Visual Analysis Essay

Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
14 min read
-10652.jpg&w=640&q=75)
People also read
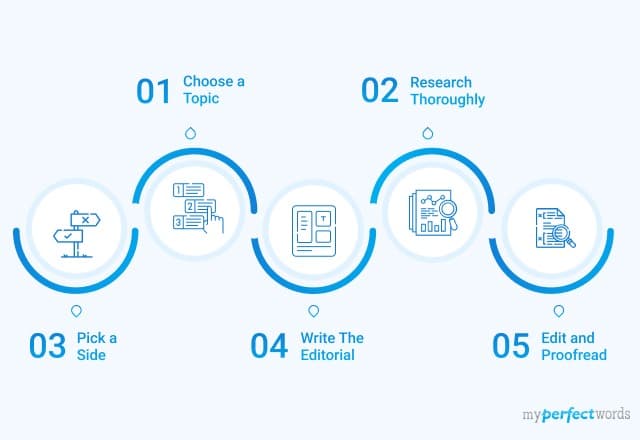
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
A visual analysis essay is a common assignment for the students of history, art, and communications. It is quite a unique type of academic essay.
Visual analysis essays are where images meet text. These essays aim to analyze the meanings embedded in the artworks, explaining visual concepts in a written form.
It may sound difficult to write a visual analysis essay, but it can be done in simple steps by following the right approach. Let’s dive into the writing steps, tips, example essays, and potential topics to help you write an excellent essay.
- 1. What is a Visual Analysis Essay
- 2. How to Write a Visual Analysis Essay - 7 Simple Steps
- 3. Tips on How to Analyze a Photograph
- 4. Tips on How to Analyze a Sculpture
- 5. Visual Analysis Essay on Advertisement
- 6. Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples
- 7. Visual Analysis Essay Topics
What is a Visual Analysis Essay
A visual analysis essay basically requires you to provide a detailed description of a specific visual work of art. It is a type of analytical essay that deals with imagery and visual art instead of texts.
The subject of a visual analysis essay could be an image, painting, photograph, or any visual medium.
In this type of essay, you need to describe the artwork and analyze its elements in detail. That is, how different elements and features fit together to make the whole work stand out. In this sense, you need to use a mixture of descriptive writing and analytical language.
To write a good visual analysis essay, you need to know the basic visual elements and principles of design. Let’s learn about these concepts first before diving into the writing steps.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job
Visual Elements for a Visual Analysis Essay
Writing a visual analysis essay involves analyzing the visual elements of a piece of art. These elements form the basis of the features and characteristics of an image.
Below you can find the common visual elements of a visual analysis essay.
Principles of Design in a Visual Analysis Essay
In addition to visual elements, you must also consider the principles of design for writing a great visual analysis essay. These principles help you identify and explain the characteristics of the image.
How to Write a Visual Analysis Essay - 7 Simple Steps
Now that you have an idea about visual elements and principles, you are now ready to proceed.
Here are the steps that you need to follow for writing a visual analysis essay. Let’s discuss them in detail.
Step 1 - Gather General Information About the Artwork
Once you have a specific artwork or image, here is how to start a visual analysis essay. You need to ask some basic questions about the work and jot down your ideas.
This pre-writing step is for brainstorming ideas. Ask these questions to begin:
- Who and what does the artwork represent?
- Who is the author of the piece?
- Who did the artist create the work for? Who is the intended audience?
- When and where was the work created? What is its historical context?
- Where was this work displayed for the first time?
- Identify which medium, materials, and techniques were used to create the image?
Step 2 - Note Down the Characteristics of the Artwork
The next thing that you need to do is identify what the image depicts. Moreover, you need to identify and describe the visual art elements and design principles used in the work.
Here’s what you need to note:
- The subject matter and its representation.
- Colors, shapes, and lines used in the composition.
- The balance, proportion, and harmony within the artwork.
- Any symbolism or metaphors present.
By pointing out such characteristics, you set the stage for a nuanced analysis in your essay.
Step 3 - Visual Analysis Essay Outline
Once you have gathered your main points by carefully studying the image, you should now organize them in an outline.
Here is how you make an outline for your visual analysis essay:
Step 4- Write the Introduction
This is the first paragraph of a visual analysis essay in which you need to provide some background information on the topic. After grabbing the readers’ attention with an interesting fact, briefly provide information on the following points.
- Talk briefly about the painting and its artist or creator.
- Provide a brief description of the painting and give historical context
- Add an interesting fact about the artist or the painting.
The introduction should end with a thesis statement. The visual analysis essay thesis states the analysis points on the artwork that you aim to discuss in your essay.
Step 5 - Provide Detailed Description, Analysis, and Interpretation
In the body section, you need to explore the artwork in detail. In the first body paragraph, simply describe the features and characteristics of the work. For instance, talk about the technique being used, shape, color, and other aspects to support your thesis.
In the next paragraphs, you can go into the analysis and interpretation of these elements and the work as a whole. Present all the details logically and discuss the relationship between the objects. Talk about the meaning, significance, and impact of the work.
Step 6 - Writing a Conclusion
Once you have completed the body section, move to the conclusion paragraph. This is the last paragraph of the essay that should be strong and well-written to create a sense of closure.
Here’s how you can do it
- Revisit the main insights gained through the analysis, summarizing the key visual elements and principles discussed.
- Emphasize the significance of cultural or historical context in interpreting the visual narrative.
- Tie together the threads of your analysis to reinforce your thesis or main argument.
- End with a memorable statement and encourage readers to carry the lessons learned from the analysis into their own encounters with art.
Step 7 - Edit & Revise Your Essay
Here’s how to end your visual analysis essay: edit and revise your first draft until it becomes the perfect version. Consider these steps for an excellent revision:
- Review for Clarity: Ensure your ideas flow logically. Clarify any ambiguous or unclear statements to enhance the overall readability of your essay.
- Trim Unnecessary Details: Trim excess information that doesn't directly contribute to your main points. Keep your analysis focused and concise.
- Check Consistency: Verify that your writing style remains consistent throughout the essay. Maintain a balance between formal language and engaging expression.
- Fine-Tune Transitions: Ensure smooth transitions between different sections of your essay. Transitions help guide your reader through the analysis, making the journey more enjoyable and comprehensible.
- Proofread for Errors: Carefully proofread your essay for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. A polished essay enhances your credibility and the overall professionalism of your work.
With these basic steps, you can craft an amazing visual analysis essay. Read on for some useful tips for analyzing different kinds of visual subjects.
Tips on How to Analyze a Photograph
Painting and photograph analysis are very similar. There are three ways in which photo visual analysis is conducted: description, reflection, and formal analysis.
Although the historical study may be used, it is not necessary.
- Description - It implies examining the picture carefully and considering all of the details. The description should be neutral, focusing on simple facts without expressing a personal viewpoint.
- Reflection - For the next stage, consider the emotions that the picture stirs in you. Every viewer will have a distinct viewpoint and feelings about the piece. Knowing some historical background might be useful when formulating an educated response.
- Formal analysis - Consider the visual components and concepts. How are they shown in the photo?
- Historical analysis - For a contextual analysis, keep an eye on the photo's surroundings. Make sure you comprehend the surrounding environment in which the photograph was taken. What era was this image shot during?
Tips on How to Analyze a Sculpture
A sculpture, unlike a painting or photograph, requires a different approach to visual analysis. It still depends on visible components and principles, however it does so in a slightly different way.
When you're writing about sculptures, keep the following in mind:
- Medium, size, and technique - What kind of material is it? Is it carved in a negative or positive method?
- Color and lightning - Describe the hue of the sculpture, whether it is painted. Was the sculptor concerned with the illumination when creating the work?
- Human body and scale - Consider how a human body is portrayed in the piece. Also, assess the sculpture's size compared to that of the viewer.
- Function - What was the sculpture's main aim? You could speak about whether it represented a religious conviction or honored someone, for example.
- Composition - Examine the placement of the piece and determine whether there is a focal point.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Visual Analysis Essay on Advertisement
In advertisements, visuals are used to pique interest or persuade the public that what is being advertised is needed. The goal of a visual argument is to generate attention and intrigue. Images are utilized in advertisements to transmit information and interact with the audience.
When conducting a visual analysis of an ad, keep the following in mind:
- Textual Elements
- Illustrations
- Composition
This all has an impact on how people perceive information and how they react to it.
When you analyze the visuals of an ad, you're performing a rhetorical analysis. The study of images and extracting information from them is known as visual rhetoric. It aids in the comprehension of typography, imagery, and the structure of elements on the page.
How to Write a Visual Analysis Paper on an Advertisement
Visual components in advertising are important. It aids in the persuasion of the audience.
Always keep the rhetorical situation in mind while analyzing visual arguments. The following are some key elements to consider:
- Audience - Who is the advertisement meant to attract?
- Purpose - What message does the photo try to get across to the audience?
- Design - What kind of visualizations are included? Are the visuals clear and easy to follow? Are there any patterns or repetitions in the design?
- Strategies - Is there any humor, celebrities, or cultural allusions in the graphic's message?
- Medium - Is the photograph surrounded by text? Is there any text within the picture? How does it interact with the picture to produce an intended effect if there is any?
- Context - What are the characters in an ad? Where are they positioned?
- Subtext - Consider the meaning of the picture's words. What are they trying to say?
Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples
Here are some visual analysis essay samples that you can read to understand this type of essay better.
Art history Visual Analysis Essay Example
Political Cartoon Visual Analysis Essay
Rhetorical and Visual Analysis Essay Sample
Mona Lisa Visual Analysis Essay
Visual Analysis Essay Topics
Here are some top visual analysis essay topics that you can choose from and begin the writing process.
- Make a review of your favorite Hollywood production and discuss the visual arts involved.
- Write about the use of color and action in TV commercials.
- Discuss how the brand name is displayed in digital media campaigns.
- Discuss different types of visual appeals used in web ads.
- What is the special about Cleo Award-winning ads?
- The Use of Light and Shadow in Caravaggio's "The Calling of Saint Matthew"
- The Symbolism of Colors in Vincent van Gogh's "Starry Night"
- What is the importance of art and culture in our life?
- How has art changed over the last 50 years?
- The use of colors in marketing and advertising.
To conclude,
From gathering information about the artwork to crafting a compelling analysis, we've navigated the essential steps you need for a visual analysis essay. Moreover, with the specific tips and examples, you have everything you need to get started.
So dive into the writing process with confidence and return to this blog whenever you need help on any step!
However, if you have gone through the whole article and are still unsure how to start your essay, we can help you.
Our professional essay writers at MyPerfectWords.com can help you with your visual analysis essay assignment. Contact us with your order details, and we will get it done for you.
We provide essay writing service for students that you can trust for better grades. Place your order now and get the best visual analysis essay writing help.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Graphic Essays and Comics
Overview | Recommended Software | Student-Made Examples | Other Examples | Instructional Video
A graphic essay (sometimes called a visual essay) uses a combination of text and images to explore a specific topic. Graphic essays can look like comics, graphic novels, magazines, collages, artist books, textbooks, or even websites. Graphic essays often first take the form of written essays and then have graphic elements added to enrich the reader experience. Unlike infographics, which also combine text and images, graphic essays are often more text-based and usually have a narrative arc or specific reading order.
Comics are a genre used to express ideas through images combined with text or other visual information. Comics can take the form of a single panel or a series of juxtaposed panels of images, sometimes called a strip. Text is conveyed via captions below the panel(s), or speech bubbles and onomatopoeias within the panel(s), to indicate dialogue, narration, sound effects, or other information. Graphic novels are often considered to be a longer form of comics, typically in book form.
A web-based graphic essay can take the form of a blog or a single page website, such as a Microsoft Sway page or an interactive Prezi. For Microsoft Sway and Prezi graphic essays, see the examples below. If you are creating a blog we recommend visiting the Web-Based Projects page .
Graphic Essay Design Tip: Graphic essays can take many forms, so we recommend being creative within the scope of your project! Get some help from DesignLab to brainstorm options and talk through the various tools available!
Make an Appointment
Recommended Software
There are many different software programs that can be used to create graphic essays. Below is a list of the software that we recommend for making a graphic essay. We organized the software by category and put the software from top to bottom from best to worst. We recommend using a software you know well or learning the software well enough to establish an easy workflow, so you can spend less time troubleshooting and spend more time on your project. Check out our Software Support page for links to tutorials for all of these programs.
General Graphic Essay Software

Web-Based Graphic Essay Software

Comic-Specific Graphic Essay Software

Student-Made Examples
Print style graphic essay.
Becoming a Witness by Jessica Posnock

Creative Graphic Essay
Virtual Communication by Max Hautala *Award Winning*

Curb Magazine (2012) by Journalism 417

Web-Based (Magazine) Graphic Essay
Curb Magazine (Current) by Journalism 417

Web-Based (Sway) Graphic Essay
Language Influences Culture, Thoughts, and Identity by Kristen Luckow *Award Winning*

Dyslexia by Maria Swanke *Award Winning*

Other Examples
Web-based (blog) graphic essay.
Switch It Up: Graphic Essay by Amanda Zieba

Graphic Novel
Graphic Novels in the Classroom by Gene Yang

Instructional Video
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Visual Rhetoric: Overview

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This section of the OWL discusses the use of rhetorical theory and rhetoric as it relates to visuals and design. "Visual rhetoric" has been used to mean anything from the use of images as argument, to the arrangement of elements on a page for rhetorical effect, to the use of typography (fonts), and more.
While we cannot hope to cover these and many other topics in depth in this resource, it will be possible for us to look at some of the common visual rhetoric problems encountered by student writers: the text elements of a page (including font choices), the use of visuals (including photographs, illustrations, and charts and graphs), and the role of overall design in composing a page rhetorically.
Note: Much of the current use of "visual rhetoric" is directed at analyzing images and other visuals that already exist. This handout is meant to help you generate visual material.
What is visual rhetoric?
The term visual rhetoric falls under an umbrella term known as visual literacy, which is generally split into three categories: visual thinking, visual learning, visual rhetoric/communication (though clearly visual thinking and visual learning must occur in order to communicate visually). The following diagram illustrates these ideas. The graphic is modified from Sandra Moriarty's diagram in her essay, "A Conceptual Map of Visual Communication" and from "Teaching Visual Literacy and Document Design in First-Year Composition" (MA Thesis) by Allen Brizee.

