

Basic tasks for creating a PowerPoint presentation
PowerPoint presentations work like slide shows. To convey a message or a story, you break it down into slides. Think of each slide as a blank canvas for the pictures and words that help you tell your story.
Choose a theme
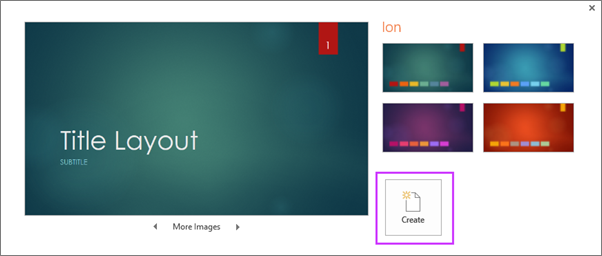
When you open PowerPoint, you’ll see some built-in themes and templates . A theme is a slide design that contains matching colors, fonts, and special effects like shadows, reflections, and more.
On the File tab of the Ribbon, select New , and then choose a theme.
PowerPoint shows you a preview of the theme, with four color variations to choose from on the right side.
Click Create , or pick a color variation and then click Create .
Read more: Use or create themes in PowerPoint
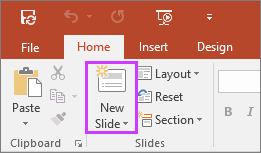
Insert a new slide
On the Home tab, click the bottom half of New Slide , and pick a slide layout.
Read more: Add, rearrange, and delete slides .
Save your presentation
On the File tab, choose Save .
Pick or browse to a folder.
In the File name box, type a name for your presentation, and then choose Save .
Note: If you frequently save files to a certain folder, you can ‘pin’ the path so that it is always available (as shown below).

Tip: Save your work as you go. Press Ctrl+S often or save the file to OneDrive and let AutoSave take care of it for you.
Read more: Save your presentation file
Select a text placeholder, and begin typing.

Format your text
Select the text.
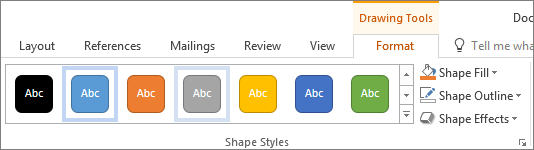
Under Drawing Tools , choose Format .

Do one of the following:
To change the color of your text, choose Text Fill , and then choose a color.
To change the outline color of your text, choose Text Outline , and then choose a color.
To apply a shadow, reflection, glow, bevel, 3-D rotation, a transform, choose Text Effects , and then choose the effect you want.
Change the fonts
Change the color of text on a slide
Add bullets or numbers to text
Format text as superscript or subscript
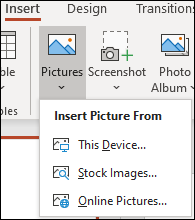
Add pictures
On the Insert tab, select Pictures , then do one of the following:
To insert a picture that is saved on your local drive or an internal server, choose This Device , browse for the picture, and then choose Insert .
(For Microsoft 365 subscribers) To insert a picture from our library, choose Stock Images , browse for a picture, select it and choose Insert .
To insert a picture from the web, choose Online Pictures , and use the search box to find a picture. Choose a picture, and then click Insert .
You can add shapes to illustrate your slide.
On the Insert tab, select Shapes , and then select a shape from the menu that appears.
In the slide area, click and drag to draw the shape.
Select the Format or Shape Format tab on the ribbon. Open the Shape Styles gallery to quickly add a color and style (including shading) to the selected shape.
Add speaker notes
Slides are best when you don’t cram in too much information. You can put helpful facts and notes in the speaker notes, and refer to them as you present.

Click inside the Notes pane below the slide, and begin typing your notes.

Add speaker notes to your slides
Print slides with or without speaker notes
Give your presentation
On the Slide Show tab, do one of the following:
To start the presentation at the first slide, in the Start Slide Show group, click From Beginning .
If you’re not at the first slide and want to start from where you are, click From Current Slide .
If you need to present to people who are not where you are, click Present Online to set up a presentation on the web, and then choose one of the following options:
Broadcast your PowerPoint presentation online to a remote audience
View your speaker notes as you deliver your slide show.
Get out of Slide Show view
To get out of Slide Show view at any time, on the keyboard, press Esc .
You can quickly apply a theme when you're starting a new presentation:
On the File tab, click New .
Select a theme.

Read more: Apply a design theme to your presentation
In the slide thumbnail pane on the left, select the slide that you want your new slide to follow.
On the Home tab, select the lower half of New Slide .
From the menu, select the layout that you want for your new slide.
Your new slide is inserted, and you can click inside a placeholder to begin adding content.
Learn more about slide layouts
Read more: Add, rearrange, and delete slides
PowerPoint for the web automatically saves your work to your OneDrive, in the cloud.
To change the name of the automatically saved file:
In the title bar, click the file name.
In the File Name box, enter the name you want to apply to the file.
If you want to change the cloud storage location, at the right end of the Location box, click the arrow symbol, then navigate to the folder you want, then select Move here .
On the Home tab, use the Font options:
Select from other formatting options such as Bold , Italic , Underline , Strikethrough , Subscript , and Superscript .
On the Insert tab, select Pictures .
From the menu, select where you want to insert the picture from:
Browse to the image you want, select it, then select Insert .
After the image is inserted on the slide, you can select it and drag to reposition it, and you can select and drag a corner handle to resize the image.
On the slide canvas, click and drag to draw the shape.
Select the Shape tab on the ribbon. Open the Shape Styles gallery to quickly add a color and style (including shading) to the selected shape.
A horizontal Notes pane appears at the bottom of the window, below the slide.
Click in the pane, then enter text.

On the Slide Show tab, select Play From Beginning .

