How to Write a History Essay with Outline, Tips, Examples and More

Before we get into how to write a history essay, let's first understand what makes one good. Different people might have different ideas, but there are some basic rules that can help you do well in your studies. In this guide, we won't get into any fancy theories. Instead, we'll give you straightforward tips to help you with historical writing. So, if you're ready to sharpen your writing skills, let our history essay writing service explore how to craft an exceptional paper.

What is a History Essay?
A history essay is an academic assignment where we explore and analyze historical events from the past. We dig into historical stories, figures, and ideas to understand their importance and how they've shaped our world today. History essay writing involves researching, thinking critically, and presenting arguments based on evidence.
Moreover, history papers foster the development of writing proficiency and the ability to communicate complex ideas effectively. They also encourage students to engage with primary and secondary sources, enhancing their research skills and deepening their understanding of historical methodology.
History Essay Outline
.png)
The outline is there to guide you in organizing your thoughts and arguments in your essay about history. With a clear outline, you can explore and explain historical events better. Here's how to make one:
Introduction
- Hook: Start with an attention-grabbing opening sentence or anecdote related to your topic.
- Background Information: Provide context on the historical period, event, or theme you'll be discussing.
- Thesis Statement: Present your main argument or viewpoint, outlining the scope and purpose of your history essay.
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context
- Provide background information on the historical context of your topic.
- Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay.
Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence
- Each paragraph should focus on a specific argument or aspect of your thesis.
- Present evidence from primary and secondary sources to support each argument.
- Analyze the significance of the evidence and its relevance to your history paper thesis.
Counterarguments (optional)
- Address potential counterarguments or alternative perspectives on your topic.
- Refute opposing viewpoints with evidence and logical reasoning.
- Summary of Main Points: Recap the main arguments presented in the body paragraphs.
- Restate Thesis: Reinforce your thesis statement, emphasizing its significance in light of the evidence presented.
- Reflection: Reflect on the broader implications of your arguments for understanding history.
- Closing Thought: End your history paper with a thought-provoking statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
References/bibliography
- List all sources used in your research, formatted according to the citation style required by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include both primary and secondary sources, arranged alphabetically by the author's last name.
Notes (if applicable)
- Include footnotes or endnotes to provide additional explanations, citations, or commentary on specific points within your history essay.
History Essay Format
Adhering to a specific format is crucial for clarity, coherence, and academic integrity. Here are the key components of a typical history essay format:
Font and Size
- Use a legible font such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri.
- The recommended font size is usually 12 points. However, check your instructor's guidelines, as they may specify a different size.
- Set 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Double-space the entire essay, including the title, headings, body paragraphs, and references.
- Avoid extra spacing between paragraphs unless specified otherwise.
- Align text to the left margin; avoid justifying the text or using a centered alignment.
Title Page (if required):
- If your instructor requires a title page, include the essay title, your name, the course title, the instructor's name, and the date.
- Center-align this information vertically and horizontally on the page.
- Include a header on each page (excluding the title page if applicable) with your last name and the page number, flush right.
- Some instructors may require a shortened title in the header, usually in all capital letters.
- Center-align the essay title at the top of the first page (if a title page is not required).
- Use standard capitalization (capitalize the first letter of each major word).
- Avoid underlining, italicizing, or bolding the title unless necessary for emphasis.
Paragraph Indentation:
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches or use the tab key.
- Do not insert extra spaces between paragraphs unless instructed otherwise.
Citations and References:
- Follow the citation style specified by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include in-text citations whenever you use information or ideas from external sources.
- Provide a bibliography or list of references at the end of your history essay, formatted according to the citation style guidelines.
- Typically, history essays range from 1000 to 2500 words, but this can vary depending on the assignment.

How to Write a History Essay?
Historical writing can be an exciting journey through time, but it requires careful planning and organization. In this section, we'll break down the process into simple steps to help you craft a compelling and well-structured history paper.
Analyze the Question
Before diving headfirst into writing, take a moment to dissect the essay question. Read it carefully, and then read it again. You want to get to the core of what it's asking. Look out for keywords that indicate what aspects of the topic you need to focus on. If you're unsure about anything, don't hesitate to ask your instructor for clarification. Remember, understanding how to start a history essay is half the battle won!
Now, let's break this step down:
- Read the question carefully and identify keywords or phrases.
- Consider what the question is asking you to do – are you being asked to analyze, compare, contrast, or evaluate?
- Pay attention to any specific instructions or requirements provided in the question.
- Take note of the time period or historical events mentioned in the question – this will give you a clue about the scope of your history essay.
Develop a Strategy
With a clear understanding of the essay question, it's time to map out your approach. Here's how to develop your historical writing strategy:
- Brainstorm ideas : Take a moment to jot down any initial thoughts or ideas that come to mind in response to the history paper question. This can help you generate a list of potential arguments, themes, or points you want to explore in your history essay.
- Create an outline : Once you have a list of ideas, organize them into a logical structure. Start with a clear introduction that introduces your topic and presents your thesis statement – the main argument or point you'll be making in your history essay. Then, outline the key points or arguments you'll be discussing in each paragraph of the body, making sure they relate back to your thesis. Finally, plan a conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your history paper thesis.
- Research : Before diving into writing, gather evidence to support your arguments. Use reputable sources such as books, academic journals, and primary documents to gather historical evidence and examples. Take notes as you research, making sure to record the source of each piece of information for proper citation later on.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate potential counterarguments to your history paper thesis and think about how you'll address them in your essay. Acknowledging opposing viewpoints and refuting them strengthens your argument and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Set realistic goals : Be realistic about the scope of your history essay and the time you have available to complete it. Break down your writing process into manageable tasks, such as researching, drafting, and revising, and set deadlines for each stage to stay on track.

Start Your Research
Now that you've grasped the history essay topic and outlined your approach, it's time to dive into research. Here's how to start:
- Ask questions : What do you need to know? What are the key points to explore further? Write down your inquiries to guide your research.
- Explore diverse sources : Look beyond textbooks. Check academic journals, reliable websites, and primary sources like documents or artifacts.
- Consider perspectives : Think about different viewpoints on your topic. How have historians analyzed it? Are there controversies or differing interpretations?
- Take organized notes : Summarize key points, jot down quotes, and record your thoughts and questions. Stay organized using spreadsheets or note-taking apps.
- Evaluate sources : Consider the credibility and bias of each source. Are they peer-reviewed? Do they represent a particular viewpoint?
Establish a Viewpoint
By establishing a clear viewpoint and supporting arguments, you'll lay the foundation for your compelling historical writing:
- Review your research : Reflect on the information gathered. What patterns or themes emerge? Which perspectives resonate with you?
- Formulate a thesis statement : Based on your research, develop a clear and concise thesis that states your argument or interpretation of the topic.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate objections to your history paper thesis. Are there alternative viewpoints or evidence that you need to address?
- Craft supporting arguments : Outline the main points that support your thesis. Use evidence from your research to strengthen your arguments.
- Stay flexible : Be open to adjusting your viewpoint as you continue writing and researching. New information may challenge or refine your initial ideas.
Structure Your Essay
Now that you've delved into the depths of researching historical events and established your viewpoint, it's time to craft the skeleton of your essay: its structure. Think of your history essay outline as constructing a sturdy bridge between your ideas and your reader's understanding. How will you lead them from point A to point Z? Will you follow a chronological path through history or perhaps dissect themes that span across time periods?
And don't forget about the importance of your introduction and conclusion—are they framing your narrative effectively, enticing your audience to read your paper, and leaving them with lingering thoughts long after they've turned the final page? So, as you lay the bricks of your history essay's architecture, ask yourself: How can I best lead my audience through the maze of time and thought, leaving them enlightened and enriched on the other side?
Create an Engaging Introduction
Creating an engaging introduction is crucial for capturing your reader's interest right from the start. But how do you do it? Think about what makes your topic fascinating. Is there a surprising fact or a compelling story you can share? Maybe you could ask a thought-provoking question that gets people thinking. Consider why your topic matters—what lessons can we learn from history?
Also, remember to explain what your history essay will be about and why it's worth reading. What will grab your reader's attention and make them want to learn more? How can you make your essay relevant and intriguing right from the beginning?
Develop Coherent Paragraphs
Once you've established your introduction, the next step is to develop coherent paragraphs that effectively communicate your ideas. Each paragraph should focus on one main point or argument, supported by evidence or examples from your research. Start by introducing the main idea in a topic sentence, then provide supporting details or evidence to reinforce your point.
Make sure to use transition words and phrases to guide your reader smoothly from one idea to the next, creating a logical flow throughout your history essay. Additionally, consider the organization of your paragraphs—is there a clear progression of ideas that builds upon each other? Are your paragraphs unified around a central theme or argument?
Conclude Effectively
Concluding your history essay effectively is just as important as starting it off strong. In your conclusion, you want to wrap up your main points while leaving a lasting impression on your reader. Begin by summarizing the key points you've made throughout your history essay, reminding your reader of the main arguments and insights you've presented.
Then, consider the broader significance of your topic—what implications does it have for our understanding of history or for the world today? You might also want to reflect on any unanswered questions or areas for further exploration. Finally, end with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action that encourages your reader to continue thinking about the topic long after they've finished reading.
Reference Your Sources
Referencing your sources is essential for maintaining the integrity of your history essay and giving credit to the scholars and researchers who have contributed to your understanding of the topic. Depending on the citation style required (such as MLA, APA, or Chicago), you'll need to format your references accordingly. Start by compiling a list of all the sources you've consulted, including books, articles, websites, and any other materials used in your research.
Then, as you write your history essay, make sure to properly cite each source whenever you use information or ideas that are not your own. This includes direct quotations, paraphrases, and summaries. Remember to include all necessary information for each source, such as author names, publication dates, and page numbers, as required by your chosen citation style.
Review and Ask for Advice
As you near the completion of your history essay writing, it's crucial to take a step back and review your work with a critical eye. Reflect on the clarity and coherence of your arguments—are they logically organized and effectively supported by evidence? Consider the strength of your introduction and conclusion—do they effectively capture the reader's attention and leave a lasting impression? Take the time to carefully proofread your history essay for any grammatical errors or typos that may detract from your overall message.
Furthermore, seeking advice from peers, mentors, or instructors can provide valuable insights and help identify areas for improvement. Consider sharing your essay with someone whose feedback you trust and respect, and be open to constructive criticism. Ask specific questions about areas you're unsure about or where you feel your history essay may be lacking.
History Essay Example
In this section, we offer an example of a history essay examining the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society. This essay demonstrates how historical analysis and critical thinking are applied in academic writing. By exploring this specific event, you can observe how historical evidence is used to build a cohesive argument and draw meaningful conclusions.

FAQs about History Essay Writing
How to write a history essay introduction, how to write a conclusion for a history essay, how to write a good history essay.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
Buffalo History Works Everyone Should Know About

Buffalo, also known as the Queen City of the Lakes, is nestled on the eastern edge of Lake Erie in upstate New York. It has a fascinating history full of ups and downs. Back in the 1800s, it was a major gateway to the American West, thanks to its prime spot along the Erie Canal and later as a key railway hub. The city peaked during the Pan-American Exposition in 1901, showing off its wealth and culture with stunning architecture. But like many industrial cities, Buffalo faced tough times in the mid-20th century. However, it's been making a comeback lately. Today, Buffalo boasts a mix of historic charm and modern innovation, with a thriving arts scene and growing tech sector, making it a city that honors its past while embracing its future. While you’re reading this interesting article, you can ask our writers to ‘ write my paper ,’ and they will gladly handle your workload.

William McKinley Assassination
William McKinley, the 25th President of the United States, met a tragic end on September 6, 1901. The assassination took place at the Pan-American Exposition in Buffalo, New York. Would you like to know how was William McKinley assassinated? As he greeted attendees in a receiving line at the Temple of Music, he was approached by Leon Czolgosz, an anarchist with a concealed revolver wrapped in a handkerchief. Czolgosz fired two shots at close range in a swift and calculated move.

The first bullet grazed McKinley's shoulder, while the second penetrated his abdomen, causing severe internal injuries. Despite initial optimism about McKinley's recovery, his condition worsened rapidly due to infection, and he succumbed to his wounds on September 14, 1901.
Czolgosz's motives were rooted in anarchist ideology. He believed in overthrowing governments and viewed McKinley as a symbol of oppressive capitalism. Czolgosz was swiftly captured and put on trial. He showed no remorse for his actions, declaring, "I killed the President because he was the enemy of the good people—the working people."
McKinley assassination sent shockwaves throughout the nation, prompting widespread mourning and outrage. McKinley was a popular president known for his leadership during the Spanish-American War and his efforts to promote American industry and prosperity through protective tariffs.
Following McKinley's death, Vice President Theodore Roosevelt assumed the presidency, embarking on a progressive agenda that would leave a lasting impact on American politics and society.
The McKinley assassination highlighted the vulnerability of public figures and led to increased security measures for presidents and other officials. It also sparked debates about the influence of radical ideologies and the need for greater vigilance against political extremism in the United States. McKinley's legacy remains a tragedy and an enduring reminder of the risks inherent in public service.
Trial and Execution of Leon Czolgosz
After the assassination of President William McKinley on September 6, 1901, Leon Czolgosz was swiftly apprehended by security and the public. Charged with murder, he faced trial in the Erie County Courthouse in Buffalo, New York. The trial began on September 23, 1901, and lasted only eight hours. Czolgosz initially pleaded not guilty but later changed his plea to guilty, refusing to offer any defense for his actions. The trial was marked by intense public interest and outrage over McKinley's assassination.

The prosecution presented evidence of Czolgosz's anarchist beliefs and his premeditated intent to kill the president. Witnesses recounted the events of the assassination, including Czolgosz's actions and statements leading up to the shooting. Despite Czolgosz's lack of legal representation, the court swiftly found him guilty of murder in the first degree.
Following his conviction, Czolgosz was sentenced to death by electrocution. His defense attorney, Robert Titus, appealed for a stay of execution, citing concerns about Czolgosz's mental state and the speed of the trial. However, the appeal was denied, and the execution proceeded as scheduled.
On October 29, 1901, just 45 days after McKinley's death, Czolgosz’s execution was performed at Auburn State Prison in New York. He was strapped into the electric chair and pronounced dead after two jolts of electricity. Czolgosz's body was later buried in an unmarked grave within the prison grounds.
The trial and execution of Leon Czolgosz highlighted the public's shock and horror at McKinley's assassination, as well as the swift and decisive response of the legal system. It also raised questions about the influence of radical ideologies and the need for heightened security measures to protect public figures. Czolgosz's actions left a lasting impact on American society, prompting increased vigilance against political extremism and further shaping the nation's approach to presidential security.
Need Assistance with Your History Essays?
Use our affordable service from seasoned academic penmen.
Lightship LV 82
Lightship LV 82, also known as the Nantucket Lightship, was a crucial navigational aid stationed off the coast of Massachusetts, marking dangerous shoals and guiding ships through the treacherous waters of Nantucket Shoals. Commissioned in 1854, this light vessel was one of many lightships operated by the United States Lighthouse Service, later the United States Coast Guard, serving as floating lighthouses in areas where traditional lighthouses couldn't be constructed.

