You are here


The Art of Case Study Research
- Robert E. Stake - University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
- Description
- Author(s) / Editor(s)
Robert E Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such questions as: How is the case selected? How do you select the case which is most likely to lead to maximizing what can be learned? How can what is learned from one case be applied to another? How can what is learned from a case be interpreted? In addition, the book covers: the differences between quantitative and qualitative approaches; data-gathering including document review; coding, sorting and pattern analysis; the roles of the researcher; triangulation; and reporting. Introduction An Intensive Study of Case Study Research Methods
This is a very useful resource for students who are evaluating case study research, or who are contemplating this as a methodology for their own research.
I have used a previous edition extensively for my own research. Yin is an essential for all case study researchers. I am delighted to have the new edition. It is a classic.
An excellent text for educator/student research methods using case study as an approach. Written in a way that makes interpretation, understanding and application easier.
This is an essential book for research using a case study approach.
Stake provides a useful step by step guide to case study methods used in qualitative inquiry. The use of workshop scenarios helps cement its application in practice.
A concise book that is so elaborate most especially for early career researchers using case study as an approach. The writing style is simple with detail examples; also the use of foot notes in the book is an “icing on the cake”.
It did not suit the needs of the actual students. This does not mean that the book would be not good - in contrary.
Classic book to go alongside Yin for a different philosophical perspective. Will advise students doing case study to read this.
Great book, essential reading for all research methods modules
This is a classic text and clearly accessible to novice and more mature researchers interested in Case Study Research. Each chapter is well defined and signposts the next chapter.
Preview this book
Robert e. stake.
Professor Stake received his B.A. in Mathematics with a minor in naval science and Spanish from the University of Nebraska in 1950. He graduated with an M.A. in educational psychology in 1954 from this university. In 1958, he received his Ph.D. in psychology from Princeton University. From 1955 to 1958, he was a Psychometric Fellow at the Educational Testing Service. Then, an Associate Professor and Faculty Research Coordinator of the College of Education at the University of Nebraska at Lincoln. In 1963, he arrived at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign where he assisted Thomas Hastings, Lee Cronbach, and Jack Easley in the... More About Author
Purchasing options
Please select a format:
Order from:
- Buy from SAGE
- Find My Rep
You are here

The Art of Case Study Research
- Robert E. Stake - University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
- Description
Robert E Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such questions as: How is the case selected? How do you select the case which is most likely to lead to maximizing what can be learned? How can what is learned from one case be applied to another? How can what is learned from a case be interpreted? In addition, the book covers: the differences between quantitative and qualitative approaches; data-gathering including document review; coding, sorting and pattern analysis; the roles of the researcher; triangulation; and reporting. Introduction An Intensive Study of Case Study Research Methods
This is an excellent book for case study research focussing on qualitative case studies. Essential for researchers looking to use this approach.
Excellent introduction into qualitative, case study research. Very well written, conveying the key issues in clear and very engaging manner. Can also serve as a very short introduction manual to qualitative research in general.
A helpful text for the those students considering case study methodologies at post graduate level.
The art of case study research is mainly focused upon an interpretivist perspective in that the cases discussed are centred on people’s stories and accounts. This book contains 10 chapters with the first chapter providing a definition of what a case study is in terms of how it focuses on the ‘uniqueness’ and ‘commonality’ of a particular problem, event, place or experience to better understand a phenomenon. This chapter also describes criterion for case selection and discusses issues related to ‘generalisation’, as well as ways in which researchers can generalise within cases. Chapter two discuses types of research questions which can be addressed through case study research and chapter three describes the characteristics of qualitative research ands its limitations for undertaking an interpretivist inquiry. Chapter four presents’ ways of gathering data and organising the data gathered from observations and interviews, with chapter five discussing data analysis and interpretation of the case, in terms of identifying patterns from within the data obtained from select paragraphs within interview transcripts. Chapter six covers the researcher’s role in the case study research in relation to where the researcher has positioned themselves within the case study with regards to: researcher as teacher, evaluator, advocate and more. Chapter seven addresses research validity in qualitative research in connection with triangulation and presents triangulation protocols as one solution to increasing the validity of case studies which employ a qualitative approach to data collection and analysis. Chapter eight provides the reader with ways in which to organise and report the findings from case studies. Chapter nine presents the author’s reflections about undertaking case study research and chapter 10 outlines a typical case study as an example for the reader to examine before undertaking their own case study research.
This text contains a useful bibliography of references and a glossary index. The language in this book is accessible to undergraduate, postgraduate and researchers seeking to employ case study approach to qualitative research projects. This text is useful for anyone seeking to undertake case study research using interpretivist methods. Of particular use are chapters six and seven as they cover the importance of the researcher’s role in case study research and triangulation as one solution to validity.
The Art of Case Study Research is an indispensable source for the case study researcher. Essential reading prior to embarking on case study research.
Many of the post-graduate students take a case study vapproach in their small scale research projects and this book will be very useful for them in develeoping their methodologies and procedures.
It is clearly evident that the author has many years experience in designing and undertaking case studies and as such this is an essential text for any researcher undertaking a case study. It is easy to read and is laid out in a clear, logical way. Thank you.
A superb supporting text for undergraduate and post graduate students conducting empirical research. Written in a logical and methodical order, workshops help students gain detailed understanding of the chosen concepts
This book will be used as a useful resource in developing learning activities and supplementary instructional handouts for students
This is an excellent text for students undertaking case study research.
For instructors
Select a purchasing option.
We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
The art of case study research
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
644 Previews
22 Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station47.cebu on June 21, 2023
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)

- Politics, Philosophy & Social Sciences
- Social Sciences
- Anthropology

Your Amazon Prime 30-day FREE trial includes:
Unlimited Premium Delivery is available to Amazon Prime members. To join, select "Yes, I want a free trial with FREE Premium Delivery on this order." above the Add to Basket button and confirm your Amazon Prime free trial sign-up.
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, you will be charged £95/year for Prime (annual) membership or £8.99/month for Prime (monthly) membership.
Buy new: £86.50 £86.50 FREE delivery: Sunday, April 14 in the UK Dispatches from: Amazon Sold by: JustAve
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. For a full refund with no deduction for return shipping, you can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition.
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method
Buy used £26.08

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet or computer – no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Follow the author

The Art of Case Study Research Paperback – 5 April 1995
Purchase options and add-ons.
This book presents a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods by drawing from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological and biographic research methods.
Robert E. Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such questions as: How is the case selected? How do you select the case which will maximize what can be learned? How can what is learned from one case be applied to another? How can what is learned from a case be interpreted? In addition, the book covers: the differences between quantitative and qualitative approaches; data-gathering including document review; coding, sorting and pattern analysis; the roles of the researcher; triangulation; and reporting.
- ISBN-10 080395767X
- ISBN-13 978-0803957671
- Edition 1st
- Publication date 5 April 1995
- Language English
- Dimensions 15.56 x 1.12 x 23.5 cm
- Print length 192 pages
- See all details
Frequently bought together

What do customers buy after viewing this item?

Product description
From the back cover, about the author, product details.
- Publisher : SAGE Publications, Inc; 1st edition (5 April 1995)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 192 pages
- ISBN-10 : 080395767X
- ISBN-13 : 978-0803957671
- Dimensions : 15.56 x 1.12 x 23.5 cm
- 650 in Under- & Postgraduate Student Guides
About the author
Robert e. stake.
Discover more of the author’s books, see similar authors, read author blogs and more
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings, help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyses reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top review from United Kingdom
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..

Top reviews from other countries
- UK Modern Slavery Statement
- Sustainability
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell on Amazon Business
- Sell on Amazon Handmade
- Sell on Amazon Launchpad
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect and build your brand
- Associates Programme
- Fulfilment by Amazon
- Seller Fulfilled Prime
- Advertise Your Products
- Independently Publish with Us
- Host an Amazon Hub
- › See More Make Money with Us
- Instalments by Barclays
- Amazon Platinum Mastercard
- Amazon Classic Mastercard
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Payment Methods Help
- Shop with Points
- Top Up Your Account
- Top Up Your Account in Store
- COVID-19 and Amazon
- Track Packages or View Orders
- Delivery Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Amazon Mobile App
- Customer Service
- Accessibility
- Netherlands
- United Arab Emirates
- United States
- Conditions of Use & Sale
- Privacy Notice
- Cookies Notice
- Interest-Based Ads Notice
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The art of case study research

1996, Library & Information Science Research
Related Papers
The Canadian Journal of Action Research
Trudie Aberdeen
Evaluation and Program Planning
ashok kumar
rizwan gujjar
Jiaheng Yao
Simon Phelan
American Journal of Orthopsychiatry
William M. Runyan
The Canadian Journal of Program Evaluation
Trista Hollweck
mubashar yaqoob
RELATED PAPERS
Jual Split Termurah DiCiteureup.
Jual Split Termurah DiCiteureup
Jhanery camarena alfaro
Revista del CESLA: International Latin American Studies Review
Silvina Merenson
Arist Automation
ARIST AUTOMATION
Actas Urológicas Españolas
Isaías Velasco Villegas
alief kurnia
Nepal Medical College Journal
anup dhungana
Journal of Vascular Surgery
Mark Farber
GEM - International Journal on Geomathematics
Hans Burchard
Herculano H De Biasi
Jurnal Teknologi Lingkungan Lahan Basah
Murti Juliandari
Bisma The Journal of Counseling
Bimbingan Konseling DKP
joko hermanianto
Khurram Niaz
Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining
Rajas Bansal
Frontiers in Physiology
Marcello Traina
The Neuroscience Journal of Shefaye Khatam
mohammad navid ebrahimi
FUTY Journal of the Environment
Ajiri Atagbaza
peter tibor nagy
Rachhpal Jassal
Proceedings of the 20th Annual European Real Estate Society Conference - Vienna, Austria
ABDIRAHMAN MOHAMED
麦考瑞大学毕业证文凭办理成绩单修改 办理澳洲MQ文凭学位证书学历认证
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
You are here

