- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

Empirical Research: Definition, Methods, Types and Examples
Content Index
Empirical research: Definition
Empirical research: origin, quantitative research methods, qualitative research methods, steps for conducting empirical research, empirical research methodology cycle, advantages of empirical research, disadvantages of empirical research, why is there a need for empirical research.
Empirical research is defined as any research where conclusions of the study is strictly drawn from concretely empirical evidence, and therefore “verifiable” evidence.
This empirical evidence can be gathered using quantitative market research and qualitative market research methods.
For example: A research is being conducted to find out if listening to happy music in the workplace while working may promote creativity? An experiment is conducted by using a music website survey on a set of audience who are exposed to happy music and another set who are not listening to music at all, and the subjects are then observed. The results derived from such a research will give empirical evidence if it does promote creativity or not.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research
You must have heard the quote” I will not believe it unless I see it”. This came from the ancient empiricists, a fundamental understanding that powered the emergence of medieval science during the renaissance period and laid the foundation of modern science, as we know it today. The word itself has its roots in greek. It is derived from the greek word empeirikos which means “experienced”.
In today’s world, the word empirical refers to collection of data using evidence that is collected through observation or experience or by using calibrated scientific instruments. All of the above origins have one thing in common which is dependence of observation and experiments to collect data and test them to come up with conclusions.
LEARN ABOUT: Causal Research
Types and methodologies of empirical research
Empirical research can be conducted and analysed using qualitative or quantitative methods.
- Quantitative research : Quantitative research methods are used to gather information through numerical data. It is used to quantify opinions, behaviors or other defined variables . These are predetermined and are in a more structured format. Some of the commonly used methods are survey, longitudinal studies, polls, etc
- Qualitative research: Qualitative research methods are used to gather non numerical data. It is used to find meanings, opinions, or the underlying reasons from its subjects. These methods are unstructured or semi structured. The sample size for such a research is usually small and it is a conversational type of method to provide more insight or in-depth information about the problem Some of the most popular forms of methods are focus groups, experiments, interviews, etc.
Data collected from these will need to be analysed. Empirical evidence can also be analysed either quantitatively and qualitatively. Using this, the researcher can answer empirical questions which have to be clearly defined and answerable with the findings he has got. The type of research design used will vary depending on the field in which it is going to be used. Many of them might choose to do a collective research involving quantitative and qualitative method to better answer questions which cannot be studied in a laboratory setting.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Research Questions and Questionnaires
Quantitative research methods aid in analyzing the empirical evidence gathered. By using these a researcher can find out if his hypothesis is supported or not.
- Survey research: Survey research generally involves a large audience to collect a large amount of data. This is a quantitative method having a predetermined set of closed questions which are pretty easy to answer. Because of the simplicity of such a method, high responses are achieved. It is one of the most commonly used methods for all kinds of research in today’s world.
Previously, surveys were taken face to face only with maybe a recorder. However, with advancement in technology and for ease, new mediums such as emails , or social media have emerged.
For example: Depletion of energy resources is a growing concern and hence there is a need for awareness about renewable energy. According to recent studies, fossil fuels still account for around 80% of energy consumption in the United States. Even though there is a rise in the use of green energy every year, there are certain parameters because of which the general population is still not opting for green energy. In order to understand why, a survey can be conducted to gather opinions of the general population about green energy and the factors that influence their choice of switching to renewable energy. Such a survey can help institutions or governing bodies to promote appropriate awareness and incentive schemes to push the use of greener energy.
Learn more: Renewable Energy Survey Template Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research
- Experimental research: In experimental research , an experiment is set up and a hypothesis is tested by creating a situation in which one of the variable is manipulated. This is also used to check cause and effect. It is tested to see what happens to the independent variable if the other one is removed or altered. The process for such a method is usually proposing a hypothesis, experimenting on it, analyzing the findings and reporting the findings to understand if it supports the theory or not.
For example: A particular product company is trying to find what is the reason for them to not be able to capture the market. So the organisation makes changes in each one of the processes like manufacturing, marketing, sales and operations. Through the experiment they understand that sales training directly impacts the market coverage for their product. If the person is trained well, then the product will have better coverage.
- Correlational research: Correlational research is used to find relation between two set of variables . Regression analysis is generally used to predict outcomes of such a method. It can be positive, negative or neutral correlation.
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis
For example: Higher educated individuals will get higher paying jobs. This means higher education enables the individual to high paying job and less education will lead to lower paying jobs.
- Longitudinal study: Longitudinal study is used to understand the traits or behavior of a subject under observation after repeatedly testing the subject over a period of time. Data collected from such a method can be qualitative or quantitative in nature.
For example: A research to find out benefits of exercise. The target is asked to exercise everyday for a particular period of time and the results show higher endurance, stamina, and muscle growth. This supports the fact that exercise benefits an individual body.
- Cross sectional: Cross sectional study is an observational type of method, in which a set of audience is observed at a given point in time. In this type, the set of people are chosen in a fashion which depicts similarity in all the variables except the one which is being researched. This type does not enable the researcher to establish a cause and effect relationship as it is not observed for a continuous time period. It is majorly used by healthcare sector or the retail industry.
For example: A medical study to find the prevalence of under-nutrition disorders in kids of a given population. This will involve looking at a wide range of parameters like age, ethnicity, location, incomes and social backgrounds. If a significant number of kids coming from poor families show under-nutrition disorders, the researcher can further investigate into it. Usually a cross sectional study is followed by a longitudinal study to find out the exact reason.
- Causal-Comparative research : This method is based on comparison. It is mainly used to find out cause-effect relationship between two variables or even multiple variables.
For example: A researcher measured the productivity of employees in a company which gave breaks to the employees during work and compared that to the employees of the company which did not give breaks at all.
LEARN ABOUT: Action Research
Some research questions need to be analysed qualitatively, as quantitative methods are not applicable there. In many cases, in-depth information is needed or a researcher may need to observe a target audience behavior, hence the results needed are in a descriptive analysis form. Qualitative research results will be descriptive rather than predictive. It enables the researcher to build or support theories for future potential quantitative research. In such a situation qualitative research methods are used to derive a conclusion to support the theory or hypothesis being studied.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Interview
- Case study: Case study method is used to find more information through carefully analyzing existing cases. It is very often used for business research or to gather empirical evidence for investigation purpose. It is a method to investigate a problem within its real life context through existing cases. The researcher has to carefully analyse making sure the parameter and variables in the existing case are the same as to the case that is being investigated. Using the findings from the case study, conclusions can be drawn regarding the topic that is being studied.
For example: A report mentioning the solution provided by a company to its client. The challenges they faced during initiation and deployment, the findings of the case and solutions they offered for the problems. Such case studies are used by most companies as it forms an empirical evidence for the company to promote in order to get more business.
- Observational method: Observational method is a process to observe and gather data from its target. Since it is a qualitative method it is time consuming and very personal. It can be said that observational research method is a part of ethnographic research which is also used to gather empirical evidence. This is usually a qualitative form of research, however in some cases it can be quantitative as well depending on what is being studied.
For example: setting up a research to observe a particular animal in the rain-forests of amazon. Such a research usually take a lot of time as observation has to be done for a set amount of time to study patterns or behavior of the subject. Another example used widely nowadays is to observe people shopping in a mall to figure out buying behavior of consumers.
- One-on-one interview: Such a method is purely qualitative and one of the most widely used. The reason being it enables a researcher get precise meaningful data if the right questions are asked. It is a conversational method where in-depth data can be gathered depending on where the conversation leads.
For example: A one-on-one interview with the finance minister to gather data on financial policies of the country and its implications on the public.
- Focus groups: Focus groups are used when a researcher wants to find answers to why, what and how questions. A small group is generally chosen for such a method and it is not necessary to interact with the group in person. A moderator is generally needed in case the group is being addressed in person. This is widely used by product companies to collect data about their brands and the product.
For example: A mobile phone manufacturer wanting to have a feedback on the dimensions of one of their models which is yet to be launched. Such studies help the company meet the demand of the customer and position their model appropriately in the market.
- Text analysis: Text analysis method is a little new compared to the other types. Such a method is used to analyse social life by going through images or words used by the individual. In today’s world, with social media playing a major part of everyone’s life, such a method enables the research to follow the pattern that relates to his study.
For example: A lot of companies ask for feedback from the customer in detail mentioning how satisfied are they with their customer support team. Such data enables the researcher to take appropriate decisions to make their support team better.
Sometimes a combination of the methods is also needed for some questions that cannot be answered using only one type of method especially when a researcher needs to gain a complete understanding of complex subject matter.
We recently published a blog that talks about examples of qualitative data in education ; why don’t you check it out for more ideas?
Since empirical research is based on observation and capturing experiences, it is important to plan the steps to conduct the experiment and how to analyse it. This will enable the researcher to resolve problems or obstacles which can occur during the experiment.
Step #1: Define the purpose of the research
This is the step where the researcher has to answer questions like what exactly do I want to find out? What is the problem statement? Are there any issues in terms of the availability of knowledge, data, time or resources. Will this research be more beneficial than what it will cost.
Before going ahead, a researcher has to clearly define his purpose for the research and set up a plan to carry out further tasks.
Step #2 : Supporting theories and relevant literature
The researcher needs to find out if there are theories which can be linked to his research problem . He has to figure out if any theory can help him support his findings. All kind of relevant literature will help the researcher to find if there are others who have researched this before, or what are the problems faced during this research. The researcher will also have to set up assumptions and also find out if there is any history regarding his research problem
Step #3: Creation of Hypothesis and measurement
Before beginning the actual research he needs to provide himself a working hypothesis or guess what will be the probable result. Researcher has to set up variables, decide the environment for the research and find out how can he relate between the variables.
Researcher will also need to define the units of measurements, tolerable degree for errors, and find out if the measurement chosen will be acceptable by others.
Step #4: Methodology, research design and data collection
In this step, the researcher has to define a strategy for conducting his research. He has to set up experiments to collect data which will enable him to propose the hypothesis. The researcher will decide whether he will need experimental or non experimental method for conducting the research. The type of research design will vary depending on the field in which the research is being conducted. Last but not the least, the researcher will have to find out parameters that will affect the validity of the research design. Data collection will need to be done by choosing appropriate samples depending on the research question. To carry out the research, he can use one of the many sampling techniques. Once data collection is complete, researcher will have empirical data which needs to be analysed.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
Step #5: Data Analysis and result
Data analysis can be done in two ways, qualitatively and quantitatively. Researcher will need to find out what qualitative method or quantitative method will be needed or will he need a combination of both. Depending on the unit of analysis of his data, he will know if his hypothesis is supported or rejected. Analyzing this data is the most important part to support his hypothesis.
Step #6: Conclusion
A report will need to be made with the findings of the research. The researcher can give the theories and literature that support his research. He can make suggestions or recommendations for further research on his topic.
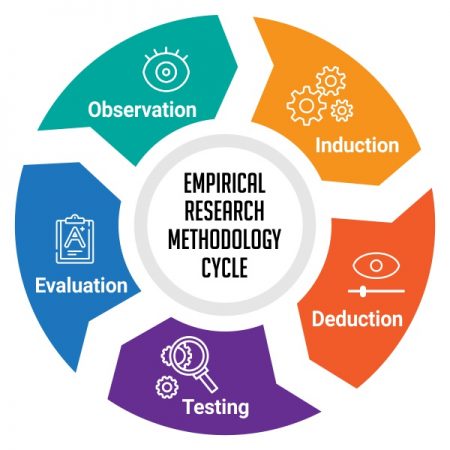
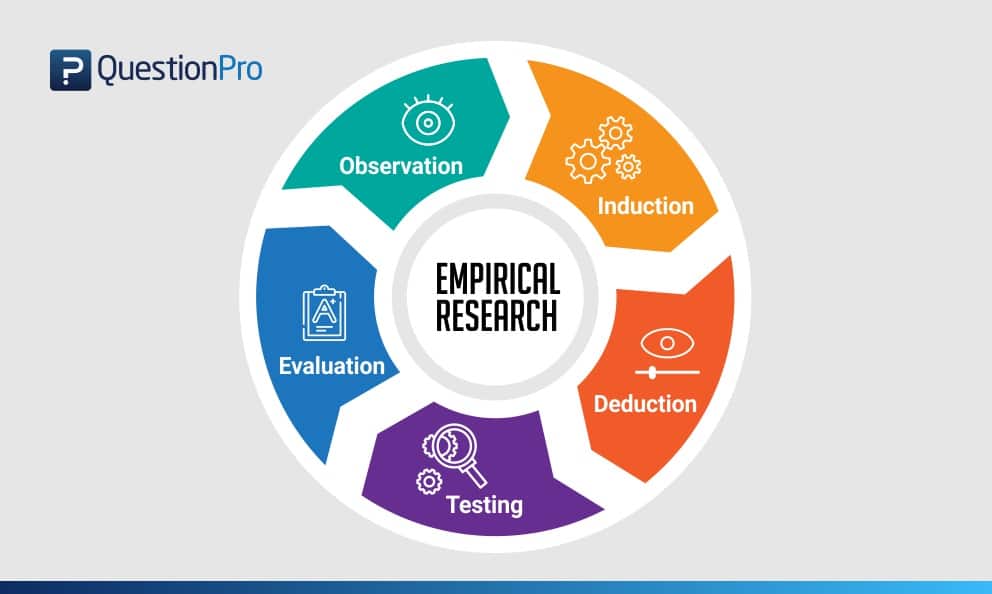
A.D. de Groot, a famous dutch psychologist and a chess expert conducted some of the most notable experiments using chess in the 1940’s. During his study, he came up with a cycle which is consistent and now widely used to conduct empirical research. It consists of 5 phases with each phase being as important as the next one. The empirical cycle captures the process of coming up with hypothesis about how certain subjects work or behave and then testing these hypothesis against empirical data in a systematic and rigorous approach. It can be said that it characterizes the deductive approach to science. Following is the empirical cycle.
- Observation: At this phase an idea is sparked for proposing a hypothesis. During this phase empirical data is gathered using observation. For example: a particular species of flower bloom in a different color only during a specific season.
- Induction: Inductive reasoning is then carried out to form a general conclusion from the data gathered through observation. For example: As stated above it is observed that the species of flower blooms in a different color during a specific season. A researcher may ask a question “does the temperature in the season cause the color change in the flower?” He can assume that is the case, however it is a mere conjecture and hence an experiment needs to be set up to support this hypothesis. So he tags a few set of flowers kept at a different temperature and observes if they still change the color?
- Deduction: This phase helps the researcher to deduce a conclusion out of his experiment. This has to be based on logic and rationality to come up with specific unbiased results.For example: In the experiment, if the tagged flowers in a different temperature environment do not change the color then it can be concluded that temperature plays a role in changing the color of the bloom.
- Testing: This phase involves the researcher to return to empirical methods to put his hypothesis to the test. The researcher now needs to make sense of his data and hence needs to use statistical analysis plans to determine the temperature and bloom color relationship. If the researcher finds out that most flowers bloom a different color when exposed to the certain temperature and the others do not when the temperature is different, he has found support to his hypothesis. Please note this not proof but just a support to his hypothesis.
- Evaluation: This phase is generally forgotten by most but is an important one to keep gaining knowledge. During this phase the researcher puts forth the data he has collected, the support argument and his conclusion. The researcher also states the limitations for the experiment and his hypothesis and suggests tips for others to pick it up and continue a more in-depth research for others in the future. LEARN MORE: Population vs Sample
LEARN MORE: Population vs Sample
There is a reason why empirical research is one of the most widely used method. There are a few advantages associated with it. Following are a few of them.
- It is used to authenticate traditional research through various experiments and observations.
- This research methodology makes the research being conducted more competent and authentic.
- It enables a researcher understand the dynamic changes that can happen and change his strategy accordingly.
- The level of control in such a research is high so the researcher can control multiple variables.
- It plays a vital role in increasing internal validity .
Even though empirical research makes the research more competent and authentic, it does have a few disadvantages. Following are a few of them.
- Such a research needs patience as it can be very time consuming. The researcher has to collect data from multiple sources and the parameters involved are quite a few, which will lead to a time consuming research.
- Most of the time, a researcher will need to conduct research at different locations or in different environments, this can lead to an expensive affair.
- There are a few rules in which experiments can be performed and hence permissions are needed. Many a times, it is very difficult to get certain permissions to carry out different methods of this research.
- Collection of data can be a problem sometimes, as it has to be collected from a variety of sources through different methods.
LEARN ABOUT: Social Communication Questionnaire
Empirical research is important in today’s world because most people believe in something only that they can see, hear or experience. It is used to validate multiple hypothesis and increase human knowledge and continue doing it to keep advancing in various fields.
For example: Pharmaceutical companies use empirical research to try out a specific drug on controlled groups or random groups to study the effect and cause. This way, they prove certain theories they had proposed for the specific drug. Such research is very important as sometimes it can lead to finding a cure for a disease that has existed for many years. It is useful in science and many other fields like history, social sciences, business, etc.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
With the advancement in today’s world, empirical research has become critical and a norm in many fields to support their hypothesis and gain more knowledge. The methods mentioned above are very useful for carrying out such research. However, a number of new methods will keep coming up as the nature of new investigative questions keeps getting unique or changing.
Create a single source of real data with a built-for-insights platform. Store past data, add nuggets of insights, and import research data from various sources into a CRM for insights. Build on ever-growing research with a real-time dashboard in a unified research management platform to turn insights into knowledge.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

21 Best Customer Advocacy Software for Customers in 2024
Apr 19, 2024

10 Quantitative Data Analysis Software for Every Data Scientist
Apr 18, 2024

11 Best Enterprise Feedback Management Software in 2024

17 Best Online Reputation Management Software in 2024
Apr 17, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Penn State University Libraries
Empirical research in the social sciences and education.
- What is Empirical Research and How to Read It
- Finding Empirical Research in Library Databases
- Designing Empirical Research
- Ethics, Cultural Responsiveness, and Anti-Racism in Research
- Citing, Writing, and Presenting Your Work
Contact the Librarian at your campus for more help!

Introduction: What is Empirical Research?
Empirical research is based on observed and measured phenomena and derives knowledge from actual experience rather than from theory or belief.
How do you know if a study is empirical? Read the subheadings within the article, book, or report and look for a description of the research "methodology." Ask yourself: Could I recreate this study and test these results?
Key characteristics to look for:
- Specific research questions to be answered
- Definition of the population, behavior, or phenomena being studied
- Description of the process used to study this population or phenomena, including selection criteria, controls, and testing instruments (such as surveys)
Another hint: some scholarly journals use a specific layout, called the "IMRaD" format, to communicate empirical research findings. Such articles typically have 4 components:
- Introduction : sometimes called "literature review" -- what is currently known about the topic -- usually includes a theoretical framework and/or discussion of previous studies
- Methodology: sometimes called "research design" -- how to recreate the study -- usually describes the population, research process, and analytical tools used in the present study
- Results : sometimes called "findings" -- what was learned through the study -- usually appears as statistical data or as substantial quotations from research participants
- Discussion : sometimes called "conclusion" or "implications" -- why the study is important -- usually describes how the research results influence professional practices or future studies
Reading and Evaluating Scholarly Materials
Reading research can be a challenge. However, the tutorials and videos below can help. They explain what scholarly articles look like, how to read them, and how to evaluate them:
- CRAAP Checklist A frequently-used checklist that helps you examine the currency, relevance, authority, accuracy, and purpose of an information source.
- IF I APPLY A newer model of evaluating sources which encourages you to think about your own biases as a reader, as well as concerns about the item you are reading.
- Credo Video: How to Read Scholarly Materials (4 min.)
- Credo Tutorial: How to Read Scholarly Materials
- Credo Tutorial: Evaluating Information
- Credo Video: Evaluating Statistics (4 min.)
- Next: Finding Empirical Research in Library Databases >>
- Last Updated: Feb 18, 2024 8:33 PM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/emp

Empirical Research in the Social Sciences and Education
What is empirical research.
- Finding Empirical Research
- Designing Empirical Research
- Ethics & Anti-Racism in Research
- Citing, Writing, and Presenting Your Work
Academic Services Librarian | Research, Education, & Engagement

Gratitude to Penn State
Thank you to librarians at Penn State for serving as the inspiration for this library guide
An empirical research article is a primary source where the authors reported on experiments or observations that they conducted. Their research includes their observed and measured data that they derived from an actual experiment rather than theory or belief.
How do you know if you are reading an empirical article? Ask yourself: "What did the authors actually do?" or "How could this study be re-created?"
Key characteristics to look for:
- Specific research questions to be answered
- Definition of the population, behavior, or phenomena being studied
- Description of the process or methodology used to study this population or phenomena, including selection criteria, controls, and testing instruments (example: surveys, questionnaires, etc)
- You can readily describe what the authors actually did
Layout of Empirical Articles
Scholarly journals sometimes use a specific layout for empirical articles, called the "IMRaD" format, to communicate empirical research findings. There are four main components:
- Introduction : aka "literature review". This section summarizes what is known about the topic at the time of the article's publication. It brings the reader up-to-speed on the research and usually includes a theoretical framework
- Methodology : aka "research design". This section describes exactly how the study was done. It describes the population, research process, and analytical tools
- Results : aka "findings". This section describes what was learned in the study. It usually contains statistical data or substantial quotes from research participants
- Discussion : aka "conclusion" or "implications". This section explains why the study is important, and also describes the limitations of the study. While research results can influence professional practices and future studies, it's important for the researchers to clarify if specific aspects of the study should limit its use. For example, a study using undergraduate students at a small, western, private college can not be extrapolated to include all undergraduates.
- Next: Finding Empirical Research >>
- Last Updated: Nov 8, 2023 4:19 PM
- URL: https://libguides.stthomas.edu/empiricalresearcheducation
© 2023 University of St. Thomas, Minnesota

