Scientific Research
- First Online: 13 October 2024

Cite this chapter

- Syed Amin Tabish 2
43 Accesses
Research involves systematic and creative efforts to expand our understanding of humans, culture, and society and to apply this knowledge in novel contexts. Scientific research specifically employs rigorous scientific methods to collect, analyze, and interpret data. Researchers classify scientific studies based on data collection techniques (such as causality and time relationships) and descriptive versus analytical features. Clinical research begins with formulating hypotheses—a way to make claims about population parameters based on sampled data. Scientific research is a neutral, systematic, and planned process that leverages existing knowledge to advance understanding beyond what is currently documented. Researchers classify studies based on data collection techniques (observational or experimental), causal relationships (descriptive or analytical), and time frames (prospective, retrospective, or cross-sectional). The foundation of scientific inquiry lies in formulating clear, specific hypotheses to address research questions, followed by rigorous testing using scientific methods. The scientific method operates neutrally, objectively, and rationally, aiming to validate or refute hypotheses. A robust research plan includes data collection procedures, variable evaluation, and ensuring analyzable data. Statistical analysis plans, subject and control calculations, and diligent data observation are essential components. Scientific research involves systematically collecting, interpreting, and evaluating data to contribute to scientific knowledge. Researchers adhere to ethical principles in medical research, including respect for humans, society, benefit, harmlessness, autonomy, and justice. Research methods guide data collection and analysis. Researchers choose methods based on data type (qualitative vs. quantitative), source (primary vs. secondary), and purpose (descriptive vs. experimental). Quantitative data analysis employs statistical methods, while qualitative data interpretation uses techniques like thematic analysis. Research methods serve as the foundational elements of scientific inquiry. They provide the essential “how” for systematically building knowledge. As researchers accumulate information, each well-designed study contributes evidence that can support, amend, refute, or deepen existing understanding. Decisions made during research—such as data collection strategies, adherence to logical rules, and bias mitigation—are critical. Learning research methods involves honing the ability to make informed decisions. Beyond traditional approaches, emerging vectors like hypothesis-driven, data-mining-inspired, and computational models expand the scientific method’s 3D space. These diverse methods will significantly influence our understanding of nature, impacting experimental design, peer review, funding, education, medical diagnostics, and legal considerations. The scientific method is a systematic process employed by researchers and scientists to explore observations and address questions. It involves several steps: asking a question, conducting background research, constructing a hypothesis, testing it through experiments, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. Scientists engage in a dynamic, open-ended investigation, following five key steps: defining a research question, making predictions, gathering data, analyzing that data, and finally drawing conclusions.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Cohen, N. and Arieli, T. (2011) Field research in conflict environments: Methodological challenges and snowball sampling. Journal of Peace Research 48 (4), pp. 423–436.
Article Google Scholar
Creswell, J. W. (2008). Educational Research: Planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River: Pearson.
Google Scholar
Eisner, E. W. (1981). “On the Differences between Scientific and Artistic Approaches to Qualitative Research”. Educational Researcher 10 (4): 5–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/1175121 .
Freshwater, D., Sherwood, G. and Drury, V. (2006) International research collaboration. Issues, benefits and challenges of the global network. Journal of Research in Nursing, 11 (4), pp 9295–303.
Gauch, Jr., H.G. (2003). Scientific method in practice. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. 2003 ISBN 0-521-81689-0 (page 3)
Abhaya Indrayan (2004). “Elements of medical research.” Indian J Med Res 119 (3): 93–100. PMID 15115159.
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Health Research and the Privacy of Health Information: The HIPAA Privacy Rule; Nass SJ, Levit LA, Gostin LO, editors. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2009. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9571/#
Kara H (2012) Research and Evaluation for Busy Practitioners: A Time-Saving Guide, p.102. Bristol: The Policy Press.
Lawson, A. (2006): Statistical Methods in Spatial Epidemiology, 2nd edition, Wiley. Lawson, A. and Cressie, N. (2000): “Spatial statistical methods for environmental epidemiology”, in Handbook of Statistics, Vol. 18, P.K. Sen and C.R. Rao (Eds.), Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 357-396.
OECD (2002) Frascati Manual: proposed standard practice for surveys on research and experimental development, 6th edition. Retrieved 27 May 2012 from www.oecd.org/sti/frascatimanual .
Schwab, Michael, and Borgdorff, Henk, eds. (2014), The Exposition of Artistic Research: Publishing Art in Academia, Leiden: Leiden University Press.