The Art of Case Study Research
- Robert E. Stake - University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
- Description
"The book is a concise and very readable guide to case study research. It includes a good introduction to the theoretical principles underlying qualitative research, and discusses a wide range of qualitative approaches, namely naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological and biographic research methods. . . . Stake offers some useful practical advice, for example, on how to conduct in-depth interviews, how to analyze qualitative data and on report writing. . . . Stake writes in a rather unusual and very personal style but this makes the text very readable. The author's obvious passion for research makes the text even more enjoyable and stimulating. . . . the book. . . seems particularly appropriate for those undertaking this type of research in the fields of education and social policy."
--Ivana La Valle in Social Research Association News
"It is gratifying to encounter a text so cogently advocating the case study method (aka: naturalistic fieldwork) as a legitimate knowledge-enhancing endeavor."
--Sala Horowitz in Academic Library Book Review
"I have just finished a qualitative case study based almost entirely on interviews with engineering students. The two sources on which I depended most heavily were Robert E. Stake's The Art of Case Study Research and Harry F. Wolcott's Writing Up Qualitative Research. I have heard others sing the praises of different works and I have referred to them, but favor the two mentioned."
--Terry C. Hall, Ed.D., Independent Scholar
"This volume consolidates and elaborates ideas Robert E. Stake articulated in earlier journal articles and chapters in a form that is useful and readily accessible to both practitioners and students of educational research methods. His unusually personal presentation style and innovative format for sharing practical tips through authentic examples add to the main treasure of his new book: an incomparable sophistication about research epistemology and practice. . . . His vast experience in the field and in the classroom and his intimate knowledge of the literature intersect, providing the reader with an unusually comprehensive portrayal of a specialized field. . . . The Art of Case Study Research is a significant contribution to research methodology literature and will undoubtedly assume quick popularity as a text."
--Linda Mabry, Indiana University, Bloomington
"A concise and readable primer for doing case study research, the fruit of many years of experience and wisdom. Robert E. Stake's book is also valuable as a genuine attempt to integrate, rather than pick arguments with, the best there is of contending approaches to qualitative inquiry."
--A. Michael Huberman, Harvard University and The Network, Inc.
" The Art of Case Study Research is most useful to novices in qualitative inquiry. I could see using it in combination with other texts or readings in an introductory course to qualitative research methods or in a research methods survey course. Because of its readable style and wellspring of examples and helpful suggestions, both graduate and undergraduate students will find the book useful. Researchers seeking to more fully understand the case study approach as perceived by one of the leaders in case study work will also pick up this book. Researchers and policymakers in social service agencies may also be interested because case studies are increasingly part of evaluation strategies."
--Corrine Glesne, University of Vermont
Unique in his approach and style, Robert E. Stake draws from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological, and biographic methods to present a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods. In his exploration, Stake uses and annotates an actual case, at Harper School, to demonstrate to readers how to resolve some of the major issues of case study research; for example, how to select the case (or cases) that will maximize learning, how to generalize what is learned from one case to another, and how to interpret what is learned from a case. Uniquely, this book legitimizes direct interpretation as a case research method. It covers such topics as the differences between quantitative and qualitative approaches to case study; data gathering, including document review; coding, sorting, and pattern analysis; the roles of the researcher, triangulation; and reporting a case study. Also provided are end-of-chapter "workshops" that help students focus on new concepts.
Written with the inspired and thought-provoking style of a master storyteller, The Art of Case Study Research helps readers chart their way through the labyrinth of case study research.
Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
We hope you'll consider this SAGE text. Email us at [email protected] , or click here to find your SAGE rep .
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
This is a very useful resource for students who are evaluating case study research, or who are contemplating this as a methodology for their own research.
I have used a previous edition extensively for my own research. Yin is an essential for all case study researchers. I am delighted to have the new edition. It is a classic.
An excellent text for educator/student research methods using case study as an approach. Written in a way that makes interpretation, understanding and application easier.
This is an essential book for research using a case study approach.
Stake provides a useful step by step guide to case study methods used in qualitative inquiry. The use of workshop scenarios helps cement its application in practice.
A concise book that is so elaborate most especially for early career researchers using case study as an approach. The writing style is simple with detail examples; also the use of foot notes in the book is an “icing on the cake”.
It did not suit the needs of the actual students. This does not mean that the book would be not good - in contrary.
Classic book to go alongside Yin for a different philosophical perspective. Will advise students doing case study to read this.
Great book, essential reading for all research methods modules
This is a classic text and clearly accessible to novice and more mature researchers interested in Case Study Research. Each chapter is well defined and signposts the next chapter.
For instructors
Select a purchasing option.
- Find My Rep
You are here

The Art of Case Study Research
- Robert E. Stake - University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
- Description
Robert E Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such questions as: How is the case selected? How do you select the case which is most likely to lead to maximizing what can be learned? How can what is learned from one case be applied to another? How can what is learned from a case be interpreted? In addition, the book covers: the differences between quantitative and qualitative approaches; data-gathering including document review; coding, sorting and pattern analysis; the roles of the researcher; triangulation; and reporting. Introduction An Intensive Study of Case Study Research Methods
This is a very useful resource for students who are evaluating case study research, or who are contemplating this as a methodology for their own research.
I have used a previous edition extensively for my own research. Yin is an essential for all case study researchers. I am delighted to have the new edition. It is a classic.
An excellent text for educator/student research methods using case study as an approach. Written in a way that makes interpretation, understanding and application easier.
This is an essential book for research using a case study approach.
Stake provides a useful step by step guide to case study methods used in qualitative inquiry. The use of workshop scenarios helps cement its application in practice.
A concise book that is so elaborate most especially for early career researchers using case study as an approach. The writing style is simple with detail examples; also the use of foot notes in the book is an “icing on the cake”.
It did not suit the needs of the actual students. This does not mean that the book would be not good - in contrary.
Classic book to go alongside Yin for a different philosophical perspective. Will advise students doing case study to read this.
Great book, essential reading for all research methods modules
This is a classic text and clearly accessible to novice and more mature researchers interested in Case Study Research. Each chapter is well defined and signposts the next chapter.
Preview this book
For instructors, purchasing options.
Please select a format:
Jump to navigation
- Bahasa Malaysia