Encyclopedia of Psychology and Religion pp 782–783 Cite as
Empirical Research
- Emeka Thaddues Njoku 3
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2020
74 Accesses
The term “empirical” entails gathered data based on experience, observations, or experimentation. In empirical research, knowledge is developed from factual experience as opposed to theoretical assumption and usually involved the use of data sources like datasets or fieldwork, but can also be based on observations within a laboratory setting. Testing hypothesis or answering definite questions is a primary feature of empirical research. Empirical research, in other words, involves the process of employing working hypothesis that are tested through experimentation or observation. Hence, empirical research is a method of uncovering empirical evidence.
Through the process of gathering valid empirical data, scientists from a variety of fields, ranging from the social to the natural sciences, have to carefully design their methods. This helps to ensure quality and accuracy of data collection and treatment. However, any error in empirical data collection process could inevitably render such...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Bibliography
Bhattacherjee, A. (2012). Social science research: Principles, methods, and practices. Textbooks Collection . Book 3.
Google Scholar
Comte, A., & Bridges, J. H. (Tr.) (1865). A general view of positivism . Trubner and Co. (reissued by Cambridge University Press, 2009).
Dilworth, C. B. (1982). Empirical research in the literature class. English Journal, 71 (3), 95–97.
Article Google Scholar
Heisenberg, W. (1971). Positivism, metaphysics and religion. In R. N. Nanshen (Ed.), Werner Heisenberg – Physics and beyond – Encounters and conversations , World Perspectives. 42. Translator: Arnold J. Pomerans. New York: Harper and Row.
Hossain, F. M. A. (2014). A critical analysis of empiricism. Open Journal of Philosophy, 2014 (4), 225–230.
Kant, I. (1783). Prolegomena to any future metaphysic (trans: Bennett, J.). Early Modern Texts. www.earlymoderntexts.com
Koch, S. (1992). Psychology’s Bridgman vs. Bridgman’s Bridgman: An essay in reconstruction. Theory and Psychology, 2 (3), 261–290.
Matin, A. (1968). An outline of philosophy . Dhaka: Mullick Brothers.
Mcleod, S. (2008). Psychology as science. http://www.simplypsychology.org/science-psychology.html
Popper, K. (1963). Conjectures and refutations: The growth of scientific knowledge . London: Routledge.
Simmel, G. (1908). The problem areas of sociology in Kurt H. Wolf: The sociology of Georg Simmel . London: The Free Press.
Weber, M. (1991). The nature of social action. In W. G. Runciman (Ed.), Weber: Selections in translation . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Political Science, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Oyo, Nigeria
Emeka Thaddues Njoku
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Emeka Thaddues Njoku .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA
David A. Leeming
Blanton-Peale Institute, New York, NY, USA
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Njoku, E.T. (2020). Empirical Research. In: Leeming, D.A. (eds) Encyclopedia of Psychology and Religion. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24348-7_200051
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24348-7_200051
Published : 12 June 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-24347-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-24348-7
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Identifying Empirical Research Articles
Identifying empirical articles.
- Searching for Empirical Research Articles
What is Empirical Research?
An empirical research article reports the results of a study that uses data derived from actual observation or experimentation. Empirical research articles are examples of primary research. To learn more about the differences between primary and secondary research, see our related guide:
- Primary and Secondary Sources
By the end of this guide, you will be able to:
- Identify common elements of an empirical article
- Use a variety of search strategies to search for empirical articles within the library collection
Look for the IMRaD layout in the article to help identify empirical research. Sometimes the sections will be labeled differently, but the content will be similar.
- I ntroduction: why the article was written, research question or questions, hypothesis, literature review
- M ethods: the overall research design and implementation, description of sample, instruments used, how the authors measured their experiment
- R esults: output of the author's measurements, usually includes statistics of the author's findings
- D iscussion: the author's interpretation and conclusions about the results, limitations of study, suggestions for further research
Parts of an Empirical Research Article
Parts of an empirical article.
The screenshots below identify the basic IMRaD structure of an empirical research article.
Introduction
The introduction contains a literature review and the study's research hypothesis.

The method section outlines the research design, participants, and measures used.

Results
The results section contains statistical data (charts, graphs, tables, etc.) and research participant quotes.

The discussion section includes impacts, limitations, future considerations, and research.

Learn the IMRaD Layout: How to Identify an Empirical Article
This short video overviews the IMRaD method for identifying empirical research.
- Next: Searching for Empirical Research Articles >>
- Last Updated: Nov 16, 2023 8:24 AM
CityU Home - CityU Catalog

What is Empirical Research? Definition, Methods, Examples
Appinio Research · 09.02.2024 · 35min read

Ever wondered how we gather the facts, unveil hidden truths, and make informed decisions in a world filled with questions? Empirical research holds the key.
In this guide, we'll delve deep into the art and science of empirical research, unraveling its methods, mysteries, and manifold applications. From defining the core principles to mastering data analysis and reporting findings, we're here to equip you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the empirical landscape.
What is Empirical Research?
Empirical research is the cornerstone of scientific inquiry, providing a systematic and structured approach to investigating the world around us. It is the process of gathering and analyzing empirical or observable data to test hypotheses, answer research questions, or gain insights into various phenomena. This form of research relies on evidence derived from direct observation or experimentation, allowing researchers to draw conclusions based on real-world data rather than purely theoretical or speculative reasoning.
Characteristics of Empirical Research
Empirical research is characterized by several key features:
- Observation and Measurement : It involves the systematic observation or measurement of variables, events, or behaviors.
- Data Collection : Researchers collect data through various methods, such as surveys, experiments, observations, or interviews.
- Testable Hypotheses : Empirical research often starts with testable hypotheses that are evaluated using collected data.
- Quantitative or Qualitative Data : Data can be quantitative (numerical) or qualitative (non-numerical), depending on the research design.
- Statistical Analysis : Quantitative data often undergo statistical analysis to determine patterns , relationships, or significance.
- Objectivity and Replicability : Empirical research strives for objectivity, minimizing researcher bias . It should be replicable, allowing other researchers to conduct the same study to verify results.
- Conclusions and Generalizations : Empirical research generates findings based on data and aims to make generalizations about larger populations or phenomena.
Importance of Empirical Research
Empirical research plays a pivotal role in advancing knowledge across various disciplines. Its importance extends to academia, industry, and society as a whole. Here are several reasons why empirical research is essential:
- Evidence-Based Knowledge : Empirical research provides a solid foundation of evidence-based knowledge. It enables us to test hypotheses, confirm or refute theories, and build a robust understanding of the world.
- Scientific Progress : In the scientific community, empirical research fuels progress by expanding the boundaries of existing knowledge. It contributes to the development of theories and the formulation of new research questions.
- Problem Solving : Empirical research is instrumental in addressing real-world problems and challenges. It offers insights and data-driven solutions to complex issues in fields like healthcare, economics, and environmental science.
- Informed Decision-Making : In policymaking, business, and healthcare, empirical research informs decision-makers by providing data-driven insights. It guides strategies, investments, and policies for optimal outcomes.
- Quality Assurance : Empirical research is essential for quality assurance and validation in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and technology. It ensures that products and processes meet established standards.
- Continuous Improvement : Businesses and organizations use empirical research to evaluate performance, customer satisfaction, and product effectiveness. This data-driven approach fosters continuous improvement and innovation.
- Human Advancement : Empirical research in fields like medicine and psychology contributes to the betterment of human health and well-being. It leads to medical breakthroughs, improved therapies, and enhanced psychological interventions.
- Critical Thinking and Problem Solving : Engaging in empirical research fosters critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and a deep appreciation for evidence-based decision-making.
Empirical research empowers us to explore, understand, and improve the world around us. It forms the bedrock of scientific inquiry and drives progress in countless domains, shaping our understanding of both the natural and social sciences.
How to Conduct Empirical Research?
So, you've decided to dive into the world of empirical research. Let's begin by exploring the crucial steps involved in getting started with your research project.
1. Select a Research Topic
Selecting the right research topic is the cornerstone of a successful empirical study. It's essential to choose a topic that not only piques your interest but also aligns with your research goals and objectives. Here's how to go about it:
- Identify Your Interests : Start by reflecting on your passions and interests. What topics fascinate you the most? Your enthusiasm will be your driving force throughout the research process.
- Brainstorm Ideas : Engage in brainstorming sessions to generate potential research topics. Consider the questions you've always wanted to answer or the issues that intrigue you.
- Relevance and Significance : Assess the relevance and significance of your chosen topic. Does it contribute to existing knowledge? Is it a pressing issue in your field of study or the broader community?
- Feasibility : Evaluate the feasibility of your research topic. Do you have access to the necessary resources, data, and participants (if applicable)?
2. Formulate Research Questions
Once you've narrowed down your research topic, the next step is to formulate clear and precise research questions . These questions will guide your entire research process and shape your study's direction. To create effective research questions:
- Specificity : Ensure that your research questions are specific and focused. Vague or overly broad questions can lead to inconclusive results.
- Relevance : Your research questions should directly relate to your chosen topic. They should address gaps in knowledge or contribute to solving a particular problem.
- Testability : Ensure that your questions are testable through empirical methods. You should be able to gather data and analyze it to answer these questions.
- Avoid Bias : Craft your questions in a way that avoids leading or biased language. Maintain neutrality to uphold the integrity of your research.
3. Review Existing Literature
Before you embark on your empirical research journey, it's essential to immerse yourself in the existing body of literature related to your chosen topic. This step, often referred to as a literature review, serves several purposes:
- Contextualization : Understand the historical context and current state of research in your field. What have previous studies found, and what questions remain unanswered?
- Identifying Gaps : Identify gaps or areas where existing research falls short. These gaps will help you formulate meaningful research questions and hypotheses.
- Theory Development : If your study is theoretical, consider how existing theories apply to your topic. If it's empirical, understand how previous studies have approached data collection and analysis.
- Methodological Insights : Learn from the methodologies employed in previous research. What methods were successful, and what challenges did researchers face?
4. Define Variables
Variables are fundamental components of empirical research. They are the factors or characteristics that can change or be manipulated during your study. Properly defining and categorizing variables is crucial for the clarity and validity of your research. Here's what you need to know:
- Independent Variables : These are the variables that you, as the researcher, manipulate or control. They are the "cause" in cause-and-effect relationships.
- Dependent Variables : Dependent variables are the outcomes or responses that you measure or observe. They are the "effect" influenced by changes in independent variables.
- Operational Definitions : To ensure consistency and clarity, provide operational definitions for your variables. Specify how you will measure or manipulate each variable.
- Control Variables : In some studies, controlling for other variables that may influence your dependent variable is essential. These are known as control variables.
Understanding these foundational aspects of empirical research will set a solid foundation for the rest of your journey. Now that you've grasped the essentials of getting started, let's delve deeper into the intricacies of research design.
Empirical Research Design
Now that you've selected your research topic, formulated research questions, and defined your variables, it's time to delve into the heart of your empirical research journey – research design . This pivotal step determines how you will collect data and what methods you'll employ to answer your research questions. Let's explore the various facets of research design in detail.
Types of Empirical Research
Empirical research can take on several forms, each with its own unique approach and methodologies. Understanding the different types of empirical research will help you choose the most suitable design for your study. Here are some common types:
- Experimental Research : In this type, researchers manipulate one or more independent variables to observe their impact on dependent variables. It's highly controlled and often conducted in a laboratory setting.
- Observational Research : Observational research involves the systematic observation of subjects or phenomena without intervention. Researchers are passive observers, documenting behaviors, events, or patterns.
- Survey Research : Surveys are used to collect data through structured questionnaires or interviews. This method is efficient for gathering information from a large number of participants.
- Case Study Research : Case studies focus on in-depth exploration of one or a few cases. Researchers gather detailed information through various sources such as interviews, documents, and observations.
- Qualitative Research : Qualitative research aims to understand behaviors, experiences, and opinions in depth. It often involves open-ended questions, interviews, and thematic analysis.
- Quantitative Research : Quantitative research collects numerical data and relies on statistical analysis to draw conclusions. It involves structured questionnaires, experiments, and surveys.
Your choice of research type should align with your research questions and objectives. Experimental research, for example, is ideal for testing cause-and-effect relationships, while qualitative research is more suitable for exploring complex phenomena.
Experimental Design
Experimental research is a systematic approach to studying causal relationships. It's characterized by the manipulation of one or more independent variables while controlling for other factors. Here are some key aspects of experimental design:
- Control and Experimental Groups : Participants are randomly assigned to either a control group or an experimental group. The independent variable is manipulated for the experimental group but not for the control group.
- Randomization : Randomization is crucial to eliminate bias in group assignment. It ensures that each participant has an equal chance of being in either group.
- Hypothesis Testing : Experimental research often involves hypothesis testing. Researchers formulate hypotheses about the expected effects of the independent variable and use statistical analysis to test these hypotheses.
Observational Design
Observational research entails careful and systematic observation of subjects or phenomena. It's advantageous when you want to understand natural behaviors or events. Key aspects of observational design include:
- Participant Observation : Researchers immerse themselves in the environment they are studying. They become part of the group being observed, allowing for a deep understanding of behaviors.
- Non-Participant Observation : In non-participant observation, researchers remain separate from the subjects. They observe and document behaviors without direct involvement.
- Data Collection Methods : Observational research can involve various data collection methods, such as field notes, video recordings, photographs, or coding of observed behaviors.
Survey Design
Surveys are a popular choice for collecting data from a large number of participants. Effective survey design is essential to ensure the validity and reliability of your data. Consider the following:
- Questionnaire Design : Create clear and concise questions that are easy for participants to understand. Avoid leading or biased questions.
- Sampling Methods : Decide on the appropriate sampling method for your study, whether it's random, stratified, or convenience sampling.
- Data Collection Tools : Choose the right tools for data collection, whether it's paper surveys, online questionnaires, or face-to-face interviews.
Case Study Design
Case studies are an in-depth exploration of one or a few cases to gain a deep understanding of a particular phenomenon. Key aspects of case study design include:
- Single Case vs. Multiple Case Studies : Decide whether you'll focus on a single case or multiple cases. Single case studies are intensive and allow for detailed examination, while multiple case studies provide comparative insights.
- Data Collection Methods : Gather data through interviews, observations, document analysis, or a combination of these methods.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
In empirical research, you'll often encounter the distinction between qualitative and quantitative research . Here's a closer look at these two approaches:
- Qualitative Research : Qualitative research seeks an in-depth understanding of human behavior, experiences, and perspectives. It involves open-ended questions, interviews, and the analysis of textual or narrative data. Qualitative research is exploratory and often used when the research question is complex and requires a nuanced understanding.
- Quantitative Research : Quantitative research collects numerical data and employs statistical analysis to draw conclusions. It involves structured questionnaires, experiments, and surveys. Quantitative research is ideal for testing hypotheses and establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
Understanding the various research design options is crucial in determining the most appropriate approach for your study. Your choice should align with your research questions, objectives, and the nature of the phenomenon you're investigating.
Data Collection for Empirical Research
Now that you've established your research design, it's time to roll up your sleeves and collect the data that will fuel your empirical research. Effective data collection is essential for obtaining accurate and reliable results.
Sampling Methods
Sampling methods are critical in empirical research, as they determine the subset of individuals or elements from your target population that you will study. Here are some standard sampling methods:
- Random Sampling : Random sampling ensures that every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. It minimizes bias and is often used in quantitative research.
- Stratified Sampling : Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into subgroups or strata based on specific characteristics (e.g., age, gender, location). Samples are then randomly selected from each stratum, ensuring representation of all subgroups.
- Convenience Sampling : Convenience sampling involves selecting participants who are readily available or easily accessible. While it's convenient, it may introduce bias and limit the generalizability of results.
- Snowball Sampling : Snowball sampling is instrumental when studying hard-to-reach or hidden populations. One participant leads you to another, creating a "snowball" effect. This method is common in qualitative research.
- Purposive Sampling : In purposive sampling, researchers deliberately select participants who meet specific criteria relevant to their research questions. It's often used in qualitative studies to gather in-depth information.
The choice of sampling method depends on the nature of your research, available resources, and the degree of precision required. It's crucial to carefully consider your sampling strategy to ensure that your sample accurately represents your target population.
Data Collection Instruments
Data collection instruments are the tools you use to gather information from your participants or sources. These instruments should be designed to capture the data you need accurately. Here are some popular data collection instruments:
- Questionnaires : Questionnaires consist of structured questions with predefined response options. When designing questionnaires, consider the clarity of questions, the order of questions, and the response format (e.g., Likert scale , multiple-choice).
- Interviews : Interviews involve direct communication between the researcher and participants. They can be structured (with predetermined questions) or unstructured (open-ended). Effective interviews require active listening and probing for deeper insights.
- Observations : Observations entail systematically and objectively recording behaviors, events, or phenomena. Researchers must establish clear criteria for what to observe, how to record observations, and when to observe.
- Surveys : Surveys are a common data collection instrument for quantitative research. They can be administered through various means, including online surveys, paper surveys, and telephone surveys.
- Documents and Archives : In some cases, data may be collected from existing documents, records, or archives. Ensure that the sources are reliable, relevant, and properly documented.
To streamline your process and gather insights with precision and efficiency, consider leveraging innovative tools like Appinio . With Appinio's intuitive platform, you can harness the power of real-time consumer data to inform your research decisions effectively. Whether you're conducting surveys, interviews, or observations, Appinio empowers you to define your target audience, collect data from diverse demographics, and analyze results seamlessly.
By incorporating Appinio into your data collection toolkit, you can unlock a world of possibilities and elevate the impact of your empirical research. Ready to revolutionize your approach to data collection?
Book a Demo
Data Collection Procedures
Data collection procedures outline the step-by-step process for gathering data. These procedures should be meticulously planned and executed to maintain the integrity of your research.
- Training : If you have a research team, ensure that they are trained in data collection methods and protocols. Consistency in data collection is crucial.
- Pilot Testing : Before launching your data collection, conduct a pilot test with a small group to identify any potential problems with your instruments or procedures. Make necessary adjustments based on feedback.
- Data Recording : Establish a systematic method for recording data. This may include timestamps, codes, or identifiers for each data point.
- Data Security : Safeguard the confidentiality and security of collected data. Ensure that only authorized individuals have access to the data.
- Data Storage : Properly organize and store your data in a secure location, whether in physical or digital form. Back up data to prevent loss.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are paramount in empirical research, as they ensure the well-being and rights of participants are protected.
- Informed Consent : Obtain informed consent from participants, providing clear information about the research purpose, procedures, risks, and their right to withdraw at any time.
- Privacy and Confidentiality : Protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Ensure that data is anonymized and sensitive information is kept confidential.
- Beneficence : Ensure that your research benefits participants and society while minimizing harm. Consider the potential risks and benefits of your study.
- Honesty and Integrity : Conduct research with honesty and integrity. Report findings accurately and transparently, even if they are not what you expected.
- Respect for Participants : Treat participants with respect, dignity, and sensitivity to cultural differences. Avoid any form of coercion or manipulation.
- Institutional Review Board (IRB) : If required, seek approval from an IRB or ethics committee before conducting your research, particularly when working with human participants.
Adhering to ethical guidelines is not only essential for the ethical conduct of research but also crucial for the credibility and validity of your study. Ethical research practices build trust between researchers and participants and contribute to the advancement of knowledge with integrity.
With a solid understanding of data collection, including sampling methods, instruments, procedures, and ethical considerations, you are now well-equipped to gather the data needed to answer your research questions.
Empirical Research Data Analysis
Now comes the exciting phase of data analysis, where the raw data you've diligently collected starts to yield insights and answers to your research questions. We will explore the various aspects of data analysis, from preparing your data to drawing meaningful conclusions through statistics and visualization.
Data Preparation
Data preparation is the crucial first step in data analysis. It involves cleaning, organizing, and transforming your raw data into a format that is ready for analysis. Effective data preparation ensures the accuracy and reliability of your results.
- Data Cleaning : Identify and rectify errors, missing values, and inconsistencies in your dataset. This may involve correcting typos, removing outliers, and imputing missing data.
- Data Coding : Assign numerical values or codes to categorical variables to make them suitable for statistical analysis. For example, converting "Yes" and "No" to 1 and 0.
- Data Transformation : Transform variables as needed to meet the assumptions of the statistical tests you plan to use. Common transformations include logarithmic or square root transformations.
- Data Integration : If your data comes from multiple sources, integrate it into a unified dataset, ensuring that variables match and align.
- Data Documentation : Maintain clear documentation of all data preparation steps, as well as the rationale behind each decision. This transparency is essential for replicability.
Effective data preparation lays the foundation for accurate and meaningful analysis. It allows you to trust the results that will follow in the subsequent stages.
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics help you summarize and make sense of your data by providing a clear overview of its key characteristics. These statistics are essential for understanding the central tendencies, variability, and distribution of your variables. Descriptive statistics include:
- Measures of Central Tendency : These include the mean (average), median (middle value), and mode (most frequent value). They help you understand the typical or central value of your data.
- Measures of Dispersion : Measures like the range, variance, and standard deviation provide insights into the spread or variability of your data points.
- Frequency Distributions : Creating frequency distributions or histograms allows you to visualize the distribution of your data across different values or categories.
Descriptive statistics provide the initial insights needed to understand your data's basic characteristics, which can inform further analysis.
Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics take your analysis to the next level by allowing you to make inferences or predictions about a larger population based on your sample data. These methods help you test hypotheses and draw meaningful conclusions. Key concepts in inferential statistics include:
- Hypothesis Testing : Hypothesis tests (e.g., t-tests, chi-squared tests) help you determine whether observed differences or associations in your data are statistically significant or occurred by chance.
- Confidence Intervals : Confidence intervals provide a range within which population parameters (e.g., population mean) are likely to fall based on your sample data.
- Regression Analysis : Regression models (linear, logistic, etc.) help you explore relationships between variables and make predictions.
- Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) : ANOVA tests are used to compare means between multiple groups, allowing you to assess whether differences are statistically significant.
Inferential statistics are powerful tools for drawing conclusions from your data and assessing the generalizability of your findings to the broader population.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis is employed when working with non-numerical data, such as text, interviews, or open-ended survey responses. It focuses on understanding the underlying themes, patterns, and meanings within qualitative data. Qualitative analysis techniques include:
- Thematic Analysis : Identifying and analyzing recurring themes or patterns within textual data.
- Content Analysis : Categorizing and coding qualitative data to extract meaningful insights.
- Grounded Theory : Developing theories or frameworks based on emergent themes from the data.
- Narrative Analysis : Examining the structure and content of narratives to uncover meaning.
Qualitative data analysis provides a rich and nuanced understanding of complex phenomena and human experiences.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is the art of representing data graphically to make complex information more understandable and accessible. Effective data visualization can reveal patterns, trends, and outliers in your data. Common types of data visualization include:
- Bar Charts and Histograms : Used to display the distribution of categorical or discrete data.
- Line Charts : Ideal for showing trends and changes in data over time.
- Scatter Plots : Visualize relationships and correlations between two variables.
- Pie Charts : Display the composition of a whole in terms of its parts.
- Heatmaps : Depict patterns and relationships in multidimensional data through color-coding.
- Box Plots : Provide a summary of the data distribution, including outliers.
- Interactive Dashboards : Create dynamic visualizations that allow users to explore data interactively.
Data visualization not only enhances your understanding of the data but also serves as a powerful communication tool to convey your findings to others.
As you embark on the data analysis phase of your empirical research, remember that the specific methods and techniques you choose will depend on your research questions, data type, and objectives. Effective data analysis transforms raw data into valuable insights, bringing you closer to the answers you seek.
How to Report Empirical Research Results?
At this stage, you get to share your empirical research findings with the world. Effective reporting and presentation of your results are crucial for communicating your research's impact and insights.
1. Write the Research Paper
Writing a research paper is the culmination of your empirical research journey. It's where you synthesize your findings, provide context, and contribute to the body of knowledge in your field.
- Title and Abstract : Craft a clear and concise title that reflects your research's essence. The abstract should provide a brief summary of your research objectives, methods, findings, and implications.
- Introduction : In the introduction, introduce your research topic, state your research questions or hypotheses, and explain the significance of your study. Provide context by discussing relevant literature.
- Methods : Describe your research design, data collection methods, and sampling procedures. Be precise and transparent, allowing readers to understand how you conducted your study.
- Results : Present your findings in a clear and organized manner. Use tables, graphs, and statistical analyses to support your results. Avoid interpreting your findings in this section; focus on the presentation of raw data.
- Discussion : Interpret your findings and discuss their implications. Relate your results to your research questions and the existing literature. Address any limitations of your study and suggest avenues for future research.
- Conclusion : Summarize the key points of your research and its significance. Restate your main findings and their implications.
- References : Cite all sources used in your research following a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Ensure accuracy and consistency in your citations.
- Appendices : Include any supplementary material, such as questionnaires, data coding sheets, or additional analyses, in the appendices.
Writing a research paper is a skill that improves with practice. Ensure clarity, coherence, and conciseness in your writing to make your research accessible to a broader audience.
2. Create Visuals and Tables
Visuals and tables are powerful tools for presenting complex data in an accessible and understandable manner.
- Clarity : Ensure that your visuals and tables are clear and easy to interpret. Use descriptive titles and labels.
- Consistency : Maintain consistency in formatting, such as font size and style, across all visuals and tables.
- Appropriateness : Choose the most suitable visual representation for your data. Bar charts, line graphs, and scatter plots work well for different types of data.
- Simplicity : Avoid clutter and unnecessary details. Focus on conveying the main points.
- Accessibility : Make sure your visuals and tables are accessible to a broad audience, including those with visual impairments.
- Captions : Include informative captions that explain the significance of each visual or table.
Compelling visuals and tables enhance the reader's understanding of your research and can be the key to conveying complex information efficiently.
3. Interpret Findings
Interpreting your findings is where you bridge the gap between data and meaning. It's your opportunity to provide context, discuss implications, and offer insights. When interpreting your findings:
- Relate to Research Questions : Discuss how your findings directly address your research questions or hypotheses.
- Compare with Literature : Analyze how your results align with or deviate from previous research in your field. What insights can you draw from these comparisons?
- Discuss Limitations : Be transparent about the limitations of your study. Address any constraints, biases, or potential sources of error.
- Practical Implications : Explore the real-world implications of your findings. How can they be applied or inform decision-making?
- Future Research Directions : Suggest areas for future research based on the gaps or unanswered questions that emerged from your study.
Interpreting findings goes beyond simply presenting data; it's about weaving a narrative that helps readers grasp the significance of your research in the broader context.
With your research paper written, structured, and enriched with visuals, and your findings expertly interpreted, you are now prepared to communicate your research effectively. Sharing your insights and contributing to the body of knowledge in your field is a significant accomplishment in empirical research.
Examples of Empirical Research
To solidify your understanding of empirical research, let's delve into some real-world examples across different fields. These examples will illustrate how empirical research is applied to gather data, analyze findings, and draw conclusions.
Social Sciences
In the realm of social sciences, consider a sociological study exploring the impact of socioeconomic status on educational attainment. Researchers gather data from a diverse group of individuals, including their family backgrounds, income levels, and academic achievements.
Through statistical analysis, they can identify correlations and trends, revealing whether individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds are less likely to attain higher levels of education. This empirical research helps shed light on societal inequalities and informs policymakers on potential interventions to address disparities in educational access.
Environmental Science
Environmental scientists often employ empirical research to assess the effects of environmental changes. For instance, researchers studying the impact of climate change on wildlife might collect data on animal populations, weather patterns, and habitat conditions over an extended period.
By analyzing this empirical data, they can identify correlations between climate fluctuations and changes in wildlife behavior, migration patterns, or population sizes. This empirical research is crucial for understanding the ecological consequences of climate change and informing conservation efforts.
Business and Economics
In the business world, empirical research is essential for making data-driven decisions. Consider a market research study conducted by a business seeking to launch a new product. They collect data through surveys, focus groups, and consumer behavior analysis.
By examining this empirical data, the company can gauge consumer preferences, demand, and potential market size. Empirical research in business helps guide product development, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns, increasing the likelihood of a successful product launch.
Psychological studies frequently rely on empirical research to understand human behavior and cognition. For instance, a psychologist interested in examining the impact of stress on memory might design an experiment. Participants are exposed to stress-inducing situations, and their memory performance is assessed through various tasks.
By analyzing the data collected, the psychologist can determine whether stress has a significant effect on memory recall. This empirical research contributes to our understanding of the complex interplay between psychological factors and cognitive processes.
These examples highlight the versatility and applicability of empirical research across diverse fields. Whether in medicine, social sciences, environmental science, business, or psychology, empirical research serves as a fundamental tool for gaining insights, testing hypotheses, and driving advancements in knowledge and practice.
Conclusion for Empirical Research
Empirical research is a powerful tool for gaining insights, testing hypotheses, and making informed decisions. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you've learned how to select research topics, collect data, analyze findings, and effectively communicate your research to the world. Remember, empirical research is a journey of discovery, and each step you take brings you closer to a deeper understanding of the world around you. Whether you're a scientist, a student, or someone curious about the process, the principles of empirical research empower you to explore, learn, and contribute to the ever-expanding realm of knowledge.
How to Collect Data for Empirical Research?
Introducing Appinio , the real-time market research platform revolutionizing how companies gather consumer insights for their empirical research endeavors. With Appinio, you can conduct your own market research in minutes, gaining valuable data to fuel your data-driven decisions.
Appinio is more than just a market research platform; it's a catalyst for transforming the way you approach empirical research, making it exciting, intuitive, and seamlessly integrated into your decision-making process.
Here's why Appinio is the go-to solution for empirical research:
- From Questions to Insights in Minutes : With Appinio's streamlined process, you can go from formulating your research questions to obtaining actionable insights in a matter of minutes, saving you time and effort.
- Intuitive Platform for Everyone : No need for a PhD in research; Appinio's platform is designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, ensuring that anyone can navigate and utilize it effectively.
- Rapid Response Times : With an average field time of under 23 minutes for 1,000 respondents, Appinio delivers rapid results, allowing you to gather data swiftly and efficiently.
- Global Reach with Targeted Precision : With access to over 90 countries and the ability to define target groups based on 1200+ characteristics, Appinio empowers you to reach your desired audience with precision and ease.
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