Visual Literacy
Essentially, a beginning definition of visual rhetoric and its applications are as follows:
- Use of images as argument
- Arrangement of elements on a page
- Use of typography (fonts, etc.)
- Analysis of existing images and visuals
Other OWL resources that are related to visual rhetoric and that may help you understand these ideas are the following:
- Visual Rhetoric Slide Presentation
- Color Theory Slide Presentation
- Using Fonts with Purpose
- Design an Effective PowerPoint Presentation
- HATS (Headings, Access, Typography, and Space) Slide Presentation: A Design Procedure for Routine Business Documents
For more information:
You may also download the pdf Works Cited and Works Referenced from "Teaching Visual Literacy and Document Design in First-Year Composition" in the Media box above. This pdf contains a number of resources on visual literacy, visual rhetoric, and document design and the uses of these concepts in composition and professional writing.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 31 October 2017
The visual essay and the place of artistic research in the humanities
- Remco Roes 1 &
- Kris Pint 1
Palgrave Communications volume 3 , Article number: 8 ( 2017 ) Cite this article
9671 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Archaeology
- Cultural and media studies
What could be the place of artistic research in current contemporary scholarship in the humanities? The following essay addresses this question while using as a case study a collaborative artistic project undertaken by two artists, Remco Roes (Belgium) and Alis Garlick (Australia). We argue that the recent integration of arts into academia requires a hybrid discourse, which has to be distinguished both from the artwork itself and from more conventional forms of academic research. This hybrid discourse explores the whole continuum of possible ways to address our existential relationship with the environment: ranging from aesthetic, multi-sensorial, associative, affective, spatial and visual modes of ‘knowledge’ to more discursive, analytical, contextualised ones. Here, we set out to defend the visual essay as a useful tool to explore the non-conceptual, yet meaningful bodily aspects of human culture, both in the still developing field of artistic research and in more established fields of research. It is a genre that enables us to articulate this knowledge, as a transformative process of meaning-making, supplementing other modes of inquiry in the humanities.
Introduction
In Being Alive: Essays on Movement, Knowledge and Description (2011), Tim Ingold defines anthropology as ‘a sustained and disciplined inquiry into the conditions and potentials of human life’ (Ingold, 2011 , p. 9). For Ingold, artistic practice plays a crucial part in this inquiry. He considers art not merely as a potential object of historical, sociological or ethnographic research, but also as a valuable form of anthropological inquiry itself, providing supplementary methods to understand what it is ‘to be human’.
In a similar vein, Mark Johnson’s The meaning of the body: aesthetics of human understanding (2007) offers a revaluation of art ‘as an essential mode of human engagement with and understanding of the world’ (Johnson, 2007 , p. 10). Johnson argues that art is a useful epistemological instrument because of its ability to intensify the ordinary experience of our environment. Images Footnote 1 are the expression of our on-going, complex relation with an inner and outer environment. In the process of making images of our environment, different bodily experiences, like affects, emotions, feelings and movements are mobilised in the creation of meaning. As Johnson argues, this happens in every process of meaning-making, which is always based on ‘deep-seated bodily sources of human meaning that go beyond the merely conceptual and propositional’ (Ibid., p. 11). The specificity of art simply resides in the fact that it actively engages with those non-conceptual, non-propositional forms of ‘making sense’ of our environment. Art is thus able to take into account (and to explore) many other different meaningful aspects of our human relationship with the environment and thus provide us with a supplementary form of knowledge. Hence Ingold’s remark in the introduction of Making: anthropology, archaeology, art and architecture (2013): ‘Could certain practices of art, for example, suggest new ways of doing anthropology? If there are similarities between the ways in which artists and anthropologists study the world, then could we not regard the artwork as a result of something like an anthropological study, rather than as an object of such study? […] could works of art not be regarded as forms of anthropology, albeit ‘written’ in non-verbal media?’ (Ingold, 2013 , p. 8, italics in original).
And yet we would hesitate to unreservedly answer yes to these rhetorical questions. For instance, it is true that one can consider the works of Francis Bacon as an anthropological study of violence and fear, or the works of John Cage as a study in indeterminacy and chance. But while they can indeed be seen as explorations of the ‘conditions and potentials of human life’, the artworks themselves do not make this knowledge explicit. What is lacking here is the logos of anthropology, logos in the sense of discourse, a line of reasoning. Therefore, while we agree with Ingold and Johnson, the problem remains how to explicate and communicate the knowledge that is contained within works of art, how to make it discursive ? How to articulate artistic practice as an alternative, yet valid form of scholarly research?
Here, we believe that a clear distinction between art and artistic research is necessary. The artistic imaginary is a reaction to the environment in which the artist finds himself: this reaction does not have to be conscious and deliberate. The artist has every right to shrug his shoulders when he is asked for the ‘meaning’ of his work, to provide a ‘discourse’. He can simply reply: ‘I don’t know’ or ‘I do not want to know’, as a refusal to engage with the step of articulating what his work might be exploring. Likewise, the beholder or the reader of a work of art does not need to learn from it to appreciate it. No doubt, he may have gained some understanding about ‘human existence’ after reading a novel or visiting an exhibition, but without the need to spell out this knowledge or to further explore it.
In contrast, artistic research as a specific, inquisitive mode of dealing with the environment requires an explicit articulation of what is at stake, the formulation of a specific problem that determines the focus of the research. ‘Problem’ is used here in the neutral, etymological sense of the word: something ‘thrown forward’, a ‘hindrance, obstacle’ (cf. probleima , Liddell-Scott’s Greek-English Lexicon). A body-in-an-environment finds something thrown before him or her, an issue that grabs the attention. A problem is something that urges us to explore a field of experiences, the ‘potentials of human life’ that are opened up by a work of art. It is often only retroactively, during a second, reflective phase of the artistic research, that a formulation of a problem becomes possible, by a selection of elements that strikes one as meaningful (again, in the sense Johnson defines meaningful, thus including bodily perceptions, movements, affects, feelings as meaningful elements of human understanding of reality). This process opens up, to borrow a term used by Aby Warburg, a ‘Denkraum’ (cf. Gombrich, 1986 , p. 224): it creates a critical distance from the environment, including the environment of the artwork itself: this ‘space for thought’ allows one to consciously explore a specific problem. Consciously here does not equal cerebral: the problem is explored not only in its intellectual, but also in its sensual and emotional, affective aspects. It is projected along different lines in this virtual Denkraum , lines that cross and influence each other: an existential line turns into a line of form and composition; a conceptual line merges into a narrative line, a technical line echoes an autobiographical line. There is no strict hierarchy in the different ‘emanations’ of a problem. These are just different lines contained within the work that interact with each other, and the problem can ‘move’ from one line to another, develop and transform itself along these lines, comparable perhaps to the way a melody develops itself when it is transposed to a different musical scale, a different musical instrument, or even to a different musical genre. But, however, abstract or technical one formulates a problem, following Johnson we argue that a problem is always a translation of a basic existential problem, emerging from a specific environment. We fully agree with Johnson when he argues that ‘philosophy becomes relevant to human life only by reconnecting with, and grounding itself in, bodily dimensions of human meaning and value. Philosophy needs a visceral connection to lived experience’ (Johnson, 2007 , p. 263). The same goes for artistic research. It too finds its relevance in the ‘visceral connection’ with a specific body, a specific situation.
Words are one way of disclosing this lived experience, but within the context of an artistic practice one can hardly ignore the potential for images to provide us with an equally valuable account. In fact, they may even prove most suited to establish the kind of space that comes close to this multi-threaded, embodied Denkraum . In order to illustrate this, we would like to present a case study, a short visual ‘essay’ (however, since the scope of four spreads offers only limited space, it is better to consider it as the image-equivalent of a short research note).
Case study: step by step reading of a visual essay
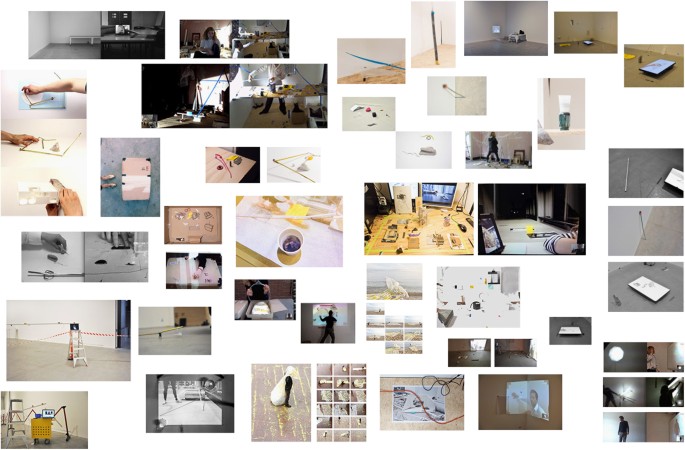
The images (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) form a short visual essay based on a collaborative artistic project 'Exercises of the man (v)' that Remco Roes and Alis Garlick realised for the Situation Symposium at Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology in Melbourne in 2014. One of the conceptual premises of the project was the communication of two physical ‘sites’ through digital media. Roes—located in Belgium—would communicate with Garlick—in Australia—about an installation that was to be realised at the physical location of the exhibition in Melbourne. Their attempts to communicate (about) the site were conducted via e-mail messages, Skype-chats and video conversations. The focus of these conversations increasingly distanced itself from the empty exhibition space of the Design Hub and instead came to include coincidental spaces (and objects) that happened to be close at hand during the 3-month working period leading up to the exhibition. The focus of the project thus shifted from attempting to communicate a particular space towards attempting to communicate the more general experience of being in(side) a space. The project led to the production of a series of small in-situ installations, a large series of video’s and images, a book with a selection of these images as well as texts from the conversations, and the final exhibition in which artefacts that were found during the collaborative process were exhibited. A step by step reading of the visual argument contained within images of this project illustrates how a visual essay can function as a tool for disclosing/articulating/communicating the kind of embodied thinking that occurs within an artistic practice or practice-based research.
Figure 1 shows (albeit in reduced form) a field of photographs and video stills that summarises the project without emphasising any particular aspect. Each of the Figs. 2 – 5 isolate different parts of this same field in an attempt to construct/disclose a form of visual argument (that was already contained within the work). In the final part of this essay we will provide an illustration of how such visual sequences can be possibly ‘read’.

