
Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.
- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Faculty of Arts & Sciences Libraries

Library Research Guide for the History of Science: Introduction
- What is a Primary Source?
- Senior Theses 2023
- Background and Context/Biography
- Exploring Your Topic
- Using HOLLIS
- What is a Secondary Source?
Page Contents
Knowing a primary source when you see one, kinds of primary sources, find primary sources in hollis, using digital libraries and collections online, using bibliographies.
- Exploring the Special Collections at Harvard
- Citing Sources & Organizing Research
Primary sources provide first-hand testimony or direct evidence concerning a topic under investigation. They are created by witnesses or recorders who experienced the events or conditions being documented.
Often these sources are created at the time when the events or conditions are occurring, but primary sources can also include autobiographies, memoirs, and oral histories recorded later.
Primary sources are characterized by their content, regardless of the format available. (Handwritten notes could be published; the published book might be digitized or put on microfilm, but those notes are still primary sources in any format).
Some types of primary sources:
- Original documents (excerpts or translations acceptable): Diaries, speeches, manuscripts, letters, interviews, news film footage, contemporary newspaper articles, autobiographies, official records, pamphlets, meeting notes, photographs, contemporary sketches
- Creative works : Poetry, drama, novels, music, art
- Relics or artifacts : Furniture, clothing, buildings
Examples of primary sources include:
- A poster from the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters' 1962 strike
- The papers of William James
- A 1970 U.S. State Dept document updating Nixon on U.S.-Soviet space cooperation activities (Harvard login)
- A British pamphlet: "Electric Lighting for Country Houses," 1898
- Phineas Gage's skull
- The text of J. Robert Oppenheimer's "Atomic Weapons" presentation to the American Philosophical Society
Outline of Primary Sources for History
Archives and Manuscripts
Archives and manuscripts are the unpublished records of persons (letters, notes, diaries, etc.) and organizations. What are Archives? Usually each archival collection has a (short) catalog record and a detailed finding aid (which is often available online).
- "Catalog record” refers to the kind of record found in library online catalogs, similar to those for books, although often a bit longer. Example of an Archive record .
- “Finding aid” (sometimes called an inventory) generally refers to a list of the folder labels for the collection, accompanied by a brief collection overview (scope and contents note) and a biographical (or institutional) note on the creator of the collection. Finding aids may be as long as needed given the size of the collection. They vary considerably according to the practices of individual repositories. Example of a Finding aid .
To find Archives and manuscripts at Harvard, go to HOLLIS Advanced search . Search your keywords or Subject terms (see the HOLLIS page of this guide ) in the Library Catalog, limiting to Resource Type: Archives/Manuscripts. You can choose the library at the right (Search Scope). Countway Medicine has abundant medical archives, and Schlesinger has many archives of women activists, many in health and reproductive rights fields. Sample search on Subject: Women health .
Library Research Guide for Finding Manuscripts and Archival Collections explains
- How to find archives and manuscripts at Harvard
- How to find archives and manuscripts elsewhere in US via search tools and via subject guides .
- How to find archives and manuscripts in Europe and elsewhere.
- Requesting digitization of archival material from Harvard and from other repositories .
For digitized archival material together with other kinds of primary sources:
- Finding Primary Sources Online offers general instructions for finding primary sources online and a list of resources by region and country
- Online Primary Source Collections for the History of Science lists digital collections at Harvard and beyond by topic.
- Online Primary Source Collections for History lists digital collections at Harvard and beyond by topic.
Methods for finding books are described under the HOLLIS page of this guide and in the Finding Primary Sources in HOLLIS box on this page.
- Book Reviews may give an indication as to how a scientific work was received. See: Finding Book Reviews .
- Numerous, especially pre-1923 books (as well as periodicals and other sources) can be found and full text searched in several digital libraries (see box on this page).
Periodicals
Scientific articles :
Web of Science Citation Indexes (Harvard Login) (1900- ) articles in all areas of science. Includes medical articles not in PubMed. You can use the Cited Reference search in the Web of Science to find primary source articles that cite a specified article, thus getting an idea of its reception. More information on the Web of Science .
PubMed (1946- ) covers, usually with abstracts, periodical articles on all areas of medicine. - --Be sure to look at the MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) at the bottom of pertinent records. Very recent articles may not as yet received their MeSH terms. So look at older records to find the MeSH terms, and use a variety of keywords as well as MeSH terms to find the new records. --The MeSH terms are the same as the Medical Subject terms found in HOLLIS. --Hit Free article or Try Harvard Library, not the publisher's name to see full text
JSTOR (Harvard Login) offers full-text of complete runs (up to about 5 years ago) of over 400 journals. JSTOR allows simultaneous or individual searching, full-text searching optional, numerous journals in a variety of fields of science and medicine. See the list at the bottom of the Advanced search screen. JSTOR searches the "Notes and News" sections of journals ( Science is especially rich in this material). In Advanced Search choose Item Type: Miscellaneous to limit largely to "Notes and News".
PsycINFO) (Harvard Login) (1872- ) indexes the professional and academic literature in psychology and related disciplines
Many more scientific periodical indexes are listed in the Library Research Guide for the History of Science .
General interest magazines and periodicals see:
American Periodicals Series Online (Harvard Login) (1740-1900) offers full text of about 1100 American periodicals. Includes several scientific and medical journals including the American Journal of Science and the Medical Repository. In cases where a periodical started before 1900, coverage is included until 1940.
British Periodicals (Harvard Login) (1681-1920) offers full text for several hundred British periodicals.
Ethnic NewsWatch (Harvard Login) (1959- ) is a full text database of the newspapers, magazines, and journals of the ethnic, minority and native press.
Periodicals Index Online (Harvard Login) indexes contents of thousands of US and European journals in the humanities and social sciences, from their first issues to 1995.
Reader's Guide Retrospective (WilsonWeb) (Harvard Login) (1890-1982) indexes many American popular periodicals.
Many more general periodical indexes are listed in Finding Articles in General and Popular Periodicals (North America and Western Europe) .
Articles in non-science fields (religion, public policy): see the list in the Library Research Guide for History .
Professional/Trade : Aimed at particular trades or professions. See the Library Research Guide for History
Newspaper articles : see the Guide to Newspapers and Newspaper Indexes .
Personal accounts . These are first person narratives recalling or describing a person’s life and opinions. These include Diaries, memoirs, autobiographies, and when delivered orally and recorded: Oral histories and Interviews.
National Library of Medicine Oral Histories
Regulatory Oral History Hub (Kenan Institute for Ethics, Duke University) offers links to digital collections containing interviews with regulators, lawyers, and judges. Mainly U.S.
Visual sources :
Records for many, but by no means all, individual Harvard University Library images are available in HOLLIS Images , an online catalog of images. Records include subjects and a thumbnail image. HOLLIS Images is included in HOLLIS searches.
Science & Society Picture Library offers over 50,000 images from the Science Museum (London), the National Museum of Photography, Film & Television and the National Railway Museum.
Database of Scientific Illustrators (DSI) includes over 12500 illustrators in natural history, medicine, technology and various sciences worldwide, c.1450-1950. Living illustrators excluded.
NYPL Digital Gallery Pictures of Science: 700 Years of Scientific and Medical Illustration
Images from the History of Medicine (IHM) includes prints and photographs from the U.S. National Library of Medicine. (The IHM is contained within a larger NLM image database, so this link goes to a specialized search).
Images From the History of the Public Health Service: a Photographic Exhibit .
Wellcome Images
Films/Videos
To find films in HOLLIS , search your topic keywords, then on the right side of the results screen, look at Resource Type and choose video/film.
To find books about films about your topic, search your topic keywords AND "in motion pictures" (in "")
Film Platform offers numerous documentary films on a wide variety of subjects. There are collections on several topics. Searches can be filtered by topic, country of production, and language.
A list of general sources for images and film is available in the Library Research Guide for History and additional sources for the history of science in Library Research Guide for the History of Science .
Government documents often concern matters of science and health policy. For Congressional documents, especially committee reports, see ProQuest Congressional (Harvard Login ).
HathiTrust Digital Library . Each full text item is linked to a standard library catalog record, thus providing good metadata and subject terms. The catalog can be searched separately. Many government documents are full text viewable. Search US government department as Author.
More sources are listed in the Library Research Guide for History
For artifacts and other objects , the Historic Scientific Instruments Collection in the Science Center includes over 15,000 instruments, often with contemporary documentation, from 1450 through the 20th century worldwide.
Waywiser, online database of the Collection of Historical Scientific Instruments .
Warren Anatomical Museum of the Center for the History of Medicine in the Countway Library of Medicine has a rich collection of medical artifacts and specimens.
Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology
Fall 2020: these collections are closed during the pandemic. Check out their links above to see what they have available online.
Primary Source Terms :
You can limit HOLLIS searches to your time period, but sources may be published later, such as a person's diary published posthumously. Find these with these special Subject terms.
You can use the following terms to search HOLLIS for primary sources:
- Correspondence
- Description and travel
- Manuscripts
- Notebooks, sketchbooks, etc.
- Personal narratives (refers to accounts of wars and diseases only)
- Pictorial works
- Sources (usually refers to collections of published primary sources)
Include these terms with your topical words in HOLLIS searches. For example: tuberculosis personal narratives
Online Primary Source Collections for the History of Science lists digital collections at Harvard and beyond by topic
Google Book Search, HathiTrust Digital Library and Internet Archives offer books and periodicals digitized from numerous libraries. Only out-of-copyright, generally post-1923, books are fully viewable. Each of these three digital libraries allows searching full text over their entire collections.
Google Book Search
HathiTrust Digital Library . Each full text item is linked to a standard library catalog record, thus providing good metadata and subject terms. The catalog can be searched separately. Many post-1923 out-of-copyright books, especially government documents, are full text viewable. You can search within copyright books to see what page your search term is on.
Internet Archive now offers a beta full text search. Put your terms (phrases or personal names, in quotation marks (""), work best) in the search box.
The Online Books Page arranges electronic texts by Library of Congress call numbers and is searchable (but not full text searchable). Includes books not in Google Books, HathiTrust, or Internet Archive. Has many other useful features.
Medical Heritage Library . Information about the Medical Heritage Library. Now searchable full text.
UK Medical Heritage Library
Biodiversity Heritage Library
Contagion: Historical Views of Diseases and Epidemics (1493-1922) provides digitized historical, manuscript, and image resources selected from Harvard University libraries and archives.
Expeditions and Discoveries (1626-1953) features nine expeditions in anthropology and archaeology, astronomy, botany, and oceanography in which Harvard University played a significant role. Includes manuscripts and records, published materials, visual works, and maps from 14 Harvard repositories.
Defining Gender Online: Five Centuries of Advice Literature for Men and Women (1450-1910).
Twentieth Century Advice Literature: North American Guides on Race, Sex, Gender, and the Family.
Many more general History digital libraries and collections: Library Research Guide for History
More History of Science digital libraries: Library Research Guide for the History of Science .
There may already be a detailed list of sources (a bibliography) for your topic.
For instance:
A bibliography of eugenics , by Samuel J. Holmes ... Berkeley, Calif., University of California press, 1924, 514 p. ( University of California publications in zoology . vol. XXV) Full text online .
Look for specialized subject bibliographies in HOLLIS Catalog . Example . WorldCat can do similar searches in the Subject Keyword field for non-Harvard holdings.
- << Previous: What is a Secondary Source?
- Next: Exploring the Special Collections at Harvard >>
- Last Updated: Apr 14, 2024 9:25 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/HistSciInfo
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
How to find resources by format
Why use primary resources.
Primary sources provide first-hand testimony or direct evidence concerning a topic under investigation. They present original thinking, report a discovery, or share new information. Use primary sources in historical research, or researching precedent or context on a particular topic.
Primary sources are created by witnesses or recorders who experienced the events or conditions being documented. They are from the time period involved and have not been filtered through subsequent interpretation or evaluation.
Determining what is a primary source can be tricky and depends on the topic, subject, and discipline you are researching. The types of information that can be considered primary sources may vary depending on the subject or discipline. Also how you are using the material in your paper or project can effect this determination. For some papers or projects it may be important to view the original object but for others a primary source that has been scanned and is online is acceptable.
The types of information that can be considered primary sources may vary depending on the subject or discipline, and also on how you are using the material. For example:
- A magazine article reporting on recent studies linking the reduction of energy consumption to the compact fluorescent light bulb would be a secondary source.
- A research article or study proving this would be a primary source.
- However, if you were studying how compact fluorescent light bulbs are presented in the popular media, the magazine article could be considered a primary source.
Tip: If you are unsure if a source you have found is primary, talk to your instructor, librarian, or archivist.
Definitions
Primary sources are original records created at the time historical events occurred or well after events in the form of memoirs and oral histories. Primary sources are distinguished from secondary sources, which are produced some time after an event, and serve to analyze or interpret primary sources.
Archives and Manuscripts consist of original unpublished, historical and contemporary material.
Primary sources in reproduction For some levels of research it is acceptable and appropriate to use primary sources that have been reproduced and published. A few examples include microfilmed newspaper articles, published diaries, and scanned images of original documents published in book form.
Search strategies
When beginning your research, searching for primary sources is similar to other kinds of research:
- Brainstorm the kinds of sources you might need. News sources? Journals from the time period? Government documents? Have a date range in mind to narrow your search.
- Diaries, letters, and other personal papers are often unique items held in archives or special collections. One trick is to google the name of the person you're researching and the word "papers." If they are being held at another institution, you might find out if they've been digitized or not.
- Brainstorm and track your keywords and subject terms. Use a thesaurus to think of more keywords or older terms you may not be familiar with, but may have been commonly used during the time period you are researching. Are the records likely to be in another language or another alphabet? Do you have expertise in this language? Knowing ahead of time might help with your search.
- Think about where records might be held. Because of historical colonialism and imperialism, some communities may not have control over their own records and materials. They may be held in another country entirely.
- Arrange a visit to our Archives and Special Collections if your topic is related to the University or Minnesota history.
- Browse our collections of online primary source databases .
Searching in the Libraries collections
The catalog provides many types of primary sources: original archival materials, print materials with the original texts, printed facsimiles, and online resources that link to digital facsimiles. You can recognize such an item if the word "sources" appears in the subject. That word and certain others, especially when searched as a subject keyword, will help narrow your search results to primary sources.
Archival materials on campus are searchable in more depth via this their description of their collections .
When searching our collection, use the Libraries' Advanced Search and enter your keywords, plus the subject term source to your search. For example, this is an Advanced search with two subject contains filters set as "Holocaust’ and ‘sources." The date range is set to start "1937" and end "1950."

