Sampling Methods In Reseach: Types, Techniques, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and convenience sampling. Proper sampling ensures representative, generalizable, and valid research results.
- Sampling : the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
- Target population : the total group of individuals from which the sample might be drawn.
- Sample: a subset of individuals selected from a larger population for study or investigation. Those included in the sample are termed “participants.”
- Generalizability : the ability to apply research findings from a sample to the broader target population, contingent on the sample being representative of that population.
For instance, if the advert for volunteers is published in the New York Times, this limits how much the study’s findings can be generalized to the whole population, because NYT readers may not represent the entire population in certain respects (e.g., politically, socio-economically).

The Purpose of Sampling
We are interested in learning about large groups of people with something in common in psychological research. We call the group interested in studying our “target population.”
In some types of research, the target population might be as broad as all humans. Still, in other types of research, the target population might be a smaller group, such as teenagers, preschool children, or people who misuse drugs.
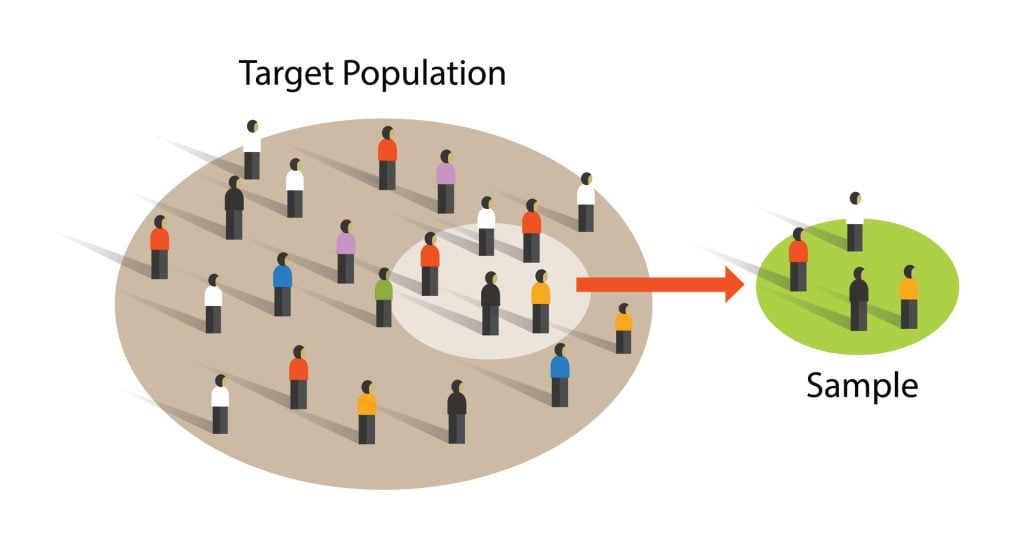
Studying every person in a target population is more or less impossible. Hence, psychologists select a sample or sub-group of the population that is likely to be representative of the target population we are interested in.
This is important because we want to generalize from the sample to the target population. The more representative the sample, the more confident the researcher can be that the results can be generalized to the target population.
One of the problems that can occur when selecting a sample from a target population is sampling bias. Sampling bias refers to situations where the sample does not reflect the characteristics of the target population.
Many psychology studies have a biased sample because they have used an opportunity sample that comprises university students as their participants (e.g., Asch ).
OK, so you’ve thought up this brilliant psychological study and designed it perfectly. But who will you try it out on, and how will you select your participants?
There are various sampling methods. The one chosen will depend on a number of factors (such as time, money, etc.).
Random Sampling
Random sampling is a type of probability sampling where everyone in the entire target population has an equal chance of being selected.
This is similar to the national lottery. If the “population” is everyone who bought a lottery ticket, then everyone has an equal chance of winning the lottery (assuming they all have one ticket each).
Random samples require naming or numbering the target population and then using some raffle method to choose those to make up the sample. Random samples are the best method of selecting your sample from the population of interest.
- The advantages are that your sample should represent the target population and eliminate sampling bias.
- The disadvantage is that it is very difficult to achieve (i.e., time, effort, and money).
Stratified Sampling
During stratified sampling , the researcher identifies the different types of people that make up the target population and works out the proportions needed for the sample to be representative.
A list is made of each variable (e.g., IQ, gender, etc.) that might have an effect on the research. For example, if we are interested in the money spent on books by undergraduates, then the main subject studied may be an important variable.
For example, students studying English Literature may spend more money on books than engineering students, so if we use a large percentage of English students or engineering students, our results will not be accurate.
We have to determine the relative percentage of each group at a university, e.g., Engineering 10%, Social Sciences 15%, English 20%, Sciences 25%, Languages 10%, Law 5%, and Medicine 15%. The sample must then contain all these groups in the same proportion as the target population (university students).
- The disadvantage of stratified sampling is that gathering such a sample would be extremely time-consuming and difficult to do. This method is rarely used in Psychology.
- However, the advantage is that the sample should be highly representative of the target population, and therefore we can generalize from the results obtained.
Opportunity Sampling
Opportunity sampling is a method in which participants are chosen based on their ease of availability and proximity to the researcher, rather than using random or systematic criteria. It’s a type of convenience sampling .
An opportunity sample is obtained by asking members of the population of interest if they would participate in your research. An example would be selecting a sample of students from those coming out of the library.
- This is a quick and easy way of choosing participants (advantage)
- It may not provide a representative sample and could be biased (disadvantage).
Systematic Sampling
Systematic sampling is a method where every nth individual is selected from a list or sequence to form a sample, ensuring even and regular intervals between chosen subjects.
Participants are systematically selected (i.e., orderly/logical) from the target population, like every nth participant on a list of names.
To take a systematic sample, you list all the population members and then decide upon a sample you would like. By dividing the number of people in the population by the number of people you want in your sample, you get a number we will call n.
If you take every nth name, you will get a systematic sample of the correct size. If, for example, you wanted to sample 150 children from a school of 1,500, you would take every 10th name.
- The advantage of this method is that it should provide a representative sample.
Sample size
The sample size is a critical factor in determining the reliability and validity of a study’s findings. While increasing the sample size can enhance the generalizability of results, it’s also essential to balance practical considerations, such as resource constraints and diminishing returns from ever-larger samples.
Reliability and Validity
Reliability refers to the consistency and reproducibility of research findings across different occasions, researchers, or instruments. A small sample size may lead to inconsistent results due to increased susceptibility to random error or the influence of outliers. In contrast, a larger sample minimizes these errors, promoting more reliable results.
Validity pertains to the accuracy and truthfulness of research findings. For a study to be valid, it should accurately measure what it intends to do. A small, unrepresentative sample can compromise external validity, meaning the results don’t generalize well to the larger population. A larger sample captures more variability, ensuring that specific subgroups or anomalies don’t overly influence results.
Practical Considerations
Resource Constraints : Larger samples demand more time, money, and resources. Data collection becomes more extensive, data analysis more complex, and logistics more challenging.
Diminishing Returns : While increasing the sample size generally leads to improved accuracy and precision, there’s a point where adding more participants yields only marginal benefits. For instance, going from 50 to 500 participants might significantly boost a study’s robustness, but jumping from 10,000 to 10,500 might not offer a comparable advantage, especially considering the added costs.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Sampling is the statistical process of selecting a subset—called a ‘sample’—of a population of interest for the purpose of making observations and statistical inferences about that population. Social science research is generally about inferring patterns of behaviours within specific populations. We cannot study entire populations because of feasibility and cost constraints, and hence, we must select a representative sample from the population of interest for observation and analysis. It is extremely important to choose a sample that is truly representative of the population so that the inferences derived from the sample can be generalised back to the population of interest. Improper and biased sampling is the primary reason for the often divergent and erroneous inferences reported in opinion polls and exit polls conducted by different polling groups such as CNN/Gallup Poll, ABC, and CBS, prior to every US Presidential election.
The sampling process
As Figure 8.1 shows, the sampling process comprises of several stages. The first stage is defining the target population. A population can be defined as all people or items ( unit of analysis ) with the characteristics that one wishes to study. The unit of analysis may be a person, group, organisation, country, object, or any other entity that you wish to draw scientific inferences about. Sometimes the population is obvious. For example, if a manufacturer wants to determine whether finished goods manufactured at a production line meet certain quality requirements or must be scrapped and reworked, then the population consists of the entire set of finished goods manufactured at that production facility. At other times, the target population may be a little harder to understand. If you wish to identify the primary drivers of academic learning among high school students, then what is your target population: high school students, their teachers, school principals, or parents? The right answer in this case is high school students, because you are interested in their performance, not the performance of their teachers, parents, or schools. Likewise, if you wish to analyse the behaviour of roulette wheels to identify biased wheels, your population of interest is not different observations from a single roulette wheel, but different roulette wheels (i.e., their behaviour over an infinite set of wheels).

The second step in the sampling process is to choose a sampling frame . This is an accessible section of the target population—usually a list with contact information—from where a sample can be drawn. If your target population is professional employees at work, because you cannot access all professional employees around the world, a more realistic sampling frame will be employee lists of one or two local companies that are willing to participate in your study. If your target population is organisations, then the Fortune 500 list of firms or the Standard & Poor’s (S&P) list of firms registered with the New York Stock exchange may be acceptable sampling frames.
Note that sampling frames may not entirely be representative of the population at large, and if so, inferences derived by such a sample may not be generalisable to the population. For instance, if your target population is organisational employees at large (e.g., you wish to study employee self-esteem in this population) and your sampling frame is employees at automotive companies in the American Midwest, findings from such groups may not even be generalisable to the American workforce at large, let alone the global workplace. This is because the American auto industry has been under severe competitive pressures for the last 50 years and has seen numerous episodes of reorganisation and downsizing, possibly resulting in low employee morale and self-esteem. Furthermore, the majority of the American workforce is employed in service industries or in small businesses, and not in automotive industry. Hence, a sample of American auto industry employees is not particularly representative of the American workforce. Likewise, the Fortune 500 list includes the 500 largest American enterprises, which is not representative of all American firms, most of which are medium or small sized firms rather than large firms, and is therefore, a biased sampling frame. In contrast, the S&P list will allow you to select large, medium, and/or small companies, depending on whether you use the S&P LargeCap, MidCap, or SmallCap lists, but includes publicly traded firms (and not private firms) and is hence still biased. Also note that the population from which a sample is drawn may not necessarily be the same as the population about which we actually want information. For example, if a researcher wants to examine the success rate of a new ‘quit smoking’ program, then the target population is the universe of smokers who had access to this program, which may be an unknown population. Hence, the researcher may sample patients arriving at a local medical facility for smoking cessation treatment, some of whom may not have had exposure to this particular ‘quit smoking’ program, in which case, the sampling frame does not correspond to the population of interest.
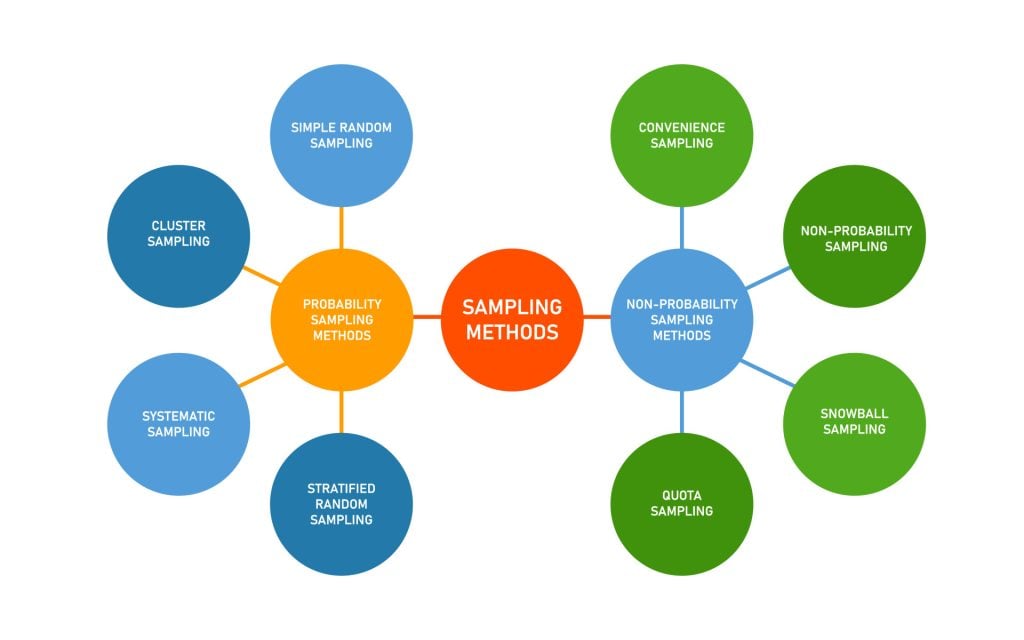
The last step in sampling is choosing a sample from the sampling frame using a well-defined sampling technique. Sampling techniques can be grouped into two broad categories: probability (random) sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling is ideal if generalisability of results is important for your study, but there may be unique circumstances where non-probability sampling can also be justified. These techniques are discussed in the next two sections.
