

Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 2 Polynomials PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 2 Comments
Case study Questions in Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 2 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions Chapter 2 Polynomials
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

These case study questions challenge students to apply their knowledge of polynomials in real-life scenarios, enhancing their problem-solving abilities. This article provides for the Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 2: Polynomials , enabling students to practice and excel in their examinations.
Polynomials Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Ankur and Ranjan start a new business together. The amount invested by both partners together is given by the polynomial p(x) = 4x 2 + 12x + 5, which is the product of their individual shares.
Coefficient of x 2 in the given polynomial is (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 12
Answer: (c) 4
Total amount invested by both, if x = 1000 is (a) 301506 (b)370561 (c) 4012005 (d)490621
Answer: (c) 4012005
The shares of Ankur and Ranjan invested individually are (a) (2x + 1),(2x + 5)(b) (2x + 3),(x + 1) (c) (x + 1),(x + 3) (d) None of these
Answer: (a) (2x + 1),(2x + 5)
Name the polynomial of amounts invested by each partner. (a) Cubic (b) Quadratic (c) Linear (d) None of these
Answer: (c) Linear
Find the value of x, if the total amount invested is equal to 0. (a) –1/2 (b) –5/2 (c) Both (a) and (b) (d) None of these
Answer: (c) Both (a) and (b)
One day, the principal of a particular school visited the classroom. The class teacher was teaching the concept of a polynomial to students. He was very much impressed by her way of teaching. To check, whether the students also understand the concept taught by her or not, he asked various questions to students. Some of them are given below. Answer them
Which one of the following is not a polynomial? (a) 4x 2 + 2x – 1 (b) y+3/y (c) x 3 – 1 (d) y 2 + 5y + 1
Answer: (b) y+3/y
The polynomial of the type ax 2 + bx + c, a = 0 is called (a) Linear polynomial (b) Quadratic polynomial (c) Cubic polynomial (d) Biquadratic polynomial
Answer: (a) Linear polynomial
The value of k, if (x – 1) is a factor of 4x 3 + 3x 2 – 4x + k, is (a) 1 (b) –2 (c) –3 (d) 3
Answer: (c) –3
If x + 2 is the factor of x 3 – 2ax 2 + 16, then value of a is (a) –7 (b) 1 (c) –1 (d) 7
Answer: (b) 1
The number of zeroes of the polynomial x 2 + 4x + 2 is (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
Answer: (b) 2
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 3. Amit and Rahul are friends who love collecting stamps. They decide to start a stamp collection club and contribute funds to purchase new stamps. They both invest a certain amount of money in the club. Let’s represent Amit’s investment by the polynomial A(x) = 3x^2 + 2x + 1 and Rahul’s investment by the polynomial R(x) = 2x^2 – 5x + 3. The sum of their investments is represented by the polynomial S(x), which is the sum of A(x) and R(x).
Q1. What is the coefficient of x^2 in Amit’s investment polynomial A(x)? (a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 1 (d) 0
Answer: (a) 3
Q2. What is the constant term in Rahul’s investment polynomial R(x)? (a) 2 (b) -5 (c) 3 (d) 0
Answer: (c) 6
Q3. What is the degree of the polynomial S(x), representing the sum of their investments? (a) 4 (b) 3 (c) 2 (d) 1
Answer: (c) 2
Q4. What is the coefficient of x in the polynomial S(x)? (a) 7 (b) -3 (c) 0 (d) 5
Answer: (b) -3
Q5. What is the sum of their investments, represented by the polynomial S(x)? (a) 5x^2 + 7x + 4 (b) 5x^2 – 3x + 4 (c) 5x^2 – 3x + 5 (d) 5x^2 + 7x + 5
Answer: (b) 5x^2 – 3x + 4
Case Study 4. A school is organizing a fundraising event to support a local charity. The students are divided into three groups: Group A, Group B, and Group C. Each group is responsible for collecting donations from different areas of the town.
Group A consists of 30 students and each student is expected to collect ‘x’ amount of money. The polynomial representing the total amount collected by Group A is given as A(x) = 2x^2 + 5x + 10.
Group B consists of 20 students and each student is expected to collect ‘y’ amount of money. The polynomial representing the total amount collected by Group B is given as B(y) = 3y^2 – 4y + 7.
Group C consists of 40 students and each student is expected to collect ‘z’ amount of money. The polynomial representing the total amount collected by Group C is given as C(z) = 4z^2 + 3z – 2.
Q1. What is the coefficient of x in the polynomial A(x)? (a) 2 (b) 5 (c) 10 (d) 0
Answer: (b) 5
Q2. What is the degree of the polynomial B(y)? (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 1
Answer: (b) 3
Q3. What is the constant term in the polynomial C(z)? (a) 4 (b) 3 (c) -2 (d) 0
Answer: (c) -2
Q4. What is the sum of the coefficients of the polynomial A(x)? (a) 2 (b) 5 (c) 10 (d) 17
Answer: (c) 10
Q5. What is the total number of students in all three groups combined? (a) 30 (b) 20 (c) 40 (d) 90
Answer: (c) 40
The Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 2: Polynomials serve as a valuable resource for students seeking to enhance their understanding of polynomial concepts and problem-solving skills. By practicing these case studies, students can strengthen their grasp of polynomials and their applications in real-life scenarios. Embrace the opportunity to engage with practical problems and excel in your mathematical journey.
By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Class 9 mcq questions for chapter 11 work and energy with answers, mcq questions of class 9 social science history chapter 5 pastoralists in the modern world with answers, cbse class 9 social science(sst) term 1 mcq questions with answers pdf download, this post has 2 comments.
I didnt understand last question
The number of zeroes of the polynomial x2 + 4x + 2 is The answer is too easy, i.e. 2
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 3 Minutes
Case Study Questions
Question 1:
On one day, principal of a particular school visited the classroom. Class teacher was teaching the concept of polynomial to students. He was very much impressed by her way of teaching. To check, whether the students also understand the concept taught by her or not, he asked various questions to students. Some of them are given below. Answer them.
(i) Which one of the following is not a polynomial? (a) 4x 2 + 2x – 1 (b) y+ (3/y) (c) x 3 – 1 (d) y 2 + 5y + 1
(ii) The polynomial of the type ax 2 + bx + c, a = 0 is called (a) Linear polynomial (b) Quadratic polynomial (c) Cubic polynomial (d) Biquadratic polynomial
(iii) The value of k, if (x – 1) is a factor of 4x 3 + 3x 2 – 4x + k, is (a) 1 (b) –2 (c) –3 (d) 3
(iv) If x + 2 is the factor of x 3 – 2ax 2 + 16, then value of a is (a) –7 (b) 1 (c) –1 (d) 7
(v) The number of zeroes of the polynomial x 2 + 4x + 2 is (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4

Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
CBSE Class 9th Maths 2023 : 30 Most Important Case Study Questions with Answers; Download PDF

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
CBSE Class 9 Maths exam 2022-23 will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. CBSE Class 9 Maths Question Bank on Case Studies given in this article can be very helpful in understanding the new format of questions.
Each question has five sub-questions, each followed by four options and one correct answer. Students can easily download these questions in PDF format and refer to them for exam preparation.
CBSE Class 9 All Students can also Download here Class 9 Other Study Materials in PDF Format.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- CBSE Class 9th 2023-24 : Science Practical Syllabus; Download PDF 19 April, 2023, 4:52 pm
- CBSE Class 9 Maths Practice Book 2023 (Released By CBSE) 23 March, 2023, 6:16 pm
- CBSE Class 9 Science Practice Book 2023 (Released By CBSE) 23 March, 2023, 5:56 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Maths 2023 : 30 Most Important Case Study Questions with Answers; Download PDF 10 February, 2023, 6:20 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Maths 2023 : Important Assertion Reason Question with Solution Download Pdf 9 February, 2023, 12:16 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Exam 2023 : Social Science Most Important Short Notes; Download PDF 16 January, 2023, 4:29 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Mathematics 2023 : Most Important Short Notes with Solutions 27 December, 2022, 6:05 pm
- CBSE Class 9th English 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answer; Download PDF 21 December, 2022, 5:16 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Science 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answers; Download PDF 20 December, 2022, 5:37 pm

