- Research Paper Guides
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- How to Write an Appendix: Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

How to Write an Appendix: Step-by-Step Guide & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
While composing your work, you may stumble upon a question on how to write an appendix.
An appendix is a supplemental section of a research paper that provides additional information, data, or materials to support the main content. The appendix is usually placed at the end of the document and is numbered with letters or numbers, such as "Appendix A," "Appendix B," etc. The purpose of an appendix is to provide readers with supplementary details that are not included in the main text but are relevant to the topic.
Once you decide on writing appendices, you should collect additional information and format your text as required. Here, we will talk about how you can work with appendices. We will also show some nuances of their preparation process using a real example. Is the deadline around the corner? Consider using professional research paper help from expert scholars.
What Is an Appendix: Definition
Experienced researchers know what an appendix in a paper is. But aspiring authors often have problems with this section of the work. First of all, you should understand that appendices are an additional section of a dissertation or any other scientific paper that includes additional information. Main points are not placed in an appendix meanwhile at the end of your work it can expand on some context or clarify author’s position on a particular issue. Also, an appendix is often placed after the citation page of a work. It is indicated with the help of references in a main text.
What Is the Purpose of an Appendix
Quite often, authors don’t understand the purpose of an appendix. This usually looks like a table and is not included in a main text. Remember that content of your dissertation should be concise and clear. It is also undesirable if you deviate from your theme so as not to confuse readers. Therefore, you can provide a reference, which will lead a reader to an appendix of a thesis. Typically, the purpose of an appendix is to extra information that is usually not included in the text's body. It expresses author's point of view, and provides additional information. It may not address the immediate topic of your dissertation or expand on current research. As a reminder, your work should be clear even without studying an appendix. So make sure you don't put important details there.
What Can You Include in an Appendix
An appendix in a paper is a supplement to a main text, not a replacement. You can put different elements there. It is better if you separate appendices, highlighting one element in each of them. Don’t forget about separate references in your text. Otherwise it will be difficult for a reader to understand your information better. Thus, the following information can be added:
- diagrams with illustrative figures;
- abbreviations ;
- interviews;
- statistics, and much more.
There are no restrictions on content added to your dissertation's appendices. Theoretically, you can attach absolutely any information that is relevant to your topic. Thus, possibilities for evidence base are almost unlimited. All you need to do is add tables or any other information.
How to Write an Appendix: Full Guide
If you already have experience working on dissertations and other scientific texts, you will not wonder how to make an appendix. However, it is still important that you get some advice on how to properly structure an appendices section. This will help add information that may be redundant in the main part of your paper. We offer 4 simple steps to create an informative and readable appendix block.
Step 1. Make an Appendix: Include Your Data
When creating an appendix, include extra data in their raw form. That is, you might not have used some details in your main paper. But you want a reader to know more information. For example, it can be calculations, some results of which are mentioned in your main text. Or maybe, you can add some statistics that clearly demonstrate your research paper conclusion . You can also include facts from other scientific sources that support your position. One thing is important — information should complement your text but not contradict it.
Step 2. Include Visual Supporting Documents in an Appendix
When you are writing an appendix, you can’t avoid visual additions that clearly demonstrate an information and save an author from lengthy descriptions in the text. Should you need to support your conclusions drawn in the scientific text, these can be used:
Don’t forget: you should quote and indicate the authorship of graphics used in your work. If you took it from any third-party sources, of course. Thus, a reader will be able to find additional data that explains the content of your text. It is good if you personally put results of your research in a graphic form. To do this, you can use Office programs, graphic editors and other programs available to PC users.
Step 3. Describe the Instruments of Your Research in Your Appendices
It is good if your appendix in the research paper has a section for indicating tools that were used during the preparation of your dissertation writing . This way, your reader will understand how you collected information and do it themselves. For example, it could be a dictaphone or tape recorder on which an interview with your expert was recorded. Or you might have used a video camera for recording facts and interviews. In such case, it is advisable to indicate these instruments in your appendix. Specialized equipment for measuring, calculating and making graphics should also be added at the beginning of the appendix. This way, you will demonstrate your skills and knowledge. Research units don’t require extra tools, so make sure they are listed. You can do it even in a short format.
Step 4. Include an Interview and Transcripts in an Appendix
When conducting interviews and surveys for collecting information, make an appendix with photocopies of handwritten materials or electronic copies of digital surveys. Their order is not important. The main thing is that your research text contains references. This will allow you to quickly study the sources. You should not only show that the source contains important data but also explain it. So, even additional content, including questions and answers, needs to be listed. But if you originally had a readable format, you don’t need to do this. In addition to interviews, also add screenshots or photos of correspondences used for surveys. For example, you can refer to a significant researcher with whom you exchanged letters. Or maybe you studied subject, together with this researcher, and they gave some comments on a particular issue. Do not know how to write a discussion section of a research paper ? Do not worry, we have the whole article dedicated to this topic.
Formatting an Appendix: Main Rules
Formatting of appendices is required in any case. First of all, provide correct citations. APA, MLA, and Chicago are the most commonly used standards. Although, you should clarify what formatting requirements your institution has. Correct formatting includes:
- Appendix title. Write it at the top of the content page, indicate its title, using letters or numbers for ordering.
- Sorted by mention. Don’t add appendices randomly, it is better to do it in chronological order. That is, as information from it is given in main text.
- Location after bibliography. This is a general requirement that cannot always be met. For example, if your professor wants the appendices to be put before the bibliography, this will have to be done.
- Page numbers. All dissertation pages should be numbered, even if they are blank. This will make the appendix block the part of main text.
Also, review your appendix before approval. Make sure that its content is clear, error-free, and correctly quoted.
Appendix Example
To do the job successfully, it is recommended to have an example of an appendix at hand. Without it, there are usually problems with a choice of font and mentions that appear in main text. We will show you what the appendix itself looks like at the end of the dissertation using a short interview as an example.

We have one more blog in case you wonder what is an abstract in a paper or need some examples and writing tips.
How to Make an Appendix: Final Thoughts
Thus, we talked about how to write an appendix. It allows you to include additional details, while avoiding writing them in the body of your text. To do this, one can use graphics, transcriptions of conversations, tables and statistics — anything that complements your research. Be sure to clarify formatting requirements of your university. Arrange appendices in an order in which they appear in your text. Try to use your own materials and not take other people's work. In case of unique findings, they can be used in your work.
Please contact us if you have any difficulties preparing an academic work! Our professional paper writers guarantee high quality and loyal prices. Just choose a writer to your liking, send your requirements and you're good to go!
Frequently Asked Questions About Appendix Writing
1. how do you add an appendix to an essay.
The inclusion of appendix to an essay is the same as to any other paper. You need to provide references in your text of an essay itself, as well as submit attachments after a bibliography. Don't forget to specify name of an appendix for easy navigation.
2. Do I add references to the appendix?
Yes, this is not only recommended but must be done. In this case the appendix will allow your reader to check the reliability of sources you used. Moreover, if you took any information from third-party sources, this protect you from plagiarism charges.
4. How do you create an appendix in Word?
It is not difficult to prepare an appendix in Word, because this Office program contains all the necessary tools. To get started, choose the same font, font size and indentation that were used in the main text, so as not to visually break away from it. We also recommend that you apply title formatting with built-in Word tools. Place the appendix titles at the top in the center of a page. In this case it will be much easier to navigate the paper.
3. What is an appendix in a report example?
You can include a wide range of information into an appendix in a report. It is better to opt for descriptive formats, though. For example, it can be graphical or mathematical research results, statistics of a certain phenomenon, and questionnaires filled in by other people.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

- How To Write A Research Paper Appendix: A Step-by-Step Guide

Think of appendices like bonus levels on your favorite video game. They are not a major part of the game, but they boost your points and they make the game worthwhile.
Appendix are important facts, calculations, or data that don’t fit into the main body of your research paper. Having an appendix gives your research paper more details, making it easier for your readers to understand your main ideas.
Let’s dive into how to create an appendix and its best practices.
Understanding the Purpose of an Appendix

If you’re looking to add some extra depth to your research, appendices are a great way to do it. They allow you to include extremely useful information that doesn’t fit neatly into the main body of your research paper, such as huge raw data, multiple charts, or very long explanations.
Think of your appendix as a treasure chest with different compartments. You can include different information including, extra data, surveys, graphs, or even detailed explanations of your methods. You can fit anything too big or detailed for the main paper in the appendix.
Planning Your Appendix

Before you dive into making your appendix, it’s a good idea to plan things out; think of it as drawing a map before going on an adventure.
You want your appendix to be organized and provide more context to your research. Not planning it will make the process time-consuming and make the appendix confusing to people reading your research paper.
How to Decide What to Include in Your Research Paper
You have to sort through the content that you will include in your appendix. Think of what your readers need to know to understand your key points. Anything that’s overly detailed, off-topic, or clutters up your paper is a good candidate for your appendix.
Tips for Organizing Your Appendix
Once you’ve figured out what to put in your appendix, it’s time to organize it. Your appendix is a place to add extra information, but it shouldn’t be cluttered or confusing to your readers. Instead, it should make your research paper easier to understand.
Use clear headings, labels, and even page numbers to help your readers find the information they need in the appendix. This way, it’s not a jumbled mess, but a well-organized part of your research paper
Formatting Guidelines

Yes, your appendix must be formatted. Most of the time, you’ll want to keep the font and margin sizes consistent with your main paper.
However, some universities and journals may have specific guidelines for appendix formatting. Verify if your institution has special guidelines, if they do, follow them, if they don’t use the same format as your main text.
Here’s a typical breakdown of how to format your appendix:
(1) Labeling and Titling
If you have different types of information in your appendix, use letters to label them, such as “Appendix A” and “Appendix B”. Then, give each appendix a title that explains the information inside it.
For example, if the first section of your appendix contains raw survey data, you could call it “Appendix A (Survey Data of People Living with Diabetes Under 18 in Texas)”. If the second section of your appendix contains charts, you could call it “Appendix B (The Effect of Sugar Tax in Curbing Diabetes in Children and Young Adults)”.
(2) Numbering Tables, Figures, and More
If you have tables, figures, or other things in your appendix, number them like a list. For example, “Table A1,” “Figure A1,” and more. This numbering helps your readers know what they’re looking at, sort of like chapters in a book.
Creating Tables and Figures