Probability sampling
Probability sampling is a technique in which every unit in the population has a chance (non-zero probability) of being selected in the sample, and this chance can be accurately determined. Sample statistics thus produced, such as sample mean or standard deviation, are unbiased estimates of population parameters, as long as the sampled units are weighted according to their probability of selection. All probability sampling have two attributes in common: every unit in the population has a known non-zero probability of being sampled, and the sampling procedure involves random selection at some point. The different types of probability sampling techniques include:
Stratified sampling. In stratified sampling, the sampling frame is divided into homogeneous and non-overlapping subgroups (called ‘strata’), and a simple random sample is drawn within each subgroup. In the previous example of selecting 200 firms from a list of 1,000 firms, you can start by categorising the firms based on their size as large (more than 500 employees), medium (between 50 and 500 employees), and small (less than 50 employees). You can then randomly select 67 firms from each subgroup to make up your sample of 200 firms. However, since there are many more small firms in a sampling frame than large firms, having an equal number of small, medium, and large firms will make the sample less representative of the population (i.e., biased in favour of large firms that are fewer in number in the target population). This is called non-proportional stratified sampling because the proportion of the sample within each subgroup does not reflect the proportions in the sampling frame—or the population of interest—and the smaller subgroup (large-sized firms) is oversampled . An alternative technique will be to select subgroup samples in proportion to their size in the population. For instance, if there are 100 large firms, 300 mid-sized firms, and 600 small firms, you can sample 20 firms from the ‘large’ group, 60 from the ‘medium’ group and 120 from the ‘small’ group. In this case, the proportional distribution of firms in the population is retained in the sample, and hence this technique is called proportional stratified sampling. Note that the non-proportional approach is particularly effective in representing small subgroups, such as large-sized firms, and is not necessarily less representative of the population compared to the proportional approach, as long as the findings of the non-proportional approach are weighted in accordance to a subgroup’s proportion in the overall population.
Cluster sampling. If you have a population dispersed over a wide geographic region, it may not be feasible to conduct a simple random sampling of the entire population. In such case, it may be reasonable to divide the population into ‘clusters’—usually along geographic boundaries—randomly sample a few clusters, and measure all units within that cluster. For instance, if you wish to sample city governments in the state of New York, rather than travel all over the state to interview key city officials (as you may have to do with a simple random sample), you can cluster these governments based on their counties, randomly select a set of three counties, and then interview officials from every office in those counties. However, depending on between-cluster differences, the variability of sample estimates in a cluster sample will generally be higher than that of a simple random sample, and hence the results are less generalisable to the population than those obtained from simple random samples.
Matched-pairs sampling. Sometimes, researchers may want to compare two subgroups within one population based on a specific criterion. For instance, why are some firms consistently more profitable than other firms? To conduct such a study, you would have to categorise a sampling frame of firms into ‘high profitable’ firms and ‘low profitable firms’ based on gross margins, earnings per share, or some other measure of profitability. You would then select a simple random sample of firms in one subgroup, and match each firm in this group with a firm in the second subgroup, based on its size, industry segment, and/or other matching criteria. Now, you have two matched samples of high-profitability and low-profitability firms that you can study in greater detail. Matched-pairs sampling techniques are often an ideal way of understanding bipolar differences between different subgroups within a given population.
Multi-stage sampling. The probability sampling techniques described previously are all examples of single-stage sampling techniques. Depending on your sampling needs, you may combine these single-stage techniques to conduct multi-stage sampling. For instance, you can stratify a list of businesses based on firm size, and then conduct systematic sampling within each stratum. This is a two-stage combination of stratified and systematic sampling. Likewise, you can start with a cluster of school districts in the state of New York, and within each cluster, select a simple random sample of schools. Within each school, you can select a simple random sample of grade levels, and within each grade level, you can select a simple random sample of students for study. In this case, you have a four-stage sampling process consisting of cluster and simple random sampling.
Non-probability sampling
Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique in which some units of the population have zero chance of selection or where the probability of selection cannot be accurately determined. Typically, units are selected based on certain non-random criteria, such as quota or convenience. Because selection is non-random, non-probability sampling does not allow the estimation of sampling errors, and may be subjected to a sampling bias. Therefore, information from a sample cannot be generalised back to the population. Types of non-probability sampling techniques include:
Convenience sampling. Also called accidental or opportunity sampling, this is a technique in which a sample is drawn from that part of the population that is close to hand, readily available, or convenient. For instance, if you stand outside a shopping centre and hand out questionnaire surveys to people or interview them as they walk in, the sample of respondents you will obtain will be a convenience sample. This is a non-probability sample because you are systematically excluding all people who shop at other shopping centres. The opinions that you would get from your chosen sample may reflect the unique characteristics of this shopping centre such as the nature of its stores (e.g., high end-stores will attract a more affluent demographic), the demographic profile of its patrons, or its location (e.g., a shopping centre close to a university will attract primarily university students with unique purchasing habits), and therefore may not be representative of the opinions of the shopper population at large. Hence, the scientific generalisability of such observations will be very limited. Other examples of convenience sampling are sampling students registered in a certain class or sampling patients arriving at a certain medical clinic. This type of sampling is most useful for pilot testing, where the goal is instrument testing or measurement validation rather than obtaining generalisable inferences.
Quota sampling. In this technique, the population is segmented into mutually exclusive subgroups (just as in stratified sampling), and then a non-random set of observations is chosen from each subgroup to meet a predefined quota. In proportional quota sampling , the proportion of respondents in each subgroup should match that of the population. For instance, if the American population consists of 70 per cent Caucasians, 15 per cent Hispanic-Americans, and 13 per cent African-Americans, and you wish to understand their voting preferences in an sample of 98 people, you can stand outside a shopping centre and ask people their voting preferences. But you will have to stop asking Hispanic-looking people when you have 15 responses from that subgroup (or African-Americans when you have 13 responses) even as you continue sampling other ethnic groups, so that the ethnic composition of your sample matches that of the general American population.
Non-proportional quota sampling is less restrictive in that you do not have to achieve a proportional representation, but perhaps meet a minimum size in each subgroup. In this case, you may decide to have 50 respondents from each of the three ethnic subgroups (Caucasians, Hispanic-Americans, and African-Americans), and stop when your quota for each subgroup is reached. Neither type of quota sampling will be representative of the American population, since depending on whether your study was conducted in a shopping centre in New York or Kansas, your results may be entirely different. The non-proportional technique is even less representative of the population, but may be useful in that it allows capturing the opinions of small and under-represented groups through oversampling.
Expert sampling. This is a technique where respondents are chosen in a non-random manner based on their expertise on the phenomenon being studied. For instance, in order to understand the impacts of a new governmental policy such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, you can sample a group of corporate accountants who are familiar with this Act. The advantage of this approach is that since experts tend to be more familiar with the subject matter than non-experts, opinions from a sample of experts are more credible than a sample that includes both experts and non-experts, although the findings are still not generalisable to the overall population at large.
Snowball sampling. In snowball sampling, you start by identifying a few respondents that match the criteria for inclusion in your study, and then ask them to recommend others they know who also meet your selection criteria. For instance, if you wish to survey computer network administrators and you know of only one or two such people, you can start with them and ask them to recommend others who also work in network administration. Although this method hardly leads to representative samples, it may sometimes be the only way to reach hard-to-reach populations or when no sampling frame is available.
Statistics of sampling
In the preceding sections, we introduced terms such as population parameter, sample statistic, and sampling bias. In this section, we will try to understand what these terms mean and how they are related to each other.
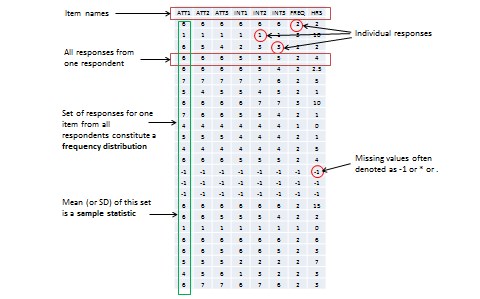
When you measure a certain observation from a given unit, such as a person’s response to a Likert-scaled item, that observation is called a response (see Figure 8.2). In other words, a response is a measurement value provided by a sampled unit. Each respondent will give you different responses to different items in an instrument. Responses from different respondents to the same item or observation can be graphed into a frequency distribution based on their frequency of occurrences. For a large number of responses in a sample, this frequency distribution tends to resemble a bell-shaped curve called a normal distribution , which can be used to estimate overall characteristics of the entire sample, such as sample mean (average of all observations in a sample) or standard deviation (variability or spread of observations in a sample). These sample estimates are called sample statistics (a ‘statistic’ is a value that is estimated from observed data). Populations also have means and standard deviations that could be obtained if we could sample the entire population. However, since the entire population can never be sampled, population characteristics are always unknown, and are called population parameters (and not ‘statistic’ because they are not statistically estimated from data). Sample statistics may differ from population parameters if the sample is not perfectly representative of the population. The difference between the two is called sampling error . Theoretically, if we could gradually increase the sample size so that the sample approaches closer and closer to the population, then sampling error will decrease and a sample statistic will increasingly approximate the corresponding population parameter.
If a sample is truly representative of the population, then the estimated sample statistics should be identical to the corresponding theoretical population parameters. How do we know if the sample statistics are at least reasonably close to the population parameters? Here, we need to understand the concept of a sampling distribution . Imagine that you took three different random samples from a given population, as shown in Figure 8.3, and for each sample, you derived sample statistics such as sample mean and standard deviation. If each random sample was truly representative of the population, then your three sample means from the three random samples will be identical—and equal to the population parameter—and the variability in sample means will be zero. But this is extremely unlikely, given that each random sample will likely constitute a different subset of the population, and hence, their means may be slightly different from each other. However, you can take these three sample means and plot a frequency histogram of sample means. If the number of such samples increases from three to 10 to 100, the frequency histogram becomes a sampling distribution. Hence, a sampling distribution is a frequency distribution of a sample statistic (like sample mean) from a set of samples , while the commonly referenced frequency distribution is the distribution of a response (observation) from a single sample . Just like a frequency distribution, the sampling distribution will also tend to have more sample statistics clustered around the mean (which presumably is an estimate of a population parameter), with fewer values scattered around the mean. With an infinitely large number of samples, this distribution will approach a normal distribution. The variability or spread of a sample statistic in a sampling distribution (i.e., the standard deviation of a sampling statistic) is called its standard error . In contrast, the term standard deviation is reserved for variability of an observed response from a single sample.
Social Science Research: Principles, Methods and Practices (Revised edition) Copyright © 2019 by Anol Bhattacherjee is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Chapter 5. Sampling
Introduction.
Most Americans will experience unemployment at some point in their lives. Sarah Damaske ( 2021 ) was interested in learning about how men and women experience unemployment differently. To answer this question, she interviewed unemployed people. After conducting a “pilot study” with twenty interviewees, she realized she was also interested in finding out how working-class and middle-class persons experienced unemployment differently. She found one hundred persons through local unemployment offices. She purposefully selected a roughly equal number of men and women and working-class and middle-class persons for the study. This would allow her to make the kinds of comparisons she was interested in. She further refined her selection of persons to interview:
I decided that I needed to be able to focus my attention on gender and class; therefore, I interviewed only people born between 1962 and 1987 (ages 28–52, the prime working and child-rearing years), those who worked full-time before their job loss, those who experienced an involuntary job loss during the past year, and those who did not lose a job for cause (e.g., were not fired because of their behavior at work). ( 244 )
The people she ultimately interviewed compose her sample. They represent (“sample”) the larger population of the involuntarily unemployed. This “theoretically informed stratified sampling design” allowed Damaske “to achieve relatively equal distribution of participation across gender and class,” but it came with some limitations. For one, the unemployment centers were located in primarily White areas of the country, so there were very few persons of color interviewed. Qualitative researchers must make these kinds of decisions all the time—who to include and who not to include. There is never an absolutely correct decision, as the choice is linked to the particular research question posed by the particular researcher, although some sampling choices are more compelling than others. In this case, Damaske made the choice to foreground both gender and class rather than compare all middle-class men and women or women of color from different class positions or just talk to White men. She leaves the door open for other researchers to sample differently. Because science is a collective enterprise, it is most likely someone will be inspired to conduct a similar study as Damaske’s but with an entirely different sample.