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics...
CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you’re looking for a comprehensive and reliable study resource and case study questions for class 9 CBSE, myCBSEguide is the perfect door to enter. With over 10,000 study notes, solved sample papers and practice questions, it’s got everything you need to ace your exams. Plus, it’s updated regularly to keep you aligned with the latest CBSE syllabus . So why wait? Start your journey to success with myCBSEguide today!
Significance of Mathematics in Class 9
Mathematics is an important subject for students of all ages. It helps students to develop problem-solving and critical-thinking skills, and to think logically and creatively. In addition, mathematics is essential for understanding and using many other subjects, such as science, engineering, and finance.
CBSE Class 9 is an important year for students, as it is the foundation year for the Class 10 board exams. In Class 9, students learn many important concepts in mathematics that will help them to succeed in their board exams and in their future studies. Therefore, it is essential for students to understand and master the concepts taught in Class 9 Mathematics .
Case studies in Class 9 Mathematics
A case study in mathematics is a detailed analysis of a particular mathematical problem or situation. Case studies are often used to examine the relationship between theory and practice, and to explore the connections between different areas of mathematics. Often, a case study will focus on a single problem or situation and will use a variety of methods to examine it. These methods may include algebraic, geometric, and/or statistical analysis.
Example of Case study questions in Class 9 Mathematics
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has included case study questions in the Class 9 Mathematics paper. This means that Class 9 Mathematics students will have to solve questions based on real-life scenarios. This is a departure from the usual theoretical questions that are asked in Class 9 Mathematics exams.
The following are some examples of case study questions from Class 9 Mathematics:
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 1
There is a square park ABCD in the middle of Saket colony in Delhi. Four children Deepak, Ashok, Arjun and Deepa went to play with their balls. The colour of the ball of Ashok, Deepak, Arjun and Deepa are red, blue, yellow and green respectively. All four children roll their ball from centre point O in the direction of XOY, X’OY, X’OY’ and XOY’ . Their balls stopped as shown in the above image.
Answer the following questions:
Answer Key:
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 2
- Now he told Raju to draw another line CD as in the figure
- The teacher told Ajay to mark ∠ AOD as 2z
- Suraj was told to mark ∠ AOC as 4y
- Clive Made and angle ∠ COE = 60°
- Peter marked ∠ BOE and ∠ BOD as y and x respectively
Now answer the following questions:
- 2y + z = 90°
- 2y + z = 180°
- 4y + 2z = 120°
- (a) 2y + z = 90°
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 3
- (a) 31.6 m²
- (c) 513.3 m³
- (b) 422.4 m²
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 4
How to Answer Class 9 Mathematics Case study questions
To crack case study questions, Class 9 Mathematics students need to apply their mathematical knowledge to real-life situations. They should first read the question carefully and identify the key information. They should then identify the relevant mathematical concepts that can be applied to solve the question. Once they have done this, they can start solving the Class 9 Mathematics case study question.
Students need to be careful while solving the Class 9 Mathematics case study questions. They should not make any assumptions and should always check their answers. If they are stuck on a question, they should take a break and come back to it later. With some practice, the Class 9 Mathematics students will be able to crack case study questions with ease.
Class 9 Mathematics Curriculum at Glance
At the secondary level, the curriculum focuses on improving students’ ability to use Mathematics to solve real-world problems and to study the subject as a separate discipline. Students are expected to learn how to solve issues using algebraic approaches and how to apply their understanding of simple trigonometry to height and distance problems. Experimenting with numbers and geometric forms, making hypotheses, and validating them with more observations are all part of Math learning at this level.
The suggested curriculum covers number systems, algebra, geometry, trigonometry, mensuration, statistics, graphing, and coordinate geometry, among other topics. Math should be taught through activities that include the use of concrete materials, models, patterns, charts, photographs, posters, and other visual aids.
CBSE Class 9 Mathematics (Code No. 041)
Class 9 Mathematics question paper design
The CBSE Class 9 mathematics question paper design is intended to measure students’ grasp of the subject’s fundamental ideas. The paper will put their problem-solving and analytical skills to the test. Class 9 mathematics students are advised to go through the question paper pattern thoroughly before they start preparing for their examinations. This will help them understand the paper better and enable them to score maximum marks. Refer to the given Class 9 Mathematics question paper design.
QUESTION PAPER DESIGN (CLASS 9 MATHEMATICS)
Mycbseguide: blessing in disguise.
Class 9 is an important milestone in a student’s life. It is the last year of high school and the last chance to score well in the CBSE board exams. myCBSEguide is the perfect platform for students to get started on their preparations for Class 9 Mathematics. myCBSEguide provides comprehensive study material for all subjects, including practice questions, sample papers, case study questions and mock tests. It also offers tips and tricks on how to score well in exams. myCBSEguide is the perfect door to enter for class 9 CBSE preparations.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
14 thoughts on “CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Case Study Questions”
This method is not easy for me
aarti and rashika are two classmates. due to exams approaching in some days both decided to study together. during revision hour both find difficulties and they solved each other’s problems. aarti explains simplification of 2+ ?2 by rationalising the denominator and rashika explains 4+ ?2 simplification of (v10-?5)(v10+ ?5) by using the identity (a – b)(a+b). based on above information, answer the following questions: 1) what is the rationalising factor of the denominator of 2+ ?2 a) 2-?2 b) 2?2 c) 2+ ?2 by rationalising the denominator of aarti got the answer d) a) 4+3?2 b) 3+?2 c) 3-?2 4+ ?2 2+ ?2 d) 2-?3 the identity applied to solve (?10-?5) (v10+ ?5) is a) (a+b)(a – b) = (a – b)² c) (a – b)(a+b) = a² – b² d) (a-b)(a+b)=2(a² + b²) ii) b) (a+b)(a – b) = (a + b
MATHS PAAGAL HAI
All questions was easy but search ? hard questions. These questions was not comparable with cbse. It was totally wastage of time.
Where is search ? bar
maths is love
Can I have more questions without downloading the app.
I love math
Hello l am Devanshu chahal and l am an entorpinior. I am started my card bord business and remanded all the existing things this all possible by math now my business is 120 crore and my business profit is 25 crore in a month. l find the worker team because my business is going well Thanks
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
NCERT solutions for class 9 maths Chapter 2 Polynomials are all about the basics of polynomials like the different types of polynomials, finding roots, or solutions to a polynomial equation. Polynomials are algebraic expressions having one variable or more. These NCERT solutions class 9 maths Chapter 2 also explain the remainder theorem and factor theory of polynomials in detail, the algebraic identities, and polynomials of various degrees.
Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2 polynomials illustrate the difference between linear, quadratic, and cubic polynomials. Important theorems mentioned are the Remainder theorem and the Factor theorem, which help identify the factors of a polynomial. Students can access the solutions from the pdf links given below and also find some of these in the exercises given below.
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.1
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.3
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.4
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.5
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 PDF
The exercises related to identifying the type of polynomial, finding the roots or solution of a polynomial equation, and finding factors of the polynomial are available for free pdf download using the four links provided below:
☛ Download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2 Polynomials
NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
These fundamental properties and theorems of polynomials form the building blocks for higher mathematics. Thus, it is very important to master the fundamentals by solving many different example exercises using the links provided above. These NCERT Solution exercises will help understand the properties of polynomials better, as well as how to utilize them. Chapter-wise detailed analysis of NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials is given below.
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.1 - 21 Questions
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.2 - 22 Questions
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.3 - 7 Questions
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.4 - 7 Questions
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.5 - 41 Questions
☛ Download Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 NCERT Book
Topics Covered: The topics that are covered under the chapter on polynomials include an explanation of polynomials as a special set of algebraic equations, different types of polynomials, solutions of polynomial equations, factor theorem, and remainder theorem. Also, these class 9 maths NCERT solutions Chapter 2 define the algebraic identities , which help in factorizing the algebraic equations.
Total Questions: Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials consists of a total of 45 questions, of which 31 are easy, 9 are moderate, and 5 are long answer type questions.
Cuemath is one of the world's leading math learning platforms that offers LIVE 1-to-1 online math classes for grades K-12 . Our mission is to transform the way children learn math, to help them excel in school and competitive exams. Our expert tutors conduct 2 or more live classes per week, at a pace that matches the child's learning needs.
List of Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2
NCERT solutions class 9 maths Chapter 2 covers lots of important concepts crucial for understanding higher grade maths. By learning to factorize a polynomial expression, one can find the roots of the polynomial equation. This is a relatively simple process that can greatly improve an individual's understanding of polynomial equations. Some important algebraic identities or formulas which help in factorization and are covered in NCERT solutions for class 9 maths chapter 2 are given below.
- ( x + y ) 2 = x 2 + 2xy + y 2
- ( x + y ) 3 = x 3 + y 3 + 3xy (x+y)
Important Questions for Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2
Video solutions for class 9 maths ncert chapter 2, faqs on ncert solutions class 9 maths chapter 2, how cbse students can utilize ncert solutions class 9 maths chapter 2 effectively.
Algebra forms the basis of higher mathematical studies. Hence, students should focus on the important terms defined in this chapter, like the degree of a polynomial, the difference between constant and variable, to get a clear understanding of the polynomials. This will help them to make their base strong to appear for their board exams and face any kind of difficult questions.
Why are Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2 Important?
The NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 includes a detailed explanation of the remainder and the factor theorem, which hold an important place in algebra. Also, the crucial algebraic identities are discussed in an elaborate manner with plenty of questions to solve for the students. A list of all key equations and concepts is available at the end of the chapter. This is a significant benefit because students can use this list whenever required instead of figuring it out from between the lengthy chapter text. Overall, these solutions cover all of the major concepts, approaches, and formulas, making them of utmost importance for class 9 math students.
How Many Questions are there in NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials?
Overall the NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 has 98 questions that can be categorized as easy, medium, and difficult ones. Roughly 70 questions are straightforward and easy to solve, 20 questions are of medium difficulty level while 8 would require some thinking as they are long-form questions.
What are the Important Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2?
The important topics that are covered under the NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 include the basic understanding of polynomials, the components of algebraic expressions, and their definitions. The chapter focuses on the types of polynomials and how to solve them, with special emphasis on factor and remainder theorem and the algebraic entities.

