Apps & Integrations
Getting started

How to use Range
A quick start guide for taking your team productiv...
Write your first Check-in
Plan your day and share your progress with these t...
Running Slack Standups with Range
Make the most of Slack standups with Range Check-i...
By Workflow
Run Better Teams
Fuel great teamwork & unlock your team’s potential
Run Better Standups
Free agenda & standup questions
Run Better Meetings
Free meeting tips
Popular posts
Amazing Icebreaker Questions for Work
Use these in Range
Team-building to build trust & connection at work
67 questions to foster psychological safety on you...
Engineering Performance Goal Examples
10 examples to help your team succeed
Breaking down the 5 decision-making models
Decisions, decisions, decisions: 5 decision-making models.
Making effective decisions is a critical leadership quality . However, settling on the best course of action is often easier said than done. When instinct and reasoning alone aren't enough to pinpoint the best decision out of your available options, it can often be helpful to utilize a decision-making model.
A decision-making model works by walking you through the decision-making process — and there are several such models available for you to choose from.
To help you improve your problem-solving abilities and make better decisions, let's take a look at five proven decision-making models and when you should use them.
Defining decision-making models
Decision-making models are frameworks designed to help you analyze possible solutions to a problem so that you can make the best possible decision. Because different decision-making models take different approaches to this goal, it's important to match the model with your unique situation and leadership style.
Given that only 20% of team members say that their organization excels at decision-making, most organizations and team leaders have a lot of room to improve in this area. If you want to improve your decision-making approach, mastering the five decision-making models is a great place to start.
The 5 main decision-making models
There are five main decision-making models designed to help leaders analyze relevant information and make optimal decisions.
Once again, each of these models takes a unique approach to decision-making, so it is important to choose the model that will work best for you and your unique situation. With that said, let's take an in-depth look at each model and the situations where each one is most applicable.
1) Rational decision-making model
The rational decision-making model involves identifying the criteria that will have the biggest impact on your decision's outcome and then evaluating possible alternatives against those criteria. The steps of the rational decision-making model are:
- Step #1) Define the problem: You'll want to start by identifying the issue you are trying to solve or the goal you are trying to achieve with your decision.
- Step #2) Define criteria: The next step is to define the criteria you are looking for in your decision. For instance, if you are deciding on a new car, you might be looking for criteria such as space, fuel efficiency, and safety.
- Step #3) Weight your criteria: If all of the criteria you define are equally important to you, then you can skip this step. If some factors are more important, you will want to assign a numerical value to your criteria based on how important each factor is.
- Step #4) Generate alternatives: Having defined and weighted the criteria you are looking for, it's time to brainstorm ideas and develop a few alternatives that meet your criteria.
- Step #5) Evaluate your alternatives: For each possible solution you come up with, you should evaluate it against your criteria, giving extra consideration to the criteria you weighted more heavily.
- Step #6) Choose the best alternative: After evaluating all possible alternatives, select the option that best matches your weighted criteria.
- Step #7) Implement the decision: The next to last step in the rational decision-making model is simply putting your decision into practice.
- Step #8) Evaluate your results: It's essential to evaluate your results anytime you make a decision. Looking at your decision from a retrospective point of view can help you decide if you should use the same decision-making process in the future.
When to use this model
The rational decision-making model is best employed when you have numerous options to consider and plenty of time to evaluate them. One example of a scenario where this model might prove useful is choosing a new hire from a pool of candidates.
2) Bounded rationality decision-making model
Sometimes, taking action quickly and choosing a "good enough" option is better than getting bogged down in searching for the best possible solution. The bounded rationality decision-making model dictates that you should limit your options to a manageable set and then choose the first option that meets your criteria rather than conducting an exhaustive analysis of each one. Going with the first option that meets your minimum threshold of requirements is a process known as "satisficing." While this may not be the best process for every decision, a willingness to satisfice can prove valuable when time constraints limit you.
The bounded rationality decision-making model is best employed when time is of the essence. It's the best model to use when inaction is more costly than not making the best decision. For example, suppose your company has encountered an issue causing extended downtime. In that case, you may want to use the bounded rationality decision-making model to quickly identify the first acceptable solution since every minute wasted is costly.
3) Vroom-Yetton decision-making model
The Vroom-Yetton decision-making model presents seven "yes or no" questions for a decision-maker to answer followed by five decision-making styles for them to choose from. It's the most complex decision-making model on our list, requiring decision-makers to utilize a decision tree to arrive at the right decision-making style based on their answers to the model's questions.
Check out this helpful resource for a complete breakdown of the Vroom-Yetton decision-making model and a copy of the decision tree template you will need to use.
The Vroom-Yetton decision-making model was specifically designed for collaborative decision-making and is best employed when you involve multiple team members in the decision-making process. In fact, one of the main objectives of this model is to determine how much weight should be given to the input from a leader's subordinates.
4) Intuitive decision-making model
Have you ever heard that it's often best to go with your gut? While making decisions based only on instinct may not seem like the best idea to those who prefer a more careful and logical approach, there are plenty of instances where going with your gut is the best way forward.
For example, if you don't have much information to consider, instinct may be the only tool for finding the best solution that you have available. Likewise, trusting your instinct can often yield the best results in cases where you are already deeply experienced with the matter at hand since nothing hones instinct better than experience.
The intuitive decision-making model probably shouldn't be the first model you turn to when you need to make a decision, but there are instances where it can be useful. We've mentioned a couple already, including cases where there isn't enough information for you to make a more informed decision and instances where your own experience is more reliable than the available information.
The intuitive decision-making model can also be useful in cases where you don't have a lot of time and need to make a decision quickly.
5) The recognition primed model
The recognition primed model is similar to the intuitive decision-making model in that it relies heavily on the decision-maker's experience and instinct. However, the recognition primed model is a little more structured than intuitive decision-making and includes the following steps:
- Step #1) Analyze available information to identify possible solutions: The first step in the recognition primed model is to brainstorm possible solutions based on your available information.
- Step #2) Run scenarios through your head: For each possible solution, run the scenario through your head and see how it plays out.
- Step #3) Make a decision: The recognition primed model dictates that the solution that leads to the best possible outcome when you visualize it in your mind is the solution that you should choose.
Like the intuitive decision-making model, the recognition primed model works best in instances where:
- You don't have a lot of information available.
- You trust your instinct and experience.
- Time constraints are a factor.
With that said, using this model effectively does require a certain degree of creativity and imagination since you will have to visualize the outcome of each possible solution.
A note on decision-making biases
Anytime you are faced with an important decision, it is essential not to let biases get in your way. Biases might be rooted in prior experiences, but that doesn't inherently mean that they are grounded in facts. In many cases, avoiding biases is also key to making an ethical decision since biases can sometimes cause you to mistreat certain people and their ideas.
Understanding the different biases
Preventing biases from getting in the way of your decision-making skills starts with identifying the types of biases you need to be aware of, including:
- Confirmation bias: Confirmation bias entails favoring or focusing on information that confirms your pre-existing beliefs and ignoring information that runs counter to those beliefs. While it's important to trust your own experience and beliefs, you don't want to subconsciously favor information just because it aligns with what you already believe to be true.
- Availability bias: Information that is easily accessible in your memory often gets undue weight, and this is known as availability bias. One example of availability bias is overestimating the likelihood of an event just because you can remember a similar event happening to you in the past.
- Survivorship bias: Survivorship bias entails focusing only on the solutions that have generated success in the past. While it's important to consider past results, ignoring possible solutions just because they are unproven will place unnecessary constraints on your decision-making process.
- Anchoring bias: Anchoring bias is the tendency to "anchor" yourself to the first piece of information you learn. Information should not get extra weight just because you have known about it for longer, and new information can be equally important to consider.
- Halo effect: The halo effect occurs when positive experiences with or impressions of one aspect of a possible solution cause you to view the entire solution positively. Rather than being blinded by the positives, seek out and consider the negatives as well.
Define your decision-making process with Range
A lot goes into making good decisions, and the decision-making models we've covered in this article can serve as excellent tools for helping you find the best possible solution to any challenge.
No matter which model you go with, communication, collaboration, and organization are key to making good decisions.
With Range, leaders and team members alike are able to effortlessly organize their ideas, communicate back and forth, share important information, and make collaborative decisions. If you want to get started using powerful team management software to organize your decision-making process, sign up for Range today.
Try Range for Free
More Related Articles

How to structure your software development team
An overview Read More...

How to prevent workplace burnout on your team
With burnout now classified as a medical condition by the World Health Organization, how should you better support your team? Read More...
Jen Dennard and Dan Pupius, Founders of Range
Setting Intentional and Effective Hybrid Policies Read More...

Work Life is Atlassian’s flagship publication dedicated to unleashing the potential of every team through real-life advice, inspiring stories, and thoughtful perspectives from leaders around the world.

Contributing Writer
Work Futurist

Senior Quantitative Researcher, People Insights
Principal Writer

This is how effective teams navigate the decision-making process
Zero Magic 8 Balls required.
Get stories like this in your inbox
Flipping a coin. Throwing a dart at a board. Pulling a slip of paper out of a hat.
Sure, they’re all ways to make a choice. But they all hinge on random chance rather than analysis, reflection, and strategy — you know, the things you actually need to make the big, meaty decisions that have major impacts.
So, set down that Magic 8 Ball and back away slowly. Let’s walk through the standard framework for decision-making that will help you and your team pinpoint the problem, consider your options, and make your most informed selection. Here’s a closer look at each of the seven steps of the decision-making process, and how to approach each one.
Step 1: Identify the decision
Most of us are eager to tie on our superhero capes and jump into problem-solving mode — especially if our team is depending on a solution. But you can’t solve a problem until you have a full grasp on what it actually is .
This first step focuses on getting the lay of the land when it comes to your decision. What specific problem are you trying to solve? What goal are you trying to achieve?
How to do it:
- Use the 5 whys analysis to go beyond surface-level symptoms and understand the root cause of a problem.
- Try problem framing to dig deep on the ins and outs of whatever problem your team is fixing. The point is to define the problem, not solve it.
⚠️ Watch out for: Decision fatigue , which is the tendency to make worse decisions as a result of needing to make too many of them. Making choices is mentally taxing , which is why it’s helpful to pinpoint one decision at a time.
2. Gather information
Your team probably has a few hunches and best guesses, but those can lead to knee-jerk reactions. Take care to invest adequate time and research into your decision.
This step is when you build your case, so to speak. Collect relevant information — that could be data, customer stories, information about past projects, feedback, or whatever else seems pertinent. You’ll use that to make decisions that are informed, rather than impulsive.
- Host a team mindmapping session to freely explore ideas and make connections between them. It can help you identify what information will best support the process.
- Create a project poster to define your goals and also determine what information you already know and what you still need to find out.
⚠️ Watch out for: Information bias , or the tendency to seek out information even if it won’t impact your action. We have the tendency to think more information is always better, but pulling together a bunch of facts and insights that aren’t applicable may cloud your judgment rather than offer clarity.
3. Identify alternatives

