Writing a Thesis and Making an Argument
Almost every assignment you complete for a history course will ask you to make an argument. Your instructors will often call this your "thesis"– your position on a subject.

What is an Argument?
An argument takes a stand on an issue. It seeks to persuade an audience of a point of view in much the same way that a lawyer argues a case in a court of law. It is NOT a description or a summary.
- This is an argument: "This paper argues that the movie JFK is inaccurate in its portrayal of President Kennedy."
- This is not an argument: "In this paper, I will describe the portrayal of President Kennedy that is shown in the movie JFK."
What is a Thesis?
A thesis statement is a sentence in which you state an argument about a topic and then describe, briefly, how you will prove your argument.
- This is an argument, but not yet a thesis: "The movie ‘JFK’ inaccurately portrays President Kennedy."
- This is a thesis: "The movie ‘JFK’ inaccurately portrays President Kennedy because of the way it ignores Kennedy’s youth, his relationship with his father, and the findings of the Warren Commission."
A thesis makes a specific statement to the reader about what you will be trying to argue. Your thesis can be a few sentences long, but should not be longer than a paragraph. Do not begin to state evidence or use examples in your thesis paragraph.
A Thesis Helps You and Your Reader
Your blueprint for writing:
- Helps you determine your focus and clarify your ideas.
- Provides a "hook" on which you can "hang" your topic sentences.
- Can (and should) be revised as you further refine your evidence and arguments. New evidence often requires you to change your thesis.
- Gives your paper a unified structure and point.
Your reader’s blueprint for reading:
- Serves as a "map" to follow through your paper.
- Keeps the reader focused on your argument.
- Signals to the reader your main points.
- Engages the reader in your argument.
Tips for Writing a Good Thesis
- Find a Focus: Choose a thesis that explores an aspect of your topic that is important to you, or that allows you to say something new about your topic. For example, if your paper topic asks you to analyze women’s domestic labor during the early nineteenth century, you might decide to focus on the products they made from scratch at home.
- Look for Pattern: After determining a general focus, go back and look more closely at your evidence. As you re-examine your evidence and identify patterns, you will develop your argument and some conclusions. For example, you might find that as industrialization increased, women made fewer textiles at home, but retained their butter and soap making tasks.
Strategies for Developing a Thesis Statement
Idea 1. If your paper assignment asks you to answer a specific question, turn the question into an assertion and give reasons for your opinion.
Assignment: How did domestic labor change between 1820 and 1860? Why were the changes in their work important for the growth of the United States?
Beginning thesis: Between 1820 and 1860 women's domestic labor changed as women stopped producing home-made fabric, although they continued to sew their families' clothes, as well as to produce butter and soap. With the cash women earned from the sale of their butter and soap they purchased ready-made cloth, which in turn, helped increase industrial production in the United States before the Civil War.
Idea 2. Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main Idea: Women's labor in their homes during the first half of the nineteenth century contributed to the growth of the national economy.
Idea 3. Spend time "mulling over" your topic. Make a list of the ideas you want to include in the essay, then think about how to group them under several different headings. Often, you will see an organizational plan emerge from the sorting process.
Idea 4. Use a formula to develop a working thesis statement (which you will need to revise later). Here are a few examples:
- Although most readers of ______ have argued that ______, closer examination shows that ______.
- ______ uses ______ and ______ to prove that ______.
- Phenomenon X is a result of the combination of ______, ______, and ______.
These formulas share two characteristics all thesis statements should have: they state an argument and they reveal how you will make that argument. They are not specific enough, however, and require more work.
As you work on your essay, your ideas will change and so will your thesis. Here are examples of weak and strong thesis statements.
- Unspecific thesis: "Eleanor Roosevelt was a strong leader as First Lady." This thesis lacks an argument. Why was Eleanor Roosevelt a strong leader?
- Specific thesis: "Eleanor Roosevelt recreated the role of the First Lady by her active political leadership in the Democratic Party, by lobbying for national legislation, and by fostering women’s leadership in the Democratic Party." The second thesis has an argument: Eleanor Roosevelt "recreated" the position of First Lady, and a three-part structure with which to demonstrate just how she remade the job.
- Unspecific thesis: "At the end of the nineteenth century French women lawyers experienced difficulty when they attempted to enter the legal profession." No historian could argue with this general statement and uninteresting thesis.
- Specific thesis: "At the end of the nineteenth century French women lawyers experienced misogynist attacks from male lawyers when they attempted to enter the legal profession because male lawyers wanted to keep women out of judgeships." This thesis statement asserts that French male lawyers attacked French women lawyers because they feared women as judges, an intriguing and controversial point.
Making an Argument – Every Thesis Deserves Its Day in Court
You are the best (and only!) advocate for your thesis. Your thesis is defenseless without you to prove that its argument holds up under scrutiny. The jury (i.e., your reader) will expect you, as a good lawyer, to provide evidence to prove your thesis. To prove thesis statements on historical topics, what evidence can an able young lawyer use?
- Primary sources: letters, diaries, government documents, an organization’s meeting minutes, newspapers.
- Secondary sources: articles and books from your class that explain and interpret the historical event or person you are writing about, lecture notes, films or documentaries.
How can you use this evidence?
- Make sure the examples you select from your available evidence address your thesis.
- Use evidence that your reader will believe is credible. This means sifting and sorting your sources, looking for the clearest and fairest. Be sure to identify the biases and shortcomings of each piece of evidence for your reader.
- Use evidence to avoid generalizations. If you assert that all women have been oppressed, what evidence can you use to support this? Using evidence works to check over-general statements.
- Use evidence to address an opposing point of view. How do your sources give examples that refute another historian’s interpretation?
Remember -- if in doubt, talk to your instructor.
Thanks to the web page of the University of Wisconsin at Madison’s Writing Center for information used on this page. See writing.wisc.edu/handbook for further information.
Module 9: The New Deal (1932-1941)
Historical arguments and thesis statements, learning objectives.
- Evaluate historical claims and thesis statements
The Research Writing Process
In an earlier historical hack, we talked about the research writing process, as shown below:
- Understand the assignment
- Select a research topic/develop a research question
- Conduct research: find and evaluate sources
- Create your claim (make an argument)
- Synthesize evidence
- Put it together
These are guidelines to help you get started, but the process is iterative, so you may cycle through these steps several times while working towards your finished product. In this hack, we want to focus on the final three steps—once you’ve done your research and have a few ideas about what to say, how do you put it together to create your finished product?
Crafting Historical Arguments
In open-ended historical research assignments, you are almost always expected to create an argument (revisit the assignment prompt or ask your instructor if you’re unsure about this). Historical arguments are not like the arguments that you and your roommate might have about the best show on T.V. or an argument you’d have with the referee at a sporting event; historical arguments require you to pick a stance on an issue and defend it with supporting evidence.
Your objective is not to create an informal persuasive essay convincing others of your viewpoint based on your personal opinions, but an argumentative one, where you defend your stance on an issue by backing it with historical evidence. Argumentative writing is done for a formal, academic purpose— you have a compelling viewpoint on a topic, and you’ve conducted research. Now you are communicating that research and using evidence to back your claim. When you write an argumentative piece, you write as if you are the authority on the topic, a subject-matter expert.
The Differences Between Persuasive and Argumentative Writing
Check out the table below for a quick breakdown of the differences between persuasive and argumentative writing.
Sometimes it can be hard to tell a topic from an argument. If someone sees you reading an article and asks, “What’s that article about?” You might say, “It’s about photography during the Great Depression.” That’s a topic, not an argument. How do we know? You can’t disagree with “photography during the Great Depression.” An argument is something you could disagree with, like “Photography during the Great Depression was essential in bringing the realities of poverty into the public eye.”
Argumentative Statements
Understand the assignment.
Don’t forget the first step in approaching a research paper or assignment—to carefully understand what you are asked to do. Some assignments are more obviously arguments than others. They may ask you to pick an obvious side, like “Was the New Deal effective or ineffective?” Or “How do you think the government should address reparations for slavery? Or “Was the American Revolution really a revolution?”
Understanding Argumentative Statements
Other times the “argument” part is less obvious. The prompt may be more generic or broad. Let’s take a look at this option for a capstone assignment in this class:
Pick a reformer or activist involved with a social movement between 1877 and 1900. Evaluate and analyze the ideas, agenda, strategies, and effectiveness of the work done by your chosen reformer or activist. You can pick one aspect of the person’s involvement or significance to the movement to focus on in your research. You should make a claim in your final report that answers one of the questions below:
- What was the influence of your person on American life during their time period?
- What is their influence and legacy today?
- What changes came about as a direct result of their activism?
- What obstacles stood in the way of this person from having a more significant impact on society?
- What activism methods used by your reformer were most effective, and why?
- How did their activism compare or contrast with other reform movements from the same time period?
- How are things different today because of their activism? In what ways are things the same?
- Why should people be aware of the work done by your chosen reformer?
- Can you draw any connections to a modern-day reform movement— what reform movement might they support today, and why?
With this prompt, you are tasked with creating an argument about the reformer or activist you chose. It is not simply a narrative or biography where you report about their lives, but you want to pick one of the listed questions to create an argument—something that shows your ability to take a stance (that could be debated by others) and support your view with evidence.
Activity #1
Give it a try—without even doing some research- what argumentative statement could you make about a 19th-century activist?
Let’s take a look at a more detailed example. For example, say that your chosen activist was Bayard Rustin , a Black activist who was instrumental in organizing the 1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. What’s an argument you could make about Rustin?
Here is one option. “While you’ve heard of Martin Luther King Jr.’s famous “I Have a Dream Speech” during the 1963 March on Washington, you may not have heard of Bayard Rustin, whose involvement in planning the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom was essential in propelling Congress to pass the Civil Rights Act of 1964. As the deputy director of the March, Rustin’s background in nonviolence and vision for the March led leaders to prioritize the civil rights movement and gave public backing to the federal law prohibiting racial discrimination.”
As you’ll learn in just a moment, this argument is what becomes the thesis statement.
Begin With a Thesis
The central claim you make in your argument is called the thesis statement . A thesis consists of a specific topic and an angle on the topic. All of the other ideas in the text support and develop the thesis.
Where in the Essay Should the Thesis Be Placed?
The thesis statement is often found in the introduction, sometimes after an initial “hook” or interesting story; sometimes, however, the thesis is not explicitly stated until the end of an essay, and sometimes it is not stated at all. In those instances, there is an implied thesis statement. You can generally extract the thesis statement by looking for a few key sentences and ideas.
Most readers expect to see the point of your argument (the thesis statement) within the first few paragraphs. This does not mean that it has to be placed there every time. Some writers place it at the very end, slowly building up to it throughout their work, to explain a point after the fact. For history essays, most professors will expect to see a clearly discernible thesis sentence in the introduction.
Characteristics of a Thesis Statement
Thesis statements vary based on the rhetorical strategy of the essay, but thesis statements typically share the following characteristics:
- Presents the main idea
- Most often is one sentence
- It tells the reader what to expect
- Is a summary of the essay topic
- Usually worded to have an argumentative edge
- Written in the third person
Crafting strong argumentative writing is a skill that teaches you how to engage in research, communicate the findings of that research, and express a point of view using supporting evidence.
Link to learning
For a few more examples of how to create arguments and thesis statements, visit this helpful writing guide .
What Makes a Good Claim?
Let’s take a closer look at this process by reviewing a worked example. For this example, we will use a topic you’ve studied recently—the FDR presidency and New Deal. Let’s imagine you’ve been assigned the following prompt:
- Did New Deal spending and programs succeed in restoring American capitalism during the Great Depression, and should the government have spent more money to help the New Deal succeed, or did the New Deal spend unprecedented amounts of money on relief and recovery efforts but ultimately fail to stimulate a full economic recovery?
You’ve already examined the prompt, selected a research topic, and conducted research, and now you are ready to make your claim. First, what claim do you want to make?
Identify the Claim
Let’s look at a sample introductory paragraph that responds to this prompt. Look for the central claim made in the argument.
Example ESSAY #1
Since the stock market crash and the onset of the depression, British economists John Maynard Keynes, Roy Harrod, and others had urged western governments to stop tinkering with monetary solutions and adopt an aggressive program of government spending, especially in the areas of public works and housing, to stimulate the economy during the depression. Keynes stressed these ideas when he met with President Roosevelt, who soon complained to labor secretary Frances Perkins: “He [Keynes] left a whole rigamarole of figures. He must be a mathematician rather than a political economist.” Roosevelt’s comments about Keynes opened a window on one fundamental reason why the president’s New Deal, despite unprecedented federal spending, never achieved full economic recovery between 1933 and 1940. Although surrounded by critical advisers such as Federal Reserve chairman Marriner Eccles, who understood Keynes and his central message about the importance of government spending, Roosevelt did not grasp these ideas intellectually. He remained at heart a fiscal conservative, little different from Herbert Hoover. Roosevelt condoned government spending when necessary to “prime the pump” for recovery and combat hunger and poverty, but not as a deliberate economic recovery tool.
Let’s look at yet another example. This also responds to this same prompt which you can find again below for reference:
Example ESSAY #2
When President Franklin Delano Roosevelt gave his inaugural address on March 4, 1933, America was in the midst of financial collapse. Banking holidays closed banks in 28 states, and investors traded their dollars for gold to have tangible wealth. The president reassured Americans” “This great Nation will endure as it has endured and will revive and will prosper.” He listed three goals to shore up capitalism through his New Deal: banking regulation, laws to curb speculation, and the establishment of a sound currency basis. Roosevelt shored up the financial sector through regulation to restore the public trust that mismanaged banks, and financial speculators had destroyed. His New Deal gave the federal government regulatory responsibility to smooth economic downturns. Over the next eight years, the New Deal’s economic practices and spending helped create recovery and restore capitalism.
Finding the Thesis Statement
You’ve found the central claims from each of these two sample essays. Quite often, the claim is the thesis statement. But sometimes, the thesis statement elaborates on the claim more by including the angle you’ll take about your claim. In the sample essay above, the thesis statement is written in reverse order, with the primary claim coming at the end, but if you read the sentences before that, you can see what the essay’s focus will be as well.”
- “Roosevelt shored up the financial sector through regulation to restore the public trust that mismanaged banks, and financial speculators had destroyed. His New Deal gave the federal government regulatory responsibility to smooth economic downturns. Over the next eight years, the New Deal’s economic practices and spending helped create recovery and restore capitalism”.”
Now we know that the rest of the essay will focus on how the New Deal’s economic practices and spending habits helped the recovery and also show 1) ways that Roosevelt shored up the financial sector and 2) gave the federal government regulatory responsibility.
Pick a reformer or activist involved with a social movement between 1877 and 1900. Pick two questions below and write a thesis statement explaining the main claim and angle you would take in an essay about the topic.
- What changes came about as a direct result of their activism?
Thesis statement #1:
Thesis statement #2:
thesis statement : a statement of the topic of the piece of writing and the angle the writer has on that topic
- Historical Hack: Crafting Historical Arguments. Authored by : Kaitlyn Connell for Lumen Learning. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Analyzing Documents Using the HAPPY Analysis. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-ushistory2/chapter/analyzing-documents-using-the-happy-analysis/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Secondary source. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secondary_source . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- What is an argument?. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/englishcomp1coreq/chapter/introduction-to-what-is-an-argument/ . Project : English Composition I Corequisite. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Did the New Deal End the Great Depression?. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:WWZKMA1o@2/12-16-%F0%9F%92%AC-Did-the-New-Deal-End-the-Great-Depression . Project : Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]
Handbook for Historians
- Choosing a Paper Topic
What is a Thesis Statement?
How to develop a thesis statement.
- What Sources Can I use?
- Gathering sources
- Find Primary Sources
- Paraphrasing and Quoting Sources
- How to create an Annotated Bibliography
- Formatting Endnotes/Footnotes
- Formatting Bibliographies
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Sample Papers
- Research Paper Checklist
The thesis statement summarizes the central argument of your paper. It is placed at the top of the outline page, and appears again in the opening paragraph. A clearly stated thesis performs three functions:
- it provides a focus for your research, helping to prevent time wasting digressions
- it furnishes an organizational theme for the paper, which then becomes easier to write
- it gives the reader precise knowledge of what the paper will argue, thereby making it easier to read
You cannot formulate a thesis statement until you know a great deal about your subject. It is often wise to begin your research in pursuit of the answer to a question about your topic - but this question is not a thesis statement. A helpful web site that can advise you on how to formulate a thesis is: http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/thesis-statements/
Guidelines for formulating the thesis statement are as follows:
- The thesis must focus on a single contention. You cannot list multiple reasons for the “truth” of your contention because the paper must follow a unified line of reasoning; a multifaceted thesis statement prevents this.
- The thesis must be precisely phrased and coherent . Generalizations and a failure to define terms results in vagueness and lack of direction in argumentation.
- The thesis must be a declarative statement. The object of your research was to answer a question; when you found the answer, you embodied it in your thesis statement. Hence a thesis can never be a question.
Here are some examples of thesis statements that strive to incorporate these recommendations...
POOR : Miguel Hidalgo’s uprising in 1810 led to a long war for independence in Mexico. WHY: The above-stated thesis is a statement of fact that provides no clue about what you plan to do with that fact in your paper. Since there is no argument here, this is not a thesis. Improved : Miguel Hidalgo’s 1810 uprising mobilized poor and native Mexicans whose violence frightened elites and prolonged the war for independence. WHY: The above-stated thesis very specifically explains why the uprising resulted in a long war for independence. What’s more, it is debatable, since there may be other explanations for the war’s length.
POOR : The creation of Israeli settlements in the West Bank and Gaza created great tension between the Israelis and Palestinians for numerous reasons. WHY : The above-stated thesis is poor because it is too general and it deals with the obvious – that there is tension between Israelis and Palestinians in the Middle East. It needs to explain what the “numerous reasons” are; focus on one of them; and drop the reference to the obvious. Remember: a thesis statement makes a specific argument and here only a vague reference to multiple reasons for tension is provided. Improved : The creation of Israeli settlements in the West Bank and Gaza was both an expression of Zionist expansionism and a means to isolate Palestinian population centers. WHY : The above-stated thesis is much better because it explains what the “numerous reasons” are and focuses on one of them. Now an argument has been created because a concrete explanation has been stated. Also, this statement removes the obvious fact that tension exists between the two ethnic groups.
POOR : Louis XIV was a strong king who broke the power of the French nobility. WHY : The above-stated thesis contains a vague judgment about Louis XIV; that he was “strong.” In addition, it fails to specify exactly how he broke the nobles’ power. Improved : The Intendant System was the most effective method used by Louis XIV to break the power of the French nobility. WHY : The above-stated thesis eliminates the vague word “strong” and specifies the mechanism Louis XIV used to break the nobles’ power. Moreover, since this was not the only policy Louis XIV used in his efforts to control the nobles, you have shown that your paper will defend a debatable position.
POOR : Gandhi was a man of peace who led the Indian resistance movement to British rule. WHY : The above-stated thesis does not clarify what about Gandhi made him a man of peace, nor does it specify anything he did to undermine British rule. Improved : Gandhi employed passive non-resistance during his Great Salt March and that enabled him to organize the Indian masses to resist British rule. WHY : The above-stated thesis specifies what has caused Gandhi to be remembered as a man of peace (his promotion of passive non-resistance to oppression) and it names one of the protests he organized against British rule. In addition, since it suggests that the technique of passive non-resistance is what made the Indian populace rally behind him, it is debatable; there were other reasons why the poor in particular were ready to protest the British monopoly on salt.
- << Previous: Outline
- Next: Main Body >>
- Last Updated: Feb 21, 2024 8:00 PM
- URL: https://resources.library.lemoyne.edu/guides/history/handbook
College of Arts and Sciences
History and American Studies
- What courses will I take as an History major?
- What can I do with my History degree?
- History 485
- History Resources
- What will I learn from my American Studies major?
- What courses will I take as an American Studies major?
- What can I do with my American Studies degree?
- American Studies 485
- For Prospective Students
- Student Research Grants
- Honors and Award Recipients
- Phi Alpha Theta
Alumni Intros
- Internships
Thesis Statements
Every paper must argue an idea and every paper must clearly state that idea in a thesis statement.
A thesis statement is different from a topic statement. A topic statement merely states what the paper is about. A thesis statement states the argument of that paper.
Be sure that you can easily identify your thesis and that the key points of your argument relate directly back to your thesis.
Topic statements:
This paper will discuss Harry Truman’s decision to drop the bomb on Hiroshima.
The purpose of this paper is to delve into the mindset behind Truman’s decision to drop the bomb on Hiroshima.
This paper will explore how Harry Truman came to the decision to drop the bomb on Hiroshima.
Thesis statements:
Harry Truman’s decision to drop the bomb on Hiroshima was motivated by racism.
The US confrontation with the Soviets was the key factor in Truman’s decision to drop the bomb on Hiroshima.
This paper will demonstrate that in his decision to drop the bomb on Hiroshima, Truman was unduly influenced by hawks in his cabinet.

