Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and major leader of the Civil Rights Movement. After his assassination, he was memorialized by Martin Luther King Jr. Day.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back.

In Focus: Martin Luther King Jr. Day
This year’s Martin Luther King Jr. Day, on January 15, coincides with the late civil rights leader ’s birthday. Had he lived, King would be turning 95 years old.
Days after his 1968 assassination , a campaign for a holiday in King’s honor began. U.S. Representative John Conyers Jr. of Michigan first proposed a bill on April 8, 1968, but the first vote on the legislation didn’t happen until 1979. King’s widow, Coretta Scott King , led the lobbying effort to drum up public support. Fifteen years after its introduction, the bill finally became law.
In 1983, President Ronald Reagan ’s signature created Martin Luther King Jr. Day of Service as a federal holiday. It’s celebrated annually on the third Monday in January. The only national day of service, Martin Luther King Jr. Day was first celebrated in 1986. The first time all 50 states recognized the holiday was in 2000.
See Martin Luther King Jr.’s life depicted onscreen in the 2018 documentary I Am MLK Jr. or the Oscar-winning movie Selma .
Who Was Martin Luther King Jr?
Quick facts, where did martin luther king jr. go to school, philosophy of nonviolence, civil rights accomplishments, "i have a dream" and other famous speeches, wife and kids, fbi surveillance, later activism, assassination.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and civil rights activist who had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States, beginning in the mid-1950s. Among his many efforts, King headed the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC). Through his nonviolent activism and inspirational speeches , he played a pivotal role in ending legal segregation of Black Americans, as well as the creation of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 . King won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964, among several other honors. He was assassinated by James Earl Ray and died on April 4, 1968, at age 39. King continues to be remembered as one of the most influential and inspirational Black leaders in history.
FULL NAME: Martin Luther King Jr. BIRTHDAY: January 15, 1929 DIED: April 4, 1968 BIRTHPLACE: Atlanta, Georgia SPOUSE: Coretta Scott King (1953-1968) CHILDREN: Yolanda, Martin III, Dexter, and Bernice King ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Capricorn
Martin Luther King Jr. was born as Michael Luther King Jr. in Atlanta. His birthday was January 15, 1929.
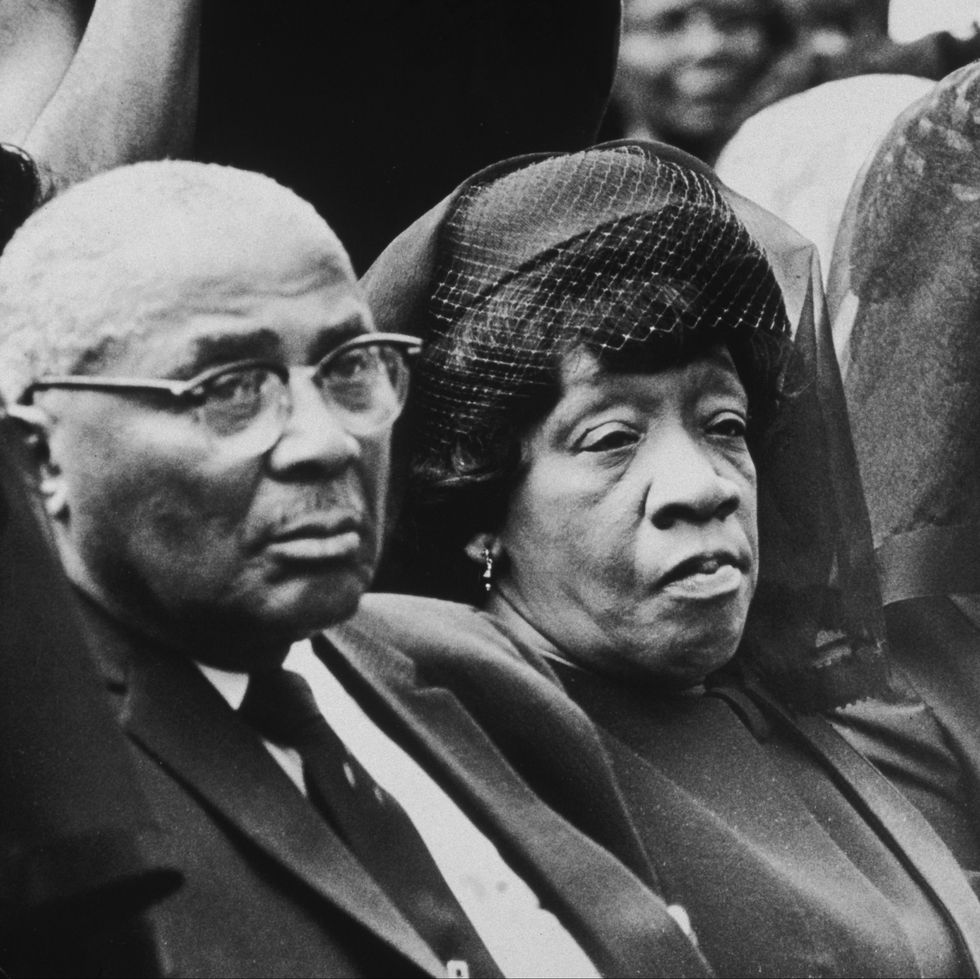

His parents were Michael Luther King Sr. and Alberta Williams King. The Williams and King families had roots in rural Georgia. Martin’s maternal grandfather, A.D. Williams, was a rural minister for years and then moved to Atlanta in 1893. He took over the small, struggling Ebenezer Baptist Church with around 13 members and made it into a forceful congregation. He married Jennie Celeste Parks, and they had one child who survived, Alberta.
Michael Sr. came from a family of sharecroppers in a poor farming community. He married Alberta in 1926 after an eight-year courtship. The newlyweds moved to A.D.’s home in Atlanta. Michael stepped in as pastor of Ebenezer Baptist Church upon the death of his father-in-law in 1931. He, too, became a successful minister and adopted the name Martin Luther King Sr. in honor of the German Protestant religious leader Martin Luther . In due time, Michael Jr. followed his father’s lead and adopt the name himself to become Martin Luther King Jr.
A middle child, Martin Jr. had an older sister, Willie, and a younger brother, Alfred. The King children grew up in a secure and loving environment. Martin Sr. was more the disciplinarian, while Alberta’s gentleness easily balanced out their father’s strict hand.
Although they undoubtedly tried, Martin Jr.’s parents couldn’t shield him completely from racism. His father fought against racial prejudice, not just because his race suffered, but also because he considered racism and segregation to be an affront to God’s will. He strongly discouraged any sense of class superiority in his children, which left a lasting impression on Martin Jr.
Growing up in Atlanta, King entered public school at age 5. In May 1936, he was baptized, but the event made little impression on him.
In May 1941, King was 12 years old when his grandmother Jennie died of a heart attack. The event was traumatic for the boy, more so because he was out watching a parade against his parents’ wishes when she died. Distraught at the news, young King jumped from a second-story window at the family home, allegedly attempting suicide.
King attended Booker T. Washington High School, where he was said to be a precocious student. He skipped both the ninth and eleventh grades and, at age 15, entered Morehouse College in Atlanta in 1944. He was a popular student, especially with his female classmates, but largely unmotivated, floating through his first two years.
Influenced by his experiences with racism, King began planting the seeds for a future as a social activist early in his time at Morehouse. “I was at the point where I was deeply interested in political matters and social ills,” he recalled in The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr . “I could envision myself playing a part in breaking down the legal barriers to Negro rights.”
The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr.