17.04.2024 | 25min read
Quota Sampling: Definition, Types, Methods, Examples

15.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Market Share? Definition, Formula, Examples

11.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Data Analysis? Definition, Tools, Examples

Empirical Research: What is empirical research?
What is empirical research.
- How do I find empirical research in databases?
- What does empirical research look like?
- How is empirical research conducted?
- What is Empirical Research?
- How do I Find Empirical Research in Databases?
- How is Empirical Research Conducted?
Ask a Librarian
Contact the reference desk.
Empirical research is based on observed and measured phenomena and derives knowledge from actual experience rather than from theory or belief.
How do you know if a study is empirical? Read the subheadings within the article, book, or report and look for a description of the research "methodology." Ask yourself: Could I recreate this study and test these results?
Key characteristics to look for:
- Specific research questions to be answered
- Definition of the population, behavior, or phenomena being studied
- Description of the process used to study this population or phenomena, including selection criteria, controls, and testing instruments (such as surveys)
Another hint: some scholarly journals use a specific layout, called the "IMRaD" format, to communicate empirical research findings. Such articles typically have 4 components:
- Introduction : sometimes called "literature review" -- what is currently known about the topic -- usually includes a theoretical framework and/or discussion of previous studies
- Methodology: sometimes called "research design" -- how to recreate the study -- usually describes the population, research process, and analytical tools
- Results : sometimes called "findings" -- what was learned through the study -- usually appears as statistical data or as substantial quotations from research participants
- Discussion : sometimes called "conclusion" or "implications" -- why the study is important -- usually describes how the research results influence professional practices or future studies
What about when research is not empirical?
Many humanities scholars do not use empirical methods. if you are looking for empirical articles in one of these subject areas, try including keywords like:.
- quantitative
- qualitative
Also, look for opportunities to narrow your search to scholarly, academic, or peer-reviewed journals articles in the database.
Adapted from " Research Methods: Finding Empirical Articles " by Jill Anderson at Georgia State University Library.
See the complete A-Z databases list for more resources
The primary content of this guide was originally created by Ellysa Cahoy at Penn State Libraries .
- Next: How do I find empirical research in databases? >>
- Last Updated: Apr 12, 2024 8:07 AM
- URL: https://geiselguides.anselm.edu/Empirical-Research
- quicklinks Academic admin council Academic calendar Academic stds cte Admission Advising African studies Alumni engagement American studies Anthropology/sociology Arabic Arboretum Archives Arcus center Art Assessment committee Athletics Athletic training Biology Biology&chem center Black faculty&staff assoc Bookstore BrandK Business office Campus event calendar Campus safety Catalog Career & prof dev Health science Ctr for civic engagement Ctr for international pgrms Chemistry Chinese Classics College communication Community & global health Community council Complex systems studies Computer science Copyright Counseling Council of student reps Crisis response Critical ethnic studies Critical theory Development Dining services Directories Disability services Donor relations East Asian studies Economics and business Educational policies cte Educational quality assmt Engineering Environmental stewardship Environmental studies English Experiential education cte Facilities management Facilities reservations Faculty development cte Faculty executive cte Faculty grants Faculty personnel cte Fellowships & grants Festival playhouse Film & media studies Financial aid First year experience Fitness & wellness ctr French Gardens & growing spaces German Global crossroads Health center Jewish studies History Hornet hive Hornet HQ Hornet sports Human resources Inclusive excellence Index (student newspaper) Information services Institutional research Institutional review board Intercultural student life International & area studies International programs Intramural sports Japanese LandSea Learning commons Learning support Lgbtqai+ student resources Library Mail and copy center Math Math/physics center Microsoft Stream Microsoft Teams Moodle Movies (ch 22 online) Music OneDrive Outdoor programs Parents' resources Payroll Phi Beta Kappa Philharmonia Philosophy Physics Physical education Political science Pre-law advising Provost Psychology Public pol & urban affairs Recycling Registrar Religion Religious & spiritual life Research Guides (libguides) Residential life Safety (security) Sexual safety Shared passages program SharePoint online Sophomore experience Spanish Strategic plan Student accounts Student development Student activities Student organizations Study abroad Support staff Sustainability Teaching and learning cte Teaching commons Theatre arts Title IX Webmail Women, gender & sexuality Writing center
Psychology Research Guide
What is empirical research, finding empirical research, what is peer review.
- Research Tips & Tricks
- Statistics This link opens in a new window
- Cite Sources
- Library FAQ This link opens in a new window

Empirical research is based on observed and measured phenomena and derives knowledge from actual experience rather than from theory or belief.
How do you know if a study is empirical? Read the subheadings within the article, book, or report and look for a description of the research "methodology." Ask yourself: Could I recreate this study and test these results?
Key characteristics to look for:
- Specific research questions to be answered
- Definition of the population, behavior, or phenomena being studied
- Description of the process used to study this population or phenomena, including selection criteria, controls, and testing instruments (such as surveys)
Another hint: some scholarly journals use a specific layout, called the "IMRaD" format, to communicate empirical research findings. Such articles typically have 4 components:
- Introduction : sometimes called "literature review" -- what is currently known about the topic -- usually includes a theoretical framework and/or discussion of previous studies
- Methodology: sometimes called "research design" -- how to recreate the study -- usually describes the population, research process, and analytical tools
- Results : sometimes called "findings" -- what was learned through the study -- usually appears as statistical data or as substantial quotations from research participants
- Discussion : sometimes called "conclusion" or "implications" -- why the study is important -- usually describes how the research results influence professional practices or future studies
Adapted from PennState University Libraries, Empirical Research in the Social Sciences and Education
Empirical research is published in books and in scholarly, peer-reviewed journals. Keep in mind that most library databases do not offer straightforward ways to identifying empirical research.
Finding Empirical Research in PsycINFO
- PsycInfo Use the "Advanced Search" Type your keywords into the search boxes Scroll down the page to "Methodology," and choose "Empirical Study" Choose other limits, such as publication date, if needed Click on the "Search" button
Finding Empirical Research in PubMed
- PubMED One technique is to limit your search results after you perform a search: Type in your keywords and click on the "Search" button To the left of your results, under "Article Types," check off the types of studies that interest you Another alternative is to construct a more sophisticated search: From PubMed's main screen, click on "Advanced" link underneath the search box On the Advanced Search Builder screen type your keywords into the search boxes Change one of the empty boxes from "All Fields" to "Publication Type" To the right of Publication Type, click on "Show Index List" and choose a methodology that interests you. You can choose more than one by holding down the "Ctrl" or "⌘" on your keyboard as you click on each methodology Click on the "Search" button
Finding Empirical Research in Library OneSearch & Google Scholar
These tools do not have a method for locating empirical research. Using "empirical" as a keyword will find some studies, but miss many others. Consider using one of the more specialized databases above.
- Library OneSearch
- Google Scholar
This refers to the process where authors who are doing research submit a paper they have written to a journal. The journal editor then sends the article to the author's peers (researchers and scholars) who are in the same discipline for review. The reviewers determine if the article should be published based on the quality of the research, including the validity of the data, the conclusions the authors' draw and the originality of the research. This process is important because it validates the research and gives it a sort of "seal of approval" from others in the research community.
Identifying a Journal is Peer-Reviewed
One of the best places to find out if a journal is peer-reviewed is to go to the journal website.
Most publishers have a website for a journal that tells you about the journal, how authors can submit an article, and what the process is for getting published.
If you find the journal website, look for the link that says information for authors, instructions for authors, submitting an article or something similar.
Finding Peer-Reviewed Articles
Start in a library database. Look for a peer-review or scholarly filter.
- PsycInfo Most comprehensive database of psychology. Filters allow you to limit by methodology. Articles without full-text can be requested via Interlibrary loan.
- Library OneSearch Search almost all the library resources. Look for a peer-review filter on the left.
- << Previous: Start Here
- Next: Research Tips & Tricks >>
- Last Updated: Apr 4, 2024 4:11 PM
- URL: https://libguides.kzoo.edu/psyc
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, empirical research methods.

Alternative Article Title: Primary Research, Scientific Research , or Field Research .
- Empirical Research may be called Primary Research, Scientific Research , or Field Research . People who conduct empirical research are typically called investigators , but they may also be called knowledge workers, scientists, empiricists, or researchers.
Empirical research is a research method that investigators use to test knowledge claims and develop new knowledge .
Empirical methods focus on observation and experimentation .
Investigators observe and conduct experiments in systematic ways
is largely determined by their rhetorical contexts. Different workplace contexts and academic disciplines have developed unique tools and techniques for gathering and interpreting information .
professions and business organizations—i.e., discourse communities , especially methodological communities.
Professions and workplaces develop unique tools and technique
Empirical research is informed by
- empiricism , a philosophy that assumes knowledge is grounded in what you can see, hear, or experience
- positivism , a philosophy that assumes the universe is an orderly place; a nonrandom order of the universe exists; events have causes and occur in regular patterns that can be determined through observation.
Investigators and discourse communities use empirical research methods
- to create new knowledge (e.g., Basic Research )
- to solve a problem at work, school, or personal life (e.g., Applied Research ).
- to conduct replication studies–i.e., repeat a study with the same methods (or with slight variations, such as changes in subjects and experimenters).
Textual research plays an important role in empirical research . Empiricists engage in some textual research in order to understand scholarly conversations around the topics that interest them. Empiricists consult archives to learn methods for conducting empirical studies. However, there are important distinctions between how scholars weight claims in textual research and how scientists weigh claims in empirical studies.
Unlike investigators who use primarily textual methods , empiricists do not consider “claims of authority, intuition, imaginative conjecture, and abstract, theoretical, or systematic reasoning as sources of reliable belief” (Duignan, Fumerton, Quinton, Quinton 2020).
Instead of relying on logical reasoning and Following Most contemporary empiricists would acknowledge that any act of observation and experimentation are somewhat subjective processes.
There are three major types of empirical research :
- e.g., numbers, mathematical equations).
- Mixed Methods (a mixture of Quantitative Methods and Qualitative Methods .
Empirical research aims to be as objective as possible by being RAD —
- (sufficient details about the research protocol is provided so the study can be repeated)
- (the results and implications of the study can be extended in future research)
- ( quantitative evidence and/or Qualitative evidence are provided to substantiate claims, results, interpretations, implications).
Key Terms: positivism ; research methods ; research methodologies .
As humans, we learn about the world from experience, observation and experimentation. Even as babies we conduct informal research: what happens when we cry and complain? If we do x , does it cause y ? Over time, we invariably learn from our experience that our actions have consequences. We sharpen our abilities to identify commons patterns (e.g., whenwe write a lot, we are more creative). Invariably, as we evolve during our lives, we come to trust our experiences, our senses, and our procedural knowledge and declarative knowledge evolves.
In work and school settings, systematic engagement at efforts of observaion are called empirical or scientific research.
Investigators conduct empirical research when the answers to research questions are not readily available from informal research or textual research , when the occasion is kairotic , when personal or financial gains are on the table. That said, most empirical research is informed by textual research: investigators review the conclusions and implications of previously published research past studies—they analyze scholarly conversations and research methods—prior to engaging in empirical studies.
Informally, as humans, we engage routinely in the intellectual strategies that inform empirical research:
- we talk with others and listen to their stories to better understand their perceptions and experiences,
- we make observations,
- we survey friends, peers, coworkers
- we cross cultures and learn about difference, and
- we make predictions about future events based on our experiences and observations.
These same intellectual strategies we use to reason from our observations and experiences also undergird empirical research methods. For example,
- a psychologist might develop a case study based on interviews
- an anthropologist or sociologist might engage in participant observation to write an ethnographic study
- a political science researcher might survey voter trends
- a stock trader may project a stock bounce based on a 30-day moving average.
The main difference between informal and formal empirical research is intentionality : Formal empirical research presupposes a Research Plan , which is sometimes referred to as as Research Protocol . When investigators want their results to be taken seriously they have to employ the research methods a methodological community has for vetting knowledge claims .
Different academic communities (e.g., Natural Sciences, Social Science, Humanities, Arts) have unique ideas about how to conduct empirical research. Professionals in the workplace — e.g., geologists, anthropologists, biologists — use entirely different tools to gather and interpret data. Being credentialed in a particular discipline or profession is tied to mastery of unique methodological practices.
Across disciplines, however, empiricists share a number of operating assumptions: Empiricists
- develop a research plan prior to engaging in research.
- seek approval from Ethics Committees when human subjects or animal testing is involved
- explain how subjects/research participants are chosen and given opportunities to opt in or opt out of studies.
Empiricists are meticulous about how they collect data because their research must be verifiable if they want other empiricists to take their work seriously. In other words, their research plan needs to be so explicit that subsequent researchers can conduct the same study.
Empirical Research is a Rhetorical Practice
Empiricists develop their research question and their research methods by considering their audience and purpose . Prior to initiating a study, researchers conduct secondary research–especially Searching as Strategic Exploration –to identify the current knowledge about a topic. As a consequence of their deep understanding of pertinent scholarly conversations on the topic, empiricists identify gaps in knowledge.
Duignan, B., Fumerton, R., Quinton, A. M., & Quinton, B. (2020). Empiricism. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/empiricism
Haswell, R. (2005). NCTE/CCCC’s recent war on scholarship. Written Communication, 22 (2), 198-223.