This chapter is all about sampling. After you have developed a research question and have a general idea of how you will collect data (observations or interviews), how do you go about actually finding people and sites to study? Although there is no “correct number” of people to interview, the sample should follow the research question and research design. You might remember studying sampling in a quantitative research course. Sampling is important here too, but it works a bit differently. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. This chapter explains why this is so and what qualities instead make a good sample for qualitative research.
Quick Terms Refresher
- The population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about.
- The sample is the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from.
- Sampling frame is the actual list of individuals that the sample will be drawn from. Ideally, it should include the entire target population (and nobody who is not part of that population).
- Sample size is how many individuals (or units) are included in your sample.
The “Who” of Your Research Study
After you have turned your general research interest into an actual research question and identified an approach you want to take to answer that question, you will need to specify the people you will be interviewing or observing. In most qualitative research, the objects of your study will indeed be people. In some cases, however, your objects might be content left by people (e.g., diaries, yearbooks, photographs) or documents (official or unofficial) or even institutions (e.g., schools, medical centers) and locations (e.g., nation-states, cities). Chances are, whatever “people, places, or things” are the objects of your study, you will not really be able to talk to, observe, or follow every single individual/object of the entire population of interest. You will need to create a sample of the population . Sampling in qualitative research has different purposes and goals than sampling in quantitative research. Sampling in both allows you to say something of interest about a population without having to include the entire population in your sample.
We begin this chapter with the case of a population of interest composed of actual people. After we have a better understanding of populations and samples that involve real people, we’ll discuss sampling in other types of qualitative research, such as archival research, content analysis, and case studies. We’ll then move to a larger discussion about the difference between sampling in qualitative research generally versus quantitative research, then we’ll move on to the idea of “theoretical” generalizability, and finally, we’ll conclude with some practical tips on the correct “number” to include in one’s sample.
Sampling People
To help think through samples, let’s imagine we want to know more about “vaccine hesitancy.” We’ve all lived through 2020 and 2021, and we know that a sizable number of people in the United States (and elsewhere) were slow to accept vaccines, even when these were freely available. By some accounts, about one-third of Americans initially refused vaccination. Why is this so? Well, as I write this in the summer of 2021, we know that some people actively refused the vaccination, thinking it was harmful or part of a government plot. Others were simply lazy or dismissed the necessity. And still others were worried about harmful side effects. The general population of interest here (all adult Americans who were not vaccinated by August 2021) may be as many as eighty million people. We clearly cannot talk to all of them. So we will have to narrow the number to something manageable. How can we do this?
First, we have to think about our actual research question and the form of research we are conducting. I am going to begin with a quantitative research question. Quantitative research questions tend to be simpler to visualize, at least when we are first starting out doing social science research. So let us say we want to know what percentage of each kind of resistance is out there and how race or class or gender affects vaccine hesitancy. Again, we don’t have the ability to talk to everyone. But harnessing what we know about normal probability distributions (see quantitative methods for more on this), we can find this out through a sample that represents the general population. We can’t really address these particular questions if we only talk to White women who go to college with us. And if you are really trying to generalize the specific findings of your sample to the larger population, you will have to employ probability sampling , a sampling technique where a researcher sets a selection of a few criteria and chooses members of a population randomly. Why randomly? If truly random, all the members have an equal opportunity to be a part of the sample, and thus we avoid the problem of having only our friends and neighbors (who may be very different from other people in the population) in the study. Mathematically, there is going to be a certain number that will be large enough to allow us to generalize our particular findings from our sample population to the population at large. It might surprise you how small that number can be. Election polls of no more than one thousand people are routinely used to predict actual election outcomes of millions of people. Below that number, however, you will not be able to make generalizations. Talking to five people at random is simply not enough people to predict a presidential election.
In order to answer quantitative research questions of causality, one must employ probability sampling. Quantitative researchers try to generalize their findings to a larger population. Samples are designed with that in mind. Qualitative researchers ask very different questions, though. Qualitative research questions are not about “how many” of a certain group do X (in this case, what percentage of the unvaccinated hesitate for concern about safety rather than reject vaccination on political grounds). Qualitative research employs nonprobability sampling . By definition, not everyone has an equal opportunity to be included in the sample. The researcher might select White women they go to college with to provide insight into racial and gender dynamics at play. Whatever is found by doing so will not be generalizable to everyone who has not been vaccinated, or even all White women who have not been vaccinated, or even all White women who have not been vaccinated who are in this particular college. That is not the point of qualitative research at all. This is a really important distinction, so I will repeat in bold: Qualitative researchers are not trying to statistically generalize specific findings to a larger population . They have not failed when their sample cannot be generalized, as that is not the point at all.
In the previous paragraph, I said it would be perfectly acceptable for a qualitative researcher to interview five White women with whom she goes to college about their vaccine hesitancy “to provide insight into racial and gender dynamics at play.” The key word here is “insight.” Rather than use a sample as a stand-in for the general population, as quantitative researchers do, the qualitative researcher uses the sample to gain insight into a process or phenomenon. The qualitative researcher is not going to be content with simply asking each of the women to state her reason for not being vaccinated and then draw conclusions that, because one in five of these women were concerned about their health, one in five of all people were also concerned about their health. That would be, frankly, a very poor study indeed. Rather, the qualitative researcher might sit down with each of the women and conduct a lengthy interview about what the vaccine means to her, why she is hesitant, how she manages her hesitancy (how she explains it to her friends), what she thinks about others who are unvaccinated, what she thinks of those who have been vaccinated, and what she knows or thinks she knows about COVID-19. The researcher might include specific interview questions about the college context, about their status as White women, about the political beliefs they hold about racism in the US, and about how their own political affiliations may or may not provide narrative scripts about “protective whiteness.” There are many interesting things to ask and learn about and many things to discover. Where a quantitative researcher begins with clear parameters to set their population and guide their sample selection process, the qualitative researcher is discovering new parameters, making it impossible to engage in probability sampling.
Looking at it this way, sampling for qualitative researchers needs to be more strategic. More theoretically informed. What persons can be interviewed or observed that would provide maximum insight into what is still unknown? In other words, qualitative researchers think through what cases they could learn the most from, and those are the cases selected to study: “What would be ‘bias’ in statistical sampling, and therefore a weakness, becomes intended focus in qualitative sampling, and therefore a strength. The logic and power of purposeful sampling like in selecting information-rich cases for study in depth. Information-rich cases are those from which one can learn a great deal about issues of central importance to the purpose of the inquiry, thus the term purposeful sampling” ( Patton 2002:230 ; emphases in the original).
Before selecting your sample, though, it is important to clearly identify the general population of interest. You need to know this before you can determine the sample. In our example case, it is “adult Americans who have not yet been vaccinated.” Depending on the specific qualitative research question, however, it might be “adult Americans who have been vaccinated for political reasons” or even “college students who have not been vaccinated.” What insights are you seeking? Do you want to know how politics is affecting vaccination? Or do you want to understand how people manage being an outlier in a particular setting (unvaccinated where vaccinations are heavily encouraged if not required)? More clearly stated, your population should align with your research question . Think back to the opening story about Damaske’s work studying the unemployed. She drew her sample narrowly to address the particular questions she was interested in pursuing. Knowing your questions or, at a minimum, why you are interested in the topic will allow you to draw the best sample possible to achieve insight.
Once you have your population in mind, how do you go about getting people to agree to be in your sample? In qualitative research, it is permissible to find people by convenience. Just ask for people who fit your sample criteria and see who shows up. Or reach out to friends and colleagues and see if they know anyone that fits. Don’t let the name convenience sampling mislead you; this is not exactly “easy,” and it is certainly a valid form of sampling in qualitative research. The more unknowns you have about what you will find, the more convenience sampling makes sense. If you don’t know how race or class or political affiliation might matter, and your population is unvaccinated college students, you can construct a sample of college students by placing an advertisement in the student paper or posting a flyer on a notice board. Whoever answers is your sample. That is what is meant by a convenience sample. A common variation of convenience sampling is snowball sampling . This is particularly useful if your target population is hard to find. Let’s say you posted a flyer about your study and only two college students responded. You could then ask those two students for referrals. They tell their friends, and those friends tell other friends, and, like a snowball, your sample gets bigger and bigger.
Researcher Note
Gaining Access: When Your Friend Is Your Research Subject
My early experience with qualitative research was rather unique. At that time, I needed to do a project that required me to interview first-generation college students, and my friends, with whom I had been sharing a dorm for two years, just perfectly fell into the sample category. Thus, I just asked them and easily “gained my access” to the research subject; I know them, we are friends, and I am part of them. I am an insider. I also thought, “Well, since I am part of the group, I can easily understand their language and norms, I can capture their honesty, read their nonverbal cues well, will get more information, as they will be more opened to me because they trust me.” All in all, easy access with rich information. But, gosh, I did not realize that my status as an insider came with a price! When structuring the interview questions, I began to realize that rather than focusing on the unique experiences of my friends, I mostly based the questions on my own experiences, assuming we have similar if not the same experiences. I began to struggle with my objectivity and even questioned my role; am I doing this as part of the group or as a researcher? I came to know later that my status as an insider or my “positionality” may impact my research. It not only shapes the process of data collection but might heavily influence my interpretation of the data. I came to realize that although my inside status came with a lot of benefits (especially for access), it could also bring some drawbacks.
—Dede Setiono, PhD student focusing on international development and environmental policy, Oregon State University
The more you know about what you might find, the more strategic you can be. If you wanted to compare how politically conservative and politically liberal college students explained their vaccine hesitancy, for example, you might construct a sample purposively, finding an equal number of both types of students so that you can make those comparisons in your analysis. This is what Damaske ( 2021 ) did. You could still use convenience or snowball sampling as a way of recruitment. Post a flyer at the conservative student club and then ask for referrals from the one student that agrees to be interviewed. As with convenience sampling, there are variations of purposive sampling as well as other names used (e.g., judgment, quota, stratified, criterion, theoretical). Try not to get bogged down in the nomenclature; instead, focus on identifying the general population that matches your research question and then using a sampling method that is most likely to provide insight, given the types of questions you have.
There are all kinds of ways of being strategic with sampling in qualitative research. Here are a few of my favorite techniques for maximizing insight:
- Consider using “extreme” or “deviant” cases. Maybe your college houses a prominent anti-vaxxer who has written about and demonstrated against the college’s policy on vaccines. You could learn a lot from that single case (depending on your research question, of course).
- Consider “intensity”: people and cases and circumstances where your questions are more likely to feature prominently (but not extremely or deviantly). For example, you could compare those who volunteer at local Republican and Democratic election headquarters during an election season in a study on why party matters. Those who volunteer are more likely to have something to say than those who are more apathetic.
- Maximize variation, as with the case of “politically liberal” versus “politically conservative,” or include an array of social locations (young vs. old; Northwest vs. Southeast region). This kind of heterogeneity sampling can capture and describe the central themes that cut across the variations: any common patterns that emerge, even in this wildly mismatched sample, are probably important to note!
- Rather than maximize the variation, you could select a small homogenous sample to describe some particular subgroup in depth. Focus groups are often the best form of data collection for homogeneity sampling.
- Think about which cases are “critical” or politically important—ones that “if it happens here, it would happen anywhere” or a case that is politically sensitive, as with the single “blue” (Democratic) county in a “red” (Republican) state. In both, you are choosing a site that would yield the most information and have the greatest impact on the development of knowledge.
- On the other hand, sometimes you want to select the “typical”—the typical college student, for example. You are trying to not generalize from the typical but illustrate aspects that may be typical of this case or group. When selecting for typicality, be clear with yourself about why the typical matches your research questions (and who might be excluded or marginalized in doing so).