First image of the visual essay. Remco Roes and Alis Garlick, as copyright holders, permit the publication of this image under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
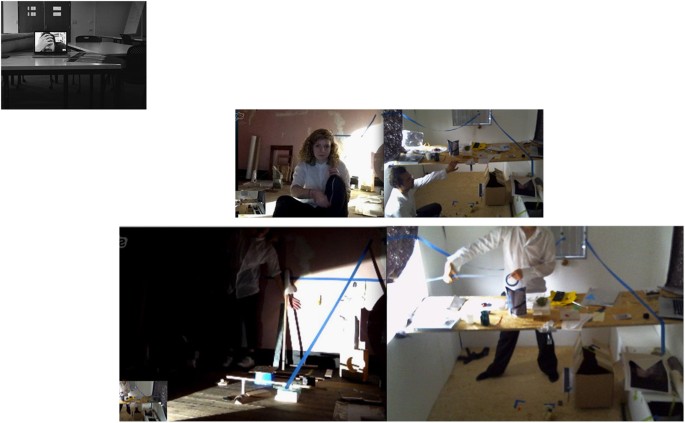

Second image of the visual essay. Remco Roes and Alis Garlick, as copyright holders, permit the publication of this image under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
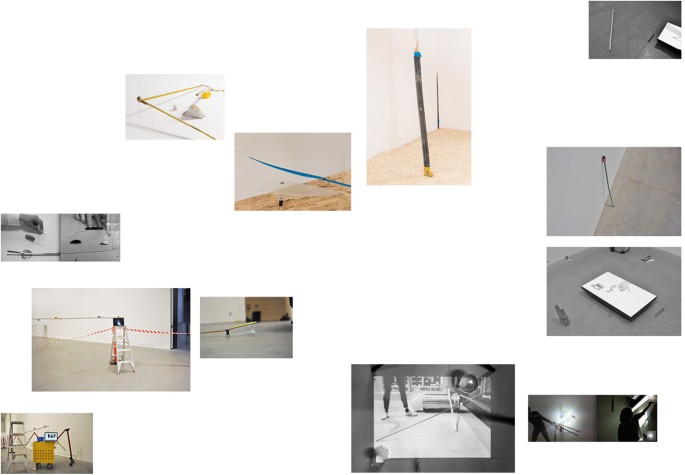

Third image of the visual essay. Remco Roes and Alis Garlick, as copyright holders, permit the publication of this image under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
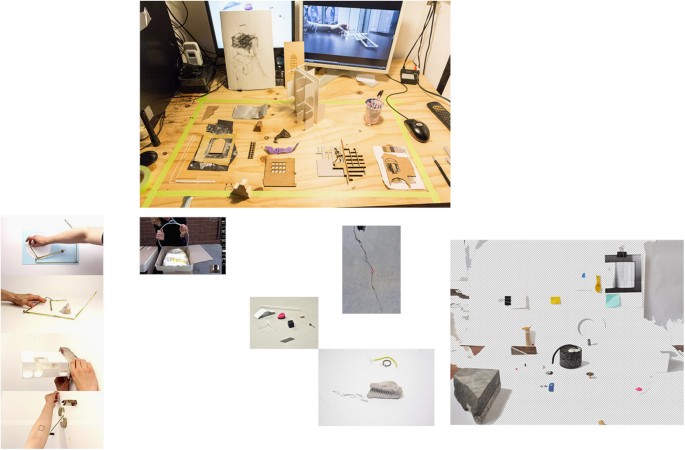

Fourth image of the visual essay. Remco Roes and Alis Garlick, as copyright holders, permit the publication of this image under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License

Fifth image of the visual essay. Remco Roes and Alis Garlick, as copyright holders, permit the publication of this image under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Figure 1 is a remnant of the first step that was taken in the creation of the series of images: significant, meaningful elements in the work of art are brought together. At first, we quite simply start by looking at what is represented in the pictures, and how they are presented to us. This act of looking almost inevitably turns these images into a sequence, an argument. Conditioned by the dominant linearity of writing, including images (for instance in a comic book) one ‘reads’ the images from left to right, one goes from the first spread to the last. Just like one could say that a musical theme or a plot ‘develops’, the series of images seem to ‘develop’ the problem, gradually revealing its complexity. The dominance of this viewing code is not to be ignored, but is of course supplemented by the more ‘holistic’ nature of visual perception (cf. the notion of ‘Gestalt’ in the psychology of perception). So unlike a ‘classic’ argumentation, the discursive sequence is traversed by resonance, by non-linearity, by correspondences between elements both in a single image and between the images in their specific positioning within the essay. These correspondences reveal the synaesthetic nature of every process of meaning-making: ‘The meaning of something is its relations, actual and potential, to other qualities, things, events, and experiences. In pragmatist lingo, the meaning of something is a matter of how it connects to what has gone before and what it entails for present or future experiences and actions’ (Johnson, 2007 , p. 265). The images operate in a similar way, by bringing together different actions, affects, feelings and perceptions into a complex constellation of meaningful elements that parallel each other and create a field of resonance. These connections occur between different elements that ‘disturb’ the logical linearity of the discourse, for instance by the repetition of a specific element (the blue/yellow opposition, or the repetition of a specific diagonal angle).
Confronted with these images, we are now able to delineate more precisely the problem they express. In a generic sense we could formulate it as follows: how to communicate with someone who does not share my existential space, but is nonetheless visually and acoustically present? What are the implications of the kind of technology that makes such communication possible, for the first time in human history? How does it influence our perception and experience of space, of materiality, of presence?
Artistic research into this problem explores the different ways of meaning-making that this new existential space offers, revealing the different conditions and possibilities of this new spatiality. But it has to be stressed that this exploration of the problem happens on different lines, ranging from the kinaesthetic perception to the emotional and affective response to these spaces and images. It would, thus, be wrong to reduce these experiences to a conceptual framework. In their actions, Roes and Garlick do not ‘make a statement’: they quite simply experiment with what their bodies can do in such a hybrid space, ‘wandering’ in this field of meaningful experiences, this Denkraum , that is ‘opened up’: which meaningful clusters of sensations, affects, feelings, spatial and kinaesthetic qualities emerge in such a specific existential space?
In what follows, we want to focus on some of these meaningful clusters. As such, these comments are not part of the visual essay itself. One could compare them to ‘reading remarks’, a short elaboration on what strikes one as relevant. These comments also do not try to ‘crack the code’ of the visual material, as if they were merely a visual and/or spatial rebus to be solved once and for all (‘ x stands for y’ ). They rather attempt to engage in a dialogue with the images, a dialogue that of course does not claim to be definitive or exhaustive.
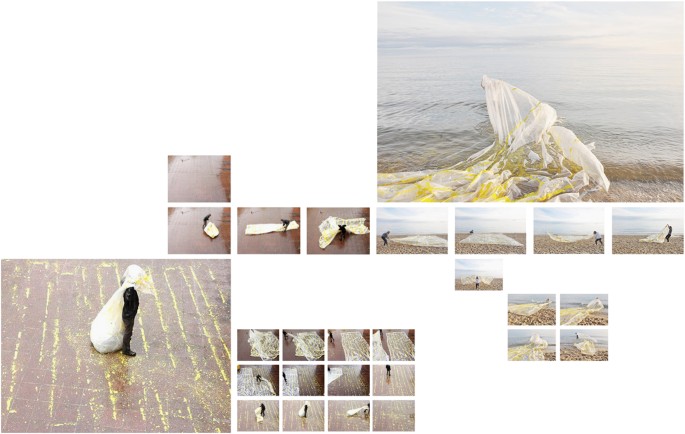
The constellation itself generates a sense of ‘lacking’: we see that there are two characters intensely collaborating and interacting with each other, while never sharing the same space. They are performing, or watching the other perform: drawing a line (imaginary or physically), pulling, wrapping, unpacking, watching, framing, balancing. The small arrangements, constructions or compositions that are made as a result of these activities are all very fragile, shaky and their purpose remains unclear. Interaction with the other occurs only virtually, based on the manipulation of small objects and fragments, located in different places. One of the few materials that eventually gets physically exported to the other side, is a kind of large plastic cover. Again, one should not ‘read’ the picture of Roes with this plastic wrapped around his head as an expression, a ‘symbol’ of individual isolation, of being wrapped up in something. It is simply the experience of a head that disappears (as a head appears and disappears on a computer screen when it gets disconnected), and the experience of a head that is covered up: does it feel like choking, or does it provide a sense of shelter, protection?
A different ‘line’ operates simultaneously in the same image: that of a man standing on a double grid: the grid of the wet street tiles and an alternative, oblique grid of colourful yellow elements, a grid which is clearly temporal, as only the grid of the tiles will remain. These images are contrasted with the (obviously staged) moment when the plastic arrives at ‘the other side’: the claustrophobia is now replaced with the openness of the horizon, the presence of an open seascape: it gives a synaesthetic sense of a fresh breeze that seems lacking in the other images.
In this case, the contrast between the different spaces is very clear, but in other images we also see an effort to unite these different spaces. The problem can now be reformulated, as it moves to another line: how to demarcate a shared space that is both actual and virtual (with a ribbon, the positioning of a computer screen?), how to communicate with each other, not only with words or body language, but also with small artefacts, ‘meaningless’ junk? What is the ‘common ground’ on which to walk, to exchange things—connecting, lining up with the other? And here, the layout of the images (into a spread) adds an extra dimension to the original work of art. The relation between the different bodies does now not only take place in different spaces, but also in different fields of representation: there is the space of the spread, the photographed space and in the photographs, the other space opened up by the computer screen, and the interaction between these levels. We see this in the Fig. 3 where Garlick’s legs are projected on the floor, framed by two plastic beakers: her black legging echoing with the shadows of a chair or a tripod. This visual ‘rhyme’ within the image reveals how a virtual presence interferes with what is present.
The problem, which can be expressed in this fundamental opposition between presence/absence, also resonates with other recurring oppositions that rhythmically structure these images. The images are filled with blue/yellow elements: blue lines of tape, a blue plexi form, yellow traces of paint, yellow objects that are used in the video’s, but the two tones are also conjured up by the white balance difference between daylight and artificial light. The blue/yellow opposition, in turn, connects with other meaningful oppositions, like—obviously—male/female, or the same oppositional set of clothes: black trousers/white shirt, grey scale images versus full colour, or the shadow and the bright sunlight, which finds itself in another opposition with the cold electric light of a computer screen (this of course also refers to the different time zones, another crucial aspect of digital communication: we do not only not share the same place, we also do not share the same time).
Yet the images also invite us to explore certain formal and compositional elements that keep recurring. The second image, for example, emphasises the importance placed in the project upon the connecting of lines, literally of lining up. Within this image the direction and angle of these lines is ‘explained’ by the presence of the two bodies, the makers with their roles of tape in hand. But upon re-reading the other spreads through this lens of ‘connecting lines’ we see that this compositional element starts to attain its own visual logic. Where the lines in image 2 are literally used as devices to connect two (visual) realities, they free themselves from this restricted context in the other images and show us the influence of circumstance and context in allowing for the successful establishing of such a connection.
In Fig. 3 , for instance, we see a collection of lines that have been isolated from the direct context of live communication. The way two parts of a line are manually aligned (in the split-screens in image 2) mirrors the way the images find their position on the page. However, we also see how the visual grammar of these lines of tape is expanded upon: barrier tape that demarcates a working area meets the curve of a small copper fragment on the floor of an installation, a crack in the wall follows the slanted angle of an assembled object, existing marks on the floor—as well as lines in the architecture—come into play. The photographs widen the scale and angle at which the line operates: the line becomes a conceptual form that is no longer merely material tape but also an immaterial graphical element that explores its own argument.
Figure 4 provides us with a pivotal point in this respect: the cables of the mouse, computer and charger introduce a certain fluidity and uncontrolled motion. Similarly, the erratic markings on the paper show that an author is only ever partially in control. The cracked line in the floor is the first line that is created by a negative space, by an absence. This resonates with the black-stained edges of the laser-cut objects, laid out on the desktop. This fourth image thus seems to transform the manifestation of the line yet again; from a simple connecting device into an instrument that is able to cut out shapes, a path that delineates a cut, as opposed to establishing a connection. The circle held up in image 4 is a perfect circular cut. This resonates with the laser-cut objects we see just above it on the desk, but also with the virtual cuts made in the Photoshop image on the right. We can clearly see how a circular cut remains present on the characteristic grey-white chessboard that is virtual emptiness. It is evident that these elements have more than just an aesthetic function in a visual argumentation. They are an integral part of the meaning-making process. They ‘transpose’ on a different level, i.e., the formal and compositional level, the central problem of absence and presence: it is the graphic form of the ‘cut’, as well as the act of cutting itself, that turns one into the other.
Concluding remarks
As we have already argued, within the frame of this comment piece, the scope of the visual essay we present here is inevitably limited. It should be considered as a small exercise in a specific genre of thinking and communicating with images that requires further development. Nonetheless, we hope to have demonstrated the potentialities of the visual essay as a form of meaning-making that allows the articulation of a form of embodied knowledge that supplements other modes of inquiry in the humanities. In this particular case, it allows for the integration of other meaningful, embodied and existential aspects of digital communication, unlikely to be ‘detected’ as such by an (auto)ethnographic, psychological or sociological framework.
The visual essay is an invitation to other researchers in the arts to create their own kind of visual essays in order to address their own work of art or that of others: they can consider their artistic research as a valuable contribution to the exploration of human existence that lies at the core of the humanities. But perhaps it can also inspire scholars in more ‘classical’ domains to introduce artistic research methods to their toolbox, as a way of taking into account the non-conceptual, yet meaningful bodily aspects of human life and human artefacts, this ‘visceral connection to lived experience’, as Johnson puts it.
Obviously, a visual essay runs the risk of being ‘shot by both sides’: artists may scorn the loss of artistic autonomy and ‘exploitation’ of the work of art in the service of scholarship, while academic scholars may be wary of the lack of conceptual and methodological clarity inherent in these artistic forms of embodied, synaesthetic meaning. The visual essay is indeed a bastard genre, the unlawful love (or perhaps more honestly: love/hate) child of academia and the arts. But precisely this hybrid, impure nature of the visual essay allows it to explore unknown ‘conditions and potentials of human life’, precisely because it combines imagination and knowledge. And while this combination may sound like an oxymoron within a scientific, positivistic paradigm, it may in fact indicate the revival, in a new context, of a very ancient alliance. Or as Giorgio Agamben formulates it in Infancy and history: on the destruction of experience (2007 [1978]): ‘Nothing can convey the extent of the change that has taken place in the meaning of experience so much as the resulting reversal of the status of the imagination. For Antiquity, the imagination, which is now expunged from knowledge as ‘unreal’, was the supreme medium of knowledge. As the intermediary between the senses and the intellect, enabling, in phantasy, the union between the sensible form and the potential intellect, it occupies in ancient and medieval culture exactly the same role that our culture assigns to experience. Far from being something unreal, the mundus imaginabilis has its full reality between the mundus sensibilis and the mundus intellegibilis , and is, indeed, the condition of their communication—that is to say, of knowledge’ (Agamben, 2007 , p. 27, italics in original).
And it is precisely this exploration of the mundus imaginabilis that should inspire us to understand artistic research as a valuable form of scholarship in the humanities.
We consider images as a broad category consisting of artefacts of the imagination, the creation of expressive ‘forms’. Images are thus not limited to visual images. For instance, the imagery used in a poem or novel, metaphors in philosophical treatises (‘image-thoughts’), actual sculptures or the imaginary space created by a performance or installation can also be considered as images, just like soundscapes, scenography, architecture.
Agamben G (2007) Infancy and history: on the destruction of experience [trans. L. Heron]. Verso, London/New York, NY
Google Scholar
Garlick A, Roes R (2014) Exercises of the man (v): found dialogues whispered to drying paint. [installation]
Gombrich EH (1986) Aby Warburg: an intellectual biography. Phaidon, Oxford, [1970]
Ingold T (2011) Being alive: essays on movement, knowledge and description. Routledge, London/New York, NY
Ingold T (2013) Making: anthropology, archaeology, art and architecture. Routledge, London/New York, NY
Johnson M (2007) The meaning of the body: Aesthetics of human understanding. Chicago University Press, Chicago
Book Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Hasselt University, Martelarenlaan 42, 3500, Hasselt, Belgium
Remco Roes & Kris Pint
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Remco Roes .
Additional information
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Publisher’s note : Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Roes, R., Pint, K. The visual essay and the place of artistic research in the humanities. Palgrave Commun 3 , 8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-017-0004-5
Download citation
Received : 29 June 2017
Accepted : 04 September 2017
Published : 31 October 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-017-0004-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9 Visual Rhetoric
Dahliani Reynolds

