techlauve.com – a knowledge base for IT professionals.
Inhale problems, exhale solutions..
- Nick’s Blog
- Active Directory
- Privacy Policy
« Outlook: “Sending and Receiving reported error (OX80040600)”
Terminal Server Does Not Accept Enough Client Connections »

Adding Sites to Internet Security Zones Using Group Policy
Sometimes it is useful to leverage the power of Group Policy in Active Directory to add sites to certain security zones in Internet Explorer. This can save the network admin the trouble of managing the security zone lists for each computer (or user) separately. In the following example, each user on the network needs to have a specific site added to the Trusted Sites list.
This tutorial assumes that group policy is in good working order on the domain and that all client users and computers can access the directory.
- Open the Group Policy Management MMC console.
- Right-click the organization unit (OU) that the policy should apply to, taking special care to consider whether the policy should apply to computers or users on this particular network.
- Select “Create and Link a GPO Here…” to create a new group policy object.
- In the “New GPO” window, enter a good, descriptive name for this new policy and click “OK”. (ex. “Trusted Sites Zone – Users” or something even more descriptive)
- Locate the newly created GPO in the left-side navigation pane, right-click it and select “Edit…”
- Expand “Administrative Templates” under either “Computer Configuration” or “User Configuration” depending on which type of OU the new policy was linked to in step 2.
- The path to the settings that this example will be using is: Administrative Templates -- Windows Components -- Internet Explorer -- Internet Control Panel -- Security Page
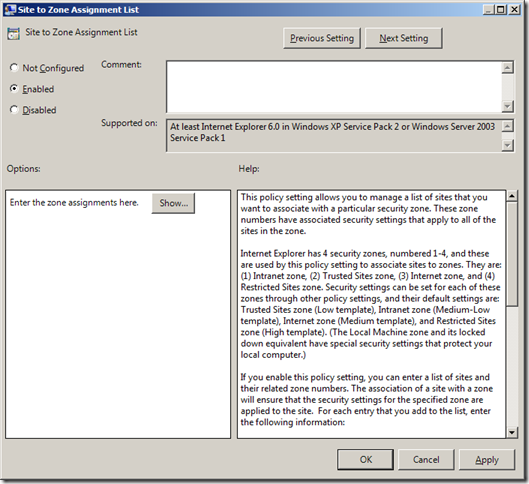
- In the right-hand pane, double-click “Site to Zone Assignment List”.
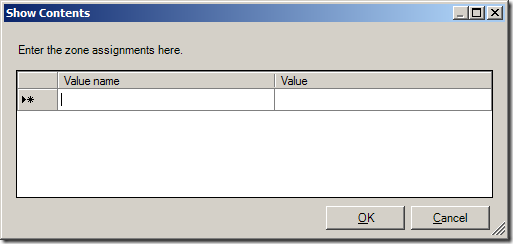
- Enable the policy and click the “Show…” button next to “Enter the zone assignments here.” This will pop up the “Show Contents” window.
- Click the “Add…” button. This will pop up the “Add Item” window.
- In the first box, labeled “Enter the name of the item to be added:”, enter the URL to the site. (ex. https://secure.ourimportantwebapp.com) . Keep in mind that wildcards can be used. (ex. https://*.ourimportantdomain.com) . Leave off any trailing slashes or sub-folders unless that type of specific control is called for.
- 1 – Intranet Zone
- 2 – Trusted Sites Zone
- 3 – Internet Zone
- 4 – Restricted Sites Zone
- Once the zone assignment has been entered, click “OK”. This will once again show the “Show Contents” window and the new entry should be present.
- Click “OK” and “OK” again to get back to the Group Policy Management Console.
The new policy will take effect at the next group policy refresh interval, which is usually 15 minutes. To test immediately, run a gpupdate /force on a user/computer that falls into the scope of the new policy and go to “Tools -> Internet Options -> Security -> Trusted Sites -> Sites”. The site(s) added should be in the list. If the sites do not show up, check the event logs for any group policy processing errors.
Related content:
- How To: Time Sync Across Windows Network
- Group Policy Not Applied To Remote VPN Users
- QuickBooks Payroll Opens/Saves the Wrong W2 Form
- Microsoft Virtual Server Web Console Constantly Asks For Password
- Group Policy: Applying Different User Policies to the Same User for Workstations and Terminal Server
No comment yet
Juicer breville says:.
November 26, 2012 at 12:11 am (UTC -5)
Hurrah, that’s what I was looking for, what a information! existing here at this web site, thanks admin of this web page.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
You may use these HTML tags and attributes: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
Submit Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Remember Me
Connect With Us
Connect with us.
Social Connect by NewsPress
Not finding the answer that you're looking for? Need more help with a problem that is addressed in one of our articles?
techlauve.com is affiliated with Rent-A-Nerd, Inc. in New Orleans, LA.
- DFS Replication (1)
- Group Policy (1)
- Microsoft Exhange (3)
- Microsoft Outlook (11)
- Copiers (1)
- Multi Function Devices (1)
- Printers (2)
- Scanners (1)
- Blackberry (1)
- Firewalls (2)
- Wireless (2)
- Hard Drives (1)
- SAN Systems (1)
- Hyper-V (3)
- Virtual Server (1)
- WordPress (1)
- Security (7)
- QuickBooks (2)
- Quicken (1)
- Antivirus/Antimalware (4)
- Backup Exec (2)
- Internet Explorer (5)
- Microsoft SQL (1)
- Licensing (2)
- Steinberg Nuendo (1)
- Mac OS X (1)
- Server 2003 (12)
- Server 2008 (14)
- Small Business Server 2003 (7)
- Terminal Server (6)
- Updates (2)
- Windows 7 (9)
- Windows XP (11)
- Reviews (1)
- Rent-A-Nerd, Inc.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Licence .
Valid XHTML 1.0 Strict Valid CSS Level 2.1
techlauve.com - a knowledge base for IT professionals. uses Graphene theme by Syahir Hakim.
- ManageEngine Products
Securing zone levels in Internet Explorer
Managing and configuring Internet Explorer can be complicated. This is especially true when users meddle with the numerous settings it houses. Users may even unknowingly enable the execution of malicious codes. This highlights the importance of securing Internet Explorer.
In this blog, we’ll talk about restricting users from changing security settings, setting trusted sites, preventing them from changing security zone policies, adding or deleting sites from security zones, and removing the Security tab altogether to ensure that users have a secure environment when using their browser.
Restricting users from changing security settings
A security zone is a list of websites at the same security level. These zones can be thought of as invisible boundaries that prevent certain web-based applications from performing unauthorized actions. These zones easily provide the appropriate level of security for the various types of web content that users are likely to encounter. Usually, sites are added or removed from a zone depending on the functionality available to users on that particular site.
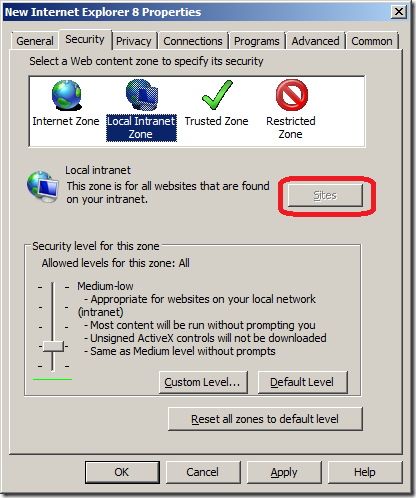
To set trusted sites via GPO
- Open the Group Policy Management Editor .
- Go to User Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page .
- Select the Site to Zone Assignment List .
- Select Enabled and click Show to edit the list. Refer to Figure 1 below. The zone values are as follows: 1 — intranet, 2 — trusted sites, 3 — internet zone, 4 — restricted sites.
- Click Apply and OK .
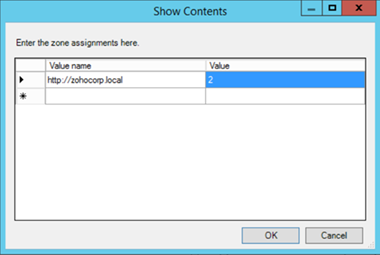
Figure 1. Assigning sites to the Trusted Sites zone.
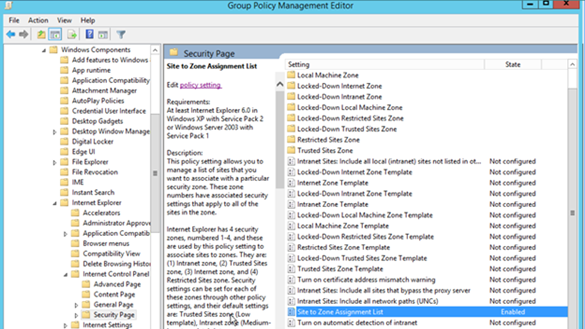
Figure 2. Enabling the Site to Zone Assignment List policy.
By enabling this policy setting, you can manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. See Figure 2.
Restricting users from changing security zone policies
- Go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer .
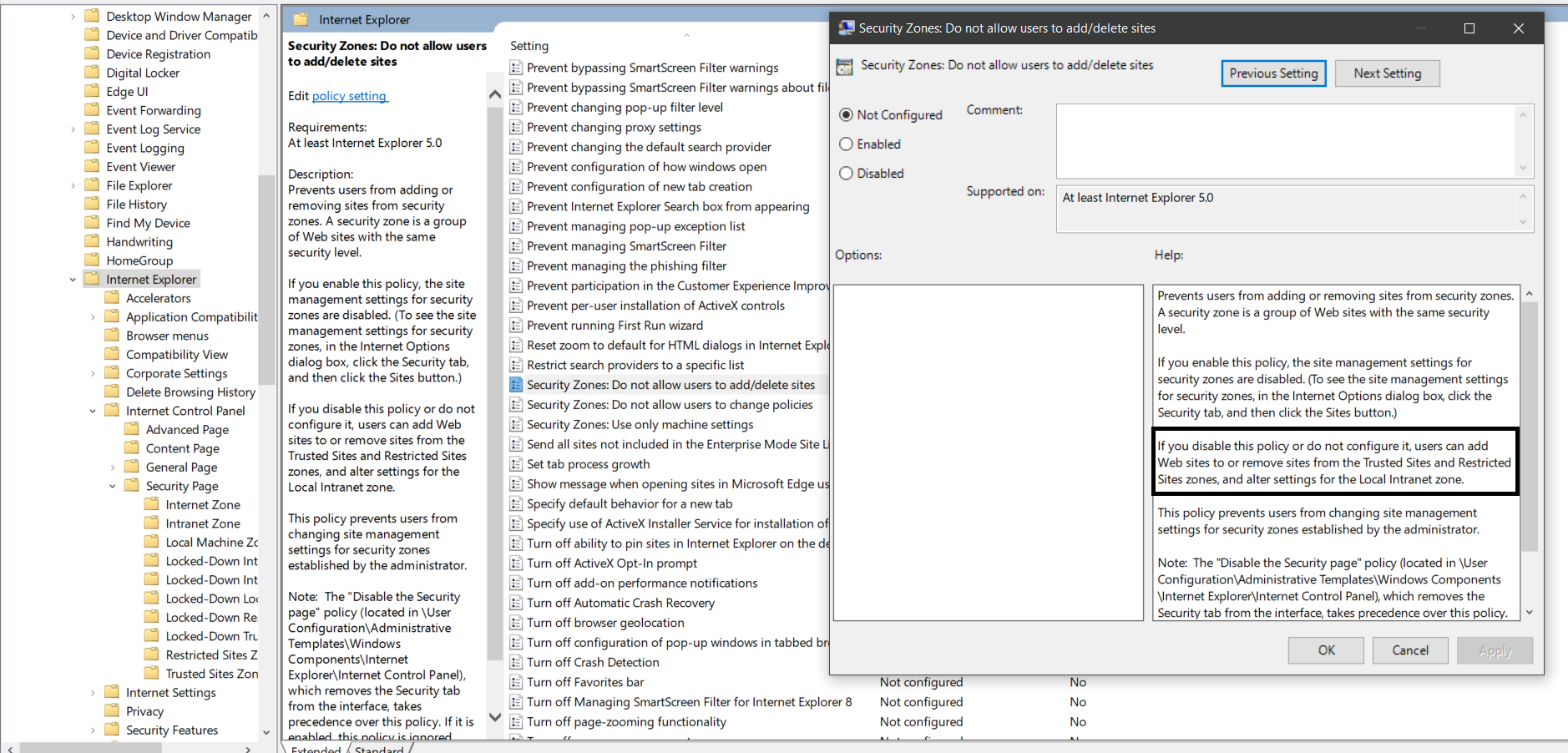
- Double-click Security Zones: Do not allow users to change policies .
- Select Enabled .
This prevents users from changing the security zone settings set by the administrator. Once enabled, this policy disables the Custom Level button and the security-level slider on the Security tab in the Internet Options dialog box. See Figure 3.
Restricting users from adding/deleting sites from security zones
- Double-click Security Zones: Do not allow users to add/delete sites .
This disables the site management settings for security zones, and prevents users from changing site management settings for security zones established by the administrator. Users won’t be able to add or remove websites from the Trusted Sites and Restricted Sites zones or alter settings for the Local Intranet zone. See Figure 3.
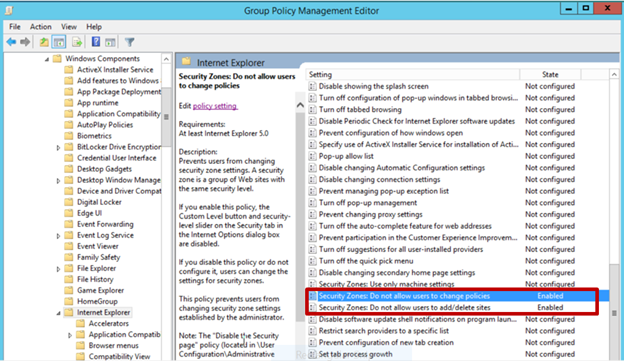
Figure 3. Enabling Security Zones: Do not allow users to change policies and Security Zones: Do not allow users to add/delete sites .
Removing the Security tab
The Security tab in Internet Explorer’s options controls access to websites by applying security settings to various download and browsing options, including defining security levels for respective security zones. By removing this tab, users will no longer be able to see or change the settings established by the administrator.
- Go to User Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel .
- Double-click Disable the Security page .
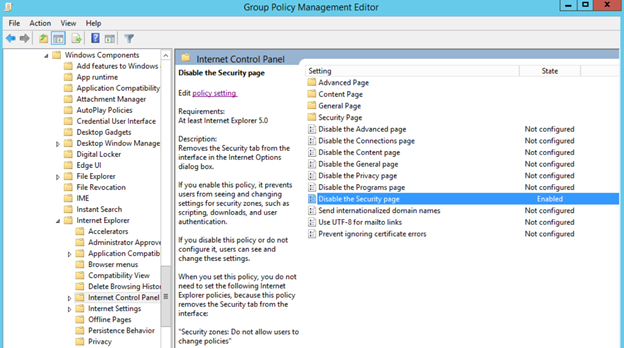
Figure 4. Enabling the Disable the Security page policy. Enabling this policy prevents users from seeing and changing settings for security zones such as scripting, downloads, and user authentication. See Figure 4.
There’s no denying the importance of securing Internet Explorer for any enterprise. By setting security levels, restricting users from changing security zone policies, preventing them from adding or deleting sites from security zones, and removing the Security tab, users will not be able to change any security settings in Microsoft Internet Explorer that have been established by the administrator. This helps you gain more control over Internet Explorer’s settings in your environment.
Derek Melber
Cancel reply.
Is there a way to enable Site to Zone assignment list and still let the user enter their own sites to the trusted list?
Hi Joe. You need to disable the below setting to achieve the requirement.
Note: Even if the policy is not configured, users can add their own sites. Only when the policy is enabled, users can’t add their own sites to trusted sites.
Thanks a lot.
Related Posts

