- SEO SOLUTIONS


TOTAL FREE HEALTH AND SAFETY DOCUMENTS DOWNLOADING SOURCE

- _HSE Trainings
- EHS Guidelines
- Risk Assessments
- Safety Posters
- Method Statements
- Health and Fitness
Friday, July 1, 2022
Permit to work system-powerpoint training.
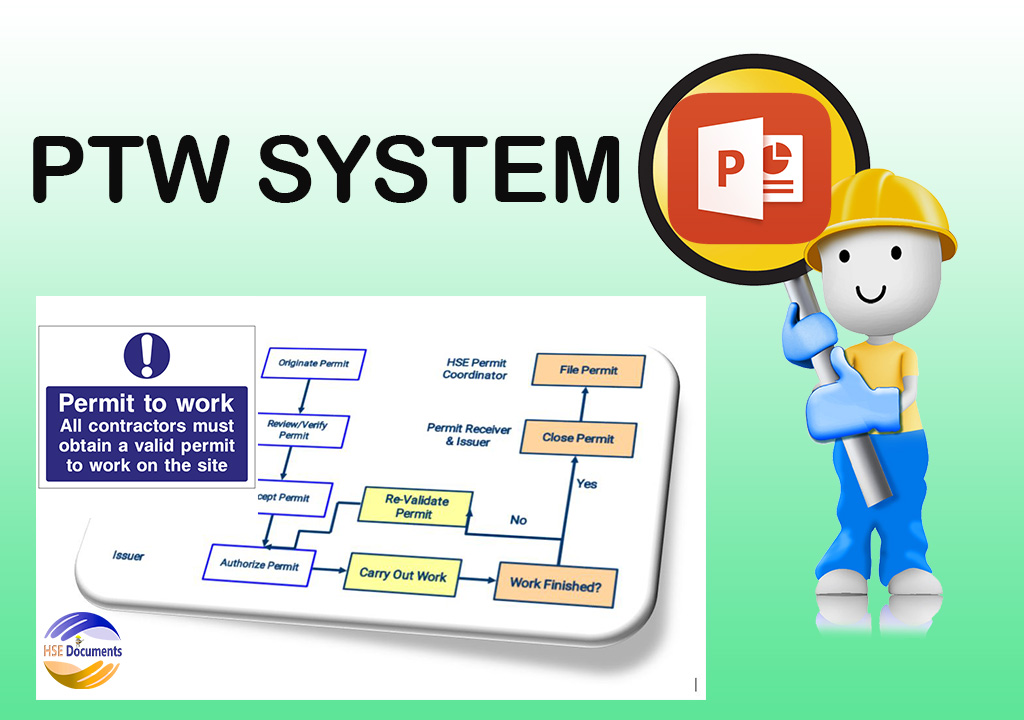
What is Permit To Work System
- The PTW system is a formal written procedure used to control access and activities of personnel in the construction
- To ensure the safety of personnel and to prevent damage to equipment
- It is also a means of communication between site management, supervisors, and operators, who carry out the work PTW normally implemented in work activities near or inside the operating facilities, there's Buried or close to the operational device, or wherein the clients assume that PTW is deemed important or near operational system or where the clients think that PTW is deemed necessary
How is work controlled within the Permit?
- To Work, SystemWork is controlled by following various steps detailed in the permit to work procedures and by using special documents called WORK PERMIT.
- Work permits are not simple permission to carry out work, but they determine how the work can be carried out safely.
Types of Permit To Work
Hot work permit, confined space entry permit.
- Electrical Permit (Energizing and Deenergizing)
Excavation Permit
Radiography permit.
- Crane Critical Lifts Man-basket Operation
- Cold Work Permit
Classified as any sort of work which involves real or ability resources of ignition and which is accomplished in a place where there can be a risk of fire or Explosion, or which contain the emission of toxic fumes from the utility of heat.
Is generally used to specify the precautions to be taken to get rid of the hazards of risky fumes, gases liquids, or solids of loss of oxygen, dangerous residues radiation, or transferring machinery from confined space or any other source before a person is permitted to enter a confined space.
Electrical Permit (Including Energizing and De-energizing)
Is normally used to cover any work on electrical equipment and precautions to be taken to eliminate the risk of electric shock/electrocution to people carrying out the work or damage to property
- Is required for any work to be carried out where existing lines or services may be buried or encountered.
- Any excavation deeper than 0.3-meter Excavation activities near existing structures (i.e. Electrical posts, buildings, Permanent Equipment, etc…)
- For excavation activities in an area classified as a safe area for excavation, a blanket permit may be requested for a long duration of time
Is normally used to cover industrial radiography – safe working practices and precautions to be taken to eliminate the risk associated with radioactive sources.
Crane Critical Lifts Permit
- A permit is needed when lifting requires Rigging Study;
- Load is 40 Tones and above Crane, lifts are performed in a “High-Risk Environment”
- Load is too big/wide to be lifted
- Lifting where 2 or more cranes are required
Man-Basket Operation
- Before the use of any man-basket suspended from a crane for hoisting personnel, the highest level of Project management must determine and be sure that conventional means are more
- Dangerous or impossible due to structural layout or worksite conditions, approval has to be signed.
- A trial lift is required before the actual riding of personnel inside the basket to make sure that the operator can safely position the man basket in the intended location
Permit Issuer Responsibilities
- In the case of an operational plant, the Company normally has its permit system.
- The manager of the affected section of the plant or his specified consultant shall be the permitted provider.
- In a non-operational area where existing facilities are already in place, The Contractor Area Construction Managers or Company Section head shall be the issuers of the permits.
- The Issuer has the sole authority to issue the permit.
- The Issuer shall be fully aware of site conditions, the type of work to be carried out, and all the requirements stated in the permit.
- The Issuer shall conduct an onsite inspection jointly together with the Receiver to make sure that website situations are secure to permit the paintings and that all necessities stated in the allow are applied earlier than the issuance of the permit.
- The Issuer shall conduct an onsite inspection together collectively with the Receiver to ensure that site conditions are safe to permit the work and that all necessities stated inside the allow are implemented earlier than the issuance of the allow.
- The Issuer shall withhold the issuance of the permit if the requirements are not met, or site conditions are not safe for the work to carry out.
- The Issuer shall, if noticing the presence of any other potential hazards, risks that may jeopardize the safety of the worker, tools, or equipment advice the Receiver of appropriate countermeasures to be taken.
- The Issuer shall ensure that all required safety monitoring measurements are properly done and so stated in the permit.
- The Issuer shall ensure all personnel involved in the work are fully aware of Emergency procedures.
- Once informed the work is completed, the Issuer shall visit the site jointly with the Receiver to ensure that the work is ceased and the site is kept clean and tidy without any smoldering existing.
- Task supervisors who are directly responsible for the work stated in the permit shall be the Receiver of the Permit. He shall define the job to be done, the exact location, and the nature of the work. Also to ensure that the situations at the allow are met incomplete
- The Receiver shall be fully aware of all requirements stated in the permit and comply with them at all times.
- The Receiver shall fully brief the work crew to ensure that requirements are clearly understood by the crew under his supervision.
