Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Chicago Manual of Style 17th Edition

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This section contains information on The Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) method of document formatting and citation. These resources follow the seventeenth edition of The Chicago Manual of Style (17t h e dition), which was issued in 2017.
Please note that although these resources reflect the most recent updates in the The Chicago Manual of Style (17 th edition) concerning documentation practices, you can review a full list of updates concerning usage, technology, professional practice, etc. at The Chicago Manual of Style Online .
Introduction
The Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) covers a variety of topics from manuscript preparation and publication to grammar, usage, and documentation, and as such, it has been lovingly dubbed the “editor's bible.”
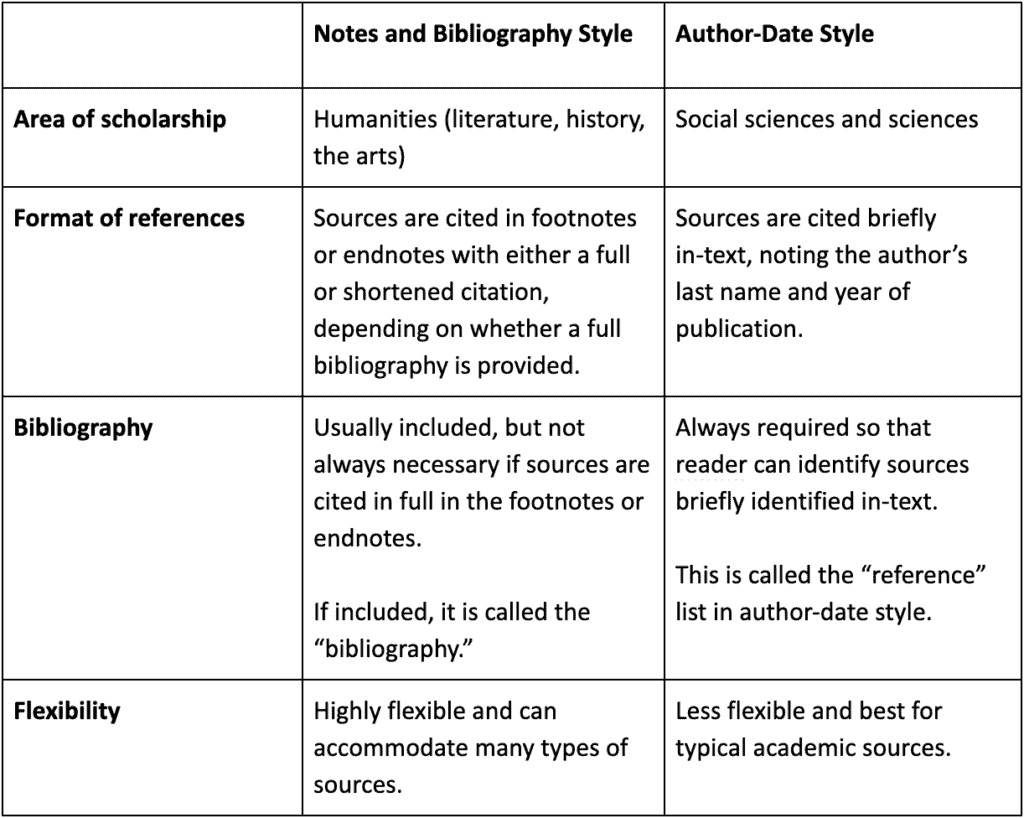
The material on this page focuses primarily on one of the two CMOS documentation styles: the Notes-Bibliography System (NB) , which is used by those working in literature, history, and the arts. The other documentation style, the Author-Date System, is nearly identical in content but slightly different in form and is preferred by those working in the social sciences.