At the time, King felt that the best way to serve that purpose was as a lawyer or a doctor. Although his family was deeply involved in the church and worship, King questioned religion in general and felt uncomfortable with overly emotional displays of religious worship. This discomfort had continued through much of his adolescence, initially leading him to decide against entering the ministry, much to his father’s dismay.
But in his junior year, King took a Bible class, renewed his faith, and began to envision a career in the ministry. In the fall of his senior year, he told his father of his decision, and he was ordained at Ebenezer Baptist Church in February 1948.
Later that year, King earned a sociology degree from Morehouse College and began attended the liberal Crozer Theological Seminary in Chester, Pennsylvania. He thrived in all his studies, was elected student body president, and was valedictorian of his class in 1951. He also earned a fellowship for graduate study.
Even though King was following his father’s footsteps, he rebelled against Martin Sr.’s more conservative influence by drinking beer and playing pool while at college. He became romantically involved with a white woman and went through a difficult time before he could break off the relationship.
During his last year in seminary, King came under the guidance of Morehouse College President Benjamin E. Mays, who influenced King’s spiritual development. Mays was an outspoken advocate for racial equality and encouraged King to view Christianity as a potential force for social change.

After being accepted at several colleges for his doctoral study, King enrolled at Boston University. In 1954, while still working on his dissertation, King became pastor of the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church of Montgomery, Alabama. He completed his doctorate and earned his degree in 1955 at age 25.
Decades after King’s death, in the late 1980s, researchers at Stanford University’s King Papers Project began to note similarities between passages of King’s doctoral dissertation and those of another student’s work. A committee of scholars appointed by Boston University determined that King was guilty of plagiarism in 1991, though it also recommended against the revocation of his degree.
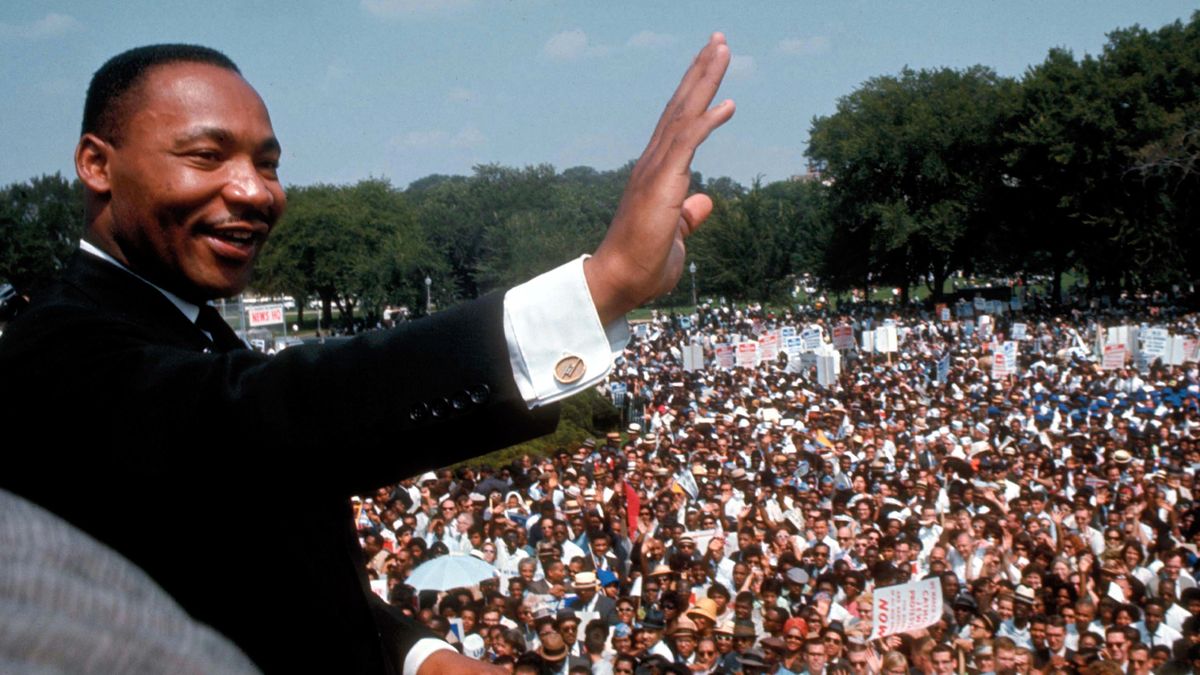

First exposed to the concept of nonviolent resistance while reading Henry David Thoreau ’s On Civil Disobedience at Morehouse, King later discovered a powerful exemplar of the method’s possibilities through his research into the life of Mahatma Gandhi . Fellow civil rights activist Bayard Rustin , who had also studied Gandhi’s teachings, became one of King’s associates in the 1950s and counseled him to dedicate himself to the principles of nonviolence.
As explained in his autobiography , King previously felt that the peaceful teachings of Jesus applied mainly to individual relationships, not large-scale confrontations. But he came to realize: “Love for Gandhi was a potent instrument for social and collective transformation. It was in this Gandhian emphasis on love and nonviolence that I discovered the method for social reform that I had been seeking.”
It led to the formation of King’s six principles of nonviolence :
- Nonviolence is a way of life for courageous people.
- Nonviolence seeks to win friendship and understanding.
- Nonviolence seeks to defeat injustice, not people.
- Nonviolence holds that suffering for a just cause can educate and transform.
- Nonviolence chooses love instead of hate.
- Nonviolence believes that the universe is on the side of justice.
In the years to come, King also frequently cited the “ Beloved Community ”—a world in which a shared spirit of compassion brings an end to the evils of racism, poverty, inequality, and violence—as the end goal of his activist efforts.
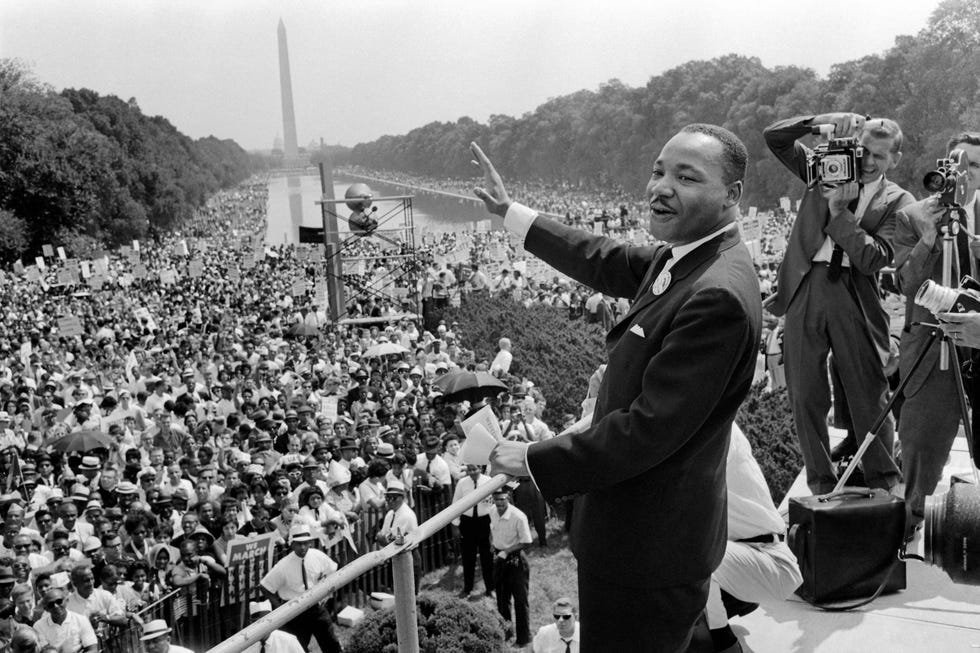