What are the Important Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2?
Since the NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 covers the polynomials from their basic structure, several definitions of important terms have been explained with their formulas, like the factor and the remainder theorem. But the most important formula would be the algebraic identities as they help in factorization itself. For example, (a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2
Do I Need to Practice all Questions Provided in NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Polynomials?
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Polynomials encompass a variety of questions that explore all the algebraic concepts related to polynomials. Hence, it would be good if the students make use of this resource and start practicing by solving the examples first, which will help them in getting an idea of what steps are to be followed when questions related to polynomials are solved.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials are provided here. Our NCERT Maths solutions contain all the questions of the NCERT textbook that are solved and explained beautifully. Here you will get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 all exercises Exercise in one place. These solutions are prepared by the subject experts and as per the latest NCERT syllabus and guidelines. CBSE Class 9 Students who wish to score good marks in the maths exam must practice these questions regularly.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials NCERT Solutions
Below we have provided the solutions of each exercise of the chapter. Go through the links to access the solutions of exercises you want. You should also check out our NCERT Class 9 Solutions for other subjects to score good marks in the exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.3

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.4

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.5

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials – Topic Discussion
Below we have listed the topics that have been discussed in this chapter. As this is one of the important topics in maths, It comes under the unit – Algebra which has a weightage of 20 marks in class 9 maths board exams.
- Polynomials in one Variable – Discussion of Linear, Quadratic and Cubic Polynomial.
- Zeroes of a Polynomial
- Real Numbers and their Decimal Expansions
- Representing Real Numbers on the Number Line Operations on Real Numbers
- Laws of Exponents for Real Numbers.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
Ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 2 polynomials| pdf download.

- Exercise 2.1 Chapter 2 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 2.2 Chapter 2 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 2.3 Chapter 2 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 2.4 Chapter 2 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 2.5 Chapter 2 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapters:
How can i download chapter 2 polynomials class 9 ncert solutions pdf , what do you mean by algebraic expressions, what is the coefficient of a zero polynomial, what is biquadratic polynomial, contact form.
CBSE Expert
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials PDF Download
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials PDF Download are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials

- Checkout: Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
- Checkout: Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions
Polynomials Case Study Questions With Answers
Case study questions class 9 maths chapter 2.
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1. Ankur and Ranjan start a new business together. The amount invested by both partners together is given by the polynomial p(x) = 4x 2 + 12x + 5, which is the product of their individual shares.
Coefficient of x 2 in the given polynomial is (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 12
Answer: (c) 4
Total amount invested by both, if x = 1000 is (a) 301506 (b)370561 (c) 4012005 (d)490621
Answer: (c) 4012005
The shares of Ankur and Ranjan invested individually are (a) (2x + 1),(2x + 5)(b) (2x + 3),(x + 1) (c) (x + 1),(x + 3) (d) None of these
Answer: (a) (2x + 1),(2x + 5)
Name the polynomial of amounts invested by each partner. (a) Cubic (b) Quadratic (c) Linear (d) None of these
Answer: (c) Linear
Find the value of x, if the total amount invested is equal to 0. (a) –1/2 (b) –5/2 (c) Both (a) and (b) (d) None of these
Answer: (c) Both (a) and (b)
Case Study 2. One day, the principal of a particular school visited the classroom. The class teacher was teaching the concept of a polynomial to students. He was very much impressed by her way of teaching. To check, whether the students also understand the concept taught by her or not, he asked various questions to students. Some of them are given below. Answer them
Which one of the following is not a polynomial? (a) 4x 2 + 2x – 1 (b) y+3/y (c) x 3 – 1 (d) y 2 + 5y + 1
Answer: (b) y+3/y
The polynomial of the type ax 2 + bx + c, a = 0 is called (a) Linear polynomial (b) Quadratic polynomial (c) Cubic polynomial (d) Biquadratic polynomial
Answer: (a) Linear polynomial
The value of k, if (x – 1) is a factor of 4x 3 + 3x 2 – 4x + k, is (a) 1 (b) –2 (c) –3 (d) 3
Answer: (c) –3
If x + 2 is the factor of x 3 – 2ax 2 + 16, then value of a is (a) –7 (b) 1 (c) –1 (d) 7
Answer: (b) 1
The number of zeroes of the polynomial x 2 + 4x + 2 is (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
Answer: (b) 2
Case Study 3. Amit and Rahul are friends who love collecting stamps. They decide to start a stamp collection club and contribute funds to purchase new stamps. They both invest a certain amount of money in the club. Let’s represent Amit’s investment by the polynomial A(x) = 3x^2 + 2x + 1 and Rahul’s investment by the polynomial R(x) = 2x^2 – 5x + 3. The sum of their investments is represented by the polynomial S(x), which is the sum of A(x) and R(x).
Q1. What is the coefficient of x^2 in Amit’s investment polynomial A(x)? (a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 1 (d) 0
Answer: (a) 3
Q2. What is the constant term in Rahul’s investment polynomial R(x)? (a) 2 (b) -5 (c) 3 (d) 0
Answer: (c) 6
Q3. What is the degree of the polynomial S(x), representing the sum of their investments? (a) 4 (b) 3 (c) 2 (d) 1
Answer: (c) 2
Q4. What is the coefficient of x in the polynomial S(x)? (a) 7 (b) -3 (c) 0 (d) 5
Answer: (b) -3
Q5. What is the sum of their investments, represented by the polynomial S(x)? (a) 5x^2 + 7x + 4 (b) 5x^2 – 3x + 4 (c) 5x^2 – 3x + 5 (d) 5x^2 + 7x + 5
Answer: (b) 5x^2 – 3x + 4
Case Study 4. A school is organizing a fundraising event to support a local charity. The students are divided into three groups: Group A, Group B, and Group C. Each group is responsible for collecting donations from different areas of the town.
Group A consists of 30 students and each student is expected to collect ‘x’ amount of money. The polynomial representing the total amount collected by Group A is given as A(x) = 2x^2 + 5x + 10.
Group B consists of 20 students and each student is expected to collect ‘y’ amount of money. The polynomial representing the total amount collected by Group B is given as B(y) = 3y^2 – 4y + 7.
Group C consists of 40 students and each student is expected to collect ‘z’ amount of money. The polynomial representing the total amount collected by Group C is given as C(z) = 4z^2 + 3z – 2.
Q1. What is the coefficient of x in the polynomial A(x)? (a) 2 (b) 5 (c) 10 (d) 0
Answer: (b) 5
Q2. What is the degree of the polynomial B(y)? (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 1
Answer: (b) 3
Q3. What is the constant term in the polynomial C(z)? (a) 4 (b) 3 (c) -2 (d) 0
Answer: (c) -2
Q4. What is the sum of the coefficients of the polynomial A(x)? (a) 2 (b) 5 (c) 10 (d) 17
Answer: (c) 10
Q5. What is the total number of students in all three groups combined? (a) 30 (b) 20 (c) 40 (d) 90
Answer: (c) 40
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Maths Polynomials Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2: Polynomials - Exercise 2.2
- NCERT Solutions

Important Topics under NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials (Ex 2.2)
Chapter 2 of the class 9 maths syllabus is on Polynomials. It is a very important chapter that is covered in class 9 and is divided into 8 major topics. Students are advised to learn from ad practice the solved questions time and again to be able to master the concept of polynomials.
The following list has been provided to give the students a glimpse at the important topics that are covered under the chapter on Polynomials.
Classification of polynomials
Degree of a polynomial
Types of polynomial based on the degree
Constant polynomial
Linear polynomial
Quadratic polynomial
Cubic polynomial
Types of polynomial based on terms
Value of a polynomial
Zero of a polynomial
Operations on polynomials
Importance of Polynomials in Class 9
Polynomials are expressions having more than two algebraic terms. They can also be defined as the sum of several terms where the same variable/variables has/have different powers.
Polynomials are practically a language used in most mathematical expressions and are used to represent appropriate relations between different variables or numbers. Students are encouraged to gather as much information from this chapter to be able to solve tricky problems based on polynomials easily in exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 teach you about polynomials. Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 PDF makes you aware of every aspect of Polynomials - be it finding value, using algebraic identities or factorization of polynomials. Our Exercise 2.2 Class 9 Maths solution explains everything about polynomials in an easy to understand way. Vedantu provides students with a Free PDF download option for all the NCERT Book Solutions of updated CBSE textbooks . Subjects like Science, Maths, English will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for Class 9 Science , Maths solutions, and solutions of other subjects that are available on Vedantu only.

