

Literature Reviews
- Introduction: What, Who & Why
- Define a topic
- Identify keywords
Identifying keywords
Comprehesive vs precise, using text mining to identify keywords.
- More search tips
- Understand & Analyse
- More resources
- Accessing help
- Systematic Style Reviews Guide
It is important to find all the relevant keywords for the topic to ensure the search is comprehensive by identifying:
- different spellings, tenses and word variants of keywords
- related concepts
- names of people or authors associated with these ideas
There are many ways to locate these terms, including
- recommended readings, textbooks and other review articles that provide an overview of the field of research
- dictionaries, thesauri, handbooks and encyclopedias that provide definitions and general information about topics.
- database thesauri or subject headings that tell you which terms are used in the databases and professional literature.
- text mining tools that allow you to analyse large amounts of text or information and identify commonly used terms in the field.
The process of searching will also help identify more terms that you should be adding to your list.
There needs to be a balance in searching between making the search comprehensive enough to encompass everything on the topic and precise enough to only capture those results that are specifically relevant.
Both approaches have advantages and disadvantages
Increasing the comprehensiveness (or sensitivity) of a search will reduce its precision and will retrieve more non-relevant articles.
Text mining will help identify how often terms come up in the literature and help identify other related terms and subject headings that have not been considered or thought of as being useful.
Text mining is a process used to look at large amounts of text and find relationships in the results by using computer programs designed to extract and analyse this data.
It is used to categorise information and identify trends and patterns which can be done across large documents or multiple sources (or both).
1. Mining for terms Use these tools to find alternate search terms that are related by identifying how often keywords appear and which other terms appear with them by number of occurrences.
2. Mine within the text Locate terms within blocks of text (e.g. an article) to find word patterns and frequency. More frequent words are more likely to be relevant to the topic.
3. Use visualising tools These tools create word clouds related to search terms
These are just some of the tools available for mining text that are available on the web. There is also both commercial and free software that can be downloaded and installed. The web pages linked below have lists of yet more tools.
Further reading:
- EPC Methods: An Exploration of the Use of Text-Mining Software in Systematic Reviews Paynter R., Bañez L. L., Berliner E., Erinoff, E., Lege-Matsuura, J., Potter, S., & Uhl, S. (2016). EPC methods: An exploration of the use of text-mining software in systematic reviews. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK362044/
- << Previous: Search the literature
- Next: More search tips >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 11:26 AM
- URL: https://libguides.jcu.edu.au/litreview


Why Keywords Are Necessary to Build a Comprehensive Literature Review
The Importance of Preparation
The quotation, “Give me six hours to chop down a tree and I will spend four sharpening my axe,” has been attributed to Abraham Lincoln. Whether or not that attribution is valid, the message of the quotation definitely applies to the development of a comprehensive literature review . With over half a billion active websites, and academic databases with hundreds of millions of entries available for search, adequate preparation for your review is critical to not only ensure that you capture accurate and relevant data, but also that you avoid wasting your most precious resource in academic research—your time!
There’s More to This than Google
The fact that the name of the search engine company has now been adopted in the global vernacular as a verb, gives some indication of the extent to which the ease of searching for anyone and anything has influenced our lives. However, the search skills you may have developed on Google will not, in themselves, automatically make you a proficient academic researcher. The databases you will be searching will probably have their data coded and sorted differently than the rankings attributed to individual websites by Google’s ever-changing search algorithms .
The World of Boolean Search
Named after the British mathematician George Boole , the creator of Boolean logic, Boolean search involves the extension of the search keywords with “operators,” (and, or, not, and near) in order to refine the logical relationships between the search terms. In the PubMed database, for example, those Boolean operators “must be entered in uppercase letters.”
Putting quotation marks around your search term (“Boolean logic”) will limit the search to that pairing, even in general search engines such as Google. The operators will allow you to start with broader keyword pairings and then to narrow the results with each iterative search request. This enables you to track or pursue a keyword pairing that you may not have originally considered in your initial list of keywords.
Moving from Quantity to Quality
When a simple search for “Boolean logic” in Google delivers 462,000 results in 0.29 seconds, you quickly realize the challenge that is facing you. You will never be short of results (unless you pick the most obscure terms imaginable), and the success of your literature review will rest on how well you plan and refine your scientific keyword search. Remember that a literature review is a process.
While your end goal will be sufficient knowledge to establish your expertise and to validate your research question, in the early stages of the process you must come to terms with not knowing what you do not know about the subject.
On that basis, every relevant search result should be assessed before proceeding. Just as goals should be SMART (specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-based), your search results can be measured using the CARS checklist:
- C – Is this a credible resource? Anyone can put up a website and claim expertise in any field. Look for evidence of credentials.
- A – How do you know the information is accurate? In this era of predatory and fabricated academic journals , “trust but verify,” should be applied at all times.
- R – Are the research assumptions reasonable? Academic publishing favors the new and counterintuitive, but that should serve as a warning for cautious interpretation of any new results that relate to your topic.
- S – Is this information supported by other sources? Citations from other journals and by other authors are one thing, but has this work ever been verified by a replication study?
Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
AI Assistance in Academia for Searching Credible Scholarly Sources
The journey of academia is a grand quest for knowledge, more specifically an adventure to…

- Manuscripts & Grants
Writing a Research Literature Review? — Here are tips to guide you through!
Literature review is both a process and a product. It involves searching within a defined…

- AI in Academia
How to Scan Through Millions of Articles and Still Cut Down on Your Reading Time — Why not do it with an AI-based article summarizer?
Researcher 1: “It’s flooding articles every time I switch on my laptop!” Researcher 2: “Why…

How to Master at Literature Mapping: 5 Most Recommended Tools to Use
This article is also available in: Turkish, Spanish, Russian, and Portuguese

- Old Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
Improving Your Chances of Publication in International Peer-reviewed Journals
Types of literature reviews Tips for writing review articles Role of meta-analysis Reporting guidelines
How to Scan Through Millions of Articles and Still Cut Down on Your Reading Time —…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Strategies to Find Sources
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Strategies to Find Sources
- Getting Started
- Introduction
- How to Pick a Topic
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
The Research Process
![why are keywords used during the literature review process Interative Litearture Review Research Process image (Planning, Searching, Organizing, Analyzing and Writing [repeat at necessary]](https://libapps.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/64450/images/ResearchProcess.jpg)
Planning : Before searching for articles or books, brainstorm to develop keywords that better describe your research question.
Searching : While searching, take note of what other keywords are used to describe your topic, and use them to conduct additional searches
♠ Most articles include a keyword section
♠ Key concepts may change names throughout time so make sure to check for variations
Organizing : Start organizing your results by categories/key concepts or any organizing principle that make sense for you . This will help you later when you are ready to analyze your findings
Analyzing : While reading, start making notes of key concepts and commonalities and disagreement among the research articles you find.
♠ Create a spreadsheet to record what articles you are finding useful and why.
♠ Create fields to write summaries of articles or quotes for future citing and paraphrasing .
Writing : Synthesize your findings. Use your own voice to explain to your readers what you learned about the literature on your topic. What are its weaknesses and strengths? What is missing or ignored?
Repeat : At any given time of the process, you can go back to a previous step as necessary.
Advanced Searching
All databases have Help pages that explain the best way to search their product. When doing literature reviews, you will want to take advantage of these features since they can facilitate not only finding the articles that you really need but also controlling the number of results and how relevant they are for your search. The most common features available in the advanced search option of databases and library online catalogs are:
- Boolean Searching (AND, OR, NOT): Allows you to connect search terms in a way that can either limit or expand your search results
- Proximity Searching (N/# or W/#): Allows you to search for two or more words that occur within a specified number of words (or fewer) of each other in the database
- Limiters/Filters : These are options that let you control what type of document you want to search: article type, date, language, publication, etc.
- Question mark (?) or a pound sign (#) for wildcard: Used for retrieving alternate spellings of a word: colo?r will retrieve both the American spelling "color" as well as the British spelling "colour."
- Asterisk (*) for truncation: Used for retrieving multiple forms of a word: comput* retrieves computer, computers, computing, etc.
Want to keep track of updates to your searches? Create an account in the database to receive an alert when a new article is published that meets your search parameters!
- EBSCOhost Advanced Search Tutorial Tips for searching a platform that hosts many library databases
- Library's General Search Tips Check the Search tips to better used our library catalog and articles search system
- ProQuest Database Search Tips Tips for searching another platform that hosts library databases
There is no magic number regarding how many sources you are going to need for your literature review; it all depends on the topic and what type of the literature review you are doing:
► Are you working on an emerging topic? You are not likely to find many sources, which is good because you are trying to prove that this is a topic that needs more research. But, it is not enough to say that you found few or no articles on your topic in your field. You need to look broadly to other disciplines (also known as triangulation ) to see if your research topic has been studied from other perspectives as a way to validate the uniqueness of your research question.
► Are you working on something that has been studied extensively? Then you are going to find many sources and you will want to limit how far back you want to look. Use limiters to eliminate research that may be dated and opt to search for resources published within the last 5-10 years.
- << Previous: How to Pick a Topic
- Next: Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
Steps in the literature review process.
- What is a literature review?
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
- You may need to some exploratory searching of the literature to get a sense of scope, to determine whether you need to narrow or broaden your focus
- Identify databases that provide the most relevant sources, and identify relevant terms (controlled vocabularies) to add to your search strategy
- Finalize your research question
- Think about relevant dates, geographies (and languages), methods, and conflicting points of view
- Conduct searches in the published literature via the identified databases
- Check to see if this topic has been covered in other discipline's databases
- Examine the citations of on-point articles for keywords, authors, and previous research (via references) and cited reference searching.
- Save your search results in a citation management tool (such as Zotero, Mendeley or EndNote)
- De-duplicate your search results
- Make sure that you've found the seminal pieces -- they have been cited many times, and their work is considered foundational
- Check with your professor or a librarian to make sure your search has been comprehensive
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of individual sources and evaluate for bias, methodologies, and thoroughness
- Group your results in to an organizational structure that will support why your research needs to be done, or that provides the answer to your research question
- Develop your conclusions
- Are there gaps in the literature?
- Where has significant research taken place, and who has done it?
- Is there consensus or debate on this topic?
- Which methodological approaches work best?
- For example: Background, Current Practices, Critics and Proponents, Where/How this study will fit in
- Organize your citations and focus on your research question and pertinent studies
- Compile your bibliography
Note: The first four steps are the best points at which to contact a librarian. Your librarian can help you determine the best databases to use for your topic, assess scope, and formulate a search strategy.
Videos Tutorials about Literature Reviews
This 4.5 minute video from Academic Education Materials has a Creative Commons License and a British narrator.
Recommended Reading
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral

Research Process :: Step by Step
- Introduction
- Select Topic
- Identify Keywords
- Background Information
- Develop Research Questions
- Refine Topic
- Search Strategy
- Popular Databases
- Evaluate Sources
- Types of Periodicals
- Reading Scholarly Articles
- Primary & Secondary Sources
- Organize / Take Notes
- Writing & Grammar Resources
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Citation Styles
- Paraphrasing
- Privacy / Confidentiality
- Research Process
- Selecting Your Topic
- Identifying Keywords
- Gathering Background Info
- Evaluating Sources

