- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans

Business Plan Example: The Industry Overview
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Wondering how to approach the industry overview section of your business plan? Having an example might help. Let's look at the industry overview for Pet Grandma, a fictional pet-based business invented for this business plan sample.
The Pet Industry
According to the American Pet Products Association, pet expenditures in the U.S. totaled slightly over $72.5 billion in 2018, up from $48 billion in 2010, an increase of 51% in eight years. This includes:
- Food: $30.32 billion
- Supplies/OTC Medicine: $16.01 billion
- Vet Care: $18.11 billion
- Live animal purchases: $2.01 billion
- Pet Services: grooming & boarding: $6.11 billion
These figures reflect the increasing humanization of pets, a trend that is showing no signs of waning. More and more people consider their pets to be people too and treat them accordingly. Karen McCullough, then director of marketing (2000-2010) for Winnipeg-based Petland Canada, which operates both company-owned and franchise stores across the country, says, "People are looking for more these days—absolutely. We see a lot now in higher-end products, people are demanding more for their pets, from treats to grooming supplies to brand-name toys and even clothing."
And, because people want the best for their pets, there is also an increasing demand for pet-care services. Across North America, the pet care business has seen an explosion of growth over the last ten years.
Our Position in the Industry
West Vancouver is an affluent area with a high pet density, an ideal market for a pet-sitting business such as Pet Grandma. People in this area not only have pets but can afford to spend money on them and are willing to do so.
Our market research has shown that nine out of 10 pet owners polled in West Vancouver would prefer to have their pets cared for in their own homes when they travel rather than be kenneled, and six out of 10 would consider having a pet sitter provide company for their dog when they were at work.
The Competition
While there are currently eight businesses offering pet sitting in West Vancouver, only three of these offer on-site pet care and none offers pet visit services for working pet owners.
Currently, there is no single company dominating the market. This may be because all of the pet-sitting businesses are relatively new; the oldest, Paula's Pet Sitting, has only been in business five years. However, half of the existing pet-sitting businesses control the majority of the market—Paula's Pet Sitting, Doggie Care Services Inc., Pet Petters, and Pet Sitters on Demand together make up 65% of the market.
Save your full competitive analysis for section four of your business plan , but briefly share competitor insights here as it relates to your industry and your unique position in it.
What Makes Pet Grandma Unique
Pet Grandma's marketing strategy is to emphasize the quality of pet care we provide. As our slogan, "A Grandma for your pet!" says, we treat people's pets as family members and strive to give them the same loving, personal care that their owners would give. In our marketing , we will be emphasizing the quality and personalized service we provide.
We will also offer some services that are currently unique, such as our pet visit services, where one of our trained staff will go to a person's home while they're at work and feed, exercise, and play with their pet, allowing dog owners who work to come home to happy, friendly companions rather than demanding, whiny animals.
Your Business Plan
That's a basic example of an industry overview for your business plan. It provides an look at your business's industry and highlights your place within it. Your plan should present well-researched information to display that you understand the industry well.
Once you have yours written, you can move on to the next section of the business plan, the market analysis .
American Pet Products Association. " Pet Industry Market Size & Ownership Statistics ." Accessed Jan. 8, 2020.
How to Write an Effective Business Plan: Industry Profile
Treana wunsch.
- December 7, 2022

Having an industry profile section in a business plan is essential for success. It serves to provide the reader with background information on the industry, along with its current trends and future projections. This section will help to assess whether or not an idea is feasible, as well as how competitive it may be in the marketplace.
The industry profile should include both qualitative and quantitative data. Qualitative data can illustrate points such as the current market share of competitors, product, price, promotion and distribution trends or any other relevant factors that may affect the business’s ability to succeed. Quantitative data consists of numerical figures like sales volume and growth rate of particular products within the industry over time.
Including this kind of information will help potential investors understand why your business should exist by highlighting its unique niche within the marketplace.
What is an industry?

An industry is an economic sector that produces goods and services. It is the driving force behind a country’s economy. Industries can range from large-scale enterprises with hundreds of employees to small, family-run businesses. As such, each industry has unique characteristics that must be taken into consideration when writing an effective business plan.
When researching an industry for your business plan, it’s important to understand the factors affecting its performance, including market trends and government regulations. Additionally, you should consider the competition in the market – both current players and potential new entrants – as well as customer habits and preferences. All this information will help you gain insight into how best to position your business within this particular industry in order to succeed.
Industry classification
When creating an industry profile, it’s important to understand the classification system used by experts in the field. This includes macro industries, subsectors, industries and even trade groups, each of which provides further detail on a company’s market.
The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) is one of the most widely used systems for classifying businesses by type of activity and geographic location. It categorizes establishments based on their primary production process or product line and assigns them a six-digit code that uniquely identifies them within their sector. The NAICS also makes it easy to compare businesses across different sectors and regions by grouping similar companies together under broader categories such as transportation or manufacturing.
How to find your industry
Finding the right industry for your company is a crucial step in the process of writing an effective business plan. Understanding what industry you are entering and who your competitors are will help determine how to structure your plan and position yourself in the market. Knowing where to start can be challenging, so here are some tips on how to find your industry and create an effective business plan.
First off, research current trends in the market and identify areas that you believe have potential for growth or represent a good fit for your company’s products or services. Look at macroeconomic data from government sources such as the Bureau of Labor Statistics, as well as industry-specific reports from organizations like Forbes or Business Insider. Analyze these reports to determine which industries may offer more potential than others, then narrow down your choices by researching key factors such as demand, competition and capital requirements within those industries.
How to find your industry NAICS code
The first step in writing an effective business plan is to identify your industry and the associated North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) code. NAICS codes are used by governments, businesses, and other organizations to classify industries according to the type of economic activity they engage in. Knowing your industry NAICS code is essential for gathering information about your industry and its competitive landscape, as well as determining which regulations apply to you.
Fortunately, it’s easy to find out what your industry NAICS code is. To begin, visit the Statistics Canada website and use their searchable database of NAICS codes. You can also contact a government agency or trade association related to your industry for more help finding your specific NAICS code.

Financial Performance Data by Industry in Canada
Financial performance data by industry in Canada is an important factor to consider when writing an effective business plan. Knowing the key financial ratios specific to your industry will help you benchmark your performance, identify potential weak spots and develop strategies for growth. Different industries have their own unique financial metrics with which they measure success. It is important to understand these ratios and how they apply to you and your target market before writing a comprehensive business plan.
By analyzing the common financial trends of businesses within certain industries in Canada, you can gain valuable insight into how successful companies in that sector operate. Using this information, you can adjust your strategy accordingly so that it meets or exceeds the expectations of investors and other stakeholders involved with your venture. The ability to effectively identify industry-specific financial indicators gives businesses a competitive edge that can result in greater profitability over time.
You can find your industry’s financial performance here . Choose the location you want data from then choose ‘total revenue’ and ‘percentage’ and ‘search for an industry’ as your other options. Then type your NAICS code that you discovered under ‘Search for an industry’ and click on ‘search’.

Your options will come up below. Choose the appropriate option and ‘create report’.

If balance sheet data is available it will also be shown.

The lower portion of the report indicates the percentage of businesses that are profitable.

You can also do an internet search of the NAICS code to see what else comes up.
Industry codes help you to discover your specific industry and define the boundaries of that industry. Understanding the health of your industry and where the future of the industry may be going offers valuable insight into how successful your business could be. You can also measure your business performance against industry performance. All of this helps you to make better decisions for your business.

FREE Business Plan Template
Click to download the Classic Google Docs Business Plan Template
Industry Lifecycle
Industry Lifecycle is an important concept for any business to understand and plan for. It is the process of a given industry maturing over time and passing through distinct stages of growth, decline, and eventual restabilization. Knowing the lifecycle of an industry can help you plan ahead by understanding where it is currently, what its likely future will be, and how to best capitalize on its strengths while minimizing weaknesses.
To write an effective business plan, an understanding of the industry’s current position in its lifecycle is essential. This knowledge will help you create realistic goals and strategies that are tailored to your specific market conditions.
This section should provide a comprehensive overview of the industry and its particular lifecycle. The lifecycle of an industry often determines how successful businesses in that sector will be and what strategies are best for them to pursue.
In order to determine the lifecycle of an industry, you must look at key factors such as trends in demand, competition from substitutes or new entrants into the market, technological advances, and changes in consumer preferences. It’s also necessary to assess potential risks within the sector including shifts in regulations or economic dips that could negatively impact performance. Additionally, you should consider how long the industry has been around and whether it’s likely to grow or decline over time.
The automotive industry is a good example of the industry lifecycle. It began with a period of introduction, followed by growth, then maturity and eventually decline. During the introduction phase, new technologies like the automobile were developed and brought to market. There was strong growth as the market for automobiles expanded. As the industry grew, it matured and reached a stable point where existing companies competed. Eventually, the industry declined as new technologies and sources of energy made it obsolete.
Industry History
It’s essential for aspiring entrepreneurs to have a basic understanding of the history of their chosen industry. Industry history is used to build an understanding of the current state of the market, as well as its potential for growth in the future. By studying past trends and developments in an industry, entrepreneurs can identify successful strategies that have been employed by previous businesses, enabling them to develop a comprehensive business plan that stands out from competitors. Moreover, they can use this information to gauge how quickly or slowly their venture may grow over time.
Industry Leaders
Industry Leaders are the heart of any successful business. Whether you’re launching a startup or expanding an existing business, understanding your industry and its leaders is essential for success. An effective business plan must include an industry profile to demonstrate comprehensive knowledge of the competitive landscape and identify strategies for establishing a foothold in the market.
An Industry Profile is a detailed analysis of your industry’s size, structure, growth rate, key players, trends and more. It begins with examining leading companies – their products/services; target markets; operations & financials; competitive advantages – and how they contribute to industry dynamics. Knowing who sets the standard in terms of quality, innovation & sustainability will also help evaluate customer preferences & overall satisfaction levels within the sector. Once identified, these insights can be used to craft actionable plans that position your company as a leader in its respective field.
Industry Threats
To create an accurate industry profile, you must carefully consider the various external factors that can potentially threaten your company’s operations. These threats may include changes in laws or regulations, economic conditions such as inflation or recession, competition from other businesses, technological advances, new entrants into the market, and customer preferences.
By analyzing these elements of your industry and assessing their potential impact on your business plan, you can better anticipate changes in the environment and develop strategies to minimize any adverse effects these threats might have on your company’s profitability.
Industry Predictions
Industry predictions can help businesses stay ahead of the curve and plan for the future. When researching your industry profile, it is essential to look at key economic indicators such as consumer spending habits, employment rates, and capital investments. Additionally, consider major disruptors like technological advancements or regulatory changes that may influence your market dynamics over time. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these factors, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions when creating your business plan and developing strategies for growth.
Tuesday Takeaways Newsletter
Industry associations.
Industry associations play an integral role in the development of a business plan. They provide industry professionals with information, resources, and contacts to help them create successful business plans and gain strategic insights into their industry. Furthermore, they can also help entrepreneurs identify potential customers and develop marketing strategies based on current industry trends.
The first step to utilizing an industry association is researching the available options and learning about their current activities. After finding one that fits the needs of your business plan, it’s important to join the organization so you have access to all the benefits they offer. Once you’ve joined, be sure to take advantage of any educational opportunities or events designed for members; these are excellent ways for entrepreneurs to network with other professionals in their field and learn more about specific trends related to their industry.
Industry Statistical Analysis
Industry statistical analysis is an important part of writing an effective business plan. Accurate and up-to-date industry data can provide invaluable insight into the current trends, potential risks, and opportunities in a particular market. Taking the time to research recent industry developments allows entrepreneurs to make more informed decisions regarding their business strategies going forward.
When conducting your own industry statistical analysis as part of a business plan, it’s important to look at both economic indicators and demographic trends for relevant market segments. Analyzing existing sales figures for similar businesses or products is also essential for understanding the size of the opportunity or assessing competitive threats. In addition, looking at various macroeconomic trends such as inflation rates or GDP growth can help inform your projections about future performance within the industry.
Putting it all together
Once you’ve gathered all your data, you’ll summarize it in your business plan. It may look like the following example:

As with any section of your business plan, this section required regular review and updating.
That's All Folks...
I hope with this information you will find it easier to write the Industry Profile section of your business plan. Up next…Marketing Strategy.
If you have questions, please comment below and I’ll be happy to answer them.
P.S. Whenever you’re ready, here are 3 ways I can help you.
Online Business Management. I will assess your business and make recommendations for improvements. Together we’ll create a plan to streamline the daily operations. My goal is to simplify your business so you can focus on what’s important.
Business Plan Writing. Take the first step to building your dreams.
Digital Marketing. If your business doesn’t have a digital marketing plan, you’re leaving money on the table.
Sharing is caring
- 'How to Write a Business Plan for Small Business' Series , Starting a Business
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Yes, add me to your mailing list
Table of Contents
Get 75% off quickbooks, master your productivity: unlocking the power of the eisenhower matrix, systemizing your business operations: the ultimate guide to maximizing efficiency in your small business, understanding the online business manager role: reach your small business goals.

You Might Also Like

Let's face it...most businesses fail. Increase your odds of success.
Get practical and actionable advice straight to your inbox every Tuesday .
This site contains affiliate links to products. We may receive a commission for purchases made through these links. However, this does not impact our reviews and comparisons. We only suggest products we’ve reviewed, and in many instances also use, in order to help you make the best choices.
Copyright 2024 © all rights reserved. design by treana wunsch.
Site hosted by Varial Hosting
Is the future of your small business uncertain?
Get straightforward advice on getting your business back on track. Every Tuesday. Straight to your inbox.
Your privacy is important to me. See my privacy policy .
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience possible on our site. Learn more

How to Write the Market Analysis Section of a Business Plan
Written by Dave Lavinsky

What is the Market Analysis in a Business Plan?
The market analysis section of your business plan is where you discuss the size of the market in which you’re competing and market trends that might affect your future potential such as economic, political, social and/or technological shifts.
This helps you and readers understand if your market is big enough to support your business’ growth, and whether future conditions will help or hurt your business. For example, stating that your market size is $56 billion, has been growing by 10% for the last 10 years, and that trends are expected to further increase the market size bodes well for your company’s success.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
What Should a Market Analysis Include?
You’ll want to address these issues in your market analysis:
- Size of Industry – How big is the overall industry?
- Projected Growth Rate of Industry – Is the industry growing or shrinking? How fast?
- Target Market – Who are you targeting with this product or service?
- Competition – How many businesses are currently in the same industry?
Learn how to write the full market analysis below.
How to Write a Market Analysis
Here’s how to write the market analysis section of a business plan.
- Describe each industry that you are competing in or will be targeting.
- Identify direct competition, but don’t forget about indirect competition – this may include companies selling different products to the same potential customer segments.
- Highlight strengths and weaknesses for both direct and indirect competitors, along with how your company stacks up against them based on what makes your company uniquely positioned to succeed.
- Include specific data, statistics, graphs, or charts if possible to make the market analysis more convincing to investors or lenders.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
Industry overview.
In your industry overview, you will define the market in which you are competing (e.g., restaurant, medical devices, etc.).
You will then detail the sub-segment or niche of that market if applicable (e.g., within restaurants there are fast food restaurants, fine dining, etc.).
Next, you will describe the key characteristics of your industry. For example, discuss how big the market is in terms of units and revenues. Let the reader know if the market is growing or declining (and at what rate), and what key industry trends are facing your market.
Use third-party market research as much as possible to validate the discussion of your industry.
Here is a list of additional items you may analyze for a complete industry overview:
- An overview of the current state of the industry . How big is it, how much does it produce or sell? What are its key differentiators from competitors? What is its target customer base like – demographic information and psychographics? How has the industry performed over time (global, domestic)?
- Analyze the macro-economic factors impacting your industry . This includes items such as economic growth opportunities, inflation, exchange rates, interest rates, labor market trends, and technological improvements. You want to make sure that all of these are trending in a positive direction for you while also being realistic about them. For example, if the economy is in shambles you might want to wait before entering the particular market.
- Analyze the political factors impacting your industry . This is an often-overlooked section of any business plan, but it can be important depending on what type of company you are starting. If you’re in a highly regulated industry (such as medical devices), this is something that you’ll want to include.
- Analyze the social factors impacting your industry . This includes analyzing society’s interest in your product or service, historical trends in buying patterns in your industry, and any effects on the industry due to changes in culture. For example, if there is a growing counter-culture trend against big oil companies you might want to position yourself differently than a company in this industry.
- Analyze the technological factors impacting your industry . This includes analyzing new technologies being developed in software, hardware, or applications that can be used to improve your product or service. It also includes emerging consumer trends and will be highly dependent on your business type. In a technology-related venture, you would analyze how these changes are impacting consumers. For an educational-related venture, you would analyze how these changes are impacting students, teachers, and/or administrators.
For each of these items, you want to provide some detail about them including their current state as well as what external factors have played a role in the recent past. You can also include many other important factors if they apply to your business including demographic trends, legal issues, environmental concerns, and sustainability issues.
When you are done analyzing all of these factors, wrap it up by summing them up in a statement that includes your view on the future of the industry. This should be positive to attract investors, potential customers, and partners.
If you’re having trouble thinking about all of these factors then it might be helpful to first develop a SWOT analysis for your business.
Once you have an understanding of the market, you’ll need to think about how you will position yourself within that potential market.
Picking Your Niche
You want to think about how large your market is for this venture. You also want to consider whether you’d like to pick a niche within the overall industry or launch yourself into the mainstream.
If you have an innovative product it can be easier to enter the mainstream market – but at the same time, you might face some additional competition if there are similar products available.
You can choose to specialize in a niche market where you’ll face less competition – but might be able to sell your services at a higher price point (this could make it easier for you to get potential customers).
Of course, if your product or service is unique then there should be no competition. But, what happens if it isn’t unique? Will you be able to differentiate yourself enough to create a competitive advantage or edge?
If you are planning on entering the mainstream market, think about whether there are different sub-niches within your specific market. For example, within the technology industry, you can choose to specialize in laptops or smartphones or tablets, or other categories. While it will be more difficult to be unique in a mainstream market, you will still be able to focus on one type or category of products.
How Will You Stand Out?
Many companies are able to stand out – whether by offering a product that is unique or by marketing their products in a way that consumers notice. For example, Steve Jobs was able to take a business idea like the iPhone and make it into something that people talked about (while competitors struggled to play catch up).
You want your venture to stand out – whether with an innovative product or service or through marketing strategies. This might include a unique brand, name, or logo. It might also include packaging that stands out from competitors.
Write down how you will achieve this goal of standing out in the marketplace. If it’s a product, then what features do you have that other products don’t? If it’s a service, then what is it about this service that will make people want to use your company rather than your competition?
You also need to think about marketing. How are you going to promote yourself or sell your product or service? You’ll need a marketing plan for this – which might include writing copy, creating an advertisement, setting up a website, and several other activities. This should include a description of each of these strategies.
If you’re struggling with the details of any of these sections, it might be helpful to research what other companies in your market are doing and how they’ve been successful. You can use this business information to inform your own strategies and plans.
Relevant Market Size & Competition
In the second stage of your analysis, you must determine the size and competition in your specific market.
Target Market Section
Your company’s relevant market size is the amount of money it could make each year if it owned a complete market share.
It’s simple.
To begin, estimate how many consumers you expect to be interested in purchasing your products or services each year.
To generate a more precise estimate, enter the monetary amount these potential customers may be ready to spend on your goods or services each year.
The size of your market is the product of these two figures. Calculate this market value here so that your readers can see how big your market opportunity is (particularly if you are seeking debt or equity funding).
You’ll also want to include an analysis of your market conditions. Is this a growing or declining market? How fast is it growing (or declining)? What are the general trends in the market? How has your market shifted over time?
Include all of this information in your own business plan to give your readers a clear understanding of the market landscape you’re competing in.
The Competition
Next, you’ll need to create a comprehensive list of the competitors in your market. This competitive analysis includes:
- Direct Competitors – Companies that offer a similar product or service
- Indirect Competitors – Companies that sell products or services that are complementary to yours but not directly related
To show how large each competitor is, you can use metrics such as revenue, employees, number of locations, etc. If you have limited information about the company on hand then you may want to do some additional research or contact them directly for more information. You should also include their website so readers can learn more if they desire (along with social media profiles).
Once you complete this list, take a step back and try to determine how much market share each competitor has. You can use different methods to do this such as market research, surveys, or conduct focus groups or interviews with target customers.
You should also take into account the barriers to entry that exist in your market. What would it take for a new company to enter the market and start competing with you? This could be anything from capital requirements to licensing and permits.
When you have all of this information, you’ll want to create a table like the one below:
Once you have this data, you can start developing strategies to compete with the other companies which will be used again later to help you develop your marketing strategy and plan.
Writing a Market Analysis Tips
- Include an explanation of how you determined the size of the market and how much share competitors have.
- Include tables like the one above that show competitor size, barriers to entry, etc.
- Decide where you’re going to place this section in your business plan – before or after your SWOT analysis. You can use other sections as well such as your company summary or product/service description. Make sure you consider which information should come first for the reader to make the most sense.
- Brainstorm how you’re going to stand out in this competitive market.
Formatting the Market Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
Now that you understand the different components of the market analysis, let’s take a look at how you should structure this section in your business plan.
Your market analysis should be divided into two sections: the industry overview and market size & competition.
Each section should include detailed information about the topic and supporting evidence to back up your claims.
You’ll also want to make sure that all of your data is up-to-date. Be sure to include the date of the analysis in your business plan so readers know when it was conducted and if there have been any major changes since then.
In addition, you should also provide a short summary of what this section covers at the beginning of each paragraph or page. You can do this by using a title such as “Industry Overview” or another descriptive phrase that is easy to follow.
As with all sections in a business plan, make sure your market analysis is concise and includes only the most relevant information to keep your audience engaged until they reach your conclusion.
A strong market analysis can give your company a competitive edge over other businesses in its industry, which is why it’s essential to include this section in your business plan. By providing detailed information about the market you’re competing in, you can show your readers that you understand the industry and know how to capitalize on current and future trends.
Business Plan Market Analysis Examples
The following are examples of how to write the market analysis section of a business plan:
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #1 – Hosmer Sunglasses, a sunglasses manufacturer based in California
According to the Sunglass Association of America, the retail sales volume of Plano (non-prescription) sunglasses, clip-on sunglasses, and children’s sunglasses (hereinafter collectively referred to as “Sunwear”) totaled $2.9 billion last year. Premium-priced sunglasses are driving the Plano Sunwear market. Plano sunglasses priced at $100 or more accounted for more than 49% of all Sunwear sales among independent retail locations last year.
The Sunglass Association of America has projected that the dollar volume for retail sales of Plano Sunwear will grow 1.7% next year. Plano sunglass vendors are also bullish about sales in this year and beyond as a result of the growth of technology, particularly the growth of laser surgery and e-commerce.
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #2 – Nailed It!, a family-owned restaurant in Omaha, NE
According to the Nebraska Restaurant Association, last year total restaurant sales in Nebraska grew by 4.3%, reaching a record high of $2.8 billion. Sales at full-service restaurants were particularly strong, growing 7% over 2012 figures. This steady increase is being driven by population growth throughout the state. The Average Annual Growth Rate (AGR) since 2009 is 2.89%.
This fast growth has also encouraged the opening of new restaurants, with 3,035 operating statewide as of this year. The restaurant industry employs more than 41,000 workers in Nebraska and contributes nearly $3 billion to the state economy every year.
Nebraska’s population continues to increase – reaching 1.9 million in 2012, a 1.5% growth rate. In addition to population, the state has experienced record low unemployment every year since 2009 – with an average of 4.7% in 2013 and 2014.
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #3 – American Insurance Company (AIC), a chain of insurance agencies in Maine
American Insurance Company (AIC) offers high-quality insurance at low prices through its chain of retail outlets in the state of Maine. Since its inception, AIC has created an extensive network of agents and brokers across the country with expanding online, call center and retail business operations.
AIC is entering a market that will more than double in size over the next 50 years according to some industry forecasts. The insurance industry is enjoying low inflation rates, steady income growth, and improving standards of living for most Americans during what has been a difficult period for much of American business. This makes this a good time to enter the insurance industry as it enjoys higher margins because customers are purchasing more coverage due to increased costs from medical care and higher liability claims.
American Insurance Company provides affordable homeowners, auto, and business insurance through high-quality fulfillment centers across America that have earned a reputation for top-notch customer service.
AIC will face significant competition from both direct and indirect competitors. The indirect competition will come from a variety of businesses, including banks, other insurance companies, and online retailers. The direct competition will come from other well-funded start-ups as well as incumbents in the industry. AIC’s competitive advantages include its low prices, high quality, and excellent customer service.
AIC plans to grow at a rate that is above average for the industry as a whole. The company has identified a market that is expected to grow by more than 100% in the next decade. This growth is due to several factors: the increase in the number of two-income households, the aging population, and the impending retirement of many baby boomers will lead to an increase in the number of people who are purchasing insurance.
AIC projects revenues of $20M in year one, which is equivalent to 100% growth over the previous year. AIC forecasts revenue growth of 40%-60% each year on average for 10 years. After that, revenue growth is expected to slow down significantly due to market saturation.
The following table illustrates these projections:
Competitive Landscape
Direct Competition: P&C Insurance Market Leaders
Indirect Competition: Banks, Other Insurance Companies, Retailers
Market Analysis Conclusion
When writing the market analysis section, it is important to provide specific data and forecasts about the industry that your company operates in. This information can help make your business plan more convincing to potential investors.
If it’s helpful, you should also discuss how your company stacks up against its competitors based on what makes it unique. In addition, you can identify any strengths or weaknesses that your company has compared to its competitors.
Based on this data, provide projections for how much revenue your company expects to generate over the next few years. Providing this information early on in the business plan will help convince investors that you know what you are talking about and your company is well-positioned to succeed.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Resources for Writing Your Business Plan
How to Write a Great Business Plan Executive Summary How to Expertly Write the Company Description in Your Business Plan The Customer Analysis Section of Your Business Plan Completing the Competitive Analysis Section of Your Business Plan The Management Team Section of Your Business Plan Financial Assumptions and Your Business Plan How to Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan Everything You Need to Know about the Business Plan Appendix Best Business Plan Software Business Plan Conclusion: Summary & Recap
Other Helpful Business Planning Articles & Templates

- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
First Steps: Writing the Industry Section of Your Business Plan This quick guide offers tips that will help you create the industry section for your business plan.
By The Staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. • Jan 4, 2015
In their book Write Your Business Plan , the staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. offer an in-depth understanding of what's essential to any business plan, what's appropriate for your venture, and what it takes to ensure success. In this edited excerpt, the authors outline what type of details you should include in the industry section of your business plan.
It isn't enough to just work hard. If you're in the wrong industry at the wrong time, making your business grow is going to be difficult. The investment community tends to believe that any business can be buoyed by an industry on the rise and that the opposite is true in an industry whose tide is ebbing. This means it's important for you to include an industry analysis in your business plan.
Readers of your business plan may want to see an industry on a fast-growth track with few established competitors and great potential. Or they may be more interested in a big, if somewhat slower-growing, market with competitors who have lost touch with the market, leaving the door open for rivals.
Whatever the facts are, you'll need to support them with a snapshot analysis of the state of your industry and any trends taking place. This can't be mere off-the-cuff thinking. You need to support your opinions with market research that identifies specific competitors and outlines their weaknesses and strengths and any barriers to entry into the market. You need to describe why your industry is valuable and how it will continue to be important. Finally, and perhaps most important, you'll have to convincingly describe what makes you better and destined to succeed.
When preparing the state of the industry section, instead of looking at your business as a self-contained system, you'll describe the whole industry in which you operate and point to your position in that universe. You then zero in on your country, your state and your local community, deepening on how far your business stretches.
This part of your plan may take a little more legwork than other sections because you'll be drawing together information from a number of outside sources. You may also be reporting on or even conducting your own original research into industry affairs.
To start preparing your industry analysis and outlook, dig up the following facts about your field:
1. What is your total industry-wide sales volume? In dollars? In units?
2. What are the trends in sales volumes within your industry?
3. Who are the major players and your key competitors? What are they like?
4. What does it take to compete? What are the barriers to entry?
5. What technological trends affect your industry?
6. What are the main modes of marketing?
7. How does government regulation affect the industry?
8. In what ways are changing consumer tastes affecting your industry?
9. Identify recent demographic trends affecting the industry.
10. How sensitive is the industry to seasons and economic cycles?
11. What are key financial measures in your industry (average profit margins, sales commissions, etc.)?
If your business addresses a trend before it's been widely recognized, you need to include this information in your business plan. Providing some statistics in the trends section of your plan can make it more convincing.
Barriers to Entry
If you want to become a semiconductor manufacturer, you'll need a billion-dollar factory or two. If you want to have a TV network, you'll need programming and cable carriage in the major markets. These problems are called barriers to entry, and they exist to some extent in all industries. The barriers may be monetary, technological, distribution or market-related, or they may simply be a matter of ownership of prime real estate.
An important part of analyzing your market is determining what the barriers to entry are and how high they stretch. If the barriers are high, as is the case with automobile manufacturing, you can be assured new competitors are likely to be slow in springing up. If the barriers are low, such as opening a nail salon, which doesn't have a huge overhead, you have more opportunity to get into the game.
Be alert for innovative competitors when writing the section of your plan in which you analyze barriers to entry. Clearly some markets are also more saturated than others, and today some are dominated by the McDonald's of their industry. For example, it's hard to open a bookstore today with Amazon changing the way people buy books. In that industry, you need to be creative and explore entry into specialty books, mystery books or another niche within the larger market. Exploring entry points in the marketplace carefully will save you from a disastrous error and will certainly demonstrate to investors that you've thought your plan through and aren't jumping to conclusions.
Identifying Competitors
You're not alone, even if you have a one-person business. You also have your competition to worry about, and your backers will worry about competition, too. Even if you're truly in the rare position of addressing a brand-new market where no competition exists, most experienced people reading your plan will have questions about companies they suspect may be competitors. For these reasons, you should devote a special section of your plan to identifying competitors.
If you had to name two competitors in the athletic shoe market, you'd quickly come up with Nike and Reebok. But these by far aren't the only competitors in the sneaker business. They're just two of the main ones, and depending on the business you're in, the other ones may be more important. If you sell soccer shoes, for instance, Adidas is a bigger player than either of the two American firms. And smaller firms such as Etonic, New Balance and Saucony also have niches where they are comparatively powerful.
You can develop a list of competitors by talking to customers and suppliers, checking with industry groups, and reading trade journals. But it's not enough to simply name your competitors. You need to know their manner of operation, how they compete.
Does a competitor stress a selective, low-volume, high-margin business, or does she emphasize sales growth at any cost, taking every job that comes along, whether or not it fits any coherent scheme or offers an attractive profit? Knowing this kind of information about competitors can help you identify their weaknesses as well as their names.
Entrepreneur Staff
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- James Clear Explains Why the 'Two Minute Rule' Is the Key to Long-Term Habit Building
- They Designed One Simple Product With a 'Focus on Human Health' — and Made $40 Million Last Year
- Lock Younger Americans Don't Necessarily Want to Retire in Florida — and the 2 Affordable States at the Top of Their List Might Surprise You
- I Tried Airchat , the Hottest New Social Media App in Silicon Valley — Here's How It Works
- Lock This Side Hustle Is Helping Farmers Earn Up to $60,000 a Year While Connecting Outdoor Lovers With Untouched Wilderness
- Are Franchises in the Clear After the Expanded Joint Employer Rule Was Struck Down? Industry Experts Answer 2 Critical Questions About What's Next.
Most Popular Red Arrow
Most people have no business starting a business. here's what to consider before you become an entrepreneur.
You need to find the right business opportunity at the right time and take the right steps to beat the odds.
AI vs. Humanity — Why Humans Will Always Win in Content Creation
With the proliferation and integration of AI across organizations and business units, PR and marketing professionals may be tempted to lean into this new technology more than recommended.
Passengers Are Now Entitled to a Full Cash Refund for Canceled Flights, 'Significant' Delays
The U.S. Department of Transportation announced new rules for commercial passengers on Wednesday.
Who You Hire Matters — Here's How to Form a Team That's Built to Last
Among the many challenges related to managing a small business, hiring a quality team of employees is one of the most important. Check out this list of tips and best practices to find the best people for your business.
Franchising Is Not For Everyone. Explore These Lucrative Alternatives to Expand Your Business.
Not every business can be franchised, nor should it. While franchising can be the right growth vehicle for someone with an established brand and proven concept that's ripe for growth, there are other options available for business owners.
7 Ways You Can Use AI to 10x Your Leadership Skills
While technology can boost individual efficiency and effectiveness, it's essential to balance their use with human intuition and creativity to avoid losing personal connection and to optimize workplace satisfaction.
Successfully copied link
How to Write a Business Plan for Your Specific Industry

10 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
When writing a business plan there are sections you should include no matter your business type. However, there may be additional industry-specific information to research and include to make your plan useful.
Check out our growing list of industry business planning guides for tips on curating your plan to succeed in your chosen industry.
- Cleaning, repairs, and maintenance
It’s only a matter of time before something breaks, needs a bit of upkeep, or even some tidying up. Ensure your cleaning, repair, or maintenance business plan is solid so your business stands out in your industry.
Auto repair shop business plan
Building a successful auto repair business requires diverse services and efficiency. Hone in on your market opportunity to stand apart from competitors.
Cleaning service business plan
Success in the cleaning industry requires exceptional service and a sharp eye for customer trends. Here’s how a business plan will help you grow.
HVAC business plan
The market for HVAC services continues to grow. But to succeed as a business, you’ll need to acquire customers and scale efficiently. A business plan can help.
Laundromat business plan
Just like a retail store or tech startup, operating a successful laundromat business takes careful planning. It also requires major upfront costs, and strict compliance with environmental regulations.
- Consulting, advertising and marketing
With a lot of career options, this industry is booming with creative talent and valued expertise. Success in this industry means staying up-to-date with consumer trends and current culture while providing quality service to your clients.
Life coaching business plan
The dynamic world of coaching presents an array of opportunities to guide clients through personal and professional growth. But just as you are developing plans for your clients you need to do the same for your business.
With the right space available to you, running a business hosting events can be a fruitful experience. From formal parties, concerts, weddings, to business conferences, smaller-scale experiences, and more, it’s important to keep your planning tidy when running an events space.
Wedding venue business plan
Whether you’ve been wanting to start a wedding venue as your primary business or a side hustle, writing a wedding venue business plan can help you say “I do” to your startup.
- Farm and agriculture
An important industry for the growth and care of our food, livestock, and sustainability, farm and agriculture are imperative for our health and wellness. Whether you are growing crops or working with wildlife, it’s important to keep things organized and running smoothly.
Agritourism business plan
Still in its infancy as an industry, agritourism offers visitors a chance to get outdoors, experience life on working agricultural enterprises like a farm or ranch, and learn about sustainable practices.
Agriculture business plan
Invest plenty of time in market research, and understand how you will reach customers, if you want to maximize your chances of running a profitable agriculture business.
- Food and beverage
An industry bursting with opportunities and equally fierce competition—to thrive here takes more than good food. Whether you’re a full-service restaurant or selling direct-to-consumer pastries you need to stay on top of technology and find a hook that sets you apart.
Bakery business plan
The style, scope, and location of your bakery will require you to pay special attention to your partnerships, branding, and starting expense forecasts.
Bar business plan
To stand out in the bar industry, build a deep knowledge of your local market and offer customers something unique.
Brewery business plan
Success is about more than brewing great beer. You need to understand how to penetrate a crowded market, build a supply chain, and more.
Coffee shop business plan
Making great coffee is one thing. To run a successful coffee shop, you’ll need to understand what your competitors are doing, and what makes your shop unique.
Fast food restaurant
The fast food industry shows remarkable resilience and despite large and established brands in the market, it can be a viable option with the right plan.
Food and beverage business plan
To make it in the food and beverage business, you must stand out from the competition, manage expenses, and maintain strong supplier relationships.
Food truck business plan
Lower operational costs and a smaller team are just the start. There’s also the unique challenge of a potentially changing location and high competition to account for.
Ice cream shop business plan
Running an ice cream shop isn’t all fun and games. You’ll need to understand the preferences of your target customers, and create a solid marketing strategy to stand out.
Small restaurant business plan
Restaurant planning comes down to matching your operational needs with market expectations. You’ll want to explore how your menu, style, employees, and even the location successfully serve potential customers.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Healthcare and medical
Made up of insurance, marketing, pharmaceuticals, tech, and administrative support—you must account for legal and regulatory compliance when writing your plan.
Assisted living business plan
Demographic trends make assisted living facilities an exciting business opportunity. But upfront costs and competition means you’ll need a plan to convince investors.
Home health care business plan
This demographic shift has driven a surge in demand for custom senior and disability care options. This presents an opportunity to start your own home health care business.
Outpatient medical practice business plan
Private medical practices often rely on the expertise of the owner and staff. This means that your team credentials and service offerings should be prioritized and display market fit in your plan.
- Online and eCommerce
Digital services and online shopping show explosive growth that is dominated by an ever-growing list of new entrants competing with larger well-established organizations. Sourcing and fulfillment, along with distinct competitive advantages, should take priority during the planning process.
Amazon FBA business plan
To take full advantage of everything Amazon’s ecosystem has to offer your business, you should create an Amazon FBA business plan. The better your plan, the better your chance at success as an Amazon FBA merchant.
eCommerce business plan
Learn how to write an eCommerce business plan and focus on the needs of your customers and what sets you apart from similar options.
Etsy business plan
As a publicly traded company, information about Etsy is not in short supply. Why is this valuable for your efforts? It helps your explore where you fit in with Etsy, and where Etsy fits in with your business idea.
Mobile app business plan
Mobile app development is a lucrative but highly competitive industry. To stand apart, you need to plan beyond the idea and consider ongoing engagement, expansion, and promotion.
Online fitness business plan
Online fitness programs focus on convenience and exclusive expertise or experiences. Your plan needs to account for how you will deliver the service, who your clients will be, and what sets you apart.
SaaS business plan
If you’re diving into the competitive world of Software as a Service, you’ll need a plan to do it. Here’s how to write a SaaS business plan.
Subscription box business plan
Similar to traditional eCommerce, subscription boxes need to account just as much for the products as the online experience.
- Real estate and rentals
Covering land, residential, commercial, and industrial property—real estate ownership is far more varied and unique than it may appear. And the types of business opportunities within this industry follow suit with various opportunities across real estate development, management, lending, and professional services.
Airbnb rental business plan
Increases in remote work and long-term travel have made renting out a residence the go-to side hustle. That unfortunately means that the competition is incredibly high and you need to find a way to stand out.
Fix-n-Flip real estate business plan
Flipping real estate is an exercise in estimating how much time and money is worth investing to see a reasonable return. To succeed, you need to keep an eye on your budget and learn how to do the work yourself.
Real estate investment business plan
Starting a real estate investment business requires intensive planning and risk management. Learn to write a business plan to improve your chances of success.
Real estate business plan
The real estate industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and market trends shaping the way people buy, sell and manage properties.
- Retail and service
Selling physical goods or an intangible service relies heavily on you understanding who your customers are and knowing why what you’re selling meets their needs. Ideally, you have a passion for what you offer and can make that quality come through within your plan.
Arcade business plan
Arcades appeal to entertainment seekers of all ages. But running a successful arcade business requires offering an experience customers can’t find elsewhere.
Artist business plan
Don’t get too caught up in your creative process and skip determining how you’ll make money. Your business model and promotional strategy can make or break your chances of being paid for your passion.
Cannabis business plan
In a crowded and regulation-heavy industry you need to plan for the legal steps and what sets you apart. Along with how you’ll cover the higher starting costs.
Clothing boutique business plan
When planning to open a boutique, you need to spend as much time explaining your operations as you do outlining your brand and specialization. What sets you apart and how do your logistical decisions support that?
Daycare center business plan
There are plenty of legal requirements to plan for when starting a daycare that depends on the kids you enroll. Not to mention setting yourself apart with safety features, education benefits, or staff expertise.
Dog grooming business plan
Dog groomers are in high demand as consumers spend more discretionary income on their pets. But you’ll need to provide a unique value to stand out.
Franchise business plan
Starting a franchise is a great way to tap into the success of a recognizable brand. However, you still need a business plan to ensure you understand the business model and how to bring it to market.
Hair and beauty salon business plan
Breaking into the beauty business requires standing out among numerous competitors. Understand your service offerings and make sure they match your customers’ needs.
Law firm business plan
Running a law firm offers flexibility and steady returns. But with so many options, you’ll need a plan that mixes deep market research and a financial strategy.
Nail salon business plan
Succeeding as a nail salon business owner requires marketing savvy and the ability to stay on top of fast-changing trends and emerging styles.
Personal shopper business plan
Do you love finding great deals and assisting others in making informed shopping decisions? If so, a personal shopper business could be an ideal move.
Yoga studio business plan
Running a yoga studio lets you turn your passion into a business. But being successful requires a plan for how you’ll separate yourself from competitors.
- Why you should keep your industry in mind when writing a business plan
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to business planning.
Yes, there is a traditional structure to keep in mind—but what you include, the tools or templates you use, and the level of detail fully depends on your needs as a business owner. It also depends on the industry that you’re entering.
Starting an eCommerce business? Make sure you have your sourcing and fulfillment as well as your marketing strategy ironed out.
Renting out an Airbnb? Be sure that you have extensive details of the market, your competition, and an accurate forecast that goes beyond the startup costs.
Understanding why businesses succeed in a given industry can help you write a better plan. It may not change the overall structure, but it will inform you where your time should be spent and what parts of your plan need to be ironclad.
- Industry business plan templates and tools
Simplify your planning efforts with free industry examples and templates.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 free real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries to inspire and guide your own plan.
Explore Sample Business Plans

Free business plan template
Keep your plan organized by downloading a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
Free Agriculture Sample Business Plan PDF + How to Write

9 Min. Read
How to Create a Unique Value Proposition + Examples

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Dog Grooming Business Plan + Free Sample Plan PDF

12 Min. Read
Free Amazon FBA Business Plan PDF [2024 Template + Sample Plan]
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Industry Overview Templates with Examples and Samples

Samradni Pradhan
In the fast-paced business world, it is important for companies to stay up-to-date with the latest industry trends and insights. The most effective way to do this is by utilizing SlideTeam’s industry overview templates. These templates help businesses analyze their industries, identify key trends and challenges, and make informed decisions about their future strategies.
In this blog, we will explore the top 10 industry overview templates that businesses can use to better understand their respective domains. We will provide examples and samples of each template, along with tips on how to use them effectively.
Whether you are a startup trying to gain a foothold in a new market or an established company looking to stay ahead of the competition, these templates will be invaluable. By leveraging the insights gained from industry overviews, businesses can make informed decisions that will help them achieve their goals and succeed in today's competitive business landscape.
If you also wish to explore some project overview templates, you can check them out here !
Template 1: Industry Overview PowerPoint Presentation Slides
Introducing the perfect tool to help you analyze and assess the potential of your industry. This visually appealing slideshow has well-designed templates equipped with the latest industry trends and growth drivers. Our well-researched market analysis PowerPoint templates enable you to identify the key drivers, such as technological advancements, social and economic changes, and political factors that affect your industry's profitability. With 32 ready-to-use slides, you can display the operational information of your competitors, such as market share and geographical presence. Furthermore, these templates can showcase your company's value chain analysis, helping you gain a competitive edge in the market. So, go ahead and add this to your cart right away!

