The distinction between qualitative and quantitative research methods is problematic
- Published: 02 March 2011
- Volume 46 , pages 1417–1429, ( 2012 )

Cite this article

- Carl Martin Allwood 1
20k Accesses
44 Citations
3 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The distinction between qualitative and quantitative research is abstract, very general and its value is usually taken for granted. In contrast, this article attempts to show that the distinction between qualitative and quantitative research is unclear, poor and therefore of limited value and that its popularity risks leading to unfortunate consequences. Various arguments are presented for this conclusion. For example, it is argued that the heterogeneity of different stand-points on important issues among qualitative researchers (for example with respect to the use of quantification and causal analysis) makes the distinction as such unstable. Moreover, the presence of substantial overlap between many features of qualitative and quantitative research often makes it difficult to separate qualitative and quantitative research. It is also shown that three obvious ways of making the distinction between qualitative and quantitative research are unsatisfactory. Use of the distinction may restrict creativity in the development of new research methods and create confusion and unnecessary work. In general, it may be preferable not to conceptualize research approaches at such abstract levels as done in the context of qualitative or quantitative approaches. Instead, it is suggested that it is more fruitful to discuss the pros and cons of specific research methods, preferably in the context of specific research problems.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Beyond qualitative/quantitative structuralism: the positivist qualitative research and the paradigmatic disclaimer.

What is Qualitative in Research

Methodology
Allwood C.M.: Vetenskapsfilosofi och psykologisk forskning, [Philosophy of science and psychological research]. In: Allwood, C.M., Erikson, M.G. (eds) Vetenskapsteori för psykologi och andra samhällsvetenskaper [Theory of science for psychology and other social sciences], pp. 444–472. Studentlitteratur, Lund (1999)
Google Scholar
Allwood C.M.: On the nature of the qualitative research approach. In: Hallberg, L. (ed.) Qualitative methods in public health research, theoretical foundations and practical examples, pp. 201–223. Studentlitteratur, Lund (2002)
Alvesson M., Kärreman D.: Taking the linguistic turn in organizational research—challenges, responses, consequences. J. Appl. Behav. Sci. 36 , 136–158 (2000)
Article Google Scholar
Bryman A.: The debate about quantitative and qualitative research: a question of method or epistemology?. Br. J. Sociol. 35 , 75–92 (1984)
Bryman A.: Quantity and quality in social research. Routledge, London (1995)
Bryman A.: Social research methods. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2001)
Bullington J., Karlsson G.: Introduction to phenomenological research. Scand. J. Psychol. 25 , 51–63 (1984)
Denzin N., Lincoln Y.S.: Introduction: entering the field of qualitative research. In: Denzin, N., Lincoln, Y.S. (eds) Strategies of qualitative inquiry, pp. 1–34. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks (1998)
Flick U.: An introduction to qualitative research. Sage Publications, London (1998)
Gelo O., Braakmann D., Benetka G.: Quantitative and qualitative research: beyond the debate. Integr. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 42 , 266–290 (2008)
Giorgi A.: An application of phenomenological method in psychology. In: Giorgi, A., Fischer, C., Murray, E. (eds) Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology, pp. 82–103. Duquesne University Press, Pittsburgh (1975)
Glazer B., Strauss A.: Discovery of grounded theory. Aldine, Chicago (1967)
Guba E.G., Lincoln Y.S.: Competing paradigms in qualitative research. In: Denzin, N., Lincoln, Y.S. (eds) The landscape of qualitative research, pp. 195–220. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks (1998)
Hamilton D.: Traditions, preferences, postures in applied qualitative research. In: Denzin, N., Lincoln, Y.S. (eds) The landscape of qualitative research, pp. 111–129. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks (1998)
Hammersley M.: Deconstructing the qualitative–quantitative divide. In: Brannen, J. (ed.) Mixing methods: qualitative and quantitative research, pp. 39–55. Ashgate Publishing Company, Aldershot (1992)
Hammersley M.: The relationship between qualitative and quantitative research: paradigm loyalty versus methodological eclecticism. In: Richardson, T.S. (ed.) Qualitative research methods in psychology and the social sciences, pp. 159–174. BPS Books, Leicester (1996)
Hoepfl, M.: Choosing qualitative research: a primer for technology education researchers. J. Technol. Educ. 9 , 47–63 (1997). http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/ejournals/JTE/v9n1/pdf/hoepfl.pdf . Accessed 21 July 2009.
Ihde, D.: Expanding hermeneutics. http://ws.cc.stonybrook.edu/philosophy/faculty/dihde/articles/expanding_hermeneutics.html (2006). Accessed 25 July 2007.
Long R.G., White M.C., Friedman W.H., Brazeal D.V.: The “qualitative” versus “quantitative” research debate: a question of metaphorical assumptions?. Int. J. Value-Based Manag. 13 , 189–197 (2000)
Mason J.: Qualitative researching. Sage Publishing, London (1996)
Masters C., Carlson D.S., Pfaldt E.: Winging it through research: an innovative approach to a basic understanding of research methodology. J. Emerg. Nurs. 32 , 382–384 (2006)
Maxwell J.A.: Causal explanation, qualitative research, and scientific inquiry in education. Educ. Res. 33 (2), 3–11 (2004a)
Maxwell J.A.: Using qualitative methods for causal explanation. Field Methods 16 , 243–264 (2004b)
Maxwell J.A.: Using numbers in qualitative research. Qual. Inq. 16 (6), 475–482 (2010)
Mays N., Pope C.: Quality in qualitative health research. In: Pope, C., Mays, N. (eds) Qualitative research in health care, pp. 89–101. BMJ Books, London (1999)
Merriam S.B.: Case study research in education. Jossey-Bass Inc. Publishers, San Francisco (1988)
Pope C., Mays N.: Qualitative methods in health research. In: Pope, C., Mays, N. (eds) Qualitative research in health care, pp. 1–10. BMJ Books, London (1999)
Rennie D.L., Watson K.D., Monteiro A.M.: The rise of qualitative research in psychology. Can. Psychol. 43 , 179–189 (2002)
Sale J.E.M., Lohfeld L.H., Brazil K.: Revisiting the quantitative–qualitative debate: implications for mixed-methods research. Qual. Quant. 36 , 43–53 (2002)
Sandelowski M., Voils C.I., Knafl G.: On quantitizing. J. Mix. Meth. Res. 3 (3), 208–222 (2009)
Schwandt T.A.: Qualitative inquiry: a dictionary of terms. Sage Publications, Thousands Oaks (1997)
Shadish W.R., Cook T.D., Campbell D.T.: Experimental and quasi-experimental design for generalized causal inference. Hughton Mifflin Company, Boston (2002)
Starrin B.: Om distinktionen kvalitativ–kvantitativ i social forskning [On the qualitative–quantitative distinction in social research]. In: Starrin, B., Svensson, P.-G. (eds) Kvalitativ metod och vetenskapsteori [Qualitative method and theory of science], pp. 11–39. Studentlitteratur, Lund (1994)
Strauss A.L., Corbin J.: Basics of qualitative research techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. 2nd edn. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks (1998)
Tesch R.: Qualitative research analysis types & software tools. Falmer Press, New York (1990)
Thorne S.E.: The implications of disciplinary agenda on quality criteria for qualitative research. In: Morse, J.M., Swanson, J.M., Kuzel, A.J. (eds) The nature of qualitative evidence, pp. 141–159. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks (2001)
Vidich A.J., Lyman S.M.: Qualitative methods: their history in sociology and anthropology. In: Denzin, N., Lincoln, Y.S. (eds) The landscape of qualitative research, pp. 41–110. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks (1998)
Wardekker W.L.: Criteria for the quality of inquiry. Mind Cult. Act. 7 , 259–272 (2000)
Ziman J.: Real science. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Book Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, University of Gothenburg, Box 500, 405 30, Gothenburg, Sweden
Carl Martin Allwood
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Carl Martin Allwood .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Allwood, C.M. The distinction between qualitative and quantitative research methods is problematic. Qual Quant 46 , 1417–1429 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-011-9455-8
Download citation
Published : 02 March 2011
Issue Date : August 2012
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-011-9455-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- The qualitative–quantitative distinction
- Qualitative approach
- Quantitative approach
- Research approach
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research in Psychology
Anabelle Bernard Fournier is a researcher of sexual and reproductive health at the University of Victoria as well as a freelance writer on various health topics.
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
- Key Differences
Quantitative Research Methods
Qualitative research methods.