- The Receiver shall ensure the work is performed by the conditions specified in the permit. He shall continue to be on the work website to supervise the work.
- The Receiver shall ensure that under no circumstances shall by his discretion or his crew change the original scope of the work, which is described in the permit.
Permit Receiver Responsibilities
- The Receiver shall request a new permit in the event a change in the scope of the work becomes necessary.
- Whenever website situations are notably changed, the Receiver shall right away forestall the paintings and tell the Issuer of the change for similarly training from him.
- Upon the occurrence of an emergency, the Receiver shall immediately stop the work and shut down all equipment.
- The Receiver shall report the completion of the work or the expiration of the validity of the permit to the Issuer and ensure that the site is kept clean and tidy without any smoldering/ignition sources.
- If the work in progress requires extending the validity stated in the permit, the Receiver shall suspend the work and request the issuance of the new permit.
HSE Permit Coordinator Responsibilities
- The HSE Permit Coordinator detailed with the aid of Area Construction Managers is answerable for the everyday coordination of the painting permits.
- He is responsible for full clerical control of the system including retention of the closed-out Work Permits for one month.
- Has the full overview of the planned, open, and suspended work permits on visual display in his permit to work office.
Operational Procedures for the Work Permit System
- A Work Permit consists of a hard and fast of three pages. The White page shall be kept by using the Receiver and stored on the work location, the Yellow page will be kept via the Issuer and the Green web page will be stored by using the HSE Permit Coordinator.
- The description of the work shall be a precise statement of the planned activity, and the location of the work by identification of the area or equipment to be worked upon. Broad scopes of labor of a preferred nature aren't appropriate.
- Method Statements, Risk Assessments, and/or Job Safety Analyses will be produced for important sports and shall be connected to and shape part of the allow. Such extra documentation will be attached to the unique Permit.
- Where additional Permits or Certificates are required, they will be attached to and form part of the Permit to Work.
- The Receiver shall produce the permit to the Contractor responsible personnel for the work requested in the permit for review and verification by 15:00 hours a day before the commencement of the activity/work.
- As rapidly as the assessment & verification were made, the PTW Receiver shall deliver the verified allow to the HSE Permit Coordinator.
- As soon as the assessment and verification had been made, the Receiver shall deliver the verified permit to the HSE Permit Coordinator.
- The HSE Permit Coordinator shall scrutinize the allow together with safety precautions and requirements stated inside the permit and deliver it to the Receiver.
- The HSE Permit Coordinator must consult HSE personnel for expert advice or hints required to paint appropriately.
- The Receiver shall bring the permit to the Issuer who shall review the permit to ensure that all required safety precautionary measures are stated and authorize the permit.
- On the day of the work, the Issuer the person together with the Receiver shall go to the site to ensure that all requirements in the permit are met And give up the allow to the Receiver
- Issuance of the permit to the Receiver in the office shall not take place.
- Upon receipt of the permit from the Issuer, the Receiver can commence the work.
- When no further work is to take place under a permit, the Receiver shall sign off and return the permit to the Issuer to close the permit.
- Upon receipt of the permit, the Issuer, and the Receiver shall inspect the work site to ensure that no smoldering is present, the work site is clean and tidy and equipment is left in a safe and hazard/risk-free condition.
- The issuer shall return the invalid PTW to the health safety and environmental Permit Coordinator for file.
Revalidation of the Permit
- When the work calls for an extension of the permit, the Receiver shall suspend the work and request an extension of the validity to the Issuer.
- The Issuer is responsible for ensuring that all precautions and requirements are still in place and the conditions in the work site are maintained safely for personnel and equipment.
- If the issuer agrees to extend the permit he shall define the time of the expiry and sign in the permit to authorize the extension.
- The Receiver returns the extended permit to the work site and resumes the work.
Emergency Situation
- When an emergency, such as a fire incident, Toxic Gas Release, or Natural calamity has taken place the Receiver shall immediately stop all work and shut down all equipment.
- All permits shall be nullified and no work shall be resumed unless new permits have been issued by the Issuer.
- Before the issuance of a new permit, the Issuer shall visit the work site to ensure that there is no imminent hazard/risk present and that the work site is safe for work.
- The Permit to Work is designed to provide a safe system of work that can be applied to works identified under perceived risks.
- This shall be applied to the Contractor controlled Construction activities on the Project.
- Permit requirements for activities other than those mentioned in this procedure will be re-evaluated especially for potentially hazardous activities where an extra degree of work control is felt to be appropriate.
Download The File Here
Permit to work system-powerpoint training, no comments:.
Post a Comment
DOWNLOAD ANDRIOD APP