Are midwife continuity of care models versus other models of care for childbearing women better for women and their babies?
Key messages
Women or their babies who received midwife continuity of care models were less likely to experience a caesarean section or instrumental birth with forceps or a ventouse suction cup, and may be less likely to experience an episiotomy (a cut made by a healthcare professional into the perineum and vaginal wall). They were more likely to experience spontaneous vaginal birth.
Women who experienced midwife continuity of care models reported more positive experiences during pregnancy, labour, and postpartum. Additionally, there were cost savings in the antenatal (care during pregnancy) and intrapartum (care during labour and birth) period.
Further evidence may change our results, and future research should focus on the impact on women with social risk factors, and those with medical complications, and understanding the implementation and scaling up of midwife continuity of care models, with emphasis on low- and middle-income countries.
What are midwife continuity of care models?
Midwife continuity of care models provide care from the same midwife or team of midwives during pregnancy, birth, and the early parenting period in collaboration with obstetric and specialist teams when required.
What did we want to find out?
We wanted to find out how outcomes differed for women or their babies who received a midwife continuity of care model compared to other models of care.
Our main outcomes were: spontaneous vaginal birth, caesarean section, regional anaesthesia (spinal or epidural block to numb the lower part of the body), intact perineum (the area between the anus and the vulva), fetal loss after 24 weeks gestation, preterm birth, and neonatal death.
We also looked at a range of other outcomes, including women’s experience and cost.
What did we do?
We searched for studies that compared midwife continuity of care models with other models of care for pregnant women. We compared and summarised the results of the studies and rated our confidence in the evidence based on factors such as study methods and size.
What did we find?
We found 17 studies involving 18,533 women in Australia, Canada, China, Ireland, and the United Kingdom.
Many of these studies largely focused on women with a lower risk of complications at the start of pregnancy, or those drawn from a specific geographical location. Midwives continued to provide midwifery care in collaboration with specialist and obstetric teams if women developed complications in pregnancy, birth, and postpartum.
Our main results
Women or their babies who received midwife continuity of care models compared to those receiving other models of care were less likely to experience a caesarean section or instrumental vaginal delivery, and may be less likely to experience an episiotomy. They were more likely to experience a spontaneous vaginal birth.
Midwife continuity care models probably make little or no difference to the likelihood of having an intact perineum, and may have little or no impact on the likelihood of preterm birth.
We are uncertain about the effect of midwife continuity of care models on regional anaesthesia, fetal loss after 24 weeks' gestation, and neonatal death.
Women who experienced care from midwife continuity of care models reported more positive experiences during pregnancy, labour, and postpartum. Additionally, there were cost savings in the antenatal and intrapartum period.
What are the limitations of the evidence?
Our confidence in these findings varies and further evidence may change our results. For instance, it is not always clear if the people assessing the outcomes knew which type of care the women received.The evidence for fetal loss after 24 weeks' gestation and neonatal death is based on a very small number of cases and there are not enough studies to be certain about some results. We lack data on important aspects like maternal health status after birth, neonatal readmissions, or infant health status.
Few studies included a specific focus on women at high risk of complications, and none focused on women from disadvantaged backgrounds, indicating a need for future research in these areas. This highlights the need for more comprehensive and diverse studies to strengthen our understanding and confidence in these findings, particularly in varied populations and across different healthcare settings.
Future research should focus on the impact on women with social risk factors, and those with medical complications, and understanding the implementation and scaling up of midwife continuity of care models, with emphasis on low- and middle-income countries.
How up-to-date is this evidence?
This is an update of our previous review. We included evidence up to 17 August 2022.
Women receiving midwife continuity of care models were less likely to experience a caesarean section and instrumental birth, and may be less likely to experience episiotomy. They were more likely to experience spontaneous vaginal birth and report a positive experience. The certainty of some findings varies due to possible risks of bias, inconsistencies, and imprecision of some estimates.
Future research should focus on the impact on women with social risk factors, and those at higher risk of complications, and implementation and scaling up of midwife continuity of care models, with emphasis on low- and middle-income countries.
Midwives are primary providers of care for childbearing women globally and there is a need to establish whether there are differences in effectiveness between midwife continuity of care models and other models of care. This is an update of a review published in 2016.
To compare the effects of midwife continuity of care models with other models of care for childbearing women and their infants.
We searched the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Trials Register, ClinicalTrials.gov, and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) (17 August 2022), as well as the reference lists of retrieved studies.
All published and unpublished trials in which pregnant women are randomly allocated to midwife continuity of care models or other models of care during pregnancy and birth.
Two authors independently assessed studies for inclusion criteria, scientific integrity, and risk of bias, and carried out data extraction and entry. Primary outcomes were spontaneous vaginal birth, caesarean section, regional anaesthesia, intact perineum, fetal loss after 24 weeks gestation, preterm birth, and neonatal death. We used GRADE to rate the certainty of evidence.
We included 17 studies involving 18,533 randomised women. We assessed all studies as being at low risk of scientific integrity/trustworthiness concerns. Studies were conducted in Australia, Canada, China, Ireland, and the United Kingdom. The majority of the included studies did not include women at high risk of complications. There are three ongoing studies targeting disadvantaged women.
Primary outcomes
Based on control group risks observed in the studies, midwife continuity of care models, as compared to other models of care, likely increase spontaneous vaginal birth from 66% to 70% (risk ratio (RR) 1.05, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.03 to 1.07; 15 studies, 17,864 participants; moderate-certainty evidence), likely reduce caesarean sections from 16% to 15% (RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.84 to 0.99; 16 studies, 18,037 participants; moderate-certainty evidence), and likely result in little to no difference in intact perineum (29% in other care models and 31% in midwife continuity of care models, average RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.98 to 1.12; 12 studies, 14,268 participants; moderate-certainty evidence). There may be little or no difference in preterm birth (< 37 weeks) (6% under both care models, average RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.16; 10 studies, 13,850 participants; low-certainty evidence).
We are very uncertain about the effect of midwife continuity of care models on regional analgesia (average RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.79 to 0.92; 15 studies, 17,754 participants, very low-certainty evidence), fetal loss at or after 24 weeks gestation (average RR 1.24, 95% CI 0.73 to 2.13; 12 studies, 16,122 participants; very low-certainty evidence), and neonatal death (average RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.43 to 1.71; 10 studies, 14,718 participants; very low-certainty evidence).
Secondary outcomes
When compared to other models of care, midwife continuity of care models likely reduce instrumental vaginal birth (forceps/vacuum) from 14% to 13% (average RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.83 to 0.96; 14 studies, 17,769 participants; moderate-certainty evidence), and may reduce episiotomy 23% to 19% (average RR 0.83, 95% CI 0.77 to 0.91; 15 studies, 17,839 participants; low-certainty evidence).
When compared to other models of care, midwife continuity of care models likely result in little to no difference in postpartum haemorrhage (average RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.03; 11 studies, 14,407 participants; moderate-certainty evidence) and admission to special care nursery/neonatal intensive care unit (average RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.03; 13 studies, 16,260 participants; moderate-certainty evidence). There may be little or no difference in induction of labour (average RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.85 to 1.00; 14 studies, 17,666 participants; low-certainty evidence), breastfeeding initiation (average RR 1.06, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.12; 8 studies, 8575 participants; low-certainty evidence), and birth weight less than 2500 g (average RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.79 to 1.08; 9 studies, 12,420 participants; low-certainty evidence).
We are very uncertain about the effect of midwife continuity of care models compared to other models of care on third or fourth-degree tear (average RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.49; 7 studies, 9437 participants; very low-certainty evidence), maternal readmission within 28 days (average RR 1.52, 95% CI 0.78 to 2.96; 1 study, 1195 participants; very low-certainty evidence), attendance at birth by a known midwife (average RR 9.13, 95% CI 5.87 to 14.21; 11 studies, 9273 participants; very low-certainty evidence), Apgar score less than or equal to seven at five minutes (average RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.72 to 1.24; 13 studies, 12,806 participants; very low-certainty evidence) and fetal loss before 24 weeks gestation (average RR 0.82, 95% CI 0.67 to 1.01; 12 studies, 15,913 participants; very low-certainty evidence). No maternal deaths were reported across three studies.
Although the observed risk of adverse events was similar between midwifery continuity of care models and other models, our confidence in the findings was limited. Our confidence in the findings was lowered by possible risks of bias, inconsistency, and imprecision of some estimates.
There were no available data for the outcomes: maternal health status, neonatal readmission within 28 days, infant health status, and birth weight of 4000 g or more.
Maternal experiences and cost implications are described narratively. Women receiving care from midwife continuity of care models, as opposed to other care models, generally reported more positive experiences during pregnancy, labour, and postpartum. Cost savings were noted in the antenatal and intrapartum periods in midwife continuity of care models.
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, the landslide traces inventory in the transition zone between the qinghai-tibet plateau and the loess plateau: a case study of jianzha county, china.