Though the two systems both convey all of the important information about each source, they differ not only in terms of the way they direct readers to these sources, but also in terms of their formatting (e.g., the position of dates in citation entries). For examples of how these citation styles work in research papers, consult our sample papers:
Author-Date Sample Paper
NB Sample Paper
In addition to consulting The Chicago Manual of Style (17th edition) for more information, students may also find it useful to consult Kate L. Turabian's Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (8th edition). This manual, which presents what is commonly known as the "Turabian" citation style, follows the two CMOS patterns of documentation but offers slight modifications suited to student texts.
Notes and Bibliography (NB) in Chicago style
The Chicago Notes and Bibliography (NB) system is often used in the humanities to provide writers with a system for referencing their sources through the use of footnotes, endnotes, and through the use of a bibliography. This offers writers a flexible option for citation and provides an outlet for commenting on those sources, if needed. Proper use of the Notes and Bibliography system builds a writer’s credibility by demonstrating their accountability to source material. In addition, it can protect writers from accusations of plagiarism, which is the intentional or accidental uncredited use of source material created by others.
Introduction to Notes
In the Notes and Bibliography system, you should include a note (endnote or footnote) each time you use a source, whether through a direct quote, paraphrase, or summary. Footnotes are added at the end of the page on which the source is referenced, while endnotes are compiled at the end of each chapter or at the end of the entire document.
In either case, a superscript number corresponding to a note, along with the bibliographic information for that source, should be placed in the text following the end of the sentence or clause in which the source is referenced.
If a work includes a bibliography, which is typically preferred, then it is not necessary to provide full publication details in notes. However, if a bibliography is not included with a work, the first note for each source should include all relevant information about the source: author’s full name, source title, and facts of publication. If you cite the same source again, or if a bibliography is included in the work, the note only needs to include the surname of the author, a shortened form of the title (if more than four words), and the page number(s). However, in a work that does not include a bibliography, it is recommended that the full citation be repeated when it is first used in a new chapter.
In contrast to earlier editions of CMOS, if you cite the same source two or more times consecutively, CMOS recommends using shortened citations. In a work with a bibliography, the first reference should use a shortened citation which includes the author’s name, the source title, and the page number(s), and consecutive references to the same work may omit the source title and simply include the author and page number. Although discouraged by CMOS, if you cite the same source and page number(s) from a single source two or more times consecutively, it is also possible to utilize the word “Ibid.,” ( from the Latin ibidem, which means “in the same place,”) as the corresponding note. If you use the same source but a draw from different new page, the corresponding note should use “Ibid.” followed by a comma and the new page number(s).
In the NB system, the footnote or endnote itself begins with the appropriate full-sized number, followed by a period and then a space.
Introduction to Bibliographies
In the NB system, the bibliography provides an alphabetical list of all sources used in a given work. This page, most often titled Bibliography, is usually placed at the end of the work preceding the index. It should include all sources cited within the work and may sometimes include other relevant sources that were not cited but provide further reading.
Although bibliographic entries for various sources may be formatted differently, all included sources (books, articles, websites, etc.) are arranged alphabetically by author’s last name. If no author or editor is listed, the title or, as a last resort, a descriptive phrase may be used.
Though useful, a bibliography is not required in works that provide full bibliographic information in the notes.
Common Elements
All entries in the bibliography will include the author (or editor, compiler, translator), title, and publication information.
Author Names
The author’s name is inverted in the bibliography, placing the last name first and separating the last name and first name with a comma; for example, John Smith becomes Smith, John.
Titles of books and journals are italicized. Titles of articles, chapters, poems, etc. are placed in quotation marks .
Publication Information
The year of publication is listed after the publisher or journal name .
Punctuation
In a bibliography, all major elements are separated by periods.
For more information and specific examples, see the sections on Books and Periodicals .
Please note that this OWL resource provides basic information regarding the formatting of entries used in the bibliography. For more information about Selected Bibliographies, Annotated Bibliographies, and Bibliographic Essays, please consult Chapter 14.61 of The Chicago Manual of Style (17th edition).