Led by his religious convictions and philosophy of nonviolence, King became one of the most prominent figures of the Civil Rights Movement . He was a founding member of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference and played key roles in several major demonstrations that transformed society. This included the Montgomery Bus Boycott that integrated Alabama’s public transit, the Greensboro Sit-In movement that desegregated lunch counters across the South, the March on Washington that led to the passage of the 1964 Civil Rights Act, and the Selma-to-Montgomery marches in Alabama that culminated in the 1965 Voting Rights Act.
King’s efforts earned him the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964 when he was 35.
Montgomery Bus Boycott
King’s first leadership role within the Civil Rights Movement was during the Montgomery Bus Boycott of 1955–1956. The 381-day protest integrated the Alabama city’s public transit in one of the largest and most successful mass movements against racial segregation in history.
The effort began on December 1, 1955, when 42-year-old Rosa Parks boarded the Cleveland Avenue bus to go home after an exhausting day at work. She sat in the first row of the “colored” section in the middle of the bus. As the bus traveled its route, all the seats in the white section filled up, then several more white passengers boarded the bus.
The bus driver noted that there were several white men standing and demanded that Parks and several other African Americans give up their seats. Three other Black passengers reluctantly gave up their places, but Parks remained seated.
The driver asked her again to give up her seat, and again she refused. Parks was arrested and booked for violating the Montgomery City Code. At her trial a week later, in a 30-minute hearing, Parks was found guilty and fined $10 and assessed $4 court fee.
The local NAACP chapter had been looking to challenge Montgomery’s segregated bus policy and had almost made 15-year-old Claudette Colvin the face of the campaign months earlier. She similarly refused to give up her bus seat to a white man on March 2, 1955, but after organizers learned Colvin was pregnant, they feared it would scandalize the deeply religious Black community and make Colvin, along with the group’s efforts, less credible in the eyes of sympathetic white people. Parks’ experience of discrimination provided another opportunity.
On the night Parks was arrested, E.D. Nixon , head of the local NAACP chapter, met with King and other local civil rights leaders to plan a Montgomery Bus Boycott. King was elected to lead the boycott because he was young, well-trained, and had solid family connections and professional standing. He was also new to the community and had few enemies, so organizers felt he would have strong credibility with the Black community.
In his first speech as the group’s president, King declared:
“We have no alternative but to protest. For many years, we have shown an amazing patience. We have sometimes given our white brothers the feeling that we liked the way we were being treated. But we come here tonight to be saved from that patience that makes us patient with anything less than freedom and justice.”
King’s skillful rhetoric put new energy into the civil rights struggle in Alabama. The Montgomery Bus Boycott began December 5, 1955, and for more than a year, the local Black community walked to work, coordinated ride sharing, and faced harassment, violence, and intimidation. Both King’s and Nixon’s homes were attacked.
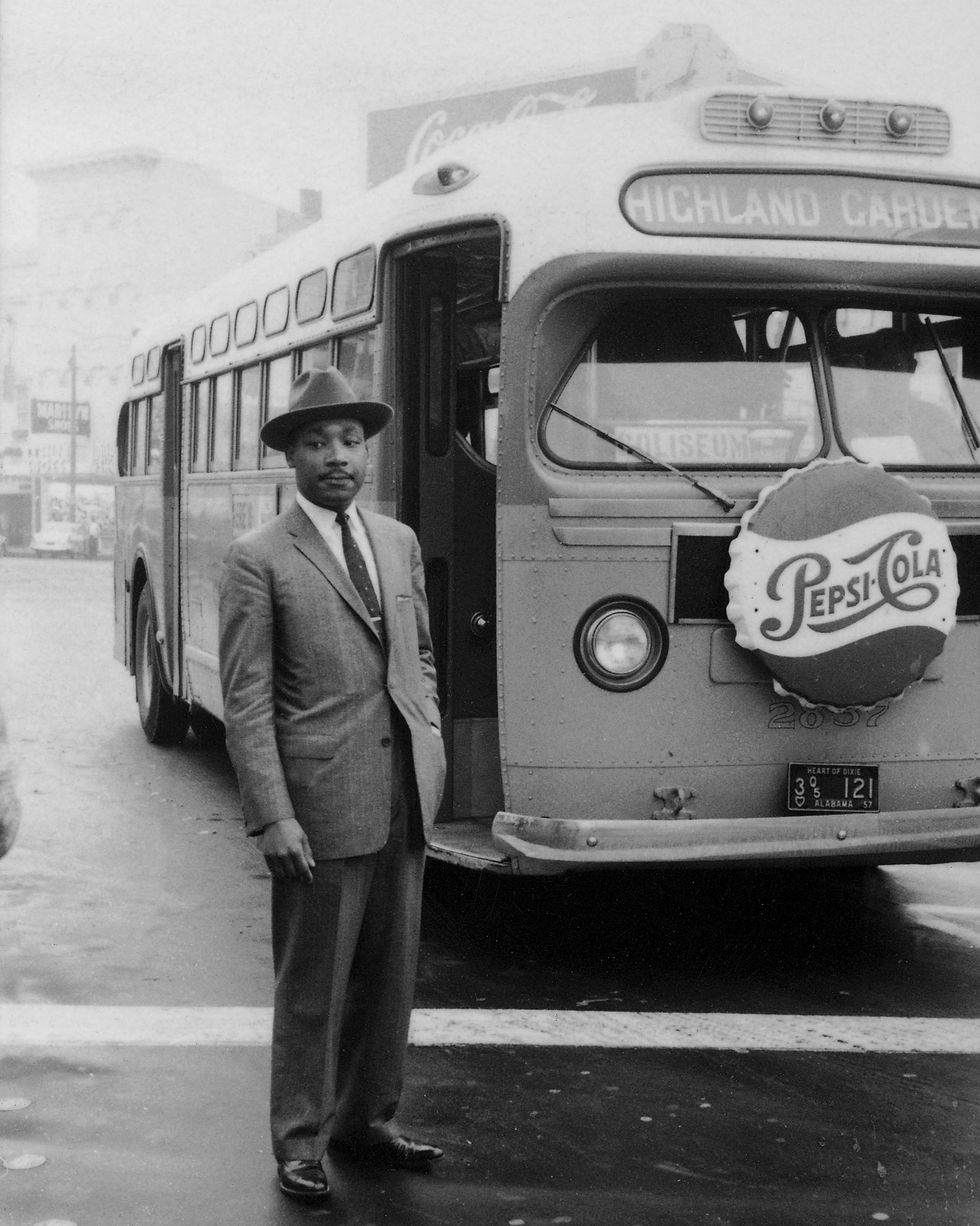
In addition to the boycott, members of the Black community took legal action against the city ordinance that outlined the segregated transit system. They argued it was unconstitutional based on the U.S. Supreme Court ’s “separate is never equal” decision in Brown v. Board of Education (1954). Several lower courts agreed, and the nation’s Supreme Court upheld the ruling in a November 13, 1956, decision that also ruled the state of Alabama’s bus segregation laws were unconstitutional.
After the legal defeats and large financial losses, the city of Montgomery lifted the law that mandated segregated public transportation. The boycott ended on December 20, 1956.
Southern Christian Leadership Conference
Flush with victory, African American civil rights leaders recognized the need for a national organization to help coordinate their efforts. In January 1957, King, Ralph Abernathy , and 60 ministers and civil rights activists founded the Southern Christian Leadership Conference to harness the moral authority and organizing power of Black churches. The SCLC helped conduct nonviolent protests to promote civil rights reform.
King’s participation in the organization gave him a base of operation throughout the South, as well as a national platform. The SCLC felt the best place to start to give African Americans a voice was to enfranchise them in the voting process. In February 1958, the SCLC sponsored more than 20 mass meetings in key southern cities to register Black voters. King met with religious and civil rights leaders and lectured all over the country on race-related issues.
Stride Toward Freedom: The Montgomery Story