- How They Relate
In psychology and other social sciences, researchers are faced with an unresolved question: Can we measure concepts like love or racism the same way we can measure temperature or the weight of a star? Social phenomena—things that happen because of and through human behavior—are especially difficult to grasp with typical scientific models.
At a Glance
Psychologists rely on quantitative and quantitative research to better understand human thought and behavior.
- Qualitative research involves collecting and evaluating non-numerical data in order to understand concepts or subjective opinions.
- Quantitative research involves collecting and evaluating numerical data.
This article discusses what qualitative and quantitative research are, how they are different, and how they are used in psychology research.
Qualitative Research vs. Quantitative Research
In order to understand qualitative and quantitative psychology research, it can be helpful to look at the methods that are used and when each type is most appropriate.
Psychologists rely on a few methods to measure behavior, attitudes, and feelings. These include:
- Self-reports , like surveys or questionnaires
- Observation (often used in experiments or fieldwork)
- Implicit attitude tests that measure timing in responding to prompts
Most of these are quantitative methods. The result is a number that can be used to assess differences between groups.
However, most of these methods are static, inflexible (you can't change a question because a participant doesn't understand it), and provide a "what" answer rather than a "why" answer.
Sometimes, researchers are more interested in the "why" and the "how." That's where qualitative methods come in.
Qualitative research is about speaking to people directly and hearing their words. It is grounded in the philosophy that the social world is ultimately unmeasurable, that no measure is truly ever "objective," and that how humans make meaning is just as important as how much they score on a standardized test.
Used to develop theories
Takes a broad, complex approach
Answers "why" and "how" questions
Explores patterns and themes
Used to test theories
Takes a narrow, specific approach
Answers "what" questions
Explores statistical relationships
Quantitative methods have existed ever since people have been able to count things. But it is only with the positivist philosophy of Auguste Comte (which maintains that factual knowledge obtained by observation is trustworthy) that it became a "scientific method."
The scientific method follows this general process. A researcher must:
- Generate a theory or hypothesis (i.e., predict what might happen in an experiment) and determine the variables needed to answer their question
- Develop instruments to measure the phenomenon (such as a survey, a thermometer, etc.)
- Develop experiments to manipulate the variables
- Collect empirical (measured) data
- Analyze data
Quantitative methods are about measuring phenomena, not explaining them.
Quantitative research compares two groups of people. There are all sorts of variables you could measure, and many kinds of experiments to run using quantitative methods.
These comparisons are generally explained using graphs, pie charts, and other visual representations that give the researcher a sense of how the various data points relate to one another.
Basic Assumptions
Quantitative methods assume:
- That the world is measurable
- That humans can observe objectively
- That we can know things for certain about the world from observation
In some fields, these assumptions hold true. Whether you measure the size of the sun 2000 years ago or now, it will always be the same. But when it comes to human behavior, it is not so simple.
As decades of cultural and social research have shown, people behave differently (and even think differently) based on historical context, cultural context, social context, and even identity-based contexts like gender , social class, or sexual orientation .
Therefore, quantitative methods applied to human behavior (as used in psychology and some areas of sociology) should always be rooted in their particular context. In other words: there are no, or very few, human universals.
Statistical information is the primary form of quantitative data used in human and social quantitative research. Statistics provide lots of information about tendencies across large groups of people, but they can never describe every case or every experience. In other words, there are always outliers.
Correlation and Causation
A basic principle of statistics is that correlation is not causation. Researchers can only claim a cause-and-effect relationship under certain conditions:
- The study was a true experiment.
- The independent variable can be manipulated (for example, researchers cannot manipulate gender, but they can change the primer a study subject sees, such as a picture of nature or of a building).
- The dependent variable can be measured through a ratio or a scale.
So when you read a report that "gender was linked to" something (like a behavior or an attitude), remember that gender is NOT a cause of the behavior or attitude. There is an apparent relationship, but the true cause of the difference is hidden.
Pitfalls of Quantitative Research
Quantitative methods are one way to approach the measurement and understanding of human and social phenomena. But what's missing from this picture?
As noted above, statistics do not tell us about personal, individual experiences and meanings. While surveys can give a general idea, respondents have to choose between only a few responses. This can make it difficult to understand the subtleties of different experiences.
Quantitative methods can be helpful when making objective comparisons between groups or when looking for relationships between variables. They can be analyzed statistically, which can be helpful when looking for patterns and relationships.
Qualitative data are not made out of numbers but rather of descriptions, metaphors, symbols, quotes, analysis, concepts, and characteristics. This approach uses interviews, written texts, art, photos, and other materials to make sense of human experiences and to understand what these experiences mean to people.
While quantitative methods ask "what" and "how much," qualitative methods ask "why" and "how."
Qualitative methods are about describing and analyzing phenomena from a human perspective. There are many different philosophical views on qualitative methods, but in general, they agree that some questions are too complex or impossible to answer with standardized instruments.
These methods also accept that it is impossible to be completely objective in observing phenomena. Researchers have their own thoughts, attitudes, experiences, and beliefs, and these always color how people interpret results.
Qualitative Approaches
There are many different approaches to qualitative research, with their own philosophical bases. Different approaches are best for different kinds of projects. For example:
- Case studies and narrative studies are best for single individuals. These involve studying every aspect of a person's life in great depth.
- Phenomenology aims to explain experiences. This type of work aims to describe and explore different events as they are consciously and subjectively experienced.
- Grounded theory develops models and describes processes. This approach allows researchers to construct a theory based on data that is collected, analyzed, and compared to reach new discoveries.
- Ethnography describes cultural groups. In this approach, researchers immerse themselves in a community or group in order to observe behavior.
Qualitative researchers must be aware of several different methods and know each thoroughly enough to produce valuable research.
Some researchers specialize in a single method, but others specialize in a topic or content area and use many different methods to explore the topic, providing different information and a variety of points of view.
There is not a single model or method that can be used for every qualitative project. Depending on the research question, the people participating, and the kind of information they want to produce, researchers will choose the appropriate approach.
Interpretation
Qualitative research does not look into causal relationships between variables, but rather into themes, values, interpretations, and meanings. As a rule, then, qualitative research is not generalizable (cannot be applied to people outside the research participants).
The insights gained from qualitative research can extend to other groups with proper attention to specific historical and social contexts.
Relationship Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
It might sound like quantitative and qualitative research do not play well together. They have different philosophies, different data, and different outputs. However, this could not be further from the truth.
These two general methods complement each other. By using both, researchers can gain a fuller, more comprehensive understanding of a phenomenon.
For example, a psychologist wanting to develop a new survey instrument about sexuality might and ask a few dozen people questions about their sexual experiences (this is qualitative research). This gives the researcher some information to begin developing questions for their survey (which is a quantitative method).
After the survey, the same or other researchers might want to dig deeper into issues brought up by its data. Follow-up questions like "how does it feel when...?" or "what does this mean to you?" or "how did you experience this?" can only be answered by qualitative research.
By using both quantitative and qualitative data, researchers have a more holistic, well-rounded understanding of a particular topic or phenomenon.
Qualitative and quantitative methods both play an important role in psychology. Where quantitative methods can help answer questions about what is happening in a group and to what degree, qualitative methods can dig deeper into the reasons behind why it is happening. By using both strategies, psychology researchers can learn more about human thought and behavior.
Gough B, Madill A. Subjectivity in psychological science: From problem to prospect . Psychol Methods . 2012;17(3):374-384. doi:10.1037/a0029313
Pearce T. “Science organized”: Positivism and the metaphysical club, 1865–1875 . J Hist Ideas . 2015;76(3):441-465.
Adams G. Context in person, person in context: A cultural psychology approach to social-personality psychology . In: Deaux K, Snyder M, eds. The Oxford Handbook of Personality and Social Psychology . Oxford University Press; 2012:182-208.
Brady HE. Causation and explanation in social science . In: Goodin RE, ed. The Oxford Handbook of Political Science. Oxford University Press; 2011. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199604456.013.0049
Chun Tie Y, Birks M, Francis K. Grounded theory research: A design framework for novice researchers . SAGE Open Med . 2019;7:2050312118822927. doi:10.1177/2050312118822927
Reeves S, Peller J, Goldman J, Kitto S. Ethnography in qualitative educational research: AMEE Guide No. 80 . Medical Teacher . 2013;35(8):e1365-e1379. doi:10.3109/0142159X.2013.804977
Salkind NJ, ed. Encyclopedia of Research Design . Sage Publishing.