To navigate through the slides, simply click the mouse or press the spacebar.
Tip: You can also use the forward and back arrow keys on your keyboard to navigate through the slide show.
Read more: Present your slide show
Stop a slide show
To get out of Slide Show view at any time, on the keyboard, press Esc.
The full-screen slide show will close, and you will be returned to the editing view of the file.
Tips for creating an effective presentation
Consider the following tips to keep your audience interested.
Minimize the number of slides
To maintain a clear message and to keep your audience attentive and interested, keep the number of slides in your presentation to a minimum.
Choose an audience-friendly font size
The audience must be able to read your slides from a distance. Generally speaking, a font size smaller than 30 might be too difficult for the audience to see.
Keep your slide text simple
You want your audience to listen to you present your information, instead of reading the screen. Use bullets or short sentences, and try to keep each item to one line.
Some projectors crop slides at the edges, so that long sentences might be cropped.
Use visuals to help express your message
Pictures, charts, graphs, and SmartArt graphics provide visual cues for your audience to remember. Add meaningful art to complement the text and messaging on your slides.
As with text, however, avoid including too many visual aids on your slide.
Make labels for charts and graphs understandable
Use only enough text to make label elements in a chart or graph comprehensible.
Apply subtle, consistent slide backgrounds
Choose an appealing, consistent template or theme that is not too eye-catching. You don't want the background or design to detract from your message.
However, you also want to provide a contrast between the background color and text color. The built-in themes in PowerPoint set the contrast between a light background with dark colored text or dark background with light colored text.
For more information about how to use themes, see Apply a theme to add color and style to your presentation .
Check the spelling and grammar
To earn and maintain the respect of your audience, always check the spelling and grammar in your presentation .
Top of Page