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles


Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.1.4: Components of a Research Project
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 85831
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
- Describe useful strategies to employ when searching for literature.
- Describe why sociologists review prior literature and how they organize their literature reviews.
- Identify the main sections contained in scholarly journal articles.
- Identify and describe the major components researchers need to plan for when designing a research project.
In this section, we’ll examine the most typical components that make up a research project, bringing in a few additional components to those we have already discussed. Keep in mind that our purpose at this stage is simply to provide a general overview of research design. The specifics of each of the following components will vary from project to project. Further, the stage of a project at which each of these components comes into play may vary. In later chapters, we will consider more specifically how these components work differently depending on the research method being employed.
Searching for Literature
Familiarizing yourself with research that has already been conducted on your topic is one of the first stages of conducting a research project and is crucial for coming up with a good research design. But where to start? How to start? In Chapter 1.3 "Beginning a Research Project" , you learned about some of the most common databases that house information about published sociological research. As you search for literature, you may have to be fairly broad in your search for articles.
I’m guessing you may feel you’ve heard enough about electronic gadget addiction in this chapter, so let’s consider a different example here. On my campus, much to the chagrin of a group of student smokers, smoking was recently banned. These students were so upset by the idea that they would no longer be allowed to smoke on university grounds that they staged several smoke-outs during which they gathered in populated areas around campus and enjoyed a puff or two together.
A student in my research methods class wanted to understand what motivated this group of students to engage in activism centered around what she perceived to be, in this age of smoke-free facilities, a relatively deviant act. Were the protesters otherwise politically active? How much effort and coordination had it taken to organize the smoke-outs? The student researcher began her research by attempting to familiarize herself with the literature on her topic. Yet her search in Sociological Abstracts for “college student activist smoke-outs,” yielded no results. Concluding there was no prior research on her topic, she informed me that she would need an alternative assignment to the annotated bibliography I required since there was no literature for her to review. How do you suppose I responded to this news? What went wrong with this student’s search for literature?
In her first attempt, the student had been too narrow in her search for articles. But did that mean she was off the hook for completing the annotated bibliography assignment? Absolutely not. Instead, she went back to Sociological Abstracts and searched again using different combinations of search terms. Rather than searching for “college student activist smoke-outs” she tried, among other sets of terms, “college student activism.” This time her search yielded a great many articles. Of course, they were not focused on prosmoking activist efforts, but they were focused on her population of interest, college students, and on her broad topic of interest, activism. I suggested that reading articles on college student activism might give her some idea about what other researchers have found in terms of what motivates college students to become involved in activist efforts. I also suggested she could play around with her search terms and look for research on activism centered on other sorts of activities that are perceived by some as deviant, such as marijuana use or veganism. In other words, she needed to be broader in her search for articles.
While this student found success by broadening her search for articles, her reading of those articles needed to be narrower than her search. Once she identified a set of articles to review by searching broadly, it was time to remind herself of her specific research focus: college student activist smoke-outs. Keeping in mind her particular research interest while reviewing the literature gave her the chance to think about how the theories and findings covered in prior studies might or might not apply to her particular point of focus. For example, theories on what motivates activists to get involved might tell her something about the likely reasons the students she planned to study got involved. At the same time, those theories might not cover all the particulars of student participation in smoke-outs. Thinking about the different theories then gave the student the opportunity to focus her research plans and even to develop a few hypotheses about what she thought she was likely to find.
Reviewing the Literature
Developing an annotated bibliography is often one of the early steps that researchers take as they begin to familiarize themselves with prior research on their topic. A second step involves a literature review in which a researcher positions his or her work within the context of prior scholarly work in the area. A literature review addresses the following matters: What sorts of questions have other scholars asked about this topic? What do we already know about this topic? What questions remain? As the researcher answers these questions, he or she synthesizes what is contained in the literature, possibly organizing prior findings around themes that are relevant to his or her particular research focus.
I once advised an undergraduate student who conducted a research project on speciesism, the belief that some species are superior to or have more value and rights than others. Her research question was “Why and how do humans construct divisions between themselves and animals?” This student organized her review of literature around the two parts of her research question: the why and the how. In the “why” section of her literature review, she described prior research that addressed questions of why humans are sometimes speciesist. She organized subsections around the three most common answers that were presented in the scholarly literature. She used the same structure in the “how” section of her literature review, arranging subsections around the answers posed in previous literature about how humans construct divisions between themselves and animals. This organizational scheme helped readers understand what we already know about the topic and what theories we rely on to help make sense of the topic. In addition, by also highlighting what we still don’t know, it helped the student set the stage for her own empirical research on the topic.
The preceding discussion about how to organize a review of scholarly literature assumes that we all know how to read scholarly literature. Yes, yes, I understand that you must know how to read. But reading scholarly articles can be a bit more challenging than reading a textbook. Here are a few pointers about how to do it successfully. First, it is important to understand the various sections that are typically contained in scholarly journals’ reports of empirical research. One of the most important and easiest to spot sections of a journal article is its abstract , the short paragraph at the beginning of an article that summarizes the author’s research question, methods used to answer the question, and key findings. The abstract may also give you some idea about the theoretical proclivities of the author. As a result, reading the abstract gives you both a framework for understanding the rest of the article and the punch line. It tells you what the author(s) found and whether the article is relevant to your area of inquiry.
After the abstract, most journal articles will contain the following sections (although exact section names are likely to vary): introduction, literature review, methodology, findings, and discussion. Of course, there will also be a list of references cited,Lists of references cited are a useful source for finding additional literature in an area. and there may be a few tables, figures, or appendices at the end of the article as well. While you should get into the habit of familiarizing yourself with articles you wish to cite in their entirety , there are strategic ways to read journal articles that can make them a little easier to digest. Once you have read the abstract and determined that this is an article you’d like to read in full, read through the discussion section at the end of the article next. Because your own review of literature is likely to emphasize findings from previous literature, you should make sure that you have a clear idea about what those findings are. Reading an article’s discussion section helps you understand what the author views as the study’s major findings and how the author perceives those findings to relate to other research.
As you read through the rest of the article, think about the elements of research design that we have covered in this chapter. What approach does the researcher take? Is the research exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory? Is it inductive or deductive? Idiographic or nomothetic? Qualitative or quantitative? What claims does the author make about causality? What are the author’s units of analysis and observation? Use what you have learned in this chapter about the promise and potential pitfalls associated with each of these research elements to help you responsibly read and understand the articles you review. Future chapters of this text will address other elements of journal articles, including choices about measurement, sampling, and research method. As you learn about these additional items, you will increasingly gain more knowledge that you can apply as you read and critique the scholarly literature in your area of inquiry.
Additional Important Components
Thinking about the overarching goals of your research project and finding and reviewing the existing literature on your topic are two of the initial steps you’ll take when designing a research project. Forming a clear research question, as discussed in Chapter 1.3 "Beginning a Research Project" , is another crucial step. There are a number of other important research design components you’ll need to consider, and we will discuss those here.
At the same time that you work to identify a clear research question, you will probably also think about the overarching goals of your research project. Will it be exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory? Will your approach be idiographic or nomothetic, inductive or deductive? How you design your project might also be determined in part by whether you aim for your research to have some direct application or if your goal is to contribute more generally to sociological knowledge about your topic. Next, think about what your units of analysis and units of observation will be. These will help you identify the key concepts you will study. Once you have identified those concepts, you’ll need to decide how to define them, and how you’ll know that you’re observing them when it comes time to collect your data. Defining your concepts, and knowing them when you see them, has to do with conceptualization and operationalization. Of course, you also need to know what approach you will take to collect your data. Thus identifying your research method is another important part of research design. You also need to think about who your research participants will be and what larger group(s) they may represent. Last, but certainly not least, you should consider any potential ethical concerns that could arise during the course of your research project. These concerns might come up during your data collection, but they might also arise when you get to the point of analyzing or sharing your research results.
Decisions about the various research components do not necessarily occur in sequential order. In fact, you may have to think about potential ethical concerns even before zeroing in on a specific research question. Similarly, the goal of being able to make generalizations about your population of interest could shape the decisions you make about your method of data collection. Putting it all together, the following list shows some of the major components you’ll need to consider as you design your research project:
- Research question
- Literature review
- Research strategy (idiographic or nomothetic, inductive or deductive)
- Research goals (basic or applied)
- Units of analysis and units of observation
- Key concepts (conceptualization and operationalization)
- Method of data collection
- Research participants (sample and population)
- Ethical concerns
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- When identifying and reading relevant literature, be broad in your search for articles, but be narrower in your reading of articles.
- Writing an annotated bibliography can be a helpful first step to familiarize yourself with prior research in your area of interest.
- Literature reviews summarize and synthesize prior research.
- Literature reviews are typically organized around substantive ideas that are relevant to one’s research question rather than around individual studies or article authors.
- When designing a research project, be sure to think about, plan for, and identify a research question, a review of literature, a research strategy, research goals, units of analysis and units of observation, key concepts, method(s) of data collection, population and sample, and potential ethical concerns.
- Find and read a complete journal article that addresses a topic that is of interest to you (perhaps using Sociological Abstracts, which is introduced in Chapter 3.1 "Beginning a Research Project" ). In four to eight sentences, summarize the author’s research question, theoretical framing, methods used, and major findings. Reread the article, and see how close you were in reporting these key elements. What did you understand and remember best? What did you leave out? What reading strategies may have helped you better recall relevant details from the article?
- Using the example of students’ electronic gadget addictions, design a hypothetical research project by identifying a plan for each of the nine components of research design that are presented in this section.
Canvas | University | Ask a Librarian
- Library Homepage
- Arrendale Library
Empirical Research: Quantitative & Qualitative
- Empirical Research
Introduction: What is Empirical Research?
Quantitative methods, qualitative methods.
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative
- Reference Works for Social Sciences Research
- Contact Us!
Call us at 706-776-0111
Chat with a Librarian
Send Us Email
Library Hours
Empirical research is based on phenomena that can be observed and measured. Empirical research derives knowledge from actual experience rather than from theory or belief.
Key characteristics of empirical research include:
- Specific research questions to be answered;
- Definitions of the population, behavior, or phenomena being studied;
- Description of the methodology or research design used to study this population or phenomena, including selection criteria, controls, and testing instruments (such as surveys);
- Two basic research processes or methods in empirical research: quantitative methods and qualitative methods (see the rest of the guide for more about these methods).
(based on the original from the Connelly LIbrary of LaSalle University)

Empirical Research: Qualitative vs. Quantitative
Learn about common types of journal articles that use APA Style, including empirical studies; meta-analyses; literature reviews; and replication, theoretical, and methodological articles.
Academic Writer
© 2024 American Psychological Association.
- More about Academic Writer ...
Quantitative Research
A quantitative research project is characterized by having a population about which the researcher wants to draw conclusions, but it is not possible to collect data on the entire population.
- For an observational study, it is necessary to select a proper, statistical random sample and to use methods of statistical inference to draw conclusions about the population.
- For an experimental study, it is necessary to have a random assignment of subjects to experimental and control groups in order to use methods of statistical inference.
Statistical methods are used in all three stages of a quantitative research project.
For observational studies, the data are collected using statistical sampling theory. Then, the sample data are analyzed using descriptive statistical analysis. Finally, generalizations are made from the sample data to the entire population using statistical inference.
For experimental studies, the subjects are allocated to experimental and control group using randomizing methods. Then, the experimental data are analyzed using descriptive statistical analysis. Finally, just as for observational data, generalizations are made to a larger population.
Iversen, G. (2004). Quantitative research . In M. Lewis-Beck, A. Bryman, & T. Liao (Eds.), Encyclopedia of social science research methods . (pp. 897-898). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc.
Qualitative Research
What makes a work deserving of the label qualitative research is the demonstrable effort to produce richly and relevantly detailed descriptions and particularized interpretations of people and the social, linguistic, material, and other practices and events that shape and are shaped by them.
Qualitative research typically includes, but is not limited to, discerning the perspectives of these people, or what is often referred to as the actor’s point of view. Although both philosophically and methodologically a highly diverse entity, qualitative research is marked by certain defining imperatives that include its case (as opposed to its variable) orientation, sensitivity to cultural and historical context, and reflexivity.
In its many guises, qualitative research is a form of empirical inquiry that typically entails some form of purposive sampling for information-rich cases; in-depth interviews and open-ended interviews, lengthy participant/field observations, and/or document or artifact study; and techniques for analysis and interpretation of data that move beyond the data generated and their surface appearances.
Sandelowski, M. (2004). Qualitative research . In M. Lewis-Beck, A. Bryman, & T. Liao (Eds.), Encyclopedia of social science research methods . (pp. 893-894). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc.
- Next: Quantitative vs. Qualitative >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 10:47 AM
- URL: https://library.piedmont.edu/empirical-research
- Ebooks & Online Video
- New Materials
- Renew Checkouts
- Faculty Resources
- Friends of the Library
- Library Services
- Request Books from Demorest
- Our Mission
- Library History
- Ask a Librarian!
- Making Citations
- Working Online
Arrendale Library Piedmont University 706-776-0111

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.2: Theory and Empirical Research
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 7203

- Jenkins-Smith et al.
- University of Oklahoma via University of Oklahoma Libraries
This book is concerned with the connection between theoretical claims and empirical data. It is about using statistical modeling; in particular, the tool of regression analysis, which is used to develop and refine theories. We define theory broadly as a set of interrelated propositions that seek to explain and, in some cases, predict an observed phenomenon.
Theory: A set of interrelated propositions that seek to explain and predict an observed phenomenon.
Theories contain three important characteristics that we discuss in detail below.
Characteristics of Good Theories Coherent and internally consistent Causal in nature Generate testable hypotheses
1.2.1 Coherent and Internally Consistent
The set of interrelated propositions that constitute a well-structured theory are based on concepts . In well-developed theories, the expected relationships among these concepts are both coherent and internally consistent. Coherence means the identification of concepts and the specified relationships among them are logical, ordered, and integrated. An internally consistent theory will explain relationships with respect to a set of common underlying causes and conditions, providing for consistency in expected relationships (and avoidance of contradictions). For systematic quantitative research, the relevant theoretical concepts are defined such that they can be measured and quantified. Some concepts are relatively easy to quantify, such as the number of votes cast for the winning Presidential candidate in a specified year or the frequency of arrests for gang-related crimes in a particular region and time period. Others are more difficult, such as the concepts of democratization, political ideology or presidential approval. Concepts that are more difficult to measure must be carefully operationalized , which is a process of relating a concept to an observation that can be measured using a defined procedure. For example, political ideology is often operationalized through public opinion surveys that ask respondents to place themselves on a Likert-type scale of ideological categories.
Concepts and Variables
A concept is a commonality across observed individual events or cases. It is a regularity that we find in a complex world. Concepts are our building blocks to understanding the world and to developing theory that explains the world. Once we have identified concepts we seek to explain them by developing theories based on them. Once we have explained a concept we need to define it. We do so in two steps. First, we give it a dictionary-like definition, called a nominal definition. Then, we develop an operational definition that identifies how we can measure and quantify it.
Once a concept has been quantified, it is employed in modeling as a variable . In statistical modeling, variables are thought of as either dependent or independent variables. A dependent variable , Y, is the outcome variable; this is the concept we are trying to explain and/or predict. The independent variable(s) , X, is the variable(s) that is used to predict or explain the dependent variable. The expected relationships between (and among) the variables are specified by the theory.
Measurement
When measuring concepts, the indicators that are used in building and testing theories should be both valid and reliable . Validity refers to how well the measurement captures the concept. Face validity, for example, refers to the plausibility and general acceptance of the measure, while the domain validity of the measure concerns the degree to which it captures all relevant aspects of the concept. Reliability, by contrast, refers to how consistent the measure is with repeated applications. A measure is reliable if, when applied to the repeated observations in similar settings, the outcomes are consistent.
Assessing the Quality of a Measure
Measurement is the process of assigning numbers to the phenomenon or concept that you are interested in. Measurement is straight-forward when we can directly observe the phenomenon. One agrees on a metric, such as inches or pounds, and then figures out how many of those units are present for the case in question. Measurement becomes more challenging when you cannot directly observe the concept of interest. In political science and public policy, some of the things we want to measure are directly observable: how many dollars were spent on a project or how many votes the incumbent receives, but many of our concepts are not observable: is issue X on the public’s agenda, how successful is a program, or how much do citizens trust the president. When the concept is not directly observable the operational definition is especially important. The operational definition explains exactly what the researcher will do to assign a number for each subject/case.
In reality, there is always some possibility that the number assigned does not reflect the true value for that case, i.e., there may be some error involved. Error can come about for any number of reasons, including mistakes in coding, the need for subjective judgments, or a measuring instrument that lacks precision. These kinds of error will generally produce inconsistent results; that is, they reduce reliability. We can assess the reliability of an indicator using one of two general approaches. One approach is a test-retest method where the same subjects are measured at two different points in time. If the measure is reliable the correlation between the two observations should be high. We can also assess reliability by using multiple indicators of the same concept and determining if there is a strong inter-correlation among them using statistical formulas such as Cronbach’s alpha or Kuder-Richardson Formula 20 (KR-20).
We can also have error when our measure is not valid. Valid indicators measure the concept we think they are measuring. The indicator should both converge with the concept and discriminate between the concept and similar yet different concepts. Unfortunately, there is no failsafe way to determine whether an indicator is valid. There are, however, a few things you can do to gain confidence in the validity of the indicator. First, you can simply look at it from a logical perspective and ask if it seems like it is valid. Does it have face validity? Second, you can see if it correlates well with other indicators that are considered valid, and in ways that are consistent with theory. This is called construct validity. Third, you can determine if it works in the way expected, which is referred to as predictive validity. Finally, we have more confidence if other researchers using the same concept agree that the indicator is considered valid. This consensual validity at least ensures that different researchers are talking about the same thing.
Measurement of Different Kinds of Concepts
Measurement can be applied to different kinds of concepts, which causes measures of different concepts to vary. There are three primary levels of measurement ; ordinal, interval, and nominal. Ordinal level measures indicate relative differences, such as more or less, but do not provide equal distances between intervals on the measurement scale. Therefore, ordinal measures cannot tell us how much more or less one observation is than another. Imagine a survey question asking respondents to identify their annual income. Respondents are given a choice of five different income levels: $0-20,000, $20,000-50,000, $50,000-$100,000, and $100,000+. This measure gives us an idea of the rank order of respondents’ income, but it is impossible for us to identify consistent differences between these responses. With an interval level measure, the variable is ordered and the differences between values are consistent. Sticking with the example of income, survey respondents are now asked to provide their annual income to the nearest ten thousand dollar mark (e.g., $10,000, $20,000, $30,000, etc.). This measurement technique produces an interval level variable because we have both a rank ordering and equal spacing between values. Ratio scales are interval measures with the special characteristic that the value of zero (0) indicates the absence of some property. A value of zero (0) income in our example may indicate a person does not have a job. Another example of a ratio scale is the Kelvin temperature scale because zero (0) degrees Kelvin indicates the complete absence of heat. Finally, a nominal level measure identifies categorical differences among observations. Numerical values assigned to nominal variables have no inherent meaning, but only differentiate one type" (e.g., gender, race, religion) from another.
1.2.2 Theories and Causality
Theories should be causal in nature, meaning that an independent variable is thought to have a causal influence on the dependent variable. In other words, a change in the independent variable causes a change in the dependent variable. Causality can be thought of as the motor" that drives the model and provides the basis for explanation and (possibly) prediction.
The Basis of Causality in Theories
- Time Ordering: The cause precedes the effect, X→Y
- Co-Variation: Changes in X are associated with changes in Y
- Non-Spuriousness: There is not a variable Z that causes both X and Y
To establish causality we want to demonstrate that a change in the independent variable is a necessary and sufficient condition for a change in the dependent variable (though more complex, interdependent relationships can also be quantitatively modeled). We can think of the independent variable as a treatment, τ, and we speculate that τ causes a change in our dependent variable, Y. The gold standard’’ for causal inference is an experiment where a) the level of ττ is controlled by the researcher and b) subjects are randomly assigned to a treatment or control group. The group that receives the treatment has outcome Y 1 and the control group has outcome Y 0 ; the treatment effect can be defined as τ=Y 1 -Y 0 . Causality is inferred because the treatment was only given to one group, and since these groups were randomly assigned other influences should wash out. Thus the difference τ=Y 1 -Y0 can be attributed to the treatment.
Given the nature of social science and public policy theorizing, we often can’t control the treatment of interest. For example, our case study in this text concerns the effect of political ideology on views about the environment. For this type of relationship, we cannot randomly assign ideology in an experimental sense. Instead, we employ statistical controls to account for the possible influences of confounding factors, such as age and gender. Using multiple regression we control for other factors that might influence the dependent variable. 1
1.2.3 Generation of Testable Hypothesis
Theory building is accomplished through the testing of hypotheses derived from theory. In simple form, a theory implies (sets of) relationships among concepts. These concepts are then operationalized. Finally, models are developed to examine how the measures are related. Properly specified hypotheses can be tested with empirical data, which are derived from the application of valid and reliable measures to relevant observations. The testing and re-testing of hypotheses develops levels of confidence that we can have for the core propositions that constitute the theory. In short, empirically grounded theories must be able to posit clear hypotheses that are testable. In this text, we discuss hypotheses and test them using relevant models and data.
As noted above, this text uses the concepts of political ideology and views about the environment as a case study in order to generate and test hypotheses about the relationships between these variables. For example, based on popular media accounts, it is plausible to expect that political conservatives are less likely to be concerned about the environment than political moderates or liberals. Therefore, we can pose the working hypothesis that measures of political ideology will be systematically related to measures of concern for the environment – with conservatives showing less concern for the environment. In classical hypothesis testing, the working hypothesis is tested against a null hypothesis . A null hypothesis is an implicit hypothesis that posits the independent variable has no effect (i.e., null effect) on the dependent variable. In our example, the null hypothesis states ideology has no effect on environmental concern.
Empirical Research
Introduction, what is empirical research, attribution.
- Finding Empirical Research in Library Databases
- Designing Empirical Research
- Case Sudies
Empirical research is based on observed and measured phenomena and derives knowledge from actual experience rather than from theory or belief.
How do you know if a study is empirical? Read the subheadings within the article, book, or report and look for a description of the research "methodology." Ask yourself: Could I recreate this study and test these results?
Key characteristics to look for:
- Specific research questions to be answered
- Definition of the population, behavior, or phenomena being studied
- Description of the process used to study this population or phenomena, including selection criteria, controls, and testing instruments (such as surveys)
Another hint: some scholarly journals use a specific layout, called the "IMRaD" format, to communicate empirical research findings. Such articles typically have 4 components:
- Introduction : sometimes called "literature review" -- what is currently known about the topic -- usually includes a theoretical framework and/or discussion of previous studies
- Methodology: sometimes called "research design" -- how to recreate the study -- usually describes the population, research process, and analytical tools
- Results : sometimes called "findings" -- what was learned through the study -- usually appears as statistical data or as substantial quotations from research participants
- Discussion : sometimes called "conclusion" or "implications" -- why the study is important -- usually describes how the research results influence professional practices or future studies
Portions of this guide were built using suggestions from other libraries, including Penn State and Utah State University libraries.
- Next: Finding Empirical Research in Library Databases >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2023 8:31 AM
- URL: https://enmu.libguides.com/EmpiricalResearch
Literature Review: 3 Essential Ingredients
The theoretical framework, empirical research and research gap
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | July 2023
Writing a comprehensive but concise literature review is no simple task. There’s a lot of ground to cover and it can be challenging to figure out what’s important and what’s not. In this post, we’ll unpack three essential ingredients that need to be woven into your literature review to lay a rock-solid foundation for your study.
This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp . In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step. If it’s your first time writing a literature review, you definitely want to use this link to get 50% off the course (limited-time offer).
Overview: Essential Ingredients
- Ingredients vs structure
- The theoretical framework (foundation of theory)
- The empirical research
- The research gap
- Summary & key takeaways
Ingredients vs Structure
As a starting point, it’s important to clarify that the three ingredients we’ll cover in this video are things that need to feature within your literature review, as opposed to a set structure for your chapter . In other words, there are different ways you can weave these three ingredients into your literature review. Regardless of which structure you opt for, each of the three components will make an appearance in some shape or form. If you’re keen to learn more about structural options, we’ve got a dedicated post about that here .