Organize the literature review into sections that present themes or identify trends, including relevant theory. You are not trying to list all the material published, but to synthesize and evaluate it according to the guiding concept of your thesis or research question.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. Occasionally you will be asked to write one as a separate assignment, but more often it is part of the introduction to an essay, research report, or thesis. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries
A literature review must do these things:
- be organized around and related directly to the thesis or research question you are developing
- synthesize results into a summary of what is and is not known
- identify areas of controversy in the literature
- formulate questions that need further research
Ask yourself questions like these:
- What is the specific thesis, problem, or research question that my literature review helps to define?
- What type of literature review am I conducting? Am I looking at issues of theory? methodology? policy? quantitative research (e.g. on the effectiveness of a new procedure)? qualitative research (e.g., studies of loneliness among migrant workers)?
- What is the scope of my literature review? What types of publications am I using (e.g., journals, books, government documents, popular media)? What discipline am I working in (e.g., nursing psychology, sociology, medicine)?
- How good was my information seeking? Has my search been wide enough to ensure I've found all the relevant material? Has it been narrow enough to exclude irrelevant material? Is the number of sources I've used appropriate for the length of my paper?
- Have I critically analyzed the literature I use? Do I follow through a set of concepts and questions, comparing items to each other in the ways they deal with them? Instead of just listing and summarizing items, do I assess them, discussing strengths and weaknesses?
- Have I cited and discussed studies contrary to my perspective?
- Will the reader find my literature review relevant, appropriate, and useful?
Ask yourself questions like these about each book or article you include:
- Has the author formulated a problem/issue?
- Is it clearly defined? Is its significance (scope, severity, relevance) clearly established?
- Could the problem have been approached more effectively from another perspective?
- What is the author's research orientation (e.g., interpretive, critical science, combination)?
- What is the author's theoretical framework (e.g., psychological, developmental, feminist)?
- What is the relationship between the theoretical and research perspectives?
- Has the author evaluated the literature relevant to the problem/issue? Does the author include literature taking positions she or he does not agree with?
- In a research study, how good are the basic components of the study design (e.g., population, intervention, outcome)? How accurate and valid are the measurements? Is the analysis of the data accurate and relevant to the research question? Are the conclusions validly based upon the data and analysis?
- In material written for a popular readership, does the author use appeals to emotion, one-sided examples, or rhetorically-charged language and tone? Is there an objective basis to the reasoning, or is the author merely "proving" what he or she already believes?
- How does the author structure the argument? Can you "deconstruct" the flow of the argument to see whether or where it breaks down logically (e.g., in establishing cause-effect relationships)?
- In what ways does this book or article contribute to our understanding of the problem under study, and in what ways is it useful for practice? What are the strengths and limitations?
- How does this book or article relate to the specific thesis or question I am developing?
Text written by Dena Taylor, Health Sciences Writing Centre, University of Toronto
http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/specific-types-of-writing/literature-review
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliography
- Next: Step 5: Cite Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 16, 2024 4:42 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/researchprocess
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.

- 53.4k views
- Title, Abstract & keywords
Q: What is the importance of keywords in a research paper?
What is the importance of keywords in a research paper?
Asked by Fred Dapaah on 27 Dec, 2016
Literature search is an important part of research writing. When you conduct a literature search online, you should be able to dig out relevant published articles. The purpose of keywords in a research paper is to help other researchers find your paper when they are conducting a search on the topic. Keywords define the field, subfield, topic, research issue, etc. that are covered by the article. Most electronic search engines, databases, or journal websites use keywords to decide whether and when to display your paper to interested readers. Keywords make your paper searchable and ensure that you get more citations. Thus, it is important to include the most relevant keywords that will help other authors find your paper.
You can read the following articles for further guidance:
- Why do journals ask for keywords?
- How to create keywords for a research paper
- How to write an effective title and abstract and choose appropriate keywords
Answered by Editage Insights on 30 Mar, 2017
- Upvote this Answer

Answered by Amani Helmi on 13 Aug, 2018
This content belongs to the Manuscript Writing Stage
Translate your research into a publication-worthy manuscript by understanding the nuances of academic writing. Subscribe and get curated reads that will help you write an excellent manuscript.
Confirm that you would also like to sign up for free personalized email coaching for this stage.
Trending Searches
- Statement of the problem
- Background of study
- Scope of the study
- Types of qualitative research
- Rationale of the study
- Concept paper
- Literature review
- Introduction in research
- Under "Editor Evaluation"
- Ethics in research
Recent Searches
- Review paper
- Responding to reviewer comments
- Predatory publishers
- Scope and delimitations
- Open access
- Plagiarism in research
- Journal selection tips
- Editor assigned
- Types of articles
- "Reject and Resubmit" status
- Decision in process
- Conflict of interest
- Library Homepage
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide: Strategies to Finding Sources
- Literature Reviews?
- Strategies to Finding Sources
- Keeping up with Research!
- Evaluating Sources & Literature Reviews
- Organizing for Writing
- Writing Literature Review
- Other Academic Writings
Useful Tool to Develop your Topic
Watch this video about Concept Mapping to become a Research Pro!
- Mind Mapping (also known as Concept Mapping) A helpful handout to show step by step how to create a concept map to map out a topic.
The Research Process
![why are keywords used during the literature review process Interative Litearture Review Research Process image (Planning, Searching, Organizing, Analyzing and Writing [repeat at necessary]](https://libapps.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/64450/images/ResearchProcess.jpg)
Planning : Before searching for articles or books, brainstorm to develop keywords that best describe your research question.
Searching : While searching take note of what other keywords are used to describe your topic and use them to do more searches
♠ Most articles include a keyword section
♠ Key concepts names may change through time so make sure to check for variations
Organizing : Start organizing your results by categories/key concepts or any organizing principle that make sense for you. This will help you later when you are ready to analyze your findings
Analyzing : While reading, start making notes of key concepts and commonalities and disagreement among the research articles you find.
♠ Create a spreadsheet document to record what articles you are finding useful and why.
♠ Create fields to write summaries of articles or quotes for future citing and paraphrasing .
Writing : Synthesize your findings. Use your own voice to explain to your readers what you learned about the literature your search; its weaknesses and strengths; what is missing or ignored
Repeat : at any given time of the process you can go back to a previous step as necessary
Advanced Searching
- Boolean Searching (AND, OR, NOT): Words that help you connect your terms in a logical way for the system understand you
- Proximity Searching (N/# or W/#): It allows you to search for two or more words that occur within a specified number of words (or fewer) of each other in the databases.
- Limiters/Filters : These are options available on the advanced page to let you control what type of document you want to search (articles), dates, language, peer-review, etc...
- Question mark (?) or a pound sign (#) for wildcard: useful when you don't know how something is spelled out, e.g. if you are looking about articles about color, if you want to find articles with the spelling colour (British English), you can use colo?r to find either spelling.
- Asterisk (*) for truncation: useful for getting results with keywords with multiple endings, e.g. comput* for computer, computers, computing , etc.
- UC Library Search Explained! Check the Search tips to better used our library catalog and articles search system
- EBSCOhost Searching Tips An useful guide about how to best search EBSCOhost databases
- ProQuest Database Search Tips An useful guide about how to best search ProQuest databases
- Are you working on an emerging topic? You are not likely to find many sources, which is good because you are trying to prove that this is a topic that needs more research. But, it is not enough to say that you found few or no articles on your topic in your field. You need to look broadly to other disciplines (also known as triangulation ) to see if your research topic has been studied from other perspectives as a way to validate the uniqueness of your research question.
- Are you working on something that has been studied extensively? Then you are going to find many sources and you will want to limit how far you want to look back. Use limiters to eliminate research that may be dated and opt to search for resources published within the last 5-10 years.
- Want to keep track of your searches , send alerts to your email when new articles in your topic are available? Create an account in any of our databases!
Following the Citation Trail!
Many databases today have special featured that show you how many times an article was cited by and by who and offer you links to those articles.
See below some recommended resources:
- Google Scholar This link opens in a new window Google Scholar not only helps you find articles on your topic, but it also offers (when available) a link called Cited by that tells you how many times the articles have been cited in their system (numbers varied depending on databases). You can click the link to see the list and access the full text of the articles (if available). Click the "Get it at UC" link to check for full text. more... less... Materials Indexed: Artworks; Audio; Biographical Information; Book Chapters; Book Reviews; Books; Business Data; Charts & Graphs; Conference Proceedings; Economic Data; Essays; Financial Data; Government Documents; Images; Journal Articles; Legal Literature; Lyrics; Magazine Articles; Maps; Monologues; Music Recordings; Musical Scores; Newsletter Articles; Newspaper Articles; Pamphlets; Patents & Trademarks; Photographs; Plays; Poetry; Poster Sessions; Preprints; Primary Sources; Prose; Public Opinion Polls; Questionnaire Responses; Radio Broadcasts; Reports; Statistics; Technical Data; Technical Reports; Television Broadcasts; Theses & Dissertations; Video
- << Previous: Literature Reviews?
- Next: Keeping up with Research! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 5, 2024 11:44 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucsb.edu/litreview
- Open access
- Published: 14 August 2018
Defining the process to literature searching in systematic reviews: a literature review of guidance and supporting studies
- Chris Cooper ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0864-5607 1 ,
- Andrew Booth 2 ,
- Jo Varley-Campbell 1 ,
- Nicky Britten 3 &
- Ruth Garside 4
BMC Medical Research Methodology volume 18 , Article number: 85 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
200k Accesses
203 Citations
118 Altmetric
Metrics details
Systematic literature searching is recognised as a critical component of the systematic review process. It involves a systematic search for studies and aims for a transparent report of study identification, leaving readers clear about what was done to identify studies, and how the findings of the review are situated in the relevant evidence.
Information specialists and review teams appear to work from a shared and tacit model of the literature search process. How this tacit model has developed and evolved is unclear, and it has not been explicitly examined before.
The purpose of this review is to determine if a shared model of the literature searching process can be detected across systematic review guidance documents and, if so, how this process is reported in the guidance and supported by published studies.
A literature review.
Two types of literature were reviewed: guidance and published studies. Nine guidance documents were identified, including: The Cochrane and Campbell Handbooks. Published studies were identified through ‘pearl growing’, citation chasing, a search of PubMed using the systematic review methods filter, and the authors’ topic knowledge.
The relevant sections within each guidance document were then read and re-read, with the aim of determining key methodological stages. Methodological stages were identified and defined. This data was reviewed to identify agreements and areas of unique guidance between guidance documents. Consensus across multiple guidance documents was used to inform selection of ‘key stages’ in the process of literature searching.
Eight key stages were determined relating specifically to literature searching in systematic reviews. They were: who should literature search, aims and purpose of literature searching, preparation, the search strategy, searching databases, supplementary searching, managing references and reporting the search process.
Conclusions
Eight key stages to the process of literature searching in systematic reviews were identified. These key stages are consistently reported in the nine guidance documents, suggesting consensus on the key stages of literature searching, and therefore the process of literature searching as a whole, in systematic reviews. Further research to determine the suitability of using the same process of literature searching for all types of systematic review is indicated.
Peer Review reports
Systematic literature searching is recognised as a critical component of the systematic review process. It involves a systematic search for studies and aims for a transparent report of study identification, leaving review stakeholders clear about what was done to identify studies, and how the findings of the review are situated in the relevant evidence.
Information specialists and review teams appear to work from a shared and tacit model of the literature search process. How this tacit model has developed and evolved is unclear, and it has not been explicitly examined before. This is in contrast to the information science literature, which has developed information processing models as an explicit basis for dialogue and empirical testing. Without an explicit model, research in the process of systematic literature searching will remain immature and potentially uneven, and the development of shared information models will be assumed but never articulated.
One way of developing such a conceptual model is by formally examining the implicit “programme theory” as embodied in key methodological texts. The aim of this review is therefore to determine if a shared model of the literature searching process in systematic reviews can be detected across guidance documents and, if so, how this process is reported and supported.
Identifying guidance
Key texts (henceforth referred to as “guidance”) were identified based upon their accessibility to, and prominence within, United Kingdom systematic reviewing practice. The United Kingdom occupies a prominent position in the science of health information retrieval, as quantified by such objective measures as the authorship of papers, the number of Cochrane groups based in the UK, membership and leadership of groups such as the Cochrane Information Retrieval Methods Group, the HTA-I Information Specialists’ Group and historic association with such centres as the UK Cochrane Centre, the NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, the Centre for Evidence Based Medicine and the National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE). Coupled with the linguistic dominance of English within medical and health science and the science of systematic reviews more generally, this offers a justification for a purposive sample that favours UK, European and Australian guidance documents.
Nine guidance documents were identified. These documents provide guidance for different types of reviews, namely: reviews of interventions, reviews of health technologies, reviews of qualitative research studies, reviews of social science topics, and reviews to inform guidance.
Whilst these guidance documents occasionally offer additional guidance on other types of systematic reviews, we have focused on the core and stated aims of these documents as they relate to literature searching. Table 1 sets out: the guidance document, the version audited, their core stated focus, and a bibliographical pointer to the main guidance relating to literature searching.
Once a list of key guidance documents was determined, it was checked by six senior information professionals based in the UK for relevance to current literature searching in systematic reviews.
Identifying supporting studies
In addition to identifying guidance, the authors sought to populate an evidence base of supporting studies (henceforth referred to as “studies”) that contribute to existing search practice. Studies were first identified by the authors from their knowledge on this topic area and, subsequently, through systematic citation chasing key studies (‘pearls’ [ 1 ]) located within each key stage of the search process. These studies are identified in Additional file 1 : Appendix Table 1. Citation chasing was conducted by analysing the bibliography of references for each study (backwards citation chasing) and through Google Scholar (forward citation chasing). A search of PubMed using the systematic review methods filter was undertaken in August 2017 (see Additional file 1 ). The search terms used were: (literature search*[Title/Abstract]) AND sysrev_methods[sb] and 586 results were returned. These results were sifted for relevance to the key stages in Fig. 1 by CC.
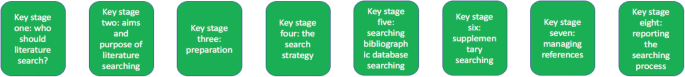
The key stages of literature search guidance as identified from nine key texts
Extracting the data
To reveal the implicit process of literature searching within each guidance document, the relevant sections (chapters) on literature searching were read and re-read, with the aim of determining key methodological stages. We defined a key methodological stage as a distinct step in the overall process for which specific guidance is reported, and action is taken, that collectively would result in a completed literature search.
The chapter or section sub-heading for each methodological stage was extracted into a table using the exact language as reported in each guidance document. The lead author (CC) then read and re-read these data, and the paragraphs of the document to which the headings referred, summarising section details. This table was then reviewed, using comparison and contrast to identify agreements and areas of unique guidance. Consensus across multiple guidelines was used to inform selection of ‘key stages’ in the process of literature searching.
Having determined the key stages to literature searching, we then read and re-read the sections relating to literature searching again, extracting specific detail relating to the methodological process of literature searching within each key stage. Again, the guidance was then read and re-read, first on a document-by-document-basis and, secondly, across all the documents above, to identify both commonalities and areas of unique guidance.
Results and discussion
Our findings.
We were able to identify consensus across the guidance on literature searching for systematic reviews suggesting a shared implicit model within the information retrieval community. Whilst the structure of the guidance varies between documents, the same key stages are reported, even where the core focus of each document is different. We were able to identify specific areas of unique guidance, where a document reported guidance not summarised in other documents, together with areas of consensus across guidance.
Unique guidance
Only one document provided guidance on the topic of when to stop searching [ 2 ]. This guidance from 2005 anticipates a topic of increasing importance with the current interest in time-limited (i.e. “rapid”) reviews. Quality assurance (or peer review) of literature searches was only covered in two guidance documents [ 3 , 4 ]. This topic has emerged as increasingly important as indicated by the development of the PRESS instrument [ 5 ]. Text mining was discussed in four guidance documents [ 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 ] where the automation of some manual review work may offer efficiencies in literature searching [ 8 ].
Agreement between guidance: Defining the key stages of literature searching
Where there was agreement on the process, we determined that this constituted a key stage in the process of literature searching to inform systematic reviews.
From the guidance, we determined eight key stages that relate specifically to literature searching in systematic reviews. These are summarised at Fig. 1 . The data extraction table to inform Fig. 1 is reported in Table 2 . Table 2 reports the areas of common agreement and it demonstrates that the language used to describe key stages and processes varies significantly between guidance documents.
For each key stage, we set out the specific guidance, followed by discussion on how this guidance is situated within the wider literature.
Key stage one: Deciding who should undertake the literature search
The guidance.
Eight documents provided guidance on who should undertake literature searching in systematic reviews [ 2 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]. The guidance affirms that people with relevant expertise of literature searching should ‘ideally’ be included within the review team [ 6 ]. Information specialists (or information scientists), librarians or trial search co-ordinators (TSCs) are indicated as appropriate researchers in six guidance documents [ 2 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ].