We live in a world saturated with images: from the images we see driving down the street (traffic signs, billboards, crosswalks), to the images we see on our screens (advertisements, memes, Kardashians), they all impart meaning. You might not have thought about it before, but something as simple as a stop sign is an example of visual rhetoric . The visual cue of the red octagon at the end of the street tells you to stop, even before you read the letters. While visual rhetoric may or may not be a familiar term for you, you are already a proficient visual rhetorician, simply through your daily life: you encounter and interpret visual information all the time.

We tend to think of rhetoric as oral or written text. In other words, well, words . Writing is traditionally understood as alphabetic text—putting letters into words into sentences into paragraphs into pages. In recent years, however, with the rise of digital media and the internet, many writing studies, rhetoric, and composition scholars have worked to redefine and expand our understanding of writing to include a variety of modalities —common ways of communicating beyond alphabetic text, that include visual, audio, and digital modes of writing. Integrating two or more modalities in a given text results in multimodal writing.
Visual rhetoric is a form of rhetoric that uses visual information—photographs, drawings, symbols, charts, maps, color, shapes, typography, white space—to communicate, to create meaning, or, more simply, to persuade (see chapter on rhetoric for a longer discussion). This visual information might be used independently, as in the stop sign example from the prior paragraph. The stop sign works alone to communicate its purpose; you don’t need additional information to correctly interpret the meaning. But you can also use visual images in combination with other visuals, or with other modes, to achieve your purpose. For example, an editorial cartoon might use a drawing and speech bubbles to effectively communicate its message. Or you might set a musical background to a photo essay to communicate a particular mood or tone to an audience. Regardless, whether you use a single visual image, multiple images, or integrate visual and textual information, the visual elements work together to create meaning.
It’s important to keep in mind that visuals are culturally dependent. This means that some visual information may be interpreted differently across cultures. Take, for example, the color white. A white dress in western cultures signifies bridal attire; in some Asian cultures, however, white is typically worn at funerals (a clothing color we would almost never see at funerals in the United States). Likewise, some casual hand gestures in the U.S., such as an okay sign, or a thumb’s up, have obscene connotations in other parts of the world. Awareness of how visual information might translate across multicultural audiences is essential for professional and public writers targeting global audiences.
Visual rhetoric is useful in many genres, particularly when we think expansively about the kinds of visual elements we might use. Professional writing might make limited use of photographs, but using white space, typography, and color helps create an appropriate ethos and strong visual design to guide and persuade readers. Writing for public audiences often uses a variety of visual elements, including photographs, charts, graphs, and maps to convey information or draw on pathos to connect with readers.
Media Attributions
- Stop_sign is licensed under a Public Domain license
- MultimodalHand © Christian Pulver is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
Thinking Rhetorically: Writing for Professional and Public Audiences Copyright © 2020 by Dahliani Reynolds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

CRAFT: Let’s Get Graphic: A Look at the Visual Essay by Nicole Breit
August 1, 2018.

If you’re keen to tell new kinds of stories – or old stories in new ways – consider these ten “visual” approaches to writing short-form memoir.
1. The Photo Essay
The art of the photo essay lies in the writer’s careful selection of images balanced with the inclusion of text. Will the photos drive the narrative, or will they fill in textual “gaps” to move the story forward? Vivek Shraya strikes an elegant balance of “showing” and “telling” in her compelling photo narrative, “ Trisha .”
2. The Concrete Essay
This form is the next evolution of concrete poetry (A.K.A. shape or pattern poems), reincarnated as CNF. Jennifer Wortman’s “ Worst-Case Scenario ” presents the story of her husband’s 35-feet fall into a gap while rock climbing, visually – via text shaped like the rocks he fell through.
3. The Illustrated Essay
There’s something so charming about a notebook doodle – perhaps because sketches convey the character of the artist in such an immediate way. I love the narrator’s personality as it comes through Randon Billings’ Noble’s drawings in “ Accidental Notes on the Syllabus .”
4. The Graphic Essay
Check out the masters of graphic memoir – Maggie McKnight , Riad Sattouf , Alison Bechdel , Marjane Satrapi, Kristen Radtke, Nicole Georges and Ellen Forney – and understand how powerful comics can be as a medium for personal storytelling.
5. The Paper Craft Essay
If you’re wondering what to do with your stockpile of scrapbooking supplies, look no further than Erica’s Trabold’s “ Swedish Rye Bread ”– an essay constructed as a collage of typed index cards, digital scans, the pages of a vintage cookbook, and scrapbooking paper.
6. The Quilted Essay
Quilting has a long history of embodying narrative in carefully chosen patterns, colours, and symbols. Learn more about textile-based narratives in Sarah Minor’s article “ What Quilting and Embroidery Can Teach Us about Narrative Form ” and by reading her visual essay, “ Log Cabin Quilt .”
7. The Schematic Essay
The Process of Becoming Informed is a found schematic essay published by The Diagram and credited to Michael K. Buckland of Library Services in Theory and Context, Pergamon Press, 1983. Where might you find a visual essay just waiting to be discovered?
8. The Graphic Hermit Crab
The hermit crab essay appropriates a found text – also known as a “false document” – as a “shell” to protect the vulnerable story it contains. The textual form’s logical progression is visual, in which a found graphic is adopted as the essay’s structure. J. Robert Lennon’s “ Turnabout: A Story Game ” is a graphic hermit crab essay that can be read starting at any point, proceeding in any direction.
9. The Video Essay
Video is a natural medium for personal narrative, and John Breslund is known as a pioneer of the visual essay form. This article includes a Q and A with Bresland and his collaborator, poet and essayist, Eula Biss, with links to some of their groundbreaking work including “Ode to Every Thing.”
10. The Interactive Essay
“Hypertext is spatial in every direction, truly nonsequential—nothing follows by necessity anything else in the essay” write Brenda Miller and Suzanne Paola in Tell It Slant . Exemplary interactive hypertext CNF include Dinty W. Moore’s “ Mr. Plimpton’s Revenge: A Google Map Essay ,” Christine Wilks’ “ Fitting the Pattern ” and the work of Eric LeMay .
I hope this survey of the visual essay, in all its weird and wonderfully varied forms, inspires you to try a new approach to telling your stories. No matter your level of skill, experience, or talent with the visual arts, you can start including visuals in your work easily – and to great effect – incorporating images or multi-media collage.
Which visual essay format appeals to you the most? I’d love to hear which visual essays inspire your next project!
2 comments for “ CRAFT: Let’s Get Graphic: A Look at the Visual Essay by Nicole Breit ”
- Pingback: CRAFT: Life Writing Tips— How Asking Questions Can Spark New Stories by Nicole Breit | Hippocampus Magazine - Memorable Creative Nonfiction
- Pingback: CRAFT: Visual CNF Forms- A Look at the Concrete Essay by Nicole Breit | Hippocampus Magazine - Memorable Creative Nonfiction
Share a Comment Cancel reply
Contributor updates.

