
- Peterborough


How to Write a Reflection Paper
Why reflective writing, experiential reflection, reading reflection.
- A note on mechanics
Reflection offers you the opportunity to consider how your personal experiences and observations shape your thinking and your acceptance of new ideas. Professors often ask students to write reading reflections. They do this to encourage you to explore your own ideas about a text, to express your opinion rather than summarize the opinions of others. Reflective writing can help you to improve your analytical skills because it requires you to express what you think, and more significantly, how and why you think that way. In addition, reflective analysis asks you to acknowledge that your thoughts are shaped by your assumptions and preconceived ideas; in doing so, you can appreciate the ideas of others, notice how their assumptions and preconceived ideas may have shaped their thoughts, and perhaps recognize how your ideas support or oppose what you read.
Types of Reflective Writing
Popular in professional programs, like business, nursing, social work, forensics and education, reflection is an important part of making connections between theory and practice. When you are asked to reflect upon experience in a placement, you do not only describe your experience, but you evaluate it based on ideas from class. You can assess a theory or approach based on your observations and practice and evaluate your own knowledge and skills within your professional field. This opportunity to take the time to think about your choices, your actions, your successes and your failures is best done within a specific framework, like course themes or work placement objectives. Abstract concepts can become concrete and real to you when considered within your own experiences, and reflection on your experiences allows you to make plans for improvement.
To encourage thoughtful and balanced assessment of readings, many interdisciplinary courses may ask you to submit a reading reflection. Often instructors will indicate to students what they expect of a reflection, but the general purpose is to elicit your informed opinions about ideas presented in the text and to consider how they affect your interpretation. Reading reflections offer an opportunity to recognize – and perhaps break down – your assumptions which may be challenged by the text(s).
Approaches to Reflective Inquiry
You may wonder how your professors assess your reflective writing. What are they looking for? How can my experiences or ideas be right or wrong? Your instructors expect you to critically engage with concepts from your course by making connections between your observations, experiences, and opinions. They expect you to explain and analyse these concepts from your own point of view, eliciting original ideas and encouraging active interest in the course material.
It can be difficult to know where to begin when writing a critical reflection. First, know that – like any other academic piece of writing – a reflection requires a narrow focus and strong analysis. The best approach for identifying a focus and for reflective analysis is interrogation. The following offers suggestions for your line of inquiry when developing a reflective response.
It is best to discuss your experiences in a work placement or practicum within the context of personal or organizational goals; doing so provides important insights and perspective for your own growth in the profession. For reflective writing, it is important to balance reporting or descriptive writing with critical reflection and analysis.
Consider these questions:
- Contextualize your reflection: What are your learning goals? What are the objectives of the organization? How do these goals fit with the themes or concepts from the course?
- Provide important information: What is the name of the host organization? What is their mission? Who do they serve? What was your role? What did you do?
- Analytical Reflection: What did you learn from this experience? About yourself? About working in the field? About society?
- Lessons from reflection: Did your experience fit with the goals or concepts of the course or organization? Why or why not? What are your lessons for the future? What was successful? Why? What would you do differently? Why? How will you prepare for a future experience in the field?
Consider the purpose of reflection: to demonstrate your learning in the course. It is important to actively and directly connect concepts from class to your personal or experiential reflection. The following example shows how a student’s observations from a classroom can be analysed using a theoretical concept and how the experience can help a student to evaluate this concept.
For Example My observations from the classroom demonstrate that the hierarchical structure of Bloom’s Taxonomy is problematic, a concept also explored by Paul (1993). The students often combined activities like application and synthesis or analysis and evaluation to build their knowledge and comprehension of unfamiliar concepts. This challenges my understanding of traditional teaching methods where knowledge is the basis for inquiry. Perhaps higher-order learning strategies like inquiry and evaluation can also be the basis for knowledge and comprehension, which are classified as lower-order skills in Bloom’s Taxonomy.
Critical reflection requires thoughtful and persistent inquiry. Although basic questions like “what is the thesis?” and “what is the evidence?” are important to demonstrate your understanding, you need to interrogate your own assumptions and knowledge to deepen your analysis and focus your assessment of the text.
Assess the text(s):
- What is the main point? How is it developed? Identify the purpose, impact and/or theoretical framework of the text.
- What ideas stood out to me? Why? Were they new or in opposition to existing scholarship?
Develop your ideas:
- What do I know about this topic? Where does my existing knowledge come from? What are the observations or experiences that shape my understanding?
- Do I agree or disagree with this argument? Why?
Make connections:
- How does this text reinforce my existing ideas or assumptions? How does this text challenge my existing ideas or assumptions?
- How does this text help me to better understand this topic or explore this field of study/discipline?
A Note on Mechanics
As with all written assignments or reports, it is important to have a clear focus for your writing. You do not need to discuss every experience or element of your placement. Pick a few that you can explore within the context of your learning. For reflective responses, identify the main arguments or important elements of the text to develop a stronger analysis which integrates relevant ideas from course materials.
Furthermore, your writing must be organized. Introduce your topic and the point you plan to make about your experience and learning. Develop your point through body paragraph(s), and conclude your paper by exploring the meaning you derive from your reflection. You may find the questions listed above can help you to develop an outline before you write your paper.
You should maintain a formal tone, but it is acceptable to write in the first person and to use personal pronouns. Note, however, that it is important that you maintain confidentiality and anonymity of clients, patients or students from work or volunteer placements by using pseudonyms and masking identifying factors.
The value of reflection: Critical reflection is a meaningful exercise which can require as much time and work as traditional essays and reports because it asks students to be purposeful and engaged participants, readers, and thinkers.

- Rasmussen University
- Transferable Skills
- Critical Thinking
- Steps 1 & 2: Reflection and Analysis
Critical Thinking: Steps 1 & 2: Reflection and Analysis
- Step 3: Acquisition of Information
- Step 4: Creativity
- Step 5: Structuring Arguments
- Step 6: Decision Making
- Steps 7 & 8: Commitment and Debate
- In the Classroom
- In the Workplace
Identify, Reflect, and Analyze
- Step 1: Reflect
- Step 2: Analyze
Step 1: Reflecting on the Issue, Problem, or Task
Reflection is an important early step in critical thinking. There are various kinds of reflection that promote deeper levels of critical thinking (click on the table to view larger):

Brockbank, A., & McGill, I. (2007). Facilitating Reflective Learning in Higher Education . Maidenhead, England: McGraw-Hill Education.
Ask yourself questions to identify the nature and essence of the issue, problem, or task. Why are you examining this subject? Why is it important that you solve this problem?

Reflective Thinking

Game: There is 1 random word below. Use it as inspiration to think of something it would be interesting if we never had in this world.
Challenge: For extra challenge, reply to someone else’s suggestion and predict how life would be different if it never was. Try and think big. Think about profound and extreme ways in which the world may be different.
Strategy: We often think about how life would be better if only we had X (X being something we would quite like). It can be a fun way to pass the time but it tends to involve adding something new to our lives. Let's go the other way around and subtract something instead. But instead of something desirable it will be something that we take for granted, something simple. Then trying to predict how it would have a profound effect changing the world around us becomes an act in following a chain reaction of influences. Creativity often involves having keen insights into how everything influences and affects everything around it in often unobvious ways. This little game is a good way to practice that thinking.
- << Previous: Steps to Critical Thinking
- Next: Step 3: Acquisition of Information >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 9:12 AM
- URL: https://guides.rasmussen.edu/criticalthinking

- Cambridge Libraries
Study Skills
Reflective practice toolkit, introduction.
- What is reflective practice?
- Everyday reflection
- Models of reflection
- Barriers to reflection
- Free writing
- Reflective writing exercise
- Bibliography

Many people worry that they will be unable to write reflectively but chances are that you do it more than you think! It's a common task during both work and study from appraisal and planning documents to recording observations at the end of a module. The following pages will guide you through some simple techniques for reflective writing as well as how to avoid some of the most common pitfalls.
What is reflective writing?
Writing reflectively involves critically analysing an experience, recording how it has impacted you and what you plan to do with your new knowledge. It can help you to reflect on a deeper level as the act of getting something down on paper often helps people to think an experience through.
The key to reflective writing is to be analytical rather than descriptive. Always ask why rather than just describing what happened during an experience.
Remember...
Reflective writing is...
- Written in the first person
- Free flowing
- A tool to challenge assumptions
- A time investment
Reflective writing isn't...
- Written in the third person
- Descriptive
- What you think you should write
- A tool to ignore assumptions
- A waste of time
Adapted from The Reflective Practice Guide: an Interdisciplinary Approach / Barbara Bassot.
You can learn more about reflective writing in this handy video from Hull University:
Created by SkillsTeamHullUni
- Hull reflective writing video transcript (Word)
- Hull reflective writing video transcript (PDF)
Where might you use reflective writing?
You can use reflective writing in many aspects of your work, study and even everyday life. The activities below all contain some aspect of reflective writing and are common to many people:
1. Job applications
Both preparing for and writing job applications contain elements of reflective writing. You need to think about the experience that makes you suitable for a role and this means reflection on the skills you have developed and how they might relate to the specification. When writing your application you need to expand on what you have done and explain what you have learnt and why this matters - key elements of reflective writing.
2. Appraisals
In a similar way, undertaking an appraisal is a good time to reflect back on a certain period of time in post. You might be asked to record what went well and why as well as identifying areas for improvement.
3. Written feedback
If you have made a purchase recently you are likely to have received a request for feedback. When you leave a review of a product or service online then you need to think about the pros and cons. You may also have gone into detail about why the product was so good or the service was so bad so other people know how to judge it in the future.
4. Blogging
Blogs are a place to offer your own opinion and can be a really good place to do some reflective writing. Blogger often take a view on something and use their site as a way to share it with the world. They will often talk about the reasons why they like/dislike something - classic reflective writing.
5. During the research process
When researchers are working on a project they will often think about they way they are working and how it could be improved as well as considering different approaches to achieve their research goal. They will often record this in some way such as in a lab book and this questioning approach is a form of reflective writing.
6. In academic writing
Many students will be asked to include some form of reflection in an academic assignment, for example when relating a topic to their real life circumstances. They are also often asked to think about their opinion on or reactions to texts and other research and write about this in their own work.
Think about ... When you reflect
Think about all of the activities you do on a daily basis. Do any of these contain elements of reflective writing? Make a list of all the times you have written something reflective over the last month - it will be longer than you think!
Reflective terminology
A common mistake people make when writing reflectively is to focus too much on describing their experience. Think about some of the phrases below and try to use them when writing reflectively to help you avoid this problem:
- The most important thing was...
- At the time I felt...
- This was likely due to...
- After thinking about it...
- I learned that...
- I need to know more about...
- Later I realised...
- This was because...
- This was like...
- I wonder what would happen if...
- I'm still unsure about...
- My next steps are...
Always try and write in the first person when writing reflectively. This will help you to focus on your thoughts/feelings/experiences rather than just a description of the experience.
Using reflective writing in your academic work