How have History & American Studies majors built careers after earning their degrees? Learn more by clicking the image above.
Recent Posts
- Fall 2023 Symposium – 12/8 – All Welcome!
- Spring ’24 Course Flyers
- Internship Opportunity – Chesapeake Gateways Ambassador
- Congratulations to our Graduates!
- History and American Studies Symposium–April 21, 2023
- The Poe Museum Internships (Richmond, VA)
- Summer Internship: Hunter House Victorian Museum (Norfolk, VA)
- View umwhistory’s profile on Facebook
- View umwhistory’s profile on Twitter

Writing a History Paper
- Reading Your Assignment
- Picking a Topic
Developing a Thesis Statement
- Subject Guide
- Planning Your Research
- Executing Your Research Plan
- Evaluating Your Research
- Writing Your Paper
- Additional Resources
- If We Don't Have What You Need
- History Homepage This link opens in a new window
Usually papers have a thesis, an assertion about your topic. You will present evidence in your paper to convince the reader of your point of view. Some ways to help you develop your thesis are by:
- stating the purpose of the paper
- asking a question and then using the answer to form your thesis statement
- summarizing the main idea of your paper
- listing the ideas you plan to include, then see if they form a group or theme
- using the ponts of controversy, ambiguity, or "issues" to develop a thesis statement
If you're having trouble with your thesis statement, ask your professor for help or visit the Student Academic Success Center: Communication Support . Your thesis may become refined, revised, or changed as your research progresses. Perhaps these sites may be helpful:
- Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences ( CMU Student Academic Success Center : Communication Support)
- Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements (Purdue OWL - Online Writing Lab)
- Developing a Thesis Statement (Writing Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison)
- Thesis Statements (The Writing Center at UNC-Chapel Hill)
- << Previous: Picking a Topic
- Next: Planning Your Research >>
- Last Updated: Oct 3, 2022 3:37 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.cmu.edu/historypaper
- Request Info
- Resource Library
How to Research and Write a Compelling History Thesis

