- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault

Cold War History
By: History.com Editors
Updated: June 26, 2023 | Original: October 27, 2009

The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension marked by competition and confrontation between communist nations led by the Soviet Union and Western democracies including the United States. During World War II , the United States and the Soviets fought together as allies against Nazi Germany . However, U.S./Soviet relations were never truly friendly: Americans had long been wary of Soviet communism and Russian leader Joseph Stalin ’s tyrannical rule. The Soviets resented Americans’ refusal to give them a leading role in the international community, as well as America’s delayed entry into World War II, in which millions of Russians died.
These grievances ripened into an overwhelming sense of mutual distrust and enmity that never developed into open warfare (thus the term “cold war”). Soviet expansionism into Eastern Europe fueled many Americans’ fears of a Russian plan to control the world. Meanwhile, the USSR came to resent what they perceived as U.S. officials’ bellicose rhetoric, arms buildup and strident approach to international relations. In such a hostile atmosphere, no single party was entirely to blame for the Cold War; in fact, some historians believe it was inevitable.
Containment
By the time World War II ended, most American officials agreed that the best defense against the Soviet threat was a strategy called “containment.” In his famous “Long Telegram,” the diplomat George Kennan (1904-2005) explained the policy: The Soviet Union, he wrote, was “a political force committed fanatically to the belief that with the U.S. there can be no permanent modus vivendi [agreement between parties that disagree].” As a result, America’s only choice was the “long-term, patient but firm and vigilant containment of Russian expansive tendencies.”
“It must be the policy of the United States,” he declared before Congress in 1947, “to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation…by outside pressures.” This way of thinking would shape American foreign policy for the next four decades.
Did you know? The term 'cold war' first appeared in a 1945 essay by the English writer George Orwell called 'You and the Atomic Bomb.'
The Cold War: The Atomic Age
The containment strategy also provided the rationale for an unprecedented arms buildup in the United States. In 1950, a National Security Council Report known as NSC–68 had echoed Truman’s recommendation that the country use military force to contain communist expansionism anywhere it seemed to be occurring. To that end, the report called for a four-fold increase in defense spending.
In particular, American officials encouraged the development of atomic weapons like the ones that had ended World War II. Thus began a deadly “ arms race .” In 1949, the Soviets tested an atom bomb of their own. In response, President Truman announced that the United States would build an even more destructive atomic weapon: the hydrogen bomb, or “superbomb.” Stalin followed suit.
As a result, the stakes of the Cold War were perilously high. The first H-bomb test, in the Eniwetok atoll in the Marshall Islands, showed just how fearsome the nuclear age could be. It created a 25-square-mile fireball that vaporized an island, blew a huge hole in the ocean floor and had the power to destroy half of Manhattan. Subsequent American and Soviet tests spewed radioactive waste into the atmosphere.
The ever-present threat of nuclear annihilation had a great impact on American domestic life as well. People built bomb shelters in their backyards. They practiced attack drills in schools and other public places. The 1950s and 1960s saw an epidemic of popular films that horrified moviegoers with depictions of nuclear devastation and mutant creatures. In these and other ways, the Cold War was a constant presence in Americans’ everyday lives.

HISTORY Vault: Nuclear Terror
Now more than ever, terrorist groups are obtaining nuclear weapons. With increasing cases of theft and re-sale at dozens of Russian sites, it's becoming more and more likely for terrorists to succeed.
The Cold War and the Space Race
Space exploration served as another dramatic arena for Cold War competition. On October 4, 1957, a Soviet R-7 intercontinental ballistic missile launched Sputnik (Russian for “traveling companion”), the world’s first artificial satellite and the first man-made object to be placed into the Earth’s orbit. Sputnik’s launch came as a surprise, and not a pleasant one, to most Americans.
In the United States, space was seen as the next frontier, a logical extension of the grand American tradition of exploration, and it was crucial not to lose too much ground to the Soviets. In addition, this demonstration of the overwhelming power of the R-7 missile–seemingly capable of delivering a nuclear warhead into U.S. air space–made gathering intelligence about Soviet military activities particularly urgent.
In 1958, the U.S. launched its own satellite, Explorer I, designed by the U.S. Army under the direction of rocket scientist Wernher von Braun, and what came to be known as the Space Race was underway. That same year, President Dwight Eisenhower signed a public order creating the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), a federal agency dedicated to space exploration, as well as several programs seeking to exploit the military potential of space. Still, the Soviets were one step ahead, launching the first man into space in April 1961.
That May, after Alan Shepard become the first American man in space, President John F. Kennedy (1917-1963) made the bold public claim that the U.S. would land a man on the moon by the end of the decade. His prediction came true on July 20, 1969, when Neil Armstrong of NASA’s Apollo 11 mission , became the first man to set foot on the moon, effectively winning the Space Race for the Americans.
U.S. astronauts came to be seen as the ultimate American heroes. Soviets, in turn, were pictured as the ultimate villains, with their massive, relentless efforts to surpass America and prove the power of the communist system.
The Cold War and the Red Scare
Meanwhile, beginning in 1947, the House Un-American Activities Committee ( HUAC ) brought the Cold War home in another way. The committee began a series of hearings designed to show that communist subversion in the United States was alive and well.
In Hollywood , HUAC forced hundreds of people who worked in the movie industry to renounce left-wing political beliefs and testify against one another. More than 500 people lost their jobs. Many of these “blacklisted” writers, directors, actors and others were unable to work again for more than a decade. HUAC also accused State Department workers of engaging in subversive activities. Soon, other anticommunist politicians, most notably Senator Joseph McCarthy (1908-1957), expanded this probe to include anyone who worked in the federal government.
Thousands of federal employees were investigated, fired and even prosecuted. As this anticommunist hysteria spread throughout the 1950s, liberal college professors lost their jobs, people were asked to testify against colleagues and “loyalty oaths” became commonplace.
The Cold War Abroad
The fight against subversion at home mirrored a growing concern with the Soviet threat abroad. In June 1950, the first military action of the Cold War began when the Soviet-backed North Korean People’s Army invaded its pro-Western neighbor to the south. Many American officials feared this was the first step in a communist campaign to take over the world and deemed that nonintervention was not an option. Truman sent the American military into Korea, but the Korean War dragged to a stalemate and ended in 1953.
In 1955, the United States and other members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) made West Germany a member of NATO and permitted it to remilitarize. The Soviets responded with the Warsaw Pact , a mutual defense organization between the Soviet Union, Albania, Poland, Romania, Hungary, East Germany, Czechoslovakia and Bulgaria that set up a unified military command under Marshal Ivan S. Konev of the Soviet Union.
Other international disputes followed. In the early 1960s, President Kennedy faced a number of troubling situations in his own hemisphere. The Bay of Pigs invasion in 1961 and the Cuban missile crisis the following year seemed to prove that the real communist threat now lay in the unstable, postcolonial “Third World.”
Nowhere was this more apparent than in Vietnam , where the collapse of the French colonial regime had led to a struggle between the American-backed nationalist Ngo Dinh Diem in the south and the communist nationalist Ho Chi Minh in the north. Since the 1950s, the United States had been committed to the survival of an anticommunist government in the region, and by the early 1960s it seemed clear to American leaders that if they were to successfully “contain” communist expansionism there, they would have to intervene more actively on Diem’s behalf. However, what was intended to be a brief military action spiraled into a 10-year conflict .
The End of the Cold War and Effects
Almost as soon as he took office, President Richard Nixon (1913-1994) began to implement a new approach to international relations. Instead of viewing the world as a hostile, “bi-polar” place, he suggested, why not use diplomacy instead of military action to create more poles? To that end, he encouraged the United Nations to recognize the communist Chinese government and, after a trip there in 1972, began to establish diplomatic relations with Beijing.
At the same time, he adopted a policy of “détente”—”relaxation”—toward the Soviet Union. In 1972, he and Soviet premier Leonid Brezhnev (1906-1982) signed the Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty (SALT I), which prohibited the manufacture of nuclear missiles by both sides and took a step toward reducing the decades-old threat of nuclear war.
Despite Nixon’s efforts, the Cold War heated up again under President Ronald Reagan (1911-2004). Like many leaders of his generation, Reagan believed that the spread of communism anywhere threatened freedom everywhere. As a result, he worked to provide financial and military aid to anticommunist governments and insurgencies around the world. This policy, particularly as it was applied in the developing world in places like Grenada and El Salvador, was known as the Reagan Doctrine .
Even as Reagan fought communism in Central America, however, the Soviet Union was disintegrating. In response to severe economic problems and growing political ferment in the USSR, Premier Mikhail Gorbachev (1931-2022) took office in 1985 and introduced two policies that redefined Russia’s relationship to the rest of the world: “glasnost,” or political openness, and “ perestroika ,” or economic reform.
Soviet influence in Eastern Europe waned. In 1989, every other communist state in the region replaced its government with a noncommunist one. In November of that year, the Berlin Wall –the most visible symbol of the decades-long Cold War–was finally destroyed, just over two years after Reagan had challenged the Soviet premier in a speech at Brandenburg Gate in Berlin: “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall.” By 1991, the Soviet Union itself had fallen apart. The Cold War was over.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

- HISTORY & CULTURE
What was the Cold War—and are we headed to another one?
The 45-year standoff between the West and the U.S.S.R. ended when the Soviet Union dissolved. Some say another could be starting as tensions with Russia rise.
As World War II dragged to an end in 1945, the leaders of the “Big Three” allied powers—the United States, Soviet Union, and Great Britain—met in Potsdam, Germany, to hash out terms to conclude the bloodiest conflict the world had ever seen. The great powers split Germany into occupation zones, recognized a Soviet-backed government in Poland, and partitioned Vietnam, monumental decisions that shaped the postwar global order. The talks were meant to forge a lasting peace, but within 18 months, a Cold War began that lasted more than four decades.
One of the most important moments at Potsdam was not captured in a memo or proclaimed at a press conference. Late in the conference, U.S. President Harry Truman took aside Soviet premier Joseph Stalin to share some explosive news: The U.S. had just successfully tested a weapon of “unusual destructive force.” It was a nuclear weapon capable of destroying entire cities, the most dangerous and powerful armament the world had ever seen.
( Subscriber exclusive: For Hiroshima's survivors, memories of the bomb are impossible to forget .)
Within weeks, the U.S. used the atomic bomb to force Japan’s surrender. With a devastating and proven weapon in its armory, the U.S. suddenly had the upper hand among the powers who were allies in the war. What followed was a dangerous struggle for supremacy between two superpowers, the U.S. and the U.S.S.R., that lasted until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991.