A MANUAL FOR WRITERS OF RESEARCH PAPERS —also known as “Turabian”—is the gold standard for college and graduate students in virtually all academic areas. An introduction to Chicago-style formatting and citation generation, the manual aids students in clear writing, citing, and research practice. At the heart of Turabian is the idea that, no matter the format, the foundations of good research remain the same: to do it carefully, present it clearly and accurately, and follow academic standards for citation, style, and format.
THE NINTH EDITION INCLUDES:
- comprehensive guidelines for formatting papers and preparing them for submission
- authoritative guidance on all matters of style
- updated to reflect The Chicago Manual of Style , 17th edition
- thorough coverage of Chicago-style formatting and citation
- extensive guidelines on conducting research in digital environments
Writers need a strong research question, an evidence-based argument, to structure their work in a logical way, and to cite their sources. A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations , remains one of the most popular books for writers because of its timeless focus on achieving these goals. The ninth edition filters decades of expertise into modern standards. Recognizing that most students will be doing their work largely or entirely online and on screens, this new edition builds information literacy by addressing digital forms of both research and writing.
Through eight decades and millions of copies, A Manual for Writers has helped generations shape their ideas into compelling research papers. This new edition continues as the gold standard for college and graduate students in virtually all academic disciplines.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / Chicago Style
Chicago/Turabian Style Guide
Need Chicago or Turabian style for a paper you are writing? This guide has everything you need to know about Chicago style according to the latest standards.
This page follows the 17th edition of The Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) and the 9th edition of the Turabian guide ( A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations ), though this guide is not officially connected with either.
Here’s a run-through of everything this page includes:
Here’s what you’ll find on this page:
What is chicago style what is turabian, paper formatting guidelines, citing your sources, notes and bibliography style, author-date style, formatting your bibliography or reference list, other chicago guides.
- Introduction to the Chicago and Turabian styles
- Paper formatting guidelines
- When and what you need to cite when writing a paper
- Notes and bibliography style
- Author-date style
- Bibliography and reference list formatting tips
You may have heard the terms “Chicago” and “Turabian” used interchangeably and wondered what the difference is. Simply put, they are just about the same.
Turabian is a simpler version of Chicago style meant for students who are writing materials that will not be published. Since the CMOS is meant for material that is intended for publication, it’s often used by scholars, publishers, and other professional academics. The Turabian guide is shorter and includes information on formatting rules, the basics of researching and writing academic papers, and citation style. Despite these differences, these two books work in tandem; both are considered to be official Chicago style.
Since Chicago style is typically used for manuscripts that will be published, The Chicago Manual of Style does not offer many guidelines for paper formatting. This is because publishers each have their own house styles and authors must follow these exactly. There are a few areas where guidance is offered.
- Manuscripts : Generally, manuscripts should be double-spaced (CMOS 2.8). Exceptions are block quotations, table titles, and lists in appendixes, which should be single-spaced, and certain front matter (e.g., table of contents), footnotes or endnotes, and bibliographies and reference lists, which should be single-spaced internally but have a blank line between each separate item (Turabian A.1.3).
- Spaces at the end of sentences and after colons : Chicago recommends one space (CMOS 2.9; Turabian A.1.3).
- Margins : Margins should be at least one inch on all four sides (CMOS 2.10). Certain forms of writing like dissertations or theses may require a larger margin on the left side to allow room for binding, but each institution will have different requirements (Turabian A.1.1).
- Justification : Text should be justified to the left (CMOS 2.10).
- Font : Turabian recommends using a font that is both readable and readily available to most people such as Times New Roman or Arial. Times New Roman font size should be no smaller than 12-point and Arial no smaller than 10-point. Footnotes and endnotes may require different sizing and you should refer to your instructor’s guidelines (Turabian A.1.2).