Get new posts by email:
Socially contacts, contact form.

Blog Archive
Social networks.
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Total Pageviews
Copyright (c) 2023 hsedocuments All Right Reseved
- Safety Officer
- Safety Quiz
- Interview Q/A
- Online Exam
- Download PPT
- Get Certificate Online
- HSE Web Story
- NEBOSH IDIP
- Fire Engineering
- Basic Safety
- Construction Safety
- Workplace Safety
- Fire Safety
- Crane Safety
- Work At Height
- Excavation Safety
- Electrical Safety
- Confined Space
- Noise Safety
- Vibration Safety
- Scaffolding
- Radiography
- HSE Calculations & Formulas
- Safety Slogan
- Tool Box Talk
- HSE Documentation
- HSE Training
- Risk Assessment
- Safety Audit
- Accident Investigation
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

Permit To Work (PTW) | Types of Work Permit | Download PPT

Table of Contents
Introduction
Permit To Work (PTW) : In the realm of workplace safety, the term “Permit to Work” or PTW is of utmost importance. It serves as a vital tool in ensuring that potentially hazardous tasks are executed with the utmost care and precaution. This article delves into the world of PTW, explaining its significance, the various types of work permits, and how to obtain one. Moreover, we will discuss the advantages of using PTW PowerPoint presentations (PPTs) and provide you with insights into its implementation across different industries.
What is a Permit to Work (PTW)?
A Permit to Work, often abbreviated as PTW, is a formal document that authorizes specific activities within a workplace. It is commonly used in environments where there are potential risks to health and safety. The primary purpose of a PTW is to ensure that the necessary precautions are taken before any hazardous work commences.
The Importance of PTW
The significance of PTW cannot be overstated. It acts as a safeguard, ensuring that potentially dangerous tasks are carried out in a controlled and safe manner. PTW also holds individuals and organizations accountable for adhering to safety protocols, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries.
Types of Work Permits
There are several types of work permits, each designed for specific work environments and activities. Let’s explore some of the most common ones:
General Work Permit
This permit is typically used for routine maintenance and non-hazardous tasks.
Hot Work Permit
Hot work permits are issued for activities involving open flames or high temperatures, such as welding and cutting.
Cold Work Permit
Cold work permits are for tasks carried out in cold conditions, where exposure to extreme temperatures is a concern.
Confined Space Entry Permit
This permit is required when working in confined spaces, which pose unique risks and challenges.
Steps to Obtain a PTW
Obtaining a PTW involves a systematic process. It typically includes identifying the task, assessing the risks, implementing safety measures, and obtaining approvals from relevant personnel.
Who Needs a PTW?
PTWs are not limited to a specific industry. They are essential in any workplace where hazardous tasks are performed. This includes manufacturing, construction, oil and gas, and many others.
Downloading a PTW PPT
To aid in the dissemination of PTW information, you can download PTW PowerPoint presentations. These PPTs provide a visual and comprehensive overview of the permit process.
What is Hazard | Risk | Accident | Incident | Near Misses with 5 Examples | Download PPT
Work At Height PPT | Hazards and Safety Precautions | Download PPT
Benefits of Using PTW PPT
Using PTW PPTs offers several advantages. They help in training and educating employees, contractors, and other stakeholders about the importance of PTW. They also serve as a reference guide for adhering to safety protocols.
In conclusion, a Permit to Work (PTW) is a fundamental tool in ensuring safety in workplaces with potential hazards. It plays a pivotal role in protecting lives and preventing accidents. By understanding the various types of work permits and their implementation, we can create safer and more secure working environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the purpose of a Permit to Work (PTW)?
A Permit to Work (PTW) serves the primary purpose of ensuring safety in the workplace. It is a formal document that authorizes specific activities, especially those with potential risks to health and safety. The PTW helps in assessing and mitigating these risks, making sure that all necessary precautions are taken before hazardous work begins.
2. Are PTWs only required in high-risk industries?
No, PTWs are not limited to high-risk industries. While they are particularly crucial in high-risk sectors like manufacturing, construction, and oil and gas, PTWs can be applicable in any workplace where potentially dangerous tasks are carried out. Safety should always be a priority, regardless of the industry.
3. How can I download a PTW PowerPoint presentation (PPT)?
You can download a PTW PowerPoint presentation (PPT) from various sources, including safety training websites, industry-specific associations, or even by creating your own based on the specific needs of your workplace. These presentations provide a visual and comprehensive overview of the PTW process and its importance.
4. What are the consequences of not following PTW procedures?
Failure to follow PTW procedures can lead to severe consequences. This may include accidents, injuries, damage to equipment, and even loss of life. Additionally, non-compliance with PTW procedures can result in legal and financial repercussions for organizations. It’s essential to adhere to PTW guidelines to ensure the safety of all individuals involved.
5. Can PTW be customized for specific industries or tasks?
Yes, PTWs can and should be customized to suit the specific requirements of different industries and tasks. Each industry and workplace may have unique risks and safety protocols. Customizing PTWs ensures that they are tailored to address these specific hazards, making them more effective in enhancing safety and compliance.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Work at height risk assessment chart | free download, 40 aramco safety engineer interview questions and sample answers | free download pdf, 43 adnoc hse officer interview questions and answers | free download pdf.
This information is very useful.safety is first priority
Great training material.
Excellent training material.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Popular Posts
Top 15 best safety slogan in hindi, easy nebosh igc exam questions and answers, 25 safety officer interview questions (with sample answers), hse engineer job vacancy : urgent requirement, top 25 best hindi safety slogan in 2024, 10 essential safety officer tips every workplace needs to know, industrial safety, safety officer & safety engineer, work at height | hazards | control measures, very important slip trip and fall hazards, personal fall arrest system, latest post, 50 fresher safety officer interview questions and answers | free download..., free requirement for safety supervisor in kuwait: salary kwd 500 –..., safety officer, safety engineer and safety supervisor hiring for kuwait oil..., safety officer, safety supervisor and safety manager hiring for saudi arabia:..., (nebosh) the national examination board in occupational safety and health, 03 safety officer jobs vacancy in saudi arabia: oil and gas..., 03 safety officer urgently required for saudi arabia: online interview, 05 hse officers urgently required in saudi arabia, 06 safety officer and safety engineer urgently required for oil and....

- Toolbox Talks
- Guest Post and Backlink
Understanding and Implementing Permit to Work Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
- by Afnan Tajuddin
- Work permit system