Though the two nations were technically at peace, the period was characterized by an aggressive and costly arms race; bloody proxy wars fought across Latin America, Africa, and Asia; and competing bids for world dominance between U.S.-led capitalist governments and the Soviet-led communist bloc.
The Cold War lasted nearly half a century. Here’s a look at why it began, how it escalated, its legacy today—and why some analysts think another Cold War is already underway.
Why’s it called the Cold War?
The term “cold war” had existed since the 1930s, when guerre froide was used in France to describe increasingly fraught relationships between European countries. In 1945, shortly after the United States dropped the atomic bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, British writer George Orwell used the term in an essay that explored what the atom bomb meant for international relations.
The atom bombs killed more than 100,000 Japanese citizens, unveiling a destructive power so terrifying that Orwell predicted it would discourage open warfare among great powers, creating instead “a state which was at once unconquerable and in a permanent state of ‘cold war’ with its neighbours.”
Orwell’s prediction of a “peace that is no peace” came true as seeds of distrust between the former allies grew.
Okay, so how did the Cold War begin?
The U.S.S.R. had borne the highest number of military and civilian casualties in the war— an estimated 24 million —while liberating huge swaths of Eastern Europe from Nazi control. Soviet leader Josef Stalin was dissatisfied with the postwar division of Europe, which he felt didn’t fairly reflect his nation’s contribution.
In the U.S., diplomat George Kennan outlined the Soviet Union’s growing distrust in the 1946 “Long Telegram,” as it is now known. Kennan warned that the U.S.S.R. was illogical and insecure and would not cooperate with the West in the long-term. In response, Washington began to pursue a policy of “containment” to prevent the spread of Soviet ideology and influence.

The U.S. soon got an opportunity to flex its new policy. In 1947, Britain announced it would withdraw aid from Greece and Turkey, which were both battling communist uprisings. President Harry Truman seized the occasion to ask Congress for funds to assist both countries, establishing what became known as the Truman Doctrine —the principle that the U.S. should support countries or people threatened by Soviet forces or communist insurrection. Stalin saw the move as the opening shot of a shadow war.
The term “Cold War” became a shorthand to describe the ideological struggle between capitalism in the West and communism in the East. American journalist Walter Lippmann popularized the term in a series of articles in 1947 as nations chose sides in the standoff.
Why was NATO created?
The U.S. wasn’t alone in worrying about Stalin’s push to extend Soviet influence westward and bring other states under communist rule. In 1948, the U.S.S.R. backed a communist coup in Czechoslovakia and launched a blockade of west Berlin, which had been divided into occupation zones controlled by communists in the east and capitalists in the west.
To demonstrate a united front, the U.S. and its allies formed a transatlantic mutual defense alliance known as the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, or NATO. On April 4, 1949, the U.S., Canada, Belgium, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxemburg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, and the U.K. signed a treaty agreeing that “an armed attack against one or more…shall be considered an attack against them all.”

The U.S.S.R. responded by creating a defensive alliance of its own. Signed in 1955, the Warsaw Pact included the Soviet Union and seven satellite states, including Poland and East Germany, reinforcing the ideological and military barrier between Eastern and Western Europe that Winston Churchill had dubbed the “ Iron Curtain ” in a 1946 speech.
How close did the world come to nuclear war?
As the two sides faced off across that Iron Curtain, the U.S. and U.S.S.R. engaged in an arms race, pouring trillions of dollars into accumulating nuclear arsenals .
The U.S. had an advantage at the start of the arms race. But once the U.S.S.R. built its own nuclear arsenal, the two sides were at a standoff over “mutually assured destruction” —the idea that if either side attacked, the other would retaliate, unleashing apocalyptic consequences for both parties.
You May Also Like

A military spouse reflects on life over two decades of war—and what comes next

What the end of the war in Afghanistan means to one mother and her family

‘A ball of blinding light’: Atomic bomb survivors share their stories
( See the abandoned Soviet bunkers hidden beneath Georgia's capital city .)
Both countries had missile defenses pointed at one another, and in 1962, the Cuban Missile Crisis brought the countries closer to the brink than any other event in the Cold War. The U.S. detected Soviet missile bases and arms in communist Cuba, just 90 miles south of Florida. Demanding they be removed, President John F. Kennedy declared that a strike on U.S. territory would trigger an immediate nuclear strike on the U.S.S.R.

The threat of imminent nuclear war hung over nearly two weeks of tense negotiations. Finally, the U.S.S.R. agreed to dismantle its weapons facilities if the U.S. pledged not to invade Cuba. Behind the scenes, the U.S. agreed to remove nuclear weapons from Turkey; that agreement did not become public until 1987.
Nevertheless, both sides’ nuclear arsenals continued to grow exponentially. By the late 1980s, the United States had an estimated 23,000 nuclear weapons to the Soviet Union’s 39,000.
How else was the Cold War fought?
Over more than four decades of Cold War, the U.S. and Soviet Union waged multiple proxy wars across the globe. In the Korean War , the Vietnam War , and other armed conflicts, the superpowers funded opposing sides or fought directly against communist or capitalist militias. Both sides funded revolutions, insurgencies, and political assassinations in Latin America, Africa, Asia, and the Middle East.
The U.S. and Soviet Union also jockeyed to prove technological dominance in a 20-year Space Race . The Soviet Union scored first with the 1957 launch of Sputnik-1, the first artificial satellite, while the U.S. was first to send a man to the moon in 1969. Only in the mid 1970s did the two nations begin to cooperate on joint missions.
( 50 years after Apollo 11, a new moon race is on .)

How did the Cold War end?
By the mid 1980s, life behind the Iron Curtain had changed. Democratic uprisings were percolating in Soviet bloc nations, and the U.S.S.R. itself struggled with economic and political chaos. The U.S. and U.S.S.R. forged a more open relationship, even brokering a nuclear treaty in 1987 that eliminated a class of particularly dangerous ground-launched missiles from the nations’ arsenals.
By 1991, the Soviet Union had lost most of its bloc to democratic revolutions, and the Warsaw Pact was formally dissolved. Mikhail Gorbachev, the last leader of the U.S.S.R., opened his country to the West and instituted economic reforms that undercut institutions that relied on nationalized goods. In December 1991, the U.S.S.R. was dissolved into separate nations.
What does all this mean now?
The U.S.S.R. is gone, and nuclear arsenals have dramatically decreased thanks to nonproliferation treaties between Washington and Moscow in the 1980s and 1990s. In recent decades, the U.S. and Russia have cooperated on a number of global issues, including Afghanistan and the war on terror.
But the Cold War still affects modern geopolitics. Both nations still have divergent geopolitical interests, large defense budgets, and international military bases. NATO still wields political power and has grown to include 30 member states. The alliance now stretches to Russia’s borders and includes former Soviet states and Warsaw Pact members, such as Poland and the Baltic States. Since the 1990s, Russia has seen the eastward expansion of NATO as a threat to its security .
Tensions between Russia and the West reached a new high point following the February 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, which had applied to take the first steps toward NATO membership in 2008, before a new president shelved the plan two years later. Some commentators have likened the current crisis to the beginnings of a new Cold War.
( Follow Ukraine's 30-year struggle for independence with this visual timeline .)
Is a 21st-century Cold War already being waged? It remains to be seen. Though historians say the decisions at Potsdam set the stage for a long post-World War II rivalry, we may not recognize the beginnings of a new Cold War until it’s visible in history’s rear-view mirror.
Related Topics
- VIETNAM WAR
- NUCLEAR WEAPONS

This pill could protect us from radiation after a nuclear meltdown

Oppenheimer: The secrets he protected and the suspicions that followed him

The true history of Einstein's role in developing the atomic bomb

How Chien-Shiung Wu changed the laws of physics

How does ‘Oppenheimer’ re-create history? We asked Christopher Nolan.
- Environment
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Gory Details
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Paid Content
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
World History Project - Origins to the Present
Course: world history project - origins to the present > unit 7.
- READ: Devastation of Old Markets
- READ: Connecting Decolonization and the Cold War
- BEFORE YOU WATCH: USA vs USSR Fight! The Cold War
- WATCH: USA vs USSR Fight! The Cold War