Use divergent thinking to generate fresh ideas in your next brainstorm
Blame the popularity of the coin toss, but making a decision often feels like choosing between only two options. Do you want heads or tails? Door number one or door number two? In reality, your options aren’t usually so cut and dried. Take advantage of this opportunity to get creative and brainstorm all sorts of routes or solutions. There’s no need to box yourselves in.
- Use the Six Thinking Hats technique to explore the problem or goal from all sides: information, emotions and instinct, risks, benefits, and creativity. It can help you and your team break away from your typical roles or mindsets and think more freely.
- Try brainwriting so team members can write down their ideas independently before sharing with the group. Research shows that this quiet, lone thinking time can boost psychological safety and generate more creative suggestions .
⚠️ Watch out for: Groupthink , which is the tendency of a group to make non-optimal decisions in the interest of conformity. People don’t want to rock the boat, so they don’t speak up.
4. Consider the evidence
Armed with your list of alternatives, it’s time to take a closer look and determine which ones could be worth pursuing. You and your team should ask questions like “How will this solution address the problem or achieve the goal?” and “What are the pros and cons of this option?”
Be honest with your answers (and back them up with the information you already collected when you can). Remind the team that this isn’t about advocating for their own suggestions to “win” — it’s about whittling your options down to the best decision.
How to do it:
- Use a SWOT analysis to dig into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the options you’re seriously considering.
- Run a project trade-off analysis to understand what constraints (such as time, scope, or cost) the team is most willing to compromise on if needed.
⚠️ Watch out for: Extinction by instinct , which is the urge to make a decision just to get it over with. You didn’t come this far to settle for a “good enough” option!
5. Choose among the alternatives
This is it — it’s the big moment when you and the team actually make the decision. You’ve identified all possible options, considered the supporting evidence, and are ready to choose how you’ll move forward.
However, bear in mind that there’s still a surprising amount of room for flexibility here. Maybe you’ll modify an alternative or combine a few suggested solutions together to land on the best fit for your problem and your team.
- Use the DACI framework (that stands for “driver, approver, contributor, informed”) to understand who ultimately has the final say in decisions. The decision-making process can be collaborative, but eventually someone needs to be empowered to make the final call.
- Try a simple voting method for decisions that are more democratized. You’ll simply tally your team’s votes and go with the majority.
⚠️ Watch out for: Analysis paralysis , which is when you overthink something to such a great degree that you feel overwhelmed and freeze when it’s time to actually make a choice.
6. Take action
Making a big decision takes a hefty amount of work, but it’s only the first part of the process — now you need to actually implement it.
It’s tempting to think that decisions will work themselves out once they’re made. But particularly in a team setting, it’s crucial to invest just as much thought and planning into communicating the decision and successfully rolling it out.
- Create a stakeholder communications plan to determine how you’ll keep various people — direct team members, company leaders, customers, or whoever else has an active interest in your decision — in the loop on your progress.
- Define the goals, signals, and measures of your decision so you’ll have an easier time aligning the team around the next steps and determining whether or not they’re successful.
⚠️Watch out for: Self-doubt, or the tendency to question whether or not you’re making the right move. While we’re hardwired for doubt , now isn’t the time to be a skeptic about your decision. You and the team have done the work, so trust the process.
7. Review your decision
9 retrospective techniques that won’t bore your team to tears.
As the decision itself starts to shake out, it’s time to take a look in the rearview mirror and reflect on how things went.
Did your decision work out the way you and the team hoped? What happened? Examine both the good and the bad. What should you keep in mind if and when you need to make this sort of decision again?
- Do a 4 L’s retrospective to talk through what you and the team loved, loathed, learned, and longed for as a result of that decision.
- Celebrate any wins (yes, even the small ones ) related to that decision. It gives morale a good kick in the pants and can also help make future decisions feel a little less intimidating.
⚠️ Watch out for: Hindsight bias , or the tendency to look back on events with the knowledge you have now and beat yourself up for not knowing better at the time. Even with careful thought and planning, some decisions don’t work out — but you can only operate with the information you have at the time.
Making smart decisions about the decision-making process
You’re probably picking up on the fact that the decision-making process is fairly comprehensive. And the truth is that the model is likely overkill for the small and inconsequential decisions you or your team members need to make.
Deciding whether you should order tacos or sandwiches for your team offsite doesn’t warrant this much discussion and elbow grease. But figuring out which major project to prioritize next? That requires some careful and collaborative thought.
It all comes back to the concept of satisficing versus maximizing , which are two different perspectives on decision making. Here’s the gist:
- Maximizers aim to get the very best out of every single decision.
- Satisficers are willing to settle for “good enough” rather than obsessing over achieving the best outcome.
One of those isn’t necessarily better than the other — and, in fact, they both have their time and place.
A major decision with far-reaching impacts deserves some fixation and perfectionism. However, hemming and hawing over trivial choices ( “Should we start our team meeting with casual small talk or a structured icebreaker?” ) will only cause added stress, frustration, and slowdowns.
As with anything else, it’s worth thinking about the potential impacts to determine just how much deliberation and precision a decision actually requires.
Decision-making is one of those things that’s part art and part science. You’ll likely have some gut feelings and instincts that are worth taking into account. But those should also be complemented with plenty of evidence, evaluation, and collaboration.
The decision-making process is a framework that helps you strike that balance. Follow the seven steps and you and your team can feel confident in the decisions you make — while leaving the darts and coins where they belong.
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.

- INTERPERSONAL SKILLS
- Decision-Making and Problem Solving
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Interpersonal Skills:
- A - Z List of Interpersonal Skills
- Interpersonal Skills Self-Assessment
- Communication Skills
- Emotional Intelligence
- Conflict Resolution and Mediation Skills
- Customer Service Skills
- Team-Working, Groups and Meetings
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
- Effective Decision Making
- Decision-Making Framework
- Introduction to Problem Solving
Identifying and Structuring Problems
Investigating Ideas and Solutions
Implementing a Solution and Feedback
- Creative Problem-Solving
Social Problem-Solving
- Negotiation and Persuasion Skills
- Personal and Romantic Relationship Skills
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
The SkillsYouNeed Guide to Interpersonal Skills

Making decisions and solving problems are two key areas in life, whether you are at home or at work. Whatever you’re doing, and wherever you are, you are faced with countless decisions and problems, both small and large, every day.
Many decisions and problems are so small that we may not even notice them. Even small decisions, however, can be overwhelming to some people. They may come to a halt as they consider their dilemma and try to decide what to do.
Small and Large Decisions
In your day-to-day life you're likely to encounter numerous 'small decisions', including, for example:
Tea or coffee?
What shall I have in my sandwich? Or should I have a salad instead today?
What shall I wear today?
Larger decisions may occur less frequently but may include:
Should we repaint the kitchen? If so, what colour?
Should we relocate?
Should I propose to my partner? Do I really want to spend the rest of my life with him/her?
These decisions, and others like them, may take considerable time and effort to make.
The relationship between decision-making and problem-solving is complex. Decision-making is perhaps best thought of as a key part of problem-solving: one part of the overall process.
Our approach at Skills You Need is to set out a framework to help guide you through the decision-making process. You won’t always need to use the whole framework, or even use it at all, but you may find it useful if you are a bit ‘stuck’ and need something to help you make a difficult decision.
Decision Making
Effective Decision-Making
This page provides information about ways of making a decision, including basing it on logic or emotion (‘gut feeling’). It also explains what can stop you making an effective decision, including too much or too little information, and not really caring about the outcome.
A Decision-Making Framework
This page sets out one possible framework for decision-making.
The framework described is quite extensive, and may seem quite formal. But it is also a helpful process to run through in a briefer form, for smaller problems, as it will help you to make sure that you really do have all the information that you need.
Problem Solving
Introduction to Problem-Solving
This page provides a general introduction to the idea of problem-solving. It explores the idea of goals (things that you want to achieve) and barriers (things that may prevent you from achieving your goals), and explains the problem-solving process at a broad level.
The first stage in solving any problem is to identify it, and then break it down into its component parts. Even the biggest, most intractable-seeming problems, can become much more manageable if they are broken down into smaller parts. This page provides some advice about techniques you can use to do so.
Sometimes, the possible options to address your problem are obvious. At other times, you may need to involve others, or think more laterally to find alternatives. This page explains some principles, and some tools and techniques to help you do so.
Having generated solutions, you need to decide which one to take, which is where decision-making meets problem-solving. But once decided, there is another step: to deliver on your decision, and then see if your chosen solution works. This page helps you through this process.
‘Social’ problems are those that we encounter in everyday life, including money trouble, problems with other people, health problems and crime. These problems, like any others, are best solved using a framework to identify the problem, work out the options for addressing it, and then deciding which option to use.
This page provides more information about the key skills needed for practical problem-solving in real life.
Further Reading from Skills You Need
The Skills You Need Guide to Interpersonal Skills eBooks.

Develop your interpersonal skills with our series of eBooks. Learn about and improve your communication skills, tackle conflict resolution, mediate in difficult situations, and develop your emotional intelligence.
Guiding you through the key skills needed in life
As always at Skills You Need, our approach to these key skills is to provide practical ways to manage the process, and to develop your skills.
Neither problem-solving nor decision-making is an intrinsically difficult process and we hope you will find our pages useful in developing your skills.
Start with: Decision Making Problem Solving
See also: Improving Communication Interpersonal Communication Skills Building Confidence
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
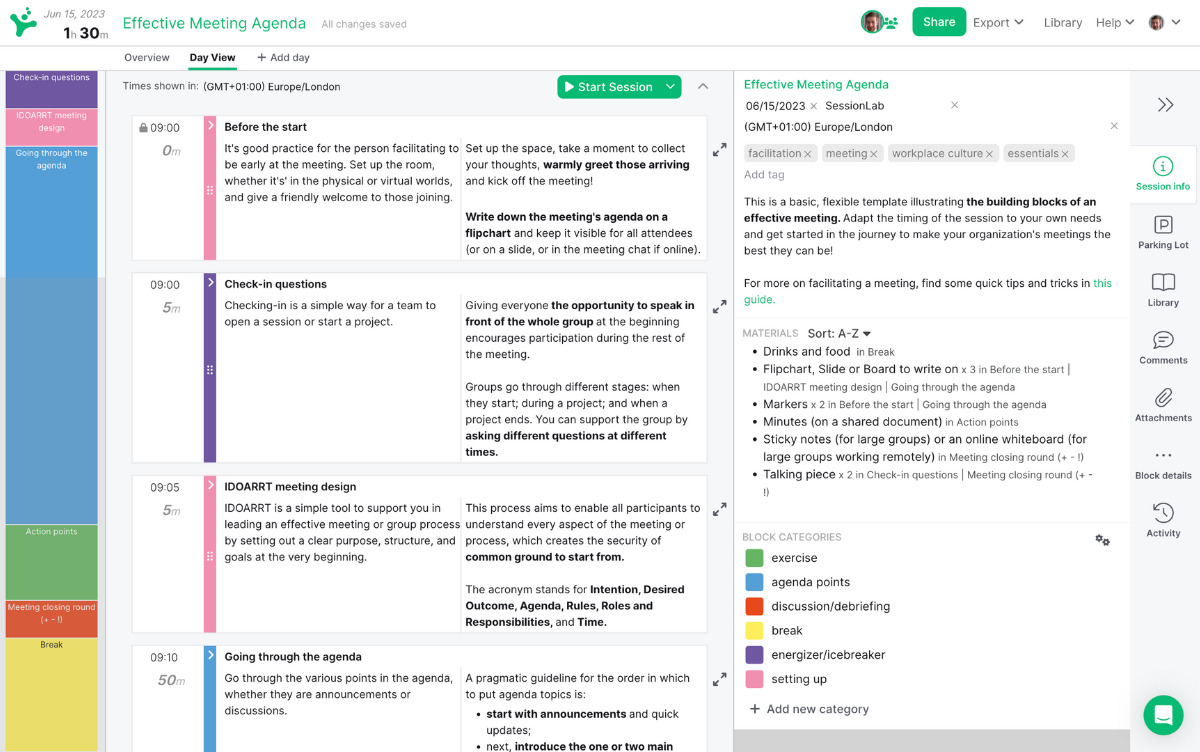
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Problem Solving and Decision Making
Introduction.
- General Approaches to Problem Solving
- Representational Accounts
- Problem Space and Search
- Working Memory and Problem Solving
- Domain-Specific Problem Solving
- The Rational Approach
- Prospect Theory
- Dual-Process Theory
- Cognitive Heuristics and Biases
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Psychology
- Counterfactual Reasoning
- Critical Thinking
- Heuristics and Biases
- Protocol Analysis
- Psychology and Law
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Data Visualization
- Remote Work
- Workforce Training Evaluation
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Problem Solving and Decision Making by Emily G. Nielsen , John Paul Minda LAST REVIEWED: 26 June 2019 LAST MODIFIED: 26 June 2019 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199828340-0246
Problem solving and decision making are both examples of complex, higher-order thinking. Both involve the assessment of the environment, the involvement of working memory or short-term memory, reliance on long term memory, effects of knowledge, and the application of heuristics to complete a behavior. A problem can be defined as an impasse or gap between a current state and a desired goal state. Problem solving is the set of cognitive operations that a person engages in to change the current state, to go beyond the impasse, and achieve a desired outcome. Problem solving involves the mental representation of the problem state and the manipulation of this representation in order to move closer to the goal. Problems can vary in complexity, abstraction, and how well defined (or not) the initial state and the goal state are. Research has generally approached problem solving by examining the behaviors and cognitive processes involved, and some work has examined problem solving using computational processes as well. Decision making is the process of selecting and choosing one action or behavior out of several alternatives. Like problem solving, decision making involves the coordination of memories and executive resources. Research on decision making has paid particular attention to the cognitive biases that account for suboptimal decisions and decisions that deviate from rationality. The current bibliography first outlines some general resources on the psychology of problem solving and decision making before examining each of these topics in detail. Specifically, this review covers cognitive, neuroscientific, and computational approaches to problem solving, as well as decision making models and cognitive heuristics and biases.
General Overviews
Current research in the area of problem solving and decision making is published in both general and specialized scientific journals. Theoretical and scholarly work is often summarized and developed in full-length books and chapter. These may focus on the subfields of problem solving and decision making or the larger field of thinking and higher-order cognition.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Psychology »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Abnormal Psychology
- Academic Assessment
- Acculturation and Health
- Action Regulation Theory
- Action Research
- Addictive Behavior
- Adolescence
- Adoption, Social, Psychological, and Evolutionary Perspect...
- Advanced Theory of Mind
- Affective Forecasting
- Affirmative Action
- Ageism at Work
- Allport, Gordon
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Ambulatory Assessment in Behavioral Science
- Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA)
- Animal Behavior
- Animal Learning
- Anxiety Disorders
- Art and Aesthetics, Psychology of
- Assessment and Clinical Applications of Individual Differe...
- Attachment in Social and Emotional Development across the ...
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Adults
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Childre...
- Attitudinal Ambivalence
- Attraction in Close Relationships
- Attribution Theory
- Authoritarian Personality
- Bayesian Statistical Methods in Psychology
- Behavior Therapy, Rational Emotive
- Behavioral Economics
- Behavioral Genetics
- Belief Perseverance
- Bereavement and Grief
- Biological Psychology
- Birth Order
- Body Image in Men and Women
- Bystander Effect
- Categorical Data Analysis in Psychology
- Childhood and Adolescence, Peer Victimization and Bullying...
- Clark, Mamie Phipps
- Clinical Neuropsychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Consistency Theories
- Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Communication, Nonverbal Cues and
- Comparative Psychology
- Competence to Stand Trial: Restoration Services
- Competency to Stand Trial
- Computational Psychology
- Conflict Management in the Workplace
- Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
- Consciousness
- Coping Processes
- Correspondence Analysis in Psychology
- Counseling Psychology
- Creativity at Work
- Cross-Cultural Psychology
- Cultural Psychology
- Daily Life, Research Methods for Studying
- Data Science Methods for Psychology
- Data Sharing in Psychology
- Death and Dying
- Deceiving and Detecting Deceit
- Defensive Processes
- Depressive Disorders
- Development, Prenatal
- Developmental Psychology (Cognitive)
- Developmental Psychology (Social)
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM...
- Discrimination
- Dissociative Disorders
- Drugs and Behavior
- Eating Disorders
- Ecological Psychology
- Educational Settings, Assessment of Thinking in
- Effect Size
- Embodiment and Embodied Cognition
- Emerging Adulthood
- Emotional Intelligence
- Empathy and Altruism
- Employee Stress and Well-Being
- Environmental Neuroscience and Environmental Psychology
- Ethics in Psychological Practice
- Event Perception
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Expansive Posture
- Experimental Existential Psychology
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Eyewitness Testimony
- Eysenck, Hans
- Factor Analysis
- Festinger, Leon
- Five-Factor Model of Personality
- Flynn Effect, The
- Forensic Psychology
- Forgiveness
- Friendships, Children's
- Fundamental Attribution Error/Correspondence Bias
- Gambler's Fallacy
- Game Theory and Psychology
- Geropsychology, Clinical
- Global Mental Health
- Habit Formation and Behavior Change
- Health Psychology
- Health Psychology Research and Practice, Measurement in
- Heider, Fritz
- History of Psychology
- Human Factors
- Humanistic Psychology
- Implicit Association Test (IAT)
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology
- Inferential Statistics in Psychology
- Insanity Defense, The
- Intelligence
- Intelligence, Crystallized and Fluid
- Intercultural Psychology
- Intergroup Conflict
- International Classification of Diseases and Related Healt...
- International Psychology
- Interviewing in Forensic Settings
- Intimate Partner Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Introversion–Extraversion
- Item Response Theory
- Law, Psychology and
- Lazarus, Richard
- Learned Helplessness
- Learning Theory
- Learning versus Performance
- LGBTQ+ Romantic Relationships
- Lie Detection in a Forensic Context
- Life-Span Development
- Locus of Control
- Loneliness and Health
- Mathematical Psychology
- Meaning in Life
- Mechanisms and Processes of Peer Contagion
- Media Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Mediation Analysis
- Memories, Autobiographical
- Memories, Flashbulb
- Memories, Repressed and Recovered
- Memory, False
- Memory, Human
- Memory, Implicit versus Explicit
- Memory in Educational Settings
- Memory, Semantic
- Meta-Analysis
- Metacognition
- Metaphor, Psychological Perspectives on
- Microaggressions
- Military Psychology
- Mindfulness
- Mindfulness and Education
- Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
- Money, Psychology of
- Moral Conviction
- Moral Development
- Moral Psychology
- Moral Reasoning
- Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
- Neuroscience of Associative Learning
- Nonergodicity in Psychology and Neuroscience
- Nonparametric Statistical Analysis in Psychology
- Observational (Non-Randomized) Studies
- Obsessive-Complusive Disorder (OCD)
- Occupational Health Psychology
- Olfaction, Human
- Operant Conditioning
- Optimism and Pessimism
- Organizational Justice
- Parenting Stress
- Parenting Styles
- Parents' Beliefs about Children
- Path Models
- Peace Psychology
- Perception, Person
- Performance Appraisal
- Personality and Health
- Personality Disorders
- Personality Psychology
- Person-Centered and Experiential Psychotherapies: From Car...
- Phenomenological Psychology
- Placebo Effects in Psychology
- Play Behavior
- Positive Psychological Capital (PsyCap)
- Positive Psychology
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Prejudice and Stereotyping
- Pretrial Publicity
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
- Procrastination
- Prosocial Behavior
- Prosocial Spending and Well-Being
- Psycholinguistics
- Psychological Literacy
- Psychological Perspectives on Food and Eating
- Psychology, Political
- Psychoneuroimmunology
- Psychophysics, Visual
- Psychotherapy
- Psychotic Disorders
- Publication Bias in Psychology
- Reasoning, Counterfactual
- Rehabilitation Psychology
- Relationships
- Reliability–Contemporary Psychometric Conceptions
- Religion, Psychology and
- Replication Initiatives in Psychology
- Research Methods
- Risk Taking
- Role of the Expert Witness in Forensic Psychology, The
- Sample Size Planning for Statistical Power and Accurate Es...
- Schizophrenic Disorders
- School Psychology
- School Psychology, Counseling Services in
- Self, Gender and
- Self, Psychology of the
- Self-Construal
- Self-Control
- Self-Deception
- Self-Determination Theory
- Self-Efficacy
- Self-Esteem
- Self-Monitoring
- Self-Regulation in Educational Settings
- Self-Report Tests, Measures, and Inventories in Clinical P...
- Sensation Seeking
- Sex and Gender
- Sexual Minority Parenting
- Sexual Orientation
- Signal Detection Theory and its Applications
- Simpson's Paradox in Psychology
- Single People
- Single-Case Experimental Designs
- Skinner, B.F.
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Small Groups
- Social Class and Social Status
- Social Cognition
- Social Neuroscience
- Social Support
- Social Touch and Massage Therapy Research
- Somatoform Disorders
- Spatial Attention
- Sports Psychology
- Stanford Prison Experiment (SPE): Icon and Controversy
- Stereotype Threat
- Stereotypes
- Stress and Coping, Psychology of
- Student Success in College
- Subjective Wellbeing Homeostasis
- Taste, Psychological Perspectives on
- Teaching of Psychology
- Terror Management Theory
- Testing and Assessment
- The Concept of Validity in Psychological Assessment
- The Neuroscience of Emotion Regulation
- The Reasoned Action Approach and the Theories of Reasoned ...
- The Weapon Focus Effect in Eyewitness Memory
- Theory of Mind
- Therapy, Cognitive-Behavioral
- Thinking Skills in Educational Settings
- Time Perception
- Trait Perspective
- Trauma Psychology
- Twin Studies
- Type A Behavior Pattern (Coronary Prone Personality)
- Unconscious Processes
- Video Games and Violent Content
- Virtues and Character Strengths
- Women and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM...
- Women, Psychology of
- Work Well-Being
- Wundt, Wilhelm
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|81.177.182.154]
- 81.177.182.154
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Discover how today’s most successful IT leaders stand out from the rest. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Read the report .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Leadership |
- 7 important steps in the decision makin ...
7 important steps in the decision making process