- Finally, it is often a good idea to look for disconfirming cases : if you are at the stage where you have a hypothesis (of sorts), you might select those who do not fit your hypothesis—you will surely learn something important there. They may be “exceptions that prove the rule” or exceptions that force you to alter your findings in order to make sense of these additional cases.
In addition to all these sampling variations, there is the theoretical approach taken by grounded theorists in which the researcher samples comparative people (or events) on the basis of their potential to represent important theoretical constructs. The sample, one can say, is by definition representative of the phenomenon of interest. It accompanies the constant comparative method of analysis. In the words of the funders of Grounded Theory , “Theoretical sampling is sampling on the basis of the emerging concepts, with the aim being to explore the dimensional range or varied conditions along which the properties of the concepts vary” ( Strauss and Corbin 1998:73 ).
When Your Population is Not Composed of People
I think it is easiest for most people to think of populations and samples in terms of people, but sometimes our units of analysis are not actually people. They could be places or institutions. Even so, you might still want to talk to people or observe the actions of people to understand those places or institutions. Or not! In the case of content analyses (see chapter 17), you won’t even have people involved at all but rather documents or films or photographs or news clippings. Everything we have covered about sampling applies to other units of analysis too. Let’s work through some examples.
Case Studies
When constructing a case study, it is helpful to think of your cases as sample populations in the same way that we considered people above. If, for example, you are comparing campus climates for diversity, your overall population may be “four-year college campuses in the US,” and from there you might decide to study three college campuses as your sample. Which three? Will you use purposeful sampling (perhaps [1] selecting three colleges in Oregon that are different sizes or [2] selecting three colleges across the US located in different political cultures or [3] varying the three colleges by racial makeup of the student body)? Or will you select three colleges at random, out of convenience? There are justifiable reasons for all approaches.
As with people, there are different ways of maximizing insight in your sample selection. Think about the following rationales: typical, diverse, extreme, deviant, influential, crucial, or even embodying a particular “pathway” ( Gerring 2008 ). When choosing a case or particular research site, Rubin ( 2021 ) suggests you bear in mind, first, what you are leaving out by selecting this particular case/site; second, what you might be overemphasizing by studying this case/site and not another; and, finally, whether you truly need to worry about either of those things—“that is, what are the sources of bias and how bad are they for what you are trying to do?” ( 89 ).
Once you have selected your cases, you may still want to include interviews with specific people or observations at particular sites within those cases. Then you go through possible sampling approaches all over again to determine which people will be contacted.
Content: Documents, Narrative Accounts, And So On
Although not often discussed as sampling, your selection of documents and other units to use in various content/historical analyses is subject to similar considerations. When you are asking quantitative-type questions (percentages and proportionalities of a general population), you will want to follow probabilistic sampling. For example, I created a random sample of accounts posted on the website studentloanjustice.org to delineate the types of problems people were having with student debt ( Hurst 2007 ). Even though my data was qualitative (narratives of student debt), I was actually asking a quantitative-type research question, so it was important that my sample was representative of the larger population (debtors who posted on the website). On the other hand, when you are asking qualitative-type questions, the selection process should be very different. In that case, use nonprobabilistic techniques, either convenience (where you are really new to this data and do not have the ability to set comparative criteria or even know what a deviant case would be) or some variant of purposive sampling. Let’s say you were interested in the visual representation of women in media published in the 1950s. You could select a national magazine like Time for a “typical” representation (and for its convenience, as all issues are freely available on the web and easy to search). Or you could compare one magazine known for its feminist content versus one antifeminist. The point is, sample selection is important even when you are not interviewing or observing people.
Goals of Qualitative Sampling versus Goals of Quantitative Sampling
We have already discussed some of the differences in the goals of quantitative and qualitative sampling above, but it is worth further discussion. The quantitative researcher seeks a sample that is representative of the population of interest so that they may properly generalize the results (e.g., if 80 percent of first-gen students in the sample were concerned with costs of college, then we can say there is a strong likelihood that 80 percent of first-gen students nationally are concerned with costs of college). The qualitative researcher does not seek to generalize in this way . They may want a representative sample because they are interested in typical responses or behaviors of the population of interest, but they may very well not want a representative sample at all. They might want an “extreme” or deviant case to highlight what could go wrong with a particular situation, or maybe they want to examine just one case as a way of understanding what elements might be of interest in further research. When thinking of your sample, you will have to know why you are selecting the units, and this relates back to your research question or sets of questions. It has nothing to do with having a representative sample to generalize results. You may be tempted—or it may be suggested to you by a quantitatively minded member of your committee—to create as large and representative a sample as you possibly can to earn credibility from quantitative researchers. Ignore this temptation or suggestion. The only thing you should be considering is what sample will best bring insight into the questions guiding your research. This has implications for the number of people (or units) in your study as well, which is the topic of the next section.
What is the Correct “Number” to Sample?
Because we are not trying to create a generalizable representative sample, the guidelines for the “number” of people to interview or news stories to code are also a bit more nebulous. There are some brilliant insightful studies out there with an n of 1 (meaning one person or one account used as the entire set of data). This is particularly so in the case of autoethnography, a variation of ethnographic research that uses the researcher’s own subject position and experiences as the basis of data collection and analysis. But it is true for all forms of qualitative research. There are no hard-and-fast rules here. The number to include is what is relevant and insightful to your particular study.
That said, humans do not thrive well under such ambiguity, and there are a few helpful suggestions that can be made. First, many qualitative researchers talk about “saturation” as the end point for data collection. You stop adding participants when you are no longer getting any new information (or so very little that the cost of adding another interview subject or spending another day in the field exceeds any likely benefits to the research). The term saturation was first used here by Glaser and Strauss ( 1967 ), the founders of Grounded Theory. Here is their explanation: “The criterion for judging when to stop sampling the different groups pertinent to a category is the category’s theoretical saturation . Saturation means that no additional data are being found whereby the sociologist can develop properties of the category. As he [or she] sees similar instances over and over again, the researcher becomes empirically confident that a category is saturated. [They go] out of [their] way to look for groups that stretch diversity of data as far as possible, just to make certain that saturation is based on the widest possible range of data on the category” ( 61 ).
It makes sense that the term was developed by grounded theorists, since this approach is rather more open-ended than other approaches used by qualitative researchers. With so much left open, having a guideline of “stop collecting data when you don’t find anything new” is reasonable. However, saturation can’t help much when first setting out your sample. How do you know how many people to contact to interview? What number will you put down in your institutional review board (IRB) protocol (see chapter 8)? You may guess how many people or units it will take to reach saturation, but there really is no way to know in advance. The best you can do is think about your population and your questions and look at what others have done with similar populations and questions.
Here are some suggestions to use as a starting point: For phenomenological studies, try to interview at least ten people for each major category or group of people . If you are comparing male-identified, female-identified, and gender-neutral college students in a study on gender regimes in social clubs, that means you might want to design a sample of thirty students, ten from each group. This is the minimum suggested number. Damaske’s ( 2021 ) sample of one hundred allows room for up to twenty-five participants in each of four “buckets” (e.g., working-class*female, working-class*male, middle-class*female, middle-class*male). If there is more than one comparative group (e.g., you are comparing students attending three different colleges, and you are comparing White and Black students in each), you can sometimes reduce the number for each group in your sample to five for, in this case, thirty total students. But that is really a bare minimum you will want to go. A lot of people will not trust you with only “five” cases in a bucket. Lareau ( 2021:24 ) advises a minimum of seven or nine for each bucket (or “cell,” in her words). The point is to think about what your analyses might look like and how comfortable you will be with a certain number of persons fitting each category.
Because qualitative research takes so much time and effort, it is rare for a beginning researcher to include more than thirty to fifty people or units in the study. You may not be able to conduct all the comparisons you might want simply because you cannot manage a larger sample. In that case, the limits of who you can reach or what you can include may influence you to rethink an original overcomplicated research design. Rather than include students from every racial group on a campus, for example, you might want to sample strategically, thinking about the most contrast (insightful), possibly excluding majority-race (White) students entirely, and simply using previous literature to fill in gaps in our understanding. For example, one of my former students was interested in discovering how race and class worked at a predominantly White institution (PWI). Due to time constraints, she simplified her study from an original sample frame of middle-class and working-class domestic Black and international African students (four buckets) to a sample frame of domestic Black and international African students (two buckets), allowing the complexities of class to come through individual accounts rather than from part of the sample frame. She wisely decided not to include White students in the sample, as her focus was on how minoritized students navigated the PWI. She was able to successfully complete her project and develop insights from the data with fewer than twenty interviewees. [1]
But what if you had unlimited time and resources? Would it always be better to interview more people or include more accounts, documents, and units of analysis? No! Your sample size should reflect your research question and the goals you have set yourself. Larger numbers can sometimes work against your goals. If, for example, you want to help bring out individual stories of success against the odds, adding more people to the analysis can end up drowning out those individual stories. Sometimes, the perfect size really is one (or three, or five). It really depends on what you are trying to discover and achieve in your study. Furthermore, studies of one hundred or more (people, documents, accounts, etc.) can sometimes be mistaken for quantitative research. Inevitably, the large sample size will push the researcher into simplifying the data numerically. And readers will begin to expect generalizability from such a large sample.
To summarize, “There are no rules for sample size in qualitative inquiry. Sample size depends on what you want to know, the purpose of the inquiry, what’s at stake, what will be useful, what will have credibility, and what can be done with available time and resources” ( Patton 2002:244 ).
How did you find/construct a sample?
Since qualitative researchers work with comparatively small sample sizes, getting your sample right is rather important. Yet it is also difficult to accomplish. For instance, a key question you need to ask yourself is whether you want a homogeneous or heterogeneous sample. In other words, do you want to include people in your study who are by and large the same, or do you want to have diversity in your sample?
For many years, I have studied the experiences of students who were the first in their families to attend university. There is a rather large number of sampling decisions I need to consider before starting the study. (1) Should I only talk to first-in-family students, or should I have a comparison group of students who are not first-in-family? (2) Do I need to strive for a gender distribution that matches undergraduate enrollment patterns? (3) Should I include participants that reflect diversity in gender identity and sexuality? (4) How about racial diversity? First-in-family status is strongly related to some ethnic or racial identity. (5) And how about areas of study?
As you can see, if I wanted to accommodate all these differences and get enough study participants in each category, I would quickly end up with a sample size of hundreds, which is not feasible in most qualitative research. In the end, for me, the most important decision was to maximize the voices of first-in-family students, which meant that I only included them in my sample. As for the other categories, I figured it was going to be hard enough to find first-in-family students, so I started recruiting with an open mind and an understanding that I may have to accept a lack of gender, sexuality, or racial diversity and then not be able to say anything about these issues. But I would definitely be able to speak about the experiences of being first-in-family.
—Wolfgang Lehmann, author of “Habitus Transformation and Hidden Injuries”
Examples of “Sample” Sections in Journal Articles
Think about some of the studies you have read in college, especially those with rich stories and accounts about people’s lives. Do you know how the people were selected to be the focus of those stories? If the account was published by an academic press (e.g., University of California Press or Princeton University Press) or in an academic journal, chances are that the author included a description of their sample selection. You can usually find these in a methodological appendix (book) or a section on “research methods” (article).
Here are two examples from recent books and one example from a recent article:
Example 1 . In It’s Not like I’m Poor: How Working Families Make Ends Meet in a Post-welfare World , the research team employed a mixed methods approach to understand how parents use the earned income tax credit, a refundable tax credit designed to provide relief for low- to moderate-income working people ( Halpern-Meekin et al. 2015 ). At the end of their book, their first appendix is “Introduction to Boston and the Research Project.” After describing the context of the study, they include the following description of their sample selection:
In June 2007, we drew 120 names at random from the roughly 332 surveys we gathered between February and April. Within each racial and ethnic group, we aimed for one-third married couples with children and two-thirds unmarried parents. We sent each of these families a letter informing them of the opportunity to participate in the in-depth portion of our study and then began calling the home and cell phone numbers they provided us on the surveys and knocking on the doors of the addresses they provided.…In the end, we interviewed 115 of the 120 families originally selected for the in-depth interview sample (the remaining five families declined to participate). ( 22 )
Was their sample selection based on convenience or purpose? Why do you think it was important for them to tell you that five families declined to be interviewed? There is actually a trick here, as the names were pulled randomly from a survey whose sample design was probabilistic. Why is this important to know? What can we say about the representativeness or the uniqueness of whatever findings are reported here?