Start with a broad search; you can always narrow it further after you begin searching.
For some topics, try a more specific subject keyword instead, for example:
- personal narratives
- autobiography
Depending on the focus of your research, there are other formats that may serve as primary source material. Here are some examples:
- advertisements
- archaeological artifacts
- birth certificates
- census material
- congressional/parliamentary hearings and reports
- correspondence
- county records
- documentary photographs
- government documents
- inscriptions
- manuscripts
- news sources
- oral histories
- organizational minutes
- records of organizations
- voting records
Subject Guides
Look for subject guides in the arts, humanities, social sciences and professional programs. Each list varies and may include recommended primary source databases or other resources in that field. Even though a list may not include a primary source section, the librarian for that subject area can suggest resources and/or strategies for your topic. Consult the complete list of subject librarians if you need assistance in other areas of research.
History, Humanities, Social Sciences
Primary sources in these disciplines are original records created at the time historical events occurred or well after events in the form of memoirs and oral histories.
Examples include: Letters, manuscripts, diaries, rare books, historical photographs, first-hand accounts, or documentary sources on a subject, person, event or issue; newspapers written at the time of an event, song, or film from time period, historical maps, government reports or data, and more.
Primary Sources in Arts, Humanities, and Social Sciences
South Asia Primary Sources
Health Sciences, Sciences, Engineering
Primary sources in the sciences are original materials or information on which other research is based. Primary sources are also sets of data, such as health statistics, which have been tabulated, but not interpreted.
Examples include: Journal articles of original research (written by person who did the research), patents, conference papers, dissertations, technical reports, or something personal like Einstein’s diary).
Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sources in the Health Sciences
Patent Research Guide
- << Previous: Patents
- Next: Standards >>
- Primary Sources
- Definitions
- Documents - Printed & Published
- Objects and Artifacts
- Sound Recordings
- Visual Materials
- Digitized Sources
- Locating Sources
- Sources By Subject
- Evaluating Sources
- Documenting Sources / Copyright
- Research Tips
- Using Archives This link opens in a new window
Primary Sources Definition
What are primary sources .
Primary sources enable the researcher to get as close as possible to the truth of what actually happened during an historical event or time period. Primary source is a term used in a number of disciplines to describe source material that is closest to the person, information, period, or idea being studied. A primary source (also called original source ) is a document, recording, artifact, or other source of information that was created at the time under study, usually by a source with direct personal knowledge of the events being described. It serves as an original source of information about the topic.
Similar definitions are used in library science , and other areas of scholarship. In journalism, a primary source can be a person with direct knowledge of a situation, or a document created by such a person. Primary sources are distinguished from secondary sources , which cite, comment on, or build upon primary sources, though the distinction is not a sharp one.
Newspaper Research
- Historical Newspapers (ProQuest) This link opens in a new window Includes the New York Times, Chicago Tribune, LA Times, Christian Science Monitor, and more. Newspapers are in PDF format and provide a visual representation of the newspaper.
- ProQuest Central This link opens in a new window Includes both newspapers and scholarly journals
- Historical Newspapers The Guardian and The Observer Search The Guardian (1821-2003) and its sister paper, The Observer (1791-2003)
- New York Newspaper Archive This link opens in a new window Access New York Newspaper Archives and discover stories of the past with NewspaperArchive.com. The archive covers New York history from 1753-2023, with lots of content from smaller, local newspapers. Articles have been scanned as PDFs and include images and advertisements, and are full text searchable.
- America's Historical Newspapers This link opens in a new window America's Historical Newspapers includes articles from local and regional American and Hispanic American newspapers from all 50 states. Coverage dates from 1690 to the early 20th century. Articles have been scanned as PDFs and include images and advertisements, and are full text searchable.
- American Periodicals Series Online This link opens in a new window includes digitized images of the pages of American magazines and journals published from colonial days to the dawn of the 20th century, 1740-1940.
- Times Digital Archive (London) This link opens in a new window Provides full-text access to back issues of The Times newspaper. Dates of coverage: 1785 to 2006.
- Hispanic American Newspapers, 1808-1980 This link opens in a new window Hispanic American Newspapers, 1808-1980 provides access to searchable digitized copies of newspapers printed in the U.S. during the 19th and 20th centuries for a Hispanic readership. It features hundreds of monolingual and bilingual newspapers in Spanish and English, including many obscure titles from the 19th century.
- Global Newsstream This link opens in a new window Full text of 300+ U.S. and international news sources. Includes coverage of 150+ major U.S. and international newspapers such as The New York Times and the Times of London, plus hundreds of other news sources and news wires.
- Gale Newspaper Sources This link opens in a new window The Gale NewsVault is a portal to several historical collections of British newspapers and periodicals. It enables full-text searching across several titles simultaneously, including the Times of London, Financial Times, and Times Literary Supplement, along with aggregate newspaper and periodical collections covering the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries.
- Access World News This link opens in a new window Access World News provides the html full text and, for some titles, the pdf "as printed" visual representation, of articles from a variety of national and international news sources, including newspapers, digital-native news websites, television and radio transcripts, blogs, college and university newspapers, journals, magazines, and some audio and video. Most international titles are English language. Dates of coverage vary from title to title, but primarily span the late 20th century to present.
The Billy Rose Theatre Collection
TITLE: [Scene from Othello with Paul Robeson as Othello and Uta Hagen as Desdemona, Theatre Guild Production, Broadway, 1943-44] http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Robeson_Hagen_Othello.jpg SOURCE:Prints and Photographs Division Washington, D.C. 20540
The Billy Rose Theatre Collection of The New York Public Library is one of the largest and most comprehensive archives devoted to the theatrical arts. This image is a work of an employee of the United States Farm Security Administration or Office of War Information domestic photographic units, created during the course of the person's official duties. As a work of the U.S. federal government, the image is in the public domain.
- Billy Rose Collection NYPL The Billy Rose Theatre Division of The New York Public Library is one of the largest and most comprehensive archives devoted to the theatrical arts.
- New York Public Library Archives & Manuscripts On this site, you can search The New York Public Library's vast holdings, initiate a research visit, submit a query to an archivist, and access digitized material. Most Broadway shows can be viewed in the special collections. You will need a NYPL library card to view them.
- ArchiveGrid This link opens in a new window Thousands of libraries, museums, and archives have contributed nearly a million collection descriptions to ArchiveGrid.
- WorldCat - FirstSearch (OCLC) This link opens in a new window Search for books and more in libraries in the U.S. and around the world. Indicates when NYU Libraries holds a copy of a book and shows you nearby libraries with holdings.
- Internet Archive Internet Archive is a non-profit digital library offering free universal access to books, movies & music, as well as 456 billion archived web pages.
- Archives Unbound This link opens in a new window NYU is currently subscribing 14 collections:African America, Communists, and the National Negro Congress; Federal Response to Radicalism; Federal Surveillance of African Americans; Feminism in Cuba - 19th through 20th century archival document; Global Missions and Theology; India from Crown Rule to Republic; Testaments to the Holocaust (Documents and Rare Printed Materials from the Wiener Library, London); The Hindu Conspiracy Cases (Activities of the Indian Independence Movement in the U.S., 1908-1933); The Indian Army and Colonial Warfare on the Frontiers of India; The International Women’s Movement (The Pan Pacific Southeast Asia Women’s Association of the USA, 1950-1985); The Middle East Online - Arab-Israeli Relations; The Middle East Online - Iraq; U.S. and Iraqi Relations: U.S. Technical Aid; and, Witchcraft in Europe.
Historical Databases
An advert for P.T. Barnum's "Feejee Mermaid" in 1842 or thereabout. Author: P. T. Barnum or an employee, Source: Newspaper advert commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/File:Barnum_mermai... This image (or other media file) is in the public domain because its copyright has expired.
- America: History and Life with Full Text This link opens in a new window ndexes literature covering the history and culture of the United States and Canada, from prehistory to the present. The database indexes 1,700 journals and also includes citations and links to book and media reviews. Strong English-language journal coverage is balanced by an international perspective on topics and events, including abstracts in English of articles published in more than 40 languages. Publication dates of coverage: 1964 to present.
- Historical Abstracts with Full Text (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window Covers the history of the world (excluding the United States and Canada) from 1450 to the present, including world history, military history, women's history, history of education, and more. Indexes more than 1,700 academic historical journals in over 40 languages. Publication dates of coverage: 1955 to present.
- Theatre in Context Collection This link opens in a new window O’Dell’s Annals of the New York Stage, the Oxford University Press Companion series, and Greenwood’s American Theatre Companies series are just a few of the many in-copyright sources included in the Theatre in Context Collection. Placed alongside thousands of playbills, posters, photographs, and related theatrical ephemera, users will be able to paint a more comprehensive picture of the life and evolution of dramatic works.
- Shakespeare Collection This link opens in a new window The Shakespeare Collection provides access to general reference data, full-text scholarly periodicals, reprinted criticism, facsimile primary source material and the full-text annotated works from The Arden Shakespeare. Users can view page images of the First Folio, key Quartos, and major editions and adaptations of Shakespeare's works, plus works by Shakespeare's contemporaries and promptbooks from the 17th to the 20th century.
- Black Thought and Culture This link opens in a new window Contains 1297 sources with 1100 authors, covering the non-fiction published works of leading African-Americans. Particular care has been taken to index this material so that it can be searched more thoroughly than ever before. Where possible the complete published non-fiction works are included, as well as interviews, journal articles, speeches, essays, pamphlets, letters and other fugitive material.
- Periodicals Archive Online This link opens in a new window Provides full-text and full-image access to hundreds of journals published in the arts, humanities, social sciences, and areas of general popular interest. Each periodical is covered back to its first issue, regardless of when it began publication. International in scope, PAO covers periodicals in a number of Western languages.
- Accessible Archives This link opens in a new window Includes the following collections: African American Newspapers, The Civil War Part I. A Newspaper Perspective, The Pennsylvania Genealogical Catalog, Pennsylvania Newspaper Record, South Carolina Newspapers, and The Liberator. ** Within these collections are papers such as The Charleston Mercury, The Christian Recorder, The Colored American, Douglass Monthly, Frederick, Douglass Paper, Freedom's Journal, Godey's Lady's Book, The Liberator, The National Era, The New York Herald, The North Star, The Pennsylvania Gazette, The Pennsylvania Packet, The Maryland Gazette, Provincial Freeman, Richmond Enquirer, The South Carolina Gazette, The Gazette of the State of South Carolina, The South Carolina Gazette and Country Journal, The South Carolina and American General Gazette, Weekly Advocate.
- Early English Books Online (EEBO) This link opens in a new window Early English Books Online (EEBO) contains digital facsimile page images of virtually every work printed in England, Ireland, Scotland, Wales and British North America and works in English printed elsewhere from 1473-1700. Searchable full text is also available for a subset of the collection.
- Eighteenth Century Journals This link opens in a new window Eighteenth Century Journals brings together rare journals printed between 1685 and 1835, primarily in the British Isles (with some publications from India, the Caribbean, and Europe). Users can view and download page images and search transcribed full text for all journals in the collection.
- C19: The 19th Century Index This link opens in a new window C19: The 19th Century Index provides bibliographic coverage of nineteenth-century books, periodicals, official documents, newspapers and archives from the English-speaking world. This database includes the Wellesley Index to Victorian Periodicals (1824-1900), Poole's Index to Periodical Literature, Palmer's Index to The Times, the Nineteenth Century Short Title Catalogue, and more.
- Sixties: Primary Documents and Personal Narratives 1960 - 1974 This link opens in a new window This resource consists of diaries, letters, autobiographies and other memoirs, written and oral histories, manifestos, government documents, memorabilia, and scholarly commentary. With 150,000 pages of material at completion, this searchable collection is a resource for students and scholars researching this period in American history, culture, and politics.
- African American Archives (via Fold3) This link opens in a new window This full text resource offers access to original documents that reveal a side of the African American story that few have seen before.
- African American Experience This link opens in a new window Full-text digital resource exploring the history and culture of African Americans, as well as the greater Black Diaspora. Features access to full-text content from more than 400 titles, 3,000 slave narratives, over 2000 images, 5,000 primary sources, and 250 vetted Web sites.
Letters & Diaries /Oral Histories
- Oral History Online This link opens in a new window Provides in-depth indexing to more than 2,700 collections of Oral History in English from around the world. The collection provides keyword searching of almost 281,000 pages of full-text by close to 10,000 individuals from all walks of life.
- American Civil War: Letters and Diaries This link opens in a new window This database contains 2,009 authors and approximately 100,000 pages of diaries, letters and memoirs. Includes 4,000 pages of previously unpublished manuscripts such as the letters of Amos Wood and his wife and the diary of Maryland Planter William Claytor. The collection also includes biographies, an extensive bibliography of the sources in the database, and material licensed from The Civil War Day-by-Day by E.B. Long.
- British and Irish Women's Letters and Diaries This link opens in a new window Includes 10,000 pages of diaries and letters revealing the experiences of approximately 500 women. The collection now includes primary materials spanning more than 300 years. The collection also includes biographies and an extensive annotated bibliography of the sources in the database.
- North American Immigrant Letters, Diaries and Oral Histories This link opens in a new window North American Immigrant Letters, Diaries and Oral Histories includes 2,162 authors and approximately 100,000 pages of information, so providing a unique and personal view of what it meant to immigrate to America and Canada between 1800 and 1950. Contains contemporaneous letters, diaries, oral histories, interviews, and other personal narratives.
- North American Women's Letters and Diaries This link opens in a new window North American Women's Letters and Diaries includes the immediate experiences of 1,325 women and 150,000 pages of diaries and letters.
Gale Primary Sources
- Gale Primary Sources This link opens in a new window Gale Artemis is a groundbreaking research environment that integrates formerly disparate digital collections to enable innovative research. Gale Artemis provides an unprecedented, seamless research experience that helps students find a starting point, search across a wide array of materials and points in time, and discover new ways to analyze information.
Victorian Popular Culture
- Victorian Popular Culture An essential resource for the study of popular entertainment in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. This innovative portal invites users into the darkened halls, small backrooms and travelling venues that hosted everything from spectacular shows and bawdy burlesque, to the world of magic and spiritualist séances. ** The resource is divided into four self-contained sections: Moving Pictures, Optical Entertainments and the Advent of Cinema; Music Hall, Theatre and Popular Entertainment; Circuses, Sideshows and Freaks; Spiritualism, Sensation and Magic
Historical Image Collections
commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/File:Cushman_in_Ha... , The American actress Charlotte Cushman advertised in William Shakespeare's Hamlet at the Washington Theater in 1861. Author:Washington Theater, SOURCE:Public Library of Congress. this image (or other media file) is in the public domain because its copyright has expired.
- American Broadsides and Ephemera This link opens in a new window American Broadsides and Ephemera offers fully searchable images of approximately 15,000 broadsides printed between 1820 and 1900 and 15,000 pieces of ephemera printed between 1760 and 1900. The remarkably diverse subjects of these broadsides range from contemporary accounts of the Civil War, unusual occurrences and natural disasters to official government proclamations, tax bills and town meeting reports. Featuring many rare items, the pieces of ephemera include clipper ship sailing cards, early trade cards, bill heads, theater and music programs, stock certificates, menus and invitations documenting civic, political and private celebrations.
- Early American Imprints, Series I. Evans, 1639-1800 This link opens in a new window Search or browse the books, pamphlets, broadsides and other imprints listed in the renowned bibliography by Charles Evans.
- Early American Imprints, Series II. Shaw-Shoemaker, 1801-1819 This link opens in a new window Search or browse the books, pamphlets, broadsides and other imprints listed in the distinguished bibliography by Ralph R. Shaw and Richard H. Shoemaker. 1801-1819
- American Antiquarian Society (AAS) Historical Periodicals Collection (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window Provide digital access to the most comprehensive collection of American periodicals published between 1691 and 1877. Included digitized images of American magazines and journals never before available outside the walls of the American Antiquarian Society. The collection is available in five series: Series 1 (1691-1820) - Series 2 (1821-1837) - Series 3 (1838-1852) - Series 4 (1853-1865) - Series 5 (1866-1877)
Link to Bobst Special Collections
- NYU Special Collections Bobst Library's Special Collections department houses significant archival resources including materials from the Downtown Collection, which documents New York City's downtown arts scene from the 1970s through the early 1990s. Maria Irene Fornés and Richard Foreman are among the many artists whose materials are housed in the Downtown Collection.
- Fales It is especially strong in English literature from the middle of the 18th century to the present, documenting developments in the novel. The Downtown Collection documents the downtown New York art, performance, and literary scenes from 1975 to the present and is extremely rich in archival holdings, including extensive film and video objects.
- Tamiment One of the finest research collections in the country documenting the history of radical politics: socialism, communism, anarchism, utopian experiments, the cultural left, the New Left, and the struggle for civil rights and civil liberties.
Guide to International Collections
- SIBMAS International Directory of Performing Arts Collections and Institutions
Books Containing Primary Source Documents
- The mediaeval stage by Chambers, E. K. (Edmund Kerchever), 1866-1954 Call Number: Online versions avail.
- The Elizabethan stage by Chambers, E. K. (Edmund Kerchever), 1866-1954 Call Number: PN2589 .C4 1965 4 vol. plus online version avail
- The diary of Samuel Pepys by Pepys, Samuel, 1633-1703 Call Number: Avail. online
- A history of theatrical art in ancient and modern times. by Mantzius, Karl, 1860-1921 Call Number: PN2106 .M313 1970 4 vol. also internet access
- Ben Jonson by Ben Jonson Call Number: online access
- << Previous: Visual Materials
- Next: Digitized Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 25, 2024 4:51 PM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/primary
Primary Sources Research Guide
- What Are Primary Sources?
- What Are Secondary Sources?
- Examples of Primary & Secondary Sources
- Where to Look for Primary Sources
Get Primary Sources by Subject
Many library subject guides contain sections on primary sources for those subjects. BELOW you can also see a list of research guides that have been tagged "primary sources."
Still have questions? Please get in touch with the librarian for your subject area for more information about specific primary sources in your field.
Defining Primary Sources
- Primary sources are original materials that provide direct evidence or first-hand testimony concerning a topic or event -- firsthand records created by people who actually participated in or remembered an event and reported on the event and their reactions to it.
- Primary sources can be contemporary sources created at the time when the event occurred (e.g., letters and newspaper articles) or later (such as, memoirs and oral history interviews).
- Primary sources may be published or unpublished. Unpublished sources include unique materials (e.g., family papers) often referred to as archives and manuscripts.
- What constitutes a primary source varies by discipline -- see Primary Sources by Discipline below . How the researcher uses the source generally determines whether it is a primary source or not.
*This material is used with permission from the University of Pittsburgh Library's research guide on Primary Sources
Primary Sources by Discipline
The definition of a primary source varies depending upon the academic discipline and the context in which it is used.
1. In the humanities , a primary source could be defined as something that was created either during the time period being studied or afterward by individuals reflecting on their involvement in the events of that time.

