TATA Steel India: Corporate Social Responsibility Case Study Project
- First Online: 04 December 2021

Cite this chapter

- Kamal Singh 4 &
- Tamanna Girdhar 4
Part of the book series: CSR, Sustainability, Ethics & Governance ((CSEG))
432 Accesses
This case study project examines the various CSR interventions and initiatives of TATA Steel India and analyses their impact on the society and on different stakeholders. The paper defines and draws meaningful conclusions about a corporate’s responsibility towards society and how they have a major role to play in sustainable development. Previous research on CSR and India’s CSR Policy formed the stepping stone for the analysis and future scope of this project. The main aim of the project is to provide a detailed understanding of CSR by providing fruitful insights about the CSR policy and interventions of TATA Steel India.
Author Note: This chapter is an outcome of a Best Case Study Innovative Practices conducted by Global Compact India Network in 2019. Content has been used with permission from relevant authorities.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Brown, K. (2001). Corporate Social Responsibility: Perceptions of Indian Business. In M. Mehra (Ed.). Retrieved from www.csmworld.org/public/pdf/social_respons.Pdf .
Banerjee, P. K. (2003). Corporate governance & business ethics in the 21st century. ICFAI Journal of Corporate Governance, III (2).
Google Scholar
Chakrabarty, B. (2013). Corporate social responsibility: Implications for small and medium enterprises in developing countries. Report was prepared by Peter Raynard and Maya Forstater in cooperation with staff of UNIDO’s Small and Medium Enterprises Branch, 2002.
Grzyb, H. (2005). Corporate Social Responsibility starts at home: Comparisons of metropolitan and rural SMEs in Western Australia. International Journal of Organisational Behaviour, 12 (1), 88–109.
Hamidu, A., Haron, H., & Amran, A. (2015). Corporate social responsibility: A review on definitions, core characteristics and theoretical perspectives. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 6 , 83–95. https://doi.org/10.5901/mjss.2015.v6n4p83
Article Google Scholar
Höllerer, M. (2012). Corporate social responsibility (CSR). In Between creed, rhetoric façade, and disregard: dissemination and theorization of corporate social responsibility in Austria (pp. 29–66). Frankfurt am Main: Peter Lang AG. Retrieved August 20, 2020, from www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctv9hj7c3.7 .
Jenkins, H. (2006). Small business champions for corporate social responsibility. Journal of Business Ethics , no. 67, 241–256.
Lepourte, J., & Heene, A. (2006). Investigating the impact of firm size on small business social responsibility: A critical review. Journal of Business Ethics , no.67, 257–273.
Rahman, H., & Singh, R. (2019). An overview of CSR taken by TATA Group.
Web Resources
https://www.tatasteel.com/media/12381/tata-steel-ir.pdf .
https://www.mca.gov.in/Ministry/pdf/CSRHLC_13092019.pdf .
http://35.154.196.254/investors/annual-report-2015-16/html/corporate-social-responsibility-activities.html .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
UN Global Compact Network India, New Delhi, India
Kamal Singh & Tamanna Girdhar
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Tamanna Girdhar .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Indian Institute of Plantation Management, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Ananda Das Gupta
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Singh, K., Girdhar, T. (2022). TATA Steel India: Corporate Social Responsibility Case Study Project. In: Das Gupta, A. (eds) A Casebook of Strategic Corporate Social Responsibility. CSR, Sustainability, Ethics & Governance. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5719-1_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5719-1_6
Published : 04 December 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-16-5718-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-16-5719-1
eBook Packages : Religion and Philosophy Philosophy and Religion (R0)

Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, collaborative corporate social responsibility praxis: case studies from india.
Social Responsibility Journal
ISSN : 1747-1117
Article publication date: 25 March 2022
Issue publication date: 26 January 2023
This study aims to explore how corporate social responsibility (CSR) has assumed a new meaning today, with the COVID-19 pandemic. This, in turn, has changed the way companies now view the impact of their activities on the environment, customers, employees, community and other stakeholders.
Design/methodology/approach
This paper uses a qualitative case study approach and draws a critical lens to document the complex interplay between dimensions of CSR, business sustainability and social issues, applying theoretical tools such as social capital theory and stakeholder theory to elucidate the nature of collaborative managerial responses to the organisation’s challenges during the pandemic. This is a case study paper. This paper applies multi method approach to develop a case study analysis through participant observation and report analysis to investigate the CSR approaches undertaken in India by Infosys Genesis, a global leader in technology services and consulting, and Akshaya Patra Foundation, a non-governmental organisation (NGO), which operates the world’s largest lunch school program. This was an appropriate methodology since the focus was on an area that was little understood, while the analysis required an in-depth understanding of a complex phenomenon through observation and a case study. In addition, case study research has been recommended for how, why and what type of research questions that focus on contemporary events (Saunders et al. , 2003; Yin, 1994), such as CSR participation in the existing business environment. Furthermore, the issue under investigation is a real-life situation where the limitations between the phenomenon and the body of knowledge are unclear (Yin, 1994). This was the case because CSR has been probed by numerous disciplines through the application of various theoretical frameworks, each interpreting the context from their own perspective. Leximancer was used for the analysis (a text-mining software for visualising the structure of concepts and themes across case studies). This process differs from the traditional content analysis in that specific word strings are not needed; instead, Leximancer recognises what concepts are present in a set of texts, permitting concepts to be automatically coded in a grounded fashion (Cretchley et al. , 2010, p. 2). The paper will be looked at from three levels comprising themes, concepts and concept profiling to create rich and reliable dimensions of a theoretical model (Myers, 2008). The themes are created in Leximancer software and are built on an algorithm that looks for hidden repeated patterns in interactions. The concepts add a layer and discover which concepts are shared by actors. The concept profiling allows to discover additional concepts and allows to do a discriminant analysis on prior concepts (Cretchley et al. , 2010). Words that come up frequently are treated as concepts. Although the limited number of cases does not represent the entire sector, it enabled collection of rich data through quotes revealing some of the most crucial aspects of large organisations and non-profits in India.
The findings demonstrate how these robust, innovative, collaborative CSR initiatives between a multinational firm and an NGO have been leveraged to combat manifold issues of education, employment and hunger during the pandemic.
Research limitations/implications
Despite significant implications, this study has limitations. A response from only two companies is investigated to the COVID-19 pandemic. The scope of this study is only India, a developing nation, thereby, cross country research is recommended. A comparative study between developed and developing countries may be conducted. A quantitative approach may be used to get empirical findings of the COVID-19 pandemic and post-pandemic policies of companies from an international perspective. Hence, there is ample opportunity to research organisations’ response to the pandemic and CSR as a strong arm to deal with critical disasters.
Practical implications
The paper offers new insights into exploring research and praxis agenda for collaborative potentials towards the evolution of CSR and sustainability.
Social implications
The findings develop new initiatives and combat manifold issues of education, employment and hunger during the pandemic to provide quick relief.
Originality/value
The paper offers new insights into how companies are considering issues related to the crisis, including avoidance of layoffs and maintaining wage payments, and may be in a better position to access fresh capital, relief programs and emergency funds. Taking proactive health and safety measures may avert legal risks to the company. It is likely that the way in which companies are responding to the crises is a real-life test on resilience and adaptation.
- Qualitative case study
- Corporate social responsibility
- Business sustainability
- Collaborative CSR
- Indian MNCs and NGOs
Chavan, M. , Gowan, S. and Vogeley, J. (2023), "Collaborative corporate social responsibility praxis: case studies from India", Social Responsibility Journal , Vol. 19 No. 2, pp. 229-248. https://doi.org/10.1108/SRJ-06-2021-0216
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2022, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
MINISTRY OF COAL YEAR END REVIEW 2023 India’s Coal Sector Achieves Record Growth among Eight Core Industries in 2023 Coal Sector giving further fillip to Economic Growth; Production likely to cross One Billion Tonne in 2023-2024 Achieved 664.37 Million Tonne Coal Production during FY 2023-24 up to 25th December 31 Mines of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Telangana offered under 9th Round of Commercial Coal Mine Auction Series of Policy Initiatives & Reforms undertaken by Coal Ministry in 2023 31 First Mile Connectivity Projects Commissioned; Four Railways Projects Commissioned for faster Coal Movement For More Efficient Coal Movement Focus on Rail- Sea-Rail Transportation Coal India Ltd taken up major projects under Corporate Social Responsibility in 2023
“ Commercial coal mining is a win- win situation for stakeholders. The industries, businesses, investments will get new resources and markets. State governments will get more revenue and a huge population of the country will get employment. It means, there will be a positive impact on every sector” - Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi
The above words of the Prime Minister aptly sums up the strategic importance of India’s Coal Sector. Relentless efforts by the Coal Ministry to ensure energy security of the nation by record increase in coal production and supply to the thermal power plants provided a special place to India’s coal sector among the core industries of the country during the year 2023. In October 2023, among eight core industries, India’s coal sector achieved a remarkable 18.4% growth, as per Core Industries Performance Index released by the Ministry of Commerce & Industries.
The Ministry of Coal has played a pivotal role in driving the above growth through various innovative reforms. These initiatives include augmenting domestic coal production, stepping up commercial coal mine auction, engaging Mine Developer cum Operators (MDOs) to ramp up domestic output and reopening of discontinued mines on a revenue-sharing model to boost production.
On 21 st December, Union Minister of Coal, Mines & Parliamentary Affairs Shri Pralhad Joshi launched the 9 th round of commercial auction. A total of 31 coal mines, including 26 under the 9 th round and 5 under the 2 nd attempt of the 7 th round, were offered in the 9 th round. These mines are spread across coal/lignite-bearing states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Telangana.