How the guidance corresponds to the published studies
The guidance is consistent with studies that call for the involvement of information specialists and librarians in systematic reviews [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ] and which demonstrate how their training as ‘expert searchers’ and ‘analysers and organisers of data’ can be put to good use [ 13 ] in a variety of roles [ 12 , 16 , 20 , 21 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. These arguments make sense in the context of the aims and purposes of literature searching in systematic reviews, explored below. The need for ‘thorough’ and ‘replicable’ literature searches was fundamental to the guidance and recurs in key stage two. Studies have found poor reporting, and a lack of replicable literature searches, to be a weakness in systematic reviews [ 17 , 18 , 27 , 28 ] and they argue that involvement of information specialists/ librarians would be associated with better reporting and better quality literature searching. Indeed, Meert et al. [ 29 ] demonstrated that involving a librarian as a co-author to a systematic review correlated with a higher score in the literature searching component of a systematic review [ 29 ]. As ‘new styles’ of rapid and scoping reviews emerge, where decisions on how to search are more iterative and creative, a clear role is made here too [ 30 ].
Knowing where to search for studies was noted as important in the guidance, with no agreement as to the appropriate number of databases to be searched [ 2 , 6 ]. Database (and resource selection more broadly) is acknowledged as a relevant key skill of information specialists and librarians [ 12 , 15 , 16 , 31 ].
Whilst arguments for including information specialists and librarians in the process of systematic review might be considered self-evident, Koffel and Rethlefsen [ 31 ] have questioned if the necessary involvement is actually happening [ 31 ].
Key stage two: Determining the aim and purpose of a literature search
The aim: Five of the nine guidance documents use adjectives such as ‘thorough’, ‘comprehensive’, ‘transparent’ and ‘reproducible’ to define the aim of literature searching [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Analogous phrases were present in a further three guidance documents, namely: ‘to identify the best available evidence’ [ 4 ] or ‘the aim of the literature search is not to retrieve everything. It is to retrieve everything of relevance’ [ 2 ] or ‘A systematic literature search aims to identify all publications relevant to the particular research question’ [ 3 ]. The Joanna Briggs Institute reviewers’ manual was the only guidance document where a clear statement on the aim of literature searching could not be identified. The purpose of literature searching was defined in three guidance documents, namely to minimise bias in the resultant review [ 6 , 8 , 10 ]. Accordingly, eight of nine documents clearly asserted that thorough and comprehensive literature searches are required as a potential mechanism for minimising bias.
The need for thorough and comprehensive literature searches appears as uniform within the eight guidance documents that describe approaches to literature searching in systematic reviews of effectiveness. Reviews of effectiveness (of intervention or cost), accuracy and prognosis, require thorough and comprehensive literature searches to transparently produce a reliable estimate of intervention effect. The belief that all relevant studies have been ‘comprehensively’ identified, and that this process has been ‘transparently’ reported, increases confidence in the estimate of effect and the conclusions that can be drawn [ 32 ]. The supporting literature exploring the need for comprehensive literature searches focuses almost exclusively on reviews of intervention effectiveness and meta-analysis. Different ‘styles’ of review may have different standards however; the alternative, offered by purposive sampling, has been suggested in the specific context of qualitative evidence syntheses [ 33 ].
What is a comprehensive literature search?
Whilst the guidance calls for thorough and comprehensive literature searches, it lacks clarity on what constitutes a thorough and comprehensive literature search, beyond the implication that all of the literature search methods in Table 2 should be used to identify studies. Egger et al. [ 34 ], in an empirical study evaluating the importance of comprehensive literature searches for trials in systematic reviews, defined a comprehensive search for trials as:
a search not restricted to English language;
where Cochrane CENTRAL or at least two other electronic databases had been searched (such as MEDLINE or EMBASE); and
at least one of the following search methods has been used to identify unpublished trials: searches for (I) conference abstracts, (ii) theses, (iii) trials registers; and (iv) contacts with experts in the field [ 34 ].
Tricco et al. (2008) used a similar threshold of bibliographic database searching AND a supplementary search method in a review when examining the risk of bias in systematic reviews. Their criteria were: one database (limited using the Cochrane Highly Sensitive Search Strategy (HSSS)) and handsearching [ 35 ].
Together with the guidance, this would suggest that comprehensive literature searching requires the use of BOTH bibliographic database searching AND supplementary search methods.
Comprehensiveness in literature searching, in the sense of how much searching should be undertaken, remains unclear. Egger et al. recommend that ‘investigators should consider the type of literature search and degree of comprehension that is appropriate for the review in question, taking into account budget and time constraints’ [ 34 ]. This view tallies with the Cochrane Handbook, which stipulates clearly, that study identification should be undertaken ‘within resource limits’ [ 9 ]. This would suggest that the limitations to comprehension are recognised but it raises questions on how this is decided and reported [ 36 ].
What is the point of comprehensive literature searching?
The purpose of thorough and comprehensive literature searches is to avoid missing key studies and to minimize bias [ 6 , 8 , 10 , 34 , 37 , 38 , 39 ] since a systematic review based only on published (or easily accessible) studies may have an exaggerated effect size [ 35 ]. Felson (1992) sets out potential biases that could affect the estimate of effect in a meta-analysis [ 40 ] and Tricco et al. summarize the evidence concerning bias and confounding in systematic reviews [ 35 ]. Egger et al. point to non-publication of studies, publication bias, language bias and MEDLINE bias, as key biases [ 34 , 35 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ]. Comprehensive searches are not the sole factor to mitigate these biases but their contribution is thought to be significant [ 2 , 32 , 34 ]. Fehrmann (2011) suggests that ‘the search process being described in detail’ and that, where standard comprehensive search techniques have been applied, increases confidence in the search results [ 32 ].
Does comprehensive literature searching work?
Egger et al., and other study authors, have demonstrated a change in the estimate of intervention effectiveness where relevant studies were excluded from meta-analysis [ 34 , 47 ]. This would suggest that missing studies in literature searching alters the reliability of effectiveness estimates. This is an argument for comprehensive literature searching. Conversely, Egger et al. found that ‘comprehensive’ searches still missed studies and that comprehensive searches could, in fact, introduce bias into a review rather than preventing it, through the identification of low quality studies then being included in the meta-analysis [ 34 ]. Studies query if identifying and including low quality or grey literature studies changes the estimate of effect [ 43 , 48 ] and question if time is better invested updating systematic reviews rather than searching for unpublished studies [ 49 ], or mapping studies for review as opposed to aiming for high sensitivity in literature searching [ 50 ].
Aim and purpose beyond reviews of effectiveness
The need for comprehensive literature searches is less certain in reviews of qualitative studies, and for reviews where a comprehensive identification of studies is difficult to achieve (for example, in Public health) [ 33 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 ]. Literature searching for qualitative studies, and in public health topics, typically generates a greater number of studies to sift than in reviews of effectiveness [ 39 ] and demonstrating the ‘value’ of studies identified or missed is harder [ 56 ], since the study data do not typically support meta-analysis. Nussbaumer-Streit et al. (2016) have registered a review protocol to assess whether abbreviated literature searches (as opposed to comprehensive literature searches) has an impact on conclusions across multiple bodies of evidence, not only on effect estimates [ 57 ] which may develop this understanding. It may be that decision makers and users of systematic reviews are willing to trade the certainty from a comprehensive literature search and systematic review in exchange for different approaches to evidence synthesis [ 58 ], and that comprehensive literature searches are not necessarily a marker of literature search quality, as previously thought [ 36 ]. Different approaches to literature searching [ 37 , 38 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 ] and developing the concept of when to stop searching are important areas for further study [ 36 , 59 ].
The study by Nussbaumer-Streit et al. has been published since the submission of this literature review [ 63 ]. Nussbaumer-Streit et al. (2018) conclude that abbreviated literature searches are viable options for rapid evidence syntheses, if decision-makers are willing to trade the certainty from a comprehensive literature search and systematic review, but that decision-making which demands detailed scrutiny should still be based on comprehensive literature searches [ 63 ].
Key stage three: Preparing for the literature search
Six documents provided guidance on preparing for a literature search [ 2 , 3 , 6 , 7 , 9 , 10 ]. The Cochrane Handbook clearly stated that Cochrane authors (i.e. researchers) should seek advice from a trial search co-ordinator (i.e. a person with specific skills in literature searching) ‘before’ starting a literature search [ 9 ].
Two key tasks were perceptible in preparing for a literature searching [ 2 , 6 , 7 , 10 , 11 ]. First, to determine if there are any existing or on-going reviews, or if a new review is justified [ 6 , 11 ]; and, secondly, to develop an initial literature search strategy to estimate the volume of relevant literature (and quality of a small sample of relevant studies [ 10 ]) and indicate the resources required for literature searching and the review of the studies that follows [ 7 , 10 ].
Three documents summarised guidance on where to search to determine if a new review was justified [ 2 , 6 , 11 ]. These focused on searching databases of systematic reviews (The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) and the Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE)), institutional registries (including PROSPERO), and MEDLINE [ 6 , 11 ]. It is worth noting, however, that as of 2015, DARE (and NHS EEDs) are no longer being updated and so the relevance of this (these) resource(s) will diminish over-time [ 64 ]. One guidance document, ‘Systematic reviews in the Social Sciences’, noted, however, that databases are not the only source of information and unpublished reports, conference proceeding and grey literature may also be required, depending on the nature of the review question [ 2 ].
Two documents reported clearly that this preparation (or ‘scoping’) exercise should be undertaken before the actual search strategy is developed [ 7 , 10 ]).
The guidance offers the best available source on preparing the literature search with the published studies not typically reporting how their scoping informed the development of their search strategies nor how their search approaches were developed. Text mining has been proposed as a technique to develop search strategies in the scoping stages of a review although this work is still exploratory [ 65 ]. ‘Clustering documents’ and word frequency analysis have also been tested to identify search terms and studies for review [ 66 , 67 ]. Preparing for literature searches and scoping constitutes an area for future research.
Key stage four: Designing the search strategy
The Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome (PICO) structure was the commonly reported structure promoted to design a literature search strategy. Five documents suggested that the eligibility criteria or review question will determine which concepts of PICO will be populated to develop the search strategy [ 1 , 4 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. The NICE handbook promoted multiple structures, namely PICO, SPICE (Setting, Perspective, Intervention, Comparison, Evaluation) and multi-stranded approaches [ 4 ].
With the exclusion of The Joanna Briggs Institute reviewers’ manual, the guidance offered detail on selecting key search terms, synonyms, Boolean language, selecting database indexing terms and combining search terms. The CEE handbook suggested that ‘search terms may be compiled with the help of the commissioning organisation and stakeholders’ [ 10 ].
The use of limits, such as language or date limits, were discussed in all documents [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ].
Search strategy structure
The guidance typically relates to reviews of intervention effectiveness so PICO – with its focus on intervention and comparator - is the dominant model used to structure literature search strategies [ 68 ]. PICOs – where the S denotes study design - is also commonly used in effectiveness reviews [ 6 , 68 ]. As the NICE handbook notes, alternative models to structure literature search strategies have been developed and tested. Booth provides an overview on formulating questions for evidence based practice [ 69 ] and has developed a number of alternatives to the PICO structure, namely: BeHEMoTh (Behaviour of interest; Health context; Exclusions; Models or Theories) for use when systematically identifying theory [ 55 ]; SPICE (Setting, Perspective, Intervention, Comparison, Evaluation) for identification of social science and evaluation studies [ 69 ] and, working with Cooke and colleagues, SPIDER (Sample, Phenomenon of Interest, Design, Evaluation, Research type) [ 70 ]. SPIDER has been compared to PICO and PICOs in a study by Methley et al. [ 68 ].
The NICE handbook also suggests the use of multi-stranded approaches to developing literature search strategies [ 4 ]. Glanville developed this idea in a study by Whitting et al. [ 71 ] and a worked example of this approach is included in the development of a search filter by Cooper et al. [ 72 ].
Writing search strategies: Conceptual and objective approaches
Hausner et al. [ 73 ] provide guidance on writing literature search strategies, delineating between conceptually and objectively derived approaches. The conceptual approach, advocated by and explained in the guidance documents, relies on the expertise of the literature searcher to identify key search terms and then develop key terms to include synonyms and controlled syntax. Hausner and colleagues set out the objective approach [ 73 ] and describe what may be done to validate it [ 74 ].
The use of limits
The guidance documents offer direction on the use of limits within a literature search. Limits can be used to focus literature searching to specific study designs or by other markers (such as by date) which limits the number of studies returned by a literature search. The use of limits should be described and the implications explored [ 34 ] since limiting literature searching can introduce bias (explored above). Craven et al. have suggested the use of a supporting narrative to explain decisions made in the process of developing literature searches and this advice would usefully capture decisions on the use of search limits [ 75 ].