The decision making process is a method of gathering information, assessing alternatives, and making a final choice with the goal of making the best decision possible. In this article, we detail the step-by-step process on how to make a good decision and explain different decision making methodologies.
We make decisions every day. Take the bus to work or call a car? Chocolate or vanilla ice cream? Whole milk or two percent?
There's an entire process that goes into making those tiny decisions, and while these are simple, easy choices, how do we end up making more challenging decisions?
At work, decisions aren't as simple as choosing what kind of milk you want in your latte in the morning. That’s why understanding the decision making process is so important.

What is the decision making process?
The decision making process is the method of gathering information, assessing alternatives, and, ultimately, making a final choice.
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

The 7 steps of the decision making process
Step 1: identify the decision that needs to be made.
When you're identifying the decision, ask yourself a few questions:
What is the problem that needs to be solved?
What is the goal you plan to achieve by implementing this decision?
How will you measure success?
These questions are all common goal setting techniques that will ultimately help you come up with possible solutions. When the problem is clearly defined, you then have more information to come up with the best decision to solve the problem.
Step 2: Gather relevant information
Gathering information related to the decision being made is an important step to making an informed decision. Does your team have any historical data as it relates to this issue? Has anybody attempted to solve this problem before?
It's also important to look for information outside of your team or company. Effective decision making requires information from many different sources. Find external resources, whether it’s doing market research, working with a consultant, or talking with colleagues at a different company who have relevant experience. Gathering information helps your team identify different solutions to your problem.
Step 3: Identify alternative solutions
This step requires you to look for many different solutions for the problem at hand. Finding more than one possible alternative is important when it comes to business decision-making, because different stakeholders may have different needs depending on their role. For example, if a company is looking for a work management tool, the design team may have different needs than a development team. Choosing only one solution right off the bat might not be the right course of action.
Step 4: Weigh the evidence
This is when you take all of the different solutions you’ve come up with and analyze how they would address your initial problem. Your team begins identifying the pros and cons of each option, and eliminating alternatives from those choices.
There are a few common ways your team can analyze and weigh the evidence of options:
Pros and cons list
SWOT analysis
Decision matrix
Step 5: Choose among the alternatives
The next step is to make your final decision. Consider all of the information you've collected and how this decision may affect each stakeholder.
Sometimes the right decision is not one of the alternatives, but a blend of a few different alternatives. Effective decision-making involves creative problem solving and thinking out of the box, so don't limit you or your teams to clear-cut options.
One of the key values at Asana is to reject false tradeoffs. Choosing just one decision can mean losing benefits in others. If you can, try and find options that go beyond just the alternatives presented.
Step 6: Take action
Once the final decision maker gives the green light, it's time to put the solution into action. Take the time to create an implementation plan so that your team is on the same page for next steps. Then it’s time to put your plan into action and monitor progress to determine whether or not this decision was a good one.
Step 7: Review your decision and its impact (both good and bad)
Once you’ve made a decision, you can monitor the success metrics you outlined in step 1. This is how you determine whether or not this solution meets your team's criteria of success.
Here are a few questions to consider when reviewing your decision:
Did it solve the problem your team identified in step 1?
Did this decision impact your team in a positive or negative way?
Which stakeholders benefited from this decision? Which stakeholders were impacted negatively?
If this solution was not the best alternative, your team might benefit from using an iterative form of project management. This enables your team to quickly adapt to changes, and make the best decisions with the resources they have.
Types of decision making models
While most decision making models revolve around the same seven steps, here are a few different methodologies to help you make a good decision.
Rational decision making models
This type of decision making model is the most common type that you'll see. It's logical and sequential. The seven steps listed above are an example of the rational decision making model.
When your decision has a big impact on your team and you need to maximize outcomes, this is the type of decision making process you should use. It requires you to consider a wide range of viewpoints with little bias so you can make the best decision possible.
Intuitive decision making models
This type of decision making model is dictated not by information or data, but by gut instincts. This form of decision making requires previous experience and pattern recognition to form strong instincts.
This type of decision making is often made by decision makers who have a lot of experience with similar kinds of problems. They have already had proven success with the solution they're looking to implement.
Creative decision making model
The creative decision making model involves collecting information and insights about a problem and coming up with potential ideas for a solution, similar to the rational decision making model.
The difference here is that instead of identifying the pros and cons of each alternative, the decision maker enters a period in which they try not to actively think about the solution at all. The goal is to have their subconscious take over and lead them to the right decision, similar to the intuitive decision making model.
This situation is best used in an iterative process so that teams can test their solutions and adapt as things change.
Track key decisions with a work management tool
Tracking key decisions can be challenging when not documented correctly. Learn more about how a work management tool like Asana can help your team track key decisions, collaborate with teammates, and stay on top of progress all in one place.
Related resources

Fix these common onboarding challenges to boost productivity

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning
Understanding dependencies in project management

How Asana uses work management for organizational planning

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Critical Thinking Models: A Comprehensive Guide for Effective Decision Making

Critical thinking models are valuable frameworks that help individuals develop and enhance their critical thinking skills . These models provide a structured approach to problem-solving and decision-making by encouraging the evaluation of information and arguments in a logical, systematic manner. By understanding and applying these models, one can learn to make well-reasoned judgments and decisions.