READ: Cold War — An Overview
- READ: The Cold War Around the World
- READ: And Then Gandhi Came — Nationalism, Revolution, and Sovereignty
- BEFORE YOU WATCH: Decolonization and Nationalism Triumphant
- WATCH: Decolonization and Nationalism Triumphant
- BEFORE YOU WATCH: Chinese Communist Revolution
- WATCH: Chinese Communist Revolution
- BEFORE YOU WATCH: Conflict in Israel and Palestine
- WATCH: Conflict in Israel and Palestine
- READ: Decolonizing Women
- End of Empires and Cold War
First read: preview and skimming for gist
Second read: key ideas and understanding content.
- According to the author, what was the basic difference at the heart of the Cold War conflict?
- What does this author identify as the three main features of the Cold War?
- Why did Stalin want to expand Soviet influence in Eastern Europe?
- What was the policy of containment and what conflicts does the author use as an example of this policy?
Third read: evaluating and corroborating
- The Cold War was a conflict that was all about methods of production and distribution that divided communities across the world along communist and capitalist lines. How would you describe the Cold War through each course frame?
Cold War: An Overview
What was the cold war, a divided europe, the cold war heats up around the world, the end of the cold war, want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
PODCAST: HISTORY UNPLUGGED J. Edgar Hoover’s 50-Year Career of Blackmail, Entrapment, and Taking Down Communist Spies
The Encyclopedia: One Book’s Quest to Hold the Sum of All Knowledge PODCAST: HISTORY UNPLUGGED
The Cold War Timeline
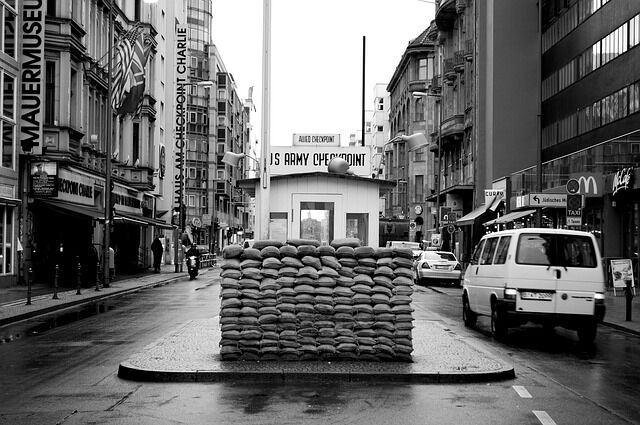

This post is a comprehensive timeline of the Cold War, from the origins of the Russian-American conflict following World War Two to the final dissolution of the Soviet Union and the fall of the Berlin Wall at the end of the 20th century.
Scroll down to learn more. Alternatively, watch this nine-minute explainer video for an overview of the Cold War.
This article is part of our larger collection of resources on the Cold War. For a comprehensive outline of the origins, key events, and conclusion of the Cold War, click here.
This article is also part of our larger selection of posts about the Vietnam War. To learn more, click here for our comprehensive guide to the Vietnam War .
This article is part of our larger selection of posts about the Cold War. To learn more, click here for our comprehensive guide to the Cold War .
Additional Resources About Cold War
What was the iron curtain and how did it collapse, the origins of the cold war timeline, cold war detente — us/soviet enmity cools, when did china become communist, cite this article.
- How Much Can One Individual Alter History? More and Less...
- Why Did Hitler Hate Jews? We Have Some Answers
- Reasons Against Dropping the Atomic Bomb
- Is Russia Communist Today? Find Out Here!
- Phonetic Alphabet: How Soldiers Communicated
- How Many Americans Died in WW2? Here Is A Breakdown
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Origins of the Cold War - A Review Essay