Shaughnessy JJ, Zechmeister EB, Zechmeister JS. Research Methods in Psychology . McGraw Hill Education.
By Anabelle Bernard Fournier Anabelle Bernard Fournier is a researcher of sexual and reproductive health at the University of Victoria as well as a freelance writer on various health topics.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research Methods & Data Analysis
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative?
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze.
Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms. Quantitative research is often used to test hypotheses, identify patterns, and make predictions.
Qualitative research , on the other hand, collects non-numerical data such as words, images, and sounds. The focus is on exploring subjective experiences, opinions, and attitudes, often through observation and interviews.
Qualitative research aims to produce rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and to uncover new insights and meanings.
Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data, such as language. Qualitative research can be used to understand how an individual subjectively perceives and gives meaning to their social reality.
Qualitative data is non-numerical data, such as text, video, photographs, or audio recordings. This type of data can be collected using diary accounts or in-depth interviews and analyzed using grounded theory or thematic analysis.
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretive, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 2)
Interest in qualitative data came about as the result of the dissatisfaction of some psychologists (e.g., Carl Rogers) with the scientific study of psychologists such as behaviorists (e.g., Skinner ).
Since psychologists study people, the traditional approach to science is not seen as an appropriate way of carrying out research since it fails to capture the totality of human experience and the essence of being human. Exploring participants’ experiences is known as a phenomenological approach (re: Humanism ).
Qualitative research is primarily concerned with meaning, subjectivity, and lived experience. The goal is to understand the quality and texture of people’s experiences, how they make sense of them, and the implications for their lives.
Qualitative research aims to understand the social reality of individuals, groups, and cultures as nearly as possible as participants feel or live it. Thus, people and groups are studied in their natural setting.
Some examples of qualitative research questions are provided, such as what an experience feels like, how people talk about something, how they make sense of an experience, and how events unfold for people.
Research following a qualitative approach is exploratory and seeks to explain ‘how’ and ‘why’ a particular phenomenon, or behavior, operates as it does in a particular context. It can be used to generate hypotheses and theories from the data.
Qualitative Methods
There are different types of qualitative research methods, including diary accounts, in-depth interviews , documents, focus groups , case study research , and ethnography.
The results of qualitative methods provide a deep understanding of how people perceive their social realities and in consequence, how they act within the social world.
The researcher has several methods for collecting empirical materials, ranging from the interview to direct observation, to the analysis of artifacts, documents, and cultural records, to the use of visual materials or personal experience. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 14)
Here are some examples of qualitative data:
Interview transcripts : Verbatim records of what participants said during an interview or focus group. They allow researchers to identify common themes and patterns, and draw conclusions based on the data. Interview transcripts can also be useful in providing direct quotes and examples to support research findings.
Observations : The researcher typically takes detailed notes on what they observe, including any contextual information, nonverbal cues, or other relevant details. The resulting observational data can be analyzed to gain insights into social phenomena, such as human behavior, social interactions, and cultural practices.
Unstructured interviews : generate qualitative data through the use of open questions. This allows the respondent to talk in some depth, choosing their own words. This helps the researcher develop a real sense of a person’s understanding of a situation.
Diaries or journals : Written accounts of personal experiences or reflections.
Notice that qualitative data could be much more than just words or text. Photographs, videos, sound recordings, and so on, can be considered qualitative data. Visual data can be used to understand behaviors, environments, and social interactions.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative research is endlessly creative and interpretive. The researcher does not just leave the field with mountains of empirical data and then easily write up his or her findings.
Qualitative interpretations are constructed, and various techniques can be used to make sense of the data, such as content analysis, grounded theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967), thematic analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006), or discourse analysis.
For example, thematic analysis is a qualitative approach that involves identifying implicit or explicit ideas within the data. Themes will often emerge once the data has been coded.
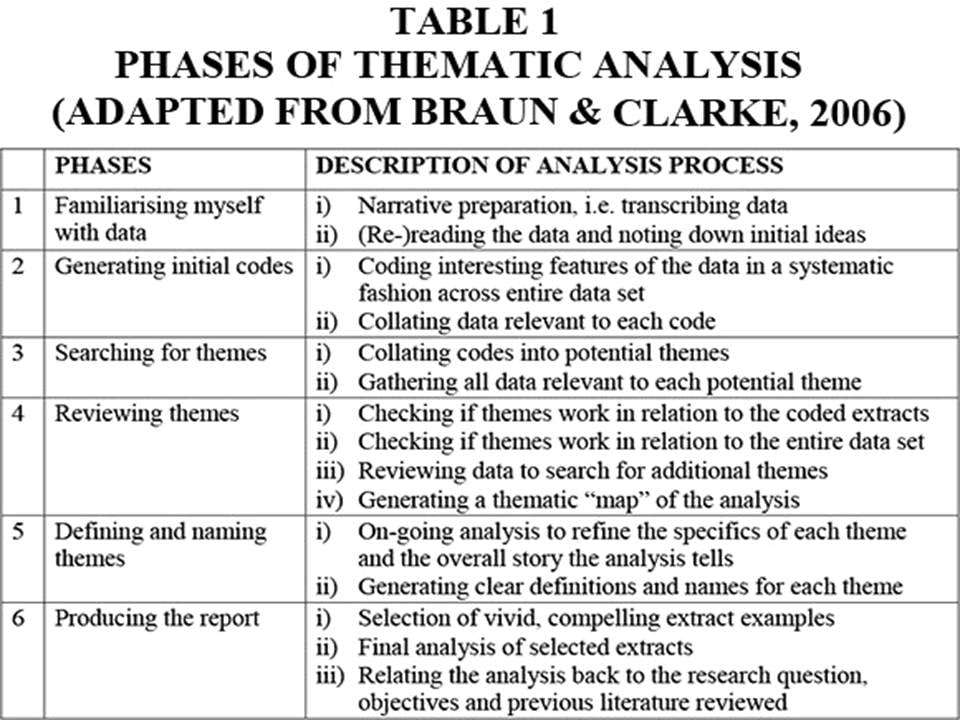
Key Features
- Events can be understood adequately only if they are seen in context. Therefore, a qualitative researcher immerses her/himself in the field, in natural surroundings. The contexts of inquiry are not contrived; they are natural. Nothing is predefined or taken for granted.
- Qualitative researchers want those who are studied to speak for themselves, to provide their perspectives in words and other actions. Therefore, qualitative research is an interactive process in which the persons studied teach the researcher about their lives.
- The qualitative researcher is an integral part of the data; without the active participation of the researcher, no data exists.
- The study’s design evolves during the research and can be adjusted or changed as it progresses. For the qualitative researcher, there is no single reality. It is subjective and exists only in reference to the observer.
- The theory is data-driven and emerges as part of the research process, evolving from the data as they are collected.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
- Because of the time and costs involved, qualitative designs do not generally draw samples from large-scale data sets.
- The problem of adequate validity or reliability is a major criticism. Because of the subjective nature of qualitative data and its origin in single contexts, it is difficult to apply conventional standards of reliability and validity. For example, because of the central role played by the researcher in the generation of data, it is not possible to replicate qualitative studies.
- Also, contexts, situations, events, conditions, and interactions cannot be replicated to any extent, nor can generalizations be made to a wider context than the one studied with confidence.
- The time required for data collection, analysis, and interpretation is lengthy. Analysis of qualitative data is difficult, and expert knowledge of an area is necessary to interpret qualitative data. Great care must be taken when doing so, for example, looking for mental illness symptoms.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Because of close researcher involvement, the researcher gains an insider’s view of the field. This allows the researcher to find issues that are often missed (such as subtleties and complexities) by the scientific, more positivistic inquiries.
- Qualitative descriptions can be important in suggesting possible relationships, causes, effects, and dynamic processes.
- Qualitative analysis allows for ambiguities/contradictions in the data, which reflect social reality (Denscombe, 2010).
- Qualitative research uses a descriptive, narrative style; this research might be of particular benefit to the practitioner as she or he could turn to qualitative reports to examine forms of knowledge that might otherwise be unavailable, thereby gaining new insight.
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research involves the process of objectively collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest.
The goals of quantitative research are to test causal relationships between variables , make predictions, and generalize results to wider populations.
Quantitative researchers aim to establish general laws of behavior and phenomenon across different settings/contexts. Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Quantitative Methods
Experiments typically yield quantitative data, as they are concerned with measuring things. However, other research methods, such as controlled observations and questionnaires , can produce both quantitative information.