Alumni & Contributor Updates: Early 2024
Contributor Updates: Fall 2023
Contributor & Alumni Updates: Spring 2023
Contributor Updates: Spring 2022
How to Write a Visual Analysis Essay: Examples & Template
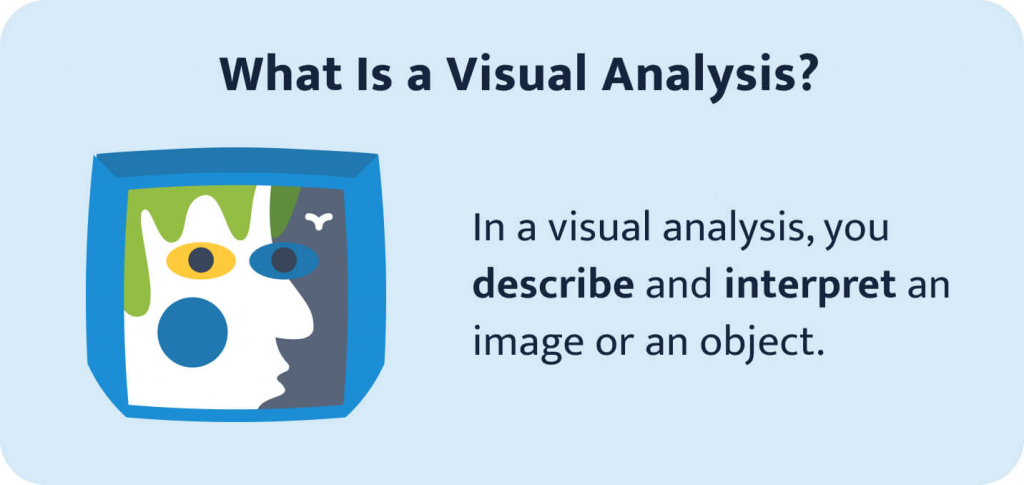
A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this article, our custom writing experts will:
- explain what a visual analysis is;
- share useful tips on how to write a good visual analysis essay;
- provide an essay sample.
- 🎨 Visual Analysis Definition
- 🏺 Artwork Analysis Tips
- ✅ Visual Analysis Writing Guide
- 📑 Example & Citation Tips
🎨 What Is a Visual Analysis?
The primary objective of visual analysis is to understand an artwork better by examining the visual elements. There are two types of visual analysis: formal and contextual.
- A formal analysis focuses on artwork elements such as texture, color, size, and line. It aims to organize visual information and translate it into words. A formal analysis doesn’t interpret the piece.
- Unlike formal analysis, contextual analysis’ primary goal is to connect artwork to its purpose or meaning within a culture. A contextual analysis includes formal analysis. Additionally, it discusses an artwork’s social purpose and significance.
Usually, students deal with formal visual analysis. Before starting to work on your essay, make sure to ask your professor whether to include contextual analysis or not.
The Purpose of Analyzing Images
Why is visual analysis important? What does it help to learn? There are several things that visual analysis helps with:
- It allows students to enhance their appreciation of art.
- It enables students to develop the ability to synthesize information.
- It encourages students to seek out answers instead of simply receiving them.
- It prompts higher-order critical thinking and helps to create a well-reasoned analysis.
- By conducting visual analysis, students learn how to support and explain their ideas by studying visual information.
What Is Formal Analysis: Art History
When we look at an artwork, we want to know why it was created, who made it, and what its function was. That’s why art historians and researchers pay special attention to the role of artworks within historical contexts.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Visual analysis is a helpful tool in exploring art. It focuses on the following aspects:
- Interpretation of subject matter ( iconography). An iconographic analysis is an explanation of the work’s meaning. Art historians try to understand what is shown and why it is depicted in a certain way.
- The analysis of function. Many works of art were designed to serve a purpose that goes beyond aesthetics. Understanding that purpose by studying their historical use helps learn more about artworks. It also establishes a connection between function and appearance.
Formal Analysis: Art Glossary
Now, let’s look at some visual elements and principles and learn how to define them.
Visual Elements :
Visual Principles :
🏺 How to Analyze Artworks: Different Types
Writing a formal analysis is a skill that requires practice. Being careful and attentive during the pre-writing stage is essential if you want to create a good and well-structured visual analysis.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
Visual analysis essay mainly consists of two components:
- Description of the selected image or object,
- Interpretation built on the visual evidence.
During the pre-writing stage:
- Collect general information about an artwork. Describe it briefly. Pay special attention to visual elements and principles:
- Develop an interpretation. Think critically. What does the information in your notes imply? How can it be interpreted?
- Support your ideas. To do it, refer to the visual elements directly. Avoid generalizing art and double-check your prompts.
How to Analyze a Painting Using the Elements of Art
To write an excellent formal visual analysis, you need to consider as many visual principles and elements as you can apply. In the formal analysis part:
- Target your description;
- Address only those elements relevant to your essay;
- Pay attention to visual elements and principles;
- Introduce the subject of the painting and describe it;
- Explain why you have decided to discuss specific elements;
- Discuss the relationship between visual elements of the artwork;
- Use the vocabulary terms.
If you are asked to do a contextual analysis , you may want to:
- Focus on the historical importance of an artwork;
- Explore the style or movement associated with an artwork;
- Learn about the historical context and the public’s reaction to the artwork;
- Learn about the author and how they’ve created the piece of art.
Painting Analysis Essay Example & Tips
Here is a template you can use for your essay.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Now, let’s take a look at an essay example.
How to Analyze a Photograph
Analyzing photos has a lot in common with paintings. There are three methods on which photo visual analysis relies: description, reflection, and formal analysis. Historical analysis can be included as well, though it is optional.
- Description . It implies looking closely at the photo and considering all the details. The description needs to be objective and consists of basic statements that don’t express an opinion.
- Reflection. For the next step, focus on the emotions that the photograph evokes. Here, every viewer will have a different opinion and feelings about the artwork. Knowing some historical context may be helpful to construct a thoughtful response.
- Formal analysis . Think of the visual elements and principles. How are they represented in the photograph?
- Historical analysis. For a contextual analysis, you need to pay attention to the external elements of the photograph. Make sure that you understand the environmental context in which the photo was taken. Under what historical circumstances was the picture made?
Photo Analysis Essay Tips
Now that we’ve talked about analyzing a photograph let’s look at some helpful tips that will help you write an essay.
How to Analyze a Sculpture
Visual analysis of a sculpture is slightly different from the one of a painting or a photograph. However, it still uses similar concepts, relies on visual elements and principles. When you write about sculpture, consider:
Visual Analysis Essay on a Sculpture: Writing Tips
A sculpture analysis consists of the following parts:
- Description . Include specific details, such as what the sculpture may represent. For instance, the human figure may be an athlete, an ancient God, a poet, etc. Consider their pose, body build, and attire.
- Formal analysis . Here, visual elements and principles become the focus. Discuss the color, shape, technique, and medium.
- Contextual analysis . If you decide to include a contextual analysis, you can talk about the sculpture’s function and how it conveys ideas and sentiments of that period. Mention its historical and cultural importance.
When it comes to sculpture analysis, you may also want to collect technical data such as:
- The size of the sculpture
- Medium (the material)
- The current condition (is it damaged, preserved as a fragment, or as a whole piece)
- Display (Was a sculpture a part of an architectural setting, or was it an independent piece of work?)
For instance, if you were to do a visual analysis of Laocoön and His Sons , you could first look up such details:
- Location: Discovered in a Roman vineyard in 1506
- Current location: Vatican
- Date: Hellenistic Period (323 BCE – 31 CE)
- Size: Height 208 cm; Width 163 cm; Depth 112 cm
- Material: Marble
- Current condition: Missing several parts.
Visual Analysis Essay: Advertisement Analysis
Visuals are used in advertisements to attract attention or convince the public that they need what is being advertised. The purpose of a visual argument is to create interest. Advertisements use images to convey information and communicate with the audience.
When writing a visual analysis of an advertisement, pay attention to the following:
- text elements,
- illustrations,
- composition.
All of this influences how the viewer perceives the information and reacts to it.
When you write about an advertisement, you conduct a rhetorical analysis of its visual elements. Visual rhetoric is mainly directed at analyzing images and extracting information from them. It helps to understand the use of typography, imagery, and the arrangement of elements on the page.
Think of the famous visual rhetoric examples such as the We can do it! poster or a Chanel №5 commercial. Both examples demonstrate how persuasive imagery has been used throughout history.

How to Write a Visual Analysis Paper on an Advertisement
The presentation of visual elements in advertising is essential. It helps to convince the audience. When you analyze visual arguments, always keep the rhetorical situation in mind. Here are some crucial elements to focus on:
✅ How to Write a Visual Analysis Paper: Step by Step
Now, we’ll focus on the paper itself and how to structure it. But first, check out the list of topics and choose what suits you best.
Visual Analysis Essay Topics
There are a lot of artworks and advertisements that can be analyzed and viewed from different perspectives. Here are some essay topics on visual analysis that you may find helpful:
- Analyze Gustav Klimt’s The Kiss (1907-1908.)
- The theme of humanity and The Son of Man (1964) by René Magritte.
- The use of visual elements in Almond Blossom by Vincent van Gogh (1888-1890.)
- Identity and Seated Harlequin (1901) by Picasso .
- Explore the themes of Paul Klee ’s The Tree of Houses , 1918.
- Objectives, activities, and instructions of Pietro Perugino’s fresco The Delivery of the Keys to Saint Peter .
- Reflection on social issues of the time in Two Fridas by Frida Kahlo and Untitled by Ramses Younan .
- Analyze the importance of Mural (1943) by Jackson Pollock .
- The political message in John Gast’s painting American Progress (1872).
- Describe the visual techniques used in Toy Pieta by Scott Avett .
- The interpretation of the painting Indian Fire God by Frederic Remington.
- Explore the historical significance and aesthetic meaning of Ognissanti Madonna by Giotto di Bondone .
- Analyze different interpretations of The Three Dancers by Pablo Picasso .
Photography:
- The idea behind Lindsay Key (1985) by Robert Mapplethorpe.
- Explore the mythical appeal of Robert Capa’s photograph The Falling Soldier (Spain,1936) from Death in Making photobook.
- Describe Two Boys with Fish (2018) from Faith series by Mario Macilau.
- Kevin Carter’s Starving Child and Vulture (1993) as the representation of photojournalism.
- The story behind Philippe Halsman’s Dali Atomicus , 1948.
- Describe The Starving Boy in Uganda photograph by Mike Wells
- Analyse the view of a historic disaster in San Francisco photograph by George R. Lawrence.
- The statement behind Eddie Adams’s photo Shooting a Viet Cong Prisoner .
- How is Steve McCurry’s perception of the world reflected in his photo Afghanistan Girl .
- Analyze the reflection of Ansel Adams’s environmental philosophy in his photo Moon and Half Dome (1960).
- Describe Girl on the Garda Lake (2016) by Giuseppe Milo.
- Combination of internal geometry and true-to-life moments in Behind the Gare Saint Lazare by Henri Cartier-Bresson .
- Modern art and Couple on Seat by Lynn Chadwick (1984.)
- Analyze the biblical context of Pieta (1498-1499) by Michelangelo.
- The use of shapes in Louise Bourgeois’ Spider (1996.)
- Analysis of the symbolism behind The Thinker (1880) by Rodin.
- The historical meaning of Fountain (1917) by Duchamp .
- Analyze the Miniature Statue of Liberty by Willard Wigan
- The combination of Egyptian culture and classical Greek ideology in statue of Osiris-Antinous .
- Reflection of the civilization values in emperor Qin’s Terracotta Army .
- The aesthetic and philosophical significance of Michelangelo’s David .
- Explore the controversial meaning of Damien Hirst’s sculpture For the Love of God (2007).
- Analyze the elements of art and design used in The Thinker by August Rodin .
- Symbolic elements in the Ancient Greek statues of Zeus .
- Depiction of the fundamental aspects of Buddhism in The Parinirvana of Siddhartha/Shakyamuni.
Advertisement:
- How Volkswagen : Think Small (1960) ad changed advertising.
- Analyze the use of figures in California Milk Processor Board: Got Milk? (1993) ad campaign .
- Analyze the use of colors in Coca-Cola — The Pause that Refreshes (1931.)
- Explore the historical context of We Can Do It! (1942) campaign.
- The importance of a slogan in 1947: A Diamond Is Forever by De Beers.
- Examine the specifics of visual advert: dogs and their humans.
- Describe the use of visual techniques in Kentucky Fried Chicken company’s advertisement.
- Analyze the multiple messages behind the print ad of JBL .
- Discuss the methods used in Toyota Highlander advertisement .
- Elucidation of people’s dependency on social networks in the advertising campaign Followers by Miller Lite.
- The use of the visual arguments in Schlitz Brewing Company advertisement .
- The role of colors and fonts in Viva la Juicy perfume advertisement .
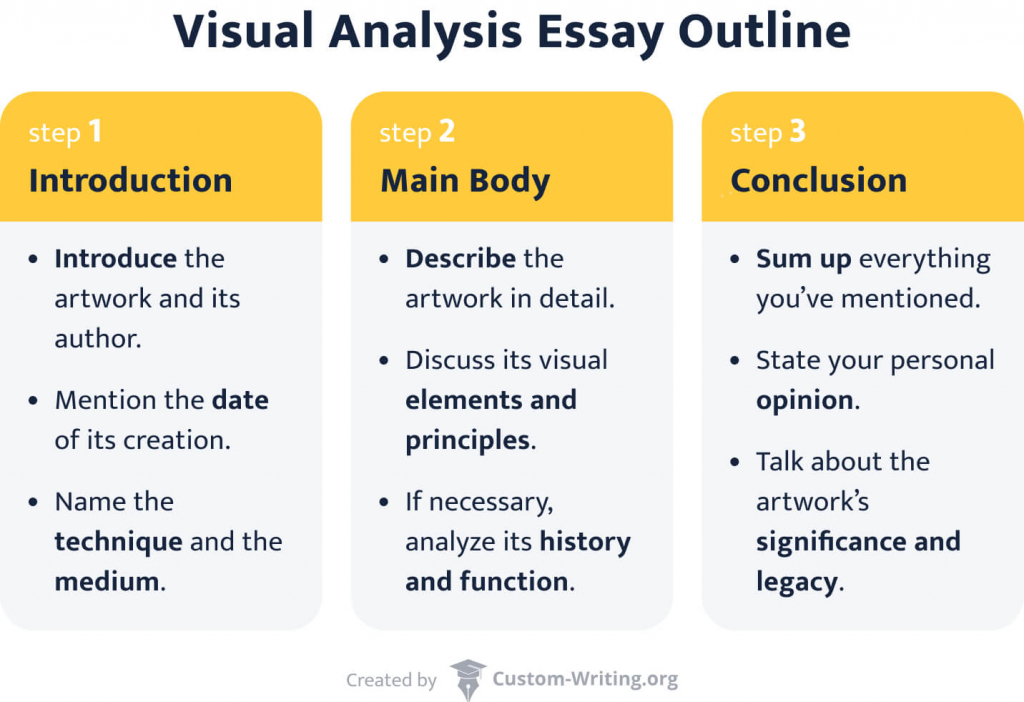
Visual Analysis Essay Outline
You can use this art analysis template to structure your essay:
How to Start an Art Essay
Every analysis starts with an introduction. In the first paragraph, make sure that:
- the reader knows that this essay is a visual analysis;
- you have provided all the necessary background information about an artwork.
It’s also important to know how to introduce an artwork. If you’re dealing with a panting or a photograph, it’s better to integrate them into the first page of your analysis. This way, the reader can see the piece and use it as a reference while reading your paper.
Art Thesis Statement Examples & Tips
Formulating a thesis is an essential step in every essay. Depending on the purpose of your paper, you can either focus your visual analysis thesis statement on formal elements or connect it with the contextual meaning.
To create a strong thesis, you should relate it to an artwork’s meaning, significance, or effect. Your interpretation should put out an argument that someone could potentially disagree with.
- For instance, you can consider how formal elements or principles impact the meaning of an artwork. Here are some options you can consider:
- If your focus is the contextual analysis, you can find the connection between the artwork and the artist’s personal life or a historical event.
How to Write Visual Analysis Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs of formal analysis consist of two parts—the description and the analysis itself. Let’s take Klimt’s The Kiss as an example:
The contextual analysis includes interpretation and evaluation.
Visual Analysis Essay Conclusion
When you work on the conclusion, try to conclude your paper without restating the thesis. At the end of your essay, you can present an interesting fact. You can also try to:
- Compare an artwork to similar ones;
- Contrast your own ideas on the piece with the reaction people had when it was first revealed.
- Talk about an artwork’s significance to the culture and art in general.
📑 Visual Analysis Essay Example & Citation Tips
In this section of the article, we will share some tips on how to reference an artwork in a paper. We will also provide an essay example.
How to Reference a Painting in an Essay
When you work on visual analysis, it is important to know how to write the title of an artwork properly. Citing a painting, a photograph, or any other visual source, will require a little more information than citing a book or an article. Here is what you will need:
- Size dimensions
- Current location
- Name of the piece
- Artist’s name
- Date when artwork was created
If you want to cite a painting or an artwork you saw online, you will also need:
- The name of the website
- Website URL
- Page’s publication date
- Date of your access
How to Properly Credit an Artwork in APA
How to properly credit an artwork in mla, how to properly credit an artwork in chicago format.
Finally, here’s a sample visual analysis of Rodin’s sculpture The Thinker in APA format. Feel free to download it below.
Many people believe that works of art are bound to be immortal. Indeed, some remarkable masterpieces have outlived their artists by many years, gaining more and more popularity with time. Among them is The Thinker, a brilliant sculpture made by Auguste Rodin, depicting a young, athletic man, immersed deep into his thoughts.
You can also look at the following essay samples to get even more ideas.
- The Protestors Cartoon by Clay Bennett: Visual Analysis
- Visual Analysis – Editorial Cartoon
- Visual Analysis: “Dust Storm” Photo by Steve McCurry
- Visual, Aural, Read & Write, Kinesthetic Analysis
- Schlitz Brewing Company Advertisement: Visual Arguments Analysis
Thanks for reading through our article! We hope you found it helpful. Don’t hesitate to share it with your friends.
Further reading:
- How to Write a Lab Report: Format, Tips, & Example
- Literature Review Outline: Examples, Approaches, & Templates
- How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step [2024 Upd.]
- How to Write a Term Paper: The Ultimate Guide and Tips
❓ Visual Analysis FAQs
To write a visual argument essay, you need to use rhetorical analysis. Visual rhetoric is directed at analyzing images and extracting the information they contain. It helps to analyze the visuals and the arrangement of elements on the page.
A well-though contextual analysis will include:
1. formal analysis, 2. some information about the artist, 3. details on when and where the piece was created, 4. the social purpose of the work, 5. its cultural meaning.
It is better to include pictures in the introduction part of your paper. Make sure to cite them correctly according to the format you’re using. Don’t forget to add the website name, the URL, and the access date.
To analyze means not only to describe but also to evaluate and synthesize visual information. To do that, you need to learn about visual elements and principles and see how and why they are used within artworks.
🔍 References
- Art History: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Visual Analysis: Duke University
- Writing a Formal Analysis in Art History: Hamilton College
- Contextual Analysis: Pine-Richland School District
- How to Analyze an Artwork: Student Art Guide
- Introduction to Art Historical Analysis: Khan Academy
- Guidelines for Analysis of Art: University of Arkansas at Little Rock
- Elements of Art: Getty.edu
- Formal or Critical Analysis: LibreTexts
- Analyzing a Photograph: University of Oregon
- Picture Composition Analysis and Photo Essay: University of Northern Iowa
- Visual Analysis Guidelines: Skidmore College
- How to Analyze Sculpture: NLA Design and Visual Arts: WordPress
- Visual Rhetoric: Purdue University
- Formal Visual Analysis: The Elements & Principles of Composition
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
![examples of verbal visual essays Critical Writing: Examples & Brilliant Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/fingers-note-report-journalist-filling-284x153.jpg)
Any critique is nothing more than critical analysis, and the word “analysis” does not have a negative meaning. Critical writing relies on objective evaluations of or a response to an author’s creation. As such, they can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves. To write a critique, you...

