
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer
Published by Rudy Brewer Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer"— Presentation transcript:

How Much Do I Remember? Are you ready to play.....

Basic Computer Vocabulary

Computer Skills Preparatory Year Presented by:

Computer Basics Whats that thingamagige?. Parts of a computer.

Chapter 1:Introduction to the world of computers

McGraw-Hill/Irwin ©2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved Plug-in B3 HARDWARE & SOFTWARE.

1 Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Computer & Information Technology Department of Computer Science & Information Systems cs98.

An Overview of the Computer System

Hardware. Basic Computer System Central Processing Unit Input Devices Output Devices Backing Storage Devices.

Introduction to Computers

Computer Systems – Hardware

What Is A Computer System?

1 Hardware - devices for Input. 2 Hardware - devices for Input Processing.

1 System Software “Background software”, manages the computer’s internal resources.

1 Introduction to Computers Prof. Sokol Computer and Information Science Brooklyn College.

Computer Parts There are many parts that work together to make a computer work.

Introduction to Computers Essential Understanding of Computers and Computer Operations.

MIS 175 Spring Learning Objectives When you finish this chapter, you will: –Recognize major components of an electronic computer. –Understand how.

Computer Skills CIS-100 CH 1.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

lesson 1-Introduction to computers.pptx

Related Papers
chitra devi
Kinoti Kaburuki
G G Rajput Rajput
SUBHAJIT PANDA
Computer, any of a class of devices capable of solving problems by processing information in discrete form. It operates on data, including magnitudes, letters, and symbols, that are expressed in binary code — i.e., using only the two digits 0 and 1. By counting, comparing, and manipulating these digits or their combinations according to a set of instructions held in its memory, a digital computer can perform such tasks as to control industrial processes and regulate the operations of machines; analyze and organize vast amounts of business data; and simulate the behaviour of dynamic systems (e.g., global weather patterns and chemical reactions) in scientific research. A typical computer system has four basic functional elements : (1) Input-output equipment, (2) Main memory, (3) Control unit, and (4) Arithmetic-logic unit.
Mahendra Pratap
Emma Greening
THE CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT & OPERATING SYSTEMS
Santino Madut Uchalla
Subhash shetty
A computer is a device that can be instructed to carry out arbitrary sequences of arithmetic or logical operations automatically. The ability of computers to follow generalized sets of operations, called programs, enables them to perform an extremely wide range of tasks. Such computers are used as control systems for a very wide variety of industrial and consumer devices. This includes simple special purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls , factory devices such as industrial robots and computer assisted design, but also in general purpose devices like personal computers and mobile devices such as smartphones. The Internet is run on computers and it connects millions of other computers. Since ancient times, simple manual devices like the abacus aided people in doing calculations. Early in the Industrial Revolution, some mechanical devices were built to automate long tedious tasks, such as guiding patterns for looms. More sophisticated electrical machines did specialized analog calculations in the early 20th century. The first digital electronic calculating machines were developed during World War II. The speed, power, and versatility of computers has increased continuously and dramatically since then. Conventionally, a modern computer consists of at least one processing element, typically a central processing unit (CPU), and some form of memory. The processing element carries out arithmetic and logical operations, and a sequencing and control unit can change the order of operations in response to stored information. Peripheral devices include input devices (keyboards, mice, joystick, etc.), output devices (monitor screens, printers, etc.), and input/output devices that perform both functions (e.g., the 2000s-era touchscreen). Peripheral devices allow information to be retrieved from an external source and they enable the result of operations to be saved and retrieved.- source = Wekipeda
osheen sharma
The central processing unit (CPU, occasionally central processor unit) is the hardware within a computer system which carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The term has been in use in the computer industry at least since the early 1960s. The form, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over the course of their history, but their fundamental operation remains much the same. A computer as shown below performs basically five major operations or functions irrespective of their size and make. These are 1) it accepts data or instructions by way of input, 2) it stores data, 3) it can process data as required by the user, 4) it gives results in the form of output, and 5) it controls all operations inside a computer. We discuss below each of these operations. 1. Input: In computing, an input device is any peripheral (piece of computer hardware equipment) used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system such as a computer or other information appliance. 2. Storage: Storage Devices are the data storage devices that are used in the computers to store the data. The computer has many types of data storage devices. Some of them can be classified as the removable data Storage Devices and the others as the non removable data Storage Devices. The memory is of two types; one is the primary memory and the other one is the secondary memory. The primary memory is the volatile memory and the secondary memory is the non volatile memory. The volatile memory is the kind of the memory that is erasable and the non volatile memory is the one where in the contents cannot be erased. Basically when we talk about the data storage devices it is generally assumed to be the secondary memory.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Policing An International Journal of Police Strategies and Management
مجلة جامعة النجاح للأبحاث العلوم الإنسانية
Revista de Administração, Contabilidade e Economia da Fundace
Marcos Campomar
Pooja Kudesia
Agnieszka Zabłocka-Kos
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Atikorn Panya
International Education Studies
Ergun Ozturk
Supplier Besar Tally Underwesar
supplier besar tally underwear
Conservation Science in Cultural Heritage
andrea natali
The Proceedings of the Annual Convention of the Japanese Psychological Association
Mela agustin
Kantonsarchäologie St.Gallen
Robert Rozema
Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology
yenny vargas
BMC Cell Biology
Dimitris Stellas
Index, revista de arte contemporáneo
Roberto Vega
Patient Safety in Surgery
Martin Sprecher
Kostas Prapoglou
Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Ali Khalifeh
arXiv (Cornell University)
Victor Efros
Manuscript Studies
Sarah Noonan
Proceedings of the International Conference on Islamic Education (ICIE 2018)
Zuriatul Khairi
Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie
Andreas Dietz
Cony B Saenger
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Computer Fundamentals and Programming in C
Reema Thareja, Assistant Professor, Institute of Information Technology and Management
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved.
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
1 st gen-1940-56
2 nd gen 1956-63
3 rd -64-71
4 th —72-89
5 th -mordern day
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SOFTWARE
- A computer is a machine that takes instructions and performs computations based on those instructions.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTERS
GENERATION OF COMPUTERS
The word generation means the state of improvement in the product development process. Similarly, computer generation refers to the different advancements of new computer technology.
First Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes
The first generation computers used very large number of vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory.
UNIVAC and ENIAC computers are prime examples of first-generation computing devices.
Advantages: Fastest calculating device of their time
Disadvantages:
1. Dissipate a lot of heat
2. Consume a lot of electricity
3. Very bulky in size
4. These computers were frequently down due to hardware failures.
5. These computers needed constant maintenance because of low mean time between failures
6. Limited commercial use because these computers were difficult to program
7. Very expensive
Second Generation (1956-1963) Transistors
- The second generation computers were manufactured using transistors.
- While first generation computers were programmed using machine language, second generation computers moved towards symbolic, or assembly languages, which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words.
- At this time, high-level programming languages like COBOL, FORTRAN, ALGOL and SNOBOL were also being developed.
- Second generation computers were first to store instructions in memory, which moved from a magnetic drum to magnetic core technology.
- Second generation computers were first developed for the atomic energy industry.
Advantages:
1. Consumed less electricity and thus dissipated less heat as compared to first generation computers
2. Faster, cheaper smaller and more reliable than first generation computers
3. Could be programmed using assembly language and high level languages
4. These computers had faster primary memory and a larger secondary memory
1. Second generation computers were manufactured using transistors that had to be assembled manually. This made commercial production of computers difficult and expensive.
Third Generation (1964-1971) Integrated Circuits
- The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the third generation of computers.
- These computers had few megabytes of main memory and magnetic disks which could store few tens of megabytes of data per disk drive.
- High level programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN were standardized by ANSI
- Some more high level programming languages like PL/I PASCAL and BASIC were introduced at this time.
- Third generation computers were the first to implement time sharing operating systems.
- Input to these computers could now be provided using keyboards and mouse.
- Faster than second generation computers and could perform 1 million transactions per second.
2. Smaller, cheaper and more reliable than their predecessors
3. These computers had faster and larger primary memory and secondary storage
4. They were widely used for scientific as well as business applications
5. During this generation of computers, standardization of existing high level languages and invention of new high level languages was done
6. These computers had time sharing operating system which allowed interactive use of computer by one or more users simultaneously thereby improving the productivity of the users.
Fourth Generation (1971-1989) Microprocessors
- The microprocessor started the fourth generation of computers with thousands of integrated circuits built onto a single silicon chip.
- Semi-conductor memories were used which were very fast, even the hard disks became cheaper, smaller in size and larger in capacity.
- For input, floppy disks (in addition to magnetic tapes) were used to port data and programs from one computer to another.
- During this period many new operating systems were developed like MS-DOS MS-Windows UNIX and Apple’s proprietary operating system.
- Development of GUIs, the mouse and handheld devices.
- In this period, several word processing packages, spreadsheet packages and graphics packages were introduced.
1. Smaller, cheaper, faster and more reliable
2. Consumed less electricity and therefore dissipated less heat
3. They had faster and larger primary memory and secondary storage
4. They could be used as general purpose computers.
5. GUIs enabled people to learn to work with computers very easily. So the use of computers in both office and home became widespread.
6. Networks allowed sharing of resources thereby efficient utilization of computer hardware and software
Fifth Generation (Present and Beyond) Artificial Intelligence
- The fifth generation computers are completely based on a new concept of artificial intelligence.
- Although such computers are still in development, there are certain applications like voice recognition which is widely being used today.
- In the fifth generation of computers the aim is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization.
- The two most common are LISP and Prolog.
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS
Computers can be broadly classified into four categories based on their speed, amount of data that they can hold and price.
Computers can be broadly classified into four categories based on their speed, amount of data that they can hold, and price .
Classification of Computers
Super Computer
Mini Computers
Mainframe Computers
Micro Computers
Intelligent Terminal
Dumb Terminal
Workstation
Cellular Telephones
H/PC Pro Devices
APPLICATIONS OF COMPUTERS
- Word Processing
- Digital Audio or Video Composition
- Desktop Publishing
- Traffic Control
- Legal System
- Retail Business
- Travel and Tourism
- Business and Industry
- Weather Forecasting
- Online Banking
- Industry and Engineering
- Decision Support Systems
- Expert Systems
BASIC ORGANIZATION OF A COMPUTER
A computer is an electronic device which basically performs five major operations which includes:
1) accepts data or instructions (input)
2) stores data
3) process data
4) displays results (output) and
5) controls and co-ordinates all operations inside a computer
CONTROL UNIT
ARITHMETIC LOGIC UNIT
Data and instructions
Flow of data and instructions
Control exercised by control unit