That September, King survived an attempt on his life when a woman with mental illness stabbed him in the chest as he signed copies of his book Stride Toward Freedom in a New York City department store. Saved by quick medical attention, King expressed sympathy for his assailant’s condition in the aftermath .
In 1959, with the help of the American Friends Service Committee, King visited Gandhi ’s birthplace in India. The trip affected him in a profound way, increasing his commitment to America’s civil rights struggle.
Greensboro Sit-In
By 1960, King was gaining national exposure. He returned to Atlanta to become co-pastor with his father at Ebenezer Baptist Church but also continued his civil rights efforts. His next activist campaign was the student-led Greensboro Sit-In movement.
In February 1960, a group of Black students in Greensboro, North Carolina , began sitting at racially segregated lunch counters in the city’s stores. When asked to leave or sit in the “colored” section, they just remained seated, subjecting themselves to verbal and sometimes physical abuse.
The movement quickly gained traction in several other cities. That April, the SCLC held a conference at Shaw University in Raleigh, North Carolina, with local sit-in leaders. King encouraged students to continue to use nonviolent methods during their protests. Out of this meeting, the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) formed and, for a time, worked closely with the SCLC. By August 1960, the sit-ins had successfully ended segregation at lunch counters in 27 southern cities. But the movement wasn’t done yet.
On October 19, 1960, King and 75 students entered a local department store and requested lunch-counter service but were denied. When they refused to leave the counter area, King and 36 others were arrested. Realizing the incident would hurt the city’s reputation, Atlanta’s mayor negotiated a truce, and charges were eventually dropped.
Soon after, King was imprisoned for violating his probation on a traffic conviction. The news of his imprisonment entered the 1960 presidential campaign when candidate John F. Kennedy made a phone call to Martin’s wife, Coretta Scott King . Kennedy expressed his concern over the harsh treatment Martin received for the traffic ticket, and political pressure was quickly set in motion. King was soon released.
Letter from Birmingham Jail
In the spring of 1963, King organized a demonstration in downtown Birmingham, Alabama. With entire families in attendance, city police turned dogs and fire hoses on demonstrators. King was jailed, along with large numbers of his supporters.
The event drew nationwide attention. However, King was personally criticized by Black and white clergy alike for taking risks and endangering the children who attended the demonstration.
In his famous Letter from Birmingham Jail , King eloquently spelled out his theory of nonviolence: “Nonviolent direct action seeks to create such a crisis and foster such a tension that a community, which has constantly refused to negotiate, is forced to confront the issue.”
1963 March on Washington
By the end of the Birmingham campaign, King and his supporters were making plans for a massive demonstration on the nation’s capital composed of multiple organizations, all asking for peaceful change. The demonstration was the brainchild of labor leader A. Philip Randolph and King’s one-time mentor Bayard Rustin .
On August 28, 1963, the historic March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom drew an estimated 250,000 people in the shadow of the Lincoln Memorial. It remains one of the largest peaceful demonstrations in American history. During the demonstration, King delivered his famed “I Have a Dream” speech .
The rising tide of civil rights agitation that had culminated in the March on Washington produced a strong effect on public opinion. Many people in cities not experiencing racial tension began to question the nation’s Jim Crow laws and the near-century of second-class treatment of African American citizens since the end of slavery. This resulted in the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 , authorizing the federal government to enforce desegregation of public accommodations and outlawing discrimination in publicly owned facilities.
Selma March
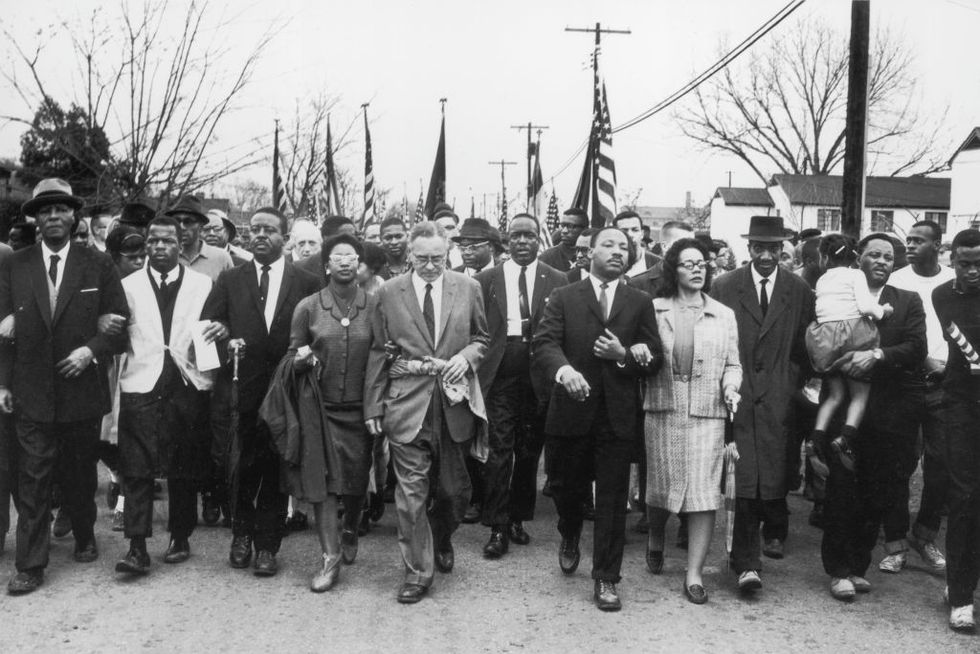

Continuing to focus on voting rights, King, the SCLC, SNCC, and local organizers planned to march peacefully from Selma, Alabama, to the state’s capital, Montgomery.
Led by John Lewis and Hosea Williams , demonstrators set out on March 7, 1965. But the Selma march quickly turned violent as police with nightsticks and tear gas met the demonstrators as they tried to cross the Edmund Pettus Bridge in Selma. The attack was televised, broadcasting the horrifying images of marchers being bloodied and severely injured to a wide audience. Of the 600 demonstrators, 58 were hospitalized in a day that became known as “ Bloody Sunday .” King, however, was spared because he was in Atlanta.
Not to be deterred, activists attempted the Selma-to-Montgomery march again. This time, King made sure he was part of it. Because a federal judge had issued a temporary restraining order on another march, a different approach was taken.
On March 9, 1965, a procession of 2,500 marchers, both Black and white, set out once again to cross the Pettus Bridge and confronted barricades and state troopers. Instead of forcing a confrontation, King led his followers to kneel in prayer, then they turned back. This became known as “Turnaround Tuesday.”
Alabama Governor George Wallace continued to try to prevent another march until President Lyndon B. Johnson pledged his support and ordered U.S. Army troops and the Alabama National Guard to protect the protestors.
On March 21, 1965, approximately 2,000 people began a march from Selma to Montgomery. On March 25, the number of marchers, which had grown to an estimated 25,000 gathered in front of the state capitol where King delivered a televised speech. Five months after the historic peaceful protest, President Johnson signed the 1965 Voting Rights Act .