Domestic coal production is very likely to cross One Billion tonne in 2023-2024. As per the latest statistics, coal production touched 664.37 million tonne during FY 2023-24 up to 25 th December. With 8.39% growth, coal dispatch to power sector during this period also touched 577.11 million tonne. Hence, the present growth of India’s coal sector aligns well with the vision of " Atmanirbhar Bharat " and contributes considerably to the nation's progress towards self-sufficiency and energy security.
Consistent efforts by the Ministry of Coal in tandem with other ministries also ensured enhanced rake availability for seamless transportation of coal during 2023. During the year, the Ministry has ensured adequate availability of quality coal to Thermal Power Plants and other crucial sectors of the economy, giving further fillip to the success saga of India’s economic growth.
The noteworthy achievements of the Ministry during 2023 is also marked by a number of reforms/policy measures centred around further enhancing overall coal production and supply, special focus on environment -friendly Underground Coal production, curtail import to the very minimum, coal gasification projects, successful commercial coal mine auction and sustainable mining practices.
Further details of the reforms and policy measures put in place by the Ministry of Coal during 2023 in line with ensuring energy security and sustainable mining practices can be summed up as follows:-
1. REFORMS & POLICY
1.1. Coal Linkage Policy implementation
- Policy for Auction of Coal Linkages to Non-Regulated Sector:
During Calendar Year 2023 ( upto November, 2023) under the NRS e-auction 24.23 MT was booked against the total offered quantity of 30.37 MT.
- Scheme for Harnessing and Allocating Koyala (Coal) Transparently in India (SHAKTI) Policy:
- Five tranches of Linkage Auction have been conducted by Coal India Limited from January to November 2023. Out of total offered quantity of 35.53 MT of coal, 27.99 MT of coal have been booked by successful bidders.
- Coal linkages granted to 11 central/state Gencos under for a capacity of 13420 MW from January to November 2023.
- Fourth round of linkage auction conducted by CIL during the period of January to November 2023. Out of total offered quantity of 8.10 MT of coal, 4.30 MT of coal was booked by successful bidders.
1.2. Land Acquisition
The land acquired u/s 9(1) and vested u/s 11 of the Coal Bearing Areas (Acquisition and Development) Act, 1957 for subsidiaries of Coal India Limited
“During the period from 01.01.2023 to 20.12.2023, a total of 9695.7215 acres of land have been acquired under section 9 (1) of the Coal Bearing Areas (Acquisition and Development) Act, 1957 for subsidiaries of Coal India Limited. A total of 4052.041 acres of land have been vested to subsidiaries of CIL under section 11(1) of the CBA (A&D) Act, 1957”.
ii) Details of land acquired by various subsidiaries of Coal India Limited under various Acts (i.e., CBA Act, RFCTLARR, Act (erstwhile LA Act, 1894) and through agreement, etc., which is uploaded on PM Gatishakti Portal total land as on 05.12.2023, are given below:-
1.3. Coal Mines (Special Provision) Rules, 2014
Coal Mines (Special Provision) Rules, 2014 have been amended and notified on 29.05.2023 incorporating additional provision for accepting the bid security in the form of online deposit.
1.4. The Coal Blocks Allocation Rules, 2017
Coal Blocks Allocation Rules, 2017 was amended through the Coal Blocks Allocation (Amendment) Rules, 2023 notified on 29.05.2023 which allows additional provision for accepting the bid security in the form of online deposit.
1.5. Guidelines on “Safety and Health Management Audit in Coal and Lignite Mines”
The focus of the safety health management system audit is a system driven, instead of individual-driven and based on the principles of risk management in place of compliance-oriented, that is, identification of hazards and assessment of risk and implementation of control to ensure risk at an acceptable level and as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA).
One of the reasons for the ineffective implementation of the present system of risk-based safety management in Indian coal mines is the lack of suitable mechanisms or processes for auditing the SMPs at regular intervals. In view of the above, Ministry of Coal issued guidelines for regular auditing to be adopted by the mine management on 14 th December 2023 for effective implementation of the Safety and Health Management system. The auditing shall be done by qualified auditors who are experienced in SHMS having domain knowledge and experience .
1.6 Amendment in timeline in CIMS Portal
After stakeholder consultations on functioning of CIMS portal and other related issues, an amendment was effected in the timeline of registration in CIMS portal. The importer can apply for registration not earlier than 60th day and till the arrival date (Zeroth Day) of consignment. The Automatic Registration Number shall remain valid for a period of 75 days. Importer shall have to enter the Registration Number and expiry date of Registration in the Bill of Entry to enable Customs for clearance of consignment.
1.7 Reforms in Coal Mines Provident Fund Organisation (CMPFO)
- Cadre Restructuring of CMPFO - Cadre Restructuring of CMPFO with a total of 934 posts has been approved by Ministry of Finance (DoE) on 26.10.2023.
- Digitization process in CMPFO - Digitization process has been initiated in CMPFO after a long time. So far, out of three phases of digitization, the Phase-I i.e. subscribers portal has been completed and employees are viewing their personal and ledger card details. Integration with the coal companies and online settlement process of claims for payment of PF and pension is covered under Phase-II which is likely to completed by December 2023. Phase-III will cover analytics and report generation process which is likely to be completed by April, 2024.
- e-office in CMPFO - e-office in CMPFO has been made operational in CMPFO since July, 2023.
2. COAL PRODUCTION/SUPPLY
2.1. Coal Production:
- The country has witnessed the highest ever coal production in the Year 2022-23. The all-India coal production in the year 2022-23 was 893.19 Million Tonne (MT) (Provisional) in comparison to 778.21 MT in the year 2021-22 with a growth of about 14.77%.
- During Calendar Year 2023 (upto 20 th December, 2023), the country has produced about 932.92 MT(Provisional) of coal as compared to about 864.25 MT(Provisional) coal during the same period of last year with a growth of about 7.95%.
2.2. Coal Supplies:
- During Calendar Year 2023 (upto 20 December, 2023), the country has supplied about 918.62 MT(Provisional) of coal as compared to about 860.19 MT(Provisional) coal during the same period of last year with a growth of about 6.79%.
- During Calendar Year 2023 (upto 20 December, 2023), the coal supply to Power Sector was 764.57 MT(Provisional) as compared to 732.88 MT coal during the same period of last year with a growth of 4.32%.
- During Calendar Year 2023 (upto 20 December, 2023), the coal supply to Non-Regulated Sector (NRS) was 154.05 MT(Provisional) as compared to 127.31 MT during the same period of last year with a growth of 21.00%.
2.3. Mission Coking Coal
With transformative measures taken by Ministry of Coal under ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative of PM, domestic raw Coking Coal production is likely to reach 140 MT by 2030, CIL has planned to increase raw coking coal production from existing mines up to 26 MT and identified ten new mines with PRC of about 22 MT by FY 2025. Also, CIL has offered eight discontinued coking coal mines on a innovative model of revenue sharing to the private sector with a PRC of 2 MT. LOA issued for 6 nos, out of which, Agreement has been signed for 3 nos.
To further enhance raw coking coal production, the Ministry of Coal has auctioned 16 coking coal blocks to the private sector with a PRC of 25 MT during the last two years. Most of these blocks are expected to start production by 2025. The Ministry has also identified four coking coal blocks and the Central Mine Planning and Design Institute (CMPDI) also will finalize GR for 4 to 6 new coking coal blocks in. These blocks may be offered in subsequent rounds of auction for private sector to further step up domestic raw coking coal supply in the country.
2.4 Setting up of Washeries
At present, domestic raw coking coal washing capacity is about 23 MT per annum including 9.26 MT of the private sector. Coal India Ltd. (CIL) is planning to set up and operationalize 9 more new washeries with a capacity of 26.5 MTPA. With setting up of new washeries, it is estimated that CIL will be able to supply about 15 MT of washed coking coal to the steel sector, thereby reducing import of coking coal. During FY 23, CIL supplied 2.15 MT washed coking coal to the steel sector and has set a target of 3.45 MT during FY24. Status of 11 Coking Coal Washeries-
• Two Coking Coal washeries are constructed and operational
• One washery commissioned
• Two under construction
• LoI/WO issued for Four washeries
• Two Washeries are to be tendered.
Additionally, 1 Non-coking Coal Washery is commissioned.
3. INFRASTRUCTURE PROJECTS
3.1. First Mile Connectivity [FMC]
Ministry of Coal takes up 103 First Mile connectivity Projects having capacity 1040 MT for seamless evacuation of coal- 31 Projects (29-CIL & 2-SCCL) of 291MTPA capacity have been commissioned.
To strengthen India’s energy security and to realize AtmaNirbhar Bharat by replacing imported coal with domestically mined coal, Ministry of Coal has set a target to produce 1.31BT in FY25 and 1.5BT in FY30. Development of coal transportation that is cost efficient, fast and environmental friendly manner is important goal of the country.
Keeping in view of increase in coal evacuation in future, Ministry of Coal is working on the development of National Coal Logistic Plan including First Mile Connectivity through railway sidings near coal mines and strengthening of Rail Network in Coalfields.
MOC has formulated a strategy to develop an integrated approach for eliminating road transportation of coal in mines and has taken steps to upgrade the mechanized coal transportation and loading system under 'First Mile Connectivity' projects. Coal Handling Plants (CHPs) and SILOs with Rapid Loading Systems will have benefits like crushing, sizing of coal and speedy computer aided loading.
MOC has undertaken 103 first mile connectivity (FMC) projects (95 – CIL, 5- SCCL & 3 – NLCIL) of 1040 MTPA capacity, out of which 31Projects (29-CIL & 2-SCCL) of 291 MTPA capacity have been commissioned. Remaining projects are to be implemented by FY2027-28
Study was undertaken through National Environmental Research Institute (NEERI), Nagpur in 2020-21. NEERI Report has established yearly carbon emissions saving, reduction in truck movement density and diesel savings of Rs 2100 cr/year for 35 projects
With reduced manual intervention, precise pre-weighed quantity and better quality of coal can be loaded. Improved loading time will bring down the wagon idling increasing their availability. Easing the load on road networks promotes cleaner environment and savings on diesel. It will be an all-round win-win situation for the company, railways and the consumers.
3.2. Initiatives under PM Gati Shakti
The Ministry of Coal, in view of cleaner environment in coal transportation has given momentum in rail evacuation and also initiating news efforts to gradually move away from road movement of coal in country. Planned construction of new broad gauge rail lines in Greenfield coal bearing areas, extending the rail links to newer loading points and doubling and tripling the rail lines in some cases will enhance rail capacity considerably.
PM launched Gati Shakti- Nation Master Plan for Infrastructure development in October 2021 with the objective to bring different Ministries together and for integrated planning and coordinated implementation of infrastructure connectivity Projects. It will incorporate the infrastructure schemes of various Ministries and State Governments and will also leverage technology extensively including spatial planning tools.
MoC has identified more than 100 layers and mapped on portal along with attributes and metadata. These data layers are being continuously monitored depending on the requirements and further layers along with their attributes may be added as and when required MoC and CMPDI is in constant touch with BISAG-N for taking immediate action on uploading of data layers
This layers will Speed ups the process of Planning by consideration of all requirements related to Ministries during the planning and execution stage in projects.
MoC on-boarded following layers on portal
a) More than 100 data layers mapped along with attributes and Metadata.
b) 51 layers are under construction
c) 24 layers are proposed to be added on portal.
East Zonal Conference
The Ministry of Coal has organized East Zonal Conference at Bhuvneshwar, Odisha on 16.2.2023 to address queries raised by Zones/States on National Logistic Policy including states-Odisha, Jharkhand, West Bengal & Bihar.
The conference aimed to bring efficiency in production and allocation of coal in Eastern Zonal States. Ministry has focused on discussion on coal logistic with special focus on digitization of difference systems. There was in-depth interaction leading to working together with national perspective among all the stake holders. The conference was attended by officials of East zonal states and different Ministries like Coal, Railways, Power, Steel, Fertilizers & Chemicals, MORTH, Shipping port & waterways along with Industries representative of East Zone.