Using tables and figures helps you organize your data neatly in your appendix. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating tables and figures in your appendix:
Choose the Right Format for Your Appendix Data
Before creating tables or figures, you need to pick the right format to display the information. Think about what makes your data most clear and understandable.
For example, a table is better for detailed numbers, while a graph is great for showing trends. The right format makes your information easy to grasp and makes your paper look organized.
How to Create Tables in Your Appendix
You can use a spreadsheet program (like Excel or Google Sheets) to create tables to arrange information neatly. Make sure to give your table a clear title so readers know what it’s about.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating tables with a spreadsheet program:
- Open Google Sheets/Excel : Access Google Sheets or Excel through the web or download the app
- Open a New Spreadsheet or Existing File : Create a new spreadsheet or open an existing one where you want to insert a table.
- Select Data : Click and drag to select the data you want to include in the table.
- Insert Table : Once your data is selected, go to the “Insert” menu, then select “Table.
- Create Table : A dialog box will appear, confirming the selected data range. Make sure the “Use the first row as headers” option is checked if your data has headers. Click “Insert .”
- Customize Your Table : After inserting the table, you can customize it by adjusting the style, format, and other table properties using the “Table” menu in Google Sheets or Excel.
You can use software like PowerPoint, Google Slides, or graphic design tools to create them. If you have a chart or graph, make sure it’s easy to understand and add a title or labels to explain it.
You can use the editing tools for images to change the size and other aspects of the image.
Stop Struggling with Research Proposals! Get Organized and Impress Reviewers with our Template
Including Raw Data
The major reasons for including raw data in your appendix are transparency and credibility. Raw data is like your research recipe; it shows exactly what you worked with to arrive at your conclusions.
Raw data also provides enough information to guide researchers in replicating your study or getting a deeper understanding of your research.
Formatting and Presenting Raw Data
Formatting your raw data makes it easy for anyone to understand. You can use tables, charts, or even lists to display your data. For example, if you did a survey, you could put the survey responses in a table with clear headings.
When presenting your raw data, clear organization is your best friend. Use headings, labels, and consistent formatting to help your readers find and understand the data. This keeps your appendix from becoming a confusing puzzle.
Citing Your Appendix
Referencing your appendix in the main text gives readers a full picture of your research while they’re reading- They don’t have to wait until the end to figure out important details of your research.
Unlike actual references and citations, citing your appendix is a very straightforward process. You can simply say, “See Appendix A for more details.”
In-Text Citations for Appendix Content
If you would like to cite information in your appendix, you usually mention the author, year, and what exactly you’re citing. This allows you to give credit to the original creator of the content, so your readers know where it came from.
For instance, if you included a chart from a book in your appendix, you’d say something like (Author, Year, p. X). Keep in mind that there are different citation styles (APA, MLA, Chicago, and others), so your appendix may look a little different.
Proofreading and Editing

Proofreading and editing your appendix is just as important as proofreading and editing the main body of your paper. A poorly written or formatted appendix can leave a negative impression on your reader and detract from the overall quality of your work.
Make sure that your appendix is consistent with the main text of your paper in terms of style and tone unless otherwise stated by your institution. Use the same font, font size, and line spacing in the appendix as you do in the main body of your paper.
Your appendix should also be free of errors in grammar, spelling, punctuation, and formatting.
Tips for Checking for Errors in Formatting, Labeling, and Content
Here are some tips for checking for errors in formatting, labeling, and content in your appendix:
- Formatting : Make sure that all of the elements in your appendix are formatted correctly, including tables, figures, and equations. Check the margins, line spacing, and font size to make sure that they are consistent with the rest of your paper.
- Labeling : All of the tables, figures, and equations in your appendix should be labeled clearly and consistently. Use a consistent numbering system and make sure that the labels match the references in the main body of your paper.
- Content : Proofread your appendix carefully to catch any errors in grammar, spelling, punctuation, and content. You can use grammar editing tools such as Grammarly to help you automatically detect errors in your context.
Appendix Checklist
Having an appendix checklist guarantees a well-organized appendix and helps you spot and correct any overlooked mistakes.
Here’s a checklist of key points to review before finalizing your appendix:
- Is all of the information in the appendix relevant and necessary?
- Is the appendix well-organized and easy to understand?
- Are all the tables, numbers, and equations clearly labeled?
- Is the appendix formatted correctly and consistently with the main body of the paper?
- Is the appendix free of errors in grammar, spelling, punctuation, and content?
Sample Appendix
We have discussed what you should include in your appendix and how to organize it. Let’s take a look at what a well-formatted appendix looks like:
Appendix A. (Raw Data of Class Scores)
The following table shows the raw data collected for the study.
How the Sample Appendix Adheres to Best Practices
- The appendix is labeled clearly and concisely as “Appendix A. (Raw Data of Class Score).”
- The appendix begins on a new page.
- The appendix is formatted consistently with the rest of the paper, using the same font, font size, and line spacing.
- The table in the appendix is labeled clearly and concisely as “Table A1.”
- The table is formatted correctly, with consistent column widths and alignment.
- The table includes all of the necessary information, including the participant number, age, gender, and score.
- The appendix is free of grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
Having an appendix easily makes your research paper impressive to reviewers, and increases your likelihood of achieving high grades or journal publication. It also makes it easier for other researchers to replicate your research, allowing you to make a significant contribution to your research field.
Ensure to use the best practices in this guide to create a well-structured and relevant appendix. Also, use the checklist provided in this article to help you carefully review your appendix before submitting it.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- appendix data
- business research
- Moradeke Owa

You may also like:
Projective Techniques In Surveys: Definition, Types & Pros & Cons
Introduction When you’re conducting a survey, you need to find out what people think about things. But how do you get an accurate and...

Subgroup Analysis: What It Is + How to Conduct It
Introduction Clinical trials are an integral part of the drug development process. They aim to assess the safety and efficacy of a new...
43 Market Research Terminologies You Need To Know
Introduction Market research is a process of gathering information to determine the needs, wants, or behaviors of consumers or...
Desk Research: Definition, Types, Application, Pros & Cons
If you are looking for a way to conduct a research study while optimizing your resources, desk research is a great option. Desk research...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
An appendix contains supplementary material that is not an essential part of the text itself but which may be helpful in providing a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem or it is information that is too cumbersome to be included in the body of the paper. A separate appendix should be used for each distinct topic or set of data and always have a title descriptive of its contents.
Tables, Appendices, Footnotes and Endnotes. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of...
Appendices are always supplementary to the research paper. As such, your study must be able to stand alone without the appendices, and the paper must contain all information including tables, diagrams, and results necessary to understand the research problem. The key point to remember when including an appendix or appendices is that the information is non-essential; if it were removed, the reader would still be able to comprehend the significance, validity , and implications of your research.
It is appropriate to include appendices for the following reasons:
- Including this material in the body of the paper that would render it poorly structured or interrupt the narrative flow;
- Information is too lengthy and detailed to be easily summarized in the body of the paper;
- Inclusion of helpful, supporting, or useful material would otherwise distract the reader from the main content of the paper;
- Provides relevant information or data that is more easily understood or analyzed in a self-contained section of the paper;
- Can be used when there are constraints placed on the length of your paper; and,
- Provides a place to further demonstrate your understanding of the research problem by giving additional details about a new or innovative method, technical details, or design protocols.
Appendices. Academic Skills Office, University of New England; Chapter 12, "Use of Appendices." In Guide to Effective Grant Writing: How to Write a Successful NIH Grant . Otto O. Yang. (New York: Kluwer Academic, 2005), pp. 55-57; Tables, Appendices, Footnotes and Endnotes. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Points to Consider
When considering whether to include content in an appendix, keep in mind the following:
- It is usually good practice to include your raw data in an appendix, laying it out in a clear format so the reader can re-check your results. Another option if you have a large amount of raw data is to consider placing it online [e.g., on a Google drive] and note that this is the appendix to your research paper.
- Any tables and figures included in the appendix should be numbered as a separate sequence from the main paper . Remember that appendices contain non-essential information that, if removed, would not diminish a reader's ability to understand the research problem being investigated. This is why non-textual elements should not carry over the sequential numbering of non-textual elements in the body of your paper.
- If you have more than three appendices, consider listing them on a separate page in the table of contents . This will help the reader know what information is included in the appendices. Note that some works list appendices in the table of contents before the first chapter while other styles list the appendices after the conclusion but before your references. Consult with your professor to confirm if there is a preferred approach.
- The appendix can be a good place to put maps, photographs, diagrams, and other images , if you feel that it will help the reader to understand the content of your paper, while keeping in mind the study should be understood without them.
- An appendix should be streamlined and not loaded with a lot information . If you have a very long and complex appendix, it is a good idea to break it down into separate appendices, allowing the reader to find relevant information quickly as the information is covered in the body of the paper.
II. Content
Never include an appendix that isn’t referred to in the text . All appendices should be summarized in your paper where it is relevant to the content. Appendices should also be arranged sequentially by the order they were first referenced in the text [i.e., Appendix 1 should not refer to text on page eight of your paper and Appendix 2 relate to text on page six].
There are very few rules regarding what type of material can be included in an appendix, but here are some common examples:
- Correspondence -- if your research included collaborations with others or outreach to others, then correspondence in the form of letters, memorandums, or copies of emails from those you interacted with could be included.
- Interview Transcripts -- in qualitative research, interviewing respondents is often used to gather information. The full transcript from an interview is important so the reader can read the entire dialog between researcher and respondent. The interview protocol [list of questions] should also be included.
- Non-textual elements -- as noted above, if there are a lot of non-textual items, such as, figures, tables, maps, charts, photographs, drawings, or graphs, think about highlighting examples in the text of the paper but include the remainder in an appendix.
- Questionnaires or surveys -- this is a common form of data gathering. Always include the survey instrument or questionnaires in an appendix so the reader understands not only the questions asked but the sequence in which they were asked. Include all variations of the instruments as well if different items were sent to different groups [e.g., those given to teachers and those given to administrators] .
- Raw statistical data – this can include any numerical data that is too lengthy to include in charts or tables in its entirety within the text. This is important because the entire source of data should be included even if you are referring to only certain parts of a chart or table in the text of your paper.
- Research instruments -- if you used a camera, or a recorder, or some other device to gather information and it is important for the reader to understand how, when, and/or where that device was used.
- Sample calculations – this can include quantitative research formulas or detailed descriptions of how calculations were used to determine relationships and significance.
NOTE: Appendices should not be a dumping ground for information. Do not include vague or irrelevant information in an appendix; this additional information will not help the reader’s overall understanding and interpretation of your research and may only distract the reader from understanding the significance of your overall study.
ANOTHER NOTE : Appendices are intended to provide supplementary information that you have gathered or created; it is not intended to replicate or provide a copy of the work of others. For example, if you need to contrast the techniques of analysis used by other authors with your own method of analysis, summarize that information, and cite to the original work. In this case, a citation to the original work is sufficient enough to lead the reader to where you got the information. You do not need to provide a copy of this in an appendix.
III. Format
Here are some general guideline on how to format appendices . If needed, consult the writing style guide [e.g., APA, MLS, Chicago] your professor wants you to use for more detail:
- Appendices may precede or follow your list of references.
- Each appendix begins on a new page.
- The order they are presented is dictated by the order they are mentioned in the text of your research paper.
- The heading should be "Appendix," followed by a letter or number [e.g., "Appendix A" or "Appendix 1"], centered and written in bold type.
- If there is a table of contents, the appendices must be listed.
- The page number(s) of the appendix/appendices will continue on with the numbering from the last page of the text.
Appendices. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Appendices. Academic Skills Office, University of New England; Appendices. Writing Center, Walden University; Chapter 12, "Use of Appendices." In Guide to Effective Grant Writing: How to Write a Successful NIH Grant . Otto O. Yang. (New York: Kluwer Academic, 2005), pp. 55-57 ; Tables, Appendices, Footnotes and Endnotes. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Lunsford, Andrea A. and Robert Connors. The St. Martin's Handbook . New York: St. Martin's Press, 1989; What To Know About The Purpose And Format Of A Research Paper Appendix. LoyolaCollegeCulion.com.
Writing Tip
Consider Putting Your Appendices Online
Appendices are useful because they provide the reader with information that supports your study without breaking up the narrative or distracting from the main purpose of your paper. If you have a lot of raw data or information that is difficult to present in textual form, consider uploading it to an online site. This prevents your paper from having a large and unwieldy set of appendices and it supports a growing movement within academe to make data more freely available for re-analysis. If you do create an online portal to your data, note it prominently in your paper with the correct URL and access procedures if it is a secured site.
Piwowar, Heather A., Roger S. Day, and Douglas B. Fridsma. “Sharing Detailed Research Data Is Associated with Increased Citation Rate.” PloS ONE (March 21, 2007); Wicherts, Jelte M., Marjan Bakker, and Dylan Molenaar. “Willingness to Share Research Data Is Related to the Strength of the Evidence and the Quality of Reporting of Statistical Results.” PLoS ONE (November 2, 2011).
- << Previous: 9. The Conclusion
- Next: 10. Proofreading Your Paper >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 10:51 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an APA Appendix
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amanda Tust is a fact-checker, researcher, and writer with a Master of Science in Journalism from Northwestern University's Medill School of Journalism.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Amanda-Tust-1000-ffe096be0137462fbfba1f0759e07eb9.jpg)
damircudric / Getty Images
- When to Use an Appendix
- What to Include
- Basic Rules
If you are writing a psychology paper for a class or for publication, you may be required to include an appendix in APA format. An APA appendix is found at the end of a paper and contains information that supplements the text but that is too unwieldy or distracting to include in the main body of the paper.
APA format is the official writing style used by the American Psychological Association . This format dictates how academic and professional papers should be structured and formatted.
Does Your Paper Need an APA Appendix?
Some questions to ask about whether you should put information in the body of the paper or in an appendix:
- Is the material necessary for the reader to understand the research? If the answer is yes, it should be in your paper and not in an appendix.
- Would including the information interrupt the flow of the paper? If the answer is yes, then it should likely appear in the appendix.
- Would the information supplement what already appears in your paper? If yes, then it is a good candidate for including in an appendix.
Your appendix is not meant to become an information dump. While the information in your appendices is supplementary to your paper and research, it should still be useful and relevant. Only include what will help readers gain insight and understanding, not clutter or unnecessary confusion.
What to Include in an APA Appendix
The APA official stylebook suggests that the appendix should include information that would be distracting or inappropriate in the text of the paper.
Some examples of information you might include in an appendix include:
- Correspondence (if it pertains directly to your research)
- Demographic details about participants or groups
- Examples of participant responses
- Extended or detailed descriptions
- Lists that are too lengthy to include in the main text
- Large amounts of raw data
- Lists of supporting research and articles that are not directly referenced in-text
- Materials and instruments (if your research relied on special materials or instruments, you might want to include images and further information about how these items work or were used)
- Questionnaires that were used as part of your research
- Raw data (presented in an organized, readable format)
- Research surveys
While the content found in the appendix is too cumbersome to include in the main text of your paper, it should still be easily presented in print format.
The appendices should always act as a supplement to your paper. The body of your paper should be able to stand alone and fully describe your research or your arguments.
The body of your paper should not be dependent upon what is in the appendices. Instead, each appendix should act to supplement what is in the primary text, adding additional (but not essential) information that provides extra insight or information for the reader.
Basic Rules for an APA Appendix
Here are some basic APA appendix rules to keep in mind when working on your paper:
- Your paper may have more than one appendix.
- Each item usually gets its own appendix section.
- Begin each appendix on a separate page.
- Each appendix must have a title.
- Use title case for your title and labels (the first letter of each word should be capitalized, while remaining letters should be lowercase).
- If your paper only has one appendix, simply title it Appendix.
- If you have more than one appendix, each one should be labeled Appendix A, Appendix B, Appendix C, and so on.
- Put the appendix label centered at the top of the page.
- On the next line under the appendix label, place the centered title of the appendix.
- If you refer to a source in your appendix, include an in-text citation just as you would in the main body of your paper and then include the source in your main reference section.
- Each appendix may contain headings, subheadings, figures, and tables.
- Each figure or table in your appendix should include a brief but explanatory title, which should be italicized.
- If you want to reference your appendix within the text of your paper, include a parenthetical note in the text. For example, you would write (See Appendix A).
Formatting an APA Appendix
How do you format an appendix in APA? An APA appendix should follow the overall rules on how to format text. Such rules specify what font and font size you should use, the size of your margins, and the spacing of the text.
Some of the APA format guidelines you need to observe:
- Use a consistent font, such as 12-point Times New Roman or 11-point Calibri
- Double-space your text
- All paragraphs should be indented on the first line
- Page numbering should be continuous with the rest of your paper
The appendix label should appear centered and bolded at the top of the page. A descriptive title should follow and should also be bolded and centered. As with other pages in your paper, your APA format appendix should be left-aligned and double-spaced. Each page should include a page number in the top right corner. You can also have more than one appendix, but each one should begin on a new page.
Data Displays in an APA Appendix
When presenting information in an appendix, use a logical layout for any data displays such as tables or figures. All tables and figures should be labeled with the words “Table” or “Figure” (sans quotation marks) and the letter of the appendix and then numbered.
For example, Table A1 would be the first table in an Appendix A. Data displays should be presented in the appendix following the same order that they first appear in the text of your paper.
In addition to following basic APA formatting rules, you should also check to see if there are additional guidelines you need to follow. Individual instructors or publications may have their own specific requirements.
Where to Include an APA Appendix
If your paper does require an appendix, it should be the very last pages of your finished paper. An APA format paper is usually structured in the following way:
Your paper may not necessarily include all of these sections. At a minimum, however, your paper may consist of a title page, abstract, main text, and reference section. Also, if your paper does not contain tables, figures, or footnotes, then the appendix would follow the references.
Never include an appendix containing information that is not referred to in your text.
A Word From Verywell
Writing a paper for class or publication requires a great deal of research, but you should pay special attention to your APA formatting. Each section of your paper, including the appendix section, needs to follow the rules and guidelines provided in the American Psychological Association’s stylebook.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