- 1 National Institute of Natural Hazards, Ministry of Emergency Management of China, Beijing, China
- 2 Key Laboratory of Compound and Chained Natural Hazards Dynamics, Ministry of Emergency Management of China, Beijing, China
- 3 Key Laboratory of Shale Gas and Geoengineering, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
- 4 Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing, China
The upper reaches of the Yellow River in China, influenced by erosion of the Yellow River and tectonic activities, are prone to landslides. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the existing landslide traces. Based on visual interpretation on high-resolution satellite images and terrain data, supplemented and validated by existing landslide records, this paper prepared the most complete and detailed landslide traces inventory in Jianzha County, Huangnan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai Province, to date. The results indicate that within the study area of 1714 km 2 , there are at least 713 landslide traces, ranging in scale from 3,556 m 2 to 11.13 km 2 , with a total area of 134.46 km 2 . The total landslide area excluding the overlap area is 126.30 km 2 . The overall landslide point density and area density in the study area are 0.42 km -2 and 7.37% respectively. The maximum point density and maximum area density of landslide traces in the area are as high as 5.69 km -2 and 98.0% respectively. The landslides are primarily distributed in the relatively low-elevation northeastern part of Jianzha County, characterized mainly by large-scale loess landslides, with 14 landslides exceeding 1×10 6 m 2 . This inventory not only supplements the landslide trace data in the transition zone between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau, but also provides an important basis for subsequent landslide risk zoning, response to climate change, and landscape evolution. Additionally, it holds significant reference value for compiling landslide inventories in similar geological environments.
1 Introduction
Worldwide, mass movements such as landslides are prevalent geological hazards, causing heavy casualties ( Petley, 2012 ; Froude and Petley, 2018 ). As far as landslide hazards are concerned, China ranks among the regions with the very frequency of landslide hazards globally ( Kirschbaum et al., 2015 ; Xu and Xu, 2021 ). According to statistics from 2004 to 2016, China experienced 463 fatal landslides not induced by earthquakes, resulting in 4,718 deaths and causing economic losses exceeding 900 million dollars ( Zhang and Huang, 2018 ). Therefore, the prevention and control of landslide hazards is crucial for people’s lives. As a key step in hazard prevention and mitigation, including the analysis of regional landslide distribution patterns, hazard assessments, and risk assessment, the construction of a regional landslide inventory is fundamental and essential. A complete and accurate inventory ensures the objectivity and precision of subsequent work ( Xu, 2015 ; Piacentini et al., 2018 ).
In the construction of China’s landslide traces inventory, many scholars have carried out a lot of work and made certain progress ( Chen et al., 2016 ; Qiu et al., 2019 ; Zhao et al., 2019 ; Zhang et al., 2020 ). In northwestern China, Huang et al. (2022) compiled a landslide traces inventory for Hualong County, Qinghai Province, consisting of 3,517 landslides through visual interpretation of high-resolution optical images. Furthermore, an in-depth study on the spatial distribution patterns of landslides was conducted based on this inventory. In central China, Li et al. (2022a) primarily utilized visual interpretation, supplemented by existing literature and hazard records, to improve and supplement the landslide traces inventory for Baoji City, Shaanxi Province. The inventory contains a total of 3,422 landslides, providing foundational data for subsequent exploration of the distribution characteristics of large-scale landslides in the region. In the western part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Cui et al. (2023) employed the Google Earth platform and visual interpretation method to identify landslide traces in the Western Himalayan Syntaxis. They established a landslide traces inventory containing 7,947 landslides. This inventory serves as a support for subsequent landslide hazard assessments. Wu et al. (2016) collected landslide data based on aerial photographs at a scale of 1:50,000 under the conditions of existing data and field survey. They mapped 328 landslides in Gangu County, Gansu Province, providing a crucial foundation for subsequent research. Lan et al. (2004) combined aerial photographs, previous landslide investigation data, and on-site verification to compile a landslide inventory for the Xiaojiang River Basin, including 574 landslide records. They conducted spatial analysis and prediction of landslide based on this inventory. The landslide data sets constructed by these studies, supported by various methods, demonstrate the ability to facilitate subsequent study on landslide in terms of accuracy and completeness. Nevertheless, accurate and complete landslide trace data are still lacking for the entire region of China.
In studies covering Jianzha County, many scholars have carried out identification work on regional landslides, or conducted research on landslide failure patterns, InSAR deformation analysis, geomorphic effects, and other aspects based on landslide data ( Ma et al., 2008 ; Guo et al., 2020a ; Wang et al., 2022 ; Tu et al., 2023 ). Yin et al. (2014) primarily utilized visual interpretation to identify 508 landslides from Sigou Gorge to Lagan Gorge in the upper reaches of the Yellow River, with many landslides distributed in Jianzha County. Tu et al. (2023) conducted landslide detection in the upper reaches of the Yellow River based on InSAR technology, and carried out detailed deformation analysis of the Lijia Gorge landslides group in Jianzha County. Du et al. (2023) combined InSAR deformation monitoring and optical images to identify 597 landslides in the upper reaches of the Yellow River. Landslides are mainly distributed in Jianzha County and its surrounding areas. Wang et al. (2022) conducted deformation analysis on the Simencun landslide in Jianzha County to explore the relationship between the failure patterns before and after the landslide occurrence. Currently, although many studies have been carried out in Jianzha County based on landslide data. However, the landslide inventory maps produced do not cover the entire Jianzha County, or the landslide data are not complete and detailed enough. Therefore, by combining the visual interpretation of high-resolution optical images with the comparison of existing literature, this study compiled a landslide traces inventory for Jianzha County, Qinghai Province. Additionally, a spatial analysis was performed on the inventory. Finally, the completeness and importance of the landslide inventory are discussed.
2 Study area
Jianzha County has a total area of approximately 1714 km 2 and is located in the transitional zone from the upper reaches of the Yellow River on the northeastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau to the Loess Plateau ( Figure 1 ) ( Ma et al., 2008 ). For a long time, the landscape evolution of this region has been influenced by the northeastward compression of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, resulting in the formation of basin and mountainous topography ( Guo et al., 2020a ; Peng et al., 2020 ). The overall terrain in the region is high in the southwest and low in the northeast. The northeastern part is the Qunke-Jianzha Basin, characterized by relatively low elevations and crossed by the main trunk of the Yellow River. On either side, there are two basins, namely, the Guide Basin and the Xunhua Basin. The Yellow River and its tributaries exert strong erosion and incision along the edges of the basins, with cutting depths exceeding 500 m. This has resulted in the formation of numerous erosion and accumulation terraces, as well as steep and rugged slopes, providing favorable conditions for landslide occurrence ( Craddock et al., 2010 ; Guo et al., 2020a ; Du et al., 2023 ).