Just as history is more than a collection of facts about past events, an effective history thesis goes beyond simply sharing recorded information. Writing a compelling history thesis requires making an argument about a historical fact and, then, researching and providing a well-crafted defense for that position.
With so many sources available—some of which may provide conflicting findings—how should a student research and write a history thesis? How can a student create a thesis that’s both compelling and supports a position that academic editors describe as “concise, contentious, and coherent”?
Key steps in how to write a history thesis include evaluating source materials, developing a strong thesis statement, and building historical knowledge.
The Importance of Research for Writing a History Thesis
Compelling theses provide context about historical events. This context, according to the reference website ThoughtCo., refers to the social, religious, economic, and political conditions during an occurrence that “enable us to interpret and analyze works or events of the past, or even the future, rather than merely judge them by contemporary standards”.
The context supports the main point of a thesis, called the thesis statement, by providing an interpretive and analytical framework of the facts, instead of simply stating them. Research uncovers the evidence necessary to make the case for that thesis statement.
To gather evidence that contributes to a deeper understanding of a given historical topic, students should reference both primary and secondary sources of research.
Primary Sources
Primary sources are firsthand accounts of events in history, according to Professor David Ulbrich, director of Norwich University’s online Master of Arts in History program. These sources provide information not only about what happened and how it happened but also why it happened.
Primary sources can include letters, diaries, photos, and videos as well as material objects such as “spent artillery shells, architectural features, cemetery headstones, chemical analysis of substances, shards of bowls or bottles, farming implements, or earth or environmental features or factors,” Ulbrich says. “The author of the thesis can tell how people lived, for example, by the ways they arranged their material lives.”
Primary research sources are the building blocks to help us better understand and appreciate history. It is critical to find as many primary sources from as many perspectives as possible. Researching these firsthand accounts can provide evidence that helps answer those “what”, “how”, and “why” questions about the past, Ulbrich says.
Secondary Sources
Secondary sources are materials—such as books, articles, essays, and documentaries—gathered and interpreted by other researchers. These sources often provide updates and evaluation of the thesis topic or viewpoints that support the theories presented in the thesis.
Primary and secondary sources are complementary types of research that form a convincing foundation for a thesis’ main points.
How to Write a History Thesis
What are the steps to write a history thesis? The process of developing a thesis that provides a thorough analysis of a historical event—and presents academically defensible arguments related to that analysis—includes the following:
1. Gather and Analyze Sources
When collecting sources to use in a thesis, students should analyze them to ensure they demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the materials. A student should evaluate the attributes of sources such as their origin and point-of-view.
An array of primary and secondary sources can help provide a thorough understanding of a historical event, although some of those sources may include conflicting views and details. In those cases, the American Historical Association says, it’s up to the thesis author to determine which source reflects the appropriate point-of-view.
2. Develop a Thesis Statement
To create a thesis statement, a student should establish a specific idea or theory that makes the main point about a historical event. Scribbr, an editing website, recommends starting with a working thesis, asking the question the thesis intends to answer, and, then, writing the answer.
The final version of a thesis statement might be argumentative, for example, taking a side in a debate. Or it might be expository, explaining a historical situation. In addition to being concise and coherent, a thesis statement should be contentious, meaning it requires evidence to support it.
3. Create an Outline
Developing a thesis requires an outline of the content that will support the thesis statement. Students should keep in mind the following key steps in creating their outline:
- Note major points.
- Categorize ideas supported by the theories.
- Arrange points according to the importance and a timeline of events addressed by the thesis.
- Create effective headings and subheadings.
- Format the outline.
4. Organize Information
Thesis authors should ensure their content follows a logical order. This may entail coding resource materials to help match them to the appropriate theories while organizing the information. A thesis typically contains the following elements.
- Abstract —Overview of the thesis.
- Introduction —Summary of the thesis’ main points.
- Literature review —Explanation of the gap in previous research addressed by this thesis.
- Methods —Outline how the author reviewed the research and why materials were selected.
- Results —Description of the research findings.
- Discussion —Analysis of the research.
- Conclusion —Statements about what the student learned.
5. Write the Thesis
Online writing guide Paperpile recommends that students start with the literature review when writing the thesis. Developing this section first will help the author gain a more complete understanding of the thesis’ source materials. Writing the abstract last can give the student a thorough picture of the work the abstract should describe.
The discussion portion of the thesis typically is the longest since it’s here that the writer will explain the limitations of the work, offer explanations of any unexpected results, and cite remaining questions about the topic.
In writing the thesis, the author should keep in mind that the document will require multiple changes and drafts—perhaps even new insights. A student should gather feedback from a professor and colleagues to ensure their thesis is clear and effective before finalizing the draft.
6. Prepare to Defend the Thesis
A committee will evaluate the student’s defense of the thesis’ theories. Students should prepare to defend their thesis by considering answers to questions posed by the committee. Additionally, students should develop a plan for addressing questions to which they may not have a ready answer, understanding the evaluation likely will consider how the author handles that challenge.
Developing Skills to Write a Compelling History Thesis
When looking for direction on how to write a history thesis, Norwich University’s online Master of Arts in History program can provide the needed skills and knowledge. The program’s tracks and several courses—taken as core classes or as electives in multiple concentrations—can provide a strong foundation for thesis work.
Master of Arts in History Tracks
In the Norwich online Master of Arts in History program, respected scholars help students improve their historical insight, research, writing, analytical, and presentation skills. They teach the following program tracks.
- Public History —Focuses on the preservation and interpretation of historic documents and artifacts for purposes of public observation.
- American History —Emphasizes the exploration and interpretation of key events associated with U.S. history.
- World History —Prepares students to develop an in-depth understanding of world history from various eras.
- Legal and Constitutional History —Provides a thorough study of the foundational legal and constitutional elements in the U.S. and Europe.
Master of Arts in History Courses
Norwich University’s online Master of Arts in History program enables students to customize studies based on career goals and personal interests through the following courses:
- Introduction to History and Historiography —Covers the core concepts of history-based study and research methodology, highlighting how these concepts are essential to developing an effective history thesis.
- Directed Readings in History —Highlights different ways to use sources that chronicle American history to assist in researching and writing a thorough and complete history thesis.
- Race, Gender, and U.S. Constitution —Explores key U.S. Supreme Court decisions relating to national race and gender relations and rights, providing a deeper context to develop compelling history theses.
- Archival Studies —Breaks down the importance of systematically overseeing archival materials, highlighting how to build historical context to better educate and engage with the public.
Start Your Path Toward Writing a Compelling History Thesis
For over two centuries, Norwich University has played a vital role in history as America’s first private military college and the birthplace of the ROTC. As such, the university is uniquely positioned to lead students through a comprehensive analysis of the major developments, events, and figures of the past.
Explore Norwich University’s online Master of Arts in History program. Start your path toward writing a compelling history thesis and taking your talents further.
Recommended Readings
Achieving Your Educational Goals: The Ultimate Guide to Getting the Most from a Master’s Degree What Can I Do With a History Degree? Defining Different Career Tracks What Is Digital History? A Guide to Digital History Resources, Museums, and Job Description
Writing History: An Introductory Guide to How History Is Produced , American Historical Association How to Write a Thesis Statement , Scribbr The Importance of Historic Context in Analysis and Interpretation , ThoughtCo. 7 Reasons Why Research Is Important , Owlcation Primary and Secondary Sources , Scribbr Secondary Sources in Research , ThoughtCo. Analysis of Sources , History Skills Research Paper Outline , Scribbr How to Structure a Thesis , Paperpile Writing Your Final Draft , History Skills How to Prepare an Excellent Thesis Defense , Paperpile
25 Thesis Statement Examples
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
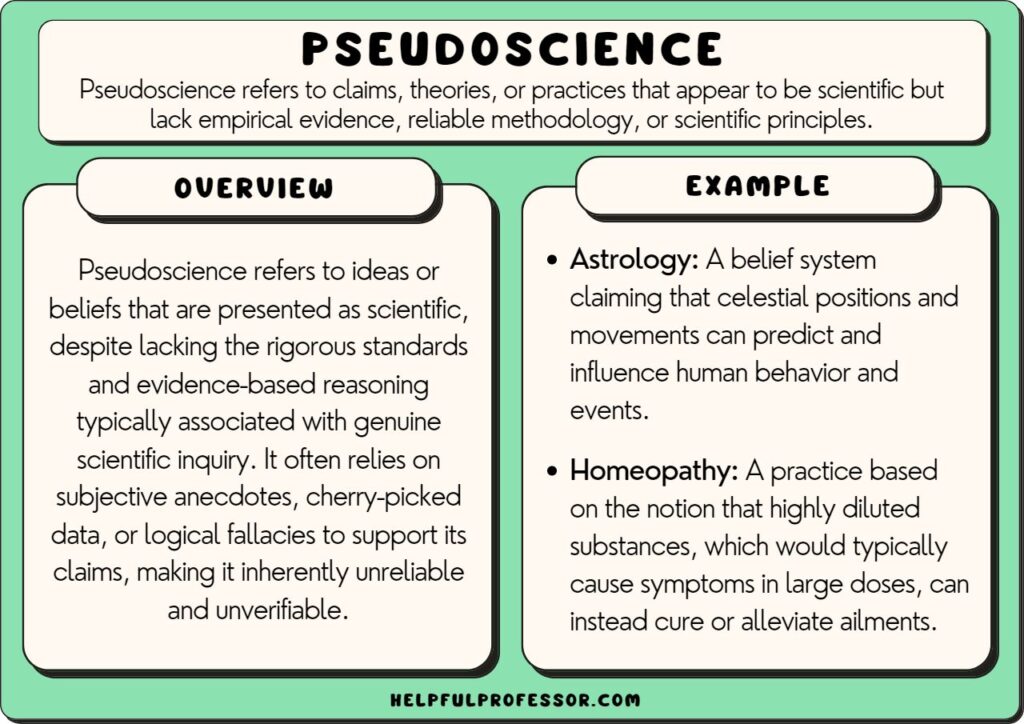
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
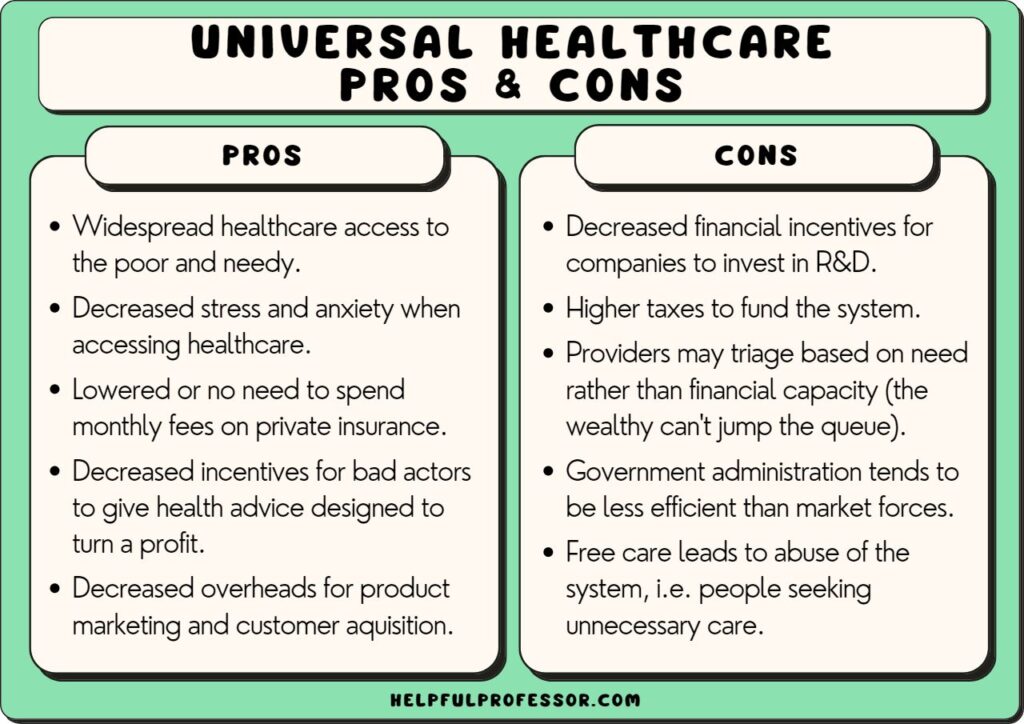
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
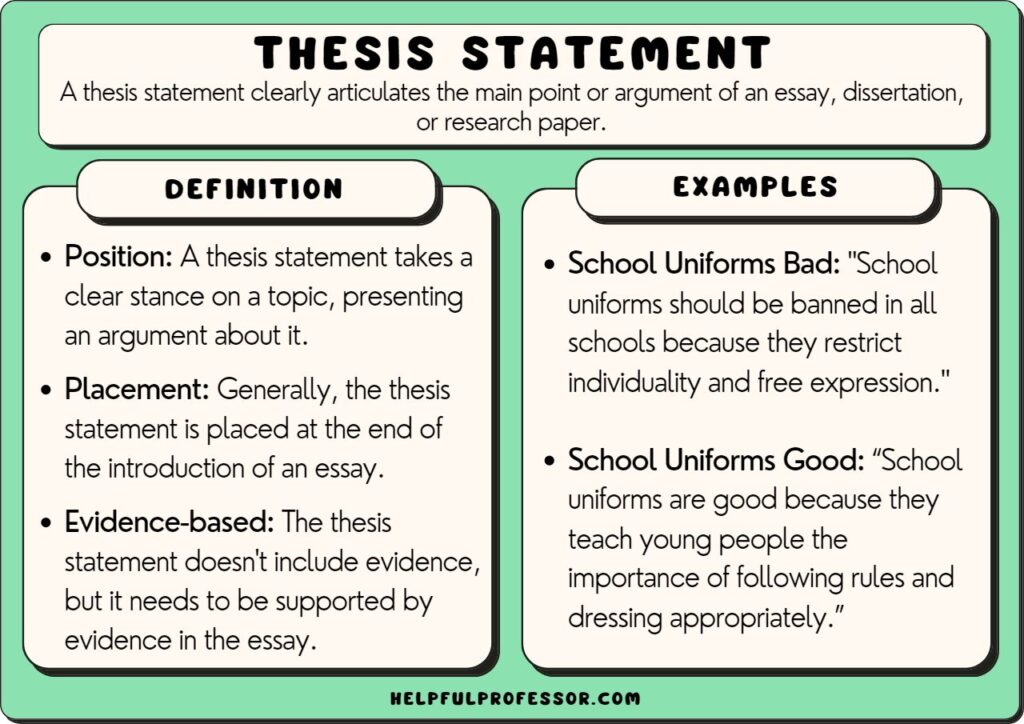
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
2021 2022 History Fair - Debate and Diplomacy in History: Writing a Thesis Statement
- What is History Fair?
- History Fair Theme
- Potential Topics
- Logging in, Creating a Project, and Sharing in Noodletools
- Building Context and Understanding Your Topic
- Writing a Thesis Statement
- Primary and Secondary Sources: What's the difference?
- Finding Secondary Sources
- Cite Secondary Sources
- Finding Primary Sources
- Cite Primary Sources
- Creating Your Website
Goals and Guiding Questions
- Understand the purpose of a thesis statement.
- Understand the parts of a thesis statement and how to write one.
- Create a thesis statement for your History Fair project.
Guiding Questions:
- How is a thesis statement different from a research question?
- What do I include in my thesis statement?
- What is my thesis statement for my HF project?
Your Thesis Statement MUST:
Give specific details
Go beyond facts to discuss the importance of a topic on history (impact, significance)
Show the topic's connection to the theme – Debate and Diplomacy

Thesis Statement Worksheet and Example
Thesis statement tips, thesis statement tips: .
1.) Don't Use the First Person
2.) Don’t ask questions in your thesis. Answer them!
3.) Don't use present tense.
4.) Avoid using “should” in your thesis.This is a historical argument, not philosophy.
5.) Avoid 'what if" history. Focus on what actually happened.
Writing Your Thesis Statement
Find the five ws:.
Who is involved in your topic?
What is happening?
Where is your topic taking place?
What time period is your topic in?
Why is this topic important? (significance, impa ct)
Look at these Thesis Statement Examples
- Thesis Statement Comparisons
- << Previous: Building Context and Understanding Your Topic
- Next: Primary and Secondary Sources: What's the difference? >>
- Last Updated: Feb 24, 2022 10:21 AM
- URL: https://mehs.morton201.libguides.com/c.php?g=1202807
How to Write a History Essay with Outline, Tips, Examples and More

Before we get into how to write a history essay, let's first understand what makes one good. Different people might have different ideas, but there are some basic rules that can help you do well in your studies. In this guide, we won't get into any fancy theories. Instead, we'll give you straightforward tips to help you with historical writing. So, if you're ready to sharpen your writing skills, let our history essay writing service explore how to craft an exceptional paper.
What is a History Essay?
A history essay is an academic assignment where we explore and analyze historical events from the past. We dig into historical stories, figures, and ideas to understand their importance and how they've shaped our world today. History essay writing involves researching, thinking critically, and presenting arguments based on evidence.
Moreover, history papers foster the development of writing proficiency and the ability to communicate complex ideas effectively. They also encourage students to engage with primary and secondary sources, enhancing their research skills and deepening their understanding of historical methodology.
History Essay Outline
.png)
The outline is there to guide you in organizing your thoughts and arguments in your essay about history. With a clear outline, you can explore and explain historical events better. Here's how to make one:
Introduction
- Hook: Start with an attention-grabbing opening sentence or anecdote related to your topic.
- Background Information: Provide context on the historical period, event, or theme you'll be discussing.
- Thesis Statement: Present your main argument or viewpoint, outlining the scope and purpose of your history essay.
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context
- Provide background information on the historical context of your topic.
- Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay.
Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence
- Each paragraph should focus on a specific argument or aspect of your thesis.
- Present evidence from primary and secondary sources to support each argument.
- Analyze the significance of the evidence and its relevance to your history paper thesis.
Counterarguments (optional)
- Address potential counterarguments or alternative perspectives on your topic.
- Refute opposing viewpoints with evidence and logical reasoning.
- Summary of Main Points: Recap the main arguments presented in the body paragraphs.
- Restate Thesis: Reinforce your thesis statement, emphasizing its significance in light of the evidence presented.
- Reflection: Reflect on the broader implications of your arguments for understanding history.
- Closing Thought: End your history paper with a thought-provoking statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
References/bibliography
- List all sources used in your research, formatted according to the citation style required by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include both primary and secondary sources, arranged alphabetically by the author's last name.
Notes (if applicable)
- Include footnotes or endnotes to provide additional explanations, citations, or commentary on specific points within your history essay.
History Essay Format
Adhering to a specific format is crucial for clarity, coherence, and academic integrity. Here are the key components of a typical history essay format:
Font and Size
- Use a legible font such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri.
- The recommended font size is usually 12 points. However, check your instructor's guidelines, as they may specify a different size.
- Set 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Double-space the entire essay, including the title, headings, body paragraphs, and references.
- Avoid extra spacing between paragraphs unless specified otherwise.
- Align text to the left margin; avoid justifying the text or using a centered alignment.
Title Page (if required):
- If your instructor requires a title page, include the essay title, your name, the course title, the instructor's name, and the date.
- Center-align this information vertically and horizontally on the page.
- Include a header on each page (excluding the title page if applicable) with your last name and the page number, flush right.
- Some instructors may require a shortened title in the header, usually in all capital letters.
- Center-align the essay title at the top of the first page (if a title page is not required).
- Use standard capitalization (capitalize the first letter of each major word).
- Avoid underlining, italicizing, or bolding the title unless necessary for emphasis.
Paragraph Indentation:
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches or use the tab key.
- Do not insert extra spaces between paragraphs unless instructed otherwise.
Citations and References:
- Follow the citation style specified by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include in-text citations whenever you use information or ideas from external sources.
- Provide a bibliography or list of references at the end of your history essay, formatted according to the citation style guidelines.
- Typically, history essays range from 1000 to 2500 words, but this can vary depending on the assignment.

How to Write a History Essay?
Historical writing can be an exciting journey through time, but it requires careful planning and organization. In this section, we'll break down the process into simple steps to help you craft a compelling and well-structured history paper.
Analyze the Question
Before diving headfirst into writing, take a moment to dissect the essay question. Read it carefully, and then read it again. You want to get to the core of what it's asking. Look out for keywords that indicate what aspects of the topic you need to focus on. If you're unsure about anything, don't hesitate to ask your instructor for clarification. Remember, understanding how to start a history essay is half the battle won!
Now, let's break this step down:
- Read the question carefully and identify keywords or phrases.
- Consider what the question is asking you to do – are you being asked to analyze, compare, contrast, or evaluate?
- Pay attention to any specific instructions or requirements provided in the question.
- Take note of the time period or historical events mentioned in the question – this will give you a clue about the scope of your history essay.
Develop a Strategy
With a clear understanding of the essay question, it's time to map out your approach. Here's how to develop your historical writing strategy:
- Brainstorm ideas : Take a moment to jot down any initial thoughts or ideas that come to mind in response to the history paper question. This can help you generate a list of potential arguments, themes, or points you want to explore in your history essay.
- Create an outline : Once you have a list of ideas, organize them into a logical structure. Start with a clear introduction that introduces your topic and presents your thesis statement – the main argument or point you'll be making in your history essay. Then, outline the key points or arguments you'll be discussing in each paragraph of the body, making sure they relate back to your thesis. Finally, plan a conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your history paper thesis.
- Research : Before diving into writing, gather evidence to support your arguments. Use reputable sources such as books, academic journals, and primary documents to gather historical evidence and examples. Take notes as you research, making sure to record the source of each piece of information for proper citation later on.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate potential counterarguments to your history paper thesis and think about how you'll address them in your essay. Acknowledging opposing viewpoints and refuting them strengthens your argument and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Set realistic goals : Be realistic about the scope of your history essay and the time you have available to complete it. Break down your writing process into manageable tasks, such as researching, drafting, and revising, and set deadlines for each stage to stay on track.