Examples from the humanities:
Art: painting, photograph, print, sculpture, film or other work of art, sketch book, architectural model or drawing, building or structure, letter, organizational records, personal account by artist History: artifact, diary, government report, interview, letter, map, news report, oral history, organizational records, photograph, speech, work of art Literature: interview, letter, manuscript, personal account by writer, poem, work of fiction or drama, contemporary review Music: score, sound recording, contemporary review, letter, personal account by composer or musician
2. In the social sciences , the definition of a primary source would be expanded to include numerical data that has been gathered to analyze relationships between people, events, and their environment.

Examples from the social sciences:
Anthropology: artifact, field notes, fossil, photograph Business: market research or surveys, anything that documents a corporation's activities, such as annual reports, meeting minutes, legal documents, marketing materials, and financial records. Communication: websites, blogs, broadcast recordings and transcripts, advertisements and commercials, public opinion polls, and magazines (e.g., Rolling Stone ). Economics: company statistics, consumer survey, data series Geography: field notes, census data, maps, satellite images, and aerial photographs. Law: code, statute, court opinion, legislative report Psychology: case study, clinical case report, experimental replication, follow-up study, longitudinal study, treatment outcome study Sociology: cultural artifact, interview, oral history, organizational records, statistical data, survey
3. In the natural sciences , a primary source could be defined as a report of original findings or ideas. These sources often appear in the form of research articles with sections on methods and results.

Examples in the natural sciences:
Biology, Chemistry, etc: research or lab notes, genetic evidence, plant specimens, technical reports, and other reports of original research or discoveries (e.g., conference papers and proceedings, dissertations, scholarly articles).
*This material is used with permission from the Lafayette College Library research guide on primary sources . Image 1: "Massachusetts Bay Colony 1776" CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 Tom Woodward: Flickr Image 2: "data" CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 CyberHades: Flickr Image 3: "Katydid 50x Magnification Wing, Coventry, CT" CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 Macroscopic Solutions: Flickr
Examples of Primary Sources
Primary sources typically include such items as:
- manuscripts, letters, first-person diaries, memoirs, personal journals, interviews, speeches, oral histories, and other materials individuals used to describe events in which they were participants or observers. Many of these materials frequently are referred to as " papers ";
- records of government agencies and other organizations, including such documents as parliamentary debates, proceedings of organization meetings, conferences, etc. Many of these materials frequently are referred to as " archives ";
- original documents such as birth certificates, marriage and baptismal registers, wills, trial transcripts, etc.;
- published materials written at the time of the event, including newspapers, news magazines, advertising, cartoons, and other ephemeral publications such as pamplets and flyers;
- contemporary creative works of literature, art, and music, such as novels, paintings, compositions, poems, etc.;
- contemporary photographs, maps, audio recordings, television and radio broadcasts, and moving pictures;
- Internet communications including email, listservs, and blogs;
- statistical and numeric data collected by various government and private agencies, including census data, opinion polls, and other surveys;
- research reports and case studies in the sciences or social sciences;
- artifacts of all kinds such as coins, clothing, fossils, furniture, and musical instruments from the time period under study
Primary sources sometimes can be ambiguous and contradictory, relecting a specific person's opinions and contemporary cultural influences on them. For that very reason such sources are invaluable tools for developing your own interpretations and reaching your own conclusions about what is going on at a point in time.
- Next: What Are Secondary Sources? >>
- Last Updated: Mar 1, 2024 9:31 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.emory.edu/main/primary_sources_overview
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Introduction to primary source research, definitions, examples of primary sources by discipline, head of bancroft public services.
- Archives terminology
- How to use library catalogs
- How to use finding aids/collection guides
- How to plan your visit to an archive
- Using digitized primary sources
- Evaluating primary sources

A primary source is an eyewitness account of an event or data obtained through original statistical or scientific research.
What are some examples of primary sources?
- Photographs
- Official records (government reports, transcripts, court records, death certificates, etc.)
- Contemporary news reports (newspapers, telecasts, radio addresses, etc.)
- Polls and Public Opinion Data
- Laws, statutes, hearings
Secondary Source
A secondary source interprets and analyzes primary sources. These sources are one or more steps removed from the event. Secondary sources may include pictures of primary sources or quotes from them. Some types of secondary sources include: journal/magazine articles, textbooks, commentaries, and encyclopedias.
Newspapers may be either primary or secondary. Most articles in newspapers are secondary, but reporters may be considered as witnesses to an event. Any topic on the media coverage of an event or phenomenon would treat newspapers as a primary source.
Source: https://guides.libraries.indiana.edu/primarysources

- Next: Archives terminology >>
- Last Updated: Apr 8, 2024 3:55 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/primarysourceresearch101
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Primary Sources
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Primary sources are materials that were either created during the time period being studied or were created at a later date by a participant in the events being studied, such as, a childhood memoir. They are original documents [i.e., they are not about another document or account] and reflect the individual viewpoint of a participant or observer. Primary sources represent direct, uninterpreted records of the subject of your research study.
NOTE : Information about identifying and using primary resources materials, particularly those held in the USC Libraries, can be found in the Libraries Primary Sources Research Guide .
Value of Primary Sources
Primary sources enable you to get as close as possible to understanding the lived experiences of others and discovering what actually happened during an event. However, what constitutes a primary or secondary source depends on the context in which it is being used. For example, David McCullough’s biography of John Adams could be a secondary source for a paper about John Adams, but a primary source for a paper about how various historians have interpreted the life of John Adams. When in doubt, ask a librarian for assistance!
Reviewing primary source material can be of value in improving your overall research paper because they :
- Are original materials,
- Were created from the time period involved,
- Have not been filtered through interpretation or evaluation by others, and
- Represent original thinking or experiences, reporting of a discovery, or the sharing of new information.
Examples of primary documents you could review as part of your overall study include :
- Artifacts [e.g. furniture or clothing, all from the time under study]
- Audio recordings [e.g. radio programs]
- Internet communications on email, listservs, blogs, Twitter, Facebook, and other social media platforms
- Interviews [e.g., oral histories, telephone, e-mail]
- Newspaper articles written at the time
- Original official documents [e.g., birth certificate, will, marriage license, trial transcript]
- Personal correspondence [e.g., letters]
- Photographs
- Proceedings of meetings, conferences and symposia
- Records of organizations, government agencies [e.g. annual report, treaty, constitution, government document]
- Survey Research [e.g., market surveys, public opinion polls]
- Transcripts of radio and television programs
- Video recordings
- Works of art, architecture, literature, and music [e.g., paintings, sculptures, musical scores, buildings, novels, poems]
Bahde, Anne. Using Primary Sources: Hands-On Instructional Exercises . Santa Barbara, CA: Libraries Unlimited, 2014; Brundage, Anthony. Going to the Sources: A Guide to Historical Research and Writing . Malden, MA: Wiley Blackwell, 2013; Daniels, Morgan and Elizabeth Yakel. “Uncovering Impact: The Influence of Archives on Student Learning.” Journal of Academic Librarianship 39 (September 2013): 414-422; Krause, Magia G. “Undergraduates in the Archives: Using an Assessment Rubric to Measure Learning.” The American Archivist 73 (Fall/Winter 2010): 507-534; Rockenbach, Barbara. “Archives, Undergraduates, and Inquiry-Based Learning: Case Studies from Yale University Library.” The American Archivist 74 (Spring/Summer 2011): 297-311; Weiner, Sharon A., Sammie Morris , and Lawrence J. Mykytiuk. "Archival Literacy Competencies for Undergraduate History Majors." The American Archivist 78 (Spring/Summer 2015): 154-180.
- << Previous: Evaluating Sources
- Next: Secondary Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 12:53 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Marquette University
Raynor Memorial Libraries
- marquette.edu //
- Contacts //

