Mental Health Research Paper

This sample mental health research paper features: 8500 words (approx. 28 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 80 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.

I. Introduction
Academic writing, editing, proofreading, and problem solving services, get 10% off with 24start discount code, ii. the sociology of mental health: a brief history, a. the development of social epidemiology of mental health and disorders, iii. the study of mental health in contemporary sociology, a. the influence of other disciplines on the sociology of mental health, b. theoretical perspectives on mental health and disorder in sociology, c. defining a unique sociological approach to mental health and illness, 1. the stressor exposure perspective, 2. the social relationships perspective, 3. the societal reaction perspective, d. the influence of psychological models on the sociology of mental health and illness, e. methodological controversies, 1. measures of mental health and disorder, 2. measures of stressor exposure, f. the social epidemiology of mental disorders, 2. socioeconomic status, 4. marital status, iv. future directions in the sociology of mental health, a. comorbidity, b. mental health services and policy, c. better measures of stress exposure, d. better measures of social resources, e. the biological perspective on mental disorders, more mental health research papers:.
- ADHD Research Paper
- Amnesia Research Paper
- Antisocial Personality Disorder Research Paper
- Anxiety Research Paper
- Autism Research Paper
- Borderline Personality Disorder Research Paper
- Conduct Disorder Research Paper
- Dementia Research Paper
- Depression Research Paper
- Eating Disorders Research Paper
- PTSD Research Paper
- Schizophrenia Research Paper
- Stress Research Paper
- Suicide Research Paper
This research paper describes the history, application, and development in sociology of the study of mental health, illness, and disorders. Mental health, mental illness, social and mental functioning, and its social indicators are a classic theme in the field of sociology. Emile Durkheim’s (1951) Suicide was a landmark study in both sociology and epidemiology, laying out a sociological course of research that remains an intellectual force in contemporary social science (Berkman and Glass 2000). The influence of the sociology of mental health and illness goes well beyond its sociological roots; its major theoretical perspectives interact with major research streams in psychiatry, psychology, anthropology, public health, and medicine (Aneshensel and Phelan 1999; Horwitz and Scheid 1999; Eaton 2001; Gallagher 2002; Cockerham 2005). The sociology of mental health also connects to numerous other fields in sociology, including general medical sociology, the sociology of aging, demography and biodemograpy, statistics, childhood studies, sociology of the life course, deviance, criminology, stratification, and studies of the quality of life.
Mental health, mental illness, and mental disorder are closely related but distinguishable concepts. Mental health refers to a state of well-being or alternatively, a state of mental normality, free of disorder or illness. Mental illness refers to a persistent state of mental abnormality. The term mental disorder is applied to a specific diagnosis of mental abnormality, such as depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, agoraphobia, mania or substance dependence.
In this research paper, the term sociology of mental health is used to refer to general theories and research that encompass the causes, development, and consequences of mental disorders and the state or symptoms of mental distress. The term also includes the study of personal and situational resources that preserve or restore the state of mental wellbeing. Sociologists who practice in the field of mental health examine a variety of outcomes and indicators of mental health as well as mental disorders.
The paper is organized into three sections: (1) a brief historical perspective on the study of mental health and illness in sociology; (2) the current state of research in the field, including its major themes and methodological problems; and (3) the future directions of the field. This research paper has four pervasive themes: (1) the interaction of the sociology of mental health and disorder with psychology, psychiatry, public health, and medicine; (2) the environmental perspective, which is the major contribution of the sociology to the mix of disciplines examining mental health in society; (3) the relationship between the study of mental health and studies of mental disorder; and (4) the emergence of the life course perspective as a dominant theoretical perspective in the sociology of mental health.
The topic of mental health has a venerable tradition in sociology. Durkheim’s classic work Suicide was translated into English in 1921, and it is still widely cited in the field. Durkheim’s work encouraged interest in the relationship of mental health and disorders with social structure, group membership, geographical location, and other indicators of social integration and organization. One of the most famous early applications of Durkheim’s perspective was Robert Merton’s (1938) work on social structure and anomie. Taken together, Durkheim and Merton introduced the influential idea that social systems can produce “stress” for individuals, who in turn may act in deviant or disordered ways (Cockerham 2005). Also applying Durkheim’s ideas, Faris and Dunham (1939) conducted a study of the distribution of schizophrenia in Chicago. Observing that people with schizophrenia clustered in high poverty areas, they argued that social isolation encouraged the development of symptoms characterizing schizophrenia.
Although Merton’s and Faris and Dunham’s theories no longer hold sway among contemporary sociologists of mental health, they are significant in their historical impact on the field. The organized field of the sociology of mental health grew out of the larger field of general medical sociology in the late 1930s and 1940s. Interest in mental illness and its causes were heightened by extraordinary events in the mid-twentieth century. The suffering of many ordinary Americans during the Great Depression, the discovery of psychiatric impairments among many World War II draftees, and the traumatic effects of combat on soldiers and civilians were powerful arguments for government support of efforts to mitigate mental illness (Kirk 1999).
The founding of the National Institutes of Mental Health (NIMH) in 1949 contributed to the development of medical sociology in general. The establishment of the Laboratory of Socio-Environmental Studies at NIMH in 1952 was a critical event in the development of studies of mental health in medical sociology. The sociologist John Clausen, who headed the laboratory, recruited and supported a number of sociologists who became leaders in the field, among them Melvin Kohn, Leonard Pearlin, Erving Goffman, and Morris Rosenberg (Kirk 1999). Using a strategy still dominant in behavioral science approaches to mental disorders, Clausen (1956) recruited social scientists from multiple disciplines as well as sociologists, stating that “the roles to be filled by sociologists within the mental health field call for collaboration with clinicians” (p. 47).
Throughout the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, NIMH was a major supporter of sociological and psychological research on mental health and illness. According to figures assembled by Kirk (1999), in 1976 more than 50 percent of NIMH research grants were to social, psychological, and behavioral scientists. A smaller proportion of grants were awarded to psychiatrists and physicians (a situation that no longer holds at NIMH).
Social epidemiology, sometimes labeled psychiatric epidemiology or social psychiatry (Gallagher 2002), is the discovery and documentation of the social and demographic distribution of mental disorders and health. The distribution of mental disorders can be documented via the study of medical records, mental hospital admissions, and surveys of the general population. Surveys in representative community populations, using clinically validated questions that identify and classify mental disorder symptoms by diagnostic categories, are the current tools used to estimate the prevalence of disorders (Cockerham 2005). The diagnostic estimates are then analyzed to determine their distribution by social and demographic group.
Hollingshead and Redlich (1958) (a sociologist and a psychiatrist) conducted an innovative study of mental disorders in New Haven, Connecticut, in which they compared mental illness inpatients and outpatients to a sample representative of the general community. Although not a study of prevalence the study had wide influence because of their findings that different types of mental disorder were distributed by social class, with more disorders among lower social class groups. The study also found that treatment for mental disorder varied by class. Because Hollingshead and Redlich’s study included only treated cases, however, they could not draw inferences about possible social causes of mental disorders.
The Midtown Manhattan Study in the 1950s (Srole et al. 1962) investigated the distribution of mental disorders using a random selection household survey design. The interview responses were rated by psychiatrists on the team. The findings from this study continue to shape social epidemiology today. Mental disorders were found to be more prevalent among respondents of lower socioeconomic status. Childhood poverty was linked to psychiatric impairment in adulthood (an early application of the life course perspective on mental health). Those who had mental disorders were less likely to be upwardly mobile. The investigators hypothesized that exposure to childhood and adult stressors played a key role in the distribution of mental disorders as well as mental health (Cockerham 2005). Many of these findings were replicated in a study of Nova Scotia communities (Leighton et al. 1963).
The environmental perspective on mental health was also advanced by studies led by social psychologists. Americans View Their Mental Health, two nationally representative interview studies conducted in 1956 and 1976 (Veroff, Douvan, and Kulka 1981), examined patterns over time in the contributions of the social environment to both positive and negative mental well-being as well as to patterns of help seeking for those who experienced mental distress.
A notable advance in the survey technology for measuring the prevalence of mental disorders and their social correlates was the Epidemiological Catchment Area (ECA) project, conducted by NIMH and five universities in the 1980s (Yale University, Johns Hopkins University, Washington University, Duke University, and the University of California at Los Angeles). A multidisciplinary team, including sociologists, psychiatrists, and psychologists developed new diagnosis instruments to detect mental disorders for use in the general population (Robins and Regier 1991). These diagnostic instruments, derived from the third version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of the American Psychiatric Association (DSMIII), were coupled with interviews that measured environmental factors, social class, race, ethnicity, stressors, social relationships, and other factors believed to correlate with the risk of developing mental disorders.
The separate samples for the ECA studies, however, were not representative of the entire population of the United States. In 1990 through 1992, NIMH funded the first national survey of mental disorders in the general U.S. population (n = 8,068), the National Comorbidity Survey (NCS; Kessler and Zhao 1999). The investigators updated the interview diagnostic measures to reflect those recently developed by the American Psychiatric Association and the World Health Organization (Kessler et al. 1994). Along with diagnostic measures of depression, mania, anxiety, substance abuse, phobias, posttraumatic stress disorder, and other mood and psychotic disorders, the NCS interviews included measures of environmental factors, personality, childhood conditions, physical health, and mental health care utilization. NCS investigated the concept of comorbidity, which is defined as the occurrence of more than one type of mental disorder in an individual.
The NCS has been widely emulated and expanded. A version of the NCS was also conducted in Canada. NIMH also funded a series of replications of the NCS in 2000 to 2003 (Kessler et al. 2005), and the method has been extended to studying mental health and illness in children. The World Health Association is currently coordinating international replications of the NCS ( http://www.hcp.med.harvard.edu/ncs/ ).
As the foregoing brief historical overview shows, the study of mental health in sociology has been influenced by multiple disciplines. It is also host to a number of competing theoretical perspectives. The most widely discussed is the tension among medical, environmental, and societal reaction perspectives on the causes, consequences, and appropriate treatment of mental disorders. As a consequence of the host of influences on the field, there is considerable disagreement over the measurement of basic concepts in research, including how to define mental health and disorders (Kessler and Zhao 1999), environmental factors such as stressors, location, and socioeconomic status (Wheaton 1999); and social consequences such as disability, labeling, and social isolation (Horwitz and Scheid 1999; Pillemer et al. 2000). In addition, there is considerable creative tension between those who concentrate on establishing the incidence and prevalence of mental disorders and those who focus more on the correlates of mental health and mental illness (Mirowsky and Ross 2002, 2004). Finally, there is considerable research on the use of mental health services and on mental health policy.
As Clausen (1956) prophetically foresaw, sociologists who specialize in mental health frequently collaborate with those in other disciplines, such as developmental and social psychology, psychiatry, epidemiology, economics (Aneshensel and Phelan 1999; Gallagher 2002), and increasingly biology (Shanahan and Hofer 2005). The National Institutes of Health has encouraged and continues to encourage multidisciplinary approaches to the study of mental illness and disorders. Psychiatrists and clinical psychologists lay claim to the definitions of mental illness and disorder through the continuing revisions of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual Mental Disorders, currently in its fourth edition (American Psychiatric Association 2000), as well as to measurements of mental distress (Radloff 1977), quality of life (Veroff et al. 1981), and social relationships and support (Cohen, Underwood, and Gottlieb 2000). Sociologists who study mental health compete for federal funds and intellectual prestige with those from other disciplines.
The presence of sociologists in interdisciplinary efforts to understand the causes, course, and consequences of mental illness and disorders is a positive situation; the influence of the sociology of mental health on other disciplines is tangible. A negative aspect of the interdisciplinary effort is that the sociology of mental health is sometimes viewed as isolated from the general field of sociology (Aneshensel and Phelan 1999). This perception may be exacerbated by the employment of sociologists of mental health (and other medical sociologists) in academic units other than Sociology departments. Members of the Sociology of Mental Health section of the American Sociological Association are employed in medical schools, schools of public health, schools of social work, and departments of human development. When theories of cause and measures of critical outcomes are shared with other disciplines, the question arises: What is the unique contribution of sociology to the study of mental health and illness? The answer to this question is pressing as there are calls for proposals that contribute to “the development, enhancement, and assembly of new data sets from existing data” and for research “that combines diverse levels of analysis” from national research and review bodies (National Institutes of Health 2004) as well as for research that examines the causes of health differences by socioeconomic status and behavioral risk factors across the life course (National Research Council 2004).
Five major perspectives, and combinations of these perspectives, are used in the contemporary sociology of mental health. The five major perspectives are (1) the medical model, (2) the environmental perspective, (3) the social psychological perspective, (4) societal reaction (or labeling), and (5) the life course perspective. The medical model views mental disorders as diseases and prescribes medical treatment as the appropriate cure. The environmental perspective asserts that factors such as social class, race, ethnicity, gender, urban location, and exposure to stressors may cause and most certainly shape risks for mental disorder. The social psychological perspective contributes insight into the social and relational factors that provide resources for adjusting to environmental stressors and restoring mental health and well-being. The social reaction perspective argues that mental illness emerges from social strain processes that produce deviance. The life course perspective views mental health and mental disorder as resulting from the accumulation of environmental stressors and exposures across the lifetime, in interaction with developmental and personal factors such as family structure, personality, and even genetic endowment. Researchers in the sociology of mental health often combine one or more of these perspectives in their research, with the life course perspective now generally seen as an emerging unifying paradigm (George 1999).
Although there is constant interaction between the mental health disciplines, several recent analyses of the state of theory in the sociology of mental health in the late twentieth century indicate the emergence of a distinct sociological approach. Horwitz and Scheid (1999) outlined two major approaches in the study of the sociology of mental health and illness. These two approaches are: (1) the social contexts producing or shaping mental health and disorder and (2) the recognition, treatment, and policy response to mental illness and disorder. In the same volume, Thoits (1999) described three major approaches that uniquely characterize the sociology of mental health: (1) stress exposure (a subset of the social context approach described by Horwitz and Scheid); (2) structural strain theory, which derives from Merton (1938); and (3) societal reaction, or labeling theory. Aneshensel and Phelan (1999) argue that the distinguishing issue in the sociological approach to mental illness is attention to how social stratification produces the unequal distribution of both disorders and mental health.
Aneshensel and Phelan also argue that a major challenge to the sociological approach to mental disorders is the debate between social causation and social selection explanations for the relationship between mental disorders and social class. The social selection approach hypothesizes that the reason there are more mental disorders in the lower economic class is because those with mental disorders are downwardly mobile economically or are unable to be upwardly mobile. This debate has many implications for interpreting how social stratification is linked to mental disorders and health (e.g., Miech et al. 1999).
The sociological approach also provides unique insight into the serious social consequences for those who have mental disorders, including socioeconomic success. The sociological approach also contributes research on the social factors that influence how institutions and individuals recognize when someone is mentally ill, how individuals are treated and how that treatment varies by social class, gender, and race, and who is more likely to use mental health care (e.g., Phelan et al. 2000).
The application of the sociological approach to mental health generates considerable empirical work that focuses on economic and other types of social stratification as determinants of mental health and mental disorder. This work is concentrated in research on stressor exposure, social relationships, and societal reaction to mental disorders.
The social context approach is a set of perspectives; the most well-known and applied outside the field of the sociology of mental health is the stress exposure perspective, which assumes that a combination or accumulation of stressors and difficulties can cause an onset of mental disorder. This perspective (Brown and Harris 1978; Dohrenwend et al. 1978), dominant in sociology, focuses on the level of change or threat posed by external events, and more recently, on the potential for chronic, unresolved stressors to threaten physical and mental health (Wheaton 1999).
Building on the strong history of social epidemiology in the field, the major assumption of this approach is that differential exposure to stressors by social class or social location is largely determined by social inequalities. In turn, the effects of prolonged stress exposure may perpetuate social inequality through the development of mental illness or disorder in disadvantaged populations (Pearlin et al. 2005). The latter point is more controversial (and in general less well developed theoretically); however the emerging life course or human developmental approach to the accumulation of disadvantage derives in some part from the stress exposure perspective (George 1999). The life course approach assumes that there is an accumulation of the negative effects of differential stressor exposure across life that perpetuates and magnifies inequalities and that many of these processes originate in childhood (e.g., McLeod and Kaiser 2004; McLeod and Nonnemaker 2000). A related stress exposure approach is stress diathesis, which assumes that stress exposure causes disorder only when there is a latent vulnerability (Eaton 2001). The diathesis approach is widely applied in psychiatric research on mental disorders.
Horwitz and Scheid (1999) add that in addition to stressor exposure, resources to help counter the negative impact of stressor exposure or to avoid stressor exposure also are differentially distributed by social class and location. The major types of social resources that vary by social class are (1) social integration, usually measured as access to meaningful and productive social roles (e.g., Pillemer et al. 2000); (2) social network characteristics (Turner and Turner 1999); (3) family structure (e.g., Turner, Sorenson, and Turner 2000); (4) received and perceived social support (Wethington and Kessler 1986); and (5) coping choices and styles (Pearlin and Schooler 1978; Pearlin et al. 1981). Thoits (1999) has pointed out that this approach, although distinct from the stressor exposure perspective, relies on stress exposure as a mechanism to activate the protective factors.
In an overview of the sociology of mental health, Thoits (1999) argued that there is no strong evidence that labeling or other societal reaction processes produce mental illness. However, the societal reaction perspective does provide an insight into social biases against those who display symptoms of mental disorder, which are often viewed as socially deviant. Aneshensel and Phelan (1999) concluded that there is a consensus among sociologists of mental health that mental disorders are objective entities and are not completely a product of social constructions. The strongest evidence for this conclusion is that symptoms of mental disorders are observed in all societies, although there are cultural variations in the ways that such symptoms are described and diagnosed.
A difficulty with this position for sociologists of mental health is that it implies there is widespread acceptance of the medical model, which can make theoretical interaction with other streams of sociology (e.g., the sociology of deviance) more contentious. Studies of the etiology of mental disorders in the population no longer routinely employ a deviance perspective. The stressor exposure model also applies a variation of the dose-response paradigm widely used in medical research. This acceptance of a variation of the medical model remains controversial and is probably related to the distance perceived between the sociology of mental health and the more mainstream sociology of stratification.
Yet another tension exists between opposing explanations of what causes social stratification in the distributions of mental disorders. On one side is the belief that routine functioning of society produces some of this stratification, as for example gender differences in the distribution of different types of disorders (Rosenfield 1999). In this view, mental distress and mental disorders can be produced by normal social processes such as gender role socialization. The stress exposure perspective, on the other hand, assumes that abnormal circumstances and events produce mental disorders and distress (Almeida and Kessler 1998). These two views are not necessarily impossible to resolve, but they continue to produce theoretical tensions.
Another factor producing distance between the sociology of mental health and the general field of sociology is the influence of social psychological theories on the field. As psychology has incorporated facets of the stress exposure perspective, sociologists of mental health have adopted ideas from social and developmental psychology on social support and relationships, coping, and life course development. An influential psychological perspective, the process of appraisal and coping, was developed by Lazarus and Folkman (1984), updated by Lazarus (1999), and has been further elaborated by Folkman and Moskowitz (2004). This perspective, dominant in the field of psychology, has emphasized how individual differences in perceptions of external stressors affect mental health. The focus of appraisal researchers on emotions as motivation for appraisal suggests commonality with biological research on emotion (Massey 2002). The theory of appraisal has been widely cited by sociologists who examine the impact of events on mental health (e.g.,Wethington and Kessler 1986).
The life course perspective (Elder 1974), now widely applied in the sociology of mental health (e.g., Wheaton and Clarke 2003; McLeod and Kaiser 2004), traces many of its components to the ecological perspective on human development pioneered by the developmental psychologist Urie Bronfenbrenner (1979). The life course perspective theorizes that developmental trajectories, developmental or socially normative timing of the stressor, and the accumulation of stressor exposure and resistance factors shape reaction to stressors (Elder, George, and Shanahan 1996). In the last decade, the life course perspective on stress accumulation has also been applied by psychologists, clinical psychologists, and neuroscientists (e.g., Singer and Ryff 1999; McEwen 2002; Repetti, Taylor, and Seeman 2002). Neuroscientists McEwen and Stellar (1993) have developed the concept of allostatic load which describes physiological mechanisms for the accumulated effects of past adaptation to stressors on health. Allostatic load is currently being adapted by sociologists to use in studies of stressor exposure across the life course and its relationship to mental health and disorder (Shanahan, Hofer and Shanahan 2003; Shanahan and Hofer 2005).
Sociological and psychological research streams on the relationship between stressor exposure and mental health are converging through collaborative efforts that examine the impact of stressor accumulation along the individual life course (Elder et al. 1996; Singer et al. 1998). A serious problem, however, is that most measures of stressor exposure available to researchers focus on recent exposures rather than the interactions of different types of stressor exposure over the long term; the majority of stressor exposure measures used in research are simple counts or sums of life events occurring over a short period of time (Wheaton 1999). Investigating the relationships between stressors over time and their combined associations with mental health and well-being is an important strategy for examining the impact of stressors over the life course (George 1999).
Issues of causality and theoretical approach are controversial in the field. Given the complexity and controversies in the sociology of mental health and illness, it is not surprising that one of the critical areas of the field is measurement. The two most disputed areas involve the measurement of outcomes and the measurement of stressor exposure.
The controversy begins with the outcomes. There is an increasing consensus that positive mental health and wellbeing is not just the absence of mental illness or disorder (Keyes 2002). There is also a controversy over whether dichotomous diagnoses of psychiatric disorder should be a proper outcome for sociological inquiry, in contrast to scales of distress symptoms (Kessler 2002; Mirowsky and Ross 2002).
Research diagnostic measures of mental disorder are controversial on many dimensions. Wakefield (1999) criticized the diagnostic measures used in the Epidemiological Catchment Area and National Comorbodity Studies for overestimating the prevalence of lifetime mental disorder in the United States. The NCS estimated that one-half of all Americans will suffer from a mental disorder over their lifetime (Kessler et al. 1994). A recent reanalysis of the NCS (Narrow et al. 2002), applying a standard of clinical seriousness based on other questions available in the survey, reduced the lifetime prevalence estimates significantly to 32 percent lifetime prevalence.
Another issue of controversy is whether a dichotomous outcome measure of disorder, one either has the disorder or not, misses levels of distress or poor social functioning that indicate considerable mental suffering (Kessler 2002; Mirowsky and Ross 2002). Persistent or recurring symptoms of sleeplessness, fatigue, sadness, loneliness, lack of appetite, and loss of interest in things in response to chronic stressors or unexpected life events can be unpleasant and disabling even if the sufferer does not show all of the symptoms of depression required for a diagnosis. The high threshold required for a diagnosis of disorder may understate emotional responses to events in the population at large. Whereas mental disorders may be relatively uncommon, symptoms of distress in response to life events are commonly observed and may indicate the presence of social dysfunction and strain in ways that surveys of mental disorders do not.
Measures of stressor exposure are particularly problematic in the sociology of mental health (Wheaton 1999). A complicating factor is that other mental health disciplines enforce higher standards of precision in measurement than does sociology. In addition, the majority of studies using stressor exposure measures do not account for any interaction between combinations of particular types of stressors. Applying the life course perspective model on mental health would ultimately require more sophisticated measures on how stressors combine and interact across time.