Along with his “I Have a Dream” and “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” speeches, King delivered several acclaimed addresses over the course of his life in the public eye.
“I Have A Dream” Speech
Date: august 28, 1963.
King gave his famous “I Have a Dream” speech during the 1963 March on Washington. Standing at the Lincoln Memorial, he emphasized his belief that someday all men could be brothers to the 250,000-strong crowd.
Notable Quote: “I have a dream that my four children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.”
“Give Us the Ballot” Speech
Date: may 17, 1957.
Six years before he told the world of his dream, King stood at the same Lincoln Memorial steps as the final speaker of the Prayer Pilgrimage for Freedom. Dismayed by the ongoing obstacles to registering Black voters, King urged leaders from various backgrounds—Republican and Democrat, Black and white—to work together in the name of justice.
Notable Quote: “Give us the ballot, and we will no longer have to worry the federal government about our basic rights. Give us the ballot, and we will no longer plead to the federal government for passage of an anti-lynching law... Give us the ballot, and we will transform the salient misdeeds of bloodthirsty mobs into the calculated good deeds of orderly citizens.”
Nobel Peace Prize Acceptance Speech
Date: december 10, 1964.
Speaking at the University of Oslo in Norway, King pondered why he was receiving the Nobel Prize when the battle for racial justice was far from over, before acknowledging that it was in recognition of the power of nonviolent resistance. He then compared the foot soldiers of the Civil Rights Movement to the ground crew at an airport who do the unheralded-yet-necessary work to keep planes running on schedule.
Notable Quote: “I think Alfred Nobel would know what I mean when I say that I accept this award in the spirit of a curator of some precious heirloom which he holds in trust for its true owners—all those to whom beauty is truth and truth, beauty—and in whose eyes the beauty of genuine brotherhood and peace is more precious than diamonds or silver or gold.”
“Our God is Marching On (How Long? Not Long)” Speech
Date: march 25, 1965.
At the end of the bitterly fought Selma-to-Montgomery march, King addressed a crowd of 25,000 supporters from the Alabama State Capitol. Offering a brief history lesson on the roots of segregation, King emphasized that there would be no stopping the effort to secure full voting rights, while suggesting a more expansive agenda to come with a call to march on poverty.
Notable Quote: “I come to say to you this afternoon, however difficult the moment, however frustrating the hour, it will not be long, because ‘truth crushed to earth will rise again.’ How long? Not long, because ‘no lie can live forever.’... How long? Not long, because the arc of the moral universe is long, but it bends toward justice.”
“Beyond Vietnam: A Time to Break Silence” Speech
Date: april 4, 1967.
One year before his assassination, King delivered a controversial sermon at New York City’s Riverside Church in which he condemned the Vietnam War. Explaining why his conscience had forced him to speak up, King expressed concern for the poor American soldiers pressed into conflict thousands of miles from home, while pointedly faulting the U.S. government’s role in escalating the war.
Notable Quote: “We still have a choice today: nonviolent coexistence or violent co-annihilation. We must move past indecision to action. We must find new ways to speak for peace in Vietnam and justice throughout the developing world, a world that borders on our doors. If we do not act, we shall surely be dragged down the long, dark, and shameful corridors of time reserved for those who possess power without compassion, might without morality, and strength without sight.”
“I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” Speech
Date: april 3, 1968.
The well-known orator delivered his final speech the day before he died at the Mason Temple in Memphis, Tennessee. King reflected on major moments of progress in history and his own life, in addition to encouraging the city’s striking sanitation workers.
Notable Quote: “I’ve seen the promised land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight that we, as a people, will get to the promised land.”
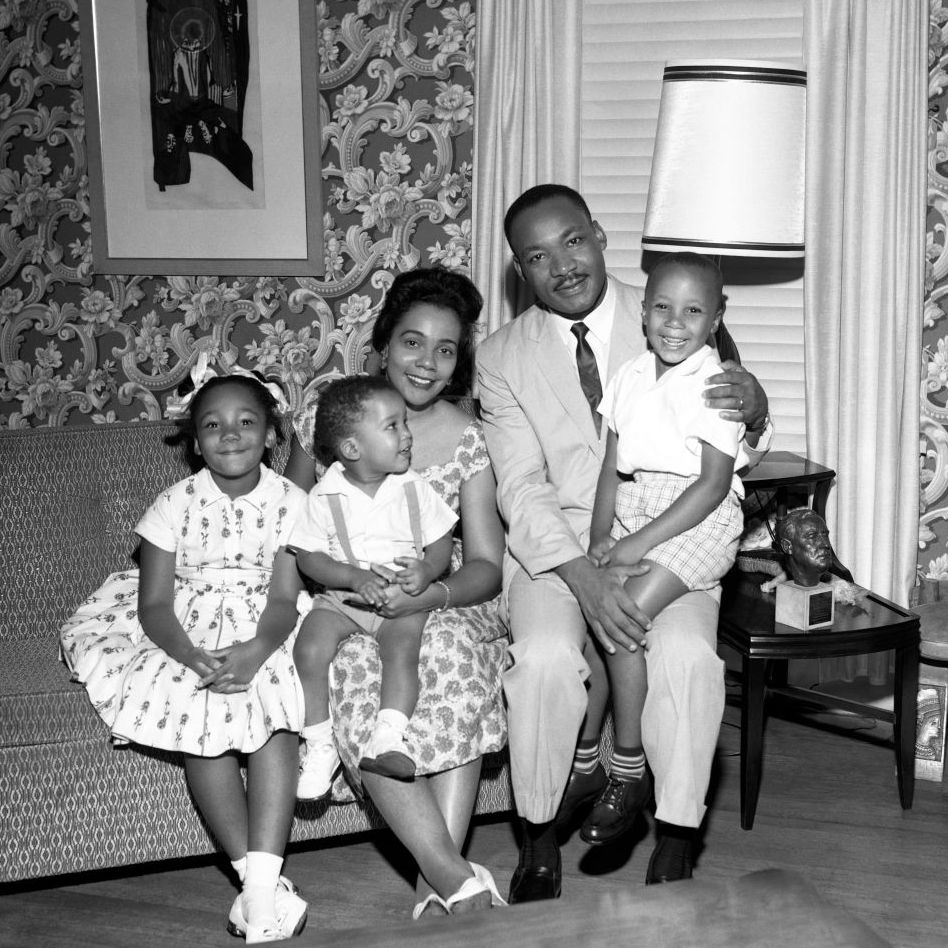
While working on his doctorate at Boston University, King met Coretta Scott , an aspiring singer and musician at the New England Conservatory school in Boston. They were married on June 18, 1953, and had four children—two daughters and two sons—over the next decade. Their oldest, Yolanda, was born in 1955, followed by sons Martin Luther King III in 1957 and Dexter in 1961. The couple welcomed Bernice King in 1963.
Although she accepted the responsibility to raise the children while King travelled the country, Coretta opened their home to organizational meetings and served as an advisor and sounding board for her husband. “I am convinced that if I had not had a wife with the fortitude, strength, and calmness of Corrie, I could not have withstood the ordeals and tensions surrounding the movement,” King wrote in his autobiography.
His lengthy absences became a way of life for their children, but Martin III remembered his father returning from the road to join the kids playing in the yard or bring them to the local YMCA for swimming. King also fostered discussions at mealtimes to make sure everyone understood the important issues he was seeking to resolve.
Leery of accumulating wealth as a high-profile figure, King insisted his family live off his salary as a pastor. However, he was known to splurge on good suits and fine dining, while contrasting his serious public image with a lively sense of humor among friends and family.
Due to his relationships with alleged Communists, King became a target of FBI surveillance and, from late 1963 until his death, a campaign to discredit the civil rights activist. While FBI wiretaps failed to produce evidence of Communist sympathies, they captured the civil rights leader’s engagement in extramarital dalliances. This led to the infamous “suicide letter” of 1964, later confirmed to be from the FBI and authorized by then-Director J. Edgar Hoover , which urged King to kill himself if he wanted to prevent news of his affairs from going public.
In 2019, historian David Garrow wrote of explosive new allegations against King following his review of recently released FBI documents. Among the discoveries was a memo suggesting that King had encouraged the rape of a parishioner in a hotel room, as well as evidence that he might have fathered a daughter with a mistress. Other historians questioned the veracity of the documentation, especially given the FBI’s known attempts to damage King’s reputation. The original surveillance tapes regarding these allegations are under judicial seal until 2027.
From late 1965 through 1967, King expanded his civil rights efforts into other larger American cities, including Chicago and Los Angeles. But he met with increasing criticism and public challenges from young Black power leaders. King’s patient, non-violent approach and appeal to white middle-class citizens alienated many Black militants who considered his methods too weak, too late, and ineffective.
To address this criticism, King began making a link between discrimination and poverty, and he began to speak out against the Vietnam War . He felt America’s involvement in Vietnam was politically untenable and the government’s conduct in the war was discriminatory to the poor. He sought to broaden his base by forming a multiracial coalition to address the economic and unemployment problems of all disadvantaged people. To that end, plans were in the works for another march on Washington to highlight the Poor People’s Campaign, a movement intended to pressure the government into improving living and working conditions for the economically disadvantaged.
By 1968, the years of demonstrations and confrontations were beginning to wear on King. He had grown tired of marches, going to jail, and living under the constant threat of death. He was becoming discouraged at the slow progress of civil rights in America and the increasing criticism from other African American leaders.
In the spring of 1968, a labor strike by Memphis, Tennessee, sanitation workers drew King to one last crusade. On April 3, 1968, he gave his final and what proved to be an eerily prophetic speech, “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop,” in which he told supporters, “Like anybody, I would like to live a long life. Longevity has its place. But I’m not concerned about that now… I’m not worried about anything. I’m not fearing any man. Mine eyes have seen the glory of the coming of the Lord.”