While Lightvessel LV 82 primarily served off the coast of Massachusetts, it has a connection to Buffalo, New York, through a significant historical event. In September 1901, President William McKinley was assassinated at the Pan-American Exposition in Buffalo. Following McKinley's death, his body was transported by train from Buffalo back to Washington, D.C., for funeral proceedings. As part of the journey, the train passed through Albany, New York, where it stopped briefly.
During this stop in Albany, the funeral train was accompanied by a guard of honor, including a contingent of U.S. Navy ships. Among these ships was Lightship LV 82, which had been temporarily moved from its station off the coast of Massachusetts to join the procession as a mark of respect for the fallen president.
The presence of the lightship as part of the funeral procession highlights its symbolic role in national events and its significance beyond its primary maritime duties. This historical moment is a reminder of the widespread impact of McKinley's assassination and how it touched various communities and institutions across the United States, including the crew of the Buffalo ship.
LV 82 faced numerous challenges throughout its decades-long service, including collisions with passing vessels and severe weather conditions. Despite these dangers, the dedicated crew aboard the lightship remained committed to their mission, ensuring the safety of countless ships navigating the waters off Nantucket. If you need a composition related to one of these topics, you can simply say, ‘ write my paper for me ,’ and our authors will do the rest.
Buffalo Grain Elevators
In the mid-19th century, Buffalo, New York, emerged as a crucial hub in the global grain trade, thanks in part to the innovative efforts of individuals like Joseph Dart. A Buffalo-based merchant and entrepreneur was the person who invented the grain elevator in 1842. This invention revolutionized the handling and storage of grain, particularly in port cities like Buffalo, where large quantities of grain were shipped and stored. In 1843, Dart introduced a groundbreaking grain-handling technology advancement – the steam-powered grain elevator. This invention revolutionized the efficiency of loading and unloading grain from ships, barges, and railroad cars, propelling Buffalo to the forefront of the grain trade.

Dart's steam-powered elevator was just one of many grain-handling innovations that transformed Buffalo's waterfront. The city's strategic location at the eastern terminus of the Erie Canal and its proximity to the Great Lakes made it an ideal location for the transshipment and storage of grain from the fertile agricultural regions of the Midwest to markets in the eastern United States and beyond.
Constructed primarily of concrete and steel, Buffalo's grain elevators rose as monumental structures along the waterfront, reaching over 100 feet. These "prairie skyscrapers," as they came to be known, featured a network of conveyor belts, chutes, and bins that facilitated the efficient transfer and storage of grain.
Dart's steam-powered elevator and other technological innovations helped solidify Buffalo's position as a dominant grain port. The city's waterfront became a bustling industrial landscape, with grain elevators dotting the skyline and processing facilities humming with activity.
While the importance of Buffalo grain elevators waned in the mid-20th century with transportation and storage technology changes, efforts have been made to preserve these iconic structures as symbols of the city's industrial heritage. Some have been repurposed for new uses, such as mixed-use developments, art spaces, and cultural attractions. In contrast, others stand as silent reminders of Buffalo's storied past as a powerhouse in the global grain trade. Through the preservation and adaptive reuse of these historic landmarks, Buffalo continues to honor its legacy as a key player in the evolution of the grain industry.
Who Can Give a Hand With My Essay?
Can I pay someone to write my paper ? Of course! You can and should pay our expert writers!
Buffalo Central Terminal
Buffalo Terminal is a testament to the city's rich railroad history and architectural grandeur. Completed in 1929, the terminal served as a major transportation hub for Buffalo, New York, connecting passengers to destinations across the United States and Canada. Designed by architects Alfred T. Fellheimer and Steward Wagner, the terminal's Art Deco style and towering structure made it an iconic landmark in the city.

Adjacent to the Central Terminal is the Buffalo Belt Line, a vital railroad corridor encircling the city. Constructed in the late 19th century, the Belt Line facilitated the movement of freight and passengers between Buffalo's industrial districts and outlying suburbs. The Belt Line played a crucial role in Buffalo's industrial boom, supporting the region's growth of manufacturing and commerce.
The Buffalo Central Terminal served as the focal point of the city's rail network, welcoming thousands of travelers daily. The terminal featured a concourse adorned with marble floors, ornate fixtures, and soaring ceilings, exuding elegance and sophistication. Its numerous platforms and tracks accommodated various trains, including long-distance passenger services, commuter trains, and freight shipments.
The city is also home to Exchange Street Station, a historic train station in Buffalo, NY. Opened in 1870, the station was a key transportation hub for passenger trains traveling between Buffalo and destinations throughout the Northeast and Midwest United States.
Buffalo-Exchange Street Station, designed by architect Thomas Rodd, originally served as the eastern terminus of the New York Central Railroad's mainline from Albany. The station's elegant Victorian-style architecture, characterized by its ornate brick facade and arched windows, reflected the grandeur of railroad travel during the late 19th century.
On September 16, 1901, the funeral procession for President William McKinley commenced from Buffalo, NY, departing the train station at approximately 8:30 AM. McKinley, who had succumbed to injuries sustained from an anarchist's bullet, passed away on September 14, following days of medical care that ultimately proved futile in controlling a severe post-operative infection.
The somber funeral train, draped in black bunting, was led by two locomotives. The first engine signaled the train's mournful journey with a long, mournful whistle as it traversed the tracks. Behind it, the second locomotive towed a series of cars, including a baggage car, a saloon car, and five Pullman lounges.
Each car held a distinct group of mourners and dignitaries. The first car accommodated members of the press, while the second housed McKinley's cabinet members. The third car was designated for the incoming President, Theodore Roosevelt, while the fourth carried McKinley's grieving family. Lastly, the final car, a glass-enclosed observation car, prominently displayed the President's coffin atop a bed of flowers, allowing the public to pay their respects as the train made its solemn journey.
Pan-American Exposition
The Pan-American Exposition of 1901 is a landmark event in American history, showcasing the achievements of the United States and its neighboring countries in the Western Hemisphere. Held in Buffalo, New York, the exposition celebrated the progress and innovation of the Americas while also serving as a platform for cultural exchange and diplomatic relations.

The Pan-American Exposition was a grand spectacle featuring elaborate exhibits, dazzling displays of technology, and architectural marvels. The centerpiece of the exposition was the Electric Tower, a towering structure illuminated by thousands of electric lights, which symbolized the rapid advancements in electrical engineering during the turn of the 20th century.
One of the most iconic features of the Pan-American Exposition was the "City of Light," a sprawling complex of illuminated buildings and gardens that dazzled visitors with its beauty and innovation. The exposition also showcased the latest inventions and innovations, including the telephone, the X-ray machine, and the motion picture camera, which captivated audiences and demonstrated the progress of American industry and ingenuity.
In addition to its technological marvels, the Pan-American Exposition highlighted the cultural diversity of the Western Hemisphere, with exhibits showcasing participating countries' art, music, and traditions. It served as a platform for cultural exchange and diplomacy, fostering connections between nations and promoting understanding and cooperation among peoples.
However, the Buffalo Pan-American Exposition was marred by tragedy when President William McKinley was assassinated on its grounds on September 6, 1901. The shocking event cast a shadow over the exposition and left a lasting impact on American history.
Despite this tragedy, the Pan-American Exposition of 1901 remains a significant moment in the nation's history, reflecting the optimism, progress, and international cooperation of the turn of the century.
Buffalo's history intersects with President William McKinley primarily through the tragic events of his assassination at the Pan-American Exposition on September 6, 1901. As the host city of the exposition, Buffalo was a vibrant industrial and commercial center during McKinley's presidency, showcasing American progress and innovation.
McKinley's visit to the exposition, where he delivered a speech promoting peace and unity among the nations of the Western Hemisphere, was cut short by the assassination perpetrated by anarchist Leon Czolgosz. The assassination cast a shadow over Buffalo and left a lasting impact on the city's identity and development.
Despite the tragedy, Buffalo continued to thrive as an industrial powerhouse, with its grain elevators, transportation networks, and cultural institutions reflecting its enduring resilience and legacy as a significant American city.

A guide to writing history essays
This guide has been prepared for students at all undergraduate university levels. Some points are specifically aimed at 100-level students, and may seem basic to those in upper levels. Similarly, some of the advice is aimed at upper-level students, and new arrivals should not be put off by it.
The key point is that learning to write good essays is a long process. We hope that students will refer to this guide frequently, whatever their level of study.
Why do history students write essays?
Essays are an essential educational tool in disciplines like history because they help you to develop your research skills, critical thinking, and writing abilities. The best essays are based on strong research, in-depth analysis, and are logically structured and well written.
An essay should answer a question with a clear, persuasive argument. In a history essay, this will inevitably involve a degree of narrative (storytelling), but this should be kept to the minimum necessary to support the argument – do your best to avoid the trap of substituting narrative for analytical argument. Instead, focus on the key elements of your argument, making sure they are well supported by evidence. As a historian, this evidence will come from your sources, whether primary and secondary.
The following guide is designed to help you research and write your essays, and you will almost certainly earn better grades if you can follow this advice. You should also look at the essay-marking criteria set out in your course guide, as this will give you a more specific idea of what the person marking your work is looking for.
Where to start
First, take time to understand the question. Underline the key words and consider very carefully what you need to do to provide a persuasive answer. For example, if the question asks you to compare and contrast two or more things, you need to do more than define these things – what are the similarities and differences between them? If a question asks you to 'assess' or 'explore', it is calling for you to weigh up an issue by considering the evidence put forward by scholars, then present your argument on the matter in hand.
A history essay must be based on research. If the topic is covered by lectures, you might begin with lecture and tutorial notes and readings. However, the lecturer does not want you simply to echo or reproduce the lecture content or point of view, nor use their lectures as sources in your footnotes. They want you to develop your own argument. To do this you will need to look closely at secondary sources, such as academic books and journal articles, to find out what other scholars have written about the topic. Often your lecturer will have suggested some key texts, and these are usually listed near the essay questions in your course guide. But you should not rely solely on these suggestions.
Tip : Start the research with more general works to get an overview of your topic, then move on to look at more specialised work.
Crafting a strong essay
Before you begin writing, make an essay plan. Identify the two-to-four key points you want to make. Organize your ideas into an argument which flows logically and coherently. Work out which examples you will use to make the strongest case. You may need to use an initial paragraph (or two) to bring in some context or to define key terms and events, or provide brief identifying detail about key people – but avoid simply telling the story.
An essay is really a series of paragraphs that advance an argument and build towards your conclusion. Each paragraph should focus on one central idea. Introduce this idea at the start of the paragraph with a 'topic sentence', then expand on it with evidence or examples from your research. Some paragraphs should finish with a concluding sentence that reiterates a main point or links your argument back to the essay question.
A good length for a paragraph is 150-200 words. When you want to move to a new idea or angle, start a new paragraph. While each paragraph deals with its own idea, paragraphs should flow logically, and work together as a greater whole. Try using linking phrases at the start of your paragraphs, such as 'An additional factor that explains', 'Further', or 'Similarly'.
We discourage using subheadings for a history essay (unless they are over 5000 words in length). Instead, throughout your essay use 'signposts'. This means clearly explaining what your essay will cover, how an example demonstrates your point, or reiterating what a particular section has added to your overall argument.
Remember that a history essay isn't necessarily about getting the 'right' answer – it's about putting forward a strong case that is well supported by evidence from academic sources. You don't have to cover everything – focus on your key points.
In your introduction or opening paragraph you could indicate that while there are a number of other explanations or factors that apply to your topic, you have chosen to focus on the selected ones (and say why). This demonstrates to your marker that while your argument will focus on selected elements, you do understand the bigger picture.
The classic sections of an essay
Introduction.
- Establishes what your argument will be, and outlines how the essay will develop it
- A good formula to follow is to lay out about 3 key reasons that support the answer you plan to give (these points will provide a road-map for your essay and will become the ideas behind each paragraph)
- If you are focusing on selected aspects of a topic or particular sources and case studies, you should state that in your introduction
- Define any key terms that are essential to your argument
- Keep your introduction relatively concise – aim for about 10% of the word count
- Consists of a series of paragraphs that systematically develop the argument outlined in your introduction
- Each paragraph should focus on one central idea, building towards your conclusion
- Paragraphs should flow logically. Tie them together with 'bridge' sentences – e.g. you might use a word or words from the end of the previous paragraph and build it into the opening sentence of the next, to form a bridge
- Also be sure to link each paragraph to the question/topic/argument in some way (e.g. use a key word from the question or your introductory points) so the reader does not lose the thread of your argument
- Ties up the main points of your discussion
- Should link back to the essay question, and clearly summarise your answer to that question
- May draw out or reflect on any greater themes or observations, but you should avoid introducing new material
- If you have suggested several explanations, evaluate which one is strongest
Using scholarly sources: books, journal articles, chapters from edited volumes
Try to read critically: do not take what you read as the only truth, and try to weigh up the arguments presented by scholars. Read several books, chapters, or articles, so that you understand the historical debates about your topic before deciding which viewpoint you support. The best sources for your history essays are those written by experts, and may include books, journal articles, and chapters in edited volumes. The marking criteria in your course guide may state a minimum number of academic sources you should consult when writing your essay. A good essay considers a range of evidence, so aim to use more than this minimum number of sources.
Tip : Pick one of the books or journal articles suggested in your course guide and look at the author's first few footnotes – these will direct you to other prominent sources on this topic.
Don't overlook journal articles as a source. They contain the most in-depth research on a particular topic. Often the first pages will summarise the prior research into this topic, so articles can be a good way to familiarise yourself with what else has 'been done'.
Edited volumes can also be a useful source. These are books on a particular theme, topic or question, with each chapter written by a different expert.
One way to assess the reliability of a source is to check the footnotes or endnotes. When the author makes a claim, is this supported by primary or secondary sources? If there are very few footnotes, then this may not be a credible scholarly source. Also check the date of publication, and prioritise more recent scholarship. Aim to use a variety of sources, but focus most of your attention on academic books and journal articles.
Paraphrasing and quotations
A good essay is about your ability to interpret and analyse sources, and to establish your own informed opinion with a persuasive argument that uses sources as supporting evidence. You should express most of your ideas and arguments in your own words. Cutting and pasting together the words of other scholars, or simply changing a few words in quotations taken from the work of others, will prevent you from getting a good grade, and may be regarded as academic dishonesty (see more below).
Direct quotations can be useful tools if they provide authority and colour. For maximum effect though, use direct quotations sparingly – where possible, paraphrase most material into your own words. Save direct quotations for phrases that are interesting, contentious, or especially well-phrased.
A good writing practice is to introduce and follow up every direct quotation you use with one or two sentences of your own words, clearly explaining the relevance of the quote, and putting it in context with the rest of your paragraph. Tell the reader who you are quoting, why this quote is here, and what it demonstrates. Avoid simply plonking a quotation into the middle of your own prose. This can be quite off-putting for a reader.
- Only include punctuation in your quote if it was in the original text. Otherwise, punctuation should come after the quotation marks. If you cut out words from a quotation, put in three dots (an ellipsis [ . . .]) to indicate where material has been cut
- If your quote is longer than 50 words, it should be indented and does not need quotation marks. This is called a block quote (use these sparingly: remember you have a limited word count and it is your analysis that is most significant)
- Quotations should not be italicised
Referencing, plagiarism and Turnitin
When writing essays or assignments, it is very important to acknowledge the sources you have used. You risk the charge of academic dishonesty (or plagiarism) if you copy or paraphrase words written by another person without providing a proper acknowledgment (a 'reference'). In your essay, whenever you refer to ideas from elsewhere, statistics, direct quotations, or information from primary source material, you must give details of where this information has come from in footnotes and a bibliography.
Your assignment may be checked through Turnitin, a type of plagiarism-detecting software which checks assignments for evidence of copied material. If you have used a wide variety of primary and secondary sources, you may receive a high Turnitin percentage score. This is nothing to be alarmed about if you have referenced those sources. Any matches with other written material that are not referenced may be interpreted as plagiarism – for which there are penalties. You can find full information about all of this in the History Programme's Quick Guide Referencing Guide contained in all course booklets.
Final suggestions
Remember that the easier it is to read your essay, the more likely you are to get full credit for your ideas and work. If the person marking your work has difficulty reading it, either because of poor writing or poor presentation, they will find it harder to grasp your points. Try reading your work aloud, or to a friend/flatmate. This should expose any issues with flow or structure, which you can then rectify.
Make sure that major and controversial points in your argument are clearly stated and well- supported by evidence and footnotes. Aspire to understand – rather than judge – the past. A historian's job is to think about people, patterns, and events in the context of the time, though you can also reflect on changing perceptions of these over time.
Things to remember
- Write history essays in the past tense
- Generally, avoid sub-headings in your essays
- Avoid using the word 'bias' or 'biased' too freely when discussing your research materials. Almost any text could be said to be 'biased'. Your task is to attempt to explain why an author might argue or interpret the past as they do, and what the potential limitations of their conclusions might be
- Use the passive voice judiciously. Active sentences are better!
- Be cautious about using websites as sources of information. The internet has its uses, particularly for primary sources, but the best sources are academic books and articles. You may use websites maintained by legitimate academic and government authorities, such as those with domain suffixes like .gov .govt .ac or .edu
- Keep an eye on word count – aim to be within 10% of the required length. If your essay is substantially over the limit, revisit your argument and overall structure, and see if you are trying to fit in too much information. If it falls considerably short, look into adding another paragraph or two
- Leave time for a final edit and spell-check, go through your footnotes and bibliography to check that your references are correctly formatted, and don't forget to back up your work as you go!
Other useful strategies and sources
- Student Learning Development , which offers peer support and one-on-one writing advice (located near the central library)
- Harvard College's guide to writing history essays (PDF)
- Harvard College's advice on essay structure
- Victoria University's comprehensive essay writing guide (PDF)
How to Write a History Essay?
04 August, 2020
10 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
There are so many types of essays. It can be hard to know where to start. History papers aren’t just limited to history classes. These tasks can be assigned to examine any important historical event or a person. While they’re more common in history classes, you can find this type of assignment in sociology or political science course syllabus, or just get a history essay task for your scholarship. This is Handmadewriting History Essay Guide - let's start!