Various critical thinking models exist, each catering to different contexts and scenarios. These models offer a step-by-step method to analyze situations, scrutinize assumptions and biases, and consider alternative perspectives. Ultimately, the goal of critical thinking models is to enhance an individual’s ability to think critically, ultimately improving their reasoning and decision-making skills in both personal and professional settings.
Key Takeaways
- Critical thinking models provide structured approaches for enhancing decision-making abilities
- These models help individuals analyze situations, scrutinize assumptions, and consider alternative perspectives
- The application of critical thinking models can significantly improve one’s reasoning and judgment skills.
Fundamentals of Critical Thinking

Definition and Importance
Critical thinking is the intellectual process of logically, objectively, and systematically evaluating information to form reasoned judgments, utilizing reasoning , logic , and evidence . It involves:
- Identifying and questioning assumptions,
- Applying consistent principles and criteria,
- Analyzing and synthesizing information,
- Drawing conclusions based on evidence.
The importance of critical thinking lies in its ability to help individuals make informed decisions, solve complex problems, and differentiate between true and false beliefs .
Core Cognitive Skills
Several core cognitive skills underpin critical thinking:
- Analysis : Breaking down complex information into smaller components to identify patterns or inconsistencies.
- Evaluation : Assessing the credibility and relevance of sources, arguments, and evidence.
- Inference : Drawing conclusions by connecting the dots between analyzed information.
- Synthesis : Incorporating analyzed information into a broader understanding and constructing one’s argument.
- Logic and reasoning : Applying principles of logic to determine the validity of arguments and weigh evidence.
These skills enable individuals to consistently apply intellectual standards in their thought process, which ultimately results in sound judgments and informed decisions.
Influence of Cognitive Biases
A key aspect of critical thinking is recognizing and mitigating the impact of cognitive biases on our thought processes. Cognitive biases are cognitive shortcuts or heuristics that can lead to flawed reasoning and distort our understanding of a situation. Examples of cognitive biases include confirmation bias, anchoring bias, and availability heuristic.
To counter the influence of cognitive biases, critical thinkers must be aware of their own assumptions and strive to apply consistent and objective evaluation criteria in their thinking process. The practice of actively recognizing and addressing cognitive biases promotes an unbiased and rational approach to problem-solving and decision-making.
The Critical Thinking Process

Stages of Critical Thinking
The critical thinking process starts with gathering and evaluating data . This stage involves identifying relevant information and ensuring it is credible and reliable. Next, an individual engages in analysis by examining the data closely to understand its context and interpret its meaning. This step can involve breaking down complex ideas into simpler components for better understanding.
The next stage focuses on determining the quality of the arguments, concepts, and theories present in the analyzed data. Critical thinkers question the credibility and logic behind the information while also considering their own biases and assumptions. They apply consistent standards when evaluating sources, which helps them identify any weaknesses in the arguments.
Values play a significant role in the critical thinking process. Critical thinkers assess the significance of moral, ethical, or cultural values shaping the issue, argument, or decision at hand. They determine whether these values align with the evidence and logic they have analyzed.
After thorough analysis and evaluation, critical thinkers draw conclusions based on the evidence and reasoning gathered. This step includes synthesizing the information and presenting a clear, concise argument or decision. It also involves explaining the reasoning behind the conclusion to ensure it is well-founded.
Application in Decision Making
In decision making, critical thinking is a vital skill that allows individuals to make informed choices. It enables them to:
- Analyze options and their potential consequences
- Evaluate the credibility of sources and the quality of information
- Identify biases, assumptions, and values that may influence the decision
- Construct a reasoned, well-justified conclusion
By using critical thinking in decision making, individuals can make more sound, objective choices. The process helps them to avoid pitfalls like jumping to conclusions, being influenced by biases, or basing decisions on unreliable data. The result is more thoughtful, carefully-considered decisions leading to higher quality outcomes.
Critical Thinking Models
Critical thinking models are frameworks that help individuals develop better problem-solving and decision-making abilities. They provide strategies for analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to reach well-founded conclusions. This section will discuss four notable models: The RED Model, Bloom’s Taxonomy, Paul-Elder Model, and The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment.
The RED Model
The RED Model stands for Recognize Assumptions, Evaluate Arguments, and Draw Conclusions. It emphasizes the importance of questioning assumptions, weighing evidence, and reaching logical conclusions.
- Recognize Assumptions: Identify and challenge assumptions that underlie statements, beliefs, or arguments.
- Evaluate Arguments: Assess the validity and reliability of evidence to support or refute claims.
- Draw Conclusions: Make well-reasoned decisions based on available information and sound reasoning.
The RED Model helps individuals become more effective problem solvers and decision-makers by guiding them through the critical thinking process ^(source) .
Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a hierarchical model that classifies cognitive skills into six levels of complexity. These levels are remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. By progressing through these levels, individuals can develop higher-order thinking skills.
- Remembering: Recall information or facts.
- Understanding: Comprehend the meaning of ideas, facts, or problems.
- Applying: Use knowledge in different situations.
- Analyzing: Break down complex topics or problems into sub-parts.
- Evaluating: Assess the quality, relevance, or credibility of information, ideas, or solutions.
- Creating: Combine elements to form a new whole, generate new ideas, or solve complex issues.
Paul-Elder Model
The Paul-Elder Model introduces the concept of “elements of thought,” focusing on a structured approach to critical thinking. This model promotes intellectual standards, such as clarity, accuracy, and relevance. It consists of three stages:
- Critical Thinking: Employ the intellectual standards to problem-solving and decision-making processes.
- Elements of Thought: Consider purpose, question at issue, information, interpretation and inference, concepts, assumptions, implications, and point of view.
- Intellectual Traits: Develop intellectual traits, such as intellectual humility, intellectual empathy, and intellectual perseverance.
This model fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation of critical thinking ^(source) .
The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment
The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment is a standardized test developed by Diane Halpern to assess critical thinking skills. The evaluation uses a variety of tasks to measure abilities in core skill areas, such as verbal reasoning, argument analysis, and decision making. Pearson, a leading publisher of educational assessments, offers this test as a means to assess individuals’ critical thinking skills ^(source) .
These four critical thinking models can be used as frameworks to improve and enhance cognitive abilities. By learning and practicing these models, individuals can become better equipped to analyze complex information, evaluate options, and make well-informed decisions.
Evaluating Information and Arguments
In this section, we will discuss the importance of evaluating information and arguments in the process of critical thinking, focusing on evidence assessment, logic and fallacies, and argument analysis.
Evidence Assessment
Evaluating the relevance, accuracy, and credibility of information is a vital aspect of critical thinking. In the process of evidence assessment, a thinker should consider the following factors:
- Source reliability : Research and understand the expertise and credibility of the source to ensure that biased or inaccurate information is not being considered.
- Currency : Check the date of the information to make sure it is still relevant and accurate in the present context.
- Objectivity : Analyze the information for potential bias and always cross-reference it with other credible sources.
When practicing critical thinking skills, it is essential to be aware of your own biases and make efforts to minimize their influence on your decision-making process.
Logic and Fallacies
Logic is crucial for deconstructing and analyzing complex arguments, while identifying and avoiding logical fallacies helps maintain accurate and valid conclusions. Some common fallacies to watch out for in critical thinking include:
- Ad Hominem : Attacking the person making the argument instead of addressing the argument itself.
- Strawman : Misrepresenting an opponent’s argument to make it easier to refute.
- False Dilemma : Presenting only two options when there may be multiple viable alternatives.
- Appeal to Authority : Assuming a claim is true simply because an authority figure supports it.
Being aware of these fallacies enables a thinker to effectively evaluate the strength of an argument and make sound judgments accordingly.
Argument Analysis
Analyzing an argument is the process of evaluating its structure, premises, and conclusion while determining its validity and soundness. To analyze an argument, follow these steps:
- Identify the premises and conclusion : Determine the main point is being argued, how it is related and substance of the argument.
- Evaluate the validity : Assess whether the conclusion logically follows from the premises and if the argument’s structure is sound.
- Test the soundness : Evaluate the truth and relevance of the premises. This may require verifying the accuracy of facts and evidence, as well as assessing the reliability of sources.
- Consider counter-arguments : Identify opposing viewpoints and counter-arguments, and evaluate their credibility to gauge the overall strength of the original argument.
By effectively evaluating information and arguments, critical thinkers develop a solid foundation for making well-informed decisions and solving problems.
Enhancing Critical Thinking
Strategies for improvement.
To enhance critical thinking, individuals can practice different strategies, including asking thought-provoking questions, analyzing ideas and observations, and being open to different perspectives. One effective technique is the Critical Thinking Roadmap , which breaks critical thinking down into four measurable phases: execute, synthesize, recommend, and communicate. It’s important to use deliberate practice in these areas to develop a strong foundation for problem-solving and decision-making. In addition, cultivating a mindset of courage , fair-mindedness , and empathy will support critical thinking development.
Critical Thinking in Education
In the field of education, critical thinking is an essential component of effective learning and pedagogy. Integrating critical thinking into the curriculum encourages student autonomy, fosters innovation, and improves student outcomes. Teachers can use various approaches to promote critical thinking, such as:
- Employing open-ended questions to stimulate ideas
- Incorporating group discussions or debates to facilitate communication and evaluation of viewpoints
- Assessing and providing feedback on student work to encourage reflection and improvement
- Utilizing real-world scenarios and case studies for practical application of concepts
Developing a Critical Thinking Mindset
To truly enhance critical thinking abilities, it’s important to adopt a mindset that values integrity , autonomy , and empathy . These qualities help to create a learning environment that encourages open-mindedness, which is key to critical thinking development. To foster a critical thinking mindset:
- Be curious : Remain open to new ideas and ask questions to gain a deeper understanding.
- Communicate effectively : Clearly convey thoughts and actively listen to others.
- Reflect and assess : Regularly evaluate personal beliefs and assumptions to promote growth.
- Embrace diversity of thought : Welcome different viewpoints and ideas to foster innovation.
Incorporating these approaches can lead to a more robust critical thinking skillset, allowing individuals to better navigate and solve complex problems.
Critical Thinking in Various Contexts
The workplace and beyond.
Critical thinking is a highly valued skill in the workplace, as it enables employees to analyze situations, make informed decisions, and solve problems effectively. It involves a careful thinking process directed towards a specific goal. Employers often seek individuals who possess strong critical thinking abilities, as they can add significant value to the organization.
In the workplace context, critical thinkers are able to recognize assumptions, evaluate arguments, and draw conclusions, following models such as the RED model . They can also adapt their thinking to suit various scenarios, allowing them to tackle complex and diverse problems.
Moreover, critical thinking transcends the workplace and applies to various aspects of life. It empowers an individual to make better decisions, analyze conflicting information, and engage in constructive debates.
Creative and Lateral Thinking
Critical thinking encompasses both creative and lateral thinking. Creative thinking involves generating novel ideas and solutions to problems, while lateral thinking entails looking at problems from different angles to find unique and innovative solutions.
Creative thinking allows thinkers to:
- Devise new concepts and ideas
- Challenge conventional wisdom
- Build on existing knowledge to generate innovative solutions
Lateral thinking, on the other hand, encourages thinkers to:
- Break free from traditional thought patterns
- Combine seemingly unrelated ideas to create unique solutions
- Utilize intuition and intelligence to approach problems from a different perspective
Both creative and lateral thinking are essential components of critical thinking, allowing individuals to view problems in a holistic manner and generate well-rounded solutions. These skills are highly valued by employers and can lead to significant personal and professional growth.
In conclusion, critical thinking is a multifaceted skill that comprises various thought processes, including creative and lateral thinking. By embracing these skills, individuals can excel in the workplace and in their personal lives, making better decisions and solving problems effectively.
Overcoming Challenges
Recognizing and addressing bias.
Cognitive biases and thinking biases can significantly affect the process of critical thinking . One of the key components of overcoming these challenges is to recognize and address them. It is essential to be aware of one’s own beliefs, as well as the beliefs of others, to ensure fairness and clarity throughout the decision-making process. To identify and tackle biases, one can follow these steps:
- Be self-aware : Understand personal beliefs and biases, acknowledging that they may influence the interpretation of information.
- Embrace diverse perspectives : Encourage open discussions and invite different viewpoints to challenge assumptions and foster cognitive diversity.
- Reevaluate evidence : Continuously reassess the relevance and validity of the information being considered.
By adopting these practices, individuals can minimize the impact of biases and enhance the overall quality of their critical thinking skills.
Dealing with Information Overload
In today’s world, information is abundant, and it can become increasingly difficult to demystify and make sense of the available data. Dealing with information overload is a crucial aspect of critical thinking. Here are some strategies to address this challenge:
- Prioritize information : Focus on the most relevant and reliable data, filtering out unnecessary details.
- Organize data : Use tables, charts, and lists to categorize information and identify patterns more efficiently.
- Break down complex information : Divide complex data into smaller, manageable segments to simplify interpretation and inferences.
By implementing these techniques, individuals can effectively manage information overload, enabling them to process and analyze data more effectively, leading to better decision-making.
In conclusion, overcoming challenges such as biases and information overload is essential in the pursuit of effective critical thinking. By recognizing and addressing these obstacles, individuals can develop clarity and fairness in their thought processes, leading to well-informed decisions and improved problem-solving capabilities.
Measuring Critical Thinking
Assessment tools and criteria.
There are several assessment tools designed to measure critical thinking, each focusing on different aspects such as quality, depth, breadth, and significance of thinking. One example of a widely used standardized test is the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal , which evaluates an individual’s ability to interpret information, draw conclusions, and make assumptions. Another test is the Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Level X and Level Z , which assess an individual’s critical thinking skills through multiple-choice questions.
Furthermore, criteria for assessing critical thinking often include precision, relevance, and the ability to gather and analyze relevant information. Some assessors utilize the Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment , which measures the application of cognitive skills such as deduction, observation, and induction in real-world scenarios.
The Role of IQ and Tests
It’s important to note that intelligence quotient (IQ) tests and critical thinking assessments are not the same. While IQ tests aim to measure an individual’s cognitive abilities and general intelligence, critical thinking tests focus specifically on one’s ability to analyze, evaluate, and form well-founded opinions. Therefore, having a high IQ does not necessarily guarantee strong critical thinking skills, as critical thinking requires additional mental processes beyond basic logical reasoning.
To build and enhance critical thinking skills, individuals should practice and develop higher-order thinking, such as critical alertness, critical reflection, and critical analysis. Using a Critical Thinking Roadmap , such as the four-phase framework that includes execution, synthesis, recommendation, and the ability to apply, individuals can continuously work to improve their critical thinking abilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main steps involved in the paul-elder critical thinking model.
The Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Model is a comprehensive framework for developing critical thinking skills. The main steps include: identifying the purpose, formulating questions, gathering information, identifying assumptions, interpreting information, and evaluating arguments. The model emphasizes clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, and fairness throughout the critical thinking process. By following these steps, individuals can efficiently analyze and evaluate complex ideas and issues.
Can you list five techniques to enhance critical thinking skills?
Here are five techniques to help enhance critical thinking skills:
- Ask open-ended questions : Encourages exploration and challenges assumptions.
- Engage in active listening: Focus on understanding others’ viewpoints before responding.
- Reflect on personal biases: Identify and question any preconceived notions or judgments.
- Practice mindfulness: Develop self-awareness and stay present in the moment.
- Collaborate with others: Exchange ideas and learn from diverse perspectives.
What is the RED Model of critical thinking and how is it applied?
The RED Model of critical thinking consists of three key components: Recognize Assumptions, Evaluate Arguments, and Draw Conclusions. To apply the RED Model, begin by recognizing and questioning underlying assumptions, being aware of personal biases and stereotypes. Next, evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of different arguments, considering evidence, logical consistency, and alternative explanations. Lastly, draw well-reasoned conclusions that are based on the analysis and evaluation of the information gathered.
How do the ‘3 C’s’ of critical thinking contribute to effective problem-solving?
The ‘3 C’s’ of critical thinking – Curiosity, Creativity, and Criticism – collectively contribute to effective problem-solving. Curiosity allows individuals to explore various perspectives and ask thought-provoking questions, while Creativity helps develop innovative solutions and unique approaches to challenges. Criticism, or the ability to evaluate and analyze ideas objectively, ensures that the problem-solving process remains grounded in logic and relevance.
What characteristics distinguish critical thinking from creative thinking?
Critical thinking and creative thinking are two complementary cognitive skills. Critical thinking primarily focuses on analyzing, evaluating, and reasoning, using objectivity and logical thinking. It involves identifying problems, assessing evidence, and drawing sound conclusions. Creative thinking, on the other hand, is characterized by the generation of new ideas, concepts, and approaches to solve problems, often involving imagination, originality, and out-of-the-box thinking.
What are some recommended books to help improve problem-solving and critical thinking skills?
There are several books that can help enhance problem-solving and critical thinking skills, including:
- “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman: This book explores the dual process theory of decision-making and reasoning.
- “The 5 Elements of Effective Thinking” by Edward B. Burger and Michael Starbird: Offers practical tips and strategies for improving critical thinking skills.
- “Critique of Pure Reason” by Immanuel Kant: A classic philosophical work that delves into the principles of reason and cognition.
- “Mindware: Tools for Smart Thinking” by Richard E. Nisbett: Presents a range of cognitive tools to enhance critical thinking and decision-making abilities.
- “The Art of Thinking Clearly” by Rolf Dobelli: Explores common cognitive biases and errors in judgment that can affect critical thinking.
You may also like