Key stage five: Determining the process of literature searching and deciding where to search (bibliographic database searching)
Table 2 summarises the process of literature searching as reported in each guidance document. Searching bibliographic databases was consistently reported as the ‘first step’ to literature searching in all nine guidance documents.
Three documents reported specific guidance on where to search, in each case specific to the type of review their guidance informed, and as a minimum requirement [ 4 , 9 , 11 ]. Seven of the key guidance documents suggest that the selection of bibliographic databases depends on the topic of review [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 10 ], with two documents noting the absence of an agreed standard on what constitutes an acceptable number of databases searched [ 2 , 6 ].
The guidance documents summarise ‘how to’ search bibliographic databases in detail and this guidance is further contextualised above in terms of developing the search strategy. The documents provide guidance of selecting bibliographic databases, in some cases stating acceptable minima (i.e. The Cochrane Handbook states Cochrane CENTRAL, MEDLINE and EMBASE), and in other cases simply listing bibliographic database available to search. Studies have explored the value in searching specific bibliographic databases, with Wright et al. (2015) noting the contribution of CINAHL in identifying qualitative studies [ 76 ], Beckles et al. (2013) questioning the contribution of CINAHL to identifying clinical studies for guideline development [ 77 ], and Cooper et al. (2015) exploring the role of UK-focused bibliographic databases to identify UK-relevant studies [ 78 ]. The host of the database (e.g. OVID or ProQuest) has been shown to alter the search returns offered. Younger and Boddy [ 79 ] report differing search returns from the same database (AMED) but where the ‘host’ was different [ 79 ].
The average number of bibliographic database searched in systematic reviews has risen in the period 1994–2014 (from 1 to 4) [ 80 ] but there remains (as attested to by the guidance) no consensus on what constitutes an acceptable number of databases searched [ 48 ]. This is perhaps because thinking about the number of databases searched is the wrong question, researchers should be focused on which databases were searched and why, and which databases were not searched and why. The discussion should re-orientate to the differential value of sources but researchers need to think about how to report this in studies to allow findings to be generalised. Bethel (2017) has proposed ‘search summaries’, completed by the literature searcher, to record where included studies were identified, whether from database (and which databases specifically) or supplementary search methods [ 81 ]. Search summaries document both yield and accuracy of searches, which could prospectively inform resource use and decisions to search or not to search specific databases in topic areas. The prospective use of such data presupposes, however, that past searches are a potential predictor of future search performance (i.e. that each topic is to be considered representative and not unique). In offering a body of practice, this data would be of greater practicable use than current studies which are considered as little more than individual case studies [ 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 ].
When to database search is another question posed in the literature. Beyer et al. [ 91 ] report that databases can be prioritised for literature searching which, whilst not addressing the question of which databases to search, may at least bring clarity as to which databases to search first [ 91 ]. Paradoxically, this links to studies that suggest PubMed should be searched in addition to MEDLINE (OVID interface) since this improves the currency of systematic reviews [ 92 , 93 ]. Cooper et al. (2017) have tested the idea of database searching not as a primary search method (as suggested in the guidance) but as a supplementary search method in order to manage the volume of studies identified for an environmental effectiveness systematic review. Their case study compared the effectiveness of database searching versus a protocol using supplementary search methods and found that the latter identified more relevant studies for review than searching bibliographic databases [ 94 ].
Key stage six: Determining the process of literature searching and deciding where to search (supplementary search methods)
Table 2 also summaries the process of literature searching which follows bibliographic database searching. As Table 2 sets out, guidance that supplementary literature search methods should be used in systematic reviews recurs across documents, but the order in which these methods are used, and the extent to which they are used, varies. We noted inconsistency in the labelling of supplementary search methods between guidance documents.
Rather than focus on the guidance on how to use the methods (which has been summarised in a recent review [ 95 ]), we focus on the aim or purpose of supplementary search methods.
The Cochrane Handbook reported that ‘efforts’ to identify unpublished studies should be made [ 9 ]. Four guidance documents [ 2 , 3 , 6 , 9 ] acknowledged that searching beyond bibliographic databases was necessary since ‘databases are not the only source of literature’ [ 2 ]. Only one document reported any guidance on determining when to use supplementary methods. The IQWiG handbook reported that the use of handsearching (in their example) could be determined on a ‘case-by-case basis’ which implies that the use of these methods is optional rather than mandatory. This is in contrast to the guidance (above) on bibliographic database searching.
The issue for supplementary search methods is similar in many ways to the issue of searching bibliographic databases: demonstrating value. The purpose and contribution of supplementary search methods in systematic reviews is increasingly acknowledged [ 37 , 61 , 62 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 ] but understanding the value of the search methods to identify studies and data is unclear. In a recently published review, Cooper et al. (2017) reviewed the literature on supplementary search methods looking to determine the advantages, disadvantages and resource implications of using supplementary search methods [ 95 ]. This review also summarises the key guidance and empirical studies and seeks to address the question on when to use these search methods and when not to [ 95 ]. The guidance is limited in this regard and, as Table 2 demonstrates, offers conflicting advice on the order of searching, and the extent to which these search methods should be used in systematic reviews.
Key stage seven: Managing the references
Five of the documents provided guidance on managing references, for example downloading, de-duplicating and managing the output of literature searches [ 2 , 4 , 6 , 8 , 10 ]. This guidance typically itemised available bibliographic management tools rather than offering guidance on how to use them specifically [ 2 , 4 , 6 , 8 ]. The CEE handbook provided guidance on importing data where no direct export option is available (e.g. web-searching) [ 10 ].
The literature on using bibliographic management tools is not large relative to the number of ‘how to’ videos on platforms such as YouTube (see for example [ 102 ]). These YouTube videos confirm the overall lack of ‘how to’ guidance identified in this study and offer useful instruction on managing references. Bramer et al. set out methods for de-duplicating data and reviewing references in Endnote [ 103 , 104 ] and Gall tests the direct search function within Endnote to access databases such as PubMed, finding a number of limitations [ 105 ]. Coar et al. and Ahmed et al. consider the role of the free-source tool, Zotero [ 106 , 107 ]. Managing references is a key administrative function in the process of review particularly for documenting searches in PRISMA guidance.
Key stage eight: Documenting the search
The Cochrane Handbook was the only guidance document to recommend a specific reporting guideline: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [ 9 ]. Six documents provided guidance on reporting the process of literature searching with specific criteria to report [ 3 , 4 , 6 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. There was consensus on reporting: the databases searched (and the host searched by), the search strategies used, and any use of limits (e.g. date, language, search filters (The CRD handbook called for these limits to be justified [ 6 ])). Three guidance documents reported that the number of studies identified should be recorded [ 3 , 6 , 10 ]. The number of duplicates identified [ 10 ], the screening decisions [ 3 ], a comprehensive list of grey literature sources searched (and full detail for other supplementary search methods) [ 8 ], and an annotation of search terms tested but not used [ 4 ] were identified as unique items in four documents.
The Cochrane Handbook was the only guidance document to note that the full search strategies for each database should be included in the Additional file 1 of the review [ 9 ].
All guidance documents should ultimately deliver completed systematic reviews that fulfil the requirements of the PRISMA reporting guidelines [ 108 ]. The guidance broadly requires the reporting of data that corresponds with the requirements of the PRISMA statement although documents typically ask for diverse and additional items [ 108 ]. In 2008, Sampson et al. observed a lack of consensus on reporting search methods in systematic reviews [ 109 ] and this remains the case as of 2017, as evidenced in the guidance documents, and in spite of the publication of the PRISMA guidelines in 2009 [ 110 ]. It is unclear why the collective guidance does not more explicitly endorse adherence to the PRISMA guidance.
Reporting of literature searching is a key area in systematic reviews since it sets out clearly what was done and how the conclusions of the review can be believed [ 52 , 109 ]. Despite strong endorsement in the guidance documents, specifically supported in PRISMA guidance, and other related reporting standards too (such as ENTREQ for qualitative evidence synthesis, STROBE for reviews of observational studies), authors still highlight the prevalence of poor standards of literature search reporting [ 31 , 110 , 111 , 112 , 113 , 114 , 115 , 116 , 117 , 118 , 119 ]. To explore issues experienced by authors in reporting literature searches, and look at uptake of PRISMA, Radar et al. [ 120 ] surveyed over 260 review authors to determine common problems and their work summaries the practical aspects of reporting literature searching [ 120 ]. Atkinson et al. [ 121 ] have also analysed reporting standards for literature searching, summarising recommendations and gaps for reporting search strategies [ 121 ].
One area that is less well covered by the guidance, but nevertheless appears in this literature, is the quality appraisal or peer review of literature search strategies. The PRESS checklist is the most prominent and it aims to develop evidence-based guidelines to peer review of electronic search strategies [ 5 , 122 , 123 ]. A corresponding guideline for documentation of supplementary search methods does not yet exist although this idea is currently being explored.
How the reporting of the literature searching process corresponds to critical appraisal tools is an area for further research. In the survey undertaken by Radar et al. (2014), 86% of survey respondents (153/178) identified a need for further guidance on what aspects of the literature search process to report [ 120 ]. The PRISMA statement offers a brief summary of what to report but little practical guidance on how to report it [ 108 ]. Critical appraisal tools for systematic reviews, such as AMSTAR 2 (Shea et al. [ 124 ]) and ROBIS (Whiting et al. [ 125 ]), can usefully be read alongside PRISMA guidance, since they offer greater detail on how the reporting of the literature search will be appraised and, therefore, they offer a proxy on what to report [ 124 , 125 ]. Further research in the form of a study which undertakes a comparison between PRISMA and quality appraisal checklists for systematic reviews would seem to begin addressing the call, identified by Radar et al., for further guidance on what to report [ 120 ].
Limitations
Other handbooks exist.
A potential limitation of this literature review is the focus on guidance produced in Europe (the UK specifically) and Australia. We justify the decision for our selection of the nine guidance documents reviewed in this literature review in section “ Identifying guidance ”. In brief, these nine guidance documents were selected as the most relevant health care guidance that inform UK systematic reviewing practice, given that the UK occupies a prominent position in the science of health information retrieval. We acknowledge the existence of other guidance documents, such as those from North America (e.g. the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) [ 126 ], The Institute of Medicine [ 127 ] and the guidance and resources produced by the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (CADTH) [ 128 ]). We comment further on this directly below.
The handbooks are potentially linked to one another
What is not clear is the extent to which the guidance documents inter-relate or provide guidance uniquely. The Cochrane Handbook, first published in 1994, is notably a key source of reference in guidance and systematic reviews beyond Cochrane reviews. It is not clear to what extent broadening the sample of guidance handbooks to include North American handbooks, and guidance handbooks from other relevant countries too, would alter the findings of this literature review or develop further support for the process model. Since we cannot be clear, we raise this as a potential limitation of this literature review. On our initial review of a sample of North American, and other, guidance documents (before selecting the guidance documents considered in this review), however, we do not consider that the inclusion of these further handbooks would alter significantly the findings of this literature review.
This is a literature review
A further limitation of this review was that the review of published studies is not a systematic review of the evidence for each key stage. It is possible that other relevant studies could help contribute to the exploration and development of the key stages identified in this review.
This literature review would appear to demonstrate the existence of a shared model of the literature searching process in systematic reviews. We call this model ‘the conventional approach’, since it appears to be common convention in nine different guidance documents.
The findings reported above reveal eight key stages in the process of literature searching for systematic reviews. These key stages are consistently reported in the nine guidance documents which suggests consensus on the key stages of literature searching, and therefore the process of literature searching as a whole, in systematic reviews.
In Table 2 , we demonstrate consensus regarding the application of literature search methods. All guidance documents distinguish between primary and supplementary search methods. Bibliographic database searching is consistently the first method of literature searching referenced in each guidance document. Whilst the guidance uniformly supports the use of supplementary search methods, there is little evidence for a consistent process with diverse guidance across documents. This may reflect differences in the core focus across each document, linked to differences in identifying effectiveness studies or qualitative studies, for instance.
Eight of the nine guidance documents reported on the aims of literature searching. The shared understanding was that literature searching should be thorough and comprehensive in its aim and that this process should be reported transparently so that that it could be reproduced. Whilst only three documents explicitly link this understanding to minimising bias, it is clear that comprehensive literature searching is implicitly linked to ‘not missing relevant studies’ which is approximately the same point.