Example 2 . In When Diversity Drops , Park ( 2013 ) examines the impact of decreasing campus diversity on the lives of college students. She does this through a case study of one student club, the InterVarsity Christian Fellowship (IVCF), at one university (“California University,” a pseudonym). Here is her description:
I supplemented participant observation with individual in-depth interviews with sixty IVCF associates, including thirty-four current students, eight former and current staff members, eleven alumni, and seven regional or national staff members. The racial/ethnic breakdown was twenty-five Asian Americans (41.6 percent), one Armenian (1.6 percent), twelve people who were black (20.0 percent), eight Latino/as (13.3 percent), three South Asian Americans (5.0 percent), and eleven people who were white (18.3 percent). Twenty-nine were men, and thirty-one were women. Looking back, I note that the higher number of Asian Americans reflected both the group’s racial/ethnic composition and my relative ease about approaching them for interviews. ( 156 )
How can you tell this is a convenience sample? What else do you note about the sample selection from this description?
Example 3. The last example is taken from an article published in the journal Research in Higher Education . Published articles tend to be more formal than books, at least when it comes to the presentation of qualitative research. In this article, Lawson ( 2021 ) is seeking to understand why female-identified college students drop out of majors that are dominated by male-identified students (e.g., engineering, computer science, music theory). Here is the entire relevant section of the article:
Method Participants Data were collected as part of a larger study designed to better understand the daily experiences of women in MDMs [male-dominated majors].…Participants included 120 students from a midsize, Midwestern University. This sample included 40 women and 40 men from MDMs—defined as any major where at least 2/3 of students are men at both the university and nationally—and 40 women from GNMs—defined as any may where 40–60% of students are women at both the university and nationally.… Procedure A multi-faceted approach was used to recruit participants; participants were sent targeted emails (obtained based on participants’ reported gender and major listings), campus-wide emails sent through the University’s Communication Center, flyers, and in-class presentations. Recruitment materials stated that the research focused on the daily experiences of college students, including classroom experiences, stressors, positive experiences, departmental contexts, and career aspirations. Interested participants were directed to email the study coordinator to verify eligibility (at least 18 years old, man/woman in MDM or woman in GNM, access to a smartphone). Sixteen interested individuals were not eligible for the study due to the gender/major combination. ( 482ff .)
What method of sample selection was used by Lawson? Why is it important to define “MDM” at the outset? How does this definition relate to sampling? Why were interested participants directed to the study coordinator to verify eligibility?
Final Words
I have found that students often find it difficult to be specific enough when defining and choosing their sample. It might help to think about your sample design and sample recruitment like a cookbook. You want all the details there so that someone else can pick up your study and conduct it as you intended. That person could be yourself, but this analogy might work better if you have someone else in mind. When I am writing down recipes, I often think of my sister and try to convey the details she would need to duplicate the dish. We share a grandmother whose recipes are full of handwritten notes in the margins, in spidery ink, that tell us what bowl to use when or where things could go wrong. Describe your sample clearly, convey the steps required accurately, and then add any other details that will help keep you on track and remind you why you have chosen to limit possible interviewees to those of a certain age or class or location. Imagine actually going out and getting your sample (making your dish). Do you have all the necessary details to get started?
Table 5.1. Sampling Type and Strategies
Further Readings
Fusch, Patricia I., and Lawrence R. Ness. 2015. “Are We There Yet? Data Saturation in Qualitative Research.” Qualitative Report 20(9):1408–1416.
Saunders, Benjamin, Julius Sim, Tom Kinstone, Shula Baker, Jackie Waterfield, Bernadette Bartlam, Heather Burroughs, and Clare Jinks. 2018. “Saturation in Qualitative Research: Exploring Its Conceptualization and Operationalization.” Quality & Quantity 52(4):1893–1907.
- Rubin ( 2021 ) suggests a minimum of twenty interviews (but safer with thirty) for an interview-based study and a minimum of three to six months in the field for ethnographic studies. For a content-based study, she suggests between five hundred and one thousand documents, although some will be “very small” ( 243–244 ). ↵
The process of selecting people or other units of analysis to represent a larger population. In quantitative research, this representation is taken quite literally, as statistically representative. In qualitative research, in contrast, sample selection is often made based on potential to generate insight about a particular topic or phenomenon.
The actual list of individuals that the sample will be drawn from. Ideally, it should include the entire target population (and nobody who is not part of that population). Sampling frames can differ from the larger population when specific exclusions are inherent, as in the case of pulling names randomly from voter registration rolls where not everyone is a registered voter. This difference in frame and population can undercut the generalizability of quantitative results.
The specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. Contrast population.
The large group of interest to the researcher. Although it will likely be impossible to design a study that incorporates or reaches all members of the population of interest, this should be clearly defined at the outset of a study so that a reasonable sample of the population can be taken. For example, if one is studying working-class college students, the sample may include twenty such students attending a particular college, while the population is “working-class college students.” In quantitative research, clearly defining the general population of interest is a necessary step in generalizing results from a sample. In qualitative research, defining the population is conceptually important for clarity.
A sampling strategy in which the sample is chosen to represent (numerically) the larger population from which it is drawn by random selection. Each person in the population has an equal chance of making it into the sample. This is often done through a lottery or other chance mechanisms (e.g., a random selection of every twelfth name on an alphabetical list of voters). Also known as random sampling .
The selection of research participants or other data sources based on availability or accessibility, in contrast to purposive sampling .
A sample generated non-randomly by asking participants to help recruit more participants the idea being that a person who fits your sampling criteria probably knows other people with similar criteria.
Broad codes that are assigned to the main issues emerging in the data; identifying themes is often part of initial coding .
A form of case selection focusing on examples that do not fit the emerging patterns. This allows the researcher to evaluate rival explanations or to define the limitations of their research findings. While disconfirming cases are found (not sought out), researchers should expand their analysis or rethink their theories to include/explain them.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
The result of probability sampling, in which a sample is chosen to represent (numerically) the larger population from which it is drawn by random selection. Each person in the population has an equal chance of making it into the random sample. This is often done through a lottery or other chance mechanisms (e.g., the random selection of every twelfth name on an alphabetical list of voters). This is typically not required in qualitative research but rather essential for the generalizability of quantitative research.
A form of case selection or purposeful sampling in which cases that are unusual or special in some way are chosen to highlight processes or to illuminate gaps in our knowledge of a phenomenon. See also extreme case .
The point at which you can conclude data collection because every person you are interviewing, the interaction you are observing, or content you are analyzing merely confirms what you have already noted. Achieving saturation is often used as the justification for the final sample size.
The accuracy with which results or findings can be transferred to situations or people other than those originally studied. Qualitative studies generally are unable to use (and are uninterested in) statistical generalizability where the sample population is said to be able to predict or stand in for a larger population of interest. Instead, qualitative researchers often discuss “theoretical generalizability,” in which the findings of a particular study can shed light on processes and mechanisms that may be at play in other settings. See also statistical generalization and theoretical generalization .
A term used by IRBs to denote all materials aimed at recruiting participants into a research study (including printed advertisements, scripts, audio or video tapes, or websites). Copies of this material are required in research protocols submitted to IRB.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Sampling Types and Methods
- First Online: 01 March 2024
Cite this chapter

- Animesh Hazari 2
138 Accesses
Sampling is the process of selecting an ideal sample that would represent the entire population of your desired study. It usually consists of a subset of individuals, items, or data points from a larger population to make inferences or draw conclusions about the entire population. Sampling in research methodology is an important step for participant recruitment once the research hypothesis, objective, and research design have been selected for the given study. The selection of the correct sampling type and method would ensure the accuracy of research data and its results. Sampling is performed before the process of data collection. It should be well understood by the researcher that sampling is different from the sample recruitment process, which often overlaps. Sampling is a prerequisite for the sample recruitment process in research. Sample recruitment is done from the pool of selected samples based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria: for instance, if a researcher wants to conduct a survey on complications of Covid-19 infection among the diabetic population within the age group of 30–40 years. Since this study involves humans, sampling process would initially involve selecting individuals with diabetes mellitus infected with Covid-19. However, the final participants’ recruitment would consist of an age group of 30–40 years, which is an inclusion criterion. There are various types of sampling methods that researchers can use to ensure that the selected subset is a representative of the whole population. In this chapter, we will learn about the commonly used sampling types and methods among allied health professionals. Examples have been for better understanding.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Health Sciences, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, Ajman, United Arab Emirates
Animesh Hazari
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Hazari, A. (2023). Sampling Types and Methods. In: Research Methodology for Allied Health Professionals. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8925-6_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8925-6_6
Published : 01 March 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-8924-9
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-8925-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
What Is Research Methodology? A Plain-Language Explanation & Definition (With Examples)
By Derek Jansen (MBA) and Kerryn Warren (PhD) | June 2020 (Last updated April 2023)
If you’re new to formal academic research, it’s quite likely that you’re feeling a little overwhelmed by all the technical lingo that gets thrown around. And who could blame you – “research methodology”, “research methods”, “sampling strategies”… it all seems never-ending!
In this post, we’ll demystify the landscape with plain-language explanations and loads of examples (including easy-to-follow videos), so that you can approach your dissertation, thesis or research project with confidence. Let’s get started.
Research Methodology 101
- What exactly research methodology means
- What qualitative , quantitative and mixed methods are
- What sampling strategy is
- What data collection methods are
- What data analysis methods are
- How to choose your research methodology
- Example of a research methodology

What is research methodology?
Research methodology simply refers to the practical “how” of a research study. More specifically, it’s about how a researcher systematically designs a study to ensure valid and reliable results that address the research aims, objectives and research questions . Specifically, how the researcher went about deciding:
- What type of data to collect (e.g., qualitative or quantitative data )
- Who to collect it from (i.e., the sampling strategy )
- How to collect it (i.e., the data collection method )
- How to analyse it (i.e., the data analysis methods )
Within any formal piece of academic research (be it a dissertation, thesis or journal article), you’ll find a research methodology chapter or section which covers the aspects mentioned above. Importantly, a good methodology chapter explains not just what methodological choices were made, but also explains why they were made. In other words, the methodology chapter should justify the design choices, by showing that the chosen methods and techniques are the best fit for the research aims, objectives and research questions.
So, it’s the same as research design?
Not quite. As we mentioned, research methodology refers to the collection of practical decisions regarding what data you’ll collect, from who, how you’ll collect it and how you’ll analyse it. Research design, on the other hand, is more about the overall strategy you’ll adopt in your study. For example, whether you’ll use an experimental design in which you manipulate one variable while controlling others. You can learn more about research design and the various design types here .
Need a helping hand?
What are qualitative, quantitative and mixed-methods?
Qualitative, quantitative and mixed-methods are different types of methodological approaches, distinguished by their focus on words , numbers or both . This is a bit of an oversimplification, but its a good starting point for understanding.
Let’s take a closer look.
Qualitative research refers to research which focuses on collecting and analysing words (written or spoken) and textual or visual data, whereas quantitative research focuses on measurement and testing using numerical data . Qualitative analysis can also focus on other “softer” data points, such as body language or visual elements.
It’s quite common for a qualitative methodology to be used when the research aims and research questions are exploratory in nature. For example, a qualitative methodology might be used to understand peoples’ perceptions about an event that took place, or a political candidate running for president.
Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and research questions are confirmatory in nature. For example, a quantitative methodology might be used to measure the relationship between two variables (e.g. personality type and likelihood to commit a crime) or to test a set of hypotheses .
As you’ve probably guessed, the mixed-method methodology attempts to combine the best of both qualitative and quantitative methodologies to integrate perspectives and create a rich picture. If you’d like to learn more about these three methodological approaches, be sure to watch our explainer video below.
What is sampling strategy?
Simply put, sampling is about deciding who (or where) you’re going to collect your data from . Why does this matter? Well, generally it’s not possible to collect data from every single person in your group of interest (this is called the “population”), so you’ll need to engage a smaller portion of that group that’s accessible and manageable (this is called the “sample”).
How you go about selecting the sample (i.e., your sampling strategy) will have a major impact on your study. There are many different sampling methods you can choose from, but the two overarching categories are probability sampling and non-probability sampling .
Probability sampling involves using a completely random sample from the group of people you’re interested in. This is comparable to throwing the names all potential participants into a hat, shaking it up, and picking out the “winners”. By using a completely random sample, you’ll minimise the risk of selection bias and the results of your study will be more generalisable to the entire population.