Online Learning and Critical Thinking: How to Choose the Right Course
Online learning gives more people access to education because of its convenience. It allows those with little time to take courses that […]

Critical Thinking and Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence has changed the way we think about the world; indeed, the very concept of a machine being able to think […]

A Student’s Guide to Critical Thinking
In the past, classroom-based learning revolved on retaining and repeating any information given. Today, schools focus on teaching the skills to learn […]

How to answer critical thinking questions
Whether you are studying and preparing to take the LSAT or looking to engage in more meaningful workplace discussions, you need to […]

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Make Great Decisions, Quickly
- Martin G. Moore

It’s a skill that will set you apart.
As a new leader, learning to make good decisions without hesitation and procrastination is a capability that can set you apart from your peers. While others vacillate on tricky choices, your team could be hitting deadlines and producing the type of results that deliver true value. That’s something that will get you — and them — noticed. Here are a few of a great decision:
- Great decisions are shaped by consideration of many different viewpoints. This doesn’t mean you should seek out everyone’s opinion. The right people with the relevant expertise need to clearly articulate their views to help you broaden your perspective and make the best choice.
- Great decisions are made as close as possible to the action. Remember that the most powerful people at your company are rarely on the ground doing the hands-on work. Seek input and guidance from team members who are closest to the action.
- Great decisions address the root cause, not just the symptoms. Although you may need to urgently address the symptoms, once this is done you should always develop a plan to fix the root cause, or else the problem is likely to repeat itself.
- Great decisions balance short-term and long-term value. Finding the right balance between short-term and long-term risks and considerations is key to unlocking true value.
- Great decisions are timely. If you consider all of the elements listed above, then it’s simply a matter of addressing each one with a heightened sense of urgency.
Where your work meets your life. See more from Ascend here .
Like many young leaders, early in my career, I thought a great decision was one that attracted widespread approval. When my colleagues smiled and nodded their collective heads, it reinforced (in my mind, at least) that I was an excellent decision maker.
- MM Martin G. Moore is the founder of Your CEO Mentor and author of No Bullsh!t Leadership and host of the No Bullsh!t Leadership podcast. His purpose is to improve the quality of leaders globally through practical, real world leadership content. For more information, please visit, www.martingmoore.com.
Partner Center

Common Problem-Solving Models & How to Use Them
Problem – solving models are step-by-step processes that provide a framework for addressing challenges. Problems arise in every facet of life. From work. to home. to friends and family, problems and conflicts can make life difficult and interfere with our physical and mental well-being. Understanding how to approach problems when they arise and implementing problem-solving techniques can make the journey through a problem less onerous on ourselves and those around us.
By building a structured problem-solving process, you can begin to build muscle memory by repeatedly practicing the same approach, and eventually, you may even begin to find yourself solving complex problems . Building a problem-solving model for each of the situations where you may encounter a problem can give you a path forward, even when the most difficult of problems arise.
This article will explore the concept of problem-solving models and dive into examples of such models and how to use them. It will also outline the benefits of implementing a problem-solving model in each area of life and why these problem-solving methods can have a large impact on your overall well-being. The goal of this article is to help you identify effective problem-solving strategies and develop critical thinking to generate solutions for any problem that comes your way.
Problem-Solving Model Defined
The first step in creating a problem-solving plan is to understand what we mean when we say problem-solving models. A problem-solving model is a step-by-step process that helps a team identify and effectively solve problems that they may encounter. This problem-solving approach gives the team the muscle memory and guide to address a conflict and resolve disputes quickly and effectively.
There are common problem-solving models that many teams have implemented, but there is also the freedom to shape a method to fit the needs of a specific situation. These models often rely on various problem-solving techniques to identify the root cause of the issue and find the best solution. This article will explore some common problem-solving models as well as general problem-solving techniques to help a team engage with and solve problems effectively.
Benefits of Implementing Problem-Solving Models
Before we discuss the exact models for problem-solving, it can be helpful to discuss why problem-solving models are beneficial in the first place. There are a variety of benefits to having a plan in place when a problem arises, but a few important benefits are listed below.
Guide Posts
When a team encounters a problem and has a guide for how to approach and solve the problem, it can be a relief to know that they have a process to fall back on when the issue cannot be resolved quickly from the beginning. A problem-solving strategy will serve as a guide for the parties to know which steps to take next and how to identify the appropriate solution.
It can also clarify when the issue needs to stay within the team, and when the issue needs to be escalated to someone in a position with more authority. It can also help the entire team solve complex problems without creating an issue out of the way the team solves the problem. It gives the team a blueprint to work from and encourages them to find a good solution.
Creative Solutions That Last
When the team or family has a way to fall back on to solve a problem, it takes some of the pressure off of coming up with the process and allows the parties to focus on identifying the relevant information and coming up with various potential solutions to the issue. By using a problem-solving method, the parties can come up with different solutions and find common ground with the best solution. This can be stifled if the team is too focused on figuring out how to solve the problem.
Additionally, the solutions that the parties come up with through problem-solving tools will often address the root cause of the issue and stop the team from having to revisit the same problem over and over again. This can lead to overall productivity and well-being and help the team continue to output quality work. By encouraging collaboration and creativity, a problem-solving technique will often keep solving problems between the parties moving forward and possibly even address them before they show up.
Common Models to Use in the Problem-Solving Process
Several models can be applied to a complex problem and create possible solutions. These range from common and straightforward to creative and in-depth to identify the most effective ways to solve a problem. This section will discuss and break down the problem-solving models that are most frequently used.
Standard Problem-Solving Process
When you search for a problem-solving technique, chances are you will find the standard model for saving problems. This model identifies and uses several important steps that will often be used in other models as well, so it can be helpful to begin the model-building process with an understanding of this model as a base. Other models often draw from this process and adapt one or more of the steps to help create additional options. Each of these steps works to accomplish a specific goal in furtherance of a solution.
Define the Problem
The first step in addressing a problem is to create a clear definition of the issue at hand. This will often require the team to communicate openly and honestly to place parameters around the issue. As the team defines the problem, it will be clear what needs to be solved and what pieces of the conflict are ancillary to the major issue. It helps to find the root causes of the issue and begin a process to address that rather than the symptoms of the problem. The team can also create a problem statement, which outlines the parameters of the problem and what needs to be fixed.
In addition to open and honest communication, other techniques can help to identify the root cause and define the problem. This includes a thorough review of the processes and steps that are currently used in the task and whether any of those steps are directly or indirectly causing the problem.
This includes reviewing how tasks are done, how communication is shared, and the current partners and team members that work together to identify if any of those are part of the issue. It is also the time to identify if some of the easy fixes or new tools would solve the problem and what the impact would be.
It is also important to gain a wide understanding of the problem from all of the people involved. Many people will have opinions on what is going on, but it is also important to understand the facts over the opinions that are affecting the problem. This can also help you identify if the problem is arising from a boundary or standard that is not being met or honored. By gathering data and understanding the source of the problem, the process of solving it can begin.
Generate Solutions
The next step in the basic process is to generate possible solutions to the problem. At this step, it is less important to evaluate how each of the options will play out and how they may change the process and more important to identify solutions that could address the issue. This includes solutions that support the goals of the team and the task, and the team can also identify short and long-term solutions.
The team should work to brainstorm as many viable solutions as possible to give them the best options to consider moving forward. They cannot pick the first solution that is proposed and consider it a successful problem-solving process.
Evaluate and Select
After a few good options have been identified, the next step is to evaluate the options and pick the most viable option that also supports the goals of the team or organization. This includes looking at each of the possible solutions and determining how they would either encourage or hinder the goals and standards of the team. These should evaluated without bias toward the solution proposed or the person putting forward the solution. Additionally, the team should consider both actual outcomes that have happened in the past and predicted instances that may occur if the solution is chosen.
Each solution should be evaluated by considering if the solution would solve the current problem without causing additional issues, the willingness of the team to buy in and implement the solution, and the actual ability of the team to implement the solution.
Participation and honesty from all team members will make the process go more smoothly and ensure that the best option for everyone involved is selected. Once the team picks the option they would like to use for the specific problem, they should clearly define what the solution is and how it should be implemented. There should also be a strategy for how to evaluate the effectiveness of the solution.
Implement the Solution and Follow Up
Once a solution is chosen, a team will often assume that the work of solving problems is complete. However, the final step in the basic model is an important step to determine if the matter is resolved or if additional options are needed. After the solution has been implemented by the team, the members of the team must provide feedback and identify any potential obstacles that may have been missed in the decision-making process.
This encourages long-term solutions for the problem and helps the team to continue to move forward with their work. It also gives the team a sense of ownership and an example of how to evaluate an idea in the future.
If the solution is not working the way that it should, the team will often need to adapt the option, or they may get to the point where they scrap the option and attempt another. Solving a problem is not always a linear process, and encouraging reform and change within the process will help the team find the answer to the issues that they face.
GROW Method
Another method that is similar to the standard method is the G.R.O.W. method. This method has very similar steps to the standard method, but the catchiness of the acronym helps a team approach the problem from the same angle each time and work through the method quickly.
The first step in the method is to identify a goal, which is what the “g” stands for in “grow.” To establish a goal, the team will need to look at the issues that they are facing and identify what they would like to accomplish and solve through the problem-solving process. The team will likely participate in conversations that identify the issues that they are facing and what they need to resolve.
The next step is to establish the current reality that the group is facing. This helps them to determine where they currently are and what needs to be done to move them forward. This can help the group establish a baseline for where they started and what they would like to change.
The next step is to find any obstacles that may be blocking the group from achieving their goal. This is where the main crux of the issues that the group is facing will come out. This is also helpful in giving the group a chance to find ways around these obstacles and toward a solution.
Way Forward
After identifying the obstacles and potential ways to avoid them, the group will then need to pick the best way to move forward and approach their goal together. Here, they will need to create steps to move forward with that goal.
Divide and Conquer
Another common problem-solving method is the divide-and-conquer method. Here, instead of the entire team working through each step of the process as a large group, they split up the issue into smaller problems that can be solved and have individual members or small groups work through the smaller problems. Once each group is satisfied with the solution to the problem, they present it to the larger group to consider along with the other options.
This process can be helpful if there is a large team attempting to solve a large and complex problem. It is also beneficial because it can be used in teams with smaller, specialized teams within it because it allows each smaller group to focus on what they know best.
However, it does encourage the parties to shy away from collaboration on the overall issue, and the different solutions that each proposes may not be possible when combined and implemented.
For this reason, it is best to use this solution when approaching complex problems with large teams and the ability to combine several problem-solving methods into one.
Six Thinking Hats
The Six Thinking Hats theory is a concept designed for a team with a lot of differing conflict styles and problem-solving techniques. This method was developed to help sort through the various techniques that people may use and help a team find a solution that works for everyone involved. It helps to organize thinking and lead the conversation to the best possible solution.
Within this system, there are six different “hats” that identify with the various aspects of the decision-making process: the overall process, idea generation, intuition and emotions, values, information gathering, and caution or critical thinking. The group agrees to participate in the process by agreeing on which of the hats the group is wearing at a given moment. This helps set parameters and expectations around what the group is attempting to achieve at any moment.
This system is particularly good in a group with different conflict styles or where people have a hard time collecting and organizing their thoughts. It can be incredibly beneficial for complex problems with many moving parts. It can also help groups identify how each of the smaller sections relates to the big picture and help create new ideas to answer the overall problem.
However, it can derail if the group focuses too heavily or for too long on one of the “hats.” The group should ensure that they have a facilitator to guide them through the process and ensure that each idea and section is considered adequately.
Trial and Error
The trial and error process takes over the evaluation and selection process and instead chooses to try out each of the alternatives to determine what the best option would be. It allows the team to gather data on each of the options and how they apply practically. It also provides the ability for the team to have an example of each possible answer to help a decision-maker determine what the best option is.
Problem-solving methods that focus on trial and error can be helpful when a team has a simple problem or a lot of time to test potential solutions, gather data, and determine an answer to the issue.
It can also be helpful when the team has a sense of the best guess for a solution but wants to test it out to determine if the data supports that option, or if they have several viable options and would like to identify the best one. However, it can be incredibly time-consuming to test each of the options and evaluate how they went. Time can often be saved by evaluating each option and selecting the best to test.
Other Problem-Solving Skills
In addition to the methods outlined above, other problem-solving skills can be used regardless of the model that is used. These techniques can round out the problem-solving process and help address either specific steps in the overall method or alter the step in some way to help it fit a specific situation.
Ask Good Questions
One of the best ways to work through any of the problem-solving models is to ask good questions. This will help the group find the issue at the heart of the problem and address that issue rather than the symptoms. The best questions will also help the group find viable solutions and pick the solution that the group can use to move forward. The more creative the questions , the more likely that they will produce innovative solutions.
Take a Step Back
Occasionally, paying attention to a problem too much can give the group tunnel vision and harm the overall processes that the group is using. Other times, the focus can lead to escalations in conflict. When this happens, it can be helpful to set aside the problem and give the group time to calm down. Once they have a chance to reconsider the options and how they apply, they can approach the issue with a new sense of purpose and determination. This can lead to additional creative solutions that may help the group find a new way forward.
Final Thoughts
Problem-solving can be a daunting part of life. However, with a good problem-solving method and the right techniques, problems can be addressed well and quickly. Applying some of these options outlined in this article can give you a head start in solving your next problem and any others that arise.
To learn more about problem-solving models, problem-solving activities, and more, contact ADR Times !
Must-read Articles:

- Recent Posts

- Mediator vs Lawyer: Finding the Best Fit - April 2, 2024
- How to Deal With a Narcissist - March 27, 2024
- How Long After Mediation Will I Get My Money? - March 19, 2024
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Psychology of Decision-Making Strategies
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Carly Snyder, MD is a reproductive and perinatal psychiatrist who combines traditional psychiatry with integrative medicine-based treatments.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/carly-935717a415724b9b9c849c26fd0450ea.jpg)
Portra / Getty Images
You have to make decisions both large and small throughout every single day of your life. What do you want to have for breakfast? What time should you meet a friend for dinner? What college should you go to? How many children do you want to have?
When faced with some decisions, you might be tempted to just flip a coin and let chance determine your fate. In most cases, we follow a certain strategy or series of strategies in order to arrive at a decision.
For many of the relatively minor decisions that we make each and every day, flipping a coin wouldn't be such a terrible approach. For some of the complex and important decisions, we are more likely to invest a lot of time, research, effort, and mental energy into coming to the right conclusion.
So how exactly does this process work? The following are some of the major decision-making strategies that you might use.
The Single-Feature Model
This approach involves hinging your decision solely on a single feature. For example, imagine that you are buying soap. Faced with a wide variety of options at your local superstore, you decide to base your decision on price and buy the cheapest type of soap available. In this case, you ignored other variables (such as scent, brand, reputation, and effectiveness) and focused on just a single feature.
The single-feature approach can be effective in situations where the decision is relatively simple and you are pressed for time. However, it is generally not the best strategy when dealing with more complex decisions.
The Additive Feature Model
This method involves taking into account all the important features of the possible choices and then systematically evaluating each option. This approach tends to be a better method when making more complex decisions.
For example, imagine that you are interested in buying a new camera. You create a list of important features that you want the camera to have, then you rate each possible option on a scale of -5 to +5.
Cameras that have important advantages might get a +5 rating for that factor, while those that have major drawbacks might get a -5 rating for that factor. Once you have looked at each option, you can then tally up the results to determine which option has the highest rating.
The additive feature model can be a great way to determine the best option for a variety of choices. As you can imagine, however, it can be quite time-consuming and is probably not the best decision-making strategy to use if you are pressed for time.
The Elimination by Aspects Model
The elimination by aspects model was first proposed by psychologist Amos Tversky in 1972. In this approach, you evaluate each option one characteristic at a time beginning with whatever feature you believe is the most important. When an item fails to meet the criteria you have established, you cross the item off your list of options. Your list of possible choices gets smaller and smaller as you cross items off the list until you eventually arrive at just one alternative.
Decision Making
The previous three processes are often used in cases where decisions are pretty straightforward, but what happens when there is a certain amount of risk, ambiguity, or uncertainty involved? For example, imagine that you are running late for your psychology class.
Should you drive above the speed limit in order to get there on time, but risk getting a speeding ticket? Or should you drive the speed limit, risk being late, and possibly get docked points for missing a scheduled pop quiz? In this case, you have to weigh the possibility that you might be late for your appointment against the probability that you will get a speeding ticket.
When making a decision in such a situation, people tend to employ two different decision-making strategies: the availability heuristic and the representativeness heuristic. Remember, a heuristic is a rule-of-thumb mental short-cut that allows people to make decisions and judgments quickly.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares a tip that can help you make better decisions.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
The Availability Heuristic
When we are trying to determine how likely something is, we often base such estimates on how easily we can remember similar events happening in the past. For example, if you are trying to determine if you should drive over the speed limit and risk getting a ticket, you might think of how many times you have seen people getting pulled over by a police officer on a particular stretch of highway.
If you cannot immediately think of any examples, you might decide to go ahead and take a chance, since the availability heuristic has led to you judge that few people get pulled over for speeding on your particular route. If you can think of numerous examples of people getting pulled over, you might decide to just play it safe and drive the suggested speed limit.
The Representativeness Heuristic
This mental shortcut involves comparing our current situation to our prototype of a particular event or behavior. For example, when trying to determine whether you should speed to get to your class on time, you might compare yourself to your image a person who is most likely to get a speeding ticket.
If your prototype is that of a careless teen that drives a hot-rod car and you are a young businesswoman who drives a sedan, you might estimate that the probability of getting a speeding ticket is quite low.
Keep in Mind
The decision-making process can be both simple (such as randomly picking out of our available options) or complex (such as systematically rating different aspects of the existing choices). The strategy we use depends on various factors, including how much time we have to make the decision, the overall complexity of the decision, and the amount of ambiguity that is involved.
- Hockenbury, D. H. & Hockenbury, S. E. (2006). Psychology. New York: Worth Publishers.
- Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1982). Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. In Daniel Kahneman, Paul Slovic, & Amos Tversky (Eds.). Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Tversky, A. (1972). Elimination by aspects: A theory of choice. Psychological Review, 80, 281-299.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Cognition: Mental Representations, Problem Solving, and Decision Making
- First Online: 01 January 2014
Cite this chapter