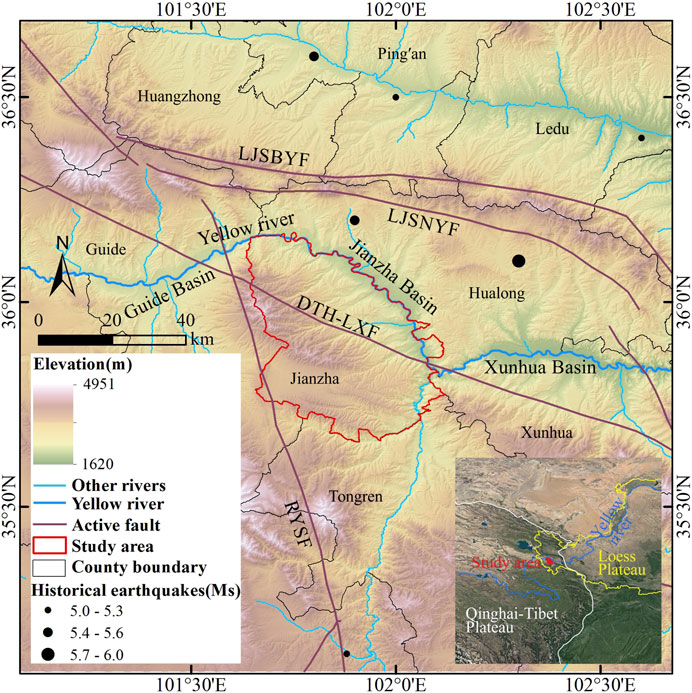
Figure 1 . Location of the study area. Surface wave magnitude (Ms) is a measure of the strength of an earthquake, calculated from surface wave. The larger the value, the stronger the earthquake. Active fault data from Deng (2007) .
The study area exhibits undulating and rugged topography with well-developed valleys and gullies. The surrounding active tectonics are developed, with the north part of the area having the Lajishanbeiyuan Fault (LJSBYF) and the Lijishannanyuan Fault (LJSNYF). The NWW-SEE trending Daotanghe-Linxia Fault (DTH-LXF) and NNW-SSE trending Riyueshan Fault (RYSF) pass through the study area. Tectonic activity and climate change contribute to the frequent geological hazards ( Yin et al., 2014 ). The large, extra-large, and giant landslides in the region are typical and representative in China ( Guo et al., 2020b ; Yin et al., 2021 ). Some studies suggest that the tectonic uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, as an internal dynamic factor, has led to the episodic incision of the Yellow River main and tributary channels, serving as the underlying cause for the formation of giant landslides ( Li et al., 2011 ). As shown in Figure 1 , there are several historical earthquakes with Ms greater than 5.0 around Jianzha County. The occurrence of landslides may be related to seismic activity or may be the result of landscape evolution, such as river erosion and high groundwater levels ( Guo et al., 2016 ; Guo et al., 2018 ).
With the advancement of remote sensing technology and improved transportation accessibility, the main methods for compiling regional landslide inventories currently include field investigation, visual interpretation of satellite images combined with computer, and automatic identification technology. Table 1 summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of the three landslide identification methods. Detailed field investigation can ensure high accuracy for landslide investigations in small-scale areas ( Huangfu et al., 2021 ). However, for large-scale regional landslide investigations, the feasibility of extensive field investigation decreases. This is primarily due to the substantial cost and time required ( Peng et al., 2016 ), as well as the difficulty in accessing rugged landslide sites. With the development of automatic identification technology, it has a significant advantage in quickly obtaining regional landslide data. However, its accuracy may be not very good ( Fayne et al., 2019 ; Zhang et al., 2020 ; Piralilou et al., 2021 ; Vecchiotti et al., 2021 ; Milledge et al., 2022 ). Combining the strengths of both approaches, the human-computer interaction visual interpretation of satellite images has gradually become an important method for constructing landslide inventory ( Xu et al., 2015 ; Shao et al., 2020 ; Li et al., 2021 ; Cui et al., 2022a ). This approach requires interpreters to have certain professional background knowledge. Compared to detailed field survey, it sacrifices a small portion of accuracy but significantly improves the efficiency of constructing landslide inventory ( Xu et al., 2014b ; Cui et al., 2022b ; Cui et al., 2022c ).
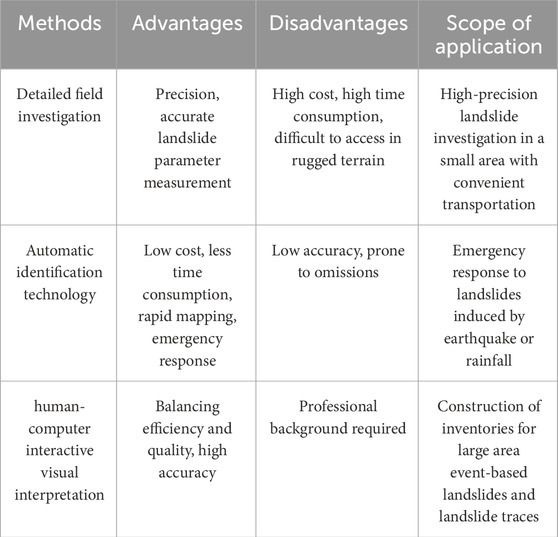
Table 1 . Advantages and disadvantages of three landslide identification methods.
This article primarily employed high-resolution optical images overlayed on terrain data for human-computer interactive visual interpretation, and combined existing landslide records in literature for validation and supplementation to construct a landslide traces inventory for Jianzha County. Google Earth Pro platform integrates a vast amount of high-resolution optical satellite image data and allows for the three-dimensional, multi-angle display of landscape by overlaying terrain data ( Crosby et al., 2012 ; Rabby and Li, 2019 ). This provides extremely convenient conditions for landslide identification. Focusing on the Jianzha County, the image quality is exceptionally high, with 100% satellite image coverage and 0% cloud coverage. Therefore, we performed repetitive basic work on landslide interpretation based on the Google Earth Pro for inventory construction. First of all, the shape and boundary of the landslide can be easily determined based on the differences between the texture, tone, shadow and vegetation development on the satellite images and the surrounding environment, combined with terrain differences and multi-angle observation. Secondly, many existing literature findings on landslides in the region will be conducted to check and supplement the inventory for ensuring the completeness and objectivity. Because different landslides have different topographic and geomorphic characteristics, there is no uniform standard applicable to the interpretation of all landslide traces. Here, some common landslide features used in landslide interpretation are listed: 1) Having an obvious armchair-shaped back wall and the phenomenon of double grooves homologous; 2) Depression in the source area, prominent topography in the accumulation area, accompanied by a distinct landslide boundary; 3) Obvious displacement between the landslide body and the surrounding environment, accompanied by cracks or differences in elevation; 4) The source area shows a brighter color, and the accumulation has transverse fissures and appears tongue-shaped; 5) Irregular stepped appearance in the accumulation body, with the terraces possibly transformed into residential areas or farmland.
4 Results and analysis
4.1 landslide traces inventory.
The landslide inventory serves as a crucial foundation for regional landslide risk assessment and prevention. Many scholars have conducted regional or individual landslide studies in Jianzha County ( Yin et al., 2014 ; Guo et al., 2020b ; Du et al., 2023 ; Tu et al., 2023 ). Although the study areas of these studies cover or partially cover Jianzha County, most have not established a complete landslide traces inventory that fully encompasses Jianzha County. Table 2 presents selected existing landslide records in Jianzha County. After objectively supplemented and validated by these records, the landslide inventory constructed in this study contains a total of 713 landslide traces ( Figure 2 ). The total area of these landslides is 134.46 km 2 . The total landslide area excluding the overlap area is 126.30 km 2 , accounting for 7.37% of the study area. The average landslide area is approximately 0.19 km 2 , with a minimum of 3,556 m 2 and a maximum of 11.13 km 2 . It can be found that landslides mainly occur on the slopes of the relatively low-elevation ridges in the northeastern part of Jianzha County. These landslides are widely distributed in towns such as Kanbula, Jiajia, Cuozhou, Maketang, and Angla, with a predominance of large-scale landslides. In the southwest, where the altitude is relatively high, landslides are sparsely distributed.
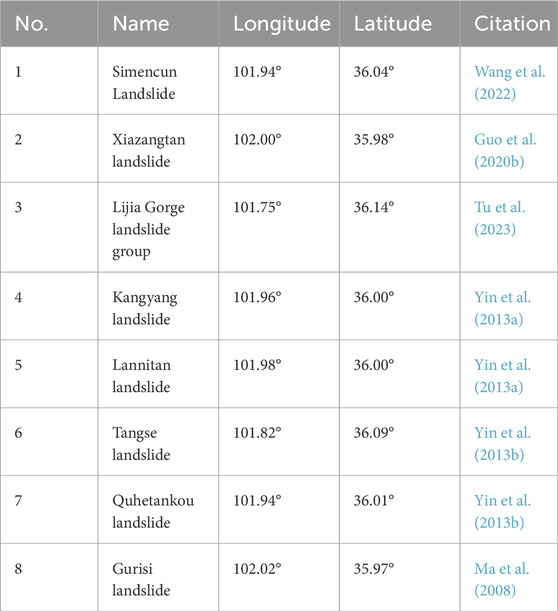
Table 2 . Selected recorded landslides in Jianzha County.
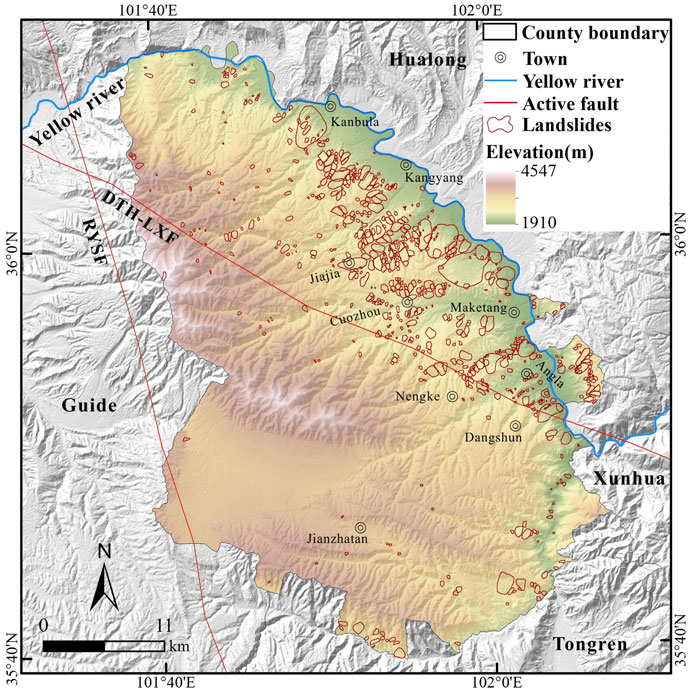
Figure 2 . Spatial distribution map of landslide traces.
4.2 Typical landslide display
In order to more intuitively display the landslides, several typical landslides were selected within the study area for display ( Figure 3 ). It can be found that the predominant landslide type is loess landslide. The landslide boundary is easily identified based on the discontinuity in texture and shape between the deposits and the surrounding environment. The material movement along the slope is evident. The displacement between the landslide deposits and the boundary visually demonstrates the movement direction and shape of the landslide. Over time, traces of human activity become visible on the deposits. After reconstruction, roads and buildings of various sizes are distributed across the deposits. These typical landslide examples can clearly capture the landslide morphology and material movement traces, which is of great value for the study of regional landslide failure mechanisms.
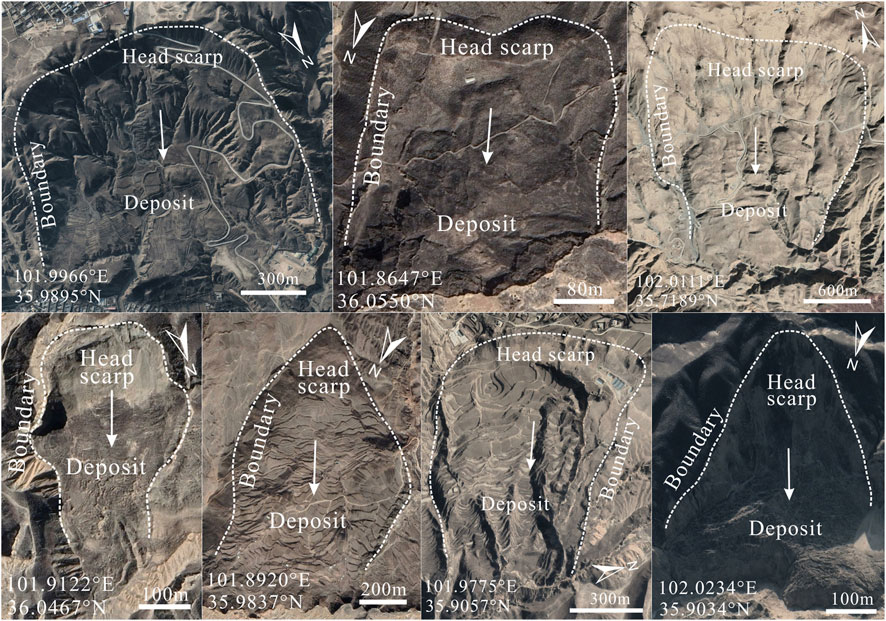