Descubra los numerosos reconocimientos de Applications Manager en 2024
Español 4 min read Read
Group Policy Central
News, Tips and Tutorials for all your Group Policy needss
How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites
As you know Group Policy Preferences are these fantastic new settings that allow IT administrators perform any configuration they want on a users group using Group Policy… well almost.. In this tutorial I will show you how to configured one of the few settings that are not controlled by preferences but can be configured using a native Group Policy.
The Internet Explore site zone assignment is one of the few settings you specifically can’t configured using preferences, as you can see (image below) the User Interface to this options has been disabled.
There is a native Group Policy that allows you to control Internet Explorer site zone list is called “Site to Zone Assignment List†which I will go thought below how to use.
Step 1. Edit the Group Policy Object that is targeted to the users you whish this setting to be applied.
Step 2 . Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page and double click on the “Site to Zone Assignment List†and check the “Enable†option then click on the “Show..†button.
Step 3. Now type the URL in the “Value name†field with the >* on the far left and then type the zone number (see table below) you want to assign to that zone.
Internet Explorer Group Policy Zone Number Mapping
| Zone Number | Zone Name |
| 1 | Intranet Zone |
| 2 | Trusted Sites zone |
| 3 | Internet zone |
| 4 | Restricted Sites zone |
As soon as you start typing the URL a new line will appear for the next URL.
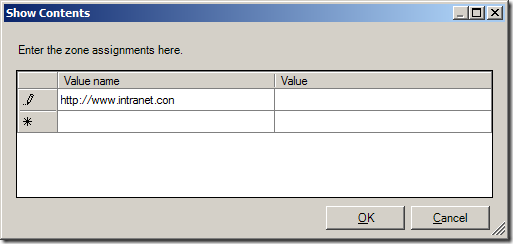
Step 4. One you have finished assigning adding the URL’s and site zone number click OK
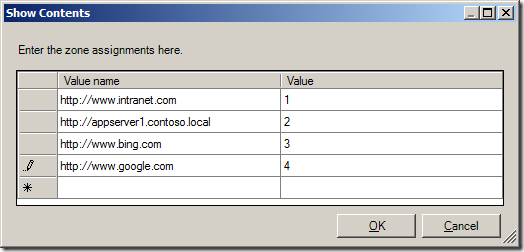
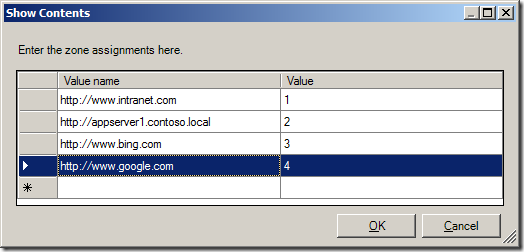
Tip: If you want to delete a row click on the button on the far left to select the row you want to delete (see image below) and then press the “Delete†key.
(sites in above list are example only)
Now the Internet Explorer Site zone list will now be populated with the zone you configured above and as you can see in the images below the Internet Explorer status bar now show the correct zone based on the that the URL’s in the address bar.
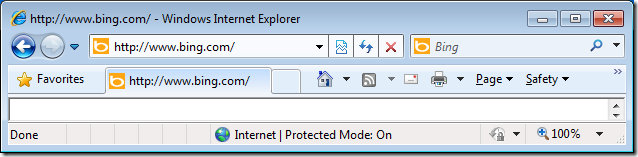
Author: Alan Burchill
Related articles.