For example, a rating scale or closed questions on a questionnaire would generate quantitative data as these produce either numerical data or data that can be put into categories (e.g., “yes,” “no” answers).
Experimental methods limit how research participants react to and express appropriate social behavior.
Findings are, therefore, likely to be context-bound and simply a reflection of the assumptions that the researcher brings to the investigation.
There are numerous examples of quantitative data in psychological research, including mental health. Here are a few examples:
Another example is the Experience in Close Relationships Scale (ECR), a self-report questionnaire widely used to assess adult attachment styles .
The ECR provides quantitative data that can be used to assess attachment styles and predict relationship outcomes.
Neuroimaging data : Neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and fMRI, provide quantitative data on brain structure and function.
This data can be analyzed to identify brain regions involved in specific mental processes or disorders.
For example, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) is a clinician-administered questionnaire widely used to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in individuals.
The BDI consists of 21 questions, each scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe depressive symptoms.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Statistics help us turn quantitative data into useful information to help with decision-making. We can use statistics to summarize our data, describing patterns, relationships, and connections. Statistics can be descriptive or inferential.
Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data. In contrast, inferential statistics are used to identify statistically significant differences between groups of data (such as intervention and control groups in a randomized control study).
- Quantitative researchers try to control extraneous variables by conducting their studies in the lab.
- The research aims for objectivity (i.e., without bias) and is separated from the data.
- The design of the study is determined before it begins.
- For the quantitative researcher, the reality is objective, exists separately from the researcher, and can be seen by anyone.
- Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
- Context: Quantitative experiments do not take place in natural settings. In addition, they do not allow participants to explain their choices or the meaning of the questions they may have for those participants (Carr, 1994).
- Researcher expertise: Poor knowledge of the application of statistical analysis may negatively affect analysis and subsequent interpretation (Black, 1999).
- Variability of data quantity: Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate analysis. Small-scale quantitative studies may be less reliable because of the low quantity of data (Denscombe, 2010). This also affects the ability to generalize study findings to wider populations.
- Confirmation bias: The researcher might miss observing phenomena because of focus on theory or hypothesis testing rather than on the theory of hypothesis generation.

Advantages of Quantitative Research
- Scientific objectivity: Quantitative data can be interpreted with statistical analysis, and since statistics are based on the principles of mathematics, the quantitative approach is viewed as scientifically objective and rational (Carr, 1994; Denscombe, 2010).
- Useful for testing and validating already constructed theories.
- Rapid analysis: Sophisticated software removes much of the need for prolonged data analysis, especially with large volumes of data involved (Antonius, 2003).
- Replication: Quantitative data is based on measured values and can be checked by others because numerical data is less open to ambiguities of interpretation.
- Hypotheses can also be tested because of statistical analysis (Antonius, 2003).
Antonius, R. (2003). Interpreting quantitative data with SPSS . Sage.
Black, T. R. (1999). Doing quantitative research in the social sciences: An integrated approach to research design, measurement and statistics . Sage.
Braun, V. & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3, 77–101.
Carr, L. T. (1994). The strengths and weaknesses of quantitative and qualitative research : what method for nursing? Journal of advanced nursing, 20(4) , 716-721.
Denscombe, M. (2010). The Good Research Guide: for small-scale social research. McGraw Hill.
Denzin, N., & Lincoln. Y. (1994). Handbook of Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications Inc.
Glaser, B. G., Strauss, A. L., & Strutzel, E. (1968). The discovery of grounded theory; strategies for qualitative research. Nursing research, 17(4) , 364.
Minichiello, V. (1990). In-Depth Interviewing: Researching People. Longman Cheshire.
Punch, K. (1998). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. London: Sage
Further Information
- Designing qualitative research
- Methods of data collection and analysis
- Introduction to quantitative and qualitative research
- Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?
- Qualitative research in health care: Analysing qualitative data
- Qualitative data analysis: the framework approach
- Using the framework method for the analysis of
- Qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research
- Content Analysis
- Grounded Theory
- Thematic Analysis
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research: Comparing the Methods and Strategies for Education Research

No matter the field of study, all research can be divided into two distinct methodologies: qualitative and quantitative research. Both methodologies offer education researchers important insights.
Education research assesses problems in policy, practices, and curriculum design, and it helps administrators identify solutions. Researchers can conduct small-scale studies to learn more about topics related to instruction or larger-scale ones to gain insight into school systems and investigate how to improve student outcomes.
Education research often relies on the quantitative methodology. Quantitative research in education provides numerical data that can prove or disprove a theory, and administrators can easily share the number-based results with other schools and districts. And while the research may speak to a relatively small sample size, educators and researchers can scale the results from quantifiable data to predict outcomes in larger student populations and groups.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research in Education: Definitions
Although there are many overlaps in the objectives of qualitative and quantitative research in education, researchers must understand the fundamental functions of each methodology in order to design and carry out an impactful research study. In addition, they must understand the differences that set qualitative and quantitative research apart in order to determine which methodology is better suited to specific education research topics.
Generate Hypotheses with Qualitative Research
Qualitative research focuses on thoughts, concepts, or experiences. The data collected often comes in narrative form and concentrates on unearthing insights that can lead to testable hypotheses. Educators use qualitative research in a study’s exploratory stages to uncover patterns or new angles.
Form Strong Conclusions with Quantitative Research
Quantitative research in education and other fields of inquiry is expressed in numbers and measurements. This type of research aims to find data to confirm or test a hypothesis.
Differences in Data Collection Methods
Keeping in mind the main distinction in qualitative vs. quantitative research—gathering descriptive information as opposed to numerical data—it stands to reason that there are different ways to acquire data for each research methodology. While certain approaches do overlap, the way researchers apply these collection techniques depends on their goal.
Interviews, for example, are common in both modes of research. An interview with students that features open-ended questions intended to reveal ideas and beliefs around attendance will provide qualitative data. This data may reveal a problem among students, such as a lack of access to transportation, that schools can help address.
An interview can also include questions posed to receive numerical answers. A case in point: how many days a week do students have trouble getting to school, and of those days, how often is a transportation-related issue the cause? In this example, qualitative and quantitative methodologies can lead to similar conclusions, but the research will differ in intent, design, and form.
Taking a look at behavioral observation, another common method used for both qualitative and quantitative research, qualitative data may consider a variety of factors, such as facial expressions, verbal responses, and body language.
On the other hand, a quantitative approach will create a coding scheme for certain predetermined behaviors and observe these in a quantifiable manner.
Qualitative Research Methods
- Case Studies : Researchers conduct in-depth investigations into an individual, group, event, or community, typically gathering data through observation and interviews.
- Focus Groups : A moderator (or researcher) guides conversation around a specific topic among a group of participants.
- Ethnography : Researchers interact with and observe a specific societal or ethnic group in their real-life environment.
- Interviews : Researchers ask participants questions to learn about their perspectives on a particular subject.
Quantitative Research Methods
- Questionnaires and Surveys : Participants receive a list of questions, either closed-ended or multiple choice, which are directed around a particular topic.
- Experiments : Researchers control and test variables to demonstrate cause-and-effect relationships.
- Observations : Researchers look at quantifiable patterns and behavior.
- Structured Interviews : Using a predetermined structure, researchers ask participants a fixed set of questions to acquire numerical data.
Choosing a Research Strategy
When choosing which research strategy to employ for a project or study, a number of considerations apply. One key piece of information to help determine whether to use a qualitative vs. quantitative research method is which phase of development the study is in.
For example, if a project is in its early stages and requires more research to find a testable hypothesis, qualitative research methods might prove most helpful. On the other hand, if the research team has already established a hypothesis or theory, quantitative research methods will provide data that can validate the theory or refine it for further testing.
It’s also important to understand a project’s research goals. For instance, do researchers aim to produce findings that reveal how to best encourage student engagement in math? Or is the goal to determine how many students are passing geometry? These two scenarios require distinct sets of data, which will determine the best methodology to employ.
In some situations, studies will benefit from a mixed-methods approach. Using the goals in the above example, one set of data could find the percentage of students passing geometry, which would be quantitative. The research team could also lead a focus group with the students achieving success to discuss which techniques and teaching practices they find most helpful, which would produce qualitative data.
Learn How to Put Education Research into Action
Those with an interest in learning how to harness research to develop innovative ideas to improve education systems may want to consider pursuing a doctoral degree. American University’s School of Education online offers a Doctor of Education (EdD) in Education Policy and Leadership that prepares future educators, school administrators, and other education professionals to become leaders who effect positive changes in schools. Courses such as Applied Research Methods I: Enacting Critical Research provides students with the techniques and research skills needed to begin conducting research exploring new ways to enhance education. Learn more about American’ University’s EdD in Education Policy and Leadership .