Start Your Research
Now that you've grasped the history essay topic and outlined your approach, it's time to dive into research. Here's how to start:
- Ask questions : What do you need to know? What are the key points to explore further? Write down your inquiries to guide your research.
- Explore diverse sources : Look beyond textbooks. Check academic journals, reliable websites, and primary sources like documents or artifacts.
- Consider perspectives : Think about different viewpoints on your topic. How have historians analyzed it? Are there controversies or differing interpretations?
- Take organized notes : Summarize key points, jot down quotes, and record your thoughts and questions. Stay organized using spreadsheets or note-taking apps.
- Evaluate sources : Consider the credibility and bias of each source. Are they peer-reviewed? Do they represent a particular viewpoint?
Establish a Viewpoint
By establishing a clear viewpoint and supporting arguments, you'll lay the foundation for your compelling historical writing:
- Review your research : Reflect on the information gathered. What patterns or themes emerge? Which perspectives resonate with you?
- Formulate a thesis statement : Based on your research, develop a clear and concise thesis that states your argument or interpretation of the topic.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate objections to your history paper thesis. Are there alternative viewpoints or evidence that you need to address?
- Craft supporting arguments : Outline the main points that support your thesis. Use evidence from your research to strengthen your arguments.
- Stay flexible : Be open to adjusting your viewpoint as you continue writing and researching. New information may challenge or refine your initial ideas.
Structure Your Essay
Now that you've delved into the depths of researching historical events and established your viewpoint, it's time to craft the skeleton of your essay: its structure. Think of your history essay outline as constructing a sturdy bridge between your ideas and your reader's understanding. How will you lead them from point A to point Z? Will you follow a chronological path through history or perhaps dissect themes that span across time periods?
And don't forget about the importance of your introduction and conclusion—are they framing your narrative effectively, enticing your audience to read your paper, and leaving them with lingering thoughts long after they've turned the final page? So, as you lay the bricks of your history essay's architecture, ask yourself: How can I best lead my audience through the maze of time and thought, leaving them enlightened and enriched on the other side?

Create an Engaging Introduction
Creating an engaging introduction is crucial for capturing your reader's interest right from the start. But how do you do it? Think about what makes your topic fascinating. Is there a surprising fact or a compelling story you can share? Maybe you could ask a thought-provoking question that gets people thinking. Consider why your topic matters—what lessons can we learn from history?
Also, remember to explain what your history essay will be about and why it's worth reading. What will grab your reader's attention and make them want to learn more? How can you make your essay relevant and intriguing right from the beginning?
Develop Coherent Paragraphs
Once you've established your introduction, the next step is to develop coherent paragraphs that effectively communicate your ideas. Each paragraph should focus on one main point or argument, supported by evidence or examples from your research. Start by introducing the main idea in a topic sentence, then provide supporting details or evidence to reinforce your point.
Make sure to use transition words and phrases to guide your reader smoothly from one idea to the next, creating a logical flow throughout your history essay. Additionally, consider the organization of your paragraphs—is there a clear progression of ideas that builds upon each other? Are your paragraphs unified around a central theme or argument?
Conclude Effectively
Concluding your history essay effectively is just as important as starting it off strong. In your conclusion, you want to wrap up your main points while leaving a lasting impression on your reader. Begin by summarizing the key points you've made throughout your history essay, reminding your reader of the main arguments and insights you've presented.
Then, consider the broader significance of your topic—what implications does it have for our understanding of history or for the world today? You might also want to reflect on any unanswered questions or areas for further exploration. Finally, end with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action that encourages your reader to continue thinking about the topic long after they've finished reading.
Reference Your Sources
Referencing your sources is essential for maintaining the integrity of your history essay and giving credit to the scholars and researchers who have contributed to your understanding of the topic. Depending on the citation style required (such as MLA, APA, or Chicago), you'll need to format your references accordingly. Start by compiling a list of all the sources you've consulted, including books, articles, websites, and any other materials used in your research.
Then, as you write your history essay, make sure to properly cite each source whenever you use information or ideas that are not your own. This includes direct quotations, paraphrases, and summaries. Remember to include all necessary information for each source, such as author names, publication dates, and page numbers, as required by your chosen citation style.
Review and Ask for Advice
As you near the completion of your history essay writing, it's crucial to take a step back and review your work with a critical eye. Reflect on the clarity and coherence of your arguments—are they logically organized and effectively supported by evidence? Consider the strength of your introduction and conclusion—do they effectively capture the reader's attention and leave a lasting impression? Take the time to carefully proofread your history essay for any grammatical errors or typos that may detract from your overall message.
Furthermore, seeking advice from peers, mentors, or instructors can provide valuable insights and help identify areas for improvement. Consider sharing your essay with someone whose feedback you trust and respect, and be open to constructive criticism. Ask specific questions about areas you're unsure about or where you feel your history essay may be lacking.
History Essay Example
In this section, we offer an example of a history essay examining the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society. This essay demonstrates how historical analysis and critical thinking are applied in academic writing. By exploring this specific event, you can observe how historical evidence is used to build a cohesive argument and draw meaningful conclusions.

FAQs about History Essay Writing
How to write a history essay introduction, how to write a conclusion for a history essay, how to write a good history essay.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
History Essay Examples

Top History Essay Examples To Get Inspired By
Published on: May 4, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
History essays are a crucial component of many academic programs, helping students to develop their critical thinking, research, and writing skills.
However, writing a great history essay is not always easy, especially when you are struggling to find the right approach. This is where history essay examples come in handy.
By reading and examining samples of successful history essays, you can gain inspiration, learn new ways to approach your topic. Moreover, you can develop a better understanding of what makes a great history essay.
In this blog, you will find a range of history essay examples that showcase the best practices in history essay writing.
Read on to find useful examples.
On This Page On This Page -->
Sample History Essays
Explore our collection of excellent history paper examples about various topics. Download the pdf examples for free and read to get inspiration for your own essay.
History Essay Samples for Middle School
The Impact of Ancient Civilizations on Modern Society
The Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire
The Causes and Consequences of the American Revolution
History Writing Samples for High School Students
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on Society
Grade 10 History Essay Example: World War 1 Causes and Effects
Grade 12 History Essay Example: The Impact of Technology on World War II
Ancient History Essay Examples
The Societal and Political Structures of the Maya Civilization
The Role of Phoenicians in the Development of Ancient Mediterranean World
The Contributions of the Indus Civilization
Medieval History Essay Examples
The Crusades Motivations and Consequences
The Beginning of Islamic Golden Age
The Black Death
Modern History Essay Examples
The Suez Crisis and the End of British Dominance
The Rise of China as an Economic Powerhouse
World History Essay Examples
The Role of the Silk Road in Shaping Global Trade and Culture
The Rise and Fall of the Ottoman Empire
The Legacy of Ancient Greek Philosophy and Thought

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
American History Essay Examples
The Civil Rights Movement and its Impact on American Society
The American Civil War and its Aftermath
The Role of Women in American Society Throughout History
African History Essay Examples
The Impact of Colonialism on African Societies
The Rise and Fall of the Mali Empire
European History Essay Examples
The Protestant Reformation and the Rise of Protestantism in Europe
The French Revolution and its Impact on European Politics and Society
The Cold War and the Division of Europe
Argumentative History Essay Examples
Was the US Civil War Primarily About Slavery or States
The Effects of British Colonization on Colonies
Art History Essay Examples
The Influence of Greek and Roman Art on Neoclassicism
The Depiction of Women in Art Throughout History
The Role of Art in the Propaganda of Fascist Regimes
How to Use History Essay Examples
History essay examples are a valuable tool for students looking for inspiration and guidance on how to approach their own essays.
By analyzing successful essays, you can learn effective writing techniques that can be expected in a high-quality history essay.
Here are some tips that will help you take full advantage of the samples above.
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples
- Analyze the Structure:
Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument.
- Study the Thesis Statement:
The thesis statement is the backbone of any successful history essay. Analyze how the author crafted their thesis statement, and consider how you can apply this to your own writing.
- Take Note of the Evidence:
Effective history essays rely on using strong evidence to support their arguments. Take note of the sources and types of evidence used in the essay. Consider how you can apply similar evidence to support your own arguments.
- Pay Attention to the Formatting and Other Academic Formalities:
The sample essays also demonstrate how you can incorporate academic formalities and standards while keeping the essay engaging. See how these essays fulfill academic standards and try to follow them in your own writing.
- Practice Writing:
While analyzing history essay examples can be helpful, it is important to also practice writing your own essays. Use the examples as inspiration, but try to craft your own unique approach to your topic.
History essays are an essential aspect of learning and understanding the past. By using history essay examples, students can gain inspiration on how to develop their history essays effectively.
Furthermore, following the tips outlined in this blog, students can effectively analyze these essay samples and learn from them.
However, writing a history essay can still be challenging.
Looking for an online essay writing service that specializes in history essays? Look no further!
Our history essay writing service is your go-to source for well-researched and expertly crafted papers.
And for an extra edge in your academic journey, explore our AI essay writing tool . Make history with your grades by choosing our online essay writing service and harnessing the potential of our AI essay writing tool.
Get started today!
Cathy A. (Law, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources will help you develop and refine the arguments in your writing.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.

70 Examples of Excellent Thesis Statements for Essays in All Subjects
Looking at examples of thesis statements can be helpful when you’re crafting a thesis statement to guide your essay.

We’ve already looked at how to write a thesis statement and the thesis statement formula . In this article, we’ll present a ton of examples of solid thesis statements for a range of different subjects.
If you’ve yet to decide on your research topic, take a look at our 85 examples of great dissertation research topics .
When you read through them, you should start to see a pattern emerge in terms of how they typically adhere to the following set of rules:
- A single sentence located at the end of your essay introduction
- The thesis statement summarizes what your opinion is and what you are going to explore.
- Directs your reader to the main arguments you will present.
A good dissertation proofreader will be able to help you ensure your thesis statement is strong and structured properly.
Alternatively, you could tap into the powers of AI and use this thesis statement generator:
Can a Thesis Statement Include More Than One Question?
A thesis statement does not need to be a single sentence. The length of your thesis statement will vary according to the complexity of the subject you are exploring.
In some cases, a solid thesis statement will consist of a single sentence. However, in other cases, you may use two, or even three, sentences.
Your overall aim should be to ensure the statement is as short and direct as possible, as this will help you to appear confident. This is particularly important in an argumentative thesis statement for argumentative essays .
Let’s remind ourselves of the basics of a good thesis statement.
How to write a thesis statement checklist:

70 Strong Thesis Statement Examples for Research Papers and Dissertations
Now we’ve covered the basis, let’s take a look at some really great examples of thesis statements you can use when writing a thesis .
15 Example Thesis Statements on the Social Sciences
- Climate change is a pressing global issue that requires immediate action, as it threatens to undermine the stability of entire ecosystems, disrupt economies, and jeopardize the health and well-being of future generations.
- The role of technology in education cannot be underestimated because it has the potential to transform the learning experience, enhance the quality of education, and provide students with access to information and resources that were previously unavailable.
- The use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower is crucial to achieving a sustainable future, as it reduces dependence on finite resources, minimizes greenhouse gas emissions, and protects the environment.
- The widespread prevalence of fake news and misinformation on social media is a growing concern, as it undermines the credibility of journalism, public trust in information, and the democratic process.
- The rise of automation and artificial intelligence in the workplace is transforming the way people work, leading to increased productivity and efficiency; however, it is also linked with job displacement and the need for workers to acquire new skills.
- The intersection of race, gender, and class has a significant impact on a person’s life opportunities and experiences, and it is crucial to understand these intersections in order to address systemic inequalities and promote social justice.
- The growing demand for food and the increasing use of industrial agriculture are putting a strain on the environment, leading to soil degradation, deforestation, and increased greenhouse gas emissions.
- The phenomenon of gentrification is transforming cities, leading to the displacement of low-income communities, the loss of cultural diversity, and the commodification of urban spaces.
- The impact of mass migration on countries and communities is complex and far-reaching, leading to both cultural enrichment and increased social and political tensions.
- The growing concern about income inequality and wealth disparity has important implications for social and economic mobility, as well as for the stability of democracies and the legitimacy of political systems.
- The rise of nationalism and populism around the world is challenging the stability of global institutions and the foundations of democratic systems. It raises important questions about the role of the nation-state in the 21st century.
- Elon Musk, the billionaire entrepreneur and innovator, has made a significant impact on the tech industry and the world as a whole through his numerous ventures and ambitious projects, making him a visionary leader and a symbol of technological progress. However, his actions and public statements have also generated controversy and criticism, calling into question the ethical and social implications of his vision for the future.
- Bitcoin, the decentralized digital currency, has revolutionized the financial industry and challenged traditional financial systems. However, the growing popularity and acceptance of Bitcoin has also brought to light important issues regarding security, regulation, and the potential for negative impacts on the economy and society as a whole.
- Quantum computing, a rapidly evolving field that harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations, has the potential to revolutionize the computing industry and solve complex problems that are beyond the capabilities of traditional computers; however, quantum computing poses a significant threat to contemporary society that should not be overlooked.
- Electric cars have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, holding great promise for reducing humanity’s dependence on fossil fuels. However, this technology is not sustainable or viable on a long-term basis