Both the biomedical and sociological streams of research on stress processes share an interest in environmental triggers of distress (Selye 1956). Following Selye, early stress researchers applied Selye’s assumption that all environmental threats activated the same or similar physiological response, using sums of exposures to different types of stressful events (Turner and Wheaton 1995). Almost immediately, sociologists and other social researchers modified this assumption, finding that more explicit and comprehensive measurement of the characteristics of stressors often increased the amount of variance explained in the mental health outcome. These measures included the estimated average “magnitude of change” scores in Social Readjustment Rating Scale (the SRRS: Holmes and Rahe 1967) and the Psychiatric Epidemiology Research Interview for Life Events (the PERI; Dohrenwend et al. 1978). Furthermore, it became clear that other characteristics of stressors, such as their type, timing, duration, severity, unexpectedness, controllability and impacts on other aspects of life make significant contributions to the stress response and mental health outcome (e.g., Brown and Harris 1978, 1989; Pearlin and Schooler 1978; Wethington, Brown, and Kessler 1995).
The stress exposure model is evolving to model the dynamic, continuous adaptation to stressors over time (e.g., Heckhausen and Schulz 1995; Lazarus 1999; Folkman and Moskowitz 2004). Sociologists have developed measures of chronic stress exposure (Pearlin and Schooler 1978) and exposure to stressors and hassles on a daily basis (Almeida, Wethington, and Kessler 2002). Researchers debate the relative reliability and validity of self-report checklist and interview measures of life events that include detailed probes that enable investigators to rate the severity of life events (Wheaton 1999). Most recently, psychologists have contributed to understanding variations in the relationships of different types of stressors (social loss vs. trauma and chronic vs. acute stressor exposure), to immune system function and cortisol activity (e.g., Dickerson and Kemeny 2004; Segerstrom and Miller 2004). Sociologists are now considering the potential for using measures of physiological activity (e.g., cortisol measurement) in their studies (Shanahan et al. 2003).
Applying the life course perspective to studying mental disorders and health over time has led to concern about the reliability and validity of retrospective measures of stressor exposure (Wethington et al. 1995; Wheaton 1999). Empirical research on memory for life events over a relatively short recall period is reassuring; most severe events can be recalled quite well over a 12-month retrospective period (Kessler and Wethington 1991). Serious concerns remain about longer retrospective recall periods. This concern is partially mitigated by the development of life history calendar methods, visual memory aids that can be used in interviews to enhance memory for life events (Freedman et al. 1988).
Despite the complexity of measurement, sociologists have pioneered the study of psychiatric sociology, or the epidemiology of mental disorders. The recent advances of measurement in the ECA and NCS studies have produced measures of outcomes that are scientifically accepted across disciplines (Cockerham 2005). These studies have also provided critical data on the use of mental health services by those who suffer from significant disorders and have had a major influence on other fields of study. The major epidemiological research questions have focused around the distribution of mental disorders and illnesses by social factors, including gender, socioeconomic status, marital status, race, and ethnicity. There is some, but more limited work, on factors such as ethnicity, migration, and location.
There is dispute whether the overall rate of mental disorders and illnesses differs by gender. The consensus before the publication of national data from the NCS was that men and women did not differ overall in rates of mental disorders; rather, different types of disorders are distributed differently. Women are more likely to report depressed affect and depressive disorders. Men, in turn, are more likely to report alcohol and drug disorders, violent behavior, and other indicators of acting out. Major psychoses such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder are not distributed unequally by gender. There is now accumulating evidence that women are also more likely to report anxiety disorders (Kessler et al. 1994, 2005), which would mean that women are overall more likely to have mental disorders. Although there is continuing interest among biological and medical scientists to find a biological cause for women’s higher rates of some disorders, particularly depression, among sociologists social cause explanations still hold sway (e.g., Rosenfield 1999).
One of the most consistent findings in the epidemiology of mental disorders is that those of lower socioeconomic status are more likely to develop mental disorders (Cockerham 2005; Gallagher 2002). This general finding was confirmed by the NCS (Kessler and Zhao 1999). There is evidence, however, that those of higher statuses are more likely to suffer from affective disorders; the overrepresentation of mental disorders is due to higher rates of schizophrenia and some personality disorders among those of lower socioeconomic status.
Among sociologists of mental health, social causation theories continue to dominate, but more attention is being given to selection processes, especially the impact of mental disorders on upward economic mobility (e.g., Miech et al. 1999). Researchers who apply the life course perspective often study selection and economic mobility processes directly, most particularly those processes that affect educational attainment in early adulthood (e.g., McLeod and Kaiser 2004).
There remains considerable controversy in the literature whether members of racial minority groups report higher rates of mental disorder than majority racial groups. Given the relationship of socioeconomic status to mental health and disorders, it is logical to predict that rates of mental disorder in African Americans would be higher than the rates among white Americans because of the average lower socioeconomic status of blacks. Such a pattern would also reflect the additional burden of discrimination and prejudice and the impact such burdens have on mental well-being (Kessler, Mickelson, and Williams 1999).
The pattern of racial and ethnic differences, however, is more complex. For example, an analysis of risk and persistence of mental disorders among U.S. ethnic groups (Breslau et al. 2005) found that Hispanics reported lower lifetime prevalence of substance use disorders than whites, and that blacks reported lower lifetime prevalence of mood (depression or mania), anxiety, and substance use disorders. However, Hispanics were more likely to report persistent mood disorders (defined as recurrence of a past disorder), and blacks were more likely to report persistent mood and anxiety disorders. Research is needed on the factors that mitigate the impact of stressors on mental health of minority groups. Other researchers call for more attention to how mental disorders are measured and diagnosed in African Americans and other minority groups (e.g., Neighbors et al. 2003).
Although there is some evidence that pattern of mental distress by marital status may be changing as cohabitation becomes more socially accepted, the consensus still holds that married people are in better mental health and report fewer mental disorders than those who are not currently married. New research (Umberson and Williams 1999) points to the quality of the marital relationship as critical to mental well-being and health; those in unsatisfying or high-conflict marriages report poor mental health. Divorce is associated with poorer mental health over time, particularly among those who did not initiate the divorce.
Evidence such as that noted above is taken to mean that marriage confers benefits on mental health and may provide some protection against mental illness. Umberson and Williams (1999) note, however, that relatively little research has been done that has pitted the benefits of marriage perspective directly against the alternative social selection perspective that those who have mental disorders are less likely to marry or to remain married. Forthofer et al. (1996) estimated the relationship of age of onset of mental disorder on the probability of subsequent marriage. They found that those who have disorders are less likely to be married and when they marry have a higher risk of divorce. Unfortunately, studies that examine both social causation and social selection perspectives on marital status and mental health remain relatively rare, most likely because of the absence of satisfactory longitudinal data that can be used to address this issue.
One of the tensions in the sociology of mental health and illness is the interdisciplinary orientation of the field. Concepts are freely borrowed along the border of sociology and psychiatry/psychology. Much work is applied, or meant to be applied, to issues of importance to social policy, such as the social costs of untreated mental disorders. The life course perspective (Elder et al. 1996) is changing how research is done and how questions are being asked. New directions in the field include (1) a focus on comorbidity and severity of illness and its social impact, (2) the need for a closer connection between epidemiology and research on mental health services and policy, (3) the press to develop better measures of stressor exposure, (4) demand for more sophisticated measures and analyses of social resources, and (5) and the challenge of biological research on the stress process to the sociological study of mental health.
The study of comorbidity of mental disorders in people has transformed some aspects of the sociology of mental health. First, the documentation of comorbidity has influenced sociologists in the field to accept that mental illness is an objective reality. Second, it has become clear that those who are comorbid for multiple disorders are severely disabled in many important life roles. Their progress through life resembles the life path of “social selection.” Third, the acceptance that mental disorders are real physical entities, and the evidence for comorbidity are challenges to the environmental perspective on mental disorders. It is likely that those who have mental disorders attract or create stressor exposure (Eaton 2001). Thus, one major direction for sociological research in the future might be an emphasis on mental disorders as predictors, rather than outcomes, of social functioning and processes.
When reviewing the state of the sociology of mental health, Horwitz and Scheid (1999) observed that research on the social contexts of mental disorder and research on mental health services do not intersect all that much. They believed that this is because the two fields of research operate on different levels of analysis, one at the individual level and the other at the social or institutional level. A challenge for future research is to connect these two levels of analysis. Research on the social epidemiology of mental health and illness can inform organizations at all levels about the costs of untreated mental disorders to organizations and society in general.
As Wheaton (1999) observed, the social stress model requires considerable new development. This research paper has pointed out a number of methodological difficulties in measuring stressor exposure and the lack of fit between the most widely used measures of stressor exposure and the newly emerging life course perspective. Another advance would come through more detailed studies of how stressors are distributed in the population at large. Does the uneven distribution of stressors in the population “explain” the negative mental health outcomes for some groups? More research is needed in this area, ideally from the life course perspective, using longitudinal samples.
There is also a need for more research on the social distribution of resources that mitigate the impact of environmental challenges and stresses. Reviews of research on social support and social integration (e.g., Berkman and Glass 2000; Cohen et al. 2000; Pillemer et al. 2000) point out deficiencies in current measures of these resources. Do minority groups gain extra protection by asserting their identity and uniqueness? What is the social distribution of protective social resources? Do differences in distribution explain group differences in mental health?
The sociology of mental health is faced with a new challenge from the field of neuroscience. This research tends to be favored by federal funding agencies because of beliefs that neuroscience can lead to the discovery of new cures or therapeutic approaches to mental disorders. Neuroscience and its measurement equipment such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and cortisol sampling have the cachet of basic or “bench” science, while the observational and epidemiological approach of sociology is being portrayed as lower-quality science. However, the rise of neuroscience in research on mental disorders does not necessarily mean that social causes are irrelevant. The power of the new neuroscience of mental disorders is that it assumes there is an interaction between social factors and biological processes (McEwen 2002).
Yet there are serious impediments to the integration of sociological and biological research. One formidable impediment in sociology is the assumption that the biological perspective would reduce the entire stress process to individual differences in physical response, thus making environmental causation moot. Another impediment is that sociologists do not yet fully appreciate how much the biological approach to stress already incorporates measures of social context and stressors in studying adjustment to stressful events and situations (Singer and Ryff 1999). Sociologists (e.g., Pearlin et al. 1981) have long pointed out that the process of adjusting to stressors is a critical component of sociological and social psychological theories of the stress process (Thoits 1995). Thus, another challenge to sociologists of mental health is to incorporate techniques and measures that will powerfully represent the social context in multidisciplinary studies of mental health and mental disorders.
Bibliography:
- Almeida, David M. and Ronald C. Kessler. 1998. “Everyday Stressors and Gender Differences in Daily Distress.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 75:670–80.
- Almeida, David M., Elaine Wethington, and Ronald C. Kessler. 2002. “The Daily Inventory of Stressful Events (DISE): An Investigator-Based Approach for Measuring Daily Stressors.” Assessment 9:41–55.
- American Psychiatric Association. 2000. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. Text revision. DSM-IV-TR. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
- Aneshensel, Carol and Jo C. Phelan. 1999. “The Sociology of Mental Health: Surveying the Field.” Pp. 3–18 in Handbook of the Sociology of Mental Health, edited by C. Aneshensel and J. C. Phelan. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Press.
- Berkman, Lisa F. and Thomas Glass. 2000. “Social Integration, Social Networks, Social Support and Health.” Pp. 137–73 in Social Epidemiology, edited by L. F. Berkman and I. Kawachi. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press.
- Breslau, Jonathan, Kenneth S. Kendler, Maxwell Su, Sergio Gaxiola-Aguilar, and Ronald C. Kessler. 2005. “Lifetime Risk and Persistence of Psychiatric Disorders across Ethnic Groups in the United States.” Psychological Medicine 35:317–27.
- Bronfenbrenner, Urie. 1979. The Ecology of Human Development: Experiments by Nature and Design. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Brown, George W. and Tirril O. Harris. 1978. Social Origins of Depression. New York: Free Press.
- Brown, George W. and Tirril O. Harris. 1989. Life Events and Illness. New York: Guilford Press.
- Clausen, John A. 1956. Sociology and the Field of Mental Health. New York: Russell Sage.
- Cockerham, William C. 2005. The Sociology of Mental Disorders. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Cohen, Sheldon, Lynn G. Underwood, and Benjamin H. Gottlieb. 2000. Social Support Measurement and Intervention: A Guide for Health and Social Scientists. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Dickerson, Susan and Margaret Kemeny. 2004. “Acute Stressors and Cortisol Responses: A Theoretical Integration and Synthesis of Laboratory Research.” Psychological Bulletin 130:355–91.
- Dohrenwend, Barbara S., Arthur Askenasy, Laurie Krasnoff, and Bruce P. Dohrenwend. 1978. “An Exemplification of a Method of Scaling Life Events: The PERI Life Events Scale.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 19:205–29.
- Durkheim, Emile. 1951. Suicide. New York: Free Press.
- Eaton, William W. 2001. The Sociology of Mental Disorders. Westport, CT: Praeger.
- Elder, Glen H. 1974. Children of the Great Depression: Social Change and Life Experiences. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Elder, Glen H., Linda K. George, and Michael J. Shanahan. 1996. “Psychosocial Stress over the Life Course.” Pp. 247–92 in Psychosocial Stress: Perspectives on Structure, Theory, Life Course, and Methods, edited by H. B. Kaplan. Orlando, FL: Academic Press.
- Faris, Robert E. and H. Warren Dunham. 1939. Mental Disorders in Urban Areas. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Folkman, Susan and Judith T. Moskowitz. 2004. “Coping: Pitfalls and Promise.” Annual Review of Psychology 55:745–74.
- Forthofer, Melinda S., Ronald C. Kessler, Amber L. Story, and Ian H. Gotlib. 1996. “The Effects of Psychiatric Disorders on the Probability and Timing of First Marriages.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 44:332–52.
- Freedman, Deborah, Arland Thornton, Donald Camburn, Duane Alwin, and Linda Young-DeMarco. 1988. “The Life History Calendar: A Technique for Collecting Retrospective Data.” Sociological Methodology 18:37–68.
- Gallagher, Bernard J. 2002. The Sociology of Mental Illness. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- George, Linda K. 1999. “Life Course Perspectives on Mental Health.” Pp. 565–84 in Handbook of the Sociology of Mental Health, edited by C. Aneshensel and J. C. Phelan. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum.
- Heckhausen, Jutta and Richard Schulz. 1995. “A Life-Span Theory of Control.” Psychological Review 102:284–304.
- Hollingshead, August B. and Frederick C. Redlich. 1958. Social Class and Mental Illness. New York: Wiley.
- Holmes, Thomas H. and Robert H. Rahe. 1967. “The Social Readjustment Rating Scale.” Journal of Psychosomatic Research 11:213–18.
- Horwitz, Allan V. and Teresa L. Scheid. 1999. “Approaches to Mental Health and Illness: Conflicting Definitions and Emphases.” Pp. 1–11 in A Handbook for the Study of Mental Illness: Social Contexts, Theories and Systems, edited by A. V. Horwitz and T. L. Scheid. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
- Kessler, Ronald C. 2002. “The Categorical versus Dimensional Assessment Controversy in the Sociology of Mental Illness.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 43:171–88.
- Kessler, Ronald C., Wait Tat Chiu, Olga Demler, and Ellen E. Walters. 2005. “Prevalence, Severity, and Comorbidity of 12-Month DSM-IV Disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication.” Archives of General Psychiatry 62:617–27.
- Kessler, Ronald C., Katherine A. McGonagle, Shanyang Zhao, Christopher B. Nelson, Michael Hughes, Suzann Eshleman, et al. 1994. “Lifetime and 12-month Prevalence of DSM-IIIR Psychiatric Disorders in the United States: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey.” Archives of General Psychiatry 51:8–19.
- Kessler, Ronald C., Kristin D. Mickelson, and David R. Williams. 1999. “The Prevalence, Distribution, and Mental Health Correlates of Perceived Discrimination in the United States.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 40:208–30.
- Kessler, Ronald C. and Elaine Wethington. 1991. “The Reliability of Life Event Reports in a Community Survey.” Psychological Medicine 21:723–38.
- Kessler, Ronald C. and Shanyang Zhao. 1999. “Overview of Descriptive Epidemiology of Mental Disorders.” Pp. 127–50 in Handbook of the Sociology of Mental Health, edited by C. Aneshensel and J. C. Phelan. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Press.
- Keyes, Corey. 2002. “The Mental Health Continuum: From Languishing to Flourishing in Life.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 43: 207–22.
- Kirk, Stuart. 1999. “Instituting Madness: The Evolution of a Federal Agency.” Pp. 539–62 in Handbook of the Sociology of Mental Health, edited by C. Aneshensel and J. C. Phelan. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Press.
- Lazarus, Richard S. 1999. Stress and Emotion. New York: Springer.
- Lazarus, Richard S. and Susan Folkman. 1984. Stress, Appraisal, and Coping. New York: Springer.
- Leighton, Dorothea C., John S. Harding, D. B. Macklin, A. M. McMillan, and Alexander H. Leighton. 1963. The Character of Danger: Psychiatric Symptoms in Selected Communities. New York: Basic Books.
- Massey, Douglas S. 2002. “Emotion and the History of Human Society.” American Sociological Review 67:1–29.
- McEwen, Bruce S. 2002. The End of Stress as We Know It. Washington, DC: Joseph Henry Press.
- McEwen, Bruce S. and Eliot Stellar. 1993. “Stress and the Individual.” Archives of Internal Medicine 153:2093–101.
- McLeod, Jane D. and Karen Kaiser. 2004. “Childhood Emotional and Behavioral Problems and Educational Attainment.” American Sociological Review 69:636–58.
- McLeod, Jane D. and James M. Nonnemaker. 2000. “Poverty and Child Emotional and Behavioral Problems: Racial/Ethnic Differences in Processes and Effects.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 41:137–61.
- Merton, Robert. 1938. “Social Structure and Anomie.” American Sociological Review 3:672–82.
- Miech, Richard A., Avshalom Caspi, Terrie E. Moffitt, Bradley R. Entner Wright, and Phil A. Silva. 1999. “Low Socioeconomic Status and Mental Disorders: A Longitudinal Study of Selection and Causation during Young Adulthood.” American Journal of Sociology 104:1096–131.
- Mirowsky, John and Catherine E. Ross. 2002. “Measurement for a Human Science.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 43:152–70.
- Mirowsky, John and Catherine E. Ross. 2004. Social Causes of Psychological Distress. 2d ed. Hawthorne, NY: Aldine de Gruyter.
- Narrow,William E., Donald S. Rae, Lee N. Robins, and Darrel A. Regier. 2002. “Revised Prevalence of Mental Disorders in the United States.” Archives of General Psychiatry 59:115–23.
- National Institutes of Health. 2004. Sociobehavioral Data Analysis and Archiving in Aging. PA-04–123. July 7.
- National Research Council. 2004. Clinical Perspectives on Racial and Ethnic Differences in Health in Late Life. Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
- Neighbors, Harold W., Steven J. Trierweiler, Briggett Ford, and Jordan R. Muroff. 2003. “Racial Differences in the Diagnostic Statistical Manual Diagnosis Using a Semistructured Instrument: The Importance of Clinical Judgment in the Diagnosis of African Americans.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 44:237–56.
- Pearlin, Leonard I., Elizabeth G. Menaghan, Morton Lieberman, and Joseph T. Mullan. 1981. “The Stress Process.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 22:337–56.
- Pearlin, Leonard I., Scott Schieman, Elena M. Fazio, and Stephen C. Meersman. 2005. “Stress, Health, and the Life Course: Some Conceptual Perspectives.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 46:205–19.
- Pearlin, Leonard and Carmi Schooler. 1978. “The Structure of Coping.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 19:2–21.
- Phelan, Jo, Bruce G. Link, Ann Stueve, and Bernice A. Pescosolido. 2000. “Public Conceptions of Mental Illness in 1950 and 1996: What Is Mental Illness and Is It to Be Feared?” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 41:188–207.
- Pillemer, Karl A., Phyllis Moen, Elaine Wethington, and Nina Glasgow. 2000. Social Integration in the Second Half of Life. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press.
- Radloff, Lenore S. 1977. “The CES-D Scale: A Self-Report Depression Scale for Research in the General Population.” Applied Psychology Measurement 1:385–401.
- Repetti, Rena, Shelley Taylor, and Teresa Seeman. 2002. “Risky Families: Family Social Environments and the Mental and Physical Health of Offspring.” Psychological Bulletin 128:330–66.
- Robins, Lee N. and Darrel A. Regier. 1991. Psychiatric Disorders in America: The Epidemiologic Catchment Area Study. New York: Free Press.
- Rosenfield, Sarah. 1999. “Gender and Mental Health: Do Women Have More Psychopathology, Men More, or Both the Same (and Why)?” Pp. 348–60 in A Handbook for the Study of Mental Health: Social Contexts, Theories, and Systems, edited by A. V. Horwitz and T. L Scheid. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
- Segerstrom, Suzanne C. and Gregory E. Miller. 2004. “Psychological Stress and the Human Immune System: A Meta-Analytic Study of 30 Years of Inquiry.” Psychological Bulletin 130:601–30.
- Selye, Hans. 1956. The Stress of Life. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Shanahan, Michael J. and Scott M. Hofer. 2005. “Social Context in Gene-environment Interactions: Retrospect and Prospect.” Journals of Gerontology 60B:65–76.
- Shanahan, Michael J., Scott M. Hofer, and Lilly Shanahan. 2003. “Biological Models of Behavior and the Life Course.” Pp. 599–622 in Handbook of the Life Course, edited by J. T. Mortimer and M. J. Shanahan. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Press.
- Singer, Burton H. and Carol D. Ryff. 1999. “Hierarchies of Life Histories and Associated Health Risks.” Pp. 96–118 in Socioeconomic Status and Health in Industrialized Nations: Social, Psychological, and Biological Pathways, Vol. 896, edited by N. Adler, M. Marmot, B. McEwen, and J. Stewart. New York: New York Academy of Sciences.
- Singer, Burton H., Carol D. Ryff, Deborah Carr, and William J. Magee. 1998. “Linking Life Histories and Mental Health: A Person-Centered Strategy.” Pp. 1–51 in Sociological Methodology, edited by A. Raftery. Washington, DC: American Sociological Association.
- Srole, Leo, Thomas S. Langer, Stanley T. Michael, Marvin K. Opler, and Thomas A. C. Rennie. 1962. Mental Health in the Metropolis: The Midtown Manhattan Study. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Thoits, Peggy A. 1995. “Stress, Coping and Social Support Processes: Where Are We? What Next?” Journal of Health and Social Behavior (extra issue):53–79.
- Thoits, Peggy A. 1999. “Sociological Approaches to Mental Illness.” Pp. 121–38 in A Handbook for the Study of Mental Illness, edited by A. V. Horwitz and T. L. Scheid. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
- Turner, R. Jay, Ann M. Sorenson, and J. Blake Turner. 2000. “Social Contingencies in Mental Health: A Seven-Year Follow-Up Study of Teenage Mothers.” Journal of Marriage and the Family 62:777–91.
- Turner, R. Jay and J. Blake Turner. 1999. “Social Integration and Support.” Pp. 301–319 in Handbook of the Sociology of Mental Health, edited by C. Aneshensel & J. C. Phelan. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum.
- Turner, R. Jay and Blair Wheaton. 1995. “Checklist Measurement of Stressful Life Events.” Pp. 29–57 in Measuring Stress: A Guide for Health and Social Scientists, edited by S. Cohen, R. C. Kessler, and L. U. Gordon. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Umberson, Debra and Kristi Williams. 1999. “Family Status and Mental Health.” Pp. 225–54 in Handbook of the Sociology of Mental Health, edited by C. Aneshensel and J. C. Phelan. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum.
- Veroff, Joseph, Elizabeth Douvan, and Richard A. Kulka. 1981. The Inner American: A Self-Portrait from 1957–1976. New York: Basic Books.
- Wakefield, Jerome C. 1999. “The Measurement of Mental Disorder.” Pp. 29–57 in A Handbook for the Study of Mental Illness, edited by A. V. Horwitz and T. L. Scheid. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
- Wethington, Elaine, George W. Brown, and Ronald C. Kessler. 1995. “Interview Measurement of Stressful Life Events.” Pp. 59–79 in Measuring Stress: A Guide for Health and Social Scientists, edited by S. Cohen, R. C. Kessler, and L. U. Gordon. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Wethington, Elaine and Ronald C. Kessler. 1986. “Perceived Support, Received Support, and Adjustment to Stressful Life Events.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 27:78–89.
- Wheaton, Blair. 1999. “Social Stress.” Pp. 277–300 in Handbook of the Sociology of Mental Health, edited by C. Aneshensel and J. C. Phelan. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Press.
- Wheaton, Blair and Philippa Clarke. 2003. “Space Meets Time: Integrating Temporal and Contextual Influences on Mental Health in Early Adulthood.” American Sociological Review 68:680–706.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 24 October 2019
A scoping review of the literature on the current mental health status of physicians and physicians-in-training in North America
- Mara Mihailescu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6878-1024 1 &
- Elena Neiterman 2
BMC Public Health volume 19 , Article number: 1363 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
26k Accesses
58 Citations
11 Altmetric
Metrics details
This scoping review summarizes the existing literature regarding the mental health of physicians and physicians-in-training and explores what types of mental health concerns are discussed in the literature, what is their prevalence among physicians, what are the causes of mental health concerns in physicians, what effects mental health concerns have on physicians and their patients, what interventions can be used to address them, and what are the barriers to seeking and providing care for physicians. This review aims to improve the understanding of physicians’ mental health, identify gaps in research, and propose evidence-based solutions.
A scoping review of the literature was conducted using Arksey and O’Malley’s framework, which examined peer-reviewed articles published in English during 2008–2018 with a focus on North America. Data were summarized quantitatively and thematically.
A total of 91 articles meeting eligibility criteria were reviewed. Most of the literature was specific to burnout ( n = 69), followed by depression and suicidal ideation ( n = 28), psychological harm and distress ( n = 9), wellbeing and wellness ( n = 8), and general mental health ( n = 3). The literature had a strong focus on interventions, but had less to say about barriers for seeking help and the effects of mental health concerns among physicians on patient care.
Conclusions
More research is needed to examine a broader variety of mental health concerns in physicians and to explore barriers to seeking care. The implication of poor physician mental health on patients should also be examined more closely. Finally, the reviewed literature lacks intersectional and longitudinal studies, as well as evaluations of interventions offered to improve mental wellbeing of physicians.
Peer Review reports