APA 7th edition - Paper Format: Appendices
- Introduction
- Mechanics of Style
- Overall Paper
- Sample Papers
- Reference List
- Tables and Figures
- APA Citations This link opens in a new window
- Additional Resources
- Writing Skills This link opens in a new window
How to Format An Appendix - Tutorial
- APA Appendices - JIBC Tip Sheet All you need to know about appendices in APA Style.
Information in this section is as outlined in the APA Publication Manual (2020), sections 2.14, 2.17, 2.24, and 7.6.
Appendices are used to include information that supplement the paper’s content but are considered distracting or inappropriate for the overall topic. It is recommended to only include an appendix if it helps the reader comprehend the study or theoretical argument being made. It is best if the material included is brief and easily presented. The material can be text, tables, figures, or a combination of these three.
Placement :
Appendices should be placed on a separate page at the end of your paper after the references, footnotes, tables, and figure. The label and title should be centre aligned. The contents of the appendix and the note should be left-aligned.
- If you are choosing to include tables and figures in your appendix, then you can list each one on a separate page or you may include multiple tables/figures in one appendix, if there is no text and each table and/or figure has its own clear number and title within the appendix.
- Tables and figures in an appendix receive a number preceded by the letter of the appendix in which it appears, e.g. Table A1 is the first table in Appendix A or of a sole appendix that is not labeled with a letter.
The follow elements are required for appendices in APA Style:
Appendix Labels:
Each appendix that you place in your paper is labelled “Appendix.” If a paper has more than one appendix, then label each with a capital letter in the order the appendices are referred to in your paper (“Appendix A” is referred to first, “Appendix B” is referred to second, etc).
- The label of the appendix should be in bold font, centre-aligned, follow Title Casing, and is located at the top of the page.
- If your appendix only contains one table or figure (and no text), then the appendix label takes the place of the table/figure number, e.g. the table may be referred to as “Appendix B” rather than “Table B1.”
Appendix Titles:
Each appendix should have a title, that describes its contents. Titles should be brief, clear, and explanatory.
- The title of the appendix should be in bold font, centre-aligned, follow Title Casing, and is one double-spaced line down from the appendix label.
- If your appendix only contains one table or figure (and no text), then the appendix title takes the place of the table/figure title.
Appendix Contents:
- Left aligned and indented; written the same as paragraphs within the body of the paper
- Double-spaced and with the same font as the rest of the paper
- If the appendix contains a table and/or figure, then the table/figure number must contain a letter to correlate the table and/or figure to the appendix and not the body of the paper, e.g. “Table A1” rather than “Table 1” to clarify that the table appears in the appendix and not in the body of the paper.
- All tables and figures in an appendix must be mentioned in the appendix and numbered in order of mention.
- All tables and figures must be aligned to the left margin, (not center aligned), and positioned after a paragraph break, preferably the paragraph in which they are referred to, with a double-spaced blank line between the table and the text.
- Each table and figure should include a note afterwards to further explain the supplement or clarify information in the table or figure to your paper/appendix and can be general, specific, and probability. See “Table Notes” in the section “Table and Figures” above for more details.
Referring to Appendices in the Text:
In your paper, refer to every appendix that you have inserted. Do not include an appendix in your work that you do not clearly explain in relation to the ideas in your paper.
- In general, only refer to the appendix by the label (“Appendix” or “Appendix A” etc.) and not the appendix title.
Reprinting or Adapting:
If you did not create the content in the appendix yourself, for instance if you found a figure on the internet, you must include a copyright attribution in a note below the figure.
- A copyright attribution is used instead of an in-text citation.
- Each work should also be listed in the reference list.
Please see pages 390-391 in the Manual for example copyright attributions.
- << Previous: Tables and Figures
- Next: Workshops >>
- Last Updated: Feb 7, 2024 1:05 PM
- URL: https://libguides.jibc.ca/apa/formatyourpaper
- Franklin University |
- Help & Support |
- Locations & Maps |

- | Research Guides
To access Safari eBooks,
- Select not listed in the Select Your Institution drop down menu.
- Enter your Franklin email address and click Go
- click "Already a user? Click here" link
- Enter your Franklin email and the password you used to create your Safari account.
Continue Close
APA Citation Style 7th Edition
- APA Style Overview
- Sample Documents & Guides
- Multiple Sources With the Same Author and Year
- Websites & Web Documents
- Course Materials (Slides, Lecture Notes, Specialty Software)
- Citing Business Databases
- Film, Videos, & Podcasts
- Art, Photos, Tables & Figures
- Legal Materials & Tax Codes
- Dissertations
- Pamphlet or Brochure
- Interviews, E-mail, Intranet, Religious Works, & Secondary Sources (7th edition)
- Footnotes This link opens in a new window
What goes into an Appendix?
Where is an appendix placed, labeling the appendix, formatting the appendix.
- Evaluating Sources This link opens in a new window
- Understanding Plagiarism
- RefWorks This link opens in a new window
"Material that supplements the content of the paper, but would be distracting or inappropriate to include in the body of the paper is to be placed in an appendix." This includes "materials that are relatively brief and that are easily presented in print format" ( Publication Manual of the APA: 6th edition , section 2.13; Publication Manual of the APA: 7th edition , section 2.14). Examples include "mathematical proofs, lists of words, a questionnaire used in the research, a detailed description of an apparatus used in the research, etc" ( Purdue OWL .)
An appendix (or appendices) follow the reference list. Use the following order for your paper:
- Abstract ( if required, start on a new page, numbered page 2)
- Text (start on a new page, numbered 3)
- References (start on a new page)
- Tables (start each on a new page)
- Figures (start each on a new page; include caption on page with figure)
- Appendices (start each on a new page)
- If only one appendix, label it Appendix
- If more than one appendix: label each one with a capital letter (Appendix A, Appendix B, etc.) in the order in which it is mentioned in the text
- Each appendix must have a title
- In the text, refer to appendices by their labels:
"produced the same results for both studies (see Appendices A and B for complete proofs)."
- Begin each appendix on a separate page
- At the top of the page, center the word Appendix and the identifying capital letters (A, B, etc.) in the order in which they are mentioned in the text.
- Center the title of the appendix using uppercase and lowercase letter on the next line
- Begin the text of the appendix flush left, followed by indented paragraphs.
A sample appendix is below:

- << Previous: Footnotes
- Next: Evaluating Sources >>
- Last Updated: Oct 25, 2023 2:14 PM
- URL: https://guides.franklin.edu/APA
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Footnotes & Appendices

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
APA style offers writers footnotes and appendices as spaces where additional, relevant information might be shared within a document; this resource offers a quick overview of format and content concerns for these segments of a document. Should additional clarification be necessary, it is always recommended that writers reach out to the individual overseeing their work (i.e., instructor, editor, etc.). For your convenience, a student sample paper is included below; please note the document is filled with Lorem Ipsum placeholder text and references to footnotes and appendices are highighlighted. Additional marginal notes also further explain specific portions of the example.
Footnotes
Footnotes are supplementary details printed at the bottom of the page pertaining to a paper’s content or copyright information. This supporting text can be utilized in any type of APA paper to support the body paragraphs.
Content-Based Footnotes
Utilizing footnotes to provide supplementary detail can enrich the body text and reinforce the main argument of the paper. Footnotes may also direct readers to an alternate source for more detail on a topic. Though content footnotes can be useful in providing additional context, it is detrimental to include tangential or convoluted information. Footnotes should detail a focused subject; lengthier sections of text are better suited for the body paragraphs.
Acknowledging Copyright
When citing long quotations, images, tables, data, or commercially published questionnaires in-text, it is important to credit the copyright information in a footnote. Functioning much like an in-text citation, a footnote copyright attribution provides credit to the original source and must also be included in a reference list. A copyright citation is needed for both direct reprinting as well as adaptations of content, and these may require express permission from the copyright owner.
Formatting Footnotes
Each footnote and its corresponding in-text callout should be formatted in numerical order of appearance utilizing superscript. As demonstrated in the example below, the superscripted numerals should follow all punctuation with the exception of dashes and parentheses.
For example:
Footnote callouts should not be placed in headings and do not require a space between the callout and superscripted number. When reintroducing a footnote that has previously been called out, refrain from replicating the callout or footnote itself; rather, format such reference as “see Footnote 4”, for example. Footnotes should be placed at the bottom of the page on which the corresponding callout is referenced. Alternatively, a footnotes page could be created to follow the reference page. When formatting footnotes in the latter manner, center and bold the label “Footnotes” then record each footnote as a double-spaced and indented paragraph. Place the corresponding superscripted number in front of each footnote and separate the numeral from the following text with a single space.
Formatting Copyright Information
To provide credit for images, tables, or figures pulled from an outside source, include the accreditation statement at the end of the note for the visual. Copyright acknowledgements for long quotations or questionnaires should simply be placed in a footnote at the bottom of the page.
When formatting a copyright accreditation, utilize the following format:
- Establish if the content was reprinted or adapted by using language such as “from” for directly copied material or “adapted from” for material that has been modified
- Include the content’s title, author, year of publication, and source
- Cite the copyright holder and year of copyright or indicate that the source is public domain or licensed under Creative Commons
- If express permission was required to reprint the material, include a statement indicating that permission was acquired
Appendices
When introducing supplementary content that may not fit within the body of a paper, an appendix can be included to help readers better understand the material without distracting from the text itself. Primarily used to introduce research materials, specific details of a study, or participant demographics, appendices are generally concise and only incorporate relevant content. Much like with footnotes, appendices may require an acknowledgement of copyright and, if data is cited, an adherence to the privacy policies that protect participant identities.
Formatting Appendices
An appendix should be created on its own individual page labelled “Appendix” and followed by a title on the next line that describes the subject of the appendix. These headings should be centered and bolded at the top of the page and written in title case. If there are multiple appendices, each should be labelled with a capital letter and referenced in-text by its specific title (for example, “see Appendix B”). All appendices should follow references, footnotes, and any tables or figures included at the end of the document.
Text Appendices
Appendices should be formatted in traditional paragraph style and may incorporate text, figures, tables, equations, or footnotes. In an appendix, all figures, tables, and other visuals should be labelled with the letter of the corresponding appendix followed by a number indicating the order in which each appears. For example, a table labelled “Table B1” would be the first table in Appendix B. If there is only one appendix in the document, the visuals should still be labelled with the letter A and a number to differentiate them from those contained in the paper itself (for example, “Figure A3” is the third figure in the singular appendix, which is not labelled with a letter in the heading).
Table or Figure Appendices
When an appendix solely contains a table or figure, the title of the figure or table should be substituted with the title of the appendix. For example, if Appendix B only includes a figure, the figure should be labelled “Appendix B” rather than “Figure B1”, as it would be named if there were multiple figures included.
If an appendix does not contain text but includes numerous figures or table, the appendix should be formatted like a text appendix. The appendix would receive a name and label, and each figure or table would be given a corresponding letter and number. For example, if Appendix C contains two tables and one figure, these visuals would be labelled “Table C1”, “Table C2”, and “Figure C1” respectively.
Sample Paper
Media File: APA 7 - Student Sample Paper (Footnotes & Appendices)
How to Write a Research Paper Appendix
Link Copied
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on LinkedIn

Presentation aced!
Writing a research paper isn’t just a work of mere writing. Writing the perfect research paper takes a lot of research, analysis, framing, formatting, and much more. Correctly writing one of the most essential and academically popular segments of a research paper, the appendix, is one such effort that goes into a dissertation. In this blog , we will discuss with you the functions of an appendix in-depth and give you some tried and tested tips to craft the perfect appendix section of a research paper! Let’s dive in!
What is an Appendix?
The appendix on a research paper is a supplementary segment at the end of a dissertation or the research paper. This section isn’t considered a part of the main body text of the dissertation, but it is an important part of doing research. Appendices often feature raw data in the form of tables, figures, maps, diagrams and statistics and thus contribute to the credibility of the research and make it a perfect research paper .
Using academic resources, books, and research tools can help frame an appendix better. Appendices are essential since they provide extra support to your research and make the dissertation seem more transparent regarding data.
However, the appendix section of a research paper should only be supplementary; thus, you cannot depend on it to help the reader understand the main text. Your dissertation text should be detailed enough to be understandable without appendices, and they should only be placed to support your arguments presented in the research report.
How to Write an Appendix for a Research Paper
Writing the perfect research paper appendix can be overwhelming if it’s your first time doing so. However, drafting the appendix section of a research paper can be quite fun if you know the basics and understand how exactly you should go about it. Here are our 5 tips on how to write the perfect appendix for your dissertation:
Step 1: Organize the Appendix
With all the raw data, stats, and information, an appendix on a research paper can be difficult to go through and understand if they’re drafted disorganizedly. So, while writing your research paper appendix, make sure you are not just ramming all information into it but organising it well so the reader can utilise it. Structure it well, for it can very well come across as a reflection of your daily choices.
Step 2: Consider Accessibility
A research paper appendix can include non-textual information like tables, diagrams, graphs, images, illustrations, etc. If you’re adding such visual data elements to your appendices, ensure the material is clear and readable so the reader can comprehend the data. You should also ensure you are labelling these elements well and adding brief descriptions to each figure.
Step 3: Review for Relevance
It is easy to lose track of the relevance of your data while preparing appendices since you have to work with many different types of data simultaneously. However, you have to remember that the goal is not to stuff your appendices with data. Rather, craft a precise, careful research paper appendix that can give your reader relevant and additional data that supports your research.
Step 4: Proofread and Revise
When it comes to dissertation writing, typos, grammatical errors, and spelling mistakes can cost you way more than just miscommunication. These seemingly harmless errors can make your work look casual and unprofessional, bringing in questions about the credibility of your work. It is a similar case when it comes to writing an appendix for a research paper.

Step 5: Seek Guidance
It is important to remember that seeking guidance when you feel stuck is pretty normal, and there is nothing to be embarrassed about it. You may feel lost while writing an appendix for a research paper, and it is the perfect time to seek guidance from your peers, advisor or even dissertation committee members.
How to Format an Appendix
Ensuring proper formatting is crucial for the seamless integration of the research paper appendix into the main body. Follow the guidelines below for a sharp-looking appendix:
Consistency with the Main Body
Formatting elements, fonts, font sizes and margins should have uniformity. Consistent and professional appearance gives your research paper a neat look.
Organisation and Structure
Use headings and subheadings to categorise your data logically. You can also use a well-structured numbering system to facilitate easy navigation.
Descriptive Elements
Introduce each content with short descriptions and paragraphs. Giving additional context makes the information more accessible and interpretable.
Consistent Formatting Style
Use a formatting style that goes well with the rest of your dissertation, along with font styles, sizes, and other formatting guidelines instructed by your academic institution.
Visual Accessibility
Any non-textual elements, such as tables, graphs, or images, should be clear and readable. Label these visual elements and add alternative texts for inclusivity in the digital appendix.
Where does the appendix go in your dissertation?
Although the appendix section of a research paper is an essential part of your dissertation, it is not to be included in the main body of the dissertation. As a compilation of supplementary material and raw data, your research paper appendix should go at the end of the dissertation, typically inserted after the reference lists. Some even present appendices as separate supplementary documents, mostly done in specially requested cases.
The format of the research paper appendix should be similar to the rest of your report for consistency. It should thus be drafted and formatted in the same style as the dissertation in terms of fonts, margins, and font sizes.
What to include in your appendix
While drafting your research paper appendix, remember that it needs to be as precise as possible. Thus, there cannot be unnecessary information in it. Typically, appendices include raw data that supports your research and is referenced in the dissertation you have prepared. Here are some of the elements that you should include in your appendix:
- Research results
- Transcribed interviews
- Survey/questionnaire details
- Table and figures
- Co-respondence
- List of abbreviations used
- Calculations and formulas
Explore student accommodations for a focused academic experience!
Book through amber today!
Referring appendix in-text
Only adding your appendix to the research paper at the end of the dissertation would not make sense if there are no references to them in the main text. To justify its existence and inclusion in the research report, you should reference the appendix at least once in the whole report. A neatly labelled and properly referred research paper appendix can make your dissertation look more professional and supported.
How to refer to an appendix
Referring to the research paper appendix within the main text is important in highlighting its relevance. Use these five methods for referencing:
In-text references
Specific references embedded in your sentences contextually shape your information. For example, "In Table 2 of Appendix B, the commonality between subjects A and B is illustrated.
Parenthetical references
You can use parentheses for concise references without disrupting the main text's flow. For instance, "The result [refer to Appendix C, Fig. 2] is not consistent with the previous findings."
Referring to the entire appendix
Refer to the entire research paper appendix in your text when appropriate. For example, "The data supporting this conclusion can be found in Appendix B."
Clarity and labelling
References should be clear and well-labelled. Proper labelling ensures easy identification of referenced material within the appendix, polishing your research paper professionally.
Cross-referencing
Cross-referencing helps you establish connections between the main text and the appendix. Phrases like "As discussed in Appendix A" guide readers to supporting material.
Crafting the perfect appendix section of a research paper involves meticulous attention to detail and adherence to formatting and referencing guidelines. As an integral part of your dissertation, the appendix contributes significantly to the transparency, credibility, and overall professionalism of your research. By following the comprehensive guidelines provided in this guide, you can ensure that your appendix not only complements your main text but also serves as a valuable resource for readers seeking additional insights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do i write in a research paper appendix, why is an appendix important for a dissertation, where is the appendix placed in the research paper, is writing a research paper appendix difficult, what are the basic guidelines for writing an appendix.
Your ideal student home & a flight ticket awaits
Follow us on :

Related Posts

How to Present a Presentation in Class?
.jpg)
Teaching Courses in Canada for International Students
.jpg)
10 Best Music Production Schools Around the World!