Following the logic of earlier scholarly debates on which side is to be blamed for the Cold War it appears that in fact both or neither: it was the inevitable consequence of the fact that two superpowers emerged after the conflagration of WWII. The ideology confrontation mattered much less vis-a-vis this immense global power shift.
Related Papers
Jonathan Morales
Bibliography of New Cold War History
Aigul Kazhenova , Tsotne Tchanturia , Marijn Mulder , Ahmet Ömer Yüce , Sergei Zakharov , Mirkamran Huseynli , Pınar Eldemir , Angela Aiello , Rastko Lompar
This bibliography attempts to present the publications on the history of the Cold War published after 1989, the beginning of the „archival revolution” in the former Soviet bloc countries. While this first edition is still far from complete, it collects a huge number of books, articles and book chapters on the topic and it is the most extensive such bibliography so far, almost 600 pages in length. An enlarged and updated edition will be completed in 2018.
Tsotne Tchanturia , Vajda Barnabás , Gökay Çınar , Barnabás Vajda , Lenka Thérová , Simon Szilvási , Irem Osmanoglu , Rastko Lompar , Aigul Kazhenova , Pınar Eldemir , Natalija Dimić Lompar , Sára Büki
This bibliography attemts to present the publications on the history of the Cold War published after 1989, the beginning of the „archival revolution” in the former Soviet bloc countries. While this first edition is still far from complete, it collects a huge number of books, articles and book chapters on the topic and it is the most extensive such bibliography so far, almost 600 pages in length. An enlarged and updated edition will be completed in 2018. So, if you are a Cold War history scholar in any country and would like us to incude all of your publications on the Cold War (published after 1989) in the second edition, we will gladly do that. Please, send us a list of your works in which books and articles/book chapters are separated and follow the format of our bibliography. The titles of non-English language entries should be translated into English in square brackets. Please, send the list to: [email protected] The Cold War History Research Center owes special thanks to the Parallel History Project on Cooperative Security (formerly: on NATO and the Warsaw Pact) in Zurich–Washington D.C. for their permission to use the Selective Bibliography on the Cold War Alliances, compiled by Anna Locher and Cristian Nünlist, available at: http://www.php.isn.ethz.ch/lory1.ethz.ch/publications/bibliography/index.html
The Bibliography of New Cold War History (second enlarged edition)
Tsotne Tchanturia , Aigul Kazhenova , Khatia Kardava
This bibliography attempts to present the publications on the history of the Cold War published after 1989, the beginning of the „archival revolution” in the former Soviet bloc countries.
Soshum: Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities
Adewunmi J Falode , Moses Yakubu
The Cold War that occurred between 1945 and 1991 was both an international political and historical event. As a political event, the Cold War laid bare the fissures, animosities, mistrusts, misconceptions and the high-stake brinksmanship that has been part of the international political system since the birth of the modern nation-state in 1648. As a historical event, the Cold War and its end marked an important epoch in human social, economic and political development. The beginning of the Cold War marked the introduction of a new form of social and political experiment in human relations with the international arena as its laboratory. Its end signaled the end of a potent social and political force that is still shaping the course of political relationship among states in the 21 st century. The historiography of the Cold War has been shrouded in controversy. Different factors have been given for the origins of the conflict. This work is a historical and structural analysis of the historiography of the Cold War. The work analyzes the competing views of the historiography of the Cold War and create an all-encompassing and holistic historiography called the Structuralist School.
Jonathan Murphy
fabio capano
In Rosella Mamoli Zorzi e Simone Francescato (eds.), American Phantasmagoria. Modes of representation in US culture
Duccio Basosi
The first section shows that the presence of ghosts in the foreign policy decision making processes of both the United States and the Soviet Union has been detected mainly in relatively recent works. The second, third and fourth sections are dedicated to distinguishing between three different kinds of apparitions—ghosts of the past, specters of the future, and phantasmagorias, respectively. The concluding section attempts some reflections on the possible meanings of such interest of Cold War historiography for spectral figures, particularly in connection with the ongoing debates about the “very notion of Cold War.”
Eliza Gheorghe
Geoffrey Roberts
Review of Jonathan Haslam's Russia's Cold War, published in International Affairs
RELATED PAPERS
Saber and Scroll, 1:3 (Fall 2012), 34-39
Tsotne Tchanturia , Dionysios Dragonas
GTU academic journal “Intellectual”
Michelle Paranzino
Roham Alvandi , Eliza Gheorghe
Diplomatic History
William C. Wohlforth
Tina Machingaidze
Békés, Csaba, Melinda Kamár (Ed.): Students on the Cold War. New Findings and Interpretations. Budapest
Torben Gülstorff
Barbara D Krasner
Akindele Boladale
European History Quarterly
Benjamin Tromly
Helen Roche
Artemy Kalinovsky
Evanthis Hatzivassiliou
henry laycock
Cold War History
Vasil Paraskevov
Cold War International History Project Working Paper #89
Priscilla Roberts
Oxford Handbook in the History of Communism, ed. Stephen Anthony Smith (Oxford: Oxford University Press)
Balazs Szalontai
Martin Grossheim
Journal of Cold War Studies
Silvio Pons
Contemporary European History
Gjert L Dyndal
The Carl Beck Papers in Russian and East …
Jeffrey Burds
Stefano Bottoni
Péter Vámos
Dithekgo Mogadime
[w:] Disintegration and Integration in East-Central Europe 1919 – post-1989, red. W. Loth, N. Păun, Cluj-Napoca 2014, s. 134-146
Jerzy Lazor
Larry L Watts
Roger Voncken
The Soviet and Post-Soviet Review
Jakub Szumski
Cold War International History Project (CWIHP) Working Paper Series
Patryk Babiracki
COLD WAR. GEOPOLITICS
Patrick Kyanda
Petar Žarković
Rachel Alberstadt
gareth dale
Elidor Mehilli
Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Why Did the Cold War Begin? Essay
Introduction, the origins of mistrust, the uneasy alliance, the iron curtain, works cited.
The Cold War was the defining conflict after the end of World War Two. Although it rarely resulted in traditional warfare, it had a tremendous effect on almost every part of western and eastern societies, from culture to technology. To fully understand it, research into its origins is required.
One of the defining aspects of the Cold War is the feeling paranoia experienced by all sides of the conflict. These feelings were not always without merit, and have origins in events preceding the Second World War. The Bolshevik Revolution of 1917 led by Vladimir Lenin and his political ideology based on the works of Karl Marx presented a strictly anti-capitalist perspective that was seen as a threat to the countries of Europe and other capitalist countries (Smith 11).
Bolsheviks were not unanimously accepted in the country either as their methods did not agree with other leftist organizations as well as the people who still supported the monarchy. These opposing forces would unite into the “White Army” which would plunge the country into a civil war (Foglesong 294). This war lasted from 1917-1922 and had taken the lives of millions. After the Revolution, Bolsheviks withdrew from the First World War leaving the allied nations worried about Germany taking over key locations that were previously protected by Russia (Foglesong 232). This has led to an Allied intervention into the Russian civil war that continued even after the First World War ended.
The Allies have supported the White Army with supplies, armaments, and troops, but due to a variety of issues, had to withdraw in 1920, with Japanese troops staying in some Russian provinces until 1925. The Red Army emerged victorious in the civil war with new knowledge that the Western leaders have no interest in cooperation.
This mindset would later fuel Stalin’s propaganda machine creating a perception of a massive international conspiracy to undermine the advances of the newly formed Soviet Union. His policies of collectivization and five-year plans would lead to millions of civilian deaths, unjust punishments without trials, and the creation of a complete police state where no one could oppose him. By creating a sense of constant opposition from the West, Stalin was able to instill a very strong “Us vs. Them” mentality among the people who made his words seem like absolute truth and the words of his critics as the words of traitors (Barghoorn 13).
Those who did not agree would disappear with the use of secret police. His authority was great enough to be able to get rid of even the members of his government and closest colleagues. Their names and actions would later be erased from documents, and their photos would be altered to discredit their previous achievements and associations (Duprat-Kushtanina 23). Paranoia and blind belief in Stalin’s authority would become the driving forces behind the next decades of the Soviet regime.
A similar paranoia grew in the United States. A fear of leftist organizations was present in the United States even before the Bolshevik Revolution, but it would reach its highest peak to date after the Bolsheviks came to power in Russia. To ensure an unopposed entry into the First World War President Woodrow Wilson with the help of the Bureau of Investigation chose to spread anti-German propaganda and organized a variety of actions against leftist groups of the United States (Goldstein 168).
A lot of these groups had a strong opposition towards the war which led to raids on their offices, arrests and legal prosecution against their members. Mass strikes were organized across America with varying results over the next several years, as well as more radical actions (Goldstein 189). Some of which include the anarchist bombings of 1919 that inspired fear of socialism in many members of the public (Goldstein 157). Books and films quickly capitalized on the newfound fear with films dramatizing the events of revolution and creating negative associations with the ideas of Bolshevism and Socialism (Goldstein 323).
This period would culminate in a false prediction of an organized overthrow of the United States government that was predicted to happen in May 1920. The event later titled “May Day Scare” involved mobilizations of thousands of policemen across the country, but did not produce any results as the opponent proved to be imaginary (Goldstein 152). This incident would end the first period of the Red Scare, but its messages would be echoed in the future.