Defining the key stages in this review helps categorise the scholarship available, and it prioritises areas for development or further study. The supporting studies on preparing for literature searching (key stage three, ‘preparation’) were, for example, comparatively few, and yet this key stage represents a decisive moment in literature searching for systematic reviews. It is where search strategy structure is determined, search terms are chosen or discarded, and the resources to be searched are selected. Information specialists, librarians and researchers, are well placed to develop these and other areas within the key stages we identify.
This review calls for further research to determine the suitability of using the conventional approach. The publication dates of the guidance documents which underpin the conventional approach may raise questions as to whether the process which they each report remains valid for current systematic literature searching. In addition, it may be useful to test whether it is desirable to use the same process model of literature searching for qualitative evidence synthesis as that for reviews of intervention effectiveness, which this literature review demonstrates is presently recommended best practice.
Abbreviations
Behaviour of interest; Health context; Exclusions; Models or Theories
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects
Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research
Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Healthcare
National Institute for Clinical Excellence
Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Setting, Perspective, Intervention, Comparison, Evaluation
Sample, Phenomenon of Interest, Design, Evaluation, Research type
STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology
Trial Search Co-ordinators
Booth A. Unpacking your literature search toolbox: on search styles and tactics. Health Information & Libraries Journal. 2008;25(4):313–7.
Article Google Scholar
Petticrew M, Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: a practical guide. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2006.
Book Google Scholar
Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). IQWiG Methods Resources. 7 Information retrieval 2014 [Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK385787/ .
NICE: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Developing NICE guidelines: the manual 2014. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/media/default/about/what-we-do/our-programmes/developing-nice-guidelines-the-manual.pdf .
Sampson M. MJ, Lefebvre C, Moher D, Grimshaw J. Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies: PRESS; 2008.
Google Scholar
Centre for Reviews & Dissemination. Systematic reviews – CRD’s guidance for undertaking reviews in healthcare. York: Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York; 2009.
eunetha: European Network for Health Technology Assesment Process of information retrieval for systematic reviews and health technology assessments on clinical effectiveness 2016. Available from: http://www.eunethta.eu/sites/default/files/Guideline_Information_Retrieval_V1-1.pdf .
Kugley SWA, Thomas J, Mahood Q, Jørgensen AMK, Hammerstrøm K, Sathe N. Searching for studies: a guide to information retrieval for Campbell systematic reviews. Oslo: Campbell Collaboration. 2017; Available from: https://www.campbellcollaboration.org/library/searching-for-studies-information-retrieval-guide-campbell-reviews.html
Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: searching for studies. In: JPT H, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; 2011.
Collaboration for Environmental Evidence. Guidelines for Systematic Review and Evidence Synthesis in Environmental Management.: Environmental Evidence:; 2013. Available from: http://www.environmentalevidence.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Review-guidelines-version-4.2-final-update.pdf .
The Joanna Briggs Institute. Joanna Briggs institute reviewers’ manual. 2014th ed: the Joanna Briggs institute; 2014. Available from: https://joannabriggs.org/assets/docs/sumari/ReviewersManual-2014.pdf
Beverley CA, Booth A, Bath PA. The role of the information specialist in the systematic review process: a health information case study. Health Inf Libr J. 2003;20(2):65–74.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Harris MR. The librarian's roles in the systematic review process: a case study. Journal of the Medical Library Association. 2005;93(1):81–7.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Egger JB. Use of recommended search strategies in systematic reviews and the impact of librarian involvement: a cross-sectional survey of recent authors. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0125931.
Li L, Tian J, Tian H, Moher D, Liang F, Jiang T, et al. Network meta-analyses could be improved by searching more sources and by involving a librarian. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(9):1001–7.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
McGowan J, Sampson M. Systematic reviews need systematic searchers. J Med Libr Assoc. 2005;93(1):74–80.
Rethlefsen ML, Farrell AM, Osterhaus Trzasko LC, Brigham TJ. Librarian co-authors correlated with higher quality reported search strategies in general internal medicine systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68(6):617–26.
Weller AC. Mounting evidence that librarians are essential for comprehensive literature searches for meta-analyses and Cochrane reports. J Med Libr Assoc. 2004;92(2):163–4.
Swinkels A, Briddon J, Hall J. Two physiotherapists, one librarian and a systematic literature review: collaboration in action. Health Info Libr J. 2006;23(4):248–56.
Foster M. An overview of the role of librarians in systematic reviews: from expert search to project manager. EAHIL. 2015;11(3):3–7.
Lawson L. OPERATING OUTSIDE LIBRARY WALLS 2004.
Vassar M, Yerokhin V, Sinnett PM, Weiher M, Muckelrath H, Carr B, et al. Database selection in systematic reviews: an insight through clinical neurology. Health Inf Libr J. 2017;34(2):156–64.
Townsend WA, Anderson PF, Ginier EC, MacEachern MP, Saylor KM, Shipman BL, et al. A competency framework for librarians involved in systematic reviews. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2017;105(3):268–75.
Cooper ID, Crum JA. New activities and changing roles of health sciences librarians: a systematic review, 1990-2012. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2013;101(4):268–77.
Crum JA, Cooper ID. Emerging roles for biomedical librarians: a survey of current practice, challenges, and changes. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2013;101(4):278–86.
Dudden RF, Protzko SL. The systematic review team: contributions of the health sciences librarian. Med Ref Serv Q. 2011;30(3):301–15.
Golder S, Loke Y, McIntosh HM. Poor reporting and inadequate searches were apparent in systematic reviews of adverse effects. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(5):440–8.
Maggio LA, Tannery NH, Kanter SL. Reproducibility of literature search reporting in medical education reviews. Academic medicine : journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges. 2011;86(8):1049–54.
Meert D, Torabi N, Costella J. Impact of librarians on reporting of the literature searching component of pediatric systematic reviews. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2016;104(4):267–77.
Morris M, Boruff JT, Gore GC. Scoping reviews: establishing the role of the librarian. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2016;104(4):346–54.
Koffel JB, Rethlefsen ML. Reproducibility of search strategies is poor in systematic reviews published in high-impact pediatrics, cardiology and surgery journals: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2016;11(9):e0163309.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Fehrmann P, Thomas J. Comprehensive computer searches and reporting in systematic reviews. Research Synthesis Methods. 2011;2(1):15–32.
Booth A. Searching for qualitative research for inclusion in systematic reviews: a structured methodological review. Systematic Reviews. 2016;5(1):74.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Egger M, Juni P, Bartlett C, Holenstein F, Sterne J. How important are comprehensive literature searches and the assessment of trial quality in systematic reviews? Empirical study. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England). 2003;7(1):1–76.
Tricco AC, Tetzlaff J, Sampson M, Fergusson D, Cogo E, Horsley T, et al. Few systematic reviews exist documenting the extent of bias: a systematic review. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(5):422–34.
Booth A. How much searching is enough? Comprehensive versus optimal retrieval for technology assessments. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2010;26(4):431–5.
Papaioannou D, Sutton A, Carroll C, Booth A, Wong R. Literature searching for social science systematic reviews: consideration of a range of search techniques. Health Inf Libr J. 2010;27(2):114–22.
Petticrew M. Time to rethink the systematic review catechism? Moving from ‘what works’ to ‘what happens’. Systematic Reviews. 2015;4(1):36.
Betrán AP, Say L, Gülmezoglu AM, Allen T, Hampson L. Effectiveness of different databases in identifying studies for systematic reviews: experience from the WHO systematic review of maternal morbidity and mortality. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005;5
Felson DT. Bias in meta-analytic research. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45(8):885–92.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Franco A, Malhotra N, Simonovits G. Publication bias in the social sciences: unlocking the file drawer. Science. 2014;345(6203):1502–5.
Hartling L, Featherstone R, Nuspl M, Shave K, Dryden DM, Vandermeer B. Grey literature in systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of the contribution of non-English reports, unpublished studies and dissertations to the results of meta-analyses in child-relevant reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17(1):64.
Schmucker CM, Blümle A, Schell LK, Schwarzer G, Oeller P, Cabrera L, et al. Systematic review finds that study data not published in full text articles have unclear impact on meta-analyses results in medical research. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0176210.
Egger M, Zellweger-Zahner T, Schneider M, Junker C, Lengeler C, Antes G. Language bias in randomised controlled trials published in English and German. Lancet (London, England). 1997;350(9074):326–9.
Moher D, Pham B, Lawson ML, Klassen TP. The inclusion of reports of randomised trials published in languages other than English in systematic reviews. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England). 2003;7(41):1–90.
Pham B, Klassen TP, Lawson ML, Moher D. Language of publication restrictions in systematic reviews gave different results depending on whether the intervention was conventional or complementary. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58(8):769–76.
Mills EJ, Kanters S, Thorlund K, Chaimani A, Veroniki A-A, Ioannidis JPA. The effects of excluding treatments from network meta-analyses: survey. BMJ : British Medical Journal. 2013;347
Hartling L, Featherstone R, Nuspl M, Shave K, Dryden DM, Vandermeer B. The contribution of databases to the results of systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16(1):127.
van Driel ML, De Sutter A, De Maeseneer J, Christiaens T. Searching for unpublished trials in Cochrane reviews may not be worth the effort. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(8):838–44.e3.
Buchberger B, Krabbe L, Lux B, Mattivi JT. Evidence mapping for decision making: feasibility versus accuracy - when to abandon high sensitivity in electronic searches. German medical science : GMS e-journal. 2016;14:Doc09.
Lorenc T, Pearson M, Jamal F, Cooper C, Garside R. The role of systematic reviews of qualitative evidence in evaluating interventions: a case study. Research Synthesis Methods. 2012;3(1):1–10.
Gough D. Weight of evidence: a framework for the appraisal of the quality and relevance of evidence. Res Pap Educ. 2007;22(2):213–28.
Barroso J, Gollop CJ, Sandelowski M, Meynell J, Pearce PF, Collins LJ. The challenges of searching for and retrieving qualitative studies. West J Nurs Res. 2003;25(2):153–78.
Britten N, Garside R, Pope C, Frost J, Cooper C. Asking more of qualitative synthesis: a response to Sally Thorne. Qual Health Res. 2017;27(9):1370–6.
Booth A, Carroll C. Systematic searching for theory to inform systematic reviews: is it feasible? Is it desirable? Health Info Libr J. 2015;32(3):220–35.
Kwon Y, Powelson SE, Wong H, Ghali WA, Conly JM. An assessment of the efficacy of searching in biomedical databases beyond MEDLINE in identifying studies for a systematic review on ward closures as an infection control intervention to control outbreaks. Syst Rev. 2014;3:135.
Nussbaumer-Streit B, Klerings I, Wagner G, Titscher V, Gartlehner G. Assessing the validity of abbreviated literature searches for rapid reviews: protocol of a non-inferiority and meta-epidemiologic study. Systematic Reviews. 2016;5:197.
Wagner G, Nussbaumer-Streit B, Greimel J, Ciapponi A, Gartlehner G. Trading certainty for speed - how much uncertainty are decisionmakers and guideline developers willing to accept when using rapid reviews: an international survey. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17(1):121.
Ogilvie D, Hamilton V, Egan M, Petticrew M. Systematic reviews of health effects of social interventions: 1. Finding the evidence: how far should you go? J Epidemiol Community Health. 2005;59(9):804–8.
Royle P, Milne R. Literature searching for randomized controlled trials used in Cochrane reviews: rapid versus exhaustive searches. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2003;19(4):591–603.
Pearson M, Moxham T, Ashton K. Effectiveness of search strategies for qualitative research about barriers and facilitators of program delivery. Eval Health Prof. 2011;34(3):297–308.
Levay P, Raynor M, Tuvey D. The Contributions of MEDLINE, Other Bibliographic Databases and Various Search Techniques to NICE Public Health Guidance. 2015. 2015;10(1):19.
Nussbaumer-Streit B, Klerings I, Wagner G, Heise TL, Dobrescu AI, Armijo-Olivo S, et al. Abbreviated literature searches were viable alternatives to comprehensive searches: a meta-epidemiological study. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;102:1–11.
Briscoe S, Cooper C, Glanville J, Lefebvre C. The loss of the NHS EED and DARE databases and the effect on evidence synthesis and evaluation. Res Synth Methods. 2017;8(3):256–7.
Stansfield C, O'Mara-Eves A, Thomas J. Text mining for search term development in systematic reviewing: A discussion of some methods and challenges. Research Synthesis Methods.n/a-n/a.
Petrova M, Sutcliffe P, Fulford KW, Dale J. Search terms and a validated brief search filter to retrieve publications on health-related values in Medline: a word frequency analysis study. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association : JAMIA. 2012;19(3):479–88.
Stansfield C, Thomas J, Kavanagh J. 'Clustering' documents automatically to support scoping reviews of research: a case study. Res Synth Methods. 2013;4(3):230–41.
PubMed Google Scholar
Methley AM, Campbell S, Chew-Graham C, McNally R, Cheraghi-Sohi S. PICO, PICOS and SPIDER: a comparison study of specificity and sensitivity in three search tools for qualitative systematic reviews. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14:579.
Andrew B. Clear and present questions: formulating questions for evidence based practice. Library Hi Tech. 2006;24(3):355–68.
Cooke A, Smith D, Booth A. Beyond PICO: the SPIDER tool for qualitative evidence synthesis. Qual Health Res. 2012;22(10):1435–43.
Whiting P, Westwood M, Bojke L, Palmer S, Richardson G, Cooper J, et al. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tests for the diagnosis and investigation of urinary tract infection in children: a systematic review and economic model. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England). 2006;10(36):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1–154.