While standing on a balcony outside his room at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee, Martin Luther King Jr. was killed by a sniper’s bullet on April 4, 1968. King died at age 39. The shocking assassination sparked riots and demonstrations in more than 100 cities across the country.
The shooter was James Earl Ray , a malcontent drifter and former convict. He initially escaped authorities but was apprehended after a two-month international manhunt. In 1969, Ray pleaded guilty to assassinating King and was sentenced to 99 years in prison.
The identity of King’s assassin has been the source of some controversy. Ray recanted his confession shortly after he was sentenced, and King’s son Dexter publicly defended Ray’s innocence after meeting with the convicted gunman in 1997. Another complicating factor is the 1993 confession of tavern owner Loyd Jowers, who said he contracted a different hit man to kill King. In June 2000, the U.S. Justice Department released a report that dismissed the alternative theories of King’s death. Ray died in prison on April 23, 1998.

King’s life had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States. Years after his death, he is the most widely known Black leader of his era.
His life and work have been honored with a national holiday, schools and public buildings named after him, and a memorial on Independence Mall in Washington, D.C.
Over the years, extensive archival studies have led to a more balanced and comprehensive assessment of his life, portraying him as a complex figure: flawed, fallible, and limited in his control over the mass movements with which he was associated, yet a visionary leader who was deeply committed to achieving social justice through nonviolent means.
- But we come here tonight to be saved from that patience that makes us patient with anything less than freedom and justice.
- There comes a time when the cup of endurance runs over and men are no longer willing to be plunged into an abyss of injustice where they experience the bleakness of corroding despair.
- Any law that uplifts human personality is just. Any law that degrades human personality is unjust.
- The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.
- Let us not seek to satisfy our thirst for freedom by drinking from the cup of bitterness and hatred.
- Darkness cannot drive out darkness: only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate: only love can do that.
- The ultimate measure of a man is not where he stands in moments of comfort and convenience, but where he stands at times of challenge and controversy. The true neighbor will risk his position, his prestige, and even his life for the welfare of others.
- We must all learn to live together as brothers, or we will all perish together as fools.
- Forgiveness is not an occasional act; it is a permanent attitude.
- I have a dream that my four children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.
- The function of education, therefore, is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically. But education which stops with efficiency may prove the greatest menace to society. The most dangerous criminal may be the man gifted with reason but with no morals.
- I’ve seen the promised land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight that we, as a people, will get to the promised land.
- Power at its best is love implementing the demands of justice. Justice at its best is love correcting everything that stands against love.
- A man who won’t die for something is not fit to live.
- At the center of non-violence stands the principle of love.
- Right, temporarily defeated, is stronger than evil triumphant.
- In the end, we will remember not the words of our enemies, but the silence of our friends.
- Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere.
- Our lives begin to end the day we become silent about things that matter.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Civil Rights Activists

Ethel Kennedy

MLK Almost Didn’t Say “I Have a Dream”

Huey P. Newton

Martin Luther King Jr. Didn’t Criticize Malcolm X

5 Crowning Achievements of Maya Angelou

30 Civil Rights Leaders of the Past and Present

Benjamin Banneker

Marcus Garvey

Madam C.J. Walker

Maya Angelou

17 Inspiring Martin Luther King Quotes

- HISTORY & CULTURE
Who was Martin Luther King, Jr.?
A civil rights legend, Dr. King fought for justice through peaceful protest—and delivered some of the 20th century's most iconic speeches.
The Reverend Martin Luther King, Jr., is a civil rights legend. In the mid-1950s, King led the movement to end segregation and counter prejudice in the United States through the means of peaceful protest. His speeches—some of the most iconic of the 20th century—had a profound effect on the national consciousness. Through his leadership, the civil rights movement opened doors to education and employment that had long been closed to Black America.
In 1983, President Ronald Reagan signed a bill creating a federal holiday to honor King for his commitment to equal rights and justice for all. Observed for the first time on January 20, 1986, it’s called Martin Luther King Jr. Day. In January 2000, Martin Luther King Jr. Day was officially observed in all 50 U.S. states . Here’s what you need to know about King’s extraordinary life.
Though King's name is known worldwide, many may not realize that he was born Michael King, Jr. in Atlanta, Georgia on January 15, 1929. His father , Michael King, was a pastor at the Ebenezer Baptist Church in Atlanta. During a trip to Germany, King, Sr. was so impressed by the history of Protestant Reformation leader Martin Luther that he changed not only his own name, but also five-year-old Michael’s.
( Read about Martin Luther King, Jr. with your kids .)
His brilliance was noted early, as he was accepted into Morehouse College , a historically Black school in Atlanta, at age 15. By the summer before his last year of college, King knew he was destined to continue the family profession of pastoral work and decided to enter the ministry. He received his Bachelor’s degree from Morehouse at age 19, and then enrolled in Crozer Theological Seminary in Chester, Pennsylvania, graduating with a Bachelor of Divinity degree in 1951. He earned a doctorate in systematic theology from Boston University in 1955.
King married Coretta Scott on June 18, 1953, on the lawn of her parents' house in her hometown of Heiberger, Alabama. They became the parents of four children : Yolanda King (1955–2007), Martin Luther King III (b. 1957), Dexter Scott King (b. 1961), and Bernice King (b. 1963).

Becoming a civil rights leader
In 1954, when he was 25 years old, Dr. King became pastor of the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church in Montgomery, Alabama. In March 1955, Claudette Colvin—a 15-year-old Black schoolgirl in Montgomery—refused to give up her bus seat to a white man, which was a violation of Jim Crow laws, local laws in the southern United States that enforced racial segregation.
YEAR-LONG ADVENTURE for every explorer on your list
( Jim Crow laws created 'slavery by another name. ')
King was on the committee from the Birmingham African-American community that looked into the case. The local chapter of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) briefly considered using Colvin's case to challenge the segregation laws, but decided that because she was so young—and had become pregnant—her case would attract too much negative attention.
Nine months later on December 1, 1955, a similar incident occurred when a seamstress named Rosa Parks was arrested for refusing to give up her seat on a city bus. The two incidents led to the Montgomery bus boycott , which was urged and planned by the President of the Alabama Chapter of the NAACP, E.D. Nixon, and led by King. The boycott lasted for 385 days.