1. The Theoretical Framework
Let’s kick off with the first essential ingredient – that is the theoretical framework , also called the foundation of theory .
The foundation of theory, as the name suggests, is where you’ll lay down the foundational building blocks for your literature review so that your reader can get a clear idea of the core concepts, theories and assumptions (in relation to your research aims and questions) that will guide your study. Note that this is not the same as a conceptual framework .
Typically you’ll cover a few things within the theoretical framework:
Firstly, you’ll need to clearly define the key constructs and variables that will feature within your study. In many cases, any given term can have multiple different definitions or interpretations – for example, different people will define the concept of “integrity” in different ways. This variation in interpretation can, of course, wreak havoc on how your study is understood. So, this section is where you’ll pin down what exactly you mean when you refer to X, Y or Z in your study, as well as why you chose that specific definition. It’s also a good idea to state any assumptions that are inherent in these definitions and why these are acceptable, given the purpose of your study.
Related to this, the second thing you’ll need to cover in your theoretical framework is the relationships between these variables and/or constructs . For example, how does one variable potentially affect another variable – does A have an impact on B, B on A, and so on? In other words, you want to connect the dots between the different “things” of interest that you’ll be exploring in your study. Note that you only need to focus on the key items of interest here (i.e. those most central to your research aims and questions) – not every possible construct or variable.
Lastly, and very importantly, you need to discuss the existing theories that are relevant to your research aims and research questions . For example, if you’re investigating the uptake/adoption of a certain application or software, you might discuss Davis’ Technology Acceptance Model and unpack what it has to say about the factors that influence technology adoption. More importantly, though, you need to explain how this impacts your expectations about what you will find in your own study . In other words, your theoretical framework should reveal some insights about what answers you might expect to find to your research questions .
If this sounds a bit fluffy, don’t worry. We deep dive into the theoretical framework (as well as the conceptual framework) and look at practical examples in Literature Review Bootcamp . If you’d like to learn more, take advantage of the limited-time offer (60% off the standard price).
Need a helping hand?
2. The Empirical Research
Onto the second essential ingredient, which is empirical research . This section is where you’ll present a critical discussion of the existing empirical research that is relevant to your research aims and questions.
But what exactly is empirical research?
Simply put, empirical research includes any study that involves actual data collection and analysis , whether that’s qualitative data, quantitative data, or a mix of both . This contrasts against purely theoretical literature (the previous ingredient), which draws its conclusions based exclusively on logic and reason , as opposed to an analysis of real-world data.
In other words, theoretical literature provides a prediction or expectation of what one might find based on reason and logic, whereas empirical research tests the accuracy of those predictions using actual real-world data . This reflects the broader process of knowledge creation – in other words, first developing a theory and then testing it out in the field.
Long story short, the second essential ingredient of a high-quality literature review is a critical discussion of the existing empirical research . Here, it’s important to go beyond description . You’ll need to present a critical analysis that addresses some (if not all) of the following questions:
- What have different studies found in relation to your research questions ?
- What contexts have (and haven’t been covered)? For example, certain countries, cities, cultures, etc.
- Are the findings across the studies similar or is there a lot of variation ? If so, why might this be the case?
- What sorts of research methodologies have been used and how could these help me develop my own methodology?
- What were the noteworthy limitations of these studies?
Simply put, your task here is to present a synthesis of what’s been done (and found) within the empirical research, so that you can clearly assess the current state of knowledge and identify potential research gaps , which leads us to our third essential ingredient.

The Research Gap
The third essential ingredient of a high-quality literature review is a discussion of the research gap (or gaps).
But what exactly is a research gap?
Simply put, a research gap is any unaddressed or inadequately explored area within the existing body of academic knowledge. In other words, a research gap emerges whenever there’s still some uncertainty regarding a certain topic or question.
For example, it might be the case that there are mixed findings regarding the relationship between two variables (e.g., job performance and work-from-home policies). Similarly, there might be a lack of research regarding the impact of a specific new technology on people’s mental health. On the other end of the spectrum, there might be a wealth of research regarding a certain topic within one country (say the US), but very little research on that same topic in a different social context (say, China).
These are just random examples, but as you can see, research gaps can emerge from many different places. What’s important to understand is that the research gap (or gaps) needs to emerge from your previous discussion of the theoretical and empirical literature . In other words, your discussion in those sections needs to start laying the foundation for the research gap.
For example, when discussing empirical research, you might mention that most studies have focused on a certain context , yet very few (or none) have focused on another context, and there’s reason to believe that findings may differ. Or you might highlight how there’s a fair deal of mixed findings and disagreement regarding a certain matter. In other words, you want to start laying a little breadcrumb trail in those sections so that your discussion of the research gap is firmly rooted in the rest of the literature review.
But why does all of this matter?
Well, the research gap should serve as the core justification for your study . Through your literature review, you’ll show what gaps exist in the current body of knowledge, and then your study will then attempt to fill (or contribute towards filling) one of those gaps. In other words, you’re first explaining what the problem is (some sort of gap) and then proposing how you’ll solve it.

Key Takeaways
To recap, the three ingredients that need to be mixed into your literature review are:
- The foundation of theory or theoretical framework
- The empirical or evidence-based research
As we mentioned earlier, these are components of a literature review and not (necessarily) a structure for your literature review chapter. Of course, you can structure your chapter in a way that reflects these three components (in fact, in some cases that works very well), but it’s certainly not the only option. The right structure will vary from study to study , depending on various factors.
If you’d like to get hands-on help developing your literature review, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the entire research journey, step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

very good , as the first writer of the thesis i will need ur advise . please give me a piece of idea on topic -impact of national standardized exam on students learning engagement . Thank you .
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Understanding Empirical Research
A deep dive into understanding empirical research, in this article….
- Introduction
What is empirical research?
Components of empirical research
- Qualitative empirical research
- Quantitative empirical research
- Approach to analysis
- Why use empirical research
You might also like…
Content creators and social media influencers in the digital economy.
by Jim Whaley
What does the state of influencer marketing look like in 2024? Discover how content creators and influencers are enmeshed in the digital economy....
Qualitative Market Research: The Complete 2023 Guide
by Chloe West
Qualitative market research helps collect key non-numerical data for analysis. Learn the qualitative research benefits, methods, and more. Inside...
Ancient Greece was an era that produced some of the greatest philosophers with unique perspectives that stemmed from equally unique beliefs. Among them were some that adhered to the dogmatic doctrines popular and commonly held at that time.

Then there were those who rejected them and instead favored evidence collected by observation of phenomenon through senses.
These were called empiricists. Their belief in this theory of knowledge was what gave birth to the concept of empiricism in scientific research . It evolved into the term empirical, which referred to data collection using evidence obtained through observation using the senses or with calibrated scientific instruments.
Based on this, empirical research is a type of investigation where the researcher infers a conclusion by testing empirical evidence. It provides a more concrete conclusion to an inquiry as it uses real-world evidence.
This approach to research is important for marketers to understand as it simplifies decision-making. For example, let’s consider a company that wants to investigate whether their web designers are more productive working from home; as a part of new remote work policies.
To test this with empirical research, they will conduct an experiment where they make two groups, sending one to work from home while the other remains in-house for a certain period. The evidence observed from this experiment will help them determine whether switching to remote work is the right decision.
Using this method of investigation, the researcher can get more in-depth data. In the example stated above, the company can assess productivity levels, individual employee performance, software effectiveness, work efficiency, etc.
Compared to empirical data, the results of a survey that simply asked for employee preference for remote work will not be as productive. The latter won’t provide verifiable evidence that is required to make a decision that impacts the productivity of the entire organization.
There are a few elements that all empirical studies contain:
- The research question , which can be obtained from previous experience, literature, or other similar studies – basically the objective of your study;
- Research design based on the research question;
- Research methodology , which refers to the method for data collection and analysis;
- Data collection , which is primary in most studies
- The sample , which should be representative of a larger population;
- Reliability , which means the results can be recreated later;

Empirical research methodology for data collection
There are essentially two methodologies the researchers use, quantitative research and qualitative research. The research methodology the researcher chooses depends on the research question and the field in which the results will be utilized.
Qualitative Empirical Research
This qualitative research methodology is collected non-numerical data and provides more detailed insights into the sample’s opinions underlying reasons regarding the hypothesis being tested.
This method is conversational and can be structures or unstructured. Researchers opt for this methodology when they want to observe the subjects’ behavior. The data gathered is more descriptive than predictive.
Some of the common methods for collecting qualitative data include:
Observation
This is when the researcher collects empirical evidence by observing the sample over a particular period. For example, a marketer can observe how their chosen sample responds to a new type of grocery store layout.
- Case Studies
Instead of collecting primary data, the researcher obtains evidence from existing cases that match the parameters and variables of the research design in question. For example, a tea company researching a blue ocean strategy may collect empirical data from existing cases where other tea companies applied this strategy.
This method is pretty self-explanatory. By asking the right questions, the researcher can obtain empirical data from people who have observed or experienced the phenomenon related to the study.
Focus Groups
A moderator guides discussion between a sampled group of people to find their opinions on the research topic. Like interviews, the online focus group questions are specific and consider the variables of the research.
Quantitative Empirical Research
This method of data collection is used when the researcher wants to obtain numerical data. The quantitative method in empirical research quantifies opinions, much like any other research. Different ways of collecting quantitative data include:
Surveys or Questionnaires
Usually deployed to a larger sample size compared to qualitative empirical research, surveys include a set of predetermined questions based on research variables and the phenomenon being studied. This method is the most commonly used (via online surveys using a market research panel or customer list) as it provides a larger amount of data.
Behavioral Data / Passive Metering
Typically permission-based, it is possible to match panelist’s online and mobile transactional behavior with survey attitude and intention responses. It is possible to track: search, shopping, purchase, ad views, media consumption, and social media activity while correlating many of these transactions.
Experiments
This is where empirical research truly shines. This is used when the researcher tests their hypothesis by setting up an experiment and manipulates the variables to observe how the phenomenon changes with each alteration.
For example, let’s consider the marketing department of a confectionary company is trying to find why their new product failed. They may set up an experiment by changing different aspects of the product, e.g., the flavor, the appearance, the packaging, and the price. This will help them figure out the cause of the failure.
Other methods of collective quantitative empirical data include causal-comparative, cross-sectional, longitudinal, and correlational research.
Approach to Analysis of Empirical Research
When you have to bring a theoretical perspective in your empirical research, you can take the inductive approach or a deductive approach.
The Inductive approach is interpretive, where you form a theory after collecting empirical evidence. It generally uses qualitative research methods and looks into how people perceive a certain phenomenon.
On the other hand, the Deductive approach is when the researcher establishes a hypothesis and develops a theoretical position before testing it against the data. Unlike the inductive approach, the deductive approach is positivist and uses quantitative methods in a highly-structured methodology.

Why Use Empirical Research
When it comes to market research, empirical research provides certain advantages over-simplistic survey analyses. It is one of the most commonly used research methods because:
- It provides data and results that can be used to confirm existing theories and authenticate traditional research through experiments and observation;
- It enables the research to observe dynamic changes in the phenomenon being observed;
- It allows the researcher to have more control over the variables involved in the study;
- It increases internal validity.
While these advantages are why empirical research is a preferred market research approach, some cons may prevent some marketers from using it.
- Empirical research is relatively more time consuming as experiments and observations for collecting primary data involve multiple variables and parameters;
- Based on the research question, the researcher may need to collect data from samples placed in different locations or environments – it can get expensive.
The importance of empirical research since is Ancient Greek beginnings has only grown. This is because human decisions rely on evidence. Marketers and decision-makers are more likely to lean on the side that can be proven and validated.
If an approach is scientifically proven to work, it is a more plausible alternative to a conclusion based solely on assumptions without investigation.

Jim Whaley is a business leader, market research expert, and writer. He posts frequently on The Standard Ovation and other industry blogs.
OvationMR is a global provider of first-party data for those seeking solutions that require information for informed business decisions.
OvationMR is a leader in delivering insights and reliable results across a variety of industry sectors around the globe consistently for market research professionals and management consultants.
Visit: https://www.ovationmr.com .

Need help with your project?
We are ready to offer you:
Our latest Panel Book
Esomar28 response, a project estimate/proposal, [email protected], +1.212.653.8750, 39 broadway, suite 2010, new york, ny 10006 usa.

- Ovation Blog
- View Panel Book
Calculators
- Sample-Size
- Margin-of-Error
- B2B Audiences
- Consumer Audiences
- Academic Surveys
- Research Design
- Start Sampling Now
- Survey Programming
Visit Us:
39 Broadway
Suite 2010
- New York, NY 10006
+1.212.653.8750

- Academic Survey Resources
- 39 Broadway
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 17 April 2024
The economic commitment of climate change
- Maximilian Kotz ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2564-5043 1 , 2 ,
- Anders Levermann ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4432-4704 1 , 2 &
- Leonie Wenz ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8500-1568 1 , 3
Nature volume 628 , pages 551–557 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
57k Accesses
3393 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental economics
- Environmental health
- Interdisciplinary studies
- Projection and prediction
Global projections of macroeconomic climate-change damages typically consider impacts from average annual and national temperatures over long time horizons 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 . Here we use recent empirical findings from more than 1,600 regions worldwide over the past 40 years to project sub-national damages from temperature and precipitation, including daily variability and extremes 7 , 8 . Using an empirical approach that provides a robust lower bound on the persistence of impacts on economic growth, we find that the world economy is committed to an income reduction of 19% within the next 26 years independent of future emission choices (relative to a baseline without climate impacts, likely range of 11–29% accounting for physical climate and empirical uncertainty). These damages already outweigh the mitigation costs required to limit global warming to 2 °C by sixfold over this near-term time frame and thereafter diverge strongly dependent on emission choices. Committed damages arise predominantly through changes in average temperature, but accounting for further climatic components raises estimates by approximately 50% and leads to stronger regional heterogeneity. Committed losses are projected for all regions except those at very high latitudes, at which reductions in temperature variability bring benefits. The largest losses are committed at lower latitudes in regions with lower cumulative historical emissions and lower present-day income.
Similar content being viewed by others