Access NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 – Polynomials
Exercise 2.2
1. Find the value of the polynomial $\text{5x - 4}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ + 3}$ at
i) $\text{x = 0}$
Ans: Let $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 5x - 4}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ + 3}$
We will simply put the value of $\text{x}$ in the given polynomial.
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = 5}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ - 4}\left( {{\text{0}}^{\text{2}}} \right)\text{ + 3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = 3}$
Hence, the value of the polynomial at $\text{x = 0}$ is $\text{3}$.
ii) $\text{x = -1}$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{-1} \right)\text{ = 5}\left( \text{-1} \right)\text{ - 4}\left[ {{\left( \text{-1} \right)}^{\text{2}}} \right]\text{ + 3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{-1} \right)\text{ = - 5 - 4 + 3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{-1} \right)\text{ = - 6}$
Hence, the value of the polynomial at $\text{x = -1}$ is $\text{-6}$.
iii) $\text{x = 2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = 5}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ - 4}\left( {{\text{2}}^{\text{2}}} \right)\text{ + 3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = 10 - 16 + 3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = - 3}$
Hence, the value of the polynomial at $\text{x = 2}$ is $\text{-3}$.
2. Find $\text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)$, $\text{p}\left( \text{1} \right)$ and $\text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)$ for each of the following polynomials:
i) $\text{p}\left( \text{y} \right)\text{ = }{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ - y + 1}$
$\text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = }{{\text{0}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ - 0 + 1}$.
So, we get the value of $\text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = 1}$.
$\text{p}\left( \text{1} \right)\text{ = }{{\text{1}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ - 1 + 1 = 1}$
So, we get the value of $\text{p}\left( \text{1} \right)\text{ = 1}$.
$\text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = }{{\text{2}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ - 2 + 1}$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = 4 - 2 + 1}$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = 3}$
So, we get the value of $\text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = 3}$.
ii) $\text{p}\left( \text{t} \right)\text{ = 2 + t + 2}{{\text{t}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ - }{{\text{t}}^{\text{3}}}$
$\text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = 2 + 0 + 2}\left( {{\text{0}}^{\text{2}}} \right)\text{ - }\left( {{\text{0}}^{\text{3}}} \right)\text{ = 2}$
So, we get the value of $\text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = 2}$.
$\text{p}\left( \text{1} \right)\text{ = 2 + 1 + 2}\left( {{\text{1}}^{\text{2}}} \right)\text{ - }\left( {{\text{1}}^{\text{3}}} \right)\text{ = 4}$
So, we get the value of $\text{p}\left( \text{1} \right)\text{ = 4}$.
$\text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = 2 + 2 + 2}\left( {{\text{2}}^{\text{2}}} \right)\text{ - }\left( {{\text{2}}^{\text{3}}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = 4 + 8 - 8}$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = 4}$
So, we get the value of $\text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = 4}$.
iii) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = }{{\text{x}}^{\text{3}}}$
$\text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = }{{\text{0}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ = 0}$
So, we get the value of $\text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = 0}$.
$\text{p}\left( \text{1} \right)\text{ = }{{\text{1}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ = 1}$
$\text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = }{{\text{2}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ = 8}$
So, we get the value of $\text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = 8}$.
iv) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ =}\left( \text{x - 1} \right)\left( \text{x + 1} \right)$
$\text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ =}\left( \text{0 - 1} \right)\left( \text{0 + 1} \right)\text{ = -1}$
So, we get the value of $\text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = -1}$.
$\text{p}\left( \text{1} \right)\text{ =}\left( \text{1 - 1} \right)\left( \text{1 + 1} \right)\text{ = 0}$
So, we get the value of $\text{p}\left( \text{1} \right)\text{ = 0}$.
$\text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ =}\left( \text{2 - 1} \right)\left( \text{2 + 1} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = }\left( \text{1} \right)\left( \text{3} \right)\text{ = 3}$
3. Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial, indicated against them.
i) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 3x + 1}$,$\text{x = -}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: We are given: $\text{x = -}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}$. If it is the zero of the polynomial $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 3x + 1}$, then $\text{p}\left( \text{-}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}} \right)$ should be $\text{0}$.
$\text{p}\left(\text{-}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\right)\text{=3}\left(\text{-}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}} \right)\text{ + 1 = -1 + 1 = 0}$
Hence, we can say that $\text{x = -}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}$ is a zero of the given polynomial.
ii) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{= 5x - }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }$ ,$\text{x = }\frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}}$
Ans: We are given: $\text{x = }\frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}}$. If it is the zero of the polynomial $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 5x - }\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }$, then $\text{p}\left( \frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}} \right)$ should be $\text{0}$.
$\text{p}\left( \frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}} \right)\text{ = 5}\left( \frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}} \right)\text{ - 3}\text{.14 = 4 - 3}\text{.14 }\ne \text{ 0}$
Hence, we can say that $\text{x = }\frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}}$ is not a zero of the given polynomial.
iii) $\text{p(x) = }{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-1, x = 1, -1}$
Ans: We are given: $\text{x = 1}$ and $\text{x = -1}$ .
If they are zeros of polynomial $\text{p(x) = }{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-1}$ , then $\text{p}\left( \text{1} \right)$ and $\text{p}\left( \text{-1} \right)$ should both be $\text{0}$.
$\text{p}\left( \text{1} \right)\text{ = }{{\left( \text{1} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-1 = 0}$
$\text{p}\left( \text{-1} \right)\text{ = }{{\left( \text{-1} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-1 = 0}$
Hence, we can say that $\text{x = 1}$ and $\text{x = -1}$ are zeroes of the given polynomial.
iv) $\text{p(x) = (x+1)(x-2), x = -1, 2}$
Ans: We are given: $\text{x = -1}$ and $\text{x = 2}$.
If they are zeroes of the polynomial $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = }\left( \text{x+1} \right)\left( \text{x-2} \right)$ , then $\text{p}\left( \text{-1} \right)$ and $\text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)$ should be $\text{0}$.
$\text{p}\left( \text{-1} \right)\text{ = }\left( \text{-1+1} \right)\left( \text{-1-2} \right)\text{ = }\left( \text{0} \right)\left( \text{-3} \right)\text{ = 0}$
$\text{p}\left( \text{2} \right)\text{ = }\left( \text{2+1} \right)\left( \text{2-2} \right)\text{ = }\left( \text{3} \right)\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = 0}$
Hence, we can say that $\text{x = -1}$ and $\text{x = 2}$ are zeroes of the given polynomial.
v) $\text{p(x) = }{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, x = 0}$
Ans: We are given $\text{x = 0}$.
If it is a zero of the polynomial $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = }{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}$ , then $\text{p}\left( \text{0} \right)$ should be $\text{0}$.
$\text{ p}\left( \text{0} \right)\text{ = }{{\left( \text{0} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{ = 0}$
Hence, we can say that $\text{x = 0}$ is a zero of the given polynomial.
vi) $\text{p(x) = lx + m, x = -}\frac{\text{m}}{\text{l}}$
Ans: We are given: $\text{x = -}\frac{\text{m}}{\text{l}}$.
If it is a zero of the polynomial $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = lx + m}$ , then $\text{p}\left( \text{-}\frac{\text{m}}{\text{l}} \right)$ should be $\text{0}$ .
Here, $\text{p}\left( \text{-}\frac{\text{m}}{\text{l}} \right)\text{ = l}\left( \text{-}\frac{\text{m}}{\text{l}} \right)\text{ + m = -m + m = 0}$
Hence, we can say that $\text{x = -}\frac{\text{m}}{\text{l}}$ is a zero of the given polynomial.
vii)$\text{p(x)=3}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-1,x=-}\frac{\text{1}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}}\text{,}\frac{\text{2}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}}$
Ans: We are given:$\text{x = }\frac{\text{-1}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}}$ and $\text{x = }\frac{\text{2}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}}$.
If they are zeroes of the polynomial $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 3}{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}\text{-1}$, then $\text{p}\left( \frac{\text{-1}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}} \right)$and $\text{p}\left( \frac{\text{2}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}} \right)$ should be $\text{0}$ .
$\text{p}\left( \frac{\text{-1}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}} \right)\text{ = 3}{{\left( \frac{\text{-1}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-1 = 3}\left( \frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}} \right)\text{-1 = 1-1 = 0}$
$\text{p}\left( \frac{\text{2}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}} \right)\text{ = 3}{{\left( \frac{\text{2}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{-1 = 3}\left( \frac{\text{4}}{\text{3}} \right)\text{-1 = 4-1 = 3}$
Hence, we can say that $\text{x = }\frac{\text{-1}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}}$ is a zero of the given polynomial.
However, the value of $\text{x = }\frac{\text{2}}{\sqrt{\text{3}}}$ is not a zero of the given polynomial.
viii) $\text{p(x) = 2x+1, x = }\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}$
Ans: We are given: $\text{x = }\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}$.
If it is a zero of polynomial $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 2x+1}$ , then $\text{p}\left( \frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}} \right)$ should be $\text{0}$
Here, $\text{p}\left( \frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}} \right)\text{ = 2}\left( \frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}} \right)\text{+1 = 1+1 = 2}$.
So, we get the value $\text{p}\left( \frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}} \right)\ne \text{0}$ .