Table of Contents
Introduction to Permit to Work Systems
In the bustling world of the petroleum, chemical, and allied industries, safety is paramount. One of the key tools to ensure this safety is the Permit-to-Work System . This system is a formal, recorded process used to control potentially hazardous work. It serves as a means of communication between site management, plant supervisors, and those who carry out the hazardous work.
Understanding the Basics of Permit to Work PTW Systems
- A permit-to-work system is a formal written system used to control certain types of work that are potentially risky. It is a document which specifies the work to be done and the precautions to be taken. Permits are an essential part of safe systems of work for many industries.
- Before initiating any task in a specific area, it’s crucial to ensure the safety of the environment and the machinery or equipment involved. To ascertain these safe conditions, a work permit system is implemented. This system specifies the conditions and procedures for the safe execution of work, allowing tasks to be carried out under controlled risk conditions.
- A permit-to-work system is not just a permission to carry out a dangerous job. It is an integral part of a system that determines how that job can be carried out safely. The issue of a permit does not, by itself, make a job safe. That can only be achieved by those preparing for the work, those supervising the work, and those carrying it out. In addition to the permit-to-work system, other precautions may need to be taken, such as process or electrical isolation, or access barriers. These will need to be identified in task risk assessments before any work is undertaken. The permit-to-work system ensures that authorised and competent people have thought about foreseeable risks and that such risks are avoided by using suitable precautions.
Aim of the Work Permit System
The primary purpose of the work permit system is to ensure that:
- Only authorized individuals are allowed to work in clearly notified hazardous areas.
- The individuals permitted to work are aware of the various safety issues involved and understand that necessary safety precautions have been taken.
- The work permit serves as a legal document between the issuer and executor for the commencement of a job inside a refinery.
- The client has implemented the work permit system to distribute equal responsibilities for the job being performed.
The Importance of Permit-to-Work Systems in Hazardous Industries
The petroleum, chemical, and allied industries store and process large quantities of hazardous substances, including flammable and toxic materials. The potential for serious incidents is clear. To prevent such incidents, it is vital that there should be effective management of hazards, including the use of safe systems of work. A permit-to-work system is an integral part of a safe system of work and can help to properly manage the wide range of activities which can take place close to these hazardous substances.
Different Types of Permits
There are several types of permits, each designed to control specific types of work activities. These include Hot Work Permit, Cold Work Permit, Electrical Work Permit, Equipment Disjointing Certificate/Breaking Containment Permit, Confined Spaces Entry Certificate, Machinery Certificate, Isolation Certificate, Excavation Certificate/Heavy Equipment Movement Certificate, Radiation Certificate, and Diving Certificate. Each of these permits has specific requirements and control measures to ensure the safety of the workers and the environment.
The Evolution of Permit to Work Systems: From Paper to Electronic
The document is primarily written around well-established paper-based permit-to-work systems, but where possible it accounts for the newer medium of electronic-based permit-to-work systems. With the advancement of technology, electronic permits have become an integral part of permit-to-work systems. These electronic systems offer several advantages, including ease of use, improved tracking, and better record-keeping. They also facilitate the transition from paper-based to electronic systems.
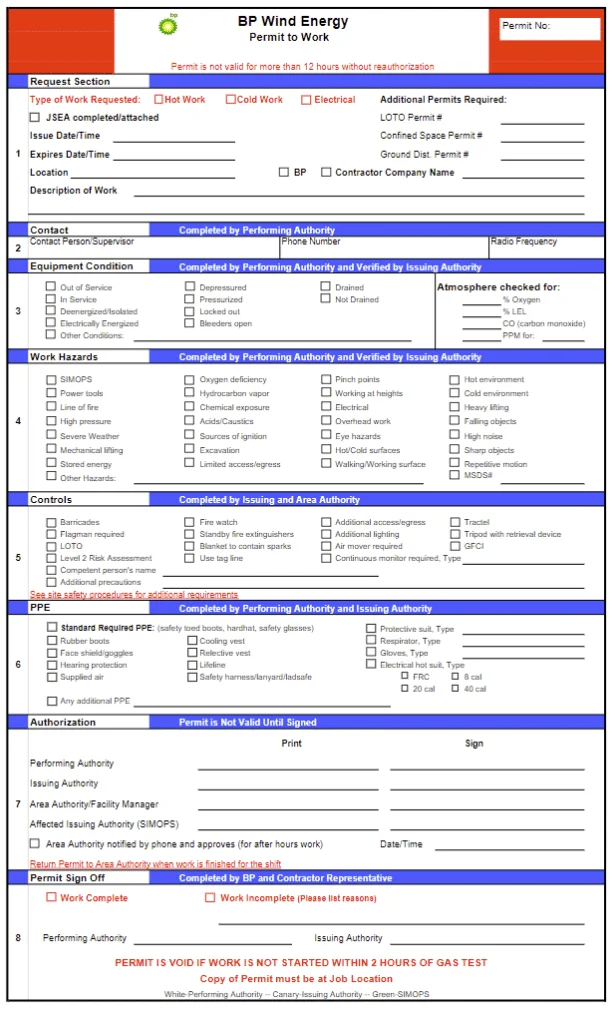
The Purpose and Function of PTW Systems