Purpose of a History Essay
Wondering how to write a history essay? First of all, it helps to understand its purpose. Secondly, this essay aims to examine the influences that lead to a historical event. Thirdly, it can explore the importance of an individual’s impact on history.
However, the goal isn’t to stay in the past. Specifically, a well-written history essay should discuss the relevance of the event or person to the “now”. After finishing this essay, a reader should have a fuller understanding of the lasting impact of an event or individual.
Need basic essay guidance? Find out what is an essay with this 101 essay guide: What is an Essay?
Elements for Success
Indeed, understanding how to write a history essay is crucial in creating a successful paper. Notably, these essays should never only outline successful historic events or list an individual’s achievements. Instead, they should focus on examining questions beginning with what , how , and why . Here’s a pro tip in how to write a history essay: brainstorm questions. Once you’ve got questions, you have an excellent starting point.
Preparing to Write

Evidently, a typical history essay format requires the writer to provide background on the event or person, examine major influences, and discuss the importance of the forces both then and now. In addition, when preparing to write, it’s helpful to organize the information you need to research into questions. For example:
- Who were the major contributors to this event?
- Who opposed or fought against this event?
- Who gained or lost from this event?
- Who benefits from this event today?
- What factors led up to this event?
- What changes occurred because of this event?
- What lasting impacts occurred locally, nationally, globally due to this event?
- What lessons (if any) were learned?
- Why did this event occur?
- Why did certain populations support it?
- Why did certain populations oppose it?
These questions exist as samples. Therefore, generate questions specific to your topic. Once you have a list of questions, it’s time to evaluate them.
Evaluating the Question

Seasoned writers approach writing history by examining the historic event or individual. Specifically, the goal is to assess the impact then and now. Accordingly, the writer needs to evaluate the importance of the main essay guiding the paper. For example, if the essay’s topic is the rise of American prohibition, a proper question may be “How did societal factors influence the rise of American prohibition during the 1920s? ”
This question is open-ended since it allows for insightful analysis, and limits the research to societal factors. Additionally, work to identify key terms in the question. In the example, key terms would be “societal factors” and “prohibition”.
Summarizing the Argument
The argument should answer the question. Use the thesis statement to clarify the argument and outline how you plan to make your case. In other words. the thesis should be sharp, clear, and multi-faceted. Consider the following tips when summarizing the case:
- The thesis should be a single sentence
- It should include a concise argument and a roadmap
- It’s always okay to revise the thesis as the paper develops
- Conduct a bit of research to ensure you have enough support for the ideas within the paper
Outlining a History Essay Plan

Once you’ve refined your argument, it’s time to outline. Notably, many skip this step to regret it then. Nonetheless, the outline is a map that shows where you need to arrive historically and when. Specifically, taking the time to plan, placing the strongest argument last, and identifying your sources of research is a good use of time. When you’re ready to outline, do the following:
- Consider the necessary background the reader should know in the introduction paragraph
- Define any important terms and vocabulary
- Determine which ideas will need the cited support
- Identify how each idea supports the main argument
- Brainstorm key points to review in the conclusion
Gathering Sources
As a rule, history essays require both primary and secondary sources . Primary resources are those that were created during the historical period being analyzed. Secondary resources are those created by historians and scholars about the topic. It’s a good idea to know if the professor requires a specific number of sources, and what kind he or she prefers. Specifically, most tutors prefer primary over secondary sources.
Where to find sources? Great question! Check out bibliographies included in required class readings. In addition, ask a campus Librarian. Peruse online journal databases; In addition, most colleges provide students with free access. When in doubt, make an appointment and ask the professor for guidance.
Writing the Essay
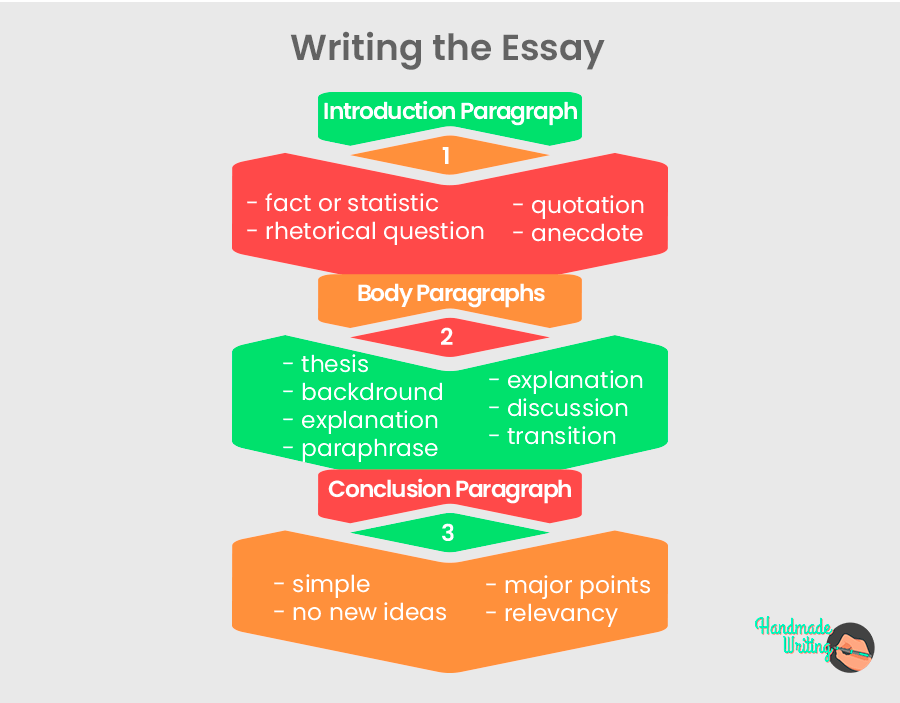
Now that you have prepared your questions, ideas, and arguments; composed the outline ; and gathered sources – it’s time to write your first draft. In particular, each section of your history essay must serve its purpose. Here is what you should include in essay paragraphs.
Introduction Paragraph
Unsure of how to start a history essay? Well, like most essays, the introduction should include an attention-getter (or hook):
- Relevant fact or statistic
- Rhetorical Question
- Interesting quotation
- Application anecdote if appropriate
Once you’ve captured the reader’s interest, introduce the topic. Similarly, present critical historic context. Namely, it is necessary to introduce any key individuals or events that will be discussed later in the essay. At last, end with a strong thesis which acts as a transition to the first argument.
Body Paragraphs
Indeed, each body paragraph should offer a single idea to support the argument. Then, after writing a strong topic sentence, the topic should be supported with correctly cited research. Consequently, a typical body paragraph is arranged as follows:
- Topic sentence linking to the thesis
- Background of the topic
- Research quotation or paraphrase #1
- Explanation and analysis of research
- Research quotation or paraphrase #2
- Transition to the next paragraph
Equally, the point of body paragraphs is to build the argument. Hence, present the weakest support first and end with the strongest. Admittedly, doing so leaves the reader with the best possible evidence.
Conclusion Paragraph
You’re almost there! Eventually, conclusion paragraphs should review the most important points in the paper. In them, you should prove that you’ve supported the argument proposed in the thesis. When writing a conclusion paragraph keep these tips in mind:
- Keep it simple
- Avoid introducing new information
- Review major points
- Discuss the relevance to today
Problems with writing Your History essay ? Try our Essay Writer Service!

Proofreading Your Essay
Once the draft is ready and polished, it’s time to proceed to final editing. What does this process imply? Specifically, it’s about removing impurities and making the essay look just perfect. Here’s what you need to do to improve the quality of your paper:
- Double check the content. In the first place, it’s recommended to get rid of long sentences, correct vague words. Also, make sure that all your paragrahps contain accurate sentences with transparent meaning.
- Pay attention to style. To make the process of digesting your essay easier, focus on crafting a paper with readable style, the one that is known to readers. Above all, the main mission here is to facilitate the perception of your essay. So, don’t forget about style accuracy.
- Practice reading the essay. Of course, the best practice before passing the paper is to read it out loud. Hence, this exercise will help you notice fragments that require rewriting or a complete removal.
History Essay Example
Did you want a history essay example? Take a look at one of our history essay papers.
Make it Shine
An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it’s achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine:
- Write a substantial introduction. Particularly, it’s the first impression the professor will have of the paper.
- State a clear thesis. A strong thesis is easier to support.
- Incorporate evidence critically. If while researching you find opposing arguments, include them and discuss their flaws.
- Cite all the research. Whether direct quotations or paraphrases, citing evidence is crucial to avoiding plagiarism, which can have serious academic consequences.
- Include primary and secondary resources. While primary resources may be harder to find, the professor will expect them—this is, after all, a history essay.
History Essay Sample
Ready to tackle the history essay format? Great! Check out this history essay sample from an upper-level history class. While the essay isn’t perfect, the professor points out its many strengths.
Remember: start early and revise, revise, revise . We can’t revise history, but you can revise your ideas until they’re perfect.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
Schoolshistory.org.uk
History resources, stories and news. Author: Dan Moorhouse

10 Tips for Writing a Perfect History Essay
No doubt, essays are one of the most popular forms of college assignments. History teachers will probably assign you many of them. And for a good reason – this type of work shows your comprehension of the subject, ability to research, analytical skills, and writing itself, of course. When preparing a history essay, one must consider all the requirements, find relevant data and come up with a logical and well-organized paper.
Your main task is to reveal the topic, demonstrating your expertise. Yes, there’s a lot of work ahead, but thanks to the tips collected below, you will easily navigate all the stages of essay writing!
However, before we begin, here’s one extra recommendation. If you struggle to finish your paper before the deadline, don’t worry! More and more learners outsource their homework to experienced authors to have their essays completed at the highest level. Basically, all you have to do is google “ write my essay ,” and a great professional will be found in no time. This is certainly the best way to manage it all when the study load is simply overwhelming.
Make Sure You Understand The Topic Right
In fact, by assigning you an essay, teachers expect you to answer the question posed. At the same time, the work must be well-argued and well-evidenced. To do this, you need to understand the given topic correctly. If it contains controversial phrases and inaccurate expressions, discuss this with the teacher. In addition, they will appreciate your efforts and desire to write a brilliant essay.
It is also important to realize the key mission. It can be one of the following:
- Explain why historical events took place;
- Interpret and analyze a topic;
- Support or disagree with a specific idea;
- Justify a certain position.
It’s a great idea to focus on keywords – they’ll be defined at the essay’s beginning. And they will help you narrow your search. Otherwise, you run the risk of spending too much time on extra research that will not relate to your topic.
Do a Profound Research
History is certainly a field where every thought requires confirmation by a fact. And for this, you will rely on sources of two types. The first is information from people who participated in the events of that historical period. It can also be photos, texts, and videos created at that time. This will serve as strong evidence.
The second group is references to the works of scientists studying those events. You can also find inspiration in documentaries and fiction books. Why? They will help you feel the spirit of the era and give some great insights.
Organize Your Sources
At first, you may be intimidated by the amount of information that you will have to read. Or vice versa – its lack. However, all history students (especially the ones from the best universities ) have proven ways to find the data they require.
- The first is positions in your reading list and bibliography course. The teachers recommended these sources for a reason, right?;
- The second is the library – try to get the most out of it. Talk to librarians, they may be able to point you to excellent materials;
- Next, come online journal databases. As a college student, you surely have access to them;
- Look through free platforms like Google Scholar. There are some high-quality academic materials. As for Wikipedia, it’s not a reliable source, but websites cited on it can help you advance your research.
Analyze The Information You’ve Gathered
Even with a lot of materials collected, you can spoil the work if you don’t analyze them properly. This can be compared to a trip to historical places . What is the point of visiting them if you didn’t come up with your conclusions? Analytical skills are some of the most vital to a researcher.
Struggling to understand whether the data is scholarly? Pay attention to these characteristics:
- Does the author have a position at the university?
- Is the book (article, review) published by the academic press?;
- What is the ending of the site that published the information? The endings “.gov” and “.edu” are best suited.
As you explore the data, be sure to take notes—let it be page numbers, specific resources, citations, or references.
Formulate Key Argument
When studying the topic, you will most likely formulate a thesis statement. With a clear idea in mind (maybe one or two sentences of it), you can move on to building a plan and a draft.
The main requirement for a thesis is that it addresses the essay’s topic and is followed by supporting arguments. By the way, you will include them in the body parts along with evidence.
Of course, the arguments may change as the essay is written (you will probably find deeper ideas during the research stage). But the main thing you will start from is a clearly defined thesis statement.
Come Up With a Plan
A plan is a skeleton of your essay. In fact, the more detailed outline you create, the easier it will be for you later. You will also be able to see how consistent your arguments are. Divide the work into three sections: introduction, main part, and conclusion.