Hence, we can say that $\text{x = }\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}$ is not a zero of the given polynomial.
4. Find the zero of the polynomial in each of the following cases:
i) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = x+5}$
Ans: If $\text{x}$ is zero of the polynomial, then we can say that $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 0}$.
Let $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x+5 = 0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x = -5}$
Therefore, $\text{x = -5}$ is a zero of the given polynomial.
ii) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = x-5}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x-5 = 0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x = 5}$
Therefore, $\text{x = 5}$ is a zero of the given polynomial.
iii) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 2x+5}$
$\Rightarrow \text{2x+5 = 0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x = -}\frac{\text{5}}{\text{2}}$
Therefore, $\text{x = -}\frac{\text{5}}{\text{2}}$ is a zero of the given polynomial.
iv) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 3x-2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{3x-2 = 0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x = }\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}$
Therefore, $\text{x = }\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}$ is a zero of the given polynomial.
v) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = 3x}$
$\Rightarrow \text{3x = 0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{x = 0}$
Therefore, $\text{x = 0}$ is a zero of the given polynomial.
vi) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = ax, a}\ne \text{0}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ax = 0}$
It is also given that $\text{a}$ is non-zero.
vii) $\text{p}\left( \text{x} \right)\text{ = cx+d, c}\ne \text{0, c, d}$ are real numbers.
$\Rightarrow \text{cx+d = 0}$
It is also given that $\text{c}$ is non-zero.
$\Rightarrow \text{x = -}\frac{\text{d}}{\text{c}}$
Therefore, $\text{x = -}\frac{\text{d}}{\text{c}}$ is a zero of the given polynomial.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 - Exercise 2.2
Vedantu’s Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 includes the following problems from polynomial-
Finding the value of polynomial when the value of the variable is randomly fixed by the teacher,For example, if I ask you to find the value of 2x + 3x when I have randomly set the value of X as 5, you will put the value - 5 in place of X and then multiply 2 and 3 with 5.
Finding whether a particular value of the variable will result in the polynomial to be equated as For example, if X equals to 5 in the equation 2X - 10, then the X = 5 is a zero of the given polynomial.
Finding which value of the variable will result in the polynomial to be equated as 0. For example, if I want to make the value of 3X+1-7 then I have to assign the value of X as 2.
What are Polynomials? Constants and Variables
Before discussing polynomials, it is necessary that you have a clear idea about variables and exponents. Consider the following equation -
2x + 3x = 10
Here we don't know at first what X is. When we solve the equation, we come to the conclusion that here X is 2. So, what X does here is it answers the ‘what’ of a question. In this equation, the question that is implied is - what should we multiply 2 and 3 with so that the addition of the product results in 10?
Again when we are confronted with the following equation -
2x + 3x = 20
the result of X changes. So, the value of X varies the situation.
This is what we call variable. This variable is generally denoted by x,y,z etc.
Again, if you look at the above two examples, the values of 2 and 3 never change. In both situations, the values of 2 and 3 remain fixed. These are called constants.
Now, look at this,
Here the value of 2 increases exponentially ( 2*2*2). The power 3 is known as an exponent.
If you look at the algebraic expression - 2x + 3x - written above, you will see there are two parts in it - 2x and 3x. These parts are called terms.
Polynomial is a mathematical expression that has multiple terms and consists of constants, variables and non-negative or non-fractionated exponents. The polynomial will only involve addition, subtraction or multiplication.
So 2x + 3x is a polynomial in the variable X.
Again, 2³ + X³ + 3² is a polynomial.
But X + 1∕X is not a polynomial since 1/x can be written as . As said earlier, a polynomial does not allow negative exponents.
Expressions that have √X are not polynomials too since √X can be written as and we know that this is not accepted by polynomials.
If you look at the expression 2x + 3x, the numbers before the variables are called coefficients.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 – Other Exercises (2.1 and 2.3)
Here are a few other exercises that you will find in the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 PDF –
Exercise 2.1
In this exercise of Class 9 Maths Chapter 2, students will be introduced to the concept of polynomials. They will obtain an indent knowledge regarding polynomials in one variable and how to solve the associated sums through shortcut techniques. Here are some important questions for exams that are provided in the exercise.
Question 1 : Finding the polynomials among the expressions in one variable and stating reasons for the answers.
Question 2 : Finding the coefficients of x2 in the provided expressions.
Question 3 : Examples of a binomial of degree 35 and monomial of degree 100.
Question 4: Determining the degree of polynomials.
Question 5 : Classifying linear, quadratic and cubic polynomial expressions.
Exercise 2.3
This chapter is a continuation of Exercise 2.2 Class 9 of NCERT maths book. Students will get in-depth knowledge about the Factor Theorem by solving all questions provided in this exercise step by step.
Question 1 : Finding the remainder when divided by expressions provided.
Question 2: Determining remainders.
Question 3: Checking if provided expressions are factors.
How Can Vedantu Help You?
Vedantu's Polynomials Class 9 solutions will help you understand all the topics included in the Polynomials chapter. NCERT guidelines specifically advise teachers to build the fundamental knowledge of the subjects in the students. Vedantu follows this NCERT advice thoroughly. That is why you will find not only solutions to the questions on polynomials but also the explanations on the logic behind our solutions. For example - in question number 2 of Ex 2.1 of our Polynomials Class 9 NCERT Solutions when we are asked to find the coefficients of given polynomials we showed how has an invisible 1 before it. So the coefficient of X² is 1.
Our answers in Class 9th Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2 include every step. No step has been skipped. You will not struggle to understand how we reached the result from a given equation. So in question 1(i) of Ex 2.2, we showed how we arrived at the answer 3 by solving the equation step by step. This will not only help the students to understand the granularities in the chapter but will also help them to get good marks.
Every Polynomial formula Class 9 has been used in our solution. The students will get to learn all the aspects of the chapter. Reading our PDF, a student can answer any question from this chapter with confidence.
The Polynomials Class 9 PDF is written in a lucid language. Apart from the Maths expressions, we have used simple, easy to understand words so that students can understand the solutions. Even the math expressions are adequately explained wherever deemed fit.
The Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 PDF has accurate solutions to every polynomials problem. The answers are written by expert teachers who know how to solve a Maths problem so that students understand the process and even the examiners get impressed by the detailed process. These teachers are well aware of NCERT guidelines and follow them to write their answers. There is no unnecessary information in our solutions.
Vedantu’s Polynomial Class 9 PDF is neatly organised. The solutions are written in an uncluttered, easy to understand way. That is why in question 1 of Ex2.3, you will find that we have used red ink to indicate the cutting off of -2x² and +2x². This visually pleasurable way of reading the solutions will help the students to maintain their focus on the solutions.
You can use our NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 to learn all the intricacies of polynomials. These solutions can provide you with everything that you need to excel in the chapter. The answers in our PDF are not written by part-time bloggers, but they are written by professional teachers who took care to make the solutions as helpful as possible.
The Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Solutions are absolutely free of cost. You don’t need to pay a single penny to download our PDF. You can simply enter your email id and we will send the download link to your email. Vedantu is not motivated by profit; we are genuinely interested in making the learning process of students better. We believe every Indian student has the right to get a quality education.
Learn Online with Vedantu’s Online Class
Our PDF on polynomials is exhaustive and can help you in finding solutions to all the questions asked in the textbook. Maths needs explanation - countless of times. You might want to ask questions about a particular solution in our PDF. So to help you, Vedantu holds online classes where you can ask questions directly to the teachers. This interaction is particularly necessary for understanding Maths chapters. The schedule of the classes is announced beforehand. We have helpful videos too which will help you understand the solutions in a much more easy and efficient way.
Our online teachers are experts in their subjects and come from respectable institutions like IITs. These teachers know how to teach Maths to students in such a way that students do not get bored. The teachers are aided by simultaneous images, videos and slides. This visual way of teaching ensures easy retention in students.
With our Master Class, you can experience a whole new learning experience. We are offering free seats in our master class for a limited period of time. These masterclasses can enhance your knowledge in ways you cannot fathom. We do not employ cheap tricks and tips. Our main focus is on building the basic knowledge of the students. Our Master Class is not just for advanced students, intermediate students can get benefit from the Master Classes as they will shed fear for Maths and grow a love for the subject.
Vedantu also has its app. This application will help the students to stay in the learning mode 24*7. The app, as of now, boasts of 1 million-plus downloads on Play Store.
Vedantu is here to help the students move forward with confidence. With Vedantu, you have a golden opportunity to make the pillars of your knowledge strong.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths
Chapter 1 - Number System
Chapter 3 - Coordinate Geometry
Chapter 4 - Linear Equations in Two Variables
Chapter 5 - Introductions to Euclid's Geometry
Chapter 6 - Lines and Angles
Chapter 7 - Triangles
Chapter 8 - Quadrilaterals
Chapter 9 - Areas of Parallelogram and Triangles
Chapter 10 - Circles
Chapter 11 - Constructions
Chapter 12 - Heron's formula
Chapter 13 - Surface area and Volumes
Chapter 14 - Statistics
Chapter 15 - Probability