Despite the relative advances of Stalin’s push for industrialization. The Soviet Union was not ready for a new war with Hitler. Stalin negotiated with Hitler to delay military action against the Soviet Union through the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact signed on August 23, 1939, in Moscow (Havers 25). Besides the neutrality, this pact divided the lands of Poland, Finland, Romania, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania between the Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. With the support of this pact, Stalin annexed the territories of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and parts of Finland and Romania (Havers 33).
The pact was terminated on June 22, 1941, when Nazi Germany started Operation Barbarossa with an attack on Soviet positions in Poland. This act of aggression was seen as a declaration of war uniting the Soviet Union with other Allied Nations (Havers 9). Despite the denouncement of the Soviet regime in previous years, the countries were forced to work together to defeat a common enemy. This war, however, would not see the return of the lands that were annexed through the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact. Stalin made sure to negotiate for these territories to remain with the Soviet Union. To facilitate his influence, Stalin made an effort to control the media of the annexed countries and established a strong presence of the communist party, as well as the secret police (Risch 69).
Some place the beginning of the Cold War at the Yalta Conference in Crimea. It was held from February 7 to 11 with a goal of deciding the future of Europe after World War Two. The three heads of the allied forces represented by the President Franklin D. Roosevelt, Premier Joseph Stalin, and Prime Minister Winston Churchill, gathered together to outline the plan for peace in Europe, and how the people of Europe would be able to govern their countries after the Nazi regime.
Each leader had their agenda making the negotiations difficult. Roosevelt pledged for Soviet support in the Pacific War, and Soviet representation in the newly formed United Nations. Churchill was focused on the free democratic elections in Eastern and Central Europe. Lastly, Stalin pressed for a Soviet sphere of influence in Eastern and Central Europe under the guise of it being crucial for the establishment of national security of the Soviet Union (Bell and Gilbert 15).
One of the important factors which could be seen as a beginning of Cold War is the change of the Polish borders. A part of its territory would be given to the Soviet Union while being compensated with a part of Germany. The spheres of influence were established during this conference, and Stalin managed to secure the Soviet regime in the previously annexed countries of Romania and Bulgaria (Bell and Gilbert 27).
Stalin’s desire for influence over the countries on the Soviet border would represent one of the first active steps toward the Cold War. With the power and numbers of the Red Army being unmatched by other nations, Stalin had major leverage during this conference, and his promises that would later be broken served as a way to prevent hostile attitudes toward his agenda.
The Potsdam Conference would prove to be another turning point at the beginning of the Cold War. The conference was held to create further plans for the future of Germany and Poland. However, it differed from the Yalta conference due to a few crucial events. Before the conference, President Roosevelt passed away and was replaced by Harry S. Truman who was not a supporter of Stalin’s regime. In fact, this conference would mark the only instance of Truman and Stalin meeting in person. Truman had strong suspicions of the Soviet Union and would prove to be less willing to agree than Roosevelt was (Bell and Gilbert 46).
The second difference came from the British elections of the Prime Minister that were held at the time of the conference (Bell and Gilbert 27). While Churchill was not a supporter of Stalin, he saw their alliance as necessary at the time. On the other hand, his political opponent Clement Attlee was much less critical of Stalin’s regime and sought to negotiate and create a functioning relationship between the countries.
He would later change his potion and become a strong anti-Soviet politician when the Cold War became inevitable. The final but perhaps the most important event before the conference was the successful test of a nuclear bomb by the United States. While the project was still secret, Stalin knew of its existence thanks to the activity of Soviet spies. Therefore, he was not surprised when Truman informed him that the United States had developed a weapon that would be able to bring a quick end to the Pacific War (Bell and Gilbert 28). This event became the start of the Nuclear Age and would serve as an example of how dangerous the next war might be.
It also removed the advantage of the Red Army, as the massive numbers of people that were involved in attacks during World War Two would easily be destroyed by a single bomb. It forever changed the concept of war and became the main reason for tension during many of the Cold War disagreements. Some of the results of this conference that became important for the Cold War included the division of Germany and Austria into four zones of occupation which would be restructured after the Truman plan, the change of the German border, and the recognition of the Soviet-controlled government of Poland (Bell and Gilbert 51).
After the conference, many of the countries bordering the Soviet Union would become Soviet satellite states. This change was not a result of the free democratic elections promised by Stalin, but a carefully orchestrated change in government by the members of the Soviet Parties of these countries. Their members worked to give themselves the majority of the power while still appearing to be democratic. These countries included Poland, Bulgaria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Romania, and Albania. East Germany also became a puppet state of the Soviet Union under the name the German Democratic Republic. Together these countries became known as the Eastern Block. The western side became represented by the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (Bell and Gilbert 61).
The growing concerns over the Soviet presence in Europe grew stronger, and in February 1946 one of the initial documents of the Cold War was created. George F. Kennan, an American diplomat, working in the US Embassy in Moscow sent a telegram outlining the US opposition to the actions of the Soviet Union. This document would later be known as the “Long Telegram.” It touched upon such topics as Soviet Union’s perceived war with capitalism, the disparity between the Soviet aggression and the views of the Russian people, and a variety of other issues (Goldgeier 404).
In turn, the Soviet government produced the Novikov telegram that declared that the United States is controlled by monopoly capitalists who are preparing for a war that would bring world domination. These telegrams would be followed by one of the most famous speeches of this period given by Winston Churchill. In this speech, Churchill calls for an Anglo-American alliance against the Soviets. He accuses the Soviets of creating an “Iron Curtain” around their territory.
The Iron Curtain represented the closed nature of the Soviet states that were blocked from contact with the western world (Levering 340). Stalin gave a strong response to this speech, comparing Churchill to Hitler and seeing his speech as a “call for war” against the Soviet Union (Levering 341). These speeches could be seen as the official proclamation of the Cold War, with two opposing blocks seeing each other as powers that have to be stopped at all costs.
The Cold War is one of the most complex periods of recent history. Its origins lie almost 30 years before its start, with a long line of events that eventually led to a possible nuclear war. Its origins are filled with subversion and paranoia effects of which are still felt today.
Barghoorn, Frederick Charles. Soviet Foreign Propaganda . Princeton University Press, 2016.
Bell, Philip, and Mark Gilbert. The World Since 1945: An International History . Bloomsbury Publishing, 2016.
Duprat-Kushtanina, Veronika. “Remembering the Repression of the Stalin Era in Russia: on the Non-Transmission of Family Memory.” Nationalities Papers , vol. 41, no. 2, 2013, pp. 225-239.
Foglesong, David. America’s Secret War Against Bolshevism: U.S. Intervention In The Russian Civil War, 1917-1920 . UNC Press Books, 2014.
Goldgeier, James. “The State of the Transatlantic Alliance.” European Foreign Affairs Review , vol. 21, no. 3, 2016, pp. 403-413.
Goldstein, Robert. Little ‘Red Scares’: Anti-Communism and Political Repression in the United States, 1921-1946 . Routledge, 2016.
Havers, Robin. The Second World War . Bloomsbury Publishing, 2014.
Levering, Ralph B. “Toward Cold War Thinking: Editorial Reactions to Churchill’s Iron Curtain Speech in North Carolina Newspapers.” Journal of Transatlantic Studies , vol. 14, no. 4, 2016, pp. 340-349.
Risch, William. “A Soviet West: Nationhood, Regionalism, and Empire in the Annexed Western Borderlands.” Nationalities Papers , vol. 43, no. 1, 2015, pp. 63-81.
Smith, Keith. “Lenin and the Bolshevik Revolution in 1917, Part 1: The Importance of Lenin’s Ideas on Revolution.” Teaching History , vol. 48, no. 2, 2014, pp. 11-13.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, February 25). Why Did the Cold War Begin? https://ivypanda.com/essays/why-did-the-cold-war-begin/
"Why Did the Cold War Begin?" IvyPanda , 25 Feb. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/why-did-the-cold-war-begin/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Why Did the Cold War Begin'. 25 February.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Why Did the Cold War Begin?" February 25, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/why-did-the-cold-war-begin/.
1. IvyPanda . "Why Did the Cold War Begin?" February 25, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/why-did-the-cold-war-begin/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Why Did the Cold War Begin?" February 25, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/why-did-the-cold-war-begin/.
- Comparative Economics of Romania
- Winston Churchill's Iron Curtain Speech
- The Significance of the Iron Curtain at World War II and the Cold War
- Journalistic Mechanisms for Covering Death in Violent Conflicts
- “The Making of a Quagmire" by David Halberstam
- Military Advances Cause Change in Social Structure
- The Vietnam War on the Network Nightly News
- The War in Vietnam: Rolling Thunder Operation Design
Essay on the Cold War: it’s Origin, Causes and Phases
After the Second World War, the USA and USSR became two Super Powers. One nation tried to reduce the power of other. Indirectly the competition between the Super Powers led to the Cold War.
Then America took the leadership of all the Capitalist Countries.
Soviet Russia took the leadership of all the Communist Countries. As a result of which both stood as rivals to each other.
Definition of the Cold War:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In the graphic language of Hartman, “Cold War is a state of tension between countries in which each side adopts policies designed to strengthen it and weaken the other by falling short by actual war”.