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

15.1: Powerpoint Learning Objectives
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 18696
Learning Objectives
If you do well in this unit, you should be able to:
- Identify the names and functions of the PowerPoint interface.
- Create, edit, save, and print presentations.
- Format presentations.
- Add a graphic to a presentation.
- Create and manipulate simple slide shows with outlines and notes.
- Create slide presentations that include text, graphics, animation, and transitions.
- Use design layouts and templates for presentations.
- Create a PowerPoint presentation.
- Introduction to Computer Applications and Concepts. Authored by : Jim Shannon. Provided by : Extended Learning Institute of Northern Virginia Community College. Located at : http://www.nvcc.edu/eli/index.html . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Great Tech Gifts for Any Occasion
- The Best Gadgets for The Beach or Pool
An Introduction to PowerPoint
Learn PowerPoint right from the beginning
- Brock University
Are you ready to dive into PowerPoint for the first time? The process might seem intimidating, but it's quite easy to learn. Follow these suggested links that will help you understand the lingo of PowerPoint, plan a successful presentation, and execute it with ease.
Information in this article applies to PowerPoint 2019, 2016, 2013, 2010, 2007; PowerPoint for Microsoft 365, and PowerPoint for Mac.
Get to Know the PowerPoint Lingo
There are terms that are specific to presentation software . The nice part is that once you learn terms specific to PowerPoint, those same terms are used in similar software programs such as Google Docs and Apple Keynote.
- The 10 Most Common PowerPoint Terms
Learn the Keys to a Successful Presentation
Most people dive right in and write their presentation as they go. However, the best presenters don't work that way; they begin by planning out their presentations.
- The Key to a Successful Presentation
- Four Parts to a Successful Presentation
Open PowerPoint for the First Time
Your first view of PowerPoint looks pretty bland. There is one large page, called a slide . Every presentation begins with a title and PowerPoint presents you with a title slide. Simply type your text into the text boxes provided.
Go to Home and select New Slide to add a blank slide with placeholders for a title and text to your presentation. This is the default slide layout and is one of many selections. There are many options to choose from for the way you want your slide to look.
- Slide Layouts in PowerPoint
- Different Ways to View PowerPoint Slides
Dress Up Your Slides
If this is your first PowerPoint presentation, you may worry that it will not give the right impression. Make it easy on yourself and use one of PowerPoint's many design themes or design templates to create a presentation that is coordinated and professional. Choose a design that fits your topic, and you're ready to go.
- Applying a Design Template in PowerPoint
Practice Your Presentation
Your audience did not come to see your PowerPoint presentation . They came to see you. You are the presentation and PowerPoint is the helper to get your message across.
Use these tips to make an effective and successful presentation.
- 10 Tips on Becoming a Better Presenter
- The 10 Most Common Presentation Mistakes
- Create Classroom Presentations Worthy of an 'A'
Insert Photos in a Presentation
Just like that old cliché says, a picture is worth a thousand words. Make an impact with your presentation by adding slides that include only pictures to make your point.
- Add Pictures or Clip Art to PowerPoint Slides
Add a Chart to Express Your Data
If your presentation is all about data, add a chart of that same data instead of text. Most people are visual learners, so seeing is believing.
Add Motion with Animations
Instill a bit of motion into your PowerPoint presentation with simple animations. Animate text so it magically appears on screen. Animate images and other graphics so they dance into view. A few animations keep your presentation alive.
- All About Animations in PowerPoint
Transition from One Slide to Another
There are two ways to create motion in a PowerPoint presentation. The first is an animation. The second advance slides in an interesting manner; these are called transitions .
- Slide Transitions for PowerPoint Slides
- 5 Tips About Slide Transitions in PowerPoint
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- How to Make a PowerPoint Presentation
- PowerPoint for Beginners - How to Use PowerPoint
- How to Add Animation to PowerPoint
- Create a Pie Chart Graphic in PowerPoint
- PowerPoint Master Slide
- Use Multiple Design Themes in the Same Powerpoint Presentation
- A Guide to Using PowerPoint Slide Layouts
- How to Draw Freehand in PowerPoint
- Using Design Themes in PowerPoint
- Simple Quizzes in PowerPoint
- Loop a PowerPoint Slide Show
- How to Use PowerPoint Slide Master Layouts
- How to Copy a PowerPoint Design Template to Another Presentation
- How to Change a Black-and-White Picture to Color in PowerPoint