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines mental health as “a state of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her community.” [ 41 ] One in four people worldwide are affected by mental health concerns [ 40 ]. Physicians are particularly vulnerable to experiencing mental illness due to the nature of their work, which is often stressful and characterized by shift work, irregular work hours, and a high pressure environment [ 1 , 21 , 31 ]. In North America, many physicians work in private practices with no access to formal institutional supports, which can result in higher instances of social isolation [ 13 , 27 ]. The literature on physicians’ mental health is growing, partly due to general concerns about mental wellbeing of health care workers and partly due to recognition that health care workers globally are dissatisfied with their work, which results in burnout and attrition from the workforce [ 31 , 34 ]. As a consequence, more efforts have been made globally to improve physicians’ mental health and wellness, which is known as “The Quadruple Aim.” [ 34 ] While the literature on mental health is flourishing, however, it has not been systematically summarized. This makes it challenging to identify what is being done to improve physicians’ wellbeing and which solutions are particularly promising [ 7 , 31 , 33 , 37 , 38 ]. The goal of our paper is to address this gap.
This paper explores what is known from the existing peer-reviewed literature about the mental health status of physicians and physicians-in-training in North America. Specifically, we examine (1) what types of mental health concerns among physicians are commonly discussed in the literature; (2) what are the reported causes of mental health concerns in physicians; (3) what are the effects that mental health concerns may have on physicians and their patients; (4) what solutions are proposed to improve mental health of physicians; and (5) what are the barriers to seeking and providing care to physicians with mental health concerns. Conducting this scoping review, our goal is to summarize the existing research, identifying the need for a subsequent systematic review of the literature in one or more areas under the study. We also hope to identify evidence-based interventions that can be utilized to improve physicians’ mental wellbeing and to suggest directions for future research [ 2 ]. Evidence-based interventions might have a positive impact on physicians and improve the quality of patient care they provide.
A scoping review of the academic literature on the mental health of physicians and physicians-in-training in North America was conducted using Arksey and O’Malley’s [ 2 ] methodological framework. Our review objectives and broad focus, including the general questions posed to conduct the review, lend themselves to a scoping review approach, which is suitable for the analysis of a broader range of study designs and methodologies [ 2 ]. Our goal was to map the existing research on this topic and identify knowledge gaps, without making any prior assumptions about the literature’s scope, range, and key findings [ 29 ].
Stage 1: identify the research question
Following the guidelines for scoping reviews [ 2 ], we developed a broad research question for our literature search, asking what does the academic literature tell about mental health issues among physicians, residents, and medical students in North America ? Burnout and other mental health concerns often begin in medical training and continue to worsen throughout the years of practice [ 31 ]. Recognizing that the study and practice of medicine plays a role in the emergence of mental health concerns, we focus on practicing physicians – general practitioners, specialists, and surgeons – and those who are still in training – residents and medical students. We narrowed down the focus of inquiry by asking the following sub-questions:
What types of mental health concerns among physicians are commonly discussed in the literature?
What are the reported causes of mental health problems in physicians and what solutions are available to improve the mental wellbeing of physicians?
What are the barriers to seeking and providing care to physicians suffering from mental health problems?
Stage 2: identify the relevant studies
We included in our review empirical papers published during January 2008–January 2018 in peer-reviewed journals. Our exclusive focus on peer-reviewed and empirical literature reflected our goal to develop an evidence-based platform for understanding mental health concerns in physicians. Since our focus was on prevalence of mental health concerns and promising practices available to physicians in North America, we excluded articles that were more than 10 years old, suspecting that they might be too outdated for our research interest. We also excluded papers that were not in English or outside the region of interest. Using combinations of keywords developed in consultation with a professional librarian (See Table 1 ), we searched databases PUBMed, SCOPUS, CINAHL, and PsychNET. We also screened reference lists of the papers that came up in our original search to ensure that we did not miss any relevant literature.
Stage 3: literature selection
Publications were imported into a reference manager and screened for eligibility. During initial abstract screening, 146 records were excluded for being out of scope, 75 records were excluded for being outside the region of interest, and 4 papers were excluded because they could not be retrieved. The remaining 91 papers were included into the review. Figure 1 summarizes the literature search and selection.
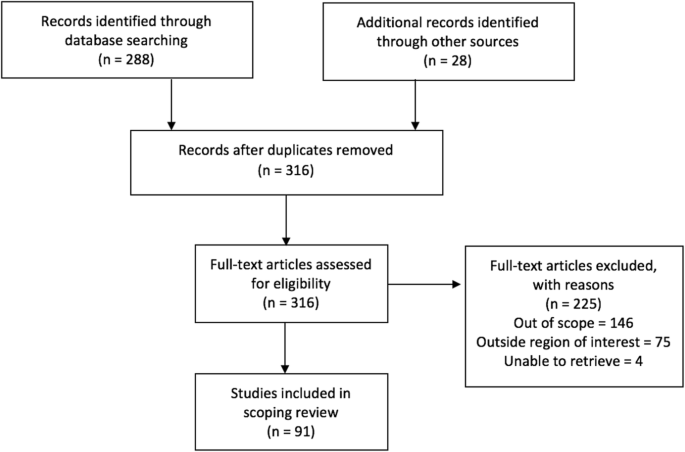
PRISMA Flow Diagram
Stage 4: charting the data
A literature extraction tool was created in Microsoft Excel to record the author, date of publication, location, level of training, type of article (empirical, report, commentary), and topic. Both authors coded the data inductively, first independently reading five articles and generating themes from the data, then discussing our coding and developing a coding scheme that was subsequently applied to ten more papers. We then refined and finalized the coding scheme and used it to code the rest of the data. When faced with disagreements on narrowing down the themes, we discussed our reasoning and reached consensus.
Stage 5: collating, summarizing, and reporting the results
The data was summarized by frequency and type of publication, mental health topics, and level of training. The themes inductively derived from the data included (1) description of mental health concerns affecting physicians and physicians-in-training; (2) prevalence of mental health concerns among this population; (3) possible causes that can explain the emergence of mental health concerns; (4) solutions or interventions proposed to address mental health concerns; (5) effects of mental health concerns on physicians and on patient outcomes; and (6) barriers for seeking and providing help to physicians afflicted with mental health concerns. Each paper was coded based on its relevance to major theme(s) and, if warranted, secondary focus. Therefore, one paper could have been coded in more than one category. Upon analysis, we identified the gaps in the literature.
Characteristics of included literature
The initial search yielded 316 records of which 91 publications underwent full-text review and were included in our scoping review. Our analysis revealed that the publications appear to follow a trend of increase over the course of the last decade reflecting the growing interest in physicians’ mental health. More than half of the literature was published in the last 4 years included in the review, from 2014 to 2018 ( n = 55), with most publications in 2016 ( n = 18) (Fig. 2 ). The majority of papers ( n = 36) focused on practicing physicians, followed by papers on residents ( n = 22), medical students ( n = 21), and those discussing medical professionals with different level of training ( n = 12). The types of publications were mostly empirical ( n = 71), of which 46 papers were quantitative. Furthermore, the vast majority of papers focused on the United States of America (USA) ( n = 83), with less than 9% focusing on Canada ( n = 8). The frequency of identified themes in the literature is broken down into prevalence of mental health concerns ( n = 15), causes of mental health concerns ( n = 18), effects of mental health concerns on physicians and patients ( n = 12), solutions and interventions for mental health concerns ( n = 46), and barriers to seeking and providing care for mental health concerns ( n = 4) (Fig. 3 ).
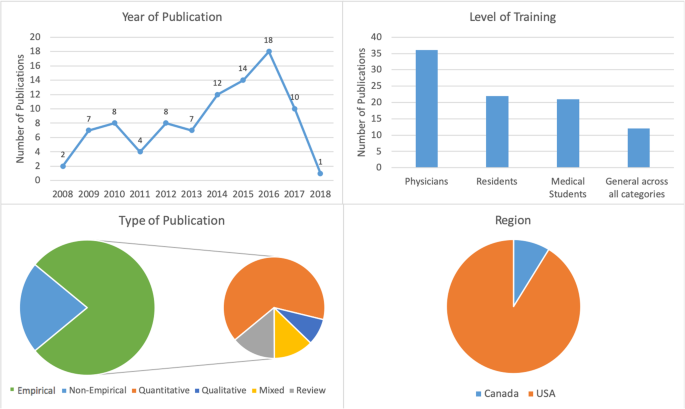
Number of sources by characteristics of included literature
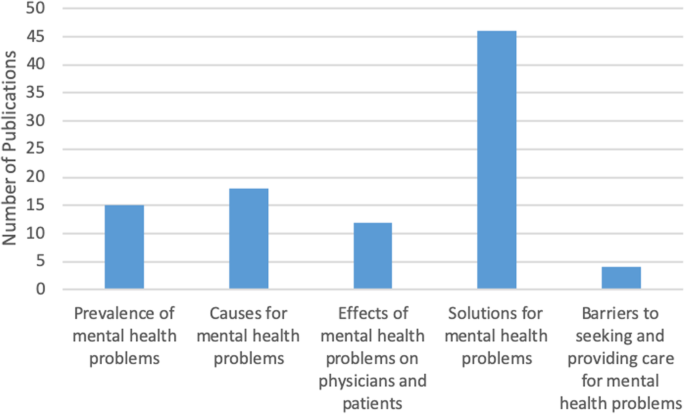
Frequency of themes in literature ( n = 91)
Mental health concerns and their prevalence in the literature
In this thematic category ( n = 15), we coded the papers discussing the prevalence of specific mental health concerns among physicians and those comparing physicians’ mental health to that of the general population. Most papers focused on burnout and stress ( n = 69), which was followed by depression and suicidal ideation ( n = 28), psychological harm and distress ( n = 9), wellbeing and wellness ( n = 8), and general mental health ( n = 3) (Fig. 4 ). The literature also identified that, on average, burnout and mental health concerns affect 30–60% of all physicians and residents [ 4 , 5 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 25 , 26 ].
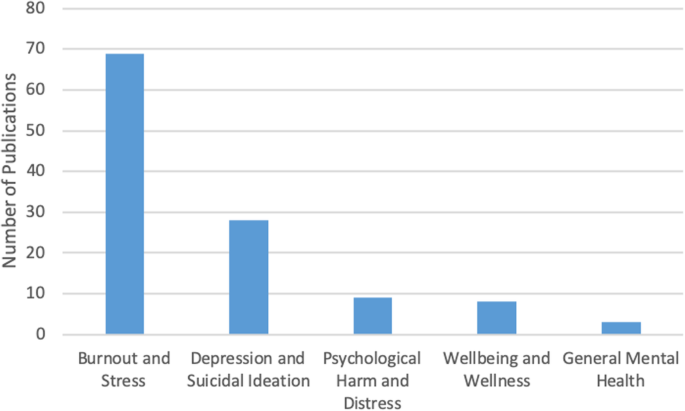
Number of sources by mental health topic discussed ( n = 91)
There was some overlap between the papers discussing burnout, depression, and suicidal ideation, suggesting that work-related stress may lead to the emergence of more serious mental health problems [ 3 , 12 , 21 ], as well as addiction and substance abuse [ 22 , 27 ]. Residency training was shown to produce the highest rates of burnout [ 4 , 8 , 19 ].
Causes of mental health concerns
Papers discussing the causes of mental health concerns in physicians formed the second largest thematic category ( n = 18). Unbalanced schedules and increasing administrative work were defined as key factors in producing poor mental health among physicians [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 13 , 15 , 27 ]. Some papers also suggested that the nature of the medical profession itself – competitive culture and prioritizing others – can lead to the emergence of mental health concerns [ 23 , 27 ]. Indeed, focus on qualities such as rigidity, perfectionism, and excessive devotion to work during the admission into medical programs fosters the selection of students who may be particularly vulnerable to mental illness in the future [ 21 , 24 ]. The third cluster of factors affecting mental health stemmed from structural issues, such as pressure from the government and insurance, fragmentation of care, and budget cuts [ 13 , 15 , 18 ]. Work overload, lack of control over work environment, lack of balance between effort and reward, poor sense of community among staff, lack of fairness and transparency by decision makers, and dissonance between one’s personal values and work tasks are the key causes for mental health concerns among physicians [ 20 ]. Govardhan et al. conceptualized causes for mental illness as having a cyclical nature - depression leads to burnout and depersonalization, which leads to patient dissatisfaction, causing job dissatisfaction and more depression [ 19 ].
Effects of mental health concerns on physicians and patients
A relatively small proportion of papers (13%) discussed the effects of mental health concerns on physicians and patients. The literature prioritized the direct effect of mental health on physicians ( n = 11) with only one paper focusing solely on the indirect effects physicians’ mental health may have on patients. Poor mental health in physicians was linked to decreased mental and physical health [ 3 , 14 , 15 ]. In addition, mental health concerns in physicians were associated with reduction in work hours and the number of patients seen, decrease in job satisfaction, early retirement, and problems in personal life [ 3 , 5 , 15 ]. Lu et al. found that poor mental health in physicians may result in increased medical errors and the provision of suboptimal care [ 25 ]. Thus physicians’ mental wellbeing is linked to the quality of care provided to patients [ 3 , 4 , 5 , 10 , 17 ].
Solutions and interventions
In this largest thematic category ( n = 46) we coded the literature that offered solutions for improving mental health among physicians. We identified four major levels of interventions suggested in the literature. A sizeable proportion of literature discussed the interventions that can be broadly categorized as primary prevention of mental illness. These papers proposed to increase awareness of physicians’ mental health and to develop strategies that can help to prevent burnout from occurring in the first place [ 4 , 12 ]. Some literature also suggested programs that can help to increase resilience among physicians to withstand stress and burnout [ 9 , 20 , 27 ]. We considered the papers referring to the strategies targeting physicians currently suffering from poor mental health as tertiary prevention . This literature offered insights about mindfulness-based training and similar wellness programs that can increase self-awareness [ 16 , 18 , 27 ], as well as programs aiming to improve mental wellbeing by focusing on physical health [ 17 ].
While the aforementioned interventions target individual physicians, some literature proposed workplace/institutional interventions with primary focus on changing workplace policies and organizational culture [ 4 , 13 , 23 , 25 ]. Reducing hours spent at work and paperwork demands or developing guidelines for how long each patient is seen have been identified by some researchers as useful strategies for improving mental health [ 6 , 11 , 17 ]. Offering access to mental health services outside of one’s place of employment or training could reduce the fear of stigmatization at the workplace [ 5 , 12 ]. The proposals for cultural shift in medicine were mainly focused on promoting a less competitive culture, changing power dynamics between physicians and physicians-in-training, and improving wellbeing among medical students and residents. The literature also proposed that the medical profession needs to put more emphasis on supporting trainees, eliminating harassment, and building strong leadership [ 23 ]. Changing curriculum for medical students was considered a necessary step for the cultural shift [ 20 ]. Finally, while we only reviewed one paper that directly dealt with the governmental level of prevention, we felt that it necessitated its own sub-thematic category because it identified the link between government policy, such as health care reforms and budget cuts, and the services and care physicians can provide to their patients [ 13 ].
Barriers to seeking and providing care
Only four papers were summarized in this thematic category that explored what the literature says about barriers for seeking and providing care for physicians suffering from mental health concerns. Based on our analysis, we identified two levels of factors that can impact access to mental health care among physicians and physicians-in-training.
Individual level barriers stem from intrinsic barriers that individual physicians may experience, such as minimizing the illness [ 21 ], refusing to seek help or take part in wellness programs [ 14 ], and promoting the culture of stoicism [ 27 ] among physicians. Another barrier is stigma associated with having a mental illness. Although stigma might be experienced personally, literature suggests that acknowledging the existence of mental health concerns may have negative consequences for physicians, including loss of medical license, hospital privileges, or professional advancement [ 10 , 21 , 27 ].
Structural barriers refer to the lack of formal support for mental wellbeing [ 3 ], poor access to counselling [ 6 ], lack of promotion of available wellness programs [ 10 ], and cost of treatment. Lack of research that tests the efficacy of programs and interventions aiming to improve mental health of physicians makes it challenging to develop evidence-based programs that can be implemented at a wider scale [ 5 , 11 , 12 , 18 , 20 ].
Our analysis of the existing literature on mental health concerns in physicians and physicians-in-training in North America generated five thematic categories. Over half of the reviewed papers focused on proposing solutions, but only a few described programs that were empirically tested and proven to work. Less common were papers discussing causes for deterioration of mental health in physicians (20%) and prevalence of mental illness (16%). The literature on the effects of mental health concerns on physicians and patients (13%) focused predominantly on physicians with only a few linking physicians’ poor mental health to medical errors and decreased patient satisfaction [ 3 , 4 , 16 , 24 ]. We found that the focus on barriers for seeking and receiving help for mental health concerns (4%) was least prevalent. The topic of burnout dominated the literature (76%). It seems that the nature of physicians’ work fosters the environment that causes poor mental health [ 1 , 21 , 31 ].
While emphasis on burnout is certainly warranted, it might take away the attention paid to other mental health concerns that carry more stigma, such as depression or anxiety. Establishing a more explicit focus on other mental health concerns might promote awareness of these problems in physicians and reduce the fear such diagnosis may have for doctors’ job security [ 10 ]. On the other hand, utilizing the popularity and non-stigmatizing image of “burnout” might be instrumental in developing interventions promoting mental wellbeing among a broad range of physicians and physicians-in-training.
Table 2 summarizes the key findings from the reviewed literature that are important for our understanding of physician mental health. In order to explicitly summarize the gaps in the literature, we mapped them alongside the areas that have been relatively well studied. We found that although non-empirical papers discussed physicians’ mental wellbeing broadly, most empirical papers focused on medical specialty (e.g. neurosurgeons, family medicine, etc.) [ 4 , 8 , 15 , 19 , 25 , 28 , 35 , 36 ]. Exclusive focus on professional specialty is justified if it features a unique context for generation of mental health concerns, but it limits the ability to generalize the findings to a broader population of physicians. Also, while some papers examined the impact of gender on mental health [ 7 , 32 , 39 ], only one paper considered ethnicity as a potential factor for mental health concerns and found no association [ 4 ]. Given that mental health in the general population varies by gender, ethnicity, age, and sexual orientation, it would be prudent to examine mental health among physicians using an intersectional analysis [ 30 , 32 , 39 ]. Finally, of the empirical studies we reviewed, all but one had a cross-sectional design. Longitudinal design might offer a better understanding of the emergence and development of mental health concerns in physicians and tailor interventions to different stages of professional career. Additionally, it could provide an opportunity to evaluate programs’ and policies’ effectiveness in improving physicians’ mental health. This would also help to address the gap that we identified in the literature – an overarching focus on proposing solutions with little demonstrated evidence they actually work.
This review has several limitations. First, our focus on academic literature may have resulted in overlooking the papers that are not peer-reviewed but may provide interesting solutions to physician mental health concerns. It is possible that grey literature – reports and analyses published by government and professional organizations – offers possible solutions that we did not include in our analysis or offers a different view on physicians’ mental health. Additionally, older papers and papers not published in English may have information or interesting solutions that we did not include in our review. Second, although our findings suggest that the theme of burnout dominated the literature, this may be the result of the search criteria we employed. Third, following the scoping review methodology [ 2 ], we did not assess the quality of the papers, focusing instead on the overview of the literature. Finally, our research was restricted to North America, specifically Canada and the USA. We excluded Mexico because we believed that compared to the context of medical practice in Canada and the USA, which have some similarities, the work experiences of Mexican physicians might be different and the proposed solutions might not be readily applicable to the context of practice in Canada and the USA. However, it is important to note that differences in organization of medical practice in Canada and the USA do exist, as do differences across and within provinces in Canada and the USA. A comparative analysis can shed light on how the structure and organization of medical practice shapes the emergence of mental health concerns.
The scoping review we conducted contributes to the existing research on mental wellbeing of American and Canadian physicians by summarizing key knowledge areas and identifying key gaps and directions for future research. While the papers reviewed in our analysis focused on North America, we believe that they might be applicable to the global medical workforce. Identifying key gaps in our knowledge, we are calling for further research on these topics, including examination of medical training curricula and its impact on mental wellbeing of medical students and residents, research on common mental health concerns such as depression or anxiety, studies utilizing intersectional and longitudinal approaches, and program evaluations assessing the effectiveness of interventions aiming to improve mental wellbeing of physicians. Focus on the effect physicians’ mental health may have on the quality of care provided to patients might facilitate support from government and policy makers. We believe that large-scale interventions that are proven to work effectively can utilize an upstream approach for improving the mental health of physicians and physicians-in-training.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
United States of America
World Health Organization
Ahmed N, Devitt KS, Keshet I, Spicer J, Imrie K, Feldman L, et al. A systematic review of the effects of resident duty hour restrictions in surgery: impact on resident wellness, training, and patient outcomes. Ann Surg. 2014;259(6):1041–53.
Article Google Scholar
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Atallah F, McCalla S, Karakash S, Minkoff H. Please put on your own oxygen mask before assisting others: a call to arms to battle burnout. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215(6):731.e1.
Baer TE, Feraco AM, Tuysuzoglu Sagalowsky S, Williams D, Litman HJ, Vinci RJ. Pediatric resident burnout and attitudes toward patients. Pediatrics. 2017;139(3):e20162163. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-2163 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Blais R, Safianyk C, Magnan A, Lapierre A. Physician, heal thyself: survey of users of the Quebec physicians health program. Can Fam Physician. 2010;56(10):e383–9.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Brennan J, McGrady A. Designing and implementing a resiliency program for family medicine residents. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2015;50(1):104–14.
Cass I, Duska LR, Blank SV, Cheng G, NC dP, Frederick PJ, et al. Stress and burnout among gynecologic oncologists: a Society of Gynecologic Oncology Evidence-based Review and Recommendations. Gynecol Oncol. 2016;143(2):421–7.
Chan AM, Cuevas ST, Jenkins J 2nd. Burnout among osteopathic residents: a cross-sectional analysis. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2016;116(2):100–5.
Chaukos D, Chad-Friedman E, Mehta DH, Byerly L, Celik A, McCoy TH Jr, et al. Risk and resilience factors associated with resident burnout. Acad Psychiatry. 2017;41(2):189–94.
Compton MT, Frank E. Mental health concerns among Canadian physicians: results from the 2007-2008 Canadian physician health study. Compr Psychiatry. 2011;52(5):542–7.
Cunningham C, Preventing MD. Burnout. Trustee. 2016;69(2):6–7 1.
PubMed Google Scholar
Daskivich TJ, Jardine DA, Tseng J, Correa R, Stagg BC, Jacob KM, et al. Promotion of wellness and mental health awareness among physicians in training: perspective of a national, multispecialty panel of residents and fellows. J Grad Med Educ. 2015;7(1):143–7.
Dyrbye LN, Shanafelt TD. Physician burnout: a potential threat to successful health care reform. JAMA. 2011;305(19):2009–10.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Epstein RM, Krasner MS. Physician resilience: what it means, why it matters, and how to promote it. Acad Med. 2013;88(3):301–3.
Evans RW, Ghosh K. A survey of headache medicine specialists on career satisfaction and burnout. Headache. 2015;55(10):1448–57.
Fahrenkopf AM, Sectish TC, Barger LK, Sharek PJ, Lewin D, Chiang VW, et al. Rates of medication errors among depressed and burnt out residents: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2008;336(7642):488–91.
Fargen KM, Spiotta AM, Turner RD, Patel S. The importance of exercise in the well-rounded physician: dialogue for the inclusion of a physical fitness program in neurosurgery resident training. World Neurosurg. 2016;90:380–4.
Gabel S. Demoralization in Health Professional Practice: Development, Amelioration, and Implications for Continuing Education. J Contin Educ Health Prof 2013 Spring. 2013;33(2):118–26.
Google Scholar
Govardhan LM, Pinelli V, Schnatz PF. Burnout, depression and job satisfaction in obstetrics and gynecology residents. Conn Med. 2012;76(7):389–95.
Jennings ML, Slavin SJ. Resident wellness matters: optimizing resident education and wellness through the learning environment. Acad Med. 2015;90(9):1246–50.
Keller EJ. Philosophy in medical education: a means of protecting mental health. Acad Psychiatry. 2014;38(4):409–13.
Krall EJ, Niazi SK, Miller MM. The status of physician health programs in Wisconsin and north central states: a look at statewide and health systems programs. WMJ. 2012;111(5):220–7.
Lemaire JB, Wallace JE. Burnout among doctors. BMJ. 2017;358:j3360.
Linzer M, Bitton A, Tu SP, Plews-Ogan M, Horowitz KR, Schwartz MD, et al. The end of the 15-20 minute primary care visit. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30(11):1584–6.
Lu DW, Dresden S, McCloskey C, Branzetti J, Gisondi MA. Impact of burnout on self-reported patient care among emergency physicians. West J Emerg Med. 2015;16(7):996–1001.
Maslach C, Schaufeli WB, Leiter MP. Job burnout. Annu Rev Psychol. 2001;52:397–422.
McClafferty H, Brown OW. Section on integrative medicine, committee on practice and ambulatory medicine, section on integrative medicine. Physician health and wellness. Pediatrics. 2014;134(4):830–5.
Miyasaki JM, Rheaume C, Gulya L, Ellenstein A, Schwarz HB, Vidic TR, et al. Qualitative study of burnout, career satisfaction, and well-being among US neurologists in 2016. Neurology. 2017;89(16):1730–8.
Peterson J, Pearce P, Ferguson LA, Langford C. Understanding scoping reviews: definition, purpose, and process. JAANP. 2016;29:12–6.
Przedworski JM, Dovidio JF, Hardeman RR, Phelan SM, Burke SE, Ruben MA, et al. A comparison of the mental health and well-being of sexual minority and heterosexual first-year medical students: a report from the medical student CHANGE study. Acad Med. 2015;90(5):652–9.
Ripp JA, Privitera MR, West CP, Leiter R, Logio L, Shapiro J, et al. Well-being in graduate medical education: a call for action. Acad Med. 2017;92(7):914–7.
Salles A, Mueller CM, Cohen GL. Exploring the relationship between stereotype perception and Residents’ well-being. J Am Coll Surg. 2016;222(1):52–8.
Shiralkar MT, Harris TB, Eddins-Folensbee FF, Coverdale JH. A systematic review of stress-management programs for medical students. Acad Psychiatry. 2013;37(3):158–64.
Sikka R, Morath J, Leape L. The quadruple aim: care, health, cost and meaning in work. BMJ Qual Saf. 2015;24(10):608–10. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004160 .
Tawfik DS, Phibbs CS, Sexton JB, Kan P, Sharek PJ, Nisbet CC, et al. Factors Associated With Provider Burnout in the NICU. Pediatrics. 2017;139(5):608. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-4134 Epub 2017 Apr 18.
Turner TB, Dilley SE, Smith HJ, Huh WK, Modesitt SC, Rose SL, et al. The impact of physician burnout on clinical and academic productivity of gynecologic oncologists: a decision analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 2017;146(3):642–6.
West CP, Dyrbye LN, Erwin PJ, Shanafelt TD. Interventions to prevent and reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2016;388(10057):2272.
Williams D, Tricomi G, Gupta J, Janise A. Efficacy of burnout interventions in the medical education pipeline. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(1):47–54.
Woodside JR, Miller MN, Floyd MR, McGowen KR, Pfortmiller DT. Observations on burnout in family medicine and psychiatry residents. Acad Psychiatry. 2008;32(1):13–9.
World Health Organization. (2001). Mental disorders affect one in four people.
World Health Organization. Promoting mental health: concepts, emerging evidence, practice (Summary Report). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not Applicable.
Not Applicable
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Telfer School of Management, University of Ottawa, 55 Laurier Ave E, Ottawa, ON, K1N 6N5, Canada
Mara Mihailescu
School of Public Health and Health Systems, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue West, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1, Canada
Elena Neiterman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M.M. and E.N. were involved in identifying the relevant research question and developing the combinations of keywords used in consultation with a professional librarian. M.M. performed the literature selection and screening of references for eligibility. Both authors were involved in the creation of the literature extraction tool in Excel. Both authors coded the data inductively, first independently reading five articles and generating themes from the data, then discussing their coding and developing a coding scheme that was subsequently applied to ten more papers. Both authors then refined and finalized the coding scheme and M.M. used it to code the rest of the data. M.M. conceptualized and wrote the first copy of the manuscript, followed by extensive drafting by both authors. E.N. was a contributor to writing the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mara Mihailescu .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Mihailescu, M., Neiterman, E. A scoping review of the literature on the current mental health status of physicians and physicians-in-training in North America. BMC Public Health 19 , 1363 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7661-9
Download citation
Received : 29 April 2019
Accepted : 20 September 2019
Published : 24 October 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7661-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mental health
- Mental illness
- Medical students
- Scoping review
- Interventions
- North America
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 07 October 2021
Young people’s mental health is finally getting the attention it needs
You have full access to this article via your institution.