- Research Guides
- Course Guides
- Primary Sources: An Introduction
Primary Sources: An Introduction: Home
Primary source research, what is a primary source, is it a primary source, what are some examples of primary sources, primary sources at marquette.
Report access issues here →
Library Liaison for History, Philosophy, Political Science, & Theology

This is introductory description of what can be considered a primary source for the purposes of a research paper. Students and faculty have access to a wide range of primary source databases. It is highly recommended that student contact a liaison librarian for a research consultation when undertaking a research project using these sources. See the link below to set up a consult:
- Schedule a Research Consultation
A primary source is a first-hand or contemporary account of an event. Primary sources date to the time an event took place and offer original account or thoughts on a topic that has not been framed by second-hand interpretation. Primary sources are usually original materials, but they may be reproduced digitally or republished in a physical format.
This guide from Fresno State University can help you determine if something is a Primary Source. If you answer 'yes' to any of the following questions, the resource is most like a Primary Source.
- Did the author personally witness or experience the subject in question?
- Does the author know about this subject because of personal experience rather than having just read about it?
- Is this source a diary, letter, memoir, autobiography, oral history, or interview of a person with first hand experience of the subject?
- Is this source an official document or record published at the time of the event by the government, courts, or another organization?
- Is this source a newspaper or magazine article written at the time of the event?
- Is this a creative work such as a novel, poem, art or music piece created by a firsthand witness of the subject in question?
- Is this an excerpt from a primary source, such as the constitution or a letter written by a Civil War soldier that has been imbedded in a secondary source, such as a textbook? Remember, secondary sources may include reprints of primary sources.
- Is this an artifact or relic such as jewelry, pottery, clothing, music, art, architecture, dance or weaponry that was used by witnesses of the subject in question?
- Is this a compilation of raw scientific data or statistics, such as census statistics published by the U.S. Census Bureau, that is being published without commentary or interpretation?
- newspapers or other news accounts
- personal accounts in diaries, letters, interviews, or oral histories
- government documents or publications
- speeches
- photographs/ video footage
- internal organizational documents
- memoirs or autobiographies
- novels, poems, or other works of art
Please note that, in the correct context, many things that are typically considered to be Secondary Sources - such as autobiographies or books about an event or historical period - can also be considered primary sources. For example, if you are writing an analysis of how historians have viewed a certain event over time, written histories on the event can be used as primary sources.
There are many resources for primary source materials at Marquette. Physical examples of these include newspaper microfilms, government or non-profit reports, reproductions of historical documents or text, and published diaries or autobiographies. The link below connects to digitized primary sources databases that can accessed by Marquette students and faculty. Please use the research consultation link above for guidance on any of these materials.
- Digital Primary Source Materials at Marquette
- Last Updated: Feb 21, 2024 9:48 AM
- URL: https://libguides.marquette.edu/primarysources
- Guide Owner
1355 W. Wisconsin Ave.
Milwaukee , WI 53233
Information Services: (414) 288-7556
Key Resources
- Library contacts
- Library floor plans
- Borrowing policies
- Library accounts
- eMarq (email)
- Desire2Learn (D2L)
Libraries A to Z
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Problem with this webpage?
Report an accessibility problem. To report another problem, please contact: [email protected]
Privacy Policy Legal Disclaimer Non-Discrimination Policy
Educator Resources

Finding Primary Sources for Teachers and Students
Finding primary sources.
Primary Sources from DocsTeach Thousands of online primary source documents from the National Archives to bring the past to life as classroom teaching tools.
National Archives Catalog Find online primary source materials for classroom & student projects from the National Archive's online catalog (OPA).
Beginning Research Activities Student activities designed to help you navigate the National Archives resources and web site.
Online Exhibits Exhibits featuring online documents, photos and primary sources from the National Archives
Our Documents 100 Milestone Documents of American History
Getting Started with Research How to start researching records at the National Archives. Finding your topic, identifying records, planning a visit, and more.
Online Research Tools & Aids Introduction to catalogs, databases, and other online resources.
Citing Primary Sources Citing Records in the National Archives of the United States
Primary Source Research and Discovery
- What are archives?
- What are primary sources?
- Where do I find primary sources for the Sciences at CSUDH?
- Where do I find primary sources at other institutions?
- What is a Finding Aid?
- How do I use and evaluate primary sources?
- How do I start?
What are Primary Sources?
Primary sources.
A primary source provides direct or firsthand evidence about an event, object, person, or work of art. Primary sources include historical and legal documents, eyewitness accounts, results of experiments, statistical data, pieces of creative writing, audio and video recordings, speeches, and art objects. Interviews, surveys, fieldwork, and Internet communications via email, blogs, listservs, and newsgroups are also primary sources. In the natural and social sciences, primary sources are often empirical studies—research where an experiment was performed or a direct observation was made. The results of empirical studies are typically found in scholarly articles or papers delivered at conferences.
Secondary Sources
Secondary sources describe, discuss, interpret, comment upon, analyze, evaluate, summarize, and process primary sources. Secondary source materials can be articles in newspapers or popular magazines, book or movie reviews, or articles found in scholarly journals that discuss or evaluate someone else's original research.
Definition courtesy of Ithaca College Library Research Guide , Primary vs Secondary section.
Clues for Identifying Primary Sources
Clues for identifying primary source characteristics.
Characteristics of Primary Sources
- Primary sources can either be first-hand observation/analysis or accounts contemporary with the events described.
- Primary sources document events, people, viewpoints of the time.
- When research is more era, rather than event-driven, the scope of possible primary sources broadens considerably.
- Primary sources represent one person's perspective; frequently will be used with secondary/tertiary sources to broaden the lens through which a researcher is looking at an event, era, or phenomenon.
- It is important when using anything as a primary source that the researcher be cognizant of and sensitive to the bias of the observer/analyzer that created the primary source, and also to the broader cultural biases of the era in which the primary source was created.
- The researcher's perspective, or the arguments or points for which a researcher plans to use a primary source as evidence, is significant in determining what sources will be primary.
- Reproductions of primary sources remain primary for many research purposes.
- Some attributes are based more on the perspective represented in the source and context in which the source is being used by researcher.
Bullet points courtesy of The University of California at Irvine Libraries .
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Examples
Primary, secondary, tertiary sources.
The infographic below gives the definition, characteristics, and examples of primary, secondary and tertiary sources. Notice, journal articles are listed for the sciences as a primary source and a secondary source for non-scientific disciplines. At the top of the graphic is the publishing timeline . As you can see primary sources are generally published first, then secondary sources. In the research timeline , secondary sources are generally consulted first to provide needed context for primary source research.
- << Previous: What are archives?
- Next: Where do I find primary sources at CSUDH? >>
- Last Updated: Jan 29, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.csudh.edu/primary-sources

Primary Sources: What They Are and Where to Find Them
What is a primary source.
- Finding Primary Sources in the UWRF Library
A primary source is an original object or document created during the time under study. Primary sources vary by discipline and can include historical and legal documents, diaries, letters, family records, speeches, interviews, autobiographies, film, government documents, eye witness accounts, results of an experiment, statistical data, pieces of creative writing, and art objects. In the natural and social sciences, the results of an experiment or study are typically found in scholarly articles or papers delivered at conferences, so those articles and papers that present the original results are considered primary sources.
A secondary source is something written about a primary source. Secondary sources include comments on, interpretations of, or discussions about the original material. You can think of secondary sources as second-hand information. If I tell you something, I am the primary source. If you tell someone else what I told you, you are the secondard source. Secondary source materials can be articles in newspapers or popular magazines, book or movie reviews, or articles found in scholarly journals that evaluate or criticize someone else's original research.
Research versus Review
Scientific and other peer reviewed journals are excellent sources for primary research sources. However, not every article in those journals will be an article with original research. Some will include book reviews and other materials that are more obviously secondary sources . More difficult to differentiate from original research articles are review articles . Both types of articles will end with a list of References (or Works Cited). Review articles are often as lengthy or even longer that original research articles. What the authors of review articles are doing is analysing and evaluating current research or investigations related to a specific topic, field, or problem. They are not primary sources since they review previously published material. They can be helpful for identifying potentially good primary sources, but they aren't primary themselves. Primary research articles can be identified by a commonly used format. If an article contains the following elements, you can count on it being a primary research article. Look for sections entitled Methods (sometimes with variations, such as Materials and Methods), Results (usually followed with charts and statistical tables), and Discussion . You can also read the abstract to get a good sense of the kind of article that is being presented. If it is a review article instead of a research article, the abstract should make that clear. If there is no abstract at all, that in itself may be a sign that it is not a primary resource. Short research articles, such as those found in Science and similar scientific publications that mix news, editorials, and forums with research reports, may not include any of those elements. In those cases look at the words the authors use, phrases such as "we tested," "we used," and "in our study, we measured" will tell you that the article is reporting on original research.
Primary or Secondary: You Decide
The distinction between types of sources can get tricky, because a secondary source may also be a primary source. DoVeanna Fulton's book on slave narratives, for example, can be looked at as both a secondary and a primary source. The distinction may depend on how you are using the source and the nature of your research. If you are researching slave narratives, the book would be a secondary source because Fulton is commenting on the narratives. If your assignment is to write a book review of Speaking Power , the book becomes a primary source, because you are commenting, evaluating, and discussing DoVeanna Fulton's ideas.
You can't always determine if something is primary or secondary just because of the source it is found in. Articles in newspapers and magazines are usually considered secondary sources. However, if a story in a newspaper about the Iraq war is an eyewitness account, that would be a primary source. If the reporter, however, includes additional materials he or she has gathered through interviews or other investigations, the article would be a secondary source. An interview in the Rolling Stone with Chris Robinson of the Black Crowes would be a primary source, but a review of the latest Black Crowes album would be a secondary source. In contrast, scholarly journals include research articles with primary materials, but they also have review articles that are not, or in some disciplines include articles where scholars are looking at primary source materials and coming to new conclusions.
For your thinking and not just to confuse you even further, some experts include tertiary sources as an additional distinction to make. These are sources that compile or, especially, digest other sources. Some reference materials and textbooks are considered tertiary sources when their chief purpose is to list or briefly summarize or, from an even further removed distance, repackage ideas. This is the reason that you may be advised not to include an encyclopedia article in a final bibliography.
The above material was adapted from the excellent explanation written by John Henderson found on Ithaca College's library website http://www.ithacalibrary.com/sp/subjects/primary and is used with permission.
- Next: Finding Primary Sources in the UWRF Library >>
- Last Updated: Nov 8, 2023 3:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uwrf.edu/primarysources

Primary Sources Guide
Understanding research sources.
- Evaluating Primary Sources
- African American Studies
- Latin American & Latina/o Studies
- Native American & Indigenous Studies
- Citing Primary Sources
We are here to help! Get help via chat, text, or email.
Click the Chat Now tab located at the top right of this page.
text 704-707-4960
You can also make an appointment with a librarian.
- What are Primary Sources?
- What are Secondary Sources?
- What are Tertiary Sources?
A primary source is a first-hand account from a person or organization who:
- Created an original work
- Participated in new scientific discoveries
- Witnessed an event
Some examples of primary sources include:
- Art and artifacts
- Autobiographies, diaries, and memoirs
- Interviews and oral histories
- Novels and poetry
- Photographs
- Data and surveys
Why are primary sources useful? Primary sources are useful to:
- Observe and analyze an event from an eyewitness perspective
- Develop your own opinions and explanations
- Learn if you agree or disagree with the authors of secondary/tertiary sources and their conclusions
A secondary source has the following qualities:
- It comments on or analyzes something
- It often summarizes or interprets primary sources
- It's usually written by someone who was not directly involved or an eyewitness
Some examples of secondary sources include:
- Analysis or criticism, such as literary criticism
- Biographies
- Essays and reviews
Why are secondary sources useful? Secondary sources are useful because they:
- Help you consider diverse viewpoints about a topic
- Organize and outline information in an approachable way
- Offer information and analysis from experts
Remember, secondary sources are often based on studying and analyzing primary sources . Another way to think about it? Your research paper is a secondary source because you're analyzing and interpreting other sources.
A tertiary source has the following qualities:
- It lists and compiles information without additional analysis
- It repackages important ideas and information from other primary and secondary sources
Some examples of tertiary sources include:
- Directories of local, state, and national organizations
- Encyclopedias and dictionaries
- Guidebooks and handbooks
Why are tertiary sources useful? Tertiary sources are useful because they help you:
- Gather background information about a topic or concept
- Find a variety of information in one source
- Provide information in a concise and compact way
Examples of Primary Sources vs. Other Sources
- Communications
One area of study at Central Piedmont where primary sources are often used is History . Here are some examples:
- Primary Source = Autobiography : Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass: An American Slave by Frederick Douglass
- Secondary Source = Biography : Frederick Douglass: Prophet of Freedom by David W. Blight

Another area of study at Central Piedmont where primary sources often come into play is English . Here are some examples:
- Primary Source = Novel : Love in the Time of Cholera by Gabriel García Márquez
- Secondary Source = Literary Criticism : Gabriel García Márquez in Retrospect: A Collection Book , edited by Gene H. Bell-Villada

One other area of study at Central Piedmont where primary sources often come into play is Communications . Here are some examples:
- Primary Sources = Memoir : Deaf Utopia: A Memoir--And a Love Letter to a Way of Life by Nyle DiMarco
- Secondary Sources = Journal Article : "Curriculum and Instruction for Deaf and Hard of Hearing Students: Evidence from the Past—Considerations for the Future" (2023) by Maria C. Hartman, Elaine R. Smolen, and Brynne Powell
- Tertiary Sources = Reference Book : American Sign Language: A Step-by-Step Guide to Signing by Suzie Chafin