Image Source: i.ytimg.com/vi/y9HjvHZfCUI/maxresdefault.jpg
Infact, Cold War is a kind of verbal war which is fought through newspapers, magazines, radio and other propaganda methods. It is a propaganda to which a great power resorts against the other power. It is a sort of diplomatic war.
Origin of Cold War:
There is no unanimity amongst scholars regarding the origin of the Cold War In 1941 when Hitler invaded Russia, Roosevelt the President of USA sent armaments to Russia. It is only because the relationship between Roosevelt and Stalin was very good. But after the defeat of Germany, when Stalin wanted to implement Communist ideology in Poland, Hungery, Bulgaria and Rumania, at that time England and America suspected Stalin.
Winston Churchill, the Prime Minister of England in his ‘Fulton Speech’ on 5 March 1946 said that Soviet Russia was covered by an Iron Curtain. It led Stalin to think deeply. As a result of which suspicion became wider between Soviet Russia and western countries and thus the Cold War took birth.
Causes of the Cold War:
Various causes are responsible for the outbreak of the Cold War. At first, the difference between Soviet Russia and USA led to the Cold War. The United States of America could not tolerate the Communist ideology of Soviet Russia. On the other hand, Russia could not accept the dominance of United States of America upon the other European Countries.
Secondly, the Race of Armament between the two super powers served another cause for the Cold War. After the Second World War, Soviet Russia had increased its military strength which was a threat to the Western Countries. So America started to manufacture the Atom bomb, Hydrogen bomb and other deadly weapons. The other European Countries also participated in this race. So, the whole world was divided into two power blocs and paved the way for the Cold War.
Thirdly, the Ideological Difference was another cause for the Cold War. When Soviet Russia spread Communism, at that time America propagated Capitalism. This propaganda ultimately accelerated the Cold War.
Fourthly, Russian Declaration made another cause for the Cold War. Soviet Russia highlighted Communism in mass-media and encouraged the labour revolution. On the other hand, America helped the Capitalists against the Communism. So it helped to the growth of Cold War.
Fifthly, the Nuclear Programme of America was responsible for another cause for the Cold War. After the bombardment of America on Hiroshima and Nagasaki Soviet Russia got afraid for her existence. So, it also followed the same path to combat America. This led to the growth of Cold War.
Lastly, the Enforcement of Veto by Soviet Russia against the western countries made them to hate Russia. When the western countries put forth any view in the Security Council of the UNO, Soviet Russia immediately opposed it through veto. So western countries became annoyed in Soviet Russia which gave birth to the Cold War.
Various Phases of the Cold War:
The Cold War did not occur in a day. It passed through several phases.
First Phase (1946-1949 ):
In this phase America and Soviet Russia disbelieved each other. America always tried to control the Red Regime in Russia. Without any hesitation Soviet Russia established Communism by destroying democracy in the Poland, Bulgaria, Rumania, Hungery, Yugoslavia and other Eastern European Countries.
In order to reduce Russia’s hegemony, America helped Greece and Turkey by following Truman Doctrine which came into force on 12 March 1947. According to Marshall Plan which was declared on 5 June, 1947 America gave financial assistance to Western European Countries.
In this phase, non withdrawal of army from Iran by Soviet Russia, Berlin blaockade etc. made the cold was more furious. After the formation of NATO in 1949, the Cold War took a halt.
Second Phase (1949-1953 ):
In this phase a treaty was signed between Australia, New Zeland and America in September, 1957 which was known as ANZUS. America also signed a treaty with Japan on 8 September, 1951. At that time by taking armaments from Russia and army from China, North Korea declared war against South Korea.
Then with the help of UNO, America sent military aid to South Korea. However, both North Korea and South Korea signed peace treaty in 1953 and ended the war. In order to reduce the impact of Soviet Communism, America spent a huge amount of dollar in propaganda against Communism. On the other hand, Soviet Russia tried to be equal with America by testing atom bomb.
Third Phase (1953-1957):
Now United States of America formed SEATO in 1954 in order to reduce Soviet Russia’s influence. In 1955 America formed MEDO in Middle East. Within a short span of time, America gave military assistance to 43 countries and formed 3300 military bases around Soviet Russia. At that time, the Vietnamese War started on 1955.
To reduce the American Power, Russia signed WARSAW PACT in 1955. Russia also signed a defence pact with 12 Countries. Germany was divided into Federal Republic of Germany which was under the American control where as German Democratic Republic was under Soviet Russia. In 1957 Soviet Russia included Sphutnick in her defence programme.
In 1953 Stalin died and Khrushchev became the President of Russia. In 1956 an agreement was signed between America and Russia regarding the Suez Crisis. America agreed not to help her allies like England and France. In fact West Asia was saved from a great danger.
Fourth Phase (1957-1962):
In 1959 the Russian President Khrushchev went on a historical tour to America. Both the countries were annoyed for U-2 accident and for Berlin Crisis. In 13 August 1961, Soviet Russia made a Berlin Wall of 25 Kilometres in order to check the immigration from eastern Berlin to Western Berlin. In 1962, Cuba’s Missile Crisis contributed a lot to the cold war.
This incident created an atmosphere of conversation between American President Kenedy and Russian President Khrushchev. America assured Russia that she would not attack Cuba and Russia also withdrew missile station from Cuba.
Fifth Phase (1962-1969 ):
The Fifth Phase which began from 1962 also marked a mutual suspicion between USA and USSR. There was a worldwide concern demanding ban on nuclear weapons. In this period Hot Line was established between the White House and Kremlin. This compelled both the parties to refrain from nuclear war. Inspite of that the Vietnam problem and the Problem in Germany kept Cold War between USA and USSR in fact.
Sixth Phase (1969-1978 ):
This phase commencing from 1969 was marked by DETENTE between USA and USSR- the American President Nixon and Russian President Brezhnev played a vital role for putting an end to the Cold War. The SALT of 1972, the summit Conference on Security’ of 1975 in Helsinki and Belgrade Conference of 1978 brought America and Russia closer.
In 1971, American Foreign Secretary Henry Kissinger paid a secret visit to China to explore the possibilities of reapproachment with China. The American move to convert Diego Garcia into a military base was primarily designed to check the Soviet presence in the Indian Ocean. During the Bangladesh crisis of 1971 and the Egypt-Israel War of 1973 the two super powers extended support to the opposite sides.
Last Phase (1979-1987 ):
In this phase certain changes were noticed in the Cold War. That is why historians call this phase as New Cold War. In 1979, the American President Carter and Russian President Brezhnev signed SALT II. But in 1979 the prospects of mitigating Cold War were marred by sudden development in Afghanistan.
Vietnam (1975), Angola (1976), Ethiopia (1972) and Afghanistan (1979) issues brought success to Russia which was unbearable for America. American President Carter’s Human Rights and Open Diplomacy were criticised by Russia. The SALT II was not ratified by the US Senate. In 1980 America boycotted the Olympic held at Moscow.
In 1983, Russia withdrew from a talk on missile with America. In 1984 Russia boycotted the Olympic game held at Los-Angeles. The Star War of the American President Ronald Regan annoyed Russia. In this way the ‘New Cold War’ between America and Russia continued till 1987.
Result of the Cold War:
The Cold War had far-reaching implications in the international affairs. At first, it gave rise to a fear psychosis which resulted in a mad race for the manufacture of more sophisticated armaments. Various alliances like NATO, SEATO, WARSAW PACT, CENTO, ANZUS etc. were formed only to increase world tension.
Secondly, Cold War rendered the UNO ineffective because both super powers tried to oppose the actions proposed by the opponent. The Korean Crisis, Cuban Missile Crisis, Vietnam War etc. were the bright examples in this direction.
Thirdly, due to the Cold War, a Third World was created. A large number of nations of Africa, Asia and Latin America decided to keep away from the military alliances of the two super powers. They liked to remain neutral. So, Non-Alignments Movement became the direct outcome of the Cold War.
Fourthly, Cold War was designed against mankind. The unnecessary expenditure in the armament production created a barrier against the progress of the world and adversely affected a country and prevented improvement in the living standards of the people.
Fifthly, the principle ‘Whole World as a Family’, was shattered on the rock of frustration due to the Cold War. It divided the world into two groups which was not a healthy sign for mankind.
Sixthly, The Cold War created an atmosphere of disbelief among the countries. They questioned among themselves how unsafe were they under Russia or America.
Finally, The Cold War disturbed the World Peace. The alliances and counter-alliances created a disturbing atmosphere. It was a curse for the world. Though Russia and America, being super powers, came forward to solve the international crisis, yet they could not be able to establish a perpetual peace in the world.
Related Articles:
- Essay on the Cold War, 1945
- Central Treaty Organisation (CENTO): Structure, Principles and Other Details
- History of The Cold War: Origin, Reasons and Other Details
- Truman Doctrine: A Policy Statement Made by US during the Cold War
- Society and Politics
- Art and Culture
- Biographies
- Publications