Cooper C, Levay P, Lorenc T, Craig GM. A population search filter for hard-to-reach populations increased search efficiency for a systematic review. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(5):554–9.
Hausner E, Waffenschmidt S, Kaiser T, Simon M. Routine development of objectively derived search strategies. Systematic Reviews. 2012;1(1):19.
Hausner E, Guddat C, Hermanns T, Lampert U, Waffenschmidt S. Prospective comparison of search strategies for systematic reviews: an objective approach yielded higher sensitivity than a conceptual one. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;77:118–24.
Craven J, Levay P. Recording database searches for systematic reviews - what is the value of adding a narrative to peer-review checklists? A case study of nice interventional procedures guidance. Evid Based Libr Inf Pract. 2011;6(4):72–87.
Wright K, Golder S, Lewis-Light K. What value is the CINAHL database when searching for systematic reviews of qualitative studies? Syst Rev. 2015;4:104.
Beckles Z, Glover S, Ashe J, Stockton S, Boynton J, Lai R, et al. Searching CINAHL did not add value to clinical questions posed in NICE guidelines. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013;66(9):1051–7.
Cooper C, Rogers M, Bethel A, Briscoe S, Lowe J. A mapping review of the literature on UK-focused health and social care databases. Health Inf Libr J. 2015;32(1):5–22.
Younger P, Boddy K. When is a search not a search? A comparison of searching the AMED complementary health database via EBSCOhost, OVID and DIALOG. Health Inf Libr J. 2009;26(2):126–35.
Lam MT, McDiarmid M. Increasing number of databases searched in systematic reviews and meta-analyses between 1994 and 2014. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2016;104(4):284–9.
Bethel A, editor Search summary tables for systematic reviews: results and findings. HLC Conference 2017a.
Aagaard T, Lund H, Juhl C. Optimizing literature search in systematic reviews - are MEDLINE, EMBASE and CENTRAL enough for identifying effect studies within the area of musculoskeletal disorders? BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16(1):161.
Adams CE, Frederick K. An investigation of the adequacy of MEDLINE searches for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of the effects of mental health care. Psychol Med. 1994;24(3):741–8.
Kelly L, St Pierre-Hansen N. So many databases, such little clarity: searching the literature for the topic aboriginal. Canadian family physician Medecin de famille canadien. 2008;54(11):1572–3.
Lawrence DW. What is lost when searching only one literature database for articles relevant to injury prevention and safety promotion? Injury Prevention. 2008;14(6):401–4.
Lemeshow AR, Blum RE, Berlin JA, Stoto MA, Colditz GA. Searching one or two databases was insufficient for meta-analysis of observational studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58(9):867–73.
Sampson M, Barrowman NJ, Moher D, Klassen TP, Pham B, Platt R, et al. Should meta-analysts search Embase in addition to Medline? J Clin Epidemiol. 2003;56(10):943–55.
Stevinson C, Lawlor DA. Searching multiple databases for systematic reviews: added value or diminishing returns? Complementary Therapies in Medicine. 2004;12(4):228–32.
Suarez-Almazor ME, Belseck E, Homik J, Dorgan M, Ramos-Remus C. Identifying clinical trials in the medical literature with electronic databases: MEDLINE alone is not enough. Control Clin Trials. 2000;21(5):476–87.
Taylor B, Wylie E, Dempster M, Donnelly M. Systematically retrieving research: a case study evaluating seven databases. Res Soc Work Pract. 2007;17(6):697–706.
Beyer FR, Wright K. Can we prioritise which databases to search? A case study using a systematic review of frozen shoulder management. Health Info Libr J. 2013;30(1):49–58.
Duffy S, de Kock S, Misso K, Noake C, Ross J, Stirk L. Supplementary searches of PubMed to improve currency of MEDLINE and MEDLINE in-process searches via Ovid. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2016;104(4):309–12.
Katchamart W, Faulkner A, Feldman B, Tomlinson G, Bombardier C. PubMed had a higher sensitivity than Ovid-MEDLINE in the search for systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(7):805–7.
Cooper C, Lovell R, Husk K, Booth A, Garside R. Supplementary search methods were more effective and offered better value than bibliographic database searching: a case study from public health and environmental enhancement (in Press). Research Synthesis Methods. 2017;
Cooper C, Booth, A., Britten, N., Garside, R. A comparison of results of empirical studies of supplementary search techniques and recommendations in review methodology handbooks: A methodological review. (In Press). BMC Systematic Reviews. 2017.
Greenhalgh T, Peacock R. Effectiveness and efficiency of search methods in systematic reviews of complex evidence: audit of primary sources. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2005;331(7524):1064–5.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hinde S, Spackman E. Bidirectional citation searching to completion: an exploration of literature searching methods. PharmacoEconomics. 2015;33(1):5–11.
Levay P, Ainsworth N, Kettle R, Morgan A. Identifying evidence for public health guidance: a comparison of citation searching with web of science and Google scholar. Res Synth Methods. 2016;7(1):34–45.
McManus RJ, Wilson S, Delaney BC, Fitzmaurice DA, Hyde CJ, Tobias RS, et al. Review of the usefulness of contacting other experts when conducting a literature search for systematic reviews. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 1998;317(7172):1562–3.
Westphal A, Kriston L, Holzel LP, Harter M, von Wolff A. Efficiency and contribution of strategies for finding randomized controlled trials: a case study from a systematic review on therapeutic interventions of chronic depression. Journal of public health research. 2014;3(2):177.
Matthews EJ, Edwards AG, Barker J, Bloor M, Covey J, Hood K, et al. Efficient literature searching in diffuse topics: lessons from a systematic review of research on communicating risk to patients in primary care. Health Libr Rev. 1999;16(2):112–20.
Bethel A. Endnote Training (YouTube Videos) 2017b [Available from: http://medicine.exeter.ac.uk/esmi/workstreams/informationscience/is_resources,_guidance_&_advice/ .
Bramer WM, Giustini D, de Jonge GB, Holland L, Bekhuis T. De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2016;104(3):240–3.
Bramer WM, Milic J, Mast F. Reviewing retrieved references for inclusion in systematic reviews using EndNote. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2017;105(1):84–7.
Gall C, Brahmi FA. Retrieval comparison of EndNote to search MEDLINE (Ovid and PubMed) versus searching them directly. Medical reference services quarterly. 2004;23(3):25–32.
Ahmed KK, Al Dhubaib BE. Zotero: a bibliographic assistant to researcher. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2011;2(4):303–5.
Coar JT, Sewell JP. Zotero: harnessing the power of a personal bibliographic manager. Nurse Educ. 2010;35(5):205–7.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097.
Sampson M, McGowan J, Tetzlaff J, Cogo E, Moher D. No consensus exists on search reporting methods for systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(8):748–54.
Toews LC. Compliance of systematic reviews in veterinary journals with preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) literature search reporting guidelines. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2017;105(3):233–9.
Booth A. "brimful of STARLITE": toward standards for reporting literature searches. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2006;94(4):421–9. e205
Faggion CM Jr, Wu YC, Tu YK, Wasiak J. Quality of search strategies reported in systematic reviews published in stereotactic radiosurgery. Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1062):20150878.
Mullins MM, DeLuca JB, Crepaz N, Lyles CM. Reporting quality of search methods in systematic reviews of HIV behavioral interventions (2000–2010): are the searches clearly explained, systematic and reproducible? Research Synthesis Methods. 2014;5(2):116–30.
Yoshii A, Plaut DA, McGraw KA, Anderson MJ, Wellik KE. Analysis of the reporting of search strategies in Cochrane systematic reviews. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2009;97(1):21–9.
Bigna JJ, Um LN, Nansseu JR. A comparison of quality of abstracts of systematic reviews including meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in high-impact general medicine journals before and after the publication of PRISMA extension for abstracts: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2016;5(1):174.
Akhigbe T, Zolnourian A, Bulters D. Compliance of systematic reviews articles in brain arteriovenous malformation with PRISMA statement guidelines: review of literature. Journal of clinical neuroscience : official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia. 2017;39:45–8.
Tao KM, Li XQ, Zhou QH, Moher D, Ling CQ, Yu WF. From QUOROM to PRISMA: a survey of high-impact medical journals' instructions to authors and a review of systematic reviews in anesthesia literature. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27611.
Wasiak J, Tyack Z, Ware R. Goodwin N. Jr. Poor methodological quality and reporting standards of systematic reviews in burn care management. International wound journal: Faggion CM; 2016.
Tam WW, Lo KK, Khalechelvam P. Endorsement of PRISMA statement and quality of systematic reviews and meta-analyses published in nursing journals: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2017;7(2):e013905.
Rader T, Mann M, Stansfield C, Cooper C, Sampson M. Methods for documenting systematic review searches: a discussion of common issues. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5(2):98–115.
Atkinson KM, Koenka AC, Sanchez CE, Moshontz H, Cooper H. Reporting standards for literature searches and report inclusion criteria: making research syntheses more transparent and easy to replicate. Res Synth Methods. 2015;6(1):87–95.
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, Cogo E, Foerster V, Lefebvre C. PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 guideline statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;75:40–6.
Sampson M, McGowan J, Cogo E, Grimshaw J, Moher D, Lefebvre C. An evidence-based practice guideline for the peer review of electronic search strategies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(9):944–52.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2017;358.
Whiting P, Savović J, Higgins JPT, Caldwell DM, Reeves BC, Shea B, et al. ROBIS: a new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;69:225–34.
Relevo R, Balshem H. Finding evidence for comparing medical interventions: AHRQ and the effective health care program. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(11):1168–77.
Medicine Io. Standards for Systematic Reviews 2011 [Available from: http://www.nationalacademies.org/hmd/Reports/2011/Finding-What-Works-in-Health-Care-Standards-for-Systematic-Reviews/Standards.aspx .
CADTH: Resources 2018.
Download references
Acknowledgements
CC acknowledges the supervision offered by Professor Chris Hyde.
This publication forms a part of CC’s PhD. CC’s PhD was funded through the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Programme (Project Number 16/54/11). The open access fee for this publication was paid for by Exeter Medical School.
RG and NB were partially supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Collaboration for Leadership in Applied Health Research and Care South West Peninsula.
The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Health Research, University of Exeter Medical School, Exeter, UK
Chris Cooper & Jo Varley-Campbell
HEDS, School of Health and Related Research (ScHARR), University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
Andrew Booth
Nicky Britten
European Centre for Environment and Human Health, University of Exeter Medical School, Truro, UK
Ruth Garside
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CC conceived the idea for this study and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. CC discussed this publication in PhD supervision with AB and separately with JVC. CC revised the publication with input and comments from AB, JVC, RG and NB. All authors revised the manuscript prior to submission. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chris Cooper .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional file
Additional file 1:.
Appendix tables and PubMed search strategy. Key studies used for pearl growing per key stage, working data extraction tables and the PubMed search strategy. (DOCX 30 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Cooper, C., Booth, A., Varley-Campbell, J. et al. Defining the process to literature searching in systematic reviews: a literature review of guidance and supporting studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 18 , 85 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0545-3
Download citation
Received : 20 September 2017
Accepted : 06 August 2018
Published : 14 August 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0545-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Literature Search Process
- Citation Chasing
- Tacit Models
- Unique Guidance
- Information Specialists
BMC Medical Research Methodology
ISSN: 1471-2288
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Literature Review Guide
Choose your topic, decide and define your scope, choose databases to search, write the review.
- APA Help This link opens in a new window
- Additional Resources
Literature Review Process
As with many other research, you’ll need to decide what you are writing about. Choosing a topic will oftentimes be tied into an assignment or research proposal, and will have to follow some guidelines based on what you are creating it for. Understanding what you are trying to accomplish with this literature review, is important, and can help you decide on a final topic. This topic decision will also help you start writing up your review once you have finished the research process, much as your thesis would help you organize your opening paragraph in a research paper.
- Tutorial: Choosing a Topic
You’ll need to ensure that your review is neither too broad, nor too narrow. To do this, the best method is to define the scope of what you are looking for. You want to decide if you are searching for a specific range of studies, years published, type of methodology, or another factor that might be more specific to your research area. Sometimes you will have to re-define your scope, once you begin the research process and you see what research has been done.
- Tutorial: Developing a Research Focus
Once you’ve decided on the scope of the research you are reviewing, you’ll also want to decide which databases or even which individual journals you will want to search. This helps you focus on what is most important to your literature review.
- DU Library Databases
At this point you’ll want to start doing the actual research. You can use your topic to help you develop keywords. Also, since you’ve defined your scope, that will help you improve your keywords. You can use that to then search the databases you’ve decided upon.
While you are doing this, remember to keep track of your search terms, so you can recreate any searches you make. You’ll want to be able to recreate the searches in case you lose track of an article you wanted to use. Use the next tab in this guide, Research , for help with the research process
- When you begin writing the review, remember that this is formatted like any other APA paper.
- Ensure you are citing your sources, use your sources to back up your argument, and consider working with an English tutor if you have questions about writing a paper.
- Write the paper with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Ensure you have a properly cited reference page, as well.
- Next: Research >>
- Last Updated: Nov 2, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://davenport.libguides.com/literature-review