Move On To the Introduction
The introduction is of key importance for the work, as it sets the overall tone of the story and intrigues the reader. First, you need to announce the topic and give a broader perspective on the problem. Your task is to make sure that the reader will be interested enough to move on to the next parts of the essay.
Also, indicate how you will answer the main question – give an overview of your arguments and the evidence you use to support them.
When Working On Body, Have a Clear Structure In Mind
This part of the essay requires special attention – it usually consists of three paragraphs:
- Argument, evidence;
- Argument, evidence.
In addition to being logical and consistent, the text must be readable and easy to perceive. For this, use transition words – they make the essay flow and link your thoughts together.
Summarize Your Key Points
A brilliant ending perfectly sums up your points of view, arguments, and evidence. Here, you are referring to the outline. Make sure that the conclusion contains the answer to the main question of the essay.
Proofread The Essay
When the last word is written, the work is still not ready. It certainly has errors and typos that are waiting to be corrected. The best advice is to rest a little after finishing the essay because you need to somewhat forget it. Then, use tools like Hemingway and Grammarly to clean up overly complex expressions, grammar errors, and long sentences.
Read the text aloud. Is it easy to read? Is the main idea clear? Great, it means proofreading went well!
To Wrap It Up
Perhaps the main mistake which students make when completing a history essay is describing events instead of analyzing them. Be sure to ask yourself the question: what is the point of this specific paragraph? How does it help support the thesis?
Another key point is references and a bibliography. There are several citation styles, so study them so as not to spoil the end of the work. Yes, it’s rather boring, but it will show the teacher your effort and diligence.
Image Sources
Featured Image: Unsplash
- ← The History of Bingo and the Evolution of the Game
- How to Create a History Essay That Will Stand Out →
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- 37470 Share on Facebook
- 2367 Share on Twitter
- 6805 Share on Pinterest
- 2955 Share on LinkedIn
- 5413 Share on Email

Subscribe to our Free Newsletter, Complete with Exclusive History Content
Thanks, I’m not interested

How to write an introduction for a history essay

Every essay needs to begin with an introductory paragraph. It needs to be the first paragraph the marker reads.
While your introduction paragraph might be the first of the paragraphs you write, this is not the only way to do it.
You can choose to write your introduction after you have written the rest of your essay.
This way, you will know what you have argued, and this might make writing the introduction easier.
Either approach is fine. If you do write your introduction first, ensure that you go back and refine it once you have completed your essay.
What is an ‘introduction paragraph’?
An introductory paragraph is a single paragraph at the start of your essay that prepares your reader for the argument you are going to make in your body paragraphs .
It should provide all of the necessary historical information about your topic and clearly state your argument so that by the end of the paragraph, the marker knows how you are going to structure the rest of your essay.
In general, you should never use quotes from sources in your introduction.
Introduction paragraph structure
While your introduction paragraph does not have to be as long as your body paragraphs , it does have a specific purpose, which you must fulfil.
A well-written introduction paragraph has the following four-part structure (summarised by the acronym BHES).
B – Background sentences
H – Hypothesis
E – Elaboration sentences
S - Signpost sentence
Each of these elements are explained in further detail, with examples, below:
1. Background sentences
The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis , your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about.
Background sentences explain the important historical period, dates, people, places, events and concepts that will be mentioned later in your essay. This information should be drawn from your background research .
Example background sentences:
Middle Ages (Year 8 Level)
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15 th and 16 th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges.
WWI (Year 9 Level)
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe.
Civil Rights (Year 10 Level)
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success.
Ancient Rome (Year 11/12 Level)
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times.
2. Hypothesis
Once you have provided historical context for your essay in your background sentences, you need to state your hypothesis .
A hypothesis is a single sentence that clearly states the argument that your essay will be proving in your body paragraphs .
A good hypothesis contains both the argument and the reasons in support of your argument.
Example hypotheses:
Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery.
Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare.
The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders.
Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1 st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state.
3. Elaboration sentences
Once you have stated your argument in your hypothesis , you need to provide particular information about how you’re going to prove your argument.
Your elaboration sentences should be one or two sentences that provide specific details about how you’re going to cover the argument in your three body paragraphs.
You might also briefly summarise two or three of your main points.
Finally, explain any important key words, phrases or concepts that you’ve used in your hypothesis, you’ll need to do this in your elaboration sentences.
Example elaboration sentences:
By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period.
Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined.
The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results.
While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period.
4. Signpost sentence
The final sentence of your introduction should prepare the reader for the topic of your first body paragraph. The main purpose of this sentence is to provide cohesion between your introductory paragraph and you first body paragraph .
Therefore, a signpost sentence indicates where you will begin proving the argument that you set out in your hypothesis and usually states the importance of the first point that you’re about to make.
Example signpost sentences:
The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20 th century.
The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Putting it all together
Once you have written all four parts of the BHES structure, you should have a completed introduction paragraph. In the examples above, we have shown each part separately. Below you will see the completed paragraphs so that you can appreciate what an introduction should look like.
Example introduction paragraphs:
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15th and 16th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges. Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies, but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery. By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period. The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe. Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare. Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined. The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success. The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders. The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results. The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20th century.
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times. Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state. While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period. The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Additional resources

What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
The UK National Charity for History
Password Sign In
Become a Member | Register for free
Essay Writing
Student Guides

- Add to My HA Add to folder Default Folder [New Folder] Add
History is not just about writing lots of essays! It is also about discussion, debate and evidence. However, there will be, as with many other subjects at A-Level, some essays to write - but it is not as tough as it looks. Essay writing is a skill that you will get better at over time, but you might find the guide below useful to help you along.
How to Write a History Essay
- Are you new to the 6th form?
- Are you already in the 6th form but worried about your essay writing skills?
- Are you moving on to study history at university?
Then this could be just what you need! This guide will not help you to get outstanding grades - that is up to you, but it will prepare you with the skills that you need to produce that masterpiece!
Key Features: The Must Haves
A-Level/Undergraduate essays should contain the following features; although it depends on the type of essay you are writing as to how far you go; for example, a personal study or dissertation will require a great deal of historiography and referencing, whereas class essays may require less. If you are unsure as to how much your teacher will expect, it is best to ask!
A well considered argument - This is VERY important to get right. It means that you will need to make sure that you clearly state your line of argument and do it convincingly. At the same time, you will also need to give full coverage to other factors/opinions/arguments that are at play - even if it is to rubbish them!
Reference to the question
An introduction
A middle - the substantive part of the essay, where you present the evidence and arguments
A conclusion
Footnotes and bibliography
Before You Start...
The key to success in any history essay is preparation. This not only includes focussed and wide reading around the topic, but also your preparation of your thoughts and arguments. Richard Harris, experienced history teacher and now lecturer in education at Southampton University provides a very good starting point for essay writing. His plan is designed to get you thinking and planning your structure before you write. You can find a copy of this planning sheet at the end of the guide.
1) Considered Argument
The key to providing a considered argument is to read widely! What is the historiography (views of different historians) surrounding the topic? What evidence is there to support different lines of argument? Your job is firstly to present these lines of argument.
Secondly, you should critically evaluate these views and evidence as you explain them. Is there evidence to counteract? By providing a considered argument - what we don't mean is that you sit on the fence! Every essay MUST have an argument, but by considered, we simply mean that you should be prepared to consider other arguments/factors, other than your own view, even if it is to critically evaluate them and dismiss their importance! But you must be convincing and be prepared to examine them fully.
At A level, the mark-schemes tend to be stepped into 5 different levels; you cannot progress beyond level 2/3 if you do not provide a well considered argument! The examiner wants to see what your opinion is, but they also want to know that you have not just "plucked" this opinion from nowhere - they want to see that you have considered the topic fully, taken account of all of the views and arguments before making your judgement. Therefore, you should stick to your line of argument throughout, but you should clearly evaluate other points of view, showing your reader how and why they are less valuable arguments than your own.
2) Reference to the question
Where possible you should show how the evidence you are presenting links back to the question. You should refer back to the question wherever a link or piece of evidence provides some clues to help formulate an answer. This should help you to avoid going off track. Always think as you are writing "does this paragraph help to present the evidence to support my line of argument or help me to answer the question?"
3) The Introduction
The introduction should set the scene. It should be short and snappy, no more than a few lines, but they are very important as you need to hook your reader in. There should be some very brief background detail to the question. You should also include some brief historiography - what is the main debate among historians about this issue? Who is saying what? You should also at this point wish to state what YOUR argument is going to be.
You should then refer back to the question by stating how you are going to measure/argue your case; a good way to do this is by referring back to the question itself. It should help you to get the question straight in your own mind too and give you some direction. For example, if you have a question asking you how significant an event was, you need to explain what is meant by significance and how you will measure this.
E.g. 'How significant was the Reichstag Fire in the Nazi revolution?'
When this question is analysed, bit by bit it helps us to explain to our reader what the essay intends to cover.
4) The Middle
This is the substantive part of the essay. This is the bit where you have to present the evidence and arguments. It should predominantly contain your analysis/argument but you must also look at the counter-arguments and the views of historians.
- Present evidence in a balanced way: You should present your argument/response to the question clearly and effectively, using the views of historians and other evidence to back up the points you make. On the other side, you should also consider the arguments against your own and critically evaluate them in order to show why they are less important/plausible than your own.
- Present your evidence in a logical order : Try to avoid jumping around. Make a plan before you write that organizes your evidence logically. This could either be in themes or in chronological order.
- Include analysis: You must make sure that you don't just fall into the trap of presenting evidence without analysis. This reads more like a list! When presenting a piece of evidence or the view of a historian, don't forget to critically analyse. Is the evidence reliable? Is the view of the historian reliable or are they writing from a specific viewpoint? Are there different interpretations? What do you think? Is it a valid point?
- Refer often to the title: Don't forget to link your points back to the question where possible. It will help your essay and your reader stay focused on the answer to the question!