Download Now
Template 2: Wellness Industry Overview PowerPoint Presentation Slides
This PPT Deck offers a comprehensive overview of the industry, covering growth rates, health and fitness club demographics, health and wellness industry overview statistics, and more. With this PPT Set, you can showcase statistics on corporate wellness and the percentage of people using health and fitness apps. Additionally, our slides illustrate the industry's products and services segments, including membership fees and personnel training services. Gain valuable insights through the SWOT analysis and learn about the challenges of entering this competitive market. Go ahead and add this template to your cart today!

Template 3: Industry Overview of Food Production Sector PowerPoint Presentation Slides
This PPT Bundle is the perfect tool for companies in the food industry looking to gain valuable insights into the competitive landscape, key trends, and economic indicators related to food production. With SWOT, PESTEL, and Porter's Five Forces techniques, there's room to include a detailed look at the sub-segments of the food production industry overview , including meat, dairy, grains, fruits, and vegetables. Furthermore, our presentation includes an action plan to adopt Industry 4.0, enhance surveillance of the food manufacturing ecosystem, better control over complex supply chains, and more. Monitor your sales and supply chain costs with our included dashboards. Go ahead and grab this deck today!

Template 4: Retail Industry Overview PowerPoint Presentation Slides
Looking to provide your audience with an in-depth insight into your business operations? We have something amazing for you! Our templates allow you to discuss the retail industry overview , including store-based, non-store-based, and service-based retail formats, as well as the key drivers for commercial growth, such as branding, positioning, leverage margin, and merchandising. Moreover, our supply chain vendor layouts enable you to discuss ways of building and sustaining relationships, while our retailing sector presentation helps you create a roadmap for customer retention, satisfaction, and engagement. With our goods and services visuals, you can illustrate the role of information technology in commercial and business operations. Don't wait. Use these templates today!

Template 5: Hospitality Management Industry Overview PowerPoints Presentation Slides
If you want to educate and inform your audience on the key statistics and scope of services in the medical services industry, we have the right template for you. With this PPT Deck, you can give a detailed account of your company's travel and event management services. Furthermore, our service industry layouts provide an in-depth understanding of hotel and lodging business operations. Utilize these designs to create a suitable business strategy, emphasizing pricing strategies, target market, and audience. Finally, take advantage of our professionally crafted tourism industry overview slideshow and engage in various analysis platforms to evaluate your services. Download today to experience the benefits firsthand.

Template 6: Tourism Industry Overview PowerPoint Presentation Slides
This slide deck is the perfect tool to showcase the important statistics and scope of the hospitality industry. This effective presentation covers key considerations, organizational structure, types of hotels, hotel business classifications, and room division. With our hotel management strategies visuals, you can showcase hotel business plans and perform a SWOT analysis of the beverage industry. This slide deck also provides information on the startup budget of the restaurant business and highlights restaurant operating expenses. It is everything you can ask for, go ahead and download it right away!

Template 7: E-Mail Security Industry Overview and Implementation Report PowerPoint Presentation Slides
This template is specifically designed to help you educate and inform your audience about the latest trends and best practices in e-mail security. This comprehensive presentation covers key topics such as cyber threats, phishing attacks, e-mail encryption, and data protection measures. With these PPT Templates, you can showcase your organization's e-mail security policies and procedures and highlight the benefits of implementing effective e-mail security measures. Whether you're an IT professional, a security consultant, or a business owner, our slides will provide you with the insights and tools you need to safeguard your organization's sensitive information. Download today and stay one step ahead of cyber threats!

Template 8: Industry Overview and Market Trends Pitchbook for Investment Bank Underwriting Deal
This comprehensive template offers an in-depth analysis which provides investors with valuable insights to make informed investment decisions. Our Pitchbook Deck covers all major sectors, including technology, healthcare, energy, and more, presenting a clear picture of the current market landscape, competitive landscape, and growth potential. Get ahead of the competition and make informed decisions with our well-developed presentation slides. Download them today!

Template 9: Key Growth Drivers of Food Manufacturing Industry Overview of Food
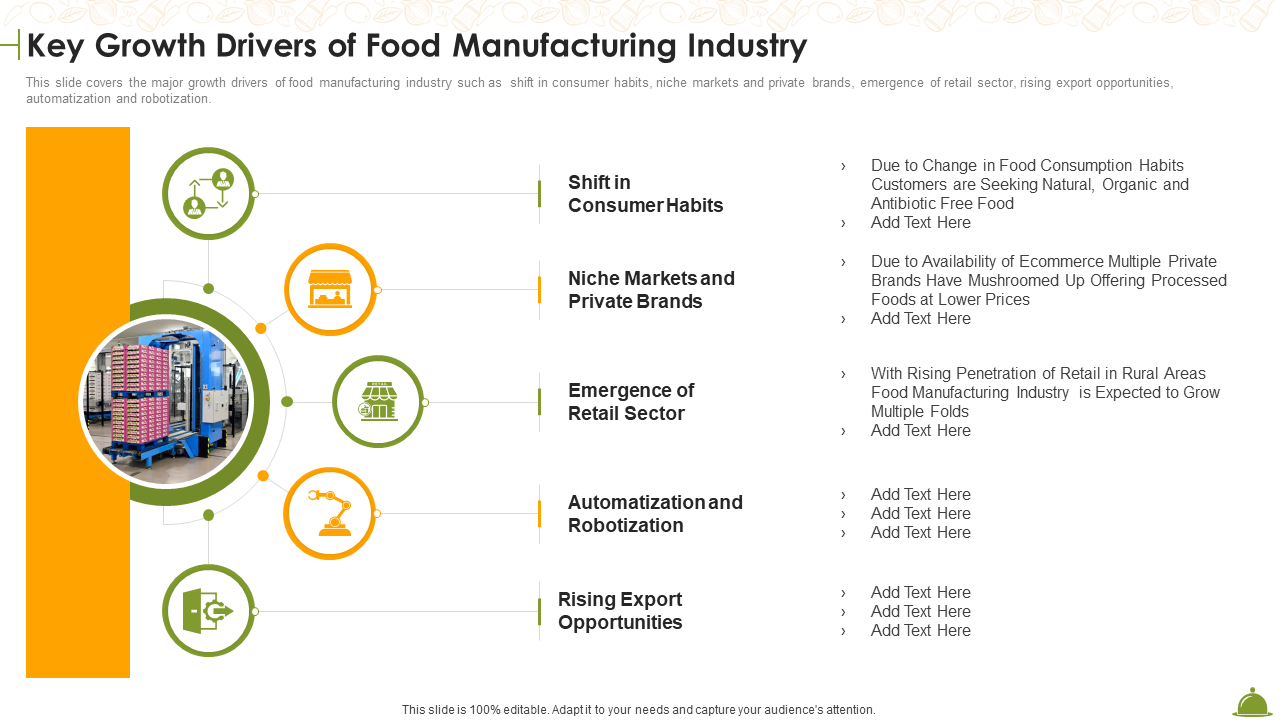
If your business is operating in the food manufacturing industry , and you need to portray a comprehensive analysis of the factors that are driving the industry growth then this template is perfect for you. This deck covers parameters like highlighting the shift in consumer habits, information on niche markets and private brands, the emergence of the retail sector, rising demand for automatization and robotization, and also some crucial information to highlight rising export opportunities. So go ahead and explore this presentation template today!
Template 10: Airlines Industry Overview Shortage of Pilots Strategies Overcome Challenge Pilot Shortage
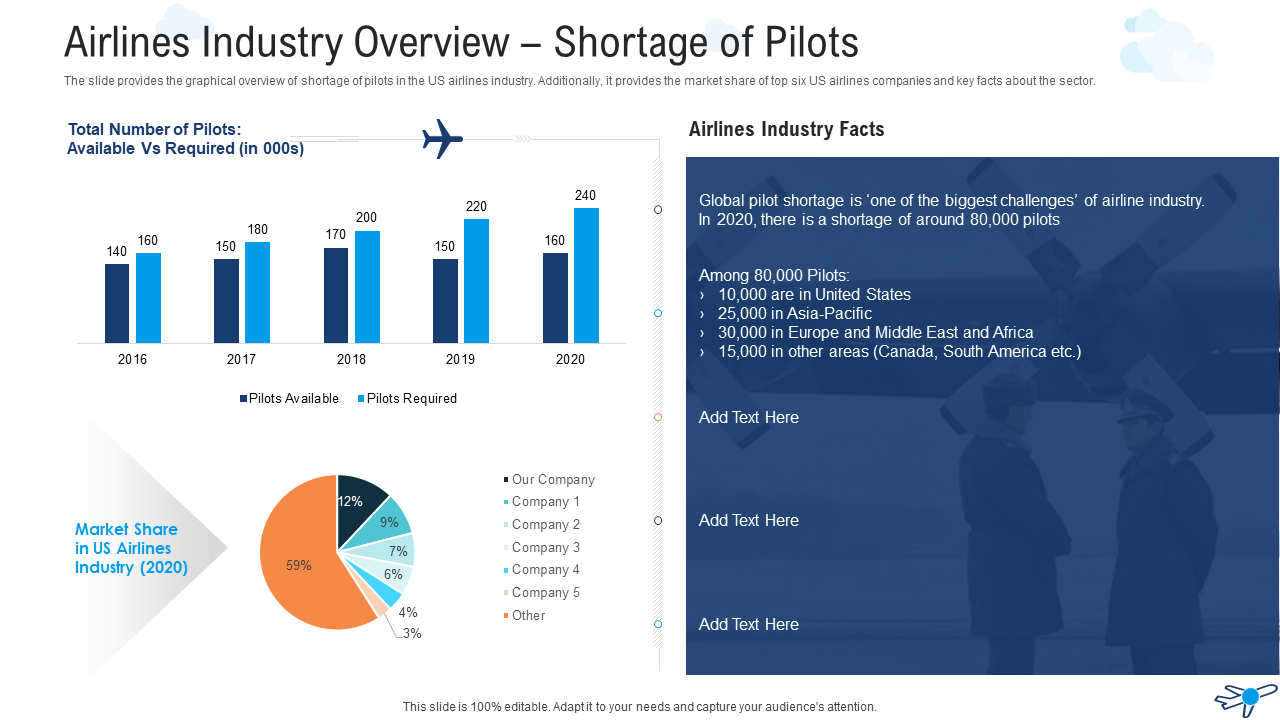
The airline industry is a vital component of global transportation, connecting people and businesses around the world. One of the important challenges that the industry is facing is the need for more pilots. If your business operates in this space, we have the perfect template for you. The layout is designed in a way to include relevant information on the number of pilots and market share of different players in the airlines industry overview . Additionally, you will find a separate section that will cover major industry drivers . So, no matter what your requirement is, you can utilize this template and make an impactful presentation.
EXPLORE THESE INDUSTRY OVERVIEW TEMPLATES TODAY!
The overall industry analysis matters the most when you want to get an impression of your business's success. And when you need to present information on the industry in general, these templates will prove to be extremely beneficial.
Download these premium PPT Slides through our monthly, semi-annual, annual, annual + custom design subscriptions here .
These templates help you understand the importance of having a professional look at your presentation. This is especially needed when discussing important information like industry analysis, market value overview, and other factors. Be sure to download and start using these professional templates today.
FAQs on Industry Overview
What is an industry overview in a business plan.
An industry overview is a critical component of a business plan that provides a comprehensive analysis of the industry in which the business operates. It helps businesses understand the competitive landscape, market trends, and key players in their industry.
It typically includes information on the market size, growth rates, and key drivers shaping the industry. It may also provide information on regulatory issues, emerging technologies, and other factors that could impact the industry's prospects.
This overview aims to help businesses identify potential opportunities and threats within their industry This enables them to make informed decisions about their strategies and investments.
What is the market and industry overview?
A market and industry overview is a comprehensive analysis of a specific market and the industry in which it operates. The market overview provides a detailed analysis of the target market's size, growth rate, and trends. It also includes information on customer behavior, preferences, and demographics. This information helps businesses to identify potential opportunities and threats within the market. The industry overview, on the other hand, provides a broader perspective of the market's competitive scenario.
By conducting a market and industry overview, businesses can better understand their target market. This information can help businesses to make important decisions about their strategies and investments and ultimately position themselves for long-term success.
What are the four types of the industry?
Industries can be broadly classified into four types:
- Primary Industries: These industries involve extracting and harvesting natural resources, such as agriculture, fishing, mining, and forestry. They are usually located in rural areas and are often characterized by low levels of technology.
- Secondary Industries: These industries involve the manufacturing and processing of raw materials into finished products. They are typically located in urban areas and are characterized by higher technology and capital investment.
- Tertiary Industries: These industries provide services to individuals and businesses. Examples include banking, healthcare, education, and tourism. These are often located in urban areas and are characterized by high customer interaction and expertise.
- Quaternary Industries: These industries involve the creation and dissemination of knowledge and information. They are typically located in urban areas and are characterized by high specialization and innovation.
Related posts:
- Top 10 Product Dashboard Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 5 Project Management Framework Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 10 Patient Dashboards Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 10 Online Dashboard Templates with Samples and Examples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

4 Must-have Process Objectives Examples with Samples and Templates
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
A lot of preparation goes into starting a business before you can open your doors to the public or launch your online store. One of your first steps should be to write a business plan . A business plan will serve as your roadmap when building your business.
Within your business plan, there’s an important section you should pay careful attention to: your market analysis. Your market analysis helps you understand your target market and how you can thrive within it.
Simply put, your market analysis shows that you’ve done your research. It also contributes to your marketing strategy by defining your target customer and researching their buying habits. Overall, a market analysis will yield invaluable data if you have limited knowledge about your market, the market has fierce competition, and if you require a business loan. In this guide, we'll explore how to conduct your own market analysis.
How to conduct a market analysis: A step-by-step guide
In your market analysis, you can expect to cover the following:
Industry outlook
Target market
Market value
Competition
Barriers to entry
Let’s dive into an in-depth look into each section:
Step 1: Define your objective
Before you begin your market analysis, it’s important to define your objective for writing a market analysis. Are you writing it for internal purposes or for external purposes?
If you were doing a market analysis for internal purposes, you might be brainstorming new products to launch or adjusting your marketing tactics. An example of an external purpose might be that you need a market analysis to get approved for a business loan .
The comprehensiveness of your market analysis will depend on your objective. If you’re preparing for a new product launch, you might focus more heavily on researching the competition. A market analysis for a loan approval would require heavy data and research into market size and growth, share potential, and pricing.
Step 2: Provide an industry outlook
An industry outlook is a general direction of where your industry is heading. Lenders want to know whether you’re targeting a growing industry or declining industry. For example, if you’re looking to sell VCRs in 2020, it’s unlikely that your business will succeed.
Starting your market analysis with an industry outlook offers a preliminary view of the market and what to expect in your market analysis. When writing this section, you'll want to include:
Market size
Are you chasing big markets or are you targeting very niche markets? If you’re targeting a niche market, are there enough customers to support your business and buy your product?
Product life cycle
If you develop a product, what will its life cycle look like? Lenders want an overview of how your product will come into fruition after it’s developed and launched. In this section, you can discuss your product’s:
Research and development
Projected growth
How do you see your company performing over time? Calculating your year-over-year growth will help you and lenders see how your business has grown thus far. Calculating your projected growth shows how your business will fare in future projected market conditions.
Step 3: Determine your target market
This section of your market analysis is dedicated to your potential customer. Who is your ideal target customer? How can you cater your product to serve them specifically?
Don’t make the mistake of wanting to sell your product to everybody. Your target customer should be specific. For example, if you’re selling mittens, you wouldn’t want to market to warmer climates like Hawaii. You should target customers who live in colder regions. The more nuanced your target market is, the more information you’ll have to inform your business and marketing strategy.
With that in mind, your target market section should include the following points:
Demographics
This is where you leave nothing to mystery about your ideal customer. You want to know every aspect of your customer so you can best serve them. Dedicate time to researching the following demographics:
Income level
Create a customer persona
Creating a customer persona can help you better understand your customer. It can be easier to market to a person than data on paper. You can give this persona a name, background, and job. Mold this persona into your target customer.
What are your customer’s pain points? How do these pain points influence how they buy products? What matters most to them? Why do they choose one brand over another?
Research and supporting material
Information without data are just claims. To add credibility to your market analysis, you need to include data. Some methods for collecting data include:
Target group surveys
Focus groups
Reading reviews
Feedback surveys
You can also consult resources online. For example, the U.S. Census Bureau can help you find demographics in calculating your market share. The U.S. Department of Commerce and the U.S. Small Business Administration also offer general data that can help you research your target industry.
Step 4: Calculate market value
You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value.
A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the two. It requires for you to calculate the entire market and then estimate how much of a share you expect your business to get. For example, let’s assume your target market consists of 100,000 people. If you’re optimistic and manage to get 1% of that market, you can expect to make 1,000 sales.
A bottom-up analysis is more data-driven and requires more research. You calculate the individual factors of your business and then estimate how high you can scale them to arrive at a projected market share. Some factors to consider when doing a bottom-up analysis include:
Where products are sold
Who your competition is
The price per unit
How many consumers you expect to reach
The average amount a customer would buy over time
While a bottom-up analysis requires more data than a top-down analysis, you can usually arrive at a more accurate calculation.
Step 5: Get to know your competition
Before you start a business, you need to research the level of competition within your market. Are there certain companies getting the lion’s share of the market? How can you position yourself to stand out from the competition?
There are two types of competitors that you should be aware of: direct competitors and indirect competitors.
Direct competitors are other businesses who sell the same product as you. If you and the company across town both sell apples, you are direct competitors.
An indirect competitor sells a different but similar product to yours. If that company across town sells oranges instead, they are an indirect competitor. Apples and oranges are different but they still target a similar market: people who eat fruits.
Also, here are some questions you want to answer when writing this section of your market analysis:
What are your competitor’s strengths?
What are your competitor’s weaknesses?
How can you cover your competitor’s weaknesses in your own business?
How can you solve the same problems better or differently than your competitors?
How can you leverage technology to better serve your customers?
How big of a threat are your competitors if you open your business?
Step 6: Identify your barriers
Writing a market analysis can help you identify some glaring barriers to starting your business. Researching these barriers will help you avoid any costly legal or business mistakes down the line. Some entry barriers to address in your marketing analysis include:
Technology: How rapid is technology advancing and can it render your product obsolete within the next five years?
Branding: You need to establish your brand identity to stand out in a saturated market.
Cost of entry: Startup costs, like renting a space and hiring employees, are expensive. Also, specialty equipment often comes with hefty price tags. (Consider researching equipment financing to help finance these purchases.)
Location: You need to secure a prime location if you’re opening a physical store.
Competition: A market with fierce competition can be a steep uphill battle (like attempting to go toe-to-toe with Apple or Amazon).
Step 7: Know the regulations
When starting a business, it’s your responsibility to research governmental and state business regulations within your market. Some regulations to keep in mind include (but aren’t limited to):
Employment and labor laws
Advertising
Environmental regulations
If you’re a newer entrepreneur and this is your first business, this part can be daunting so you might want to consult with a business attorney. A legal professional will help you identify the legal requirements specific to your business. You can also check online legal help sites like LegalZoom or Rocket Lawyer.
Tips when writing your market analysis
We wouldn’t be surprised if you feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information needed in a market analysis. Keep in mind, though, this research is key to launching a successful business. You don’t want to cut corners, but here are a few tips to help you out when writing your market analysis:
Use visual aids
Nobody likes 30 pages of nothing but text. Using visual aids can break up those text blocks, making your market analysis more visually appealing. When discussing statistics and metrics, charts and graphs will help you better communicate your data.
Include a summary
If you’ve ever read an article from an academic journal, you’ll notice that writers include an abstract that offers the reader a preview.
Use this same tactic when writing your market analysis. It will prime the reader of your market highlights before they dive into the hard data.
Get to the point
It’s better to keep your market analysis concise than to stuff it with fluff and repetition. You’ll want to present your data, analyze it, and then tie it back into how your business can thrive within your target market.
Revisit your market analysis regularly
Markets are always changing and it's important that your business changes with your target market. Revisiting your market analysis ensures that your business operations align with changing market conditions. The best businesses are the ones that can adapt.
Why should you write a market analysis?
Your market analysis helps you look at factors within your market to determine if it’s a good fit for your business model. A market analysis will help you:
1. Learn how to analyze the market need
Markets are always shifting and it’s a good idea to identify current and projected market conditions. These trends will help you understand the size of your market and whether there are paying customers waiting for you. Doing a market analysis helps you confirm that your target market is a lucrative market.
2. Learn about your customers
The best way to serve your customer is to understand them. A market analysis will examine your customer’s buying habits, pain points, and desires. This information will aid you in developing a business that addresses those points.
3. Get approved for a business loan
Starting a business, especially if it’s your first one, requires startup funding. A good first step is to apply for a business loan with your bank or other financial institution.
A thorough market analysis shows that you’re professional, prepared, and worth the investment from lenders. This preparation inspires confidence within the lender that you can build a business and repay the loan.
4. Beat the competition
Your research will offer valuable insight and certain advantages that the competition might not have. For example, thoroughly understanding your customer’s pain points and desires will help you develop a superior product or service than your competitors. If your business is already up and running, an updated market analysis can upgrade your marketing strategy or help you launch a new product.
Final thoughts
There is a saying that the first step to cutting down a tree is to sharpen an axe. In other words, preparation is the key to success. In business, preparation increases the chances that your business will succeed, even in a competitive market.
The market analysis section of your business plan separates the entrepreneurs who have done their homework from those who haven’t. Now that you’ve learned how to write a market analysis, it’s time for you to sharpen your axe and grow a successful business. And keep in mind, if you need help crafting your business plan, you can always turn to business plan software or a free template to help you stay organized.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