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Computer Fundamentals and Programming in C
Reema Thareja, Assistant Professor, Institute of Information Technology and Management
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved.
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
1 st gen-1940-56
2 nd gen 1956-63
3 rd -64-71
4 th —72-89
5 th -mordern day
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SOFTWARE
- A computer is a machine that takes instructions and performs computations based on those instructions.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTERS
GENERATION OF COMPUTERS
The word generation means the state of improvement in the product development process. Similarly, computer generation refers to the different advancements of new computer technology.
First Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes
The first generation computers used very large number of vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory.
UNIVAC and ENIAC computers are prime examples of first-generation computing devices.
Advantages: Fastest calculating device of their time
Disadvantages:
1. Dissipate a lot of heat
2. Consume a lot of electricity
3. Very bulky in size
4. These computers were frequently down due to hardware failures.
5. These computers needed constant maintenance because of low mean time between failures
6. Limited commercial use because these computers were difficult to program
7. Very expensive
Second Generation (1956-1963) Transistors
- The second generation computers were manufactured using transistors.
- While first generation computers were programmed using machine language, second generation computers moved towards symbolic, or assembly languages, which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words.
- At this time, high-level programming languages like COBOL, FORTRAN, ALGOL and SNOBOL were also being developed.
- Second generation computers were first to store instructions in memory, which moved from a magnetic drum to magnetic core technology.
- Second generation computers were first developed for the atomic energy industry.
Advantages:
1. Consumed less electricity and thus dissipated less heat as compared to first generation computers
2. Faster, cheaper smaller and more reliable than first generation computers
3. Could be programmed using assembly language and high level languages
4. These computers had faster primary memory and a larger secondary memory
1. Second generation computers were manufactured using transistors that had to be assembled manually. This made commercial production of computers difficult and expensive.
Third Generation (1964-1971) Integrated Circuits
- The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the third generation of computers.
- These computers had few megabytes of main memory and magnetic disks which could store few tens of megabytes of data per disk drive.
- High level programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN were standardized by ANSI
- Some more high level programming languages like PL/I PASCAL and BASIC were introduced at this time.
- Third generation computers were the first to implement time sharing operating systems.
- Input to these computers could now be provided using keyboards and mouse.
- Faster than second generation computers and could perform 1 million transactions per second.
2. Smaller, cheaper and more reliable than their predecessors
3. These computers had faster and larger primary memory and secondary storage
4. They were widely used for scientific as well as business applications
5. During this generation of computers, standardization of existing high level languages and invention of new high level languages was done
6. These computers had time sharing operating system which allowed interactive use of computer by one or more users simultaneously thereby improving the productivity of the users.
Fourth Generation (1971-1989) Microprocessors
- The microprocessor started the fourth generation of computers with thousands of integrated circuits built onto a single silicon chip.
- Semi-conductor memories were used which were very fast, even the hard disks became cheaper, smaller in size and larger in capacity.
- For input, floppy disks (in addition to magnetic tapes) were used to port data and programs from one computer to another.
- During this period many new operating systems were developed like MS-DOS MS-Windows UNIX and Apple’s proprietary operating system.
- Development of GUIs, the mouse and handheld devices.
- In this period, several word processing packages, spreadsheet packages and graphics packages were introduced.
1. Smaller, cheaper, faster and more reliable
2. Consumed less electricity and therefore dissipated less heat
3. They had faster and larger primary memory and secondary storage
4. They could be used as general purpose computers.
5. GUIs enabled people to learn to work with computers very easily. So the use of computers in both office and home became widespread.
6. Networks allowed sharing of resources thereby efficient utilization of computer hardware and software
Fifth Generation (Present and Beyond) Artificial Intelligence
- The fifth generation computers are completely based on a new concept of artificial intelligence.
- Although such computers are still in development, there are certain applications like voice recognition which is widely being used today.
- In the fifth generation of computers the aim is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization.
- The two most common are LISP and Prolog.
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS
Computers can be broadly classified into four categories based on their speed, amount of data that they can hold and price.
Computers can be broadly classified into four categories based on their speed, amount of data that they can hold, and price .
Classification of Computers
Super Computer
Mini Computers
Mainframe Computers
Micro Computers
Intelligent Terminal
Dumb Terminal
Workstation
Cellular Telephones
H/PC Pro Devices
APPLICATIONS OF COMPUTERS
- Word Processing
- Digital Audio or Video Composition
- Desktop Publishing
- Traffic Control
- Legal System
- Retail Business
- Travel and Tourism
- Business and Industry
- Weather Forecasting
- Online Banking
- Industry and Engineering
- Decision Support Systems
- Expert Systems
BASIC ORGANIZATION OF A COMPUTER
A computer is an electronic device which basically performs five major operations which includes:
1) accepts data or instructions (input)
2) stores data
3) process data
4) displays results (output) and
5) controls and co-ordinates all operations inside a computer
CONTROL UNIT
ARITHMETIC LOGIC UNIT
Data and instructions
Flow of data and instructions
Control exercised by control unit
The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Microsoft PowerPoint: From Newbie to Master
You will need to give a presentation one day. This beginner’s guide to Microsoft PowerPoint should give you a great start to a wonderful slideshow.
Microsoft PowerPoint has been a staple for creating presentations for many years. But like anything, not everyone is an expert right off the bat. You have to start somewhere, right? So, let this beginner's guide to PowerPoint be that first step.
For those beginner's who are using PowerPoint for the first time, haven't used it in a while, or just want a simple reference for the basics, this your guide to the desktop version. And, many of these same features apply if you use it online. So, if you are still deciding between PowerPoint Online and PowerPoint 2016 , this guide can come in handy either way.
What Is Microsoft PowerPoint?
Microsoft PowerPoint is basically a presentation creation tool. You can make slideshows with text, images, shapes, animations, audio, and much more. Then, pop your presentation onto the big screen to display it to others or save it as a visual document for yourself.
From Microsoft :
"PowerPoint is a slideshow presentation program that's part of the Microsoft office suite of tools. PowerPoint makes it easy to create, collaborate, and present your ideas in dynamic, visually compelling ways."
For business, educational, and personal situations, PowerPoint offers the flexibility to make the simplest presentations stand out with its host of features.
General Uses for PowerPoint
- Business presentations for products and services
- Educational slideshows for classrooms and lectures
- Personal visuals such as mind maps and family photo slideshows
- Sales and marketing materials
- Event presentations like weddings, anniversaries, or family reunions
- Project, budget, and financial presentations
- Certificates, calendars, reports, diagrams, and charts for any industry
You can create almost any type of visual in PowerPoint. But first, you should become familiar with the general terms of the application.
Basic Terms Used in PowerPoint
You will see many words and terms used frequently throughout this guide. So, taking a moment to review them will help you follow the processes and explanations much easier.
Slideshow and Presentation : When talking about PowerPoint, you may see these two terms become interchangeable. They each represent the overall document you create in the application.
Slides : Each slideshow in PowerPoint contains slides, just like with a physical slideshow. You can think of slides as pages that you can add to your presentation and then move through them one-by-one.
Animations : Animations are visual effects that can give your slide a unique appearance. They allow you to add movement and pizzazz to the elements on your slide.
Transitions : Transitions are also visual tools, but you will see as one slide moves to the next. By using a transition, you can make your presentation stand out to your audience or use it to create a dramatic effect.