Shuttleworth, Martyn (2008). “Definition of Research”. Explorable . Explorable.com . Retrieved 14 August 2011.
What is Original Research? Original research is considered a primary source. Thomas G. Carpenter Library, University of North Florida. Archived from the original on 2011-07-09. Retrieved 9 Aug 2014.
Wilson, Nick and van Ruiten, Schelte/ELIA, eds. (2013), SHARE Handbook for Artistic Research Education , Amsterdam: Valand Academy, p. 249.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Sher-i-Kashmir Inst. of Medical Sciences, Srinagar, India
Syed Amin Tabish
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Tabish, S.A. (2024). Scientific Research. In: Health Care Management: Principles and Practice. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-3879-3_27
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-3879-3_27
Published : 13 October 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-97-3878-6
Online ISBN : 978-981-97-3879-3
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Download Free PDF
Research Methodology: An Introduction

Related papers
According to Mugenda & Mugenda (2010), research is process of carrying out a diligent inquiry or a critical examination of a given phenomenonexhaustive study that follows some logical sequence. Mouly defines research as a process of arriving at effective solutions to problems through systematic collection, analysis and interpretation of data. Research also involves a critical analysis of existing conclusions or theories with regard to newly discovered facts Research is the continued search for knowledge and understanding of the world around us. Clifford Woody argues that research is the process of designing and redefining problems, formulating hypothesis or suggested solutions, collecting, organizing and evaluating data, making deductions and reaching conclusions and carefully testing the conclusions to determine whether they fit the formulated hypothesis.
Research is any original and systematic investigation undertaken to increase knowledge and understanding and to establish facts and principles. It comprises the creation of ideas and generation of new knowledge that lead to new and improved insights and the development of new material, devices, products and processes. The word " research " perhaps originates from the old French word recerchier that meant to 'search again'. It implicitly assumes that the earlier search was not exhaustive and complete and hence a repeated search is called for.
Educational Journal, 2023
In the simplest of terms, the research definition is a process of seeking out knowledge. This knowledge can be new, or it can support an already known fact. The purpose of research is to inform and is based on collected and analyzed data. This exploration occurs systematically, where it is either tested or investigated to add to a body of knowledge. Research is a systematic and scientific approach to understanding the world around us. It is a process of inquiry that involves the collection and analysis of data to answer questions or solve problems.
It is an investigation of finding solutions to scientific and social problems through objective and systematic analysis. It is a search for knowledge, that is, a discovery of hidden truths. Here knowledge means information about matters. The information might be collected from different sources like experience, human beings, books, journals, nature, etc. A research can lead to new contributions to the existing knowledge. Only through research is it possible to make progress in a field. Research is indeed civilization and determines the economic, social and political development of a nation. The results of scientific research very often force a change in the philosophical view of problems which extend far beyond the restricted domain of science itself. Research is not confined to science and technology only. There are vast areas of research in other disciplines such as languages, literature, history and sociology. Whatever might be the subject, research has to be an active, diligent and systematic process of inquiry in order to discover, interpret or revise facts, events, behaviours and theories. Applying the outcome of research for the refinement of knowledge in other subjects, or in enhancing the quality of human life also becomes a kind of research and development. Research is done with the help of study, experiment, observation, analysis, comparison and reasoning. Research Methods and Research Methodology Research methods are the various procedures, schemes and algorithms used in research. All the methods used by a researcher during a research study are termed as research methods. They are essentially planned, scientific and value-neutral. They include theoretical procedures, experimental studies, numerical schemes, statistical approaches, etc. Research methods help us collect samples, data and find a solution to a problem. Particularly, scientific research methods call for explanations based on collected facts, measurements and observations and not on reasoning alone. They accept only those explanations which can be verified by experiments. Research methodology is a systematic way to solve a problem. Foundations of research are built and conducted over a structure called methodology (Remenyi et al. 1998) and a valid study will always adapt encouraging research methodology (Buckley et al. 1975). It is a science of studying how research is to be carried out. Essentially, the procedures by which researchers go about their work of describing, explaining and predicting phenomena are called research methodology. It is also defined as the study of methods by which knowledge is gained. Its aim is to give the work plan of research. It consists a logical sequence of steps or actions that are necessary to effectively solve a research problem.
Research may be very broadly defined as systematic gathering of data and information and its analysis for advancement of knowledge in any subject. research attempts to find answer intellectual and practical questions through application of systematic methods. Types of research can be classified in many different ways.