15 Sample Thesis Statements for Literary Analysis Essays
- The political and social developments of the 18th century had a significant impact on the development of the English novel, which reflected both the ideals and the realities of the time.
- The Romantic movement in English literature constituted a notable divergence from the Enlightenment ideas of reason and order by emphasizing emotion, imagination, and individualism.
- Although Jane Austen is well known for her wit and social satire, her writings also serve as a commentary on the discrimination that women encountered in early 19th-century England.
- The manner in which authors of the Victorian era portrayed non-European cultures and peoples is one way to show how colonialism and imperialism had an impact on English literature.
- The literature of the Victorian era reflects the position of women in English society at the time, with female characters frequently acting as icons of moral and cultural values.
- The use of symbolism within English literature serves as a potent instrument for examining complicated themes and ideas, from the profound to the ridiculous.
- When writers like James Joyce and Virginia Woolf introduced the stream-of-consciousness narrative approach, the English novel underwent a revolution that allowed for a new degree of depth and reflection in storytelling.
- The writings of English Romantic poets, like William Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge, marked a turning point in the development of English literature by ushering in a novel kind of writing that praised the natural world, human emotion, and unique experiences.
- From Beowulf to Paradise Lost, the evolution of the English epic poem reflects the shifting morals and ideologies of English society over time, as well as its changing perception of who we are and where we belong in the world.
- The three Bronte sisters—Charlotte, Emily, and Anne—used literature to question the restrictions and standards that were imposed on women in 19th-century England, setting a new precedent for female emancipation.
- With its rigid structure and rhyme schemes, the English sonnet tradition has been a well-liked and enduring manner to convey one’s thoughts on both the political and personal levels as well as the human condition.
- With its emphasis on experimentation, fragmentation, and psychological depth, the Modernist movement in English literature marked a significant shift from the realism and naturalism of older literary traditions.
- The evolution of English literature in the 20th century was greatly influenced by the writings of T.S. Eliot and W.B. Yeats, which capture the period’s intellectual and cultural upheaval as well as the significant changes evident in European society.
- The expansion of the English empire and its influence over the world had a significant impact on the literature of the nation, influencing new kinds of storytelling as well as the themes, writing techniques, and perspectives of its authors.
- From the biblical account of the Fall to the Greek myth of Orpheus and Eurydice, the use of allegory and myth in English literature has been a potent means of examining difficult concepts and universal truths.
10 Sample Thesis Statements on History
- Beginning in 1789, the French Revolution marked a significant turning point in European history that eventually resulted in the collapse of the monarchy and the foundation of a democratic republic.
- The American Civil War, which took place between 1861 and 1865, was a pivotal event in the history of the nation, influencing its political structure, identity, and values for a number of years.
- An important turning point in world economic and social history, the Industrial Revolution, which started in England in the late 18th century, fundamentally changed how products were created and consumed, leading to significant changes in the lives of people all over the world.
- One of the biggest and most influential empires in history, the Roman Empire, which ruled from 27 BC to 476 AD, had an impact on the growth of art, architecture, law, and language throughout the Mediterranean region.
- The Enlightenment, an intellectual and cultural movement that began in Europe in the 18th century, represented an important turning point in the history of ideas and gave rise to new ways of thinking about politics, religion, and society.
- One of the deadliest and most significant conflicts in modern history, the First World War, which raged from 1914 to 1918, drastically altered the political, social, and economic climate of Europe and other parts of the world.
- The Cold War, which lasted from 1945 to 1991, marked a pivotal period in the history of the 20th century, impacting the advancement of science, technology, and culture as well as the political and military landscape of the world.
- The 1754–1763 French and Indian War was a pivotal period in the history of the American colonies, paving the way for the ultimate independence of the United States and determining the course of the nation’s future.
- Capitalism, which first appeared in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries, marked a significant turning point in the development of modern market economies and the lives of millions of people.
- An important turning point in the history of the American colonies was the American Revolution, which took place between 1775 and 1783 and ultimately resulted in the independence of the United States and the development of a new system of government.
10 Example Thesis Statements on Art
- The Italian Renaissance, which started in the 14th century and lasted until the 17th, was a time of great artistic and cultural revival. The painting, sculpture, and architectural expressions that emerged during this time had a significant influence on Western art and culture.
- A time of great artistic and cultural diversity, the Baroque period was characterized by the emergence of new forms of artistic expression, such as painting, sculpture, and music, that reflected the religious, political, and cultural values of the day.
- The late 19th-century French Impressionist style was a ground-breaking trend in painting that aimed to represent the fleeting, transient effects of light and color in the natural world.
- Mid-20th-century modern art movement known as Abstract Expressionism, which emphasized spontaneous, expressive brushwork and explored the emotional and psychological components of the creative process, was a prominent force in the world of contemporary art.
- Pop Art, a modern art movement that began in the middle of the 20th century in response to the Abstract Expressionist movement, was distinguished by its use of common objects, commercial imagery, and vibrant colors to produce a fresh kind of art that was approachable and pertinent to popular culture.
- Surrealism, a modern art movement that began in the 1920s, used methods like automatic drawing and dream-like images to produce a new kind of work that was both strange and enticing while prompting an investigation of the subconscious mind.
- The 1920s and 1930s saw the emergence of the Art Deco movement, which aspired to create a new genre of modern art that was elegant, sophisticated, and representative of the contemporary world. It was distinguished by its use of geometric shapes, brilliant colors, and metallic finishes.
- Gothic Art, a key influence on Medieval art that first appeared in the 12th century, is known for its concentration on lofty cathedrals, exquisite stained glass, and ornate sculptures that capture the period’s religious and cultural values.
- The Romanesque period was a time of great artistic and cultural rebirth. Painting, sculpture, and architectural styles all emerged during this time, and they had a significant influence on Western art and culture.
- The 19th-century art movement known as realism tried to portray the world as it actually was by employing precise, lifelike depictions of people, places, and things to produce a new kind of art that was both realistic and compelling on an emotional level.
15 Examples of English Language Thesis Statements
- Due to historical, cultural, and social influences on the development of the English language, numerous dialects and variations have emerged all over the world. For individuals, groups, and cultures, the emergence of English as a world language has yielded both benefits and challenges and had a profound impact on global language education and language policy.
- Understanding the structure, purposes, and meanings of English allows us to better comprehend how language both influences and is influenced by human cognition, perception, and interaction.
- The widespread use of English in digital communication and social media has given rise to new linguistic elements and conventions, like emoticons, acronyms, and hashtags, which have significantly changed how our ability to express ourselves and interact with others.
- The English language has taken on a greater significance in higher education because it is frequently the language of instruction and research in many academic subjects and is necessary for worldwide communication and collaboration.
- Studying English as a second or foreign language requires not only learning linguistic abilities but also gaining intercultural competence and the capacity to deal with diversity and cultural differences.
- The influence of the English language on other languages has led to phenomena such as word borrowing, grammar borrowing, and punctuation changes. This has led to a fundamental change in language boundaries and the emergence of hybrid forms of language.
- English usage in the workplace has become crucial for successful communication and career advancement, especially in multinational organizations and international industries. This has resulted in the growth of specialized linguistic abilities and discourse patterns.
- Language diversity and linguistic justice have become ethical and political hot topics as a result of how English has affected the identities and cultural practices of speakers of other languages, led to the extinction of indigenous languages, and initiated negotiations over language rights and language maintenance.
- Understanding the cultural, historical, and social circumstances in which literary works were created helps us to examine and interpret the literary works’ artistic and aesthetic qualities as well as its larger relevance and societal effects.
- The widespread use of English in popular culture, such as music, film, and television, has significantly influenced the language’s acceptance around the world and sparked the development of new genres, styles, and modes of expression.
- By studying English as a discourse community and examining its norms, practices, and communication techniques, it is possible to get insight into the power structures and social hierarchies that influence how people use language and formulate language ideologies.
- English’s use in the tourism sector as a universal language and a vehicle for cross-cultural engagement has had economic and social repercussions for both host communities and guests, sparking discussions about how globalization is affecting regional cultures and identities.
- English should be taught to all children since it not only fosters language proficiency but also creativity, social responsibility, and critical thinking.
- The impact of English on the linguistic landscape of cities and communities, including the use of English in media, ads, and public signs, reflects language interaction dynamics and the negotiation of linguistic identities and rights.
- The impact of English on the linguistic landscape of cities and communities, including the use of English in public signs, advertisements, and media, reflects the dynamics of language contact and the negotiation of linguistic identities and rights.
As you will see from all the example thesis statements shared above, a solid thesis statement follows a general formula.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on September 14, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master’s program or a capstone to a bachelor’s degree.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation , it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: choosing a relevant topic , crafting a proposal , designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement for Master’s programs, and is also sometimes required to complete a bachelor’s degree in liberal arts colleges.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
- In other countries (particularly the UK), a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807” by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: “’A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man’: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947″ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the “Insert Caption” feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialized or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetize the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyzes the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasize what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense , your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5–7% of your overall word count.
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation , you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimizing confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A thesis is typically written by students finishing up a bachelor’s or Master’s degree. Some educational institutions, particularly in the liberal arts, have mandatory theses, but they are often not mandatory to graduate from bachelor’s degrees. It is more common for a thesis to be a graduation requirement from a Master’s degree.
Even if not mandatory, you may want to consider writing a thesis if you:
- Plan to attend graduate school soon
- Have a particular topic you’d like to study more in-depth
- Are considering a career in research
- Would like a capstone experience to tie up your academic experience
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 20, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
- Editing Services
- Academic Editing Services
- Admissions Editing Services
- Admissions Essay Editing Services
- AI Content Editing Services
- APA Style Editing Services
- Application Essay Editing Services
- Book Editing Services
- Business Editing Services
- Capstone Paper Editing Services
- Children's Book Editing Services
- College Application Editing Services
- College Essay Editing Services
- Copy Editing Services
- Developmental Editing Services
- Dissertation Editing Services
- eBook Editing Services
- English Editing Services
- Horror Story Editing Services
- Legal Editing Services
- Line Editing Services
- Manuscript Editing Services
- MLA Style Editing Services
- Novel Editing Services
- Paper Editing Services
- Personal Statement Editing Services
- Research Paper Editing Services
- Résumé Editing Services
- Scientific Editing Services
- Short Story Editing Services
- Statement of Purpose Editing Services
- Substantive Editing Services
- Thesis Editing Services
Proofreading
- Proofreading Services
- Admissions Essay Proofreading Services
- Children's Book Proofreading Services
- Legal Proofreading Services
- Novel Proofreading Services
- Personal Statement Proofreading Services
- Research Proposal Proofreading Services
- Statement of Purpose Proofreading Services
Translation
- Translation Services
Graphic Design
- Graphic Design Services
- Dungeons & Dragons Design Services
- Sticker Design Services
- Writing Services
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
Related Posts

How to Prove a Thesis Statement: Analyzing an Argument

How to Select the Right Journal for Publication
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?

3 Point Thesis Statement
A 3-point thesis statement is a concise yet potent tool that outlines the main arguments of your paper. By presenting three key points, it guides readers through your central ideas and supports your position. In this guide, we’ll explore how to create compelling 3-point thesis statements , along with valuable tips to ensure clarity, coherence, and persuasive strength in your academic writing.
Definition of a 3 Point Thesis Statement
A 3-point thesis statement is a succinct and focused sentence that outlines the main arguments or points you intend to address in your paper. It serves as a roadmap for your readers, indicating the core topics or themes you’ll explore while presenting your stance or perspective on a particular issue.
Example of a 3 Point Thesis Statement
Topic: The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
Thesis Statement: “The accelerating effects of climate change threaten global biodiversity through temperature shifts, habitat degradation, and altered migration patterns.”
In this example, the 3-point thesis statement clearly presents the three main points that will be discussed in the paper: temperature shifts, habitat degradation, and altered migration patterns. These points provide a structured framework for the upcoming argumentative analysis.
100 Three Point Thesis Statement Examples