- Pagination : Pagination of the body of the paper and back matter should use arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.). Front matter like the title page and table of contents should use lowercase roman numerals (i, ii, iii, etc.). For the placement of page numbers, the general rule is to adhere to local guidelines and be consistent. (Turabian A.1.4)
For more specific formatting guidelines, you can take a look at the appendix “Paper Format and Submission” in the Turabian manual.
Chicago style has two citation styles to let readers know that you used information from somewhere else and to show them where to find it.
- notes and bibliography style
- author-date style.
Though different, each style allows you to tell your readers how you found your information. If you’re wondering how these two styles differ from parenthetical citations, this guide on footnotes, end notes, and parentheticals contains more details on each method.
The 2 styles
The first style is the notes and bibliography style . This style uses footnotes or endnotes to point readers to the original source of the information. This style also often provides a bibliography at the end that readers consult, but this is not always necessary if sources are cited in full in your text.
The second style is called author-date style . This style uses parenthetical in-text citation to let readers know to look at the reference list at the end to find the full citation for the information you have used.
Here’s a chart to compare these two citation styles:
You must cite your source in any of the following situations:
- If you quote a source exactly
- If you reword ideas from a source
- If you use any material (e.g., statistics, data, methodology) from a source you read while writing
When citing your sources, you usually need a few key pieces of information:
- Who created the source? This might be an author, editor, translator, or corporate body.
- How can you identify the source? This information will likely include a title, page numbers, volume or issue numbers, and edition.
- What is the publication information? This might include the name of the publishing company, the year of publication, and the name of the journal or book the information is in.
- Where can others find the source? This is important for online sources and singular material like that found in rare book collections or archives. For online material, you’ll want to record a URL or database name if possible. For rare book or archival material, you’ll need the name of the place you found it and the collection name.
Why citing your sources is important Telling your readers where you found your information is a very important part of the writing process. It gives credit to the hard work others have done . It also lets readers know that your information is reliable—they don’t just have to take it from you; they can go see what other researchers have written about the topic.
Citing your sources also helps readers to understand the context of your project . You can show that you understand the work that has already been done and where your own research fits in.
Finally, your readers might want to build on your research. Citing helps them to know where you found your information when readers do their own research. They might even cite you if you formally published your work. You can read more about how to integrate the research of others into your paper in Chapter 7 of the Turabian manual or Chapter 13 in the CMOS.
This style uses superscript numbers at the ends of sentences. These numbers alert readers that the sentence contains information from another source. Each superscript number refers to a note.
The notes are located at the bottom of the page (footnotes) or at the end of the paper, chapter, or book (endnotes).
- Footnotes make it very easy for readers to find your source, but they can interrupt the document flow.
- Endnotes tend to reduce distraction on the page, but then the reader must flip pages to find the source you cite.
Unless your instructor has told you otherwise, the choice between footnotes and endnotes is up to you. You just need to be consistent and stick to one style or the other.

Updates to “Ibid” It’s important to note that previous editions of the CMOS encouraged the use of “ibid” when the same source was cited multiple times in a row. “Ibid” is a Latin word meaning “in the same place.”
The 17th edition of the CMOS, however, overturns this recommendation because the use of “ibid” can be confusing for readers and authors can easily cite to the wrong source if they are not careful.
The current recommendation of the CMOS is to always use the shortened form of the citation. If you refer to the same work multiple times in a row, you may leave out the shortened title and just list the author’s last name and the page number to which you are citing (See CMOS 14.34 for more information.).
Full Bibliography If you are including a full bibliography, you might choose only to use shortened citation forms in your footnotes or endnotes. You may also use the shortened structure that omits the title for sources that you cite several times in a row.
Keep in mind that if you cite a different source, you need to use the full shortened structure the next time you cite from a source you have used before. Here’s an example:
- Robisheaux, Langenburg , 58
- Robisheaux, 59.
- Robisheaux, 70.
- Cyrus, Scribes , 80.
- Robisheaux, Langenburg , 95.