King’s prominent and outspoken role in the boycott led to numerous threats against his life, and his house was firebombed. He was arrested during the campaign, which concluded with a United States District Court ruling in Browder v. Gayle ( in which Colvin was a plaintiff ) that ended racial segregation on all Montgomery public buses. King's role in the bus boycott transformed him into a national figure and the best-known spokesman of the civil rights movement.
Fighting for change through nonviolent protest
From the early days of the Montgomery boycott, King had often referred to India’s Mahatma Gandhi as “the guiding light of our technique of nonviolent social change.”
You May Also Like

The perfect storm that led to the Jonestown massacre

Who built this mysterious settlement in Madagascar? Scientists have a new theory

What was the Stonewall uprising?
In 1957, King, Ralph Abernathy, Fred Shuttlesworth, Joseph Lowery, and other civil rights activists founded the Southern Christian Leadership Conference to harness the organizing power of Black churches to conduct nonviolent protests to ultimately achieve civil rights reform. The group was part of what was called “The Big Five” of civil rights organizations, which included the NAACP, the National Urban League, the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee, and the Congress on Racial Equality.
Through his connections with the Big Five civil rights groups, overwhelming support from Black America and with the support of prominent individual well-wishers, King’s skill and effectiveness grew exponentially. He organized and led marches for Blacks' right to vote, desegregation, labor rights, and other basic civil rights.
( How the U.S. Voting Rights Act was won—and why it's under fire today .)
On August 28, 1963, The March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom became the pinnacle of King’s national and international influence. Before a crowd of 250,000 people, he delivered the legendary “I Have A Dream” speech on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial. That speech, along with many others that King delivered, has had a lasting influence on world rhetoric .
In 1964, King was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for his civil rights and social justice activism. Most of the rights King organized protests around were successfully enacted into law with the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the 1965 Voting Rights Act .
Economic justice and the Vietnam War
King’s opposition to the Vietnam War became a prominent part of his public persona. On April 4, 1967—exactly one year before his death—he gave a speech called “Beyond Vietnam” in New York City, in which he proposed a stop to the bombing of Vietnam. King also suggested that the United States declare a truce with the aim of achieving peace talks, and that the U.S. set a date for withdrawal.
( King's advocacy for human rights around the world still inspires today .)
Ultimately, King was driven to focus on social and economic justice in the United States. He had traveled to Memphis, Tennessee in early April 1968 to help organize a sanitation workers’ strike, and on the night of April 3, he delivered the legendary “I've Been to the Mountaintop" speech , in which he compared the strike to the long struggle for human freedom and the battle for economic justice, using the New Testament's Parable of the Good Samaritan to stress the need for people to get involved.
Assassination
But King would not live to realize that vision. The next day, April 4, 1968, King was gunned down on the balcony of the Lorraine Motel in Memphis by James Earl Ray , a small-time criminal who had escaped the year before from a maximum-security prison. Ray was charged and convicted of the murder and sentenced to 99 years in prison on March 10, 1969. But Ray changed his mind after three days in jail, claiming he was not guilty and had been framed. He spent the rest of his life fighting unsuccessfully for a trial, despite the ultimate support of some members of the King family and the Reverend Jesse Jackson.
The turmoil that flowed from King’s assassination led many Black Americans to wonder if that dream he had spoken of so eloquently had died with him. But, today, young people around the world still learn about King's life and legacy—and his vision of equality and justice for all continue to resonate.
Related Topics
- CIVIL RIGHTS

The birth of the Holy Roman Empire—and the unlikely king who ruled it

The quest for the Holy Grail began long before King Arthur

Meet the ruthless king who unified the Kingdom of Hawai'i

Who is Hanuman, the Hindu god with the face of a monkey?

Who was the first king of England? The answer is … complicated.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

The New Definitive Biography of Martin Luther King Jr.
“King: A Life,” by Jonathan Eig, is the first comprehensive account of the civil rights icon in decades.
Credit... PS Spencer
Supported by
- Share full article
By Dwight Garner
- Published May 8, 2023 Updated May 28, 2023
- Apple Books
- Barnes and Noble
- Books-A-Million
- Bookshop.org
When you purchase an independently reviewed book through our site, we earn an affiliate commission.
KING: A Life , by Jonathan Eig
Listen to This Article
Growing up, he was called Little Mike, after his father, the Baptist minister Michael King. Later he sometimes went by M.L. Only in college did he drop his first name and began to introduce himself as Martin Luther King Jr. This was after his father visited Germany and, inspired by accounts of the reform-minded 16th-century friar Martin Luther, adopted his name.
King Jr. was born in 1929. Were he alive he would be 94, the same age as Noam Chomsky. The prosperous King family lived on Auburn Avenue in Atlanta. One writer, quoted by Jonathan Eig in his supple, penetrating, heartstring-pulling and compulsively readable new biography, “King: A Life,” called it “the richest Negro street in the world.”
Eig’s is the first comprehensive biography of King in three decades. It draws on a landslide of recently released White House telephone transcripts, F.B.I. documents, letters, oral histories and other material, and it supplants David J. Garrow’s 1986 biography “Bearing the Cross” as the definitive life of King, as Garrow himself deposed recently in The Spectator . It also updates the material in Taylor Branch’s magisterial trilogy about America during the King years.
King and his two siblings had the trappings of middle-class life in Atlanta: bicycles, a dog, allowances. But they were sickly aware of the racism that made white people shun them, that kept them out of most of the city’s parks and swimming pools, among other degradations.
Their father expected a lot from his children. He had a temper. He was a stern disciplinarian who spanked with a belt. Their mother was a calmer, sweeter, more stable presence. King would inherit qualities from both.
One of the stranger moments in King’s childhood, and thus in American history, occurred on Dec. 15, 1939. That was the night Clark Gable, Carole Lombard and other Hollywood stars converged on Atlanta for the premiere of “Gone With the Wind,” the highly anticipated film version of Margaret Mitchell’s Pulitzer Prize-winning 1936 novel.
“Gone With the Wind” was already controversial in the Black community for its placid and romantic depiction of slavery. To the dismay of some of his peers, King’s father allowed his church’s choir to perform at the premiere. It was only a movie, he thought, and not an entirely inaccurate one. Choir members wore slave costumes, their heads wrapped with cloth. “Martin Luther King Jr., dressed as a young slave, sat in the choir’s first row, singing along,” Eig writes.
King was a sensitive child. When things upset him, he twice tried to commit suicide, if halfheartedly, by leaping out of a second-story window of his house. (Both times, he wasn’t seriously hurt.) He was bright and skipped several grades in school. He thought he might be a doctor or a lawyer; the high emotion in church embarrassed him.
When he arrived in 1944 at nearby Morehouse College, one of the most distinguished all-Black, all-male colleges in America, he was 15 and short for his age. He picked up the nickname Runt. He majored in sociology. He read Henry David Thoreau’s essay “Civil Disobedience” and it was a vital early influence. He began to think about life as a minister, and he practiced his sermons in front of a mirror.
He was small, but he was a natty dresser and possessed a trim mustache and a dazzling smile. Women were already throwing themselves at him, and they would never stop doing so.
He attended Crozer Theological Seminary in Pennsylvania, where he fell in love with and nearly married a white woman, but that would have ended any hope of becoming a minister in the South. Eig, who has also written artful biographies of Muhammad Ali and Lou Gehrig, describes how several young women attended King’s graduation from Crozer and how — as if in a scene from a Feydeau farce — each expected to be introduced to his parents as his fiancée.