The primary purpose of a permit-to-work system is to ensure the proper authorisation of designated work. This work may be of certain types or work of any type within certain designated areas other than normal operations. The system makes clear to people carrying out the work the exact identity, nature, and extent of the job and the hazards involved. It also specifies the precautions to be taken, including safe isolation from potential risks such as hazardous substances, electricity, and other energy forms.
The Role of Permit-to-Work Systems in Risk Management
A permit-to-work system aims to ensure that proper consideration is given to the risks of a particular job or simultaneous activities at site. Whether it is manually or electronically generated, the permit is a detailed document which authorises certain people to carry out specific work at a specific site at a certain time, and which sets out the main precautions needed to complete the job safely.
The Communication Aspect of Permit-to-Work Systems
The permit-to-work system is also a means of communication between site management, supervisors, and those carrying out the work. The system ensures that everyone involved in the work is aware of the risks and the necessary precautions. This communication is crucial to ensure the safety of all workers and to prevent accidents.
The Objectives and Functions of Permit-to-Work Systems
The objectives and functions of a permit to work system can be summarised as ensuring the proper authorisation of designated work, making clear to people carrying out the work the exact identity, nature, and extent of the job, and the hazards involved. It also specifies the precautions to be taken, including safe isolation from potential risks such as hazardous substances, electricity, and other energy forms.
When are Permit-to-Work Systems Required?
PTW systems are typically required for non-production work such as maintenance, repair, inspection, testing, alteration, construction, dismantling, adaptation, modification, and cleaning. They are also necessary for non-routine operations and jobs where two or more individuals or groups need to coordinate activities to complete the job safely. Additionally, they are used when there is a transfer of work and responsibilities from one group to another.
Identifying Situations that Require a Permit-to-Work System
Permit to work systems are normally considered most appropriate to non-production work, non-routine operations, jobs where two or more individuals or groups need to co-ordinate activities to complete the job safely, and jobs where there is a transfer of work and responsibilities from one group to another. However, permit-to-work systems should not be applied to all activities, as experience has shown that their overall effectiveness may be weakened. Permits-to-work are not normally required for controlling general visitors to site or routine maintenance tasks in non-hazardous areas.
The Limitations of Permit-to-Work Systems
While Work permit system are a crucial tool for managing hazardous work, they are not a panacea for all safety issues. They should not be seen as an easy way to eliminate hazard or reduce risk. The issue of a permit does not, by itself, make a job safe – that can only be achieved by those preparing for the work, those supervising the work, and those carrying it out. In addition to the permit-to-work system, other precautions may need to be taken, and these will need to be identified in task risk assessments before any work is undertaken.
The Role of Work permit system in Non-Routine Operations
Non-routine operations often involve a higher level of risk than regular operations. These operations may involve unfamiliar procedures, unfamiliar equipment, or working in unfamiliar areas. In these situations, a permit-to-work system can be particularly valuable. The system ensures that the work is properly planned, that all risks are identified and mitigated, and that everyone involved in the work is aware of the precautions they need to take.
Work Not Requiring a Permit
- Routine work in established workshops and adjacent yards with boundaries.
- Routine material handling work in warehouses and lay down areas.
- Routine office work.
- Visual inspection or checking without using any tools in operation areas with verbal permission from assistant custodians.
- Work carried out by operation employees as part of their daily start-up and shutdown of the plant.
- Work carried out in designated areas declared as work permit-free by the client.
- Any work approved by the client on special request by the contractor.