Grade 12 - The Cold War
How did the Cold War period shape international relations after the Second World War?
After the Second World War, there was a struggle between two world powers, the US and Russia. Why was it called the ‘Cold War’ ? The reason lay in the threat of new and even deadlier weapons of nuclear technology that prevented outright open warfare. The Cold War was characterised by conflict through proxy wars, the manipulation of more vulnerable states through extensive military and financial aid, espionage, propaganda, rivalry over technology, space and nuclear races, and sport. Besides periods of tense crisis in this bi-polar world, the Cold War deeply affected the newly independent countries in Africa and the liberation struggles in southern Africa from the 1960s until the 1990s, when the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) was dismantled.
Did you know? The term “Cold War” was first used by George Orwell, author of the book satirizing Stalinism, “Animal Farm”.
The detente (friendship) that existed between the Allied powers (The US, France and Russia) after 1945 was no more. That military aid would be offered to each other when faced with Nazism fell away, and increased hostility was the order of the day. Some historians argue that it was the formulation and implementation of common policy documents by the USSR for its East European territories that heralded the beginning of different spheres of influence. Quickly, two distinct blocs emerged.
Also see: National Senior Certificate Grd 12, History Paper 1, November 2014 and National Senior Certificate Grd 12, History Paper 2, November 2014 .
Most learners will understand that a ‘war’ involves conflict between warring parties; that a ‘war’ involves the use of weaponry amongst ‘warring parties’ BUT what is meant by a ‘COLD’ war as opposed to a ‘HOT’ one? Common reference to any war usually involves the type of war that involves weaponry, personnel, devastation, explosions, and most of the images of war. A “COLD” war would refer to a battle of ideologies where the protagonists do not face each other, or fight, each other DIRECTLY.
The Cold War was characteristics by different ideologies being imposed or sold to other countries.
It dissected the world into spheres of influence, with the United States of America (USA) as a champion of democracy (and incidentally, Capitalism, as well) pitted against the USSR (Russia), which stood as a beacon of Communism. These divisions played themselves out in the exporting of influence...and then arms and money....to countries sympathetic to either cause.
The Cold War, which occurred from 1945 until 1989/1990 had far-reaching consequences for the world in general. Much of the literature during this period focussed on the bi-polar nature of the globe. Nation-states across the world, whatever explicit or not, empathised with either Russia or the USA. These countries became the battlefields for the competing influences of Democracy/Capitalism against Communism/Centrally-planned economies.
So, learners might ask as to why this Cold War did not escalate into a ‘Hot’ war, where conventional means of warfare were employed. The reason lies in the proliferation (increase) of nuclear weapons so that if these weapons were ever used, the destruction that would follow would result in a global destruction. So, this Cold War was fought behind the threat of a nuclear war. The Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) was probably the closest that the world got to a full-blown conventional war.
The Cold War was a period of increased hostility between two blocs of power, the USA and its allies on the one hand; and the USSR and China, on the other. From the end of the Cold War until the early 1990s, world politics and events were primarily viewed through this lens the battle to exert control and influence globally. The Cold War spread outside Europe to every region of the world, and drew to a close by end of the late 1980s / early 1990s. Towards the end of the 1980s, Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev held conferences with USA President Ronald Reagan. The USSR introduced reform policies aimed at restructuring (perestroika) and opening the Russian economy (glasnost).
In December 1989, after more than four decades, Russian President Gorbachev and American President G. H.W Bush declared the Cold War officially over.
Timeline (Source: “ Timeline of events in the Cold War ” [ Accesssed: 23 January 2015])
- 1945: Cold War begins
- 1946: Winston Churchill delivers his ‘ Iron Curtain’ speech
- 1947: Marshall Plan is announced
- 1948 : February, Communists take over Czechoslovakia
- 1948 : June, The ‘Berlin Blockade’ begins
- 1949 : July, NATO is ratified
- 1950 : February, McCarthy begins communist witchunt
- 1954 : KGB established. CIA assists in overthrowing ‘unfriendly’ regimes in Iran and Guatemala
- 1961 : Bay of Pigs invasion. Construction of Berlin Wall begins. US involvement in Vietnam increases ( troops were dispatched in 1965)
- 1962 : Cuban Missile Crisis
- 1965 : 150000 troops dispatched to Vietnam
- 1970 : US President Nixon extends the war to Cambodia.
- 1973 : Ceasefire between the US and Vietnam.
- 1975 : North Vietnam defeats South Vietnam.
- 1979 : USSR invades Afghanistan
- 1983 : Ronald Reagan proposes Star Wars
- 1989 : Soviet troops withdraw from Afghanistan. Communist governments collapse in Poland, East Germany, Hungary, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia and Romania. The Soviet Empire ( USSR ) ends.
http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/what%20was%20the%20cold%20war.htm
http://www.amazon.com/The-Cold-War-New-History/dp/0143038273
USSR and USA and the creation of spheres of interest :
- installation of Soviet-friendly governments in satellite states;
- USA’s policy of containment: Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan;
- Berlin Crises from 1949 to 1961 (broad understanding of the crises); and
- opposing military alliances: NATO and Warsaw Pact (broadly)
Containment and brinkmanship: the Cuban crisis (as an example of containment and brinkmanship)
Collections in the Archives
Know something about this topic.
Towards a people's history
The Cold War (1945-1989) essay
The Cold War is considered to be a significant event in Modern World History. The Cold War dominated a rather long time period: between 1945, or the end of the World War II, and 1990, the collapse of the USSR. This period involved the relationships between two superpowers: the United States and the USSR. The Cold War began in Eastern Europe and Germany, according to the researchers of the Institute of Contemporary British History (Warner 15). Researchers state that “the USSR and the United States of America held the trump cards, nuclear bombs and missiles” (Daniel 489). In other words, during the Cold War, two nations took the fate of the world under their control. The progression of the Cold War influenced the development of society, which became aware of the threat of nuclear war. After the World War II, the world experienced technological progress, which provided “the Space Race, computer development, superhighway construction, jet airliner development, the creation of international phone system, the advent of television, enormous progress in medicine, and the creation of mass consumerism, and many other achievements” (Daniel 489). Although the larger part of the world lived in poverty and lacked technological progress, the United States and other countries of Western world succeeded in economic development. The Cold War, which began in 1945, reflected the increased role of technological progress in the establishment of economic relationships between two superpowers. The Cold War involved internal and external conflicts between two superpowers, the United States and the USSR, leading to eventual breakdown of the USSR.
- The Cold War: background information
The Cold War consisted of several confrontations between the United States and the USSR, supported by their allies. According to researchers, the Cold War was marked by a number of events, including “the escalating arms race, a competition to conquer space, a dangerously belligerent for of diplomacy known as brinkmanship, and a series of small wars, sometimes called “police actions” by the United States and sometimes excused as defense measures by the Soviets” (Gottfried 9). The Cold War had different influences on the United States and the USSR. For the USSR, the Cold War provided massive opportunities for the spread of communism across the world, Moscow’s control over the development of other nations and the increased role of the Soviet Communist party.
In fact, the Cold War could split the wartime alliance formed to oppose the plans of Nazi Germany, leaving the USSR and the United States as two superpowers with considerable economic and political differences. The USSR was based on a single-party Marxist–Leninist system, while the United States was a capitalist state with democratic governance based on free elections.
The key figure in the Cold War was the Soviet leader Gorbachev, who was elected in 1985. He managed to change the direction of the USSR, making the economies of communist ruled states independent. The major reasons for changing in the course were poor technological development of the USSR (Gottfried 115). Gorbachev believed that radical changes in political power could improve the Communist system. At the same time, he wanted to stop the Cold War and tensions with the United States. The cost of nuclear arms race had negative impact on the economy of the USSR. The leaders of the United States accepted the proposed relationships, based on cooperation and mutual trust. The end of the Cold War was marked by signing the INF treaty in 1987 (Gottfried 115).
- The origins of the Cold War
Many American historians state that the Cold War began in 1945. However, according to Russian researchers, historians and analysts “the Cold War began with the Bolshevik Revolution in 1917, for this was when the capitalist world began its systematic opposition to and effort to undermine the world’s first socialist state and society” (Warner13). For Russians, the Cold War was hot in 1918-1922, when the Allied Intervention policy implemented in Russia during the Russian Civil War. According to John W. Long, “the U.S. intervention in North Russia was a policy formulated by President Wilson during the first half of 1918 at the urgent insistence of Britain, France and Italy, the chief World War I allies” (380).
Nevertheless, there are some other opinions regarding the origins of the Cold War. For example, Geoffrey Barraclough, an outstanding English historian, states that the events in the Far East at the end of the century contributed to the origins of the Cold War. He argues that “during the previous hundred years, Russia and the United States has tended to support each other against England; but now, as England’s power passed its zenith, they came face to face across the Pacific” (Warner 13). According to Barraclough, the Cold War is associated with the conflict of interests, which involved European countries, the Middle East and South East Asia. Finally, this conflict divided the world into two camps. Thus, the Cold War origins are connected with the spread of ideological conflict caused by the emergence of the new power in the early 20-th century (Warner 14). The Cold War outbreak was associated with the spread of propaganda on the United States by the USSR. The propagandistic attacks involved the criticism of the U.S. leaders and their policies. These attacked were harmful to the interests of American nation (Whitton 151).
- The major causes of the Cold War
The United States and the USSR were regarded as two superpowers during the Cold War, each having its own sphere of influence, its power and forces. The Cold War had been the continuing conflict, caused by tensions, misunderstandings and competitions that existed between the United States and the USSR, as well as their allies from 1945 to the early 1990s (Gottfried 10). Throughout this long period, there was the so-called rivalry between the United States and the USSR, which was expressed through various transformations, including military buildup, the spread of propaganda, the growth of espionage, weapons development, considerable industrial advances, and competitive technological developments in different spheres of human activity, such as medicine, education, space exploration, etc.
There four major causes of the Cold War, which include:
- Ideological differences (communism v. capitalism);
- Mutual distrust and misperception;
- The fear of the United State regarding the spread of communism;
- The nuclear arms race (Gottfried 10).
The major causes of the Cold War point out to the fact that the USSR was focused on the spread of communist ideas worldwide. The United States followed democratic ideas and opposed the spread of communism. At the same time, the acquisition of atomic weapons by the United States caused fear in the USSR. The use of atomic weapons could become the major reason of fear of both the United States and the USSR. In other words, both countries were anxious about possible attacks from each other; therefore, they were following the production of mass destruction weapons. In addition, the USSR was focused on taking control over Eastern Europe and Central Asia. According to researchers, the USSR used various strategies to gain control over Eastern Europe and Central Asia in the years 1945-1980. Some of these strategies included “encouraging the communist takeover of governments in Eastern Europe, the setting up of Comecon, the Warsaw Pact, the presence of the Red Army in Eastern Europe, and the Brezhnev Doctrine” (Phillips 118). These actions were the major factors for the suspicions and concerns of the United States. In addition, the U.S. President had a personal dislike of the Soviet leader Joseph Stalin and his policies. In general, the United States was concerned by the Soviet Union’s actions regarding the occupied territory of Germany, while the USSR feared that the United States would use Western Europe as the major tool for attack.
- The consequences of the Cold War
The consequences of the Cold War include both positive and negative effects for both the United States and the USSR.
- Both the United States and the USSR managed to build up huge arsenals of atomic weapons of mass destruction and ballistic missiles.
- The Cold War provided opportunities for the establishment of the military blocs, NATO and the Warsaw Pact.
- The Cold War led to the emergence of the destructive military conflicts, like the Vietnam War and the Korean War, which took the lives of millions of people (Gottfried13).
- The USSR collapsed because of considerable economic, political and social challenges.
- The Cold War led to the destruction of the Berlin Wall and the unification of the two German nations.
- The Cold War led to the disintegration of the Warsaw Pact (Gottfried 136).
- The Cold war provided the opportunities for achieving independence of the Baltic States and some former Soviet Republics.
- The Cold War made the United States the sole superpower of the world because of the collapse of the USSR in 1990.
- The Cold War led to the collapse of Communism and the rise of globalization worldwide (Phillips 119).
The impact of the Cold War on the development of many countries was enormous. The consequences of the Cold War were derived from numerous internal problems of the countries, which were connected with the USSR, especially developing countries (India, Africa, etc.). This fact means that foreign policies of many states were transformed (Gottfried 115).
The Cold War (1945-1989) essay part 2
Do you like this essay?
Our writers can write a paper like this for you!
Order your paper here .
Home — Essay Samples — War — Cold War
Essays on Cold War
Hook examples for cold war essays, the tension-building anecdote hook.
Start your essay with a gripping anecdote from the Cold War era, such as a close encounter between opposing forces, a spy's daring mission, or a pivotal diplomatic negotiation.
The Iron Curtain Metaphor Hook
Draw parallels between the Iron Curtain that divided Europe during the Cold War and modern-day geopolitical divisions. Explore how historical lessons can inform contemporary politics.
The Cuban Missile Crisis Revelation Hook
Begin with a revelation about the Cuban Missile Crisis, a pivotal event during the Cold War. Discuss the world's reaction to this crisis and its implications for global peace.
The Space Race Innovation Hook
Highlight the innovative aspects of the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union. Discuss the technological advancements and the impact on science and society.
The Proxy Wars Connection Hook
Start by exploring the concept of proxy wars during the Cold War. Discuss how these conflicts shaped the global political landscape and their relevance in today's world.
The Nuclear Arms Race Factoid Hook
Begin with startling facts about the nuclear arms race between superpowers. Discuss the fear of nuclear annihilation and its lasting effects on international relations.