Planning to Study Abroad ?

Your ideal student accommodation is a few steps away! Please fill in your details below so we can find you a new home!
We have got your response

amber © 2024. All rights reserved.
4.8/5 on Trustpilot
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by students
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by Students
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
Published on 15 August 2022 by Kirsten Dingemanse and Tegan George. Revised on 25 October 2022.
An appendix is a supplementary document that facilitates your reader’s understanding of your research but is not essential to your core argument. Appendices are a useful tool for providing additional information or clarification in a research paper , dissertation , or thesis without making your final product too long.
Appendices help you provide more background information and nuance about your topic without disrupting your text with too many tables and figures or other distracting elements.
We’ve prepared some examples and templates for you, for inclusions such as research protocols, survey questions, and interview transcripts. All are worthy additions to an appendix. You can download these in the format of your choice below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What is an appendix in a research paper, what to include in an appendix, how to format an appendix, how to refer to an appendix, where to put your appendices, other components to consider, appendix checklist.
In the main body of your research paper, it’s important to provide clear and concise information that supports your argument and conclusions . However, after doing all that research, you’ll often find that you have a lot of other interesting information that you want to share with your reader.
While including it all in the body would make your paper too long and unwieldy, this is exactly what an appendix is for.
As a rule of thumb, any detailed information that is not immediately needed to make your point can go in an appendix. This helps to keep your main text focused but still allows you to include the information you want to include somewhere in your paper.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
An appendix can be used for different types of information, such as:
- Supplementary results : Research findings are often presented in different ways, but they don’t all need to go in your paper. The results most relevant to your research question should always appear in the main text, while less significant results (such as detailed descriptions of your sample or supplemental analyses that do not help answer your main question), can be put in an appendix.
- Statistical analyses : If you conducted statistical tests using software like Stata or R, you may also want to include the outputs of your analysis in an appendix.
- Further information on surveys or interviews : Written materials or transcripts related to things such as surveys and interviews can also be placed in an appendix.
You can opt to have one long appendix, but separating components (like interview transcripts, supplementary results, or surveys) into different appendices makes the information simpler to navigate.
Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Always start each appendix on a new page.
- Assign it both a number (or letter) and a clear title, such as ‘Appendix A. Interview transcripts’. This makes it easier for your reader to find the appendix, as well as for you to refer back to it in your main text.
- Number and title the individual elements within each appendix (e.g., ‘Transcripts’) to make it clear what you are referring to. Restart the numbering in each appendix at 1.
It is important that you refer to each of your appendices at least once in the main body of your paper. This can be done by mentioning the appendix and its number or letter, either in parentheses or within the main part of a sentence. It is also possible to refer to a particular component of an appendix.
Appendix B presents the correspondence exchanged with the fitness boutique. Example 2. Referring to an appendix component These results (see Appendix 2, Table 1) show that …
It is common to capitalise ‘Appendix’ when referring to a specific appendix, but it is not mandatory. The key is just to make sure that you are consistent throughout your entire paper, similarly to consistency in capitalising headings and titles in academic writing.
However, note that lowercase should always be used if you are referring to appendices in general. For instance, ‘The appendices to this paper include additional information about both the survey and the interviews.’
The simplest option is to add your appendices after the main body of your text, after you finish citing your sources in the citation style of your choice . If this is what you choose to do, simply continue with the next page number. Another option is to put the appendices in a separate document that is delivered with your dissertation.
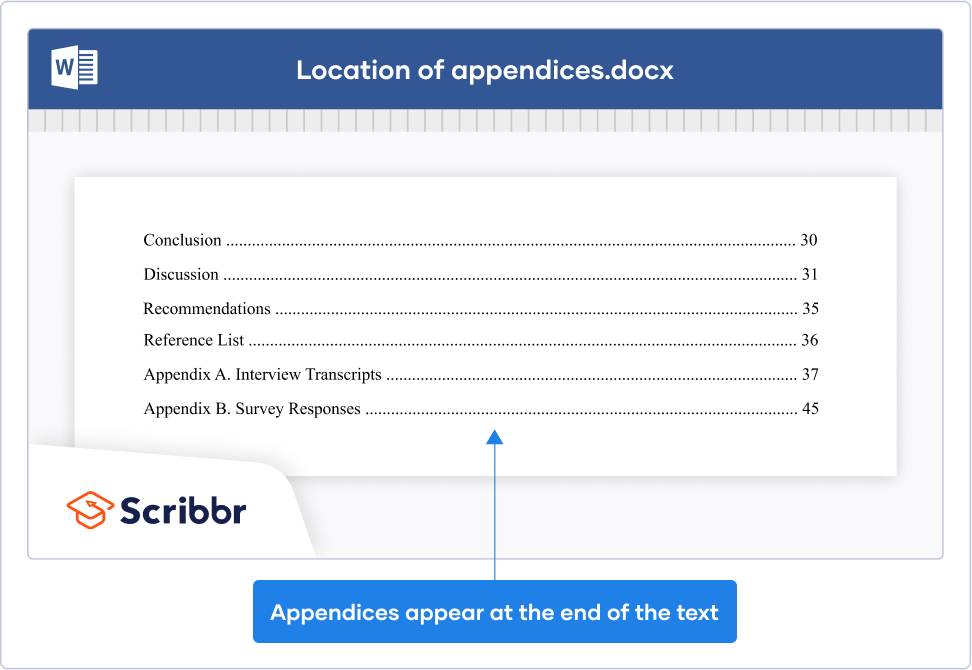
Remember that any appendices should be listed in your paper’s table of contents .
There are a few other supplementary components related to appendices that you may want to consider. These include:
- List of abbreviations : If you use a lot of abbreviations or field-specific symbols in your dissertation, it can be helpful to create a list of abbreviations .
- Glossary : If you utilise many specialised or technical terms, it can also be helpful to create a glossary .
- Tables, figures and other graphics : You may find you have too many tables, figures, and other graphics (such as charts and illustrations) to include in the main body of your dissertation. If this is the case, consider adding a figure and table list .
Checklist: Appendix
All appendices contain information that is relevant, but not essential, to the main text.
Each appendix starts on a new page.
I have given each appendix a number and clear title.
I have assigned any specific sub-components (e.g., tables and figures) their own numbers and titles.
My appendices are easy to follow and clearly formatted.
I have referred to each appendix at least once in the main text.
Your appendices look great! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Dingemanse, K. & George, T. (2022, October 25). Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/appendix/
Is this article helpful?
Kirsten Dingemanse
Other students also liked, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, dissertation title page, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
What is an appendix in a paper
What is an appendix?
What type of information includes an appendix, the format of an appendix, frequently asked questions about appendices in papers, related articles.
An appendix is a section of a paper that features supporting information not included in the main text.
The appendix of a paper consists of supporting information for the research that is not necessary to include in the text. This section provides further insight into the topic of research but happens to be too complex or too broad to add to the body of the paper. A paper can have more than one appendix, as it is recommended to divide them according to topic.
➡️ Read more about what is a research paper?
An appendix can take many types of forms. Here are some examples:
- Surveys. Since many researchers base their methodology on surveys, these are commonly found attached as appendices. Surveys must be included exactly as they were presented to the respondents, and exactly how they were answered so the reader can get a real picture of the findings.
- Interviews . Whether it’s a transcript or a recording, interviews are usually included as an appendix. The list of questions and the real answers must be presented for complete transparency.
- Correspondence . All types of communication with collaborators regarding the research should be included as an appendix. These can be emails, text messages, letters, transcripts of audio messages, etc.
- Research tools . Any instrument used to perform the research should be acknowledged in an appendix to give the reader insight into the process. For instance, audio recorders, cameras, special software, etc.
- Non-textual items . If the research includes too many graphs, tables, figures, illustrations, photos or charts, these should be added as an appendix.
- Statistical data . When raw data is too long, it should be attached to the research as an appendix. Even if only one part of the data was used, the complete data must be given.
➡️ Learn more about surveys, interviews, and other research methodologies .
The format of an appendix will vary based on the type of citation style you’re using, as well as the guidelines of the journal or class for which the paper is being written. Here are some general appendix formatting rules:
- Appendices should be divided by topic or by set of data.
- Appendices are included in the table of contents.
The most common heading for an appendix is Appendix A or 1, centered, in bold, followed by a title describing its content.
- An appendix should be located before or after the list of references.
- Each appendix should start on a new page.
- Each page includes a page number.
- Appendices follow a sequential order, meaning they appear in the order in which they are referred to throughout the paper.
An appendix is usually added before or after the list of references.
There is no specific space limit to an appendix, but make sure to consult the guidelines of the citation format you are using.
Yes, all appendices must be included in the table of contents.
Appendices feature different types of material, for instance interviews, research tools, surveys, raw statistical data, etc.