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2: Polynomials - Exercise 2.2
1. Give a brief description of the topic.
Polynomial is acquired from the word “poly” which means “many” and the word “nominal” refers to “term”. In Math subject, a polynomial expression consists of variables which are also known as coefficients and indeterminates. The coefficients require the operations of addition, subtraction, non-negative integer exponents of variables and multiplication.
Polynomials are utterances with one or more phrases with a non-zero coefficient. A polynomial can also have one or more than one number of terms. In the form of a polynomial, each utterance in it is known as a term. Suppose x 2 + 4x+ 2 is polynomial, then the expressions x 2 , 4x, and 2 are the terms of the polynomial. Each term of the polynomial has a coefficient. For example, if 4x+1 is the polynomial, then the coefficient of x is 4.
2. What are the important terms of a polynomial?
A term might either be a variable or a single digit or it also could be a sequence of the variable with digits.
The degree of the polynomial is the most distinguished power of the variable in a polynomial.
A polynomial of degree 1 will be termed as a linear polynomial.
A polynomial of degree 2 will be described as a quadratic polynomial.
A polynomial of degree 3 is termed as a cubic polynomial.
A polynomial of 1 term is termed as a monomial.
A polynomial of 2 terms is termed as binomial.
A polynomial of 3 terms is termed as a trinomial.
A real number ‘a’ is a zero of a polynomial p(x) if p(a) = 0, where a is also termed as root of the equation p(x) = 0.
A linear polynomial in one variable holds an individual zero, a polynomial of a non-zero constant has no zero, and every real character is a zero of the zero polynomial.
3. What are the topics that are covered in this chapter?
Polynomial is an algebraic expression which includes constants, variables and exponents. It is the expression where the variables have just certain elemental powers. The topics that are covered in this chapter are:
Introduction
Polynomials in One Variable
Zeros of Polynomials
Remainder Theorem
Factorisation of Polynomials
Algebraic Identities
Polynomial expressions are algebraic equations which will have two or more terms with the equal variables of different exponents. This is one of the notable topics for class 9 Mathematics, which students require to learn in order to gain profound knowledge about complex algebraic expressions. Mathematics is one of those subjects that serve as a foundation of numbers, analysis, figures and logic.
4. Are the answers provided by Vedantu, sufficient to attain accurate marks?
Our answers are made to the point and they are drafted to aid you from the exam portion of the view. Answers to the exercising questions are certainly given with examples and they are 100% curate. Our answers will make your learning easy for the exam as they are fitted to be compatible with the tips given with the assistance of using CBSE maths Syllabus and NCERT Book.
Our answers will assist you in advancing a conceptual basis with all the principal ideas in a comprehensible language. The exercising covers all of the vital topics and subtopics of the chapter which might occur for your Class 9 maths exams. You also can clear all of your doubts from here and in this manner, you can definitely perform well in your Class 9 maths exam.
5. Do I need to practice all the questions given in the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2?
The NCERT textbook is the best textbook to prepare for the final exams as it is where most of the questions are asked in the final exam. The exercises and the examples are explained in a simpler manner for all students to understand. Important concepts are also explained in the PDFs. It is important that you practice all the questions and concepts while preparing for the exam. You should not leave any questions. Being thorough with all the questions will help you score good marks in the final exam. You can visit the Vedantu website or download the Vedantu app to access these resources at free of cost.
6. How many exercises are there in this chapter?
Chapter 2 of Maths from the NCERT textbook has three exercises- 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3. Each exercise and its solution is explained step by step in the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2. Not a single question or step has been skipped where they are explained. The examples from within the chapter are also explained. The solutions have been written by professionals with the aim of making it easier for all the students depending on their calibre to understand.
7. How many questions are there in each exercise?
There are a total of three exercises in the Chapter 2 of Class 10 NCERT Maths textbook. Exercise 2.1 has five questions that cover introduction to polynomials and linear and quadratic linear expressions. Exercise 2.2 has four questions that mainly concentrate on finding the value of the polynomials. The last exercise is 2.3 which focuses on the factor theorem. The questions ask to find the remainders and their division.
8. What are constants and variables?
Constants are the numeric values attached to a variable (x,y) in any equation. They stay the same and do not change. They help you determine the value of the variable. Variables are the X or Y attached to a constant whose value needs to be determined. It may vary in different situations. It is a result of the constants and the answer on the other side that helps determine the value of the variables.
9. Is Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions enough to revise for the final exam?
The NCERT Solutions for each subject and chapter provides summaries and revision notes for the students to refer to and prepare from. These are sufficient as they cover every aspect of the chapter and do not exclude any topic. The students can take the help of the Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to prepare for the exam and revise by going through the revision notes provided. The formulas and concepts are explained in an easy and systematic manner.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9
Cbse study materials for class 9, cbse study materials.
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 9
- NCERT 9 Maths
- Chapter 2: Polynomial
- Exercise 2.5
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 - Polynomials Exercise 2.5
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 – Polynomials Exercise 2.5 are given here. These NCERT Maths solutions are created by our subject experts, who make it easy for students to learn. The students use NCERT Class 9 Maths Solutions for reference while solving the exercise problems. The fifth exercise in Polynomials- Exercise 2.5 discusses the Algebraic Identities.
The experts provide a detailed and stepwise explanation of each answer to the questions given in the exercises in the NCERT textbook for Class 9. The NCERT solutions are always prepared by following NCERT guidelines so that it should cover the whole syllabus accordingly. These are very helpful in scoring well in board examinations.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2- Polynomials Exercise 2.5
carouselExampleControls111