The Espionage and Spy Games Hook
Introduce your essay by delving into the world of espionage during the Cold War. Discuss famous spies, intelligence agencies, and the intrigue of espionage operations.
The Cultural Cold War Reference Hook
Start with references to the cultural aspects of the Cold War, including the influence of literature, music, and art. Discuss how cultural diplomacy played a role in the conflict.
The End of the Cold War Paradox Hook
Begin with the paradox of the peaceful end of the Cold War. Explore the factors that contributed to its conclusion and the subsequent geopolitical shifts.
The Lessons from History Hook
Start by reflecting on the lessons that can be learned from the Cold War. Discuss how understanding this historical period can inform contemporary foreign policy and global relations.
Consequences of The Truman Doctrine
Alas, babylon: analysis, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Differences Between Stalin and Khrushchev
The cold war between the united states and the soviet union, analysis of how did the cold war shaped american politics, society, and economy, the cold war: an era of fear, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Understanding The Effects of The Cold War
The policy of containment during the cold war, how the atomic bomb invention contributed to the ww2 and the cold war, the end of the cold war as a turning point in the history of global civil society, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Beginning of The Cuban Missile Crisis
The role of "cold war" in bringing international order, american policy of containment during the cold war and its consequences, fears of america and the emergence of the cold war, america's leadership position at an international stage, the impact of world war ii and the cold war on the development of science in the 20th century, ronald reagan and mikhail gorbachev: discussion on resolving the cold war, analysis of the influence behind the actions of the united states army, cuban missile crisis as a world changing event, the korean war – a conflict between the soviet union and the united states, apocalypse now - cold war perspectives, the political situation in brazil during the cold war, the development of the peace corps in america, the geography of the cold war: why the us embarked on a containment policy, religion as one of the causes of the cold war, red scare: incitement to hatred of anarchy and communism, beware the red scare: another red threat to america, american containment strategy and the end of the cold war, history of american life in the early postwar era, advantages, disadvantages, and application of aip in modern submarines.
12 March 1947 – 26 December 1991 (44 years and 9 months)
North Atlantic Treaty Organization, Soviet Union, United States, Warsaw Treaty Organization.
Winston Churchill, Joseph Stalin, Harry S. Truman, Dwight D. Eisenhower, Nikita Khrushchev, John F. Kennedy, Ronald Reagan
Cuban missile crisis, Nuclear Test-Ban Treaty, Strategic Arms Limitation Talks, Berlin crisis of 1961, collapse of the Soviet Union
The Cold War was a period of political tension and military rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, lasting roughly from the late 1940s to the early 1990s. It emerged in the aftermath of World War II when ideological differences and geopolitical interests between the two superpowers intensified. The historical context of the Cold War can be traced back to the division of Europe after World War II, with the United States championing democratic principles and capitalism, while the Soviet Union sought to spread communism and establish spheres of influence. This ideological divide led to a series of confrontations and proxy wars fought between the two powers and their respective allies. The development of nuclear weapons added a dangerous dimension to the conflict, as both sides engaged in an arms race to gain a strategic advantage. The Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962, a standoff between the United States and the Soviet Union over the placement of nuclear missiles in Cuba, brought the world to the brink of nuclear war.
The division of the world into two ideological blocs: The capitalist bloc led by the United States and the communist bloc led by the Soviet Union. The arms race and nuclear proliferation, leading to the stockpiling of nuclear weapons by both superpowers and the development of advanced military technology. The establishment of military alliances such as NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) and the Warsaw Pact, which solidified the division between the Western and Eastern blocs. Proxy wars and conflicts fought between the United States and the Soviet Union or their respective allies, such as the Korean War, the Vietnam War, and various conflicts in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. The spread of communism to several countries, including Eastern European nations that became part of the Soviet-dominated Eastern Bloc. The Cuban Missile Crisis, a tense standoff between the United States and the Soviet Union in 1962, which brought the world to the brink of nuclear war. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, marking the end of the Cold War and the transition to a unipolar world with the United States as the dominant superpower.
One of the major effects of the Cold War was the division of the world into two competing blocs, the United States-led capitalist bloc and the Soviet Union-led communist bloc. This ideological divide created a bipolar world order and fueled numerous proxy wars and conflicts around the world, such as the Korean War and the Vietnam War. The arms race between the United States and the Soviet Union was another significant consequence of the Cold War. Both superpowers invested heavily in the development and stockpiling of nuclear weapons, leading to an unprecedented level of global military buildup. The fear of nuclear annihilation and the doctrine of mutually assured destruction shaped military strategies and had a lasting impact on international security policies. The Cold War also had economic ramifications. The United States and the Soviet Union competed for influence and sought to spread their respective economic systems, capitalism and communism, across the globe. This led to the creation of economic alliances and aid programs, such as the Marshall Plan, as well as the establishment of the Soviet-dominated Eastern Bloc and the NATO alliance. Furthermore, the Cold War influenced the course of decolonization and independence movements in many countries. The superpowers often supported or opposed regimes based on their alignment with capitalist or communist ideologies, leading to political instability and conflicts in various regions. In addition, the Cold War had cultural and social effects. It fostered a climate of suspicion and fear, which manifested in widespread political repression, surveillance, and the suppression of civil liberties. The ideological struggle between capitalism and communism influenced cultural productions, including literature, art, and film.
Studying and writing essays on the topic of the Cold War is essential for students due to its multidimensional significance. Firstly, exploring the Cold War provides students with a deeper understanding of the complexities of international relations, diplomacy, and ideological conflicts. It offers insights into the strategies, policies, and motivations of the superpowers involved, such as the United States and the Soviet Union. Secondly, writing essays on the Cold War promotes critical thinking and analytical skills. Students are encouraged to examine primary and secondary sources, analyze different perspectives, and evaluate the long-term consequences of historical events. This process enhances their ability to form well-reasoned arguments and develop a nuanced understanding of complex historical phenomena. Additionally, the Cold War has left a lasting impact on society, culture, and global dynamics. By exploring this topic, students can gain insights into the origins of the arms race, the nuclear age, the space race, and the proliferation of proxy wars. They can also examine the impact of the Cold War on civil rights, technological advancements, popular culture, and the formation of alliances.
1. The term "Cold War" was coined by the American financier and presidential adviser Bernard Baruch in a speech in 1947. It referred to the absence of direct military confrontation between the superpowers, but the ongoing ideological and political struggle between them. 2. The Cold War was characterized by a state of non-military confrontation between the United States and the Soviet Union. 3. The space race played a significant role during the Cold War, prompting the establishment of NASA and fueling competition between the superpowers. 4. The proxy wars fought between the United States and the Soviet Union during the Cold War resulted in the loss of numerous lives, with casualties reaching millions. 5. Notable "hot" conflicts of the Cold War period included the Korean War, the unsuccessful Bay of Pigs invasion in Cuba, and the Vietnam War. These conflicts involved direct military engagement or support from the superpowers, leading to significant human suffering and loss.
1. Gaddis, J. L. (2005). The Cold War: A new history. Penguin Books. 2. Westad, O. A. (2012). The Cold War: A world history. Basic Books. 3. Leffler, M. P. (2008). For the soul of mankind: The United States, the Soviet Union, and the Cold War. Hill and Wang. 4. Beschloss, M. R. (1997). Mayday: Eisenhower, Khrushchev, and the U-2 affair. HarperCollins. 5. Zubok, V. M., & Pleshakov, C. (2007). Inside the Kremlin's cold war: From Stalin to Khrushchev. Harvard University Press. 6. Hogan, M. J. (Ed.). (2015). The Cold War in retrospect: The formative years. Oxford University Press. 7. LaFeber, W. (2002). America, Russia, and the Cold War, 1945-2000. McGraw-Hill. 8. Lynch, T. (2010). The Cold War: A very short introduction. Oxford University Press. 9. Matlock, J. F. (1995). Reagan and Gorbachev: How the Cold War ended. Random House. 10. McMahon, R. J. (2003). The Cold War: A very short introduction. Oxford University Press.
Relevant topics
- Vietnam War
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Cold War was an ongoing political rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies that developed after World War II.This hostility between the two superpowers was first given its name by George Orwell in an article published in 1945. Orwell understood it as a nuclear stalemate between "super-states": each possessed weapons of mass destruction and was ...
The term 'cold war' first appeared in a 1945 essay by the English writer George Orwell called 'You and the Atomic Bomb.' The Cold War: The Atomic Age .
The Cold War originated in the breakdown of relations between the two main victors in World War II: United States and the Soviet Union, and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc, in the years 1945-1949.. The origins derive from diplomatic (and occasional military) confrontations stretching back decades, followed by the issue of political boundaries in Central Europe ...
The 45-year standoff between the West and the U.S.S.R. ended when the Soviet Union dissolved. Some say another could be starting as tensions with Russia rise. Although the U.S. and Soviet Union ...
Cold War Introduction. The uneasy alliance between the United States, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union that defeated Nazi Germany began to unravel after World War II, giving rise to an ongoing political rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies that became known as the Cold War, a name coined ...
READ: Cold War — An Overview. Google Classroom. The aftermath of World War Two shifted the global balance of power and created a bi-polar world led by two competing superpowers: The United States (US) and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR). We call this global competition the Cold War. The article below uses "Three Close Reads".
As a historical period, the Cold War may be seen as a rivalry between two nuclear superpowers that threatened global destruction. The rivalry took place within a common frame of reference, in which a new historical relationship between imperialism and nationalism worked in remarkably parallel ways across the superpower divide.
David Engerman's essay on the origins of the Origins, begins, refreshingly, not during or just after World War II, but rather in 191 7 with the originating ideologues, Wilson and Lenin. Endings concludes with an essay by G. John ... Piero Gleijeses's essay, "Cuba and the Cold War, 1959-1980," begins with a surprising claim, whose significance ...
The American people (140 million) cheered their nation's victories at the end of WW II. In the 1930s joblessness and insecurity had pushed up the suicide rate and dampened the marriage rate—war had banished the blight of depression. The economy faltered in the initial postwar years as the gross national product slumped in 1946 and 1947 from ...
This post is a comprehensive timeline of the Cold War, from the origins of the Russian-American conflict following World War Two to the final dissolution of the Soviet Union and the fall of the Berlin Wall at the end of the 20th century. ... START: The Strategic Arms Reduction treaty was signed between Russia and the USA: 25th December 1991 ...
At the end of World War II, English writer George Orwell used cold war, as a general term, in his essay "You and the Atomic Bomb", published 19 October 1945 in the British newspaper Tribune.Contemplating a world living in the shadow of the threat of nuclear warfare, Orwell looked at James Burnham's predictions of a polarized world, writing: . Looking at the world as a whole, the drift for many ...
The Bibliography of New Cold War History (second enlarged edition) 2018 •. Tsotne Tchanturia, Aigul Kazhenova, Khatia Kardava. This bibliography attempts to present the publications on the history of the Cold War published after 1989, the beginning of the „archival revolution" in the former Soviet bloc countries. Download Free PDF.
The Cold War was the defining conflict after the end of World War Two. Although it rarely resulted in traditional warfare, it had a tremendous effect on almost every part of western and eastern societies, from culture to technology. To fully understand it, research into its origins is required. We will write a custom essay on your topic.
7. What is brinkmanship? Why is the handling of the Cuban missile crisis referred to as an example of brinkmanship? 8. Evaluate John F. Kennedy's leadership between January 1961 and his assassination in November 1963. Did Kennedy's presidency escalate or ease Cold War tensions? 9.
After the Second World War, the USA and USSR became two Super Powers. One nation tried to reduce the power of other. Indirectly the competition between the Super Powers led to the Cold War. Then America took the leadership of all the Capitalist Countries. Soviet Russia took the leadership of all the Communist Countries. As a result of which both stood as rivals to each other. Definition of the ...
The Cold War was a period of increased hostility between two blocs of power, the USA and its allies on the one hand; and the USSR and China, on the other. From the end of the Cold War until the early 1990s, world politics and events were primarily viewed through this lens the battle to exert control and influence globally.
The Cold War dominated a rather long time period: between 1945, or the end of the World War II, and 1990, the collapse of the USSR. This period involved the relationships between two superpowers: the United States and the USSR. The Cold War began in Eastern Europe and Germany, according to the researchers of the Institute of Contemporary ...
Essay and Discussion Questions from Contemporary History. Contemporary History Post-1945 High School Questions. Print. Help students understand how events since 1945 have shaped today's world through these essay and discussion questions. ... What are the major factors that explain why the Cold War stayed cold? ...
Hook Examples for Cold War Essays. The Tension-Building Anecdote Hook. Start your essay with a gripping anecdote from the Cold War era, such as a close encounter between opposing forces, a spy's daring mission, or a pivotal diplomatic negotiation. The Iron Curtain Metaphor Hook
The War Of The Cold War Essay. One major war ended and another to begin. The Cold war lasted about 45 years. There were no direct military campaigns between the United States and Soviet Union. However, billions of dollars and millions of lives were lost. The United States emerged as the greatest power from World War 2.
The Cold War began due to a multitude of reasons. It was a political, ideological, and economic struggle between the U.S.A. and the U.S.S.R. It began when Nazi Germany surrendered and the alliance between the U.S. and U.S.S.R. started to fall apart. The "iron curtain" as referenced in Document 1 was an imaginary line that separated East and ...