How to Structure Paragraphs:
It is important to structure your points within the scaffolding of the paragraph well. A good way to do this is to PEE all over your paragraphs!!!
Of course, don't take this literally and ruin your essay - what we mean is to use the PEE formula:
E - Example
E - Explanation.
This is a good habit to get into and a good way to provide structure. Simply make your point, give an example or piece of evidence to back it up, then explain it. What is the context? How or why is it significant/insignificant? How does it fit into the topic? How does it help to answer the question?
Test yourself:
See if you can spot the PEE on this paragraph which forms part of an answer to the question "Was Edward IV a new monarch?"
"Edward's power did not increase at the expense of the nobility; a key criteria for new monarch status. Edward continued the tradition of letting powerful magnates rule the peripheral regions of the country, such as the North and Wales. This resulted in the creation of a number of large power bases including the Herberts in Wales, Gloucester in the North, the Percys in the eastern marshes and the Woodvilles in London. This was largely due to the small number of noble creations in his reign - he only made nine promotions to high nobility. On the one hand this shows that he was in form control as he had sufficient power and stability without having to make lots of noble creations to gain support, yet on the other hand he was creating a volatile situation as rivalries built up between powerful factions and Edward was cresting a potentially explosive situation which only he could control."
5) Conclusion
This is the end of the essay. This is the bit where you are expected to answer the question! Here you should sum up in a couple of sentences what your argument is, and why it is the most plausible explanation, being careful to remind the reader of supportive evidence. Finally, you should put the essay in context. Explain the wider context to the question. It might be that there are longer-term or under the surface issues that need further exploration, or it may be that there is a bigger picture in play. By putting your answer in context, we don't mean just adding some extra facts about the period at the end - your setting in context should display your broader understanding of the period. A good example of this is when a student was writing about the Golden Age of Spain:
"In conclusion, the extent to whether this period can be deemed as a "Golden Age" ultimately rests on the context of the time. Although it is true to say that Spain was making advances in several areas, in terms of power, unity, wealth, economy, culture, empire and discovery. The extent of religious and racial persecution however, could be deemed as less golden in terms of morality, even if both policies were successful in terms of strengthening Spain's power base. In the wider context of the time, Spain's achievements seem less golden than they may at first appear. We have to remember that this period saw the Renaissance. The Renaissance affected practically every area of life at the time, and was a new dawn of discovery and thinking - Leonardo Da Vinci, William Harvey, Martin Luther, Copernicus and Galileo were but a few of the characters that shaped the time; therefore, if Spain had a golden age, so too did many other countries."
- Re-state your argument using the key words from the title
- Be confident in your argument
- Hint at a broader context
- What other issues would you explore, given more time?
6) Footnotes and Bibliography
At A-Level and undergraduate level, you will be expected to footnote your essays. Because you are not expected to do this at GCSE, this may be a new skill for you, but it is very easy!
What are footnotes?
When you quote evidence or the views of a historian from a book or periodical, you are expected to let your reader know where you got this evidence from, so that if they wished (very few would) they could go and check your evidence. You can do this by including citations or footnotes.
How to Footnote
The process of footnoting is slightly different on different computer programs and may differ again if you are using a MAC, but the process is the same, even if you are handwriting.
Footnotes should be numbered and should either appear at the bottom of the page on which they are cited or in a list at the end of the essay. They should include the following information:
1.) Author's name (surname first)
2.) Date and place of publication (found on the first page of the book usually)
3.) Title of book (in italics)
4.) Page reference.
How to footnote on the computer
If you have Microsoft Office, the simplest way to insert a footnote is by going to the references section on the tool-bar and then following the instructions above. If you are using an earlier version of Office, you should click on insert and then select footnote from the list.
Below is an example to illustrate what a footnote should look like:
"Leo, the holy pope in Rome, passed away; and in this year there was a great pestilence among cattle than man could remember for many years..." [1]
Footnote extras
- If the book is a collection of articles or a reproduction of primary source material, it will not have an author, but an editor instead. If the main name on the book is an editor, you need to write the letters (ed.) next to the name.
- If your next footnote in the sequence is from the same book, but a different page, you do not need to write out all of the information again, you can simply write the word "Ibid" which means same source and then cite the page number. However, you should only do this once in any given sequence. If you have 3 quotes in a row from the same book, the third time, you should write out the information again.
What is a bibliography?
A bibliography is the list of books that you have used to help you write your essay. This may include books that you have quoted from or used as part of your reading.
You should always include a bibliography at the end of your essay which lists the books that you have used. You can use the same format as you would for footnotes. Below is a sample to show you how it should look.
1.) Campbell, J (ed) Cambridge 1982 - The Anglo-Saxons
2.) Swanton, M (ed) J.M Dent 1997 - The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The Harvard Footnote System
Another option to make sure you have referenced correctly is to use the simpler Harvard system. This may be a preferred method for the writing of normal class essays, although for a personal study, the use of traditional footnoting is still recommended. Harvard referencing uses the author and the date of the work in the main body of the text, and then has a reference list at the end of the essay which contains the references cited in alphabetical order by author. The reference list contains the full details of the book or journal cited. Because you only refer to a shortened form of works in the main essay (author, date) your essay doesn't get filled with too much reference material. The use of the author/date shorthand does make it easy to locate works in the reference list.
An example from the main body of a text:
Within the last ten years, teachers who have attended INSET courses have reported that the courses have helped to increase their competence and confidence in using IT (see, for example, Higham and Morris, 1993; ESRC 1990), yet despite the fact that the passing years have presented opportunities for more teachers to increase their skills in IT, weaknesses identified by McCoy (1992) seem to be still evident (Gillmon, 1998; Goldstein 1997). This suggests that we need to look for explanations other than attendance at INSET courses for the reasons for the apparently poor state of teachers' competence and confidence in IT.
In this text the author is citing entire works by other researchers to support her argument. Notice the use of brackets and the author/s and dates of all works.
Another example from the main body of a text:
One resource provided in the secondary speech genre is the "posited author" (Bakhtin, 1981, p. 312).
Here the quotation is a direct one so a page number has been added. Quotations of no more than two sentences can be incorporated into the main text and marked off with quotation marks, but if you quote a longer passage it must be placed in a separate paragraph and indented from the left and right margins of the main text.
_______________
[1] Swanton, Michael (ed), J.M Dent 1997, The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, pg. 185
Attached files:
- Essay Planning Sheet 54.5 KB Word document
- How to write a synoptic essay
- A-level 'how to' guides
How to memorise essays and long responses

Lauren Condon
Marketing Specialist at Atomi

When it comes to memorising essays or long responses for your exams, there are three big things to consider.
- Should you even try to memorise an essay?
- Do you know how to adapt your memorised response to the exam question?
- How on earth are you meant to memorise a 1,200 word essay??
It’s a lot to weigh up but we can help you out here. If you want an answer to the first question, here’s one we prepared earlier. But wait, there’s more! If you’re super keen to read more about question #2, then go ahead and click here .
And for that third point on how to actually memorise a long essay? Well, all you have to do is keep reading...
1. Break it down
Your essay/long response/creative writing piece could be anywhere between 800 and 1,200 words long. Yeah… that’s a lot. So when it comes to memorising the whole thing, it’s a lot easier to break the answer down into logical chunks and work on memorising it bit by bit.
So if you want to memorise your Discovery Essay, you might have something like this:
- Introduction
- Theme 1 with the assigned text
- Theme 1 with the related text
- Theme 2 with the assigned text
- Theme 2 with the related text
You’re going to want to memorise the paragraphs and pay attention to the structure then you can piece it all together in the exam. Having a killer structure makes it a lot easier to remember the overall bones of this situation and if you’re finding this effective, you can even break those body paragraphs down further like topic sentence > example > explanation > connection to thesis.
2. Use memory tricks
Now, there are lots of different strategies and approaches when it comes to memorising a long piece of writing. Moving in sections, you can try reading it out loud over again (slowly looking at the paper less and less) or the classic look-cover-write-check approach. If you’re really struggling, make some of your own flashcards that have the first sentence on one side and the next sentence on the back so you can test your progress.
You could also enlist the help of some creative mnemonics (memory tricks) to remind you which sentence or section needs to come next. Pick one keyword from each sentence in the paragraph and turn them into a silly sentence to help you remember the structure of the paragraph and to make sure you don’t forget one of your awesome points.
3. Play to your strengths
Not all of us are super geniuses that can just read an essay and then memorise the entire thing but we’re all going to have our own strengths. There’s going to be something whether it’s art, music, writing, performance or sport that just ‘clicks’ in your brain and this is what you want to capitalise on. So for me, I was really into debating and public speaking (hold back the jokes please) and was used to giving speeches and remembering them. So whenever I wanted to memorise a long response, I would write out the essay onto palm cards and then practice it out loud like a speech. Did it annoy my family? Yes. Was I too embarrassed to tell people my strategy? Yes. Did it work? Absolutely. 💯
Whatever your strengths are, find a way to connect them to your essay and come up with a creative way of learning your long response that will be much easier and more effective for you!
4. Start early
So you know how there’s that whole long-term/short-term memory divide? Yeah well that’s going to be pretty relevant when it comes to memorising. You’re going to have a much better chance of remembering your long response if you start early and practice it often, instead of trying to cram it in the night before… sorry.
The good news is, you still have a couple of months before the HSC so try to get your prepared response written, get good feedback from your teachers and then make it perfect so it’s ready to go for the HSC. Then, the next step is to start memorising the essay now and test yourself on it fairly regularly all the way up to your exams. This way, you have plenty of time to really lock it deep into your memory.
5. Test yourself
The final and maybe even most important step is to test yourself. And not with flashcards or the look-cover-check-repeat anymore. Once you’ve got the essay memorised pretty well, you want to spend the weeks coming up to HSC doing past questions so you can practice
- Having the essay memorised
- Being able to recall it under pressure
- Adapting it to any question so that all your hard work will actually pay off
For this to work, you really need to commit 100% to exam conditions (no cheating!) and it’s definitely worth sending those responses to your teacher to get them marked. That way, you will actually know if you’re doing a good job of remembering the core of your argument but also tailoring it perfectly to the question.
Any subject with essays or long responses can be super daunting so if you want to have a pre-written, adaptable response ready to go then it’s worth making sure you can actually memorise it for your exam. Remember to break down the essay into sections, play to your memory strengths and make sure you consistently test yourself all the way up to HSC. That should do the trick. 👌
Published on
July 28, 2017
Recommended reads

The syllabus: your key to smashing your studies

How to make a personalised study timetable

How to use Atomi’s 2023 study plans and timetables
What's atomi.
Engaging, curriculum-specific videos and interactive lessons backed by research, so you can study smarter, not harder.
With tens of thousands of practice questions and custom revision sessions, you won’t just think you’re ready. You’ll know you are!
Study skills strategies and tips, AI-powered revision recommendations and progress insights help you stay on track.
Short, curriculum-specific videos and interactive content that’s easy to understand and backed by the latest research.
Active recall quizzes, topic-based tests and exam practice enable students to build their skills and get immediate feedback.
Our AI understands each student's progress and makes intelligent recommendations based on their strengths and weaknesses.
How to Research Effectively for History Essays
Published by rahul narain on 16th january 2024 16th january 2024.
The key to crafting an insightful and compelling history essay lies in effective research. This isn’t just about gathering facts and dates; it’s about diving deep into historical contexts and weaving together narratives that bring the past to life.
Researching for history essays can often feel like a journey through time, but knowing where to start and how to navigate the vast sea of information is key. In the age of digital resources, students frequently turn to essay writer service that write essays online, seeking assistance in framing and articulating their historical arguments. From identifying reliable sources to synthesizing conflicting viewpoints, these seven tips are designed to equip you with the tools necessary for delving into history with confidence and curiosity.

1. Identify Credible Sources
The first step in effective history research is distinguishing between credible and less reliable sources. Academic journals, books published by university presses, and documents from reputable institutions are generally trustworthy. They undergo strict fact-checking processes. For instance, when researching the Civil War, a journal article from the American Historical Review would be more credible than a generic web article.
In contrast, be cautious with sources like personal blogs, opinion pieces, and unverified online content. While they might offer unique perspectives or interpretations, their accuracy and credibility might not stand up to academic scrutiny.
2. Utilize Digital Libraries and Archives
Digital libraries and archives have revolutionized historical research, providing access to a plethora of resources right at your fingertips:
- Library of Congress: A rich repository of American history documents and photos.
- JSTOR: Access to a wide range of academic journals and books.
- Google Scholar: For scholarly articles and legal documents.
- Project MUSE: Offers books and journals from university presses.
- British Library’s Online Gallery: Access to historical manuscripts and rare books.
- EuroDocs: Primary historical documents from Western Europe.
- National Archives: U.S. government documents and records.
- World Digital Library: Resources from countries globally.
- HathiTrust Digital Library: Digital versions of books from various libraries.
After familiarizing yourself with these resources, create a system to organize your findings. Bookmark essential web pages and maintain digital or physical notes for easy reference. This systematic approach will save you time and help streamline your research process.
3. Read Critically and Take Effective Notes
Adequate research requires meaningful engagement with sources. As you delve into sources, question the author’s perspective, the context in which it was written, and its potential biases.
Note-taking is an essential component of this critical engagement. Whether you prefer digital notes or the traditional pen-and-paper method, develop a system that works for you. Outline fundamental facts, jot down your ideas, and note page numbers for easy referencing. These notes will be invaluable when you start writing your essay, providing a roadmap for your research journey.
4. Synthesize Diverse Perspectives
Aim to include a range of viewpoints in your research. For instance, if you’re researching the American Civil Rights Movement, examine sources that cover different racial, political, and socio-economic perspectives. This approach enriches your understanding.
Synthesizing these perspectives involves comparing and contrasting different viewpoints, looking for common themes, and understanding how they interact with each other. This synthesis allows you to develop a well-rounded argument in your essay, showing that you’ve considered the topic in its full complexity.

5. Manage Time and Set Research Goals
Effective research also means managing your time wisely and setting clear goals.
- Set specific research goals.
- Use a research journal.
- Use bibliographies of good sources.
- Prioritize quality over quantity.
- Regularly review and adjust your goals.
- Keep track of deadlines.
By setting clear objectives and allocating enough time for research, you can avoid last-minute cramming and ensure a thorough and thoughtful research process.
6. Engage with Primary Sources
Primary sources are the raw materials of history, offering first-hand accounts of past events. Engaging with these sources, like letters, diaries, official documents, or even artifacts, can provide a direct window into the time you’re studying.
When working with primary sources, consider their root, intent, and the context in which they were created. This analysis helps you understand the source’s reliability and its place in the broader historical narrative. It also allows you to make your own interpretations and draw conclusions that can add depth and originality to your essay.
7. Evaluate Secondary Sources
Secondary sources, such as books and articles written by historians, provide interpretations and analyses of historical events. These sources offer context and scholarly perspectives to help shape your understanding of a topic.
However, it’s essential to evaluate these sources critically. Consider the historian’s credentials, the arguments they present, and how they interpret their primary sources. Look for potential biases or assumptions that might color their analysis.
Wrapping Up
Remember, researching for history essays is a skill that develops over time. Each essay is an opportunity to refine your techniques, from identifying credible sources to synthesizing diverse viewpoints. You can also seek guidance from professional writers. An Essay Service review can help you find a researcher to collaborate with. Receiving help and continuously learning is vital in honing your skills as both a researcher and a writer. By applying these strategies, you enrich your essays with depth and insight and grow as a history student, equipped to explore the past with a discerning eye and a curious mind.

RAHUL NARAIN
Principal partner - BaseKamp Rahul has over 18 years of business & operations experience in the education domain. He is committed to bringing positive change to the education ecosystem merging improved learning with financial viability for all stakeholders. Rahul has been responsible for setting up K - 12 schools as well as vocational learning centres for premier education institutions like Aptech , EuroKids , iDiscoveri & Sesame Street . He has built a sustainable franchisee network and robust channel management. As a principal partner of Basekamp he brings entrepreneurial zeal & hands-on experience of building and raising projects successfully right from scratch. Rahul is a post-graduate in Business Management and certified in Business Environment & Strategic Management from IIT Delhi .
Related Posts
Truly amazing: 8 fun facts about the korean language.
Reading Time: 3 minutes The Korean language is the official spoken language of North and South Korea. This captivating language has gained people’s interest worldwide, notably the Korean alphabet and Korean words, thanks to the products of Korean culture Read more…
Discovering the Advantages of Enrolling in an International School in Hong Kong
Reading Time: 4 minutes Discovering the Advantages of Enrolling in an International School in Hong Kong In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and globalization, it has become increasingly relevant for students to gain an international perspective on Read more…
9 Reasons to Apply for an Online School in Your 30s
Reading Time: 3 minutes Reaching your 30s is a transformative period marked by increased responsibilities, career aspirations, and personal growth. While the idea of returning to school may seem challenging amidst the demands of adulthood, it’s never too late Read more…
Remember, SCOTUS—Presidential Immunity Would Apply to Joe Biden, Too
We’re all nervous about what donald trump would do with immunity for official acts. but remember, two can play that game..