What’s the Difference Between Educational Equity and Equality?
EdD vs. PhD in Education: Requirements, Career Outlook, and Salary
Top Education Technology Jobs for Doctorate in Education Graduates
American University, EdD in Education Policy and Leadership
Edutopia, “2019 Education Research Highlights”
Formplus, “Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data: 15 Key Differences and Similarities”
iMotion, “Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research: What Is What?”
Scribbr, “Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research”
Simply Psychology, “What’s the Difference Between Quantitative and Qualitative Research?”
Typeform, “A Simple Guide to Qualitative and Quantitative Research”
Request Information

New Scholar
- Tips for Publishing
- Publishing Process Overview
- Selecting a Journal Overview
- Conference Presentation or Poster Session Overview
- Predatory Publishers
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research
Types of empirical research, list of journals friendly to qualitative work.
- Understanding Research Impact This link opens in a new window
Quantitative Research is used to quantify the problem by way of generating numerical data or data that can be transformed into useable statistics. It is used to quantify attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and other defined variables – and generalize results from a larger sample population.
Qualitative Research is primarily exploratory research. It is used to gain an understanding of underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations. This data is usually gathered using conversational methods such as interviews or focus groups.
Some journals and even some disciplines may have a preference as to what type of empirical research they wish to publish. Some authors who have written an article that is primarily qualitative in nature, may seek out journals that are "qualitative research friendly." We have listed a few such journals below.

- International Journal of Qualitative Methods
- Journal of Mixed Methods Research
- Quality & Quantity
- List of qualitative research journals compiled by Saint Louis University
You can also look through the last few issues of a journal to see if the articles they publish tend to be more qualitative or quantitative in nature.
- << Previous: Predatory Publishers
- Next: Understanding Research Impact >>
- Last Updated: Mar 12, 2024 2:40 PM
- URL: https://libguides.lib.rochester.edu/newscholar
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Prev Med Public Health
- v.56(1); 2023 Jan
Qualitative Research in Healthcare: Necessity and Characteristics
1 Department of Preventive Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
2 Ulsan Metropolitan City Public Health Policy’s Institute, Ulsan, Korea
3 Department of Nursing, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea
Eun Young Choi
4 College of Nursing, Sungshin Women’s University, Seoul, Korea
Seung Gyeong Jang
5 Department of Preventive Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Quantitative and qualitative research explore various social phenomena using different methods. However, there has been a tendency to treat quantitative studies using complicated statistical techniques as more scientific and superior, whereas relatively few qualitative studies have been conducted in the medical and healthcare fields. This review aimed to provide a proper understanding of qualitative research. This review examined the characteristics of quantitative and qualitative research to help researchers select the appropriate qualitative research methodology. Qualitative research is applicable in following cases: (1) when an exploratory approach is required on a topic that is not well known, (2) when something cannot be explained fully with quantitative research, (3) when it is necessary to newly present a specific view on a research topic that is difficult to explain with existing views, (4) when it is inappropriate to present the rationale or theoretical proposition for designing hypotheses, as in quantitative research, and (5) when conducting research that requires detailed descriptive writing with literary expressions. Qualitative research is conducted in the following order: (1) selection of a research topic and question, (2) selection of a theoretical framework and methods, (3) literature analysis, (4) selection of the research participants and data collection methods, (5) data analysis and description of findings, and (6) research validation. This review can contribute to the more active use of qualitative research in healthcare, and the findings are expected to instill a proper understanding of qualitative research in researchers who review qualitative research reports and papers.
Graphical abstract

INTRODUCTION
The definition of research varies among studies and scholars, and it is difficult to devise a single definition. The Oxford English Dictionary defines research as “a careful study of a subject, especially in order to discover new facts or information about it” [ 1 ], while Webster’s Dictionary defines research as “studious inquiry or examination - especially: investigation or experimentation aimed at the discovery and interpretation of facts, revision of accepted theories or laws in the light of new facts, or practical application of such new or revised theories or laws” [ 2 ]. Moreover, research is broadly defined as the process of solving unsolved problems to broaden human knowledge [ 3 ]. A more thorough understanding of research can be gained by examining its types and reasons for conducting it.
The reasons for conducting research may include practical goals, such as degree attainment, job promotion, and financial profit. Research may be based on one’s own academic curiosity or aspiration or guided by professors or other supervisors. Academic research aims can be further divided into the following: (1) accurately describing an object or phenomenon, (2) identifying general laws and establishing well-designed theories for understanding and explaining a certain phenomenon, (3) predicting future events based on laws and theories, and (4) manipulating causes and conditions to induce or prevent a phenomenon [ 3 ].
The appropriate type of research must be selected based on the purpose and topic. Basic research has the primary purpose of expanding the existing knowledge base through new discoveries, while applied research aims to solve a real problem. Descriptive research attempts to factually present comparisons and interpretations of findings based on analyses of the characteristics, progression, or relationships of a certain phenomenon by manipulating the variables or controlling the conditions. Experimental or analytical research attempts to identify causal relationships between variables through experiments by arbitrarily manipulating the variables or controlling the conditions [ 3 ]. In addition, research can be quantitative or qualitative, depending on the data collection and analytical methods. Quantitative research relies on statistical analyses of quantitative data obtained primarily through investigation and experiment, while qualitative research uses specific methodologies to analyze qualitative data obtained through participant observations and in-depth interviews. However, as these types of research are not polar opposites and the criteria for classifying research types are unclear, there is some degree of methodological overlap.
What is more important than differentiating types of research is identifying the appropriate type of research to gain a better understanding of specific questions and improve problems encountered by people in life. An appropriate research type or methodology is essential to apply findings reliably. However, quantitative research based on the philosophical ideas of empiricism and positivism has been the mainstay in the field of healthcare, with academic advancement achieved through the application of various statistical techniques to quantitative data [ 4 ]. In particular, there has been a tendency to treat complicated statistical techniques as more scientific and superior, with few qualitative studies in not only clinical medicine, but also primary care and social medicine, which are relatively strongly influenced by the social sciences [ 5 , 6 ].
Quantitative and qualitative research use different ways of exploring various social phenomena. Both research methodologies can be applied individually or in combination based on the research topic, with mixed quantitative and qualitative research methodologies becoming more widespread in recent years [ 7 ]. Applying these 2 methods through a virtuous cycle of integration from a complementary perspective can provide a more accurate understanding of human phenomena and solutions to real-world problems.
This review aimed to provide a proper understanding of qualitative research to assist researchers in selecting the appropriate research methodology. Specifically, this review examined the characteristics of quantitative and qualitative research, the applicability of qualitative research, and the data sources collected and analyzed in qualitative research.
COMPARISON OF QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
A clearer understanding of qualitative research can be obtained by comparing qualitative and quantitative research, with which people are generally familiar [ 8 , 9 ]. Quantitative research focuses on testing the validity of hypotheses established by the researcher to identify the causal relationships of a specific phenomenon and discovering laws to predict that phenomenon ( Table 1 ). Therefore, it emphasizes controlling the influence of variables that may interfere with the process of identifying causality and laws. In contrast, qualitative research aims to discover and explore new hypotheses or theories based on a deep understanding of the meaning of a specific phenomenon. As such, qualitative research attempts to accept various environmental factors naturally. In quantitative research, importance is placed on the researcher acting as an outsider to take an objective view by keeping a certain distance from the research subject. In contrast, qualitative research encourages looking inside the research subjects to understand them deeply, while also emphasizing the need for researchers to take an intersubjective view that is formed and shared based on a mutual understanding with the research subjects.
Comparison of methodological characteristics between quantitative research and qualitative research
The data used in quantitative research can be expressed as numerical values, and data accumulated through questionnaire surveys and tests are often used in analyses. In contrast, qualitative research uses narrative data with words and images collected through participant observations, in-depth interviews, and focus group discussions used in the analyses. Quantitative research data are measured repeatedly to enhance their reliability, while the analyses of such data focus on superficial aspects of the phenomenon of interest. Qualitative research instead focuses on obtaining deep and rich data and aims to identify the specific contents, dynamics, and processes inherent within the phenomenon and situation.