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
The process of writing a literature review

Writing a literature review is a complex and non-linear process. It usually involves reiterations of all or any of the following steps:
Conducting a Library search for sources
- Taking notes while critically reading and analysing the literature
- Structuring the literature review
- Styling the language of the literature review.
One of the first and important steps in carrying out a literature review is to conduct an effective Library search which will help you identify the most relevant sources for your research topic.
If you need some assistance with searching the literature strategically, you might want to work through the Strategies and Resources for Searching the Literature module in this collection. Amongst other things, this module will help you to effectively:
- form key words or descriptors for your topic
- create a search query
- find different and relevant types of resources
- use more advanced searching techniques.
Taking notes
Taking effective notes is another key part of the process of writing up your literature review.
There is a variety of ways that one can use to take notes. These include:
- highlighting and writing notes in margins
- drawing a diagram or a mind map
- using the Cornell note-taking system .
In this module, we will focus on using an annotated bibliography as a note-taking technique.
Using an annotated bibliography to take notes
An annotated bibliography can be a useful way of taking notes as you read the literature and think about what you are reading. It allows you to collect both a summary of the key points from different readings as well as a critical assessment of the literature. It also allows you to provide comments about how a text relates both to your own research and to other literature.
An annotated bibliography has two main sections:
- A reference (bibliographic information or citation) in your chosen citation style.
- An annotation (description and comments on the source). The annotation usually provides:
- a summary of the key points or arguments the source makes
- a reflection on how the source contributes to your field of knowledge and how it might be useful in your own research
- a critical analysis or evaluation of the ideas presented.
What to include in a summary?
When writing an annotated bibliography, start with a summary or description for each source. As you read, take notes in your own words of the aim of the research, the methodologies that have been used, the main arguments and overall findings, and the scope and limitations of the study. This will form the basis of your summary which will be in the form of a coherent 50–100-word paragraph or just two or three sentences.
How to reflect on the relevance of a source to your own research?
Writing a reflection for your annotated bibliography includes writing a few sentences explaining in what ways the source is useful for, or relates to, the overall theme of your research. This section of the annotation will be particularly helpful when you come to building an argument for your research in your literature review.
Ask yourself:
- What does this source contribute to the ideas I am developing in my research or to the argument/s I am making?
It is worth mentioning that while your reflection states your personal ideas and evaluations, it should still be objective and unemotional.
What to include in a critical analysis?
- What are the strengths and limitations of the source in terms of aim, methodology, and findings?
- Are the findings sound, logical and well researched?
- Is the source original, important and of a high standard?
- How does this source add to the research in the field?
- Where is its place — and relationship — in the wider field of research and scholarly discussions?
Research and Writing Skills for Academic and Graduate Researchers Copyright © 2022 by RMIT University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Research Techniques pp 23–33 Cite as
Use of Libraries, Literature Search and Review
- Habeeb Adewale Ajimotokan 2
- First Online: 20 September 2022
907 Accesses
Part of the book series: SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology ((BRIEFSAPPLSCIENCES))
The objectives of this chapter are to
Describe the use of the library and specify how to research using it;
Define the terms literature search and review;
Outline the importance of literature search and review;
Specify and briefly describe the sources of archival literature;
Specify and describe the types of publications; and
Define the term search strategy and specify the approaches to literature search.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Lues, L., & Lategan, L. O. K. (2006). RE: Search ABC (1st ed.). Sun Press.
Google Scholar
Walliman, N. (2011). Your research project: Designing and planning your work . Sage Publications Ltd.
Bell, J. (2010). Doing your research project: A guide for first-time researchers in education and social science (5th ed.). Open University Press.
Baker, S. (1999). Finding and searching information sources. In Doing your research project: A guide for first-time researchers in education and social science (Ch. 5, 3rd ed.). Open University Press.
Thiel, D. V. (2014). Research methods for engineers . Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Patent. (2019). Patent, Wikipedia the Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Patent
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, Nigeria
Habeeb Adewale Ajimotokan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Ajimotokan, H.A. (2023). Use of Libraries, Literature Search and Review. In: Research Techniques. SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13109-7_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13109-7_3
Published : 20 September 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-13108-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-13109-7
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
Literature search for research planning and identification of research problem
Anju grewal.
Department of Anaesthesiology, Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India
Hanish Kataria
1 Department of Surgery, Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh, India
2 Department of Cardiac Anaesthesia, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India
Literature search is a key step in performing good authentic research. It helps in formulating a research question and planning the study. The available published data are enormous; therefore, choosing the appropriate articles relevant to your study in question is an art. It can be time-consuming, tiring and can lead to disinterest or even abandonment of search in between if not carried out in a step-wise manner. Various databases are available for performing literature search. This article primarily stresses on how to formulate a research question, the various types and sources for literature search, which will help make your search specific and time-saving.
INTRODUCTION
Literature search is a systematic and well-organised search from the already published data to identify a breadth of good quality references on a specific topic.[ 1 ] The reasons for conducting literature search are numerous that include drawing information for making evidence-based guidelines, a step in the research method and as part of academic assessment.[ 2 ] However, the main purpose of a thorough literature search is to formulate a research question by evaluating the available literature with an eye on gaps still amenable to further research.
Research problem[ 3 ] is typically a topic of interest and of some familiarity to the researcher. It needs to be channelised by focussing on information yet to be explored. Once we have narrowed down the problem, seeking and analysing existing literature may further straighten out the research approach.
A research hypothesis[ 4 ] is a carefully created testimony of how you expect the research to proceed. It is one of the most important tools which aids to answer the research question. It should be apt containing necessary components, and raise a question that can be tested and investigated.
The literature search can be exhaustive and time-consuming, but there are some simple steps which can help you plan and manage the process. The most important are formulating the research questions and planning your search.
FORMULATING THE RESEARCH QUESTION
Literature search is done to identify appropriate methodology, design of the study; population sampled and sampling methods, methods of measuring concepts and techniques of analysis. It also helps in determining extraneous variables affecting the outcome and identifying faults or lacunae that could be avoided.
Formulating a well-focused question is a critical step for facilitating good clinical research.[ 5 ] There can be general questions or patient-oriented questions that arise from clinical issues. Patient-oriented questions can involve the effect of therapy or disease or examine advantage versus disadvantage for a group of patients.[ 6 ]
For example, we want to evaluate the effect of a particular drug (e.g., dexmedetomidine) for procedural sedation in day care surgery patients. While formulating a research question, one should consider certain criteria, referred as ‘FINER’ (F-Feasible, I-Interesting, N-Novel, E-Ethical, R-Relevant) criteria.[ 5 ] The idea should be interesting and relevant to clinical research. It should either confirm, refute or add information to already done research work. One should also keep in mind the patient population under study and the resources available in a given set up. Also the entire research process should conform to the ethical principles of research.
The patient or study population, intervention, comparison or control arm, primary outcome, timing of measurement of outcome (PICOT) is a well-known approach for framing a leading research question.[ 7 , 8 ] Dividing the questions into key components makes it easy and searchable. In this case scenario:
- Patients (P) – What is the important group of patients? for example, day care surgery
- Intervention (I) – What is the important intervention? for example, intravenous dexmedetomidine
- Comparison (C) – What is the important intervention of comparison? for example, intravenous ketamine
- Outcome (O) – What is the effect of intervention? for example, analgesic efficacy, procedural awareness, drug side effects
- Time (T) – Time interval for measuring the outcome: Hourly for first 4 h then 4 hourly till 24 h post-procedure.
Multiple questions can be formulated from patient's problem and concern. A well-focused question should be chosen for research according to significance for patient interest and relevance to our knowledge. Good research questions address the lacunae in available literature with an aim to impact the clinical practice in a constructive manner. There are limited outcome research and relevant resources, for example, electronic database system, database and hospital information system in India. Even when these factors are available, data about existing resources is not widely accessible.[ 9 ]
TYPES OF MEDICAL LITERATURE
(Further details in chapter ‘Types of studies and research design’ in this issue).
Primary literature
Primary sources are the authentic publication of an expert's new evidence, conclusions and proposals (case reports, clinical trials, etc) and are usually published in a peer-reviewed journal. Preliminary reports, congress papers and preprints also constitute primary literature.[ 2 ]
Secondary literature
Secondary sources are systematic review articles or meta-analyses where material derived from primary source literature are infererred and evaluated.[ 2 ]
Tertiary literature
Tertiary literature consists of collections that compile information from primary or secondary literature (eg., reference books).[ 2 ]
METHODS OF LITERATURE SEARCH
There are various methods of literature search that are used alone or in combination [ Table 1 ]. For past few decades, searching the local as well as national library for books, journals, etc., was the usual practice and still physical literature exploration is an important component of any systematic review search process.[ 10 , 11 ] With the advancement of technology, the Internet is now the gateway to the maze of vast medical literature.[ 12 ] Conducting a literature review involves web-based search engines, i.e., Google, Google Scholar, etc., [ Table 2 ], or using various electronic research databases to identify materials that describe the research topic or those homologous to it.[ 13 , 14 ]
Methods of literature search