Many courses will also expect you to reflect on your own learning as you progress through a particular programme. You may be asked to keep some type of reflective journal or diary. Depending on the needs of your course this may or may not be assessed but if you are using one it's important to write reflectively. This can help you to look back and see how your thinking has evolved over time - something useful for job applications in the future. Students at all levels may also be asked to reflect on the work of others, either as part of a group project or through peer review of their work. This requires a slightly different approach to reflection as you are not focused on your own work but again this is a useful skill to develop for the workplace.
You can see some useful examples of reflective writing in academia from Monash University , UNSW (the University of New South Wales) and Sage . Several of these examples also include feedback from tutors which you can use to inform your own work.
Laptop/computer/broswer/research by StockSnap via Pixabay licenced under CC0.
Now that you have a better idea of what reflective writing is and how it can be used it's time to practice some techniques.
This page has given you an understanding of what reflective writing is and where it can be used in both work and study. Now that you have a better idea of how reflective writing works the next two pages will guide you through some activities you can use to get started.
- << Previous: Barriers to reflection
- Next: Free writing >>
- Last Updated: Jun 21, 2023 3:24 PM
- URL: https://libguides.cam.ac.uk/reflectivepracticetoolkit
© Cambridge University Libraries | Accessibility | Privacy policy | Log into LibApps
Critical And Creative Thinking Community Site
Graduate program in critical and creative thinking, university of massachusetts boston, reflective practice portfolio.
A portfolio often means a showcase or a display for others of achievements, but the “Reflective Practice (and Metacognitive) Portfolio” (RPP) is designed to be a revelation of the journey that one has taken through the (MA) program. The outcome serves as a self-customized tool box and set of reminders that students intend to use in their ongoing learning and practice (including their work beyond/after CCT), embedded in a narrative. The portfolio should be created along the way of the CCT study in order to best capture your reflection close in time to the points that represent the milestones of your journey (that is, it is not recommended to wait until the end of the degree program to put together the parts all at once). Asking students to build this kind of portfolio during their studies matches the goals of personal and professional development captured by the Program overview, excerpted below.
Requirements
The portfolio is a compilation of a set of exhibits (assignments from the courses), and an additional narrative writing that goes along with each of them. Toward this end, students should choose one specific assignment from every course taken as part of the MA (including electives taken from other graduate programs during your time of study, but excluding any courses taken prior to CCT matriculation at other institutions that were brought in as transfer credits). The section at the bottom of this page gives examples of a possible choice of assignment from many of the courses. Each course’s instructor may also recommend a specific assignment as a good option for your selected assignment. Ultimately, though, it is up to the student to choose the most appropriate assignment. This assignment is one that best illustrates a key shift or change in thinking that you experienced through that course or conveys an important insight about yourself that you want to continue to move into your own practice.
Once you select the representative assignment from a course, develop a narrative that explains why this assignment was meaningful to your development. The narrative should be 2-4 paragraphs of writing (about one double-spaced page per assignment) that shows your reflection on why that is the case, and how you notice your thinking, assumptions, and/or awareness changing. The narrative uses a metacognitive approach — is a type of “guided tour” of your thinking.
Note: If your selected assignment is a final paper or other lengthy work, do not submit the entire paper as the assignment. In this case, submit an excerpt of a single relevant section (or at least indicate in your narrative which section is relevant) so that the reader knows where to focus.
Note that the above description implies that the narrative should not :
- be general commentary on the course as a whole or a broad appreciation for the course; that is, keep the narrative focused on the one specific selected assignment and its particular importance
- explain instructions for the assignment (you can mention its purpose or goal but keep that to a sentence or two)
- merely give a summary/abstract of the content of the assignment; your narrative must go beyond what is included there. Address deeper reflection on how the assignment represents important shifts in your thinking during that period, or as part of your overall development as a reflective practitioner through the CCT program. Assume that the reader can refer to the assignment itself if they want to get into the full content.
Students are strongly encouraged to submit a sample of your ongoing portfolio no later than the mid-semester point of your final term to confirm that your work meets the requirements here.
The format for creating the portfolio is flexible. At a minimum, develop the portfolio in a way that allows you to eventually capture the entire contents as a single PDF file. You may develop the portfolio as a running document where you update the narratives after each term, and then add the selected assignments as attachments. You may also develop the portfolio as a personal web site or blog, where you set up one page on the site for each course term, and then add the narratives and attached selected assignments on that page (or similar variations).
Submit the final Reflective Practice Portfolio to [email protected] (any documents or links to your site, plus a PDF compilation of the entire contents of the portfolio) no later than one week after the final Synthesis project has been submitted (typically during the CrCrTh 694 course). If you have remaining course requirements to fulfill after finishing CrCrTh 694, wait to submit the portfolio until all courses are finalized.
Portfolios are publicly viewable for at least one year after your graduation (and then longer until you ask for it to be removed). If you submit your portfolio as a link to a personal blog or web site, it is requested that you keep this site live for (at least) one year after graduation. The portfolios serve as examples for future students to help them reflect and be inspired, and so these should generally be regarded as accessible to public. It is therefore ok to be selective about what/how much you share; you may hide or redact some sections or private information within the original assignments that you don’t want to be seen by others.
Occasional CCT orientations may use past examples of portfolios to demonstrate to incoming students how these have been constructed.
Selected Examples of Portfolios
Note: Some examples below were produced before the RPP became a formal program requirement and still in piloting stage, so content may or may not fully cover the current guidelines as students used their own distinctive approaches. Refer to the sections above for current guidelines.
Andrew Castagna Billie Charles Emily Flaherty Hans Helgeson Matthew Jose Ivy Madden Bradford O’Brien Randy Valdez April Baptiste Robertson Yin Chan Geoff Keston Annie McCluskey Erin McCoy Timothy Brian Nuryadi Cynthia Romer Evan Schapiro Russell Suereth Michael Teachey Kyle Lemstrom Cara Tuttle Nadjia Edwards Timizay Ruiz Pineda Caitlin Quarrington Casey Andrews Erik Anker ( overview | documents ) Meghan Callaghan Russell DeLuca-Kavanagh David Kooharian Rhoda Maurer Lauren Taub
Suggested Selected Assignments for Courses
(others may be substituted as appropriate)
- CrCrTh 601: Critical Thinking Manifesto, or individual Reflection Paper
- CrCrTh 602: Second Reflective Review of Diary
- CrCrTh 603: Weekly Paper or Final Paper
- CrCrTh 611: Process Review, or Final Written Plan
- CrCrTh 612: Self-Reflective Assessment, or Reflection Assignment
- CrCrTh 615: Manifesto, or Final Project
- CrCrTh 616: Final Paper or individual discussion posts
- CrCrTh 618: Plan for Practice; Critical Reflection Paper
- CrCrTh 619: Short Paper
- CrCrTh 627: Current Issues Analysis Paper
- CrCrTh 630: selection from Creative Products
- CrCrTh 640: Research Plan
- CrCrTh 645: Final Paper
- CrCrTh 649: Education Unit/Curriculum
- CrCrTh 650: selection from Creative Products
- CrCrTh 651: General Principles Journal/Summary
- CrCrTh 652: General Principles Journal/Summary
- CrCrTh 655: Plan for Classroom Implementation
- CrCrTh 670: Expert Teaching and Learning Portfolio
- CrCrTh 688: Progress Report or Plan for Practice
- CrCrTh 692: Self-assessment
- CrCrTh 693: Process Review
- CrCrTh 694: Excerpts from Synthesis paper; Exit Self-assessment
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples
What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples
Published on May 30, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment .
To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources .
Critical thinking skills help you to:
- Identify credible sources
- Evaluate and respond to arguments
- Assess alternative viewpoints
- Test hypotheses against relevant criteria
Table of contents
Why is critical thinking important, critical thinking examples, how to think critically, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about critical thinking.
Critical thinking is important for making judgments about sources of information and forming your own arguments. It emphasizes a rational, objective, and self-aware approach that can help you to identify credible sources and strengthen your conclusions.
Critical thinking is important in all disciplines and throughout all stages of the research process . The types of evidence used in the sciences and in the humanities may differ, but critical thinking skills are relevant to both.
In academic writing , critical thinking can help you to determine whether a source:
- Is free from research bias
- Provides evidence to support its research findings
- Considers alternative viewpoints
Outside of academia, critical thinking goes hand in hand with information literacy to help you form opinions rationally and engage independently and critically with popular media.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Critical thinking can help you to identify reliable sources of information that you can cite in your research paper . It can also guide your own research methods and inform your own arguments.
Outside of academia, critical thinking can help you to be aware of both your own and others’ biases and assumptions.
Academic examples
However, when you compare the findings of the study with other current research, you determine that the results seem improbable. You analyze the paper again, consulting the sources it cites.
You notice that the research was funded by the pharmaceutical company that created the treatment. Because of this, you view its results skeptically and determine that more independent research is necessary to confirm or refute them. Example: Poor critical thinking in an academic context You’re researching a paper on the impact wireless technology has had on developing countries that previously did not have large-scale communications infrastructure. You read an article that seems to confirm your hypothesis: the impact is mainly positive. Rather than evaluating the research methodology, you accept the findings uncritically.
Nonacademic examples
However, you decide to compare this review article with consumer reviews on a different site. You find that these reviews are not as positive. Some customers have had problems installing the alarm, and some have noted that it activates for no apparent reason.
You revisit the original review article. You notice that the words “sponsored content” appear in small print under the article title. Based on this, you conclude that the review is advertising and is therefore not an unbiased source. Example: Poor critical thinking in a nonacademic context You support a candidate in an upcoming election. You visit an online news site affiliated with their political party and read an article that criticizes their opponent. The article claims that the opponent is inexperienced in politics. You accept this without evidence, because it fits your preconceptions about the opponent.
There is no single way to think critically. How you engage with information will depend on the type of source you’re using and the information you need.
However, you can engage with sources in a systematic and critical way by asking certain questions when you encounter information. Like the CRAAP test , these questions focus on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
When encountering information, ask:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert in their field?
- What do they say? Is their argument clear? Can you summarize it?
- When did they say this? Is the source current?
- Where is the information published? Is it an academic article? Is it peer-reviewed ?
- Why did the author publish it? What is their motivation?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence? Does it rely on opinion, speculation, or appeals to emotion ? Do they address alternative arguments?
Critical thinking also involves being aware of your own biases, not only those of others. When you make an argument or draw your own conclusions, you can ask similar questions about your own writing:
- Am I only considering evidence that supports my preconceptions?
- Is my argument expressed clearly and backed up with credible sources?
- Would I be convinced by this argument coming from someone else?
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Critical thinking skills include the ability to:
You can assess information and arguments critically by asking certain questions about the source. You can use the CRAAP test , focusing on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
Ask questions such as:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence?
A credible source should pass the CRAAP test and follow these guidelines:
- The information should be up to date and current.
- The author and publication should be a trusted authority on the subject you are researching.
- The sources the author cited should be easy to find, clear, and unbiased.
- For a web source, the URL and layout should signify that it is trustworthy.
Information literacy refers to a broad range of skills, including the ability to find, evaluate, and use sources of information effectively.
Being information literate means that you:
- Know how to find credible sources
- Use relevant sources to inform your research
- Understand what constitutes plagiarism
- Know how to cite your sources correctly
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search, interpret, and recall information in a way that aligns with our pre-existing values, opinions, or beliefs. It refers to the ability to recollect information best when it amplifies what we already believe. Relatedly, we tend to forget information that contradicts our opinions.
Although selective recall is a component of confirmation bias, it should not be confused with recall bias.
On the other hand, recall bias refers to the differences in the ability between study participants to recall past events when self-reporting is used. This difference in accuracy or completeness of recollection is not related to beliefs or opinions. Rather, recall bias relates to other factors, such as the length of the recall period, age, and the characteristics of the disease under investigation.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/critical-thinking/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, student guide: information literacy | meaning & examples, what are credible sources & how to spot them | examples, applying the craap test & evaluating sources, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Academic Resources
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Catalog
- Academic Success
- BlueM@il (Email)
- Campus Connect
- DePaul Central
- Desire2Learn (D2L)
Campus Resources
- Campus Security
- Campus Maps
University Resources
- Technology Help Desk
Information For
- Alumni & Friends
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Teaching Guides
- How Students Learn
- Course Design
- Instructional Methods
- Aligning with Learning Goals
- Critical Thinking
- Deterring Plagiarism
- Integrative Learning
- Feedback & Grading
- Learning Activities
- Flex Teaching
- Online Teaching
- Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Reflective Practice
- Inclusive Teaching
- Teaching at DePaul
- Support Services
- Technology Tools
Teaching Commons > Teaching Guides > Assignment Design > Critical Thinking
Designing Assignments for Critical Thinking