Organizing Academic Research Papers: Appendices
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
An appendix contains supplementary material that is not an essential part of the text itself but which may be helpful in providing a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem and/or is information which is too cumbersome to be included in the body of the paper. A separate appendix should be used for each distinct topic or set of data and always have a title descriptive of its contents .
Importance of...
Your research paper must be complete without the appendices, and it must contain all information including tables, diagrams, and results necessary to address the research problem. The key point to remember when you are writing an appendix is that the information is non-essential; if it were removed, the paper would still be understandable.
It is appropriate to include appendices...
- When the incorporation of material in the body of the work would make it poorly structured or it would be too long and detailed and
- To ensure inclusion of helpful, supporting, or essential material that would otherwise clutter or break up the narrative flow of the paper, or it would be distracting to the reader.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Points to Consider
When considering whether to include content in an appendix, keep in mind the following points:
- It is usually good practice to include your raw data in an appendix, laying it out in a clear format so the reader can re-check your results. Another option if you have a large amount of raw data is to consider placing it online and note this as the appendix to your research paper.
- Any tables and figures included in the appendix should be numbered as a separate sequence from the main paper . Remember that appendices contain non-essential information that, if removed, would not diminish a reader's understanding of the overall research problem being investigated. This is why non-textual elements should not carry over the sequential numbering of elements in the paper.
- If you have more than three appendices, consider listing them on a separate page at the beginning of your paper . This will help the reader know before reading the paper what information is included in the appendices [always list the appendix or appendices in a table of contents].
- The appendix can be a good place to put maps, photographs, diagrams, and other non-textual elements , if you feel that it will help the reader to understand the content of your paper, but remembering that the paper should be understandable without them.
- An appendix should be streamlined and not loaded with a lot information . If you have a very long and complex appendix, it is a good idea to break it down into separate appendices, allowing the reader to find relevant information quickly.
II. Contents
Appendices may include some of the following, all of which should be referred to or summarized in the text of your paper:
- Supporting evidence [e.g. raw data]
- Contributory facts or specialized data [raw data appear in the appendix, but with summarized data appearing in the body of the text].
- Sample calculations
- Technical figures, graphs, tables, statistics
- Detailed description of research instruments
- Maps, charts, photographs, drawings
- Letters, emails, and other copies of correspondance
- Questionnaire/survey instruments, with the results appearing in the text
- Complete transcripts of interviews
- Complete field notes from observations
- Specification or data sheets
NOTE: Do not include vague or irrelevant information in an appendix; this additional information will not help the reader’s overall understanding and interpretation of your research and may only succeed in distracting the reader from understanding your research study.
III. Format
Here are some general guideline on how to format appendices, but consult the writing style guide [e.g., APA] your professor wants you to use for the class, if needed:
- Appendices may precede or follow your list of references.
- Each appendix begins on a new page.
- The order they are presented is dictated by the order they are mentioned in the text of your research paper.
- The heading should be "Appendix," followed by a letter or number [e.g., "Appendix A" or "Appendix 1"], centered and written in bold.
- Appendices must be listed in the table of contents [if used].
- The page number(s) of the appendix/appendices will continue on with the numbering from the last page of the text.
Appendices . The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Tables, Appendices, Footnotes and Endnotes . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Lunsford, Andrea A. and Robert Connors. The St. Martin's Handbook. New York: St. Martin's Press, 1989.
- << Previous: 9. The Conclusion
- Next: 10. Proofreading Your Paper >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
General Research Paper Guidelines: Appendices
If you have some information you would like to include in your research but it could potentially be distracting to readers or inappropriate within the body of your research paper, you can always include supplemental information as an appendix to your work. An appendix or appendices should always be inserted after your Reference List; however, the appropriateness of appendix content really depends on the nature and scope of your research paper.
For a more in-depth review of what supplemental materials might be included in a social science appendix, be sure to review Section 2.14 “Appendices” (pp. 41-42) of your 7 th edition APA manual.
Appendices Formatting
APA 7 addresses appendices and supplemental materials in Section 2.14 and on page 41:
- The appendices follow the reference list.
- They are lettered "Appendix A," "Appendix B," "Appendix C," and so forth. If you have only one appendix, however, simply label it Appendix.
- Put figures and tables in separate appendices. The appendix title serves as the title for a table if it is the only table in the appendix.
- If you decide that certain figures and tables should appear in the same appendix, number them A1, A2, A3, and so forth, according to the appendix in which they appear.
- The materials in the appendix must not extend beyond the margins of the rest of the paper: Reduce the appendix materials as needed.
As a general guide, appendices are appropriate for any material that, if presented in the main body of the document, would unnecessarily interrupt the flow of the writing. Note that it is unlikely that you will use appendices in Walden course papers. For doctoral capstone studies, you might include some appendices with supplementary information.
- Previous Page: References
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Easy Guide on How to Write an Appendix

Understanding What Is an Appendix
Many students ask, 'What is an appendix in writing?'. Essentially, an appendix is a compilation of the references cited in an academic paper, prevalent in academic journals, which can be found in any academic publication, including books. Professors frequently require their students to include an appendix in their work.
Incorporating an appendix in your written piece can aid readers in comprehending the information presented. It is important to note that different professors may have varying guidelines on how to write an appendix. To learn more about how to write an appendix for a research paper according to APA, Chicago, and MLA styles, check out the following paragraphs prepared by our PRO nursing essay writing service !
Meanwhile, note that an appendix comprises all the information utilized in a paper, including references and statistics from several authors and sources (the number varies according to the type of academic paper). The purpose of the appendix is to prevent vague or irrelevant information and improve the reader's understanding of the paper.
The Purpose of an Appendix
To understand what an appendix tries to accomplish and how to write an appendix example, after all, we must first answer the key question, 'What is the purpose of an appendix?'. In short, an appendix is crucial for further explaining complex information that may be difficult to fully convey within the main text of an essay. It is intended to offer readers additional information about the topic addressed in the paper.
The material presented in an appendix has the potential to bolster the argument and sway the reader's opinion. Nonetheless, you should try to incorporate supporting material and examples toward the end of the paper to avoid disrupting the flow of the main text. Furthermore, the likelihood of including an appendix increases as a paper becomes more advanced. The use of an appendix is especially prevalent in the academic writing of a research document and journal-style scientific paper, in which extra information is usually needed to support a main point of view.
How to Structure an Appendix
While there are variations between formats, each one follows a basic structure. Thus, understanding the general structure is an essential first step in learning about this topic. No matter if you're tasked with 'how to write an appendix MLA or APA style?' - remember that both adhere to this structure, despite their differences:

Order an Essay Now & Get These Features For Free :
Every Appendix Should Contain:
- A clear title: The title of the appendix should be concise and descriptive, clearly indicating what information is contained within it. For example, 'Appendix A: Data Tables for Study Results or 'Appendix B: Images of Experimental Setup.'
- A list of contents: Including a table of contents in the appendix can be helpful for readers to navigate the information provided. For example:
Table of Contents:
A. Data Tables for Study Results
B. Images of Experimental Setup
C. Survey Questions and Responses
D. Sample Interview Transcripts
- Page numbers: The appendix should be a separate page, independently numbered from the main body of the paper, and specified uniformly (e.g., 'Appendix A,' 'Appendix B,' etc.). For example:
Page 1 of 5
- Relevant information: The appendix should contain all the relevant information supporting the main arguments of the document, including tables of data, raw statistical data, charts, or other documents. For example:
Figure 1: Experimental Results
[insert graph or chart here]
- Proper formatting: The appendix should be formatted in accordance with the specific requirements of the chosen citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). For example:
Appendix B: Survey Questions and Responses
[insert survey questions and responses here, formatted following APA style guidelines]
- Clear labeling: Each element should have a clear appendix label so readers can easily understand its relevance to the paper. For example:
Table 1: Demographic Characteristics of Survey Respondents
- Concise explanation: It is important to provide short detailed descriptions of each element in the Appendix so that readers can understand its importance. For example:
Appendix C: Sample Interview Transcripts
Transcripts of the three interviews with the study participants shall be included for reference. These interviews provide further insights into the experiences of participants and their views on the subject addressed in this document.
Need college essay help ? You can always ask us to do a custom term paper from our professional writers.
General Appendix Format
To ensure proper formatting, it is important to understand the basics of how to structure an appendix. Although it may seem overwhelming, the basic format is relatively easy to comprehend and serves as a foundation for understanding the APA and MLA formats. Additionally, mastering the basic format can be helpful when writing an appendix for a book or dissertation.