Web based methods of literature search

The various databases available for literature search include databases for original published articles in the journals [ Table 2 ] and evidence-based databases for integrated information available as systematic reviews and abstracts [ Table 3 ].[ 12 , 14 ] Most of these are not freely available to the individual user. PubMed ( http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ ) is the largest available resource since 1996; however, a large number of sources now provide free access to literature in the biomedical field.[ 15 ] More than 26 million citations from Medline, life science journals and online books are included in PubMed. Links to the full-text material are included in citations from PubMed Central and publisher web sites.[ 16 ] The choice of databases depends on the subject of interest and potential coverage by the different databases. Education Resources Information Centre is a free online digital library of education research and information sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences of the U.S. Department of Education, available at http://eric.ed.gov/ . No one database can search all the medical literature. There is need to search several different databases. At a minimum, PubMed or Medline, Embase and the Cochrane central trials Registry need to be searched. When searching these databases, emphasis should be given to meta-analysis, systematic reviews randomised controlled trials and landmark studies.
Electronic source of Evidence-Based Database

Time allocated to the search needs attention as exploring and selecting data are early steps in the research method and research conducted as part of academic assessment have narrow timeframes.[ 17 ] In Indian scenario, limited outcome research and accessibility to data leads to less thorough knowledge of nature of research problem. This results in the formulation of the inappropriate research question and increases the time to literature search.
TYPES OF SEARCH
Type of search can be described in different forms according to the subject of interest. It increases the chances of retrieving relevant information from a search.
Translating research question to keywords
This will provide results based on any of the words specified; hence, they are the cornerstone of an effective search. Synonyms/alternate terms should be considered to elicit further information, i.e., barbiturates in place of thiopentone. Spellings should also be taken into account, i.e., anesthesia in place of anaesthesia (American and British). Most databases use controlled word-stock to establish common search terms (or keywords). Some of these alternative keywords can be looked from database thesaurus.[ 4 ] Another strategy is combining keywords with Boolean operators. It is important to keep a note of keywords and methods used in exploring the literature as these will need to be described later in the design of search process.
‘Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) is the National Library of Medicine's controlled hierarchical vocabulary that is used for indexing articles in PubMed, with more specific terms organised underneath more general terms’.[ 17 ] This provides a reliable way to retrieve citations that use different terminology for identical ideas, as it indexes articles based on content. Two features of PubMed that can increase yield of specific articles are ‘Automatic term mapping’ and ‘automatic term explosion’.[ 4 ]
For example, if the search keyword is heart attack, this term will match with MeSH transcription table heading and then explode into various subheadings. This helps to construct the search by adding and selecting MeSH subheadings and families of MeSH by use of hyperlinks.[ 4 ]
We can set limits to a clinical trial for retrieving higher level of evidence (i.e., randomised controlled clinical trial). Furthermore, one can browse through the link entitled ‘Related Articles’. This PubMed feature searches for similar citations using an intricate algorithm that scans titles, abstracts and MeSH terms.[ 4 ]
Phrase search
This will provide pages with only the words typed in the phrase, in that exact order and with no words in between them.
Boolean operators
AND, OR and NOT are the three Boolean operators named after the mathematician George Boole.[ 18 ] Combining two words using ‘AND’ will fetch articles that mention both the words. Using ‘OR’ will widen the search and fetch more articles that mention either subject. While using the term ‘NOT’ to combine words will fetch articles containing the first word but not the second, thus narrowing the search.
Filters can also be used to refine the search, for example, article types, text availability, language, age, sex and journal categories.
Overall, the recommendations for methodology of literature search can be as below (Creswell)[ 19 ]
- Identify keywords and use them to search articles from library and internet resources as described above
- Search several databases to search articles related to your topic
- Use thesaurus to identify terms to locate your articles
- Find an article that is similar to your topic; then look at the terms used to describe it, and use them for your search
- Use databases that provide full-text articles (free through academic libraries, Internet or for a fee) as much as possible so that you can save time searching for your articles
- If you are examining a topic for the first time and unaware of the research on it, start with broad syntheses of the literature, such as overviews, summaries of the literature on your topic or review articles
- Start with the most recent issues of the journals, and look for studies about your topic and then work backward in time. Follow-up on references at the end of the articles for more sources to examine
- Refer books on a single topic by a single author or group of authors or books that contain chapters written by different authors
- Next look for recent conference papers. Often, conference papers report the latest research developments. Contact authors of pertinent studies. Write or phone them, asking if they know of studies related to your area of interest
- The easy access and ability to capture entire articles from the web make it attractive. However, check these articles carefully for authenticity and quality and be cautious about whether they represent systematic research.
The whole process of literature search[ 20 ] is summarised in Figure 1 .

Process of literature search
Literature search provides not only an opportunity to learn more about a given topic but provides insight on how the topic was studied by previous analysts. It helps to interpret ideas, detect shortcomings and recognise opportunities. In short, systematic and well-organised research may help in designing a novel research.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Identifying keywords. It is important to find all the relevant keywords for the topic to ensure the search is comprehensive by identifying: There are many ways to locate these terms, including. dictionaries, thesauri, handbooks and encyclopedias that provide definitions and general information about topics. database thesauri or subject headings ...
The Importance of Preparation. The quotation, "Give me six hours to chop down a tree and I will spend four sharpening my axe," has been attributed to Abraham Lincoln. Whether or not that attribution is valid, the message of the quotation definitely applies to the development of a comprehensive literature review.
The main steps in this research process are: Planning: Before searching for articles or books, brainstorm to develop keywords that better describe your research question. Searching: While searching, take note of what other keywords are used to describe your topic, and use them to conduct additional searches. ♠ Most articles include a keyword ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Literature review can be an iterative process. Researchers need to pilot the review and decide what is manageable. Sometimes, the research question needs to be narrowed down. Deeper understanding can be gained during the review process, requiring a change in keywords and/or analytical methods.
Literature Review and Research Design by Dave Harris This book looks at literature review in the process of research design, and how to develop a research practice that will build skills in reading and writing about research literature--skills that remain valuable in both academic and professional careers. Literature review is approached as a process of engaging with the discourse of scholarly ...
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply: be thorough, use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and. look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. ... Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. ... Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process. Create a matrix of the ...
Overall, the process can be divided into five main steps: 1. Come up with a statement of purpose, to establish why you need to do the review in the first place. 2. Come up with key words, so that you can plug these into search engines or scientific databases, to identify relevant papers. 3.
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your ...
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations. EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic.
Researchers often face challenges already in the early stages of a literature review, and thus, struggle in getting started with the search and in organizing the process. ... The identification of potential keywords is a crucial and iterative part of the search process. During the think alouds, we observed different strategies for identifying ...
Answer: Literature search is an important part of research writing. When you conduct a literature search online, you should be able to dig out relevant published articles. The purpose of keywords in a research paper is to help other researchers find your paper when they are conducting a search on the topic. Keywords define the field, subfield ...
The main steps in this research process are: Planning: Before searching for articles or books, brainstorm to develop keywords that best describe your research question. Searching: While searching take note of what other keywords are used to describe your topic and use them to do more searches. ♠ Most articles include a keyword section
A literature search is distinguished from, but integral to, a literature review. Literature reviews are conducted for the purpose of (a) locating information on a topic or identifying gaps in the literature for areas of future study, (b) synthesising conclusions in an area of ambiguity and (c) helping clinicians and researchers inform decision-making and practice guidelines.
The purpose of this review is to determine if a shared model of the literature searching process can be detected across systematic review guidance documents and, if so, how this process is reported in the guidance and supported by published studies. A literature review. Two types of literature were reviewed: guidance and published studies.
INTRODUCTION. Librarians and information specialists are often involved in the process of preparing and completing systematic reviews (SRs), where one of their main tasks is to identify relevant references to include in the review [].Although several recommendations for the process of searching have been published [2-6], none describe the development of a systematic search strategy from ...
Write the Review. When you begin writing the review, remember that this is formatted like any other APA paper. Ensure you are citing your sources, use your sources to back up your argument, and consider working with an English tutor if you have questions about writing a paper. Write the paper with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Writing a literature review is a complex and non-linear process. It usually involves reiterations of all or any of the following steps: Conducting a Library search for sources; Taking notes while critically reading and analysing the literature; Structuring the literature review; Styling the language of the literature review.
3.6 Chapter Summary. The use of the library and scholarly web-based search may offer quick access to the archival literature, which is always ordered according to its date of publication and disciplines. A literature search and review is an essential component in the design and implementation of a research project.
keywords. These keywords are then used by the Associate Editors when selecting appropriate reviewers for articles as they enter the review process. The online system allows the Associate Editors to search by the keywords identified in the article, which helps to filter the list of possible reviewers. This ensures that
Abstract. Literature search is a key step in performing good authentic research. It helps in formulating a research question and planning the study. The available published data are enormous; therefore, choosing the appropriate articles relevant to your study in question is an art. It can be time-consuming, tiring and can lead to disinterest or ...