Introduction to Computers
Sep 11, 2009
2.02k likes | 3.43k Views
Introduction to Computers. By Rave Harpaz Computer Science Dept. Brooklyn College. What Is A Computer?.
Share Presentation
- electronic spreadsheet
- so powerful
- own memory unit
- computer know
- control unit
- auxiliary storage devices

Presentation Transcript
Introduction to Computers By Rave Harpaz Computer Science Dept. Brooklyn College
What Is A Computer? A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions (software) stored in its own memory unit, that can accept data (input), manipulate data (process), and produce information (output) from the processing. Generally, the term is used to describe a collection of devices that function together as a system.
Devices that comprise a computer system Monitor (output) Speaker (output) System unit (processor, memory…) Printer (output) Storage devices (CD-RW, Floppy, Hard disk, zip,…) Mouse (input) Scanner (input) Keyboard (input)
What Does A Computer Do? Computers can perform four general operations, which comprise the information processing cycle. Input Process Output Storage
Data and Information • All computer processing requires data, which is a collection of raw facts, figures and symbols, such as numbers, words, images, video and sound, given to the computer during the input phase. • Computers manipulate data to create information. Information is data that is organized, meaningful, and useful. • During the output Phase, the information that has been created is put into some form, such as a printed report. • The information can also be put in computer storage for future use.
Why Is A Computer So Powerful? • The ability to perform the information processing cycle with amazing speed. • Reliability (low failure rate). • Accuracy. • Ability to store huge amounts of data and information. • Ability to communicate with other computers.
How Does a Computer Know what to do? • It must be given a detailed list of instructions, called a compute program or software, that tells it exactly what to do. • Before processing a specific job, the computer program corresponding to that job must be stored in memory. • Once the program is stored in memory the compute can start the operation by executing the program instructions one after the other.
What Are The Primary Components Of A Computer ? • Input devices. • Central Processing Unit (containing the control unit and the arithmetic/logic unit). • Memory. • Output devices. • Storage devices.
Input Devices • Keyboard. • Mouse.
The Keyboard The most commonly used input device is the keyboard on which data is entered by manually keying in or typing certain keys. A keyboard typically has 101 or 105 keys.
The Mouse Is a pointing device which is used to control the movement of a mouse pointer on the screen to make selections from the screen. A mouse has one to five buttons. The bottom of the mouse is flat and contains a mechanism that detects movement of the mouse.
The Central processing Unit The central processing unit (CPU) contains electronic circuits that cause processing to occur. The CPU interprets instructions to the computer, performs the logical and arithmetic processing operations, and causes the input and output operations to occur. It is considered the “brain” of the computer.
Memory Memory also called Random Access Memory or RAM (temporary memory) is the main memory of the computer. It consists of electronic components that store data including numbers, letters of the alphabet, graphics and sound. Any information stored in RAM is lost when the computer is turned off. Read Only Memory or ROM is memory that is etched on a chip that has start-up directions for your computer. It is permanent memory.
Amount Of RAM In Computers The amount of memory in computers is typically measured in kilobytes or megabytes. One kilobyte (K or KB) equals approximately 1,000 memory locations and one megabyte (M or MB) equals approximately one million locations A memory location, or byte, usually stores one character. Therefore, a computer with 8 MB of memory can store approximately 8 million characters. One megabyte can hold approximately 500 pages of text information.
Output Devices Output devices make the information resulting from the processing available for use. The two output devices more commonly used are the printer and the computer screen. The printer produces a hard copy of your output, and the computer screen produces a soft copy of your output.
Storage Devices Auxiliary storage devices are used to store data when they are not being used in memory. The most common types of auxiliary storage used on personal computers are floppy disks, hard disks and CD-ROM drives.
Floppy Disks A floppy disk is a portable, inexpensive storage medium that consists of a thin, circular, flexible plastic disk with a magnetic coating enclosed in a square-shaped plastic shell.
Structure Of Floppy Disks • Initially Floppy disks were 8-inches wide, they then shrank to 5.25 inches, and today the most widely used folly disks are 3.5 inches wide and can typically store 1.44 megabytes of data. • A folly disk is a magnetic disk, which means that it used magnetic patterns to store data. • Data in floppy disks can be read from and written to. • Formatting is the process of preparing a disk for reading and writing. • A track is a narrow recording band that forms a full circle on the surface of the disk.
The disk’s storage locations are divided into pie-shaped sections called sectors. • A sectors is capable of holding 512 bytes of data. • A typical floppy stores data on both sides and has 80 tracks on each side with 18 sectors per track.
Hard Disks • Another form of auxiliary storage is a hard disk. A hard disk consists of one or more rigid metal plates coated with a metal oxide material that allows data to be magnetically recorded on the surface of the platters. • The hard disk platters spin at a high rate of speed, typically 5400 to 7200 revolutions per minute (RPM). • Storage capacites of hard disks for personal computers range from 10 GB to 120 GB (one billion bytes are called a gigabyte).
Compact Discs • A compact disk (CD), also called an optical disc, is a flat round, portable storage medium that is usually 4.75 inch in diameter. • A CD-ROM (read only memory), is a compact disc that used the same laser technology as audio CDs for recording music. In addition it can contain other types of data such as text, graphics, and video. • The capacity of a CD-ROM is 650 MB of data.
Computer Software Computer software is the key to productive use of computers. Software can be categorized into two types: Operating system software Application software.
Operating System Software Operating system software tells the computer how to perform the functions of loading, storing and executing an application and how to transfer data. Today, many computers use an operating system that has a graphical user interface (GUI) that provides visual clues such as icon symbols to help the user. Microsoft Windows 98 is a widely used graphical operating system. DOS (Disk Operating System) is an older but still widely used operating system that is text-based.
Application Software Application Software consists of programs that tell a computer how to produce information. Some of the more commonly used packages are: Word processing Electronic spreadsheet Database Presentation graphics
Word Processing • Word Processing software is used to create and print documents. A key advantage of word processing software is that users easily can make changes in documents.
Electronic Spreadsheets • Electronic spreadsheet software allows the user to add, subtract, and perform user-defined calculations on rows and columns of numbers. These numbers can be changed and the spreadsheet quickly recalculates the new results.
Database Software • Allows the user to enter, retrieve, and update data in an organized and efficient manner, with flexible inquiry and reporting capabilities.
Presentation Graphics • Presentation graphic software allows the user to create documents called slides to be used in making the presentations. Using special projection devices, the slides display as they appear on the computer screen.
- More by User