The Ribbon and Tabs in PowerPoint
Just like with other Microsoft Office applications, the PowerPoint ribbon contains the buttons that you will use inside tabs. You can customize the ribbon to remove or add both tabs and buttons. But, you will likely see the tabs below by default.
Here is a brief description of what each one is for and which tab group you can see.
- File : Create a new presentation, open an existing one, save, print, and share slideshows.
- Home : Control the clipboard, slides, font, paragraph, drawing, and editing.
- Insert : Insert slides, tables, images, illustrations, links, comments, text, and media.
- Design : Select a theme, pick a variant, customize slides, and get design ideas.
- Transitions : Choose a transition, preview it, adjust the effects, and add timing.
- Animations : Pick an animation, preview it, adjust the effects, use advanced features, and add timing.
- Slide Show : Start a slideshow, set one up, pick a monitor, and use presentation view.
- Review : Use tools for proofreading, accessibility, language, comments, and comparisons.
- View : Change the presentation view, adjust the master views, zoom in or out, select colors, and work with windows and macros.
You should also see the Help tab and Tell me what you want to do box. If you need assistance or want more information on a feature, just open Help or enter the keyword into the Tell me box and view your results.
The PowerPoint Quick Access Toolbar
Like the tabs and ribbon with other Microsoft Office products, you also have the Quick Access Toolbar. You might already be familiar with this handy tool, but if not, this is the toolbar at the very top left of the PowerPoint window. As the name implies, this feature allows you to perform quick actions.
The Save button lets you easily save the file you are working on with the current file name.
If you make a mistake and want to undo it, just click the Undo button. If you click it once, it will undo the last action you took. If you keep clicking it, it will undo each previous action by moving backward. Alternatively, you can click the arrow next to the Undo button and highlight all actions you want to undo.
If you undo an action with the button, the Redo button will then be clickable. This lets you redo what you have just undone. Like the Undo button, you can redo your last action with one click or use the arrow next to the Redo button to redo multiple actions.
The Presentation button lets you start your slideshow as it will be viewed by others. It should take up your entire screen for a nice view of the presentation at any time during your creating or editing processes.
You can select the arrow on the right of the Quick Access Toolbar to add or remove buttons from it easily. You can also see more commands available or move the toolbar below the ribbon.
How to Work With PowerPoint Slides
Slides are the foundations of your slideshows. So knowing the ins and outs of how to work with them effectively can have a big impact on your creation. Here are the basics you should know to work with your PowerPoint slides.
Add a PowerPoint Slide
On the Home tab, you should see a section on the ribbon for Slides . You can quickly add a slide by clicking the New Slide button. This will add a slide just like the one you have currently selected.
Alternatively, you can click the arrow on the New Slide button. This allows you to choose which type of slide you want to add such as a blank slide, a title with content, or a picture with caption.
Change the Layout of a Slide
The Layout button on your ribbon lets you change the type of the currently selected slide. So you can easily change a title slide to one with a title and content or a picture with caption slide to a content with a caption. Or you can get a slide ready for you to insert a PDF directly .
Slide Icons
Some slide types are easy to understand right from the start. For instance, if you choose a title slide, you will see the text areas instructing you to click to add your title and subtitle. But other slide layouts, like those that let you add media, contain icons for you to insert your content.
If you use this type of slide, just click the corresponding icon to insert your item.
- Insert Table : Create a table by choosing the number of columns and rows.
- Insert Chart : Create a chart with a variety of options like line, pie, bar, and area.
- Insert SmartArt graphic : Create a visual like a matrix, pyramid, or process diagram.
- Pictures : Insert an image from your computer.
- Online Pictures : Insert an image from the gallery or search the web for one.
- Insert video : Insert a video from a file, YouTube, or embed code.
You can also get more details on embedding YouTube videos or adding music to your PowerPoint presentations .
Delete a Slide
If you want to delete a slide, the simplest way is to select it and click Delete on your keyboard. You can also right-click on the slide and choose Delete Slide from the context menu.
Using PowerPoint Sections
You might want to organize your slideshow into different sections. Click the Section button, select Add Section , and then give it a name. You can then add slides separately within each section. The Section button arrow lets you also remove, rename, collapse, and expand sections.
Other Common Slide Actions
- Easily rearrange slides with a drag-and-drop action.
- Duplicate slides or create them from an outline using the New Slide button arrow or right-clicking and using the context menu.
- Return a slide to its default layout by clicking the Reset button or right-clicking and using the context menu.
Work With Presentation Notes
PowerPoint offers a terrific speaker note feature that can come in handy. You can add a note to a slide for your own reference or for speaking to your audience during a presentation. The note section appears directly below each slide within PowerPoint.
If you cannot see it, just click the Notes button in the task bar at the bottom of your PowerPoint window. Or, open the View tab and click the Notes button on your ribbon. Then, simply click inside the note section to add yours.
Using Notes in Your Presentations
When you present your slideshow to an audience, only you can see your notes. This makes it a great tool to hold your descriptions, explanations, or instructions as you present your slideshow. Here is the view that you will see containing your notes as you display your presentation.
Printing Your Presentation Notes
If you print your presentation so that your audience has a reference, you can include your notes if you like. To see how it will look, click the View tab and then Notes Page in the Presentation Views section of the ribbon.
If you would like to change how your notes look when you print them, click the Notes Master button in the Master Views section of the ribbon. This allows you to select the design, layout, and page setup options. Also, note the Handout Master button directly to the left which lets you customize the entire handout appearance as well.
Add Animation to PowerPoint
If you are considering adding animations to your slides, it's super easy to do. Animations can be effective for slideshows you create for education like classroom presentations or college lectures. They can also give your presentation a fun effect for personal slideshows like a family reunion or wedding display.
Animation Options
These are the basic features available on the Animations tab.
- Animation : Choose from a variety of options by clicking the arrow in the Animation You can apply an animation to an element when it enters or exits the slide, use it for emphasis, or give it a motion path.
- Effect Options : Different animations have extra options for you to pick from. For instance, the Wheel animation lets you pick the number of spokes while the Spin options lets you select the direction and amount of spins.
- Advanced Animation : Here you can add an animation, open the Animation Pane for more working room, set up a trigger, or use the Animation Painter. But for simple slideshow animations, the basic features should suit you fine.
- Timing : Decide how you want your animations to appear on the slide. They can start when you click during the presentation or right after or with the previous animation. You can also pick a duration time, delay time, and reorder your animations.
- Preview : Once you add an animation you can see a quick view of how it will look without exiting the editing mode or opening the presentation view.
Create Your First PowerPoint Animation
First, select the slide and then the element on the slide that you want to animate. Then, just pick the type from the Animation box. It's that easy! You can then use the tools described above to add effects, advanced items, or timing if you like.
Notice that when you add an animation to an element, a number appears next to it. Each animation you add will be numbered sequentially so that you can easily identify it, work with it, or reorder it. Remember to think of each animated element on its own. This means you can have multiple animations with their own effects all on the same slide.
If you use the Animation Pane on the right, the numbers make it simple to see one animation at a time. There, you can add the same types of effects that you see on the ribbon. Just click the arrow corresponding to the animation and a dropdown menu will appear.
And if you are inserting Excel charts into your presentation , you can animate those too.
Apply PowerPoint Transition Effects
Inserting transitions between your slides can be another effective way to keep your audience's attention, similar to animations. You can apply a unique visual, with or without sound, as you move through the slides of your presentation.