There are clear distinctions in the advantages, disadvantages, and goals of quantitative and qualitative research. On one hand, quantitative research has the advantages of reliability and generalizability of the findings, and advances in data collection and analysis methods have increased reliability and generalizability. However, quantitative research presents difficulties with an in-depth analysis of dynamic phenomena that cannot be expressed by numbers alone and interpreting the results analyzed in terms numbers. On the other hand, qualitative research has the advantage of validity, which refers to how accurately or appropriately a phenomenon was measured. However, qualitative research also has the disadvantage of weak generalizability, which determines whether an observed phenomenon applies to other cases.
APPLICATIONS OF QUALITATIVE RESEARCH AND ITS USEFULNESS IN THE HEALTHCARE FIELD
Qualitative research cannot be the solution to all problems. A specific methodology should not be applied to all situations. Therefore, researchers need to have a good understanding of the applicability of qualitative research. Generally, qualitative research is applicable in following cases: (1) when an exploratory approach is required on a topic that is not well known, (2) when something cannot be explained fully with quantitative research, (3) when it is necessary to newly present a specific view on a research topic that is difficult to explain with existing views, (4) when it is inappropriate to present the rationale or theoretical proposition for designing hypotheses, as in quantitative research, and (5) when conducting research that requires detailed descriptive writing with literary expressions [ 7 ]. In particular, qualitative research is useful for opening new fields of research, such as important topics that have not been previously examined or whose significance has not been recognized. Moreover, qualitative research is advantageous for examining known topics from a fresh perspective.
In the healthcare field, qualitative research is conducted on various topics considering its characteristics and strengths. Quantitative research, which focuses on hypothesis validation, such as the superiority of specific treatments or the effectiveness of specific policies, and the generalization of findings, has been the primary research methodology in the field of healthcare. Qualitative research has been mostly applied for studies such as subjective disease experiences and attitudes with respect to health-related patient quality of life [ 10 - 12 ], experiences and perceptions regarding the use of healthcare services [ 13 - 15 ], and assessments of the quality of care [ 16 , 17 ]. Moreover, qualitative research has focused on vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, children, disabled [ 18 - 20 ], minorities, and socially underprivileged with specific experiences [ 21 , 22 ].
For instance, patient safety is considered a pillar of quality of care, which is an aspect of healthcare with increasing international interest. The ultimate goal of patient safety research should be the improvement of patient safety, for which it is necessary to identify the root causes of potential errors and adverse events. In such cases, qualitative rather than quantitative research is often required. It is also important to identify whether there are any barriers when applying measures for enhancing patient safety to clinical practice. To identify such barriers, qualitative research is necessary to observe healthcare workers directly applying the solutions step-by-step during each process, determine whether there are difficulties in applying the solutions to relevant stakeholders, and ask how to improve the process if there are difficulties.
Patient safety is a very broad topic, and patient safety issues could be categorized into preventing, recognizing, and responding to patient safety issues based on related metrics [ 23 ]. Responding to issues that pertain to the handling of patient safety incidents that have already occurred has received relatively less interest than other categories of research on this topic, particularly in Korea. Until 2017, almost no research was conducted on the experiences of and difficulties faced by patients and healthcare workers who have been involved in patient safety incidents. This topic can be investigated using qualitative research.
A study in Korea investigated the physical and mental suffering experienced during the process of accepting disability and medical litigation by a patient who became disabled due to medical malpractice [ 21 ]. Another qualitative case study was conducted with participants who lost a family member due to a medical accident and identified psychological suffering due to the incident, as well as secondary psychological suffering during the medical litigation process, which increased the expandability of qualitative research findings [ 24 ]. A quantitative study based on these findings confirmed that people who experienced patient safety incidents had negative responses after the incidents and a high likelihood of sleep or eating disorders, depending on their responses [ 25 ].
A study that applied the grounded theory to examine the second victim phenomenon, referring to healthcare workers who have experienced patient safety incidents, and presented the response stages experienced by second victims demonstrated the strength of qualitative research [ 26 ]. Subsequently, other studies used questionnaire surveys on physicians and nurses to quantify the physical, mental, and work-related difficulties experienced by second victims [ 27 , 28 ]. As such, qualitative research alone can produce significant findings; however, combining quantitative and qualitative research produces a synergistic effect. In the healthcare field, which remains unfamiliar with qualitative research, combining these 2 methodologies could both enhance the validity of research findings and facilitate open discussions with other researchers [ 29 ].
In addition, qualitative research has been used for diverse sub-topics, including the experiences of patients and guardians with respect to various diseases (such as cancer, myocardial infarction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, depression, falls, and dementia), awareness of treatment for diabetes and hypertension, the experiences of physicians and nurses when they come in contact with medical staff, awareness of community health environments, experiences of medical service utilization by the general public in medically vulnerable areas, the general public’s awareness of vaccination policies, the health issues of people with special types of employment (such as delivery and call center workers), and the unmet healthcare needs of persons with vision or hearing impairment.
GENERAL WORKFLOW OF QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Rather than focusing on deriving objective information, qualitative research aims to discern the quality of a specific phenomenon, obtaining answers to “why” and “how” questions. Qualitative research aims to collect data multi-dimensionally and provide in-depth explanations of the phenomenon being researched. Ultimately, the purpose of qualitative research is set to help researchers gain an understanding of the research topic and reveal the implications of the research findings. Therefore, qualitative research is generally conducted in the following order: (1) selection of a research topic and question, (2) selection of a theoretical framework and methods, (3) literature analysis, (4) selection of the research participants (or participation target) and data collection methods, (5) data analysis and description of findings, and (6) research validation ( Figure 1 ) [ 30 ]. However, unlike quantitative research, in which hypothesis setting and testing take place unidirectionally, a major characteristic of qualitative research is that the process is reversible and research methods can be modified. In other words, the research topic and question could change during the literature analysis process, and theoretical and analytical methods could change during the data collection process.

General workflow of qualitative research.
Selection of a Research Topic and Question
As with any research, the first step in qualitative research is the selection of a research topic and question. Qualitative researchers can select a research topic based on their interests from daily life as a researcher, their interests in issues within the healthcare field, and ideas from the literature, such as academic journals. The research question represents a more specific aspect of the research topic. Before specifically starting to conduct research based on a research topic, the researcher should clarify what is being researched and determine what research would be desirable. When selecting a research topic and question, the research should ask: is the research executable, are the research topic and question worth researching, and is this a research question that a researcher would want to research?
Selection of Theoretical Framework and Methods
A theoretical framework refers to the thoughts or attitudes that a researcher has about the phenomenon being researched. Selecting the theoretical framework first could help qualitative researchers not only in selecting the research purpose and problem, but also in carrying out various processes, including an exploration of the precedent literature and research, selection of the data type to be collected, data analysis, and description of findings. In qualitative research, theoretical frameworks are based on philosophical ideas, which affect the selection of specific qualitative research methods. Representative qualitative research methods include the grounded theory, which is suitable for achieving the goal of developing a theory that can explain the processes involved in the phenomenon being researched; ethnographic study, which is suitable for research topics that attempt to identify and interpret the culture of a specific group; phenomenology, which is suitable for research topics that attempt to identify the nature of research participants’ experiences or the phenomenon being researched; case studies, which aim to gain an in-depth understanding of a case that has unique characteristics and can be differentiated from other cases; action research, which aims to find solutions to problems faced by research participants, with the researchers taking the same position as the participants; and narrative research, which is suitable for research topics that attempt to interpret the entire life or individual experiences contained within the stories of research participants. Other methodologies include photovoice research, consensual qualitative research, and auto-ethnographic research.
Literature Analysis
Literature analysis results can be helpful in specifically selecting the research problem, theoretical framework, and research methods. The literature analysis process compels qualitative researchers to contemplate the new knowledge that their research will add to the academic field. A comprehensive literature analysis is encouraged both in qualitative and quantitative research, and if the prior literature related to the subject to be studied is insufficient, it is sometimes evaluated as having low research potential or research value. Some have claimed that a formal literature review should not be performed before the collection of field data, as it could create bias, thereby interfering with the investigation. However, as the qualitative research process is cyclic rather than unidirectional, the majority believes that a literature review can be performed at any time. Moreover, an ethical review prior to starting the research is a requirement; therefore, the research protocol must be prepared and submitted for review and approval prior to conducting the research. To prepare research protocols, the existing literature must be analyzed at least to a certain degree. Nonetheless, qualitative researchers must keep in mind that their emotions, bias, and expectations may interject themselves during the literature review process and should strive to minimize any bias to ensure the validity of the research.