3.3. Railway Projects Commissioned during 2023
- Bhadrachalam Road-Sattupalli New BG rail Line: 54 Km length new rail to facilitate unconnected areas of Telangana and coal transportation.
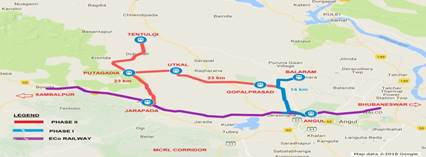
- Angul — Balaram — Putagadia — Jarapada along with the link from Putagadia to Tentuloi(68 Km) (MCRL Rail Corridor in Odisha): This rail line will provide proximity to Talcher coalfields to nearby Paradip and Damra port and make it amenable to provide cheaper and alternative means of coal supply to distant location on east and west coast power plants and other users through sea route and ships relieving the existing congestion in upcoming rail routes.
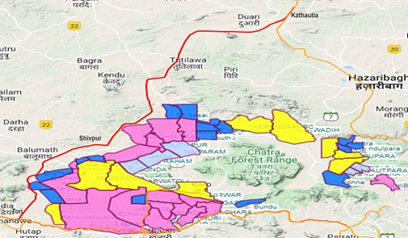
- Tori-Shivpur-Kathautia Railway Line: This new rail line of 49km, shall provide coal evacuation capacity of about 125 MT by rail and play major role in eliminating coal transportation by road via Koderma, Jharkhand to the trunk railway line from Howrah to Delhi.
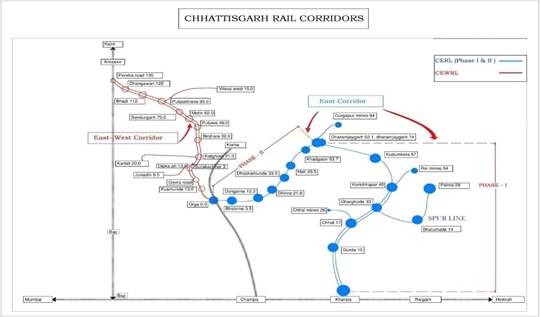
- CERL ( Kharsia-Dharamjaygarh Rail Link) Phase-I:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 14 th September 2023 dedicated to the nation South Eastern Coalfields Limited's (SECL) East Rail Corridor Phase-1, built at a cost of approximately ₹ 3,055 crore, at Raigarh, Chhattisgarh.
This 124 km track length line between Kharsia and Dharamjaygarh will help in transporting coal and other raw materials to various end-use projects including power generation projects from coal mines of SECL and other coal mines of Mand-Raigad Coalfield spread in Raigarh district, added the statement from PRO.
The annual capacity of the project is 62 million tonnes per year. In future, with the development of passenger transport facilities, people of this tribal-domina.
3.4 Coastal Shipping of Coal
The Ministry of Coal has taken an initiative to promote Rail-Sea-Rail which aims to integrate Rail-Sea-Rail (RSR) transportation for the efficient movement of domestic coal. This multimodal transportation system allows for the seamless transportation of coal from mines to ports and then to end-users, reducing transportation costs and improving logistic efficiency.
In the financial year FY’23, the major coal-producing states such as Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, along with parts of Madhya Pradesh, accounted for approximately 75% of the total domestic raw coal despatch. Recognizing the need to increased coal production, the Ministry of Coal has projected nearly doubling of coal production in India with a CAGR of ~7.7% by FY’ 30.