Lesson 11A Introduction to Computers Types of Graphics File
745 views • 19 slides

Introduction to Computers A World of Computers Next What is computer literacy ? Knowledge and understanding of computers and their uses Computers are everywhere p. 4-5 Fig. 1-1 Important Concepts … computer competency
1.08k views • 47 slides

Lesson 2A Introduction to Computers Keyboard Alphanumeric keys Modifier keys Numeric keypad Function keys Cursor-movement keys Special-purpose keys Click to Enlarge How the Computer Accepts Input from the Keyboard Keyboard controller Keyboard buffer Scan code Interrupt request
1.09k views • 23 slides

Introduction to Computers. Seminar I. Parts of the Computer. Personal Computer a PC (any non-Mac computer) has four major pieces of hardware--keyboard, mouse, monitor, central processing unit (CPU). Macs have the same four components, but use different software for the operating system.
1.08k views • 32 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS. EPROG COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS & PROGRAMMING FOR ENGINEERING STUDENTS. <<professor>>. What is a computer?. an electronic device that manipulates information, or "data“ not a glorified typewriter has the ability to store , retrieve , and process data.
1.22k views • 80 slides

Introduction to Computers. Lecture By K. Ezirim. What is a Computer?. An electronic device Desktops, Notebooks, Mobile Devices, Calculators etc. Require instructions to operate Comprises of Hardware Software. Basic operations of Computers. Input – accept data for processing
148 views • 0 slides

Introduction to Computers. and How to Purchase Computers and Mobile Devices. Objectives. Define the term computer and discuss the four basic computer operations: input, process, output, and storage Define data and information
784 views • 54 slides

Introduction to Computers. What is a Computer?. An electronic, programmable device that: Accepts data in the form of Input Manipulates that data by Processing Produces results in the form of Output Stores for future use through Storage devices. Slide . Information Processing Cycle.
362 views • 21 slides

Introduction to Computers. Course Introduction. Welcome to your online course!. What will I learn?. Getting Started. Go to: www.imagineschoolslakewoodranch Login (top right of screen) User Name: firstname.lastname Password: Firstname Click on “My Classes” at the top of the screen
247 views • 8 slides

Introduction to Computers. What is a Computer?. A COMPUTER is an electronic device that can: Receive information Perform processes Produce output Store info for future use. Information Processing Cycle. Input Process Output Storage. Hardware vs. Software.
348 views • 21 slides

Introduction to Computers. Essential Understanding of Computers and Computer Operations. Topics. The term “computer” Four basic computer operations Data and information Principal components of computer Data storage devices and usage Software The Internet & WWW .
385 views • 24 slides

Introduction to Computers. Rabie A. Ramadan, PhD. About my self. Rabie A. Ramadan My website and publications http://www.rabieramadan.org. Class Information. I am not here to punish you Trust yourself and do your best. Class Information. You can bring anything to drink but
609 views • 45 slides

Valia Mitsou Computer and Information Science Brooklyn College Source: Introductory Concepts and Techniques, A preliminary edition was prepared by Rave Harpaz. Introduction to Computers. A computer is an electronic device that can: - accept data ( input ) - manipulate data ( process )
825 views • 28 slides

Introduction to Computers. Welcome to. Sherry Wilson (Instructor). Bachelors Degree In Computer Graphics Been working with computers for over 15 years Currently work at a local printing as a PrePress / Large Format Designer. Resources & Supplies You will need for this class:. Goals.
388 views • 16 slides

Introduction to Computers. Parts. Monitor. CRT Cathode Ray Tube Flat Panel Dual Screen. Graphics Array. These are drivers for hardware. Sometimes old software has to have old drivers. CGA 16 320 x 200 EGA 64 480 x 320
420 views • 34 slides

Introduction to Computers. Michael R. Izzo [email protected] 401-942-3850. Introduction to Computers Syllabus VISUALIZING TECHNOLOGY WEEK CHAPTER READING ASSIGNMENT ASSIGNMENT
246 views • 11 slides

Introduction To Computers
Introduction To Computers. Module Objectives:. Define Computers Identify Hardware Components Become proficient at using Windows Explore Software Explore Microsoft Word, Excel and Publisher Tour the Desktop Use the Start Menu Work with, and Close, Windows
2.38k views • 158 slides

Introduction to Computers. Power Point. Opening and Viewing Presentations. Click on the Start button (bottom-left of your screen). From the popup menu displayed click on All Programs. Click on a submenu option called Microsoft Office. Finally click on Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007.
296 views • 25 slides

Introduction to computers
Introduction to computers. MS WORD. Starting Microsoft Word 2007. Start >> All programs >> Microsoft Office>> Microsoft Office Word 2007. At desktop>>mouse right click>>new>>Microsoft office word document. Office Button. Office Button. Ribbon Tabs.
407 views • 38 slides

Introduction to computers. Excel. Functions. Searching and replacing data. Worksheets. Renaming a worksheet. Click on the Sheet1 tab to display the first worksheet. Double click on the Sheet1 tab and you will be able to type in a new name. Inserting a new worksheet. Deleting a worksheet.
285 views • 26 slides

Introduction to Computers. MS Word. Paragraph Formatting. What is paragraph formatting?. Paragraph formatting includes items such as alignment and indenting as well as numbering and bulleting of lists. If you click on the Home tab, you will see a paragraph section within the Ribbon
321 views • 29 slides

Introduction to Computers. By Engr. Abdul Hannan Zahid Lecturer Dept. of Chemical Engineering. Chapter 1. Introducing Computer Systems. Book: Introduction to Computers By Peter Norton 6th Edition. Learning Objectives:.
857 views • 72 slides
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Introduction to PowerPoint
- Computer Science

Microsoft PowerPoint is essentially a graphics presentation software application that comes in the same package of software as MS Access, MS Excel, MS Word, and MS Paint, issued by Microsoft Office . It is a software that helps the user in formulating and arranging their data and information in the form of slides, which enhances the clarity and communication of the subject, along with adding a visual aspect to the data which makes it more appealing and presentable.
Thus, it can be used for presenting business ideas and plans, and visually presenting the data also makes learning with the data a lot easier, thus can be used by teachers in schools for making learning fun and uncomplicated.