- Tim van Gelder from the University of Melbourne offers some guidelines for teaching critical thinking based on key ideas from cognitive science in his article "Teaching Critical Thinking: Some Lessons fro m Cognitive Science".
- The IDEA Center at Kansas State University offers information on designing assignments and learning environments that enhance thinking skills.
- The University of Nebraska at Lincoln offers an overview of teaching critical thinking , including a number of examples across the disciplines
Stephen Brookfield On Critical And Creative Thinking
The 2012 Fall Forum on Teaching and Learning featured a keynote presentation by the noted expert on adult education, Stephen Brookfield, who is the John Ireland Endowed Chair at the University of St. Thomas in St. Paul, Minnesota. You can watch the keynote below.
TLA Handouts On Teaching For Critical Thinking
- Definitions of Critical Thinking
- Argument mapping allows students to see the underlying structure of an argument.
- Creating cognitive dissonance to help students question their pre-existing or intuitive ideas.
- Scaffolding assignments so that they gradually increase in cognitive complexity.
- Teaching for transfer to help students understand their critical thinking process.
- Critical thinking Internet resources and selected bibliography.
Further Resources
Bean, J.C. (2001). Engaging Ideas: The Professor's Guide to Integrating Writing, Critical Thinking, and Active Learning in the Classroom. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Brookfield, Stephen. (2011). Teaching for Critical Thinking: Tools and Techniques to Help Students Question Their Assumptions. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Critical Reflection
Critical reflection is a “meaning-making process” that helps us set goals, use what we’ve learned in the past to inform future action and consider the real-life implications of our thinking. It is the link between thinking and doing, and at its best, it can be transformative (Dewey, 1916/1944; Schön, 1983; Rodgers, 2002). Without reflection, experience alone might cause us to “reinforce stereotypes…, offer simplistic solutions to complex problems and generalize inaccurately based on limited data” (Ash & Clayton, 2009, p.26). Engaging in critical reflection, however, helps us articulate questions, confront bias, examine causality, contrast theory with practice and identify systemic issues all of which helps foster critical evaluation and knowledge transfer (Ash & Clayton, 2009, p. 27). While critical reflection may come more easily for some students than others, it is a skill that can be learned through practice and feedback (Dewey, 1933, Rodgers, 2002).
Guidelines for Integrating Reflections into Your Course
Incorporating the following characteristics into the design of your reflective activities can help make the reflective process as effective as possible.
Create Curiosity. When students learn new concepts or subject matter, they often experience a sense of uncertainty and disequilibrium until they can make sense of the new information. Critical reflection is necessary to assimilate the new information and resolve the state of disequilibrium. It takes time to do well; sparking students’ curiosity can motivate them to engage in the reflective process(Dewey, 1933; Rodgers, 2002). Providing appropriate question prompts, activities, problems and tasks can help spark the necessary curiosity. See CTE's online resource: Reflection Framework and Prompts .
Make it Continual. Build in “periodic, structured opportunities to reflect and integrate learning” (Kuh, O’Donnell & Reed, 2013). Because critical reflection is a defined way of thinking, students have to have numerous opportunities throughout the course and the program to practice and receive feedback.
Connect It. Activities to promote reflection can range from writing/rewriting exercises, problem solving activities, discussions, role playing/simulations, and group work to name a few. To be effective, though, be sure to explicitly connect the reflective activities to course/program learning outcomes, specific assignments, course concepts or experiences . For an example of role playing/simulations, please see CTE's resource, an interview (YouTube) with Dr. Veronica Kitchen about Using Simulations in the Classroom .
Give it Context. Design reflective activities to support integration of learning across courses and to engage students with “big questions” related to community/public issues that matter beyond the classroom. Ideally, reflective activities should ask students to consider messy, ill-defined problems that do not have a ‘right’ answer (Moon, 1999). This helps move them towards higher order thinking and higher levels of reflection.
Consider your Class Size. Assessing and providing feedback to reflections require time and resources. For smaller classes, it might be manageable to assess individual reflections through journals, logs, and blogs. For larger classes, consider facilitating whole class discussions and opportunities for peer feedback. Dividing a large class into smaller groups for discussions and small group brainstorming sessions can provide the practice and feedback students need without all the feedback having to come from you, the instructor. Having students share reflections through ePortfolios is yet another way for students to receive feedback from peers. See CTE's online resource about ePortfolios .
Model the Reflective Process. During class discussions, model the reflective process by asking the kinds of questions that members of your discipline ask. Explicitly point out how you support a claim with evidence. As you go through the process, explain how you are modeling the critical reflection process. Providing students with a rubric may help them practice the process themselves.
Breakdown the Assignment. When you provide students with details for a particular assignment, lead a discussion asking them as a group to outline a process for tackling the assignment. Have each student then create a personal plan for addressing the areas which might cause them more difficulty. Ask students to hand in different pieces of the assignment throughout the term, providing feedback to the various components. Over time, less guidance and feedback will be required to help students with the reflective thinking process.
Encourage Multiple Perspectives. Being exposed to different perspectives (through discussions with classmates, or through resources such readings, websites, case studies, simulations that represent different points of view), and being able to participate in a dialogue with others (peers, instructors) about matters of importance is critical to the reflective thinking process. Having students work on collaborative projects can facilitate this; they learn to listen to others and consider different approaches to solving problems.
Provide a Safe Environment where students can explore and articulate emotional responses. Students might not mind sharing their knowledge and understanding about content with their classmates but may be less inclined to share emotional responses with others. In these cases, consider splitting up the task so that the descriptive, non-personal component is done in class and the articulation of learning part is handed in individually to a TA or instructor.
Assess It. Making reflections part of a course grade encourages students to engage in the reflective process, helps them track their growth and development over time, and signals to them that critical reflection is a worthwhile and valued activity. Provide students with ‘frequent, timely and constructive feedback’ to the reflective activities.
Provide Clear Marking Criteria and Exemplars. Clearly state the criteria for success and show students an example of a good reflection. Explain why the example is a good one (e.g., show how the reflection provides concrete examples to support the observations, and ties the observations back to the course content/learning outcome). Provide students with opportunities to self-assess or provide peer-feedback using the rubric that you will use to assess their reflections.
Assignment and Rubric Examples:
See the links below for examples of critical reflection assignments that have been shared with CTE. Some of the instructors have also included their assessment rubrics along with the assignment instructions.
- Reflecting on Professional Skill Development
- Becoming Reflexive Practitioners
- ePortfolio: Inspired Insights, Magnificent Failures, and Unanticipated Connections
- AAC&U Integrative Learning VALUE rubric
- Higher Levels of Reflection Rubric
Choose Prompts that Suit Your Goals
Use language that suits your course and discipline. The term ‘reflection’ has come to mean different things to different people (Rodgers, 2002). Use a term that makes sense to your discipline. Science students might roll their eyes if asked to reflect on personal development in a chemistry course. Is there a term that your discipline uses instead of the term reflection (design notes, lab notes, documentation of bugs)?
Choose the type of reflection that suits your goals. Reflective activities can be of two types: one type helps students focus on their growth and development, and on their personal learning process and another type fosters students’ capacity to think deeply about content and concepts. Be sure to choose reflective prompts that align with your course goals.
- Process Reflection. This type of reflection promptsstudents to think about their progress and the strategies they are using while they are working on a project or assignment (e.g., where are you with your project? What challenges are you having? What are you planning to do about those challenges? What problems did you encounter in completing the assignment? How did you troubleshoot them? What still needs work?) This can be done individually or, in large classes, consider using small group discussions.
- Inward-Looking Reflection. When reflecting inward, students focus on their personal strengths, gaps, resources, standards, values, response to challenges, strategies, etc.
- Outward-Looking Reflection. By observing others, students can build their awareness of alternative perspectives and ways of doing things. When contrasts are noted, students can give examples to support their observations.
- Forward-Looking Reflection. At the beginning of a course, project, or assignment, prompt students to think about which components look familiar and which look more challenging and difficult, and why. Towards the end of the course, hand these lists back to the students and have them discuss whether they have met their goals. As a class, have the students list which of the goals they believe they achieved, and which they did not. Alternatively, have students write a letter to the students who take the course next, giving advice and encouragement.
- Backward-Looking Reflection . At the end of a project, work term or volunteer experience a backward-looking reflection is a good way for students to take stock of their experience.
Examples of Reflection Models and Reflection Questions:
- Sample Reflection Questions
- Eight Reflection Models
- Reflections to Foster Deep Thinking & Connection Making
If you would like support applying these tips to your own teaching, CTE staff members are here to help. View the CTE Support page to find the most relevant staff member to contact.
- AAC&U Integrative Learning VALUE rubrics retrieved from https://www.aacu.org/value-rubrics
- Habits of Mind: The Questions Intelligent Thinkers Ask that Help Them Solve Problems and Make Decisions retrieved from https://www.edutopia.org/pdfs/stw/edutopia-stw-assessment-high-sch-humanities-habits-of-mind.pdf
- Sample reflection questions retrieved from https://www.edutopia.org/pdfs/stw/edutopia-stw-replicatingPBL-21stCAcad-reflection-questions.pdf
- Teaching Metacognitive Skills CTE tipsheet retrieved from https://uwaterloo.ca/centre-for-teaching-excellence/teaching-resources/teaching-tips/metacognitive
- Ash, S.L., & Clayton, P. H. (2009). Generating, deepening, and documenting learning: The power of critical reflection in applied learning. Journal of Applied Learning in Higher Education, 1(1), 25-48.
- Boss, S. (2009). High tech reflection strategies make learning stick retrieved from http://www.edutopia.org/student-reflection-blogs-journals-technology
- Dewey, J. (1916/1944). Democracy and education: An introduction to the philosophy of education. New York: The Free Press.
- Kalman, C.S., Sobhanzadeh, M., Thompson, R., Ibrahim, A., Wang, X. (2015). Combination of interventions can change students’ epistemological beliefs. Physical Review Special Topics Physics Education Research, 11(2):020136-. doi:10.1103/PhysRevSTPER.11.020136
- Kuh, G. D., O’Donnell, K., & Reed, S. (2013). Ensuring quality and taking high-impact practices to scale. Washington, DC: Association of American Colleges and Universities .
- Moon, J. (1999). Reflection in learning and professional development. Abingdon, Oxon: RoutledgeFalmer.
- Rodgers, C. (2002). Defining reflection: Another look at John Dewey and reflective thinking. The Teachers College Record , 104 (4), 842-866.
- Schön, D. A. (1983). The reflective practitioner: How professionals think in action (Vol. 5126). Basic books.
Catalog search
Teaching tip categories.
- Assessment and feedback
- Blended Learning and Educational Technologies
- Career Development
- Course Design
- Course Implementation
- Inclusive Teaching and Learning
- Learning activities
- Support for Student Learning
- Support for TAs
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
Reflective writing is a process of identifying, questioning, and critically evaluating course-based learning opportunities, integrated with your own observations, experiences, impressions, beliefs, assumptions, or biases, and which describes how this process stimulated new or creative understanding about the content of the course.
A reflective paper describes and explains in an introspective, first person narrative, your reactions and feelings about either a specific element of the class [e.g., a required reading; a film shown in class] or more generally how you experienced learning throughout the course. Reflective writing assignments can be in the form of a single paper, essays, portfolios, journals, diaries, or blogs. In some cases, your professor may include a reflective writing assignment as a way to obtain student feedback that helps improve the course, either in the moment or for when the class is taught again.
How to Write a Reflection Paper . Academic Skills, Trent University; Writing a Reflection Paper . Writing Center, Lewis University; Critical Reflection . Writing and Communication Centre, University of Waterloo; Tsingos-Lucas et al. "Using Reflective Writing as a Predictor of Academic Success in Different Assessment Formats." American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education 81 (2017): Article 8.
Benefits of Reflective Writing Assignments
As the term implies, a reflective paper involves looking inward at oneself in contemplating and bringing meaning to the relationship between course content and the acquisition of new knowledge . Educational research [Bolton, 2010; Ryan, 2011; Tsingos-Lucas et al., 2017] demonstrates that assigning reflective writing tasks enhances learning because it challenges students to confront their own assumptions, biases, and belief systems around what is being taught in class and, in so doing, stimulate student’s decisions, actions, attitudes, and understanding about themselves as learners and in relation to having mastery over their learning. Reflection assignments are also an opportunity to write in a first person narrative about elements of the course, such as the required readings, separate from the exegetic and analytical prose of academic research papers.
Reflection writing often serves multiple purposes simultaneously. In no particular order, here are some of reasons why professors assign reflection papers:
- Enhances learning from previous knowledge and experience in order to improve future decision-making and reasoning in practice . Reflective writing in the applied social sciences enhances decision-making skills and academic performance in ways that can inform professional practice. The act of reflective writing creates self-awareness and understanding of others. This is particularly important in clinical and service-oriented professional settings.
- Allows students to make sense of classroom content and overall learning experiences in relation to oneself, others, and the conditions that shaped the content and classroom experiences . Reflective writing places you within the course content in ways that can deepen your understanding of the material. Because reflective thinking can help reveal hidden biases, it can help you critically interrogate moments when you do not like or agree with discussions, readings, or other aspects of the course.
- Increases awareness of one’s cognitive abilities and the evidence for these attributes . Reflective writing can break down personal doubts about yourself as a learner and highlight specific abilities that may have been hidden or suppressed due to prior assumptions about the strength of your academic abilities [e.g., reading comprehension; problem-solving skills]. Reflective writing, therefore, can have a positive affective [i.e., emotional] impact on your sense of self-worth.
- Applying theoretical knowledge and frameworks to real experiences . Reflective writing can help build a bridge of relevancy between theoretical knowledge and the real world. In so doing, this form of writing can lead to a better understanding of underlying theories and their analytical properties applied to professional practice.
- Reveals shortcomings that the reader will identify . Evidence suggests that reflective writing can uncover your own shortcomings as a learner, thereby, creating opportunities to anticipate the responses of your professor may have about the quality of your coursework. This can be particularly productive if the reflective paper is written before final submission of an assignment.
- Helps students identify their tacit [a.k.a., implicit] knowledge and possible gaps in that knowledge . Tacit knowledge refers to ways of knowing rooted in lived experience, insight, and intuition rather than formal, codified, categorical, or explicit knowledge. In so doing, reflective writing can stimulate students to question their beliefs about a research problem or an element of the course content beyond positivist modes of understanding and representation.
- Encourages students to actively monitor their learning processes over a period of time . On-going reflective writing in journals or blogs, for example, can help you maintain or adapt learning strategies in other contexts. The regular, purposeful act of reflection can facilitate continuous deep thinking about the course content as it evolves and changes throughout the term. This, in turn, can increase your overall confidence as a learner.
- Relates a student’s personal experience to a wider perspective . Reflection papers can help you see the big picture associated with the content of a course by forcing you to think about the connections between scholarly content and your lived experiences outside of school. It can provide a macro-level understanding of one’s own experiences in relation to the specifics of what is being taught.
- If reflective writing is shared, students can exchange stories about their learning experiences, thereby, creating an opportunity to reevaluate their original assumptions or perspectives . In most cases, reflective writing is only viewed by your professor in order to ensure candid feedback from students. However, occasionally, reflective writing is shared and openly discussed in class. During these discussions, new or different perspectives and alternative approaches to solving problems can be generated that would otherwise be hidden. Sharing student's reflections can also reveal collective patterns of thought and emotions about a particular element of the course.
Bolton, Gillie. Reflective Practice: Writing and Professional Development . London: Sage, 2010; Chang, Bo. "Reflection in Learning." Online Learning 23 (2019), 95-110; Cavilla, Derek. "The Effects of Student Reflection on Academic Performance and Motivation." Sage Open 7 (July-September 2017): 1–13; Culbert, Patrick. “Better Teaching? You Can Write On It “ Liberal Education (February 2022); McCabe, Gavin and Tobias Thejll-Madsen. The Reflection Toolkit . University of Edinburgh; The Purpose of Reflection . Introductory Composition at Purdue University; Practice-based and Reflective Learning . Study Advice Study Guides, University of Reading; Ryan, Mary. "Improving Reflective Writing in Higher Education: A Social Semiotic Perspective." Teaching in Higher Education 16 (2011): 99-111; Tsingos-Lucas et al. "Using Reflective Writing as a Predictor of Academic Success in Different Assessment Formats." American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education 81 (2017): Article 8; What Benefits Might Reflective Writing Have for My Students? Writing Across the Curriculum Clearinghouse; Rykkje, Linda. "The Tacit Care Knowledge in Reflective Writing: A Practical Wisdom." International Practice Development Journal 7 (September 2017): Article 5; Using Reflective Writing to Deepen Student Learning . Center for Writing, University of Minnesota.