34 thoughts on “ How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites ”
Blog Post: How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites http://bit.ly/bNHowK
How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites http://bit.ly/bNHowK
- Pingback: Group Policy Center » Blog Archive » Group Policy Setting of the Week 18 – Allow file downlaod (Internet Explorer)
- Pingback: Group Policy Center » Blog Archive » How to use Group Policy to mitigate security issue KB981374
Yup, that is right and excately how we do it, however there is one problem that is of slight concern 🙁
Once the Zones are set via this GP the user can not add his own and as banks etc. today rely on Trusted Zones this is a slight problem. Our IT policy allow for users to use their PC for personal business as well as work and thus it is a slight problem that they cant add Zones for eg. their bank etc.
I have been thinking, maybe one could make a script to set Zones and deploy this via SCCM 2007.
I have not tried this for a while but i believe you can still do this if you configure it under the Internet Explorer Maintainence section of Group Policy…
The configuration for regular zones works fine. Bu the real pain starts when trying to cover zones for “Enahanced Security Configuration” which require other hives in the registry (e.g. “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\ESCDomains\MyDomain”). I have not seen a Microsoft solution for that so far. If anybody knows a smart solution and would share it, I’d really appreciate that.
You will not have to resort to a script and SCCM. Contrary to what this blog entry says can’t be done, we do use GPP to set sites into speicfic security zones. But we don’t set it as a GPP Internet Setting. We use GPP to assign the sites to their proper zones in HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains. Doing it this way we configure the sites we need configured for the organization but do not block the users’ ability to add sites they need set for their individual machines.
Ditto. This was my conclusion a few years ago when researching the various IE management methods. Have been scripting the site/zone assignment manually since then. Primarily with GPP which is fairly simple to manage Colin
GPP is server 2008 only and requires client side software correct? Anyway to do achieve the same results (managed IE Zones without disabling user access) in a 2003 AD environment?
Is there somebody who know how to do the same but with Cookies ?
Because of that, I still have to use IEM which sucks…
@AdamFowler_IT this is how you do IE zones http://t.co/uKug8h9h /cc @auteched
@alanburchill @auteched Worth noting that IE zones via this method http://t.co/qiaLSFK7 will wipe out settings from the old method!!!
with this GPO can we block all internet traffic except google and some other sites to users in the domain??
- Pingback: Best Practice: Roaming Profiles and Folder Redirection (a.k.a. User State Virtualization) : The Digital Jedi's Blog
If I understand GPOs properly, configuring this policy setting will centrally manage this setting without allowing the user to add/delete/modify any of the site to zone settings. Wouldn’t it be preferable to configure these directly in the user’s registry by use of “Preference” registry settings? I.e. creating records in “User Configuration\Preferences\Windows Settings\Registry”.
Hi, Quick question. Is it possible to have multiple sites assigned to “Intranet Zone”? If I try and add additional sites with the same zone number it states that this is not allowed. Can the links be broken up with ; , or something similar? Thanks,
you add each url in separate lines and repeat the zone number code on the right as many times in the list as you like for that zone. Each url will appear listed in that zone then.
I have a question, when you apply this group policy, users cannot add trusted website anymore by themselves. Did you know how to manage that ?
For those trying to find the answer for the above this post may be useful: http://blog.thesysadmins.co.uk/group-policy-internet-explorer-security-zones.html
It covers two methods. The first method will remove the option for the end user to edit or change the security zones, the second will allow the user to add or remove sites.
- Pingback: How to configure Roaming Profiles and Folder Redirection
- Pingback: genuine uggs
Is there a trick to copy/pasting in multiple Value names at once? I have like 100+ IP addresses to insert… Do I have to enter them in 1 at a time?!?
I found this extremely helpful and thank you for posting this. However, for some reason, on my PC when I test the GPO, my trusted sites are affected by the GPO but the only thing that happens is that I can no longer add them; the list is empty. I added about 10 sites to the list using the method above but they are not showing up. I checked to make sure the policy was being applied correctly and it is being applied; it is making it impossible to add to my trusted sites, but the list is empty. With IE 9, the GPO would do the opposite, it would add the sites but the end-user could still add more. I used IEAK for IE 9 years ago and never had a problem, but when I installed IEAK 10 or 11, it never worked.
OK, never mind! To answer my own question, in IE 10, it no longer displays the security zone on the status bar, which stinks, but one can right-click + properties (in an empty space in the body of the webpage) and it will tell the zone you are in. Looks like the zones I added are at least showing in trusted sites. That is good enough for me I guess. Thanks for the original post once again!
I too miss the security bar on IE 10. Will be interesting to review the browser user growths next year.
any news on the copying and pasting I have 100 ips to add need help with the distribution T
Computer specialists are often called IT experts/ advisors or business development advisors, and the division of a corporation or institution of higher education that deals with software technology is often called the IT sector. Countless IT service providers such as The Roots International are offering different facilities like real estate, IT solutions and many more.
I think I have a weird question/request. I want to include my whole domain such as http://www.domain.com as a trusted site. Although, I want to exclude a single web page such as http://www.my.domain.com .
I have *www.domain.com, can http://www.my.domain.com be excluded in any way?
Well, it will provide the internet user user better experience to use internet and surfing websites through internet explorer.
Invaluable discussion ! Coincidentally , if your company has been searching for a a form , my business discovered a blank version here http://goo.gl/eJ3ETg
دم شما گرم.
- Pingback: Allow Previously Unused ActiveX Controls To Run Without Prompt - PC Moment
- Pingback: Internet Options to add Trusted Site Greyed Out - SysPreped Windows 10 LTSB - Boot Panic
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Site sponsor, featured post.
Popular Posts

- Best Practice (40)
- Group Policy FAQ (3)
- KB Focus (5)
- Other Site Links (15)
- Podcast (2)
- ScreenCast (4)
- Security (33)
- Setting of the Week (41)
- Site News (19)
- TechEd (35)
- Tutorials (117)
- Uncategorized (6)
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments

Personal blog on Microsoft technologies (Exchange, Skype for Business, SharePoint, Office 365,Azure, Intune, SCCM...)