Selection of the Research Participants and Data Collection Methods
The subjects of qualitative research are not necessarily humans. It is more important to find the research subject(s) from which the most in-depth answers to the research problem can be obtained. However, the subjects in most qualitative studies are humans, as most research question focus on humans. Therefore, it is important to obtain research participants with sufficient knowledge, experience, and attitudes to provide the most appropriate answers to the research question. Quantitative research, which views generalizability as a key research goal, emphasizes the selection of research participants (i.e., the research sample that can represent the study’s population of interest), whereas qualitative research emphasizes finding research participants who can best describe and demonstrate the phenomenon of interest.
In qualitative research, the participant selection method is referred to as purposeful sampling (or purposive sampling), which can be divided into various types. Sampling methods have various advantages, disadvantages, and characteristics. For instance, unique sampling (extreme case sampling) has the advantage of being able to obtain interesting research findings by researching phenomena that have previously received little or no interest, and the disadvantage of deriving research findings that are interesting to only some readers if the research is conducted on an overly unique situation. Maximum variation sampling, also referred to as theoretical sampling, is commonly used in qualitative research based on the grounded theory. Selecting the appropriate participant sampling method that suits the purpose of research is crucial ( Table 2 ).
Sampling methods of selecting research participants in qualitative research
Once the researcher has decided how to select study participants, the data collection methods must be determined. Just as with participant sampling, various data collection methods are available, all of which have various advantages and disadvantages; therefore, the method must be selected based on the research question and circumstances. Unlike quantitative research, which usually uses a single data source and data collection method, the use of multiple data sources and data collection methods is encouraged in qualitative research [ 30 ]. Using a single data source and data collection method could cause data collection to be skewed by researcher bias; therefore, using multiple data sources and data collection methods is ideal. In qualitative research, the following data types are commonly used: (1) interview data obtained through one-on-one in-depth interviews and focus group discussions, (2) observational data from various observation levels, (3) documented data collected from personal or public documents, and (4) image data, such as photographs and videos.
Interview data are the most commonly used data source in qualitative research [ 31 ]. In qualitative research, an interview refers to communication that takes place based on a clear sense of purpose of acquiring certain information, unlike conversations that typically take place in daily life. The level of data acquired through interviews varies significantly depending on the researcher’s personal qualifications and abilities, as well as his or her level of interest and knowledge regarding the research topic. Therefore, interviewers must be trained to go beyond simply identifying the clearly expressed experiences of research participants to exploring their inner experiences and emotions [ 32 ]. Interview data can be classified based on the level of structuralization of the data collection method, sample size, and interview method. The characteristics of each type of interview are given in Table 3 .
Detailed types of interview methods according to the characteristics of in-depth interviews and focus group discussion
Observations, which represent a key data collection method in anthropology, refer to a series of actions taken by the researcher in search of a deep understanding by systematically examining the appearances of research participants that take place in natural situations [ 33 ]. Observations can be categorized as participant and non-participant, insider and outsider, disguised and undisguised, short- and long-term, and structured and unstructured. However, a line cannot be drawn clearly to differentiate these categories, and the degree of each varies along a single spectrum. Therefore, it is necessary for a qualitative researcher to select the appropriate data collection method based on the circumstances and characteristics of the research topic.
Various types of document data can be used in qualitative research. Personal documents include diaries, letters, and autobiographies, while public documents include legal documents, public announcements, and civil documents. Online documents include emails and blog or bulletin board postings, while other documents include graffiti. All these document types may be used as data sources in qualitative research. In addition, image data acquired by the research participant or researcher, such as photographs and videos, serve as useful data sources in qualitative research. Such data sources are relatively objective and easily accessible, while they contain a significant amount of qualitative meaning despite the low acquisition cost. While some data may have been collected for research purposes, other data may not have been originally produced for research. Therefore, the researcher must not distort the original information contained in the data source and must verify the accuracy and authenticity of the data source in advance [ 30 ].
This review examined the characteristics of qualitative research to help researchers select the appropriate qualitative research methodology and identify situations suitable for qualitative research in the healthcare field. In addition, this paper analyzed the selection of the research topic and problem, selection of the theoretical framework and methods, literature analysis, and selection of the research participants and data collection methods. A forthcoming paper will discuss more specific details regarding other qualitative research methodologies, such as data analysis, description of findings, and research validation. This review can contribute to the more active use of qualitative research in the healthcare field, and the findings are expected to instill a proper understanding of qualitative research in researchers who review and judge qualitative research reports and papers.
Ethics Statement
Since this study used secondary data source, we did not seek approval from the institutional review board. We also did not have to ask for the consent of the participants.
Acknowledgments
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: Pyo J, Lee W, Choi EY, Jang SG, Ock M. Data curation: Pyo J, Ock M. Formal analysis: Pyo J, Ock M. Funding acquisition: None. Validation: Lee W, Choi EY, Jang SG. Writing - original draft: Pyo J, Ock M. Writing - review & editing: Pyo J, Lee W, Choi EY, Jang SG, Ock M.

What is the difference between Qualitative and Quantitative Variables?
Table of Contents
Qualitative and quantitative variables are two types of data that are used in research and data analysis. Qualitative variables are descriptive and do not have numerical values, while quantitative variables are numerical and can be measured or counted.
The main difference between the two is that qualitative variables are based on qualities or characteristics, while quantitative variables are based on quantity or numerical values. Qualitative variables are often used to describe and categorize things, such as gender, ethnicity, or occupation. On the other hand, quantitative variables are used to measure and compare data, such as height, weight, or income.
Another key difference is that qualitative variables are often subjective and can be interpreted differently by different individuals, while quantitative variables are more objective and can be measured and compared using statistical methods.
In summary, the main distinction between qualitative and quantitative variables lies in their nature and purpose. Qualitative variables provide descriptive information, while quantitative variables provide numerical data that can be analyzed and used for statistical purposes. Understanding the difference between these two types of variables is crucial in conducting accurate and meaningful research.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Variables: What’s the Difference?
In statistics, there are two types of variables:
1. Quantitative Variables: Sometimes referred to as “numeric” variables, these are variables that represent a measurable quantity. Examples include:
- Number of students in a class
- Number of square feet in a house
- Population size of a city
- Age of an individual
- Height of an individual
2. Qualitative Variables: Sometimes referred to as “categorical” variables, these are variables that take on names or labels and can fit into categories. Examples include:
- Eye color (e.g. “blue”, “green”, “brown”)
- Gender (e.g. “male”, “female”)
- Breed of dog (e.g. “lab”, “bulldog”, “poodle”)
- Level of education (e.g. “high school”, “Associate’s degree”, “Bachelor’s degree”)
- Marital status (e.g. “married”, “single”, “divorced”)
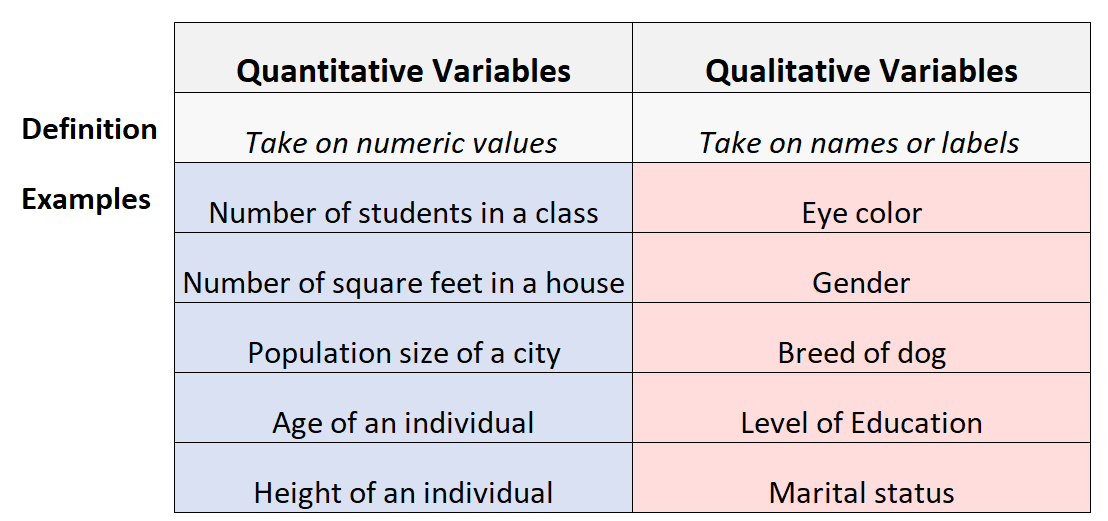
Every single variable you will ever encounter in statistics can be classified as either quantitative or qualitative.