How to Approach Writing a Reflection Paper
Thinking About Reflective Thinking
Educational theorists have developed numerous models of reflective thinking that your professor may use to frame a reflective writing assignment. These models can help you systematically interpret your learning experiences, thereby ensuring that you ask the right questions and have a clear understanding of what should be covered. A model can also represent the overall structure of a reflective paper. Each model establishes a different approach to reflection and will require you to think about your writing differently. If you are unclear how to fit your writing within a particular reflective model, seek clarification from your professor. There are generally two types of reflective writing assignments, each approached in slightly different ways.
1. Reflective Thinking about Course Readings
This type of reflective writing focuses on thoughtfully thinking about the course readings that underpin how most students acquire new knowledge and understanding about the subject of a course. Reflecting on course readings is often assigned in freshmen-level, interdisciplinary courses where the required readings examine topics viewed from multiple perspectives and, as such, provide different ways of analyzing a topic, issue, event, or phenomenon. The purpose of reflective thinking about course readings in the social and behavioral sciences is to elicit your opinions, beliefs, and feelings about the research and its significance. This type of writing can provide an opportunity to break down key assumptions you may have and, in so doing, reveal potential biases in how you interpret the scholarship.
If you are assigned to reflect on course readings, consider the following methods of analysis as prompts that can help you get started :
- Examine carefully the main introductory elements of the reading, including the purpose of the study, the theoretical framework being used to test assumptions, and the research questions being addressed. Think about what ideas stood out to you. Why did they? Were these ideas new to you or familiar in some way based on your own lived experiences or prior knowledge?
- Develop your ideas around the readings by asking yourself, what do I know about this topic? Where does my existing knowledge about this topic come from? What are the observations or experiences in my life that influence my understanding of the topic? Do I agree or disagree with the main arguments, recommended course of actions, or conclusions made by the author(s)? Why do I feel this way and what is the basis of these feelings?
- Make connections between the text and your own beliefs, opinions, or feelings by considering questions like, how do the readings reinforce my existing ideas or assumptions? How the readings challenge these ideas or assumptions? How does this text help me to better understand this topic or research in ways that motivate me to learn more about this area of study?
2. Reflective Thinking about Course Experiences
This type of reflective writing asks you to critically reflect on locating yourself at the conceptual intersection of theory and practice. The purpose of experiential reflection is to evaluate theories or disciplinary-based analytical models based on your introspective assessment of the relationship between hypothetical thinking and practical reality; it offers a way to consider how your own knowledge and skills fit within professional practice. This type of writing also provides an opportunity to evaluate your decisions and actions, as well as how you managed your subsequent successes and failures, within a specific theoretical framework. As a result, abstract concepts can crystallize and become more relevant to you when considered within your own experiences. This can help you formulate plans for self-improvement as you learn.
If you are assigned to reflect on your experiences, consider the following questions as prompts to help you get started :
- Contextualize your reflection in relation to the overarching purpose of the course by asking yourself, what did you hope to learn from this course? What were the learning objectives for the course and how did I fit within each of them? How did these goals relate to the main themes or concepts of the course?
- Analyze how you experienced the course by asking yourself, what did I learn from this experience? What did I learn about myself? About working in this area of research and study? About how the course relates to my place in society? What assumptions about the course were supported or refuted?
- Think introspectively about the ways you experienced learning during the course by asking yourself, did your learning experiences align with the goals or concepts of the course? Why or why do you not feel this way? What was successful and why do you believe this? What would you do differently and why is this important? How will you prepare for a future experience in this area of study?
NOTE: If you are assigned to write a journal or other type of on-going reflection exercise, a helpful approach is to reflect on your reflections by re-reading what you have already written. In other words, review your previous entries as a way to contextualize your feelings, opinions, or beliefs regarding your overall learning experiences. Over time, this can also help reveal hidden patterns or themes related to how you processed your learning experiences. Consider concluding your reflective journal with a summary of how you felt about your learning experiences at critical junctures throughout the course, then use these to write about how you grew as a student learner and how the act of reflecting helped you gain new understanding about the subject of the course and its content.
ANOTHER NOTE: Regardless of whether you write a reflection paper or a journal, do not focus your writing on the past. The act of reflection is intended to think introspectively about previous learning experiences. However, reflective thinking should document the ways in which you progressed in obtaining new insights and understandings about your growth as a learner that can be carried forward in subsequent coursework or in future professional practice. Your writing should reflect a furtherance of increasing personal autonomy and confidence gained from understanding more about yourself as a learner.
Structure and Writing Style
There are no strict academic rules for writing a reflective paper. Reflective writing may be assigned in any class taught in the social and behavioral sciences and, therefore, requirements for the assignment can vary depending on disciplinary-based models of inquiry and learning. The organization of content can also depend on what your professor wants you to write about or based on the type of reflective model used to frame the writing assignment. Despite these possible variations, below is a basic approach to organizing and writing a good reflective paper, followed by a list of problems to avoid.
Pre-flection
In most cases, it's helpful to begin by thinking about your learning experiences and outline what you want to focus on before you begin to write the paper. This can help you organize your thoughts around what was most important to you and what experiences [good or bad] had the most impact on your learning. As described by the University of Waterloo Writing and Communication Centre, preparing to write a reflective paper involves a process of self-analysis that can help organize your thoughts around significant moments of in-class knowledge discovery.
- Using a thesis statement as a guide, note what experiences or course content stood out to you , then place these within the context of your observations, reactions, feelings, and opinions. This will help you develop a rough outline of key moments during the course that reflect your growth as a learner. To identify these moments, pose these questions to yourself: What happened? What was my reaction? What were my expectations and how were they different from what transpired? What did I learn?
- Critically think about your learning experiences and the course content . This will help you develop a deeper, more nuanced understanding about why these moments were significant or relevant to you. Use the ideas you formulated during the first stage of reflecting to help you think through these moments from both an academic and personal perspective. From an academic perspective, contemplate how the experience enhanced your understanding of a concept, theory, or skill. Ask yourself, did the experience confirm my previous understanding or challenge it in some way. As a result, did this highlight strengths or gaps in your current knowledge? From a personal perspective, think introspectively about why these experiences mattered, if previous expectations or assumptions were confirmed or refuted, and if this surprised, confused, or unnerved you in some way.
- Analyze how these experiences and your reactions to them will shape your future thinking and behavior . Reflection implies looking back, but the most important act of reflective writing is considering how beliefs, assumptions, opinions, and feelings were transformed in ways that better prepare you as a learner in the future. Note how this reflective analysis can lead to actions you will take as a result of your experiences, what you will do differently, and how you will apply what you learned in other courses or in professional practice.
Basic Structure and Writing Style
Reflective Background and Context
The first part of your reflection paper should briefly provide background and context in relation to the content or experiences that stood out to you. Highlight the settings, summarize the key readings, or narrate the experiences in relation to the course objectives. Provide background that sets the stage for your reflection. You do not need to go into great detail, but you should provide enough information for the reader to understand what sources of learning you are writing about [e.g., course readings, field experience, guest lecture, class discussions] and why they were important. This section should end with an explanatory thesis statement that expresses the central ideas of your paper and what you want the readers to know, believe, or understand after they finish reading your paper.
Reflective Interpretation
Drawing from your reflective analysis, this is where you can be personal, critical, and creative in expressing how you felt about the course content and learning experiences and how they influenced or altered your feelings, beliefs, assumptions, or biases about the subject of the course. This section is also where you explore the meaning of these experiences in the context of the course and how you gained an awareness of the connections between these moments and your own prior knowledge.
Guided by your thesis statement, a helpful approach is to interpret your learning throughout the course with a series of specific examples drawn from the course content and your learning experiences. These examples should be arranged in sequential order that illustrate your growth as a learner. Reflecting on each example can be done by: 1) introducing a theme or moment that was meaningful to you, 2) describing your previous position about the learning moment and what you thought about it, 3) explaining how your perspective was challenged and/or changed and why, and 4) introspectively stating your current or new feelings, opinions, or beliefs about that experience in class.
It is important to include specific examples drawn from the course and placed within the context of your assumptions, thoughts, opinions, and feelings. A reflective narrative without specific examples does not provide an effective way for the reader to understand the relationship between the course content and how you grew as a learner.
Reflective Conclusions
The conclusion of your reflective paper should provide a summary of your thoughts, feelings, or opinions regarding what you learned about yourself as a result of taking the course. Here are several ways you can frame your conclusions based on the examples you interpreted and reflected on what they meant to you. Each example would need to be tied to the basic theme [thesis statement] of your reflective background section.
- Your reflective conclusions can be described in relation to any expectations you had before taking the class [e.g., “I expected the readings to not be relevant to my own experiences growing up in a rural community, but the research actually helped me see that the challenges of developing my identity as a child of immigrants was not that unusual...”].
- Your reflective conclusions can explain how what you learned about yourself will change your actions in the future [e.g., “During a discussion in class about the challenges of helping homeless people, I realized that many of these people hate living on the street but lack the ability to see a way out. This made me realize that I wanted to take more classes in psychology...”].
- Your reflective conclusions can describe major insights you experienced a critical junctures during the course and how these moments enhanced how you see yourself as a student learner [e.g., "The guest speaker from the Head Start program made me realize why I wanted to pursue a career in elementary education..."].
- Your reflective conclusions can reconfigure or reframe how you will approach professional practice and your understanding of your future career aspirations [e.g.,, "The course changed my perceptions about seeking a career in business finance because it made me realize I want to be more engaged in customer service..."]
- Your reflective conclusions can explore any learning you derived from the act of reflecting itself [e.g., “Reflecting on the course readings that described how minority students perceive campus activities helped me identify my own biases about the benefits of those activities in acclimating to campus life...”].
NOTE: The length of a reflective paper in the social sciences is usually less than a traditional research paper. However, don’t assume that writing a reflective paper is easier than writing a research paper. A well-conceived critical reflection paper often requires as much time and effort as a research paper because you must purposeful engage in thinking about your learning in ways that you may not be comfortable with or used to. This is particular true while preparing to write because reflective papers are not as structured as a traditional research paper and, therefore, you have to think deliberately about how you want to organize the paper and what elements of the course you want to reflect upon.
ANOTHER NOTE: Do not limit yourself to using only text in reflecting on your learning. If you believe it would be helpful, consider using creative modes of thought or expression such as, illustrations, photographs, or material objects that reflects an experience related to the subject of the course that was important to you [e.g., like a ticket stub to a renowned speaker on campus]. Whatever non-textual element you include, be sure to describe the object's relevance to your personal relationship to the course content.
Problems to Avoid
A reflective paper is not a “mind dump” . Reflective papers document your personal and emotional experiences and, therefore, they do not conform to rigid structures, or schema, to organize information. However, the paper should not be a disjointed, stream-of-consciousness narrative. Reflective papers are still academic pieces of writing that require organized thought, that use academic language and tone , and that apply intellectually-driven critical thinking to the course content and your learning experiences and their significance.
A reflective paper is not a research paper . If you are asked to reflect on a course reading, the reflection will obviously include some description of the research. However, the goal of reflective writing is not to present extraneous ideas to the reader or to "educate" them about the course. The goal is to share a story about your relationship with the learning objectives of the course. Therefore, unlike research papers, you are expected to write from a first person point of view which includes an introspective examination of your own opinions, feelings, and personal assumptions.
A reflection paper is not a book review . Descriptions of the course readings using your own words is not a reflective paper. Reflective writing should focus on how you understood the implications of and were challenged by the course in relation to your own lived experiences or personal assumptions, combined with explanations of how you grew as a student learner based on this internal dialogue. Remember that you are the central object of the paper, not the research materials.
A reflective paper is not an all-inclusive meditation. Do not try to cover everything. The scope of your paper should be well-defined and limited to your specific opinions, feelings, and beliefs about what you determine to be the most significant content of the course and in relation to the learning that took place. Reflections should be detailed enough to covey what you think is important, but your thoughts should be expressed concisely and coherently [as is true for any academic writing assignment].
Critical Reflection . Writing and Communication Centre, University of Waterloo; Critical Reflection: Journals, Opinions, & Reactions . University Writing Center, Texas A&M University; Connor-Greene, Patricia A. “Making Connections: Evaluating the Effectiveness of Journal Writing in Enhancing Student Learning.” Teaching of Psychology 27 (2000): 44-46; Good vs. Bad Reflection Papers , Franklin University; Dyment, Janet E. and Timothy S. O’Connell. "The Quality of Reflection in Student Journals: A Review of Limiting and Enabling Factors." Innovative Higher Education 35 (2010): 233-244: How to Write a Reflection Paper . Academic Skills, Trent University; Amelia TaraJane House. Reflection Paper . Cordia Harrington Center for Excellence, University of Arkansas; Ramlal, Alana, and Désirée S. Augustin. “Engaging Students in Reflective Writing: An Action Research Project.” Educational Action Research 28 (2020): 518-533; Writing a Reflection Paper . Writing Center, Lewis University; McGuire, Lisa, Kathy Lay, and Jon Peters. “Pedagogy of Reflective Writing in Professional Education.” Journal of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning (2009): 93-107; Critical Reflection . Writing and Communication Centre, University of Waterloo; How Do I Write Reflectively? Academic Skills Toolkit, University of New South Wales Sydney; Reflective Writing . Skills@Library. University of Leeds; Walling, Anne, Johanna Shapiro, and Terry Ast. “What Makes a Good Reflective Paper?” Family Medicine 45 (2013): 7-12; Williams, Kate, Mary Woolliams, and Jane Spiro. Reflective Writing . 2nd edition. London: Red Globe Press, 2020; Yeh, Hui-Chin, Shih-hsien Yang, Jo Shan Fu, and Yen-Chen Shih. “Developing College Students’ Critical Thinking through Reflective Writing.” Higher Education Research and Development (2022): 1-16.
Writing Tip
Focus on Reflecting, Not on Describing
Minimal time and effort should be spent describing the course content you are asked to reflect upon. The purpose of a reflection assignment is to introspectively contemplate your reactions to and feeling about an element of the course. D eflecting the focus away from your own feelings by concentrating on describing the course content can happen particularly if "talking about yourself" [i.e., reflecting] makes you uncomfortable or it is intimidating. However, the intent of reflective writing is to overcome these inhibitions so as to maximize the benefits of introspectively assessing your learning experiences. Keep in mind that, if it is relevant, your feelings of discomfort could be a part of how you critically reflect on any challenges you had during the course [e.g., you realize this discomfort inhibited your willingness to ask questions during class, it fed into your propensity to procrastinate, or it made it difficult participating in groups].
Writing a Reflection Paper . Writing Center, Lewis University; Reflection Paper . Cordia Harrington Center for Excellence, University of Arkansas.
Another Writing Tip
Helpful Videos about Reflective Writing
These two short videos succinctly describe how to approach a reflective writing assignment. They are produced by the Academic Skills department at the University of Melbourne and the Skills Team of the University of Hull, respectively.
- << Previous: Writing a Policy Memo
- Next: Writing a Research Proposal >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning

About this free course
Become an ou student, download this course, share this free course.

Start this free course now. Just create an account and sign in. Enrol and complete the course for a free statement of participation or digital badge if available.
4 Models of reflection – core concepts for reflective thinking
The theories behind reflective thinking and reflective practice are complex. Most are beyond the scope of this course, and there are many different models. However, an awareness of the similarities and differences between some of these should help you to become familiar with the core concepts, allow you to explore deeper level reflective questions, and provide a way to better structure your learning.
Boud’s triangular representation (Figure 2) can be viewed as perhaps the simplest model. This cyclic model represents the core notion that reflection leads to further learning. Although it captures the essentials (that experience and reflection lead to learning), the model does not guide us as to what reflection might consist of, or how the learning might translate back into experience. Aligning key reflective questions to this model would help (Figure 3).
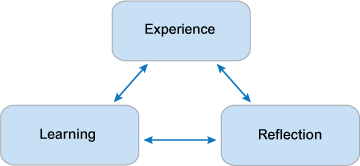
This figure contains three boxes, with arrows linking each box. In the boxes are the words ‘Experience’, ‘Learning’ and ‘Reflection’.
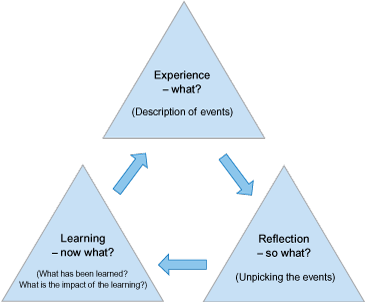
This figure contains three triangles, with arrows linking each one. In the top triangle is the text ‘Experience - what? (Description of events)’. In the bottom-left triangle is the text ‘Learning - now what? (What has been learned? What is the impact of the learning?’. In the bottom-right triangle is the text ‘Reflection - so what? (Unpicking the events)’.
Gibbs’ reflective cycle (Figure 4) breaks this down into further stages. Gibbs’ model acknowledges that your personal feelings influence the situation and how you have begun to reflect on it. It builds on Boud’s model by breaking down reflection into evaluation of the events and analysis and there is a clear link between the learning that has happened from the experience and future practice. However, despite the further break down, it can be argued that this model could still result in fairly superficial reflection as it doesn’t refer to critical thinking or analysis. It doesn’t take into consideration assumptions that you may hold about the experience, the need to look objectively at different perspectives, and there doesn’t seem to be an explicit suggestion that the learning will result in a change of assumptions, perspectives or practice. You could legitimately respond to the question ‘what would you do or decide next time?’ by answering that you would do the same, but does that constitute deep level reflection?
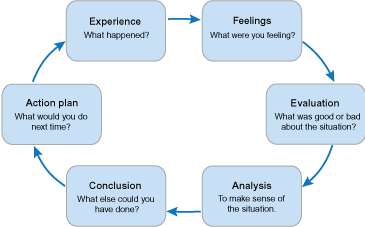
This figure shows a number of boxes containing text, with arrows linking the boxes. From the top left (and going clockwise) the boxes display the following text: ‘Experience. What happened?’; ‘Feeling. What were you feeling?’; ‘Evaluation. What was good or bad about the situation?’; ‘Analysis. To make sense of the situation’; ‘Conclusion. What else could you have done?’; ‘Action plan. What would you do next time?’.
Atkins and Murphy (1993) address many of these criticisms with their own cyclical model (Figure 5). Their model can be seen to support a deeper level of reflection, which is not to say that the other models are not useful, but that it is important to remain alert to the need to avoid superficial responses, by explicitly identifying challenges and assumptions, imagining and exploring alternatives, and evaluating the relevance and impact, as well as identifying learning that has occurred as a result of the process.
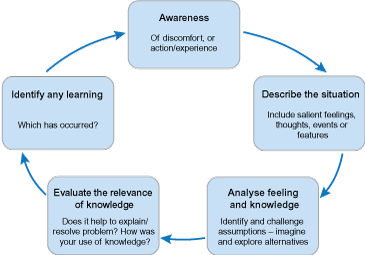
This figure shows a number of boxes containing text, with arrows linking the boxes. From the top (and going clockwise) the boxes display the following text: ‘Awareness. Of discomfort, or action/experience’; ‘Describe the situation. Include saliant feelings, thoughts, events or features’; ‘Analyse feeling and knowledge. Identify and challenge assumptions - imagine and explore alternatives’; ‘Evaluate the relevance of knowledge. Does it help to explain/resolve the problem? How was your use of knowledge?’; ‘Identify any learning. Which has occurred?’
You will explore how these models can be applied to professional practice in Session 7.
- My UCalgary
- Class Schedule
- UCalgary Directory
- Continuing Education
- Active Living
- Academic Calendar
- UCalgary Maps
- Close Faculty Websites List Viewing: Faculty Websites
- Cumming School of Medicine
- Faculty of Arts
- Faculty of Graduate Studies
- Faculty of Kinesiology
- Faculty of Law
- Faculty of Nursing
- Faculty of Nursing (Qatar)
- Faculty of Science
- Faculty of Social Work
- Faculty of Veterinary Medicine
- Haskayne School of Business
- School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape
- School of Public Policy
- Schulich School of Engineering
- Werklund School of Education
- Taylor Institute for Teaching and Learning
- Resource Library
- Academic integrity
- Artificial Intelligence
- Blended and online learning
- Curriculum review and development
- Designing learning
- Educational leadership and mentorship
- Equity, diversity, inclusion and accessibility
- Experiential learning
- Indigenous Ways of Knowing
- Mental health and wellness
- Scholarship of teaching and learning
- Teaching assistants
- Teaching continuity
- Teaching dossiers
- Search the catalogue
- Learning modules

Lesson 2: Designing critical reflection assignments
The design of critical reflection assignments should be intentional and aligned with desired learning outcomes. We invite you below to consider two models for designing critical reflection, the DEAL model, and Kolb’s Experiential Learning Cycle, and to articulate the desired learning outcomes informing your use of critical reflection.
Reflection question:
Consider the experiential learning activities relevant to instructional practice.
What would you want your students to learn from these experiential learning activities? With a specific experiential learning opportunity in mind, write down 3 desired learning outcomes that would inform your design of a critical reflection assignment.
Examples of experiential learning activities
Capstone projects.
Students draw upon the knowledge, skills, and abilities they developed across a degree program in a senior culminating experience to demonstrate the breadth of their learning. Capstones may engage students with external organizations or industry partners.
Case studies
Students put learning into action by applying theory to real-world or simulated scenarios with pre-set qualities and conditions.
Community-engaged learning
Students connect disciplinary learning and theoretical concepts while developing skills through activities designed with or for a community organization to achieve mutually beneficial outcomes.
Course-based research experiences (CURE)
Students engage with an inquiry project or set of coordinated, research-based assignments to build their scholarly skills and self-efficacy within a course-setting for academic credit.
Creative performance/exhibits/installations
Students produce, manage, curate or participate in a creative undertaking such as drama, dance, or musical performance or an exhibit of photograph, studio art, design, or mixed-media for a live or virtual audience to demonstrate their artistic repertoire and sensibilities.
Field schools/trips/excursions
Students engage in embodied or hands-on learning or place-based experience such as data collection or analysis in a field location, sometimes with guest experts or Elders as guides in addition to the instructor.
Pitch competitions/case studies/hackathons
Pitch competitions: Students prepare and deliver a compelling idea for a product or solution to a panel of expert judges as part of an academic course or co-curricular activity.
Hackathons: Students collaborate in teams to develop solutions to a real-life problem via an intense, time-limited challenge often in a competition that ranks the outputs.
Simulations and VR
Students engage in hands-on, structured scenarios or activities that are typically case-based or designed to mimic possible or actual events with a range of technological tools and/or human actors. These scenarios may include one or more of the following: human simulation, high-fidelity simulations, virtual simulation, virtual labs, augmented reality, virtual reality, game simulation, or standardized patient actors.
Clinical placements
Students learn and perform duties under the supervision of a practicing professional in a workplace setting. In some cases, such placements are required for professional certification.
For-credit internships (work-integrated learning)
Students participate in a discipline-specific, supervised, and structured work term. An internship may be paid or unpaid but is awarded academic credit. The length of internship can vary by program.
Study abroad/group study abroad/research abroad
Students engage in international and cross-cultural academic experiences such as exchanges, group study programs, study or research assistantships abroad, and collaborative virtual or online intercultural learning, often in conjunction with programs at partner universities or with research placements around the world.
Design/prototyping
Students apply and develop complex problem-solving and teamwork skills by engaging with a real-world challenge in a course setting often using a computerized/digital or physical model, typically with oversight and mentorship from an instructor and/or practicing professional.
Models for designing critical reflection
There are numerous evidence-based models that can guide the design of critical reflection assignments. Below we outline Ash and Clayton’s (2009) DEAL model and Kolb’s (1984) Experiential Learning Cycle.
The DEAL Model
The DEAL model developed by Ash and Clayton (2009) provides an evidence-based model to guide the design of critical reflection assignments by segmenting the structure of a critical reflection into three sequential parts: Describe, Examine, and Articulate Learning.
Description the experience in an objective and detailed manner.
Examination of experiences in light of specific learning goals or objectives.
Articulate Learning
Articulation of learning, including goals for future action that can then be taken forward into the next experience for improved practice and further refinement of learning.
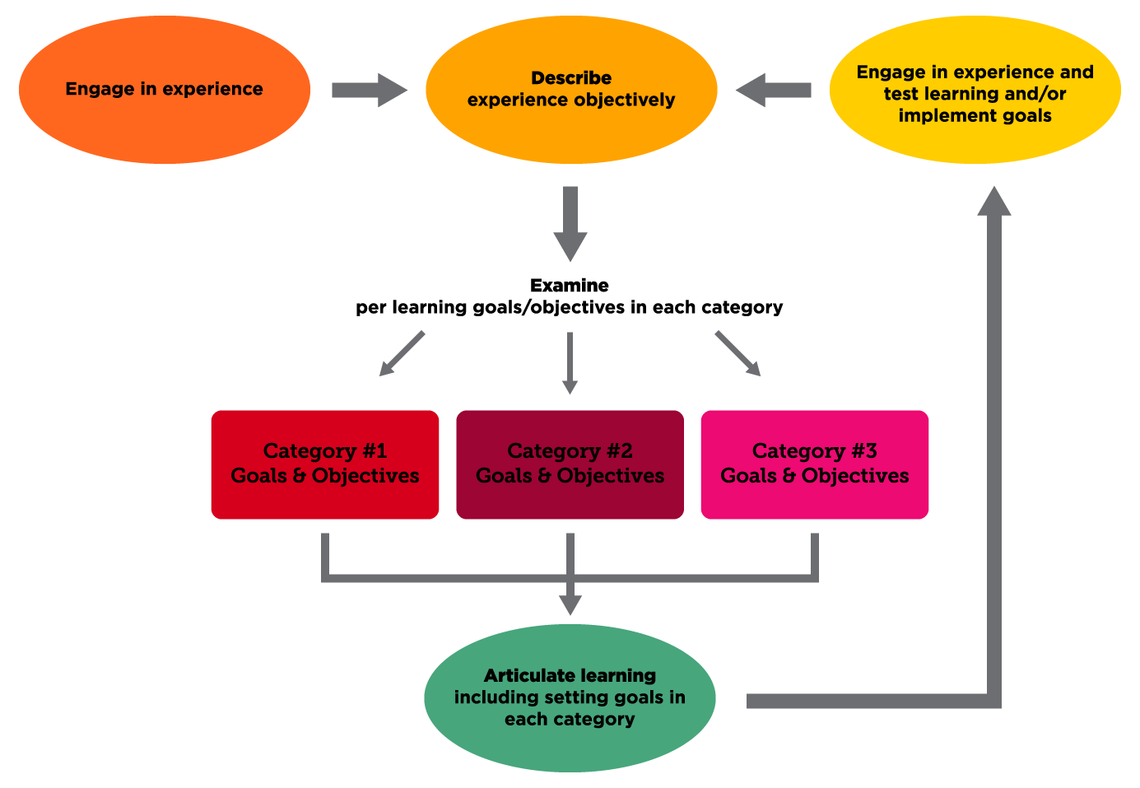
Schematic Overview of the DEAL Model for Critical Reflection (Ash and Clayton, 2009).
The Experiential Learning Cycle
Kolb’s (1984) Experiential Learning Cycle provides a cyclical model that highlights the continuous and iterative nature of critical reflection. The four stages of the Experiential Learning Cycle are Do, Review, Conclude, and Redo.
Doing or having an experience. This stage speaks to the actual experience students learn from and reflect on.
Reviewing or reflecting on the experience. This stage is for reflective observation.
Concluding learning outcomes or learning from the experience. This stage is about abstract conceptualization where students articulate the relationship between broader ideas, concepts, and ideals to their experience.
Planning or trying out learned skills and applying one’s learned knowledge. This stage involves students actively experimenting and practicing their new skills and knowledges. This stage leads to a new concrete experience.
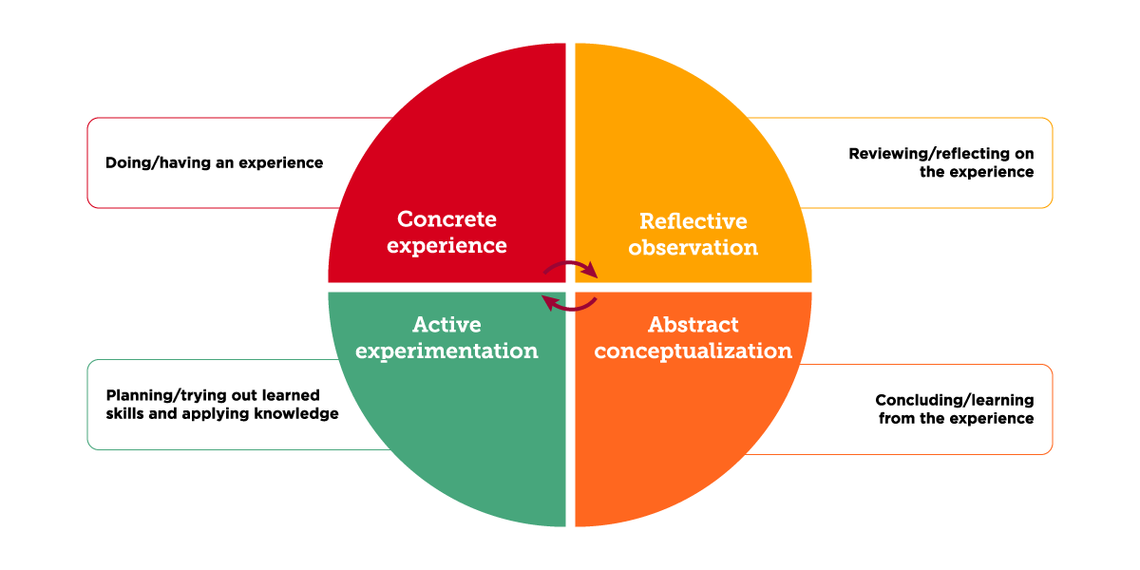
Additional resources
Critical reflection from the centre for teaching excellence.
University of Waterloo
View resource
Lesson checklist
Reflect on what experiential learning opportunities are part of your instructional practice
Review DEAL and Experiential Learning Cycle models of reflection
Articulate your desired learning outcomes for critical reflection
Check out additional resource
Ash, S. L., & Clayton, P. H. (2009). Generating, deepening, and documenting learning: The power of critical reflection in applied learning. Journal of Applied Learning in Higher Education , 1(1), 25-48.
Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experiential learning: Experience as the source of learning and development (Vol. 1). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall
McRae, N. (2018) The P.E.A.R. Framework for experiential learning: Institutional level [PowerPoint slides, PDF file]. Retrieved from https://uwaterloo.ca/centre-for-teaching-excellence/sites/default/files/uploads/files/waterloo_exl_norah_mcrae_final.pdf
More lessons