If you are assigned to write a rhetorical analysis essay, you have one significant advantage. You can choose a text from an almost infinite number of resources. The most important thing is that you analyze the statement addressed to an audience. The task of a rhetorical analysis essay is to...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

As a student, you may be asked to write a book review. Unlike an argumentative essay, a book review is an opportunity to convey the central theme of a story while offering a new perspective on the author’s ideas. Knowing how to create a well-organized and coherent review, however, is...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...

You don’t need to be a nerd to understand the general idea behind cause and effect essays. Let’s see! If you skip a meal, you get hungry. And if you write an essay about it, your goal is achieved! However, following multiple rules of academic writing can be a tough...
![examples of verbal visual essays How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/young-writer-taking-notes-284x153.jpg)
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays. While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to...
![examples of verbal visual essays How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...

The conclusion is the last paragraph in your paper that draws the ideas and reasoning together. However, its purpose does not end there. A definite essay conclusion accomplishes several goals: Therefore, a conclusion usually consists of: Our experts prepared this guide, where you will find great tips on how to...
![examples of verbal visual essays How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/closeup-shot-woman-working-studying-from-home-with-red-coffee-cup-nearby-284x153.jpg)
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present...
do you review and edit visual arts extended essay

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

10.8: A Sample Visual Argument Analysis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 82027

- Saramanda Swigart
- City College of San Francisco
Media Alternative
Listen to an audio version of this page (28 sec):
The essay "An Image Is Worth a Thousand Calls to Arms" by Saramanda Swigart analyzes a visual argument.
- Sample visual argument analysis essay "An Image Is Worth a Thousand Calls to Arms" in PDF with margin notes
- Sample visual argument analysis essay "An Image Is Worth a Thousand Calls to Arms" accessible version with notes in parentheses
Visual Rhetorical Analysis
This essay about the influential power of visual rhetoric, exemplified by Shepard Fairey’s “Hope” poster from Barack Obama’s 2008 campaign, analyzes its strategic composition and symbolic elements. It highlights how visual rhetoric, through deliberate imagery and symbolism, shapes collective perceptions and inspires action. Beyond mere aesthetics, the essay explores the profound socio-cultural impact of visual communication, emphasizing its role in provoking emotions and fostering shared values. Through this lens, it underscores the importance of understanding visual rhetoric as a vital tool for critical discourse in today’s visually-dominated society.
How it works
In the vast realm of human communication, the potency of language transcends mere verbal or written expression. Visual rhetoric, an artful orchestration of images and symbols, exerts a profound influence on our perceptions, beliefs, and actions. From captivating advertisements to thought-provoking political campaigns, visual rhetoric saturates our daily existence, wielding the power to sway, provoke, and inspire. In this illuminating essay, we embark on a journey of visual rhetorical analysis, delving into its intricate tapestry, deciphering its subtle strategies, and uncovering its profound socio-cultural impact.
Deciphering Visual Rhetoric: Visual rhetoric encompasses the deliberate manipulation of images, symbols, and visual elements to convey messages and elicit responses from audiences. Unlike conventional rhetoric, which relies predominantly on verbal argumentation, visual rhetoric taps into the sensory experience, evoking emotions, values, and instincts. Through careful orchestration of design principles such as composition, color theory, and symbolism, visual rhetoric constructs narratives and shapes collective perceptions.
An Illustrative Case Study: The “Hope” Poster Phenomenon: One emblematic instance of visual rhetoric in action is the renowned “Hope” poster created by artist Shepard Fairey during Barack Obama’s historic 2008 presidential campaign. This iconic artwork features a stylized portrait of Obama, embellished with the word “HOPE” emblazoned in vibrant, captivating colors below his visage. Through this seemingly simple yet profoundly impactful composition, Fairey encapsulates the essence of Obama’s aspirational message, stirring sentiments of optimism, unity, and progress.
Analytical Insights: The effectiveness of the “Hope” poster lies in its astute utilization of visual elements to convey a persuasive narrative. Firstly, Fairey’s deliberate selection of imagery is noteworthy. By portraying Obama in a dignified, almost heroic light, with his gaze fixed resolutely ahead and an aura of determination, Fairey elevates him as a symbol of hope and leadership. The striking contrast of vivid hues, particularly the juxtaposition of warm reds and cool blues, not only commands attention but also reinforces the theme of unity and inclusivity.
Moreover, the strategic placement of the word “HOPE” directly beneath Obama’s image serves as a focal point, accentuating the overarching message of the campaign. Rendered in a bold, sans-serif font, the word exudes a sense of urgency and significance, compelling viewers to internalize its message. Through this visual hierarchy, Fairey ensures that the viewer’s gaze is inexorably drawn to the central theme of hope and renewal.
Furthermore, the poster employs symbolism to resonate with its audience on a deeper level. The stylized portrayal of Obama, reminiscent of iconic propaganda posters and contemporary pop art, taps into collective cultural references and archetypes, imbuing the image with layers of meaning and resonance. Additionally, the word “HOPE” functions not merely as a slogan but as a potent symbol of collective aspiration and possibility, inviting viewers to project their own hopes and dreams onto the image, fostering a sense of emotional connection and shared purpose.
Impact and Legacy: The “Hope” poster swiftly attained iconic status, emblematic of Obama’s transformative campaign and the spirit of optimism it embodied. Its ubiquitous presence across diverse media platforms, from billboards to social media profiles, amplified its reach and influence, cementing its place in political and cultural lore. Beyond its immediate political context, the poster continues to reverberate as a powerful testament to the potential of visual rhetoric in galvanizing social change and inspiring collective action.
Conclusion: In an age dominated by visual stimuli, the language of images assumes paramount significance, shaping our perceptions, beliefs, and identities in profound ways. Through the prism of visual rhetorical analysis, we gain insights into the nuanced strategies employed by artists and communicators to convey messages, provoke emotions, and catalyze social change. As we navigate an increasingly visual landscape, understanding the grammar of visual rhetoric becomes indispensable for discerning meaning, questioning assumptions, and engaging in critical discourse. Just as words wield the power to shape our reality, so too do images, and through the lens of visual rhetorical analysis, we unravel the intricate tapestry of visual communication, illuminating the enduring impact of imagery on our collective consciousness and societal narratives.
Cite this page
Visual Rhetorical Analysis. (2024, Apr 14). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/visual-rhetorical-analysis/
"Visual Rhetorical Analysis." PapersOwl.com , 14 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/visual-rhetorical-analysis/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Visual Rhetorical Analysis . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/visual-rhetorical-analysis/ [Accessed: 8 May. 2024]
"Visual Rhetorical Analysis." PapersOwl.com, Apr 14, 2024. Accessed May 8, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/visual-rhetorical-analysis/
"Visual Rhetorical Analysis," PapersOwl.com , 14-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/visual-rhetorical-analysis/. [Accessed: 8-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Visual Rhetorical Analysis . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/visual-rhetorical-analysis/ [Accessed: 8-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Template Lists
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides How to Use Visual Communication: Definition, Examples, Templates
How to Use Visual Communication: Definition, Examples, Templates
Written by: Midori Nediger Aug 27, 2020

With so many businesses and organizations now operating online, visual communication is more important than ever.
Whether you’re an executive looking to align your team on new organizational processes, or a marketer looking for ways to differentiate on social media, you may wonder how best to use visuals to really connect with your audience.
In this guide, I’ll give you some trade secrets from my experience as an information designer. I’ll show you how to leverage design and visual communications best practices to engage your audience while avoiding information overload.
Table of contents:
- What is visual communication?
What are some of the most common types of visual communication?
Why does visual communication matter, how to use visual communication in the workplace, how to make your visual communications look professional, what is visual communication visual communication defined:.
Visual communication is the practice of using visual elements to convey a message, inspire change, or evoke emotion.
It’s one part communication design— crafting a message that educates, motivates, and engages, and one part graphic design— using design principles to communicate that message so that it’s clear and eye-catching.
Effective visual communication should be equally appealing and informative.

Visual communication is really about picking the right elements (usually text, icons, shapes, imagery and data visualizations) to create meaning for your audience. You can also communicate visually with video. For example, you can use a free screen recorder to show a colleague how to complete a task rather than sharing a document.
Some common visual communication strategies include:
- Using data visualization to show the impact of your work
- Using shapes and lines to outline relationships, processes, and flows
- Using symbols and icons to make information more memorable
- Using visuals and data to tell stories
- Using color to indicate importance and draw attention
When you think about visual communication, your mind might first jump to design-heavy content like social media graphics or infographics .
And while visual communication certainly plays a role in those cases, there are a ton of other types of content that fall under the visual communication umbrella.
Some common types of visual communications in the workplace include:
- Process Diagrams
- Flow Charts
- Charts and Graphs
- Visual Reports
- Presentations

NEW! Introducing: Marketing Statistics Report 2022
It’s 2022 already. Marketers, are you still using data from pre-COVID times?
Don’t make decisions based on outdated data that no longer applies. It’s time you keep yourself informed of the latest marketing statistics and trends during the past two years, and learn how COVID-19 has affected marketing efforts in different industries — with this FREE marketing statistics report put together by Venngage and HubSpot .
The report uses data gathered from over 100,000 customers of HubSpot CRM. In addition to that, you’ll also know about the trends in using visuals in content marketing and the impacts of the pandemic on visual content, from 200+ marketers all over the world interviewed by Venngage.