Size: 643 KB
A 3-point thesis statement succinctly outlines central arguments, providing a roadmap for focused discussions. Below are 100 examples spanning various subjects, each followed by a brief 60-word description:
- Cyberbullying Effects on Adolescents Cyberbullying adversely impacts adolescents’ mental health, self-esteem, and academic performance. This thesis addresses the detrimental effects of cyberbullying on adolescents’ psychological well-being, academic achievement, and self-perception.
- Renewable Energy Solutions Renewable energy systems contribute to sustainability through reduced emissions, resource conservation, and energy independence. This thesis explores the multifaceted benefits of renewable energy, including its role in combating climate change, conserving resources, and fostering energy autonomy.
- Gender Stereotypes in Media Media perpetuates gender stereotypes through representation, roles, and normalized behaviors. Focusing on media’s influence, this thesis analyzes how gender stereotypes are reinforced through portrayal, societal roles, and the reinforcement of normalized behaviors.
- The Impact of Social Media on Politics Social media shapes political discourse by influencing awareness, engagement, and public opinion. Examining the intersection of technology and politics, this thesis delves into how social media platforms shape political discussions by impacting awareness, engagement, and public sentiment.
- Cultural Diversity in Education Incorporating diverse perspectives in education enhances critical thinking, empathy, and global understanding. This thesis underscores the significance of integrating diverse viewpoints into educational curricula, fostering skills such as critical thinking, empathy, and cross-cultural awareness.
- Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Job Market Artificial intelligence transforms employment landscapes by reshaping job roles, skill demands, and the need for adaptability. Investigating AI’s influence on jobs, this thesis explores how automation shifts job responsibilities, necessitates new skills, and emphasizes the importance of adaptability.
- Effects of Social Media on Teenage Body Image Social media shapes teenage body image through comparisons, idealized representations, and societal beauty standards. This thesis delves into how social media influences teenagers’ perceptions of body image by promoting comparisons, unrealistic ideals, and cultural beauty norms.
- Ethical Implications of Genetic Engineering Genetic engineering raises ethical concerns over altering organisms, patenting life forms, and unforeseen ecological consequences. Analyzing the ethical dimensions, this thesis examines debates surrounding genetic modification, including ethical dilemmas, intellectual property, and environmental risks.
- Education’s Role in Addressing Poverty Education is a catalyst for poverty alleviation by fostering skills, knowledge, and socio-economic mobility. This thesis emphasizes education’s pivotal role in breaking the cycle of poverty through skill development, knowledge acquisition, and improved economic prospects.
- Media’s Influence on Political Polarization Media exacerbates political polarization by disseminating biased information, echo chambers, and fostering extremism. Investigating media’s role, this thesis explores how biased reporting, echo chambers, and extremist content contribute to the widening political divide.
- Environmental Conservation and Economic Growth Environmental conservation and economic growth can coexist through sustainable practices, green technologies, and eco-tourism. This thesis examines the compatibility of preserving the environment and promoting economic development by emphasizing sustainable practices, technology, and eco-friendly industries.
- Impacts of Social Media on Interpersonal Relationships Social media alters interpersonal relationships by affecting communication dynamics, intimacy, and personal interactions. Exploring technology’s influence on relationships, this thesis analyzes how social media shapes communication patterns, intimacy levels, and face-to-face interactions.
- Globalization’s Effects on Cultural Diversity Globalization both enriches and endangers cultural diversity through cultural exchange, homogenization, and cultural appropriation. This thesis examines globalization’s dual effects, including the enrichment of cultural exchange and the challenges of cultural homogenization and appropriation.
- The Role of Education in Promoting Environmental Stewardship Education fosters environmental stewardship by instilling awareness, responsibility, and sustainable behaviors. Addressing the intersection of education and the environment, this thesis underscores how education cultivates environmental consciousness, accountability, and sustainable practices.
- Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare Diagnostics Artificial intelligence revolutionizes healthcare diagnostics through precise analysis, early detection, and improved patient outcomes. Exploring AI’s impact on healthcare, this thesis assesses how AI enhances medical diagnoses by providing accurate analyses, detecting conditions earlier, and optimizing patient care.
- Media’s Influence on Consumer Behavior Media shapes consumer behavior by creating desires, trends, and influencing purchasing decisions. Focusing on media’s sway, this thesis examines how advertising and media content drive consumer desires, shape trends, and impact buying choices.
- Education’s Role in Fostering Tolerance and Inclusion Education cultivates tolerance and inclusion by promoting empathy, understanding, and dismantling stereotypes. This thesis highlights how education plays a vital role in creating inclusive societies through empathy-building, stereotype deconstruction, and fostering understanding.
- Ethical Considerations in Artificial Intelligence Development Ethical concerns surround AI development due to bias, privacy invasion, and the potential for autonomous decision-making. Addressing the ethical dimensions, this thesis evaluates the moral implications associated with AI development, including issues of bias, privacy, and decision-making autonomy.
- Media’s Influence on Political Engagement Media influences political engagement by shaping public opinion, mobilizing activism, and framing political narratives. Examining media’s role in politics, this thesis analyzes how media outlets shape public perceptions, drive activism, and contribute to the framing of political issues.
- Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security Sustainable agriculture ensures food security through ecological practices, crop diversity, and responsible resource management. Investigating the relationship between agriculture and food security, this thesis explores how sustainable practices, diverse crops, and resource conservation bolster global food supplies
- Technology’s Impact on Education Technology transforms education through online learning, personalized instruction, and innovative teaching methods. Examining the intersection of technology and education, this thesis assesses how digital tools reshape learning environments, enhance personalization, and revolutionize teaching techniques.
- Effects of Social Media on Mental Health Social media affects mental health through comparison, cyberbullying, and the pressure of maintaining online personas. Investigating mental health implications, this thesis explores how social media contributes to anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges through comparison, bullying, and curated online identities.
- The Role of Literature in Shaping Societal Norms Literature shapes societal norms by reflecting culture, challenging conventions, and fostering critical discourse. Examining literature’s impact, this thesis analyzes how literary works influence societal values, prompt reflection, and challenge established norms.
- Online Privacy and Personal Data Protection Online privacy hinges on protecting personal data from breaches, surveillance, and unauthorized use. Addressing digital security, this thesis explores the complexities of safeguarding personal information from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and surveillance.
- Media’s Role in Shaping Historical Narratives Media influences historical narratives by framing events, shaping memory, and emphasizing certain perspectives. Focusing on media’s historical impact, this thesis examines how media narratives influence collective memory, historical understanding, and the framing of significant events.
- Economic Inequality and Access to Education Economic inequality affects education access through disparities in resources, quality, and opportunities. Addressing the connection between wealth disparity and education, this thesis explores how economic inequalities impact access to quality education and opportunities.
- Influence of Social Media on Democracy Social media affects democracy by shaping political discourse, enabling citizen participation, and disseminating information. Examining the intersection of technology and politics, this thesis assesses how social media platforms influence democratic processes, political engagement, and information dissemination.
- Effects of Climate Change on Coastal Communities Climate change poses risks to coastal communities through rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and erosion. Investigating climate impacts, this thesis explores how rising temperatures and changing weather patterns threaten coastal areas with sea-level rise, storms, and erosion.
- The Role of Art in Cultural Preservation Art contributes to cultural preservation by conveying heritage, identity, and historical narratives. Focusing on artistic expression, this thesis examines how art serves as a vessel for cultural memory, preservation of traditions, and the portrayal of historical stories.
- Media’s Influence on Beauty Standards Media shapes beauty standards through idealized images, promoting unrealistic ideals, and setting cultural norms. Analyzing media’s role in shaping perceptions of beauty, this thesis explores how media images influence cultural definitions of attractiveness and self-worth.
- The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Ethics Artificial intelligence raises ethical concerns related to bias, decision-making, and the potential for autonomous systems. Addressing the ethical dimensions of AI, this thesis evaluates how machine learning technologies introduce ethical dilemmas in areas such as bias, decision-making, and autonomy.
- Literature’s Exploration of Social Injustice Literature critiques social injustice by depicting marginalized experiences, advocating for change, and prompting reflection. This thesis analyzes how literary works shed light on societal inequalities, advocate for marginalized voices, and inspire social change.
- Effects of Video Games on Cognitive Development Video games impact cognitive development through problem-solving, spatial awareness, and enhanced multitasking skills. Examining the influence of gaming, this thesis explores how interactive digital entertainment contributes to cognitive skill development in areas such as problem-solving and multitasking.
- The Role of Education in Gender Equality Education empowers gender equality by challenging stereotypes, promoting opportunities, and fostering inclusive mindsets. Addressing the intersection of education and gender, this thesis emphasizes how educational systems contribute to dismantling gender stereotypes, increasing opportunities, and promoting gender inclusivity.
- Effects of Social Media on News Consumption Social media shapes news consumption patterns through personalized feeds, viral content, and the spread of misinformation. Investigating media’s impact on news consumption, this thesis examines how social media algorithms, viral content, and misinformation affect the way individuals access and interpret news.
- Urbanization’s Impact on Mental Health Urbanization affects mental health through overcrowding, noise pollution, and limited access to green spaces. Exploring the psychological consequences of urban living, this thesis analyzes how city environments influence mental well-being through factors such as noise, density, and lack of natural spaces.
- The Role of Literature in Empathy Cultivation Literature cultivates empathy by portraying diverse experiences, fostering emotional connections, and promoting understanding. This thesis explores how literary narratives foster empathy by encouraging readers to connect emotionally with characters from various backgrounds and circumstances.
- Effects of Online Learning on Educational Equity Online learning impacts educational equity by addressing accessibility, offering flexible options, and widening disparities. Focusing on digital education, this thesis examines how online learning platforms both address and exacerbate disparities in education access and quality.
- Media’s Influence on Public Health Attitudes Media shapes public health attitudes by disseminating health information, addressing stigmas, and promoting healthy behaviors. Examining media’s role in health communication, this thesis analyzes how media platforms influence public perceptions, spread health-related information, and contribute to behavior change.
- Impact of Technology on Family Dynamics Technology affects family dynamics by altering communication, screen time habits, and the balance between virtual and face-to-face interactions. This thesis explores how technology influences the ways families communicate, spend time together, and navigate the integration of digital devices into daily life
- Impacts of Social Media on Teen Mental Health Social media influences teen mental health through comparison, online bullying, and the pressure to curate a perfect image. Focusing on adolescent well-being, this thesis examines how social media usage affects mental health, contributing to issues such as low self-esteem, anxiety, and depression.
- The Role of Literature in Empowerment Literature empowers individuals by providing representation, voicing marginalized perspectives, and fostering a sense of agency. Addressing the transformative power of literature, this thesis explores how literary works empower individuals by offering diverse role models, amplifying underrepresented voices, and encouraging self-expression.
- Effects of Screen Time on Child Development Excessive screen time influences child development through cognitive impacts, sedentary behaviors, and altered social interactions. Investigating digital media’s impact on children, this thesis analyzes how prolonged screen time affects cognitive development, physical activity, and social skills in early childhood.
- Media’s Role in Shaping Cultural Identities Media influences cultural identities by reflecting representation, perpetuating stereotypes, and shaping societal perceptions. This thesis examines how media shapes cultural identities by influencing how different groups are represented, constructing stereotypes, and influencing cultural perceptions.
- The Impact of Online Shopping on Retail Industry Online shopping transforms the retail industry through convenience, global access, and the rise of e-commerce platforms. Focusing on the evolving retail landscape, this thesis explores how digital commerce platforms have revolutionized shopping behaviors, affecting traditional retail structures.
- The Role of Literature in Social Change Literature drives social change by sparking awareness, prompting activism, and encouraging critical engagement with societal issues. This thesis delves into how literature serves as a catalyst for social transformation by raising awareness, mobilizing readers, and advocating for change.
- Effects of Technology on Sleep Patterns Technology disrupts sleep patterns through blue light exposure, screen time before bed, and the impact on circadian rhythms. This thesis examines how technology usage, particularly before sleep, affects sleep quality, circadian rhythms, and overall well-being.
- Media’s Influence on Consumerism Media drives consumerism through advertising, influencing purchasing behavior, and shaping materialistic values. Investigating media’s impact on consumption, this thesis analyzes how advertisements, marketing strategies, and media content influence consumer choices and materialistic attitudes.
- The Impact of Virtual Reality on Education Virtual reality transforms education through immersive learning experiences, simulations, and interactive engagement. Exploring the intersection of technology and education, this thesis assesses how virtual reality enhances learning by creating immersive environments, simulations, and interactive content.
- Effects of Social Media on Friendship Dynamics Social media affects friendship dynamics by redefining connection, altering communication, and influencing group dynamics. Analyzing the digitalization of friendships, this thesis explores how social media platforms impact the nature of friendships, communication patterns, and group interactions.
- The Role of Literature in Fostering Resilience Literature fosters resilience by portraying characters’ coping strategies, resilience narratives, and encouraging emotional growth. This thesis highlights how literary narratives provide readers with insights into resilience strategies, offering examples of characters overcoming adversity and promoting emotional growth.
- Effects of Technology on Workplace Productivity Technology influences workplace productivity through automation, remote work tools, and digital communication platforms. Examining technology’s influence on work environments, this thesis assesses how digital tools enhance efficiency, promote remote collaboration, and reshape traditional work structures.
- Media’s Role in Public Opinion Formation Media shapes public opinion by framing news, influencing perceptions, and molding societal attitudes toward current events. Investigating media’s impact on public discourse, this thesis analyzes how media outlets influence public perceptions, frame news narratives, and contribute to the formation of public opinions.
- The Impact of Music on Mood Regulation Music influences mood regulation through emotional resonance, stress reduction, and the ability to evoke specific feelings. Focusing on the therapeutic effects of music, this thesis examines how music selection and listening habits impact emotional well-being, stress management, and mood enhancement.
- The Role of Literature in Environmental Awareness Literature raises environmental awareness by highlighting ecological issues, inspiring stewardship, and promoting sustainable values. Addressing the environmental impact of literature, this thesis explores how literary works contribute to environmental consciousness, advocacy for sustainable practices, and the dissemination of ecological knowledge.
- Effects of Online Communication on Language Evolution Online communication affects language evolution through text abbreviations, emojis, and the emergence of digital linguistic norms. Exploring the linguistic impact of digital communication, this thesis assesses how online platforms influence language evolution, leading to the emergence of new linguistic norms, abbreviations, and visual symbols.
- Media’s Influence on Political Participation Media shapes political participation by influencing voter engagement, political awareness, and mobilization efforts. Focusing on media’s role in democracy, this thesis analyzes how media platforms impact political engagement, disseminate information, and influence citizens’ participation in political processes.
- The Impact of Technology on Creative Expression Technology transforms creative expression through digital tools, online platforms, and innovative art forms. This thesis examines how technology empowers artists to explore new mediums, collaborate globally, and redefine creative boundaries in the digital age.
- The Role of Literature in Historical Preservation Literature preserves history by documenting cultural narratives, recording lived experiences, and offering insights into past societies. Addressing literature’s historical significance, this thesis explores how literary works serve as windows into past eras, preserving cultural memories and societal contexts.
- Effects of Video Game Violence on Aggression Video game violence influences aggression through desensitization, aggressive thoughts, and altered social behaviors. Investigating the psychological impact of gaming, this thesis analyzes how exposure to violent video games affects aggression levels, cognitive responses, and social interactions
- The Impact of Technology on Family Communication Technology alters family communication through digital devices, social media, and virtual interactions. Focusing on family dynamics, this thesis explores how technology affects communication patterns, family bonding, and the challenges of maintaining meaningful connections in the digital era.
- Effects of Social Media on Political Polarization Social media exacerbates political polarization through filter bubbles, echo chambers, and the reinforcement of ideological beliefs. Analyzing the relationship between social media and politics, this thesis investigates how online platforms contribute to the polarization of public opinion by reinforcing preexisting beliefs and narrowing exposure to diverse perspectives.
- The Role of Literature in Identity Formation Literature contributes to identity formation by reflecting cultural heritage, exploring self-discovery, and examining personal narratives. Addressing the intersection of literature and identity, this thesis explores how literary works contribute to the formation of individual and cultural identities, fostering self-awareness and cultural understanding.
- Effects of Technology on Human Relationships Technology impacts human relationships by altering social interactions, intimacy dynamics, and the balance between virtual and real-world connections. Investigating the influence of digital devices on interpersonal connections, this thesis examines how technology shapes the nature of relationships, emotional intimacy, and face-to-face interactions.
- Media’s Influence on Fear and Perception Media shapes fear and perception through sensationalism, framing, and the selective presentation of information. Focusing on media’s psychological impact, this thesis analyzes how media content affects public perceptions, triggers fear responses, and influences the framing of news events.
- The Impact of Technology on Privacy Technology challenges privacy through data collection, surveillance, and the blurring of online and offline boundaries. Addressing privacy concerns in the digital age, this thesis explores how technology threatens personal privacy by enabling data collection, surveillance practices, and the erosion of traditional boundaries between public and private spaces.
- Effects of Social Media on Body Image Social media influences body image through comparison, unrealistic beauty ideals, and promoting appearance-focused self-worth. Examining the psychological effects of digital media, this thesis assesses how social media platforms impact body image perceptions, self-esteem, and psychological well-being.
- The Role of Literature in Challenging Authority Literature challenges authority by critiquing power structures, questioning norms, and advocating for social change. Focusing on literature’s subversive potential, this thesis explores how literary works engage with themes of power, resistance, and social critique, challenging established authority and advocating for reform.
- Effects of Technology on Mental Health Technology influences mental health through screen addiction, social isolation, and the pressure to maintain an ideal online image. Investigating the relationship between technology usage and psychological well-being, this thesis analyzes how digital devices impact mental health, contributing to issues such as addiction, isolation, and negative self-comparisons.
- Media’s Role in Promoting Health Behaviors Media influences health behaviors by disseminating health information, promoting positive habits, and shaping public health narratives. Addressing media’s impact on public health, this thesis explores how media platforms contribute to health awareness, behavioral change, and the dissemination of health-related information.
- The Impact of Technology on Education Equity Technology impacts education equity by addressing access barriers, facilitating personalized learning, and promoting digital literacy. Focusing on technology’s educational implications, this thesis examines how digital tools can both bridge and exacerbate educational disparities, fostering access, inclusivity, and skills development.
- Effects of Social Media on Political Activism Social media amplifies political activism through digital mobilization, online advocacy, and the spread of social causes. Analyzing the role of technology in political engagement, this thesis assesses how social media platforms empower individuals and groups to mobilize for political change, share advocacy messages, and influence social issues.
- The Role of Literature in Promoting Empathy Literature fosters empathy by immersing readers in diverse experiences, building emotional connections, and enhancing understanding. Investigating literature’s capacity to cultivate compassion, this thesis explores how narrative empathy promotes understanding, encourages readers to embrace diverse perspectives, and fosters emotional resonance.
- Effects of Technology on Attention Span Technology impacts attention span through constant stimuli, information overload, and the allure of multitasking. Addressing technology’s cognitive effects, this thesis examines how digital devices influence attentional capabilities, cognitive focus, and the challenges of sustained concentration in a digitalized world.
- Media’s Influence on Political Disinformation Media platforms contribute to political disinformation through the spread of false information, echo chambers, and the manipulation of public opinion. Examining media’s role in disseminating misinformation, this thesis investigates how fake news, echo chambers, and algorithmic biases impact the accuracy of public discourse and democratic decision-making.
- The Impact of Technology on Creativity Technology enhances creativity through digital tools, collaborative platforms, and the democratization of creative expression. Focusing on the relationship between technology and creative processes, this thesis explores how digital innovations empower individuals to explore new artistic mediums, collaborate across boundaries, and engage in creative experimentation.