The Essentials of PTW Systems
A permit-to-work system has several essential features. These include clear identification of who may authorise particular jobs and who is responsible for specifying the necessary precautions. The
system also requires training and instruction in the issue, use, and closure of permits. Furthermore, it includes monitoring and auditing to ensure that the system works as intended.

The Key Elements of a Permit-to-Work System
The key elements of a permit-to-work system include clear identification of who may authorise particular jobs and who is responsible for specifying the necessary precautions. The system also requires training and instruction in the issue, use, and closure of permits. Furthermore, it includes monitoring and auditing to ensure that the system works as intended.
The Process of Display, Suspension, and Handover in Permit-to-Work Systems
The Work permit system should include a process for the display of permits, the suspension of work, and the handover of work. The display of permits ensures that everyone involved in the work is aware of the permit and its conditions. The suspension of work allows for the safe stoppage of work if necessary. The handover of work ensures that when work is transferred from one group to another, all parties are aware of the status of the work and the precautions that need to be taken.
Understanding Permit Interaction and Hand-back Procedures
Permit interaction refers to the situation where multiple permits are in effect at the same time. This can occur when different groups are working on different aspects of a job, or when different jobs are being carried out in close proximity. The permit-to-work system should include procedures for managing permit interaction to ensure that all work is carried out safely. Hand-back procedures are also important to ensure that when work is completed, the site is returned to a safe condition.
Attachments of Work Permit
The work permit may require several attachments, including:
- Work method statement
- Work permit risk assessment
- Issuer, Executor, and permit holder PTW card copies
- Safety certificate of equipment
- Lifting plan if lifting activity is involved
- Drawing of location
- Entrant & Attendant copy if it’s a confined space permit, etc.
Authorisation and Supervision in Permit-to-Work Systems
The authorisation and supervision of work are crucial aspects of a permit-to-work system. The system should clearly identify who may authorise particular jobs and who is responsible for supervising the work. This ensures that the work is carried out safely and in accordance with the conditions of the permit.
The Importance of Authorisation in Permit-to-Work Systems
Authorisation is a crucial aspect of a permit-to-work system. It ensures that only competent individuals who understand the risks and precautions associated with the work are allowed to carry out the work. The authorisation process also ensures that the work is properly planned and that all necessary precautions are taken.
The Role of Supervision in Ensuring the Effectiveness of Permit-to-Work Systems
Supervision is another crucial aspect of a PTW system. Supervisors play a key role in ensuring that the work is carried out safely and in accordance with the conditions of the permit. They are responsible for monitoring the work, ensuring that all necessary precautions are taken, and intervening if necessary to prevent unsafe work.
The Challenges of Supervising a Large Number of Permits
Supervising a large number of permits can be a challenging task. It requires a high level of organisation and attention to detail. Supervisors must be able to keep track of all active permits, ensure that all work is carried out in accordance with the conditions of the permits, and intervene if necessary to prevent unsafe work. Despite these challenges, effective supervision is crucial for the success of a permit-to-work system.
Responsibilities in Permit-to-Work Systems
Various roles and responsibilities are associated with a permit-to-work system. These include employers or duty holders, site or installation managers, contractors and subcontractors, supervisory personnel, and individuals. Each of these roles has specific responsibilities within the system to ensure its effective operation.
The Responsibilities of Employers or Duty Holders in Permit-to-Work Systems
Employers or duty holders have a key role in a permit-to-work system. They are responsible for ensuring that the system is properly implemented and maintained. This includes ensuring that all necessary resources are provided, that all personnel are properly trained, and that the system is regularly audited and reviewed.
The Role of Site or Installation Managers in Permit-to-Work Systems
Site or installation managers also have important responsibilities in a permit-to-work system. They are responsible for overseeing the implementation of the system, ensuring that all work is properly authorised and supervised, and that all necessary precautions are taken. They are also responsible for ensuring that all personnel are properly trained and competent to carry out their roles within the system.
Understanding the Responsibilities of Contractors and Subcontractors
Contractors and subcontractors have a crucial role in a permit-to-work system. They are responsible for ensuring that they understand and comply with the conditions of the permit, that they carry out the work safely, and that they report any issues or concerns to the supervisor. They are also responsible for ensuring that they are properly trained and competent to carry out the work.
Training and Competence in Permit-to-Work Systems
Training and competence are crucial elements of a permit-to-work system. All personnel involved in the system must receive appropriate training and demonstrate competence in their roles. This ensures that everyone understands the system and can effectively carry out their responsibilities.
The Importance of Training in PTW Systems
Training is a crucial aspect of a permit-to-work system. It ensures that all personnel understand the system and can effectively carry out their roles. Training should cover the purpose and function of the system, the roles and responsibilities of different personnel, the process of issuing, using, and closing permits, and the procedures for managing permit interaction and hand-back.
Developing Competence in Permit-to-Work Systems