Grab your copy now — it’s not like any other marketing reports out there, plus it’s 100% free!
These can look very different when used in different industries, but they all use the same visual communication strategies and design principles to accurately present information and create meaning for audiences.
Let’s take a look at some visual communication strategies used across different types of organizations.
Nonprofit organizations
Nonprofit organizations often combine data visualization and visual storytelling to gain the trust of their audiences and establish the credibility of their organization.
This might take the form of a statistical infographic or an impact report that they share with their donors and supporters:

They may also create public-facing informational posters or brochures to build awareness around their organization and foster support for their cause.

Another place where visual communication is key for larger nonprofits is to update stakeholders on campaign or research results. These reports often combine storytelling with data visualization to inform and convince.

Healthcare organizations
A visual communication strategy often applied in healthcare is the use of plain language and simple iconography to communicate with audiences with lower health literacy.
For example, a public health unit might create an infographic factsheet to ensure that recommended protocols are followed, like these recent COVID-19 guidelines from Public Health Ontario:

In fact, the CDC recommends the use of visuals to boost understanding of health information for external communications in healthcare.
These types of visual guides aren’t just helpful for external communication. Similar tactics can be used to remind staff of workplace best practices, like patient safety and infection prevention practices.

Learn more: Venngage for Healthcare Organizations
Business consulting organizations
Business development organizations may use diagrams like process maps to communicate high-level strategy to clients , which can help make their value more tangible.
A simple roadmap or summary of strategy recommendations can go a long way towards communicating and aligning with clients.

Visuals can help create understanding where words alone cannot.
They can help bridge the gap between concepts and words, especially when appealing to an audience with diverse needs and backgrounds.
It’s clear that visual communication is top-of-mind for many. When we surveyed marketers about their use of visual content , 74% of the marketers we surveyed stated that more than 70% of their content contained some form of visual.

Plus, it’s been demonstrated time and time again that in addition to making information more engaging, visuals can actually help with the comprehension of information.
But when should you consider making your content more visual?
You can use visual communication to:
- Engage your audience
- Communicate complex information
- Tell a story and convey emotion
- Simplify information
- Communicate the impact of your data
Let’s take a look at how this can apply in the workplace.
You might think that visual communication isn’t really necessary in your day-to-day work.
But visuals, in the right hands, can be used as a tool to influence what your audience pays attention to, thinks about, and understands.
1. How to make boring topics engaging
Creating engaging content that shows the value of your business can be a challenge when you work in a “boring” or technical industry like finance, business development, engineering or healthcare.
But it’s this kind of challenge where visual communication shines. Creating unique visuals can help you position yourself as the innovative solution in the market.
Here are some simple strategies to consider:
Use stylized icons to make technical information feel concrete and approachable
This infographic about credit card merchant processing, for example, takes advantage of a playful icon style and a modern design treatment to capture your attention and keep you reading.

This might be the perfect way to signal to young business owners that you’re different from the traditional big banks, and that you’re right for them. It feels so much more approachable than a wall of text on a web page.
Just applying some basic visual communication strategies can make this “boring” technical information a bit more accessible and relatable to your target audience —ready to boost engagement on social media, your blog, or your newsletter.
Use visual metaphors to get your audience thinking
Visual metaphors are another way to make old ideas feel fresh and exciting, and can even help foster deeper understanding of your subject matter.
The use of women running in the infographic below, for example, helps me think about NPS scores in a new way:

By allowing the visual presentation to drive how you position the value of your product or service, you can find new ways to reach your customers.
Read more: Common symbols and meanings and how to use them in design
To sum up, here are some visual communication tips for how to make boring topics engaging:
- Use visuals and icons to make technical information feel approachable
- Choose a graphic design style that will resonate with your target audience
- Think outside of the box: use a unique visual presentation to get your audience thinking
If your visual presentation is unique, your information doesn’t have to be revolutionary to give you an edge over your competitors.
Read more: Infographic ideas to make your information engaging.
2. How to communicate process changes and improvements
Being able to quickly re-align your team on process changes has never been more important.
Visuals can make processes easier to understand and more memorable. They can also help boost employee alignment and engagement.
Here’s how you can use process documentation to help align your team.
Show both high-level and low-level changes with hierarchical process diagrams
Breaking down processes into discrete visual steps can make new processes much easier to grasp.
And breaking down steps into even smaller sections can help you communicate both high-level concepts and specific details in the same place, like in this process diagram below.

Providing these process documents to employees can help quickly align teams on new strategies, like an action plan to address a crisis or a shift into a new market, while also acting as a reference point in the future.

- Provide presentation slides as a post-meeting reference guide
With remote work becoming the norm, you likely spend many of your days in back-to-back Zoom calls.
If you’re holding a meeting to discuss major process changes or company updates, it may be worth your while to whip up some quick meeting slides to help clarify changes and ensure your team is aligned.
Including a slide deck can help reinforce the importance of what’s discussed, and act as a reference when your team digs into their work.

Provide checklists to help your team keep track of complex processes
Providing a checklist of steps for your team to follow can help you delegate work with confidence, while giving your team the confidence to know that they’re doing things right.
Checklists are particularly helpful for communicating complex or proprietary internal processes, as they can help remove any anxiety from the process.

Build out a library of internal training documents that you can update periodically
Building out a library of training documents, while it might take a bit of time up front, can really save time and money in the long run, because a team that’s aligned is a team that’s productive.
Onboarding guides, FAQs for new employees (like the fun onboarding FAQs below), and other process documentation can all help make remote onboarding easier, and help new employees feel comfortable and in control.

HR onboarding checklists can help avoid the headache of overlooked paperwork and unclear expectations. Having one checklist for the employee and one for your HR department will help keep everyone aligned and on top of their tasks.

If you’re ramping up to hire a mass of new employees, it may even be worth rethinking the design of your offer letter . After your new employee signs, you can send on their package of matching onboarding documents.

And once you create those documents, they should be easy to update and disseminate to new and existing team members, making your job even easier.
To summarize, here are your tips for communicating process changes on the fly:
- Show high- and low-level changes with hierarchical process diagrams
- Help your team keep track of changes with checklists
- Build a library of internal training documents that you can update periodically
3. How to simplify complex information with visuals
Perhaps the most powerful use of visual communication is to simplify complex information.
Just take this image that HubSpot posted on Twitter recently, for example. With one simple visual, they manage to position their product as the perfect solution to three problems experienced across three different teams:

This doesn’t just work for external communications on social media.
It can be the perfect approach for consultants looking to communicate their ideas and strategies to clients, in a quick and digestible way.
Or B2B organizations in technical fields looking to demystify the products and services they offer to differentiate from their competitors, without using a ton of technical language:

Or healthcare organizations looking to make recommendations clear to patients:

The four key steps for simplifying complex information with visuals are:
- Remove as much text as possible
- Use shapes like circles and rectangles to indicate groupings
- Use lines and borders to indicate flows and relationships
- Use color and size to draw attention to key information
Read More: How to Summarize Information Visually
4. How to visualize data and insights
Effective data visualization does more than just display some data from a spreadsheet.
It should communicate insights and capture ideas. It should communicate the why behind the trends.
It should help you answer the question often asked by busy people with competing demands: why should I care?
- Use the right chart for your data and your goal
The first thing to consider when visualizing data is what visual form will best communicate your insight.
At Venngage, we’ve developed the ICCOR method to help you choose the best charts for your infographic. The ICCOR method is a framework aimed to help you use a visualization type that aligns with your communication goal.
Your communication goal might be to:
- Inform : convey a single important message or data point that doesn’t require much context to understand
- Compare : show similarities or differences among values or parts of a whole
- Show Change : visualize trends over time or space
- Organize : show groups, patterns, rank or order
- Reveal Relationships : show correlations among variables or values
Each of these different goals will be best communicated with a different type of chart.
For example, icons arrays (also called ‘pictograms’) have been shown to be more effective than bar or pie charts for communicating risk , which is particularly important for healthcare providers and public health workers who want to support good decision making in their patients.
Bar charts, on the other hand, are perfect for handling larger amounts of data and highlighting comparisons between sets of data, which might be more important for those working in finance:

For access to professional templates, and a simple editor to visualize financial information, check out: Venngage for Finance
For the full ICCOR framework, check out: How to choose the best types of charts for your data
Choosing a chart is just one part of the process. How do you actually make an impact with your data?
- Tell a story with your data to inspire your audience
A plain old bar graph won’t do much to inspire your audience. But a creative combination of charts, visuals, text, and statistics that tells a story can.
By highlighting the right numbers and pulling in text and other visuals, you can show the impact of your organization in a more holistic way, and tell the story behind the data.

Storytelling with data is as much about crafting a narrative as it is about understanding and communicating the insights in your data.
The first step to crafting your narrative is understanding your audience. Think about:
- What’s going on in their lives?
- What knowledge do they have on the subject?
- What context do they need from you?
Once you understand your audience, it should be easy to pull out the insights that will make an impact, and present them in an impactful way. That’s the difference between an engaging design and your standard Excel chart.
Another common practice in data storytelling is the use of icon stories to draw viewers in and make abstract ideas more concrete.
Take this report from UNICEF, for example. The simple, universal icons are combined in different ways to create and reinforce key ideas, creating an impactful report that will be memorable for readers.

- Call out key insights and action items in the data
The impact of your hard work can easily get lost in a monthly or quarterly report.
But you can apply the design techniques typically used in infographics to make sure your efforts stand out of more traditional summative reports.
The trick is to do more with less. Get rid of data that doesn’t say anything, and emphasize the data that’s meaningful. Remove the noise to pull focus towards what’s useful.
Highlight key data points and add annotations to provide context to the most important data:

Here’s what to consider when visualizing your data and insights:
- Understand your audience and design with their knowledge in mind
Read more: Data visualization examples and best practices

If you’re not a full-time designer, one of your main concerns might be making sure your visual communications look professional.
You want to make sure you’re producing content that elevates your brand, and inspires your colleagues, donors, and stakeholders.
Here’s what you should think about:
Establish a cohesive visual brand for any external communications
It’s critical for any growing business to establish cohesive visual branding.
Especially for consumer-facing communications, like for your blog or social media, the quality of your visual brand signals to your customers about the quality of your organization.
Luckily, it’s pretty easy to ensure your branding feels consistent. Here’s how:
- Include the same header and footer with your logo across infographics, one-pagers, reports, and flyers
- Apply your brand fonts and colors consistently across all of your collateral
- Use the same style of symbols and icons across every document

As a shortcut, you can use Venngage’s Brand Kit to add your brand logos, fonts and colors to your designs with just a few clicks.
Read more: Don’t have your brand guidelines built out yet? Learn how to choose fonts and how to pick colors for designs, first.
Repurpose and reuse designs to keep your communications consistent
Reusing and repurposing existing designs can truly be a game changer.
For one, it’ll speed up your workflow. But more importantly, it’ll ensure that you’re producing communications that are consistent and cohesive.
Did I mention yet that your communications need to be cohesive?
You can repurpose the documents you’ve created for one client or project, add different content and tweak it a bit for a new client or a different target audience, to get a ton of mileage out of a small amount of design work.
Even if you’re just creating documents to share internally, like project summaries or company newsletters, you can set yourself and your team apart by producing documents that have a consistent visual style.
The recent rapid transition to remote work has propelled visual communication from a “nice-to-have” into an integral part of communication at work.
I hope you’ve already started thinking about how you can use visuals to amplify your communications.
Just remember to keep these design and visual communication principles in mind:
- Use modern design and visuals to make boring information engaging and differentiate yourself from your competitors
- Simplify your information to make an impact
- Use data visualization techniques to show the value of your work
- Create designs with a cohesive visual brand and reuse them to keep your communications consistent
For help getting started with visual communication and infographics, check out this guide: How to make an infographic in 5 steps .
Discover popular designs