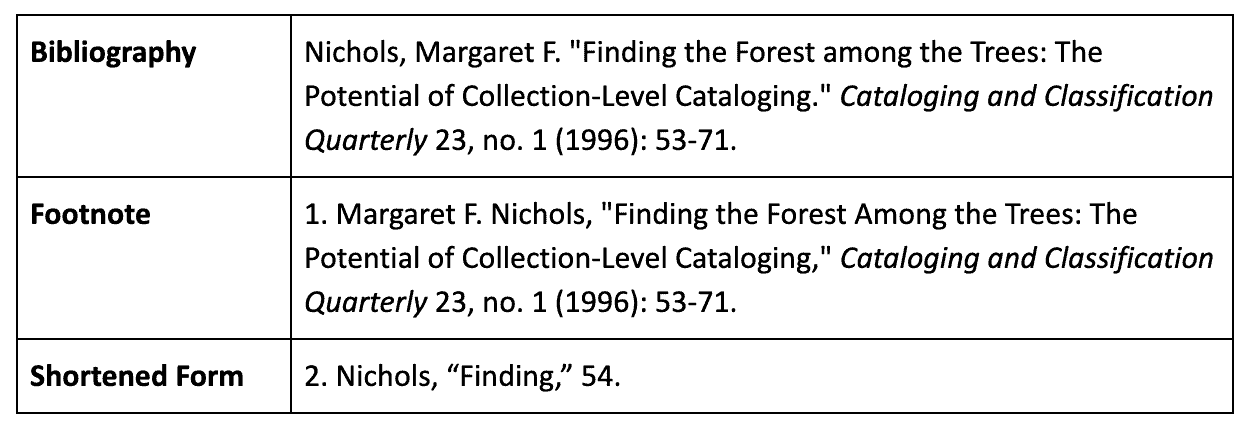
Citation Examples Here are a few examples of citation structures in the notes and bibliography style. For more examples and information on this style, check out the EasyBib Chicago footnotes guide.
Journal article:
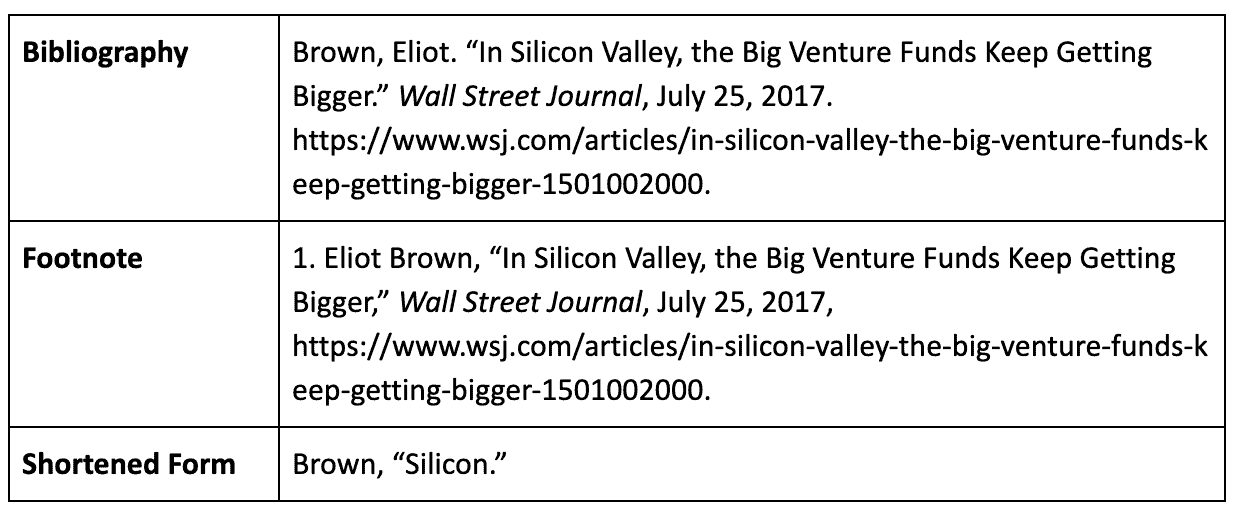
Newspaper or magazine article:
This style uses parenthetical in-text citations and a reference list to guide readers to the sources you cite. The in-text citation generally includes the:
- Author’s last name
- Year of publication
- Page numbers referenced
Using the parenthetical citation, the reader can then look at the reference list and find full information for the source.The reference list for this style is usually titled “References” or “Works Cited” and is organized in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. The parenthetical in-text citation always comes at the end of a sentence, and is placed before the final punctuation.