Analyze your market like a pro with this step-by-step guide + insider tips
Don’t fall into the trap of assuming that you already know enough about your market.
No matter how fantastic your product or service is, your business cannot succeed without sufficient market demand .
You need a clear understanding of who will buy your product or service and why .
You want to know if there is a clear market gap and a market large enough to support the survival and growth of your business.
Industry research and market analysis will help make sure that you are on the right track .
It takes time , but it is time well spent . Thank me later.
WHAT is Market Analysis?
The Market Analysis section of a business plan is also sometimes called:
- Market Demand, Market Trends, Target Market, The Market
- Industry Analysis & Trends, Industry & Market Analysis, Industry and Market Research
WHY Should You Do Market Analysis?
First and foremost, you need to demonstrate beyond any reasonable doubt that there is real need and sufficient demand for your product or service in the market, now and going forward.
- What makes you think that people will buy your products or services?
- Can you prove it?
Your due diligence on the market opportunity and validating the problem and solution described in the Product and Service section of your business plan are crucial for the success of your venture.
Also, no company operates in a vacuum. Every business is part of a larger overall industry, the forces that affect your industry as a whole will inevitably affect your business as well.
Evaluating your industry and market increases your own knowledge of the factors that contribute to your company’s success and shows the readers of your business plan that you understand the external business conditions.
External Support
In fact, if you are seeking outside financing, potential backers will most definitely be interested in industry and market conditions and trends.
You will make a positive impression and have a better chance of getting their support if you show market analysis that strengthens your business case, combining relevant and reliable data with sound judgement.
Let’s break down how to do exactly that, step by step:
HOW To Do Market Analysis: Step-by-Step
So, let’s break up how market analysis is done into three steps:
- Industry: the total market
- Target Market: specific segments of the industry that you will target
- Target Customer: characteristics of the customers that you will focus on
Step 1: Industry Analysis
How do you define an industry.
For example, the fashion industry includes fabric suppliers, designers, companies making finished clothing, distributors, sales representatives, trade publications, retail outlets online and on the high street.
How Do You Analyze an Industry?
Briefly describe your industry, including the following considerations:
1.1. Economic Conditions
Outline the current and projected economic conditions that influence the industry your business operates in, such as:
- Official economic indicators like GDP or inflation
- Labour market statistics
- Foreign trade (e.g., import and export statistics)
1.2. Industry Description
Highlight the distinct characteristic of your industry, including:
- Market leaders , major customer groups and customer loyalty
- Supply chain and distribution channels
- Profitability (e.g., pricing, cost structure, margins), financials
- Key success factors
- Barriers to entry preventing new companies from competing in the industry
1.3. Industry Size and Growth
Estimate the size of your industry and analyze how industry growth affects your company’s prospects:
- Current size (e.g., revenues, units sold, employment)
- Historic and projected industry growth rate (low/medium/high)
- Life-cycle stage /maturity (emerging/expanding/ mature/declining)
1.4. Industry Trends
- Industry Trends: Describe the key industry trends and evaluate the potential impact of PESTEL (political / economic / social / technological / environmental / legal) changes on the industry, including the level of sensitivity to:
- Seasonality
- Economic cycles
- Government regulation (e.g. environment, health and safety, international trade, performance standards, licensing/certification/fair trade/deregulation, product claims) Technological change
- Global Trends: Outline global trends affecting your industry
- Identify global industry concerns and opportunities
- International markets that could help to grow your business
- Strategic Opportunity: Highlight the strategic opportunities that exist in your industry
Step 2: Target Customer Identification
Who is a target customer.
One business can have–and often does have–more than one target customer group.
The success of your business depends on your ability to meet the needs and wants of your customers. So, in a business plan, your aim is to assure readers that:
- Your customers actually exist
- You know exactly who they are and what they want
- They are ready for what you have to offer and are likely to actually buy
How Do You Identify an Ideal Target Customer?
2.1. target customer.
- Identify the customer, remembering that the decision-maker who makes the purchase can be a different person or entity than the end-user.
2.2. Demographics
- For consumers ( demographics ): Age, gender, income, occupation, education, family status, home ownership, lifestyle (e.g., work and leisure activities)
- For businesses ( firmographic ): Industry, sector, years in business, ownership, size (e.g., sales, revenues, budget, employees, branches, sq footage)
2.3. Geographic Location
- Where are your customers based, where do they buy their products/services and where do they actually use them
2.4 Purchasing Patterns
- Identify customer behaviors, i.e., what actions they take
- how frequently
- and how quickly they buy
2.5. Psychographics
- Identify customer attitudes, i.e., how they think or feel
- Urgency, price, quality, reputation, image, convenience, availability, features, brand, customer service, return policy, sustainability, eco-friendliness, supporting local business
- Necessity/luxury, high involvement bit ticket item / low involvement consumable
Step 3: Target Market Analysis
What is a target market.
Target market, or 'target audience', is a group of people that a business has identified as the most likely to purchase its offering, defined by demographic, psychographic, geographic and other characteristics. Target market may be broken down to target customers to customize marketing efforts.
How Do You Analyze a Target Market?
So, how many people are likely to become your customers?
To get an answer to this questions, narrow the industry into your target market with a manageable size, and identify its key characteristics, size and trends:
3.1. Target Market Description
Define your target market by:
- Type: B2C, B2B, government, non-profits
- Geographic reach: Specify the geographic location and reach of your target market
3.2. Market Size and Share
Estimate how large is the market for your product or service (e.g., number of customers, annual purchases in sales units and $ revenues). Explain the logic behind your calculation:
- TAM (Total Available/Addressable/Attainable Market) is the total maximum demand for a product or service that could theoretically be generated by selling to everyone in the world who could possibly buy from you, regardless of competition and any other considerations and restrictions.
- SAM (Serviceable Available Market) is the portion of the TAM that you could potentially address in a specific market. For example, if your product/service is only available in one country or language.
- SOM (Service Obtainable Market / Share of Market) is the share of the SAM that you can realistically carve out for your product or service. This the target market that you will be going after and can reasonably expect to convert into a customer base.
3.3. Market Trends
Illustrate the most important themes, changes and developments happening in your market. Explain the reasons behind these trends and how they will favor your business.
3.4. Demand Growth Opportunity
Estimate future demand for your offering by translating past, current and future market demand trends and drivers into forecasts:
- Historic growth: Check how your target market has grown in the past.
- Drivers past: Identify what has been driving that growth in the past.
- Drivers future: Assess whether there will be any change in influence of these and other drivers in the future.
How Big Should My Target Market Be?
Well, if the market opportunity is small, it will limit how big and successful your business can become. In fact, it may even be too small to support a successful business at all.
On the other hand, many businesses make the mistake of trying to appeal to too many target markets, which also limits their success by distracting their focus.

What If My Stats Look Bad?
Large and growing market suggests promising demand for your offering now and into the future. Nevertheless, your business can still thrive in a smaller or contracting market.
Instead of hiding from unfavorable stats, acknowledge that you are swimming against the tide and devise strategies to cope with whatever lies ahead.
Step 4: Industry and Market Analysis Research
The market analysis section of your business plan should illustrate your own industry and market knowledge as well as the key findings and conclusions from your research.
Back up your findings with external research sources (= secondary research) and results of internal market research and testing (= primary research).
What is Primary and Secondary Market Research?
Yes, there are two main types of market research – primary and secondary – and you should do both to adequately cover the market analysis section of your business plan:
- Primary market research is original data you gather yourself, for example in the form of active fieldwork collecting specific information in your market.
- Secondary market research involves collating information from existing data, which has been researched and shared by reliable outside sources . This is essentially passive desk research of information already published .
Unless you are working for a corporation, this exercise is not about your ability to do professional-level market research.
Instead, you just need to demonstrate fundamental understanding of your business environment and where you fit in within the market and broader industry.
Why Do You Need To Do Primary & Secondary Market Research?
There are countless ways you could go collecting industry and market research data, depending on the type of your business, what your business plan is for, and what your needs, resources and circumstances are.
For tried and tested tips on how to properly conduct your market research, read the next section of this guide that is dedicated to primary and secondary market research methods.
In any case, tell the reader how you carried out your market research. Prove what the facts are and where you got your data. Be as specific as possible. Provide statistics, numbers, and sources.
When doing secondary research, always make sure that all stats, facts and figures are from reputable sources and properly referenced in both the main text and the Appendix of your business plan. This gives more credibility to your business case as the reader has more confidence in the information provided.
Go to the Primary and Secondary Market Research post for my best tips on industry, market and competitor research.
7 TOP TIPS For Writing Market Analysis
1. realistic projections.
Above all, make sure that you are realistic in your projections about how your product or service is going to be accepted in the market, otherwise you are going to seriously undermine the credibility of your entire business case.
2. Laser Focus
Discuss only characteristic of your target market and customers that are observable, factual and meaningful, i.e. directly relate to your customers’ decision to purchase.
Always relate the data back to your business. Market statistics are meaningless until you explain where and how your company fits in.
For example, as you write about the market gap and the needs of your target customers, highlight how you are uniquely positioned to fill them.
In other words, your goal is to:
- Present your data
- Analyze the data
- Tie the data back to how your business can thrive within your target market
3. Target Audience
On a similar note, tailor the market analysis to your target audience and the specific purpose at hand.
For example, if your business plan is for internal use, you may not have to go into as much detail about the market as you would have for external financiers, since your team is likely already very familiar with the business environment your company operates in.
4. Story Time
Make sure that there is a compelling storyline and logical flow to the market information presented.
The saying “a picture is worth a thousand words” certainly applies here. Industry and market statistics are easier to understand and more impactful if presented as a chart or graph.
6. Information Overload
Keep your market analysis concise by only including pertinent information. No fluff, no repetition, no drowning the reader in a sea of redundant facts.
While you should not assume that the reader knows anything about your market, do not elaborate on unnecessary basic facts either.
Do not overload the reader in the main body of the business plan. Move everything that is not essential to telling the story into the Appendix. For example, summarize the results of market testing survey in the main body of the business plan document, but move the list of the actual survey questions into the appendix.
7. Marketing Plan
Note that market analysis and marketing plan are two different things, with two distinct chapters in a business plan.
As the name suggests, market analysis examines where you fit in within your desired industry and market. As you work thorugh this section, jot down your ideas for the marketing and strategy section of your business plan.
Final Thoughts
Remember that the very act of doing the research and analysis is a great opportunity to learn things that affect your business that you did not know before, so take your time doing the work.
Related Questions
What is the purpose of industry & market research and analysis.
The purpose of industry and market research and analysis is to qualitatively and quantitatively assess the environment of a business and to confirm that the market opportunity is sufficient for sustainable success of that business.
Why are Industry & Market Research and Analysis IMPORTANT?
Industry and market research and analysis are important because they allow you to gain knowledge of the industry, the target market you are planning to sell to, and your competition, so you can make informed strategic decisions on how to make your business succeed.
How Can Industry & Market Research and Analysis BENEFIT a Business?
Industry and market research and analysis benefit a business by uncovering opportunities and threats within its environment, including attainable market size, ideal target customers, competition and any potential difficulties on the company’s journey to success.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
What Is an Industry Size Business Plan?
An industry size business plan is necessary for budgeting and marketing, especially for those who will seek third-party financing. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
An industry size business plan is necessary for budgeting and marketing, especially for those who will seek third-party financing. Most venture capitalists want to know the potential size of the market for the businesses they're investing in. Ultimately, the size of the potential market for the products or services your business is offering determines the value of your business, and to most venture capitalists, the larger that market, the better.
TAM, or Total Available Market, refers to the maximum size of the market for a business's offerings, and it may include both people and revenue. SAM, or Served Available Market, refers to the segment of the TAM consisting of people who will be able to use the business's solution. The SAM will be the business's target market.
Market Size Presentation
The section of your business plan pertaining to market size can be presented in any number of ways. One of the easiest ways to do this is with a simple columnar format that outlines the TAM and SAM now and in five years. This will allow the investor to quickly determine the potential size of the market and its growth over the course of your business plan.
While sizing of the market is important, it is only a plan. The market size section of your business plan can only provide an educated guess at how large the available market will be. This is your opportunity to demonstrate your plans for a successful launch and continued growth.
Available Data and Statistics
Market sizing is largely based on trade association data and any other available statistics. Begin with verifiable base data, including government statistics when available. Cross-reference your information with alternative sources whenever possible. Make sure that your findings make sense.
You should also be specific. For example, you wouldn't want to say, "There are millions of properties in the world with pools, and if we take a small percentage of that, our business plan will work." Rather, keep the industry definition very narrow.
Your analysis will differ depending on whether or not you're dealing with a pre-existing market or a new market. If you're dealing with an existing product, there will be industry and market data available to you. If you're dealing with a new product , you may need to conduct market research, consult with potential customers, and go from there.
Determining Your Market Size
Determining your market size will help you make a clear distinction between two categories:
- Addressable market - the total revenue opportunity for your product or service
- Available market - the portion of the addressable market you can realistically compete with
If you don't have a firm grip on your market size, you'll put your business's success at risk, both in these early stages and through its life cycle.
Estimating Your Market Size
Market sizing will allow you to gain a sense of current market trends. It can help you uncover the drivers of demand, since movements or changes in the market tend to continue for a period of time. Furthermore, studying these trends can reveal whether there's another product on the way that could potentially affect your market size.
When estimating market size, the best place to start is to consider the problem you intend to solve and how much value your product or service will have to consumers. This is actually something many entrepreneurs tend to overlook because they become engrossed in the product they've developed and not its benefits to the audience.
To estimate your market size, follow these steps:
- Clearly define the customer you're targeting.
- Estimate how many customers you will be targeting.
- Figure out your penetration rate.
- Calculate both the volume and the value to your potential market size.
- Apply the data.
Determining Your Market Potential
It doesn't matter if you're seeking third-party financing or not. Understanding the potential for your market will help you in the following areas:
- Product development
- Organizational design
- Distribution
- Partnerships
- Employee skills
Beyond this, understanding your market potential will help you address more mundane issues, such as selecting a bank, hiring an account, or seeking legal counsel .
If you need help with your industry size business plan, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Market Analysis: Everything You Need To Know
- Business Plan for New Company
- IT Company Business Plan
- Creating a Business Plan
- How to Value a Company
- Business Plan Outline: Everything You Need To Know
- How to Evaluate a Startup
- Real Estate Rental Business Plan
- Parts of Business Plan and Definition
- Import Export Business Plan
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Business Plans
How to Write a Business Plan Industry Analysis
How do you conduct industry analysis for a business plan? Do you need help conducting market research and industry analysis for your business plan? Then I advice you read on. So you have a great business idea, you have refined and fine-tuned it, and you are ready to launch. You are going to offer a product or service with a clearly defined customer base, and you are confident that you will be successful in the long term.
Well, if the above applies perfectly to you, then you have not completed your assignment. What happens when you enter an examination hall without having studied for the exam at all? You’d spend all your time in the hall blaming yourself for being silly, right? Now, starting a business is even much more important because there’s a lot more at stake than passing or failing a grade. So, you must not leave out any aspect of research undone.
In this section of your business plan, you will demonstrate that the industry’s market size is worth going after, who your main competitors will be if you decide to take a plunge, and how you will be able to carve out a niche for yourself and give your competitors a run for their money. Planning a business goes beyond analyzing the potential of your offer. You must analyze the following three factors as well:
- The strengths and weaknesses of your business
- The competition
- Who your customers are, what they want, and how they want it
These are the major components of a business plan’s market or industrial analysis and it is also known as a SWOT (Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analysis. This section of your business plan reveals the chances of your business to achieve success with its offers. And that’s why the industry analysis is a very important section of your business plan, which must be carefully conducted and documented.
So in this article, we will be looking at how to conduct industry analysis for a business plan. If you are a budding entrepreneur, or you are planning to start a new business; then below are the exact steps to follow when conducting an industry analysis for a new business:
How to Conduct Industry Analysis for a Business Plan
1. analyze the competition.
Of the three factors listed above, the competition may prove the most difficult to analyze, especially if you are new to the industry. But there are ways to simplify the task. You can start by looking at your direct competitors. If you are planning to start a new restaurant in an area, your direct competitors are other restaurants within that locality, while your indirect competitors are those that are slightly remote but still around.
Now, you are not just counting the number of rivals you have. You are trying to see how you can push ahead of them by filling a loophole they never noticed all these while. Some people find it hard to leave their workplace for the restaurant at lunchtime, but it’s either they do it or go hungry. You can disrupt the market’s status quo by offering to deliver lunch to people right in their workplaces. Filling loopholes like this one should be your goal.
If you don’t device strategies for pushing ahead of the competition, you will just enter the industry and join the survival race that you may never win. So, you need to introduce an innovation that will threaten your rivals. Remember, it’s either you differentiate or you fizzle out fast!
2. Assess the industry / market size
After analyzing your direct and indirect competitors, you will need to analyze your chances of standing firm even in the face of stiffer competition. Your first step in market research is to get an idea of how big the opportunity is and why it’s worth going after.
This means finding out how many customers you are catering to and much revenue you are likely to make. This is a convincing first step to lure in whoever is reading your business plan to become intrigued and dig further into your findings. Here are some factors you should consider:
- The individual strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
- The rate at which new competitors enter the market or the rate at which old competitors are leaving the market.
- The products or services that fetch most revenue for your competitors.
- How you will overcome the threat of substitute goods.
You can get lots of helpful information about your market from government sources, trade associations, financial services firms, online data providers, and free resources on the web.
3. Analyze industry forces and trends
You will need to outline what’s happening in the industry from many perspectives that would help the reader get the full gist on whether the market is lucrative or not. A great general-purpose tool for doing just that is the PEST Analysis. Here’s what it stands for and what you should consider:
- P – Political factors ( the role government plays in your industry )
- E – Economic factors ( the state of the economy on both local and national level )
- S – Social factors ( relevant changes in matters like lifestyle trends, demographics, consumer attitudes, buying patterns and opinions )
- T – Technological factors ( the impact of changing technological trends on your industry )
4. Develop your marketing plan
Developing your marketing plan entails answering the following questions:
- What products or services are you offering?
- How much will you charge for your offers?
- Where will you sell your product, and who are your target customers?
- What special incentives would you use to encourage customers to buy your product?
In short, this section of your industry analysis outlines how you will deliver your product to the customers and how you will win customers to your side.
5. Craft your growth plan
While some entrepreneurs are of the opinion that this step should come only after you have established your business, crafting your market development plan helps you envision your company growing in a few years. Your growth plan should address the following questions:
- According to recent data, is the market for your product growing or dwindling?
- Do you plan to introduce new products or line extensions in the next few years?
- If you plan to introduce new offers, would they be closely related to your current offers or within another niche entirely?
- Are there strategies for giving your business the competitive advantage in the industry?
- Are there plans to handle increasing demand?
6. Fine-tune your analysis
After the steps discussed above, cross check your analyses to ensure that your findings are factual and your figures are accurate. Another handy tool to have in your arsenal when conducting industry research is the almighty Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis . ( Don’t worry if you’ve never attended a business strategy class in your life, it’s actually quite straightforward ). Here’s the breakdown:
Threat of new entrants
How difficult ( or easy ) is it for someone to enter your specific vertical? If it’s very easy then most likely the space will be crowded with competitors fighting for margins. Conversely, if it’s very difficult, that that in itself can become a competitive advantage.
Threat of substitute products or services
How likely is it that another product or service could decrease demand or displace you and potentially the entire industry all together?
Bargaining power of customers
When it comes to pricing and terms, how much power does your customer have? Are they organized enough to exercise their purchase power, or is there so much competition that they have their pick resulting in pricing wars amongst providers?
Bargaining power of suppliers
This refers to how dependent you are on a given supplier to operate your business. If it’s difficult or near impossible for you to switch, that means they have the upper hand, whereas, if the switching costs are low, you can negotiate better terms for yourself.
Competitive rivalry of the market
Factoring in the first four forces, you can arrive at a good understanding of the playing field and whether it’s in your favor if you enter it, how long you’ll be able to last, through what means you’ll carve a space for yourself, and what you’re up against.
As a final note, you must never forget that the industry analysis is a vital part of your business plan and it will probably be the most extensive portion of it. So, take your time to conduct extensive research on your competitors and market trends over the recent years.
- Go to Chapter 9 Part B: Writing a Business Plan Competitive Market Analysis
- Go Back to Chapter 8: Writing your Company’s Profile
- Go Back to Introduction and Table of Content
More on Business Plans
24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
Published: February 06, 2024
I believe that reading sample business plans is essential when writing your own.

hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'e9d2eacb-6b01-423a-bf7a-19d42ba77eaa', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
As you explore business plan examples from real companies and brands, it’s easier for you to learn how to write a good one.
But what does a good business plan look like? And how do you write one that’s both viable and convincing. I’ll walk you through the ideal business plan format along with some examples to help you get started.
Table of Contents
Business Plan Format
Business plan types, sample business plan templates, top business plan examples.
Ask any successful sports coach how they win so many games, and they’ll tell you they have a unique plan for every single game. To me, the same logic applies to business.
If you want to build a thriving company that can pull ahead of the competition, you need to prepare for battle before breaking into a market.
Business plans guide you along the rocky journey of growing a company. And if your business plan is compelling enough, it can also convince investors to give you funding.
With so much at stake, I’m sure you’re wondering where to begin.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Fill out the form to get your free template.
First, you’ll want to nail down your formatting. Most business plans include the following sections.
1. Executive Summary
I’d say the executive summary is the most important section of the entire business plan.
Why? Essentially, it's the overview or introduction, written in a way to grab readers' attention and guide them through the rest of the business plan. This is important, because a business plan can be dozens or hundreds of pages long.
There are two main elements I’d recommend including in your executive summary:
Company Description
This is the perfect space to highlight your company’s mission statement and goals, a brief overview of your history and leadership, and your top accomplishments as a business.
Tell potential investors who you are and why what you do matters. Naturally, they’re going to want to know who they’re getting into business with up front, and this is a great opportunity to showcase your impact.
Need some extra help firming up those business goals? Check out HubSpot Academy’s free course to help you set goals that matter — I’d highly recommend it
Products and Services
To piggyback off of the company description, be sure to incorporate an overview of your offerings. This doesn’t have to be extensive — just another chance to introduce your industry and overall purpose as a business.
In addition to the items above, I recommend including some information about your financial projections and competitive advantage here too.:
Keep in mind you'll cover many of these topics in more detail later on in the business plan. So, keep the executive summary clear and brief, and only include the most important takeaways.
Executive Summary Business Plan Examples
This example was created with HubSpot’s business plan template:

This executive summary is so good to me because it tells potential investors a short story while still covering all of the most important details.
.webp?width=500&height=418&name=executive-summary-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
Image Source
Tips for Writing Your Executive Summary
- Start with a strong introduction of your company, showcase your mission and impact, and outline the products and services you provide.
- Clearly define a problem, and explain how your product solves that problem, and show why the market needs your business.
- Be sure to highlight your value proposition, market opportunity, and growth potential.
- Keep it concise and support ideas with data.
- Customize your summary to your audience. For example, emphasize finances and return on investment for venture capitalists.
Check out our tips for writing an effective executive summary for more guidance.
2. Market Opportunity
This is where you'll detail the opportunity in the market.
The main question I’d ask myself here is this: Where is the gap in the current industry, and how will my product fill that gap?
More specifically, here’s what I’d include in this section:
- The size of the market
- Current or potential market share
- Trends in the industry and consumer behavior
- Where the gap is
- What caused the gap
- How you intend to fill it
To get a thorough understanding of the market opportunity, you'll want to conduct a TAM, SAM, and SOM analysis and perform market research on your industry.
You may also benefit from creating a SWOT analysis to get some of the insights for this section.
Market Opportunity Business Plan Example
I like this example because it uses critical data to underline the size of the potential market and what part of that market this service hopes to capture.

Tips for Writing Your Market Opportunity Section
- Focus on demand and potential for growth.
- Use market research, surveys, and industry trend data to support your market forecast and projections.
- Add a review of regulation shifts, tech advances, and consumer behavior changes.
- Refer to reliable sources.
- Showcase how your business can make the most of this opportunity.
3. Competitive Landscape
Since we’re already speaking of market share, you'll also need to create a section that shares details on who the top competitors are.
After all, your customers likely have more than one brand to choose from, and you'll want to understand exactly why they might choose one over another.
My favorite part of performing a competitive analysis is that it can help you uncover:
- Industry trends that other brands may not be utilizing
- Strengths in your competition that may be obstacles to handle
- Weaknesses in your competition that may help you develop selling points
- The unique proposition you bring to the market that may resonate with customers
Competitive Landscape Business Plan Example
I like how the competitive landscape section of this business plan below shows a clear outline of who the top competitors are.
.webp?width=500&height=405&name=competitive-landscape-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
It also highlights specific industry knowledge and the importance of location, which shows useful experience in this specific industry.
This can help build trust in your ability to execute your business plan.
Tips for Writing Your Competitive Landscape
- Complete in-depth research, then emphasize your most important findings.
- Compare your unique selling proposition (USP) to your direct and indirect competitors.
- Show a clear and realistic plan for product and brand differentiation.
- Look for specific advantages and barriers in the competitive landscape. Then, highlight how that information could impact your business.
- Outline growth opportunities from a competitive perspective.
- Add customer feedback and insights to support your competitive analysis.
4. Target Audience
Use this section to describe who your customer segments are in detail. What is the demographic and psychographic information of your audience?
If your immediate answer is "everyone," you'll need to dig deeper. Here are some questions I’d ask myself here:
- What demographics will most likely need/buy your product or service?
- What are the psychographics of this audience? (Desires, triggering events, etc.)
- Why are your offerings valuable to them?
I’d also recommend building a buyer persona to get in the mindset of your ideal customers and be clear on why you're targeting them.
Target Audience Business Plan Example
I like the example below because it uses in-depth research to draw conclusions about audience priorities. It also analyzes how to create the right content for this audience.
Tips for Writing Your Target Audience Section
- Include details on the size and growth potential of your target audience.
- Figure out and refine the pain points for your target audience , then show why your product is a useful solution.
- Describe your targeted customer acquisition strategy in detail.
- Share anticipated challenges your business may face in acquiring customers and how you plan to address them.
- Add case studies, testimonials, and other data to support your target audience ideas.
- Remember to consider niche audiences and segments of your target audience in your business plan.
5. Marketing Strategy
Here, you'll discuss how you'll acquire new customers with your marketing strategy. I’d suggest including information:
- Your brand positioning vision and how you'll cultivate it
- The goal targets you aim to achieve
- The metrics you'll use to measure success
- The channels and distribution tactics you'll use
I think it’s helpful to have a marketing plan built out in advance to make this part of your business plan easier.
Marketing Strategy Business Plan Example
This business plan example includes the marketing strategy for the town of Gawler.
In my opinion, it really works because it offers a comprehensive picture of how they plan to use digital marketing to promote the community.
Tips for Writing Your Marketing Strategy
- Include a section about how you believe your brand vision will appeal to customers.
- Add the budget and resources you'll need to put your plan in place.
- Outline strategies for specific marketing segments.
- Connect strategies to earlier sections like target audience and competitive analysis.
- Review how your marketing strategy will scale with the growth of your business.
- Cover a range of channels and tactics to highlight your ability to adapt your plan in the face of change.
6. Key Features and Benefits
At some point in your business plan, you'll need to review the key features and benefits of your products and/or services.
Laying these out can give readers an idea of how you're positioning yourself in the market and the messaging you're likely to use. It can even help them gain better insight into your business model.
Key Features and Benefits Business Plan Example
In my opinion, the example below does a great job outlining products and services for this business, along with why these qualities will attract the audience.

Tips for Writing Your Key Features and Benefits
- Emphasize why and how your product or service offers value to customers.
- Use metrics and testimonials to support the ideas in this section.
- Talk about how your products and services have the potential to scale.
- Think about including a product roadmap.
- Focus on customer needs, and how the features and benefits you are sharing meet those needs.
- Offer proof of concept for your ideas, like case studies or pilot program feedback.
- Proofread this section carefully, and remove any jargon or complex language.
7. Pricing and Revenue
This is where you'll discuss your cost structure and various revenue streams. Your pricing strategy must be solid enough to turn a profit while staying competitive in the industry.
For this reason, here’s what I’d might outline in this section:
- The specific pricing breakdowns per product or service
- Why your pricing is higher or lower than your competition's
- (If higher) Why customers would be willing to pay more
- (If lower) How you're able to offer your products or services at a lower cost
- When you expect to break even, what margins do you expect, etc?
Pricing and Revenue Business Plan Example
I like how this business plan example begins with an overview of the business revenue model, then shows proposed pricing for key products.

Tips for Writing Your Pricing and Revenue Section
- Get specific about your pricing strategy. Specifically, how you connect that strategy to customer needs and product value.
- If you are asking a premium price, share unique features or innovations that justify that price point.
- Show how you plan to communicate pricing to customers.
- Create an overview of every revenue stream for your business and how each stream adds to your business model as a whole.
- Share plans to develop new revenue streams in the future.
- Show how and whether pricing will vary by customer segment and how pricing aligns with marketing strategies.
- Restate your value proposition and explain how it aligns with your revenue model.
8. Financials
To me, this section is particularly informative for investors and leadership teams to figure out funding strategies, investment opportunities, and more.
According to Forbes , you'll want to include three main things:
- Profit/Loss Statement - This answers the question of whether your business is currently profitable.
- Cash Flow Statement - This details exactly how much cash is incoming and outgoing to give insight into how much cash a business has on hand.
- Balance Sheet - This outlines assets, liabilities, and equity, which gives insight into how much a business is worth.
While some business plans might include more or less information, these are the key details I’d include in this section.
Financials Business Plan Example
This balance sheet is a great example of level of detail you’ll need to include in the financials section of your business plan.
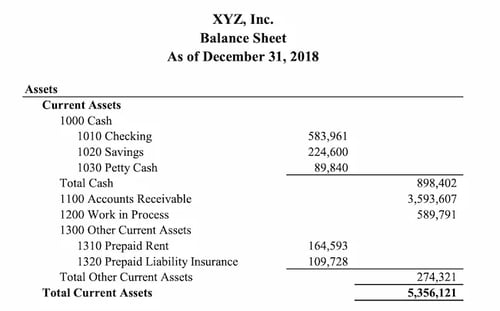
Tips for Writing Your Financials Section
- Growth potential is important in this section too. Using your data, create a forecast of financial performance in the next three to five years.
- Include any data that supports your projections to assure investors of the credibility of your proposal.
- Add a break-even analysis to show that your business plan is financially practical. This information can also help you pivot quickly as your business grows.
- Consider adding a section that reviews potential risks and how sensitive your plan is to changes in the market.
- Triple-check all financial information in your plan for accuracy.
- Show how any proposed funding needs align with your plans for growth.
As you create your business plan, keep in mind that each of these sections will be formatted differently. Some may be in paragraph format, while others could be charts or graphs.
The formats above apply to most types of business plans. That said, the format and structure of your plan will vary by your goals for that plan.
So, I’ve added a quick review of different business plan types. For a more detailed overview, check out this post .
1. Startups
Startup business plans are for proposing new business ideas.
If you’re planning to start a small business, preparing a business plan is crucial. The plan should include all the major factors of your business.
You can check out this guide for more detailed business plan inspiration .
2. Feasibility Studies
Feasibility business plans focus on that business's product or service. Feasibility plans are sometimes added to startup business plans. They can also be a new business plan for an already thriving organization.
3. Internal Use
You can use internal business plans to share goals, strategies, or performance updates with stakeholders. In my opinion, internal business plans are useful for alignment and building support for ambitious goals.
4. Strategic Initiatives
Another business plan that's often for sharing internally is a strategic business plan. This plan covers long-term business objectives that might not have been included in the startup business plan.
5. Business Acquisition or Repositioning
When a business is moving forward with an acquisition or repositioning, it may need extra structure and support. These types of business plans expand on a company's acquisition or repositioning strategy.
Growth sometimes just happens as a business continues operations. But more often, a business needs to create a structure with specific targets to meet set goals for expansion. This business plan type can help a business focus on short-term growth goals and align resources with those goals.
Now that you know what's included and how to format a business plan, let's review some of my favorite templates.
1. HubSpot's One-Page Business Plan
Download a free, editable one-page business plan template..
The business plan linked above was created here at HubSpot and is perfect for businesses of any size — no matter how many strategies we still have to develop.
Fields such as Company Description, Required Funding, and Implementation Timeline give this one-page business plan a framework for how to build your brand and what tasks to keep track of as you grow.
Then, as the business matures, you can expand on your original business plan with a new iteration of the above document.
Why I Like It
This one-page business plan is a fantastic choice for the new business owner who doesn’t have the time or resources to draft a full-blown business plan. It includes all the essential sections in an accessible, bullet-point-friendly format. That way, you can get the broad strokes down before honing in on the details.
2. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

We also created a business plan template for entrepreneurs.
The template is designed as a guide and checklist for starting your own business. You’ll learn what to include in each section of your business plan and how to do it.
There’s also a list for you to check off when you finish each section of your business plan.
Strong game plans help coaches win games and help businesses rocket to the top of their industries. So if you dedicate the time and effort required to write a workable and convincing business plan, you’ll boost your chances of success and even dominance in your market.
This business plan kit is essential for the budding entrepreneur who needs a more extensive document to share with investors and other stakeholders.
It not only includes sections for your executive summary, product line, market analysis, marketing plan, and sales plan, but it also offers hands-on guidance for filling out those sections.
3. LiveFlow’s Financial Planning Template with built-in automation
This free template from LiveFlow aims to make it easy for businesses to create a financial plan and track their progress on a monthly basis.
The P&L Budget versus Actual format allows users to track their revenue, cost of sales, operating expenses, operating profit margin, net profit, and more.
The summary dashboard aggregates all of the data put into the financial plan sheet and will automatically update when changes are made.
Instead of wasting hours manually importing your data to your spreadsheet, LiveFlow can also help you to automatically connect your accounting and banking data directly to your spreadsheet, so your numbers are always up-to-date.
With the dashboard, you can view your runway, cash balance, burn rate, gross margins, and other metrics. Having a simple way to track everything in one place will make it easier to complete the financials section of your business plan.
This is a fantastic template to track performance and alignment internally and to create a dependable process for documenting financial information across the business. It’s highly versatile and beginner-friendly.
It’s especially useful if you don’t have an accountant on the team. (I always recommend you do, but for new businesses, having one might not be possible.)
4. ThoughtCo’s Sample Business Plan

One of the more financially oriented sample business plans in this list, BPlan’s free business plan template dedicates many of its pages to your business’s financial plan and financial statements.
After filling this business plan out, your company will truly understand its financial health and the steps you need to take to maintain or improve it.
I absolutely love this business plan template because of its ease-of-use and hands-on instructions (in addition to its finance-centric components). If you feel overwhelmed by the thought of writing an entire business plan, consider using this template to help you with the process.
6. Harvard Business Review’s "How to Write a Winning Business Plan"
Most sample business plans teach you what to include in your business plan, but this Harvard Business Review article will take your business plan to the next level — it teaches you the why and how behind writing a business plan.
With the guidance of Stanley Rich and Richard Gumpert, co-authors of " Business Plans That Win: Lessons From the MIT Enterprise Forum ", you'll learn how to write a convincing business plan that emphasizes the market demand for your product or service.
You’ll also learn the financial benefits investors can reap from putting money into your venture rather than trying to sell them on how great your product or service is.
This business plan guide focuses less on the individual parts of a business plan, and more on the overarching goal of writing one. For that reason, it’s one of my favorites to supplement any template you choose to use. Harvard Business Review’s guide is instrumental for both new and seasoned business owners.
7. HubSpot’s Complete Guide to Starting a Business
If you’re an entrepreneur, you know writing a business plan is one of the most challenging first steps to starting a business.
Fortunately, with HubSpot's comprehensive guide to starting a business, you'll learn how to map out all the details by understanding what to include in your business plan and why it’s important to include them. The guide also fleshes out an entire sample business plan for you.
If you need further guidance on starting a business, HubSpot's guide can teach you how to make your business legal, choose and register your business name, and fund your business. It will also give small business tax information and includes marketing, sales, and service tips.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of starting a business, in addition to writing your business plan, with a high level of exactitude and detail. So if you’re in the midst of starting your business, this is an excellent guide for you.
It also offers other resources you might need, such as market analysis templates.
8. Panda Doc’s Free Business Plan Template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
Once you fill it out, you’ll fully understand your business’ nitty-gritty details and how all of its moving parts should work together to contribute to its success.
This template has two things I love: comprehensiveness and in-depth instructions. Plus, it’s synced with PandaDoc’s e-signature software so that you and other stakeholders can sign it with ease. For that reason, I especially love it for those starting a business with a partner or with a board of directors.
9. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers several free business plan templates that can be used to inspire your own plan.
Before you get started, you can decide what type of business plan you need — a traditional or lean start-up plan.
Then, you can review the format for both of those plans and view examples of what they might look like.
We love both of the SBA’s templates because of their versatility. You can choose between two options and use the existing content in the templates to flesh out your own plan. Plus, if needed, you can get a free business counselor to help you along the way.
I’ve compiled some completed business plan samples to help you get an idea of how to customize a plan for your business.
I chose different types of business plan ideas to expand your imagination. Some are extensive, while others are fairly simple.
Let’s take a look.
1. LiveFlow
One of the major business expenses is marketing. How you handle your marketing reflects your company’s revenue.
I included this business plan to show you how you can ensure your marketing team is aligned with your overall business plan to get results. The plan also shows you how to track even the smallest metrics of your campaigns, like ROI and payback periods instead of just focusing on big metrics like gross and revenue.
Fintech startup, LiveFlow, allows users to sync real-time data from its accounting services, payment platforms, and banks into custom reports. This eliminates the task of pulling reports together manually, saving teams time and helping automate workflows.
"Using this framework over a traditional marketing plan will help you set a profitable marketing strategy taking things like CAC, LTV, Payback period, and P&L into consideration," explains LiveFlow co-founder, Lasse Kalkar .
When it came to including marketing strategy in its business plan, LiveFlow created a separate marketing profit and loss statement (P&L) to track how well the company was doing with its marketing initiatives.
This is a great approach, allowing businesses to focus on where their marketing dollars are making the most impact. Having this information handy will enable you to build out your business plan’s marketing section with confidence. LiveFlow has shared the template here . You can test it for yourself.
2. Lula Body

Sometimes all you need is a solid mission statement and core values to guide you on how to go about everything. You do this by creating a business plan revolving around how to fulfill your statement best.
For example, Patagonia is an eco-friendly company, so their plan discusses how to make the best environmentally friendly products without causing harm.
A good mission statement should not only resonate with consumers but should also serve as a core value compass for employees as well.
Patagonia has one of the most compelling mission statements I’ve seen:
"Together, let’s prioritise purpose over profit and protect this wondrous planet, our only home."
It reels you in from the start, and the environmentally friendly theme continues throughout the rest of the statement.
This mission goes on to explain that they are out to "Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, and use business to protect nature."
Their mission statement is compelling and detailed, with each section outlining how they will accomplish their goal.
4. Vesta Home Automation

This executive summary for a smart home device startup is part of a business plan created by students at Mount Royal University .
While it lacks some of the sleek visuals of the templates above, its executive summary does a great job of demonstrating how invested they are in the business.
Right away, they mention they’ve invested $200,000 into the company already, which shows investors they have skin in the game and aren’t just looking for someone else to foot the bill.
This is the kind of business plan you need when applying for business funds. It clearly illustrates the expected future of the company and how the business has been coming along over the years.
5. NALB Creative Center
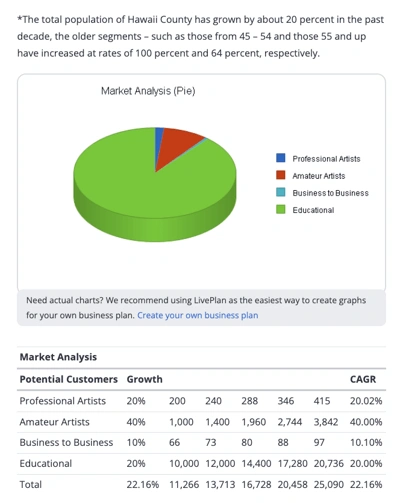
This fictional business plan for an art supply store includes everything one might need in a business plan: an executive summary, a company summary, a list of services, a market analysis summary, and more.
One of its most notable sections is its market analysis summary, which includes an overview of the population growth in the business’ target geographical area, as well as a breakdown of the types of potential customers they expect to welcome at the store.
This sort of granular insight is essential for understanding and communicating your business’s growth potential. Plus, it lays a strong foundation for creating relevant and useful buyer personas .
It’s essential to keep this information up-to-date as your market and target buyer changes. For that reason, you should carry out market research as often as possible to ensure that you’re targeting the correct audience and sharing accurate information with your investors.
Due to its comprehensiveness, it’s an excellent example to follow if you’re opening a brick-and-mortar store and need to get external funding to start your business .
6. Curriculum Companion Suites (CSS)
If you’re looking for a SaaS business plan example, look no further than this business plan for a fictional educational software company called Curriculum Companion Suites.
Like the business plan for the NALB Creative Center, it includes plenty of information for prospective investors and other key stakeholders in the business.
One of the most notable features of this business plan is the executive summary, which includes an overview of the product, market, and mission.
The first two are essential for software companies because the product offering is so often at the forefront of the company’s strategy. Without that information being immediately available to investors and executives, then you risk writing an unfocused business plan.
It’s essential to front-load your company’s mission if it explains your "Why?" and this example does just that. In other words, why do you do what you do, and why should stakeholders care? This is an important section to include if you feel that your mission will drive interest in the business and its offerings.
7. Culina Sample Business Plan