Unicorn seal. Indian Museum Kolkata H-53. Sign 336. baṭa 'rimless, wide-mouthed pot' rebus: bhaṭa 'furnace' PLUS muka 'ladle' (Tamil)(DEDR 4887) Rebus: mūh 'ingot' (Santali) Vikalpa. ḍabu 'an iron spoon' (Santali) Rebus: ḍab, ḍhimba, ḍhompo 'lump (ingot?). Thus, together, furnace ingots. kolom 'three' rebus: kolimi 'smithy, forge' kāṇḍa, kãṝ ʻstalk, arrow'(CDIAL 3023) rebus: khaṇḍa 'implements'.(Oriya) Cargo manifest smithy ingots implements maritime treasure guard-Invoiced, delivered on jāngaḍa 'on approval basis' accounting system-system in vogue even today for high-value diamond transactions
Java script para bootstrap
ARGUMENT, 2011
La Scuola Cattolica, 2024
Skepticism (New Problems of Philosophy), 2022
Biologia: Ensino, Pesquisa e Extensão - Uma Abordagem do Conhecimento Científico nas Diferentes Esferas do Saber - Volume 2, 2021
International Journal of Language Studies, 2024
The American Journal of Cardiology, 1983
Hereditary Cancer in Clinical Practice, 2008
Folia Forestalia Polonica: Series A - Forestry, 2009
International Scholarly Research Notices, 2014
Endocrine Reviews, 2019

Related topics
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Harris, Trump Voters Differ Over Election Security, Vote Counts and Hacking Concerns
Just 20% of voters are highly confident the supreme court would be politically neutral if it rules on legal issues in 2024 election, table of contents.
- Other findings: Voters’ plans for casting ballots, confidence in Supreme Court to be politically neutral if it must resolve 2024 election challenges
- Confidence in poll workers, state election officials
- Are the parties committed to fair and accurate elections?
- GOP confidence in absentee ballot counts remains low
- 2. Confidence in voting access and integrity; expectations for whether and when the election results will be clear
- How easy will it be to vote this year?
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology

Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand Americans’ views of voting and their expectations around the 2024 presidential election.
For this analysis, we surveyed 5,110 U.S. adults – including 4,025 registered voters – from Sept. 30 to Oct. 6, 2024. Everyone who took part in this survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), a group of people recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses who have agreed to take surveys regularly. This kind of recruitment gives nearly all U.S. adults a chance of selection. Surveys were conducted either online or by telephone with a live interviewer. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other factors. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this report , the topline and the survey methodology .
With voting underway in the 2024 presidential race, majorities of American voters are at least somewhat confident that the election will be run smoothly, that votes will be counted accurately and that ineligible voters will be prevented from casting ballots.
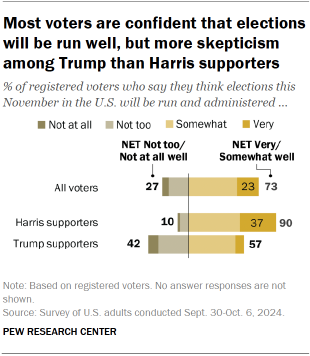
But supporters of Kamala Harris and Donald Trump have sharply different expectations for how this year’s election may unfold. In many cases, these differences are as wide as they were in the lead-up to the 2020 election .
Harris supporters are more optimistic about the way the election will be run: 90% say they are at least somewhat confident that elections across the United States will be administered well. This compares with 57% of Trump supporters who are confident the election will be run smoothly.
This pattern in views extends to other aspects of the presidential race:
- Harris supporters are more confident than Trump supporters that, after all the votes are counted, it will be clear who won (85% vs. 58%).
- Harris supporters are much more confident that mail-in ballots will be counted as voters intend (85% vs. 38%).
- Harris supporters also are more confident that election systems across the U.S. are secure from hacking and other technological threats (73% vs. 32%).
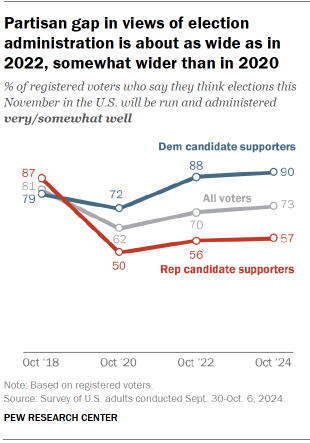
The latest national survey by Pew Research Center, conducted among 5,110 U.S. adults (including 4,025 registered voters) from Sept. 30 to Oct. 6, 2024, finds that voters who support Harris are more confident in the way the 2024 election will unfold than President Joe Biden’s supporters were four years ago.