Internet Explorer – Define site to zone assignment by GPO
You may want to define an Internet Explorer setting called Security Zone using a group policy.
This settings allows you to assign some specific URL’s to an Internet security zone; each security zone has specific settings such as automatic authentication, Active X control behavior…

So, to define this settings using GPO, you have to open your Group Policy management console, create a new GPO and edit it.
The GPO settings is Computer Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page\Site to Zone Assignment List
When you edit this setting (Site to Zone Assignment List) you have to define the URL and the security zone (using a number from 1 (Intranet) to 4 (Restricted Sites) [2: Trusted Sites, 3: Internet].
BUT, if you are using Internet Explorer 7 or later with this setting configured, your end-users will not be able to add their own URL’s (such as their banking site).

So, if you want to configure site to zone assignment while allowing end-users to add their own URL’s, you must use another setting: Internet Explorer Maintenance .
This settings is User Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Internet Explorer Maintenance\Security\Security Zone and Content Ratings
Open the Security Zone and Content Ratings and choose Import the current security zones and privacy settings

By hitting the Modify Settings button you can assign the URL to the Security Zone you want to use as well as the security configuration (user authentication, Active X…).
This time, your Site to Zone configuration is deployed to your end users while you’re allowing them to add their own URL too.

Related Posts
Windows server 2008 r2 – microsoft directaccess connectivity assistant.
The Microsoft DirectAccess Connectivity Assistant (DCA) helps organizations reduce the cost of supporting DirectAccess users and significantly improve their connectivity experience. This Solution Accelerator is…
Windows 7 – Windows Troubleshooting Pack Designer
This is a prerelease of updates to a Windows 7 SDK tool that helps you write Windows 7 Troubleshooting Packs. View the demo http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/dd572173.aspx https://connect.microsoft.com/site919
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Don't subscribe All new comments Replies to my comments Notify me of followup comments via e-mail. You can also subscribe without commenting.

Managing Internet Explorer Trusted Sites with Group Policy
Internet Explorer Maintenance is dead. We all have our regrets, missed chances, and memories. But we have to move on. Depending on your love for power, you have two options. You can take the totalitarian route (known as Administrative Templates) or the benevolent method (known as Group Policy Preferences). Here are the two ways that you can configure Internet Explorer Trusted Sites with Group Policy.
Configuring IE Trusted Sites with Administrative Templates
Site to Zone Mapping allows you to configure trusted sites with Group Policy Administrative Templates. This setting can be found at:
- Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Internet Explorer / Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Site to Zone Assignment List
- User Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Internet Explorer / Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Site to Zone Assignment List
When possible, use the computer configuration option as it will not impact user logons. When you enable the setting, you will be prompted for a value name (the website) and a value (the zone list). Here are the possible values and the zone that they correspond to:
- 1 = Intranet/Local Zone
- 2 = Trusted Sites
- 3 = Internet/Public Zone
- 4 = Restricted Sites

The screenshot above shows one trusted site and one restricted site. There is a potential downside to managing trusted sites with Administrative Templates. You will not be able to edit the trusted sites list within Internet Explorer. If you have more than four items listed, you won’t be able to see the entire list in the IE Trusted Sites window. If you view the site properties (Alt – File – Properties), you can check a specific site’s zone though. Remember this trick as it will help you when troubleshooting! You can view the entire list in the Registry by navigating to HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains. If you are an administrator, you can edit/add/remote items from this list for testing. Just be sure to run a GPUpdate /force to undo your changes.
Bonus Points : Leave a comment below explaining why a GPUpdate /force is required to undo your changes. Super Bonus Points if you answer in a haiku.
Configuring IE Trusted Sites with Group Policy Preferences Registry
You would think that Group Policy Preferences Internet Settings could set trusted sites. Unfortunately, that setting is greyed out.

You can still configure IE site mappings with Group Policy Registry Preferences though.* The benefit of this is that your users can edit the zone lists and view all of the added sites. To set this up, create a new user side registry preference. This trick will not work under computer configuration. Enter in the following details:
- Keypath: Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains\WEBSITENAME
- Value Name: http
- Value Type: REG_DWORD
- Value Data: 2
Here is an example showing DeployHappiness being set as a trusted site with registry preferences:

If your site isn’t being placed in the Trusted Sites list, add it manually and then navigate to the registry location above. Ensure that the manual addition exactly matches your registry preference. You will also need to ensure that no Administrative Template Site to Zone settings are applied. If they are, they will wipe out your preference settings. Remember that Policies always win!
You can search your domain for site to zone settings by using this Group Policy Search script. Alan Burchill taught me this trick.
To see additional ways to configure site to zone mappings, read this very in depth example guide.
24 thoughts on “ Managing Internet Explorer Trusted Sites with Group Policy ”
I hope to replace our Site to Zone list to allow our users to enter their own in but I am not sure how to enter our entries that don’t specify a specific protocal such as http or https. So can someone tell me how I would create an entry for this:
*://*.sharepoint.com
and what about something like this – how would this be entered?
https://192.192.192.192 .:9443 (example only)
As for your first question, this info should help: https://community.spiceworks.com/topic/326140-add-trusted-sites-via-gpo-but-still-allow-users-to-add-trusted-sites?page=1#entry-2849140
As for the second question, I don’t know of a way to handle ports. In reference to your example, a link like that would be entered like this: *://192.192.192.192
This is excellent – I have used the GP preferences to add trused sites without locking users out of the setting if they need to add a site. But what about this – a program in the startup group – it is a shortcut to a file on a server – a member server of the local domain – domain.local. I want to prevent this program from prompting end-users to run it, and make sure it will run without prompting. Can this be accomplished with a GP preference as well? If so, do I need to add it to trusted sites, or to the local intranet zone or local machine zone? It would seem to be a local intranet or local machine zone I am working with here. I am not sure how to add it – whether I just need to add the local domain, or the computer name FQDN, or the path to the shared folder and the file. thanks!
This sounds like two different problems: 1. How do I get an app to run without prompting? 2. How do I make it run on startup with group policy?
The latter is easy, create it as a scheduled task that runs on startup. The former depends on what type of script it is. If it’s a vbscript then run it with cscript /b “name.vbs”.
With the old approach we had a file under trusted sites to allow the file to run. It has stopped working under 2012. Could I use this with a file? The old setting was:
file:\\Domain.com\netlogon\AsmallExe.exe
See this article on what you can configure with trusted sites: http://evilgpo.blogspot.com/2016/03/internet-explorer-site-to-zone.html
Just the ticket. Thanks a lot.
I have double-checked that the site to zone assignment policy is not configured, both under user and computer settings. We used group policy preferences because we do not want to lock down the trusted sites – only to push out the sites we want to be trusted. But for some absurd reason, the trusted sites are locked down and greyed out half the time – one day I will look and the sites are not dimmed out and will let me add or remove them. Then the next day they will be greyed out again. It is amazingly ridiculous. I am the only admin; no one else knows how to mess with the settings even if they had the admin credentials. So I have no clue why it keeps reverting back to the wrong settings. I thing our active directory needs to have dcdiag run on it a few times. Any ideas will be sincerely appreciated.
If it is locked down, it is a GP policy that is doing it (the site to zone assignment one) or a registry key that is enabling that site to zone assignment.
When you see one that does it, run a GPResult /h report.htm /f and look through that report.htm. You will see any GP settings that would block it then.
A reply to my own post – the problem was corrupted group policy on the Windows 7 computers – some of the computers were working fine. The ones that were not working, we had to delete the corrupt policy (it was preventing the updated policy settings from being applied). It was in the path C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Group Policy\History\{policy GUID}. After deleting the corrupt policy and rebooting, it fixed the problem!
Thanks for the update Sam!
You’re welcome! I am still having some issues with the trusted sites being greyed out in IE, even though I made certain not to use site to zone assignment in the policy, and only used GP preferences to add registry items for the sites in the trusted zone. Do you know what registry key I need to be looking for, that might be causing this issue?
Many thanks! Sam S.
Are you making sure that you’re applying it under HKCU, and not under HKLM? If you configure it under HKCU, users will still have the ability to add their own entries. But if you configure it under HKLM, the option to add entries will be greyed out.
Yes, I definitely deployed the preferences under the Users GP Preferences and not computer policy/preferences. However, there are some policy settings that I set in both computer and user settings in the GPO. None of these are site to zone assignments though. These settings are for all the security settings within the zones, like, download signed activeX controls – enable, download unsigned activeX controls, Prompt… etc.. – these settings are set in the computer policy and the user policy which is probably what is wrong. I should probably just disable the computer policies in the GPO. I will try that and see if it helps. Why are all these settings available in the computer side and the user side both? Is there a reason someone would set these settings in one policy over the other?
A computer side policy is available for every user that logs in already. These are generally faster to apply and are my preferred way to configure something. However, times like this are when a user side policy would be the best route for you. Remove the computer side settings and try John’s suggestions. Let us know what you find out.
Sam, another thing you can try is to access the GPO from a Windows 7 workstation running IE 9 (and make sure that there are no current Internet Explorer policies being applied to the workstation; put it in an OU that is blocking inheritance if you have to), then drill down to “User Config\Policies\Windows Settings\Internet Explorer Maintenance\Security\Security Zones and Content Ratings”. Double-click on “Security Zones and Content Ratings”, then choose “Import…” under “Security Zones and Privacy’, click “Continue” when prompted, then click “Modify Settings, then “Trusted Sites”, then the “Sites” button. You can then make whatever changes you want (add a site, remove a site, remove the check from the https box, etc). This should give you the freedom you’re looking for :).
i`ve add multiple Sites to the Site to Zone assigment list (Trusted Sites). After a new logon, i`ve check my settings, start IE11, visit the site i`ve add to the list, press Alt – File – Properties and check the Zone. Some of the sites are correct, shown in the trusted site zone, some of them not, they are in an unkown zone (mixed). I want to check the registry path Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains but this key is empty, for HKLM and HKCU. What`s wrong?
Thanks and Regards Patrick
Are you deploying the trusted sites with Policies or registry preferences?
> comment below explaining why GPUpdate /force is required to undo your changes.
For Group Policy to apply efficiently changes trigger it.
Exceptions apply. GPUPDate force is one. Security too.
Less obtusely said: “Group Policy will normally only reprocess client side extensions that have at least one policy element that changed. The exceptions to this are Security Option settings which reapply every ~16 hours on most machines and every 5 minutes on Domain Controllers. The other exceptions are when you run a gpupdate /force, and any CSEs you configure to auto-reapply. You can view this decision tree by enabling UserEnv logging as described in http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc775423%28v=ws.10%29.aspx ” … But not as haiku.
Hi, Is it possible to select the users you want that this GPO applies? It is because I need to add a web to trusted sites, but only to two users. Any idea?
You would need to configure these settings under user configuration. Then change the scope of the GPO from authenticated users to a group containing those two users.
With regards to deploying trusted sites via GPO, while allowing users to add their own entries, see if this post helps: http://community.spiceworks.com/topic/post/2849140
I’m finding that when I deploy Trusted Sites using GPP and the registry, users aren’t able to add entries themselves (it allows them to add to the list, but the entries don’t stick and are gone as soon as you reopen the dialog). Any ideas?
You sir, have a good last name! 🙂
Do you have any delete preferences configured to that registry key? If you manually browse to that key, do you see what the user added?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Security Essentials
- Deploying Windows 10 (without touching a client)
- Group Policy – Preferences to Software and Everything In Between
- OneNote Can Centralize Your Documentation
- Lunch and Learn: PowerShell 3
- Lunch and Learn: Software Extraction
- Disclosure Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Rebuild the Administrative Start Menu
- Guest Posting
- What’s This? Q&A on Sponsored Posts
- Blogs that I Follow – 2018 Edition
- Books to Boost Your Career!
- Top Articles to Teach You Now!
- Top Gadgets to be more Productive!
- Software Tools
- Other – eBooks, Virtual labs, etc
- My Articles
- Clients and Desktops
- Group Policy
- Deployment/MDT
- About DeployHappiness
- February 2024
- October 2023
- January 2023
- October 2021
- November 2020
- October 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- November 2019
- October 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- August 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- Group Policy (85)
- Best Practice (90)
- Hardware (9)
- Management (100)
- Networking (3)
- Office 365 (8)
- Performance (23)
- Quick Tip (26)
- PowerShell (87)
- Security (28)
- Server (16)
- Thinking about IT (14)
- Training (6)
- TroubleShooting (36)
- Uncategorized (29)
- Walkthrough (109)
- Entries (RSS)
- Comments (RSS)

a blog by Sander Berkouwer
- The things that are better left unspoken
HOWTO: Add the required Hybrid Identity URLs to the Local Intranet list of Internet Explorer and Edge

Most Microsoft-based Hybrid Identity implementations use Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) Servers, Web Application Proxies and Azure AD Connect installations. In this series, labeled Hardening Hybrid Identity , we’re looking at hardening these implementations, using recommended practices.
In this part of the series, we’ll look at the required Hybrid Identity URLs that you want to add to the Intranet Sites list in Internet Explorer.
Note: This is the first part for adding Microsoft Cloud URLs to Internet Explorer’s zone. In this part we look at the Local Intranet zone. In the next part we look at the Trusted Sites zone.
Note: Adding URLs to the Local Intranet zone for Internet Explorer, also applies to Microsoft Edge.
Why look at the Intranet Sites?
Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), and certain functionality in Azure Active Directory leverage Windows Integrated Authentication to allow for Single Sign-on. (SSO).
Single Sign-on reduces prompt fatigue in people and thus makes them more aware of the moments when password prompts happen and (and this is the theory…) paying more attention to what they are doing with their passwords.
I’m not a psychologist, but I do know how to make Windows Integrated Authentication work with Internet Explorer.
Intranet Sites vs. Trusted Sites (with Default settings)
Internet Explorer offers built-in zones:
- Local intranet
- Trusted sites
- Restricted sites
Per zone, Internet Explorer is allowed specific functionality. Restricted Sites is the most restricted zone and Internet Explorer deploys the maximum safeguards and fewer secure features (like Windows Integrated Authentication) are enabled.
The Local intranet zone, by default, offers a medium-low level of security, where Trusted sites allows for medium-level security. By default, the Local intranet zone allows for the following functionality beyond the Trusted sites zone:
- Local intranet does not allow ActiveX Filtering
- Local intranet allows Scriptlets
- Local intranet allows accessing data sources across domains (Trusted sites prompt)
- Local intranet allows scripting of Microsoft web browser control
- Sites in the Local intranet zone don’t prompt for client certificate selection when only one certificate exists
- Sites in the Local intranet zone may launch applications and unsafe files
- Sites in the Local intranet zone may navigate windows and frames across different domains
- Local intranet sites do not use the Pop-up Blocker feature
- Local intranet sites do not use the Defender SmartScreen feature
- Local intranet sites allow programmatic clipboard access
- Local intranet sites do not use the XSS Filter feature
- Local intranet sites allow user authentication
Possible negative impact (What could go wrong?)
Internet Explorer’s zones are defined with specific default settings to lower the security features for websites added to these zones.
When you use a Group Policy object to add websites that don’t need the functionality of the Local intranet zone to the zone, the systems in scope for the Group Policy object are opened up to these websites. This may result in unwanted behavior of the browser such as browser hijacks, identity theft and remote code executions.
While this does not represent a clear and immediate danger, it is a situation to avoid.
Getting ready
The best way to manage Internet Explorer zones is to use Group Policy.
To create a Group Policy object, manage settings for the Group Policy object and link it to an Organizational Unit, Active Directory site and/or Active Directory domain, log into a system with the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) installed with an account that is either:
- A member of the Domain Admins group, or;
- The current owner of the Group Policy Object, and have the Link GPOs permission on the Organizational Unit(s), Site(s) and/or Domain(s) where the Group Policy Object is to be linked, or;
- Delegated the Edit Settings or Edit settings, delete and modify security permission on the GPO, and have the Link GPOs permission on the Organizational Unit(s), Site(s) and/or Domain(s) where the Group Policy Object is to be linked.