A kite-flying festival in a refugee camp near Syria’s border with Turkey. The event was organized in July 2020 to support the health and well-being of children fleeing violence in Syria. Credit: Muhammed Said/Anadolu Agency/Getty
Worldwide, at least 13% of people between the ages of 10 and 19 live with a diagnosed mental-health disorder, according to the latest State of the World’s Children report , published this week by the United Nations children’s charity UNICEF. It’s the first time in the organization’s history that this flagship report has tackled the challenges in and opportunities for preventing and treating mental-health problems among young people. It reveals that adolescent mental health is highly complex, understudied — and underfunded. These findings are echoed in a parallel collection of review articles published this week in a number of Springer Nature journals.
Anxiety and depression constitute more than 40% of mental-health disorders among young people (those aged 10–19). UNICEF also reports that, worldwide, suicide is the fourth most-common cause of death (after road injuries, tuberculosis and interpersonal violence) among adolescents (aged 15–19). In eastern Europe and central Asia, suicide is the leading cause of death for young people in that age group — and it’s the second-highest cause in western Europe and North America.

Collection: Promoting youth mental health
Sadly, psychological distress among young people seems to be rising. One study found that rates of depression among a nationally representative sample of US adolescents (aged 12 to 17) increased from 8.5% of young adults to 13.2% between 2005 and 2017 1 . There’s also initial evidence that the coronavirus pandemic is exacerbating this trend in some countries. For example, in a nationwide study 2 from Iceland, adolescents (aged 13–18) reported significantly more symptoms of mental ill health during the pandemic than did their peers before it. And girls were more likely to experience these symptoms than were boys.
Although most mental-health disorders arise during adolescence, UNICEF says that only one-third of investment in mental-health research is targeted towards young people. Moreover, the research itself suffers from fragmentation — scientists involved tend to work inside some key disciplines, such as psychiatry, paediatrics, psychology and epidemiology, and the links between research and health-care services are often poor. This means that effective forms of prevention and treatment are limited, and lack a solid understanding of what works, in which context and why.
This week’s collection of review articles dives deep into the state of knowledge of interventions — those that work and those that don’t — for preventing and treating anxiety and depression in young people aged 14–24. In some of the projects, young people with lived experience of anxiety and depression were co-investigators, involved in both the design and implementation of the reviews, as well as in interpretation of the findings.
Quest for new therapies
Worldwide, the most common treatment for anxiety and depression is a class of drug called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, which increase serotonin levels in the brain and are intended to enhance emotion and mood. But their modest efficacy and substantial side effects 3 have spurred the study of alternative physiological mechanisms that could be involved in youth depression and anxiety, so that new therapeutics can be developed.