The coastal shipping mode of transportation, which is an economical and eco-friendly system for moving goods, has the potential to revolutionize India's logistics industry. The ongoing efforts to augment coal evacuation such as RS/RSR, strives to achieve full capacity utilization of the ports along the Southern and Western coasts. This will enable efficient transportation of more coal to power houses in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Andhra Pradesh. Initiatives are underway to optimise the costs of delivering coal through RSR. Opting for Rail-Sea-Rail could potentially save around Rs. 760-1300 per ton in logistics costs for end users located in Southern India. Presently, for supply of Coal from MCL (Paradip) to Western/Northern TPPs the total cost increases by around Rs 2500/ton over ARR but still it is cheaper than the total landed cost of imported coal.
The Ministry of Coal's efforts to promote Rail-Sea-Rail are yielding significant results as Rail-Sea-Rail transportation of coal has significant growth of around 125% over the past four years. With coal production in India expected to nearly double in the next seven years, the Rail Sea Rail as an alternative mode of transportation, becomes crucial for efficient Coal evacuation to consumption centres in India, ensuring a seamless and uninterrupted power supply.
4. COAL BLOCK ALLOCATION
4.1. Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957
Under the provisions of Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 and the Rules made thereunder, 34 coal blocks have been successfully auctioned.
4.2. Commercial Mining
Commercial Coal Mining : -
To reduce import of coal and to promote domestic production, auction-based regime introduced in 2014 allowed private sector participation, however, it was limited to captive usage in own end use plants. The sector has been opened up for commercial coal mining by private players in 2020 and first ever successful auction of commercial mining was launched by the Prime Minister on 18.06.2020 and concluded with allocation of 20 coal mines
- As of now total 91 coal mines have successfully been auctioned under commercial mining having Peak Rated Capacity (PRC) of ~220.90 MTPA. Once fully operational these mines will generate employment potential of about 2, 98,650 persons and would attract capital investment of more than Rs. 33,100 Crores.
- Further, Ministry of Coal has also launched the auction process of 8 th round offering 39 coal mines on Nov 15 2023 and 9 th round offering 31 coal mines on Dec 2023
- In Calendar Year 2023 Vesting Orders have been issued for 36 coal mines and Coal Mining Development and Production Agreement ( CMDPAs) have been signed for 37 coal mines.
5. ASSET MONETIZATION
In the year 2022-2023 against the NITI Aayog Target of ₹30000 crore Ministry of Coal achieved ₹ 57179.99 crore.
Status of Asset Monetization in FY 2023-24 till November 2023 against NITI Aayog Target of ₹ 50118 crore is as follows:
Ministry of Coal achieved Capex Target for the FY 2022-23 of Rs. 23400.22 Cr which is 109.24% of the annual capex target. Detail of Capex Achieved in FY 2022-23 and in FY 2023-24 till November 2023 is given below:
6. CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSBILITY
6.1. Corporate Social Responsibility
CSR Expenditure
As part of CSR, SCCL spend Rs.13.44 Cr. on CSR activities in 2023 for development of nearby villages, towns, environment measures etc. Compare to Rs. 11.39 crs during the same period last year.
CIL spent Rs. 517.93 cr. on a consolidated basis during FY 22-23 which was 17% more than the statutory requirement. For the ongoing financial year i.e. FY 23-24, the statutory target is Rs. 428.20 cr. 62% of which i.e. Rs. 264.37 cr. have been utilized upto 18.12.2023. On a consolidated basis, CIL has been one of the top ten corporate spenders in the country.
Major projects taken up during the year
- Replicating successful schemes such as ‘CCL Ke Laal/Laadli’ in other subsidiaries such as TARASH Super 30 in WCL for JEE & NEET coaching and SECL Ke Sushrut in SECL for NEET coaching. Under these schemes, free residential coaching is provided to meritorious underprivileged students for engineering/medical entrance examinations.
- Construction of women’s hostels at National Institute of Technology (NIT), Rourkela and Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Bombay
- Establishment of centralized kitchen in Ramgarh, Jharkhand for providing mid-day meals to 50,000 students
- Providing MRI machine for neurological treatment in Kolkata, West Bengal
- Construction of 5,000 seater library in Ranchi, Jharkhand
- Commencement of 3 rd phase of Thalassemia Bal Sewa Yojana. Under this scheme, financial assistance of upto Rs. 10 lakhs is provided for Bone Marrow Transplants (BMTs) of Thalassemia and Aplastic Anemia patients in eleven major hospitals of the country. The processing of cases is through a portal which was also launched along with the 3 rd phase of the scheme.
Skill Development
During FY 22-23, CIL on a consolidated basis covered 11,816 persons under its skilling/livelihood activities. For FY 23-24, the skilling/livelihood enhancement coverage target has been set at 8,000 persons.
Major events/happenings
- Inauguration of 500 bedded medical college and Hospital constructed by MCL at Talcher, Angul district, Odisha at a cost of Rs. 493 cr.
- Reaching the milestone of 400 beneficiaries by Thalassemia Bal Sewa Yojana, which was celebrated at Narayana Hrudyalaya Bengaluru
6.2 Mission Mode Recruitment
5910 appointment letters for various posts (CIL-5091 & NLCIL- 819) were issued under Mission Mode Recruitment upto November 2023.
7. SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT & JUST TRANSITION
- During January 2023 to November, 2023, Coal/Lignite PSUs planted 53.48 lakh saplings on 2,711 Ha.
- Coal/Lignite PSUs achieved a cumulative plantation area of 10,735 Ha with 234.52 lakh saplings since FY 2019-20 and doubled the target/achievement of plantation since 2019.
- In adherence to Accredited Compensatory Afforestation (ACA) guidelines, 3003 Ha of de-coaled afforested land have been identified to create ACA land bank for future coal mining projects.