The URLs to add
You’ll want to add the following URLs to the Local intranet zone, depending on the way you’ve setup your Hybrid Identity implementation:
https:// <YourADFSFarmName>
When you use federation with Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), the URL for the AD FS Farm needs to be added to the Local Intranet zone. As AD FS is authenticated against, it need to be added to the Local intranet zone as, by default, this is the only zone for websites to allow for user authentication.
https://login.microsoftonline.com
Https://secure.aadcdn.microsoftonline-p.com.
The https://login.microsoftonline.com and https://secure.aadcdn.microsoftonline-p.com URLs are the main URLs for authenticating to Microsoft cloud services. As these URLs are used to authenticate against, they need to be added to the Local intranet zone as, by default, this is the only zone for websites to allow for user authentication.
https://aadg.windows.net.nsatc.net
- https://autologon.microsoftazuread-sso.com
If you use the Seamless Single Sign-On (3SO) feature in Azure AD Connect, then you’ll want to add the following URLS to the Local intranet zone:
- https://aadg.windows.net.nsatc.net and
These URLs need to be added to the Local intranet zone on all devices where people in the organization use the 3SO feature, as these are the URLs where they will authenticate against. Trusted sites, by default, do not allow this functionality.
If you don’t use the 3SO functionality, don’t add the above URLs.
https://account.activedirectory.windowsazure.com
It is still one of Microsoft’s recommendation to add the https://account.activedirectory.windowsazure.com URL to the Local intranet zone. However, an enhanced experience is available that no longer points employees to this URL, but instead to the https://myprofile.microsoft.com URL, that uses the normal authentication URLs.
The new enhanced experience is available in the Azure portal, under User settings , Manage user feature preview settings (in the User feature previews area) named Users can use preview features for registering and managing security info – enhanced .
If you’ve enabled the enhanced preview, don’t add the above URL.
How to add the URLs to the Local Intranet zone
To add the URLs to the Local Intranet zone, perform these steps:
- Log into a system with the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) installed.
- Open the Group Policy Management Console ( gpmc.msc )
- In the left pane, navigate to the Group Policy objects node.
- Locate the Group Policy Object that you want to use and select it, or right-click the Group Policy Objects node and select New from the menu.
- Right-click the Group Policy object and select Edit… from the menu. The Group Policy Management Editor window appears.
- In the main pane of the Group Policy Management Editor window, expand the Computer Configuration node, then Policies , Administrative Templates , Windows Components , Internet Explorer , Internet Control Panel and then the Security Page node.

- In the main pane, double-click the Sites to Zone Assignment List setting.
- Enable the Group Policy setting by selecting the Enabled option in the top pane.
- Click the Show… button in the left pane. The Show Contents window appears.

- Add the above URLs to the Local Intranet zone by entering the URL in the Value name column and the number 1 in the Value column for each of the URLs.
- Click OK when done.
- Close the Group Policy Editor window.
- In the left navigation pane of the Group Policy Management Console, navigate to the Organization Unit (OU) where you want to link the Group Policy object.
- Right-click the OU and select Link an existing GPO… from the menu.
- In the Select GPO window, select the GPO.
- Click OK to link the GPO.
Repeat the last three steps to link the GPO to all OUs that require it. Take Block Inheritance into account for OUs by linking the GPO specifically to include all people in scope.
To enable functionality in a Hybrid Identity implementation, we need to open up the web browser to allow functionality for specific web addresses. By enabling the right URLs we minimize our efforts in enabling the functionality and also minimize the negative effect on browser security.
There is no need to add all the URLs to specific Internet Explorer zones, when you don’t need to functionality. However, do not forget to add the specific URLs when you enable specific functionality like Seamless Single Sign-on and remove specific URLs when you move away from specific functionality.
Further reading
Office 365 URLs and IP address ranges Group Policy – Internet Explorer Security Zones Add Site to Local Intranet Zone Group Policy
Posted on October 15, 2019 by Sander Berkouwer in Active Directory , Entra ID , Security
5 Responses to HOWTO: Add the required Hybrid Identity URLs to the Local Intranet list of Internet Explorer and Edge

If you use the GPO methode (S2ZAL) the zone get's 'locked' so the user cannot add url's to the zone himself. If you want them to allow this ( yeah i know this shoudln't be 🙂 ) you can use a reg import with GPO Preferences instead.
Yes, indeed you can.

Very well done and written! I've only just begun writing myself just recently and realized that a lot of blogs merely rework old content but add very little of worth. It's good to see a beneficial post of some true valuue to your readers and I. It is actually going down on the list of things I need to emulate being a nnew blogger. Visitor engagement and content quality are king. Many great ideas; you've unquestionably made it on my list of sites to follow!
Continue the great work!
it's done,work fine,thanks you
Nice detail, well explained. Good work.
leave your comment cancel
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Advertisement

Search this site
Dirteam.com / activedir.org blogs.
- Strategy and Stuff
- Dave Stork's IMHO
- The way I did it
- Sergio's Shack
- Things I do
- Tomek's DS World
Microsoft MVP (2009-2025)
Veeam vanguard (2016-2024), vmware vexpert (2019-2022).

Xcitium Security MVP (2023)

Recent Posts
- I'm co-presenting at Whitehall Media’s Identity Management Europe event
- Join Raymond and me as we discuss “UnOauthorized” with Eric Woodruff
- I’m speaking at NT Konferenca 2024
- What's New in Entra ID for August 2024
- On-premises Identity-related updates and fixes for August 2024
Recent Comments
- Arian van der Pijl on Sympathy for the devil, empathy for the Identity professional
- disa pointid on On-premises Identity-related updates and fixes for August 2024
- Frank Keough on Hardening SMB on Domain Controllers, Step 1: Reporting on SMBv1 connections , SMBv2 connections and SMB null sessions
- Sander Berkouwer on TODO: Upgrade the Certificates for your Windows Server 2016-based Domain Controllers (and up) to enable Windows Hello for Business Hybrid Scenarios
- Jeff McGowan on TODO: Upgrade the Certificates for your Windows Server 2016-based Domain Controllers (and up) to enable Windows Hello for Business Hybrid Scenarios
The information on this website is provided for informational purposes only and the authors make no warranties, either express or implied. Information in these documents, including URL and other Internet Web site references, is subject to change without notice. The entire risk of the use or the results from the use of this document remains with the user. Active Directory, Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, Windows NT, and Windows Server are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