- Heading “Appendix #” . Contains a number or letter, that could be 1 or A.
- Reference List.
- Index Table followed a list of appendices.
- Page Number.
Do You Need More Help With Your APPENDIX?
Get help from professional writers asap!
How to Write an Appendix in Different Styles
There are two distinct styles for creating an appendix, and it's important to familiarize yourself with both since a professor may request one or the other. Our expert writers have compiled guidelines and rules for both formats - the Appendix APA format and the Appendix MLA format. Although they share some similarities, they also have unique features and regulations that must be strictly followed.
Appendix APA
Many professors require students to write an appendix in a paper of this format. To master how to write an appendix APA format and get the structure correct, it's a good idea to follow these guidelines and rules:
The guidelines for Appendix APA:
- The appendix begins with the heading 'Appendix' followed by ABC.
- It should also be written on top of the appendix title.
- Every appendix follows the order of the stated information in the paper.
- Include the appendix after the reference list.
- Include page numbers for each appendix.
- Appendices are to have their own page, regardless of the size.
- Include Footnotes.
The general rules for Appendix APA are to be followed when writing. This is what professors look for when a paper is required when apprentices are to be written in this format. Learn the general rules to master how to write an appendix APA style and get you onto the right path to success. You may find it useful to memorize this information or keep a note of it.
Rules for APA:
- All appendices should include their own point.
- Include a title for each appendix.
- For multiple appendices, use ABC for tilting them.
- For reference within the body, include (see appendix a) after the text.
- The title should be centered.
- All appendices are to have their own page, regardless of the size.
- Paragraph One should be written without indents.
- The rest of the paragraphs should have the intended formatting.
- Include double spacing.
Whether you're tackling how to write an interview paper in APA appendix or any other type of academic work, the following example can serve as a valuable blueprint to guide you through the process.
Appendix Chicago Style
Writing an appendix Chicago style is rather similar to APA. Though, there are some minor differences. Take a look at these guidelines for this form of an appendix.
Guidelines for an Appendix Chicago Style
- More than one appendix is described as appendices.
- The font required for the appendix Chicago style is Times New Roman.
- The text size should be 12 points.
- The page numbers should be displayed on the top right of each page.
- The page numbers should also be labeled as 'Page 1,2,3'.
- Avoid including a page number on the front cover.
- The bibliography should be the final new page. It should not share a page with any other content.
- It is possible to include footnotes in the bibliography.
To better comprehend how to write an appendix in Chicago style, glance through the example below:
Appendix MLA Format
The guidelines and regulations for creating an appendix in MLA format are largely similar to those in APA format. However, there are some differences between the two, the most notable being that the MLA appendix is placed before the reference list.
The guidelines for MLA Format:
- The appendix is included before the list of references.
It may be useful to follow the example of an appendix to better understand how to write an appendix in MLA style. Doing so can increase the chances of getting a grasp of the MLA rules to fulfill the requirements of your professor on your academic paper.
Rules for MLA
- The title is to be centered.
- The list should be double-spaced.
- The first line should include each reference in the left margin. Every subsequent line is to be formatted so it's invented. This can be referred to as 'hanging indent' to make things easier.
- The reference list must be in alphabetical order. This can be done with the first letter of the title of the reference. Though, this is usually done if the writer is unknown. If the writer is known, you can also use the first letter of the surname.
- If you include the name of the known writer, use this order. SURNAME, FIRST NAME, YEAR.
- Italic fonts are required for the titles of complete writings, internet sites, books, and recordings.
- It is important not to use an italic font on reference titles that only refer to the part of a source. This includes poetry, short papers, tabloids, sections of a PDF, and scholarly entries.
Before we conclude, let's dive deeper into the world of appendix writing by exploring an example of how to write an appendix MLA style.
Let's wrap this up! It's safe to say that following the APA, Chicago, and MLA formats is crucial when crafting an appendix. As we've seen, starting with an APA appendix example can help ease you in mastering how to write an appendix of paper. Once you have a handle on the precise formats and guidelines, creating an appendix becomes a piece of cake. Also, memorizing the format can help you whip up accurate appendices for any type of paper, whether an essay or a dissertation. Trust us, mastering this topic is a must if you want to excel in knowing how to write an appendix in a report or any other academic work.
Moreover, if you ever find yourself in need of additional academic assistance, be sure to check out our resources on how to write an article review . Or, better yet, why not let us handle your most challenging tasks with ease by simply sending us a ' write my paper request? We are here to support you every step of the way.
Get Immediate Writing Help
Our appendix pages are written with the customer’s needs in mind, and plagiarism-free. Why not give it a try?
What Is An Appendix In Writing?
What is the purpose of an appendix, how to format an appendix, related articles.
.webp)
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What the data says about crime in the U.S.
A growing share of Americans say reducing crime should be a top priority for the president and Congress to address this year. Around six-in-ten U.S. adults (58%) hold that view today, up from 47% at the beginning of Joe Biden’s presidency in 2021.
We conducted this analysis to learn more about U.S. crime patterns and how those patterns have changed over time.
The analysis relies on statistics published by the FBI, which we accessed through the Crime Data Explorer , and the Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS), which we accessed through the National Crime Victimization Survey data analysis tool .
To measure public attitudes about crime in the U.S., we relied on survey data from Pew Research Center and Gallup.
Additional details about each data source, including survey methodologies, are available by following the links in the text of this analysis.
With the issue likely to come up in this year’s presidential election, here’s what we know about crime in the United States, based on the latest available data from the federal government and other sources.
How much crime is there in the U.S.?
It’s difficult to say for certain. The two primary sources of government crime statistics – the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS) – paint an incomplete picture.
The FBI publishes annual data on crimes that have been reported to law enforcement, but not crimes that haven’t been reported. Historically, the FBI has also only published statistics about a handful of specific violent and property crimes, but not many other types of crime, such as drug crime. And while the FBI’s data is based on information from thousands of federal, state, county, city and other police departments, not all law enforcement agencies participate every year. In 2022, the most recent full year with available statistics, the FBI received data from 83% of participating agencies .
BJS, for its part, tracks crime by fielding a large annual survey of Americans ages 12 and older and asking them whether they were the victim of certain types of crime in the past six months. One advantage of this approach is that it captures both reported and unreported crimes. But the BJS survey has limitations of its own. Like the FBI, it focuses mainly on a handful of violent and property crimes. And since the BJS data is based on after-the-fact interviews with crime victims, it cannot provide information about one especially high-profile type of offense: murder.
All those caveats aside, looking at the FBI and BJS statistics side-by-side does give researchers a good picture of U.S. violent and property crime rates and how they have changed over time. In addition, the FBI is transitioning to a new data collection system – known as the National Incident-Based Reporting System – that eventually will provide national information on a much larger set of crimes , as well as details such as the time and place they occur and the types of weapons involved, if applicable.
Which kinds of crime are most and least common?
Property crime in the U.S. is much more common than violent crime. In 2022, the FBI reported a total of 1,954.4 property crimes per 100,000 people, compared with 380.7 violent crimes per 100,000 people.
By far the most common form of property crime in 2022 was larceny/theft, followed by motor vehicle theft and burglary. Among violent crimes, aggravated assault was the most common offense, followed by robbery, rape, and murder/nonnegligent manslaughter.
BJS tracks a slightly different set of offenses from the FBI, but it finds the same overall patterns, with theft the most common form of property crime in 2022 and assault the most common form of violent crime.
How have crime rates in the U.S. changed over time?
Both the FBI and BJS data show dramatic declines in U.S. violent and property crime rates since the early 1990s, when crime spiked across much of the nation.
Using the FBI data, the violent crime rate fell 49% between 1993 and 2022, with large decreases in the rates of robbery (-74%), aggravated assault (-39%) and murder/nonnegligent manslaughter (-34%). It’s not possible to calculate the change in the rape rate during this period because the FBI revised its definition of the offense in 2013 .
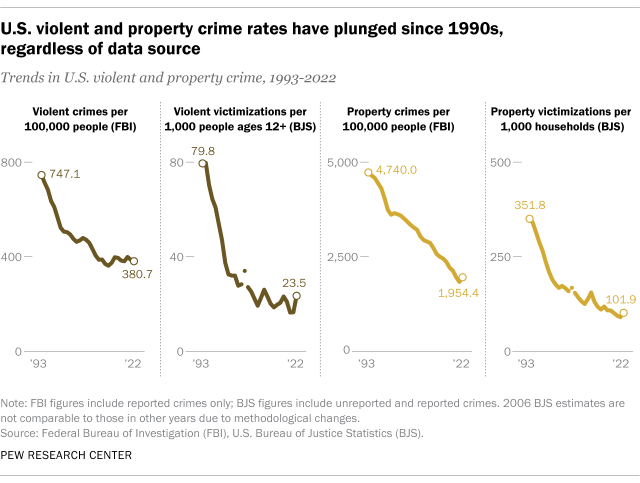
The FBI data also shows a 59% reduction in the U.S. property crime rate between 1993 and 2022, with big declines in the rates of burglary (-75%), larceny/theft (-54%) and motor vehicle theft (-53%).
Using the BJS statistics, the declines in the violent and property crime rates are even steeper than those captured in the FBI data. Per BJS, the U.S. violent and property crime rates each fell 71% between 1993 and 2022.
While crime rates have fallen sharply over the long term, the decline hasn’t always been steady. There have been notable increases in certain kinds of crime in some years, including recently.
In 2020, for example, the U.S. murder rate saw its largest single-year increase on record – and by 2022, it remained considerably higher than before the coronavirus pandemic. Preliminary data for 2023, however, suggests that the murder rate fell substantially last year .
How do Americans perceive crime in their country?
Americans tend to believe crime is up, even when official data shows it is down.
In 23 of 27 Gallup surveys conducted since 1993 , at least 60% of U.S. adults have said there is more crime nationally than there was the year before, despite the downward trend in crime rates during most of that period.
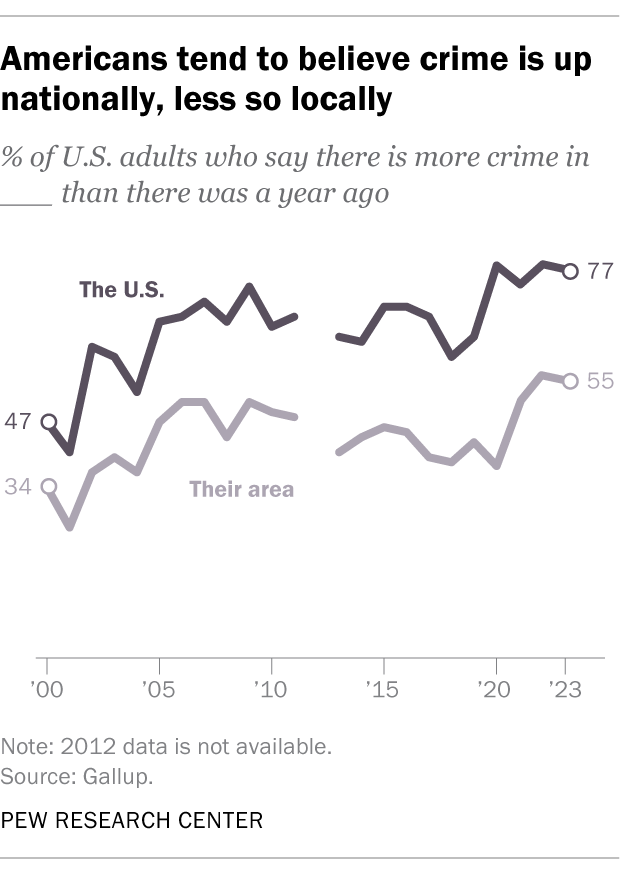
While perceptions of rising crime at the national level are common, fewer Americans believe crime is up in their own communities. In every Gallup crime survey since the 1990s, Americans have been much less likely to say crime is up in their area than to say the same about crime nationally.
Public attitudes about crime differ widely by Americans’ party affiliation, race and ethnicity, and other factors . For example, Republicans and Republican-leaning independents are much more likely than Democrats and Democratic leaners to say reducing crime should be a top priority for the president and Congress this year (68% vs. 47%), according to a recent Pew Research Center survey.
How does crime in the U.S. differ by demographic characteristics?
Some groups of Americans are more likely than others to be victims of crime. In the 2022 BJS survey , for example, younger people and those with lower incomes were far more likely to report being the victim of a violent crime than older and higher-income people.
There were no major differences in violent crime victimization rates between male and female respondents or between those who identified as White, Black or Hispanic. But the victimization rate among Asian Americans (a category that includes Native Hawaiians and other Pacific Islanders) was substantially lower than among other racial and ethnic groups.
The same BJS survey asks victims about the demographic characteristics of the offenders in the incidents they experienced.
In 2022, those who are male, younger people and those who are Black accounted for considerably larger shares of perceived offenders in violent incidents than their respective shares of the U.S. population. Men, for instance, accounted for 79% of perceived offenders in violent incidents, compared with 49% of the nation’s 12-and-older population that year. Black Americans accounted for 25% of perceived offenders in violent incidents, about twice their share of the 12-and-older population (12%).
As with all surveys, however, there are several potential sources of error, including the possibility that crime victims’ perceptions about offenders are incorrect.
How does crime in the U.S. differ geographically?
There are big geographic differences in violent and property crime rates.
For example, in 2022, there were more than 700 violent crimes per 100,000 residents in New Mexico and Alaska. That compares with fewer than 200 per 100,000 people in Rhode Island, Connecticut, New Hampshire and Maine, according to the FBI.
The FBI notes that various factors might influence an area’s crime rate, including its population density and economic conditions.
What percentage of crimes are reported to police? What percentage are solved?
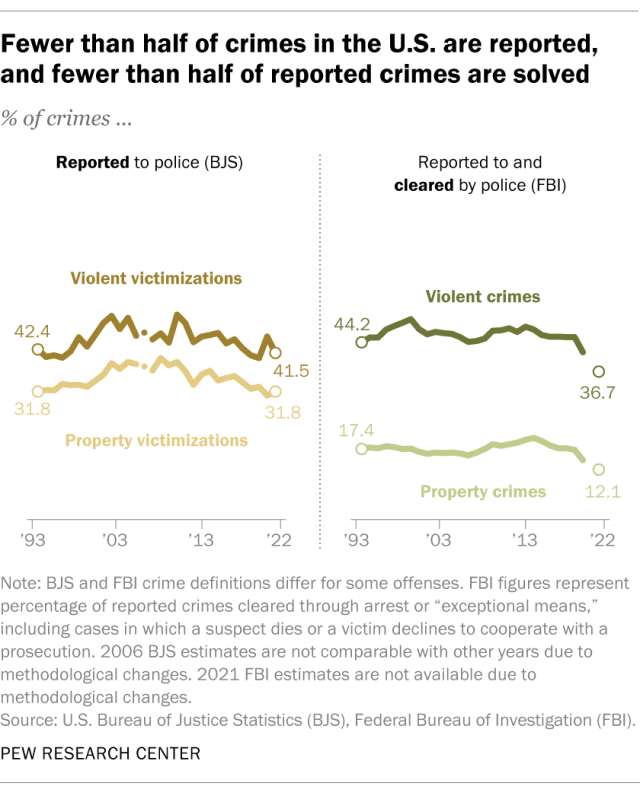
Most violent and property crimes in the U.S. are not reported to police, and most of the crimes that are reported are not solved.
In its annual survey, BJS asks crime victims whether they reported their crime to police. It found that in 2022, only 41.5% of violent crimes and 31.8% of household property crimes were reported to authorities. BJS notes that there are many reasons why crime might not be reported, including fear of reprisal or of “getting the offender in trouble,” a feeling that police “would not or could not do anything to help,” or a belief that the crime is “a personal issue or too trivial to report.”
Most of the crimes that are reported to police, meanwhile, are not solved , at least based on an FBI measure known as the clearance rate . That’s the share of cases each year that are closed, or “cleared,” through the arrest, charging and referral of a suspect for prosecution, or due to “exceptional” circumstances such as the death of a suspect or a victim’s refusal to cooperate with a prosecution. In 2022, police nationwide cleared 36.7% of violent crimes that were reported to them and 12.1% of the property crimes that came to their attention.
Which crimes are most likely to be reported to police? Which are most likely to be solved?
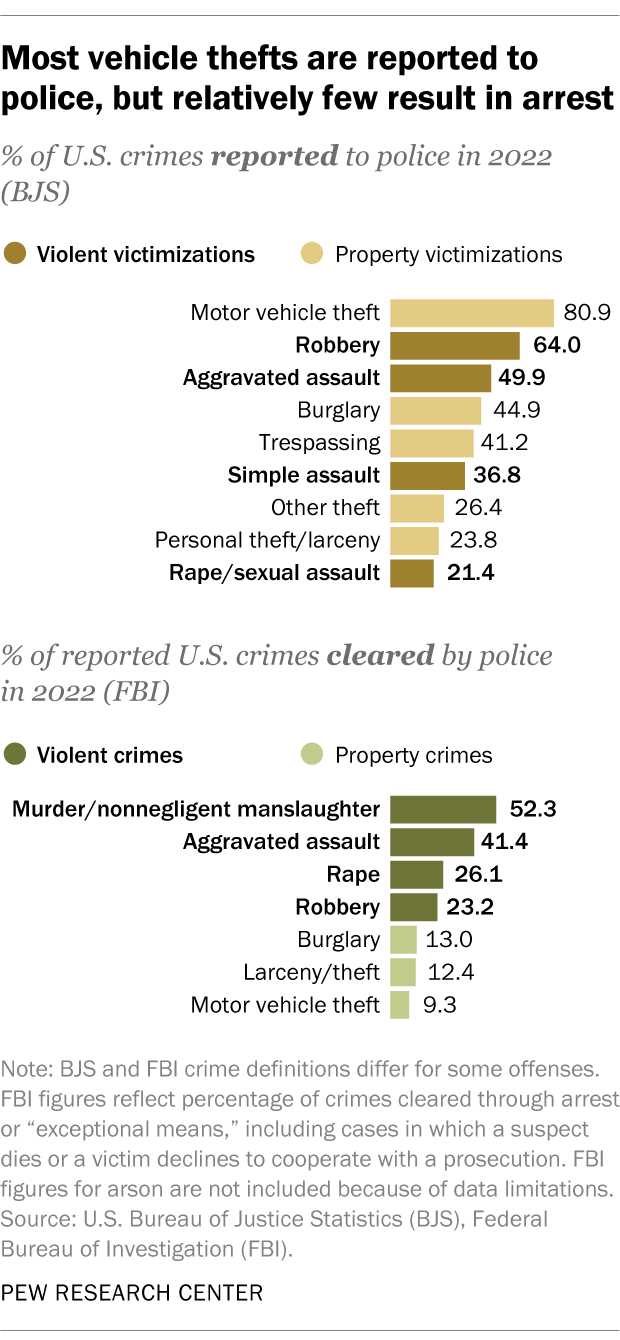
Around eight-in-ten motor vehicle thefts (80.9%) were reported to police in 2022, making them by far the most commonly reported property crime tracked by BJS. Household burglaries and trespassing offenses were reported to police at much lower rates (44.9% and 41.2%, respectively), while personal theft/larceny and other types of theft were only reported around a quarter of the time.
Among violent crimes – excluding homicide, which BJS doesn’t track – robbery was the most likely to be reported to law enforcement in 2022 (64.0%). It was followed by aggravated assault (49.9%), simple assault (36.8%) and rape/sexual assault (21.4%).
The list of crimes cleared by police in 2022 looks different from the list of crimes reported. Law enforcement officers were generally much more likely to solve violent crimes than property crimes, according to the FBI.
The most frequently solved violent crime tends to be homicide. Police cleared around half of murders and nonnegligent manslaughters (52.3%) in 2022. The clearance rates were lower for aggravated assault (41.4%), rape (26.1%) and robbery (23.2%).
When it comes to property crime, law enforcement agencies cleared 13.0% of burglaries, 12.4% of larcenies/thefts and 9.3% of motor vehicle thefts in 2022.
Are police solving more or fewer crimes than they used to?
Nationwide clearance rates for both violent and property crime are at their lowest levels since at least 1993, the FBI data shows.
Police cleared a little over a third (36.7%) of the violent crimes that came to their attention in 2022, down from nearly half (48.1%) as recently as 2013. During the same period, there were decreases for each of the four types of violent crime the FBI tracks:
- Police cleared 52.3% of reported murders and nonnegligent homicides in 2022, down from 64.1% in 2013.
- They cleared 41.4% of aggravated assaults, down from 57.7%.
- They cleared 26.1% of rapes, down from 40.6%.
- They cleared 23.2% of robberies, down from 29.4%.
The pattern is less pronounced for property crime. Overall, law enforcement agencies cleared 12.1% of reported property crimes in 2022, down from 19.7% in 2013. The clearance rate for burglary didn’t change much, but it fell for larceny/theft (to 12.4% in 2022 from 22.4% in 2013) and motor vehicle theft (to 9.3% from 14.2%).
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on Nov. 20, 2020.
- Criminal Justice