During last week’s oral arguments in United States v. Trump, it sure sounded like there might be five Supreme Court justices willing to conclude that a president should indeed have lifetime immunity from legal reprisal for official acts committed as president. This prospect is terrifying because it would hand a President Trump a nearly blank check to do anything he wants—to the Constitution, to his political opponents, to the executive branch—and there will be no way to stop him unless 67 votes emerge in the Senate to convict him of high crimes and misdemeanors and remove him from office, which seems a near impossibility, given Republicans’ excessive fealty to and fear of the man and his movement.
But then it occurred to me over the weekend: Well, wait a second. Donald Trump isn’t president. Joe Biden is. And if presidential immunity for official acts were to apply to a future President Trump, would it not also apply to current President Biden?
Of course it would. And I hope that fact has them doing some thinking in the Biden White House. Democrats should drive the point home to Republicans and the nation that two can play this game.
What “official acts” might Biden undertake once Samuel Alito, Clarence Thomas, Neil Gorsuch, Bret Kavanaugh, and possibly John Roberts declare him to be above the law? Well, let’s have some fun here.
Let’s start with the Supreme Court itself. Biden could wake up one day and announce that the court should have 13 members, or 15, and he could set about appointing the new associate justices and doing his best to ram them through the Senate, offering Joe Manchin trillions in economic development for West Virginia to secure the retiring senator’s support, between now and Election Day.
Politically risky? Sure. But maybe not as politically risky as most pundits would assume—and not nearly as costly to the republic as the things Trump is contemplating doing. Remember, the Constitution calls for no set number of justices. Biden would be within even his pre-immunity rights to try to change it. T wo polls came out last fall asking respondents whether they’d favor court expansion, and the affirmative view prevailed in both: It was 54-46 in one, and 44-35 (with 22 percent having no opinion) in the other. That looks like a winnable political fight to me.
Biden would need only to make two arguments. Number one, this court delegitimized itself when it took away a half-century-old right, the right to a safe and legal abortion, in the Dobbs ruling. Every one of the justices who voted to strip that right away from women vowed in his or her confirmation hearing about their deep respect for precedent. They all lied. Number two, this very court gave me the power to do this! I’m only doing what this very Supreme Court just ruled a president was within his rights to do.
Okay. We all know Biden is not going to do that. He’s too respectful of tradition, and Democrats are too fearful of the right-wing noise machine, which would kick into an unprecedented outrage gear if Biden actually tried to make use of the tools the Supreme Court just handed him.
But here’s my point. If this court were to give presidents a grant of immunity for official acts, Biden should most certainly use the occasion to play some hardball. Make some threats about what he might do with this power. Get the American public thinking about some things they just don’t think about enough, leading public opinion in the direction of reforming aspects of our democratic system that badly need reform.
Take the Electoral College. Democrats have won seven of the last eight presidential elections, in popular vote terms, but this archaic and reactionary system that was put into place to give presidential candidates from slaveholding states an advantage has helped elect two Republicans who lost the popular vote.
I don’t think Biden should just unilaterally end the Electoral College—although, if he had immunity for all official acts, he could certainly give it a whirl, let conservatives bring a civil lawsuit, and see what his new 13-member Supreme Court thinks of the idea.
Less audaciously, he could certainly find some legal way to put an end to all these MAGA-driven attempts to seat alternate electors in states whose outcomes they dispute, which they did in seven states in 2020 and by all accounts are preparing to do again this year. Yes, the GOP-led House would impeach him, but so what? There’d never be 67 votes in the Senate to convict. And as with court expansion, if it were clear that he had really won the disputed states, public opinion would be on Biden’s side, and he’d have pushed the Overton window dramatically in the direction of eventual abolition of the Electoral College.
Okay, this, too, is a little out there for Biden. More seriously, he could use an immunity grant to issue a series of rulings and orders that would be aimed toward two ends: one, shoring up some of his policy decisions against the inevitable Trump reversals should Trump be elected, and two, preemptively making it harder for Trump to do some of the things that the infamous Project 2025 pledges he will do.
On the former, for example, the Biden administration could undertake a number of administrative moves on the civil rights and labor fronts to make it harder for Trump to undo what Team Biden has done. And on the latter, Biden can find a way to make it basically impossible for Trump to implement his so-called Schedule F plans , under which Trump would give himself the authority to fire more federal workers and replace them with lackeys. And that’s just for starters. With immunity for official acts, Biden could preemptively defang a lot of what promises to be undemocratic and authoritarian about a Trump second term.
Of course, the Supreme Court might not even issue a ruling on immunity. It might just remand it back to the Washington, D.C., appeals court that ruled in February that Citizen Trump was not immune from prosecution—that is, the high court’s real intent may just have been to delay the prosecution of Trump on January 6 insurrection charges, not to shield him from prosecution.
But I hope we’ve all learned by now never to underestimate the cynical perfidy of this court majority. They may well limit presidential immunity, thinking they’re helping Trump remake the country in his fascist fashion. They’ll calculate that the old institutionalist Biden would never use his new powers in the closing months and weeks of his term. It would be delicious to see him prove them wrong.
Michael Tomasky is the editor of The New Republic.

Philip Seymour Hoffman's sister pens essay remembering brother's talent and coping with his loss 10 years after death
Emily Barr recalled saving magazine clippings to remember her brother.
Philip Seymour Hoffman's sister, Emily Barr, recalled her brother's talent and detailed in part how she coped with his death, in a new essay titled "Encyclopedia Brown: A Story for My Brother, Philip Seymour Hoffman."
In the essay, published in The Paris Review on Monday, Barr recalled approaching the librarian at her public library in order to collect magazine clippings that mentioned her late brother in order to keep his memory alive.
"I didn't want to read these articles. But I didn't want children cutting them up in class next year. More importantly, I didn't want one of my children to be sitting in art class and get handed one of these magazines and open it up to see their uncle Phil."
Barr began the essay describing trips to the library with her brother and discussing some of Hoffman's favorite mystery movies and books, identifying "Encyclopedia Brown" books and "The Adventure of Sherlock Holmes' Smarter Brother" with Gene Wilder as a preferred choice.

"I could swear that Phil based much of his acting technique on watching Gene Wilder scenes like this over and over as a kid," wrote Barr. "The physical comedy is subtle in that the main character is unaware of his buffoonery—only the audience is in on the joke. Phil did this a lot: we would know that something was up, but the character himself was often clueless."
MORE: Remembering Actor Philip Seymour Hoffman
Barr cited examples of this technique in classic Hoffman films like "Along Came Polly," "Boogie Nights," and "The Talented Mr. Ripley."
The Oscar winner, who was notoriously private about his personal life, died in 2014 of an overdose. Hoffman's family released the following statement after the actor's untimely death:
"We are devastated by the loss of our beloved Phil and appreciate the outpouring of love and support we have received from everyone. This is a tragic and sudden loss and we ask that you respect our privacy during this time of grieving. Please keep Phil in your thoughts and prayers."
Editor’s Picks
Remembering actor philip seymour hoffman.

See why this librarian is going viral on TikTok

Why Sam Rockwell dedicated his Oscar to 'good friend' Philip Seymour Hoffman
Hoffman won the Best Actor Academy Award and the Golden Globe for Best Performance by an Actor in a Motion Picture Drama for his leading role in the 2005 film "Capote," which detailed the five-year period during which author Truman Capote penned "In Cold Blood."
MORE: Vanessa Bryant posts throwback photos with Kobe Bryant to mark wedding anniversary
He was nominated for three Best Supporting Actor Oscars for "The Master," "Doubt," and "Charlie Wilson's War."
Barr ended the essay by guessing how her late brother may have reacted to her plan to save his articles.
"I walked home in the snow, thinking about the mystery I'd created for her with the missing pieces and also how Phil would think I was ridiculous for doing all this. He'd wrap his big arm around me, and we would walk a little quicker as the temperature dropped and the sun set lower in the sky.We would talk, like when we were kids, imagining the story of Encyclopedia Brown trying to solve The Case of the Vanishing Actor, which takes place in a library with a small wooden door."
Read Barr's full essay here .
Top Stories

'Surprising' and 'disturbing': Legal experts react to SCOTUS on Trump immunity case
- Apr 30, 6:52 AM

College protests updates: Columbia asks NYPD to 'retain a presence' through May 17
- 3 hours ago

Barbra Streisand asks Melissa McCarthy about Ozempic, sparking debate on weight
- Apr 30, 4:15 PM

This congresswoman was born and raised in Ukraine. She just voted against aid for her homeland
- Apr 29, 12:11 AM

Trump says 'it depends' if there will be violence if he loses 2024 election to Biden
- Apr 30, 1:24 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
Oral History Offers a Model for How Schools Can Introduce Students to Complex Topics

- Share article
As historian David McCullough said, history is the study of who we are and why we are the way we are.
That’s why teachers in the Memphis-Shelby County public schools, as racially isolated now as they were when the U.S. Supreme Court outlawed school segregation, have launched a curriculum to introduce their students to the 13 children who helped integrate these Tennessee city schools in 1961.
Memphis-Shelby County teachers, researchers from the University of Memphis, and the local Memphis 13 Foundation worked with seven of the 10 surviving members of the Memphis 13—a group of Black 1st graders who peacefully enrolled in four all-white schools at the height of the civil rights era—to develop teacher training, lesson plans, and oral history activities for elementary students.

“Just going home and talking to grandparents or talking to the elders in their community was never going to be enough,” said Anna Falkner, an assistant professor at the University of Memphis and a co-developer of the curriculum, “because it wouldn’t provide [students] with the context that they needed in order to understand what happened and understand the ongoing effects of, for example, the way segregation looks today.”
The Memphis 13 project offers a model for how schools can introduce complex subjects to students, even in early grades, while also giving them opportunities to investigate social studies in their communities
“Really consider the context,” Falkner said. “What are the specifics that can help students understand their Southern context or the context wherever they are and what that means in relation to the larger experience. It’s not just focusing on that national narrative, not just sharing Brown v. Board , but really thinking about, what did this look like in my backyard? What did it look like for my family members or my community members?”
For example, teachers met with surviving members of the Memphis 13 to identify projects for students in 2nd and 5th grades, when Tennessee social studies standards cover civil rights issues. Sheila Malone, one of the students who first integrated into the district’s Bruce Elementary as a 1st grader, suggested that 5th graders record the experiences of others who had attended the district schools during desegregation.
“[Malone] wanted the students to go back home and share the story and have intergenerational conversations about the history of our schools,” said Gina Tillis, the director of curriculum and instruction for the Memphis 13 Foundation, who co-developed the Memphis curriculum. “One of the things that I’ve noticed with the members of Memphis 13 is, as they’re sharing their stories, they’re unpacking memories that have been silenced. … This is a really powerful space for students to reflect on their education, their parents’ and their elders’ education, and what we’re doing collectively to create a more inclusive and equitable school system.”
Second graders, for example, watch documentaries and review news accounts about the school desegregation decisions in Memphis and other cities, identifying ways children their age participated. In 5th grade , students review collected oral history interviews and collect their own, as well as analyze modern policies related to school integration. Tillis said the project plans to expand the curriculum to 8th and 11th grades in the future.
Building school integration history projects
Emerging technology has made it easier for educators to engage their students in active historical research, according to the Center for Public History and Digital Humanities at Cleveland State University in Ohio. The center, for example, has developed apps to help students record interviews and archive historical documents.
Efforts like those of the Memphis 13 helped integrate public schools in the decades following the landmark U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Brown v. Board of Education . However, these trends began to reverse in the 1990s and have worsened to this day, even as the overall public school population has grown more diverse. Studies find schools serving high populations of students of color continue to have on average fewer educational opportunities —including challenging courses, experienced teachers, and other resources—compared with schools serving mostly white students.
While the Memphis 13 are well known, Tillis stressed that schools can use community history to engage students regardless of where they are. “Everyone has a school desegregation story. Every district, every person ... and every district story is unique,” she said. “It’s, I think, one of the most powerful stories to share because it offers you this platform to really deconstruct what’s going on in our schools.”
Researchers recommended that schools interested in developing similar projects:
- Work with local historians and groups to identify social studies topics and events that had strong effects on the local community. This can include school district librarians or archivists, for example.
- Provide teachers with training in both the historical context and strategies and tools for documenting community history.
- Focus on topics that encourage students to make connections between history and current issues in their community.
“One of the lessons that we’re hoping to share with other school districts is just the power of listening to your community members who are historians, even if they don’t work for the local archive: the neighbor down the street who kept all the newspapers, the person who knew everybody in the neighborhood,” Falkner said. “Finding those community members and making a meaningful way for them to participate in the curriculum development is the most important piece.”
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

Doris Kearns Goodwin and husband Dick Goodwin lived, observed, created and chronicled the 1960s

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Book Review
An Unfinished Love Story: A Personal History of the 1960s
By Doris Kearns Goodwin Simon & Schuster: 480 pages, $35 If you buy books linked on our site, The Times may earn a commission from Bookshop.org , whose fees support independent bookstores.
“An Unfinished Love Story: A Personal History of the 1960s” isn’t precisely the book that presidential historian Doris Kearns Goodwin set out to write.
Dominating this often fascinating volume is both the colossal presence and the sudden absence of Richard “Dick” Goodwin, Doris’ late husband, whose speechwriting talents defined some of the most memorable moments of the 1960s. The couple’s aim was to co-write a book based on his extraordinary archive — 300 boxes! — of personal papers and curios, from voluminous speech drafts to a shattered police club from the 1968 Democratic Convention in Chicago.
Husband and wife spent years perusing and discussing those treasures, an effort short-circuited by his death in 2018, at 86, of cancer. Amid her grief and a move from their rambling home in Concord, Mass., to a Boston condo, Goodwin took up the project on her own.

She describes the result as a hybrid of history, biography and memoir. At its most poignant, “An Unfinished Love Story” is, as the title indicates, an account of personal loss. It also turns out to be a reflection on the process of constructing history, suggesting how time, perspective and stories left unwritten can shape our view of the past.