Mental health: build predictive models to steer policy
For example, researchers have been investigating potential links between depression and inflammatory disorders — such as asthma, cardiovascular disease and inflammatory bowel disease. This is because, in many cases, adults with depression also experience such disorders. Moreover, there’s evidence that, in mice, changes to the gut microbiota during development reduce behaviours similar to those linked to anxiety and depression in people 4 . That suggests that targeting the gut microbiome during adolescence could be a promising avenue for reducing anxiety in young people. Kathrin Cohen Kadosh at the University of Surrey in Guildford, UK, and colleagues reviewed existing reports of interventions in which diets were changed to target the gut microbiome. These were found to have had minimal effect on youth anxiety 5 . However, the authors urge caution before such a conclusion can be confirmed, citing methodological limitations (including small sample sizes) among the studies they reviewed. They say the next crop of studies will need to involve larger-scale clinical trials.
By contrast, researchers have found that improving young people’s cognitive and interpersonal skills can be more effective in preventing and treating anxiety and depression under certain circumstances — although the reason for this is not known. For instance, a concept known as ‘decentring’ or ‘psychological distancing’ (that is, encouraging a person to adopt an objective perspective on negative thoughts and feelings) can help both to prevent and to alleviate depression and anxiety, report Marc Bennett at the University of Cambridge, UK, and colleagues 6 , although the underlying neurobiological mechanisms are unclear.
In addition, Alexander Daros at the Campbell Family Mental Health Institute in Toronto, Canada, and colleagues report a meta-analysis of 90 randomized controlled trials. They found that helping young people to improve their emotion-regulation skills, which are needed to control emotional responses to difficult situations, enables them to cope better with anxiety and depression 7 . However, it is still unclear whether better regulation of emotions is the cause or the effect of these improvements.
Co-production is essential
It’s uncommon — but increasingly seen as essential — that researchers working on treatments and interventions are directly involving young people who’ve experienced mental ill health. These young people need to be involved in all aspects of the research process, from conceptualizing to and designing a study, to conducting it and interpreting the results. Such an approach will lead to more-useful science, and will lessen the risk of developing irrelevant or inappropriate interventions.