And those who support Trump are deeply skeptical about the way the election will be conducted – expressing even less confidence on some election issues than his supporters did four years ago.
Wide partisan gaps in election confidence since 2020
In 2018, Republican candidate supporters were 8 percentage points more likely than Democratic candidate supporters to say that year’s midterm election would be run well. By 2020, Biden’s supporters were 22 points more likely than Trump’s to expect the election to run smoothly. The gap this year is even wider: 33 points between Harris and Trump supporters.
Harris, Trump supporters differ on whether votes will be counted accurately
As was the case four years ago, Trump supporters are particularly skeptical that absentee and mail-in ballots will be counted as voters intend.
Harris supporters are more than twice as likely as Trump supporters to say they are very or somewhat confident that absentee and mail-in ballots will be counted accurately (85% vs. 38%).
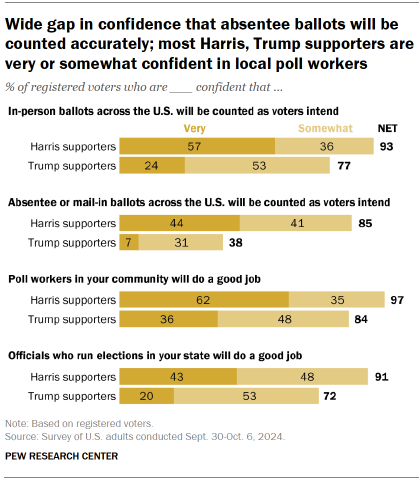
By contrast, sizable majorities of both coalitions (93% of Harris supporters, 77% of Trump supporters) are at least somewhat confident that in-person votes will be counted accurately.
However, far more Harris (57%) than Trump (24%) supporters are very confident this will happen.
There is broad confidence among voters overall that local poll workers and state election officials will do a good job during the upcoming election.
Yet Harris supporters are more likely than Trump supporters to express a high degree of confidence in these administrators.
Read more on views of election administration and vote counting in Chapter 1
Related: Key facts about U.S. poll workers
Voters’ views of illegal voting, access to voting
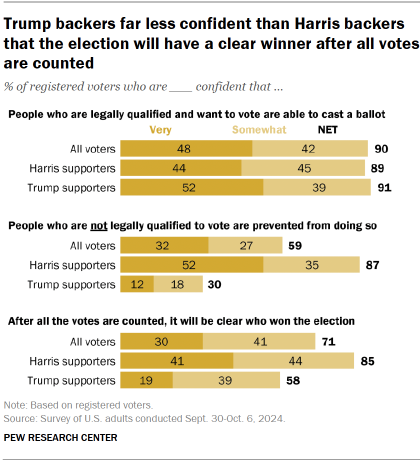
Roughly nine-in-ten among both Trump and Harris supporters are confident that eligible voters will be able to cast a ballot if they want to.
But there are bigger divisions on whether people who are ineligible to vote will be prevented from doing so.
Today, 87% of Harris voters are at least somewhat confident that ineligible voters will be prevented from casting ballots. Just 30% of Trump supporters say this.
Most voters are at least somewhat confident that it will be clear which candidate won the election after all the votes are counted. But here again, Harris backers (85%) are much more likely than Trump supporters (58%) to express confidence that the winner will be clear.
Do voters think election systems in the U.S. are safe from hacking?
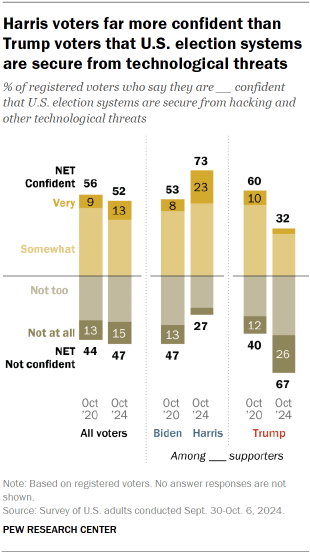
Overall, 52% of voters are at least somewhat confident that U.S. election systems are secure from hacking and other technological threats. Nearly as many voters (47%) are not confident about this.
- 73% of Harris supporters say they are confident that election systems are secure. This is higher than the share of Biden supporters who said this in the weeks before the 2020 election (53%).