Transition Options
These are the basic features available on the Transitions tab.
- Transition to This Slide : Pick from the transition options by clicking the arrow in the box. You can apply a transition that is subtle, exciting, or dynamic. Keep in mind that this is the effect for transitioning to the current slide .
- Effect Options : Different transitions have extra options that you can apply. For example, the Wipe, Wind, and Orbit transitions let you pick the direction.
- Timing : Here you can add a sound to go with your transition, pick a duration time, and apply these items to all slides. In addition, you can decide to advance to the next slide upon your mouse click or automatically after a certain period of time.
- Preview : Once you add a transition you can see a quick view of how it will look without exiting the editing mode or opening the presentation view.
Create a Slide Transition
This works basically much the same way as the animation only with one step less. Simply select the slide and pick the transition. You can then optionally apply any of the above-described effects that you would like. Pretty easy, right?
While transitions, like animations, may not have their place in every type of slideshow, they can be eye-catching for casual gatherings or fun events. Even for business presentations, a simple Fade effect can eliminate a clunky transition between slides.
Use Different Presentation Views
Not everyone works the same way when it comes being creative. Luckily PowerPoint offers different built-in views to accommodate this. Just select the View tab and take a look at the ways in which you can work with your slideshow.
The Presentation Views section holds five unique ways to create or edit your slideshow. One of those is the Notes Page which you read about above. And, here are the other four with brief explanations.
- Normal : As you can probably guess, this is the basic, normal view. You should see your slides on the left as numbered thumbnails and the current slide in the largest section to the right. This view works well if you prefer to jump between slides visually.
- Outline View : For those who prefer to write or create using outlines, this view is ideal. You can write directly within the outline pane on the left or paste an existing outline from Microsoft Word directly in. Here again, the current slide is in the largest section to the right.
- Slide Sorter : This is a terrific way to see all of your slides at a glance. Taking up the entire center window, you can see each slide and can reorder them easily with a drag-and-drop action.
- Reading View : If you want to see your entire presentation without switching to full-screen mode, then just click this button. You can view your slideshow with animations and transitions easily.
Along with the Slide Sorter view, the Normal and Outline Views allow you to quickly reorder your slides. Just select one and then drag it to its new location.
Collaborate on PowerPoint Presentations
Like other Microsoft Office applications, you have features to easily collaborate with others on your PowerPoint presentations. So if your sales team, fellow educators, or classmates will work on the slideshow together, you have a few options.
Share your slideshow as a PowerPoint presentation saved to OneDrive or as a PDF. Just click the Share button from the menu on the upper right corner. Then, invite others in the sidebar that opens, send the slideshow as an attachment, or obtain a link to share.
Let others make notes on the presentation with the Comments button which is right next to the Share button on the menu. (Assuming your collaborators open the presentation in PowerPoint.) You can view their comments, pop in a reply, move, and delete comments.
View the version history once you start collaborating. If your collaborators are able to make edits to the presentation, you can see the previous versions. A button will appear in the menu in between the Share and Comments buttons. You can then open previous versions of the slideshow if needed.
Slideshow Options
Once your presentation is complete, it's time to review and set up your slideshow. Head over to the Slide Show tab and check out the following options.
Start Slide Show
- From Beginning : Watch your slideshow from the first slide as your audience will see it.
- From Current Slide : Watch your slideshow start from the slide you select.
- Present Online : Use the Office Presentation Service to view your slideshow in a browser.
- Custom Slide Show : Create a custom presentation with the slides in a particular order.
- Set Up Slide Show : Choose the show type, show options, which slides to display, how to advance the slides, and any multiple monitor options you need.
- Hide Slide : This hides any slide that you select from the presentation.
- Rehearse Timings : You can practice presenting your slideshow and see the amount of time you spend on each slide and the slideshow in total. You also have an option to save your timings which is helpful for improving the presentation time if needed.
- Record Slide Show : Easily record your slideshow from the beginning or a specific slide. This is ideal for distributing to others who could not attend the presentation.
- Enable or Disable narrations, timings, and media controls with the convenient checkboxes.
Select a connected monitor from the dropdown box for where your presentation should display. You can also enable or disable Presenter View.
Presenter View provides you with a different view of your slideshow. This allows you to see your presentation with speaker notes on one screen while your slideshow displays on another. In addition, you can control your presentation in this view.
- Change the display settings or duplicate the slideshow.
- Access tools like a laser pointer, pen, or highlighter to use throughout your presentation.
- Zoom in on a slide.
- Black or unblack the slideshow.
- Advance to another slide.
- End the slideshow.
Start the PowerPoint Slideshow
Once you have the above options set for your slideshow, have rehearsed it, and are ready to start, the rest is easy.
Open PowerPoint on your computer, select which monitor to use, and then present it. You can start the slideshow with either the From Beginning button on the Slide Show tab or with the Start from Beginning button on the Quick Access Toolbar . This is the same process you would have followed when you reviewed your presentation.
If you decide to use the Presenter View during your slideshow, then you already know the tools you have at your fingertips to control the show. But if you choose not to or are only working with one monitor, you can still maneuver your presentation.
Simply right-click on the slideshow once it begins to open the context menu. You can then see all of the slides, zoom in, adjust the screen or printer options, and end the show.
Design With Powerpoint Templates
One final part of this beginner's guide is the templates you can use to boost your productivity in PowerPoint. Using a template, you can get a head start on your presentation. PowerPoint offers a variety of built-in templates and you can find those from online third-parties.
Use Featured PowerPoint Templates
To view options within PowerPoint, click File > New . You will then see a number of featured templates you can use along with categories you can pick from and a search box if you want something in particular.
The built-in templates range from basic business cards and diagrams to lengthy and detailed presentations for most any industry.
If you see a template you would like to check out, click on it and then review its description and download size in the popup window. If you want to use it, click the Create button.
Use Third-Party PowerPoint Templates
While templates for Microsoft Word or Microsoft Excel seem to be more plentiful, you can still check out these great suggestions for third-party options that include Microsoft PowerPoint templates.
- 5 PowerPoint Templates for Efficient Meetings
- The Best PowerPoint Templates for Educational Presentations
- Need a Gantt Chart Template for Excel or PowerPoint? Here Are 10 Unique Options
- The Best Free Microsoft Office Calendar Templates for Staying Organized
- The Best Flowchart Templates for Microsoft Office
Let the PowerPoint Presentation Begin
If you have never used it before, then this beginner's guide to Microsoft PowerPoint should give you a great start to a wonderful slideshow. Whether you are preparing your first professional presentation or just want to get creative with family photos, these basics should have you covered.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