Competence is another crucial aspect of a permit-to-work system. All personnel involved in the system must demonstrate competence in their roles. This includes understanding the system, being able to carry out their roles effectively, and being able to identify and manage risks. Competence can be developed through training, experience, and ongoing assessment.
The Role of Training in Enhancing Safety Performance
Training plays a crucial role in enhancing safety performance in a permit-to-work system. By ensuring that all personnel are properly trained and competent, employers can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and incidents. Training should be ongoing and should include both initial training for new personnel and refresher training for existing personnel.
The Future of Permit-to-Work Systems
With the advancement of technology and the increasing complexity of industrial operations, the future of permit-to-work systems is likely to involve significant changes. These changes may include the increased use of electronic systems, the integration of permit-to-work systems with other safety management systems, and the use of advanced analytics to improve the effectiveness of the system.
The Impact of Technological Advancements on Permit-to-Work Systems
Technological advancements are likely to have a significant impact on permit-to-work systems. The increased use of electronic systems can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the system, making it easier to issue, track, and close permits. Technology can also facilitate the integration of the permit-to-work system with other safety management systems, providing a more holistic approach to safety management.
The Potential of AI and Machine Learning in Permit-to-Work Systems
The potential of AI and machine learning in permit-to-work systems is significant. These technologies can be used to analyse data from the system, identify patterns and trends, and provide insights that can be used to improve the effectiveness of the system. For example, machine learning algorithms could be used to predict the likelihood of accidents based on historical data, allowing for proactive measures to prevent accidents.
The Future Challenges and Opportunities for Permit-to-Work Systems
The future of permit-to-work systems is likely to involve both challenges and opportunities. Challenges may include the need to adapt to new technologies, the increasing complexity of industrial operations, and the need to integrate the permit-to-work system with other safety management systems. Opportunities may include the potential to improve the effectiveness of the system through the use of advanced analytics, the potential to improve safety performance through better training and competence development, and the potential to reduce the risk of accidents through more effective risk management.
In conclusion, permit-to-work systems are a crucial tool for managing hazardous work in the petroleum, chemical, and allied industries. By ensuring the proper authorisation of work, providing a means of communication between different parties, and specifying the necessary precautions, these systems can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and incidents. However, to be effective, these systems require the commitment of all personnel, from employers and managers to contractors and individuals. With the right training, competence development, and technological support, permit-to-work systems can contribute significantly to safety performance in these industries.
Legal Requirements and Standards
Relevant legal requirements.
There are several legal requirements relevant to Permit-to-Work systems. These include the Health and Safety at Work etc Act 1974 , Confined Spaces Regulations 1997 , Control of Major Accident Hazards Regulations 1999, and many more.
Various standards and guidelines provide further guidance on Permit-to-Work systems. These include The safe isolation of plant and equipment Guidance HSE Books 1997, Task Risk Assessment Guide Step Change In Safety, and others.
FAQs on Permit to Work PTW Systems
1. what is a permit to work system.
A permit-to-work system is a formal, recorded process used to control work that is identified as potentially hazardous. It serves as a means of communication between site management, plant supervisors, and those who carry out the hazardous work. It is not just a permission to carry out a dangerous job, but an integral part of a system that determines how that job can be carried out safely.
2. Why are PTW systems important in hazardous industries?
Permit-to-work systems are vital in hazardous industries like the petroleum, chemical, and allied industries that store and process large quantities of hazardous substances. These systems help prevent serious incidents by ensuring effective management of hazards, including the use of safe systems of work. They ensure that only authorised and competent people carry out specific work at a specific site at a certain time, and that all necessary precautions are taken to complete the job safely.
3. How has the permit-to-work system evolved over time?
The permit-to-work system has evolved from being a paper-based system to an electronic one. With the advancement of technology, electronic permits have become an integral part of permit-to-work systems. These electronic systems offer several advantages, including ease of use, improved tracking, and better record-keeping. They also facilitate the transition from paper-based to electronic systems.
4. When is a permit-to-work system required?
Permit-to-work systems are typically required for non-production work such as maintenance, repair, inspection, testing, alteration, construction, dismantling, adaptation, modification, and cleaning. They are also necessary for non-routine operations and jobs where two or more individuals or groups need to coordinate activities to complete the job safely. Additionally, they are used when there is a transfer of work and responsibilities from one group to another.
5. What are the key elements of a permit-to-work system?
6. how does the process of authorisation and supervision work in a permit-to-work system, 7. what are the responsibilities of different stakeholders in a permit-to-work system, 8. why is training important in a permit-to-work system, 9. how can technology impact the future of permit-to-work systems, 10. what are the challenges and opportunities for permit-to-work systems in the future, share this:, leave a reply cancel reply.