Science careers and mental health
Two such young people are co-authors in a review from Karolin Krause at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health in Toronto, Canada, and colleagues. The review explored whether training in problem solving helps to alleviate depressive symptoms 8 . The two youth partners, in turn, convened a panel of 12 other youth advisers, and together they provided input on shaping how the review of the evidence was carried out and on interpreting and contextualizing the findings. The study concluded that, although problem-solving training could help with personal challenges when combined with other treatments, it doesn’t on its own measurably reduce depressive symptoms.
The overarching message that emerges from these reviews is that there is no ‘silver bullet’ for preventing and treating anxiety and depression in young people — rather, prevention and treatment will need to rely on a combination of interventions that take into account individual needs and circumstances. Higher-quality evidence is also needed, such as large-scale trials using established protocols.
Along with the UNICEF report, the studies underscore the transformational part that funders must urgently play, and why researchers, clinicians and communities must work together on more studies that genuinely involve young people as co-investigators. Together, we can all do better to create a brighter, healthier future for a generation of young people facing more challenges than ever before.
Nature 598 , 235-236 (2021)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-02690-5
Twenge, J. M., Cooper, A. B., Joiner, T. E., Duffy, M. E. & Binau, S. G. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 128 , 185–199 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Thorisdottir, I. E. et al. Lancet Psychiatr. 8 , 663–672 (2021).
Article Google Scholar
Murphy, S. E. et al. Lancet Psychiatr. 8 , 824–835 (2021).
Murray, E. et al. Brain Behav. Immun. 81 , 198–212 (2019).
Cohen Kadosh, K. et al. Transl. Psychiatr. 11 , 352 (2021).
Bennett, M. P. et al. Transl Psychiatr. 11 , 288 (2021).
Daros, A. R. et al. Nature Hum. Behav . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01191-9 (2021).
Krause, K. R. et al. BMC Psychiatr. 21 , 397 (2021).
Download references
Reprints and permissions

Related Articles

- Psychiatric disorders
- Public health
Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
News & Views 24 APR 24

The rise of eco-anxiety: scientists wake up to the mental-health toll of climate change
News Feature 10 APR 24
Use fines from EU social-media act to fund research on adolescent mental health
Correspondence 09 APR 24

How ignorance and gender inequality thwart treatment of a widespread illness
Outlook 09 MAY 24

Bird flu in US cows: where will it end?
News 08 MAY 24

US funders to tighten oversight of controversial ‘gain-of-function’ research
News 07 MAY 24
Japan can embrace open science — but flexible approaches are key
Correspondence 07 MAY 24
Beware of graphene’s huge and hidden environmental costs
Countering extreme wildfires with prescribed burning can be counterproductive
W3-Professorship (with tenure) in Inorganic Chemistry
The Institute of Inorganic Chemistry in the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences at the University of Bonn invites applications for a W3-Pro...
53113, Zentrum (DE)
Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität
Principal Investigator Positions at the Chinese Institutes for Medical Research, Beijing
Studies of mechanisms of human diseases, drug discovery, biomedical engineering, public health and relevant interdisciplinary fields.
Beijing, China
The Chinese Institutes for Medical Research (CIMR), Beijing
Research Associate - Neural Development Disorders
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Staff Scientist - Mitochondria and Surgery
Recruitment of talent positions at shengjing hospital of china medical university.
Call for top experts and scholars in the field of science and technology.
Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Custom Essay, Term Paper & Research paper writing services
- testimonials
Toll Free: +1 (888) 354-4744
Email: [email protected]
Writing custom essays & research papers since 2008
60 popular mental health research paper topics.