Non-probability sampling , on the other hand, doesn’t use a random sample . For example, it might involve using a convenience sample, which means you’d only interview or survey people that you have access to (perhaps your friends, family or work colleagues), rather than a truly random sample. With non-probability sampling, the results are typically not generalisable .
To learn more about sampling methods, be sure to check out the video below.
What are data collection methods?
As the name suggests, data collection methods simply refers to the way in which you go about collecting the data for your study. Some of the most common data collection methods include:
- Interviews (which can be unstructured, semi-structured or structured)
- Focus groups and group interviews
- Surveys (online or physical surveys)
- Observations (watching and recording activities)
- Biophysical measurements (e.g., blood pressure, heart rate, etc.)
- Documents and records (e.g., financial reports, court records, etc.)
The choice of which data collection method to use depends on your overall research aims and research questions , as well as practicalities and resource constraints. For example, if your research is exploratory in nature, qualitative methods such as interviews and focus groups would likely be a good fit. Conversely, if your research aims to measure specific variables or test hypotheses, large-scale surveys that produce large volumes of numerical data would likely be a better fit.
What are data analysis methods?
Data analysis methods refer to the methods and techniques that you’ll use to make sense of your data. These can be grouped according to whether the research is qualitative (words-based) or quantitative (numbers-based).
Popular data analysis methods in qualitative research include:
- Qualitative content analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA)
- Visual analysis (of photographs, videos, art, etc.)
Qualitative data analysis all begins with data coding , after which an analysis method is applied. In some cases, more than one analysis method is used, depending on the research aims and research questions . In the video below, we explore some common qualitative analysis methods, along with practical examples.
Moving on to the quantitative side of things, popular data analysis methods in this type of research include:
- Descriptive statistics (e.g. means, medians, modes )
- Inferential statistics (e.g. correlation, regression, structural equation modelling)
Again, the choice of which data collection method to use depends on your overall research aims and objectives , as well as practicalities and resource constraints. In the video below, we explain some core concepts central to quantitative analysis.
How do I choose a research methodology?
As you’ve probably picked up by now, your research aims and objectives have a major influence on the research methodology . So, the starting point for developing your research methodology is to take a step back and look at the big picture of your research, before you make methodology decisions. The first question you need to ask yourself is whether your research is exploratory or confirmatory in nature.
If your research aims and objectives are primarily exploratory in nature, your research will likely be qualitative and therefore you might consider qualitative data collection methods (e.g. interviews) and analysis methods (e.g. qualitative content analysis).
Conversely, if your research aims and objective are looking to measure or test something (i.e. they’re confirmatory), then your research will quite likely be quantitative in nature, and you might consider quantitative data collection methods (e.g. surveys) and analyses (e.g. statistical analysis).
Designing your research and working out your methodology is a large topic, which we cover extensively on the blog . For now, however, the key takeaway is that you should always start with your research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread). Every methodological choice you make needs align with those three components.
Example of a research methodology chapter
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of a research methodology from an actual dissertation, as well as an overview of our free methodology template .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

199 Comments
Thank you for this simple yet comprehensive and easy to digest presentation. God Bless!
You’re most welcome, Leo. Best of luck with your research!
I found it very useful. many thanks
This is really directional. A make-easy research knowledge.
Thank you for this, I think will help my research proposal
Thanks for good interpretation,well understood.
Good morning sorry I want to the search topic
Thank u more
Thank you, your explanation is simple and very helpful.
Very educative a.nd exciting platform. A bigger thank you and I’ll like to always be with you
That’s the best analysis
So simple yet so insightful. Thank you.
This really easy to read as it is self-explanatory. Very much appreciated…
Thanks for this. It’s so helpful and explicit. For those elements highlighted in orange, they were good sources of referrals for concepts I didn’t understand. A million thanks for this.
Good morning, I have been reading your research lessons through out a period of times. They are important, impressive and clear. Want to subscribe and be and be active with you.
Thankyou So much Sir Derek…
Good morning thanks so much for the on line lectures am a student of university of Makeni.select a research topic and deliberate on it so that we’ll continue to understand more.sorry that’s a suggestion.
Beautiful presentation. I love it.
please provide a research mehodology example for zoology
It’s very educative and well explained
Thanks for the concise and informative data.
This is really good for students to be safe and well understand that research is all about
Thank you so much Derek sir🖤🙏🤗
Very simple and reliable
This is really helpful. Thanks alot. God bless you.
very useful, Thank you very much..
thanks a lot its really useful
in a nutshell..thank you!
Thanks for updating my understanding on this aspect of my Thesis writing.
thank you so much my through this video am competently going to do a good job my thesis
Thanks a lot. Very simple to understand. I appreciate 🙏
Very simple but yet insightful Thank you
This has been an eye opening experience. Thank you grad coach team.
Very useful message for research scholars
Really very helpful thank you
yes you are right and i’m left
Research methodology with a simplest way i have never seen before this article.
wow thank u so much
Good morning thanks so much for the on line lectures am a student of university of Makeni.select a research topic and deliberate on is so that we will continue to understand more.sorry that’s a suggestion.
Very precise and informative.
Thanks for simplifying these terms for us, really appreciate it.
Thanks this has really helped me. It is very easy to understand.
I found the notes and the presentation assisting and opening my understanding on research methodology
Good presentation
Im so glad you clarified my misconceptions. Im now ready to fry my onions. Thank you so much. God bless
Thank you a lot.
thanks for the easy way of learning and desirable presentation.
Thanks a lot. I am inspired
Well written
I am writing a APA Format paper . I using questionnaire with 120 STDs teacher for my participant. Can you write me mthology for this research. Send it through email sent. Just need a sample as an example please. My topic is ” impacts of overcrowding on students learning
Thanks for your comment.
We can’t write your methodology for you. If you’re looking for samples, you should be able to find some sample methodologies on Google. Alternatively, you can download some previous dissertations from a dissertation directory and have a look at the methodology chapters therein.
All the best with your research.
Thank you so much for this!! God Bless
Thank you. Explicit explanation
Thank you, Derek and Kerryn, for making this simple to understand. I’m currently at the inception stage of my research.
Thnks a lot , this was very usefull on my assignment
excellent explanation
I’m currently working on my master’s thesis, thanks for this! I’m certain that I will use Qualitative methodology.
Thanks a lot for this concise piece, it was quite relieving and helpful. God bless you BIG…
I am currently doing my dissertation proposal and I am sure that I will do quantitative research. Thank you very much it was extremely helpful.
Very interesting and informative yet I would like to know about examples of Research Questions as well, if possible.
I’m about to submit a research presentation, I have come to understand from your simplification on understanding research methodology. My research will be mixed methodology, qualitative as well as quantitative. So aim and objective of mixed method would be both exploratory and confirmatory. Thanks you very much for your guidance.
OMG thanks for that, you’re a life saver. You covered all the points I needed. Thank you so much ❤️ ❤️ ❤️
Thank you immensely for this simple, easy to comprehend explanation of data collection methods. I have been stuck here for months 😩. Glad I found your piece. Super insightful.
I’m going to write synopsis which will be quantitative research method and I don’t know how to frame my topic, can I kindly get some ideas..
Thanks for this, I was really struggling.
This was really informative I was struggling but this helped me.
Thanks a lot for this information, simple and straightforward. I’m a last year student from the University of South Africa UNISA South Africa.
its very much informative and understandable. I have enlightened.
An interesting nice exploration of a topic.
Thank you. Accurate and simple🥰
This article was really helpful, it helped me understanding the basic concepts of the topic Research Methodology. The examples were very clear, and easy to understand. I would like to visit this website again. Thank you so much for such a great explanation of the subject.
Thanks dude
Thank you Doctor Derek for this wonderful piece, please help to provide your details for reference purpose. God bless.
Many compliments to you
Great work , thank you very much for the simple explanation
Thank you. I had to give a presentation on this topic. I have looked everywhere on the internet but this is the best and simple explanation.
thank you, its very informative.
Well explained. Now I know my research methodology will be qualitative and exploratory. Thank you so much, keep up the good work
Well explained, thank you very much.
This is good explanation, I have understood the different methods of research. Thanks a lot.
Great work…very well explanation
Thanks Derek. Kerryn was just fantastic!
Great to hear that, Hyacinth. Best of luck with your research!
Its a good templates very attractive and important to PhD students and lectuter
Thanks for the feedback, Matobela. Good luck with your research methodology.
Thank you. This is really helpful.
You’re very welcome, Elie. Good luck with your research methodology.
Well explained thanks
This is a very helpful site especially for young researchers at college. It provides sufficient information to guide students and equip them with the necessary foundation to ask any other questions aimed at deepening their understanding.
Thanks for the kind words, Edward. Good luck with your research!
Thank you. I have learned a lot.
Great to hear that, Ngwisa. Good luck with your research methodology!
Thank you for keeping your presentation simples and short and covering key information for research methodology. My key takeaway: Start with defining your research objective the other will depend on the aims of your research question.
My name is Zanele I would like to be assisted with my research , and the topic is shortage of nursing staff globally want are the causes , effects on health, patients and community and also globally
Thanks for making it simple and clear. It greatly helped in understanding research methodology. Regards.
This is well simplified and straight to the point
Thank you Dr
I was given an assignment to research 2 publications and describe their research methodology? I don’t know how to start this task can someone help me?
Sure. You’re welcome to book an initial consultation with one of our Research Coaches to discuss how we can assist – https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Thanks a lot I am relieved of a heavy burden.keep up with the good work
I’m very much grateful Dr Derek. I’m planning to pursue one of the careers that really needs one to be very much eager to know. There’s a lot of research to do and everything, but since I’ve gotten this information I will use it to the best of my potential.
Thank you so much, words are not enough to explain how helpful this session has been for me!
Thanks this has thought me alot.
Very concise and helpful. Thanks a lot
Thank Derek. This is very helpful. Your step by step explanation has made it easier for me to understand different concepts. Now i can get on with my research.
I wish i had come across this sooner. So simple but yet insightful
really nice explanation thank you so much
I’m so grateful finding this site, it’s really helpful…….every term well explained and provide accurate understanding especially to student going into an in-depth research for the very first time, even though my lecturer already explained this topic to the class, I think I got the clear and efficient explanation here, much thanks to the author.
It is very helpful material
I would like to be assisted with my research topic : Literature Review and research methodologies. My topic is : what is the relationship between unemployment and economic growth?
Its really nice and good for us.
THANKS SO MUCH FOR EXPLANATION, ITS VERY CLEAR TO ME WHAT I WILL BE DOING FROM NOW .GREAT READS.
Short but sweet.Thank you
Informative article. Thanks for your detailed information.
I’m currently working on my Ph.D. thesis. Thanks a lot, Derek and Kerryn, Well-organized sequences, facilitate the readers’ following.
great article for someone who does not have any background can even understand
I am a bit confused about research design and methodology. Are they the same? If not, what are the differences and how are they related?
Thanks in advance.
concise and informative.
Thank you very much
How can we site this article is Harvard style?
Very well written piece that afforded better understanding of the concept. Thank you!
Am a new researcher trying to learn how best to write a research proposal. I find your article spot on and want to download the free template but finding difficulties. Can u kindly send it to my email, the free download entitled, “Free Download: Research Proposal Template (with Examples)”.
Thank too much
Thank you very much for your comprehensive explanation about research methodology so I like to thank you again for giving us such great things.
Good very well explained.Thanks for sharing it.
Thank u sir, it is really a good guideline.
so helpful thank you very much.
Thanks for the video it was very explanatory and detailed, easy to comprehend and follow up. please, keep it up the good work
It was very helpful, a well-written document with precise information.
how do i reference this?
MLA Jansen, Derek, and Kerryn Warren. “What (Exactly) Is Research Methodology?” Grad Coach, June 2021, gradcoach.com/what-is-research-methodology/.
APA Jansen, D., & Warren, K. (2021, June). What (Exactly) Is Research Methodology? Grad Coach. https://gradcoach.com/what-is-research-methodology/
Your explanation is easily understood. Thank you
Very help article. Now I can go my methodology chapter in my thesis with ease
I feel guided ,Thank you
This simplification is very helpful. It is simple but very educative, thanks ever so much
The write up is informative and educative. It is an academic intellectual representation that every good researcher can find useful. Thanks
Wow, this is wonderful long live.