Climate damage projections beyond annual temperature
Paul Waidelich, Fulden Batibeniz, … Sonia I. Seneviratne
Investment incentive reduced by climate damages can be restored by optimal policy
Sven N. Willner, Nicole Glanemann & Anders Levermann
Climate economics support for the UN climate targets
Martin C. Hänsel, Moritz A. Drupp, … Thomas Sterner
Projections of the macroeconomic damage caused by future climate change are crucial to informing public and policy debates about adaptation, mitigation and climate justice. On the one hand, adaptation against climate impacts must be justified and planned on the basis of an understanding of their future magnitude and spatial distribution 9 . This is also of importance in the context of climate justice 10 , as well as to key societal actors, including governments, central banks and private businesses, which increasingly require the inclusion of climate risks in their macroeconomic forecasts to aid adaptive decision-making 11 , 12 . On the other hand, climate mitigation policy such as the Paris Climate Agreement is often evaluated by balancing the costs of its implementation against the benefits of avoiding projected physical damages. This evaluation occurs both formally through cost–benefit analyses 1 , 4 , 5 , 6 , as well as informally through public perception of mitigation and damage costs 13 .
Projections of future damages meet challenges when informing these debates, in particular the human biases relating to uncertainty and remoteness that are raised by long-term perspectives 14 . Here we aim to overcome such challenges by assessing the extent of economic damages from climate change to which the world is already committed by historical emissions and socio-economic inertia (the range of future emission scenarios that are considered socio-economically plausible 15 ). Such a focus on the near term limits the large uncertainties about diverging future emission trajectories, the resulting long-term climate response and the validity of applying historically observed climate–economic relations over long timescales during which socio-technical conditions may change considerably. As such, this focus aims to simplify the communication and maximize the credibility of projected economic damages from future climate change.
In projecting the future economic damages from climate change, we make use of recent advances in climate econometrics that provide evidence for impacts on sub-national economic growth from numerous components of the distribution of daily temperature and precipitation 3 , 7 , 8 . Using fixed-effects panel regression models to control for potential confounders, these studies exploit within-region variation in local temperature and precipitation in a panel of more than 1,600 regions worldwide, comprising climate and income data over the past 40 years, to identify the plausibly causal effects of changes in several climate variables on economic productivity 16 , 17 . Specifically, macroeconomic impacts have been identified from changing daily temperature variability, total annual precipitation, the annual number of wet days and extreme daily rainfall that occur in addition to those already identified from changing average temperature 2 , 3 , 18 . Moreover, regional heterogeneity in these effects based on the prevailing local climatic conditions has been found using interactions terms. The selection of these climate variables follows micro-level evidence for mechanisms related to the impacts of average temperatures on labour and agricultural productivity 2 , of temperature variability on agricultural productivity and health 7 , as well as of precipitation on agricultural productivity, labour outcomes and flood damages 8 (see Extended Data Table 1 for an overview, including more detailed references). References 7 , 8 contain a more detailed motivation for the use of these particular climate variables and provide extensive empirical tests about the robustness and nature of their effects on economic output, which are summarized in Methods . By accounting for these extra climatic variables at the sub-national level, we aim for a more comprehensive description of climate impacts with greater detail across both time and space.
Constraining the persistence of impacts
A key determinant and source of discrepancy in estimates of the magnitude of future climate damages is the extent to which the impact of a climate variable on economic growth rates persists. The two extreme cases in which these impacts persist indefinitely or only instantaneously are commonly referred to as growth or level effects 19 , 20 (see Methods section ‘Empirical model specification: fixed-effects distributed lag models’ for mathematical definitions). Recent work shows that future damages from climate change depend strongly on whether growth or level effects are assumed 20 . Following refs. 2 , 18 , we provide constraints on this persistence by using distributed lag models to test the significance of delayed effects separately for each climate variable. Notably, and in contrast to refs. 2 , 18 , we use climate variables in their first-differenced form following ref. 3 , implying a dependence of the growth rate on a change in climate variables. This choice means that a baseline specification without any lags constitutes a model prior of purely level effects, in which a permanent change in the climate has only an instantaneous effect on the growth rate 3 , 19 , 21 . By including lags, one can then test whether any effects may persist further. This is in contrast to the specification used by refs. 2 , 18 , in which climate variables are used without taking the first difference, implying a dependence of the growth rate on the level of climate variables. In this alternative case, the baseline specification without any lags constitutes a model prior of pure growth effects, in which a change in climate has an infinitely persistent effect on the growth rate. Consequently, including further lags in this alternative case tests whether the initial growth impact is recovered 18 , 19 , 21 . Both of these specifications suffer from the limiting possibility that, if too few lags are included, one might falsely accept the model prior. The limitations of including a very large number of lags, including loss of data and increasing statistical uncertainty with an increasing number of parameters, mean that such a possibility is likely. By choosing a specification in which the model prior is one of level effects, our approach is therefore conservative by design, avoiding assumptions of infinite persistence of climate impacts on growth and instead providing a lower bound on this persistence based on what is observable empirically (see Methods section ‘Empirical model specification: fixed-effects distributed lag models’ for further exposition of this framework). The conservative nature of such a choice is probably the reason that ref. 19 finds much greater consistency between the impacts projected by models that use the first difference of climate variables, as opposed to their levels.
We begin our empirical analysis of the persistence of climate impacts on growth using ten lags of the first-differenced climate variables in fixed-effects distributed lag models. We detect substantial effects on economic growth at time lags of up to approximately 8–10 years for the temperature terms and up to approximately 4 years for the precipitation terms (Extended Data Fig. 1 and Extended Data Table 2 ). Furthermore, evaluation by means of information criteria indicates that the inclusion of all five climate variables and the use of these numbers of lags provide a preferable trade-off between best-fitting the data and including further terms that could cause overfitting, in comparison with model specifications excluding climate variables or including more or fewer lags (Extended Data Fig. 3 , Supplementary Methods Section 1 and Supplementary Table 1 ). We therefore remove statistically insignificant terms at later lags (Supplementary Figs. 1 – 3 and Supplementary Tables 2 – 4 ). Further tests using Monte Carlo simulations demonstrate that the empirical models are robust to autocorrelation in the lagged climate variables (Supplementary Methods Section 2 and Supplementary Figs. 4 and 5 ), that information criteria provide an effective indicator for lag selection (Supplementary Methods Section 2 and Supplementary Fig. 6 ), that the results are robust to concerns of imperfect multicollinearity between climate variables and that including several climate variables is actually necessary to isolate their separate effects (Supplementary Methods Section 3 and Supplementary Fig. 7 ). We provide a further robustness check using a restricted distributed lag model to limit oscillations in the lagged parameter estimates that may result from autocorrelation, finding that it provides similar estimates of cumulative marginal effects to the unrestricted model (Supplementary Methods Section 4 and Supplementary Figs. 8 and 9 ). Finally, to explicitly account for any outstanding uncertainty arising from the precise choice of the number of lags, we include empirical models with marginally different numbers of lags in the error-sampling procedure of our projection of future damages. On the basis of the lag-selection procedure (the significance of lagged terms in Extended Data Fig. 1 and Extended Data Table 2 , as well as information criteria in Extended Data Fig. 3 ), we sample from models with eight to ten lags for temperature and four for precipitation (models shown in Supplementary Figs. 1 – 3 and Supplementary Tables 2 – 4 ). In summary, this empirical approach to constrain the persistence of climate impacts on economic growth rates is conservative by design in avoiding assumptions of infinite persistence, but nevertheless provides a lower bound on the extent of impact persistence that is robust to the numerous tests outlined above.
Committed damages until mid-century
We combine these empirical economic response functions (Supplementary Figs. 1 – 3 and Supplementary Tables 2 – 4 ) with an ensemble of 21 climate models (see Supplementary Table 5 ) from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP-6) 22 to project the macroeconomic damages from these components of physical climate change (see Methods for further details). Bias-adjusted climate models that provide a highly accurate reproduction of observed climatological patterns with limited uncertainty (Supplementary Table 6 ) are used to avoid introducing biases in the projections. Following a well-developed literature 2 , 3 , 19 , these projections do not aim to provide a prediction of future economic growth. Instead, they are a projection of the exogenous impact of future climate conditions on the economy relative to the baselines specified by socio-economic projections, based on the plausibly causal relationships inferred by the empirical models and assuming ceteris paribus. Other exogenous factors relevant for the prediction of economic output are purposefully assumed constant.
A Monte Carlo procedure that samples from climate model projections, empirical models with different numbers of lags and model parameter estimates (obtained by 1,000 block-bootstrap resamples of each of the regressions in Supplementary Figs. 1 – 3 and Supplementary Tables 2 – 4 ) is used to estimate the combined uncertainty from these sources. Given these uncertainty distributions, we find that projected global damages are statistically indistinguishable across the two most extreme emission scenarios until 2049 (at the 5% significance level; Fig. 1 ). As such, the climate damages occurring before this time constitute those to which the world is already committed owing to the combination of past emissions and the range of future emission scenarios that are considered socio-economically plausible 15 . These committed damages comprise a permanent income reduction of 19% on average globally (population-weighted average) in comparison with a baseline without climate-change impacts (with a likely range of 11–29%, following the likelihood classification adopted by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); see caption of Fig. 1 ). Even though levels of income per capita generally still increase relative to those of today, this constitutes a permanent income reduction for most regions, including North America and Europe (each with median income reductions of approximately 11%) and with South Asia and Africa being the most strongly affected (each with median income reductions of approximately 22%; Fig. 1 ). Under a middle-of-the road scenario of future income development (SSP2, in which SSP stands for Shared Socio-economic Pathway), this corresponds to global annual damages in 2049 of 38 trillion in 2005 international dollars (likely range of 19–59 trillion 2005 international dollars). Compared with empirical specifications that assume pure growth or pure level effects, our preferred specification that provides a robust lower bound on the extent of climate impact persistence produces damages between these two extreme assumptions (Extended Data Fig. 3 ).
Estimates of the projected reduction in income per capita from changes in all climate variables based on empirical models of climate impacts on economic output with a robust lower bound on their persistence (Extended Data Fig. 1 ) under a low-emission scenario compatible with the 2 °C warming target and a high-emission scenario (SSP2-RCP2.6 and SSP5-RCP8.5, respectively) are shown in purple and orange, respectively. Shading represents the 34% and 10% confidence intervals reflecting the likely and very likely ranges, respectively (following the likelihood classification adopted by the IPCC), having estimated uncertainty from a Monte Carlo procedure, which samples the uncertainty from the choice of physical climate models, empirical models with different numbers of lags and bootstrapped estimates of the regression parameters shown in Supplementary Figs. 1 – 3 . Vertical dashed lines show the time at which the climate damages of the two emission scenarios diverge at the 5% and 1% significance levels based on the distribution of differences between emission scenarios arising from the uncertainty sampling discussed above. Note that uncertainty in the difference of the two scenarios is smaller than the combined uncertainty of the two respective scenarios because samples of the uncertainty (climate model and empirical model choice, as well as model parameter bootstrap) are consistent across the two emission scenarios, hence the divergence of damages occurs while the uncertainty bounds of the two separate damage scenarios still overlap. Estimates of global mitigation costs from the three IAMs that provide results for the SSP2 baseline and SSP2-RCP2.6 scenario are shown in light green in the top panel, with the median of these estimates shown in bold.
Damages already outweigh mitigation costs
We compare the damages to which the world is committed over the next 25 years to estimates of the mitigation costs required to achieve the Paris Climate Agreement. Taking estimates of mitigation costs from the three integrated assessment models (IAMs) in the IPCC AR6 database 23 that provide results under comparable scenarios (SSP2 baseline and SSP2-RCP2.6, in which RCP stands for Representative Concentration Pathway), we find that the median committed climate damages are larger than the median mitigation costs in 2050 (six trillion in 2005 international dollars) by a factor of approximately six (note that estimates of mitigation costs are only provided every 10 years by the IAMs and so a comparison in 2049 is not possible). This comparison simply aims to compare the magnitude of future damages against mitigation costs, rather than to conduct a formal cost–benefit analysis of transitioning from one emission path to another. Formal cost–benefit analyses typically find that the net benefits of mitigation only emerge after 2050 (ref. 5 ), which may lead some to conclude that physical damages from climate change are simply not large enough to outweigh mitigation costs until the second half of the century. Our simple comparison of their magnitudes makes clear that damages are actually already considerably larger than mitigation costs and the delayed emergence of net mitigation benefits results primarily from the fact that damages across different emission paths are indistinguishable until mid-century (Fig. 1 ).
Although these near-term damages constitute those to which the world is already committed, we note that damage estimates diverge strongly across emission scenarios after 2049, conveying the clear benefits of mitigation from a purely economic point of view that have been emphasized in previous studies 4 , 24 . As well as the uncertainties assessed in Fig. 1 , these conclusions are robust to structural choices, such as the timescale with which changes in the moderating variables of the empirical models are estimated (Supplementary Figs. 10 and 11 ), as well as the order in which one accounts for the intertemporal and international components of currency comparison (Supplementary Fig. 12 ; see Methods for further details).
Damages from variability and extremes
Committed damages primarily arise through changes in average temperature (Fig. 2 ). This reflects the fact that projected changes in average temperature are larger than those in other climate variables when expressed as a function of their historical interannual variability (Extended Data Fig. 4 ). Because the historical variability is that on which the empirical models are estimated, larger projected changes in comparison with this variability probably lead to larger future impacts in a purely statistical sense. From a mechanistic perspective, one may plausibly interpret this result as implying that future changes in average temperature are the most unprecedented from the perspective of the historical fluctuations to which the economy is accustomed and therefore will cause the most damage. This insight may prove useful in terms of guiding adaptation measures to the sources of greatest damage.
Estimates of the median projected reduction in sub-national income per capita across emission scenarios (SSP2-RCP2.6 and SSP2-RCP8.5) as well as climate model, empirical model and model parameter uncertainty in the year in which climate damages diverge at the 5% level (2049, as identified in Fig. 1 ). a , Impacts arising from all climate variables. b – f , Impacts arising separately from changes in annual mean temperature ( b ), daily temperature variability ( c ), total annual precipitation ( d ), the annual number of wet days (>1 mm) ( e ) and extreme daily rainfall ( f ) (see Methods for further definitions). Data on national administrative boundaries are obtained from the GADM database version 3.6 and are freely available for academic use ( https://gadm.org/ ).
Nevertheless, future damages based on empirical models that consider changes in annual average temperature only and exclude the other climate variables constitute income reductions of only 13% in 2049 (Extended Data Fig. 5a , likely range 5–21%). This suggests that accounting for the other components of the distribution of temperature and precipitation raises net damages by nearly 50%. This increase arises through the further damages that these climatic components cause, but also because their inclusion reveals a stronger negative economic response to average temperatures (Extended Data Fig. 5b ). The latter finding is consistent with our Monte Carlo simulations, which suggest that the magnitude of the effect of average temperature on economic growth is underestimated unless accounting for the impacts of other correlated climate variables (Supplementary Fig. 7 ).
In terms of the relative contributions of the different climatic components to overall damages, we find that accounting for daily temperature variability causes the largest increase in overall damages relative to empirical frameworks that only consider changes in annual average temperature (4.9 percentage points, likely range 2.4–8.7 percentage points, equivalent to approximately 10 trillion international dollars). Accounting for precipitation causes smaller increases in overall damages, which are—nevertheless—equivalent to approximately 1.2 trillion international dollars: 0.01 percentage points (−0.37–0.33 percentage points), 0.34 percentage points (0.07–0.90 percentage points) and 0.36 percentage points (0.13–0.65 percentage points) from total annual precipitation, the number of wet days and extreme daily precipitation, respectively. Moreover, climate models seem to underestimate future changes in temperature variability 25 and extreme precipitation 26 , 27 in response to anthropogenic forcing as compared with that observed historically, suggesting that the true impacts from these variables may be larger.
The distribution of committed damages
The spatial distribution of committed damages (Fig. 2a ) reflects a complex interplay between the patterns of future change in several climatic components and those of historical economic vulnerability to changes in those variables. Damages resulting from increasing annual mean temperature (Fig. 2b ) are negative almost everywhere globally, and larger at lower latitudes in regions in which temperatures are already higher and economic vulnerability to temperature increases is greatest (see the response heterogeneity to mean temperature embodied in Extended Data Fig. 1a ). This occurs despite the amplified warming projected at higher latitudes 28 , suggesting that regional heterogeneity in economic vulnerability to temperature changes outweighs heterogeneity in the magnitude of future warming (Supplementary Fig. 13a ). Economic damages owing to daily temperature variability (Fig. 2c ) exhibit a strong latitudinal polarisation, primarily reflecting the physical response of daily variability to greenhouse forcing in which increases in variability across lower latitudes (and Europe) contrast decreases at high latitudes 25 (Supplementary Fig. 13b ). These two temperature terms are the dominant determinants of the pattern of overall damages (Fig. 2a ), which exhibits a strong polarity with damages across most of the globe except at the highest northern latitudes. Future changes in total annual precipitation mainly bring economic benefits except in regions of drying, such as the Mediterranean and central South America (Fig. 2d and Supplementary Fig. 13c ), but these benefits are opposed by changes in the number of wet days, which produce damages with a similar pattern of opposite sign (Fig. 2e and Supplementary Fig. 13d ). By contrast, changes in extreme daily rainfall produce damages in all regions, reflecting the intensification of daily rainfall extremes over global land areas 29 , 30 (Fig. 2f and Supplementary Fig. 13e ).
The spatial distribution of committed damages implies considerable injustice along two dimensions: culpability for the historical emissions that have caused climate change and pre-existing levels of socio-economic welfare. Spearman’s rank correlations indicate that committed damages are significantly larger in countries with smaller historical cumulative emissions, as well as in regions with lower current income per capita (Fig. 3 ). This implies that those countries that will suffer the most from the damages already committed are those that are least responsible for climate change and which also have the least resources to adapt to it.
Estimates of the median projected change in national income per capita across emission scenarios (RCP2.6 and RCP8.5) as well as climate model, empirical model and model parameter uncertainty in the year in which climate damages diverge at the 5% level (2049, as identified in Fig. 1 ) are plotted against cumulative national emissions per capita in 2020 (from the Global Carbon Project) and coloured by national income per capita in 2020 (from the World Bank) in a and vice versa in b . In each panel, the size of each scatter point is weighted by the national population in 2020 (from the World Bank). Inset numbers indicate the Spearman’s rank correlation ρ and P -values for a hypothesis test whose null hypothesis is of no correlation, as well as the Spearman’s rank correlation weighted by national population.
To further quantify this heterogeneity, we assess the difference in committed damages between the upper and lower quartiles of regions when ranked by present income levels and historical cumulative emissions (using a population weighting to both define the quartiles and estimate the group averages). On average, the quartile of countries with lower income are committed to an income loss that is 8.9 percentage points (or 61%) greater than the upper quartile (Extended Data Fig. 6 ), with a likely range of 3.8–14.7 percentage points across the uncertainty sampling of our damage projections (following the likelihood classification adopted by the IPCC). Similarly, the quartile of countries with lower historical cumulative emissions are committed to an income loss that is 6.9 percentage points (or 40%) greater than the upper quartile, with a likely range of 0.27–12 percentage points. These patterns reemphasize the prevalence of injustice in climate impacts 31 , 32 , 33 in the context of the damages to which the world is already committed by historical emissions and socio-economic inertia.
Contextualizing the magnitude of damages
The magnitude of projected economic damages exceeds previous literature estimates 2 , 3 , arising from several developments made on previous approaches. Our estimates are larger than those of ref. 2 (see first row of Extended Data Table 3 ), primarily because of the facts that sub-national estimates typically show a steeper temperature response (see also refs. 3 , 34 ) and that accounting for other climatic components raises damage estimates (Extended Data Fig. 5 ). However, we note that our empirical approach using first-differenced climate variables is conservative compared with that of ref. 2 in regard to the persistence of climate impacts on growth (see introduction and Methods section ‘Empirical model specification: fixed-effects distributed lag models’), an important determinant of the magnitude of long-term damages 19 , 21 . Using a similar empirical specification to ref. 2 , which assumes infinite persistence while maintaining the rest of our approach (sub-national data and further climate variables), produces considerably larger damages (purple curve of Extended Data Fig. 3 ). Compared with studies that do take the first difference of climate variables 3 , 35 , our estimates are also larger (see second and third rows of Extended Data Table 3 ). The inclusion of further climate variables (Extended Data Fig. 5 ) and a sufficient number of lags to more adequately capture the extent of impact persistence (Extended Data Figs. 1 and 2 ) are the main sources of this difference, as is the use of specifications that capture nonlinearities in the temperature response when compared with ref. 35 . In summary, our estimates develop on previous studies by incorporating the latest data and empirical insights 7 , 8 , as well as in providing a robust empirical lower bound on the persistence of impacts on economic growth, which constitutes a middle ground between the extremes of the growth-versus-levels debate 19 , 21 (Extended Data Fig. 3 ).
Compared with the fraction of variance explained by the empirical models historically (<5%), the projection of reductions in income of 19% may seem large. This arises owing to the fact that projected changes in climatic conditions are much larger than those that were experienced historically, particularly for changes in average temperature (Extended Data Fig. 4 ). As such, any assessment of future climate-change impacts necessarily requires an extrapolation outside the range of the historical data on which the empirical impact models were evaluated. Nevertheless, these models constitute the most state-of-the-art methods for inference of plausibly causal climate impacts based on observed data. Moreover, we take explicit steps to limit out-of-sample extrapolation by capping the moderating variables of the interaction terms at the 95th percentile of the historical distribution (see Methods ). This avoids extrapolating the marginal effects outside what was observed historically. Given the nonlinear response of economic output to annual mean temperature (Extended Data Fig. 1 and Extended Data Table 2 ), this is a conservative choice that limits the magnitude of damages that we project. Furthermore, back-of-the-envelope calculations indicate that the projected damages are consistent with the magnitude and patterns of historical economic development (see Supplementary Discussion Section 5 ).