John Gramlich is an associate director at Pew Research Center
8 facts about Black Lives Matter
#blacklivesmatter turns 10, support for the black lives matter movement has dropped considerably from its peak in 2020, fewer than 1% of federal criminal defendants were acquitted in 2022, before release of video showing tyre nichols’ beating, public views of police conduct had improved modestly, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates. Published on August 4, 2022 by Tegan George and Kirsten Dingemanse. Revised on July 18, 2023. An appendix is a supplementary document that facilitates your reader's understanding of your research but is not essential to your core argument. Appendices are a useful tool for providing additional information or clarification in a research paper ...
Appendix format example. The appendix label appears at the top of the page, bold and centered. On the next line, include a descriptive title, also bold and centered. The text is presented in general APA format: left-aligned, double-spaced, and with page numbers in the top right corner. Start a new page for each new appendix.
Here's an example of an appendix for a research paper on the topic of "The Effects of Exercise on Mental Health": Appendix A: Survey Questionnaire. This questionnaire was administered to participants in the study "The Effects of Exercise on Mental Health.". Section 1: Demographic Information. Section 2: Exercise Habits.
Step 1. Make an Appendix: Include Your Data. When creating an appendix, include extra data in their raw form. That is, you might not have used some details in your main paper. But you want a reader to know more information. For example, it can be calculations, some results of which are mentioned in your main text.
Insert Table: Once your data is selected, go to the "Insert" menu, then select "Table. Create Table: A dialog box will appear, confirming the selected data range. Make sure the "Use the first row as headers" option is checked if your data has headers. Click "Insert.".
For example, in a research paper, an appendix might include raw data tables or graphs that were used to support the study's conclusions. Including technical details: Appendices can be used to include technical details that may be of interest to a specialized audience. For example, in a technical report, an appendix might include detailed ...
Another option if you have a large amount of raw data is to consider placing it online [e.g., on a Google drive] and note that this is the appendix to your research paper. Any tables and figures included in the appendix should be numbered as a separate sequence from the main paper. Remember that appendices contain non-essential information that ...
Put the appendix label centered at the top of the page. On the next line under the appendix label, place the centered title of the appendix. If you refer to a source in your appendix, include an in-text citation just as you would in the main body of your paper and then include the source in your main reference section.
Information in this section is as outlined in the APA Publication Manual (2020), sections 2.14, 2.17, 2.24, and 7.6. Appendices are used to include information that supplement the paper's content but are considered distracting or inappropriate for the overall topic. It is recommended to only include an appendix if it helps the reader ...
Begin each appendix on a separate page. At the top of the page, center the word Appendix and the identifying capital letters (A, B, etc.) in the order in which they are mentioned in the text. Center the title of the appendix using uppercase and lowercase letter on the next line. Begin the text of the appendix flush left, followed by indented ...
The appendix would receive a name and label, and each figure or table would be given a corresponding letter and number. For example, if Appendix C contains two tables and one figure, these visuals would be labelled "Table C1", "Table C2", and "Figure C1" respectively. Sample Paper
Example of an appendix in a research paper. This business research paper is an example of a paper that includes an appendix. It contains only one appendix because all the supplemental data consists of tables. The appendix begins on page 33, not immediately below the references on page 32.
Step 2: Consider Accessibility. A research paper appendix can include non-textual information like tables, diagrams, graphs, images, illustrations, etc. If you're adding such visual data elements to your appendices, ensure the material is clear and readable so the reader can comprehend the data. You should also ensure you are labelling these ...
Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates. Published on 15 August 2022 by Kirsten Dingemanse and Tegan George. Revised on 25 October 2022. An appendix is a supplementary document that facilitates your reader's understanding of your research but is not essential to your core argument. Appendices are a useful tool for providing additional information or clarification in a research paper ...
An appendix is a section of a paper that features supporting information not included in the main text. The appendix of a paper consists of supporting information for the research that is not necessary to include in the text. This section provides further insight into the topic of research but happens to be too complex or too broad to add to ...
Each appendix begins on a new page. The order they are presented is dictated by the order they are mentioned in the text of your research paper. The heading should be "Appendix," followed by a letter or number [e.g., "Appendix A" or "Appendix 1"], centered and written in bold. Appendices must be listed in the table of contents [if used].
The following pages are sample appendices that can help you with the format and organization of the document. Appendices should be designated with letters. The figures and tables are numbered in the straight numbering style. This means that the figures and tables are numbered consecutively throughout the document.
An appendix or appendices should always be inserted after your Reference List; however, the appropriateness of appendix content really depends on the nature and scope of your research paper. For a more in-depth review of what supplemental materials might be included in a social science appendix, be sure to review Section 2.14 "Appendices ...
Meanwhile, note that an appendix comprises all the information utilized in a paper, including references and statistics from several authors and sources (the number varies according to the type of academic paper). The purpose of the appendix is to prevent vague or irrelevant information and improve the reader's understanding of the paper.
The definition of this term is simple. An appendix is an academic work section that contains additional information (statistics, references, tables, figures, etc.) that cannot be included in the main text. This component is usually placed after the reference list at the end of a research paper or dissertation. The purpose of this text component ...
An appendix can be a helpful way to provide additional information to your readers in a clear and organized manner. In this video, we'll take you to step by ...
For some papers and reports, you may choose to add a table, graph, chart, or image within the body of the draft. Or you may choose to include an appendix at the end of your paper. These can help to provide a visual representation of data or other information that you wish to relay to your reader. Follow the guidance below to understand when and ...
To measure public attitudes about crime in the U.S., we relied on survey data from Pew Research Center and Gallup. Additional details about each data source, including survey methodologies, are available by following the links in the text of this analysis. ... For example, in 2022, there were more than 700 violent crimes per 100,000 residents ...