King then pursued a doctorate at Boston University. (He nearly went to the University of Edinburgh in Scotland instead, a notion that is mind-bending to contemplate.) He was said to be the most eligible young Black man in the city.
In Boston he fell in love with Coretta Scott, he said, over the course of a single telephone call. She had attended Antioch College in Ohio and was studying voice at the New England Conservatory; she hoped to become a concert singer. Their love story is beautifully related. They were married in Alabama, at the Scott family’s home near Marion. They spent the first night of their marriage in the guest bedroom of a funeral parlor, because no local hotel would accommodate them.
The Kings moved to Montgomery, Ala., in 1954, when he took over as pastor at the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church. A year later, a seamstress named Rosa Parks refused to give up her seat to white passengers on a Montgomery bus. Thus began the Montgomery bus boycott, an action that established the city as a crucible of the civil rights movement. The young pastor was about to rise to a great occasion, and to step into history.
“As I watched them,” he wrote about the men and women who participated in the long and difficult boycott, “I knew that there is nothing more majestic than the determined courage of individuals willing to suffer and sacrifice for their freedom and dignity.”
By this point in “King: A Life,” Eig has established his voice. It’s a clean, clear, journalistic voice, one that employs facts the way Saul Bellow said they should be employed, each a wire that sends a current. He does not dispense two-dollar words; he keeps digressions tidy and to a minimum; he jettisons weight, on occasion, for speed. He appears to be so in control of his material that it is difficult to second-guess him.
By the time we’ve reached Montgomery, King’s reputation has been flyspecked. Eig flies low over his penchant for plagiarism, in academic papers and elsewhere. (King was a synthesizer of ideas, not an original scholar.) His womanizing only got worse over the years. This is a very human, and quite humane, portrait.
Many readers will be familiar with what follows: the long fight in Montgomery, in which the world came to realize that this wasn’t merely about bus seats, and it wasn’t merely Montgomery’s problem. Later, the whole world was watching as Bull Connor, Birmingham’s commissioner of public safety, sicced police dogs on peaceful protesters. In prison, King would compose what is now known as “Letter From Birmingham Jail” on napkins, toilet paper and in the margins of newspapers. Later came the 1963 March on Washington and King’s partly improvised “I Have a Dream” speech.
During these years, King was imprisoned on 29 separate occasions. He never got used to it. He had shotguns fired into his family’s house. Bombs were found on his porch. Crosses were burned on his lawn. He was punched in the face more than once. In 1958, in Harlem, he was stabbed in the chest with a seven-inch letter opener. He was told that had he even sneezed before doctors could remove it, he might have died.
Eig is adept at weaving in other characters, and other voices. He makes it plain that King was not acting in a vacuum, and he traces the work of organizations like the N.A.A.C.P., CORE and SNCC, and of men like Thurgood Marshall, John Lewis, Julian Bond and Ralph Abernathy. He shows how King was too progressive for some, and vastly too conservative for others, Malcolm X central among them.
As this book moves into its final third, you sense the author echolocating between two other major biographies, Robert Caro’s multivolume life of Lyndon Johnson and Beverly Gage’s powerful recent biography of J. Edgar Hoover, the longtime F.B.I. director.
King’s relationships with John F. Kennedy and Robert Kennedy were complicated; his relationship with Johnson was even more so. King and Johnson were driven apart when King began to speak out against the Vietnam War, which Johnson considered a betrayal.
The details about Hoover’s relentless pursuit of King, via wiretaps and other methods, are repulsive. American law enforcement was more interested in tarring King with whatever they could dig up than in protecting him. Hoover tried to paint him as a communist; he wasn’t one.
King was under constant surveillance. Hoover’s F.B.I. agents bugged his hotel rooms and reported that he was having sex with many women, in many cities; they tried to drive him to suicide by threatening to release the tapes. King, in one bureau report, is said to have “participated in a sex orgy.” There is also an allegation, about which Eig is dubious, that King looked on during a rape. Complete F.B.I. recordings and transcripts are scheduled to be released in 2027.
Eig catches King in private moments. He had health issues; the stresses of his life aged him prematurely. He rarely got enough sleep, but he didn’t seem to need it. Writing about his demeanor in general, the writer Louis Lomax called King the “foremost interpreter of the Negro’s tiredness.”
King loved good Southern food and ate like a country boy. When the meal was especially delicious, he liked to eat with his hands. He argued, laughing, that utensils only got in the way.
Once, when his daughter skinned her knee by a swimming pool, he took a piece of fried chicken and jokingly pretended to apply it to the wound. “Let’s put some fried chicken on that,” he said. “Yes, a little piece of chicken, that’s always the best thing for a cut.”
Eig has read everything, from W.E.B. Du Bois through Norman Mailer and Murray Kempton and Caro and Gage. He argues that we have sometimes mistaken King’s nonviolence for passivity. He doesn’t put King on the couch, but he considers the lifelong guilt King felt about his privileged upbringing, and how he was driven by competitiveness with his father, who had moral failures of his own.
He lingers on the cadences of King’s speeches, explaining how he learned to work his audience, to stretch and rouse them at the same time. He had the best material on his side, and he knew it. Eig puts it this way: “Here was a man building a reform movement on the most American of pillars: the Bible, the Declaration of Independence, the American dream.”
Eig’s book is worthy of its subject.
Audio produced by Kate Winslett .
KING: A Life | By Jonathan Eig | Illustrated | 669 pp. | Farrar, Straus & Giroux | $35
Dwight Garner has been a book critic for The Times since 2008. His new book, “The Upstairs Delicatessen: On Eating, Reading, Reading About Eating, and Eating While Reading,” is out this fall. More about Dwight Garner
Explore More in Books
Want to know about the best books to read and the latest news start here..
100 Best Books of the 21st Century: As voted on by 503 novelists, nonfiction writers, poets, critics and other book lovers — with a little help from the staff of The New York Times Book Review.
Examining Joan Didion: Since her death, Didion has become a literary subject as popular for her image and writing as for the fascination she inspired for almost half a century.
A Dutch Love Story in a Time of Silence: In Yael van der Wouden’s debut novel, “The Safekeep,” the writer spins an erotic thriller out of the Netherlands’ failure to face up to the horrors of the Holocaust.
Aleksei Navalny’s Prison Diaries: In the Russian opposition leader’s posthumous memoir, compiled with help from his widow, Yulia Navalnaya, Navalny faced the fact that Vladimir Putin might succeed in silencing him .
The Book Review Podcast: Each week, top authors and critics talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here .
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and civil rights activist who had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States, beginning in the mid-1950s. Among his many...
FBI director J. Edgar Hoover personally ordered surveillance of King, with the intent to undermine his power as a civil rights leader. The Church Committee, a 1975 investigation by the U.S. Congress, found that "From December 1963 until his death in 1968, Martin Luther King Jr. was the target of an intensive campaign by the Federal Bureau of Investigation to 'neutralize' him as an effective civil ri…
At the age of thirty-five, Martin Luther King, Jr., was the youngest man to have received the Nobel Peace Prize. When notified of his selection, he announced that he would turn over the prize money of $54,123 to the furtherance of the …
Who was Martin Luther King, Jr.? A civil rights legend, Dr. King fought for …
Introduction. Martin Luther King, Jr., made history, but he was also transformed by his deep …
The New Definitive Biography of Martin Luther King Jr. “King: A Life,” by Jonathan Eig, is the first comprehensive account of the civil rights icon in decades. Credit...