Meaning of PowerPoint
PowerPoint is a software that is designed to make graphical presentations in the form of individual pages also known as slides.
Features of PowerPoint
Some of the features available in Microsoft PowerPoint are stated below.
Customising Colour Schemes
Adding Animations
Creating and Adding tables
Adding images
Adding and Managing Hyperlinks
Creating Custom Shows
Creating and Importing Charts
Easy exporting to MS Word
How to Start PowerPoint?
To start powerpoint:.
Click on Start

Click the following in sequence stated: All Programs->Microsoft Office->Microsoft Office PowerPoint
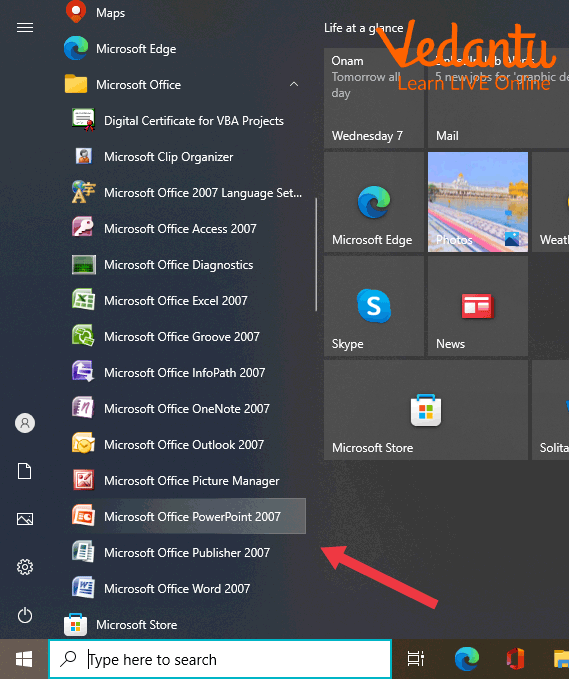
Starting PowerPoint
The Microsoft Office PowerPoint window will appear, starting the software.
How to Open a Blank Presentation?
By default, when we open PowerPoint for the first time, it opens to a new presentation but for future purposes, if we want to open a new presentation, we can do so by following the below-given steps.
Click on New Presentation link on Getting Started pane on the left which results in the appearance of a new window.
Select on Blank Presentation, when the new presentation appears along with it a Layout pane on the right will also appear.
Select any desired layout from the list.
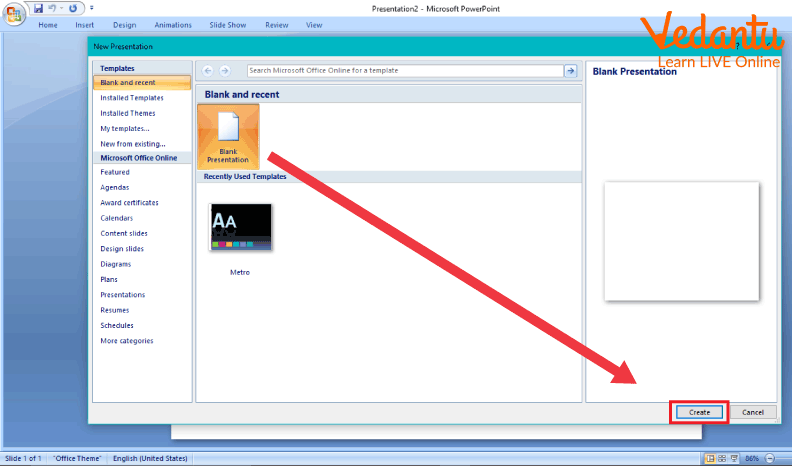
Opening a New Presentation
Uses of PowerPoint
Uses of PowerPoint in Education:
Since PowerPoint offers the feature of adding images and animations, learning by visualisation makes the learning experience more fun and simplified, and researchers state that visual information is retained for a longer amount of time thus it makes the whole process more beneficial.
Uses of PowerPoint in Business:
Business is mainly about creating a well-laid out roadmap and planning for the project at hand and then executing it. With PowerPoint we can assure a more organised output with a solid structure.
Uses of PowerPoint for Government and Citizen Services:
PowerPoint is also a good option, from other software bundled within MS Office, for storing records and since it's also printable, it provides easy access to the records for government and citizen services to the seekers.
MS Office PowerPoint is an application for making graphical presentations thus adding a visual aspect to our data, enhancing its concept, and leading to easier communication. The software offers various features like Customising colour schemes, adding graphics, images, and animation, etc. Thus it serves as a salient software under MS Offices.
Sample Questions
1. How can we view or run a presentation?
Ans: To run a presentation, either click on the F5 key or select Play from Beginning on the Slideshow Pane.
2. How can we add a blank slide to our presentation?
Ans: For adding a new slide in the same presentation simply click on the Slide icon on the Insert tab and choose the type of slide you want to add from the drop-down menu which unfolds on the screen.
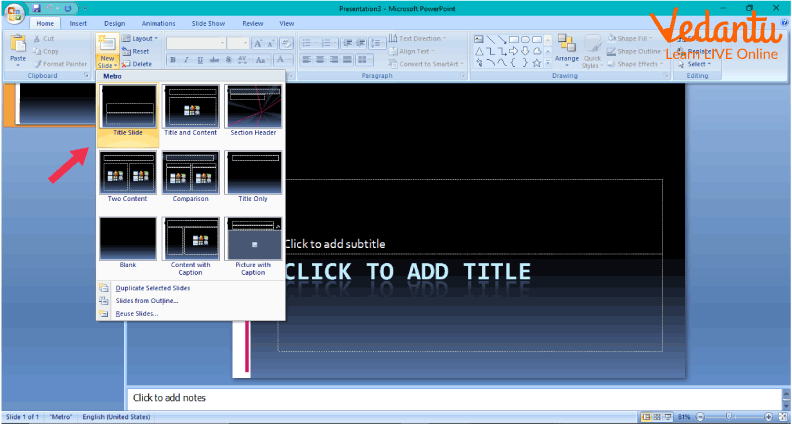
Adding a New Slide
Practice Questions
State whether the following statements are True or False :
In PowerPoint we can use animations.
PowerPoint cannot be used to store records.
PowerPoint allows us to graphically represent data.
We can not export data from PowerPoint to Word.
False
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate answers:
We can add _______, ________ and _________ which gives our presentation a visual aspect.
PowerPoint is a software designed and issued by _______
PowerPoint presents information in the form of individual sheets termed as ________.
Graphics, images, animations
Microsoft Offices