- The pattern is reversed among Trump supporters: 32% now say election systems are secure from hacking and other technological threats, down from 60% four years ago.
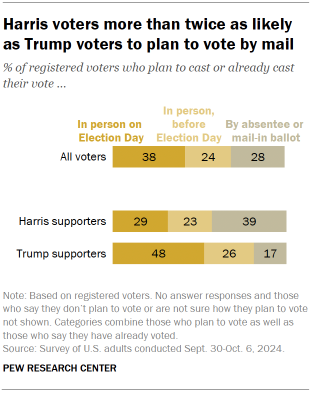
A smaller share of voters plan to cast ballots by mail compared with 2020. Four years ago, during the COVID-19 pandemic, a record share of voters cast ballots by mail in the presidential election . Today, a much smaller share of voters plan to vote by mail (39% then, 28% today). But as in 2020 amid the Biden-Trump matchup , Harris supporters are about twice as likely as Trump supporters to say they plan to cast a ballot via mail.
Read more on voters’ expectations around voting in Chapter 3
Trump backers who plan to vote by mail are more confident that mail-in ballots will be counted accurately. Though most Trump supporters plan to cast a ballot in person, 17% say they plan to vote absentee or by mail. These voters express far more confidence in the accuracy of mail-in ballots than do those who plan to vote in person (67% vs. 31%).
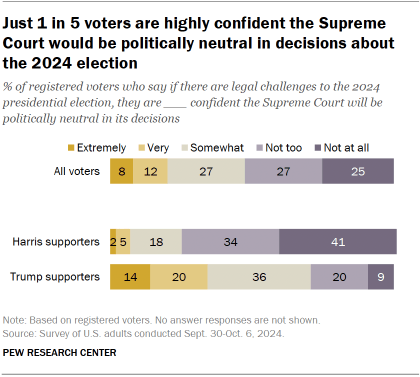
Most voters are not confident the Supreme Court would be politically neutral if it had to resolve legal challenges related to the 2024 election. Overall, just 20% of voters are extremely or very confident the court would remain politically neutral if it had to resolve any legal challenges that stemmed from the 2024 election. But Trump voters express more confidence than Harris voters do (34% vs. 6%).
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Election 2024
- Election System & Voting Process
- Supreme Court
- U.S. Democracy
Most Voters Say Harris Will Concede – and Trump Won’t – If Defeated in the Election
How voters expect harris’ and trump’s policies to affect different groups in society, in tight u.s. presidential race, latino voters’ preferences mirror 2020, americans in both parties are concerned over the impact of ai on the 2024 presidential campaign, americans view walz more positively than vance, but many aren’t familiar with either vp nominee, most popular, report materials.
- Questionnaire
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan, nonadvocacy fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It does not take policy positions. The Center conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, computational social science research and other data-driven research. Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts , its primary funder.
© 2024 Pew Research Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research is also considered as the application of scientific method in solving the problems. It is a systematic, formal and intensive process of carrying on the scientific method of analysis. There are many ways of obtaining knowledge. They are intuition, revelation, and
A research methodology is defined as the study of how scientific research is conducted. According to Mishra and Alok (2022), a research methodology outlines what research is about, how to proceed ...
1 Curiosity and research 1 1.1 Course goals 1 1.2 Kinds of questions 1 1.3 Research methods for science 3 1.4 Putting methods together 15 Assignments 15 2 Overview of experimental analysis and design 18 2.1 Hypothesis-driven experiments 18 2.2 Measuring values 30 2.3 Improving experiments 39 2.4 Safety and ethics 43 Assignments 48 3 Statistics 51
3. Note the method or tool you selected to answer the question. 4. Make a list of other methods you might employ to answer your original question. 5. Reflect on how identifying alternative research methods might lead you to different answers to your original question, then make a new research plan.
and the scientific method is the arrangement that has so far. proved most fruitf ul for the explanation of objective. phenomena.. Accumulation. Science is an acc umulative and integrated system ...
data collection, analysis, and interpretation. The selection of a research approach includes the research problem or issue being addressed, the researchers' persona. experiences, and the audiences for the study. Thus, in this book, philosophical assumptions, research approaches, research designs, and research methods are four key terms ...
4.2 Research methodology, theory and research method selection A research methodology is 'a general approach to studying research topics' (Hussey and Hussey, 1997: 56), which is distinct from a research method. A research method is a tool or a technique that is used to gather data (Bailey, 1994). In contrast, a research methodology ...