Figure 3 . Display of seven typical landslide traces in the study area.
4.3 Landslide density statistics
In order to quantitatively analyze the spatial distribution of landslides, landslide point density and area density are used to characterize the distribution and aggregation of landslides. After kernel density calculation with the search radius set to 2 km, the results are shown in Figure 4 . High point density areas are primarily concentrated in the northeastern part of the study area ( Figure 4A ), with the maximum density reaching 5.69 km -2 . This indicates that landslides in these areas are numerically dominant. The maximum landslide area density is 98.0% ( Figure 4B ). High area density areas are different from high point density areas in distribution. For instance, landslide area density is more significant relative to point density in areas close to the Kanbula Town. This indicates that the landslides in this area tend to be larger in scale.
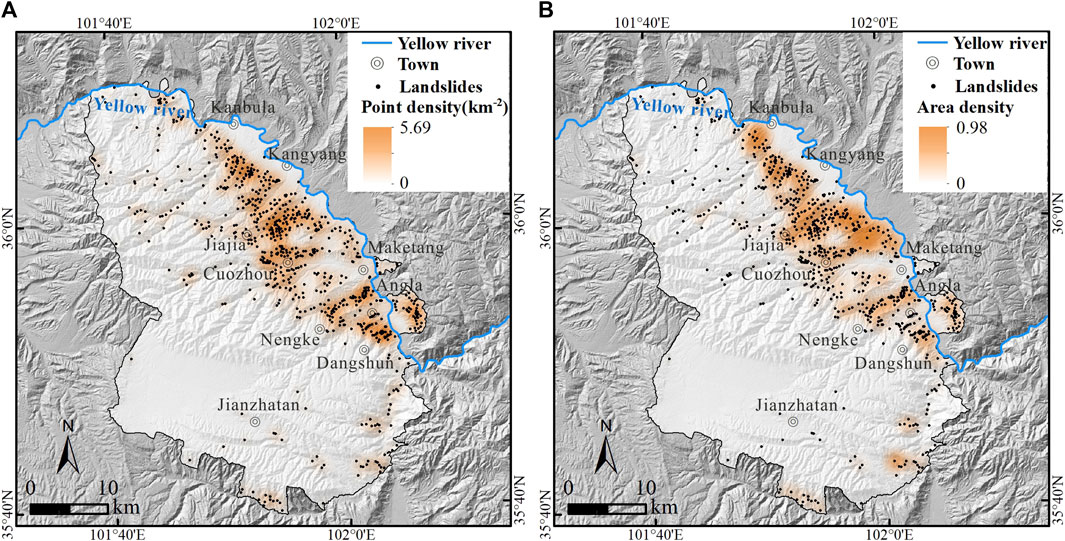
Figure 4 . Landslide density map. (A) point density map; (B) area density map.
5 Discussion
5.1 landslide scale and the completeness analysis.
To explore the scale of landslides in Jianzha County, the cumulative landslide number was plotted against the landslide area in a double logarithmic coordinate system to show the relationship between them ( Figure 5 ). Where N represents the number of landslides exceeding a given area, A. It can be observed that the majority of landslides have a scale smaller than 1×10 6 m 2 , with only 14 landslides exceeding 1×10 6 m 2 in scale. The fitting formula for all landslides is l g N A = − 0.728 l g A + 5.957 , with R 2 =0.882. For landslides with an area larger than 1×10 5 m 2 , the fitting formula is l g N A = − 1.210 l g A + 8.552 , with R 2 =0.99, indicating that these data are relatively complete. For landslides with an area smaller than 1×10 4 m 2 , the curve exhibits a smoother trend, possibly due to the less distinct image change characteristics in the exposed loess areas, making them difficult to identify.
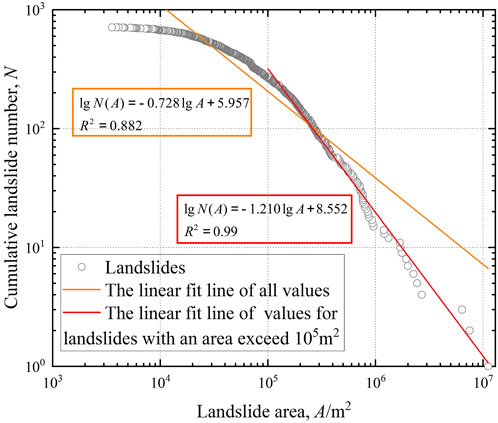
Figure 5 . Curve depicting correlation between the cumulative landslide number and the landslide area.
As shown in Figure 5 , landslides with an area greater than 1×10 5 m 2 are fitted as l g N A = − 1.210 l g A + 8.552 . In previous studies, this formula was often used in the statistics of coseismic landslide inventories to evaluate the completeness. For example, in the nearly complete coseismic landslide inventory established by Xu et al. (2014a) after the Wenchuan earthquake, landslides within a certain area are defined by the equation l g N A = − 2.0745 l g A + 13 , and the landslides exhibit a rolling trend. Similarly, coseismic landslide inventories for the Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake ( Xu et al., 2014b ) and Maerkang earthquake ( Chen et al., 2023 ) also show a similar trend, with the slopes and intercepts of the corresponding fitting equations are −1.341 and 6.02 (Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake) and −1.1052 and 5.7839 (Maerkang earthquake), respectively. Although the scale of landslides may vary due to different environmental conditions. However, it can be observed that whether it is the landslide traces inventory of this article or the coseismic landslide inventory, the landslides show a similar trend of change. In particular, in the work of establishing a landslide inventory with similar landslide scales, Li et al. (2022b) constructed a landslide traces inventory containing 3,757 landslides around the Baihetan Hydropower Station reservoir in China. The relationship between the cumulative number and area of landslides with an area greater than 1×10 5 m 2 is l g N A = − 1.275 l g A + 6.26 . Upon comparison, this is very close to the results of this article, which also proves the completeness of our inventory to a certain extent. By comparing the completeness of landslide inventories in different categories, it is concluded that landslide inventories of the same category have more reference value than those of different categories.
5.2 Objective assessment of methods
A complete and detailed landslide inventory is of great significance for regional landslide research and risk management. The human-computer interaction visual interpretation method, as one of the primary approaches for establishing regional landslide inventory, possesses advantages that are irreplaceable by field investigation and automatic identification techniques ( Guzzetti et al., 2012 ; Tian et al., 2019 ; Xu et al., 2020 ). While this study primarily relied on such a method to construct a relatively objective landslide traces inventory for Jianzha County, there are still some limitations. For small-scale landslides, due to the resolution limitations of satellite images, the coverage of topographic and geomorphic features, and the subjective factors from interpreters, it is inevitable that landslides with unclear identification characteristics will be missed. Compared with detailed field investigation, the visual interpretation method consumes less cost and time. Compared with automatic identification method, it is superior in accuracy and is currently a widely used method for identifying regional landslides ( Cui et al., 2021 ; Li et al., 2022a ; Sun et al., 2024 ). This method sacrifices some accuracy compared to field investigation, but greatly improves efficiency. Balancing the efficiency of automatic identification and the accuracy of field investigation is an exploratory and challenging task.
5.3 The importance of the landslide inventory
Landslide susceptibility refers to the probability of slope failure in a specific geological environment without considering triggering factors ( Akgun, 2012 ; Nikoobakht et al., 2022 ). As a fundamental component, landslide inventory plays an indispensable role in landslide susceptibility assessment. It provides essential information about landslides, including the number, scale, location. Based on landslide inventory, one can select a single assessment method and specific influencing factors for landslide susceptibility assessment ( Huangfu et al., 2021 ; Nanehkaran et al., 2021 ; Cemiloglu et al., 2023 ). Alternatively, one can choose several different assessment methods for comparative analysis to find the optimal results ( Azarafza et al., 2021 ; Nanehkaran et al., 2022 ; Mao et al., 2024 ). With the development of landslide assessment, machine learning has demonstrated outstanding performance among many methods, gradually becoming the preferred approach for assessment ( Nanehkaran et al., 2023 ). Based on susceptibility assessment, triggering factors are added to evaluate landslide hazard, while carrier indicators are added for vulnerability assessment. Risk assessment is then performed by overlaying hazard and vulnerability. However, regardless of which assessment method is chosen and which landslide influencing factors are considered, the susceptibility assessment, hazard assessment, vulnerability assessment, and risk assessment all need to be based on landslide data. The landslide inventory can not only be used to validate the results obtained through predictive modeling, but also provide an important reference for exploring factors involved in the occurrence of new landslides. Many studies have been carried out on incomplete landslide inventories and updated the inventories, effectively enhancing the understanding of subsequent landslide development and assessment research. For example, the Hokkaido earthquake ( Kasai and Yamada, 2019 ; Cui et al., 2021 ), Wenchuan earthquake ( Dai et al., 2011 ; Xu et al., 2014a ), and Jiuzhaigou earthquake ( Tian et al., 2019 ; Sun et al., 2024 ). The work of compiling a complete and detailed landslide inventory is not only of great value and significance, but also has important supporting value for subsequent research on landslide failure mechanisms, landscape evolution, especially landslide susceptibility assessment.
6 Conclusion
This study established a landslide traces inventory in Jianzha County, Qinghai Province, China, and conducted a statistical analysis of their number, area, and density. A total of 713 landslides were identified, mainly loess landslides. The total area of landslides is 134.46 km 2 , ranging in scale from 3556 m 2 to 11.13 km 2 . The landslides are primarily concentrated in the low-elevation regions of the northeastern part of the study area. This inventory is more similar in scale and completeness to other loess landslide inventories. Furthermore, it is more complete and detailed than previous landslide traces records in Jianzha County. The study compiled the most complete and detailed landslide traces inventory in Jianzha County so far, which is of great significance to landslide scientific research. In future, relevant research on loess landslide development characteristics, failure mechanisms, susceptibility assessment and risk zoning can be conducted based on this landslide inventory.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
TL: Investigation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. CX: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing–review and editing. LL: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. JX: Investigation, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Institute of Natural Hazards, Ministry of Emergency Management of China (2023-JBKY-57) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42077259).
Acknowledgments
Deep thanks are extended to the reviewers for their beneficial review and valuable comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Akgun, A. (2012). A comparison of landslide susceptibility maps produced by logistic regression, multi-criteria decision, and likelihood ratio methods: a case study at İzmir, Turkey. Landslides 9 (1), 93–106. doi:10.1007/s10346-011-0283-7
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Azarafza, M., Azarafza, M., Akgün, H., Atkinson, P. M., and Derakhshani, R. (2021). Deep learning-based landslide susceptibility mapping. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 24112. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-03585-1
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cemiloglu, A., Zhu, L., Mohammednour, A. B., Azarafza, M., and Nanehkaran, Y. A. (2023). Landslide susceptibility assessment for Maragheh County, Iran, using the logistic regression algorithm. Land 12 (7), 1397. doi:10.3390/land12071397
Chen, W., Chai, H., Zhao, Z., Wang, Q., and Hong, H. (2016). Landslide susceptibility mapping based on GIS and support vector machine models for the Qianyang county, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 75, 474. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-5093-0
Chen, Z., Huang, Y., He, X., Shao, X., Li, L., Xu, C., et al. (2023). Landslides triggered by the 10 June 2022 Maerkang earthquake swarm, Sichuan, China: spatial distribution and tectonic significance. Landslides 20, 2155–2169. doi:10.1007/s10346-023-02080-0
Craddock, W. H., Kirby, E., Harkins, N. W., Zhang, H., Shi, X., and Liu, J. (2010). Rapid fluvial incision along the Yellow River during headward basin integration. Nat. Geosci. 3 (3), 209–213. doi:10.1038/ngeo777
Crosby, C. J., Whitmeyer, S. J., De Paor, D. G., Bailey, J., and Ornduff, T. (2012). Lidar and Google Earth: simplifying access to high-resolution topography data. Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 492, 37–47. doi:10.1130/2012.2492(03)
Cui, Y., Bao, P., Xu, C., Ma, S., Zheng, J., and Fu, G. (2021). Landslides triggered by the 6 September 2018 Mw6.6 Hokkaido, Japan: an updated inventory and retrospective hazard assessment. Earth Sci. Inf. 14, 247–258. doi:10.1007/s12145-020-00544-8
Cui, Y., Hu, J., Xu, C., Miao, H., and Zheng, J. (2022b). Landslides triggered by the 1970 Ms7.7 Tonghai earthquake in Yunnan, China: an inventory, distribution characteristics, and tectonic significance. J. Mt. Sci. 19 (6), 1633–1649. doi:10.1007/s11629-022-7321-x
Cui, Y., Hu, J., Zheng, J., Fu, G., and Xu, C. (2022a). Susceptibility assessment of landslides caused by snowmelt in a typical loess area in the Yining County, Xinjiang, China. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeology 55 (1), qjegh2021–2024. doi:10.1144/qjegh2021-024
Cui, Y., Jin, J., Huang, Q., Yuan, K., and Xu, C. (2022c). A data-driven model for spatial shallow landslide probability of occurrence due to a typhoon in Ningguo City, Anhui Province, China. Forests 13 (5), 732. doi:10.3390/f13050732
Cui, Y., Yang, W., Xu, C., and Wu, S. (2023). Distribution of ancient landslides and landslide hazard assessment in the Western Himalayan Syntaxis area. Front. Earth Sci. 11, 1135018. doi:10.3389/feart.2023.1135018
Dai, F., Xu, C., Yao, X., Xu, L., Tu, X., and Gong, Q. (2011). Spatial distribution of landslides triggered by the 2008 Ms8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 40 (4), 883–895. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.04.010
Deng, Q. (2007). Map of active tectonics in China . Beijing: Seismological Press . (In Chinese)