The best way to write a good mental health research paper is to select a topic that you will enjoy working on. If you are looking for some interesting mental health research paper topics to work on, here is a list of 60 ideas to choose from.
Perfect for students as well as experts these topics have ample scope to experiment, share ideas and arguments on, and find substantial evidence to support your view. Take a look –
Mental Health Topics for Research Paper
When you are writing a paper for a graded assignment, it is important to have some great research paper topics about mental health to pick from. Here are some to consider –
- Mental traumas from physical injuries and how to help recover
- Resilience building – why is it important for children?
- Friendships in men and how they contribute to mental health?
- The role of parenting in building good mental health in children
- What is normal emotional health and mental functioning?
- Anti-depressants and their side effects.
- Indicators suggesting medication for depression can be stopped
- Effects of colors on mental health
- How and why does lack of sleep effect emotional mental health?
- Effect of exercise on a patient’s mental health
- Effective methods to boost brain health and emotional quotient as we age
- Mental health developmental stages in children from birth to 5 years of age
- Why is play important for mental health in children
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder – what causes it and how to manage?
- ADHD — how to identify if someone has it?
Critical Analysis Research Paper Topics in Mental Health
For psychology students looking for effective research paper topics mental health offers many arenas for critical analysis. Here are some good topics to pick from –
- Relevance of Freud in modern day psychiatry
- Abortion care – the ethics and the procedures to facilitate emotional wellbeing
- Are women facing more mental health issues than men?
- Suicide – The reasons, trauma, and dealing with it
- How does peer pressure change mental wellness and how to deal with it?
- Effect of child abuse on toddlers’ mental health and resilience
- Does Obesity affect mental health?
- Is the damage on mental health caused by sexual abuse permanent?
- Hormonal imbalances and their effect on women’s mental health
- How to identify signs of mental illness in a loved one?
Music Therapy Research Paper Topics Mental Health
Music plays a significant role in enhancing mental health. Here are some mental health research paper topics on the role of music therapy in the field of mental health and treatments:
- Music therapy a complimentary approach to biomedicine
- Does music therapy facilitate enhanced healing?
- Efficacy of music therapy for older adults
- The role of music therapy in rehabilitation of mental health patients
- Music based interventions and the effects of music therapy
- Eating disorders and can music therapy help?
- Can music therapy help with mental health during menopause?
- Music therapy and its role in PTSD
Mental Health Nursing Research Paper Topics
If you are a nursing student you will certainly find these research paper topics for mental health useful for your assignment –
- Psychiatric care in adult patients of mental health disorders
- Non-chemical practices in bipolar disorder
- Mental health care for patients dealing with alcohol addiction
- Managing PTSD in armed forces veterans
- Ethics to deal with psychiatric patients
- Postpartum depression and how to identify and assist in early stages
- Identifying the signs and managing patients with eating disorder
- Mental illnesses common in soldiers returning from war
- Signs of mental illness that must never be ignored
- How to manage self-destructive mental health patients?
Controversial Research Paper Topics About Mental Health
Some mental health topics are controversial, but also well scoring if handled well. Take a look at some such topics worth considering –
- Do natural alternatives to anti-depressants work?
- Extreme postpartum depression leading to child harming tendencies
- Infertility and its effects on mental health of the couple
- Are more women suicidal than men?
- Effect of teen relationship problems on mental health
- The relationship between mental health and child abusers
- Physical abuse in marriage and its effect on mental health
- Rape and managing the emotional scars for effective healing
- Self-destructive tendencies in children – causes and cures
- Is it possible that there are people without conscience?
- Are video games making children violent and aggressive?
- Should criminals facing trial be subjected to genetic testing for impulse control?
- Mental health in teenagers and why they cut themselves
- Phobias – some of the most common and unusual fears people have
- Divorce and how it affects the mental health of children
- Is mental illness genetic
- Does discovery of being adopted affect mental health of a child?
If you are a college student wondering what is the best way to write a research paper or how to write an effective submission that will get you good grades, you can get in touch with us for writing help. Our team offers fast and cheap assistance with writing papers that are appropriate for your level of education.
55 research questions about mental health
Last updated
11 March 2024
Reviewed by
Brittany Ferri, PhD, OTR/L
Research in the mental health space helps fill knowledge gaps and create a fuller picture for patients, healthcare professionals, and policymakers. Over time, these efforts result in better quality care and more accessible treatment options for those who need them.
Use this list of mental health research questions to kickstart your next project or assignment and give yourself the best chance of producing successful and fulfilling research.
- Why does mental health research matter?
Mental health research is an essential area of study. It includes any research that focuses on topics related to people’s mental and emotional well-being.
As a complex health topic that, despite the prevalence of mental health conditions, still has an unending number of unanswered questions, the need for thorough research into causes, triggers, and treatment options is clear.
Research into this heavily stigmatized and often misunderstood topic is needed to find better ways to support people struggling with mental health conditions. Understanding what causes them is another crucial area of study, as it enables individuals, companies, and policymakers to make well-informed choices that can help prevent illnesses like anxiety and depression.
- How to choose a strong mental health research topic
As one of the most important parts of beginning a new research project, picking a topic that is intriguing, unique, and in demand is a great way to get the best results from your efforts.
Mental health is a blanket term with many niches and specific areas to explore. But, no matter which direction you choose, follow the tips below to ensure you pick the right topic.
Prioritize your interests and skills
While a big part of research is exploring a new and exciting topic, this exploration is best done within a topic or niche in which you are interested and experienced.
Research is tough, even at the best of times. To combat fatigue and increase your chances of pushing through to the finish line, we recommend choosing a topic that aligns with your personal interests, training, or skill set.
Consider emerging trends
Topical and current research questions are hot commodities because they offer solutions and insights into culturally and socially relevant problems.
Depending on the scope and level of freedom you have with your upcoming research project, choosing a topic that’s trending in your area of study is one way to get support and funding (if you need it).
Not every study can be based on a cutting-edge topic, but this can be a great way to explore a new space and create baseline research data for future studies.
Assess your resources and timeline
Before choosing a super ambitious and exciting research topic, consider your project restrictions.
You’ll need to think about things like your research timeline, access to resources and funding, and expected project scope when deciding how broad your research topic will be. In most cases, it’s better to start small and focus on a specific area of study.
Broad research projects are expensive and labor and resource-intensive. They can take years or even decades to complete. Before biting off more than you can chew, consider your scope and find a research question that fits within it.
Read up on the latest research
Finally, once you have narrowed in on a specific topic, you need to read up on the latest studies and published research. A thorough research assessment is a great way to gain some background context on your chosen topic and stops you from repeating a study design. Using the existing work as your guide, you can explore more specific and niche questions to provide highly beneficial answers and insights.
- Trending research questions for post-secondary students
As a post-secondary student, finding interesting research questions that fit within the scope of your classes or resources can be challenging. But, with a little bit of effort and pre-planning, you can find unique mental health research topics that will meet your class or project requirements.
Examples of research topics for post-secondary students include the following:
How does school-related stress impact a person’s mental health?
To what extent does burnout impact mental health in medical students?
How does chronic school stress impact a student’s physical health?
How does exam season affect the severity of mental health symptoms?
Is mental health counseling effective for students in an acute mental crisis?
- Research questions about anxiety and depression
Anxiety and depression are two of the most commonly spoken about mental health conditions. You might assume that research about these conditions has already been exhausted or that it’s no longer in demand. That’s not the case at all.
According to a 2022 survey by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 12.5% of American adults struggle with regular feelings of worry, nervousness, and anxiety, and 5% struggle with regular feelings of depression. These percentages amount to millions of lives affected, meaning new research into these conditions is essential.
If either of these topics interests you, here are a few trending research questions you could consider:
Does gender play a role in the early diagnosis of anxiety?
How does untreated anxiety impact quality of life?
What are the most common symptoms of anxiety in working professionals aged 20–29?
To what extent do treatment delays impact quality of life in patients with undiagnosed anxiety?
To what extent does stigma affect the quality of care received by people with anxiety?
Here are some examples of research questions about depression:
Does diet play a role in the severity of depression symptoms?
Can people have a genetic predisposition to developing depression?
How common is depression in work-from-home employees?
Does mood journaling help manage depression symptoms?
What role does exercise play in the management of depression symptoms?
- Research questions about personality disorders
Personality disorders are complex mental health conditions tied to a person’s behaviors, sense of self, and how they interact with the world around them. Without a diagnosis and treatment, people with personality disorders are more likely to develop negative coping strategies during periods of stress and adversity, which can impact their quality of life and relationships.
There’s no shortage of specific research questions in this category. Here are some examples of research questions about personality disorders that you could explore:
What environments are more likely to trigger the development of a personality disorder?
What barriers impact access to care for people with personality disorders?
To what extent does undiagnosed borderline personality disorder impact a person’s ability to build relationships?
How does group therapy impact symptom severity in people with schizotypal personality disorder?
What is the treatment compliance rate of people with paranoid personality disorder?
- Research questions about substance use disorders
“Substance use disorders” is a blanket term for treatable behaviors and patterns within a person’s brain that lead them to become dependent on illicit drugs, alcohol, or prescription medications. It’s one of the most stigmatized mental health categories.
The severity of a person’s symptoms and how they impact their ability to participate in their regular daily life can vary significantly from person to person. But, even in less severe cases, people with a substance use disorder display some level of loss of control due to their need to use the substance they are dependent on.
This is an ever-evolving topic where research is in hot demand. Here are some example research questions:
To what extent do meditation practices help with craving management?
How effective are detox centers in treating acute substance use disorder?
Are there genetic factors that increase a person’s chances of developing a substance use disorder?
How prevalent are substance use disorders in immigrant populations?
To what extent do prescription medications play a role in developing substance use disorders?
- Research questions about mental health treatments
Treatments for mental health, pharmaceutical therapies in particular, are a common topic for research and exploration in this space.
Besides the clinical trials required for a drug to receive FDA approval, studies into the efficacy, risks, and patient experiences are essential to better understand mental health therapies.
These types of studies can easily become large in scope, but it’s possible to conduct small cohort research on mental health therapies that can provide helpful insights into the actual experiences of the people receiving these treatments.
Here are some questions you might consider:
What are the long-term effects of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) for patients with severe depression?
How common is insomnia as a side effect of oral mental health medications?
What are the most common causes of non-compliance for mental health treatments?
How long does it take for patients to report noticeable changes in symptom severity after starting injectable mental health medications?
What issues are most common when weaning a patient off of an anxiety medication?
- Controversial mental health research questions
If you’re interested in exploring more cutting-edge research topics, you might consider one that’s “controversial.”
Depending on your own personal values, you might not think many of these topics are controversial. In the context of the research environment, this depends on the perspectives of your project lead and the desires of your sponsors. These topics may not align with the preferred subject matter.
That being said, that doesn’t make them any less worth exploring. In many cases, it makes them more worthwhile, as they encourage people to ask questions and think critically.
Here are just a few examples of “controversial” mental health research questions:
To what extent do financial crises impact mental health in young adults?
How have climate concerns impacted anxiety levels in young adults?
To what extent do psychotropic drugs help patients struggling with anxiety and depression?
To what extent does political reform impact the mental health of LGBTQ+ people?
What mental health supports should be available for the families of people who opt for medically assisted dying?
- Research questions about socioeconomic factors & mental health
Socioeconomic factors—like where a person grew up, their annual income, the communities they are exposed to, and the amount, type, and quality of mental health resources they have access to—significantly impact overall health.
This is a complex and multifaceted issue. Choosing a research question that addresses these topics can help researchers, experts, and policymakers provide more equitable and accessible care over time.
Examples of questions that tackle socioeconomic factors and mental health include the following:
How does sliding scale pricing for therapy increase retention rates?
What is the average cost to access acute mental health crisis care in [a specific region]?
To what extent does a person’s environment impact their risk of developing a mental health condition?
How does mental health stigma impact early detection of mental health conditions?
To what extent does discrimination affect the mental health of LGBTQ+ people?
- Research questions about the benefits of therapy
Therapy, whether that’s in groups or one-to-one sessions, is one of the most commonly utilized resources for managing mental health conditions. It can help support long-term healing and the development of coping mechanisms.
Yet, despite its popularity, more research is needed to properly understand its benefits and limitations.
Here are some therapy-based questions you could consider to inspire your own research:
In what instances does group therapy benefit people more than solo sessions?
How effective is cognitive behavioral therapy for patients with severe anxiety?
After how many therapy sessions do people report feeling a better sense of self?
Does including meditation reminders during therapy improve patient outcomes?
To what extent has virtual therapy improved access to mental health resources in rural areas?
- Research questions about mental health trends in teens
Adolescents are a particularly interesting group for mental health research due to the prevalence of early-onset mental health symptoms in this age group.
As a time of self-discovery and change, puberty brings plenty of stress, anxiety, and hardships, all of which can contribute to worsening mental health symptoms.
If you’re looking to learn more about how to support this age group with mental health, here are some examples of questions you could explore:
Does parenting style impact anxiety rates in teens?
How early should teenagers receive mental health treatment?
To what extent does cyberbullying impact adolescent mental health?
What are the most common harmful coping mechanisms explored by teens?
How have smartphones affected teenagers’ self-worth and sense of self?
- Research questions about social media and mental health
Social media platforms like TikTok, Instagram, YouTube, Facebook, and X (formerly Twitter) have significantly impacted day-to-day communication. However, despite their numerous benefits and uses, they have also become a significant source of stress, anxiety, and self-worth issues for those who use them.
These platforms have been around for a while now, but research on their impact is still in its infancy. Are you interested in building knowledge about this ever-changing topic? Here are some examples of social media research questions you could consider:
To what extent does TikTok’s mental health content impact people’s perception of their health?
How much non-professional mental health content is created on social media platforms?
How has social media content increased the likelihood of a teen self-identifying themselves with ADHD or autism?
To what extent do social media photoshopped images impact body image and self-worth?
Has social media access increased feelings of anxiety and dread in young adults?
- Mental health research is incredibly important
As you have seen, there are so many unique mental health research questions worth exploring. Which options are piquing your interest?
Whether you are a university student considering your next paper topic or a professional looking to explore a new area of study, mental health is an exciting and ever-changing area of research to get involved with.
Your research will be valuable, no matter how big or small. As a niche area of healthcare still shrouded in stigma, any insights you gain into new ways to support, treat, or identify mental health triggers and trends are a net positive for millions of people worldwide.
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Most Popular
11 days ago
Into vs In to
How to reference a movie in an essay, how to write a position paper, is gen z actually lazy this admission consultant doesn’t think so, how do you spell, mental health awareness thesis statement examples.
unsplash.com

Mental health awareness is a crucial topic in contemporary society that seeks to educate individuals on mental health disorders, reduce stigma, and advocate for accessible treatment. When constructing a thesis on this topic, a decisive, clear, and specific thesis statement is imperative. This text will provide and analyze good and bad thesis statement examples on mental health awareness to guide students in developing robust research arguments.
Good Thesis Statement Examples
Specific and Clear: “The research quantitatively analyzes the impact of school-based mental health awareness programs on adolescents’ levels of depression and anxiety.” Bad: “School programs about mental health awareness are important.”
The good example is specific and clear, offering a quantitative approach, focus group (adolescents), and measurable outcomes (levels of depression and anxiety). Conversely, the bad example is vague, lacking clear metrics or specific focus areas.
Well-defined Scope: “This thesis explores the role of social media in propagating mental health stigma among adults in the United States.” Bad: “Social media plays a role in mental health.”
The good statement precisely defines the scope, focusing on stigma propagation, the adult demographic, and limiting the study to the United States. The bad example is too broad and lacks specificity on the aspect of mental health and target demographic.
Arguable and Debatable: “The availability of teletherapy services significantly improves access to mental health care for rural populations facing transportation barriers.” Bad: “Teletherapy services are beneficial.”
The good thesis is arguable and presents a specific claim about teletherapy’s impact on rural populations and access barriers, whereas the bad example is non-debatable and too general without a particular focus or claim.
Bad Thesis Statement Examples
Overly Broad: “Mental health is important for everyone.”
This statement, while true, is too broad and general. It doesn’t guide the reader towards a specific aspect of mental health, making it ineffective for a thesis.
Lack of Clear Argument: “Mental health issues affect people in different ways.”
While this statement is factual, it lacks a clear argument or focus, leaving the reader without direction or understanding of the paper’s purpose. Seeking paraphrasing help can enhance the clarity and focus of your statement, ensuring your paper effectively communicates its purpose.
Unmeasurable and Unresearchable: “Positive thinking can cure mental disorders.”
This statement is not only scientifically incorrect but also unmeasurable and unresearchable, making it inappropriate for scholarly research.
A strong thesis statement is pivotal for the success of a thesis on Mental Health Awareness. As illustrated, good thesis statements are clear, specific, and arguable with a well-defined scope, guiding the reader effortlessly through the research’s purpose and objectives. In contrast, bad thesis statements are often overly broad, lack clear arguments, and are not measurable or researchable, leading to confusion and a lack of direction. By carefully considering these examples, students can craft thesis statements that offer clarity, precision, and a roadmap for their research on the vital and complex issue of mental health awareness.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from Thesis Statement Examples and Samples