In-text citation example Nicholson’s study reveals a great deal about the general practices of ARL institutions in regard to the technical processing of these personal libraries. About half of the institutions kept the personal libraries shelved together and half used a Library of Congress classification scheme (Nicholson 2010, 114-115).
In the reference list, the citation would appear as follows:
Nicholson, Joseph R. 2010. “Making Personal Libraries More Public: A Study of the Technical Processing of Personal Libraries in ARL Institutions.” RBM: A Journal of Rare Books, Manuscripts, and Cultural Heritage 11, no. 2 (Fall): 106-133.
Additional Examples Here are more examples of parenthetical in-text citations and their full citations as they would appear in the reference list. There are even more guides linked at the bottom of this page.


Social media:

In-text citation examples
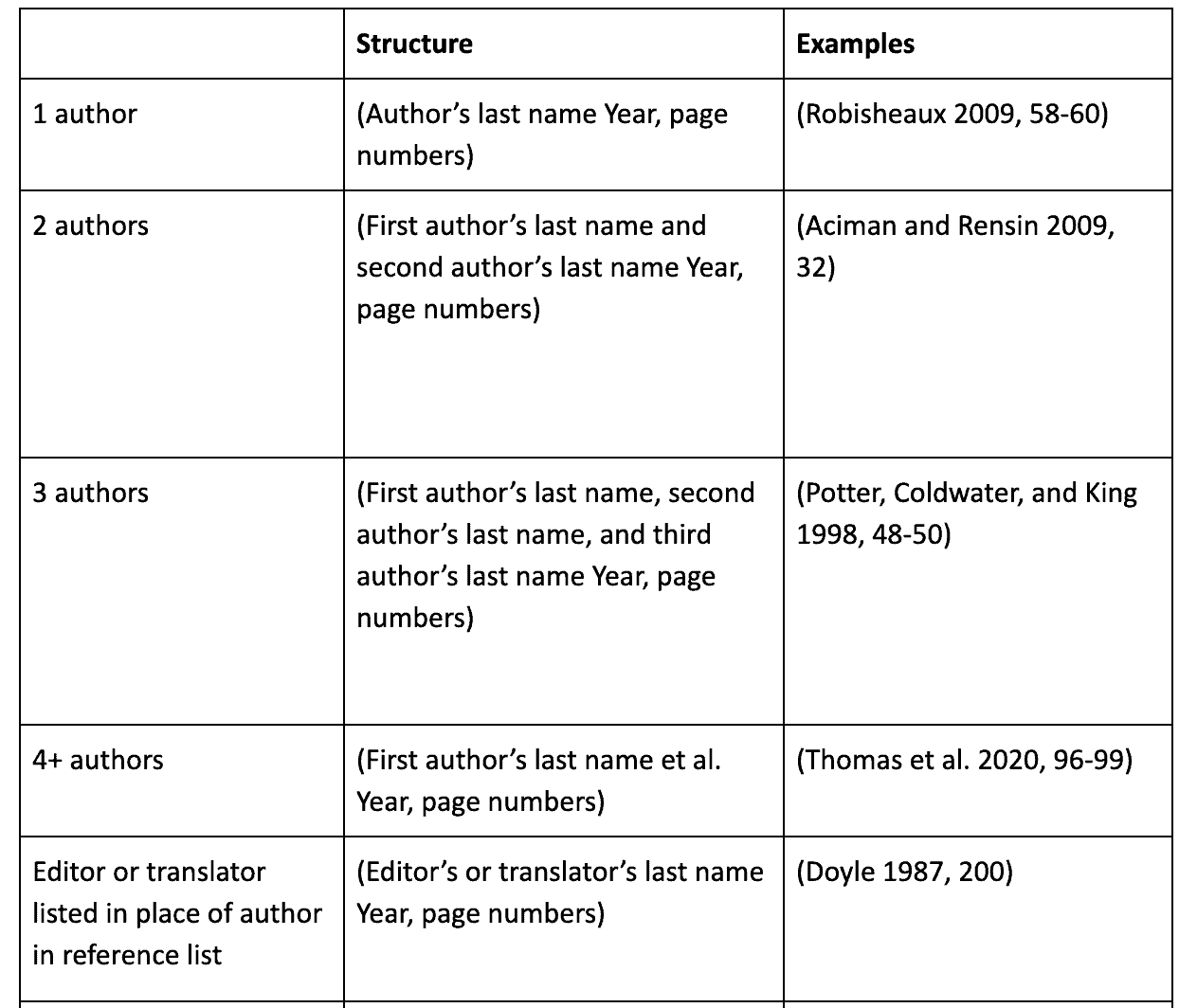
When building in-text citations, you might come across more complicated citations. This chart shows some of the most common citation types you will come across and how to build in-text citations for them.
Bibliographies and reference lists are located at the end of your paper. You should include every source you cite in your bibliography or reference list.
Here are a few guidelines to follow:
- Center your title (either “Bibliography” or “Reference List”) at the top of the page.
- Organize entries alphabetically by the last name of the author (or title if no author is known).
- Each entry should be single-spaced with a blank line between entries.
- Each entry should also have a half-inch hanging indent.
3-em dashes
While sometimes 3-em dashes are used in bibliographies and reference lists in repeated list entries under the same author, the 17th edition of CMOS actually recommends that authors not do this in citation lists (CMOS 14.67 and 15.17).