Credit : Austin Community College's Primary Sources guide served as the inspiration and model for this LibGuide.
Additional Help
- Next: Evaluating Primary Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 5, 2024 8:10 AM
- URL: https://researchguides.cpcc.edu/primary-sources
Fall library services
SPECIAL COLLECTIONS AND ARCHIVES
- MAIN LIBRARY HOURS Loading...
- SPECIAL COLLECTIONS HOURS Loading...
- MUSIC LIBRARY HOURS Loading...
- SCIENCE LIBRARY HOURS Loading...
- Furman University
- Special Collections & Archives
Information For Students
I have to write a research paper using primary sources. where do i start.
- What are Special Collections and Archives?
- What is the difference between Primary and Secondary sources?
- How do I cite primary source materials?
Primary sources are created by individuals who participated in or witnessed an event and recorded that event during or immediately after the event.
Explanation:
A student activist during the war writing about protest activities has created a memoir. This would be a primary source because the information is based on her own involvement in the events she describes. Similarly, an antiwar speech is a primary source. So is the arrest record of student protesters. A newspaper editorial or article, reporting on a student demonstration is also a primary source.
Deeds, wills, court documents, military records, tax records, census records, diaries, journals, letters, account books, advertisements, newspapers, photographs, and maps are primary sources.
Secondary sources are created by someone who was either not present when the event occurred or removed from it in time. We use secondary sources for overview information, and to help familiarize ourselves with a topic and compare that topic with other events in history.
History books, encyclopedias, historical dictionaries, and academic articles are secondary sources.
If you've never written a research paper using primary sources, it is important to understand that the process is different from using only secondary sources. Many students discover that finding and gaining access to primary source documents can be difficult. The Library website has a valuable guide to locating primary source documents. Follow the link below to be redirected to that guide:
https://libguides.furman.edu/resources/primary-sources
- Students are encouraged to seek help from the Special Collections Librarian or Research Librarians to aid in their research projects. Librarians will be able to aid students in a variety of ways including helping to locate primary source materials.
After locating appropriate primary sources, it is necessary for students to analyze and interpret them. To many students, this task can seem arduous, if not overwhelming. There are many resources available in the library as well as online, which are helpful. The National Archives website has very useful analysis worksheets that can help students to determine the significance of primary source documents. Links to PDF files of these worksheets are listed below:
Written Document | Artifact | Cartoon | Map | Motion Picture | Photograph | Poster | Sound Recording
- << Previous: What is the difference between Primary and Secondary sources?
- Next: How do I cite primary source materials? >>
- Last Updated: Oct 21, 2021 2:47 PM
- URL: https://libguides.furman.edu/special-collections/for-students
What Is a Primary Source?
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms - Definition and Examples
Diane Diederich / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In research and academics, a primary source refers to information collected from sources that witnessed or experienced an event firsthand. These can be historical documents , literary texts, artistic works, experiments, journal entries, surveys, and interviews. A primary source, which is very different from a secondary source , is also called primary data.
The Library of Congress defines primary sources as "the raw materials of history—original documents and objects which were created at the time under study," in contrast to secondary sources , which are "accounts or interpretations of events created by someone without firsthand experience," ("Using Primary Sources").
Secondary sources are often meant to describe or analyze a primary source and do not give firsthand accounts; primary sources tend to provide more accurate depictions of history but are much harder to come by.
Characteristics of Primary Sources
There are a couple of factors that can qualify an artifact as a primary source. The chief characteristics of a primary source, according to Natalie Sproull, are: "(1) [B]eing present during the experience, event or time and (2) consequently being close in time with the data. This does not mean that data from primary sources are always the best data."
Sproull then goes on to remind readers that primary sources are not always more reliable than secondary sources. "Data from human sources are subject to many types of distortion because of such factors as selective recall, selective perceptions, and purposeful or nonpurposeful omission or addition of information. Thus data from primary sources are not necessarily accurate data even though they come from firsthand sources," (Sproull 1988).
Original Sources
Primary sources are often called original sources, but this is not the most accurate description because you're not always going to be dealing with original copies of primary artifacts. For this reason, "primary sources" and "original sources" should be considered separate. Here's what the authors of "Undertaking Historical Research in Literacy," from Handbook of Reading Research , have to say about this:
"The distinction also needs to be made between primary and original sources . It is by no means always necessary, and all too often it is not possible, to deal only with original sources. Printed copies of original sources, provided they have been undertaken with scrupulous care (such as the published letters of the Founding Fathers), are usually an acceptable substitute for their handwritten originals." (E. J. Monaghan and D. K. Hartman, "Undertaking Historical Research in Literacy," in Handbook of Reading Research , ed. by P. D. Pearson et al. Erlbaum, 2000)
When to Use Primary Sources
Primary sources tend to be most useful toward the beginning of your research into a topic and at the end of a claim as evidence, as Wayne Booth et al. explain in the following passage. "[Primary sources] provide the 'raw data' that you use first to test the working hypothesis and then as evidence to support your claim . In history, for example, primary sources include documents from the period or person you are studying, objects, maps, even clothing; in literature or philosophy, your main primary source is usually the text you are studying, and your data are the words on the page. In such fields, you can rarely write a research paper without using primary sources," (Booth et al. 2008).
When to Use Secondary Sources
There is certainly a time and place for secondary sources and many situations in which these point to relevant primary sources. Secondary sources are an excellent place to start. Alison Hoagland and Gray Fitzsimmons write: "By identifying basic facts, such as year of construction, secondary sources can point the researcher to the best primary sources , such as the right tax books. In addition, a careful reading of the bibliography in a secondary source can reveal important sources the researcher might otherwise have missed," (Hoagland and Fitzsimmons 2004).
Finding and Accessing Primary Sources
As you might expect, primary sources can prove difficult to find. To find the best ones, take advantage of resources such as libraries and historical societies. "This one is entirely dependent on the assignment given and your local resources; but when included, always emphasize quality. ... Keep in mind that there are many institutions such as the Library of Congress that make primary source material freely available on the Web," (Kitchens 2012).
Methods of Collecting Primary Data
Sometimes in your research, you'll run into the problem of not being able to track down primary sources at all. When this happens, you'll want to know how to collect your own primary data; Dan O'Hair et all tell you how: "If the information you need is unavailable or hasn't yet been gathered, you'll have to gather it yourself. Four basic methods of collecting primary data are field research, content analysis, survey research, and experiments. Other methods of gathering primary data include historical research, analysis of existing statistics, ... and various forms of direct observation," (O'Hair et al. 2001).
- Booth, Wayne C., et al. The Craft of Research . 3rd ed., University of Chicago Press, 2008.
- Hoagland, Alison, and Gray Fitzsimmons. "History." Recording Historic Structures. 2nd. ed., John Wiley & Sons, 2004.
- Kitchens, Joel D. Librarians, Historians, and New Opportunities for Discourse: A Guide for Clio's Helpers . ABC-CLIO, 2012.
- Monaghan, E. Jennifer, and Douglas K. Hartman. "Undertaking Historical Research in Literacy." Handbook of Reading Research. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2002.
- O'Hair, Dan, et al. Business Communication: A Framework for Success . South-Western College Pub., 2001.
- Sproull, Natalie L. Handbook of Research Methods: A Guide for Practitioners and Students in the Social Sciences. 2nd ed. Scarecrow Press, 1988.
- "Using Primary Sources." Library of Congress .
- Secondary Sources in Research
- Primary and Secondary Sources in History
- How to Prove Your Family Tree Connections
- Research in Essays and Reports
- Five Steps to Verifying Online Genealogy Sources
- Pros and Cons of Secondary Data Analysis
- Understanding Secondary Data and How to Use It in Research
- Documentation in Reports and Research Papers
- What Is a Research Paper?
- 6 Skills Students Need to Succeed in Social Studies Classes
- How to Use Libraries and Archives for Research
- How to Cite Genealogy Sources
- Glossary of Historical Terms
- Definition and Examples of Quotation in English Grammar
- How to Determine a Reliable Source on the Internet
- Fashion Throughout History
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples
Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples
Published on January 14, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 12, 2024.
Primary research is a research method that relies on direct data collection , rather than relying on data that’s already been collected by someone else. In other words, primary research is any type of research that you undertake yourself, firsthand, while using data that has already been collected is called secondary research .
Primary research is often used in qualitative research , particularly in survey methodology, questionnaires, focus groups, and various types of interviews . While quantitative primary research does exist, it’s not as common.
Table of contents
When to use primary research, types of primary research, examples of primary research, advantages and disadvantages of primary research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
Primary research is any research that you conduct yourself. It can be as simple as a 2-question survey, or as in-depth as a years-long longitudinal study . The only key is that data must be collected firsthand by you.
Primary research is often used to supplement or strengthen existing secondary research. It is usually exploratory in nature, concerned with examining a research question where no preexisting knowledge exists. It is also sometimes called original research for this reason.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Primary research can take many forms, but the most common types are:
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Observational studies
- Interviews and focus groups
Surveys and questionnaires collect information about a group of people by asking them questions and analyzing the results. They are a solid choice if your research topic seeks to investigate something about the characteristics, preferences, opinions, or beliefs of a group of people.
Surveys and questionnaires can take place online, in person, or through the mail. It is best to have a combination of open-ended and closed-ended questions, and how the questions are phrased matters. Be sure to avoid leading questions, and ask any related questions in groups, starting with the most basic ones first.
Observational studies are an easy and popular way to answer a research question based purely on what you, the researcher, observes. If there are practical or ethical concerns that prevent you from conducting a traditional experiment , observational studies are often a good stopgap.
There are three types of observational studies: cross-sectional studies , cohort studies, and case-control studies. If you decide to conduct observational research, you can choose the one that’s best for you. All three are quite straightforward and easy to design—just beware of confounding variables and observer bias creeping into your analysis.
Similarly to surveys and questionnaires, interviews and focus groups also rely on asking questions to collect information about a group of people. However, how this is done is slightly different. Instead of sending your questions out into the world, interviews and focus groups involve two or more people—one of whom is you, the interviewer, who asks the questions.
There are 3 main types of interviews:
- Structured interviews ask predetermined questions in a predetermined order.
- Unstructured interviews are more flexible and free-flowing, proceeding based on the interviewee’s previous answers.
- Semi-structured interviews fall in between, asking a mix of predetermined questions and off-the-cuff questions.
While interviews are a rich source of information, they can also be deceptively challenging to do well. Be careful of interviewer bias creeping into your process. This is best mitigated by avoiding double-barreled questions and paying close attention to your tone and delivery while asking questions.
Alternatively, a focus group is a group interview, led by a moderator. Focus groups can provide more nuanced interactions than individual interviews, but their small sample size means that external validity is low.
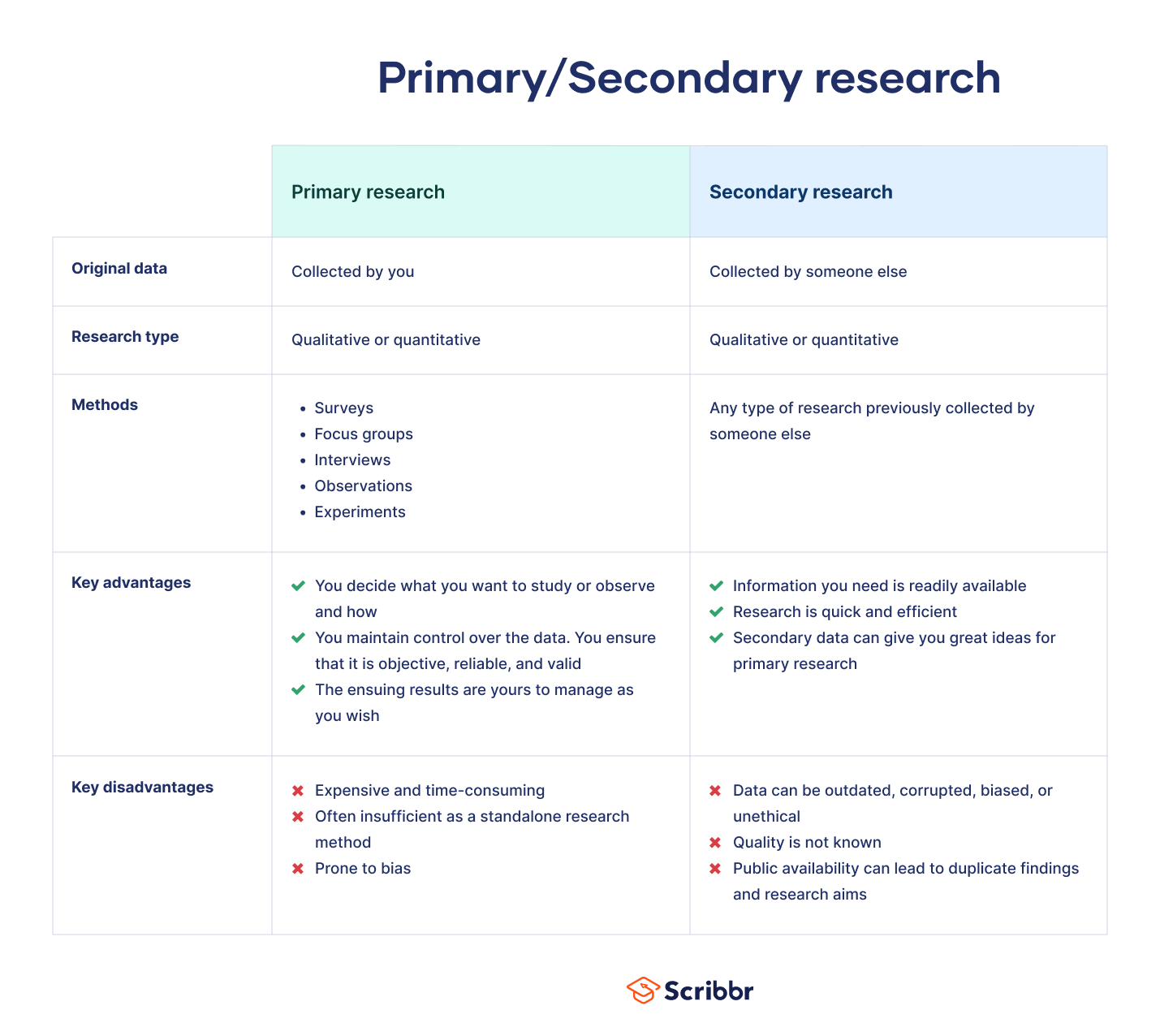
Primary research can often be quite simple to pursue yourself. Here are a few examples of different research methods you can use to explore different topics.
Primary research is a great choice for many research projects, but it has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of primary research
Advantages include:
- The ability to conduct really tailored, thorough research, down to the “nitty-gritty” of your topic . You decide what you want to study or observe and how to go about doing that.
- You maintain control over the quality of the data collected, and can ensure firsthand that it is objective, reliable , and valid .
- The ensuing results are yours, for you to disseminate as you see fit. You maintain proprietary control over what you find out, allowing you to share your findings with like-minded individuals or those conducting related research that interests you for replication or discussion purposes.