Reckoning with long shadow of 1960s counterculture
Max Ludington’s ‘Thorn Tree’ suggests the divisions of the 1960s await a moment to reemerge. But strong writing is weighed down by tonal and structural problems.
April 13, 2024
Goodwin, the author of award-winning biographies of Lyndon B. Johnson, Franklin and Eleanor Roosevelt, Abraham Lincoln, Theodore Roosevelt and others, has a nice touch as a storyteller. Here she successfully navigates the awkward feat of weaving together the couple’s gently probing conversations, her husband’s archival documentation, other historical sources and her own reporting.
“An Unfinished Love Story” offers a bird’s-eye view of familiar events, and of a decade marked by both idealism and political violence. “Too often,” Goodwin writes, with her characteristic optimism, “memories of assassination, violence, and social turmoil have obscured the greatest illumination of the Sixties, the spark of communal idealism and belief that kindled social justice and love for a more inclusive vision of America.”
While arguing for this rosier perspective, the book provides nuance and detail on matters such as the origins of the Peace Corps and the Alliance for Progress, Robert F. Kennedy’s private agonies over whether to challenge LBJ for the Democratic presidential nomination in 1968, and Jackie Kennedy’s emotional struggles after her husband’s 1963 assassination. In a 1966 letter from Hawaii, Jackie addresses Dick Goodwin, her close friend, as a fellow “lost soul” and complains of “memories that drag you down into a life that can never be the same.” That is a sentiment that Doris Kearns Goodwin understands.
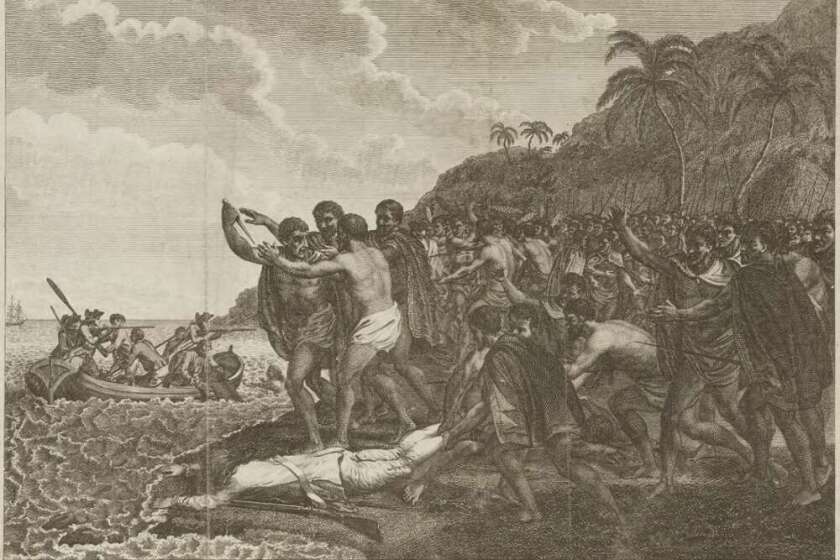

The canonized and vilified Capt. James Cook is ready for a reassessment
In Hampton Sides’ telling, this explorer’s final mission, ending with his death on the shores of Hawaii’s Big Island, has room for both condemnation and celebration.
April 2, 2024
She and the then-married Goodwin — with his “curly, disheveled black hair,” “thick, unruly eyebrows” and “pockmarked face” — met at Harvard in 1972, where she taught a popular course on the American presidency. He had left the Johnson administration in 1965, three years before she joined it, and had become disillusioned with the Vietnam War. Despite having penned her own antiwar piece for the New Republic, she would become an LBJ confidante, an aide on his presidential memoirs and a lifelong admirer.
Not just a speechwriter but a policy advisor and political strategist, Dick Goodwin enjoyed a Zelig-like march through 20th century American history. President of the Harvard Law Review and law clerk to U.S. Supreme Court Justice Felix Frankfurter, Goodwin worked for two presidents, John F. Kennedy and Johnson, and several would-be presidents, including Eugene McCarthy and Robert F. Kennedy. He later wrote the concession speech that Al Gore delivered after the Supreme Court stopped the recount of the 2000 presidential election vote in Florida.
According to his widow, Goodwin idolized the coolly self-possessed JFK, fused with LBJ, regarded McCarthy as “the most original mind” he’d encountered in politics and adored RFK, his best friend of the bunch. (No mention is made here of the seamier side of these politicians’ lives, or how their sexual indiscretions bear on their legacies.)
Nearly every Democratic leader seems to have sought the services of the brilliant, cigar-smoking, workaholic Goodwin. But, as “An Unfinished Love Story” makes clear, he was more than a pen for hire. Goodwin had passionately held views about civil rights, the alleviation of poverty and other issues. As Johnson’s principal speechwriter, he helped fashion both the title and the programs of the Great Society. He was responsible for LBJ’s single most powerful speech, on behalf of the 1965 Voting Rights Act, which coopted the anthem of the civil rights movement: “We Shall Overcome.”

How Keith Haring’s art transcended critics, bigotry and a merciless virus
Biographer Brad Gooch’s “Radiant” reveals how much life and creativity artist Keith Haring packed into 31 years before he died of AIDS.
March 15, 2024
Goodwin left the Johnson administration, against the president’s wishes, to pursue a solo writing career. Over time, his public stance against American involvement in Vietnam pitted him against his former boss. “It’s like being bitten by your own dog,” Johnson said of Goodwin’s defection.
Goodwin was, at heart, deeply loyal, his widow suggests, even if he sometimes chose loyalty to principles over personal attachments. On the other hand, when a previously hesitant Bobby Kennedy entered the 1968 Democratic primary race against McCarthy, friendship prevailed, and Goodwin switched sides, as he had earlier warned McCarthy he would. The RFK assassination, following victory in the California Democratic primary (and Martin Luther King Jr.’s murder earlier that year), was shattering for Goodwin, as for so many others.
“An Unfinished Love Story” is at its most moving when it touches on the Goodwins’ long, happy, occasionally contentious marriage; its bumpy origins (after becoming a widower, he wasn’t as ready to commit as she was); and his emotional farewell. Always attuned to relationships, Goodwin is an astute chronicler of her own.
Beyond underlining the brighter side of the 1960s, the archive and the conversations it prompted changed the couple’s views of the two presidents they served. She gained a deeper appreciation of the impact of Kennedy’s idealism, she writes, while her husband moderated his long-standing bitterness toward Johnson. Embedded in that rapprochement is an unstated hope: that more knowledge and informed debate might somehow ease our country’s current political polarization as well.
Julia M. Klein is a cultural reporter and critic in Philadelphia.
More to Read

How people of color carry the burden of untold stories
April 3, 2024

Column: For years, the Reagans’ daughter regretted some things she wrote. Now she’s at peace
Feb. 6, 2024

Letters to the Editor: Congratulations to George Skelton on 50 years covering California’s good, bad and in-between
Jan. 21, 2024
A cure for the common opinion
Get thought-provoking perspectives with our weekly newsletter.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
More From the Los Angeles Times
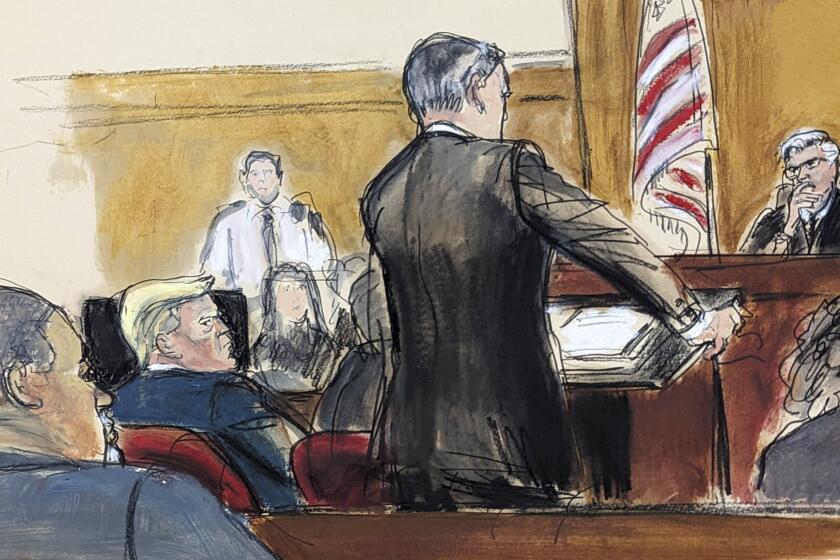

Litman: Donald Trump was just fined for contempt of court. Could he go to jail next time?

Opinion: California’s budget deficit will force difficult cuts. This one should be the easiest
April 30, 2024

Goldberg: What we keep getting wrong about protests like those at USC, Columbia and other campuses

Granderson: Here’s one way to bring college costs back in line with reality
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Prepare for a History Exam
Last Updated: January 10, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Carrie Adkins, PhD . Carrie Adkins is the cofounder of NursingClio, an open access, peer-reviewed, collaborative blog that connects historical scholarship to current issues in gender and medicine. She completed her PhD in American History at the University of Oregon in 2013. While completing her PhD, she earned numerous competitive research grants, teaching fellowships, and writing awards. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 15 testimonials and 83% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 366,830 times.
History is full of dates, names, and places that can make your head spin. Try making flashcards to remember lots of information. Mnemonic devices are another great memorization tool that can add a little silliness to studying. In addition to memorizing facts, you should also be able to connect the dots. Take notes each class session, and make study guides, timelines, and other visual aids to help you see the larger themes. To increase your shot at passing the test, study a bit every day instead of cramming, and try to get rest and eat well just before the test.
Memorizing Information

- If you have trouble coming up with a list, try asking your teacher what key dates, figures, and other information might show up on the test.

- You could also try recording yourself reading your textbook or flashcards. As you listen to the recording, follow along in your notes or flashcards.

- For example, the mnemonic device Neighbors Actually Persuaded Lovely Yvonne To Shut Her Window will help you memorize the British royal families in chronological order: Norman, Angevin, Plantagenet, Lancaster, York, Tudor, Stuart, Hanover, and Windsor. [3] X Research source
Connecting the Dots

- Ask yourself, “How does the syllabus organize these facts and figures? Does it mention or hint at any key critical questions? What connections does it make between individual class sessions?”
Carrie Adkins, PhD
"For most people, rote memorization of dates, names, and events is incredibly difficult," adds Carrie Adkins, PhD in History. "Depending on what you’re studying or why you’re memorizing, I would suggest that having a deeper understanding of the historical narrative will help. It’s much easier to remember events and dates if you understand why they mattered and how they connect with one another."

- Your study guide won’t do you much good if it simply copies your class notes. Look for key themes in your class notes, pull out the essential information, and put it in your outline.
- For example, if you’re outlining class sessions on the Wars of the Roses, you could list key members (along with their dates and titles) of the houses of Lancaster and York in one section of your study guide. Then, you could outline underlying causes of the rivalry between the houses. Finally, you could list key battles and their dates, temporary truces and how they broke down, and the conflict’s resolution.

- For example, making family trees and a timeline would come in handy if you’re trying to prepare for an exam on the Wars of the Roses.

- For example, ask them what the exam's format will be, what the unit's main theses (or key ideas) are, and what information is most important.
Creating a Study Strategy

- Multiple choice or fill in the blank tests stress memorization, so you’ll know that you should put your flashcards to good use.
- If your test includes or is only made up of essays, you should be prepared to analyze a set of historical facts or compare and contrast two interpretations.

- Study groups are great for coming up with potential test questions, since everyone can make up a question and quiz each other.

- You can also find exam tips, sample responses, and other useful resources on CollegeBoard. Just search for whichever standardized test you’ll be taking.

- If you feel like you need to study, just review your outlines and hard facts. Try to be confident and avoid overwhelming yourself or getting too nervous.
Studying for Specific Exam Types

- When you take the test, make sure to read the question clearly and try to eliminate at least half of the available answer options. [10] X Research source

- When studying, refer to your list of key terms and concepts, and make sure you can concisely define them.
- Have someone quiz you on your flashcards. Try to get to the point that you can give a complete but brief answer without asking for any hints.

- Understand the unit's main concepts, then use the facts and figures you've memorized to back up those key points. Remember there's no "U" in history: leave personal opinions out of essays!

- Look for words like analyze or compare and contrast, then plan your essay accordingly. For example, historians disagree about the degree to which feudalism in the Late Middle Ages set the stage for the Wars of the Roses. Your exam could include an essay asking you to defend one position and explain why it’s a more accurate interpretation.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.educationcorner.com/history-study-skills-guide.html
- ↑ https://www.thoughtco.com/how-to-study-history-terms-1857067
- ↑ https://www.mnemonic-device.com/history/neighbors-actually-persuaded-lovely-yvonne-to-shut-her-window/
- ↑ http://www.historyguide.org/guide/exam1a.html
- ↑ https://depts.washington.edu/pswrite/essayex.html
- ↑ https://subjecttestspractice.collegeboard.org/practice/sat-subject-test-preparation/us-history
- ↑ https://www.thoughtco.com/studying-for-multiple-choice-exam-3212071
- ↑ https://www.kaptest.com/study/ap-us-history/ap-u-s-history-multiple-choice-practice-questions/
- ↑ http://www.societyforhistoryeducation.org/pdfs/Maxwell.pdf
- ↑ https://www.kaptest.com/study/ap-us-history/how-to-approach-the-ap-u-s-history-long-essay-question/
About This Article

If you have a history exam you need to prepare for, make flashcards of the key terms, people, and dates covered in the lessons and study the flashcards in the days leading up to the test. If you have one, read the course syllabus to help you identify overarching themes in the material that will help you tie facts together, then make an outline or study guide to synthesize that information. For tips on studying based on the test’s format, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
May 17, 2019
Did this article help you?