Example: Classifying Quantitative & Qualitative Variables
Consider the following dataset with information about 10 different basketball players:
There are five total variables in this dataset. Two of them are qualitative variables and three of them are quantitative variables:
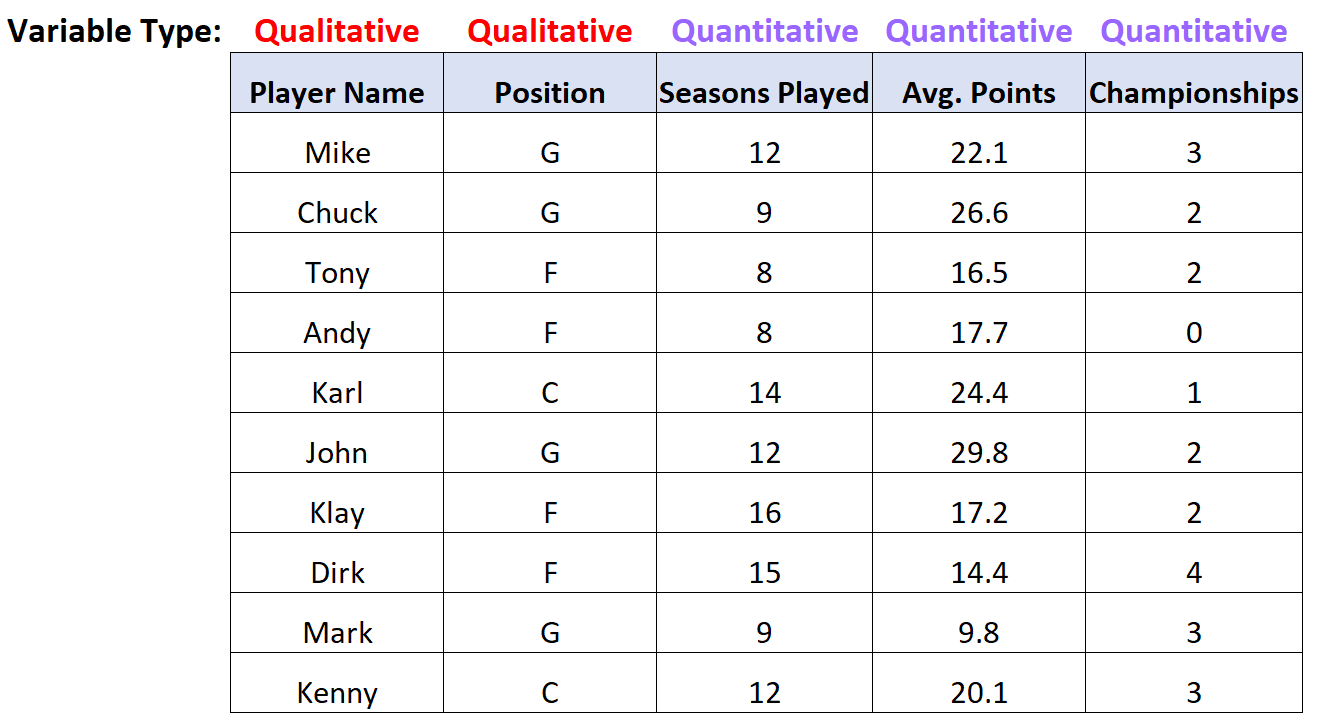
Summarizing Quantitative & Qualitative Variables
We can use many different metrics to summarize quantitative variables , including:
- Measures of central tendency like the mean, median, and mode.
- Measures of dispersion like the range, interquartile range, and standard deviation.
However, we can only use frequency tables and relative frequency tables to summarize qualitative variables .
To illustrate this, let’s once again consider the dataset from the previous example:
For the quantiative variable Seasons Played , we can calculate the following metrics:
- Mean: 11.5
- Median: 12
- Interquartile Range: 4.5
- Standard Deviation: 2.915
These metrics give us a good idea of where the center value is located as well as how spread out the values are for this variable.
And for the qualitative variable Position , we can create a frequency table to describe how often different values occur:
This table lets us quickly see how frequently each position (G=guard, F=forward, C=center) occurred in the dataset.
Additional Resources
Descriptive vs. Inferential Statistics Statistic vs. Parameter Levels of Measurement: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio
Related terms:
- What’s the Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Variables?
- QUALITATIVE VERSUS QUANTITATIVE DIFFERENCES
- What are Categorical vs. Quantitative Variables?
- What is the difference between independent and dependent variables?
- What is the difference between Endogenous and Exogenous Variables?
- Participant Variables (Subject Variables)
- What is the difference between Within-Group and Between Group Variation in ANOVA?
- Qualitative Method
- Qualitative Variable
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables: What is the Difference?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Living within blurry boundaries: The value of distinguishing between qualitative and quantitative research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 12(3), 268-279. Crossref. ISI. Google Scholar. Morgan D. L. (2018b). Rebuttal. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 12(3), 260-261. Google Scholar. National Research Council. (2002).
Here, we use network research as an example to illustrate how quantitative and qualitative approaches, techniques, and data are mixed along a continuum of fusion between quantitative and ...
The paradigmatic differences between qualitative and quantitative research (see Table 2) have led to intense disagreements between their proponents and opponents, and the long-running debate is referred to as the paradigm war (Bryman, 2007; Coates, 2021; Denzin, 2010; Gage, 1989; Glogowska, 2011; Johnson & Onwuegbuzie, 2004; van Griensven et al ...
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge. Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions.
Quantitative research focuses on numbers and graphs, while qualitative research emphasizes words and definitions. Overall, qualitative research often is based on observations, interviews, and previously published papers, whereas quantitative methods utilize math, surveys, and hands-on experiments. Hence, when researchers want to understand ...
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
The distinction between qualitative and quantitative research is abstract, very general and its value is usually taken for granted. In contrast, this article attempts to show that the distinction between qualitative and quantitative research is unclear, poor and therefore of limited value and that its popularity risks leading to unfortunate consequences. Various arguments are presented for ...
This chapter highlights some of the differences between quantitative and qualitative research, but also how they can be used in a complementary manner in the same programme of research. Quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research (MMR) come from different underlying assumptions of what is reality and what is knowledge. Broadly speaking ...
At a Glance. Psychologists rely on quantitative and quantitative research to better understand human thought and behavior. Qualitative research involves collecting and evaluating non-numerical data in order to understand concepts or subjective opinions. Quantitative research involves collecting and evaluating numerical data.
between qualitative and quantitative research designs is about the question of scale or depth versus. breath (Sayer, 1992). There are limited preliminary changes between both re search designs ...
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze. Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms.
It is so easy to confuse the words "quantitative" and "qualitative," it's best to use "empirical" and "qualitative" instead. Hint: An excellent clue that a scholarly journal article contains empirical research is the presence of some sort of statistical analysis
The qualitative vs. quantitative debate is a dichotomy but it is a false one. The terms qualitative and quantitative assume that the various research approaches such as RCTs, case studies, cohort studies, grounded theory, discourse analysis, feminist research, phenomenology, ethnography, action research - the list goes on - somehow fit ...
Educators use qualitative research in a study's exploratory stages to uncover patterns or new angles. Form Strong Conclusions with Quantitative Research. Quantitative research in education and other fields of inquiry is expressed in numbers and measurements. This type of research aims to find data to confirm or test a hypothesis.
For example, qualitative research usually relies on interviews, observations, and textual analysis to explore subjective experiences and diverse perspectives. While quantitative data collection methods include surveys, experiments, and statistical analysis to gather and analyze numerical data. The differences between the two research approaches ...
Quantitative Research is used to quantify the problem by way of generating numerical data or data that can be transformed into useable statistics. It is used to quantify attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and other defined variables - and generalize results from a larger sample population. Qualitative Research is primarily exploratory research.
COMPARISON OF QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH. A clearer understanding of qualitative research can be obtained by comparing qualitative and quantitative research, with which people are generally familiar [8,9].Quantitative research focuses on testing the validity of hypotheses established by the researcher to identify the causal relationships of a specific phenomenon and discovering laws ...
The main difference between the two is that qualitative variables are based on qualities or characteristics, while quantitative variables are based on quantity or numerical values. Qualitative variables are often used to describe and categorize things, such as gender, ethnicity, or occupation. On the other hand, quantitative variables are used ...