- Effects of Social Media on Political Engagement Social media influences political engagement through information dissemination, fostering online communities, and encouraging civic participation. This thesis investigates how social media platforms amplify political involvement by facilitating information-sharing, building virtual communities, and motivating individuals to engage in civic activities.
- The Role of Literature in Teaching Moral Lessons Literature imparts moral lessons by portraying ethical dilemmas, consequences of actions, and encouraging ethical reflection. Exploring literature’s moral dimensions, this thesis examines how literary narratives serve as vehicles for discussing ethical challenges, prompting readers to contemplate consequences and engage in moral reasoning.
- Effects of Technology on Physical Health Technology impacts physical health through sedentary behaviors, screen-related health issues, and disruptions to sleep patterns. Investigating the relationship between technology and physical well-being, this thesis analyzes how digital devices influence physical activity levels, posture, and overall health outcomes.
- Media’s Influence on Social Perception Media shapes social perception through portrayal, stereotypes, and influencing attitudes toward various societal groups. Analyzing media’s role in shaping public perceptions, this thesis assesses how media content constructs societal narratives, influences attitudes, and contributes to the formation of stereotypes
- The Impact of Technology on Privacy in Relationships Technology affects privacy in relationships through digital communication, surveillance concerns, and the blurring of boundaries. Focusing on the interplay of technology and personal relationships, this thesis explores how digital devices influence privacy dynamics, communication norms, and the challenges of maintaining boundaries.
- Effects of Social Media on Youth Empowerment Social media empowers youth through digital activism, amplification of voices, and the mobilization of social change. Investigating the role of social media in youth engagement, this thesis assesses how online platforms enable young individuals to advocate for causes, share perspectives, and shape societal narratives.
- The Role of Literature in Exploring Identity Literature explores identity by examining cultural heritage, personal experiences, and the journey of self-discovery. This thesis delves into how literature serves as a vehicle for individuals to explore their identities, offering insight into cultural backgrounds, personal struggles, and the quest for self-understanding.
- Effects of Technology on Memory and Cognitive Skills Technology impacts memory and cognitive skills through information overload, reliance on digital aids, and altered memory retention. Addressing technology’s cognitive effects, this thesis examines how digital devices influence memory processes, cognitive skills, and the capacity for deep learning and critical thinking.
- Media’s Influence on Political Trust Media shapes political trust through framing, information credibility, and influencing public perceptions of political figures. Analyzing media’s impact on political relationships, this thesis assesses how media coverage contributes to public trust or distrust in political institutions, leaders, and the information presented.
- The Impact of Technology on Language Evolution Technology influences language evolution through digital communication, new linguistic norms, and the emergence of online language varieties. Focusing on the linguistic impact of technology, this thesis explores how digital communication platforms contribute to the evolution of language, including the development of new forms and conventions.
- Effects of Social Media on Youth Mental Health Social media affects youth mental health through cyberbullying, the pressure to conform, and the impact of online peer comparisons. Investigating mental health challenges among young individuals, this thesis analyzes how social media contributes to anxiety, depression, and self-esteem issues among adolescents.
- The Role of Literature in Promoting Social Justice Literature advocates for social justice by depicting injustice, amplifying marginalized voices, and inspiring collective action. Addressing literature’s role in advocating for equality, this thesis explores how literary narratives illuminate social injustices, empower marginalized communities, and prompt readers to engage in activism.
- Effects of Technology on Human Productivity Technology influences human productivity through automation, digital distractions, and the challenges of multitasking. Examining the interplay of technology and productivity, this thesis assesses how digital devices both enhance and hinder efficiency, time management, and task completion.
- Media’s Influence on Cultural Appropriation Media shapes cultural appropriation through portrayal, perpetuating stereotypes, and commodifying cultural elements. Focusing on media’s impact on cultural understanding, this thesis analyzes how media content contributes to cultural appropriation by presenting distorted portrayals and commodifying cultural practices.
- The Impact of Technology on Parenting Styles Technology influences parenting styles through digital device usage, screen time management, and the challenge of balancing virtual and real-world interactions. Investigating the intersection of technology and parenting, this thesis explores how digital devices shape parenting approaches, influence family dynamics, and affect children’s development.
- Effects of Social Media on Political Information Seeking Social media influences political information seeking through personalized news feeds, echo chambers, and filter bubbles. This thesis examines how social media platforms impact the way individuals access, interpret, and seek out political information, contributing to the customization and potential polarization of news consumption.
- The Role of Literature in Addressing Mental Health Stigma Literature challenges mental health stigma by portraying mental health experiences, fostering empathy, and promoting open conversations. Focusing on the intersection of literature and mental health, this thesis explores how literary narratives contribute to destigmatizing mental health challenges by portraying characters’ struggles, emotions, and journeys to recovery.
- Effects of Technology on Social Interaction Technology influences social interaction through digital communication, altered face-to-face interactions, and the challenges of maintaining personal connections. Analyzing technology’s impact on human relationships, this thesis assesses how digital devices shape the ways individuals connect, communicate, and experience social interactions.
- Media’s Influence on Political Spin and Manipulation Media platforms contribute to political spin through biased reporting, framing, and the manipulation of public perception. Investigating media’s role in political communication, this thesis analyzes how media outlets shape public opinion by framing news narratives, promoting specific agendas, and influencing political discourse.
- The Impact of Technology on Learning Styles Technology transforms learning styles through personalized education, online resources, and the shift toward digital learning environments. Focusing on educational advancements, this thesis explores how technology accommodates diverse learning styles, fosters individualized instruction, and alters the way students engage with educational content.
- Effects of Social Media on Civic Engagement Social media influences civic engagement through digital activism, online petitions, and the mobilization of collective action. This thesis examines how social media platforms empower individuals to engage in civic activities, advocate for social change, and participate in online campaigns.
- The Role of Literature in Navigating Grief and Loss Literature provides solace in grief and loss by depicting the complexities of mourning, offering catharsis, and promoting emotional healing. Addressing literature’s role in emotional support, this thesis explores how literary narratives provide readers with ways to navigate the emotional challenges of grief, loss, and mourning.
- Effects of Technology on Environmental Awareness Technology impacts environmental awareness through online campaigns, virtual experiences, and the dissemination of environmental information. Investigating technology’s ecological impact, this thesis analyzes how digital platforms raise awareness about environmental issues, connect individuals with nature, and inspire pro-environmental behaviors.
- Media’s Influence on Public Perception of Climate Change Media shapes public perception of climate change through framing, information presentation, and the portrayal of scientific consensus. Focusing on the media’s role in environmental discourse, this thesis assesses how media coverage impacts public understanding of climate change, influencing attitudes, policy discussions, and societal responses.
3 Point Thesis Statement Examples for Argumentative Essay
- Gun Control Stricter gun control laws can reduce firearm-related violence by limiting access, implementing background checks, and regulating firearm sales. In an argumentative essay, explore the effectiveness of stricter gun control measures in curbing gun violence through access restrictions, background checks, and sales regulations.
- Climate Change Human activities are the primary drivers of climate change evidenced by rising temperatures, shrinking ice caps, and increasing carbon emissions. In this essay, argue that human actions are responsible for climate change, citing evidence like temperature increases, melting ice, and escalating carbon emissions.
- Education Reform Education reform requires revising curricula, enhancing teacher training, and implementing student-centered learning approaches to improve learning outcomes. Addressing education reform, argue that curricular updates, teacher preparation, and student-centered teaching methods are pivotal for enhancing academic achievements.
- Capital Punishment Capital punishment should be abolished due to the risk of wrongful execution, moral concerns, and lack of proven deterrence effect. In an argumentative context, advocate for the abolition of the death penalty by discussing the potential for wrongful executions, moral dilemmas, and the lack of conclusive evidence of deterrence.
- Online Privacy Stricter regulations, user education, and enhanced data encryption are necessary to safeguard online privacy in the digital age. Argue for improved online privacy by discussing the need for stringent regulations, educating users about digital risks, and implementing robust data encryption.
- Animal Testing Animal testing should be replaced with alternative methods such as in vitro testing, computer simulations, and human cell studies to ensure ethical research. Take a stance against animal testing by arguing for the adoption of humane alternatives, including in vitro experiments, computer models, and human cell research.
- School Uniforms School uniforms foster a sense of belonging, minimize socio-economic disparities, and create a focused learning environment conducive to academic success. Present a case for school uniforms, highlighting their benefits in promoting inclusivity, reducing inequality, and cultivating a focused educational environment.
- Social Media Addiction Social media addiction requires intervention through awareness campaigns, setting digital boundaries, and promoting face-to-face interactions. Argue against the harmful effects of social media addiction, advocating for strategies like awareness initiatives, self-regulation, and prioritizing offline connections.
- Genetic Engineering Genetic engineering raises ethical concerns due to potential ecological disruption, unforeseen health risks, and the alteration of natural genetic diversity. Present an argument against genetic engineering by discussing ecological impacts, health uncertainties, and potential consequences for biodiversity.
- Universal Healthcare The adoption of universal healthcare improves public health outcomes by providing equitable access to medical services, reducing financial burdens, and promoting preventive care. Advocate for universal healthcare by discussing its potential to ensure healthcare equity, alleviate financial strain, and prioritize preventative measures.
3 Point Thesis Statement Examples for an Essay
- Happiness Happiness is attainable through positive relationships, meaningful pursuits, and a balanced approach to life’s challenges. In this essay, explore the avenues to achieve happiness through fostering connections, pursuing fulfilling goals, and embracing life’s complexities.
- Travel Travel enriches personal growth by broadening cultural perspectives, encouraging adaptability, and promoting experiential learning. Discuss the benefits of travel, emphasizing its role in expanding cultural horizons, developing adaptability, and facilitating hands-on education.
- Leadership Effective leadership encompasses clear communication, empathetic understanding, and the ability to inspire and motivate others. Delve into the qualities of a successful leader, focusing on communication skills, empathy, and the capacity to inspire and lead by example.
- Dreams Pursuing dreams requires determination, overcoming obstacles, and embracing failure as a stepping stone towards eventual success. Explore the journey toward realizing dreams, emphasizing the importance of resilience, facing challenges, and learning from setbacks.
- Time Management Efficient time management involves setting priorities, utilizing effective strategies, and maintaining a healthy work-life balance. Discuss the significance of managing time wisely, covering aspects like prioritization, productivity techniques, and maintaining personal well-being.
- Healthy Eating Maintaining a healthy diet necessitates balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep to promote overall well-being and academic success. In this essay, advocate for healthy eating habits by discussing the importance of nutritional balance, exercise, and sufficient sleep in supporting academic performance.
- Creativity Nurturing creativity involves embracing curiosity, seeking inspiration from various sources, and welcoming experimentation without fear of failure. Examine the facets of creativity, emphasizing curiosity-driven exploration, diverse sources of inspiration, and the courage to experiment.
- Friendship Meaningful friendships are built on trust, mutual support, and shared experiences, contributing to emotional fulfillment and personal growth. Explore the essence of friendship, discussing the core elements of trust, mutual assistance, and the impact of shared moments.
- Resilience Resilience emerges from facing adversity, developing coping strategies, and maintaining a positive outlook during challenging times. Highlight the concept of resilience, showcasing how it evolves through confronting hardships, developing coping mechanisms, and nurturing optimism.
- Nature Conservation Nature conservation demands sustainable practices, community involvement, and legislative support to preserve biodiversity and ecological balance. Discuss the importance of protecting the environment, emphasizing sustainable behaviors, community engagement, and legal measures to maintain biodiversity.
3 Point Thesis Statement Examples in Middle School
- Bullying Bullying prevention requires awareness campaigns, fostering empathy, and promoting open communication to create a safe and inclusive school environment. In middle school, discuss strategies to combat bullying by raising awareness, cultivating empathy, and encouraging open dialogue among students.
- Internet Safety Internet safety education involves responsible online behavior, recognizing digital risks, and safeguarding personal information to ensure a secure online experience. Address the importance of internet safety for middle school students, focusing on responsible online conduct, cyber awareness, and protecting personal data.
- Healthy Lifestyle Adopting a healthy lifestyle entails balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep to promote overall well-being and academic success. Discuss the significance of healthy habits for middle schoolers, emphasizing the role of balanced nutrition, exercise, and sufficient sleep in supporting academic performance.
- Peer Pressure Navigating peer pressure requires assertiveness, making informed choices, and seeking positive influences to maintain personal values and self-confidence. Address the challenges of peer pressure among middle school students, advocating for strategies like assertiveness training, informed decision-making, and seeking supportive friendships.
- Environmental Awareness Fostering environmental awareness involves learning about ecosystems, practicing eco-friendly habits, and participating in conservation efforts to protect the planet. Explore the importance of environmental education for middle schoolers, encouraging them to learn about ecosystems, adopt eco-conscious behaviors, and engage in conservation projects.
- Friendship Dynamics Nurturing positive friendships involves empathy, effective communication, and resolving conflicts to foster healthy and supportive relationships. Address the complexities of middle school friendships, emphasizing empathy, communication skills, and conflict resolution techniques for building strong connections.
- Time Management Developing time management skills encompasses setting priorities, using organizational tools, and establishing routines to balance academics and leisure activities. Discuss the relevance of time management for middle school students, introducing strategies like prioritization, organization, and establishing effective routines.
- Goal Setting Goal setting involves defining aspirations, breaking tasks into manageable steps, and persevering in the face of challenges to achieve personal ambitions. Explore the concept of goal setting among middle schoolers, encouraging them to define aspirations, create actionable plans, and cultivate resilience.
- Cultural Diversity Embracing cultural diversity involves understanding different perspectives, promoting inclusion, and celebrating various traditions to create a harmonious school community. Address cultural diversity in middle school, advocating for cultural understanding, inclusivity, and the importance of respecting diverse backgrounds.
- Cyberbullying Combating cyberbullying requires reporting incidents, practicing digital citizenship, and creating a culture of kindness to ensure online safety and well-being. Discuss the implications of cyberbullying for middle schoolers, emphasizing the importance of reporting, practicing responsible online behavior, and fostering a positive digital environment.
3 Point Thesis Statement Examples in Literature
- The Great Gatsby “The Great Gatsby” portrays the disillusionment of the American Dream through characters’ pursuit of wealth, the facade of social status, and the inability to attain lasting happiness. Discuss the themes of disillusionment and the American Dream in F. Scott Fitzgerald’s novel, exploring how characters’ materialistic pursuits and social aspirations lead to unfulfilled desires.
- To Kill a Mockingbird “To Kill a Mockingbird” highlights social injustice through the lens of racism, the loss of innocence, and the importance of empathy in understanding others’ perspectives. Analyze Harper Lee’s novel, focusing on its exploration of racial inequality, the loss of innocence, and the value of empathy in addressing societal prejudices.
- Romeo and Juliet “Romeo and Juliet” examines the consequences of impulsivity, the impact of familial feuds, and the significance of love transcending societal boundaries. Explore William Shakespeare’s tragedy, discussing the themes of impulsive actions, familial conflicts, and the enduring power of love that defies societal constraints.
- 1984 “1984” critiques totalitarianism by depicting government surveillance, manipulation of language, and the suppression of individuality as dystopian manifestations of power. Analyze George Orwell’s dystopian novel, focusing on its portrayal of authoritarian control, the manipulation of information, and the degradation of personal freedoms.
- Pride and Prejudice “Pride and Prejudice” explores societal norms, gender expectations, and the complexities of love and self-discovery as characters navigate social hierarchies. Examine Jane Austen’s classic work, delving into its examination of social class, gender roles, and the transformative power of genuine affection in overcoming biases.
- The Catcher in the Rye “The Catcher in the Rye” presents the alienation of youth, the search for authenticity, and the complexities of growing up as Holden Caulfield navigates the challenges of adolescence. Discuss J.D. Salinger’s novel, focusing on the protagonist’s feelings of alienation, his quest for authenticity, and the portrayal of teenage angst and identity formation.
- The Lord of the Rings “The Lord of the Rings” explores the battle between good and evil, the hero’s journey, and the significance of fellowship as characters embark on an epic quest to save Middle-earth. Analyze J.R.R. Tolkien’s epic fantasy, discussing its themes of morality, heroism, and the power of camaraderie as characters confront the forces of darkness.
- Frankenstein “Frankenstein” delves into the consequences of unchecked ambition, the ethical implications of scientific creation, and the alienation of the outsider as Victor Frankenstein grapples with his monstrous creation. Examine Mary Shelley’s novel, addressing themes of ambition, ethics, and societal rejection as Victor Frankenstein’s scientific endeavors lead to unintended consequences.
- The Scarlet Letter “The Scarlet Letter” explores the consequences of societal judgment, the complexities of sin and redemption, and the resilience of the human spirit as Hester Prynne navigates the aftermath of her actions. Analyze Nathaniel Hawthorne’s work, discussing its examination of guilt, societal norms, and the capacity for personal growth in the face of adversity.
- Brave New World “Brave New World” critiques a dystopian future by depicting a society driven by consumerism, the suppression of individuality, and the manipulation of happiness as the ultimate goal. Explore Aldous Huxley’s dystopian vision, discussing its commentary on technological control, the pursuit of pleasure, and the loss of authentic human experience.
3 Point Thesis Statement Examples for Graphic Organizers
- Solar System Understanding the solar system involves recognizing the sun as the center, identifying planets and their characteristics, and comprehending the roles of asteroids, comets, and moons. Discuss the solar system using a graphic organizer, highlighting its key components including the sun, planets, asteroids, comets, and moons, along with their distinctive features.
- Ecosystems Exploring ecosystems involves categorizing biomes, understanding food chains and webs, and recognizing the importance of biodiversity in maintaining ecological balance. Utilize a graphic organizer to depict various biomes within ecosystems, illustrate food chains and webs, and emphasize the significance of biodiversity for ecological stability.
- Literary Elements Analyzing literature entails identifying plot elements, character traits, and thematic concepts to gain a comprehensive understanding of narrative structure and meaning. Create a graphic organizer to analyze literary works, mapping out key elements such as plot, characters, and themes to enhance comprehension of narrative elements.
- Historical Events Studying historical events requires sequencing chronological occurrences, contextualizing historical contexts, and identifying influential figures and their contributions. Construct a graphic organizer to explore historical events, arranging them chronologically, providing contextual information, and highlighting notable individuals and their impacts.
- Plant Life Cycle Exploring the plant life cycle involves identifying stages from seed germination to reproduction, understanding the roles of roots, stems, leaves, and flowers, and grasping the significance of pollination. Employ a graphic organizer to depict the plant life cycle, depicting stages from seed germination to pollination and reproduction, while illustrating the roles of different plant parts.
- Literary Genres Understanding literary genres requires categorizing fiction, non-fiction, poetry, drama, and identifying distinguishing characteristics that define each genre’s narrative style. Use a graphic organizer to differentiate literary genres, classifying fiction, non-fiction, poetry, and drama while highlighting the unique features that define each genre.
- Elements of a Story Analyzing the elements of a story involves identifying the exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution to gain insight into narrative structure and development. Create a graphic organizer to explore the elements of a story, mapping out the key stages from exposition to resolution, enhancing comprehension of narrative progression.
- Food Groups Understanding dietary balance entails categorizing food groups such as fruits, vegetables, grains, proteins, and dairy, and recognizing their nutritional contributions to overall health. Utilize a graphic organizer to depict food groups, categorizing fruits, vegetables, grains, proteins, and dairy while emphasizing their roles in providing essential nutrients.
- Biographical Information Exploring biographies involves organizing key details like birth, achievements, contributions, and impact to gain insights into notable individuals’ lives and legacies. Construct a graphic organizer to analyze biographical information, arranging details such as birth, accomplishments, significant contributions, and lasting impact on society.
- Cause and Effect Relationships Understanding cause and effect relationships entails identifying triggers and outcomes, recognizing the interconnectedness of events, and comprehending the implications of actions. Design a graphic organizer to explore cause and effect relationships, mapping out causal factors and corresponding effects to illustrate the interconnected nature of events.
Free 3 Point Thesis Statement Worksheets Download
Download our free 3 Point Thesis Statement Worksheets to enhance your writing skills. These comprehensive resources provide structured guidance on crafting impactful thesis statements for various topics. Through step-by-step exercises, you’ll learn to formulate clear arguments with three supporting points, fostering effective communication and analytical thinking. Elevate your essay writing by mastering the art of concise and persuasive thesis statements with our downloadable worksheets.
3 Point Thesis Statement Worksheet