Green cover on reclaimed OB dump of JVR OC-II of SCCL
- Ministry of Coal and Coal/Lignite PSUs have prioritized the development of eco- parks and tourism sites to promote mine tourism.
- During January 2023 to November, 2023, Coal/Lignite PSUs developed 4 Eco-park/Mine Tourism sites.
- From FY 2019-20 to FY 2023-24 (as of November, 2023), Coal/Lignite PSUs have successfully established 15 Eco-Parks & Mine Tourism sites, with 7 sites integrated into the local tourism circuit, emphasizing a commitment to sustainable and accessible mine tourism experiences.
- It is also planned to develop 19 new Eco-Parks/Tourism sites in coal mining areas.

Chandra Sekhar Azad Eco- Park at Bina Project, NCL
- Mine water is crucial for diverse community needs such as domestic use, irrigation, groundwater recharge, and industrial applications.
- During January 2023 to November, 2023, 2,513 LKL volume of treated mine water has been supplied for community purposes of which 1,193 LKL has been supplied for drinking purpose and 2,320 LKL has been supplied for irrigation purposes.
- Between FY 2018-19 and FY 2023-24 (as on November, 2023), Coal/Lignite PSUs have supplied a cumulative volume of around 18,582 Lakh Kilo Liters (LKL) of treated mine water for community purposes, benefiting annually approximately 17.70 lakh people in 981 villages across 9 states, showcasing the vital role of mine water in promoting community welfare and sustainable development.

Mine Water Treatment Plant at ECL
- To promote Circular Economy (Waste to Wealth in Coal Sector), during January 2023 to November 2023, 2 numbers of OB to M-sand Plants have been commissioned by Coal/Lignite PSUs making it a total of 4 OB Processing Plants and 5 OB to M-sand Plants till November, 2023.
- 6 more such plants are under various stages of development.

Overburden to M-Sand Plant at Amlohri Plant at NCL
- Efficient use of energy resources and their conservation assume tremendous significance as one unit of energy saved at the consumption level ultimately translates into equivalent reduction of carbon footprint.
- Coal/lignite PSUs have taken of various energy conservation and efficiency measures during January 2023 to November 2023, such as replacement of 1.50 lakh conventional lights with LED lights, 2,562 energy efficient ACs, 45,325 Super Fans, deployment of 136 E-vehicles, 655 Efficient Water Heaters, 235 Energy Efficient Motors for Pumps, 624 Auto-timer in street lights and installation of Capacitor Banks.
8. OTHER ACTIVITIES
8.1. Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav
"Meri Maati Mera Desh", with the tagline `Mitti ko naman, veeron ka vandan`, is a nationwide and people led “Jan bhagidari” initiative to commemorate 75 years of India's independence. "Meri Maati Mera Desh” is the finale of Azaadi ka Amrit Mahotsav program to celebrate many achievements of the nation. It involves paying tribute to the 'Veers' who protect our nation. At Ministry of Coal, ceremonies were conducted at the level of village, Panchayat, Block, Urban Local body, State and National level with a motive to affirm our bond to the nourishing earth and honor our braves with the following simple actions:
- Dedication of Shilaphalakam-installation of nameplate of Veers.
- Taking the Panch Pran Pledge.
- Vasudha Vandan—creation of Amrit Vatika with 75 saplings of indigenous tree.
- Veeron Ka Vandan- honoring freedom fighters/braves who protect the nation and families of braves.
- Hoisting of National Flag and singing of National Anthem.
Mitti from the villages of India was collected at block level and then finally brought to the Capital along with volunteers from each block that would assemble at Kartavya Path. An Amrit Vatika would be planted in the Capital and the Prime Minister would administer the Panch Pran pledge to volunteers. As per the schedule prescribed, the level 1 (Village level) was completed during the period 1st September to 30th September 2023. During the said period, following activities/programmes were done by all Coal PSU in respective subsidiaries spread across the country.
- Collection of soil or rice in Amrit Kalash from houses in every village in a festive environment.
- During the collection of soil and rice in Amrit Kalash the group was accompanied by the people playing Dholaks, Nagadas.
- Panch Pran pledge was taken at time of soil and rice collection.
A total of 956 Kalash were collected from 21 districts by organizing Amrit Kalash yatras. Around 1 Lakh people participated in the yatras organized by the Coal Companies of Ministry of Coal at various urban blocks and villages.

8.2. Special Campaign for disposal of pendencies 3.0
In line with Government of India’s vision for enhancing operational efficiency, the Ministry of Coal conducted Special Campaign 3.0 from 2nd October 2023 to 31st October 2023 with resounding success. This focused initiative aimed at institutionalizing cleanliness and streamlining processes to mitigate pending matters. The Ministry achieved noteworthy success of effectively addressing public grievances leading to more public interface, references from Members of Parliament, and Parliament Assurances. A comprehensive Cleanliness drive, coupled with the meticulous disposal of scrap and the systematic weeding out of files, constituted the multifaceted approach.
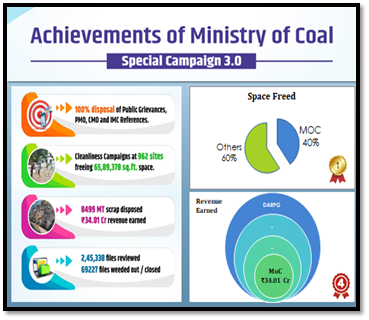
The Ministry of Coal has completed the Special Campaign 3.0 with remarkable success. The achievements of the Ministry during the Special Campaign 3.0 are as under:
- 100% target achieved in disposal of Public Grievances, PMO References, CMO References and IMC.
- 65,89,378 sq.ft. space was freed. Ministry of Coal is in the top position under the 'Space Freed' Category amongst all Ministries/Departments in the Government of India.
- Cleanliness Campaigns were conducted at 962 sites, against the initial target of 763 sites identified during the Preparatory phase, by the Ministry and its CPSEs.
- Revenue of Rs.34.01Cr. earned through disposal of 8499 MT scrap. MoC is at 4th position in the category of 'Revenue earned from Scrap' amongst all Ministries/Departments in the Government of India.
- 1, 39,969 physical files and 1,05,369 e-files were reviewed and total of 69,227 files were weeded out/closed.
The space freed up from scrap & waste disposal is being used for various purposes like plantations, horticultural activities, beautification, wider passages, parking space, office sitting arrangements, storage etc.
1. An unused room has been modified to office cabins for three officers in SECL