Using 3-em dashes can cause a number of problems and it is best to just use the author’s name each time, especially if submitting your work for formal publication.
If your editor or publisher wants to use the 3-em dash, they will insert them where necessary. You can also check with your teacher and see what they want you to do.
For more guidelines for formatting bibliographies and reference lists, see CMOS 14 and 15 and Chapters 16 and 18 in the Turabian guide.
Citation Basics
- Fundamentals of Chicago Citation
- How to Cite a Book
- How to Cite a Chapter
- How to Cite an E-book
- How to Cite the Bible
Periodicals
- How to Cite a Journal
- How to Cite a Newspaper
- How to Cite a Magazine
Online Content
- How to Cite a Blog
- How to Cite a Website
- How to Cite a Tweet
- How to Cite a Video on YouTube
Audio / Video / Photo / Art
- How to Cite a Film
- How to Cite a Musical Recording
- How to Cite a Painting
- How to Cite a Podcast
- How to Cite a Photo
- How to Cite Sheet Music
- How to Cite a TV/Radio Broadcast
Academic Sources
- How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation
- How to Cite a Conference Paper
- How to Cite a Lecture
Other Source Types
- How to Cite a Report
- How to Cite Interview
- How to Cite a Mobile App
Reference Materials
- How to Cite an Encyclopedia
- How to Cite a Dictionary
Bibliography:
The Chicago Manual of Style , 17th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2017. https://doi.org/10.7208/cmos17.
Turabian, Kate L. A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations , 9th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2018.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated April 9, 2020.
Written by Janice Hansen . Janice has a doctorate in literature and a master’s degree in library science. She spends a lot of time with rare books and citations.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Chicago Citation Examples
Chicago Formatting
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