Size: 360 KB
3 Point Thesis Statement Worksheet Sample

Size: 160 KB
Three Point Thesis Statement Worksheet Download

Size: 170 KB
How to Write a 3 Point Thesis Statement? – Step by Step Guide
Crafting a compelling 3 Point Thesis Statement involves careful planning and a structured approach. Follow this step-by-step guide to create a clear and impactful thesis that effectively outlines your main argument and supporting points:
- Choose Your Topic: Select a specific topic that you want to address in your essay. Ensure it’s focused enough to be thoroughly explored within the scope of your work.
- Identify Your Main Argument: Determine the central point or argument you want to make about the chosen topic. This main idea will serve as the foundation for your thesis statement.
- Brainstorm Supporting Points: Identify three key points that support and reinforce your main argument. These points will guide your essay’s structure and content.
- Craft Your Thesis Statement: Combine your main argument and the three supporting points into a single, concise sentence. Ensure it clearly conveys the overall message of your essay.
- Order and Coherence: Arrange your supporting points logically. Typically, present them in the order you’ll address them in your essay, from strongest to weakest or chronologically.
- Avoid Ambiguity: Make sure your thesis statement is specific and unambiguous. Avoid vague language that might confuse or mislead readers.
- Precision and Clarity: Use clear and precise language in your thesis statement. Each word should contribute to the overall clarity and accuracy of your message.
- Revise for Consistency: Check that your thesis statement aligns with the content of your essay. Any deviations should be addressed to maintain coherence.
- Seek Feedback: Share your thesis statement with peers or mentors for feedback. Their insights can help you refine and strengthen your argument.
- Refine and Edit: Revise your thesis statement based on the feedback you receive. Edit for grammar, style, and conciseness.
- Finalize Your Thesis Statement: Once satisfied, incorporate your refined thesis statement into your essay’s introduction, ensuring it provides a roadmap for readers.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can create a powerful 3 Point Thesis Statement that effectively communicates your main argument and supporting points, setting the tone for a well-structured and persuasive essay.
Tips for Writing a 3 Point Thesis Statment
- Clarity is Key: Keep your thesis statement clear and straightforward, avoiding vague or convoluted language.
- Singular Focus: Center your thesis around a single, focused argument to maintain a clear message.
- Strong Supporting Points: Select three robust supporting points that directly bolster your main argument.
- Parallel Structure: Use consistent grammatical structure for your supporting points to enhance organization.
- Logical Order: Arrange supporting points logically, from strongest to weakest or in a coherent sequence.
- Specific Examples: Back up your points with concrete evidence, avoiding general statements.
- Avoid First-Person: Keep your thesis objective by refraining from using first-person pronouns.
- Highlight Importance: Explain the significance or broader implications of your main argument and points.
- Feedback Matters: Seek input from others to refine and strengthen your thesis statement.
- Connect and Transition: Ensure your thesis smoothly leads into the content of your essay’s body.
Mastering the art of crafting impactful 3 Point Thesis Statements elevates your writing prowess. With a clear main argument and well-chosen supporting points, your essays gain depth and structure. Following expert tips ensures clarity, conciseness, and logical organization. This skill empowers you to communicate effectively, fostering a deeper connection with readers and enhancing the overall impact of your work.

AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
How long should a chapter be, similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and responsible writing, you may also like, similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and..., what is a master’s thesis: a guide for..., should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., what are the benefits of generative ai for..., how to avoid plagiarism tips and advice for..., plagiarism checkers vs. ai content detection: navigating the..., plagiarism prevention: why you need a plagiarism check..., what is a literature review how to write....
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Human Trafficking — Thesis Statement for Human Trafficking
Thesis Statement for Human Trafficking
- Categories: Human Trafficking
About this sample

Words: 612 |
Published: Mar 20, 2024
Words: 612 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Prevalence of human trafficking, causes of human trafficking, impact on victims, measures to combat human trafficking.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 783 words
3 pages / 1172 words
3 pages / 1267 words
5 pages / 2332 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Human Trafficking
The term forced labor is often associated with historical atrocities, but unfortunately, it remains a pervasive issue in the modern world. This essay delves into the complex and distressing phenomenon of forced labor, examining [...]
Human trafficking is a despicable crime that continues to plague societies around the world, robbing individuals of their freedom and dignity. It is a heinous violation of human rights and a global issue that demands immediate [...]
Human trafficking is a modern-day form of slavery that involves the illegal trade of human beings for exploitation or commercial gain. It is a grave violation of human rights that affects millions of people around the world, [...]
Sex trafficking is a global issue that has gained significant attention in recent years. It involves the exploitation of individuals, primarily women and children, for the purpose of forced labor, sexual exploitation, and other [...]
Human trafficking is a devastating and egregious violation of human rights that affects millions of people around the world. This modern-day form of slavery involves the recruitment, transportation, and exploitation of [...]
Child trafficking is a heinous crime that continues to plague our society, robbing innocent children of their childhood and basic human rights. From forced labor to sexual exploitation, the trafficking of children remains a [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Your thesis statement is one of the most important parts of your paper. It expresses your main argument succinctly and explains why your argument is historically significant. Think of your thesis as a promise you make to your reader about what your paper will argue. Then, spend the rest of your paper-each body paragraph-fulfilling that promise.
Thesis statements vary based on the rhetorical strategy of the essay, but thesis statements typically share the following characteristics: Presents the main idea. Most often is one sentence. Tells the reader what to expect. Is a summary of the essay topic. Usually worded to have an argumentative edge.
These formulas share two characteristics all thesis statements should have: they state an argument and they reveal how you will make that argument. They are not specific enough, however, and require more work. Refine. As you work on your essay, your ideas will change and so will your thesis. Here are examples of weak and strong thesis statements.
Crafting a good thesis is one of the most challenging parts of the writing process, so do not expect to perfect it on the first few tries. Successful writers revise their thesis statements again and again. A successful thesis statement: • makes a historical argument. • takes a position that requires defending. • is historically specific.
Thesis statements vary based on the rhetorical strategy of the essay, but thesis statements typically share the following characteristics: Presents the main idea. Most often is one sentence. It tells the reader what to expect. Is a summary of the essay topic. Usually worded to have an argumentative edge.
The thesis statement summarizes the central argument of your paper. It is placed at the top of the outline page, and appears again in the opening paragraph. A clearly stated thesis performs three functions: it provides a focus for your research, helping to prevent time wasting digressions. it furnishes an organizational theme for the paper ...
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
Thesis statements: Harry Truman's decision to drop the bomb on Hiroshima was motivated by racism. The US confrontation with the Soviets was the key factor in Truman's decision to drop the bomb on Hiroshima. This paper will demonstrate that in his decision to drop the bomb on Hiroshima, Truman was unduly influenced by hawks in his cabinet.
done, for example, in their junior tutorial essays. This is, of course, just fine; and you can even use some of the material from said essays in your thesis if you must (it's not necessary to reinvent the wheel). However, your senior thesis should be a completely new project. If you wrote on William
Some ways to help you develop your thesis are by: stating the purpose of the paper. asking a question and then using the answer to form your thesis statement. summarizing the main idea of your paper. listing the ideas you plan to include, then see if they form a group or theme. using the ponts of controversy, ambiguity, or "issues" to develop a ...
Of course, a thesis statement does not prove your argument. Your evidence and analysis, combined with your writing's eloquence, will help persuade readers. But a strong thesis statement will make for a more compelling essay and, as Toynbee advised, demonstrate that history is more than just "one damned thing after another." Debate that.
example, then the thesis statement of any historical work (such as a history exam essay) is the philosophy as yet embellished by example, the analysis as yet buttressed by evidence, the spool of interpretive thread that you will subsequently unravel and weave throughout the body of your essay (for more on weaving your thesis, see #4 below).
In writing the thesis, the author should keep in mind that the document will require multiple changes and drafts—perhaps even new insights. A student should gather feedback from a professor and colleagues to ensure their thesis is clear and effective before finalizing the draft. 6. Prepare to Defend the Thesis.
Evidence supports your thesis statement. Your thesis statement should be based on careful consideration of the evidence you have assembled. Select the strongest, most relevant facts and examples to explain your claim. Your evidence will include examples, information, and quotations that support your thesis. Depending on the
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
2021 2022 History Fair - Debate and Diplomacy in History: Writing a Thesis Statement. What is History Fair? History Fair Theme; Potential Topics; Logging in, Creating a Project, and Sharing in Noodletools ... Thesis Statement Worksheet and Example. Thesis Statement Tips. Thesis Statement Tips: 1.) Don't Use the First Person . Incorrect ...
Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay. Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence. Each paragraph should focus on a specific argument or aspect of your thesis. Present evidence from primary and secondary sources to support each argument.
B. Thesis statement. The Trail of Tears was a devastating event that resulted in the displacement and suffering of many Native American tribes, highlighting the detrimental effects of government policies and the disregard for indigenous rights. II. Historical Context.
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples. Analyze the Structure: Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument. Study the Thesis Statement:
Pollution is bad for the environment. This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is ...
10 Example Thesis Statements on Art. The Italian Renaissance, which started in the 14th century and lasted until the 17th, was a time of great artistic and cultural revival. The painting, sculpture, and architectural expressions that emerged during this time had a significant influence on Western art and culture.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute. An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic. Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's ...
The Second Amendment and the right to bear arms. To truly understand the debate on gun control, we must first look at the historical context of the Second Amendment. Enshrined in the United States Constitution, the Second Amendment was originally intended to ensure the right of citizens to bear arms as a means of self-defense and protection ...
Thesis Statement: It is imperative to prioritize mental health and provide support for individuals struggling with mental illness in order to promote overall well-being and prevent the negative consequences of neglecting mental health. Body 1. The Importance of Mental Health Awareness and Support. Mental health is a fundamental aspect of our overall well-being, and it is essential to raise ...
Example of a 3 Point Thesis Statement. Topic: The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity. Thesis Statement: "The accelerating effects of climate change threaten global biodiversity through temperature shifts, habitat degradation, and altered migration patterns.". In this example, the 3-point thesis statement clearly presents the three ...
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
In conclusion, gun violence is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention and action. By addressing the causes of gun violence and implementing solutions that focus on strengthening gun laws, investing in mental health resources, and addressing root causes of violence, we can work towards reducing gun violence in our society.
The debate over abortion has been ongoing for many years, and it has raised important ethical, legal, and medical issues. While some argue that abortion is a woman's right to choose, others believe that it is morally wrong and goes against the sanctity of life. This essay will analyze the various perspectives on abortion, the ethical ...
Human trafficking is a heinous crime that violates the fundamental human rights of individuals across the globe. This essay aims to explore the various aspects of human trafficking, including its prevalence, causes, impact on victims, and measures to combat this abhorrent practice. By examining the statistics, evidence, and reputable sources ...