The scientific method, or research method, is a set of systematic techniques used to acquire, modify, and integrate knowledge concerning observable and measurable phenomena. Science is one wayofknowing about the world by making use of the scientific method to acquire knowledge. Answers: 1. The scientific method is a set of systematic techniques ...
Science and scientific research. Science and scientific research. Thinking like a researcher. Thinking like a researcher. Thinking like a researcher. The research process. The research process. The research process. Theories in scientific research. Theories in scientific research. Theories in scientific research. Research design
The methods for conducting scientific research that have been developed over the past centuries include the following: • Observation • Hypothesis • Experimentation • Interpretation lt is important to understand the nature of these meth ods and how each method should be used to conduct research. OBSERVATIONS
Chapter 1 The Scientific Method and Relevant Components- -3 Therefore, utilizing and following the tenets of a sound research design is one of the most fundamental aspects of the scientific method. Put simply, the research design is the structure of investigation, conceived so as to obtain the "answer" to research questions or hypotheses.
engage in scientific research. The course in which you are now enrolled will provide you with information about conducting scientific research. Some students might feel that understanding research is important only for professional scientists. But, as Table 1.1 reveals, there are many reasons why students should take a research methods course. One
The scientific method provides an organized way to think about and solve problems based on data. Most scientists describe it as the following steps: 1. State the problem. State the problem that you will study as clearly and concisely as possible. 2. Form the hypothesis.
The method of science, or. reflective inquiry, is the fourth way of knowing or fixing belief. To Peirce and to scientists in general, it is the most . reliable. way of knowing. Peirce argues that the method of science provides a means to fix beliefs in such a way that the "ultimate conclusion of every man must be the same. . . . There are real
Research Methods Lecture 1: Scientific Method and Critical Thinking 1.1 Scientific Methods Most beginning science courses describe the scientific method. They mean something fairly specific, which is often outlined as Hypothesis . 1. State a hypothesis; that is, a falsifiable statement about the world. 2. Design an experimental procedure to ...
Most scientists, but not all, are interested in three goals: understanding, prediction, and control. Of these three goals, two of them, understanding and prediction, are sought by all scientists. The third goal, control, is sought only by those scientists who can manipulate the phenomena they study.
Research refers to a perpetual pursuit of knowledge and comprehension. Scientific research differs substantially from other types of research in its use of scientific methods for conducting studies. Research is an organized and systematic way of finding answers to questions. Systematic: A defined set of steps and procedures must be followed ...
ster sessions.Summary There are seven steps to the scientific method: Question, Research, Hypothesis, Experiment, Data Analysis, Concl. sion, and Communication. Although scientists may modify, reorder, or revisit steps on occasion, scientists generally use thi.
Research methodology is a systematic way to solve a problem. Foundations of research are built and conducted over a structure called methodology (Remenyi et al. 1998) and a valid study will always adapt encouraging research methodology (Buckley et al. 1975). It is a science of studying how research is to be carried out.
Quantitative methods are research techniques that are used to gather quantitative data, data that can be sorted, classified, measured. This following section outlines the core quantitative research methods used in social research. Quantitative survey What is the method? Surveys are a popular method of collecting primary data. The broad
4.4.2 Quasi Experimental Research 4.5 Methods of Research 4.5.1 Non-Experimental Methods 4.5.1.1 Naturalistic Observation 4.5.1.2 Archival Research 4.5.1.3 Content Analysis 4.5.2 Surveys 4.5.3 Field Studies 4.5.4 Case Studies 4.6 Experimental Methods 4.6.1 Laboratory Experiments 4.6.2 Field Experiment 4.7 Let Us Sum Up 4.8 Unit End Questions 4. ...
The scientific method is the strategy of science to generate knowledge. Its implementation is carried out by scientific research. Scientific research is employed in the three phases of the ...
NYS Standard 1 - Students will use mathematical analysis, scientific inquiry, and engineering design, as appropriate, to pose questions, seek answers, and develop solutions. NYS Standard 4 - Students will understand and apply scientific concepts, principles, and theories pertaining to the physical setting and living environment and recognize ...
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century. The scientific method involves careful observation coupled with rigorous scepticism, because cognitive assumptions can distort the interpretation of the observation.Scientific inquiry includes creating a hypothesis through inductive reasoning ...
Due to their characteristics, each of these methods is more. suitable for one of the three objectives of scientific research: exploratory, descriptive and explanatory. Keywords: Exploratory ...
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan, nonadvocacy fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It does not take policy positions. The Center conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, computational social science research and other data-driven research.