Lesson 3: Confronting discomfort and subjectivity

Lesson 4: Critical reflection prompts

Lesson 5: Critical reflection assessment
<< Go back to Critical Reflection Learning Module
Have questions?
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
You will be using throughout CRIT 602 to explore the larger context for your field of study and its associated professions will be critical inquiry:
“ Critical inquiry is the process of gathering and evaluating information , ideas, and assumptions from multiple perspectives to produce well-reasoned analysis and understanding , and leading to new ideas, applications and questions ” (“Critical Inquiry,” n.d.).
A high stakes example of critical inquiry is clinical diagnosis and treatment of physical or mental illness, which involves the doctor asking an entire matrix of complex questions at every stage of the process and knowledge of a body of research that is continually changing, as well as the ability to determine how each set of questions intersects with the body of research.
In a work setting, critical inquiry might be used to solve an organizational problem, such as poor morale among support staff. A director must ask: how can we identify the cause of the decline in morale that we’re experiencing now? When did it start? What factors could have led to it? Have there been changes in management? Have there been changes in our business practices? Could any external factors have caused or contributed to the decline in morale among these staff? Are organizations similar to ours experiencing a similar problem locally? Regionally? Nationally? Has research been done that we could use to find solutions to the problem? What’s been written in the professional literature for our industry that might help us solve our morale problem? Should we bring in a consultant?
In daily life, you might use critical inquiry to buy a car. What kind of vehicle will best meet my needs and the needs of my family? Truck, car, SUV? What about reliability history for the make and model I’m considering? What price range can I afford? How can I find out what is a fair price for the make and model I’m considering? Should I go with dealer financing or get the loan directly through my own bank or credit union? Why is this guy trying to sell me an extended warranty when I’ve already been here for three hours, and I want to go home?
The Role of Reflection in Critical Inquiry
Reflective learning is included in one of the three primary skills goals for CRIT 602: Reflect on learning to guide professional practice. The Center for Simplified Strategic Planning (CSSP) identifies reflection as a critical skill for strategic thinkers:
“Critical Skill #6: [Strategic thinkers] are committed lifelong learners and learn from each of their experiences. They use their experiences to enable them to think better on strategic issues” (“Strategic Thinking,” n.d.) .
We learn from experience by reflecting on it: Simply put, reflection is thinking about new experiences, connecting them to prior experiences, and learning something useful for the future.
In “Defining Reflection: Another Look at John Dewey and Reflective Thinking,” Carol R. Rodgers (2002) defines reflection in a way that aligns particularly well with the critical inquiry you will be conducting into the larger context for your field of study and its associated professions:
1. Reflection is a meaning-making process that moves a learner from one experience into the next with deeper understanding of its relationships with and connections to other experiences and ideas. It is the thread that makes continuity of learning possible, and ensures the progress of the individual and, ultimately, society. It is a means to essentially moral ends.
[Analytical Thinking Goal: You break concepts or evidence into parts and explain how the parts are related to each other.]
2. Reflection is a systematic, rigorous, disciplined way of thinking, with its roots in scientific inquiry.
[Analytical Thinking Goal: Your conclusion is logically tied to information. You have identified consequences and implications clearly.]
3. Reflection needs to happen in community, in interaction with others.
[ CCSP “Critical Skill #8: [Strategic thinkers] are committed to and seek advice from others. They may use a coach, a mentor, a peer advisory group or some other group that they can confide in and offer up ideas for feedback.”] (“Strategic Thinking,” n.d.)
4. Reflection requires attitudes that value the personal and intellectual growth of oneself and others.
[Developing a Community of Practice]
Critical Inquiry (AFCI 101). (n.d.). Retrieved September 10, 2022, from University of South Carolina Aiken website: https://www.usca.edu/academic-affairs/general-education/critical-inquiry.dot
Rodgers, C. (2002). Defining Reflection Another Look at John Dewey and Reflective Thinking. Teachers College Record, 104(4), 842-866.(1).pdf
Strategic thinking: 11 critical thinking skills. (n.d.). Retrieved September 10, 2018, from Center for Simplified Strategic Planning website: https://www.cssp.com/CD0808b/ CriticalStrategicThinkingSkills/
Feel free to check out the full article if you’re interested! (John Dewey was a top influencer in the field of public education.)
- Defining Reflection: Ano ther Look at John Dewey and Reflective Thinking
CRIT 602 Readings and Resources Copyright © 2019 by Granite State College (USNH) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Deakin University
- Learning and Teaching
Critical reflection for assessments and practice
- Critical reflection writing
Critical reflection for assessments and practice: Critical reflection writing
- Reflective practice
- Critical reflection
- How to reflect
- Recount and reflect
Critically reflective language and writing
"Our language is the reflection of ourselves..."
Mahatma Ghandi - Cries of Never (1916)
Our language is part of our identity. How we speak or write or paint or move when communicating shapes our sense of self and our presence in this world. Critical reflection uses particular language and writing styles.
What is reflective writing?
Critical reflection uses particular language and writing styles, often linked to your study area. For example, critical reflection in Health disciplines is linked to evidence-based practice and therefore uses a combination of clinical language and first-hand clinician perspective. In contrast, critical reflective writing for a dance student may have technical terms and creative language. Regardless of area, reflective writing at uni needs you to link your reflection to theories. This means that there is a formal tone to reflective writing assessments.
What does critical reflective writing include?
Critical reflective writing is not just a summary or description of an event or something that you have observed. Description is needed for context in a critical reflection but the core of good reflective writing is exploring the significance of events (the ‘why’ and ‘how’) by providing analysis and insights into your thinking.
In critical reflective writing you need to:

This helps you to develop new insights and perspectives which can inform your future practice.
Language of reflective writing

The language used in reflective writing allows you to discuss your personal experiences, feelings and ideas. It’s fine to refer to yourself and use “I”, “my” and “me”.
You can also use action verbs when writing about your feelings and opinions, for example, “I felt…”, “I think…”, “I realise…”.
Remember you also need to include theory to support what you are saying. Take a look at the language of reflective writing for more support in this area.
What? So What? Now What? Model
Just as there are models to help you critically reflect on your actions, thoughts and feelings, there are also models to help you write critical reflections.
The 'What? So What? Now What?' model guides your own reflections and learning from events that are significant for you. It gives you prompts to help you identify and discuss the different components of critical reflective writing.
Click on the plus symbols (+) below to see what is discussed in each section.
What? So What? Now What? template
To help you put this model into practice for your own context, download the template provided below to use for assessments.
- What? So What? Now What? template
Essay versus critical reflection essay
At uni a common form of critical reflection writing is the critical reflection essay. For a quick recap on the major differences, look at this table.
Try to express your reactions, feelings, attitudes and views in an open and honest way. Avoid writing what you think others ‘want to hear’.
Remember that a critical reflection should describe, analyse and evaluate? Use this checklist to shape up a draft critical reflection based on a recent experience. Don’t forget to use the SWOT model to help prompt your writing
- A brief description of the event or context
- What you noticed
- What you were thinking and feeling
- Why this learning is significant to you
- What you have learnt from this experience
- How this will inform future practice.
- << Previous: How to reflect
- Next: Recount and reflect >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 4:53 PM
- URL: https://deakin.libguides.com/critical-reflection-guide
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
Examples of Reflective Writing
Types of reflective writing assignments.
A journal requires you to write weekly entries throughout a semester. May require you to base your reflection on course content.
A learning diary is similar to a journal, but may require group participation. The diary then becomes a place for you to communicate in writing with other group members.
A logbook is often used in disciplines based on experimental work, such as science. You note down or 'log' what you have done. A log gives you an accurate record of a process and helps you reflect on past actions and make better decisions for future actions.
A reflective note is often used in law. A reflective note encourages you to think about your personal reaction to a legal issue raised in a course.
An essay diary can take the form of an annotated bibliography (where you examine sources of evidence you might include in your essay) and a critique (where you reflect on your own writing and research processes).
a peer review usually involves students showing their work to their peers for feedback.
A self-assessment task requires you to comment on your own work.
Some examples of reflective writing
Social science fieldwork report (methods section), engineering design report, learning journal (weekly reflection).
Brookfield, S 1987, Developing critical thinkers: challenging adults to explore alternative ways of thinking and acting , Open University Press, Milton Keynes.
Mezirow, J 1990, Fostering critical reflection in adulthood: a guide to transformative and emancipatory learning , Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
Schön, DA 1987, Educating the reflective practitioner , Jossey-Bass. San Francisco.
We thank the students who permitted us to feature examples of their writing.
Prepared by Academic Skills, UNSW. This guide may be distributed or adapted for educational purposes. Full and proper acknowledgement is required.
Essay and assignment writing guide
- Essay writing basics
- Essay and assignment planning
- Answering assignment questions
- Editing checklist
- Writing a critical review
- Annotated bibliography
- How do I write reflectively?
- Examples of reflective writing
- ^ More support
Study Hacks Workshops | All the hacks you need! 7 Feb – 10 Apr 2024
Discover your Library: Main Library 21 – 23 May 2024

Fostering critical thinking with reflective journals
Timely, frequent and constructive feedback has a powerful influence on student achievement. However, its impact on higher education students is hotly debated and often highly variable
Lesley Gardner
.css-76pyzs{margin-right:0.25rem;} ,, udayangi muthupoltotage.