Sep 30 2023
Gender & Sexuality Studies Thesis Statement Examples

Criminal Justice Reform Thesis Statement Examples

Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Thesis Statement Examples
Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email

Latest Issue
Psychiatry’s new frontiers
Hope amid crisis
Recent Issues
- AI explodes Taking the pulse of artificial intelligence in medicine
- Health on a planet in crisis
- Real-world health How social factors make or break us
- Molecules of life Understanding the world within us
- The most mysterious organ Unlocking the secrets of the brain
- All Articles
- The spice sellers’ secret
- ‘And yet, you try’
- Making sense of smell
- Before I go
- My favorite molecule
- View all Editors’ Picks
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
- Infectious Diseases
- View All Articles
Reasons for hope
Solutions for the mental health crisis emerge through innovative research, diagnostics and treatments
By Nina Bai
Illustration by Jules Julien
Photography by Leslie Williamson

It’s the spring of hope for mental health, astir with novel discoveries, life-changing therapies and more openness than ever before — yet, for many, it feels like the winter of despair. The pandemic years, that crucible of stress, isolation and uncertainty, fueled and exposed mental health problems. In 2022, nearly 1 in 4 American adults (about 59 million people) said they experienced a mental illness in the previous year, but only half of those afflicted reported receiving any mental health treatment.
Among children and adolescents, the prevalence of mental illness, which had been steadily creeping upward, jumped during the pandemic, according to the U.S. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. In 2019, 15.7% of American adolescents aged 12-17 reported experiencing a major depressive episode in the past year. In 2022, that number was 19.5%. That same year, 13.4% of adolescents — just over 1 in 8 — seriously thought about killing themselves.
And even as the pandemic has stoked demand for mental health care, it also has worn down the mental health workforce, already short-handed, with early retirements and widespread burnout. Access to affordable, effective interventions remains a daunting barrier. People face long waiting lists and lack of insurance coverage. Many treatable conditions remain undiagnosed because people lack a way to obtain assessments.
Yet, below this perfect storm of mental health crisis, there is a strong undercurrent of hope that begins in the lab. Research is leading the way toward treatments that are more effective, more personalized and more accessible.
“The manner in which we know the brain now, compared with what we knew in previous decades, is incredibly different,” said Victor Carrión , MD, the John A. Turner, MD, Endowed Professor for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and vice chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences.

Direct impact on patients
New imaging technologies allow researchers to see the neural circuitry that goes awry in neuropsychiatric disorders, lab-grown clumps of brain tissue — known as organoids — can simulate the impact of genetics in autism, and artificial intelligence can surmise signals that predict the onset of depression and anxiety.
Moreover, these discoveries, rather than moving slowly through specialist silos, can now rapidly inform new treatments. “Collaboration is vital for translation, and our departmental awards and programs promote and emphasize synergy between research and clinical practice,” said Laura Roberts , MD, the Katharine Dexter McCormick and Stanley McCormick Memorial Professor and chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences.
“Our bench scientists doing tremendous research also work alongside our clinicians to make sure that new knowledge translates to the clinical setting and has a direct impact on patient care,” she said.
Researchers developing transcranial magnetic stimulation, for example, work with clinicians who treat patients with severe depression to design clinical trials, and their techniques are informed by teams inventing new ways to measure the flow of brain signals and those building virtual reality models of the brain.
A clearer understanding of the biology of mental health disorders not only leads to breakthrough treatments — but just as powerfully, helps dissipate stigma.
“There’s been a large shift in stigma in the past 25 years,” said Heather Gotham , PhD, clinical professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, who leads the coordination of a nationwide network of centers dedicated to implementing evidence-based mental health care.
The Mental Health Technology Transfer Center Network, funded by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, offers training in preventing school violence, substance use in the workplace, adolescent depression and more, and it offers support for mental health providers seeing refugees and asylum seekers.
“Collaboration is vital for translation, and our departmental awards and programs promote and emphasize synergy between research and clinical practice.” Laura Roberts, the Katharine Dexter McCormick and Stanley McCormick Memorial Professor and chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences
“One thing that’s made a difference is the greater understanding that mental health disorders and substance use disorders are chronic, relapsing disorders of the body, just like diabetes and heart disease,” Gotham said.
With this new awareness, more people want to be mental health literate. In the past few years, Gotham has seen a surge of interest, from a broader community, in the network’s online courses — from teachers, for example, who want to be more responsive to the needs of students and reduce stigma in the classroom.
Less stigma also means more money for research and mental health services. Funding for mental health has become a rare bipartisan issue. In 2022, Congress passed the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act, which has provided $245 million to fund mental health services like training for school personnel, first responders and law enforcement and expanding the 988 suicide and crisis lifeline.
Stanford Medicine researchers know that to make the most impact with their discoveries they must reach those who need help the most — through online symptom screenings, virtual therapy, group therapy, inclusive clinical trials and community interventions.
They are training mental health professionals locally and globally in new evidence-based techniques. Providers in more than 38 countries, for example, have been trained in cue-centered therapy, a 15-week treatment program developed at Stanford Medicine to help children and teens recover from chronic trauma. Recently, pro bono training in cue-centered therapy was provided to clinicians in Ukraine.
What gives Roberts hope is that a more open conversation on mental health is drawing together experts from different fields with a shared purpose. “It used to be that clinicians would stay in their clinical practice and refer to journals for new research, and researchers would stay in the lab and never see a patient — and we don’t have that now,” she said. “I see more openness and more flexibility from the current generation of researchers and clinicians.”
Read on in this issue of Stanford Medicine to learn about some of the ways Stanford Medicine researchers and clinicians are advancing the understanding of mental health and sharing that knowledge.
Nina Bai is a science writer in the Stanford Medicine Office of Communications.
Email the author
Mental Health: Assessment and Screening Research Paper
First of all, it is useful to properly understand the difference between screening and assessment processes. The former means the evaluation to determine whether some disorder is present. Hence, it is usually broad enough to cover different possibilities. In many instances, the screening may serve as a tool to begin a difficult discussion or frame assessment on sensitive issues (CAMH, 2019a). The latter is focused on providing an in-depth understanding of issues acquired through screening. However, because of the heavy workload at the mental health department, great emphasis should be placed on developing coherent screening strategies.
Different strategies for intake interviews may be conducted separately or combined. Saskatchewan Health Authority (n.d.) identifies four of the most common ones: interviews, physical examinations, lab tests, and written tests. Interviews are an indispensable part of the screening, especially if they are combined with some diary notes or recordings of symptoms. However, it seems that it will be more effective to include a written test as an intermediate part between two interview sessions. The initial interview will be some form of informal exchange that will create a calmer atmosphere. Afterward, a written self-report is the best continuation of the session because there are many peer-reviewed test samples that help determine the type of disorder and common symptoms (CAMH, 2019b). For example, Symptom Checklist-90-Revised, found effective by scholars (Abiri & Shairi, 2019), helps identify the broad range of psychological problems. Through 12-15 minutes, patients will complete this test, which greatly fits into the time limits of the discussed medical facility.
The after-test interview will be more informed of the symptoms and the possible disorders. After that, it is good to give recommendations to make lab tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), electroencephalogram (EEG), computed tomography (CT), and others (Saskatchewan Health Authority, n.d.). Physical examination may also be added to the session if needed. It will add more objectivity to the screening giving broader understanding to the specialist.
Akhavan Abiri, F., & Shairi, M. R. (2020). Validity and reliability of symptom checklist-90-revised (SCL-90-R) and brief symptom inventory-53 (BSI-53). Clinical Psychology and Personality , 17 (2), 169-195. Web.
CAMH. (2019a). Suicide risk: Detecting & assessing suicidality . Web.
CAMH. (2019b). PTSD: Screening & assessment . Web.
Saskatchewan Health Authority. (n.d.). Mental health assessment . Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, May 6). Mental Health: Assessment and Screening. https://ivypanda.com/essays/mental-health-assessment-and-screening/
"Mental Health: Assessment and Screening." IvyPanda , 6 May 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/mental-health-assessment-and-screening/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Mental Health: Assessment and Screening'. 6 May.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Mental Health: Assessment and Screening." May 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/mental-health-assessment-and-screening/.
1. IvyPanda . "Mental Health: Assessment and Screening." May 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/mental-health-assessment-and-screening/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Mental Health: Assessment and Screening." May 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/mental-health-assessment-and-screening/.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Shortening Techniques
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Understanding the Visuals
- Magnetic Resonance Scanning on Infants and Children
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder and Tourette Syndrome
- Suicidal Deaths: Mental Support
- Mental Illness: Jessie's Case Analysis
- Breaking Barriers: Mental Health Advocacy in the US
- Mental Health Stigma in Rural America

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This research paper describes the history, application, and development in sociology of the study of mental health, illness, and disorders. Mental health, mental illness, social and mental functioning, and its social indicators are a classic theme in the field of sociology. Emile Durkheim's (1951) Suicide was a landmark study in both ...
Moreover, when it comes to the research on mental health (vis-a-viz physical health), promotive and preventive mental health aspects have received less attention vis-a-viz physical health. Instead, greater emphasis has been given to the illness aspect, such as research on psychopathology, mental disorders, and treatment ( 19 , 20 ).
found mental health concerns can cause a student to have difficulty in school. with poor academic performance, even chronic absenteeism, and disciplinary. concerns. Weist (2005) notes that in the prior two decades, "school mental health. programs have increased due to the recognition of the crisis in children's mental.
Abstract. Social media are responsible for aggravating mental health problems. This systematic study summarizes the effects of social network usage on mental health. Fifty papers were shortlisted from google scholar databases, and after the application of various inclusion and exclusion criteria, 16 papers were chosen and all papers were ...
Koehler, Sarah Nichole and Parrell, Bobbie Rose, "THE IMPACT OF SOCIAL MEDIA ON MENTAL HEALTH: A MIXED-METHODS RESEARCH OF SERVICE PROVIDERS' AWARENESS" (2020). Electronic Theses, Projects, ... I would like to dedicate this research paper to my family, friends, and loved ones. A special acknowledgment to my significant other, Donnie, for
This paper examines the impact of social media on mental health, focusing on the role of online platforms in shaping psy chological well-b eing. T he abstract provides a concise summary of the
Children and adolescent mental health. The World Health Organization (WHO, Citation 2017) reported that 10-20% of children and adolescents worldwide experience mental health problems.It is estimated that 50% of all mental disorders are established by the age of 14 and 75% by the age of 18 (Kessler et al., Citation 2007; Kim-Cohen et al., Citation 2003).
A scoping review of the academic literature on the mental health of physicians and physicians-in-training in North America was conducted using Arksey and O'Malley's [] methodological framework.Our review objectives and broad focus, including the general questions posed to conduct the review, lend themselves to a scoping review approach, which is suitable for the analysis of a broader range ...
How does school mental health affect students' academic and social-emotional outcomes? This paper reviews the current status of the research and suggests future directions for this important topic ...
It is pertinent to summarize and study mental health research during the pandemic, because many psychological problems have arisen as a result, and there has been significant interest in research on such issues in the previous two years. ... Due to the limited training sample of academic papers at present, it is difficult to predict the ...
This qualitative study explores the lived experience of mental distress within college. student identity. The purposes of this study is to: (1) address a gap in extant literature on mental. health as an aspect of college identity from students' own voice, (2) add to literature that.
For example, children and young people have diminished educational opportunities if they have poor mental health (Thomas & Morris, Citation 2003; Wickersham et al., ... This paper describes four mental health research goals which were the product of these discussions across the mental health sector. The goals are intended to be a guide rather ...
Sadly, psychological distress among young people seems to be rising. One study found that rates of depression among a nationally representative sample of US adolescents (aged 12 to 17) increased ...
Property cluster models are an approach that proposes that networks of mechanistic clusters cause mental health problems. For example, Kendler et al. ( 2011) argue that this model is the best way of understanding mental health problems as it acknowledges that mental health problems are multi-factorial or "fuzzy".
The quality of life and mental health of the participants are highly connected with their age, gender, year level, and family socioeconomic situation. ... Discover the world's research. 25 ...
The COVID-19 pandemic represents an unprecedented threat to mental health in high, middle, and low-income countries. In addition to flattening the curve of viral transmission, priority needs to be given to the prevention of mental disorders (e.g. major depressive disorder, PTSD, as well as suicide).
Critical Analysis Research Paper Topics in Mental Health. For psychology students looking for effective research paper topics mental health offers many arenas for critical analysis. Here are some good topics to pick from -. Relevance of Freud in modern day psychiatry. Abortion care - the ethics and the procedures to facilitate emotional ...
Mental health and related conditions are a hot-button healthcare topic in 2024. With an estimated one in five Americans living with a mental health condition, ongoing research into the causes, treatment options, and possible triggers has never been more necessary.. Research in the mental health space helps fill knowledge gaps and create a fuller picture for patients, healthcare professionals ...
Good Thesis Statement Examples. Specific and Clear: "The research quantitatively analyzes the impact of school-based mental health awareness programs on adolescents' levels of depression and anxiety." Bad: "School programs about mental health awareness are important." The good example is specific and clear, offering a quantitative approach, focus group (adolescents), and measurable ...
Short abstract. This study aimed to establish what is known about the mental health of researchers based on the existing literature. The literature identified focuses mainly on stress in the academic workforce and contributory factors in the academic workplace. Keywords: Depression, Scientific Professions, Workforce Management, Workplace ...
The present research paper explored to study the level of mental health among adolescents. Method: The present study consisted sample of 40 subjects divided in two groups (Boys and Girls) each ...
A mental health crisis looms, but less stigma means more funding, more research and new efforts to reach those in need. ... Less stigma also means more money for research and mental health services. Funding for mental health has become a rare bipartisan issue. In 2022, Congress passed the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act, which has provided ...
APPLICATIONS OF ESM IN THE MENTAL HEALTH RESEARCH FIELD. ... Good examples are anhedonia and avolition, ... The second and third author contributed equally to this paper. This work was supported by a Research Foundation Flanders (FWO) Odysseus grant (G0F8416N) and a European Research Council consolidator grant (ERC‐2012‐StG, project 309767 ...
We will write a custom essay on your topic a custom Research Paper on Mental Health: Assessment and Screening. 808 writers online . ... For example, Symptom Checklist-90-Revised, found effective by scholars (Abiri & Shairi, 2019), helps identify the broad range of psychological problems. Through 12-15 minutes, patients will complete this test ...