- Frank E. Ritter 4 ,
- Gordon D. Baxter 5 &
- Elizabeth F. Churchill 6
100k Accesses
There are several higher level structures built upon the basic structures of memory, attention, and learning in the user’s cognitive architecture. These representations and behaviors include mental models, problem solving, and decision making. These structures and processes form the basics of higher level cognition when interacting with technology, and describe some of the ways that users represent systems and interfaces, and how users interact with and use systems. Mental models are used to understand systems and to interact with systems. When the user’s mental models are inaccurate, systems are hard to use. Problem solving is used when it is not clear what to do next. Problem solving uses mental models, forms a basis for learning, and can be supported in a variety of ways. Decision making is a more punctuated form of problem solving, made about and with systems. It is not always as clear or accurate as one would like (or expect), and there are ways to support and improve it. There are some surprises in each of these areas where folk psychology concepts and theories are inaccurate.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bibby, P. A., & Payne, S. J. (1996). Instruction and practice in learning to use a device. Cognitive Science, 20 (4), 539–578.
Article Google Scholar
Byrne, M. D., & Bovair, S. (1997). A working memory model of a common procedural error. Cognitive Science, 21 (1), 31–61.
Cacciabue, P. C., Decortis, F., Drozdowicz, B., Masson, M., & Nordvik, J. (1992). COSIMO: A cognitive simulation model of human decision making and behavior in accident management of complex plants. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 22 (5), 1058–1074.
Cacioppo, J. T., & Petty, R. E. (1982). The need for cognition. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 42 (1), 116–131.
Carroll, J. M., & Olson, J. (Eds.). (1987). Mental models in human-computer interaction: Research issues about what the user of software knows . Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Google Scholar
Chase, W. G., & Simon, H. A. (1973). Perception in chess. Cognitive Psychology, 4 , 55–81.
Dawes, R. M. (1994). House of cards: Psychology and psychotherapy built on myth . New York, NY: The Free Press.
Dunning, D., Heath, C., & Suls, J. M. (2004). Flawed self-assessment: Implications for health, education, and the workplace. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 5 (3), 69–106.
Dunning, D., Johnson, K., Ehrlinger, J., & Kruger, J. (2003). Why people fail to recognize their own incompetence. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 12 (3), 83–87.
Evans, J. St. B. T. (1990). Biases in human reasoning . Hove, UK: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Fogg, B. J. (2003). Persuasive technology: Using computers to change what we think and do . San Francisco, CA: Morgan Kaufmann.
Gentner, D., & Stevens, A. L. (Eds.). (1983). Mental models . Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Gigerenzer, G., Todd, P. M., & the ABC Research Group (1999). Simple heuristics that make us smart . New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Gobet, F., Richman, H., Staszewski, J., & Simon, H. A. (1997). Goals, representations, and strategies in a concept attainment task: The EPAM model. The Psychology of Learning and Motivation, 37 , 265–290.
Gobet, F., & Simon, H. A. (1996a). Templates in chess memory: A mechanism for recalling several boards. Cognitive Psychology, 31 , 1–40.
Gobet, F., & Simon, H. A. (1996b). The roles of recognition processes and look-ahead search in time-constrained expert problem solving: Evidence from grandmaster level chess. Psychological Science, 7 , 52–55.
Hayes, J. R. (1981). The complete problem solver . Philadelphia: The Franklin Institute Press.
Hoffman, R. R., Crandall, B., & Shadbolt, N. R. (1998). Use of the critical decision method to elicit expert knowledge: A case study in the methodology of cognitive task analysis. Human Factors, 40 , 254–276.
Johnson-Laird, P. N. (1983). Mental models . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Johnson-Laird, P. N., Legrenzi, P., & Sonio Legrenzi, M. (1972). Reasoning and a sense of reality. British Journal of Psychology, 63 , 395–400.
Kahneman, D. (2013). Thinking, fast and slow . New York, NY: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
Kahneman, D., Slovic, P., & Tversky, A. (Eds.). (1982). Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases . Cambridge: Cambridge, UK.
Kaplan, C. (1989). Hatching a theory of incubation: Does putting a problem aside really help? If so, why? , Carnegie-Mellon University, University Microfilms International, Catalog #9238813.
Klein, G. A. (1997). Recognition-primed decision making: Looking back, looking forward . Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Krug, S. (2005). Don’t make me think: A common sense approach to web usability (2nd ed.). Berkeley, CA: New Riders Press.
Larkin, J. H., McDermott, J., Simon, D. P., & Simon, H. A. (1980). Expert and novice performance in solving physics problems. Science, 208 , 1335–1342.
Lehto, M. R. (1997). Decision making. In G. Salvendy (Ed.), Handbook of human factors and ergonomics (pp. 1201–1248). New York, NY: Wiley.
Levitt, S., & Dubner, S. J. (2005). Freakonomics: A rogue economist explores the hidden side of everything . New York, NY: William Morrow/HarperCollins.
Luchins, A. S. (1942). Mechanization in problem solving: The effect of Einstellung. Psychological Monographs, 54 (6), 1–95.
Moray, N. (1996). A taxonomy and theory of mental models. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society 40th Annual Meeting (Vol. 1, pp. 164–168).
Moray, N. (1999). Mental models in theory and practice. In D. Gopher & A. Koriat (Eds.), Attention and performance XVII: Cognitive regulation of performance: Interaction of theory and application (pp. 223–258). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Norman, D. A. (1983). Design rules based on analysis of human error. Communications of the ACM, 26 (4), 254–258.
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Norman, D. A. (1988). The psychology of everyday things . New York, NY: Basic Books.
Norman, D. A. (2013). The design of everyday things . New York, NY: Basic Books.
NTSB. (1990). Aircraft accident report. United Airlines flight 232. Mc Donnell Douglas DC - 10 - 10. Sioux Gateway airport. Sioux City, Iowa, July 19, 1989 . Washington DC: National Transportation Safety Board.
Payne, S. J. (1995). Naive judgments of stimulus-response compatibility. Human Factors, 37 , 495–506.
Quinlan, P., & Dyson, B. (2008). Cognitive psychology . Harlow, UK: Pearson.
Rasmussen, J. (1983). Skills, rules, knowledge: Signals, signs and symbols and other distinctions in human performance models. IEEE Transactions: Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, SMC - 13 , 257–267.
Revell, K. M. A., & Stanton, N. A. (2012). Models of models: Filtering and bias rings in depiction of knowledge structures and their implications for design. Ergonomics, 55 (9), 1073–1092.
Ries, A., & Trout, J. (1986/2000). Positioning: The battle for your mind . New York, NY: McGraw-Hill International.
Ritter, F. E., & Bibby, P. A. (2008). Modeling how, when, and what learning happens in a diagrammatic reasoning task. Cognitive Science, 32 , 862–892.
Ritter, F. E., Jones, R. M., & Baxter, G. D. (1998). Reusable models and graphical interfaces: Realising the potential of a unified theory of cognition. In U. Schmid, J. Krems, & F. Wysotzki (Eds.), Mind modeling—a cognitive science approach to reasoning, learning and discovery (pp. 83–109). Lengerich, Germany: Pabst Scientific Publishing.
Schwartz, B. (2004). The paradox of choice: Why more is less . New York, NY: Harper Perennial.
Simon, H. A. (1997). Administrative behavior (4th ed.). New York, NY: The Free Press.
Simon, H. A., & Chase, W. G. (1973). Skill in chess. American Scientist, 61 , 393–403.
Smallman, H. S., & St. John, M. (2005). Naïve realism: Misplaced faith in the utility of realistic displays. Ergonomics in Design, 13 (Summer), 6–13.
Sternberg, R. J. (2004). Why smart people can be so foolish. European Psychologist, 9 (3), 145–150.
Sternberg, R. J., & Davidson, J. E. (1995). The nature of insight . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Tverksy, A., & Kahneman, D. (1981). The framing of decisions and the psychology of choice. Science, 211 , 453–458.
Tverksy, A., & Kahneman, D. (1986). Rational choice and the framing of decisions. Journal of Business, 59 , 251–278.
Wason, P. C. (1960). On the failure to eliminate hypotheses in a conceptual task. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 12 , 129–140.
Wilson, J. R., & Rutherford, A. (1989). Mental models: Theory and application in human factors. Human Factors, 31 , 617–634.
Winne, P. H., & Jamieson-Noel, D. (2002). Exploring students’ calibration of self reports about study tactics and achievement. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 27 (4), 551–572.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of IST, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA
Frank E. Ritter
School of Computer Science, University of St Andrews, St Andrews, Fife, UK
Gordon D. Baxter
eBay Research Labs, San Jose, CA, USA
Elizabeth F. Churchill
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Frank E. Ritter .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer-Verlag London
About this chapter
Ritter, F.E., Baxter, G.D., Churchill, E.F. (2014). Cognition: Mental Representations, Problem Solving, and Decision Making. In: Foundations for Designing User-Centered Systems. Springer, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-5134-0_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-5134-0_6
Published : 12 April 2014
Publisher Name : Springer, London
Print ISBN : 978-1-4471-5133-3
Online ISBN : 978-1-4471-5134-0
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
- MEDICAL ASSISSTANT
- Abdominal Key
- Anesthesia Key
- Basicmedical Key
- Otolaryngology & Ophthalmology
- Musculoskeletal Key
- Obstetric, Gynecology and Pediatric
- Oncology & Hematology
- Plastic Surgery & Dermatology
- Clinical Dentistry
- Radiology Key
- Thoracic Key
- Veterinary Medicine
- Gold Membership
Making Decisions and Solving Problems
CHAPTER 6 Making Decisions and Solving Problems Rose Aguilar Welch This chapter describes the key concepts related to problem solving and decision making. The primary steps of the problem-solving and decision-making processes, as well as analytical tools used for these processes, are explored. Moreover, strategies for individual or group problem solving and decision making are presented. Objectives • Apply a decision-making format to list options to solve a problem, identify the pros and cons of each option, rank the options, and select the best option. • Evaluate the effect of faulty information gathering on a decision-making experience. • Analyze the decision-making style of a nurse leader/manager. • Critique resources on the Internet that focus on critical thinking, problem solving, and decision making. Terms to Know autocratic creativity critical thinking decision making democratic optimizing decision participative problem solving satisficing decision The Challenge Vickie Lemmon RN, MSN Director of Clinical Strategies and Operations, WellPoint, Inc., Ventura, California Healthcare managers today are faced with numerous and complex issues that pertain to providing quality services for patients within a resource-scarce environment. Stress levels among staff can escalate when problems are not resolved, leading to a decrease in morale, productivity, and quality service. This was the situation I encountered in my previous job as administrator for California Children Services (CCS). When I began my tenure as the new CCS administrator, staff expressed frustration and dissatisfaction with staffing, workload, and team communications. This was evidenced by high staff turnover, lack of teamwork, customer complaints, unmet deadlines for referral and enrollment cycle times, and poor documentation. The team was in crisis, characterized by in-fighting, blaming, lack of respectful communication, and lack of commitment to program goals and objectives. I had not worked as a case manager in this program. It was hard for me to determine how to address the problems the staff presented to me. I wanted to be fair but thought that I did not have enough information to make immediate changes. My challenge was to lead this team to greater compliance with state-mandated performance measures. What do you think you would do if you were this nurse? Introduction Problem solving and decision making are essential skills for effective nursing practice. Carol Huston (2008) identified “expert decision-making skills” as one of the eight vital leadership competencies for 2020. These processes not only are involved in managing and delivering care but also are essential for engaging in planned change. Myriad technologic, social, political, and economic changes have dramatically affected health care and nursing. Increased patient acuity, shorter hospital stays, shortage of healthcare providers, increased technology, greater emphasis on quality and patient safety, and the continuing shift from inpatient to ambulatory and home health care are some of the changes that require nurses to make rational and valid decisions. Moreover, increased diversity in patient populations, employment settings, and types of healthcare providers demands efficient and effective decision making and problem solving. More emphasis is now placed on involving patients in decision making and problem solving and using multidisciplinary teams to achieve results. Nurses must possess the basic knowledge and skills required for effective problem solving and decision making. These competencies are especially important for nurses with leadership and management responsibilities. Definitions Problem solving and decision making are not synonymous terms. However, the processes for engaging in both processes are similar. Both skills require critical thinking, which is a high-level cognitive process, and both can be improved with practice. Decision making is a purposeful and goal-directed effort that uses a systematic process to choose among options. Not all decision making begins with a problem situation. Instead, the hallmark of decision making is the identification and selection of options or alternatives. Problem solving, which includes a decision-making step, is focused on trying to solve an immediate problem, which can be viewed as a gap between “what is” and “what should be.” Effective problem solving and decision making are predicated on an individual’s ability to think critically. Although critical thinking has been defined in numerous ways, Scriven and Paul (2007) refer to it as “ the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action.” Effective critical thinkers are self-aware individuals who strive to improve their reasoning abilities by asking “why,” “what,” or “how.” A nurse who questions why a patient is restless is thinking critically. Compare the analytical abilities of a nurse who assumes a patient is restless because of anxiety related to an upcoming procedure with those of a nurse who asks if there could be another explanation and proceeds to investigate possible causes. It is important for nurse leaders and managers to assess staff members’ ability to think critically and enhance their knowledge and skills through staff-development programs, coaching, and role modeling. Establishing a positive and motivating work environment can enhance attitudes and dispositions to think critically. Creativity is essential for the generation of options or solutions. Creative individuals can conceptualize new and innovative approaches to a problem or issue by being more flexible and independent in their thinking. It takes just one person to plant a seed for new ideas to generate . The model depicted in Figure 6-1 demonstrates the relationship among related concepts such as professional judgment, decision making, problem solving, creativity, and critical thinking. Sound clinical judgment requires critical or reflective thinking. Critical thinking is the concept that interweaves and links the others. An individual, through the application of critical-thinking skills, engages in problem solving and decision making in an environment that can promote or inhibit these skills. It is the nurse leader’s and manager’s task to model these skills and promote them in others. FiGURE 6-1 Problem-solving and decision-making model. Decision Making This section presents an overview of concepts related to decision models, decision-making styles, factors affecting decision making, group decision making (advantages and challenges), and strategies and tools. The phases of the decision-making process include defining objectives, generating options, identifying advantages and disadvantages of each option, ranking the options, selecting the option most likely to achieve the predefined objectives, implementing the option, and evaluating the result. Box 6-1 contains a form that can be used to complete these steps. BOX 6-1 Decision-Making Format Objective: _____________________________________ Options Advantages Disadvantages Ranking Add more rows as necessary. Rank priority of options, with “1” being most preferred. Select the best option. Implementation plan: ______________________________________________________________________________ Evaluation plan: __________________________________________________________________________________ A poor-quality decision is likely if the objectives are not clearly identified or if they are inconsistent with the values of the individual or organization. Lewis Carroll illustrates the essential step of defining the goal, purpose, or objectives in the following excerpt from Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland: One day Alice came to a fork in the road and saw a Cheshire Cat in a tree. “Which road do I take?” she asked. His response was a question: “Where do you want to go?” “I don’t know,” Alice answered. “Then,” said the cat, “it doesn’t matter.” Decision Models The decision model that a nurse uses depends on the circumstances. Is the situation routine and predictable or complex and uncertain? Is the goal of the decision to make a decision conservatively that is just good enough or one that is optimal? If the situation is fairly routine, nurse leaders and managers can use a normative or prescriptive approach. Agency policy, standard procedures, and analytical tools can be applied to situations that are structured and in which options are known. If the situation is subjective, non-routine, and unstructured or if outcomes are unknown or unpredictable, the nurse leader and manager may need to take a different approach. In this case, a descriptive or behavioral approach is required. More information will need to be gathered to address the situation effectively. Creativity, experience, and group process are useful in dealing with the unknown. In the business world, Camillus described complex problems that are difficult to describe or resolve as “wicked” (as cited in Huston, 2008 ). This term is apt in describing the issues that nurse leaders face. In these situations, it is especially important for nurse leaders to seek expert opinion and involve key stakeholders. Another strategy is satisficing. In this approach, the decision maker selects the solution that minimally meets the objective or standard for a decision. It allows for quick decisions and may be the most appropriate when time is an issue. Optimizing is a decision style in which the decision maker selects the option that is best, based on an analysis of the pros and cons associated with each option. A better decision is more likely using this approach, although it does take longer to arrive at a decision. For example, a nursing student approaching graduation is contemplating seeking employment in one of three acute care hospitals located within a 40-mile radius of home. The choices are a medium-size, not-for-profit community hospital; a large, corporate-owned hospital; and a county facility. A satisficing decision might result if the student nurse picked the hospital that offered a decent salary and benefit packet or the one closest to home. However, an optimizing decision is more likely to occur if the student nurse lists the pros and cons of each acute care hospital being considered such as salary, benefits, opportunities for advancement, staff development, and mentorship programs. Decision-Making Styles The decision-making style of a nurse manager is similar to the leadership style that the manager is likely to use. A manager who leans toward an autocratic style may choose to make decisions independent of the input or participation of others. This has been referred to as the “decide and announce” approach, an authoritative style. On the other hand, a manager who uses a democratic or participative approach to management involves the appropriate personnel in the decision-making process. It is imperative for managers to involve nursing personnel in making decisions that affect patient care. One mechanism for doing so is by seeking nursing representation on various committees or task forces. Participative management has been shown to increase work performance and productivity, decrease employee turnover, and enhance employee satisfaction. Any decision style can be used appropriately or inappropriately. Like the tenets of situational leadership theory, the situation and circumstances should dictate which decision-making style is most appropriate. A Code Blue is not the time for managers to democratically solicit volunteers for chest compressions! The autocratic method results in more rapid decision making and is appropriate in crisis situations or when groups are likely to accept this type of decision style. However, followers are generally more supportive of consultative and group approaches. Although these approaches take more time, they are more appropriate when conflict is likely to occur, when the problem is unstructured, or when the manager does not have the knowledge or skills to solve the problem. Exercise 6-1 Interview colleagues about their most preferred decision-making model and style. What barriers or obstacles to effective decision making have your colleagues encountered? What strategies are used to increase the effectiveness of the decisions made? Based on your interview, is the style effective? Why or why not? Factors Affecting Decision Making Numerous factors affect individuals and groups in the decision-making process. Tanner (2006) conducted an extensive review of the literature to develop a Clinical Judgment Model. Out of the research, she concluded that five principle factors influence decision making. (See the Literature Perspective below.) Literature Perspective Resource: Tanner, C. A. (2006). Thinking like a nurse: A research-based model of clinical judgment in nursing. Journal of Nursing Education, 45 (6), 204-211. Tanner engaged in an extensive review of 200 studies focusing on clinical judgment and clinical decision making to derive a model of clinical judgment that can be used as a framework for instruction. The first review summarized 120 articles and was published in 1998. The 2006 article reviewed an additional 71 studies published since 1998. Based on an analysis of the entire set of articles, Tanner proposed five conclusions which are listed below. The reader is referred to the article for detailed explanation of each of the five conclusions. The author considers clinical judgment as a “problem-solving activity.” She notes that the terms “clinical judgment,” “problem solving,” “decision making,” and “critical thinking” are often used interchangeably. For the purpose of aiding in the development of the model, Tanner defined clinical judgment as actions taken based on the assessment of the patient’s needs. Clinical reasoning is the process by which nurses make their judgments (e.g., the decision-making process of selecting the most appropriate option) ( Tanner, 2006 , p. 204): 1. Clinical judgments are more influenced by what nurses bring to the situation than the objective data about the situation at hand. 2. Sound clinical judgment rests to some degree on knowing the patient and his or her typical pattern of responses, as well as an engagement with the patient and his or her concerns. 3. Clinical judgments are influenced by the context in which the situation occurs and the culture of the nursing care unit. 4. Nurses use a variety of reasoning patterns alone or in combination. 5. Reflection on practice is often triggered by a breakdown in clinical judgment and is critical for the development of clinical knowledge and improvement in clinical reasoning. The Clinical Judgment Model developed through the review of the literature involves four steps that are similar to problem-solving and decision-making steps described in this chapter. The model starts with a phase called “Noticing.” In this phase, the nurse comes to expect certain responses resulting from knowledge gleaned from similar patient situations, experiences, and knowledge. External factors influence nurses in this phase such as the complexity of the environment and values and typical practices within the unit culture. The second phase of the model is “Interpreting,” during which the nurse understands the situation that requires a response. The nurse employs various reasoning patterns to make sense of the issue and to derive an appropriate action plan. The third phase is “Responding,” during which the nurse decides on the best option for handling the situation. This is followed by the fourth phase, “Reflecting,” during which the nurse assesses the patient’s responses to the actions taken. Tanner emphasized that “reflection-in-action” and “reflection-on-action” are major processes required in the model. Reflection-in-action is real-time reflection on the patient’s responses to nursing action with modifications to the plan based on the ongoing assessment. On the other hand, reflection-on-action is a review of the experience, which promotes learning for future similar experiences. Nurse educators and managers can employ this model with new and experienced nurses to aid in understanding thought processes involved in decision making. As Tanner (2006) so eloquently concludes, “If we, as nurse educators, help our students understand and develop as moral agents, advance their clinical knowledge through expert guidance and coaching, and become habitual in reflection-on-practice, they will have learned to think like a nurse” ( p. 210 ). Implications for Practice Nurse educators and managers can employ this model with new and experienced nurses to aid in understanding thought processes involved in decision making. For example, students and practicing nurses can be encouraged to maintain reflective journals to record observations and impressions from clinical experiences. In clinical post-conferences or staff development meetings, the nurse educator and manager can engage them in applying to their lived experiences the five conclusions Tanner proposed. The ultimate goal of analyzing their decisions and decision-making processes is to improve clinical judgment, problem-solving, decision-making, and critical-thinking skills. Internal and external factors can influence how the situation is perceived. Internal factors include variables such as the decision maker’s physical and emotional state, personal philosophy, biases, values, interests, experience, knowledge, attitudes, and risk-seeking or risk-avoiding behaviors. External factors include environmental conditions, time, and resources. Decision-making options are externally limited when time is short or when the environment is characterized by a “we’ve always done it this way” attitude. Values affect all aspects of decision making, from the statement of the problem/issue through the evaluation. Values, determined by one’s cultural, social, and philosophical background, provide the foundation for one’s ethical stance. The steps for engaging in ethical decision making are similar to the steps described earlier; however, alternatives or options identified in the decision-making process are evaluated with the use of ethical resources. Resources that can facilitate ethical decision making include institutional policy; principles such as autonomy, nonmaleficence, beneficence, veracity, paternalism, respect, justice, and fidelity; personal judgment; trusted co-workers; institutional ethics committees; and legal precedent. Certain personality factors, such as self-esteem and self-confidence, affect whether one is willing to take risks in solving problems or making decisions. Keynes (2008) asserts that individuals may be influenced based on social pressures. For example, are you inclined to make decisions to satisfy people to whom you are accountable or from whom you feel social pressure? Characteristics of an effective decision maker include courage, a willingness to take risks, self-awareness, energy, creativity, sensitivity, and flexibility. Ask yourself, “Do I prefer to let others make the decisions? Am I more comfortable in the role of ‘follower’ than leader? If so, why?” Exercise 6-2 Identify a current or past situation that involved resource allocation, end-of-life issues, conflict among healthcare providers or patient/family/significant others, or some other ethical dilemma. Describe how the internal and external factors previously described influenced the decision options, the option selected, and the outcome. Group Decision Making There are two primary criteria for effective decision making. First, the decision must be of a high quality; that is, it achieves the predefined goals, objectives, and outcomes. Second, those who are responsible for its implementation must accept the decision. Higher-quality decisions are more likely to result if groups are involved in the problem-solving and decision-making process. In reality, with the increased focus on quality and safety, decisions cannot be made alone. When individuals are allowed input into the process, they tend to function more productively and the quality of the decision is generally superior. Taking ownership of the process and outcome provides a smoother transition. Multidisciplinary teams should be used in the decision-making process, especially if the issue, options, or outcome involves other disciplines. Research findings suggest that groups are more likely to be effective if members are actively involved, the group is cohesive, communication is encouraged, and members demonstrate some understanding of the group process. In deciding to use the group process for decision making, it is important to consider group size and composition. If the group is too small, a limited number of options will be generated and fewer points of view expressed. Conversely, if the group is too large, it may lack structure, and consensus becomes more difficult. Homogeneous groups may be more compatible; however, heterogeneous groups may be more successful in problem solving. Research has demonstrated that the most productive groups are those that are moderately cohesive. In other words, divergent thinking is useful to create the best decision. For groups to be able to work effectively, the group facilitator or leader should carefully select members on the basis of their knowledge and skills in decision making and problem solving. Individuals who are aggressive, are authoritarian, or manifest self-oriented behaviors tend to decrease the effectiveness of groups. The nurse leader or manager should provide a nonthreatening and positive environment in which group members are encouraged to participate actively. Using tact and diplomacy, the facilitator can control aggressive individuals who tend to monopolize the discussion and can encourage more passive individuals to contribute by asking direct, open-ended questions. Providing positive feedback such as “You raised a good point,” protecting members and their suggestions from attack, and keeping the group focused on the task are strategies that create an environment conducive to problem solving. Advantages of Group Decision Making The advantages of group decision making are numerous. The adage “two heads are better than one” illustrates that when individuals with different knowledge, skills, and resources collaborate to solve a problem or make a decision, the likelihood of a quality outcome is increased. More ideas can be generated by groups than by individuals functioning alone. In addition, when followers are directly involved in this process, they are more apt to accept the decision, because they have an increased sense of ownership or commitment to the decision. Implementing solutions becomes easier when individuals have been actively involved in the decision-making process. Involvement can be enhanced by making information readily available to the appropriate personnel, requesting input, establishing committees and task forces with broad representation, and using group decision-making techniques. The group leader must establish with the participants what decision rule will be followed. Will the group strive to achieve consensus, or will the majority rule? In determining which decision rule to use, the group leader should consider the necessity for quality and acceptance of the decision. Achieving both a high-quality and an acceptable decision is possible, but it requires more involvement and approval from individuals affected by the decision. Groups will be more committed to an idea if it is derived by consensus rather than as an outcome of individual decision making or majority rule. Consensus requires that all participants agree to go along with the decision. Although achieving consensus requires considerable time, it results in both high-quality and high-acceptance decisions and reduces the risk of sabotage. Majority rule can be used to compromise when 100% agreement cannot be achieved. This method saves time, but the solution may only partially achieve the goals of quality and acceptance. In addition, majority rule carries certain risks. First, if the informal group leaders happen to fall in the minority opinion, they may not support the decision of the majority. Certain members may go so far as to build coalitions to gain support for their position and block the majority choice. After all, the majority may represent only 51% of the group. In addition, group members may support the position of the formal leader, although they do not agree with the decision, because they fear reprisal or they wish to obtain the leader’s approval. In general, as the importance of the decision increases, so does the percentage of group members required to approve it. To secure the support of the group, the leader should maintain open communication with those affected by the decision and be honest about the advantages and disadvantages of the decision. The leader should also demonstrate how the advantages outweigh the disadvantages, suggest ways the unwanted outcomes can be minimized, and be available to assist when necessary.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Related posts:
- Patient Safety
- Developing the Role of Manager
- Care Delivery Strategies
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Comments are closed for this page.