11 templates

66 templates

teacher appreciation

9 templates

memorial day
12 templates

pediatrician
27 templates
Computer Workshop for Beginners
Computer workshop for beginners presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
Many people’s jobs, public administration, friendships, art…almost everything is computer- or internet based these days, but there are still loads of people who have just been passed over by this development, be it for lack of access or comprehension. Ready to explain to this clientele how those weird, scary computer thingies can actually be your friend? A noble endeavor, and to help you we have created a light and fun Google Slides & PowerPoint template (with a desktop layout, of course) so your workshop will be easily comprehensible. Download it and make your beginners’ computer workshop amazing!
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 30 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Computer Basics
If you're new to computers or just want to update your skills, you've come to the right place. New videos coming soon!

Introduction
- 1 About This Tutorial arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn what's covered in this free course.
- 2 What is a Computer? arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn what a computer is and how it functions.
Hardware Basics
- 3 Basic Parts of a Computer arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn the basic parts of a computer, including the monitor, computer case, and keyboard.
- 4 Buttons and Ports on a Computer arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn the various ports and buttons on a computer.
- 5 Inside a Computer arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn what's inside a computer.
- 6 Laptop Computers arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn more about laptop computers and how they differ from traditional desktop computers.
- 7 Mobile Devices arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn how mobile devices work.
Software Basics
- 8 Understanding Operating Systems arrow_forward_ios ✓ Get a better understanding of operating systems and how they function.
- 9 Understanding Applications arrow_forward_ios ✓ Better understand applications and how they work.
Using a Computer
- 10 Setting Up a Computer arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn know how to set up a computer.
- 11 Getting Started with Your First Computer arrow_forward_ios ✓ Get started with your first computer.
- 12 Getting to Know the OS arrow_forward_ios ✓ Get to know your computer's operating system.
Using the Internet
- 13 Connecting to the Internet arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn how to get online and start using the Internet.
- 14 Getting Started with the Internet arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn how to get started with and navigate the Internet.
- 15 Understanding the Cloud arrow_forward_ios ✓ Gain a greater understanding of the cloud and how it works.
Safety and Maintenance
- 16 Keeping Your Computer Clean arrow_forward_ios ✓ Use these tips to keep your computer clean.
- 17 Protecting Your Computer arrow_forward_ios ✓ Employ these strategies to keep your computer well protected from threats.
- 18 Creating a Safe Workspace arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn tips for creating a safe space at work.
- 19 Basic Troubleshooting Techniques arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn these basic troubleshooting techniques.
- 20 How to Use Your Computer's Built-in Help arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn how to use your computer's built-in help function.
- 21 Learning a New Program arrow_forward_ios ✓ Use these tips for learning a new program, whatever it may be.
- 22 Bringing Your Files with You arrow_forward_ios ✓ Learn how you can bring your computer files and folders with you wherever you go.
- 23 Using Accessibility Features arrow_forward_ios ✓ Here's how to use your computer's various accessibility functions.
- 24 Computer Basics Quiz arrow_forward_ios ✓ Test your knowledge of computer basics by taking our quiz.

COMPUTER BASICS
Mar 21, 2019
10.85k likes | 24.63k Views
COMPUTER BASICS. Module Review. After completing the Computer Basics Terms Worksheet, use this presentation to review any concepts you had questions on or to check your answers to the worksheet.
Share Presentation
- main memory
- computer basics
- computer chip
- computer include reports
- computer basics terms worksheet

Presentation Transcript
COMPUTER BASICS Module Review
After completing the Computer Basics Terms Worksheet, use this presentation to review any concepts you had questions on or to check your answers to the worksheet. On the next slide, click on the section button that you would like to review. When you have completed that section, click TOPIC to go back to the choices. Click END when you are finished reviewing for the test.
TOPICSSelect from the following topics: Input and Output Computers Memory and Storage Hardware/ Software History END
INPUT • Examples of input include words or symbols, pictures, temperature from a thermometer, music or voice audio signals, instructions from another computer • Input devices include keyboard, scanners, joystick • Gathers information and transforms it into a series of electronic signals for the computer.
OUTPUT • Examples of output from a computer include reports, pictures, graphs, and documents. • Output devices include speakers, monitors, and printers. • Displays, prints or transmits the results of processing. • It is useful information that leaves the system (processed information). TOPICS
COMPUTERS A computer and its associated storage devices that are accessed remotely over a network by users is a server.
COMPUTERS A large, powerful, expensive computer system capable of accommodating hundreds of users doing a variety of computing tasks is a mainframe.
COMPUTERS A personal computer based on a microprocessor is a desktop microcomputer.
COMPUTERS The original design of personal computers was based on the IBM PC design.
COMPUTERS A device with a keyboard, mouse and system components all in one compact unit is a laptop. TOPICS
MEMORY • RAM (Random Access Memory) is the main memory and stores data and programs while the computer is running. When the computer is turned off anything in main memory disappears. Computer can read from and write to this memory. • ROM (Read Only Memory) is a computer chip that stores specific instructions to manage the computer’s operation. Unlike main memory, this type of memory is non-volatile—the instructions remain permanently on the chip and cannot be changed.
MEMORY AND STORAGE • BIT is the fundamental unit of information with just two possible values (0 or 1) • A sequence of adjacent bits (usually 8) operated on as a unit by a computer is a BYTE.
STORAGE • Hard Disk is a rigid magnetic disk mounted permanently in a computer drive unit. • A small plastic magnetic disk enclosed in a stiff envelope with a radial slit is a floppy disk. • Zip disk is a magnetic disk storage device that has more capacity than a floppy disk. (Not used much) • CD-ROM is a compact disk that functions as a read-only memory.
HANDLING DISKS/FILES • Write-protected is used to modify (file or disk) so that its data cannot be edited or erased. • Format is used to prepare a disk for use on a specific type of drive by imprinting the disk with the information it needs to work in that particular kind of drive. Make sure you know what you are doing when you format a disk, because everything on the disk will be erased.
Processor speed is measured by MegaHertz (MHz) TOPICS
HARDWARE • Hardware is the electronic and mechanical peripheral devices that make up a computer. • The stuff you can touch!
HARDWARE • The central processing unit (CPU) is the “brains” of the computer which is housed on a tiny silicon chip. This is where the mathematical calculations and logical comparisons are done.
HARDWARE • Pentium is the name given to Intel’s P5 chip, the successor to the 80486.
SOFTWARE • Program is a series of commands and executable files that produce an expected result.
SOFTWARE • Operating system software is a type of software that provides an interface between the user or application software and the computer hardware. • Application software is a type of software program that performs a specific function such as presentations (i.e. PowerPoint, Word, Excel, etc.)
SOFTWARE • A computer interface that enables a user to launch commands by pointing and clicking at graphical objects such as windows, icons, and menu items is GUI (Graphical User Interface) • ICON is an image that represents an executable file. TOPICS
HISTORY • Charles Babbage invented the difference machine. • Grace Hopper coined the term debugging as she found a moth was causing the computer relay to not work.
HISTORY • Bill Gates’ system (i.e. Windows) and application (i.e. Microsoft Office) software is what made him rich. • Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak were two creators of Apple Corporation. TOPICS
Are you ready for the test now? Good luck!
- More by User