Du, J., Li, Z., Song, C., Zhu, W., Ji, Y., Zhang, C., et al. (2023). InSAR-based active landslide detection and characterization along the upper reaches of the Yellow River. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 16, 3819–3830. doi:10.1109/jstars.2023.3263003
Fayne, J. V., Ahamed, A., Roberts-Pierel, J., Rumsey, A. C., and Kirschbaum, D. (2019). Automated satellite-based landslide identification product for Nepal. Earth Interact. 23 (3), 1–21. doi:10.1175/ei-d-17-0022.1
Froude, M. J., and Petley, D. N. (2018). Global fatal landslide occurrence from 2004 to 2016. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 18 (8), 2161–2181. doi:10.5194/nhess-18-2161-2018
Guo, X., Forman, S. L., Marin, L., and Li, X. (2018). Assessing tectonic and climatic controls for late quaternary fluvial terraces in Guide, Jianzha, and Xunhua basins along the Yellow River on the northeastern Tibetan plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 195, 109–121. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.07.005
Guo, X., Sun, Z., Lai, Z., Lu, Y., and Li, X. (2016). Optical dating of landslide-dammed lake deposits in the upper Yellow River, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Quat. Int. 392, 233–238. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2015.06.021
Guo, X., Wei, J., Lu, Y., Song, Z., and Liu, H. (2020a). Geomorphic effects of a dammed pleistocene lake formed by landslides along the upper Yellow River. Water 12 (5), 1350. doi:10.3390/w12051350
Guo, X., Wei, J., Song, Z., Lai, Z., and Yu, L. (2020b). Optically stimulated luminescence chronology and geomorphic imprint of Xiazangtan landslide upon the upper Yellow River valley on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Geol. J. 55 (7), 5498–5507. doi:10.1002/gj.3754
Guzzetti, F., Mondini, A. C., Cardinali, M., Fiorucci, F., Santangelo, M., and Chang, K.-T. (2012). Landslide inventory maps: new tools for an old problem. Earth-Science Rev. 112 (1-2), 42–66. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.02.001
Huang, Y., Xu, C., Li, L., He, X., Cheng, J., Xu, X., et al. (2022). Inventory and spatial distribution of ancient landslides in Hualong county, China. Land 12 (1), 136. doi:10.3390/land12010136
Huangfu, W., Wu, W., Zhou, X., Lin, Z., Zhang, G., Chen, R., et al. (2021). Landslide geo-hazard risk mapping using logistic regression modeling in Guixi, Jiangxi, China. Sustainability 13 (9), 4830. doi:10.3390/su13094830
Kasai, M., and Yamada, T. (2019). Topographic effects on frequency-size distribution of landslides triggered by the Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake in 2018. Earth, Planets Space 71 (1), 89–12. doi:10.1186/s40623-019-1069-8
Kirschbaum, D., Stanley, T., and Zhou, Y. (2015). Spatial and temporal analysis of a global landslide catalog. Geomorphology 249, 4–15. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.03.016
Lan, H. X., Zhou, C. H., Wang, L. J., Zhang, H. Y., and Li, R. H. (2004). Landslide hazard spatial analysis and prediction using GIS in the Xiaojiang watershed, Yunnan, China. Eng. Geol. 76 (1), 109–128. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.06.009
Li, L., Xu, C., Xu, X., Zhang, Z., and Cheng, J. (2021). Inventory and distribution characteristics of large-scale landslides in Baoji city, Shaanxi province, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Information 11 (1), 10. doi:10.3390/ijgi11010010
Li, L., Xu, C., Yang, Z., Zhang, Z., and Lv, M. (2022a). An inventory of large-scale landslides in Baoji city, Shaanxi province, China. Data 7 (8), 114. doi:10.3390/data7080114
Li, L., Xu, C., Yao, X., Shao, B., Ouyang, J., Zhang, Z., et al. (2022b). Large-scale landslides around the reservoir area of Baihetan hydropower station in Southwest China: analysis of the spatial distribution. Nat. Hazards Res. 2 (3), 218–229. doi:10.1016/j.nhres.2022.07.002
Li, X., Guo, X., and Li, W. (2011). Mechanism of giant landslides from Longyangxia valley to Liujiaxia valley along upper Yellow River. J. Eng. Geol. 19 (4), 516–529 [in Chinese, with English summary].
Google Scholar
Ma, X., Wang, L., Lv, B., and Ju, S. (2008). An investigation of geological hazards based on IRS-P 6 remote sensing data, Jianzha county, Qinghai province. Northwest. Geol. 41 (2), 93–100 [in Chinese, with English summary].
Mao, Y., Li, Y., Teng, F., Sabonchi, A. K. S., Azarafza, M., and Zhang, M. (2024). Utilizing hybrid machine learning and soft computing techniques for landslide susceptibility mapping in a Drainage Basin. Water 16 (3), 380. doi:10.3390/w16030380
Milledge, D. G., Bellugi, D. G., Watt, J., and Densmore, A. L. (2022). Automated determination of landslide locations after large trigger events: advantages and disadvantages compared to manual mapping. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 22 (2), 481–508. doi:10.5194/nhess-22-481-2022
Nanehkaran, Y. A., Chen, B., Cemiloglu, A., Chen, J., Anwar, S., Azarafza, M., et al. (2023). Riverside landslide susceptibility overview: leveraging artificial neural networks and machine learning in accordance with the United Nations (UN) sustainable development goals. Water 15 (15), 2707. doi:10.3390/w15152707
Nanehkaran, Y. A., Licai, Z., Chen, J., Azarafza, M., and Yimin, M. (2022). Application of artificial neural networks and geographic information system to provide hazard susceptibility maps for rockfall failures. Environ. Earth Sci. 81 (19), 475. doi:10.1007/s12665-022-10603-6
Nanehkaran, Y. A., Mao, Y., Azarafza, M., Kockar, M. K., and Zhu, H.-H. (2021). Fuzzy-based multiple decision method for landslide susceptibility and hazard assessment: a case study of Tabriz, Iran. Geomechanics Eng. 24 (5), 407–418. doi:10.12989/gae.2021.24.5.407
Nikoobakht, S., Azarafza, M., Akgün, H., and Derakhshani, R. (2022). Landslide susceptibility assessment by using convolutional neural network. Appl. Sci. 12 (12), 5992. doi:10.3390/app12125992
Peng, D., Xu, Q., Qi, X., Fan, X., Dong, X., Li, S., et al. (2016). Study on early recognition of loess landslides based on field investigation. Int. J. Georesources Environment-IJGE Former. Int'l J Geohazards Environ. 2 (2), 35–52. doi:10.15273/ijge.2016.02.006
Peng, J., Lan, H., Qian, H., Wang, W., Li, R., Li, Z., et al. (2020). Scientific research framework of livable Yellow River. J. Eng. Geol. 28 (2), 189–201 [in Chinese, with English summary].
Petley, D. (2012). Global patterns of loss of life from landslides. Geology 40 (10), 927–930. doi:10.1130/g33217.1
Piacentini, D., Troiani, F., Daniele, G., and Pizziolo, M. (2018). Historical geospatial database for landslide analysis: the catalogue of landslide occurrences in the Emilia-Romagna region (CLOCkER). Landslides 15 (4), 811–822. doi:10.1007/s10346-018-0962-8
Piralilou, S. T., Shahabi, H., and Pazur, R. (2021). Automatic landslide detection using bi-temporal sentinel 2 imagery. GI_Forum 9, 39–45. doi:10.1553/giscience2021_01_s39
Qiu, H., Cui, Y., Yang, D., Pei, Y., Hu, S., Ma, S., et al. (2019). Spatiotemporal distribution of nonseismic landslides during the last 22 years in Shaanxi province, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Information 8 (11), 505. doi:10.3390/ijgi8110505
Rabby, Y. W., and Li, Y. (2019). An integrated approach to map landslides in Chittagong Hilly Areas, Bangladesh, using Google Earth and field mapping. Landslides 16 (3), 633–645. doi:10.1007/s10346-018-1107-9
Shao, X., Ma, S., Xu, C., Shen, L., and Lu, Y. (2020). Inventory, distribution and geometric characteristics of landslides in Baoshan city, Yunnan province, China. Sustainability 12 (6), 2433. doi:10.3390/su12062433
Sun, J., Shao, X., Feng, L., Xu, C., Huang, Y., and Yang, W. (2024). An essential update on the inventory of landslides triggered by the Jiuzhaigou Mw6. 5 earthquake in China on 8 August 2017, with their spatial distribution analyses. Heliyon 10 (2), e24787. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24787
Tian, Y., Xu, C., Ma, S., Xu, X., Wang, S., and Zhang, H. (2019). Inventory and spatial distribution of landslides triggered by the 8th August 2017 Mw 6.5 Jiuzhaigou earthquake, China. J. Earth Sci. 30 (1), 206–217. doi:10.1007/s12583-018-0869-2
Tu, K., Ye, S., Zou, J., Hua, C., and Guo, J. (2023). InSAR displacement with high-resolution optical remote sensing for the early detection and deformation analysis of active landslides in the upper Yellow River. Water 15 (4), 769. doi:10.3390/w15040769
Vecchiotti, F., Tilch, N., and Kociu, A. (2021). The use of TERRA-ASTER satellite for landslide detection. Geosciences 11 (6), 258. doi:10.3390/geosciences11060258
Wang, L., Qiu, H., Zhou, W., Zhu, Y., Liu, Z., Ma, S., et al. (2022). The post-failure spatiotemporal deformation of certain translational landslides may follow the pre-failure pattern. Remote Sens. 14 (10), 2333. doi:10.3390/rs14102333
Wu, Y., Li, W., Liu, P., Bai, H., Wang, Q., He, J., et al. (2016). Application of analytic hierarchy process model for landslide susceptibility mapping in the Gangu County, Gansu Province, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 75, 422. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-5194-9
Xu, C. (2015). Preparation of earthquake-triggered landslide inventory maps using remote sensing and GIS technologies: principles and case studies. Geosci. Front. 6 (6), 825–836. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2014.03.004
Xu, C., Xu, X., and Shyu, J. B. H. (2015). Database and spatial distribution of landslides triggered by the Lushan, China Mw6.6 earthquake of 20 April 2013. Geomorphology 248, 77–92. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.07.002
Xu, C., Xu, X., Shyu, J. B. H., Zheng, W., and Min, W. (2014b). Landslides triggered by the 22 July 2013 Minxian–Zhangxian, China, Mw5.9 earthquake: inventory compiling and spatial distribution analysis. J. Asian Earth Sci. 92, 125–142. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.06.014
Xu, C., Xu, X., Yao, X., and Dai, F. (2014a). Three (nearly) complete inventories of landslides triggered by the May 12, 2008 Wenchuan Mw7.9 earthquake of China and their spatial distribution statistical analysis. Landslides 11, 441–461. doi:10.1007/s10346-013-0404-6
Xu, X., and Xu, C. (2021). Natural Hazards Research: an eternal subject of human survival and development. Nat. Hazards Res. 1 (1), 1–3. doi:10.1016/j.nhres.2020.12.003
Xu, Y., Allen, M. B., Zhang, W., Li, W., and He, H. (2020). Landslide characteristics in the Loess Plateau, northern China. Geomorphology 359, 107150. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107150
Yin, Z., Qin, X., and Zhao, W. (2014). “Characteristics of landslides from sigou gorge to lagan gorge in the upper reaches of Yellow River. Landslide Science for a Safer Geoenvironment: vol. 1,” in The international programme on landslides (IPL) ( Springer ).
Yin, Z., Qin, X., Zhao, W., and Wei, G. (2013a). Characteristics of landslides in upper reaches of Yellow River with multiple data of remote sensing. J. Eng. Geol. 21 (5), 779–787 [in Chinese, with English summary].
Yin, Z., Wei, G., Qi, X., and Zhou, C. (2013b). Spatial and temporal characteristics of landslides and there response to climatic change from Sigou to Lagan gorges in upper reaches of Yellow River. J. Eng. Geol. 21 (1), 129–137 [in Chinese, with English summary].
Yin, Z., Wei, G., Qin, X., Li, W., and Zhao, W. (2021). Research progress on landslides and dammed lakes in the upper reaches of the Yellow River, northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Earth Sci. Front. 28 (2), 46–57 [in Chinese, with English summary].
Zhang, F., and Huang, X. (2018). Trend and spatiotemporal distribution of fatal landslides triggered by non-seismic effects in China. Landslides 15 (8), 1663–1674. doi:10.1007/s10346-018-1007-z
Zhang, P., Xu, C., Ma, S., Shao, X., Tian, Y., and Wen, B. (2020a). Automatic extraction of seismic landslides in large areas with complex environments based on deep learning: an example of the 2018 Iburi earthquake, Japan. Remote Sens. 12 (23), 3992. doi:10.3390/rs12233992
Zhang, Z., Wang, T., and Wu, S. (2020b). Distribution and features of landslides in the tianshui basin, northwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 17 (3), 686–708. doi:10.1007/s11629-019-5595-4
Zhao, B., Wang, Y., Chen, M., Luo, Y., Liang, R., and Li, J. (2019). Typical characteristics of large-scale landslides in the transition belt between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau. Arabian J. Geosciences 12, 470. doi:10.1007/s12517-019-4612-9
Keywords: landslide traces inventory, upper reaches of the yellow river, loess landslides, Jianzha County, visual interpretation
Citation: Li T, Xu C, Li L and Xu J (2024) The landslide traces inventory in the transition zone between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau: a case study of Jianzha County, China. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1370992. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1370992
Received: 15 January 2024; Accepted: 19 March 2024; Published: 05 April 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Li, Xu, Li and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chong Xu, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Prevention, Mitigation, and Relief of Compound and Chained Natural Hazards