Before After
2. Waiting Lounge is made after clearing up space at Barkasayal Area, CCL

Before After
3. Parking Space created through removing unused materials at CMPDI (HQ), Ranchi, Jharkhand

Before After
New Initiatives undertaken in Special Campaign 3.0
1. Plastic to Paver
Eastern Coalfields Limited collected single use plastic. After segregation of the plastic, it was processed into Paver Blocks/tiles at Bankola area.

Before After
2. Scrap to Sculpture
SECL’s Jamuna Kotma Area has undertaken the initiative of “Scrap to Sculpture” under Special Campaign 3.0 activities. The main objective of this project was to convert scrap materials of coal mines into various creative sculptures.
The colliery has established a public park to house and display these sculptures made from scrap at Bankim Vihar, Jamuna Kotma Area in Anuppur district of Madhya Pradesh. Among the scrap-made sculptures installed prominent ones are of a coal mine worker, a lion, a crane bird and a flower.

Before After
3. Punarutthan Charkha Udyan
In Neyveli Township, a garbage dump area was repurposed and "Punarutthan Charkha Udyan" was established

At Ministry of Coal the campaign witnessed widespread participation and significant outcomes have been achieved which can be seen at
Ministry of Coal has successfully completed special campaign 3.0 by achieving 100% success rate in disposal of pendency and earned the revenue of 34.01 Crore. Watch & Subscribe for daily updates - https://t.co/ESKiSPQqys pic.twitter.com/bq2KKwvZVy — Ministry of Coal (@CoalMinistry) December 21, 2023
Awards to Best Performers in Special Campaign 3.0
To appreciate the commendable efforts put forth by the Ministry & the coal companies for the success of Special Campaign 3.0 an award ceremony was organized in the presence of Minister of Coal, Mines and parliamentary affairs Shri Prahlad Joshi. The awards were given to winners in the below categories.
8.3. Awards for Star Rating of Coal & Lignite Mines
Ministry of Coal organized prestigious Star Rating Awards ceremony on December 20, 2023, to recognize the exceptional performance of Coal and Lignite mines. With a steadfast commitment to elevating industry standards, the Ministry has implemented a well-defined mechanism to enhance performance across key criteria, promoting responsible coal mining practices for sustained growth and development. The Minister of Coal, Mines and Parliamentary Affairs, Shri Pralhad Joshi graced the occasion as the chief guest.

Ministry of Coal is committed to sustainability of Coal and Lignite mining, enhancing overall performance of coal mines in the country by championing sustainable mining practices and fostering competitiveness among mines. Therefore, the Ministry has formulated Star Rating Policy to distinguish outstanding performance of coal mines and accord them the recognition. The Star rating policy outlines Star Rating criteria across seven comprehensive modules: “Mining Operations, Environmental factors, Adoption of Technologies-Best Mining Practices, Economic Performance, Rehabilitation & Resettlement, Worker related Compliance, and Safety & Security.”
The Star Ratings are awarded on a scale from Five Star to No Star, evaluating each mine’s achievements holistically. In the last four years (2018-19, 2019-20, 2020-21, 2021-22), a total of 68 mines have qualified for 5 star rating, scoring more than 91%. Among them, 39 mines have ranked 1st 2nd & 3rd prize.
8.4. IT/Media Initiatives
- Ministry of Coal has striven hard and taken lead towards standardization and improvement in IT working environment and service delivery through various portals and implementation of e-Governance Projects like Single Window Clearance System, Coal Import Monitoring System (CIMS), Coal Projects Monitoring Portal, Star Rating of Coal Mines etc.
- Keeping the priority accorded to Cyber Security, necessary steps are being taken by Ministry of Coal and PSUs under the Ministry of Coal on regular basis, to ensure and enhance Cyber Security like Nomination of Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), Preparation of Cyber Crisis Management Plan (CCMP), compliance of security guidelines etc.
- During the month of October'23, which has been observed as National Cyber Security Awareness Month, Ministry of Coal organized a “ Workshop on Cyber Security ” to sensitize the PSUs and organizations under the administrative control of the Ministry about current cyber security challenges and adapt best cyber security practices to implement in their organizations.
- Additionally, information about Cyber Hygiene is being disseminated through Social Media Handles and also through banners/standees placed at different locations of Ministry/PSUs for maximum awareness.
- Ministry of Coal has made remarkable accomplishments in its media outreach to connect people. Through, the regular press releases, the Ministry has effectively communicated key initiatives, policies, and achievements. Ministry of Coal has active presence on various social media platforms, including X(Twitter), Facebook, Koo, Instagram, thread and LinkedIn showcased real-time updates, fostering engagement and transparency. Additionally, Ministry has contributed to informed public discourse through articles in prominent newspapers and magazines, providing in-depth insights into the coal sector’s development along with sustainability. This media strategy underscores the ministry's commitment to effective communication and public awareness.
9. FUTURISTIC AGENDA
9.1. Coal Gasification Project
With comfortable coal availability in the country, the Government of India has decided to promote gasification of coal in a big way. Coal gasification can yield multiple energy, chemical and petro-chemical products, most of which are presently being imported.
In order to set up 02 Coal based and one lignite based gasification project to promote indigenous gasification technology, Coal India Limited has signed two MOUs with BHEL and GAIL on 12.10.2022 to set up coal based gasification projects at MCL Odisha to produce ammonium nitrate using high ash coal and at ECL West Bengal to produce Synthetic Natural Gas with low ash coal. NLCIL has signed MOU with BHEL for Methanol from Lignite in Tamil Nadu under the aegis of Ministry of Coal.
9.2 Diversification of Coal companies