FAQs on Introduction to PowerPoint
1. What is the difference between the transition effect and the animation effect in MS Office PowerPoint?
Transition effects are used on transitioning from one slide to another, whereas Animation effects can be used on the text or the images on the slide.
2. Can we insert sound in a presentation?
Yes we can also insert sound in our presentation.
3. Is Microsoft Office PowerPoint a software?
Yes MS Office PowerPoint is a software application issued by MS Offices.

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is PowerPoint: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
What is PowerPoint? This blog provides the essence of PowerPoint, a versatile presentation software by Microsoft. Discover its features, uses, and the art of crafting compelling slideshows. Whether you're a student, professional, or simply curious, explore the power of PowerPoint and learn how to create impactful presentations effortlessly.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals (ERP) MB920
- Microsoft Access Training
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals (CRM) MB910
- Microsoft Word Course
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Marketing MB220

According to Glassdoor , a PowerPoint designer's average salary in the UK is about £37,811 annually. In this blog, you will learn What is PowerPoint, its key features, its benefits, and how to use it, as well as learn some tips for creating effective presentations.
Table of contents
1) What is PowerPoint?
2) Understanding the PowerPoint Interface
3) Key Features of PowerPoint
4) How to use PowerPoint to create a presentation?
5) Benefits of PowerPoint
6) Tips for Creating Effective PowerPoint Presentations
7) Conclusion
What is PowerPoint?
PowerPoint is a versatile and popular presentation software developed by Microsoft (MS). It is a part of the Microsoft Office Suite and offers various features and tools to create visually appealing and engaging presentations. MS PowerPoint allows users to combine text, graphics, multimedia elements, and animations to convey information effectively .
Evolution of PowerPoint