Nice initiative
thank you the video was helpful to me.
Thank you very much for your simple and clear explanations I’m really satisfied by the way you did it By now, I think I can realize a very good article by following your fastidious indications May God bless you
Thanks very much, it was very concise and informational for a beginner like me to gain an insight into what i am about to undertake. I really appreciate.
very informative sir, it is amazing to understand the meaning of question hidden behind that, and simple language is used other than legislature to understand easily. stay happy.
This one is really amazing. All content in your youtube channel is a very helpful guide for doing research. Thanks, GradCoach.
research methodologies
Please send me more information concerning dissertation research.
Nice piece of knowledge shared….. #Thump_UP
This is amazing, it has said it all. Thanks to Gradcoach
This is wonderful,very elaborate and clear.I hope to reach out for your assistance in my research very soon.
This is the answer I am searching about…
realy thanks a lot
Thank you very much for this awesome, to the point and inclusive article.
Thank you very much I need validity and reliability explanation I have exams
Thank you for a well explained piece. This will help me going forward.
Very simple and well detailed Many thanks
This is so very simple yet so very effective and comprehensive. An Excellent piece of work.
I wish I saw this earlier on! Great insights for a beginner(researcher) like me. Thanks a mil!
Thank you very much, for such a simplified, clear and practical step by step both for academic students and general research work. Holistic, effective to use and easy to read step by step. One can easily apply the steps in practical terms and produce a quality document/up-to standard
Thanks for simplifying these terms for us, really appreciated.
Thanks for a great work. well understood .
This was very helpful. It was simple but profound and very easy to understand. Thank you so much!
Great and amazing research guidelines. Best site for learning research
hello sir/ma’am, i didn’t find yet that what type of research methodology i am using. because i am writing my report on CSR and collect all my data from websites and articles so which type of methodology i should write in dissertation report. please help me. i am from India.
how does this really work?
perfect content, thanks a lot
As a researcher, I commend you for the detailed and simplified information on the topic in question. I would like to remain in touch for the sharing of research ideas on other topics. Thank you
Impressive. Thank you, Grad Coach 😍
Thank you Grad Coach for this piece of information. I have at least learned about the different types of research methodologies.
Very useful content with easy way
Thank you very much for the presentation. I am an MPH student with the Adventist University of Africa. I have successfully completed my theory and starting on my research this July. My topic is “Factors associated with Dental Caries in (one District) in Botswana. I need help on how to go about this quantitative research
I am so grateful to run across something that was sooo helpful. I have been on my doctorate journey for quite some time. Your breakdown on methodology helped me to refresh my intent. Thank you.
thanks so much for this good lecture. student from university of science and technology, Wudil. Kano Nigeria.
It’s profound easy to understand I appreciate
Thanks a lot for sharing superb information in a detailed but concise manner. It was really helpful and helped a lot in getting into my own research methodology.
Comment * thanks very much
This was sooo helpful for me thank you so much i didn’t even know what i had to write thank you!
You’re most welcome 🙂
Simple and good. Very much helpful. Thank you so much.
This is very good work. I have benefited.
Thank you so much for sharing
This is powerful thank you so much guys
I am nkasa lizwi doing my research proposal on honors with the university of Walter Sisulu Komani I m on part 3 now can you assist me.my topic is: transitional challenges faced by educators in intermediate phase in the Alfred Nzo District.
Appreciate the presentation. Very useful step-by-step guidelines to follow.
I appreciate sir
wow! This is super insightful for me. Thank you!
Indeed this material is very helpful! Kudos writers/authors.
I want to say thank you very much, I got a lot of info and knowledge. Be blessed.
I want present a seminar paper on Optimisation of Deep learning-based models on vulnerability detection in digital transactions.
Need assistance
Dear Sir, I want to be assisted on my research on Sanitation and Water management in emergencies areas.
I am deeply grateful for the knowledge gained. I will be getting in touch shortly as I want to be assisted in my ongoing research.
The information shared is informative, crisp and clear. Kudos Team! And thanks a lot!
hello i want to study
Hello!! Grad coach teams. I am extremely happy in your tutorial or consultation. i am really benefited all material and briefing. Thank you very much for your generous helps. Please keep it up. If you add in your briefing, references for further reading, it will be very nice.
All I have to say is, thank u gyz.
Good, l thanks
thank you, it is very useful
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] the literature review is to inform the choice of methodology for your own research. As we’ve discussed on the Grad Coach blog,…
- Free Download: Research Proposal Template (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Research design (methodology) […]
- Dissertation vs Thesis: What's the difference? - Grad Coach - […] and thesis writing on a daily basis – everything from how to find a good research topic to which…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Increase Font Size
21 Introduction to Sampling
1. Introduction:
The purpose of research is basically to explore relationship between various variables which may be related to human behavior, materials, actions, etc. For example, one may try to find out the relationship between intelligence and performance and in such a case the researcher may define the research problem as “The effect of human intelligence on academic performance.” In deterioration of material, the researcher may try to find out the influence of the environmental factors, on the extent of deterioration and therefore, the research is trying to find out the relationship between two variables. In summary, the purpose of research is to establish the nature and extent of relationship between two variables. In establishing such a relationship, the sample used for the study becomes very vital and selection procedure adopted by the researcher in any research is also of paramount importance. The results of the study can be generalized to the population effectively when the right type of sample is used in the research. Therefore, enormous attention should be given to sample selection. This chapter deals with the concept of Census, Sampling Methods, Sampling frame, advantages and limitations of sampling, sampling and non-sampling errors, etc.
2. Learning objectives:
At the end of the session you will be able to:
- Understand ‘Census’, its features, advantages and limitations.
- Comprehend the importance of sampling in research and know about its principles.
- Conceptualize what is a sampling frame.
- Know about the various Sampling and Non- Sampling errors.
3. CENSUS
A study of all items in the ‘population’ is known as a census. It can be assumed that in census, when all items are covered, no element of chance is left and highest accuracy is obtained. But in practice this may not be true. Even a minute bias in such an inquiry will get larger as the number of observation increases. Moreover, there is no way of checking the element of bias or its extent except through a resurvey. Besides, this consumes a great deal of time, money and energy. Therefore, when the population is large, this method becomes difficult to adopt, because of the resources involved. At times, this method is not feasible for ordinary researchers. It is possible only for the Government to get the complete enumeration carried out. Government adopts this in cases such as population census conducted once in a ten years. Further, every time, it is not possible to study every item in the population, and sometimes it is possible to obtain sufficiently accurate results by studying only a part of the total population. In such cases there is no utility of census surveys.
A census can provide detailed information on all or most elements in the population, thereby enabling totals for rare population groups or small geographic areas. A census and a sample survey have many features in common, such as the use of a questionnaire to collect information, the need to process and edit the data, and the susceptibility to various sources of error.
The census method can be applied in a situation where the separate data for every unit in the population is to be collected, such that the separate actions for each are taken. For example, the preparation of the voter’s list for election purposes, income tax assessment, recruitment of personnel, etc. are some of the areas where the census method is adopted. This method can be used where the population is comprised of heterogeneous items, i.e. different characteristics.
3.1 Advantages of Census Method:
1. Concentrated study : the researcher can have an in depth study about a problem and also can gather a lot of information about the entire population.
2. Accuracy: there are more chances of the census data to be highly accurate when compared to other methods of data collection. The smaller the population, higher is the degree of accuracy.
3. Adapts to heterogeneous groups: Census method is the only data collection method that can be adopted for a population which is heterogeneous in nature.
3.2 Disadvantages of census method:
1. Inconvenient: it is a highly inconvenient method because it involves a lot of manual efforts.
2. Time & cost consuming: besides being inconvenient, census method demands spending a lot of time and money to get the data collected.
3. Unsuitable for all study: census method cannot be suitable for all kinds of study. Its adaptability is very limited i.e. only to a few circumstances where the population is limited and does not require vast area of study.
4. SAMPLING
Sampling refers to the process of selecting few representatives from the whole group of items in any field of inquiry. The whole group is referred to as ‘population ‘or ‘universe’. Hence sampling refers to choosing few items of the population which would serve as representative group that can be used to estimate or predict unknown information about the population. Sampling seems to be a pre-requisite when the population is a bigger one and when there is practical difficulty in studying the entire population which is going to be time, cost and energy consuming.
Eg. Suppose you want to estimate the average age of the students in your class. There are two ways of doing this. The first method is to contact all students in the class, find out their ages, add them up and then divide this by the number of students (the procedure for calculating an average). The second method is to select a few students from the class (the small group of students selected is called the Sample ), ask them their ages, add them up and then divide by the number of students you have asked. From this you can make an estimate of the average age of the class
4.1 PRINCIPLES OF SAMPLING:
There are two important principles on which the sampling theory works:
4.1.1 PRINCIPLE OF STATISTICAL REGULARITY
The principle of statistical regularity is derived from the theory of probability in mathematics. According to this principle, when a large number of items are selected at random from the universe, then it is likely to possess the same characteristics as that of the entire population.
This principle claims that the sample selection is random, i.e. every item has an equal and likely chance of being selected. It is believed that sample selected randomly and not deliberately acts as a true representative of the population. Thus, this principle is characterized by the large sample size and the random selection of a representative sample.
4.1.2 PRINCIPLE OF INERTIA OF LARGE NUMBERS
The principle of Inertia of large numbers states that the larger the size of the sample the more accurate the conclusion is likely to be. This principle is based on the notion, that large numbers are more stable in their characteristics than the small numbers, and the variation in the aggregate of large numbers is insignificant. It does not mean that there is no variation in the large numbers, there is, but is less than in the smaller numbers.
4.2 SAMPLING METHOD:
A sample is considered to be a true representative of the population. The data gathered from the sample is expected to be applicable to the entire population but many times, such generalizations are questioned citing flaws in the sampling methods. For example, the researcher wants to select 200 girls from a group of 2000 for a research on the nutritional value of a product developed or to evaluate the usage of cloth in particular material (cotton/synthetic etc.) and in this case the sample is 10% of the population. What is the guarantee that the 200 persons selected as the sample truly represent the characteristics of the 2000 persons? This may be possible if the sampling method applies ensures that every person of the population has a high probability of getting selected as one among the 200 persons. Such samples are called probability samples indicating that every person of the population has a chance of getting selected. The results obtained from the probability samples are mostly objective in nature and the generalizing ability factor is fairly high. There are also possibilities that the 200 girls sometimes represent a particular geographical area or in cases volunteers too and therefore, they will not be the true representatives of the population. Such samples are called non-probability samples. The results emerging from non-probability samples are sometimes subjective and cannot be generalized to the population. The different types of probability and non-probability samples are enumerated in the following sections of this chapter.
SAMPLING METHODS
Probability Sampling is further classified as follows:
- Simple random sampling
- Systematic sampling
- Stratified random sampling
- Multistage sampling
- Cluster sampling
Non- Probability Sampling is further classified as follows:
- Convenience sampling
- Judgmental sampling
- Quota sampling
- Snow ball sampling
- Accidental sampling
4.3 Advantages of Sampling:
- Every unit in the population has a chance of getting selected, as far as probability sampling is concerned.
- As the sample is mostly the true representative of the population, the probability of generalizability of the results too is very high.
- Direct and reliable data can be acquired, as each and every unit is being dealt with.
- Accuracy of data is high
- Sampling involves less cost and is convenient
- Organizational problems are very low when the population sample is taken for study.
- Facilitates better rapport between the researcher and the respondents.
- Intensive and exhaustive data can be collected.
4.4 Limitations:
1. Less suitable for homogeneous groups as the generalizability factor gets affected.
E.g . a researcher wants to study the attitude of students towards curriculum and in case the population of students belongs to a school, which admits only meritorious students, then the population becomes largely homogeneous and in such case, the generalizability of the responses obtained from them to the entire student population may be low
2. Requires a lot of controls in sample selection which costs time and resources. Also assuring a truly representative sample is difficult.
3. There are chances of bias.
4. Sampling is difficult in case the population is too small or too heterogeneous.
5. SAMPLING FRAME:
Sampling frame is nothing but the unit of a population from which the sample is selected for the study. The definition of the population also determines the sample frame. For example, a researcher wants to study the papers published by the Home Science teachers of a University, then all the Home Science teachers together become the population for the study and every teacher becomes the sampling frame. Simply stated, all the individual unit of the defined population is a sampling frame. If the Chief Educational Officer wants to gather information on availability of laboratories in secondary schools in a district then every secondary school in that location becomes the sampling frame and the total list of the secondary schools becomes the population. Sampling unit does not mean human beings alone used in census but any entity that is used as a sample for the research. Companies which carryout market research of sale of products uses a particular product as the sample frame and so on.