Missing impacts and spatial spillovers
Despite assessing several climatic components from which economic impacts have recently been identified 3 , 7 , 8 , this assessment of aggregate climate damages should not be considered comprehensive. Important channels such as impacts from heatwaves 31 , sea-level rise 36 , tropical cyclones 37 and tipping points 38 , 39 , as well as non-market damages such as those to ecosystems 40 and human health 41 , are not considered in these estimates. Sea-level rise is unlikely to be feasibly incorporated into empirical assessments such as this because historical sea-level variability is mostly small. Non-market damages are inherently intractable within our estimates of impacts on aggregate monetary output and estimates of these impacts could arguably be considered as extra to those identified here. Recent empirical work suggests that accounting for these channels would probably raise estimates of these committed damages, with larger damages continuing to arise in the global south 31 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 .
Moreover, our main empirical analysis does not explicitly evaluate the potential for impacts in local regions to produce effects that ‘spill over’ into other regions. Such effects may further mitigate or amplify the impacts we estimate, for example, if companies relocate production from one affected region to another or if impacts propagate along supply chains. The current literature indicates that trade plays a substantial role in propagating spillover effects 43 , 44 , making their assessment at the sub-national level challenging without available data on sub-national trade dependencies. Studies accounting for only spatially adjacent neighbours indicate that negative impacts in one region induce further negative impacts in neighbouring regions 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , suggesting that our projected damages are probably conservative by excluding these effects. In Supplementary Fig. 14 , we assess spillovers from neighbouring regions using a spatial-lag model. For simplicity, this analysis excludes temporal lags, focusing only on contemporaneous effects. The results show that accounting for spatial spillovers can amplify the overall magnitude, and also the heterogeneity, of impacts. Consistent with previous literature, this indicates that the overall magnitude (Fig. 1 ) and heterogeneity (Fig. 3 ) of damages that we project in our main specification may be conservative without explicitly accounting for spillovers. We note that further analysis that addresses both spatially and trade-connected spillovers, while also accounting for delayed impacts using temporal lags, would be necessary to adequately address this question fully. These approaches offer fruitful avenues for further research but are beyond the scope of this manuscript, which primarily aims to explore the impacts of different climate conditions and their persistence.
Policy implications
We find that the economic damages resulting from climate change until 2049 are those to which the world economy is already committed and that these greatly outweigh the costs required to mitigate emissions in line with the 2 °C target of the Paris Climate Agreement (Fig. 1 ). This assessment is complementary to formal analyses of the net costs and benefits associated with moving from one emission path to another, which typically find that net benefits of mitigation only emerge in the second half of the century 5 . Our simple comparison of the magnitude of damages and mitigation costs makes clear that this is primarily because damages are indistinguishable across emissions scenarios—that is, committed—until mid-century (Fig. 1 ) and that they are actually already much larger than mitigation costs. For simplicity, and owing to the availability of data, we compare damages to mitigation costs at the global level. Regional estimates of mitigation costs may shed further light on the national incentives for mitigation to which our results already hint, of relevance for international climate policy. Although these damages are committed from a mitigation perspective, adaptation may provide an opportunity to reduce them. Moreover, the strong divergence of damages after mid-century reemphasizes the clear benefits of mitigation from a purely economic perspective, as highlighted in previous studies 1 , 4 , 6 , 24 .
Historical climate data
Historical daily 2-m temperature and precipitation totals (in mm) are obtained for the period 1979–2019 from the W5E5 database. The W5E5 dataset comes from ERA-5, a state-of-the-art reanalysis of historical observations, but has been bias-adjusted by applying version 2.0 of the WATCH Forcing Data to ERA-5 reanalysis data and precipitation data from version 2.3 of the Global Precipitation Climatology Project to better reflect ground-based measurements 49 , 50 , 51 . We obtain these data on a 0.5° × 0.5° grid from the Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project (ISIMIP) database. Notably, these historical data have been used to bias-adjust future climate projections from CMIP-6 (see the following section), ensuring consistency between the distribution of historical daily weather on which our empirical models were estimated and the climate projections used to estimate future damages. These data are publicly available from the ISIMIP database. See refs. 7 , 8 for robustness tests of the empirical models to the choice of climate data reanalysis products.
Future climate data
Daily 2-m temperature and precipitation totals (in mm) are taken from 21 climate models participating in CMIP-6 under a high (RCP8.5) and a low (RCP2.6) greenhouse gas emission scenario from 2015 to 2100. The data have been bias-adjusted and statistically downscaled to a common half-degree grid to reflect the historical distribution of daily temperature and precipitation of the W5E5 dataset using the trend-preserving method developed by the ISIMIP 50 , 52 . As such, the climate model data reproduce observed climatological patterns exceptionally well (Supplementary Table 5 ). Gridded data are publicly available from the ISIMIP database.
Historical economic data
Historical economic data come from the DOSE database of sub-national economic output 53 . We use a recent revision to the DOSE dataset that provides data across 83 countries, 1,660 sub-national regions with varying temporal coverage from 1960 to 2019. Sub-national units constitute the first administrative division below national, for example, states for the USA and provinces for China. Data come from measures of gross regional product per capita (GRPpc) or income per capita in local currencies, reflecting the values reported in national statistical agencies, yearbooks and, in some cases, academic literature. We follow previous literature 3 , 7 , 8 , 54 and assess real sub-national output per capita by first converting values from local currencies to US dollars to account for diverging national inflationary tendencies and then account for US inflation using a US deflator. Alternatively, one might first account for national inflation and then convert between currencies. Supplementary Fig. 12 demonstrates that our conclusions are consistent when accounting for price changes in the reversed order, although the magnitude of estimated damages varies. See the documentation of the DOSE dataset for further discussion of these choices. Conversions between currencies are conducted using exchange rates from the FRED database of the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis 55 and the national deflators from the World Bank 56 .
Future socio-economic data
Baseline gridded gross domestic product (GDP) and population data for the period 2015–2100 are taken from the middle-of-the-road scenario SSP2 (ref. 15 ). Population data have been downscaled to a half-degree grid by the ISIMIP following the methodologies of refs. 57 , 58 , which we then aggregate to the sub-national level of our economic data using the spatial aggregation procedure described below. Because current methodologies for downscaling the GDP of the SSPs use downscaled population to do so, per-capita estimates of GDP with a realistic distribution at the sub-national level are not readily available for the SSPs. We therefore use national-level GDP per capita (GDPpc) projections for all sub-national regions of a given country, assuming homogeneity within countries in terms of baseline GDPpc. Here we use projections that have been updated to account for the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the trajectory of future income, while remaining consistent with the long-term development of the SSPs 59 . The choice of baseline SSP alters the magnitude of projected climate damages in monetary terms, but when assessed in terms of percentage change from the baseline, the choice of socio-economic scenario is inconsequential. Gridded SSP population data and national-level GDPpc data are publicly available from the ISIMIP database. Sub-national estimates as used in this study are available in the code and data replication files.
Climate variables
Following recent literature 3 , 7 , 8 , we calculate an array of climate variables for which substantial impacts on macroeconomic output have been identified empirically, supported by further evidence at the micro level for plausible underlying mechanisms. See refs. 7 , 8 for an extensive motivation for the use of these particular climate variables and for detailed empirical tests on the nature and robustness of their effects on economic output. To summarize, these studies have found evidence for independent impacts on economic growth rates from annual average temperature, daily temperature variability, total annual precipitation, the annual number of wet days and extreme daily rainfall. Assessments of daily temperature variability were motivated by evidence of impacts on agricultural output and human health, as well as macroeconomic literature on the impacts of volatility on growth when manifest in different dimensions, such as government spending, exchange rates and even output itself 7 . Assessments of precipitation impacts were motivated by evidence of impacts on agricultural productivity, metropolitan labour outcomes and conflict, as well as damages caused by flash flooding 8 . See Extended Data Table 1 for detailed references to empirical studies of these physical mechanisms. Marked impacts of daily temperature variability, total annual precipitation, the number of wet days and extreme daily rainfall on macroeconomic output were identified robustly across different climate datasets, spatial aggregation schemes, specifications of regional time trends and error-clustering approaches. They were also found to be robust to the consideration of temperature extremes 7 , 8 . Furthermore, these climate variables were identified as having independent effects on economic output 7 , 8 , which we further explain here using Monte Carlo simulations to demonstrate the robustness of the results to concerns of imperfect multicollinearity between climate variables (Supplementary Methods Section 2 ), as well as by using information criteria (Supplementary Table 1 ) to demonstrate that including several lagged climate variables provides a preferable trade-off between optimally describing the data and limiting the possibility of overfitting.
We calculate these variables from the distribution of daily, d , temperature, T x , d , and precipitation, P x , d , at the grid-cell, x , level for both the historical and future climate data. As well as annual mean temperature, \({\bar{T}}_{x,y}\) , and annual total precipitation, P x , y , we calculate annual, y , measures of daily temperature variability, \({\widetilde{T}}_{x,y}\) :
the number of wet days, Pwd x , y :
and extreme daily rainfall:
in which T x , d , m , y is the grid-cell-specific daily temperature in month m and year y , \({\bar{T}}_{x,m,{y}}\) is the year and grid-cell-specific monthly, m , mean temperature, D m and D y the number of days in a given month m or year y , respectively, H the Heaviside step function, 1 mm the threshold used to define wet days and P 99.9 x is the 99.9th percentile of historical (1979–2019) daily precipitation at the grid-cell level. Units of the climate measures are degrees Celsius for annual mean temperature and daily temperature variability, millimetres for total annual precipitation and extreme daily precipitation, and simply the number of days for the annual number of wet days.
We also calculated weighted standard deviations of monthly rainfall totals as also used in ref. 8 but do not include them in our projections as we find that, when accounting for delayed effects, their effect becomes statistically indistinct and is better captured by changes in total annual rainfall.
Spatial aggregation
We aggregate grid-cell-level historical and future climate measures, as well as grid-cell-level future GDPpc and population, to the level of the first administrative unit below national level of the GADM database, using an area-weighting algorithm that estimates the portion of each grid cell falling within an administrative boundary. We use this as our baseline specification following previous findings that the effect of area or population weighting at the sub-national level is negligible 7 , 8 .
Empirical model specification: fixed-effects distributed lag models
Following a wide range of climate econometric literature 16 , 60 , we use panel regression models with a selection of fixed effects and time trends to isolate plausibly exogenous variation with which to maximize confidence in a causal interpretation of the effects of climate on economic growth rates. The use of region fixed effects, μ r , accounts for unobserved time-invariant differences between regions, such as prevailing climatic norms and growth rates owing to historical and geopolitical factors. The use of yearly fixed effects, η y , accounts for regionally invariant annual shocks to the global climate or economy such as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation or global recessions. In our baseline specification, we also include region-specific linear time trends, k r y , to exclude the possibility of spurious correlations resulting from common slow-moving trends in climate and growth.
The persistence of climate impacts on economic growth rates is a key determinant of the long-term magnitude of damages. Methods for inferring the extent of persistence in impacts on growth rates have typically used lagged climate variables to evaluate the presence of delayed effects or catch-up dynamics 2 , 18 . For example, consider starting from a model in which a climate condition, C r , y , (for example, annual mean temperature) affects the growth rate, Δlgrp r , y (the first difference of the logarithm of gross regional product) of region r in year y :
which we refer to as a ‘pure growth effects’ model in the main text. Typically, further lags are included,
and the cumulative effect of all lagged terms is evaluated to assess the extent to which climate impacts on growth rates persist. Following ref. 18 , in the case that,
the implication is that impacts on the growth rate persist up to NL years after the initial shock (possibly to a weaker or a stronger extent), whereas if
then the initial impact on the growth rate is recovered after NL years and the effect is only one on the level of output. However, we note that such approaches are limited by the fact that, when including an insufficient number of lags to detect a recovery of the growth rates, one may find equation ( 6 ) to be satisfied and incorrectly assume that a change in climatic conditions affects the growth rate indefinitely. In practice, given a limited record of historical data, including too few lags to confidently conclude in an infinitely persistent impact on the growth rate is likely, particularly over the long timescales over which future climate damages are often projected 2 , 24 . To avoid this issue, we instead begin our analysis with a model for which the level of output, lgrp r , y , depends on the level of a climate variable, C r , y :
Given the non-stationarity of the level of output, we follow the literature 19 and estimate such an equation in first-differenced form as,
which we refer to as a model of ‘pure level effects’ in the main text. This model constitutes a baseline specification in which a permanent change in the climate variable produces an instantaneous impact on the growth rate and a permanent effect only on the level of output. By including lagged variables in this specification,
we are able to test whether the impacts on the growth rate persist any further than instantaneously by evaluating whether α L > 0 are statistically significantly different from zero. Even though this framework is also limited by the possibility of including too few lags, the choice of a baseline model specification in which impacts on the growth rate do not persist means that, in the case of including too few lags, the framework reverts to the baseline specification of level effects. As such, this framework is conservative with respect to the persistence of impacts and the magnitude of future damages. It naturally avoids assumptions of infinite persistence and we are able to interpret any persistence that we identify with equation ( 9 ) as a lower bound on the extent of climate impact persistence on growth rates. See the main text for further discussion of this specification choice, in particular about its conservative nature compared with previous literature estimates, such as refs. 2 , 18 .
We allow the response to climatic changes to vary across regions, using interactions of the climate variables with historical average (1979–2019) climatic conditions reflecting heterogenous effects identified in previous work 7 , 8 . Following this previous work, the moderating variables of these interaction terms constitute the historical average of either the variable itself or of the seasonal temperature difference, \({\hat{T}}_{r}\) , or annual mean temperature, \({\bar{T}}_{r}\) , in the case of daily temperature variability 7 and extreme daily rainfall, respectively 8 .
The resulting regression equation with N and M lagged variables, respectively, reads:
in which Δlgrp r , y is the annual, regional GRPpc growth rate, measured as the first difference of the logarithm of real GRPpc, following previous work 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 18 , 19 . Fixed-effects regressions were run using the fixest package in R (ref. 61 ).
Estimates of the coefficients of interest α i , L are shown in Extended Data Fig. 1 for N = M = 10 lags and for our preferred choice of the number of lags in Supplementary Figs. 1 – 3 . In Extended Data Fig. 1 , errors are shown clustered at the regional level, but for the construction of damage projections, we block-bootstrap the regressions by region 1,000 times to provide a range of parameter estimates with which to sample the projection uncertainty (following refs. 2 , 31 ).
Spatial-lag model
In Supplementary Fig. 14 , we present the results from a spatial-lag model that explores the potential for climate impacts to ‘spill over’ into spatially neighbouring regions. We measure the distance between centroids of each pair of sub-national regions and construct spatial lags that take the average of the first-differenced climate variables and their interaction terms over neighbouring regions that are at distances of 0–500, 500–1,000, 1,000–1,500 and 1,500–2000 km (spatial lags, ‘SL’, 1 to 4). For simplicity, we then assess a spatial-lag model without temporal lags to assess spatial spillovers of contemporaneous climate impacts. This model takes the form:
in which SL indicates the spatial lag of each climate variable and interaction term. In Supplementary Fig. 14 , we plot the cumulative marginal effect of each climate variable at different baseline climate conditions by summing the coefficients for each climate variable and interaction term, for example, for average temperature impacts as:
These cumulative marginal effects can be regarded as the overall spatially dependent impact to an individual region given a one-unit shock to a climate variable in that region and all neighbouring regions at a given value of the moderating variable of the interaction term.
Constructing projections of economic damage from future climate change
We construct projections of future climate damages by applying the coefficients estimated in equation ( 10 ) and shown in Supplementary Tables 2 – 4 (when including only lags with statistically significant effects in specifications that limit overfitting; see Supplementary Methods Section 1 ) to projections of future climate change from the CMIP-6 models. Year-on-year changes in each primary climate variable of interest are calculated to reflect the year-to-year variations used in the empirical models. 30-year moving averages of the moderating variables of the interaction terms are calculated to reflect the long-term average of climatic conditions that were used for the moderating variables in the empirical models. By using moving averages in the projections, we account for the changing vulnerability to climate shocks based on the evolving long-term conditions (Supplementary Figs. 10 and 11 show that the results are robust to the precise choice of the window of this moving average). Although these climate variables are not differenced, the fact that the bias-adjusted climate models reproduce observed climatological patterns across regions for these moderating variables very accurately (Supplementary Table 6 ) with limited spread across models (<3%) precludes the possibility that any considerable bias or uncertainty is introduced by this methodological choice. However, we impose caps on these moderating variables at the 95th percentile at which they were observed in the historical data to prevent extrapolation of the marginal effects outside the range in which the regressions were estimated. This is a conservative choice that limits the magnitude of our damage projections.
Time series of primary climate variables and moderating climate variables are then combined with estimates of the empirical model parameters to evaluate the regression coefficients in equation ( 10 ), producing a time series of annual GRPpc growth-rate reductions for a given emission scenario, climate model and set of empirical model parameters. The resulting time series of growth-rate impacts reflects those occurring owing to future climate change. By contrast, a future scenario with no climate change would be one in which climate variables do not change (other than with random year-to-year fluctuations) and hence the time-averaged evaluation of equation ( 10 ) would be zero. Our approach therefore implicitly compares the future climate-change scenario to this no-climate-change baseline scenario.
The time series of growth-rate impacts owing to future climate change in region r and year y , δ r , y , are then added to the future baseline growth rates, π r , y (in log-diff form), obtained from the SSP2 scenario to yield trajectories of damaged GRPpc growth rates, ρ r , y . These trajectories are aggregated over time to estimate the future trajectory of GRPpc with future climate impacts:
in which GRPpc r , y =2020 is the initial log level of GRPpc. We begin damage estimates in 2020 to reflect the damages occurring since the end of the period for which we estimate the empirical models (1979–2019) and to match the timing of mitigation-cost estimates from most IAMs (see below).
For each emission scenario, this procedure is repeated 1,000 times while randomly sampling from the selection of climate models, the selection of empirical models with different numbers of lags (shown in Supplementary Figs. 1 – 3 and Supplementary Tables 2 – 4 ) and bootstrapped estimates of the regression parameters. The result is an ensemble of future GRPpc trajectories that reflect uncertainty from both physical climate change and the structural and sampling uncertainty of the empirical models.
Estimates of mitigation costs
We obtain IPCC estimates of the aggregate costs of emission mitigation from the AR6 Scenario Explorer and Database hosted by IIASA 23 . Specifically, we search the AR6 Scenarios Database World v1.1 for IAMs that provided estimates of global GDP and population under both a SSP2 baseline and a SSP2-RCP2.6 scenario to maintain consistency with the socio-economic and emission scenarios of the climate damage projections. We find five IAMs that provide data for these scenarios, namely, MESSAGE-GLOBIOM 1.0, REMIND-MAgPIE 1.5, AIM/GCE 2.0, GCAM 4.2 and WITCH-GLOBIOM 3.1. Of these five IAMs, we use the results only from the first three that passed the IPCC vetting procedure for reproducing historical emission and climate trajectories. We then estimate global mitigation costs as the percentage difference in global per capita GDP between the SSP2 baseline and the SSP2-RCP2.6 emission scenario. In the case of one of these IAMs, estimates of mitigation costs begin in 2020, whereas in the case of two others, mitigation costs begin in 2010. The mitigation cost estimates before 2020 in these two IAMs are mostly negligible, and our choice to begin comparison with damage estimates in 2020 is conservative with respect to the relative weight of climate damages compared with mitigation costs for these two IAMs.
Data availability
Data on economic production and ERA-5 climate data are publicly available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4681306 (ref. 62 ) and https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/datasets/reanalysis-datasets/era5 , respectively. Data on mitigation costs are publicly available at https://data.ene.iiasa.ac.at/ar6/#/downloads . Processed climate and economic data, as well as all other necessary data for reproduction of the results, are available at the public repository https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10562951 (ref. 63 ).
Code availability
All code necessary for reproduction of the results is available at the public repository https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10562951 (ref. 63 ).
Glanemann, N., Willner, S. N. & Levermann, A. Paris Climate Agreement passes the cost-benefit test. Nat. Commun. 11 , 110 (2020).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Burke, M., Hsiang, S. M. & Miguel, E. Global non-linear effect of temperature on economic production. Nature 527 , 235–239 (2015).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Kalkuhl, M. & Wenz, L. The impact of climate conditions on economic production. Evidence from a global panel of regions. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 103 , 102360 (2020).
Article Google Scholar
Moore, F. C. & Diaz, D. B. Temperature impacts on economic growth warrant stringent mitigation policy. Nat. Clim. Change 5 , 127–131 (2015).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Drouet, L., Bosetti, V. & Tavoni, M. Net economic benefits of well-below 2°C scenarios and associated uncertainties. Oxf. Open Clim. Change 2 , kgac003 (2022).
Ueckerdt, F. et al. The economically optimal warming limit of the planet. Earth Syst. Dyn. 10 , 741–763 (2019).
Kotz, M., Wenz, L., Stechemesser, A., Kalkuhl, M. & Levermann, A. Day-to-day temperature variability reduces economic growth. Nat. Clim. Change 11 , 319–325 (2021).
Kotz, M., Levermann, A. & Wenz, L. The effect of rainfall changes on economic production. Nature 601 , 223–227 (2022).
Kousky, C. Informing climate adaptation: a review of the economic costs of natural disasters. Energy Econ. 46 , 576–592 (2014).
Harlan, S. L. et al. in Climate Change and Society: Sociological Perspectives (eds Dunlap, R. E. & Brulle, R. J.) 127–163 (Oxford Univ. Press, 2015).