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


COMMENTS
Here is a six-step process to follow when using a problem-solving model: 1. Define the problem. First, determine the problem that your team needs to solve. During this step, teams may encourage open and honest communication so everyone feels comfortable sharing their thoughts and concerns.
There are 4 modules in this course. Problem-solving and effective decision-making are essential skills in today's fast-paced and ever-changing workplace. Both require a systematic yet creative approach to address today's business concerns. This course will teach an overarching process of how to identify problems to generate potential ...
Perhaps the best-known of commercially available problem-solving training is provided by Kepner-Tregoe, a firm named after its founders, Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe. They published their classic book about problem solving and decision making in 1965. It was titled . The Rational Manager. Later, in 1981, they published an updated version ...
A decision-making model works by walking you through the decision-making process — and there are several such models available for you to choose from. To help you improve your problem-solving abilities and make better decisions, let's take a look at five proven decision-making models and when you should use them. Defining decision-making ...
The decision-making process is a seven-step framework for making a big decision with careful consideration, collaboration, and confidence. ... Most of us are eager to tie on our superhero capes and jump into problem-solving mode — especially if our team is depending on a solution. ... And the truth is that the model is likely overkill for the ...
The chapter introduces principles of rational choice suggested by classical decision theory, followed by a discussion of research on human decision making which has led to the new perspectives of behavioral decision theory and behavioral economics, and naturalistic decision models. It addresses the topic of decision support and problem solving ...
Decision-making is perhaps best thought of as a key part of problem-solving: one part of the overall process. Our approach at Skills You Need is to set out a framework to help guide you through the decision-making process. You won't always need to use the whole framework, or even use it at all, but you may find it useful if you are a bit ...
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly . The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it's easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions.
Decision making is the process of selecting and choosing one action or behavior out of several alternatives. Like problem solving, decision making involves the coordination of memories and executive resources. Research on decision making has paid particular attention to the cognitive biases that account for suboptimal decisions and decisions ...
Effective decision-making involves creative problem solving and thinking out of the box, so don't limit you or your teams to clear-cut options. ... The creative decision making model involves collecting information and insights about a problem and coming up with potential ideas for a solution, similar to the rational decision making model. ...
These models provide a structured approach to problem-solving and decision-making by encouraging the evaluation of information and arguments in a logical, systematic manner. By understanding and applying these models, one can learn to make well-reasoned judgments and decisions.
The right people with the relevant expertise need to clearly articulate their views to help you broaden your perspective and make the best choice. Great decisions are made as close as possible to ...
The chapter introduces principles of rational choice suggested by classical decision theory, followed by a discussion of research on human decision making which has led to the new perspectives of behavioral decision theory and behavioral economics, and naturalistic decision models. It addresses the topic of decision support and problem solving ...
Decision-making is the process of choosing a solution based on your judgment, situation, facts, knowledge or a combination of available data. The goal is to avoid potential difficulties. Identifying opportunity is an important part of the decision-making process. Making decisions is often a part of problem-solving.
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
The Six Step Problem Solving Model Problem solving models are used to address the many challenges that arise in the workplace. While many people regularly solve problems, there are a range of different approaches that can be used to find a solution. Complex challenges for teams, working groups and boards etc., are usually solved more quickly by ...
The first step in creating a problem-solving plan is to understand what we mean when we say problem-solving models. A problem-solving model is a step-by-step process that helps a team identify and effectively solve problems that they may encounter. This problem-solving approach gives the team the muscle memory and guide to address a conflict ...
Keep in Mind. The decision-making process can be both simple (such as randomly picking out of our available options) or complex (such as systematically rating different aspects of the existing choices). The strategy we use depends on various factors, including how much time we have to make the decision, the overall complexity of the decision ...
Easton's Models of Decision-Making. In essence: There are four variables or "streams" that circulate in a kind of Brownian movement in a fixed decision space, that decision space being the garbage can; those four variables are: problems, decision participants, choice opportunities, and solutions.
Problem solving uses mental models, forms a basis for learning, and can be supported in a variety of ways. Decision making is a more punctuated form of problem solving, made about and with systems. It is not always as clear or accurate as one would like (or expect), and there are ways to support and improve it.
In the "Problem Solving" section of this chapter, we discuss diagnosis of the conflict and also the development of alternative possibilities for resolving a conflict. In "Decision Making," we consider a range of the kinds of decisions people involved in resolving conflict have to make, both individually and together, including choice among the ...
The Z-Model for Problem Solving. Jolie Bain Pillsbury. A common approach to problem solving can enhance a group's ability to make decisions together. The Z-Model is such an approach. When used in conjunction with a consensus process, such as Proposal-Based Decision Making (PBDM)1, group decision making is more effective. 1.
An individual, through the application of critical-thinking skills, engages in problem solving and decision making in an environment that can promote or inhibit these skills. It is the nurse leader's and manager's task to model these skills and promote them in others. FiGURE 6-1 Problem-solving and decision-making model.