Created in partnership with

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
A diy guide to starting your own journal, universities, ai and the common good, artificial intelligence and academic integrity: striking a balance, create an onboarding programme for neurodivergent students.
Students and staff frequently voice their dissatisfaction with assessment feedback . The common complaint is that students do not engage with nor act on it. They can often see it as more critical than constructive. Learning as a transaction frequently produces a passive attitude to feedback, with students expecting to be “told” what to do to achieve a high grade.
At the University of Auckland, we wanted students to take responsibility for developing their knowledge, skills and critical thinking, so we introduced a continuous reflective journal task into a postgraduate information systems course. The aim was to offer students a way to dissect, reflect on and understand feedback so that they could identify areas for improvement. To facilitate this, we encouraged students to provide evidence of their evolving thought processes and details on how they acted on the feedback and found meaning in their learning experiences. The journal was linked to standard assignments and peer review features accessible via Canvas, the University’s teaching and learning portal. We wanted to create a shared and transparent process that students and staff trusted, to shift the common framing of students as consumers and instead empower them to take an active role in their learning.
We designed a set of in-classroom activities to facilitate students’ understanding of our assessment:
- A series of discussions and interactive sessions focused on reflective writing
- Rubric interpretation
- Giving and receiving feedback.
In these sessions, we held group discussions to create and clarify a shared understanding of the reflective writing assessment and its rubrics. We scaffolded students’ understanding of feedback and their role in constructing and writing peer feedback. We distilled the work from the sessions into a set of resources, namely rubric interpretation, reflective writing and appropriate methods of giving and receiving feedback materials that were stored and available on canvas, to help students develop constructive feedback language.
For staff, we followed the notion that students learn best when they receive feedback quickly and frequently and recognised that the class size made returning feedback within a specific timeframe challenging.
We therefore leveraged existing electronic tools such as Turnitin e-rater and Grammarly to provide feedback. We involved students in designing rubrics within Canvas to enable automatic marking and facilitate detailed feedback that could be processed quickly. Finally, we leveraged peer-marking rubrics in Canvas to enable peer-to-peer marking. Thus, a student would receive four different types of feedback for each piece of work.
- Resources on teaching and learning in higher education
- Let’s talk: how to connect with your students in a blended learning environment
- Encouraging effective teamwork in the classroom
After the trial, we wanted to find out if the task did improve learning. We collected a wide range of data, including students’ background information, GPA, language competency and attitude before the intervention. Then we reviewed their performance data at different periods in the semester and looked at individual feedback and their journals. We then invited students to focus groups. From informal and formal feedback, we found students engaged well with reflective journals. Students told us that their expectations and effort highly influenced their response to feedback. They were able to demonstrate a deeper understanding of recurring themes that impeded their learning. This encouraged them to spend more time on self-reflection and self-evaluation.
Students appreciated the nuanced feedback and said the process revealed the importance of understanding and acting on it. They also appreciated the availability of instructors to provide clarification. They tended to prefer the individualised feedback and felt it was more useful than generic rubric marking.
For teaching staff, the reflective journal task created opportunities to identify, understand and address weaknesses in current feedback processes, which can and do reduce student engagement. Staff learned how to create a trusting atmosphere and use an appropriate tone when providing feedback.
Our three key takeaways are:
- Students interpret marking rubrics in different ways. More work is needed to develop a common understanding of how marking works. Upon reflection of the assessment and its activities, we chose to separate activities into different classes, over two weeks.
- The reflective journals enhanced students’ self-regulation and performance over time.
- Better automation using readily available digital tools would help to reduce increased staff workload. We are reviewing the mechanisms available to us through our learning management system and its available plug-in tools.
In the meantime, we continue to use the reflective journals and improve the model.
Lesley Gardner is an associate professor and Udayangi Muthupoltotage is a lecturer at the University of Auckland Business School.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
Global perspectives: navigating challenges in higher education across borders, how to help young women see themselves as coders, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, authentic assessment in higher education and the role of digital creative technologies, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
- Columbia University in the City of New York
- Office of Teaching, Learning, and Innovation
- University Policies
- Columbia Online
- Academic Calendar
- Resources and Technology
- Resources and Guides
Getting Started with Creative Assignments
Creative teaching and learning can be cultivated in any course context to increase student engagement and motivation, and promote thinking skills that are critical to problem-solving and innovation. This resource features examples of Columbia faculty who teach creatively and have reimagined their course assessments to allow students to demonstrate their learning in creative ways. Drawing on these examples, this resource provides suggestions for creating a classroom environment that supports student engagement in creative activities and assignments.
On this page:
- The What and Why of Creative Assignments
Examples of Creative Teaching and Learning at Columbia
- How To Get Started
Cite this resource: Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (2022). Getting Started with Creative Assignments. Columbia University. Retrieved [today’s date] from https://ctl.columbia.edu/resources-and-technology/resources/creative-assignments/
The What and Why of Creative Assignments
Creative assignments encourage students to think in innovative ways as they demonstrate their learning. Thinking creatively involves combining or synthesizing information or course materials in new ways and is characterized by “a high degree of innovation, divergent thinking, and risk-taking” (AAC&U). It is associated with imagination and originality, and additional characteristics include: being open to new ideas and perspectives, believing alternatives exist, withholding judgment, generating multiple approaches to problems, and trying new ways to generate ideas (DiYanni, 2015: 41). Creative thinking is considered an important skill alongside critical thinking in tackling contemporary problems. Critical thinking allows students to evaluate the information presented to them while creative thinking is a process that allows students to generate new ideas and innovate.
Creative assignments can be integrated into any course regardless of discipline. Examples include the use of infographic assignments in Nursing (Chicca and Chunta, 2020) and Chemistry (Kothari, Castañeda, and McNeil, 2019); podcasting assignments in Social Work (Hitchcock, Sage & Sage, 2021); digital storytelling assignments in Psychology (Sheafer, 2017) and Sociology (Vaughn and Leon, 2021); and incorporating creative writing in the economics classroom (Davis, 2019) or reflective writing into Calculus assignment ( Gerstle, 2017) just to name a few. In a 2014 study, organic chemistry students who elected to begin their lab reports with a creative narrative were more excited to learn and earned better grades (Henry, Owens, and Tawney, 2015). In a public policy course, students who engaged in additional creative problem-solving exercises that included imaginative scenarios and alternative solution-finding showed greater interest in government reform and attentiveness to civic issues (Wukich and Siciliano, 2014).
The benefits of creative assignments include increased student engagement, motivation, and satisfaction (Snyder et al., 2013: 165); and furthered student learning of course content (Reynolds, Stevens, and West, 2013). These types of assignments promote innovation, academic integrity, student self-awareness/ metacognition (e.g., when students engage in reflection through journal assignments), and can be made authentic as students develop and apply skills to real-world situations.
When instructors give students open-ended assignments, they provide opportunities for students to think creatively as they work on a deliverable. They “unlock potential” (Ranjan & Gabora and Beghetto in Gregerson et al., 2013) for students to synthesize their knowledge and propose novel solutions. This promotes higher-level thinking as outlined in the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy’s “create” cognitive process category: “putting elements together to form a novel coherent whole or make an original product,” this involves generating ideas, planning, and producing something new.
The examples that follow highlight creative assignments in the Columbia University classroom. The featured Columbia faculty taught creatively – they tried new strategies, purposefully varied classroom activities and assessment modalities, and encouraged their students to take control of what and how they were learning (James & Brookfield, 2014: 66).

Dr. Cruz changed her course assessment by “moving away from high stakes assessments like a final paper or a final exam, to more open-ended and creative models of assessments.” Students were given the opportunity to synthesize their course learning, with options on topic and format of how to demonstrate their learning and to do so individually or in groups. They explored topics that were meaningful to them and related to the course material. Dr. Cruz noted that “This emphasis on playfulness and creativity led to fantastic final projects including a graphic novel interpretation, a video essay that applied critical theory to multiple texts, and an interactive virtual museum.” Students “took the opportunity to use their creative skills, or the skills they were interested in exploring because some of them had to develop new skills to produce these projects.” (Dr. Cruz; Dead Ideas in Teaching and Learning , Season 3, Episode 6). Along with their projects, students submitted an artist’s statement, where they had to explain and justify their choices.
Dr. Cruz noted that grading creative assignments require advanced planning. In her case, she worked closely with her TAs to develop a rubric that was shared with students in advance for full transparency and emphasized the importance of students connecting ideas to analytical arguments discussed in the class.
Watch Dr. Cruz’s 2021 Symposium presentation. Listen to Dr. Cruz talk about The Power of Blended Classrooms in Season 3, Episode 6 of the Dead Ideas in Teaching and Learning podcast. Get a glimpse into Dr. Cruz’s online classroom and her creative teaching and the design of learning experiences that enhanced critical thinking, creativity, curiosity, and community by viewing her Voices of Hybrid and Online Teaching and Learning submission.