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Types of communication

Ivan Andreev
Demand Generation & Capture Strategist, Valamis
January 19, 2021 · updated April 2, 2024
9 minute read
After reading this guide, you will better understand the four main types of communication: Verbal, non-verbal, written, and visual.
You will be able to use this information to improve your own communication and make sure that you are promoting effective communication skills within your organisation.
- Non-verbal communication
- Verbal communication
- Written communication
- Visual communication
4 Types of communication
While it is easy to think of communication as simply the verbal transmission of information from one person to another, it is so much more than that.
Communication ranges from non-verbal, such as a glance and raised eyebrows, to verbal, such as a change in pitch and tone. Let’s take an in-depth look at all the ways that we communicate with each other.
1. Non-verbal communication
It is interesting to note that non-verbal communication is used both intentionally and unintentionally.
Most people do not have perfect control over their facial expressions – we all have heard an unprofessional comment and raised our eyebrows in response, regardless of whether or not it was wise to do so.
By learning more about how we use non-verbal communication, you will be better able to master yours and ensure that you are conveying your message exactly the way you wish to.
Facial expressions
We often use facial expressions as a way to communicate that we are listening and engaged with the person speaking.
A smile, furrowed eyebrows, or a quizzical expression all convey information to the speaker about how you are responding to their conversation.
They work to help grease the conversation, keeping it going without having to interject verbally to confirm your continued interest.
If you have ever spoken to a stone-faced person, you will know how important facial expressions are in a conversation.
How you position yourself during a conversation is important.
If you angle yourself towards the person, with a relaxed and open posture, you invite them to engage with you more fully.
Leaning back, crossing arms, or turning away from the speaker conveys a very different message – and not a positive one.
Just as no one wants to have a conversation with the back of someone’s head, talking to someone with an extremely closed posture creates a more difficult and unpleasant conversation.
Gestures and physical touch
Depending on the person, and their country of origin, they may use gestures and physical touch a lot, or almost never. However, there is a lot of information conveyed in these actions.
A gentle touch on the arm can signal encouragement, while an overly strong handshake can be an act of dominance.
Someone fidgeting with their hands while talking to you about a problem can signal guilt or avoidance and using many grand gestures while presenting an idea could convey excitement or confidence.
Eye contact
We all know the importance of eye contact.
When someone is unable to maintain eye contact, we take this to mean that they are being untruthful, shifty, or not paying attention.
Being able to maintain eye contact while listening will ensure that the speaker knows that you are present and engaged.
While speaking, it shows that you are connecting with the listener, and in cases where you are delivering unpleasant news, is doubly important.
Being able to tell someone an unpleasant message while looking them directly in the eye shows that you respect them and are an honest and sincere person.
2. Verbal communication
When we speak, we are communicating much more than just the content of our words.
We are also using pitch and tone, as well as the level of formality we use to convey important subtext to the person we are speaking with.
By carefully choosing how we use each of these aspects, we can be sure that our message is received exactly as intended.
From greeting coworkers to leading a client pitch meeting to present in front of the entire company, verbal communication factors into our work lives in a massive way.
When speaking, our emotions can often come into play.
If we are angry, upset, or frustrated, our pitch might raise, conveying to the listener that we are experiencing a strong emotion.
This is not necessarily a bad thing, but being able to control it allows you to make sure that you are effectively communicating.
We all encounter situations that are frustrating or upsetting.
Allowing that to change our tone from calm and professional to curt, short, or rude is always a mistake.
Tone conveys a lot of information to the listener about how the speaker views them.
To build positive interpersonal relationships in an office environment, we should all endeavour to speak in a professional and respectful tone.
Of course, content is the most important part of verbal communication. What we say, and the words we choose to use, are crucial.
While most office communications tend to be more formal than, for example, meeting a friend for coffee, we should make sure that we leave space for personal chats and relationship building.
Think also about how technical your content is. If you are talking with developers about specific aspects of code, you should use different terms than when talking to the marketing team about new developments within the app.
3. Written communication
Effective communication by writing is a massively important skill, especially as more people are working remotely and keep in touch throughout the workday through Skype, Slack, or other digital mediums.
From a Slack message to an email to a customer to a new employee’s training guide, we write every day and it is crucial that we understand how to do so effectively.
In fact, as we increasingly rely on written communication, we are all faced with just how easy it is to create misunderstandings when using this medium.
Unclear messages, the information gone missing, or an incorrect understanding of tone or content are all problems that happen with written communication every day.
Sometimes the reader will misread the tone of a message because they are having a bad day, or just had a run-in with an unpleasant person.
No matter what, one important skill to have when relying on written communication is knowing when you need to stop using it. A simple call, in almost all cases, can solve these communication problems.
If you sense that there is a miscommunication happening, or just starting, nip it in the bud with a quick verbal chat and you’ll save a lot of time and frustration for all parties.
When writing, it is important to think about how you are presenting the information. Using paragraphs and line breaks are necessary.
Creating an impenetrable wall of text will disengage the reader – understanding and applying a proper structure will let the reader take in the information in digestible chunks.
Present your argument or thesis, take the time to back it up with clear proof, add in the relevant information to make sure that the reader understands the point fully, then close with a conclusion.
It is a hard balance to strike between over or under explaining concepts. If you are writing instructions for a new employee, how detailed should you be?
Of course, this depends on the person, but over-explaining a little bit is much better than leaving the reader clueless.
Be thoughtful about your audience, what will they know and what do you need to explain in more detail?
Written content tends to be a bit more formal than verbal.
Leave out the slang, use proper punctuation and spelling, and remember that anything written – especially in the digital age – will remain, even if you delete it.
Err on the side of professionalism every time you write something. Messages on Slack, for example, do not need to be written as formally as a cover letter, but they should be polite, professional, and well-written.
Be aware that written jokes can fall flat without the added context of tone or facial expressions.
4. Visual communication
Visual has become the most used type of communication, driven by social media, YouTube, and other platforms of the digital era.
As more and more people and organisations use these channels of communication, the more we are used to, and even dependent upon, using visual communication to stand out in a crowded platform.
Understanding that your visual communication must be in line with your brand and marketing, and knowing that there must be a developed and cohesive strategy for that, is crucial.
We rely heavily on visual communication.
There are many ways that visual communication, like charts, photographs, sketches, video, graphs, and even emojis and GIFs, can help improve the understanding of your message.
Think about how charts can bring data to life, making it much easier to understand than presenting a long stream of numbers, or how a sketch of a new UX is much more effective than a text description.
We rely on visuals to elevate our understanding of complex ideas.
While it is tempting to include visuals to add a bit of diversity and interest, you should consider what they bring to the table.
- Are they helpful?
- Are they necessary?
- Do they add to the overall message?
Not all communications need to have visuals added, and in some cases, they might detract from what you are trying to communicate.
You should endeavour to make sure that you are not adding fluff to your message, but rather strengthening your audience’s understanding of it.
As with all communications, make sure that you are meeting your audience where they are.
If you are presenting complex data, include the relevant descriptions, at the right technical level, so that your audience can follow.
Don’t use images that are graphic or could be upsetting, and remember the same rule applies to visual communication as does to writing: don’t create anything that you wouldn’t want to have associated with you in the future.
Develop and maintain a strategy-driven learning culture
Upgrade your organization’s learning culture with clear, actionable strategies to address the challenges.
You might be interested in
Career development plan
Learn what a career development plan is and how to create it. Discover examples and download the career development planning template in PDF.

No workforce can be effective with underlying skills gaps. Here we cover how to identify and address different skill gaps.

Gamification
Learn what gamification with real examples and find out how to develop effective gamification for your employees.
We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
Essays on the verbal and visual arts : proceedings of the 1966 annual spring meeting.
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
some text runs into the gutter.
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
115 Previews
3 Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
EPUB and PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station15.cebu on August 6, 2019
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Bigger Audience. Better yet, these sorts of essays can be shared online to make your argument to a larger audience. For example, not too many people will read your essay on homelessness, but many people might want to see your essay on the lives of homeless people in your town and the people who help the homeless in a soup kitchen (see "Depression Slideshow" or "My Photo Memory: Helping Others ...
A visual analysis essay is a common assignment for the students of history, art, and communications. It is quite a unique type of academic essay. Visual analysis essays are where images meet text. These essays aim to analyze the meanings embedded in the artworks, explaining visual concepts in a written form.
These examples help to show some of the basic strengths of this format which attempts ... vigorous - form of the visual essay. The relations between visual, auditory and verbal parts can be played out in many different ways. Both tight and loose relations between these expressive systems may be ... visual essays (e.g. Good Company, 1982 ...
A graphic essay (sometimes called a visual essay) uses a combination of text and images to explore a specific topic. Graphic essays can look like comics, graphic novels, magazines, collages, artist books, textbooks, or even websites. Graphic essays often first take the form of written essays and then have graphic elements added to enrich the ...
Visual Rhetoric: Overview. This section of the OWL discusses the use of rhetorical theory and rhetoric as it relates to visuals and design. "Visual rhetoric" has been used to mean anything from the use of images as argument, to the arrangement of elements on a page for rhetorical effect, to the use of typography (fonts), and more.
Explain the central theme or argument of your visual essay using simple visual and verbal communication. Keep your speech clear and concise while avoiding unnecessary complexity. Structuring Your ...
WHAT IS A VISUAL ESSAY? A visual essay can be an entirely visual piece or it can combine image and writing. The length of these essays varies (usually between 6 and 12 pages). A visual essay can focus on any social or political aspect of visual communication, it can be a response to the visual work of others, a commentary on visual processes ...
Visual essays can be powerful tools for conveying information and engaging audiences, as they appeal to both visual and verbal learners. They can also provide a creative outlet for writers and artists to express themselves and explore new ways of presenting information. ... Remember that visual essay examples are the key to success, because ...
Step 3: Create Your Outline. Creating an outline is one of the most important steps in crafting a great visual essay. An outline will help keep you focused on the task at hand and ensure that all of the information is organized in a logical manner. Start by making a list of main points or arguments that need to be addressed in the essay and ...
However, the poster's text clarifies its appeal and makes it explicit: "Join the Navy, the Service for Fighting Men." (Note: Here the argument shifts again into an analysis of the emotional appeal being made there. The characterization of the Navy as the "Service for Fighting Men," combined with the rodeo cowboy imagery, the inherent ...
The visual essay is an invitation to other researchers in the arts to create their own kind of visual essays in order to address their own work of art or that of others: they can consider their ...
Integrating two or more modalities in a given text results in multimodal writing. Visual rhetoric is a form of rhetoric that uses visual information—photographs, drawings, symbols, charts, maps, color, shapes, typography, white space—to communicate, to create meaning, or, more simply, to persuade (see chapter on rhetoric for a longer ...
The Video Essay. Video is a natural medium for personal narrative, and John Breslund is known as a pioneer of the visual essay form. This article includes a Q and A with Bresland and his collaborator, poet and essayist, Eula Biss, with links to some of their groundbreaking work including "Ode to Every Thing." 10. The Interactive Essay
The relationship, however, between the lingual and the visual tends to be one of asymmetry. The visual tends to be held in lower regard and thought of as 'dispensable embellishment' (Millard, E. and J. Marsh. [2001]. Words with pictures: the role of visual literacy in writing and its implication for schooling.
Visual analysis is a helpful tool in exploring art. It focuses on the following aspects: Interpretation of subject matter (iconography). An iconographic analysis is an explanation of the work's meaning. Art historians try to understand what is shown and why it is depicted in a certain way. The analysis of function.
The essay "An Image Is Worth a Thousand Calls to Arms" by Saramanda Swigart analyzes a visual argument. Sample visual argument analysis essay "An Image Is Worth a Thousand Calls to Arms" in PDF with margin notes; Sample visual argument analysis essay "An Image Is Worth a Thousand Calls to Arms" accessible version with notes in parentheses
Visual Rhetorical Analysis. In the vast realm of human communication, the potency of language transcends mere verbal or written expression. Visual rhetoric, an artful orchestration of images and symbols, exerts a profound influence on our perceptions, beliefs, and actions. From captivating advertisements to thought-provoking political campaigns ...
Some common visual communication strategies include: Using data visualization to show the impact of your work. Using shapes and lines to outline relationships, processes, and flows. Using symbols and icons to make information more memorable. Using visuals and data to tell stories. Using color to indicate importance and draw attention.
Verbal Visual Essay Examples - Ms. Lee's Class. Summatives 2016. Speech Assignment 2015/2016. ENG 1D. ENG 2D. ENG 4U.
Step 2: choose / create at least 6 visuals that relate to your quotes. Step 3: Combine quotes and visuals to create your 'Verbal-Visual Essay Project' in a creative and complete way (could be multimedia, poster, video, art, etc) Step 4: Separately, write a 3 paragraph description that explains your quotes, your visuals and information about ...
ÐÏ à¡± á> þÿ 9 ...
4 Types of communication. While it is easy to think of communication as simply the verbal transmission of information from one person to another, it is so much more than that. Communication ranges from non-verbal, such as a glance and raised eyebrows, to verbal, such as a change in pitch and tone. Let's take an in-depth look at all the ways ...
Advanced embedding details, examples, and help! Favorite. Share. Flag. Flag this item for. Graphic Violence ... Essays on the verbal and visual arts : proceedings of the 1966 annual spring meeting. by American Ethnological Society. Publication date 1967 Topics Ethnology Publisher Seattle : Distributed by the University of Washington Press ...