Understanding the PowerPoint Interface
The PowerPoint interface provides a user-friendly environment for creating and editing presentations. Familiarising yourself with its essential components will help you navigate the software efficiently. Here's a breakdown of the MS PowerPoint interface:
1) Ribbon : The Ribbon is located at the top of the MS PowerPoint window and consists of multiple tabs, such as Home, Insert, Design, Transitions, and more.
2) Slides pane : The Slides pane is on the left side of the PowerPoint window. It displays thumbnail images of your presentation slides, allowing you to navigate and rearrange them easily. You can add, delete, duplicate, or hide slides from this pane.
3) Notes pane : The Notes pane is located below the Slides pane. It provides space for adding speaker notes or additional information related to each slide.
4) Slide area : The Slide area occupies the central part of the PowerPoint window. It displays the selected slide, where you can add and arrange content such as text, images, charts, and multimedia elements .
5) Task panes : Task panes are additional panels on the PowerPoint window's right side. They offer various functionalities such as formatting options, slide layouts, animations, etc. Task panes can be opened or closed based on your specific needs.
Understanding the MS PowerPoint interface will help you navigate the software effectively and make the most of its features. Whether you are creating slides, adding content, or applying formatting, having a good grasp of the interface ensures a smooth and productive experience .
Key Features of PowerPoint
When it comes to creating captivating and professional presentations, MS PowerPoint stands out as versatile and feature-rich software. Its array of tools and functionalities enables users to bring their imagination and ideas to life. Moreover, it also helps engage their audience effectively .
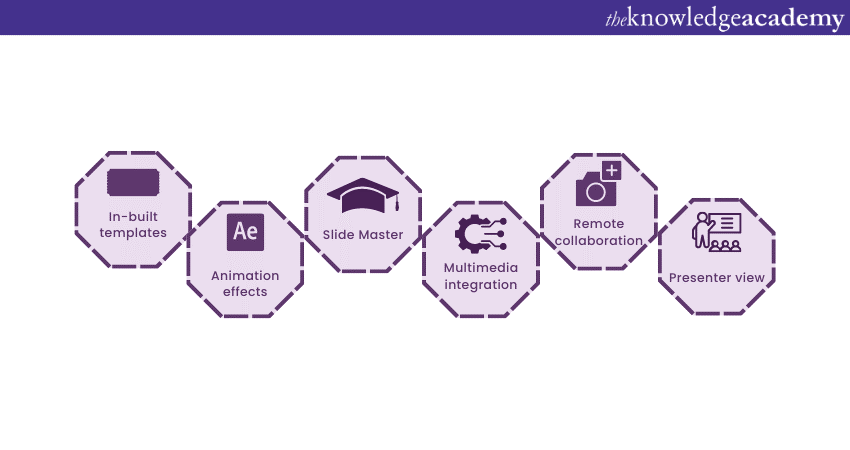
1) Slide Templates : PowerPoint provides a collection of pre-designed templates that make it easy to create visually appealing slides.
2) Slide Master : The Slide Master feature allows users to define the overall layout, font styles, and colour scheme for the entire presentation .
3) Animations and transitions : PowerPoint offers various animation effects and slide transitions to add visual interest and captivate the audience .
4) Multimedia integration : Users can embed images, videos, and audio files directly into their presentations, enhancing the overall impact .
5) Collaboration tools : MS PowerPoint allows multiple users to work on a presentation simultaneously, making it ideal for team projects and remote collaboration .
6) Presenter View : The Presenter View feature gives presenters access to speaker notes, a timer, and a preview of upcoming slides, enabling a seamless presentation experience .
These features collectively contribute to PowerPoint's versatility and make it a powerful tool for developing engaging and impactful presentations.
How to use PowerPoint to create a presentation?
Creating a presentation in PowerPoint is a straightforward process. Whether it's simple animations or explainer videos learning H ow to use PowerPoint is an extremely valuable skill. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a presentation:
1) Launch PowerPoint and choose a template or start with a blank slide.
2) Add slides by clicking "New Slide" or using the shortcut key (Ctrl + M).
3) Customise slide content by entering text and inserting visuals.
4) Rearrange slides for a logical flow by dragging them in the slide navigation pane.
5) Apply slide transitions for visual effects in the "Transitions" tab.
6) Add animations to objects in the "Animations" tab.
7) Preview your presentation by clicking "Slide Show".
8) Save your presentation and choose a format (.pptx or .pdf).
9) Share your presentation via email, cloud storage, or collaboration tools.
By following these steps, you can create a well-structured and visually appealing presentation in Microsoft PowerPoint. Remember to keep your content concise, use engaging visuals, and practice your presentation skills to deliver an impactful presentation .
Benefits of PowerPoint
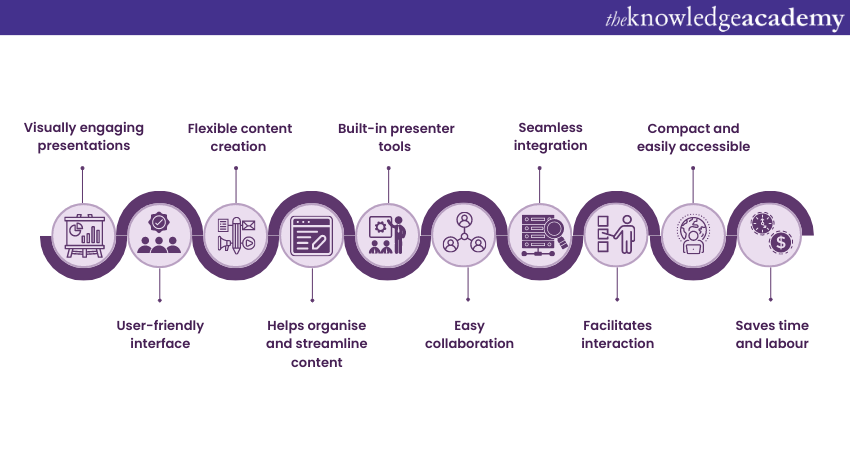
1) Visual appeal : Microsoft PowerPoint allows you to create visually appealing presentations with its wide range of design tools and features. You can use templates, themes, and customisable layouts to make your slides visually engaging and professional .
2) Easy to use : PowerPoint has a user-friendly interface, making it accessible to users of all levels. The intuitive tools and straightforward navigation make it easy to create, edit, and deliver presentations efficiently .
3) Flexibility : PowerPoint provides flexibility in terms of content creation. You can include various types of content, such as text, images, charts, graphs, videos, and audio files, to enhance your message and engage your audience effectively.
4) Organisation and structure : PowerPoint offers features to help you organise and structure your content. You can create multiple slides, use slide masters for consistent formatting, and arrange the sequence of slides to create a logical flow .
5) Presenter tools : PowerPoint includes built-in presenter tools that aid in delivering presentations smoothly. You can use presenter view to see your notes and upcoming slides while your audience sees only the presentation. Additionally, features like slide transitions and animations add visual interest and help you control the flow of information .
6) Collaboration and sharing : PowerPoint allows for easy collaboration and sharing of presentations. Several users can simultaneously work on the same presentation, making it convenient for team projects. You can also share your presentations via email, cloud storage, or online platforms, ensuring easy access for viewers .
7) Integration with other tools : PowerPoint can seamlessly integrate with other Microsoft Office applications, such as Word and Excel. You can import data and charts from Excel or copy and paste content between different Office applications, saving time and effort .
8) Presenter-audience interaction : PowerPoint provides features that facilitate interaction between the presenter and the audience. You can include interactive elements like hyperlinks, buttons, and quizzes to engage your audience and make your presentations more dynamic.
9) Portable and accessible : PowerPoint presentations can be saved in various formats, such as .pptx or .pdf, making them easily accessible on different devices. This portability allows you to deliver presentations on laptops, tablets, or even projectors without compatibility issues .
10) Time and effort savings : PowerPoint simplifies the process of creating presentations, saving you time and effort. The pre-designed templates, slide layouts, and formatting options enable you to create professional-looking presentations efficiently .
Unleash your creativity to deliver captivating presentations that leave a lasting impact with our Microsoft PowerPoint Masterclass – Sign up now!
Tips for Creating Effective PowerPoint Presentations
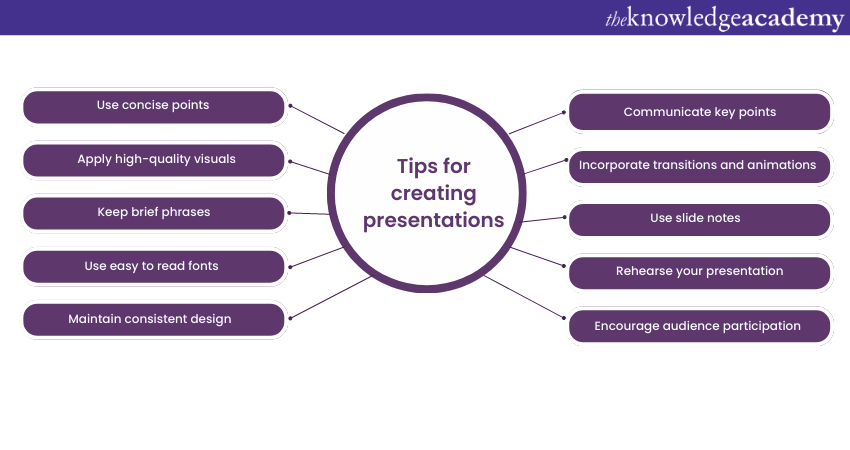
1) Simplicity is key : Keep your slides clean and uncluttered. Use concise bullet points and simple visuals to convey your message effectively .
2) Visuals matter : Incorporate relevant, high-quality visuals such as images, charts, and diagrams to enhance understanding and engagement .
3) Limit text : Avoid overwhelming your audience with excessive text on slides. Use brief phrases or keywords to communicate key points .
4) Choose legible fonts : Opt for clear and readable fonts that are easy to read, even from a distance. Maintain consistency in font styles throughout your presentation .
5) Consistent design : Maintain a consistent design theme, including colours, fonts, and layout, to create a visually appealing and professional presentation.
6) Emphasise important points : Use visual hierarchy techniques, such as font size, colour, and formatting, to draw attention to essential information .
7) Use transitions and animations sparingly : Incorporate slide transitions and animations thoughtfully, focusing on enhancing content and transitions without distracting the audience .
8) S lide notes for guidance : Utilise the slide notes feature to include additional details, explanations, or reminders for a well-prepared and confident presentation.
9) Practice and time yourself : Rehearse your presentation to ensure smooth delivery and stay within the allocated time. Practice helps you refine your content and delivery.
10) Engage the audience : Encourage audience participation through interactive elements, questions, or discussions to foster engagement and make your presentation more memorable.