Culina's sample business plan is an excellent example of how to lay out your business plan so that it flows naturally, engages readers, and provides the critical information investors and stakeholders need.
You can use this template as a guide while you're gathering important information for your own business plan. You'll have a better understanding of the data and research you need to do since Culina’s plan outlines these details so flawlessly for inspiration.
8. Plum Sample Business Plan

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![industry overview business plan example How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![industry overview business plan example 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![industry overview business plan example The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
How to Conduct an Industry Analysis? Steps, Template, Examples
Appinio Research · 16.11.2023 · 39min read

Are you ready to unlock the secrets of Industry Analysis, equipping yourself with the knowledge to navigate markets and make informed strategic decisions? Dive into this guide, where we unravel the significance, objectives, and methods of Industry Analysis.
Whether you're an entrepreneur seeking growth opportunities or a seasoned executive navigating industry shifts, this guide will be your compass in understanding the ever-evolving business terrain.
What is Industry Analysis?
Industry analysis is the process of examining and evaluating the dynamics, trends, and competitive forces within a specific industry or market sector. It involves a comprehensive assessment of the factors that impact the performance and prospects of businesses operating within that industry. Industry analysis serves as a vital tool for businesses and decision-makers to gain a deep understanding of the environment in which they operate.
Key components of industry analysis include:
- Market Size and Growth: Determining the overall size of the market, including factors such as revenue, sales volume, and customer base. Analyzing historical and projected growth rates provides insights into market trends and opportunities.
- Competitive Landscape: Identifying and analyzing competitors within the industry. This includes assessing their market share, strengths, weaknesses, and strategies. Understanding the competitive landscape helps businesses position themselves effectively.
- Customer Behavior and Preferences: Examining consumer behavior , preferences, and purchasing patterns within the industry. This information aids in tailoring products or services to meet customer needs.
- Regulatory and Legal Environment: Assessing the impact of government regulations, policies, and legal requirements on industry operations. Compliance and adaptation to these factors are crucial for business success.
- Technological Trends: Exploring technological advancements and innovations that affect the industry. Staying up-to-date with technology trends can be essential for competitiveness and growth.
- Economic Factors: Considering economic conditions, such as inflation rates, interest rates, and economic cycles, that influence the industry's performance.
- Social and Cultural Trends: Examining societal and cultural shifts, including changing consumer values and lifestyle trends that can impact demand and preferences.
- Environmental and Sustainability Factors: Evaluating environmental concerns and sustainability issues that affect the industry. Industries are increasingly required to address environmental responsibility.
- Supplier and Distribution Networks: Analyzing the availability of suppliers, distribution channels, and supply chain complexities within the industry.
- Risk Factors: Identifying potential risks and uncertainties that could affect industry stability and profitability.
Objectives of Industry Analysis
Industry analysis serves several critical objectives for businesses and decision-makers:
- Understanding Market Dynamics: The primary objective is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the industry's dynamics, including its size, growth prospects, and competitive landscape. This knowledge forms the basis for strategic planning.
- Identifying Growth Opportunities: Industry analysis helps identify growth opportunities within the market. This includes recognizing emerging trends, niche markets, and underserved customer segments.
- Assessing Competitor Strategies: By examining competitors' strengths, weaknesses, and strategies, businesses can formulate effective competitive strategies. This involves positioning the company to capitalize on its strengths and exploit competitors' weaknesses.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities specific to the industry allows businesses to develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of adverse events.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Industry analysis provides the data and insights necessary for informed strategic decision-making. It guides decisions related to market entry, product development, pricing strategies, and resource allocation.
- Resource Allocation: By understanding industry dynamics, businesses can allocate resources efficiently. This includes optimizing marketing budgets, supply chain investments, and talent recruitment efforts.
- Innovation and Adaptation: Staying updated on technological trends and shifts in customer preferences enables businesses to innovate and adapt their offerings effectively.
Importance of Industry Analysis in Business
Industry analysis holds immense importance in the business world for several reasons:
- Strategic Planning: It forms the foundation for strategic planning by providing a comprehensive view of the industry's landscape. Businesses can align their goals, objectives, and strategies with industry trends and opportunities.
- Risk Management: Identifying and assessing industry-specific risks allows businesses to manage and mitigate potential threats proactively. This reduces the likelihood of unexpected disruptions.
- Competitive Advantage: In-depth industry analysis helps businesses identify opportunities for gaining a competitive advantage. This could involve product differentiation, cost leadership, or niche market targeting .
- Resource Optimization: Efficient allocation of resources, both financial and human, is possible when businesses have a clear understanding of industry dynamics. It prevents wastage and enhances resource utilization.
- Informed Investment: Industry analysis assists investors in making informed decisions about allocating capital. It provides insights into the growth potential and risk profiles of specific industry sectors.
- Adaptation to Change: As industries evolve, businesses must adapt to changing market conditions. Industry analysis facilitates timely adaptation to new technologies, market shifts, and consumer preferences .
- Market Entry and Expansion: For businesses looking to enter new markets or expand existing operations, industry analysis guides decision-making by evaluating the feasibility and opportunities in target markets.
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding the regulatory environment is critical for compliance and risk avoidance. Industry analysis helps businesses stay compliant with relevant laws and regulations.
In summary, industry analysis is a fundamental process that empowers businesses to make informed decisions, stay competitive, and navigate the complexities of their respective markets. It is an invaluable tool for strategic planning and long-term success.
How to Prepare for Industry Analysis?
Let's start by going through the crucial preparatory steps for conducting a comprehensive industry analysis.
1. Data Collection and Research
- Primary Research: When embarking on an industry analysis, consider conducting primary research . This involves gathering data directly from industry sources, stakeholders, and potential customers. Methods may include surveys , interviews, focus groups , and observations. Primary research provides firsthand insights and can help validate secondary research findings.
- Secondary Research: Secondary research involves analyzing existing literature, reports, and publications related to your industry. Sources may include academic journals, industry-specific magazines, government publications, and market research reports. Secondary research provides a foundation of knowledge and can help identify gaps in information that require further investigation.
- Data Sources: Explore various data sources to collect valuable industry information. These sources may include industry-specific associations, government agencies, trade publications, and reputable market research firms. Make sure to cross-reference data from multiple sources to ensure accuracy and reliability.
2. Identifying Relevant Industry Metrics
Understanding and identifying the right industry metrics is essential for meaningful analysis. Here, we'll discuss key metrics that can provide valuable insights:
- Market Size: Determining the market's size, whether in terms of revenue, units sold, or customer base, is a fundamental metric. It offers a snapshot of the industry's scale and potential.
- Market Growth Rate: Assessing historical and projected growth rates is crucial for identifying trends and opportunities. Understanding how the market has evolved over time can guide strategic decisions.
- Market Share Analysis: Analyzing market share among industry players can help you identify dominant competitors and their respective positions. This metric also assists in gauging your own company's market presence.
- Market Segmentation : Segmenting the market based on demographics, geography, behavior, or other criteria can provide deeper insights. Understanding the specific needs and preferences of various market segments can inform targeted strategies.
3. Gathering Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence is the cornerstone of effective industry analysis. To gather and utilize information about your competitors:
- Competitor Identification: Begin by creating a comprehensive list of your primary and potential competitors. Consider businesses that offer similar products or services within your target market. It's essential to cast a wide net to capture all relevant competitors.
- SWOT Analysis : Conduct a thorough SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis for each competitor. This analysis helps you identify their internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats they face.
- Market Share Analysis: Determine the market share held by each competitor and how it has evolved over time. Analyzing changes in market share can reveal shifts in competitive dynamics.
- Product and Pricing Analysis: Evaluate your competitors' product offerings and pricing strategies . Identify any unique features or innovations they offer and consider how your own products or services compare.
- Marketing and Branding Strategies: Examine the marketing and branding strategies employed by competitors. This includes their messaging, advertising channels, and customer engagement tactics. Assess how your marketing efforts stack up.
Industry Analysis Frameworks and Models
Now, let's explore essential frameworks and models commonly used in industry analysis, providing you with practical insights and examples to help you effectively apply these tools.
Porter's Five Forces Model
Porter's Five Forces is a powerful framework developed by Michael Porter to assess the competitive forces within an industry. This model helps you understand the industry's attractiveness and competitive dynamics.
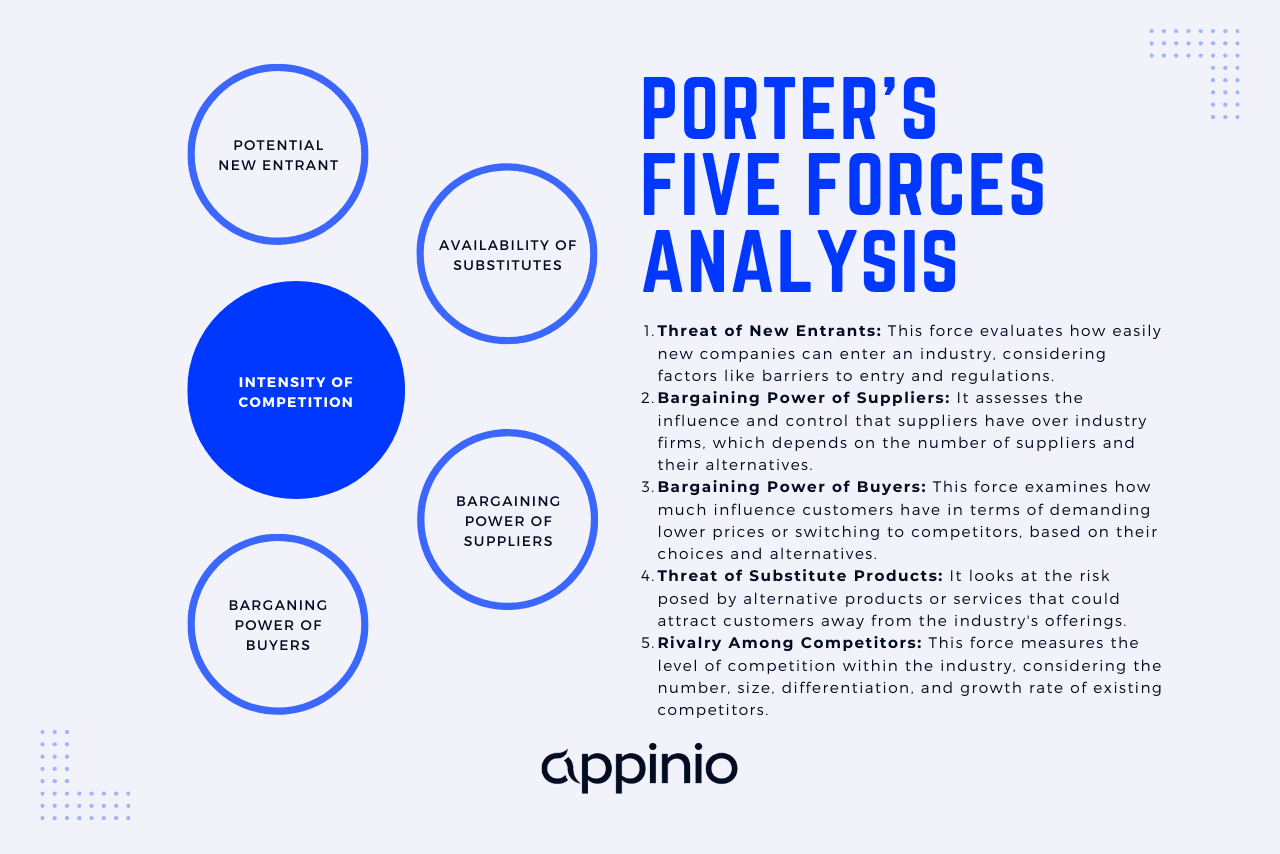
It consists of five key forces:
- Threat of New Entrants: This force evaluates how easy or difficult it is for new companies to enter the industry. Factors that increase barriers to entry include high capital requirements, strong brand loyalty among existing players, and complex regulatory hurdles. For example, the airline industry has significant barriers to entry due to the need for large capital investments in aircraft, airport facilities, and regulatory approvals.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: This force examines the influence suppliers have on the industry's profitability. Powerful suppliers can demand higher prices or impose unfavorable terms. For instance, in the automotive industry, suppliers of critical components like microchips can wield significant bargaining power if they are few in number or if their products are highly specialized.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: The bargaining power of buyers assesses how much influence customers have in negotiating prices and terms. In industries where buyers have many alternatives, such as the smartphone market, they can demand lower prices and better features, putting pressure on manufacturers to innovate and compete.
- Threat of Substitutes: This force considers the availability of substitute products or services that could potentially replace what the industry offers. For example, the rise of electric vehicles represents a significant threat to the traditional gasoline-powered automotive industry as consumers seek eco-friendly alternatives.
- Competitive Rivalry: Competitive rivalry assesses the intensity of competition among existing firms in the industry. A highly competitive industry, such as the smartphone market, often leads to price wars and aggressive marketing strategies as companies vie for market share.
Example: Let's consider the coffee shop industry . New entrants face relatively low barriers, as they can set up a small shop with limited capital. However, the bargaining power of suppliers, such as coffee bean producers, can vary depending on the region and the coffee's rarity. Bargaining power with buyers is moderate, as customers often have several coffee shops to choose from. Threats of substitutes may include energy drinks or homemade coffee, while competitive rivalry is high, with numerous coffee chains and independent cafes competing for customers.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is a versatile tool used to assess an organization's internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. By conducting a SWOT analysis, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of your industry and formulate effective strategies.
- Strengths: These are the internal attributes and capabilities that give your business a competitive advantage. For instance, if you're a tech company, having a talented and innovative team can be considered a strength.
- Weaknesses: Weaknesses are internal factors that hinder your business's performance. For example, a lack of financial resources or outdated technology can be weaknesses that need to be addressed.
- Opportunities: Opportunities are external factors that your business can capitalize on. This could be a growing market segment, emerging technologies, or changing consumer trends.
- Threats: Threats are external factors that can potentially harm your business. Examples of threats might include aggressive competition, economic downturns, or regulatory changes.
Example: Let's say you're analyzing the fast-food industry. Strengths could include a well-established brand, a wide menu variety, and efficient supply chain management. Weaknesses may involve a limited focus on healthy options and potential labor issues. Opportunities could include the growing trend toward healthier eating, while threats might encompass health-conscious consumer preferences and increased competition from delivery apps.
PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL Analysis examines the external macro-environmental factors that can impact your industry. The acronym stands for:
- Political: Political factors encompass government policies, stability, and regulations. For example, changes in tax laws or trade agreements can affect industries like international manufacturing.
- Economic: Economic factors include economic growth, inflation rates, and exchange rates. A fluctuating currency exchange rate can influence export-oriented industries like tourism.
- Social: Social factors encompass demographics, cultural trends, and social attitudes. An aging population can lead to increased demand for healthcare services and products.
- Technological: Technological factors involve advancements and innovations. Industries like telecommunications are highly influenced by technological developments, such as the rollout of 5G networks.
- Environmental: Environmental factors cover sustainability, climate change, and ecological concerns. Industries such as renewable energy are directly impacted by environmental regulations and consumer preferences.
- Legal: Legal factors encompass laws, regulations, and compliance requirements. The pharmaceutical industry, for instance, faces stringent regulatory oversight and patent protection laws.
Example: Consider the automobile manufacturing industry. Political factors may include government incentives for electric vehicles. Economic factors can involve fluctuations in fuel prices affecting consumer preferences for fuel-efficient cars. Social factors might encompass the growing interest in eco-friendly transportation options. Technological factors could relate to advancements in autonomous driving technology. Environmental factors may involve emissions regulations, while legal factors could pertain to safety standards and recalls.
Industry Life Cycle Analysis
Industry Life Cycle Analysis categorizes industries into various stages based on their growth and maturity. Understanding where your industry stands in its life cycle can help shape your strategies.
- Introduction: In the introduction stage, the industry is characterized by slow growth, limited competition, and a focus on product development. New players enter the market, and consumers become aware of the product or service. For instance, electric scooters were introduced as a new mode of transportation in recent years.
- Growth: The growth stage is marked by rapid market expansion, increased competition, and rising demand. Companies focus on gaining market share, and innovation is vital. The ride-sharing industry, exemplified by companies like Uber and Lyft, experienced significant growth in this stage.
- Maturity: In the maturity stage, the market stabilizes, and competition intensifies. Companies strive to maintain market share and differentiate themselves through branding and customer loyalty programs. The smartphone industry reached maturity with multiple established players.
- Decline: In the decline stage, the market saturates, and demand decreases. Companies must adapt or diversify to survive. The decline of traditional print media is a well-known example.
Example: Let's analyze the video streaming industry . The introduction stage saw the emergence of streaming services like Netflix. In the growth stage, more players entered the market, and the industry saw rapid expansion. The industry is currently in the maturity stage, with established platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ competing for market share. However, with continued innovation and changing consumer preferences, the decline stage may eventually follow.
Value Chain Analysis
Value Chain Analysis dissects a company's activities into primary and support activities to identify areas of competitive advantage. Primary activities directly contribute to creating and delivering a product or service, while support activities facilitate primary activities.
- Primary Activities: These activities include inbound logistics (receiving and storing materials), operations (manufacturing or service delivery), outbound logistics (distribution), marketing and sales, and customer service.
- Support Activities: Support activities include procurement (acquiring materials and resources), technology development (R&D and innovation), human resource management (recruitment and training), and infrastructure (administrative and support functions).
Example: Let's take the example of a smartphone manufacturer. Inbound logistics involve sourcing components, such as processors and displays. Operations include assembly and quality control. Outbound logistics cover shipping and distribution. Marketing and sales involve advertising and retail partnerships. Customer service handles warranty and support.
Procurement ensures a stable supply chain for components. Technology development focuses on research and development of new features. Human resource management includes hiring and training skilled engineers. Infrastructure supports the company's administrative functions.
By applying these frameworks and models effectively, you can better understand your industry, identify strategic opportunities and threats, and develop a solid foundation for informed decision-making.
Data Interpretation and Analysis
Once you have your data, it's time to start interpreting and analyzing the data you've collected during your industry analysis.
You can unlock the full potential of your data with Appinio 's comprehensive research platform. Beyond aiding in data collection, Appinio simplifies the intricate process of data interpretation and analysis. Our intuitive tools empower you to effortlessly transform raw data into actionable insights, giving you a competitive edge in understanding your industry.
Whether it's assessing market trends, evaluating the competitive landscape, or understanding customer behavior, Appinio offers a holistic solution to uncover valuable findings. With our platform, you can make informed decisions, strategize effectively, and stay ahead of industry shifts.
Experience the ease of data collection and interpretation with Appinio – book a demo today!
Book a Demo
1. Analyze Market Size and Growth
Analyzing the market's size and growth is essential for understanding its dynamics and potential. Here's how to conduct a robust analysis:
- Market Size Calculation: Determine the total market size in terms of revenue, units sold, or the number of customers. This figure serves as a baseline for evaluating the industry's scale.
- Historical Growth Analysis: Examine historical data to identify growth trends. This includes looking at past year-over-year growth rates and understanding the factors that influenced them.
- Projected Growth Assessment: Explore industry forecasts and projections to gain insights into the expected future growth of the market. Consider factors such as emerging technologies, changing consumer preferences, and economic conditions.
- Segmentation Analysis: If applicable, analyze market segmentation data to identify growth opportunities in specific market segments. Understand which segments are experiencing the most significant growth and why.
2. Assess Market Trends
Stay ahead of the curve by closely monitoring and assessing market trends. Here's how to effectively evaluate trends within your industry.
- Consumer Behavior Analysis: Dive into consumer behavior data to uncover shifts in preferences, buying patterns, and shopping habits. Understand how technological advancements and cultural changes influence consumer choices.
- Technological Advancements: Keep a keen eye on technological developments that impact your industry. Assess how innovations such as AI, IoT, blockchain, or automation are changing the competitive landscape.
- Regulatory Changes: Stay informed about regulatory shifts and their potential consequences for your industry. Regulations can significantly affect product development, manufacturing processes, and market entry strategies.
- Sustainability and Environmental Trends: Consider the growing importance of sustainability and environmental concerns. Evaluate how your industry is adapting to eco-friendly practices and how these trends affect consumer choices.
3. Evaluate Competitive Landscape
Understanding the competitive landscape is critical for positioning your business effectively. To perform a comprehensive evaluation:
- Competitive Positioning: Determine where your company stands in comparison to competitors. Identify your unique selling propositions and areas where you excel.
- Market Share Analysis: Continuously monitor market share among industry players. Identify trends in market share shifts and assess the strategies that lead to such changes.
- Competitive Advantages and Weaknesses: Analyze your competitors' strengths and weaknesses. Identify areas where you can capitalize on their weaknesses and where you need to fortify your own strengths.
4. Identify Key Success Factors
Recognizing and prioritizing key success factors is crucial for developing effective strategies. To identify and leverage these factors:
- Customer Satisfaction: Prioritize customer satisfaction as a critical success factor. Satisfied customers are more likely to become loyal advocates and contribute to long-term success.
- Quality and Innovation: Focus on product or service quality and continuous innovation. Meeting and exceeding customer expectations can set your business apart from competitors.
- Cost Efficiency: Strive for cost efficiency in your operations. Identifying cost-saving opportunities can lead to improved profitability.
- Marketing and Branding Excellence: Invest in effective marketing and branding strategies to create a strong market presence. Building a recognizable brand can drive customer loyalty and growth.
5. Analyze Customer Behavior and Preferences
Understanding your target audience is central to success. Here's how to analyze customer behavior and preferences:
- Market Segmentation: Use market segmentation to categorize customers based on demographics, psychographics , and behavior. This allows for more personalized marketing and product/service offerings.
- Customer Surveys and Feedback: Gather customer feedback through surveys and feedback mechanisms. Understand their pain points, preferences, and expectations to tailor your offerings.
- Consumer Journey Mapping: Map the customer journey to identify touchpoints where you can improve engagement and satisfaction. Optimize the customer experience to build brand loyalty.
By delving deep into data interpretation and analysis, you can gain valuable insights into your industry, uncover growth opportunities, and refine your strategic approach.
How to Conduct Competitor Analysis?
Competitor analysis is a critical component of industry analysis as it provides valuable insights into your rivals, helping you identify opportunities, threats, and areas for improvement.
1. Identify Competitors
Identifying your competitors is the first step in conducting a thorough competitor analysis. Competitors can be classified into several categories:
- Direct Competitors: These are companies that offer similar products or services to the same target audience. They are your most immediate competitors and often compete directly with you for market share.
- Indirect Competitors: Indirect competitors offer products or services that are related but not identical to yours. They may target a slightly different customer segment or provide an alternative solution to the same problem.
- Potential Competitors: These companies could enter your market in the future. Identifying potential competitors early allows you to anticipate and prepare for new entrants.
- Substitute Products or Services: While not traditional competitors, substitute products or services can fulfill the same customer needs or desires. Understanding these alternatives is crucial to your competitive strategy.
2. Analyze Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
Once you've identified your competitors, you need to analyze their strengths and weaknesses. This analysis helps you understand how to position your business effectively and identify areas where you can gain a competitive edge.
- Strengths: Consider what your competitors excel at. This could include factors such as brand recognition, innovative products, a large customer base, efficient operations, or strong financial resources.
- Weaknesses: Identify areas where your competitors may be lacking. Weaknesses could involve limited product offerings, poor customer service, outdated technology, or financial instability.
3. Competitive Positioning
Competitive positioning involves defining how you want your business to be perceived relative to your competitors. It's about finding a unique position in the market that sets you apart. Consider the following strategies:
- Cost Leadership: Strive to be the low-cost provider in your industry. This positioning appeals to price-conscious consumers.
- Differentiation: Focus on offering unique features or attributes that make your products or services stand out. This can justify premium pricing.
- Niche Market: Target a specific niche or segment of the market that may be underserved by larger competitors. Tailor your offerings to meet their unique needs.
- Innovation and Technology: Emphasize innovation and technology to position your business as a leader in product or service quality.
- Customer-Centric: Prioritize exceptional customer service and customer experience to build loyalty and a positive reputation.
4. Benchmarking and Gap Analysis
Benchmarking involves comparing your business's performance and practices with those of your competitors or industry leaders. Gap analysis helps identify areas where your business falls short and where improvements are needed.
- Performance Benchmarking: Compare key performance metrics, such as revenue, profitability, market share, and customer satisfaction, with those of your competitors. Identify areas where your performance lags behind or exceeds industry standards.
- Operational Benchmarking: Analyze your operational processes, supply chain, and cost structures compared to your competitors. Look for opportunities to streamline operations and reduce costs.
- Product or Service Benchmarking: Evaluate the features, quality, and pricing of your products or services relative to competitors. Identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Marketing and Sales Benchmarking: Assess your marketing strategies, customer acquisition costs, and sales effectiveness compared to competitors. Determine whether your marketing efforts are performing at a competitive level.
Market Entry and Expansion Strategies
Market entry and expansion strategies are crucial for businesses looking to enter new markets or expand their presence within existing ones. These strategies can help you effectively target and penetrate your chosen markets.
Market Segmentation and Targeting
- Market Segmentation: Begin by segmenting your target market into distinct groups based on demographics , psychographics, behavior, or other relevant criteria. This helps you understand the diverse needs and preferences of different customer segments.
- Targeting: Once you've segmented the market, select specific target segments that align with your business goals and capabilities. Tailor your marketing and product/service offerings to appeal to these chosen segments.
Market Entry Modes
Selecting the proper market entry mode is crucial for a successful expansion strategy. Entry modes include:
- Exporting: Sell your products or services in international markets through exporting. This is a low-risk approach, but it may limit your market reach.
- Licensing and Franchising: License your brand, technology, or intellectual property to local partners or franchisees. This allows for rapid expansion while sharing the risk and control.
- Joint Ventures and Alliances: Partner with local companies through joint ventures or strategic alliances. This approach leverages local expertise and resources.
- Direct Investment: Establish a physical presence in the target market through subsidiaries, branches, or wholly-owned operations. This offers full control but comes with higher risk and investment.
Competitive Strategy Formulation
Your competitive strategy defines how you will compete effectively in the target market.
- Cost Leadership: Strive to offer products or services at lower prices than competitors while maintaining quality. This strategy appeals to price-sensitive consumers.
- Product Differentiation: Focus on offering unique and innovative products or services that stand out in the market. This strategy justifies premium pricing.
- Market Niche: Target a specific niche or segment within the market that is underserved or has particular needs. Tailor your offerings to meet the unique demands of this niche.
- Market Expansion : Expand your product or service offerings to capture a broader share of the market. This strategy involves diversifying your offerings to appeal to a broader audience.
- Global Expansion: Consider expanding internationally to tap into new markets and diversify your customer base. This strategy involves thorough market research and adaptation to local cultures and regulations.
International Expansion Considerations
If your expansion strategy involves international markets, there are several additional considerations to keep in mind.
- Market Research: Conduct in-depth market research to understand the target country's cultural, economic, and legal differences.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with international trade regulations, customs, and import/export laws.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Adapt your marketing and business practices to align with the cultural norms and preferences of the target market.
- Localization: Consider adapting your products, services, and marketing materials to cater to local tastes and languages.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate the political, economic, and legal risks associated with operating in the target country. Develop risk mitigation strategies.
By carefully analyzing your competitors and crafting effective market entry and expansion strategies, you can position your business for success in both domestic and international markets.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Risk assessment and mitigation are crucial aspects of industry analysis and strategic planning. Identifying potential risks, assessing vulnerabilities, and implementing effective risk management strategies are essential for business continuity and success.
1. Identify Industry Risks
- Market Risks: These risks pertain to factors such as changes in market demand, economic downturns, shifts in consumer preferences, and fluctuations in market prices. For example, the hospitality industry faced significant market risks during the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in decreased travel and tourism .
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks: Regulatory changes, compliance requirements, and government policies can pose risks to businesses. Industries like healthcare are particularly susceptible to regulatory changes that impact operations and reimbursement.
- Technological Risks: Rapid technological advancements can disrupt industries and render existing products or services obsolete. Companies that fail to adapt to technological shifts may face obsolescence.
- Operational Risks: These risks encompass internal factors that can disrupt operations, such as supply chain disruptions, equipment failures, or cybersecurity breaches.
- Financial Risks: Financial risks include factors like liquidity issues, credit risk , and market volatility. Industries with high capital requirements, such as real estate development, are particularly vulnerable to financial risks.
- Competitive Risks: Intense competition and market saturation can pose challenges to businesses. Failing to respond to competitive threats can result in loss of market share.
- Global Risks: Industries with a worldwide presence face geopolitical risks, currency fluctuations, and international trade uncertainties. For instance, the automotive industry is susceptible to trade disputes affecting the supply chain.
2. Assess Business Vulnerabilities
- SWOT Analysis: Revisit your SWOT analysis to identify internal weaknesses and threats. Assess how these weaknesses may exacerbate industry risks.
- Financial Health: Evaluate your company's financial stability, debt levels, and cash flow. Identify vulnerabilities related to financial health that could hinder your ability to withstand industry-specific challenges.
- Operational Resilience: Assess the robustness of your operational processes and supply chain. Identify areas where disruptions could occur and develop mitigation strategies.
- Market Positioning: Analyze your competitive positioning and market share. Recognize vulnerabilities in your market position that could be exploited by competitors.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Ensure that your business complies with relevant regulations and standards. Identify vulnerabilities related to non-compliance or regulatory changes.
3. Risk Management Strategies
- Risk Avoidance: In some cases, the best strategy is to avoid high-risk ventures or markets altogether. This may involve refraining from entering certain markets or discontinuing products or services with excessive risk.
- Risk Reduction: Implement measures to reduce identified risks. For example, diversifying your product offerings or customer base can reduce dependence on a single revenue source.
- Risk Transfer: Transfer some risks through methods such as insurance or outsourcing. For instance, businesses can mitigate cybersecurity risks by purchasing cyber insurance.
- Risk Acceptance: In cases where risks cannot be entirely mitigated, it may be necessary to accept a certain level of risk and have contingency plans in place to address potential issues.
- Continuous Monitoring: Establish a system for continuous risk monitoring. Regularly assess the changing landscape and adjust risk management strategies accordingly.
4. Contingency Planning
Contingency planning involves developing strategies and action plans to respond effectively to unforeseen events or crises. It ensures that your business can maintain operations and minimize disruptions in the face of adverse circumstances. Key elements of contingency planning include:
- Risk Scenarios: Identify potential risk scenarios specific to your industry and business. These scenarios should encompass a range of possibilities, from minor disruptions to major crises.
- Response Teams: Establish response teams with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. Ensure that team members are trained and ready to act in the event of a crisis.
- Communication Plans: Develop communication plans that outline how you will communicate with employees, customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders during a crisis. Transparency and timely communication are critical.
- Resource Allocation: Determine how resources, including personnel, finances, and equipment, will be allocated in response to various scenarios.
- Testing and Simulation: Regularly conduct tests and simulations of your contingency plans to identify weaknesses and areas for improvement. Ensure your response teams are well-practiced and ready to execute the plans effectively.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Maintain comprehensive documentation of contingency plans, response procedures, and communication protocols. This documentation should be easily accessible to relevant personnel.
- Review and Update: Continuously review and update your contingency plans to reflect changing industry dynamics and evolving risks. Regularly seek feedback from response teams to make improvements.
By identifying industry risks, assessing vulnerabilities, implementing risk management strategies, and developing robust contingency plans, your business can navigate the complexities of the industry landscape with greater resilience and preparedness.
Industry Analysis Template
When embarking on the journey of Industry Analysis, having a well-structured template is akin to having a reliable map for your exploration. It provides a systematic framework to ensure you cover all essential aspects of the analysis. Here's a breakdown of an industry analysis template with insights into each section.
Industry Overview
- Objective: Provide a broad perspective of the industry.
- Market Definition: Define the scope and boundaries of the industry, including its products, services, and target audience.
- Market Size and Growth: Present current market size, historical growth trends, and future projections.
- Key Players: Identify major competitors and their market share.
- Market Trends: Highlight significant trends impacting the industry.
Competitive Analysis
- Objective: Understand the competitive landscape within the industry.
- Competitor Identification: List direct and indirect competitors.
- Competitor Profiles: Provide detailed profiles of major competitors, including their strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market positioning.
- SWOT Analysis: Conduct a SWOT analysis for each major competitor.
- Market Share Analysis: Analyze market share distribution among competitors.
Market Analysis
- Objective: Explore the characteristics and dynamics of the market.
- Customer Segmentation: Define customer segments and their demographics, behavior, and preferences.
- Demand Analysis: Examine factors driving demand and customer buying behavior.
- Supply Chain Analysis: Map out the supply chain, identifying key suppliers and distribution channels.
- Regulatory Environment: Discuss relevant regulations, policies, and compliance requirements.
Technological Analysis
- Objective: Evaluate the technological landscape impacting the industry.
- Technological Trends: Identify emerging technologies and innovations relevant to the industry.
- Digital Transformation: Assess the level of digitalization within the industry and its impact on operations and customer engagement.
- Innovation Opportunities: Explore opportunities for leveraging technology to gain a competitive edge.
Financial Analysis
- Objective: Analyze the financial health of the industry and key players.
- Revenue and Profitability: Review industry-wide revenue trends and profitability ratios.
- Financial Stability: Assess financial stability by examining debt levels and cash flow.
- Investment Patterns: Analyze capital expenditure and investment trends within the industry.
Consumer Insights
- Objective: Understand consumer behavior and preferences.
- Consumer Surveys: Conduct surveys or gather data on consumer preferences, buying habits , and satisfaction levels.
- Market Perception: Gauge consumer perception of brands and products in the industry.
- Consumer Feedback: Collect and analyze customer feedback and reviews.
SWOT Analysis for Your Business
- Objective: Assess your own business within the industry context.
- Strengths: Identify internal strengths that give your business a competitive advantage.
- Weaknesses: Recognize internal weaknesses that may hinder your performance.
- Opportunities: Explore external opportunities that your business can capitalize on.
- Threats: Recognize external threats that may impact your business.
Conclusion and Recommendations
- Objective: Summarize key findings and provide actionable recommendations.
- Summary: Recap the most critical insights from the analysis.
- Recommendations: Offer strategic recommendations for your business based on the analysis.
- Future Outlook: Discuss potential future developments in the industry.
While this template provides a structured approach, adapt it to the specific needs and objectives of your Industry Analysis. It serves as your guide, helping you navigate through the complex landscape of your chosen industry, uncovering opportunities, and mitigating risks along the way.
Remember that the depth and complexity of your industry analysis may vary depending on your specific goals and the industry you are assessing. You can adapt this template to focus on the most relevant aspects and conduct thorough research to gather accurate data and insights. Additionally, consider using industry-specific data sources, reports, and expert opinions to enhance the quality of your analysis.
Industry Analysis Examples
To grasp the practical application of industry analysis, let's delve into a few diverse examples across different sectors. These real-world scenarios demonstrate how industry analysis can guide strategic decision-making.
Tech Industry - Smartphone Segment
Scenario: Imagine you are a product manager at a tech company planning to enter the smartphone market. Industry analysis reveals that the market is highly competitive, dominated by established players like Apple and Samsung.
Use of Industry Analysis:
- Competitive Landscape: Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, identifying areas where they excel (e.g., Apple's brand loyalty ) and where they might have vulnerabilities (e.g., consumer demand for more affordable options).
- Market Trends: Identify trends like the growing demand for sustainable technology and 5G connectivity, guiding product development and marketing strategies.
- Regulatory Factors: Consider regulatory factors related to intellectual property rights, patents, and international trade agreements that can impact market entry and operations.
- Outcome: Armed with insights from industry analysis, you decide to focus on innovation, emphasizing features like eco-friendliness and affordability. This niche approach helps your company gain a foothold in the competitive market.
Healthcare Industry - Telehealth Services
Scenario: You are a healthcare entrepreneur exploring opportunities in the telehealth sector, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Industry analysis is critical due to rapid market changes.
- Market Size and Growth: Evaluate the growing demand for telehealth services, driven by the need for remote healthcare during the pandemic and convenience factors.
- Regulatory Environment: Understand the evolving regulatory landscape, including changes in telemedicine reimbursement policies and licensing requirements.
- Technological Trends: Explore emerging technologies such as AI-powered diagnosis and remote monitoring that can enhance service offerings.
- Outcome: Industry analysis underscores the potential for telehealth growth. You adapt your business model to align with regulatory changes, invest in cutting-edge technology, and focus on patient-centric care, positioning your telehealth service for success.
Food Industry - Plant-Based Foods
Scenario: As a food industry entrepreneur , you are considering entering the plant-based foods market, driven by increasing consumer interest in health and sustainability.
- Market Trends: Analyze the trend toward plant-based diets and sustainability, reflecting changing consumer preferences.
- Competitive Landscape: Assess the competitive landscape, understanding that established companies and startups are vying for market share.
- Consumer Behavior: Study consumer behavior, recognizing that health-conscious consumers seek plant-based alternatives.
- Outcome: Informed by industry analysis, you launch a line of plant-based products emphasizing both health benefits and sustainability. Effective marketing and product quality gain traction among health-conscious consumers, making your brand a success in the plant-based food industry.
These examples illustrate how industry analysis can guide strategic decisions, whether entering competitive tech markets, navigating dynamic healthcare regulations, or capitalizing on shifting consumer preferences in the food industry. By applying industry analysis effectively, businesses can adapt, innovate, and thrive in their respective sectors.
Industry Analysis is the compass that helps businesses chart their course in the vast sea of markets. By understanding the industry's dynamics, risks, and opportunities, you gain a strategic advantage that can steer your business towards success. From identifying competitors to mitigating risks and formulating competitive strategies, this guide has equipped you with the tools and knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the business world.
Remember, Industry Analysis is not a one-time task; it's an ongoing journey. Keep monitoring market trends, adapting to changes, and staying ahead of the curve. With a solid foundation in industry analysis, you're well-prepared to tackle challenges, seize opportunities, and make well-informed decisions that drive your business toward prosperity. So, set sail with confidence and let industry analysis be your guiding star on the path to success.
How to Conduct Industry Analysis in Minutes?
Introducing Appinio , the real-time market research platform that transforms how you conduct Industry Analysis. Imagine getting real-time consumer insights in minutes, putting the power of data-driven decision-making at your fingertips. With Appinio, you can:
- Gain insights swiftly: Say goodbye to lengthy research processes. Appinio delivers answers fast, ensuring you stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
- No research degree required: Our intuitive platform is designed for everyone. You don't need a PhD in research to harness its capabilities.
- Global reach, local insights: Define your target group precisely from over 1200 characteristics and access consumer data in over 90 countries.
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