As part of his standard practice, Dr. Yesilevskiy scaffolds assignments – from less complex to more complex – to ensure students integrate the concepts they learn in the class into their projects or new experiments. For example, in Laboratory 1, Dr. Yesilevskiy slowly increases the amount of independence in each experiment over the semester: students are given a full procedure in the first experiment and by course end, students are submitting new experiment proposals to Dr. Yesilevskiy for approval. This is creative thinking in action. Students not only learned how to “replicate existing experiments, but also to formulate and conduct new ones.”
Watch Dr. Yesilevskiy’s 2021 Symposium presentation.
How Do I Get Started?: Strategies to Support Creative Assignments
The previous section showcases examples of creative assignments in action at Columbia. To help you support such creative assignments in your classroom, this section details three strategies to support creative assignments and creative thinking. Firstly, re-consider the design of your assignments to optimize students’ creative output. Secondly, scaffold creative assignments using low-stakes classroom activities that build creative capacity. Finally, cultivate a classroom environment that supports creative thinking.
Design Considerations for Creative Assignments
Thoughtfully designed open-ended assignments and evaluation plans encourage students to demonstrate their learning in authentic ways. When designing creative assignments, consider the following suggestions for structuring and communicating to your students about the assignment.
Set clear expectations . Students may feel lost in the ambiguity and complexity of an open-ended assignment that requires them to create something new. Communicate the creative outcomes and learning objectives for the assignments (Ranjan & Gabora, 2013), and how students will be expected to draw on their learning in the course. Articulare how much flexibility and choice students have in determining what they work on and how they work on it. Share the criteria or a rubric that will be used to evaluate student deliverables. See the CTL’s resource Incorporating Rubrics Into Your Feedback and Grading Practices . If planning to evaluate creative thinking, consider adapting the American Association of Colleges and Universities’ creative thinking VALUE rubric .
Structure the project to sustain engagement and promote integrity. Consider how the project might be broken into smaller assignments that build upon each other and culminate in a synthesis project. The example presented above from Dr. Yesilevskiy’s teaching highlights how he scaffolded lab complexity, progressing from structured to student-driven. See the section below “Activities to Prepare Students for Creative Assignments” for sample activities to scaffold this work.
Create opportunities for ongoing feedback . Provide feedback at all phases of the assignment from idea inception through milestones to completion. Leverage office hours for individual or group conversations and feedback on project proposals, progress, and issues. See the CTL’s resource on Feedback for Learning . Consider creating opportunities for structured peer review for students to give each other feedback on their work. Students benefit from learning about their peers’ projects, and seeing different perspectives and approaches to accomplishing the open-ended assignment. See the CTL’s resource Peer Review: Intentional Design for Any Course Context .
Share resources to support students in their work. Ensure all students have access to the resources they will need to be successful on the assigned project. Connect students with campus resources that can help them accomplish the project’s objectives. For instance, if students are working on a research project – connect them to the Library instruction modules “ From Books to Bytes: Navigating the Research Ecosystem ,” encourage them to schedule a consultation with a specialist for research support through Columbia Libraries , or seek out writing support. If students will need equipment to complete their project, remind them of campus resources such as makerspaces (e.g., The Makerspace @ Columbia in Room 254 Engineering Terrace/Mudd; Design Center at Barnard College); borrowing equipment (e.g., Instructional Media and Technology Services (IMATS) at Barnard; Gabe M. Wiener Music & Arts Library ).
Ask students to submit a self-reflection with their project. Encourage students to reflect on their process and the decisions they made in order to complete the project. Provide guiding questions that have students reflect on their learning, make meaning, and engage their metacognitive thinking skills (see the CTL’s resource of Metacognition ). Students can be asked to apply the rubric to their work or to submit a creative statement along with their work that describes their intent and ownership of the project.
Collect feedback from students and iterate. Invite students to give feedback on the assigned creative project, as well as the classroom environment and creative activities used. Tell students how you will use their suggestions to make improvements to activities and assignments, and make adjustments to the classroom environment. See the CTL’s resource on Early and Mid-Semester Student Feedback .
Low-Stakes Activities to Prepare Students for Creative Assignments
The activities described below are meant to be scaffolded opportunities leading to a larger creative project. They are low-stakes, non-graded activities that make time in the classroom for students to think, brainstorm, and create (Desrochers and Zell, 2012) and prepare them to do the creative thinking needed to complete course assignments. The activities can be adapted for any course context, with or without the use of technology, and can be done individually or collaboratively (see the CTL’s resource on Collaborative Learning to explore digital tools that are available for group work).
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a process that students can engage in to generate as many ideas as possible related to a topic of study or an assignment topic (Sweet et al., 2013: 87). As they engage in this messy and jugement-free work, students explore a range of possibilities. Brainstorming reveals students’ prior knowledge (Ambrose et al., 2010: 29). Brainstorm activities are useful early on to help create a classroom culture rooted in creativity while also serving as a potential icebreaker activity that helps instructors learn more about what prior knowledge and experiences students are bringing to the course or unit of study. This activity can be done individually or in groups, and in class or asynchronously. Components may include:
- Prompt students to list off (individually or collaboratively) their ideas on a whiteboard, free write in a Google Doc or some other digital space.
- Provide formative feedback to assist students to further develop their ideas.
- Invite students to reflect on the brainstorm process, look over their ideas and determine which idea to explore further.
Mind mapping
A mind map, also known as a cognitive or concept map, allows students to visually display their thinking and knowledge organization, through lines connecting concepts, arrows showing relationships, and other visual cues (Sweet et al., 2013: 89; Ambrose et al. 2010: 63). This challenges students to synthesize and be creative as they display words, ideas, tasks or principles (Barkley, 2010: 219-225). A mind mapping activity can be done individually or in groups, and in class or asynchronously. This activity can be an extension of a brainstorming session, whereby students take an idea from their brainstormed list and further develop it.
Components of a mind mapping activity may include:
- Prompt students to create a map of their thinking on a topic, concept, or question. This can be done on paper, on a whiteboard, or with digital mind mapping or whiteboard tools such as Google Drawing.
- Provide formative feedback on the mind maps.
- Invite students to reflect on their mind map, and determine where to go next.
Digital storytelling
Digital storytelling involves integrating multimedia (images, text, video, audio, etc.) and narrative to produce immersive stories that connect with course content. Student-produced stories can promote engagement and learning in a way that is both personal and universal (McLellan, 2007). Digital storytelling contributes to learning through student voice and creativity in constructing meaning (Rossiter and Garcia, 2010).
Tools such as the CTL-developed Mediathread as well as EdDiscussion support collaborative annotation of media objects. These annotations can be used in writing and discussions, which can involve creating a story. For freeform formats, digital whiteboards allow students to drop in different text and media and make connections between these elements. Such storytelling can be done collaboratively or simply shared during class. Finally, EdBlogs can be used for a blog format, or Google Slides if a presentation format is better suited for the learning objective.
Asking questions to explore new possibilities
Tap into student imagination, stimulate curiosity, and create memorable learning experiences by asking students to pose “What if?” “why” and “how” questions – how might things be done differently; what will a situation look like if it is viewed from a new perspective?; or what could a new approach to solving a problem look like? (James & Brookfield, 2014: 163). Powerful questions are open-ended ones where the answer is not immediately apparent; such questions encourage students to think about a topic in new ways, and they promote learning as students work to answer them (James & Brookfield, 2014: 163). Setting aside time for students to ask lots of questions in the classroom and bringing in questions posed on CourseWorks Discussions or EdDiscussion sends the message to students that their questions matter and play a role in learning.
Cultivate Creative Thinking in the Classroom Environment
Create a classroom environment that encourages experimentation and thinking from new and diverse perspectives. This type of environment encourages students to share their ideas without inhibition and personalize the meaning-making process. “Creative environments facilitate intentional acts of divergent (idea generation, collaboration, and design thinking) and convergent (analysis of ideas, products, and content created) thinking processes.” (Sweet et al., 2013: 20)
Encourage risk-taking and learning from mistakes . Taking risks in the classroom can be anxiety inducing so students will benefit from reassurance that their creativity and all ideas are welcome. When students bring up unexpected ideas, rather than redirecting or dismissing, seize it as an opportunity for a conversation in which students can share, challenge, and affirm ideas (Beghetto, 2013). Let students know that they can make mistakes, “think outside of the box” without penalty (Desrochers and Zell, 2012), and embrace failure seeing it as a learning opportunity.
Model creative thinking . Model curiosity and how to ask powerful questions, and encourage students to be curious about everything (Synder et al., 2013, DiYanni, 2015). Give students a glimpse into your own creative thinking process – how you would approach an open-ended question, problem, or assignment? Turn your own mistakes into teachable moments. By modeling creative thinking, you are giving students permission to engage in this type of thinking.
Build a community that supports the creative classroom environment. Have students get to know and interact with each other so that they become comfortable asking questions and taking risks in front of and with their peers. See the CTL’s resource on Community Building in the Classroom . This is especially important if you are planning to have students collaborate on creative activities and assignments and/or engage in peer review of each other’s work.
Plan for play. Play is integral to learning (Cavanagh, 2021; Eyler, 2018; Tatter, 2019). Play cultivates a low stress, high trust, inclusive environment, as students build relationships with each. This allows students to feel more comfortable in the classroom and motivates them to tackle more difficult content (Forbes, 2021). Set aside time for play (Ranjan & Gabora, 2013; Sinfield, Burns, & Abegglen, 2018). Design for play with purpose grounded in learning goals. Create a structured play session during which students experiment with a new topic, idea, or tool and connect it to curricular content or their learning experience. Play can be facilitated through educational games such as puzzles, video games, trivia competitions, scavenger hunts or role-playing activities in which students actively apply knowledge and skills as they act out their role (Eyler, 2018; Barkley, 2010). For an example of role-playing games explore Reacting to the Past , an active learning pedagogy of role-playing games developed by Mark Carnes at Barnard College.
The CTL is here to help!
CTL consultants are happy to support instructors as they design activities and assignments that promote creative thinking. Email [email protected] to schedule a consultation.
Ambrose et al. (2010). How Learning Works: 7 Research-Based Principles for Smart Teaching. Jossey-Bass.
Barkley, E. F., Major, C. H., and Cross, K. P. (2014). Collaborative Learning Techniques: A Handbook for College Faculty .
Barkley, E. F. (2010) Student Engagement Techniques: A Handbook for College Faculty.
Beghetto, R. (2013). Expect the Unexpected: Teaching for Creativity in the Micromoments. In M.B. Gregerson, H.T. Snyder, and J.C. Kaufman (Eds.). Teaching Creatively and Teaching Creativity . Springer.
Cavanagh, S. R. (2021). How to Play in the College Classroom in a Pandemic, and Why You Should . The Chronicle of Higher Education. February 9, 2021.
Chicca, J. and Chunta, K, (2020). Engaging Students with Visual Stories: Using Infographics in Nursing Education . Teaching and Learning in Nursing. 15(1), 32-36.
Davis, M. E. (2019). Poetry and economics: Creativity, engagement and learning in the economics classroom. International Review of Economics Education. Volume 30.
Desrochers, C. G. and Zell, D. (2012). Gave projects, tests, or assignments that required original or creative thinking! POD-IDEA Center Notes on Instruction.
DiYanni, R. (2015). Critical and creative thinking : A brief guide for teachers . John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Eyler, J. R. (2018). How Humans Learn. The Science and Stories Behind Effective College Teaching. West Virginia University Press.
Forbes, L. K. (2021). The Process of Play in Learning in Higher Education: A Phenomenological Study. Journal of Teaching and Learning. Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 57-73.
Gerstle, K. (2017). Incorporating Meaningful Reflection into Calculus Assignments. PRIMUS. Problems, Resources, and Issues in Mathematics Undergraduate Studies. 29(1), 71-81.
Gregerson, M. B., Snyder, H. T., and Kaufman, J. C. (2013). Teaching Creatively and Teaching Creativity . Springer.
Henry, M., Owens, E. A., and Tawney, J. G. (2015). Creative Report Writing in Undergraduate Organic Chemistry Laboratory Inspires Non Majors. Journal of Chemical Education , 92, 90-95.
Hitchcock, L. I., Sage, T., Lynch, M. and Sage, M. (2021). Podcasting as a Pedagogical Tool for Experiential Learning in Social Work Education. Journal of Teaching in Social Work . 41(2). 172-191.
James, A., & Brookfield, S. D. (2014). Engaging imagination : Helping students become creative and reflective thinkers . John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Jackson, N. (2008). Tackling the Wicked Problem of Creativity in Higher Education.
Jackson, N. (2006). Creativity in higher education. SCEPTrE Scholarly Paper , 3 , 1-25.
Kleiman, P. (2008). Towards transformation: conceptions of creativity in higher education.
Kothari, D., Hall, A. O., Castañeda, C. A., and McNeil, A. J. (2019). Connecting Organic Chemistry Concepts with Real-World Context by Creating Infographics. Journal of Chemistry Education. 96(11), 2524-2527.
McLellan, H. (2007). Digital Storytelling in Higher Education. Journal of Computing in Higher Education. 19, 65-79.
Ranjan, A., & Gabora, L. (2013). Creative Ideas for Actualizing Student Potential. In M.B. Gregerson, H.T. Snyder, and J.C. Kaufman (Eds.). Teaching Creatively and Teaching Creativity . Springer.
Rossiter, M. and Garcia, P. A. (2010). Digital Storytelling: A New Player on the Narrative Field. New Directions for Adult and Continuing Education. No. 126, Summer 2010.
Sheafer, V. (2017). Using digital storytelling to teach psychology: A preliminary investigation. Psychology Learning & Teaching. 16(1), 133-143.
Sinfield, S., Burns, B., & Abegglen, S. (2018). Exploration: Becoming Playful – The Power of a Ludic Module. In A. James and C. Nerantzi (Eds.). The Power of Play in Higher Education . Palgrave Macmillan.
Reynolds, C., Stevens, D. D., and West, E. (2013). “I’m in a Professional School! Why Are You Making Me Do This?” A Cross-Disciplinary Study of the Use of Creative Classroom Projects on Student Learning. College Teaching. 61: 51-59.
Sweet, C., Carpenter, R., Blythe, H., and Apostel, S. (2013). Teaching Applied Creative Thinking: A New Pedagogy for the 21st Century. Stillwater, OK: New Forums Press Inc.
Tatter, G. (2019). Playing to Learn: How a pedagogy of play can enliven the classroom, for students of all ages . Harvard Graduate School of Education.
Vaughn, M. P. and Leon, D. (2021). The Personal Is Political Art: Using Digital Storytelling to Teaching Sociology of Sexualities. Teaching Sociology. 49(3), 245-255.
Wukich, C. and Siciliano, M. D. (2014). Problem Solving and Creativity in Public Policy Courses: Promoting Interest and Civic Engagement. Journal of Political Science Education . 10, 352-368.
CTL resources and technology for you.
- Overview of all CTL Resources and Technology
This website uses cookies to identify users, improve the user experience and requires cookies to work. By continuing to use this website, you consent to Columbia University's use of cookies and similar technologies, in accordance with the Columbia University Website Cookie Notice .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Week 1 Assignment: Critical Thinking Reflection Critical thinking, just like any other concept out there, has a history. Critical thinking dates to the late 1950s when it was introduced to the K-12 system. But what does this concept of critical thinking mean? There are various definitions from various scholars on what it means to think critically.
Critical Thinking Reflection In the late 1950s is when critical thinking was brought into grades k-12 (Norris, S. P. (2014)). What does critical thinking mean to you? Critical thinking has many definitions, but to me it means evaluating situations and thinking outside the box. Every person uses critical thinking whether they know it or not.
Critical thinking is a habit of mind characterized by the comprehensive exploration of issues, ideas, artifacts, and events before accepting or formulating an opinion or conclusion (Rhodes, 2010). Citizens in a democracy must be able to adapt to the changes as presented and ... reflective writing assignments. Theoretical Framework
Critical reflection is not a reading assignment, a summary of an activity, or an emotional outlet. Rather, the goal is to change your thinking about a subject, and thus change your behaviour. Tip: Critical reflections are common in coursework across all disciplines, but they can take very different forms. Your instructor may ask you to develop ...
Develop your point through body paragraph (s), and conclude your paper by exploring the meaning you derive from your reflection. You may find the questions listed above can help you to develop an outline before you write your paper. You should maintain a formal tone, but it is acceptable to write in the first person and to use personal pronouns.
Identify, Reflect, and Analyze. Step 1: Reflect. Step 2: Analyze. Step 1: Reflecting on the Issue, Problem, or Task. Reflection is an important early step in critical thinking. There are various kinds of reflection that promote deeper levels of critical thinking (click on the table to view larger): Brockbank, A., & McGill, I. (2007).
In many of your reflective writing assignments, you will be required to write at either the second (analytical) and third (critical) levels. Reflections at the descriptive level tend to be more like diary entries, and are not usually appropriate for university assignments. Levels of reflection - from descriptive to critical reflection Descriptive
This manuscript deals with the problematic question of how students' critical reflection is manifested when reflecting on their experiences of learning critical thinking in higher education. Critical reflection is understood as the fusion of personal experience with new knowledge and study content, leading to a new understanding and a new sense of the meaning of oneself, one's learning ...
Reflection can also be useful when constructing an academic argument as you will have to think about how all the evidence fits with your own understanding of a topic. Being able to reflect on something is also an important part of critical thinking and writing as it allows you to question arguments made in the literature, be open minded about ...
Once you select the representative assignment from a course, develop a narrative that explains why this assignment was meaningful to your development. The narrative should be 2-4 paragraphs of writing (about one double-spaced page per assignment) that shows your reflection on why that is the case, and how you notice your thinking, assumptions ...
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
Reflective Practice; Inclusive Teaching; Teaching Commons > Teaching Guides > Assignment Design > Critical Thinking. Designing Assignments for Critical Thinking Critical thinking is a catchall phrase used to describe the ability of students to think for themselves, to reason well, and to approach problems and issues in a systematic and logical ...
Critical Reflection. Critical reflection is a "meaning-making process" that helps us set goals, use what we've learned in the past to inform future action and consider the real-life implications of our thinking. It is the link between thinking and doing, and at its best, it can be transformative (Dewey, 1916/1944; Schön, 1983; Rodgers ...
Thinking About Reflective Thinking. Educational theorists have developed numerous models of reflective thinking that your professor may use to frame a reflective writing assignment. These models can help you systematically interpret your learning experiences, thereby ensuring that you ask the right questions and have a clear understanding of what should be covered.
4 Applying critical and reflective thinking in academic and professional contexts: examples. 5 Summary and reflection. ... 3.1 What assessors will be looking for in your postgraduate assignments. 3.2 Evidence of critical thinking in academic writing. ... The theories behind reflective thinking and reflective practice are complex. Most are ...
The design of critical reflection assignments should be intentional and aligned with desired learning outcomes. We invite you below to consider two models for designing critical reflection, the DEAL model, and Kolb's Experiential Learning Cycle, and to articulate the desired learning outcomes informing your use of critical reflection.
1. Reflection is a meaning-making process that moves a learner from one experience into the next with deeper understanding of its relationships with and connections to other experiences and ideas. It is the thread that makes continuity of learning possible, and ensures the progress of the individual and, ultimately, society. It is a means to ...
of thinking in class and in assignments; give them feedback; and repeat. Thinking is an active process. ... Creative thinking, critical thinking, reflective thinking, problem solving, decision ...
Critical reflection uses particular language and writing styles, often linked to your study area. For example, critical reflection in Health disciplines is linked to evidence-based practice and therefore uses a combination of clinical language and first-hand clinician perspective. ... What you were thinking and feeling ; Why this learning is ...
Types of reflective writing assignments. ... Developing critical thinkers: challenging adults to explore alternative ways of thinking and acting, Open University Press, Milton Keynes. Mezirow, J 1990, Fostering critical reflection in adulthood: a guide to transformative and emancipatory learning, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco. Schön, ...
Students interpret marking rubrics in different ways. More work is needed to develop a common understanding of how marking works. Upon reflection of the assessment and its activities, we chose to separate activities into different classes, over two weeks. The reflective journals enhanced students' self-regulation and performance over time.
Critical thinking allows students to evaluate the information presented to them while creative thinking is a process that allows students to generate new ideas and innovate. ... Gerstle, K. (2017). Incorporating Meaningful Reflection into Calculus Assignments. PRIMUS. Problems, Resources, and Issues in Mathematics Undergraduate Studies. 29(1 ...
COMM227 Interpersonal and Critical Thinking Skills WINTER 2024 Instructor: Karim Boulos Individual Reflection Paper on Experience of Leading a Small Group Assessment Purpose The primary purpose of this assignment is for students to experience leading a small group and to reflect on their experiences. Each student will practice leadership skills by taking the lead in their group to coordinate a ...