Previous Next
Access Other Exercise Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 2- Polynomials
The Exercise wise links for NCERT Class 9 Solutions Maths Chapter 2 are given below.
Exercise 2.1 Solutions 5 Questions Exercise 2.2 Solutions 4 Questions Exercise 2.3 Solutions 3 Questions Exercise 2.4 Solutions 5 Questions
Access Answers to NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 – Polynomials Exercise 2.5
1. Use suitable identities to find the following products:
(i) (x+4)(x +10)
Using the identity, (x+a)(x+b) = x 2 +(a+b)x+ab
(x+4)(x+10) = x 2 +(4+10)x+(4×10)
= x 2 +14x+40
(ii) (x+8)(x –10)
(x+8)(x−10) = x 2 +(8+(−10))x+(8×(−10))
= x 2 +(8−10)x–80
= x 2 −2x−80
(iii) (3x+4)(3x–5)
(3x+4)(3x−5) = (3x) 2 +[4+(−5)]3x+4×(−5)
= 9x 2 +3x(4–5)–20
= 9x 2 –3x–20
(iv) (y 2 +3/2)(y 2 -3/2)
Using the identity, (x+y)(x–y) = x 2 –y 2
(y 2 +3/2)(y 2 –3/2) = (y 2 ) 2 –(3/2) 2
2. Evaluate the following products without multiplying directly:
(i) 103×107
103×107= (100+3)×(100+7)
Using identity, [(x+a)(x+b) = x 2 +(a+b)x+ab
Here, x = 100
We get, 103×107 = (100+3)×(100+7)
= (100) 2 +(3+7)100+(3×7)
= 10000+1000+21
(ii) 95×96
95×96 = (100-5)×(100-4)
Using identity, [(x-a)(x-b) = x 2 -(a+b)x+ab
We get, 95×96 = (100-5)×(100-4)
= (100) 2 +100(-5+(-4))+(-5×-4)
= 10000-900+20
(iii) 104×96
104×96 = (100+4)×(100–4)
Using identity, [(a+b)(a-b)= a 2 -b 2 ]
Here, a = 100
We get, 104×96 = (100+4)×(100–4)
= (100) 2 –(4) 2
3. Factorize the following using appropriate identities:
(i) 9x 2 +6xy+y 2
9x 2 +6xy+y 2 = (3x) 2 +(2×3x×y)+y 2
Using identity, x 2 +2xy+y 2 = (x+y) 2
Here, x = 3x
= (3x+y)(3x+y)
(ii) 4y 2 −4y+1
4y 2 −4y+1 = (2y) 2 –(2×2y×1)+1
Using identity, x 2 – 2xy + y 2 = (x – y) 2
Here, x = 2y
4y 2 −4y+1 = (2y) 2 –(2×2y×1)+1 2
= (2y–1)(2y–1)
(iii) x 2 –y 2 /100
x 2 –y 2 /100 = x 2 –(y/10) 2
Using identity, x 2 -y 2 = (x-y)(x+y)
Here, x = x
= (x–y/10)(x+y/10)
4. Expand each of the following, using suitable identities:
(i) (x+2y+4z) 2
(ii) (2x−y+z) 2
(iii) (−2x+3y+2z) 2
(iv) (3a –7b–c) 2
(v) (–2x+5y–3z) 2
(vi) ((1/4)a-(1/2)b +1) 2
Using identity, (x+y+z) 2 = x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2xy+2yz+2zx
(x+2y+4z) 2 = x 2 +(2y) 2 +(4z) 2 +(2×x×2y)+(2×2y×4z)+(2×4z×x)
= x 2 +4y 2 +16z 2 +4xy+16yz+8xz
(ii) (2x−y+z) 2
Here, x = 2x
(2x−y+z) 2 = (2x) 2 +(−y) 2 +z 2 +(2×2x×−y)+(2×−y×z)+(2×z×2x)
= 4x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –4xy–2yz+4xz
Here, x = −2x
(−2x+3y+2z) 2 = (−2x) 2 +(3y) 2 +(2z) 2 +(2×−2x×3y)+(2×3y×2z)+(2×2z×−2x)
= 4x 2 +9y 2 +4z 2 –12xy+12yz–8xz
Using identity (x+y+z) 2 = x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2xy+2yz+2zx
Here, x = 3a
(3a –7b– c) 2 = (3a) 2 +(– 7b) 2 +(– c) 2 +(2×3a ×– 7b)+(2×– 7b ×– c)+(2×– c ×3a)
= 9a 2 + 49b 2 + c 2 – 42ab+14bc–6ca
Here, x = –2x
(–2x+5y–3z) 2 = (–2x) 2 +(5y) 2 +(–3z) 2 +(2×–2x × 5y)+(2× 5y×– 3z)+(2×–3z ×–2x)
= 4x 2 +25y 2 +9z 2 – 20xy–30yz+12zx
(vi) ((1/4)a-(1/2)b+1) 2
Here, x = (1/4)a
y = (-1/2)b
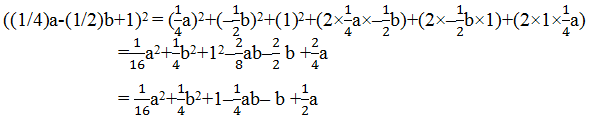
5. Factorize:
(i) 4x 2 +9y 2 +16z 2 +12xy–24yz–16xz
(ii ) 2x 2 +y 2 +8z 2 –2√2xy+4√2yz–8xz
We can say that, x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2xy+2yz+2zx = (x+y+z) 2
4x 2 +9y 2 +16z 2 +12xy–24yz–16xz = (2x) 2 +(3y) 2 +(−4z) 2 +(2×2x×3y)+(2×3y×−4z)+(2×−4z×2x)
= (2x+3y–4z) 2
= (2x+3y–4z)(2x+3y–4z)
(ii) 2x 2 +y 2 +8z 2 –2√2xy+4√2yz–8xz
Using identity, (x +y+z) 2 = x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2xy+2yz+2zx
2x 2 +y 2 +8z 2 –2√2xy+4√2yz–8xz
= (-√2x) 2 +(y) 2 +(2√2z) 2 +(2×-√2x×y)+(2×y×2√2z)+(2×2√2×−√2x)
= (−√2x+y+2√2z) 2
= (−√2x+y+2√2z)(−√2x+y+2√2z)
6. Write the following cubes in expanded form:
(i) (2x+1) 3
(ii) (2a−3b) 3
(iii) ((3/2)x+1) 3
(iv) (x−(2/3)y) 3
Using identity,(x+y) 3 = x 3 +y 3 +3xy(x+y)
(2x+1) 3 = (2x) 3 +1 3 +(3×2x×1)(2x+1)
= 8x 3 +1+6x(2x+1)
= 8x 3 +12x 2 +6x+1
Using identity,(x–y) 3 = x 3 –y 3 –3xy(x–y)
(2a−3b) 3 = (2a) 3 −(3b) 3 –(3×2a×3b)(2a–3b)
= 8a 3 –27b 3 –18ab(2a–3b)
= 8a 3 –27b 3 –36a 2 b+54ab 2
((3/2)x+1) 3 =((3/2)x) 3 +1 3 +(3×(3/2)x×1)((3/2)x +1)
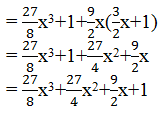
(iv) (x−(2/3)y) 3
Using identity, (x –y) 3 = x 3 –y 3 –3xy(x–y)
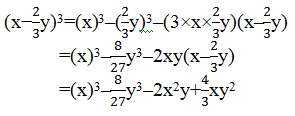
7. Evaluate the following using suitable identities:
(ii) (102) 3
(iii) (998) 3
We can write 99 as 100–1
(99) 3 = (100–1) 3
= (100) 3 –1 3 –(3×100×1)(100–1)
= 1000000 –1–300(100 – 1)
= 1000000–1–30000+300
We can write 102 as 100+2
(100+2) 3 =(100) 3 +2 3 +(3×100×2)(100+2)
= 1000000 + 8 + 600(100 + 2)
= 1000000 + 8 + 60000 + 1200
We can write 99 as 1000–2
(998) 3 =(1000–2) 3
=(1000) 3 –2 3 –(3×1000×2)(1000–2)
= 1000000000–8–6000(1000– 2)
= 1000000000–8- 6000000+12000
= 994011992
8. Factorise each of the following:
(i) 8a 3 +b 3 +12a 2 b+6ab 2
(ii) 8a 3 –b 3 –12a 2 b+6ab 2
(iii) 27–125a 3 –135a +225a 2
(iv) 64a 3 –27b 3 –144a 2 b+108ab 2
(v) 27p 3 –(1/216)−(9/2) p 2 +(1/4)p
The expression, 8a 3 +b 3 +12a 2 b+6ab 2 can be written as (2a) 3 +b 3 +3(2a) 2 b+3(2a)(b) 2
8a 3 +b 3 +12a 2 b+6ab 2 = (2a) 3 +b 3 +3(2a) 2 b+3(2a)(b) 2
= (2a+b)(2a+b)(2a+b)
Here, the identity, (x +y) 3 = x 3 +y 3 +3xy(x+y) is used.
The expression, 8a 3 –b 3 −12a 2 b+6ab 2 can be written as (2a) 3 –b 3 –3(2a) 2 b+3(2a)(b) 2
8a 3 –b 3 −12a 2 b+6ab 2 = (2a) 3 –b 3 –3(2a) 2 b+3(2a)(b) 2
= (2a–b)(2a–b)(2a–b)
Here, the identity,(x–y) 3 = x 3 –y 3 –3xy(x–y) is used.
(iii) 27–125a 3 –135a+225a 2
The expression, 27–125a 3 –135a +225a 2 can be written as 3 3 –(5a) 3 –3(3) 2 (5a)+3(3)(5a) 2
27–125a 3 –135a+225a 2 = 3 3 –(5a) 3 –3(3) 2 (5a)+3(3)(5a) 2
= (3–5a)(3–5a)(3–5a)
Here, the identity, (x–y) 3 = x 3 –y 3 -3xy(x–y) is used.
The expression, 64a 3 –27b 3 –144a 2 b+108ab 2 can be written as (4a) 3 –(3b) 3 –3(4a) 2 (3b)+3(4a)(3b) 2
64a 3 –27b 3 –144a 2 b+108ab 2 = (4a) 3 –(3b) 3 –3(4a) 2 (3b)+3(4a)(3b) 2
=(4a–3b)(4a–3b)(4a–3b)
Here, the identity, (x – y) 3 = x 3 – y 3 – 3xy(x – y) is used.
(v) 27p 3 – (1/216)−(9/2) p 2 +(1/4)p
The expression, 27p 3 –(1/216)−(9/2) p 2 +(1/4)p can be written as
(3p) 3 –(1/6) 3 −(9/2) p 2 +(1/4)p = (3p) 3 –(1/6) 3 −3(3p)(1/6)(3p – 1/6)
Using (x – y) 3 = x 3 – y 3 – 3xy (x – y)
27p 3 –(1/216)−(9/2) p 2 +(1/4)p = (3p) 3 –(1/6) 3 −3(3p)(1/6)(3p – 1/6)
Taking x = 3p and y = 1/6
= (3p–1/6) 3
= (3p–1/6)(3p–1/6)(3p–1/6)
(i) x 3 +y 3 = (x+y)(x 2 –xy+y 2 )
(ii) x 3 –y 3 = (x–y)(x 2 +xy+y 2 )
We know that, (x+y) 3 = x 3 +y 3 +3xy(x+y)
⇒ x 3 +y 3 = (x+y) 3 –3xy(x+y)
⇒ x 3 +y 3 = (x+y)[(x+y) 2 –3xy]
Taking (x+y) common ⇒ x 3 +y 3 = (x+y)[(x 2 +y 2 +2xy)–3xy]
⇒ x 3 +y 3 = (x+y)(x 2 +y 2 –xy)
(ii) x 3 –y 3 = (x–y)(x 2 +xy+y 2 )
We know that,(x–y) 3 = x 3 –y 3 –3xy(x–y)
⇒ x 3 −y 3 = (x–y) 3 +3xy(x–y)
⇒ x 3 −y 3 = (x–y)[(x–y) 2 +3xy]
Taking (x+y) common ⇒ x 3 −y 3 = (x–y)[(x 2 +y 2 –2xy)+3xy]
⇒ x 3 +y 3 = (x–y)(x 2 +y 2 +xy)
10. Factorize each of the following:
(i) 27y 3 +125z 3
(ii) 64m 3 –343n 3
The expression, 27y 3 +125z 3 can be written as (3y) 3 +(5z) 3
27y 3 +125z 3 = (3y) 3 +(5z) 3
We know that, x 3 +y 3 = (x+y)(x 2 –xy+y 2 )
= (3y+5z)[(3y) 2 –(3y)(5z)+(5z) 2 ]
= (3y+5z)(9y 2 –15yz+25z 2 )
The expression, 64m 3 –343n 3 can be written as (4m) 3 –(7n) 3
64m 3 –343n 3 = (4m) 3 –(7n) 3
We know that, x 3 –y 3 = (x–y)(x 2 +xy+y 2 )
= (4m–7n)[(4m) 2 +(4m)(7n)+(7n) 2 ]
= (4m–7n)(16m 2 +28mn+49n 2 )
11. Factorise: 27x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –9xyz
The expression 27x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –9xyz can be written as (3x) 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3(3x)(y)(z)
27x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –9xyz = (3x) 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3(3x)(y)(z)
We know that, x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3xyz = (x+y+z)(x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –xy –yz–zx)
= (3x+y+z)[(3x) 2 +y 2 +z 2 –3xy–yz–3xz]
= (3x+y+z)(9x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –3xy–yz–3xz)
12. Verify that:
x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3xyz = (1/2) (x+y+z)[(x–y) 2 +(y–z) 2 +(z–x) 2 ]
We know that,
x 3 +y 3 +z 3 −3xyz = (x+y+z)(x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –xy–yz–xz)
⇒ x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3xyz = (1/2)(x+y+z)[2(x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –xy–yz–xz)]
= (1/2)(x+y+z)(2x 2 +2y 2 +2z 2 –2xy–2yz–2xz)
= (1/2)(x+y+z)[(x 2 +y 2 −2xy)+(y 2 +z 2 –2yz)+(x 2 +z 2 –2xz)]
= (1/2)(x+y+z)[(x–y) 2 +(y–z) 2 +(z–x) 2 ]
13. If x+y+z = 0, show that x 3 +y 3 +z 3 = 3xyz.
x 3 +y 3 +z 3 -3xyz = (x +y+z)(x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –xy–yz–xz)
Now, according to the question, let (x+y+z) = 0,
then, x 3 +y 3 +z 3 -3xyz = (0)(x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –xy–yz–xz)
⇒ x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3xyz = 0
⇒ x 3 +y 3 +z 3 = 3xyz
Hence Proved
14. Without actually calculating the cubes, find the value of each of the following:
(i) (−12) 3 +(7) 3 +(5) 3
(ii) (28) 3 +(−15) 3 +(−13) 3
Let a = −12
We know that if x+y+z = 0, then x 3 +y 3 +z 3 =3xyz.
Here, −12+7+5=0
(−12) 3 +(7) 3 +(5) 3 = 3xyz
= 3×-12×7×5
(28) 3 +(−15) 3 +(−13) 3
We know that if x+y+z = 0, then x 3 +y 3 +z 3 = 3xyz.
Here, x+y+z = 28–15–13 = 0
(28) 3 +(−15) 3 +(−13) 3 = 3xyz
= 0+3(28)(−15)(−13)
15. Give possible expressions for the length and breadth of each of the following rectangles, in which their areas are given:
(i) Area : 25a 2 –35a+12
(ii) Area : 35y 2 +13y–12
Using the splitting the middle term method,
We have to find a number whose sum = -35 and product =25×12=300
We get -15 and -20 as the numbers [-15+-20=-35 and -15×-20=300]
25a 2 –35a+12 = 25a 2 –15a−20a+12
= 5a(5a–3)–4(5a–3)
= (5a–4)(5a–3)
Possible expression for length = 5a–4
Possible expression for breadth = 5a –3
We have to find a number whose sum = 13 and product = 35×-12 = 420
We get -15 and 28 as the numbers [-15+28 = 13 and -15×28=420]
35y 2 +13y–12 = 35y 2 –15y+28y–12
= 5y(7y–3)+4(7y–3)
= (5y+4)(7y–3)
Possible expression for length = (5y+4)
Possible expression for breadth = (7y–3)
16. What are the possible expressions for the dimensions of the cuboids whose volumes are given below?
(i) Volume : 3x 2 –12x
(ii) Volume : 12ky 2 +8ky–20k
3x 2 –12x can be written as 3x(x–4) by taking 3x out of both the terms.
Possible expression for length = 3
Possible expression for breadth = x
Possible expression for height = (x–4)
(ii) Volume: 12ky 2 +8ky–20k
12ky 2 +8ky–20k can be written as 4k(3y 2 +2y–5) by taking 4k out of both the terms.
12ky 2 +8ky–20k = 4k(3y 2 +2y–5)
= 4k(3y 2 +5y–3y–5)
= 4k[y(3y+5)–1(3y+5)]
= 4k(3y+5)(y–1)
Possible expression for length = 4k
Possible expression for breadth = (3y +5)
Possible expression for height = (y -1)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Thank you for this This is helpful
I like this app whole information I got
Excellent it is really very helpful for doubt solving
Very Helpful 🙂 !!
Thank you for this And this is most helpful for us
It is very helpful thankyou so much
Thanks BYJU’S is very helpful 😊
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Ankur and Ranjan start a new business together. The amount invested by both partners together is given by the polynomial p (x) = 4x 2 + 12x + 5, which is the product of their individual shares.
Case Study Questions Question 1: On one day, principal of a particular school visited the classroom. Class teacher was teaching the concept of polynomial to students. He was very much impressed by her way of teaching. To check, whether the students also understand the concept taught by her or not, he asked variousquestions to students. … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 9 ...
Download Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams 2023-24. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 9 so that they can score 100% in Exams. Case study questions play a pivotal role in enhancing students' problem-solving skills.
CBSE Class 9 Maths Question Bank on Case Studies given in this article can be very helpful in understanding the new format of questions. Each question has five sub-questions, each followed by four options and one correct answer. Students can easily download these questions in PDF format and refer to them for exam preparation. Case Study Questions.
Welcome to our Class 9 Maths exam preparation series for the academic year 2023-24! In this video, we dive deep into Case Study Questions from Chapter 2: Pol...
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 2. Read the Source/Text given below and answer any four questions: Maths teacher draws a straight line AB shown on the blackboard as per the following figure. Now he told Raju to draw another line CD as in the figure. The teacher told Ajay to mark ∠ AOD as 2z.
To prepare for Class 9 exams, students will require notes to study. These notes are of great help when they have to revise chapter 2 polynomials before the exam. ... The important algebraic identities used in Class 9 Maths chapter 2 polynomials are listed below: (x + y + z) 2 = x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2xy + 2yz + 2zx (x + y) ... Polynomials Class 9 ...
Total Questions: Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials consists of a total of 45 questions, of which 31 are easy, 9 are moderate, and 5 are long answer type questions. Cuemath is one of the world's leading math learning platforms that offers LIVE 1-to-1 online math classes for grades K-12. Our mission is to transform the way children learn math ...
Ans: Crucial Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 questions titled Polynomials assist students in preparing for the Class 9 Mathematics Test. This will give you a general sense of the types of questions you could encounter in the test and from which chapter. Understanding what to study in a subject makes learning easier and faster since it requires less time.
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 - Polynomials solved by expert Maths teachers on Vedantu as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 2 - Polynomials exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations. Download free Class 9 Maths to amp up ...
These questions will help the 9th class students to get acquainted with a wide variety of questions and develop the confidence to solve polynomial questions more efficiently. 1. Give an example of a monomial and a binomial having degrees of 82 and 99, respectively. Solution: An example of a monomial having a degree of 82 = x 82.
List of Exercises in Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials. Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials contains 5 exercises. Based on the concept of polynomials, each exercise provides a number of questions. Click on the below links to access the exercise-wise NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 polynomials. Exercise 2.1 Solutions 5 Questions
Every NCERT Solution is provided to make the study simple and interesting on Vedantu. Subjects like Science, Maths, and English will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for Class 9 Science, Maths solutions, and solutions of other subjects.. Chapter 2 of the class 9 maths syllabus includes Polynomials, which is a very important chapter in mathematics that is covered in ...
Here you will get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 all exercises Exercise in one place. These solutions are prepared by the subject experts and as per the latest NCERT syllabus and guidelines. CBSE Class 9 Students who wish to score good marks in the maths exam must practice these questions regularly.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths. Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.2 solved by Expert Teachers as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks.
Subjective Case Based Questions -🔥Polynomials Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 | CBSE Board Exam 2022 Preparation | NCERT Solutions | #VedantuClass9and10 Are all wor... CBSE Exam, class 10
Answer. (i) coefficients of x2 = 1. (ii) coefficients of x2 = -1. (iii) coefficients of x2 = π / 2. (iv) coefficients of x2 = 0. 3. Give one example each of a binomial of degree 35, and of a monomial of degree 100. Answer. 3 x35 +7 and 4 x100.
Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Case Study 1. Ankur and Ranjan start a new business together. The amount invested by both partners together is given by the polynomial p (x) = 4x 2 + 12x + 5, which is the product of their individual shares. Coefficient of x2 in the given polynomial is.
For example in our NCERT Maths Class 9 Exercise 2.3 Solutions , question number 1 (v) tells us to find the remainder when X³ + 3X² + 3X + 1 is divided by 5 + 2X. We employed Long division method and divided the first Polynomial with the second. We went on dividing the Polynomial until the variable was finally eliminated.
Join this channel to get access to perks:https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCsozUYGJWc3kYdQFiMv_BXw/join Maths 👇 class 9 exercise 1.1https://youtu.be/fs_4QLVM...
Answer: b. Explanation: The coefficient of x 2 in equation 3x 3 +2x 2 -x+1 is the multiple of x 2. 3) A binomial of degree 20 in the following is: a. 20x + 1. b. x/20 + 1. c. x 20 +1. d. x 2 +20. Answer: c. Explanation: A polynomial having two terms and the highest degree 20 is called a binomial of degree 20.
The AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Exam in Alaska must begin between 1 and 2 p.m. local time. AP African American Studies Exam Pilot: For the 2024 AP Exam administration, only schools that are participating in the 2023-24 AP African American Studies Exam Pilot can order and administer the exam.
Join us at 6 PM (WAT) this Thursday May 9, 2024, as our distinguish guest will be discussing the topic: GEN-Z ACCOUNTANTS: Redefining Traditional...
This chapter is a continuation of Exercise 2.2 Class 9 of NCERT maths book. Students will get in-depth knowledge about the Factor Theorem by solving all questions provided in this exercise step by step. Question 1: Finding the remainder when divided by expressions provided. Question 2: Determining remainders.
Access Other Exercise Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 2- Polynomials. The Exercise wise links for NCERT Class 9 Solutions Maths Chapter 2 are given below.. Exercise 2.1 Solutions 5 Questions Exercise 2.2 Solutions 4 Questions Exercise 2.3 Solutions 3 Questions Exercise 2.4 Solutions 5 Questions. Access Answers to NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 - Polynomials Exercise 2.5