Windows security encyclopedia
#microsoft #windows #security
Search form
Site to zone assignment list.
This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all of the sites in the zone.Internet Explorer has 4 security zones numbered 1-4 and these are used by this policy setting to associate sites to zones. They are: (1) Intranet zone (2) Trusted Sites zone (3) Internet zone and (4) Restricted Sites zone. Security settings can be set for each of these zones through other policy settings and their default settings are: Trusted Sites zone (Low template) Intranet zone (Medium-Low template) Internet zone (Medium template) and Restricted Sites zone (High template). (The Local Machine zone and its locked down equivalent have special security settings that protect your local computer.)If you enable this policy setting you can enter a list of sites and their related zone numbers. The association of a site with a zone will ensure that the security settings for the specified zone are applied to the site. For each entry that you add to the list enter the following information:Valuename – A host for an intranet site or a fully qualified domain name for other sites. The valuename may also include a specific protocol. For example if you enter http://www.contoso.com as the valuename other protocols are not affected. If you enter just www.contoso.com then all protocols are affected for that site including http https ftp and so on. The site may also be expressed as an IP address (e.g. 127.0.0.1) or range (e.g. 127.0.0.1-10). To avoid creating conflicting policies do not include additional characters after the domain such as trailing slashes or URL path. For example policy settings for www.contoso.com and www.contoso.com/mail would be treated as the same policy setting by Internet Explorer and would therefore be in conflict.Value - A number indicating the zone with which this site should be associated for security settings. The Internet Explorer zones described above are 1-4.If you disable or do not configure this policy users may choose their own site-to-zone assignments.
Policy path:
Scope: , supported on: , registry settings: , filename: , related content.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Group Policy and Internet Explorer's Site to Zone assignment issues?
We are using GPO to apply Site to Zone assignements for our users so that we can add some specific addresses into their Internet Explorer's Intranet and Trusted zones.
Using the Site to Zone GPO setting I have setup..
*.domain.com 1
The "domain.com" is our internal domain so I want anywebsite.domain.com to be treated as an intranet site to allow for SSO authentication to some of these websites that support it.
However this does not seem to work, adding *.domain in the local intranet zone prompts for a password when trying to hit websites that make use of SSO.
When I add the complete address of the internal site that prompts for a password "mywebsite.domain.com" to the local intranet zone then SSO works and the user is not prompted for a password.
I am trying to set this up so we don't always have to add websites into this GPO setting and wait for it to apply on client computers etc.. instead use *.domain.com to cover any subdomain.
Why can't we use wild cards in the site to zone assignment for local intranet or is my syntax incorrect?
To recap, a setting like this does not allow SSO:
This works:
mywebsite.domain.com 1 support.domain.com 1
The number "1" is the zone assignment, in this case "Local Intranet Zone" in Internet Explorer.
- group-policy
- authentication
- internet-explorer
- single-sign-on
- Does it work if you use domain.com not *.domain.com? – Greg Askew Commented May 7, 2015 at 15:54
- I have not tried, I figured it may need the wildcard to cover all sub-domains; will try this. – user146882 Commented May 7, 2015 at 16:20
- that did not work as well, changing *.domain.com to domain.com has no effect – user146882 Commented May 7, 2015 at 16:49
- Is the problem that the site is not showing in the Intranet zone, or that SSO is not working for that site when it is in the Intranet zone? – Greg Askew Commented May 7, 2015 at 16:50
- did you add http:// or https:// in front of *.domain.com? Did IE recognize host.domain.com as intranet (in status bar)? – strongline Commented May 7, 2015 at 16:50
Easy thing. Just say http://*.DOMAIN.COM 1
*.domain.com isnt enough
- this worked, added a record for http://*.domain.com, https://*.domain.com, and *.domain.com as local intranet zone (1), tested via IE and SSO works; now I can take out the mymanysubdomains.domain.com out of the GPO :) Thanks!! – user146882 Commented May 7, 2015 at 19:13
You must log in to answer this question.
- The Overflow Blog
- Masked self-attention: How LLMs learn relationships between tokens
- Deedy Das: from coding at Meta, to search at Google, to investing with Anthropic
- Featured on Meta
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Preventing unauthorized automated access to the network
Hot Network Questions
- How many natural operations on subsets are there?
- Can I use named pipes to achieve temporal uncoupling?
- Is a 1500w inverter suitable for a 10a portable band saw?
- What happened with the 31.5 ft giant in Jubbulpore district (now Jabalpur), India, August 8, 1934?
- Book where the humans discover tachyon technology and use this against a race of liquid metal beings
- How do you measure exactly 31 minutes by burning the ropes?
- Used car dealership refused to let me use my OBDII on their car, is this a red flag?
- Evil machine/Alien entity kills man but his consciousness/brain remains alive within it, and he spends eons reading its mind to defeat it and escape
- Story where the main character is hired as a FORTH interpreter. We pull back and realise he is a computer program living in a circuit board
- White (king and 2 bishops) vs Black (king and 1 knight). White to play and mate in 2
- Taking out the film from the roll can it still work?
- Why is my Lenovo ThinkPad running Ubuntu using the e1000e Ethernet driver?
- Problems regressing y on x/y?
- How similar were the MC6800 and MOS 6502?
- Is this a balanced way to implement the "sparks" spell from Skyrim into D&D?
- Help with unidentified character denoting temperature, 19th century thermodynamics
- Remove an entire inner list that has any zeros
- Where is this NPC's voice coming from?
- Are logic and mathematics the only fields in which certainty (proof) can be obtained?
- How can I draw the intersection of a plane with a dome tent?
- What "Texas and federal law"s is SpaceX "in violation of"?
- If a 'fire temple' was built in a gigantic city, with many huge perpetual flames inside, how could they keep smoke from bothering non-worshippers?
- In big band horn parts, should I write double flats (sharps) or the enharmonic equivalent?
- Inconsistency in answers while solving a 2nd order differential equation using operator method

an endpoint admin's journal
- Recent Posts
- Popular Posts
- Recent Comments

Deploy Trusted sites zone assignment using Intune
November 6, 2023

Zoom Desktop Client – Download older build versions from Zoom
October 31, 2023

Uninstall Teams chat app using remediation script and a configuration profile in Intune
October 30, 2023

Intune Last Check-in date not updating for Windows device
October 25, 2023

How to use Event Viewer to check cause of Blue screen of Death (BSOD)
October 23, 2023
5 Quick Mac OS Terminal commands to make a Mac user life easier

Powershell : Find disabled users and computers in AD
- Active Directory (1)
- Windows (7)
- November 2023
- October 2023
Deploy a set of trusted sites overriding users’ ability to add trusted sites themselves. To acheive this, an Intune configuration profile Trusted site zone assignment can be deployed to devices/users group as required.
Login to Intune Portal and navigate to: Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles .
Hit the Create button and Select New policy

From the Create a profile menu, select Windows 10 and later for Platform , Templates for Profile type. Select Administrative templates and click Create .

Give the profile desired name and click Next .

In Configurations settings, select Computer Configuration and search for keyword “ Site to Zone “, Site to Zone Assignment List setting will be listed under search results. Go ahead click on it to Select it.

Once selected, a Site to Zone Assignment List page will appear on right side explaining different zones and values required for these zone for setup. Since this profile is being used for trusted sites, we will use the Value “2” . Go ahead and select Enabled button and start entering the trusted sites as required. please ensure to set each value to “2” . See example below:
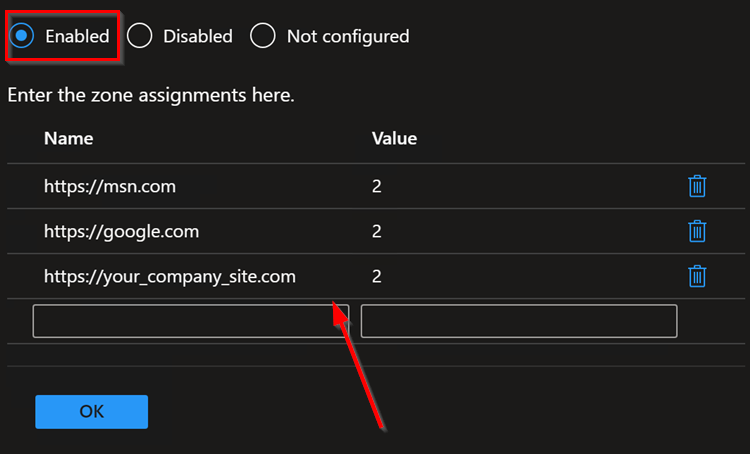
Once done adding the list of sites, click OK to close it and Hit Next on Configuration settings page.
Add Scope tags if needed.
Under Assignments , Click Add groups to target the policy deployment to specific group of devices/users. You can also select Add all users / All all devices .
Hit Next . Then Hit Review + Save button to save.
Tags: Intune Windows
You may also like...