A good sampling frame will:
- Include all the individuals that belong to the target population
- Exclude all the individuals that do not comprise the target population
- Includes all accurate information about each unit of the population
- List all the units in an order and organizes with a numerical identifier.
- Avoids repetition of units and thereby the possible errors.
5.1 PROBLEMS WITH SAMPLING FRAME
- Missing elements: Some members of the population are not included in the frame.
- Foreign elements: The non-members of the population are included in the frame.
- Duplicate entries: A member of the population is surveyed more than once.
- Groups or clusters: The frame lists clusters instead of individuals.
6. SAMPLING AND NON-SAMPLING ERRORS
In a research, the error may result because of the flaw in selection of the right sample. Unless the sample is the true representation of the population, the results are bound to be suspect and therefore, such errors emerging out of the results are certainly sampling errors . The researcher should definitely minimize the sampling error in research and therefore, probability sample procedure is advisable.
The research may result in non-sampling errors too which emerge due to the faulty methodology. In research, use of measurement tools, forming of the right hypothesis, use of the right statistical applications, interpretation of data, etc., also determine the quality and outcomes of the research and any error in these areas may also make the research outcomes suspect. Some of these potential non-sampling errors are enumerated as follows:
6.1 Errors due to the measurement tools:
In research, the researcher develops a tool to collect data or else an existing tool may also be used. When researcher develops the tool – whether it is a questionnaire or a rating scale or an inventory and so on – the reliability and validity should also be established in order to gather accurate data. Reliability ensures the stability of the tool whereas the validity indicates its true worthiness. Sometimes, the test may be reliable but need not be valid and therefore, the researcher has to use appropriate methods to ensure a high reliability and validity of the tools to collect data.
This can be explained through a simple example. Suppose one wants to buy 5 meters of cloth and the shop keeper measures 5 times in front of the customer using a measurement scale which considered one meter by the customer on its face value. As the procedure of measuring is repeated five times using that scale, the customer assumes that it is five meter. In this exercise, the procedure of measurement is reliable because of the consistency in the repetition of the task by 5 times. However, the customer later finds that the actual length is only 4.9 meters and on further verification finds out that the actual length of the measurement tool is only 98 centimeters. This indicates that the tool is not a valid one as it does not contain the real measurement of a meter. Therefore, good sampling technique but a poor tool may not bring out an objective outcome of the research thus resulting in a non-sampling error.
6.2 Errors due to the application of wrong research design.
The broad classification of research designs may be enumerated as follows:
1. Descriptive studies – A research design which simply describes the phenomenon or explain “what it is” of the research
2. Causal Comparative Studies – This approach is used to explore relationship between variables but not able to establish the cause and effect relationship between them.
3. Correlation studies – This approach helps in measuring the magnitude of relationship between variables
4. Experimental research – This research tries to establish the cause and effect relationship between variables.
Though the sampling is good, the researcher may not use the right design for the research which may bring faulty outcomes too. Applying experimental design when there are no proper controls, trying to establish cause and effect relationship between the variables through a causal-comparative study, etc., may contribute to sampling errors.
6.3 Errors due to wrong selection of variables:
Researchers sometimes commit mistakes in determining the variables of the research study. The following descriptions help in understanding different variables in order to know where the researcher can err.
- Independent variable : A variable that can be manipulated as per the objective of the study
- Dependent variable : The variable that is treated normally as the criterion or effect in the research study
- Antecedent Variables : Variables, which are believed to have an effect on the results of the overall study, particularly in explaining the variance, are called antecedent variables.
- Extraneous Variables : In addition to independent variables used in the study and the antecedent variables undetected, some other variables such as the test itself, interest level in taking test, etc., which affect the generalization of the results are called extraneous variables.
In order to get the real impact of the independent variables on the criterion of the study, it is preferable to control the effect of the extraneous variables. Lack of such control may also result in non-sampling error of the study.
6.4 . Errors due to application of inappropriate statistical procedures:
Some research studies may use statistical applications but usage of the inappropriate technique may also result in errors in the study though the sampling procedure is correct. Two broad procedures in statistics and their usage are described below:
6.4.1 Parametric statistical procedures
Parametric statistical procedures make the following assumptions:
o the distributions compared are normal
o the variances of distributions are equal; and
o the subjects of the distributions are independent of each other.
Analysis of Variance: Procedure used to compare the effects when more than two variables are used in the study. Use of ANOVA reduces the error compared to doing pair-wise comparisons. ANOVA uses F test.
Analysis of Covariance: Adjusting the post-test scores on the basis of new variables and then comparing the difference between the experimental group and control group.
Canonical Correlation: When the researcher is interested in computing correlation between a set of independent variables and a set of dependent variables, the canonical correlation technique is used.
Multiple Regression: The process of using more predictors in order to explain the variance in the criterion is called multiple regression.
6.4.2 Non-parametric statistical procedures
Non-parametric statistical procedures are used when the distributions do not satisfy any pre-determined assumptions.
Chi-square, Mann-Whitney, Biserial Correlation, Point biserial correlation tests are some of the commonly used non-parametric statistical procedures.
6.5 Errors due to inappropriate hypothesis:
Hypothesis in a study is nothing but an educated guess. A null-hypothesis is non-directional and usually used in exploration studies. A researcher may use directional hypothesis when there is better control over variables. Non-directional hypotheses work better in the case of confirmatory studies. Hypothesis testing involves application of statistics too. Sometimes the researcher may reject the null hypothesis when it is tenable and this error is called Type I error. Type II error occurs when the researcher retains the null hypothesis when it is false. A good research study tries to control the Type II error. Though the researcher may adopt the right sampling procedure, the error may result through the wrong application of hypotheses too.
Well, we have discussed the concepts of Census, Sampling Methods, Sampling frame, advantages and limitations of sampling, probable and non-probable sampling, and sampling errors in this lesson. We have also enumerated the advantages and limitations of each sampling technique. We have described the errors that may occur in research due to other factors such as research design, tools for the study, analysis techniques, etc., and how care must be taken in the selection of the sample considering these factors. Sample selection is not an independent process in research but an inter-dependent aspect to make the research study more effective. However, among all procedures used in research, selection of sample is a very important feature and we should try to reduce the sampling error to make the research more accurate. The time and energy spent on research will go waste if the results of the study do not have an impact on the population and therefore, utmost care is necessary in sample selection. Review of related literature on sampling procedure will also help you to make the sampling technique appropriate in your research. I also urge you to go through the research studies conducted in home science and other disciplines and see how the researchers have selected samples. The knowledge gained through this lesson will definitely give you insights in reviewing the sampling techniques adopted by other researchers for various research designs.
- http://psychology.ucdavis.edu/rainbow/html/fact_sample.html
- http://www.analytictech.com/mb313/sampling.htm
- http://zebu.uoregon.edu/1996/es202/l1.html
- https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4612-9998-1_3
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sampling_(statistics)
Suggested References
- C.R. Kothari (2004), Research Methodology, methods & techniques second edition, revised. New Delhi, India: New Age Publishing Company, P55-67
- Ranjit Kumar (2011), Research Methodology a step-by-step guide for beginners, third edition, New Delhi, India, Sage Publications , P 175- 189
- Santhosh Gupta(2001) Research Methodology and Statistical technique, , New Delhi, India , Deep& Deep publications ISBN 81-7100-501-2
- G.R. Basotia &K.K. Sharma (2002) Research Methodology, Jaipur, India , Mangal Deep Publications, ISBN: 81-7594-090-5 P.Saravanavel (2007) Research Methodology, Allahabad, India, Kitab Mahal Publications, ISBN: 81-2225-0010-2
- R.Panneerselvam(2004), New Delhi, India, Phi Learning Private Limited, ISBN: 978-81-203-2452-7
- Welter R. Borg & Meredith D. Gall, Educational Research- An Introduction, fourth edition, New York & London, Longman Publications, ISBN: 0-582-28246-2

COMMENTS
2. Systematic sampling. Systematic sampling is similar to simple random sampling, but it is usually slightly easier to conduct. Every member of the population is listed with a number, but instead of randomly generating numbers, individuals are chosen at regular intervals. Example: Systematic sampling.
This is often used to ensure that the sample is representative of the population as a whole. Cluster Sampling: In this method, the population is divided into clusters or groups, and then a random sample of clusters is selected. Then, all members of the selected clusters are included in the sample. Multi-Stage Sampling: This method combines two ...
Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and convenience sampling. Proper sampling ensures representative, generalizable, and valid research results.
Simple random sampling. Simple random sampling involves selecting participants in a completely random fashion, where each participant has an equal chance of being selected.Basically, this sampling method is the equivalent of pulling names out of a hat, except that you can do it digitally.For example, if you had a list of 500 people, you could use a random number generator to draw a list of 50 ...
Understand sampling methods in research, from simple random sampling to stratified, systematic, and cluster sampling. Learn how these sampling techniques boost data accuracy and representation, ensuring robust, reliable results. Check this article to learn about the different sampling method techniques, types and examples.
The sampling method will depend on the research question. For instance, the researcher may want to understand an issue in greater detail for one particular population rather than worry about the ' generalizability' of these results. ... Please note that "random sample" does not mean arbitrary sample. For example, if the researcher ...
8. Sampling. Sampling is the statistical process of selecting a subset—called a 'sample'—of a population of interest for the purpose of making observations and statistical inferences about that population. Social science research is generally about inferring patterns of behaviours within specific populations. We cannot study entire ...
Step 1: Define your population. Like other methods of sampling, you must decide upon the population that you are studying. In systematic sampling, you have two choices for data collection: You can select your sample ahead of time from a list and then approach the selected subjects to collect data, or.
Linear systematic sampling is a statistical sampling technique that involves selec ting every kth element from a. list or population after a random starting point has been det ermined. This method ...
The sample is the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. Sampling frame is the actual list of individuals that the sample will be drawn from. Ideally, it should include the entire target population (and nobody who is not part of that population). Sample size is how many individuals (or units) are included in your sample.
Abstract. Sampling is the process of selecting an ideal sample that would represent the entire population of your desired study. It usually consists of a subset of individuals, items, or data points from a larger population to make inferences or draw conclusions about the entire population. Sampling in research methodology is an important step ...
The four steps of simple random sampling are (1) defining the population, (2) constructing a list of all members, (3) drawing the sample, and (4) contacting the members of the sample. Stratified random sampling is a form of probability sampling in which individuals are randomly selected from specified subgroups (strata) of the population.
Nonprobability sampling or judgment sampling depends on subjective judgment. [Salant, p62] The nonprobability method of sampling is a process where probabilities cannot be assigned to the units objectively, and hence it becomes difficult to determine the reliability of the sample results in terms of probability.
As we mentioned, research methodology refers to the collection of practical decisions regarding what data you'll collect, from who, how you'll collect it and how you'll analyse it. Research design, on the other hand, is more about the overall strategy you'll adopt in your study. For example, whether you'll use an experimental design ...
The main methodological issue that influences the generalizability of clinical research findings is the sampling method. In this educational article, we are explaining the different sampling ...
Qualitative Research Methodology. This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
1.3.2 Non-probability Sampling 1.3.3 Choice of the Sampling Method 1.3.4 Characteristics of a Good Sample 1.3.5 Determination of Sample Size 1.4 Key Points at a Glance 1.5 Let Us Sum up 1.6 Glossary 1.7 Check Your Progress: The Key 1.0 INTRODUCTION In order to carry out a research study, you have to first acquire relevant information on the ...
1.Inconvenient: it is a highly inconvenient method because it involves a lot of manual efforts. 2.Time & cost consuming: besides being inconvenient, census method demands spending a lot of time and money to get the data collected. 3. Unsuitable for all study: census method cannot be suitable for all kinds of study.
"Chapter Ten: Understanding Populations and Sampling" 1. ** Definition of a Research Population **: The concept of a research population or universe, which includes all individuals, groups, organizations, documents, campaigns, or incidents relevant to a study. 2. ** Sample Selection from a Population **: Guidance on selecting a sample from a population, including identifying a target ...