By implementing these tips, you can create effective MS PowerPoint presentations that capture attention, communicate information clearly, and engage your audience effectively.
Conclusion
We hope this blog has helped you understand What is PowerPoint and how it can help you. It offers powerful features with a user-friendly interface for creating visually appealing presentations. With its tools for organising information, incorporating text and visuals, and delivering impactful content, PowerPoint is a valuable tool for beginners to communicate their ideas effectively .
Master the art of effective communication and productivity and unlock your potential with our comprehensive Microsoft Office Training – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming office applications resources batches & dates.
Thu 16th May 2024
Thu 6th Jun 2024
Thu 4th Jul 2024
Thu 8th Aug 2024
Thu 5th Sep 2024
Thu 10th Oct 2024
Thu 7th Nov 2024
Thu 5th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
CS4670/5670 - Introduction to Computer Vision
- Geometry / Physics of image formation
- Properties of images and basic image processing
- 3D reconstruction
- Grouping (of image pixels into objects)
- Machine learning in computer vision: basics, hand-designed feature vectors, convolutional networks
- Detecting and localizing objects
Office Hour Calendar
Lectures / notes:.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Download ppt "Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer". Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according to specified rules, produce information (output), and store the information for future use.
55. Slide 55 of 84 TOPIC CHAPTER 1: Introduction To Computers Front view 3.5-inch floppy disk drive 3.5-inch floppy disk Rear view of floppy disk drive Data cable Power cable Floppy Disk Drives (FDD) FDD is a personal computer storage device that reads data from, and writes data to, removable disks made of flexible Mylar plastic covered with a magnetic coating and enclosed in a stiff ...
These are 1) it accepts data or instructions by way of input, 2) it stores data, 3) it can process data as required by the user, 4) it gives results in the form of output, and 5) it controls all operations inside a computer. We discuss below each of these operations. 1. Input: In computing, an input device is any peripheral (piece of computer ...
A computer is an electronic device which basically performs five major operations which includes: 1) accepts data or instructions (input) 2) stores data. 3) process data. 4) displays results (output) and. 5) controls and co-ordinates all operations inside a computer. .
1.97k likes | 4.85k Views. Computer Basics 1. Computer Basic 1 includes two lessons: Lesson 1: Introduction to Computers Lesson 2: Common Computer Terminology. Lesson 1 - Introduction to Computer Objectives. After completing lesson 1, you will be able to: Describe the importance of computers in today's world. Download Presentation.
It covers the following points, viz., 1. Introduction to Computer 2. Main Parts of Computer 3. Types of Computer 4. Storage Unit vs. Memory Unit 5. Classification on Working System 6. Types of Network 7. Classification of Computer- Based on Size 8. Some Important Extensions. The above points were discussed in this powerpoint presentation. Read less
Introduction ¤ Its an electronic device which accepts input, processes data, stores data, and produces output ¤ Input refer to whatever is sent to a Computer system ¤ Data refer to the symbols that represent facts, objects, and ideas ¤ A computer processes data in a device called the central processing unit (CPU)
Presentation Transcript. Introduction to computer fundamentals. The Computer Defined • A computer is an electronic device that processes data, converting it into information that is useful to people. Analog and Digital Computer • Analog systems represent data as variable points along a continuous spectrum of values.
The idea of making a PowerPoint presentation is to show your information in the simplest way possible for your audience. Step 2: Create a new document in PowerPoint. Once you check that all the functions are working fine with the software, please open it and go to the File tab. If you've ever used Word or Excel, you'll probably find this Home ...
Step 1.When you start the computer, certain operating system files are loaded into RAM from the hard disk. The operating system displays the user interface on the screen. Operating system interface Operating system instructions Step 2.When you start a Web browser, the program's instructions are loaded into RAM from the hard disk.
Learn everything you need to know to get started using Microsoft PowerPoint! You'll learn all the basics plus more, including: how to choose a design theme...
Nov 4, 2015 •. 10 likes • 12,609 views. J. Jibin Sr. Plamoottukada. Introduction to computer Powerpoint Presentation for plus one Accountancy 11 chapter. Technology. 1 of 30. Download Now. Download to read offline.
Learning Objectives. If you do well in this unit, you should be able to: Identify the names and functions of the PowerPoint interface. Create, edit, save, and print presentations. Format presentations. Add a graphic to a presentation. Create and manipulate simple slide shows with outlines and notes. Create slide presentations that include text ...
Slides in a presentation are similar to pages in a word processing document. All slides and graphics are saved in one file (example: keys.xppt). Use the PowerPoint file to present the information in the following ways: • On-screen slide show: The keys.xppt file displays the slide show on a monitor or computer-projected large screen.
This is the beginning Microsoft PowerPoint course that you've been waiting for! Learn everything you need to effectively use PowerPoint by watching just one ...
Open PowerPoint for the First Time. Your first view of PowerPoint looks pretty bland. There is one large page, called a slide. Every presentation begins with a title and PowerPoint presents you with a title slide. Simply type your text into the text boxes provided. Go to Home and select New Slide to add a blank slide with placeholders for a ...
Introduction to Computers. Power Point. Opening and Viewing Presentations. Click on the Start button (bottom-left of your screen). From the popup menu displayed click on All Programs. Click on a submenu option called Microsoft Office. Finally click on Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007. 294 views • 25 slides
MS Office PowerPoint is an application for making graphical presentations thus adding a visual aspect to our data, enhancing its concept, and leading to easier communication. The software offers various features like Customising colour schemes, adding graphics, images, and animation, etc. Thus it serves as a salient software under MS Offices.
7. INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS History of Computer Mid 1800's - Babbage designed "analytical engine" expanded upon mechanical calculators, but programmable via punch-cards described general layout of modern computers never functional, beyond technology of the day 1890 - Hollerith invented tabulating machine used for 1890 U.S. Census stored data on punch-cards, could sort and tabulate using ...
Definitions. Architecture: (also ISA: instruction set architecture) The parts of a processor design that one needs to understand for writing correct machine/assembly code. Examples: instruction set specification, registers. Machine Code: The byte-level programs that a processor executes.
PowerPoint is a versatile and popular presentation software developed by Microsoft (MS). It is a part of the Microsoft Office Suite and offers various features and tools to create visually appealing and engaging presentations. MS PowerPoint allows users to combine text, graphics, multimedia elements, and animations to convey information ...
3. Computer Components Any kind of computers consists of HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE. Hardware: Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that constitutes a computer system. Computer hardware refers to the physical parts or components of a computer such as the monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, hard drive disk (HDD), system unit (graphic cards, sound cards, memory ...
Overview: This course will serve as a detailed introduction to computer vision. The emphasis will be on covering the fundamentals which underly both computer vision research and applications. A tentative list of topics is below: Geometry / Physics of image formation. Properties of images and basic image processing. 3D reconstruction.