17.04.2024 | 25min read
Quota Sampling: Definition, Types, Methods, Examples

15.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Market Share? Definition, Formula, Examples

11.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Data Analysis? Definition, Tools, Examples
Restaurant Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Restaurant Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your restaurant business plan.
We have helped over 100,000 entrepreneurs and business owners with how to write a restaurant business plan to help them start or grow their restaurants.
Below is a restaurant business plan template to help you create each section of your business plan.
Restaurant Business Plan Example
Executive summary, business overview.
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse is a new restaurant and steakhouse located in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma. The menu of Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will include bistro-type dishes that are authentically created and crafted by acclaimed Chef Peter Logan. It will be located in the trendy part of town, known as the Plaza District. The restaurant will be surrounded by classy art galleries, live theater, high-end restaurants and bars, and expensive shopping.
Owned by emerging restaurant operators Chef Peter Logan and Anastasia Gillette, Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse’s mission is to become Oklahoma City’s best, new restaurant for patrons to celebrate their next big event, have a nice date night, or gather with friends or family for a fun evening while dining over finely crafted entrees, desserts, and cocktails.
Products Served
The following are the menu items to be offered by Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse:
- Soups & Salads
- Gourmet sides
- Wine, Beer & Spirits
Customer Focus
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will target adult men and women between the ages of 21 – 65 with disposable income in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma. Within this demographic are millennials, young professionals, newlyweds, young families, more established families, and retirees. Because of the pricing structure of the menu, the patrons will likely be upper middle class to the wealthy population of Oklahoma City.
Management Team
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse is owned and operated by fellow Oklahoma City natives and culinary enthusiasts, Chef Peter Logan and Anastasia Gillette. Both come with a unique skill set and complement each other perfectly. They formerly worked together at another OKC fine dining establishment and made a great team for serving guests delectable food and wine while ensuring the highest level of customer service.
Chef Peter will manage the kitchen operations of Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse, while Anastasia will oversee front of the house operations, maintain and ensure customer service, and manage all reservations.
Financial Highlights
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse is seeking $300,000 in debt financing to open its start-up restaurant. The funding will be dedicated for the build-out and design of the restaurant, kitchen, bar and lounge, as well as cooking supplies and equipment, working capital, three months worth of payroll expenses and opening inventory. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Restaurant Build-Out and Design – $100,000
- Kitchen supplies and equipment – $100,000
- Opening inventory – $25,000
- Working capital (to include 3 months of overhead expenses) – $25,000
- Marketing (advertising agency) – $25,000
- Accounting firm (3 months worth and establishment/permitting of business) – $25,000
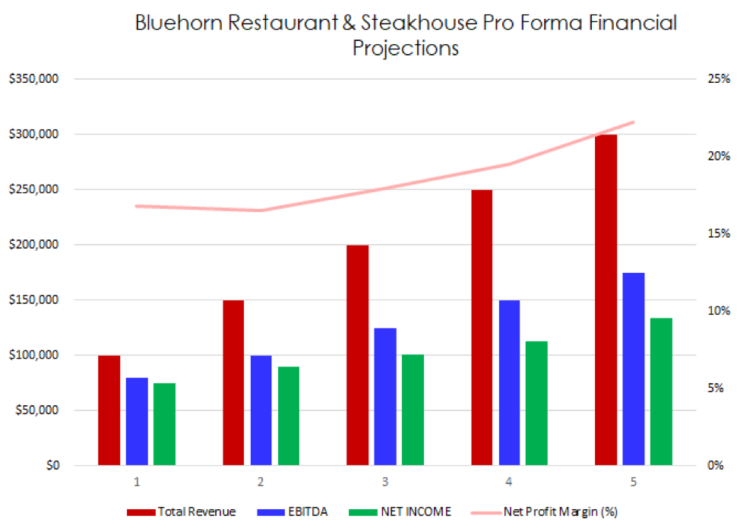
Company Overview
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse is a new restaurant and steakhouse located in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma. Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will serve a wide variety of dishes and beverages and will cater to the upper middle class to wealthier population of Oklahoma City. The menu of Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will include bistro-type dishes that are authentically created and crafted by acclaimed Chef Peter Logan. It will be located in the trendy part of town, known as the Plaza District. The Plaza District is one of Oklahoma’s trendy neighborhoods and is considered the “it” area for newlyweds, millennials, professionals, and young singles. The restaurant will be surrounded by classy art galleries, live theater, high-end restaurants and bars, and expensive shopping.
Owned by emerging restaurant operators Chef Peter Logan and Anastasia Gillette, the restaurant’s mission statement is to become the best new steak restaurant in OKC. The following are the types of menu items Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will serve- shareables, steaks, soups, gourmet sides and salads.
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse History
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse is owned by two Oklahoma City natives, Chef Peter Logan and Anastasia Gillette. They have both worked around the country in fine dining establishments and have a combined twenty years in the restaurant industry. Upon working alongside each other at another fine dining establishment in Oklahoma City, the two of them became good friends and decided to venture into owning their own restaurant.
Chef Peter is the kitchen guru and critically acclaimed chef, while Anastasia manages the front of the house and is a certified Sommelier. Together, with both of their expertise and knowledge, Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse is destined to become Oklahoma City’s next big restaurant.
Industry Analysis
The Restaurant industry is expected to grow to over $220 billion in the next five years.
Consumer spending is projected to grow. The Consumer Confidence Index, a leading indicator of spending patterns, is expected to also grow strongly, which will boost restaurant industry growth over the next five years. The growth in consumer confidence also suggests that more consumers may opt to segment their disposable income to eating outside the home.
Additionally, an increase in the number of households earning more than $100,000 annually further contributes to the industry growth, supporting industry operators that offer more niche, higher-end products. This group is expected to continue to grow in size over the next five years.
The urban population represents a large market for the industry. Specifically, time-strapped individuals living in urban areas will likely frequent industry establishments to save time on cooking. The urban population is expected to increase, representing a potential opportunity for the industry.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market, customer segmentation.
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will primarily target the following customer profile:
- Upper middle class to wealthier population
- Millennials
- Young professionals
- Households with an average income of at least $75k
- Foodies and culture enthusiasts
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will be competing with other restaurants in Oklahoma City. A profile of each competitor is below. The Press Located in the trendy area known as the Plaza District, The Press has reimagined our favorite foods of the surrounding regions through the lens of home.
The menu consists of appetizers, soups, burgers and sandwiches, bowls, main dishes, sides, desserts, and a large selection of alcoholic beverages. The Press serves craft beer, domestic beer, wine spritzers, house cocktails, wine, and mimosas. They also offer brunch. The menu of The Press is affordable with the most expensive dish being $16. The wine menu is also not pretentious as the wine is sold either by the glass or bottle, with the most expensive bottle being $52 for the Gruet Sparkling Brut Rose. Oak & Ore Oak & Ore is a craft beer and restaurant in OKC’s Plaza District. They have a 36-tap beer selection and offer vegetarian, vegan, and gluten free dining options. Oak & Ore offers a rotating, 36-tap selection of their favorite brews from Oklahoma and around the world. Each beer is thoughtfully paired with a craft beer-inspired dining experience.
The food menu of Oak & Ore offers starters, salads, wings, fried chicken, sandwiches, tacos, banh mi, and sides. They also have a selection of kids dishes so the whole family can enjoy comfort food while sampling one of their delectable beers.
The Mule OKC The Mule is a casual, hip restaurant offering a large beer and cocktail menu plus sandwiches and more. Located in the constantly growing and buzzing hub that is the Plaza District, The Mule takes the timeless favorite and contorts it into a whole menu of wild offerings.
There is also a fantastic assortment of soups offered and The Mule shakes up a seasonal list of cocktails designed by their bar staff. During the winter months, patrons can stave off the cold with their versions of hot toddies and buttered rum. For the beer drinkers, they always have a reliable line-up of fresh cold brews on draft, as well as a wide selection of can.
Competitive Advantage
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse offers several advantages over its competition. Those advantages are:
- Gourmet dishes elegantly prepared to the finest standard.
- Selection of steaks sourced from local Oklahoma farms.
- An exclusive and unique wine menu that includes a wine selection of all price points.
- Highly sought after location: Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will be located in the trendy and attractive neighborhood known as The Plaza District.
- Trendy, welcoming, and energetic ambiance that will be perfect for a night out or a celebration.
Marketing Plan
Promotions strategy.
The marketing strategy for Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse is as follows: Location Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse’s location is a promotions strategy in itself. The Plaza District is a destination spot for locals, tourists, and anyone looking for the trendiest food fare in Oklahoma City. The Plaza District is home to OKC’s most popular bars and restaurants, art galleries, theaters, and boutique shopping. The millennials, young professionals, and foodies will frequent Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse for the location itself.
Social Media Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will use social media to cater to the millennials and Oklahoma City residents. Chef Peter and Anastasia plan to hire an advertising agency to take professional photographs of the menu items and location to create appealing posts to reach a greater audience. The posts will include pictures of the menu items, as well as upcoming featured options. SEO Website Marketing Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse plans to invest funds into maintaining a strong SEO presence on search engines like Google and Bing. When a person types in “local fine dining restaurant” or “Oklahoma City restaurant”, Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will appear in the top three choices. The website will include the full menu, location, hours, and lots of pictures of the food, drinks, and steaks. Third Party Delivery Sites Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will maintain a presence on sites like GrubHub, Uber Eats, Doordash, and Postmates so that people looking for local food to be delivered will see Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse listed near the top.
Operations Plan
Operation functions:.
The company will hire the following:
- 4 sous chefs
- 2 bartenders
- 2 hostesses
- The company will hire an advertising agency and an accounting firm
Milestones:
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse aims to open in the next 6 months. The following are the milestones needed in order to obtain this goal.
7/1/202X – Execute lease for prime location in the Plaza District.
7/2/202X – Begin construction of restaurant build-out.
7/10/202X – Finalize menu.
7/17/202X – Hire advertising company to begin developing marketing efforts.
8/15/202X – Start of marketing campaign
8/22/202X – Final walk-thru of completed restaurant build-out.
8/25/202X – Hire team of sous chefs, servers, and bussers.
9/1/202X – Decoration and set up of restaurant.
9/15/202X – Grand Opening of Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will be owned and operated by Chef Peter Logan and Anastasia Gillette. Each will have a 50% ownership stake in the restaurant.
Chef Peter Logan, Co-Owner
Chef Peter Logan is an Oklahoma City native and has been in the restaurant industry for over ten years. He was trained in a prestigious Le Cordon Bleu Culinary Academy in San Francisco and has worked in some of the nation’s most prestigious fine dining restaurants. His tenure has took him from the west coast to the east coast, and now he’s back doing what he loves in his hometown of Oklahoma City.
Chef Peter will manage the kitchen operations of Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse. He will train and oversee the sous chefs, manage inventory, place food inventory orders, deal with the local food vendors, and ensure the highest customer satisfaction with the food.
Anastasia Gillette, Co-Owner
Anastasia Gillette was born and raised in Oklahoma City and has garnered over ten years in the restaurant industry as well. While in college, Anastasia worked as a hostess at one of the area’s most prestigious restaurant establishments. While there, she was eventually promoted to Front of the House Manager where she oversaw the hostesses, servers, bussers, bartenders, and reservations. Her passion always led to the beverage portion of the restaurant so she obtained her Sommelier certificate in 2019. With her wine education, Anastasia is able to cultivate an interesting and elegant wine selection for the restaurant.
Anastasia will oversee front of the house operations, maintain and ensure customer service, and manage all reservations. She will also be in charge of the bar and wine ordering, training of front of the house staff, and will manage the restaurant’s social media accounts once they are set up.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse will come from the food and drink menu items being offered daily.
The cost drivers will be the ingredients and products needed to make the menu items as well as the cooking materials. A significant cost driver is the fine dining equipment, serving dishes, and beer and wine glasses. Other cost drivers will be the overhead expenses of payroll for the employees, accounting firm, and cost of the advertising agency.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Bluehorn Restaurant & Steakhouse is seeking $300,000 in debt financing to open its start-up restaurant. The breakout of the funding is below:
Financial Projections
Income Statement
Balance Sheet
Cash Flow Statement
Restaurant Business Plan FAQs
What is a restaurant business plan.
A restaurant business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your restaurant business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your restaurant business plan using our Restaurant Business Plan Template here .
What Are the Main Types of Restaurants?
There are many types of restaurant businesses. Restaurants can range in type from fast food, fast casual, moderate casual, fine dining, and bar and restaurant types. Restaurants also come in a variety of different ethnic or themed categories, such as Mexican restaurants, Asian restaurants, American, etc. Some restaurants also go mobile and have food trucks.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Restaurant Business Plan?
Restaurant businesses are most likely to receive funding from banks. Typically you will find a local bank and present your business plan to them. Another option for a restaurant business is to obtain a small business loan. SBA loans are a popular option as they offer longer loan terms with lower interest rates.
What are the Steps To Start a Restaurant Business?
1. Develop A Restaurant Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed restaurant business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your restaurant business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your restaurant business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Restaurant Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your restaurant business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your restaurant business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Restaurant Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your restaurant business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your restaurant business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful restaurant business:
- How to Start a Restaurant Business
Where Can I Get a Restaurant Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free restaurant business plan template PDF here . This is a sample restaurant business plan template you can use in PDF format.

How to Write a Business Plan Industry Analysis
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business Plans
How do you conduct industry analysis for a business plan? Do you need help conducting market research and industry analysis for your business plan? Then I advice you read on. So you have a great business idea, you have refined and fine-tuned it, and you are ready to launch. You are going to offer a product or service with a clearly defined customer base, and you are confident that you will be successful in the long term.
Well, if the above applies perfectly to you, then you have not completed your assignment. What happens when you enter an examination hall without having studied for the exam at all? You’d spend all your time in the hall blaming yourself for being silly, right? Now, starting a business is even much more important because there’s a lot more at stake than passing or failing a grade. So, you must not leave out any aspect of research undone.
In this section of your business plan, you will demonstrate that the industry’s market size is worth going after, who your main competitors will be if you decide to take a plunge, and how you will be able to carve out a niche for yourself and give your competitors a run for their money. Planning a business goes beyond analyzing the potential of your offer. You must analyze the following three factors as well:
- The strengths and weaknesses of your business
- The competition
- Who your customers are, what they want, and how they want it
These are the major components of a business plan’s market or industrial analysis and it is also known as a SWOT (Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analysis. This section of your business plan reveals the chances of your business to achieve success with its offers. And that’s why the industry analysis is a very important section of your business plan, which must be carefully conducted and documented.
So in this article, we will be looking at how to conduct industry analysis for a business plan. If you are a budding entrepreneur, or you are planning to start a new business; then below are the exact steps to follow when conducting an industry analysis for a new business:
How to Conduct Industry Analysis for a Business Plan
1. analyze the competition.
Of the three factors listed above, the competition may prove the most difficult to analyze, especially if you are new to the industry. But there are ways to simplify the task. You can start by looking at your direct competitors. If you are planning to start a new restaurant in an area, your direct competitors are other restaurants within that locality, while your indirect competitors are those that are slightly remote but still around.
Now, you are not just counting the number of rivals you have. You are trying to see how you can push ahead of them by filling a loophole they never noticed all these while. Some people find it hard to leave their workplace for the restaurant at lunchtime, but it’s either they do it or go hungry. You can disrupt the market’s status quo by offering to deliver lunch to people right in their workplaces. Filling loopholes like this one should be your goal.
If you don’t device strategies for pushing ahead of the competition, you will just enter the industry and join the survival race that you may never win. So, you need to introduce an innovation that will threaten your rivals. Remember, it’s either you differentiate or you fizzle out fast!
2. Assess the industry / market size
After analyzing your direct and indirect competitors, you will need to analyze your chances of standing firm even in the face of stiffer competition. Your first step in market research is to get an idea of how big the opportunity is and why it’s worth going after.
This means finding out how many customers you are catering to and much revenue you are likely to make. This is a convincing first step to lure in whoever is reading your business plan to become intrigued and dig further into your findings. Here are some factors you should consider:
- The individual strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
- The rate at which new competitors enter the market or the rate at which old competitors are leaving the market.
- The products or services that fetch most revenue for your competitors.
- How you will overcome the threat of substitute goods.
You can get lots of helpful information about your market from government sources, trade associations, financial services firms, online data providers, and free resources on the web.
3. Analyze industry forces and trends
You will need to outline what’s happening in the industry from many perspectives that would help the reader get the full gist on whether the market is lucrative or not. A great general-purpose tool for doing just that is the PEST Analysis. Here’s what it stands for and what you should consider:
- P – Political factors ( the role government plays in your industry )
- E – Economic factors ( the state of the economy on both local and national level )
- S – Social factors ( relevant changes in matters like lifestyle trends, demographics, consumer attitudes, buying patterns and opinions )
- T – Technological factors ( the impact of changing technological trends on your industry )
4. Develop your marketing plan
Developing your marketing plan entails answering the following questions:
- What products or services are you offering?
- How much will you charge for your offers?
- Where will you sell your product, and who are your target customers?
- What special incentives would you use to encourage customers to buy your product?
In short, this section of your industry analysis outlines how you will deliver your product to the customers and how you will win customers to your side.
5. Craft your growth plan
While some entrepreneurs are of the opinion that this step should come only after you have established your business, crafting your market development plan helps you envision your company growing in a few years. Your growth plan should address the following questions:
- According to recent data, is the market for your product growing or dwindling?
- Do you plan to introduce new products or line extensions in the next few years?
- If you plan to introduce new offers, would they be closely related to your current offers or within another niche entirely?
- Are there strategies for giving your business the competitive advantage in the industry?
- Are there plans to handle increasing demand?
6. Fine-tune your analysis
After the steps discussed above, cross check your analyses to ensure that your findings are factual and your figures are accurate. Another handy tool to have in your arsenal when conducting industry research is the almighty Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis . ( Don’t worry if you’ve never attended a business strategy class in your life, it’s actually quite straightforward ). Here’s the breakdown:
Threat of new entrants
How difficult ( or easy ) is it for someone to enter your specific vertical? If it’s very easy then most likely the space will be crowded with competitors fighting for margins. Conversely, if it’s very difficult, that that in itself can become a competitive advantage.
Threat of substitute products or services
How likely is it that another product or service could decrease demand or displace you and potentially the entire industry all together?
Bargaining power of customers
When it comes to pricing and terms, how much power does your customer have? Are they organized enough to exercise their purchase power, or is there so much competition that they have their pick resulting in pricing wars amongst providers?
Bargaining power of suppliers
This refers to how dependent you are on a given supplier to operate your business. If it’s difficult or near impossible for you to switch, that means they have the upper hand, whereas, if the switching costs are low, you can negotiate better terms for yourself.
Competitive rivalry of the market
Factoring in the first four forces, you can arrive at a good understanding of the playing field and whether it’s in your favor if you enter it, how long you’ll be able to last, through what means you’ll carve a space for yourself, and what you’re up against.
As a final note, you must never forget that the industry analysis is a vital part of your business plan and it will probably be the most extensive portion of it. So, take your time to conduct extensive research on your competitors and market trends over the recent years.
- Go to Chapter 9 Part B: Writing a Business Plan Competitive Market Analysis
- Go Back to Chapter 8: Writing your Company’s Profile
- Go Back to Introduction and Table of Content
Related Posts:
- How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary [Sample Template]
- 9 Most Important Elements & Components of a Business Plan
- How to Write a Marketing Plan Strategy for a New Product
- Buying a Business Plan Software – 10 Factors to Consider
- 10 Reasons Why Business Plan Pro Software is the Best

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Let's look at the industry overview for Pet Grandma, a fictional pet-based business invented for this business plan sample. The Pet Industry According to the American Pet Products Association, pet expenditures in the U.S. totaled slightly over $72.5 billion in 2018, up from $48 billion in 2010, an increase of 51% in eight years.
An example of the industry analysis in a business plan of an Indian soap company: Market overview: The market is estimated to be at INR 195 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at 7% annually ...
Follow the steps below to start drafting a business overview to include in your business plan: 1. Start with your pitch. The first sentence of your business overview should serve as a sort of elevator pitch for your company—a quick summary that defines who you are and what you do. In your pitch, you may include your offerings as a company and ...
Business Plan Example and Template. Learn how to create a business plan. Over 1.8 million professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. ... Industry Overview. The industry overview section provides information about the specific industry that the business operates in. Some of the information provided in this ...
Choose the location you want data from then choose 'total revenue' and 'percentage' and 'search for an industry' as your other options. Then type your NAICS code that you discovered under 'Search for an industry' and click on 'search'. Your options will come up below. Choose the appropriate option and 'create report'.
Here's how to write the market analysis section of a business plan. Describe each industry that you are competing in or will be targeting. Identify direct competition, but don't forget about indirect competition - this may include companies selling different products to the same potential customer segments.
Whether you write it all out in a formal business plan or not, when you're doing your industry analysis, you're looking at the following: Industry participants. Distribution patterns. Competition and buying patterns. Everything in your industry that happens outside of your business will affect your company.
By The Staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. • Jan 4, 2015. In their book Write Your Business Plan, the staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. offer an in-depth understanding of what's essential to any ...
Why you should keep your industry in mind when writing a business plan. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to business planning. Yes, there is a traditional structure to keep in mind—but what you include, the tools or templates you use, and the level of detail fully depends on your needs as a business owner. It also depends on the industry that you're entering.
Template 3: Industry Overview of Food Production Sector PowerPoint Presentation Slides. ... What is an industry overview in a business plan? An industry overview is a critical component of a business plan that provides a comprehensive analysis of the industry in which the business operates. It helps businesses understand the competitive ...
Step 2: Provide an industry outlook. An industry outlook is a general direction of where your industry is heading. Lenders want to know whether you're targeting a growing industry or declining ...
7 TOP TIPS For Writing Market Analysis. 1. Realistic Projections. Above all, make sure that you are realistic in your projections about how your product or service is going to be accepted in the market, otherwise you are going to seriously undermine the credibility of your entire business case. 2.
An industry size business plan is necessary for budgeting and marketing, especially for those who will seek third-party financing. Most venture capitalists want to know the potential size of the market for the businesses they're investing in. Ultimately, the size of the potential market for the products or services your business is offering ...
How to Conduct Industry Analysis for a Business Plan. 1. Analyze the competition. Of the three factors listed above, the competition may prove the most difficult to analyze, especially if you are new to the industry. But there are ways to simplify the task. You can start by looking at your direct competitors.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
8. Panda Doc's Free Business Plan Template. PandaDoc's free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
Bottom Line. Writing an executive summary doesn't need to be difficult if you've already done the work of writing the business plan itself. Take the elements from the plan and summarize each ...
Industry analysis in a business plan is a tool that enables a company to understand its position relative to other companies that produce similar products or services like it. While considering the strategic planning process, a company must understand the overall industry's forces.
Here's how to conduct a robust analysis: Market Size Calculation: Determine the total market size in terms of revenue, units sold, or the number of customers. This figure serves as a baseline for evaluating the industry's scale. Historical Growth Analysis: Examine historical data to identify growth trends.
The funding will be dedicated for the build-out and design of the restaurant, kitchen, bar and lounge, as well as cooking supplies and equipment, working capital, three months worth of payroll expenses and opening inventory. The breakout of the funding is below: Restaurant Build-Out and Design - $100,000. Kitchen supplies and equipment ...
How to Conduct Industry Analysis for a Business Plan. 1. Analyze the competition. Of the three factors listed above, the competition may prove the most difficult to analyze, especially if you are new to the industry. But there are ways to simplify the task. You can start by looking at your direct competitors.