Computer Basics
Computer Basics Which computer should I buy? What do I get for an extra $775 and do I even need it ? Desktop We need to understand several things before going out and buying a computer . What are the different components of a computer system and how do they work?
2.86k views • 31 slides

Computer Basics. Computer Hardware and Software 2008-2009. The Information Processing Cycle. What is a computer?. accepts data processes data produces output stores results. A computer is an electronic device that executes the instructions in a program.
1.17k views • 22 slides
Computer Basics. The Computer (Generic). Processor executes commands. Memory stores program and data. Input devices transfer information from outside world into computer. Output devices are vice versa. Inputs. Memory. Outputs. Processor. NXT. USB communications port.
681 views • 11 slides
Computer Basics. Introduction to Computer. Computer Types. Operating Systems. By Gustavo Alatta. Introduction to Computers.
905 views • 18 slides
Computer Basics. Mr. Reese. Introduction to Computers. Lesson 1. 1.1 Describe the Importance of Computers in Today’s World. Computer an electronic device that you can use to store and process information. 1.1 Describe the Importance of Computers in Today’s World.
798 views • 46 slides

Computer Basics. Chris G7j. What is a computer?. An electronic device Store Receive Process. What are the types of computer?. Desktop Computer Laptop Computer Tablet Computers Mobile phones Gaming consoles TV. How are they used?. Communicating Socializing Doing work Playing games.
1.17k views • 25 slides

Computer basics
Computer basics. By Prim G7J. What and why 1,3. Learning about computer basics Why? Because you need to know for a good job Most children don’t know about computers You should know how to put a computer together To pass ICT class. What is a computer? 2.
553 views • 19 slides

Computer Basics. Lesson 5 - Output. What is Output?. Output is data that has been processed into useful form, now called Information. Types of Output: Hard copy: printed on paper or other permanent media Soft copy: displayed on screen or by other non-permanent means.
552 views • 29 slides

Computer Basics. Lesson 2 - Applications. What is an Application?. An application is another word for a program running on the computer. Whether or not it is a good application depends on how well it performs the tasks it is designed to do and how easy it is for the user to use.
548 views • 17 slides
COMPUTER BASICS. WHAT IS A COMPUTER?. A device, usually electronic, that processes data according to a set of instructions. TYPES OF COMPUTER. There are four main categories, namely: Super Computer Mainframe Computer Mini Computer Micro Computer. COMPONENTS OF THE COMPUTER SYSTEM.
1.17k views • 7 slides

Computer Basics. Instructors: Connie Hutchison & Christopher McCoy. Objectives. Describe the importance of computers in today's world. Explain the basics of computer performance and how it relates to productivity. Explain the difference between memory and storage. Objectives.
1.37k views • 38 slides

Computer Basics. Tech Lit Mrs. Lesher. Keyboard. Media Center. Function Keys. Special or Dedicated Keys. Function Keys. Special or Dedicated Keys. Alphanumeric Keys. Numeric, Insertion Point Control, and Special Keys. Insertion Point Control Keys. Windows Desktop. Shortcuts Start
660 views • 39 slides

Computer Basics. Unit 1. Getting to Know Computers. Ch. 1. Computer. An electronic device that manipulates information, or "data." Watch What is a computer?. Computer. Has the ability to store , retrieve , and process data. Computers Simplified. Two basic parts Hardware
1.11k views • 40 slides

Computer Basics. What’s that thingamagige?. Parts of a computer. Tower. The container for the CPU , memory, motherboard, video graphic card and drives. Floppy Disk Drive. A drive used to read a floppy disk. CD ROM Drive and Burner.
735 views • 26 slides

Computer basics. How to build your own pc. Choosing parts. Motherboard Processor Memory (RAM) Disk drive Graphics card Power supply Case Blu-ray/DVD drive Cooling Operating system. motherboard. Most important component Links all other parts together and supplies them with power
796 views • 12 slides

Computer Basics. Topic 1: The Role of Computers. Objective: Describe the role of computers in our daily life. The Role of Computers:.
4.16k views • 131 slides

Computer Basics. There are many types of computers including:. Types of Computers. Supercomputers...are used to process very large amounts of information including processing information to predict hurricanes, satellite images and navigation, and process military war scenarios.
680 views • 25 slides

Computer Basics. Kitsap Regional Library. Lesson Plan Objectives. Students will gain a basic understanding of the library computers Students will be able to log-on and off the library computers using their library card and pin
1.04k views • 19 slides

1.18k views • 25 slides

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Computer Basics.
Published by Freddie Finchum Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Computer Basics."— Presentation transcript:

Transition Plus Services

Computer Parts There are many parts that work together to make a computer work.

Basic Computer for Small Business

4.03 IT PowerPoint Objective 4.03—Understand Information Technology activities and careers.

© Paradigm Publishing, Inc. 2-1 Chapter 2 Input and Processing Chapter 2 Input and Processing.

The physical parts of Computer

Computer Basics 1 Computer Basic 1 includes two lessons:

Computer Basics Dayton Metro Library Place photo here May 20, 2015.

Intro to Computer Hardware. Computer Hardware Hardware – the physical parts of the computer system that you can see and touch.

Hardware of Personal Computers

Parts of a Computer.

Getting to know your computer…
Hardware and Software Basics. Computer Hardware Central Processing Unit - also called “The Chip”, a CPU, a processor, or a microprocessor Memory (RAM)

History of computers What your computer can do depends upon two things: the hardware your computer has, and the software that can be run on your computer.

Information Technology Ms. Abeer Helwa. Computer Generations First Generation (Vacuum Tubes) -They relied on the machine language to perform operations.

Introduction To Computers

COMPUTER PARTS There are many parts that work together to make a computer work.

Bellringer Do you think students should study computers? Why or why not?