[Windows 10] How to completely uninstall Flash player
- Previous Zoom Desktop Client – Download older build versions from Zoom
thanks! I was just looking for this exact solution!
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Troubleshoot "Internet Explorer Zonemapping" failures when processing Group Policy
- 2 contributors
When you execute GPUpdate /force , you may see the following output:
When you run GPRESULT /H GPReport.html and examine the report, you see the following information under Component Status :
The System event log contains an event ID 1085 that indicates a Group Policy processing error related to "Internet Explorer ZoneMapping," like the following one:
This event can occur if you enter an invalid entry within the Site To Zone Assignment List policy in the following paths:
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page
User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page
The "Site To Zone Assignment List" policy
The format of the Site To Zone Assignment List policy is described within the policy. This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all sites in the zone.
Internet Explorer has four security zones, which are used by this policy setting to associate sites with zones. They're numbered 1 to 4 and defined in descending order of most to least trusted:
- Local Intranet zone
- Trusted Sites zone
- Internet zone
- Restricted Sites zone
The security settings can be set for each of these zones through other policy settings, and their default settings are:
- Trusted Sites zone (Low template)
- Intranet zone (Medium-Low template)
- Internet zone (Medium template)
- Restricted Sites zone (High template)
The Local Machine zone and its locked-down equivalent have special security settings that protect your local computer.
If you enable this policy setting, you can enter a list of sites and their related zone numbers. The association of a site with a zone ensures that the security settings for the specified zone are applied to that site. For each entry that you add to the list, enter the following information:
Valuename : It's used to specify a host for an intranet site, or a fully qualified domain name for other sites. The valuename may also include a specific protocol. For example, if you enter https://www.contoso.com as the valuename , other protocols aren't affected. If you just enter www.contoso.com , all protocols for that site are affected, including http, https, ftp, and so on. The site may also be expressed as an IP address (such as 127.0.0.1) or a range (such as 127.0.0.1-10). To avoid creating conflicting policies, don't include other characters after the domain, such as a trailing slash or URL path. For example, the policy settings for www.contoso.com and www.contoso.com/mail would be treated as the same policy setting by Internet Explorer, and therefore, conflict.
Value : It's the number of the zone you want to associate the site with security settings. The Value of the above Internet Explorer zones is 1 to 4 .
When you enter data in the Group Policy Editor, there's no syntax or logical error checking available. This error checking is performed on the client when the Internet Explorer Zonemapping Group Policy Extension converts the registry into the format used by Internet Explorer. During that conversion, the same methods are implemented when you manually add a site to a specific security zone. If an entry is rejected when you add it manually, the conversion also fails if the Group Policy is used and the event 1085 is issued. For example, when you try to add a wildcard entry to a top-level domain (TLD) (like *.com or *.co.uk ) while adding a site, the wildcard entry is rejected. Now, the question is, which entries are treated as TLDs; by default, the following schemes are treated as TLDs in Internet Explorer:
- Flat domains (such as .com ).
- Two-letter domains in a two-letter TLD (such as .co.uk ).
The following blog post includes a granular explanation of domains:
Understanding Domain Names in Internet Explorer
To identify incorrect entries in the policy, download and run the IEDigest tool. After creating a report and opening it in your web browser, you'll see a Warnings section where incorrect entries are named. These entries need to be removed (or corrected) in the Group Policy. Here's an example of how it looks like when trying to add *.com to a zone:
Warnings Description Key Name Value Invalid entry in Site to Zone Assignment List. Click here for more info HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMapKey *.com is invalid
More information
- Intranet site is identified as an Internet site when you use an FQDN or an IP address
- Security Zones in Microsoft Edge
Third-party contact disclaimer
Microsoft provides third-party contact information to help you find additional information about this topic. This contact information may change without notice. Microsoft does not guarantee the accuracy of third-party contact information.
Additional resources

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In the second box, labeled "Enter the value of the item to be added:", enter the number that corresponds to the Internet Explorer security zone that the site should be added to. The zone assignments are as follows: 1 - Intranet Zone; 2 - Trusted Sites Zone; 3 - Internet Zone; 4 - Restricted Sites Zone; Once the zone assignment has ...
3.Clearing ZoneMap Entries: Instead of relying solely on modifying the "site to zone assignment list" template, you can consider using a startup script in a GPO to delete the unwanted entries from the ZoneMap registry key. This script can run with elevated privileges and remove the obsolete entries. You can use PowerShell or batch scripting to ...
In the main pane, double-click the Sites to Zone Assignment List setting. Enable the Group Policy setting by selecting the Enabled option in the top pane. Click the Show ... Add the above URLs to the Trusted Sites zone by entering the URL in the Value name column and the number 2 in the Value column for each of the URLs. Click OK when done.
Select the Site to Zone Assignment List. Select Enabled and click Show to edit the list. Refer to Figure 1 below. The zone values are as follows: 1 — intranet, 2 — trusted sites, 3 — internet zone, 4 — restricted sites. Click OK. Click Apply and OK. Figure 1. Assigning sites to the Trusted Sites zone. Figure 2.
Put simply we are going to setup the IE Zone registry keys manually using Group Policy Preferences… However it's a little complicated as the URL that is in the Site to Zone mapping is actually stored as the name of the key. Finally the protocol is the registry value with a number that assigns it to the corresponding zone.
Step 4: Add URLs to the list and assign a zone. Add the FQDN and then assign the zone; the zone numbers are: 1 = Local Intranet Zone 2 = Trusted Sites Zone 3 = Internet Zone 4 = Restricted Sites Zone. Once you have created your list and zones just apply the GPO to the OU, refresh the policy which will grey-out the option for the user to modify ...
These registry entries are located in the following registry subkey: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\<ZoneNumber>. In this registry subkey, <ZoneNumber> is a zone such as 0 (zero). The 1200 registry entry and the 2000 registry entry each contain a setting that is named Administrator approved.
Step 2. Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page and double click on the “Site to Zone Assignment List†and check the “Enable†option then click on the “Show..†button. Step 3.
Users can use the Internet Control Panel to assign specific sites to Zones and to configure the permission results for each zone. In managed environments, administrators can use Group Policy to assign specific sites to Zones (via "Site to Zone Assignment List" policy) and specify the settings for URLActions on a per-zone basis.
When you edit this setting (Site to Zone Assignment List) you have to define the URL and the security zone (using a number from 1 (Intranet) to 4 (Restricted Sites) [2: Trusted Sites, 3: Internet]. BUT, if you are using Internet Explorer 7 or later with this setting configured, your end-users will not be able to add their own URL's (such as ...
When you enable the setting, you will be prompted for a value name (the website) and a value (the zone list). Here are the possible values and the zone that they correspond to: 1 = Intranet/Local Zone. 2 = Trusted Sites. 3 = Internet/Public Zone. 4 = Restricted Sites.
Especially a long list of URLs in the "site to zone assignment" setting. However it seems that one URL still falls into the "internet zone" even when assigned to the "trusted zone". In earlier versions of internet explorer one could easily determine from the status bar into which zone an URL falls.
In the main pane, double-click the Sites to Zone Assignment List setting. Enable the Group Policy setting by selecting the Enabled option in the top pane. Click the Show ... Add the above URLs to the Local Intranet zone by entering the URL in the Value name column and the number 1 in the Value column for each of the URLs. Click OK when done.
Site to Zone Assignment List. This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all of the sites in the zone.Internet Explorer has 4 security zones numbered 1-4 and these are used by this policy setting to ...
For example, I have a list with two entries named like following. https://something.domain.local. https://something.domain.local:123. After some quick googling I found out that some are saying that while the list is being processed, it just strippes out the port. Which I now assume, I could just go with the first entry in the list and delete ...
Click the Show button. In the Value name field, enter the server name in the following format: "file://servername" (replace "servername" with the actual name of the server). In the Value field, enter the corresponding zone number for the zone that you want to add the server to: 1 for Intranet zone. 2 for Trusted Sites zone.
Re: Site to Zone Assignment List - Powershell. # Step 2: Navigate to the Site to Zone Assignment List # This step is manual and requires navigating through the Group Policy Management Editor interface. # Step 3: Enable the Policy and Specify Zone Assignments # Define the list of URLs and their corresponding zone assignments.
2. We are using GPO to apply Site to Zone assignements for our users so that we can add some specific addresses into their Internet Explorer's Intranet and Trusted zones. Using the Site to Zone GPO setting I have setup.. *.domain.com 1. The "domain.com" is our internal domain so I want anywebsite.domain.com to be treated as an intranet site to ...
These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all of the sites in the zone. Internet Explorer has 4 security zones, numbered 1-4, and these are used by this policy setting to associate sites to zones. They are: (1) Intranet zone, (2) Trusted Sites zone, (3) Internet zone, and (4) Restricted Sites zone.
Deploy a set of trusted sites overriding users' ability to add trusted sites themselves. To acheive this, an Intune configuration profile Trusted site zone assignment can be deployed to devices/users group as required. Login to Intune Portal and navigate to: Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles. Hit the Create button and Select New ...
host.domain.fqdn. *.domain.fqdn. protocol://host.domain.fqdn. protocol://*.domain.fqdn. Essentially each entry is made of 2 mandatory choices: either "all protocols" or "this specific protocol", and "all hosts for this domain & subdomains" or "this specific host". Entries that are more restrictive take precedence (though I can never remember ...
The Site to Zone Assignment List policy setting associates sites to zones by using the following values for the Internet security zones: Intranet zone; Trusted Sites zone; Internet zone; Restricted Sites zone; If you set this policy setting to Enabled, you can enter a list of sites and their related zone numbers. By associating a site to a zone ...
The "Site To Zone Assignment List" policy. The format of the Site To Zone Assignment List policy is described within the policy. This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all sites in the zone.