Disadvantages of primary research
Disadvantages include:
- In order to be done well, primary research can be very expensive and time consuming. If you are constrained in terms of time or funding, it can be very difficult to conduct your own high-quality primary research.
- Primary research is often insufficient as a standalone research method, requiring secondary research to bolster it.
- Primary research can be prone to various types of research bias . Bias can manifest on the part of the researcher as observer bias , Pygmalion effect , or demand characteristics . It can occur on the part of participants as a Hawthorne effect or social desirability bias .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
The 3 main types of primary research are:
Exploratory research aims to explore the main aspects of an under-researched problem, while explanatory research aims to explain the causes and consequences of a well-defined problem.
There are several methods you can use to decrease the impact of confounding variables on your research: restriction, matching, statistical control and randomization.
In restriction , you restrict your sample by only including certain subjects that have the same values of potential confounding variables.
In matching , you match each of the subjects in your treatment group with a counterpart in the comparison group. The matched subjects have the same values on any potential confounding variables, and only differ in the independent variable .
In statistical control , you include potential confounders as variables in your regression .
In randomization , you randomly assign the treatment (or independent variable) in your study to a sufficiently large number of subjects, which allows you to control for all potential confounding variables.
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analyzing data from people using questionnaires.
When conducting research, collecting original data has significant advantages:
- You can tailor data collection to your specific research aims (e.g. understanding the needs of your consumers or user testing your website)
- You can control and standardize the process for high reliability and validity (e.g. choosing appropriate measurements and sampling methods )
However, there are also some drawbacks: data collection can be time-consuming, labor-intensive and expensive. In some cases, it’s more efficient to use secondary data that has already been collected by someone else, but the data might be less reliable.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2024, January 12). Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/primary-research/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, data collection | definition, methods & examples, observer bias | definition, examples, prevention, what is qualitative research | methods & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

Performing Academic Research: Primary and secondary sources
- The research process
- Creating a research plan
- Primary and secondary sources
- Academic vs. non-academic information
- Evaluating information: The PAARC test
Identifying Primary and Secondary Sources
What is a primary source.
Primary sources are firsthand accounts of events, ideas, or statements. They are usually created at the time of an event or very soon after.
Primary sources can come in many different forms, including diaries, letters, photographs, art, maps, video and film, sound recordings, interviews, newspapers, magazines, novels, poems, short stories, autobiographies, or memoirs. The exact form of a primary source is not important. It is the content and context of the material that makes it a primary source. For example, a novel written in 2012 about the Peloponnesian War isn’t a primary source for information about the Peloponnesian War (unless the author is somehow over two thousand years old). However, the same novel is a primary source for information about the author’s ideas, philosophy, and writing style.
When trying to identify a Primary Source, ask yourself:
- Was it created at the time of an event, or very soon after?
- Was it created by someone who saw or heard an event themselves?
- Is it a personal record of an event?
If you answer to any of the above is “yes,” then it is likely that you are looking at a Primary Source.
What is a Secondary Source?
Secondary sources report, describe, comment on, or analyze the experiences or work of others.
A secondary source is at least once removed from the primary source. It reports on the original work, the direct observation, or the firsthand experience. It will often use primary sources as examples.
Secondary sources can include books, textbooks, newspapers, biographies, journal articles, movies and magazines. As with primary sources, the format is less important than the information being presented. If the source seeks to report, describe, comment on or analyze an original work, direct observation, or firsthand experience of another person, it is a secondary source.
Eamon, Michael. “Defining Primary and Secondary Sources.” Library and Archives Canada , Library and Archives Canada,
27 May 2010, https://www.collectionscanada.gc.ca/education/008-3010-e.html.
Payton, Melissa. The Prentice Hall Guide to Evaluating Online Resources with Research Navigator 2004 . Pearson Education Inc., 2004.
- << Previous: Creating a research plan
- Next: Academic vs. non-academic information >>
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2024 11:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.marianopolis.edu/research


Research Basics
- What Is Research?
- Types of Research
- Secondary Research | Literature Review
- Developing Your Topic
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Evaluating Sources
- Responsible Conduct of Research
- Additional Help
What Is a Primary or Secondary Source?
At its simplest, a primary source is an account of something that happened by the people who were there, such as participants or witnesses. A secondary source is an account of something that happened by people who were NOT there, often framed as a review, summary, or analysis. Technically, a secondary source is a review or analysis of primary sources—there’s also what’s called a tertiary source, that analyzes secondary sources, and so on.
What Does That Mean to Me As a Student or Researcher at Illinois Tech?
The most common type of primary source used at Illinois Tech is the research paper written by the researcher(s) who actually carried out the work. These papers are typically published as articles in peer-reviewed journals but could also be in the form of a thesis or dissertation, research report, case study, clinical trial, etc. In addition to written reports, various ancillary materials can be primary sources. These include data, surveys, questionnaires, interviews, computer code, images, and other supporting materials that were generated or collected as part of the work.
Secondary sources may be published in peer-reviewed journals as well but most often occur in popular media, like websites, blogs, newspapers, etc. Secondary sources in peer-reviewed journals are easy to identify because they use the word “review” in the title or abstract and don’t present any new research. Also considered as secondary sources are any ancillary materials that were re-used or repurposed from other research.
Interestingly, primary source research papers almost always include a review of prior research as part of the introduction or as a “literature review” section. The primary source material only includes those parts that talk about the new research: the methodology, results, discussion of results, conclusions, or other similar sections.
Why Is It Important to Use Primary Sources?
Simply put, people make mistakes. There’s an old party game called Telephone where a phrase is whispered from one person to the next around the room and at the end of the game, everybody is amused at how the phrase or its meaning has changed. Using secondary, tertiary, or other sources is like playing Telephone with your research. Reviews and other secondary accounts are summaries, so even at their best they omit parts of the original research and lack the detail and nuance of the original paper. At worst, a review author could entirely misunderstand or misrepresent the original research.
Does That Mean I Should Only Use Primary Sources?
No, not at all. For older, well-established research that’s had ample time to be reviewed and consolidated into the general knowledge of the field, there’s no need to go back to primary source material unless you’re challenging the conventional interpretation.
- << Previous: Developing Your Topic
- Next: Evaluating Sources >>
- Last Updated: Dec 21, 2023 3:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.iit.edu/research_basics

Organizing Academic Research Papers: Primary Sources
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
Primary sources were either created during the time period being studied or were created at a later date by a participant in the events being studied, such as, a childhood memoir. They are original documents (i.e., they are not about another document or account) and reflect the individual viewpoint of a participant or observer. Primary sources represent direct, uninterpreted records of the subject of your research study.
Value of Primary Sources
Primary sources enable you to get as close as possible to understanding the lived experiences of others and discovering what actually happened during an event. However, what constitutes a primary or secondary source depends on the context in which it is being used. For example, David McCullough’s biography of John Adams could be a secondary source for a paper about John Adams, but a primary source for a paper about how various historians have interpreted the life of John Adams. When in doubt, ask a librarian for assistance!
Reviewing primary source material can be of value in improving your overall research paper because they :
- Are original materials,
- Were created from the time period involved,
- Have not been filtered through interpretation or evaluation by others, and
- Represent original thinking or experiences, reporting of a discovery, or the sharing of new information.
Examples of primary documents you could review as part of your overall study include : * Artifacts (e.g. furniture or clothing, all from the time under study); * Audio recordings (e.g. radio programs) * Diaries; * Internet communications on email, listservs; * Interviews (e.g., oral histories, telephone, e-mail); * Letters; * Newspaper articles written at the time; * Original Documents (i.e. birth certificate, will, marriage license, trial transcript); * Patents; * Photographs * Proceedings of Meetings, conferences and symposia; * Records of organizations, government agencies (e.g. annual report, treaty, constitution, government document); * Speeches; * Survey Research (e.g., market surveys, public opinion polls); * Transcripts of radio and television programs * Video recordings; * Works of art, architecture, literature, and music (e.g., paintings, sculptures, musical scores, buildings, novels, poems).
- << Previous: Evaluating Sources
- Next: Secondary Sources >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON

- Master Your Homework
- Do My Homework
Exploring Research Papers as Primary Sources
The use of research papers as primary sources is an increasingly important yet often overlooked component of modern scholarly inquiry. In this article, we will explore the potential that exists in utilizing research papers to enhance one’s understanding and appreciation of a given subject matter. We will examine how these documents can provide invaluable insight into historical trends, reveal nuances about particular individuals or groups, and broaden our collective knowledge base across multiple disciplines. Furthermore, by delving into the ways in which researchers are deploying such works as primary source material within their own research processes, we hope to expand upon existing techniques while uncovering new methods for employing them effectively.
I. Introduction to Exploring Research Papers as Primary Sources
Research papers can provide insightful primary sources for conducting research . Research paper are often used as the basis of exploratory or in-depth studies. By examining a particular topic from different angles and perspectives, they offer an opportunity to make discoveries that wouldn’t otherwise be possible through traditional methods. It is important to understand the role of research papers when exploring primary sources.
In this section, we will discuss how research papers are primary sources , what types of information they contain, and why it is beneficial to use them as part of your exploration process. We will also cover some strategies on where to find quality research material and look at ways in which you can critically assess the validity of any given source before incorporating it into your project. Ultimately, understanding how are research papers primary sources , will enable you to conduct meaningful and rigorous investigations into various topics with confidence!
II. Analyzing the Data Contained in a Research Paper
When analyzing data contained in a research paper, it is important to consider if the information being presented can be considered primary source material or not. Research papers are often based on existing studies and findings; therefore, they may use another person’s work as their own evidence. It is essential for readers to determine if the content within a research paper should be regarded as original or secondary sources of information before deciding whether to rely upon it.
In order to identify primary sources from secondary ones, there must firstly be an understanding that research papers are primary sources when written by experts in the field and designed specifically with the purpose of examining new theories and ideas related to particular topics. In addition, those researching similar fields who add citations from different literature into their works also indicate that such materials could potentially serve as primary source documents too.
On one hand, readers need confirmation that any claims made within these papers are , indeed authentic; while on the other hand every piece requires careful analysis so far-reaching conclusions can drawn about what has been discussed throughout them – this will require ensuring all aspects have been properly researched using quality resources which provide verifiable evidence.
- For example, investigating which type of statistical tests were used alongside qualitative methods like interviews will help reader form concrete understandings regarding both results obtained from experiments.
- Moreover, establishing how authors collected raw data– either through participant surveys/observations etc.– further establishes credibility around assertions proposed throughout these reports.
. Lastly it’s vital for those reading academic journals or other forms of literary pieces connected with scientific discourse ascertain whether supporting references provided by authors including journal articles cited in bibliographies etc., are , themselves valid or else risk making invalid claims stemming from false knowledge bases found therein .
III. Interpreting Results from Published Studies
In order to interpret results from published studies, it is important to understand the difference between primary and secondary sources of research papers. Primary sources are those that provide original data or information directly related to a specific research question. Secondary sources may present ideas based on analysis of existing data, but they do not generally contain new data or facts about the topic under investigation.
Interpreting results from published studies requires a comprehensive understanding of both primary and secondary source materials as well as an appreciation for how researchers use these resources in their work. In evaluating whether any given piece of literature can be considered “primary” one must consider several factors including its reliability and timeliness: is the paper reporting original findings which have been rigorously tested? Are research papers primary sources? If so, how does this impact our interpretation? Additionally, we need to ask if other authors have come to similar conclusions when citing the same study; often multiple interpretations exist depending upon who read it and what aspect was being studied in particular detail at any given time period by different authors/researchers!
IV. Examining the Methodology of a Study
and understanding.
In this section, we will look into examining the methodology of a study to understand if research papers are primary sources in scientific inquiry.
One of the most important things that must be determined when conducting any type of research is what kind of data should be collected, as well as how it should be collected. For example, while experiments can provide empirical evidence and surveys can capture opinions or attitudes – neither approach is suitable for all types of studies. This means researchers need to identify an appropriate methodology based on the goals and objectives they set out to achieve with their study. Furthermore, certain methodological approaches may determine whether or not a research paper is considered a primary source.
- Observational studies involve collecting information about behavior without directly manipulating or intervening.
The main purpose here is usually descriptive rather than causal; observers simply record what they see without influencing outcomes through manipulation/intervention so these studies often lack proof that one thing caused another which means their results cannot conclusively prove cause-effect relationships between variables – though they could indicate something worth exploring further.
- Experiments
, on the other hand, manipulate one or more independent variables (IVs) by either introducing new treatments/stimuli or withholding existing ones in order to compare how different levels influence one dependent variable (DV). Experiments offer direct evidence supporting causality between manipulated IVs and observed DVs making them highly reliable sources – however if conducted incorrectly there may still remain doubts regarding validity.
For any researcher studying a topic using methods from both observational data collection techniques and experimental interventions involving human subjects it’s critical for them to consider carefully whether their output falls under ‘primary’ sources criteria before attempting publication since much relies upon such distinction – particularly related questions like: Are Research Papers Primary Sources? A thorough review process within respected peer-reviewed journals is generally required prior to acceptance which involves assessing whether authors have followed accepted rules & standards during project execution including proper measures taken throughout ethical considerations linked with experimentation if relevant among many other factors ultimately dictating journal approval decision once adequately evaluated according to protocol established by particular institution(s).
V. Assessing Implications and Application of Findings
In the field of research and scholarly work, there are two main sources available: primary and secondary resources. Primary sources are original documents or artifacts created during a certain time period that contain information about a particular topic. When considering whether research papers can be classified as primary sources it is important to consider several factors such as authorship, format, purpose, accuracy/validity of content and currency.
- Authorship – Are the authors credible? Do they have expertise in their given subject matter?
- Format – Is the material presented in an easily understood way for readers to comprehend its contents?
VI. Evaluating Criticisms and Strengths of a Research Paper VII. Conclusion: The Value of Using Research Papers as Primary Sources
The importance of research papers as primary sources has been established in the discussion so far. Evaluating criticisms and strengths is key to determining whether these papers are useful for academic work or not. To do this, certain aspects need to be taken into account when assessing a paper.
- Research Gap: The first thing that should be evaluated is the originality of the paper; its ability to fill gaps in existing knowledge by providing innovative solutions.
- Methodology Used: It’s also important to consider how data was collected and what methods were used during analysis, e.g., qualitative/quantitative techniques.
- Clarity of Writing: Another element worth exploring is the way ideas have been conveyed through language – does it lack clarity? Are complex words being overused? Does it use jargon unnecessarily?
These questions can help identify both potential strengths and weaknesses which will ultimately decide if research papers are valuable primary sources or not. Nevertheless, there may still remain some ambiguity when examining these criteria due to differences in personal interpretations regarding research quality.
In conclusion, understanding where one stands with regards to evaluating criticism and strengths for any given piece of work related to research papers helps answer many lingering questions about their value as primary sources.. Researching well-defined topics enables more accurate evaluations than subjective opinions from individuals who may only possess general familiarity with a particular field. Are research papers primary source material then depends on looking at all evidence objectively within an appropriate context. . With reliable information comes confidence that one’s own decisions based on valid arguments will stand up against scrutiny since rigorous assessment has already taken place when researching if a paper qualifies as a suitable primary source . In summary, an informed evaluation process allows one make rational choices between multiple options effectively without compromising accuracy of using them as legitimate resources where appropriate . English: The exploration of research papers as primary sources can be a highly rewarding experience for those interested in history and related topics. While the process may at first appear daunting, understanding how to effectively source these materials can greatly enrich one’s learning and provide valuable insight into past events. With some dedication, persistence, and care, it is possible to take full advantage of this invaluable resource while furthering our knowledge of times gone by.
info This is a space for the teal alert bar.
notifications This is a space for the yellow alert bar.