Intro to Computer Hardware
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Computer Basics: Powerpoint
- Hardware vs. software
- Troubleshooting
- Solve Problems Yourself
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Class Notebook
- RAMLINK Tutorials
- Computer Operating System
Use PowerPoint to make great presentations
PowerPoint Basics
- Basic tasks for creating a PowerPoint presentation
- What is a slide layout?
- Office 365 Access
- 5 Things that the West Library Can Do for You
- Computer Basics
PowerPoint Toolbar

- << Previous: Excel
- Next: OneNote >>
- Last Updated: May 8, 2024 1:01 PM
- URL: https://westlibrary.txwes.edu/computerbasics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
S. sluget. Learn to identify parts of a computer, hardware and software, operate the mouse and keyboard and become familiar with the MS Windows X/P Operating System. Technology Entertainment & Humor. 1 of 12. Download now. Computer Basics 101 Slide Show Presentation - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Microsoft PowerPoint is a presentation design software that is part of Microsoft 365. This software allows you to design presentations by combining text, images, graphics, video, and animation on slides in a simple and intuitive way. Over time, PowerPoint has evolved and improved its accessibility to users.
Computer Basics 1 Computer Basic 1 includes two lessons: • Lesson 1: Introduction to Computers • Lesson 2: Common Computer Terminology. Lesson 1 - Introduction to Computer Objectives After completing lesson 1, you will be able to: Describe the importance of computers in today's world. Identify the main parts of a computer. Identify the steps for starting a computer.
It perform four primary operations are: 1. INPUT - entering data into the computer 2. PROCESSING - performing operations on the data 3. OUTPUT - presenting the results 4. STORAGE - saving data, or output for future use. 4. 4 Data • Data is a collection of facts, figures and statistics related to an object.
One of the basics of PowerPoint presentations is to have a consistent color palette throughout. With these PowerPoint basics covered, let's change the slide background color on slide two. To start, click on the slide background. Next, click on the Design tab. In the toolbar, click on the Format Background button.
Part 4: What are Types. Secondary Storage 650. Secondary Storage Single. Secondary Storage A. Secondary Storage A. Various Types of. Part 5: Introduction to computer hardware - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Learn everything you need to know to get started using Microsoft PowerPoint! You'll learn all the basics plus more, including: how to choose a design theme...
Computer Basics 101 Slide Show Presentation sluget Introduction to computing, Analog Computers, Hybrid computers, TYPES OF COMPUTER, Parts of the Computer , Software, Hardware, data, Users, Input and output devices, Introduction to computing
Under Drawing Tools, choose Format. Do one of the following: To change the color of your text, choose Text Fill, and then choose a color. To change the outline color of your text, choose Text Outline, and then choose a color. To apply a shadow, reflection, glow, bevel, 3-D rotation, a transform, choose Text Effects, and then choose the effect ...
A computer is an electronic device which basically performs five major operations which includes: 1) accepts data or instructions (input) 2) stores data. 3) process data. 4) displays results (output) and. 5) controls and co-ordinates all operations inside a computer. .
Insert Chart: Create a chart with a variety of options like line, pie, bar, and area. Insert SmartArt graphic: Create a visual like a matrix, pyramid, or process diagram. Pictures: Insert an image from your computer. Online Pictures: Insert an image from the gallery or search the web for one.
Blue Technology Illustration Education School Cute Workshop Computer Editor's Choice Internet Computing Editable in Canva. Yes, computers can be your friend! Be at ease running your beginners' computer workshop with this fun Google Slides & PPT template with a desktop layout!
Click and drag the slide to the location to which you want to move it. Deleting Slides To delete a slide from a presentation: 1. Right-click on the slide thumbnail and select Delete Slide on the menu that appears. OR 2. Click on a slide thumbnail and press Delete or Backspace on the keyboard. Working with Text Placeholders
Presentations 101: The Absolute Basics of Making a Presentation. This post is part of a series called Presentation Fundamentals. Presentations don't require PowerPoint, Keynote, or any specific app. They don't require a projector, a laser pointer, or a long stick. And they definitely don't require bullet points, animations, and soundtracks.
Desktop vs Laptop. Desktop. vs Laptop. Desktop. vs Laptop 5:00. Desktop: A computer is an electronic device that processes information. With a computer you can create documents like resumes, look up information on the Internet, watch movies, play games, and much more.
A computer is an electronic device that processes data to perform various tasks, consisting of hardware components like the central processing unit (CPU), memory (RAM), storage devices (hard drive, SSD), input devices (keyboard, mouse), and output devices (monitor, printer). On the software side, computers rely on operating systems to manage ...
8 Presentation A presentation program (also called a presentation graphics program) is a computer software package used to display information, normally in the form of a slide show. It typically includes three major functions: an editor that allows text to be inserted and formatted, a method for inserting and manipulating graphic images and a ...
21 likes • 21,890 views. Vicente Antofina. Computer lesson. Education. 1 of 29. Download now. Download to read offline. Beginning computer basics - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
4. Buttons and Ports on a Computer Learn the various ports and buttons on a computer. 5. Inside a Computer Learn what's inside a computer. 6. Laptop Computers Learn more about laptop computers and how they differ from traditional desktop computers. 7. Mobile Devices Learn how mobile devices work.
COMPUTER BASICS Module Review. After completing the Computer Basics Terms Worksheet, use this presentation to review any concepts you had questions on or to check your answers to the worksheet. On the next slide, click on the section button that you would like to review. When you have completed that section, click TOPIC to go back to the choices.
COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre. 2. What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is composed of hardware and software, and can exist in a variety of sizes and configurations. 3.
Embed. Download presentation. Presentation on theme: "Computer Basics."—. Presentation transcript: 1 Computer Basics. 2 Topic 1: The Role of Computers. 3 Objective: Describe the role of computers in our daily life. 4 The Role of Computers: A computer is an electronic device that you can use to store and process information.
Eunice & James L. West Library. 1201 Wesleyan Street Fort Worth, TX 76105 (817) 531-4800 Facebook Twitter YouTube Instagram Provide Feedback