Cathrienne Annah Martinez
Jul 7, 2016
May 5, 2017
Aug 25, 2017
Fathumathul Fasna
Aug 22, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
This Isn’t the China I Remember

By Gish Jen
Ms. Jen, an American novelist whose family hails from Shanghai, wrote from Shanghai.
In 1979 my mother pulled out a Band-Aid in a Nanjing hospital. The nurses clustered around it, amazed. “The West has everything!” they said.
We were on a family visit to China, where my Shanghai relatives were similarly wowed by our excellent teeth and ample body fat, not to mention our descriptions of American dishwashers, refrigerators and air-conditioning. And with the general awe came V.I.P. treatment. Hosts broke out bottles of expensive orange soda that they freely mixed with expensive warm beer. We could not escape drinking this any more than we could escape our government-assigned “guide,” whose job was to strictly monitor visitors like us. Relatives or not, we were foreigners.
I returned to teach English at the Shandong Mining Institute in 1981. My students were coal mining engineers preparing to study abroad, so that they might bring back safer mining techniques. I was their “foreign expert.” As such, I had not only a sit-down toilet in the apartment provided to me, but also running hot water, an unheard-of luxury. My ayi, or housekeeper, would make a fire under a vat of water on the roof and, when it was ready, turn the faucet handle in my bathtub.
After class, my students would bring stools out to the basketball court where, each facing a different direction, they would sit and study for hours on end. Loving their country and wanting to make it strong, they were grateful for Westerners like me. Foreign as we were, we were a help.
Fast forward a few decades to a booming China. In my many visits over the years — as a teacher, as a visiting artist and as a tourist — Shanghai hotel staff had always returned my credit card to me with two hands, a bow of the head, and a smile. But with a quarter of the world’s construction cranes said to be in the city during China’s boom years, raising skyscrapers from what had been rice paddies, attitudes had changed. My credit card was returned with one hand; the receptionist barely looked up. My relatives no longer asked that I bring American goods for them, either. “China has everything,” they said then. As many proudly proclaimed, the 20th century was America’s; the 21st was China’s.
One seldom hears that triumphalist tone today. Instead, the talk is of a loss of confidence and trust in the Chinese government. People remain proud of their city, which now boasts excellent, cosmopolitan food and spotless streets. There are huge new sports centers featuring tennis and paddle-boarding, there is an artificial beach with pink sand. The city is far greener than in years past, too. Magnolia and cherry trees bloom everywhere and even the strips under the freeways have been landscaped. And thanks to the ubiquitous security cameras, Shanghai is spectacularly safe.
Yet below the surface lurks a sense of malaise. In this famously cosmopolitan city, there are weirdly few foreigners compared to before, many having left due to the stifling policies during the pandemic or because international companies have pulled out staff, or other reasons. Clothing shops are empty and many other stores have closed. The Nanjing West Road shopping district, previously a sea of humans, is strangely underpopulated.
Shanghainese are still outraged at having been locked down for two months in the spring of 2022 to stem a surge in Covid-19 cases with little time to prepare. Such were the shortages of essentials that Tylenol was for sale by the pill. And so heavy-handed were even the post-lockdown policies that residents took to the streets in protest .
But for many, the pandemic debacle only capped a series of governmental blunders starting with Premier Li Keqiang urging young people to open their own businesses in 2014. This and other missteps cost wave after wave of people their life savings and many Chinese now blame government ineptitude and erraticism for bringing the economy to a standstill. As a Shanghainese friend put it, the government has turned China around and around until, like spinning cars, people’s engines have stalled and their wheels have locked up.
The result has been so steep and unrelenting a fall in real estate prices that elderly people, like my friend’s parents, can’t sell their apartments to pay for nursing or assisted living. And they are hardly the only ones affected by the downturn. Doctors find themselves squeezed — many patients don’t have money for operations — while businesspeople sit on their hands, unwilling to make investments in so unpredictable an environment. Many college graduates, faced with a grim job market, are essentially dropping out, or “lying flat,” as it’s called in China. Not even schoolchildren, it seems, have been spared the general despondency. As one teacher I spoke to observed, when the society is sick, the children pay the price. Too many parents know a child who has had to leave school because of depression.
Of course, for all of this the West is scapegoated — having opposed, people say, China’s rise — as is China’s other favorite enemy, Japan, whose brutal 1930s invasion and ensuing occupation of China still rankles. (One sequence of a CGI video shown in my recent Shanghai spin class featured huge coronaviruses studded with Japanese temples.)
Whoever is to blame, emigration is on the rise . According to U.N. figures, more than 310,000 Chinese left the country in each of the past two years, a 62 percent increase from the earlier average of around 191,000 per year over the decade through 2019. Those in Shanghai with the means to do so talk endlessly about “running away,” even to officially reviled countries like the United States .
This is not always an answer. One friend of mine has come back to China to stay, having spent six years attending graduate school in Boston, saying she missed the warmth of Chinese family life. And no one has illusions about the difficulty of getting established in another country. People in China speak of a whole new class of emigrants, women who have left high-powered careers to accompany their children to the United States early enough for them to assimilate — ideally, in middle or high school. As for the fruits of their sacrifice, it’s too early to say. Can the children really become Westerners? Will they — like me decades earlier — become the foreigners?
Things in China could change. Those “lying flat” are not asleep. They are watching and could someday rise up. But in the meantime, people in Shanghai are simply, as they put it, “xin lei ”: Their hearts are tired.
Gish Jen is an American novelist and the author of “Thank You, Mr. Nixon.” She is currently teaching at N.Y.U. Shanghai.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computation and Language
Title: can gpt-4 do l2 analytic assessment.
Abstract: Automated essay scoring (AES) to evaluate second language (L2) proficiency has been a firmly established technology used in educational contexts for decades. Although holistic scoring has seen advancements in AES that match or even exceed human performance, analytic scoring still encounters issues as it inherits flaws and shortcomings from the human scoring process. The recent introduction of large language models presents new opportunities for automating the evaluation of specific aspects of L2 writing proficiency. In this paper, we perform a series of experiments using GPT-4 in a zero-shot fashion on a publicly available dataset annotated with holistic scores based on the Common European Framework of Reference and aim to extract detailed information about their underlying analytic components. We observe significant correlations between the automatically predicted analytic scores and multiple features associated with the individual proficiency components.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Opinion Dogs are our greatest creation. And we might be theirs.
Tommy Tomlinson is the author of “ Dogland .” He lives in Charlotte with his wife, her mother and a cat named Jack Reacher.
The dog is humankind’s greatest invention. The wheel, the lightbulb, concrete — all amazing. Top of the line. But nothing in human creation has been as essential and adaptable as the countless descendants of the ancient gray wolf.
How did we do it? I spent three years following the traveling carnival of American dog shows — like a Grateful Dead tour with Milk-Bones — in search of the answer. My journey culminated in the dog world’s most prestigious event: the Westminster Dog Show. Show dogs are bred from the purest stock, culled from litters at just a few weeks old, trained with the dedication of Olympic gymnasts — and groomed like supermodels. They’d be unrecognizable to their ancient kin — and to ours.
The American Kennel Club, arbiter of bloodlines, now recognizes about 200 breeds, while tracking crossbreeds like goldendoodles, and even mutts. From the most massive mastiff to the tiniest teacup chihuahua, all dogs trace back to the same common ancestors.
Scientists think this weird and powerful companionship of humans and dogs might have started somewhere between 15,000 and 30,000 years ago. Humans of that era were mainly hunters traveling in camps. They ate meat by the fire. The cooking meat attracted wolves who were drawn to the aroma but stayed safely out of range of the flames. Every so often, a human would fling a bone into the darkness. The wolves gnawed on the bones. They trailed the humans to the next campsite, still keeping their distance. There was an unspoken arrangement. The wolves alerted the humans to intruders, and the humans fed the wolves well.
Over time the wolves crept closer. One fateful night a curious wolf came all the way into the firelight. The humans didn’t chase it off.
Slowly, the humans mingled with the wolves. After days or months or generations or centuries, a wolf curled up at a human’s feet. Maybe got its belly rubbed. That was the first dog.
As far as we can tell, dogs are the first animals that humans ever tamed. The wolves that hung out with humans found themselves changing inside and out. They developed shorter muzzles and smaller teeth. Their instinct to run became a desire to stay close. With time, dogs were manufactured through breeding to meet different human needs. We made huskies to pull sleds and Newfoundlands to pull fish nets and dachshunds to catch badgers.
Dogs taught humans the early science of designer genes. In the mid-19th century, as we moved off the farm and into the factory, we created dogs we could bring indoors at the end of a workday. And we created dogs we could bring to work: French bulldogs (now the most popular breed in America ) started out as literal lap dogs for lace-makers in France. We molded dogs to be friends, companions, playmates and unofficial therapists.
So dogs are not just humanity’s greatest invention but also its longest-running experiment.
That’s one way to look at it.
Now switch out the frame. Swap the subject and the object. Change the verbs.
Here’s another view:
Around the time early humans evolved, Neanderthals also walked the planet. At some point — roughly 40,000 years ago — humans started to thrive while Neanderthals died off. And this is about the time when those first curious wolves began to evolve into dogs. Some scientists believe the timing is not a coincidence. Maybe the dog was the key advantage in the triumph of humankind.
Dogs enabled humans to settle down and stop their endless wandering. Dogs protected humans at this vulnerable transition from nomadic to settled life. Dogs did work that humans did not have the strength or stamina to do: guarding, herding, hunting, pulling sleds. They created time for humans to build and think and create without having to focus every moment on the next meal or the next threat.
We domesticated dogs, and they domesticated us.
Today, dogs provide not just companionship but also an uncomplicated kind of love in an ever more complicated world. And for those restless souls wandering from town to town, chasing job after job — nomads again — a dog can be an anchor, something to hold on to on a lonely night.
From the gray wolf by the ancient fire to a coifed Pomeranian prancing around the show ring, dogs have been with us nearly as long as we have been human.
They might be our greatest creation. And we might be theirs.
About guest opinion submissions
The Washington Post accepts opinion articles on any topic. We welcome submissions on local, national and international issues. We publish work that varies in length and format, including multimedia. Submit a guest opinion or read our guide to writing an opinion article .
- Opinion | ‘Kristi, darling, I understand completely,’ by Cruella De Vil April 29, 2024 Opinion | ‘Kristi, darling, I understand completely,’ by Cruella De Vil April 29, 2024
- Opinion | The wartime outrage in Israel that no one is talking about April 29, 2024 Opinion | The wartime outrage in Israel that no one is talking about April 29, 2024
- Opinion | Is another Trump coup case really necessary? Yes. Arizona matters. April 28, 2024 Opinion | Is another Trump coup case really necessary? Yes. Arizona matters. April 28, 2024


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Common Types of History Papers History papers come in all shapes and sizes. Some papers are narrative (organized like a story according to chronology, or the sequence of events), and some are analytical (organized like an essay according to the topic's internal logic). Some papers are concerned with history (not just what happened,
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context. Provide background information on the historical context of your topic. Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay. Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence.
To write an effective essay, students should examine the question, understand its focus and requirements, acquire information and evidence through research, then construct a clear and well-organised response. Writing a good history essay should be rigorous and challenging, even for stronger students. As with other skills, essay writing develops ...
Analysis Over Recitation: Remember, a history essay isn't just a timeline of events. While it's important to mention key dates and happenings, the heart of your essay should focus on the analysis. Don't just list events; dive deep into the why and how. Dissect motives, evaluate the implications of actions, and discuss the larger themes at play.
Step 1: Understand the History Paper Format. You may be assigned one of several types of history papers. The most common are persuasive essays and research papers. History professors might also ask you to write an analytical paper focused on a particular source or an essay that reviews secondary sources.
Things to remember. Write history essays in the past tense; Generally, avoid sub-headings in your essays; Avoid using the word 'bias' or 'biased' too freely when discussing your research materials. Almost any text could be said to be 'biased'. Your task is to attempt to explain why an author might argue or interpret the past as they do, and ...
Historical essay writing is based upon the thesis. A thesis is a statement, an argument which will be presented by the writer. The thesis is in effect, your position, your particular interpretation, your way of seeing a problem. Resist the temptation, which many students have, to think of a thesis as simply "restating" an instructor's question.
Write in the past tense when discussing history. If a historical event took place in the past, write about it in the past. Be precise. Focus on your thesis and only provide information that is needed to support or develop your argument. Be formal. Try not to use casual language, and avoid using phrases like "I think.".
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece. Most essays will require you to write: 1 Introduction Paragraph. 3 Body Paragraphs. 1 Concluding Paragraph.
history papers come in all shapes and sizes. some papers are narrative (organized like a story according to chronology, or the sequence of events), and some are analytical (organized like an essay according to the topic's ... remember that historical actors were not privy to contemporary values or assumptions and that no historical generation ...
Make it Shine. An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it's achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine: Write a substantial introduction.
Writing a history essay requires a lot of work and experience. A student needs to show a high level of knowledge and understanding of historical events, as well analytical and research skills. No wonder many students find it challenging to compose a well-written essay! To achieve success, use the following tips to level-up your writing abilities
It is also important to realize the key mission. It can be one of the following: Explain why historical events took place; Interpret and analyze a topic; Support or disagree with a specific idea; Justify a certain position. It's a great idea to focus on keywords - they'll be defined at the essay's beginning.
1. Background sentences. The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis, your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about. Background sentences explain the important historical ...
Rather, it requires explication. It requires, as well, that you connect it to your thesis. Remember that you bring evidence in support of your thesis and evidence that's evidence that does not serve that purpose should be excluded. (4) Weave your thesis throughout the body of your essay - Once delineated in your introduction, be sure to weave ...
Download Article. 1. Have a clear structure. When you come to write the body of the essay it is important that you have a clear structure to your argument and to your prose. If your essay drifts, loses focus, or becomes a narrative of events then you will find your grade dropping.
Use several resources to ensure the accuracy of your historic research. 4. Write down connections between the chronological notes you take. Studying history can often feel like you're memorizing a bunch of disconnected dates, names, and places. Avoid this by making the connections explicit in the notes that you take.
History is not just about writing lots of essays! It is also about discussion, debate and evidence. However, there will be, as with many other subjects at A-Level, some essays to write - but it is not as tough as it looks. Essay writing is a skill that you will get better at over time, but you might find the guide below useful to help you along.
Break the essay down into small sections. Depending on the length of the essay, each section might be a few sentences, one paragraph, or even one page. [2] 3. Memorize a little bit each day. Start early when you need to memorize something. Give yourself 1 day for every paragraph or page.
So when it comes to memorising the whole thing, it's a lot easier to break the answer down into logical chunks and work on memorising it bit by bit. So if you want to memorise your Discovery Essay, you might have something like this: Introduction. Theme 1 with the assigned text. Theme 1 with the related text. Theme 2 with the assigned text.
Remember, researching for history essays is a skill that develops over time. Each essay is an opportunity to refine your techniques, from identifying credible sources to synthesizing diverse viewpoints. You can also seek guidance from professional writers. An Essay Service review can help you find a researcher to collaborate with. Receiving ...
During last week's oral arguments in United States v.Trump, it sure sounded like there might be five Supreme Court justices willing to conclude that a president should indeed have lifetime ...
Philip Seymour Hoffman's sister pens essay remembering brother's talent and coping with his loss 10 years after death. Emily Barr recalled saving magazine clippings to remember her brother.
OPINION: History tells humanity a remarkable tale, but it only does us any good if we're able to remember it ("How Ronald Reagan handled campus protests," web, April 29).
Work with local historians and groups to identify social studies topics and events that had strong effects on the local community. This can include school district librarians or archivists, for ...
Book Review. An Unfinished Love Story: A Personal History of the 1960s. By Doris Kearns Goodwin Simon & Schuster: 480 pages, $35 If you buy books linked on our site, The Times may earn a ...
1. Make flashcards of key terms, people, and dates. Studying history involves memorizing lots of dates, names, events, and other facts. Look through your notes and textbook and identify keywords. Make a list of them, then create flashcards with a word on one side and its definition or explanation on the other.
Fast forward a few decades to a booming China. In my many visits over the years — as a teacher, as a visiting artist and as a tourist — Shanghai hotel staff had always returned my credit card ...
Automated essay scoring (AES) to evaluate second language (L2) proficiency has been a firmly established technology used in educational contexts for decades. Although holistic scoring has seen advancements in AES that match or even exceed human performance, analytic scoring still encounters issues as it inherits flaws and shortcomings from the human scoring process. The recent introduction of ...
The dog is humankind's greatest invention. The wheel, the lightbulb, concrete — all amazing. Top of the line. But nothing in human creation has been as essential and adaptable as the countless ...