Research Process
- Brainstorming
- Explore Google This link opens in a new window
- Explore Web Resources
- Explore Background Information
- Explore Books
- Explore Scholarly Articles
- Narrowing a Topic
- Primary and Secondary Resources
- Academic, Popular & Trade Publications
- Scholarly and Peer-Reviewed Journals
- Grey Literature
- Clinical Trials
- Evidence Based Treatment
- Scholarly Research
- Database Research Log
- Search Limits
- Keyword Searching
- Boolean Operators
- Phrase Searching
- Truncation & Wildcard Symbols
- Proximity Searching
- Field Codes
- Subject Terms and Database Thesauri
- Reading a Scientific Article
- Website Evaluation
- Article Keywords and Subject Terms
- Cited References
- Citing Articles
- Related Results
- Search Within Publication
- Database Alerts & RSS Feeds
- Personal Database Accounts
- Persistent URLs
- Literature Gap and Future Research
- Web of Knowledge
- Annual Reviews
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- Finding Seminal Works
- Exhausting the Literature
- Finding Dissertations
- Researching Theoretical Frameworks
- Research Methodology & Design
- Tests and Measurements
- Organizing Research & Citations This link opens in a new window
- Scholarly Publication
- Learn the Library This link opens in a new window
Primary Sources
Primary resources contain first-hand information, meaning that you are reading the author’s own account on a specific topic or event that s/he participated in. Examples of primary resources include scholarly research articles, books, and diaries. Primary sources such as research articles often do not explain terminology and theoretical principles in detail. Thus, readers of primary scholarly research should have foundational knowledge of the subject area. Use primary resources to obtain a first-hand account to an actual event and identify original research done in a field. For many of your papers, use of primary resources will be a requirement.
Examples of a primary source are:
- Original documents such as diaries, speeches, manuscripts, letters, interviews, records, eyewitness accounts, autobiographies
- Empirical scholarly works such as research articles, clinical reports, case studies, dissertations
- Creative works such as poetry, music, video, photography
How to locate primary research in NU Library:
- From the Library's homepage, begin your search in NavigatorSearch or select a subject-specific database from the A-Z Databases .
- Use the Scholarly/Peer-Reviewed Journal limiter to narrow your search to journal articles.
- Once you have a set of search results, remember to look for articles where the author has conducted original research. A primary research article will include a literature review, methodology, population or set sample, test or measurement, discussion of findings and usually future research directions.
Secondary Sources
Secondary sources describe, summarize, or discuss information or details originally presented in another source; meaning the author, in most cases, did not participate in the event. This type of source is written for a broad audience and will include definitions of discipline specific terms, history relating to the topic, significant theories and principles, and summaries of major studies/events as related to the topic. Use secondary sources to obtain an overview of a topic and/or identify primary resources. Refrain from including such resources in an annotated bibliography for doctoral level work unless there is a good reason.
Examples of a secondary source are:
- Publications such as textbooks, magazine articles, book reviews, commentaries, encyclopedias, almanacs
Locate secondary resources in NU Library within the following databases:
- Annual Reviews (scholarly article reviews)
- Credo Reference (encyclopedias, dictionaries, handbooks & more)
- Ebook Central (ebooks)
- ProQuest (book reviews, bibliographies, literature reviews & more )
- SAGE Reference Methods, SAGE Knowledge & SAGE Navigator (handbooks, encyclopedias, major works, debates & more)
- Most other Library databases include secondary sources.
Beginning the Resarch Process Workshop
This workshop introduces to the beginning stages of the research process, focusing on identifying different types of information, as well as gathering background information through electronic books.
- Beginning the Research Process Workshop Outline
Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Determining Information Needs
- Next: Academic, Popular & Trade Publications >>
- Last Updated: Apr 14, 2024 12:14 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchprocess

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information
ENGLISH 206: Women in Literature
- Primary vs Secondary Sources
- Research Help
Ask A Librarian
About this guide.
This guide explains the differences between primary and secondary sources. Because the definitions can often change depending on the subject you are studying, ask your instructor if you have questions.
Primary Sources
A primary source is a document or piece of evidence written or created during the time period you are studying. A primary source allows you to examine evidence firsthand without being affected by other opinions.
Types of Primary Sources:
- Memos/E-mails
- Speeches (both the text of the speech & the giving of the speech)
- Manuscripts
- Autobiographies
- Laws, legislation, court rulings
- Newspaper & magazine articles as an event happened
- News footage
- Artifacts: buildings, clothes, jewelry, toys, fossils
- Journal articles reporting original research or an experiment
- Official records of governments, agencies, organizations: meeting minutes, reports, vital records (e.g., Census records)
- Creative works: poetry, novels, drama, music, art, photography, movies, scripts, performances
- Technical reports (i.e., accounts of work done on research projects)
Secondary Sources
A secondary source describes or analyzes a primary source. These sources are one step removed from the actual event and allow you to understand what scholars and other experts know about your topic.
Types of Secondary Sources:
- Books or articles that explain or review research works
- Histories and critical commentaries
- Encyclopedias, dictionaries, and other reference materials
- Newspaper articles, magazine articles, and webpages authored by people who had nothing to do with the actual research
- Journal article that summarizes the results of other researchers' experiments
Comparing Sources: Primary vs. Secondary
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Research Help >>
- Last Updated: Apr 12, 2024 12:43 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uwgb.edu/english206
AI Index Report
Welcome to the seventh edition of the AI Index report. The 2024 Index is our most comprehensive to date and arrives at an important moment when AI’s influence on society has never been more pronounced. This year, we have broadened our scope to more extensively cover essential trends such as technical advancements in AI, public perceptions of the technology, and the geopolitical dynamics surrounding its development. Featuring more original data than ever before, this edition introduces new estimates on AI training costs, detailed analyses of the responsible AI landscape, and an entirely new chapter dedicated to AI’s impact on science and medicine.
Read the 2024 AI Index Report
The AI Index report tracks, collates, distills, and visualizes data related to artificial intelligence (AI). Our mission is to provide unbiased, rigorously vetted, broadly sourced data in order for policymakers, researchers, executives, journalists, and the general public to develop a more thorough and nuanced understanding of the complex field of AI.
The AI Index is recognized globally as one of the most credible and authoritative sources for data and insights on artificial intelligence. Previous editions have been cited in major newspapers, including the The New York Times, Bloomberg, and The Guardian, have amassed hundreds of academic citations, and been referenced by high-level policymakers in the United States, the United Kingdom, and the European Union, among other places. This year’s edition surpasses all previous ones in size, scale, and scope, reflecting the growing significance that AI is coming to hold in all of our lives.
Steering Committee Co-Directors

Ray Perrault
Steering committee members.

Erik Brynjolfsson

John Etchemendy

Katrina Ligett

Terah Lyons

James Manyika

Juan Carlos Niebles

Vanessa Parli

Yoav Shoham

Russell Wald
Staff members.

Loredana Fattorini

Nestor Maslej
Letter from the co-directors.
A decade ago, the best AI systems in the world were unable to classify objects in images at a human level. AI struggled with language comprehension and could not solve math problems. Today, AI systems routinely exceed human performance on standard benchmarks.
Progress accelerated in 2023. New state-of-the-art systems like GPT-4, Gemini, and Claude 3 are impressively multimodal: They can generate fluent text in dozens of languages, process audio, and even explain memes. As AI has improved, it has increasingly forced its way into our lives. Companies are racing to build AI-based products, and AI is increasingly being used by the general public. But current AI technology still has significant problems. It cannot reliably deal with facts, perform complex reasoning, or explain its conclusions.
AI faces two interrelated futures. First, technology continues to improve and is increasingly used, having major consequences for productivity and employment. It can be put to both good and bad uses. In the second future, the adoption of AI is constrained by the limitations of the technology. Regardless of which future unfolds, governments are increasingly concerned. They are stepping in to encourage the upside, such as funding university R&D and incentivizing private investment. Governments are also aiming to manage the potential downsides, such as impacts on employment, privacy concerns, misinformation, and intellectual property rights.
As AI rapidly evolves, the AI Index aims to help the AI community, policymakers, business leaders, journalists, and the general public navigate this complex landscape. It provides ongoing, objective snapshots tracking several key areas: technical progress in AI capabilities, the community and investments driving AI development and deployment, public opinion on current and potential future impacts, and policy measures taken to stimulate AI innovation while managing its risks and challenges. By comprehensively monitoring the AI ecosystem, the Index serves as an important resource for understanding this transformative technological force.
On the technical front, this year’s AI Index reports that the number of new large language models released worldwide in 2023 doubled over the previous year. Two-thirds were open-source, but the highest-performing models came from industry players with closed systems. Gemini Ultra became the first LLM to reach human-level performance on the Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) benchmark; performance on the benchmark has improved by 15 percentage points since last year. Additionally, GPT-4 achieved an impressive 0.97 mean win rate score on the comprehensive Holistic Evaluation of Language Models (HELM) benchmark, which includes MMLU among other evaluations.
Although global private investment in AI decreased for the second consecutive year, investment in generative AI skyrocketed. More Fortune 500 earnings calls mentioned AI than ever before, and new studies show that AI tangibly boosts worker productivity. On the policymaking front, global mentions of AI in legislative proceedings have never been higher. U.S. regulators passed more AI-related regulations in 2023 than ever before. Still, many expressed concerns about AI’s ability to generate deepfakes and impact elections. The public became more aware of AI, and studies suggest that they responded with nervousness.
Ray Perrault Co-director, AI Index
Our Supporting Partners

Analytics & Research Partners

Stay up to date on the AI Index by subscribing to the Stanford HAI newsletter.
Prestigious cancer research institute has retracted 7 studies amid controversy over errors