Bolton, P. et al. The Green Swan (BIS Books, 2020).
Alogoskoufis, S. et al. ECB Economy-wide Climate Stress Test: Methodology and Results European Central Bank, 2021).
Weber, E. U. What shapes perceptions of climate change? Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Change 1 , 332–342 (2010).
Markowitz, E. M. & Shariff, A. F. Climate change and moral judgement. Nat. Clim. Change 2 , 243–247 (2012).
Riahi, K. et al. The shared socioeconomic pathways and their energy, land use, and greenhouse gas emissions implications: an overview. Glob. Environ. Change 42 , 153–168 (2017).
Auffhammer, M., Hsiang, S. M., Schlenker, W. & Sobel, A. Using weather data and climate model output in economic analyses of climate change. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 7 , 181–198 (2013).
Kolstad, C. D. & Moore, F. C. Estimating the economic impacts of climate change using weather observations. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 14 , 1–24 (2020).
Dell, M., Jones, B. F. & Olken, B. A. Temperature shocks and economic growth: evidence from the last half century. Am. Econ. J. Macroecon. 4 , 66–95 (2012).
Newell, R. G., Prest, B. C. & Sexton, S. E. The GDP-temperature relationship: implications for climate change damages. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 108 , 102445 (2021).
Kikstra, J. S. et al. The social cost of carbon dioxide under climate-economy feedbacks and temperature variability. Environ. Res. Lett. 16 , 094037 (2021).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar
Bastien-Olvera, B. & Moore, F. Persistent effect of temperature on GDP identified from lower frequency temperature variability. Environ. Res. Lett. 17 , 084038 (2022).
Eyring, V. et al. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 9 , 1937–1958 (2016).
Byers, E. et al. AR6 scenarios database. Zenodo https://zenodo.org/records/7197970 (2022).
Burke, M., Davis, W. M. & Diffenbaugh, N. S. Large potential reduction in economic damages under UN mitigation targets. Nature 557 , 549–553 (2018).
Kotz, M., Wenz, L. & Levermann, A. Footprint of greenhouse forcing in daily temperature variability. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 118 , e2103294118 (2021).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Myhre, G. et al. Frequency of extreme precipitation increases extensively with event rareness under global warming. Sci. Rep. 9 , 16063 (2019).
Min, S.-K., Zhang, X., Zwiers, F. W. & Hegerl, G. C. Human contribution to more-intense precipitation extremes. Nature 470 , 378–381 (2011).
England, M. R., Eisenman, I., Lutsko, N. J. & Wagner, T. J. The recent emergence of Arctic Amplification. Geophys. Res. Lett. 48 , e2021GL094086 (2021).
Fischer, E. M. & Knutti, R. Anthropogenic contribution to global occurrence of heavy-precipitation and high-temperature extremes. Nat. Clim. Change 5 , 560–564 (2015).
Pfahl, S., O’Gorman, P. A. & Fischer, E. M. Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation. Nat. Clim. Change 7 , 423–427 (2017).
Callahan, C. W. & Mankin, J. S. Globally unequal effect of extreme heat on economic growth. Sci. Adv. 8 , eadd3726 (2022).
Diffenbaugh, N. S. & Burke, M. Global warming has increased global economic inequality. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 116 , 9808–9813 (2019).
Callahan, C. W. & Mankin, J. S. National attribution of historical climate damages. Clim. Change 172 , 40 (2022).
Burke, M. & Tanutama, V. Climatic constraints on aggregate economic output. National Bureau of Economic Research, Working Paper 25779. https://doi.org/10.3386/w25779 (2019).
Kahn, M. E. et al. Long-term macroeconomic effects of climate change: a cross-country analysis. Energy Econ. 104 , 105624 (2021).
Desmet, K. et al. Evaluating the economic cost of coastal flooding. National Bureau of Economic Research, Working Paper 24918. https://doi.org/10.3386/w24918 (2018).
Hsiang, S. M. & Jina, A. S. The causal effect of environmental catastrophe on long-run economic growth: evidence from 6,700 cyclones. National Bureau of Economic Research, Working Paper 20352. https://doi.org/10.3386/w2035 (2014).
Ritchie, P. D. et al. Shifts in national land use and food production in Great Britain after a climate tipping point. Nat. Food 1 , 76–83 (2020).
Dietz, S., Rising, J., Stoerk, T. & Wagner, G. Economic impacts of tipping points in the climate system. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 118 , e2103081118 (2021).
Bastien-Olvera, B. A. & Moore, F. C. Use and non-use value of nature and the social cost of carbon. Nat. Sustain. 4 , 101–108 (2021).
Carleton, T. et al. Valuing the global mortality consequences of climate change accounting for adaptation costs and benefits. Q. J. Econ. 137 , 2037–2105 (2022).
Bastien-Olvera, B. A. et al. Unequal climate impacts on global values of natural capital. Nature 625 , 722–727 (2024).
Malik, A. et al. Impacts of climate change and extreme weather on food supply chains cascade across sectors and regions in Australia. Nat. Food 3 , 631–643 (2022).
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Kuhla, K., Willner, S. N., Otto, C., Geiger, T. & Levermann, A. Ripple resonance amplifies economic welfare loss from weather extremes. Environ. Res. Lett. 16 , 114010 (2021).
Schleypen, J. R., Mistry, M. N., Saeed, F. & Dasgupta, S. Sharing the burden: quantifying climate change spillovers in the European Union under the Paris Agreement. Spat. Econ. Anal. 17 , 67–82 (2022).
Dasgupta, S., Bosello, F., De Cian, E. & Mistry, M. Global temperature effects on economic activity and equity: a spatial analysis. European Institute on Economics and the Environment, Working Paper 22-1 (2022).
Neal, T. The importance of external weather effects in projecting the macroeconomic impacts of climate change. UNSW Economics Working Paper 2023-09 (2023).
Deryugina, T. & Hsiang, S. M. Does the environment still matter? Daily temperature and income in the United States. National Bureau of Economic Research, Working Paper 20750. https://doi.org/10.3386/w20750 (2014).
Hersbach, H. et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 146 , 1999–2049 (2020).
Cucchi, M. et al. WFDE5: bias-adjusted ERA5 reanalysis data for impact studies. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 12 , 2097–2120 (2020).
Adler, R. et al. The New Version 2.3 of the Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) Monthly Analysis Product 1072–1084 (University of Maryland, 2016).
Lange, S. Trend-preserving bias adjustment and statistical downscaling with ISIMIP3BASD (v1.0). Geosci. Model Dev. 12 , 3055–3070 (2019).
Wenz, L., Carr, R. D., Kögel, N., Kotz, M. & Kalkuhl, M. DOSE – global data set of reported sub-national economic output. Sci. Data 10 , 425 (2023).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gennaioli, N., La Porta, R., Lopez De Silanes, F. & Shleifer, A. Growth in regions. J. Econ. Growth 19 , 259–309 (2014).
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US). U.S. dollars to euro spot exchange rate. https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/AEXUSEU (2022).
World Bank. GDP deflator. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.DEFL.ZS (2022).
Jones, B. & O’Neill, B. C. Spatially explicit global population scenarios consistent with the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Environ. Res. Lett. 11 , 084003 (2016).
Murakami, D. & Yamagata, Y. Estimation of gridded population and GDP scenarios with spatially explicit statistical downscaling. Sustainability 11 , 2106 (2019).
Koch, J. & Leimbach, M. Update of SSP GDP projections: capturing recent changes in national accounting, PPP conversion and Covid 19 impacts. Ecol. Econ. 206 (2023).
Carleton, T. A. & Hsiang, S. M. Social and economic impacts of climate. Science 353 , aad9837 (2016).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bergé, L. Efficient estimation of maximum likelihood models with multiple fixed-effects: the R package FENmlm. DEM Discussion Paper Series 18-13 (2018).
Kalkuhl, M., Kotz, M. & Wenz, L. DOSE - The MCC-PIK Database Of Subnational Economic output. Zenodo https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.4681305 (2021).
Kotz, M., Wenz, L. & Levermann, A. Data and code for “The economic commitment of climate change”. Zenodo https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.10562951 (2024).
Dasgupta, S. et al. Effects of climate change on combined labour productivity and supply: an empirical, multi-model study. Lancet Planet. Health 5 , e455–e465 (2021).
Lobell, D. B. et al. The critical role of extreme heat for maize production in the United States. Nat. Clim. Change 3 , 497–501 (2013).
Zhao, C. et al. Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 114 , 9326–9331 (2017).
Wheeler, T. R., Craufurd, P. Q., Ellis, R. H., Porter, J. R. & Prasad, P. V. Temperature variability and the yield of annual crops. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 82 , 159–167 (2000).
Rowhani, P., Lobell, D. B., Linderman, M. & Ramankutty, N. Climate variability and crop production in Tanzania. Agric. For. Meteorol. 151 , 449–460 (2011).
Ceglar, A., Toreti, A., Lecerf, R., Van der Velde, M. & Dentener, F. Impact of meteorological drivers on regional inter-annual crop yield variability in France. Agric. For. Meteorol. 216 , 58–67 (2016).
Shi, L., Kloog, I., Zanobetti, A., Liu, P. & Schwartz, J. D. Impacts of temperature and its variability on mortality in New England. Nat. Clim. Change 5 , 988–991 (2015).
Xue, T., Zhu, T., Zheng, Y. & Zhang, Q. Declines in mental health associated with air pollution and temperature variability in China. Nat. Commun. 10 , 2165 (2019).
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Liang, X.-Z. et al. Determining climate effects on US total agricultural productivity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 114 , E2285–E2292 (2017).
Desbureaux, S. & Rodella, A.-S. Drought in the city: the economic impact of water scarcity in Latin American metropolitan areas. World Dev. 114 , 13–27 (2019).
Damania, R. The economics of water scarcity and variability. Oxf. Rev. Econ. Policy 36 , 24–44 (2020).
Davenport, F. V., Burke, M. & Diffenbaugh, N. S. Contribution of historical precipitation change to US flood damages. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 118 , e2017524118 (2021).
Dave, R., Subramanian, S. S. & Bhatia, U. Extreme precipitation induced concurrent events trigger prolonged disruptions in regional road networks. Environ. Res. Lett. 16 , 104050 (2021).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financing from the Volkswagen Foundation and the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH on behalf of the Government of the Federal Republic of Germany and Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ).
Open access funding provided by Potsdam-Institut für Klimafolgenforschung (PIK) e.V.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Research Domain IV, Research Domain IV, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Potsdam, Germany
Maximilian Kotz, Anders Levermann & Leonie Wenz
Institute of Physics, Potsdam University, Potsdam, Germany
Maximilian Kotz & Anders Levermann
Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change, Berlin, Germany
Leonie Wenz
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the design of the analysis. M.K. conducted the analysis and produced the figures. All authors contributed to the interpretation and presentation of the results. M.K. and L.W. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Leonie Wenz .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature thanks Xin-Zhong Liang, Chad Thackeray and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data figures and tables
Extended data fig. 1 constraining the persistence of historical climate impacts on economic growth rates..
The results of a panel-based fixed-effects distributed lag model for the effects of annual mean temperature ( a ), daily temperature variability ( b ), total annual precipitation ( c ), the number of wet days ( d ) and extreme daily precipitation ( e ) on sub-national economic growth rates. Point estimates show the effects of a 1 °C or one standard deviation increase (for temperature and precipitation variables, respectively) at the lower quartile, median and upper quartile of the relevant moderating variable (green, orange and purple, respectively) at different lagged periods after the initial shock (note that these are not cumulative effects). Climate variables are used in their first-differenced form (see main text for discussion) and the moderating climate variables are the annual mean temperature, seasonal temperature difference, total annual precipitation, number of wet days and annual mean temperature, respectively, in panels a – e (see Methods for further discussion). Error bars show the 95% confidence intervals having clustered standard errors by region. The within-region R 2 , Bayesian and Akaike information criteria for the model are shown at the top of the figure. This figure shows results with ten lags for each variable to demonstrate the observed levels of persistence, but our preferred specifications remove later lags based on the statistical significance of terms shown above and the information criteria shown in Extended Data Fig. 2 . The resulting models without later lags are shown in Supplementary Figs. 1 – 3 .
Extended Data Fig. 2 Incremental lag-selection procedure using information criteria and within-region R 2 .
Starting from a panel-based fixed-effects distributed lag model estimating the effects of climate on economic growth using the real historical data (as in equation ( 4 )) with ten lags for all climate variables (as shown in Extended Data Fig. 1 ), lags are incrementally removed for one climate variable at a time. The resulting Bayesian and Akaike information criteria are shown in a – e and f – j , respectively, and the within-region R 2 and number of observations in k – o and p – t , respectively. Different rows show the results when removing lags from different climate variables, ordered from top to bottom as annual mean temperature, daily temperature variability, total annual precipitation, the number of wet days and extreme annual precipitation. Information criteria show minima at approximately four lags for precipitation variables and ten to eight for temperature variables, indicating that including these numbers of lags does not lead to overfitting. See Supplementary Table 1 for an assessment using information criteria to determine whether including further climate variables causes overfitting.
Extended Data Fig. 3 Damages in our preferred specification that provides a robust lower bound on the persistence of climate impacts on economic growth versus damages in specifications of pure growth or pure level effects.
Estimates of future damages as shown in Fig. 1 but under the emission scenario RCP8.5 for three separate empirical specifications: in orange our preferred specification, which provides an empirical lower bound on the persistence of climate impacts on economic growth rates while avoiding assumptions of infinite persistence (see main text for further discussion); in purple a specification of ‘pure growth effects’ in which the first difference of climate variables is not taken and no lagged climate variables are included (the baseline specification of ref. 2 ); and in pink a specification of ‘pure level effects’ in which the first difference of climate variables is taken but no lagged terms are included.
Extended Data Fig. 4 Climate changes in different variables as a function of historical interannual variability.
Changes in each climate variable of interest from 1979–2019 to 2035–2065 under the high-emission scenario SSP5-RCP8.5, expressed as a percentage of the historical variability of each measure. Historical variability is estimated as the standard deviation of each detrended climate variable over the period 1979–2019 during which the empirical models were identified (detrending is appropriate because of the inclusion of region-specific linear time trends in the empirical models). See Supplementary Fig. 13 for changes expressed in standard units. Data on national administrative boundaries are obtained from the GADM database version 3.6 and are freely available for academic use ( https://gadm.org/ ).
Extended Data Fig. 5 Contribution of different climate variables to overall committed damages.
a , Climate damages in 2049 when using empirical models that account for all climate variables, changes in annual mean temperature only or changes in both annual mean temperature and one other climate variable (daily temperature variability, total annual precipitation, the number of wet days and extreme daily precipitation, respectively). b , The cumulative marginal effects of an increase in annual mean temperature of 1 °C, at different baseline temperatures, estimated from empirical models including all climate variables or annual mean temperature only. Estimates and uncertainty bars represent the median and 95% confidence intervals obtained from 1,000 block-bootstrap resamples from each of three different empirical models using eight, nine or ten lags of temperature terms.
Extended Data Fig. 6 The difference in committed damages between the upper and lower quartiles of countries when ranked by GDP and cumulative historical emissions.
Quartiles are defined using a population weighting, as are the average committed damages across each quartile group. The violin plots indicate the distribution of differences between quartiles across the two extreme emission scenarios (RCP2.6 and RCP8.5) and the uncertainty sampling procedure outlined in Methods , which accounts for uncertainty arising from the choice of lags in the empirical models, uncertainty in the empirical model parameter estimates, as well as the climate model projections. Bars indicate the median, as well as the 10th and 90th percentiles and upper and lower sixths of the distribution reflecting the very likely and likely ranges following the likelihood classification adopted by the IPCC.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, peer review file, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kotz, M., Levermann, A. & Wenz, L. The economic commitment of climate change. Nature 628 , 551–557 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07219-0
Download citation
Received : 25 January 2023
Accepted : 21 February 2024
Published : 17 April 2024
Issue Date : 18 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07219-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Human-Computer Interaction
Title: empirical research methods for human-computer interaction.
Abstract: Most attendees at CHI conferences will agree that an experiment (user study) is the hallmark of good research in human-computer interaction. But what constitutes an experiment? And how does one go from an experiment to a CHI paper? This course will teach how to pose testable research questions, how to make and measure observations, and how to design and conduct an experiment. Specifically, attendees will participate in a real experiment to gain experience as both an investigator and as a participant. The second session covers the statistical tools typically used to analyze data. Most notably, attendees will learn how to organize experiment results and write a CHI paper.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Types and methodologies of empirical research. Empirical research can be conducted and analysed using qualitative or quantitative methods. Quantitative research: Quantitative research methods are used to gather information through numerical data. It is used to quantify opinions, behaviors or other defined variables.
Empirical research is based on observed and measured phenomena and derives knowledge from actual experience rather than from theory or belief. ... to communicate empirical research findings. Such articles typically have 4 components: Introduction: sometimes called "literature review" -- what is currently known about the topic ...
A scientist gathering data for her research. Empirical research is research using empirical evidence.It is also a way of gaining knowledge by means of direct and indirect observation or experience. Empiricism values some research more than other kinds. Empirical evidence (the record of one's direct observations or experiences) can be analyzed quantitatively or qualitatively.
An empirical research article is a primary source where the authors reported on experiments or observations that they conducted. Their research includes their observed and measured data that they derived from an actual experiment rather than theory or belief. ... There are four main components: Introduction: aka "literature review". This ...
Another hint: some scholarly journals use a specific layout, called the "IMRaD" format, to communicate empirical research findings. Such articles typically have 4 components: Introduction: sometimes called "literature review" -- what is currently known about the topic -- usually includes a theoretical framework and/or discussion of previous studies
'Empirical Research' published in 'Encyclopedia of Psychology and Religion' During the seventeenth and the eighteenth centuries, thinkers such as David Hume and John Locke popularized and entrenched empiricism as a major core in philosophical investigation by applying the method in their philosophical inquiry (Matin 1968, pp. 33-47).They further posited that, "experience provides the marks ...
Identifying Empirical Research Articles. Look for the IMRaD layout in the article to help identify empirical research.Sometimes the sections will be labeled differently, but the content will be similar. Introduction: why the article was written, research question or questions, hypothesis, literature review; Methods: the overall research design and implementation, description of sample ...
Empirical research is characterized by several key features: Observation and Measurement: It involves the systematic observation or measurement of variables, events, or behaviors. Data Collection: Researchers collect data through various methods, such as surveys, experiments, observations, or interviews.
Another hint: some scholarly journals use a specific layout, called the "IMRaD" format, to communicate empirical research findings. Such articles typically have 4 components: Introduction: sometimes called "literature review" -- what is currently known about the topic -- usually includes a theoretical framework and/or discussion of previous studies
Description of the process used to study this population or phenomena, including selection criteria, controls, and testing instruments (such as surveys) Another hint: some scholarly journals use a specific layout, called the "IMRaD" format, to communicate empirical research findings. Such articles typically have 4 components:
Empirical research is a research method that investigators use to test knowledge claims and develop new knowledge.. Empirical methods focus on observation and experimentation.. Investigators observe and conduct experiments in systematic ways. is largely determined by their rhetorical contexts. Different workplace contexts and academic disciplines have developed unique tools and techniques for ...
Depending on your research and subject, some of the followings sub-headings within the Methods section can be used: Participants (or Subjects in animal research): Who participated in the study (include drop-out, return rates, and exclusion information), their key demographic information, and how they were selected/recruited and compensated.
Share this content. Empirical research is research that is based on observation and measurement of phenomena, as directly experienced by the researcher. The data thus gathered may be compared against a theory or hypothesis, but the results are still based on real life experience. The data gathered is all primary data, although secondary data ...
Using the example of students' electronic gadget addictions, design a hypothetical research project by identifying a plan for each of the nine components of research design that are presented in this section. 2.1.4: Components of a Research Project is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.
Description of the methodology or research design used to study this population or phenomena, including selection criteria, controls, and testing instruments (such as surveys); Two basic research processes or methods in empirical research: quantitative methods and qualitative methods (see the rest of the guide for more about these methods).
This page titled 1.2: Theory and Empirical Research is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Jenkins-Smith et al. (University of Oklahoma Libraries) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request.
The second one is empirical research where data are gathered via direct experience, observation, experimentation, interviews, and questionnaires—this type of research, therefore, uses mainly primary data. It is possible to conduct academic research, which is an amalgam of the two and, therefore, they are not watertight closed boxes.
Description of the process used to study this population or phenomena, including selection criteria, controls, and testing instruments (such as surveys) Another hint: some scholarly journals use a specific layout, called the "IMRaD" format, to communicate empirical research findings. Such articles typically have 4 components:
To recap, the three ingredients that need to be mixed into your literature review are: The foundation of theory or theoretical framework. The empirical or evidence-based research. The research gap. As we mentioned earlier, these are components of a literature review and not (necessarily) a structure for your literature review chapter.
The empirical research papers could have four components: 1- Introduction: sometimes called literature review - what is currently known about the topic -- usually includes a theoretical framework ...
Empirical Research Article Components of an Empirical Article When analyzing an empirical article, it is crucial to briefly review the abstract to comprehend the fundamental idea of the article. This includes understanding its primary focus, the individuals who participated in the study, the subject matter being investigated, and the ...
Components of empirical research . There are a few elements that all empirical studies contain: The research question, which can be obtained from previous experience, literature, or other similar studies - basically the objective of your study;; Research design based on the research question;; Research methodology, which refers to the method for data collection and analysis;
Non-cognitive factors, such as personal academic passion, have been shown in some empirical studies to significantly influence the development of research talent (H. D ... (2019). Components of positive research training environment: Qualitative research on the team of universities' major R&D projects. Journal of Beijing Institute of ...
Global projections of macroeconomic climate-change damages typically consider impacts from average annual and national temperatures over long time horizons1-6. Here we use recent empirical ...
The methods section is typically one of the most complex parts of an empirical research paper. Select an empirical article. What are the components included in the methods section? Why are the components different in the methods section of an empirical article and other types of research papers? Does a literature review have a methods section?
View a PDF of the paper titled Empirical research methods for human-computer interaction, by I. Scott MacKenzie and 2 other authors View PDF HTML (experimental) Abstract: Most attendees at CHI conferences will agree that an experiment (user study) is the hallmark of good research in human-computer interaction.
In terms of research samples and methods, this paper selects Chinese listed companies as research objects, and in the future, it can focus on specific industries (e.g., chemical industry, iron and steel industry, etc.) to carry out empirical evidence or case studies, to obtain more typical and targeted research results.