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Art of Case Study Research is a significant contribution to research methodology literature and will undoubtedly assume quick popularity as a text."--Linda Mabry, Indiana University, Bloomington "A concise and readable primer for doing case study research, the fruit of many years of experience and wisdom. Robert E. Stake's book is also ...
The Art of Case Study Research. Robert E. Stake. SAGE, Apr 5, 1995 - Education - 175 pages. This book presents a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods by drawing from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological and biographic research methods. Robert E. Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such ...
The Art of Case Study Research. This book presents a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods by drawing from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological and biographic research methods. Robert E. Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such questions as: How is the case selected?
The Art of Case Study Research. This book presents a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods by drawing from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenologic and biographic research methods. Robert E Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such questions as: How is the case selected?
The Art of Case Study Research. This book presents a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods by drawing from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenologic and biographic research methods. Robert E Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such questions as: How is the case selected?
The Art of Case Study Research is a significant contribution to research methodology literature and will undoubtedly assume quick popularity as a text."--Linda Mabry, Indiana University, Bloomington "A concise and readable primer for doing case study research, the fruit of many years of experience and wisdom. Robert E. Stake′s book is also ...
The art of case study research is mainly focused upon an interpretivist perspective in that the cases discussed are centred on people's stories and accounts. This book contains 10 chapters with the first chapter providing a definition of what a case study is in terms of how it focuses on the 'uniqueness' and 'commonality' of a ...
Case study is the study of the particularity and complexity of a single case, coming to understand its activity within important circumstances. In this book, [the author develops] a view of case studies that draws from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological, and biographic research methods. . . . [The author briefly presents] a disciplined, qualitative mode of inquiry into the ...
The art of case study research by Stake, Robert E. Publication date 1995 Topics Education -- Research -- Methodology, Case method Publisher Thousand Oaks : Sage Publications Collection inlibrary; printdisabled; internetarchivebooks Contributor Internet Archive Language English. xv, 175 p. : 24 cm
Robert E. Stake. 3.90. 144 ratings7 reviews. This book presents a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods by drawing from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological and biographic research methods. Robert E. Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such questions How is the case selected?
R. Stake. Published 1995. Art, Education. Introduction An Intensive Study of Case Study Research Methods The Unique Case Research Questions The Nature of Qualitative Research Data Gathering Analysis and Interpretation Case Researcher Roles Triangulation Writing the Report Reflections Harper School. View via Publisher.
The The Art Of Case Study Research is an adequate introduction to Robert Stake's approach to case study research, and is a well-respected and seminal text in the field. Case study researchers should at least be familiar with Robert Stake and this text. Read more. 27 people found this helpful.
This book presents a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods by drawing from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological and biographic research methods.Robert E. Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such questions as: How is the case...
The Art of Case Study Research Paperback - 5 April 1995. by Dr. Robert E. Stake (Author) 4.7 125 ratings. See all formats and editions. This book presents a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods by drawing from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological and biographic research methods.
The Art of Case Study Research. Thousand oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1995. 175 pp. $23.50 (paperback). (ISBN -8039-5767-X). Reviewed by ReijD Savolainen, Acting Associate Professor, Department of Information Studies, University of Tampere, Finland, P.O.B. 607, FIN-33101 Finland [email protected]>. The book has its roots in evaluation research ...
The Art of Case Study Research, by Robert Stake, 1995. March 2014. Conference: IIM Bangalore internal. Authors: Pavan Soni. Inflexion Point Consulting.
The Art of Case Study Research . Robert E. Stake - University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA; Courses: Case Study Research | Qualitative Research in Business & Management. April 1995 | 192 pages | SAGE Publications, Inc . Download flyer. Description; Contents; Reviews ...
Reflections on the State-of-the-Art of Case Study Research Key Findings. There is a vast body of methodology literature to support case study researchers and there have been ongoing debates in several management disciplines about the role and quality of case study research. As the innovation management community has not previously reflected on ...
The Art of Case Study Research. This book presents a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods by drawing from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenologic and biographic research methods. Robert E Stake uses and annotates an actual case study to answer such questions as: How is the case selected?
The case study method is a research strategy that aims to gain an in-depth understanding of a specific phenomenon by collecting and analyzing specific data within its true context (Rebolj, 2013 ...
The Art of Case Study Research. Kindle Edition. by Robert E. Stake (Author) Format: Kindle Edition. 133. See all formats and editions. This book presents a disciplined, qualitative exploration of case study methods by drawing from naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological and biographic research methods.Robert E. Stake uses and ...
We are very uncertain about the effect of midwife continuity of care models compared to other models of care on third or fourth-degree tear (average RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.49; 7 studies, 9437 participants; very low-certainty evidence), maternal readmission within 28 days (average RR 1.52, 95% CI 0.78 to 2.96; 1 study, 1195 participants; very ...
Cornell's colleges and schools encompass more than 100 fields of study, with locations in Ithaca, New York, New York City and Doha, Qatar. ... which is not the case for primary city-regions. Our results show extensive interconnectedness among urban centres and with their surrounding areas, with 3.2 billion people having physical access to ...
The study compiled the most complete and detailed landslide traces inventory in Jianzha County so far, which is of great significance to landslide scientific research. In future, relevant research on loess landslide development characteristics, failure mechanisms, susceptibility assessment and risk zoning can be conducted based on this ...