Seven studies from researchers at the prestigious Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have been retracted over the last two months after a scientist blogger alleged that images used in them had been manipulated or duplicated.
The retractions are the latest development in a monthslong controversy around research at the Boston-based institute, which is a teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School.
The issue came to light after Sholto David, a microbiologist and volunteer science sleuth based in Wales, published a scathing post on his blog in January, alleging errors and manipulations of images across dozens of papers produced primarily by Dana-Farber researchers . The institute acknowledged errors and subsequently announced that it had requested six studies to be retracted and asked for corrections in 31 more papers. Dana-Farber also said, however, that a review process for errors had been underway before David’s post.
Now, at least one more study has been retracted than Dana-Farber initially indicated, and David said he has discovered an additional 30 studies from authors affiliated with the institute that he believes contain errors or image manipulations and therefore deserve scrutiny.
The episode has imperiled the reputation of a major cancer research institute and raised questions about one high-profile researcher there, Kenneth Anderson, who is a senior author on six of the seven retracted studies.
Anderson is a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and the director of the Jerome Lipper Multiple Myeloma Center at Dana-Farber. He did not respond to multiple emails or voicemails requesting comment.
The retractions and new allegations add to a larger, ongoing debate in science about how to protect scientific integrity and reduce the incentives that could lead to misconduct or unintentional mistakes in research.
The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute has moved relatively swiftly to seek retractions and corrections.
“Dana-Farber is deeply committed to a culture of accountability and integrity, and as an academic research and clinical care organization we also prioritize transparency,” Dr. Barrett Rollins, the institute’s integrity research officer, said in a statement. “However, we are bound by federal regulations that apply to all academic medical centers funded by the National Institutes of Health among other federal agencies. Therefore, we cannot share details of internal review processes and will not comment on personnel issues.”
The retracted studies were originally published in two journals: One in the Journal of Immunology and six in Cancer Research. Six of the seven focused on multiple myeloma, a form of cancer that develops in plasma cells. Retraction notices indicate that Anderson agreed to the retractions of the papers he authored.
Elisabeth Bik, a microbiologist and longtime image sleuth, reviewed several of the papers’ retraction statements and scientific images for NBC News and said the errors were serious.
“The ones I’m looking at all have duplicated elements in the photos, where the photo itself has been manipulated,” she said, adding that these elements were “signs of misconduct.”
Dr. John Chute, who directs the division of hematology and cellular therapy at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and has contributed to studies about multiple myeloma, said the papers were produced by pioneers in the field, including Anderson.
“These are people I admire and respect,” he said. “Those were all high-impact papers, meaning they’re highly read and highly cited. By definition, they have had a broad impact on the field.”
Chute said he did not know the authors personally but had followed their work for a long time.
“Those investigators are some of the leading people in the field of myeloma research and they have paved the way in terms of understanding our biology of the disease,” he said. “The papers they publish lead to all kinds of additional work in that direction. People follow those leads and industry pays attention to that stuff and drug development follows.”
The retractions offer additional evidence for what some science sleuths have been saying for years: The more you look for errors or image manipulation, the more you might find, even at the top levels of science.
Scientific images in papers are typically used to present evidence of an experiment’s results. Commonly, they show cells or mice; other types of images show key findings like western blots — a laboratory method that identifies proteins — or bands of separated DNA molecules in gels.
Science sleuths sometimes examine these images for irregular patterns that could indicate errors, duplications or manipulations. Some artificial intelligence companies are training computers to spot these kinds of problems, as well.
Duplicated images could be a sign of sloppy lab work or data practices. Manipulated images — in which a researcher has modified an image heavily with photo editing tools — could indicate that images have been exaggerated, enhanced or altered in an unethical way that could change how other scientists interpret a study’s findings or scientific meaning.
Top scientists at big research institutions often run sprawling laboratories with lots of junior scientists. Critics of science research and publishing systems allege that a lack of opportunities for young scientists, limited oversight and pressure to publish splashy papers that can advance careers could incentivize misconduct.
These critics, along with many science sleuths, allege that errors or sloppiness are too common , that research organizations and authors often ignore concerns when they’re identified, and that the path from complaint to correction is sluggish.
“When you look at the amount of retractions and poor peer review in research today, the question is, what has happened to the quality standards we used to think existed in research?” said Nick Steneck, an emeritus professor at the University of Michigan and an expert on science integrity.
David told NBC News that he had shared some, but not all, of his concerns about additional image issues with Dana-Farber. He added that he had not identified any problems in four of the seven studies that have been retracted.
“It’s good they’ve picked up stuff that wasn’t in the list,” he said.
NBC News requested an updated tally of retractions and corrections, but Ellen Berlin, a spokeswoman for Dana-Farber, declined to provide a new list. She said that the numbers could shift and that the institute did not have control over the form, format or timing of corrections.
“Any tally we give you today might be different tomorrow and will likely be different a week from now or a month from now,” Berlin said. “The point of sharing numbers with the public weeks ago was to make clear to the public that Dana-Farber had taken swift and decisive action with regard to the articles for which a Dana-Farber faculty member was primary author.”
She added that Dana-Farber was encouraging journals to correct the scientific record as promptly as possible.
Bik said it was unusual to see a highly regarded U.S. institution have multiple papers retracted.
“I don’t think I’ve seen many of those,” she said. “In this case, there was a lot of public attention to it and it seems like they’re responding very quickly. It’s unusual, but how it should be.”
Evan Bush is a science reporter for NBC News. He can be reached at [email protected].
Children excluded in primary school less likely to pass GCSEs, new research warns
Charity Chance UK has conducted a study into the long-term impacts of children being excluded or suspended in primary school - finding that almost all pupils excluded at that age had a special education need or disability.

News correspondent @AlicePorterTV
Monday 15 April 2024 05:57, UK

The majority of children excluded in primary school don't pass their GCSEs in English and Maths, according to new research.
The charity Chance UK looked at the long-term impact of children being excluded or suspended in primary school .
The study tracked various year groups across their school lives and included data from 3.2 million pupils in England.
They found that 97% of those excluded at primary school had a special educational need or disability.
Mary-Anne's* son has ADHD, before his diagnosis schools struggled to cope with his behaviour.
She said: "My son was permanently excluded at five years old; they referred him to go to a pupil referral unit.
"He would have been the only five year old in the building. I was like 'No, we're not doing this'.
More on Education

Labour commits to keeping Tories' free childcare expansion plans

Nearly a quarter of teachers use alcohol to cope with stresses of the job, survey suggests

'Transgender ideology is a cult', sacked teacher tells employment tribunal
Related Topics:
"My son was the angry boy. I was saying there must be a reason why he gets so angry and then be completely calm - but they [the teachers] were just like 'no he's really naughty'."

More than 22,000 children aged six years and under were excluded or suspended in primary schools in England in 2022.
But teaching unions have raised concerns that, since the pandemic, behaviour in classrooms has significantly worsened with teachers struggling to cope.
Tom Bennett, Department for Education behaviour advisor, says exclusions are a last resort.
He said: "Exclusions are done in the most extreme circumstances for example when a child is violent towards a teacher or abused another student or persistently disrupted lessons.
"You can't teach a lesson if someone is throwing chairs at you. Exclusions are incredibly rare; the average primary school excludes one child every 17 years."
Read more from Sky News: Minibus of football fans overturns in crash with 17 people injured Injured survivors from Manchester bombing suing MI5 Lockdown famous osprey welcomes earliest egg of season

Keep up with all the latest news from the UK and around the world by following Sky News
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

Mary-Anne's son was helped by Chance UK which matches students with mentors to provide support to children with behavioural and emotional difficulties.
The charity is calling on the government for additional funding for specialist support in primary schools.
A Department for Education spokesperson said: "For pupils at risk of exclusion, we've set out a new model for alternative provision schools to work with mainstream schools and provide targeted support early on, helping improve behaviour, attendance and reduce the risk of exclusions."
*Real names have been omitted in this report.
Related Topics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Enrich your research with primary sources Enrich your research with primary sources. Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more. ... Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016) Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
For digitized archival material together with other kinds of primary sources: Finding Primary Sources Online offers general instructions for finding primary sources online and a list of resources by region and country; Online Primary Source Collections for the History of Science lists digital collections at Harvard and beyond by topic.
U.S. History Primary Sources Timeline - Explore important topics and moments in U.S. history through historical primary sources from the Library's collections. Search the online collections Successful searches of the online collections of the Library of Congress, as with any archival research institution, begin with an understanding of what ...
When you do research, you have to gather information and evidence from a variety of sources. Primary sources provide raw information and first-hand evidence. Examples include interview transcripts, statistical data, and works of art. Primary research gives you direct access to the subject of your research. Secondary sources provide second-hand ...
Primary sources in the sciences are original materials or information on which other research is based. Primary sources are also sets of data, such as health statistics, which have been tabulated, but not interpreted. ... Journal articles of original research (written by person who did the research), patents, conference papers, dissertations ...
Primary sources enable the researcher to get as close as possible to the truth of what actually happened during an historical event or time period. Primary source is a term used in a number of disciplines to describe source material that is closest to the person, information, period, or idea being studied. A primary source (also called original ...
Primary sources may be published or unpublished. Unpublished sources include unique materials (e.g., family papers) often referred to as archives and manuscripts. What constitutes a primary source varies by discipline -- see Primary Sources by Discipline below. How the researcher uses the source generally determines whether it is a primary ...
A primary source is an eyewitness account of an event or data obtained through original statistical or scientific research. What are some examples of primary sources? Secondary Source. A secondary source interprets and analyzes primary sources. These sources are one or more steps removed from the event. Secondary sources may include pictures of ...
Reviewing primary source material can be of value in improving your overall research paper because they: Are original materials, Were created from the time period involved, Have not been filtered through interpretation or evaluation by others, and; Represent original thinking or experiences, reporting of a discovery, or the sharing of new ...
This is introductory description of what can be considered a primary source for the purposes of a research paper. Students and faculty have access to a wide range of primary source databases. It is highly recommended that student contact a liaison librarian for a research consultation when undertaking a research project using these sources.
Finding Primary Sources. Primary Sources from DocsTeach Thousands of online primary source documents from the National Archives to bring the past to life as classroom teaching tools.. National Archives Catalog Find online primary source materials for classroom & student projects from the National Archive's online catalog (OPA).. Beginning Research Activities Student activities designed to help ...
In the natural and social sciences, primary sources are often empirical studies—research where an experiment was performed or a direct observation was made. The results of empirical studies are typically found in scholarly articles or papers delivered at conferences.
A primary source is an original object or document created during the time under study. Primary sources vary by discipline and can include historical and legal documents, diaries, letters, family records, speeches, interviews, autobiographies, film, government documents, eye witness accounts, results of an experiment, statistical data, pieces of creative writing, and art objects.
A primary source is a first-hand account from a person or organization who: Created an original work; Participated in new scientific discoveries; Witnessed an event; ... Your research paper is a secondary source because you're analyzing and interpreting other sources.
Primary Sources Handout (2018) What are primary sources & why should you use them in your research papers? Primary sources are the raw materials of history. They are firsthand resources created by eyewitnesses — people who actually see or participate in an event and record it and their reactions to it. Primary sources have not been edited ...
If you've never written a research paper using primary sources, it is important to understand that the process is different from using only secondary sources. Many students discover that finding and gaining access to primary source documents can be difficult. The Library website has a valuable guide to locating primary source documents.
In history, for example, primary sources include documents from the period or person you are studying, objects, maps, even clothing; in literature or philosophy, your main primary source is usually the text you are studying, and your data are the words on the page. In such fields, you can rarely write a research paper without using primary ...
Primary research is any research that you conduct yourself. It can be as simple as a 2-question survey, or as in-depth as a years-long longitudinal study. The only key is that data must be collected firsthand by you. Primary research is often used to supplement or strengthen existing secondary research.
Secondary sources report, describe, comment on, or analyze the experiences or work of others. A secondary source is at least once removed from the primary source. It reports on the original work, the direct observation, or the firsthand experience. It will often use primary sources as examples. Secondary sources can include books, textbooks ...
The most common type of primary source used at Illinois Tech is the research paper written by the researcher(s) who actually carried out the work. These papers are typically published as articles in peer-reviewed journals but could also be in the form of a thesis or dissertation, research report, case study, clinical trial, etc.
Reviewing primary source material can be of value in improving your overall research paper because they: Represent original thinking or experiences, reporting of a discovery, or the sharing of new information. * Works of art, architecture, literature, and music (e.g., paintings, sculptures, musical scores, buildings, novels, poems).
The use of research papers as primary sources is an increasingly important yet often overlooked component of modern scholarly inquiry. In this article, we will explore the potential that exists in utilizing research papers to enhance one's understanding and appreciation of a given subject matter.
Thus, readers of primary scholarly research should have foundational knowledge of the subject area. Use primary resources to obtain a first-hand account to an actual event and identify original research done in a field. For many of your papers, use of primary resources will be a requirement. Examples of a primary source are:
Tertiary Sources. These are sources that index, abstract, organize, compile, or digest other sources. Some reference materials and textbooks are considered tertiary sources when their main purpose is to list or summarize other information. Tertiary sources are usually not credited to a particular author. Examples of Tertiary Sources:
A secondary source describes or analyzes a primary source. These sources are one step removed from the actual event and allow you to understand what scholars and other experts know about your topic. Types of Secondary Sources: Books or articles that explain or review research works; Histories and critical commentaries; Textbooks
With respect to the individual components of the primary end point, a first hospitalization for heart failure occurred in 118 patients (3.6%) in the empagliflozin group and in 153 patients (4.7% ...
Mission. The AI Index report tracks, collates, distills, and visualizes data related to artificial intelligence (AI). Our mission is to provide unbiased, rigorously vetted, broadly sourced data in order for policymakers, researchers, executives, journalists, and the general public to develop a more thorough and nuanced understanding of the complex field of AI.
Research papers rely on other people's writing as a foundation to create new ideas, but you can't just use someone else's words. That's why paraphrasing is an essential writing technique for academic writing.. Paraphrasing rewrites another person's ideas, evidence, or opinions in your own words.With proper attribution, paraphrasing helps you expand on another's work and back up ...
Critics of science research and publishing systems allege that a lack of opportunities for young scientists, limited oversight and pressure to publish splashy papers that can advance careers could ...
The majority of children excluded in primary school don't pass their GCSEs in English and Maths, according to new research. The charity Chance UK looked at the long-term impact of children being ...