CIL, SCCL and NLCIL have planned to diversify its business in area of solar power generation, setting up of Coal/Lignite gasification plants, setting up of supercritical Thermal Power Plants, critical minerals mining and Pump Storage Plants. These companies have set target to achieve net-zero target by installing Renewable Energy project and till date, installed total RE projects having capacity of 1655 MW.
Beena Yadav/R K Pillai/ Shuhaib T

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This case study project examines the various CSR interventions and initiatives of TATA Steel India and analyses their impact on the society and on different stakeholders. The paper defines and draws meaningful conclusions about a corporate's responsibility...
Case Studies. This section publishes exclusive Case Stories on CSR, Sustainability, SDGs and Corporate Governance, Business Innovation I India CSR is the largest tech-led platform for information on CSR, Corporate Governance and sustainability in India offering diverse content across multispectral issues. It writes on Sustainable Development ...
TCS from the FY 2017-18 to FY 2021-22. The study concentrates on aspects like CSR activities, CSR spending patterns and the effect of CSR on the share prices of TCS. KEYWORDS: Corporate Social Responsibility, CSR activities and spending, Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), Share price. INTRODUCTION The concept of corporate social responsibility ...
Published Oct 27, 2023. Introduction. In the realm of corporate social responsibility (CSR), Infosys stands as an exemplar of a transformative force for society. As a community of C-suite ...
Collaborative corporate social responsibility praxis: case studies from India - Author: Meena Chavan, Sunaina Gowan, Joanna Vogeley. This study aims to explore how corporate social responsibility (CSR) has assumed a new meaning today, with the COVID-19 pandemic. This, in turn, has changed the way companies now view the impact of their ...
The notion of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is on the rise all over the world, and in India as well. CSR is not new to India; in fact, historically speaking, CSR is a well- established phenomenon in the country, and India has one of the world's richest traditions. of CSR. "In 1965, Lai Bahadur Shastri, then the prime minister of India ...
Abstract Case Intro 1 Case Intro 2 Excerpts Abstract. This case is about Coca-Cola's corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives in India. It details the activities taken up by Coca-Cola India's management and employees to contribute to the society and community in which the company operates.
8 Activities which may be included by companies in their Corporate Social Responsibility Policies: Activities relating to:— 1 [(i) Eradicating hunger, poverty and malnutrition, 2 ['promoting health care including preventive health care'] and sanitation 4 [including contribution to the Swach Bharat Kosh set-up by the Central Government for the promotion of sanitation] and making available ...
For a century, Tata Steel has provided a level of compassion that is unmatched in its sector or its country. But the onslaught of global competition and, crucially, global capital markets have sparked serious debate on the role, level and the sustainability of social spending at Tata Steel. In particular, a new emphasis on EVA risks upsetting the century-old commitment to CSR.
Corporate Social Responsibility in India: A Case Study of Public and Private Sector DOI: 10.9790/487X-1906046774 www.iosrjournals.org 68 | Page how such decisions affect firm performance and second, is that the firms can achieve a competitive advantage ... Corporate Social Responsibility in India: A Case Study of Public and Private Sector
This book provides a comprehensive overview of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in Indian corporations following the 2013 legal mandate on corporate spending of profits for CSR. Bringing together authors hailing from diverse walks of life, the book pursues a 'hands-on' approach, with real-world case studies and examples that help the reader feel the dynamic pulse of India immediately ...
the prices of Dollar was witnessed. Corporate Social Responsibility became a matter of utmost importance for diverse groups demanding change in the business. During the 1980's to 2000, corporations recognized and started accepting a responsibility towards society. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) focuses on the wealth
Corporate Social Respon sibility refers to the. management is a management model. according to which business firms take care of. the society and e nvironment as their social. responsibility. The ...
The Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) mandate in India under the Companies Act, 2013, has been a historical event not only in India, but also to the world at large, when one is debating about ...
Abstract and Figures. This paper attempts to understand the work done by a public sector and private sector organization in the field of corporate social responsibility (CSR). This study is based ...
NEW DELHI (India CSR): To celebrate a decade of the mandated Corporate Social Responsibility, under the Companies Act, 2013, the book, "A Decade of Mandated Corporate Social Responsibility: Interventions, Insights, Impact and more" was launched at the Tamarind Hall of the India Habitat Centre, New Delhi.Chief Guest Hon'ble Deputy Chairperson of the Rajya Sabha Shri Harivansh Narayan ...
IIMS Journal of Management Science 91. Corporate Social Responsibility in India: I ssues and challenges. Rabinarayan Samantara and Shivangi Dhawan. ABSTRACT. It is rightly said that "It is easy ...
of Corporate Social Responsibility. The Case Study of India. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis, 62(4): 605-611. Corporate social responsibility is in the focus of many companies in recent years. It becomes a way of sustainability for many companies on the market. It expresses a voluntary commitment
Corporate Social Responsibility Case Studies, Corporate Social Responsibility Case Study, ICMR develops Case Studies, Micro Case Studies, Latest Case Studies, Best Selling Case Studies, Short Case Studies, business research reports, courseware - in subjects like Corporate Social Responsibility Cases, Marketing, Finance, Human Resource Management, Operations, Project Management, Business Ethics ...
Corporate Social Responsibility has constantly been a part of the State Bank of India covering various social, environmental, and well-being actions [43]. The main determination of the Ban k's CSR
6. CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSBILITY . 6.1. Corporate Social Responsibility . CSR Expenditure. As part of CSR, SCCL spend Rs.13.44 Cr. on CSR activities in 2023 for development of nearby villages, towns, environment measures etc. Compare to Rs. 11.39 crs during the same period last year.