Shopping Cart
No products in the cart.
Permit to Work & Lock Out Tag Out
Watch snapshots of the course.
Course Content

Course Includes
- Course Certificate
Ratings and Reviews
It's very helpful, thank you😊
The quality of information you can get in this PTW&LOTO course on trainovate is amazing. salamat
Email Address
Remember Me
Registration confirmation will be emailed to you.
There was a problem reporting this post.
Block Member?
Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
- See blocked member's posts
- Mention this member in posts
- Invite this member to groups
- Message this member
- Add this member as a connection
Please note: This action will also remove this member from your connections and send a report to the site admin. Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.

Leaving so soon?
Get 25% off when you purchase this course using this code:

Get 25% Off!
Purchase the course now and get discount using this code:

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Permit to Work System Orientation Training PTWS – PI & PH Orientation Training.
Published by Dayna Wiggins Modified over 8 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Permit to Work System Orientation Training PTWS – PI & PH Orientation Training."— Presentation transcript:

Safety Absolutes Green Lake

Managing the Health and Safety of Contractors

Work Health Safety Regulations Regulations Module: Workplace WHS requirements Workbook page 8.

Permit to Work System Permit Orientation Training PTWS – Permit Orientation Training.

HSSE Policy Z Contractor HSSE Induction V2. HSSE Policy Z Contractor HSSE Induction V2.

Contractor Coordination. Agenda Training Objectives Definitions Law and Regulatory Requirements Responsibilities Implementation Scenarios.

Work with a valid work permit when required
Contractor Safety Management

Hazard identification and Risk assessment

Rev: Section 6 Alternative Fall Protection.

Risk Management (Safe Work Method Statements)

BUILD WITH US. ™ Contractors

W504 - Management of asbestos containing materials.

OH&S Management System

Risk Assessment – An Essential Standard

Review Quiz 1. OHS Legislation 4. Incident Response Introduction 2. Hazards & Controls 3. OHS Communication EASY GUIDES Australia.

1 CHCOHS312A Follow safety procedures for direct care work.

WORKPLACE HAZARD MANAGEMENT PLATFORM UPGRADE KEY ELEMENTS IDENTIFY PLAN AND DOCUMENT COMMUNICATEMANAGEMONITOR.

Work Health and Safety (National Uniform Legislation) Act and Regulations NT WorkSafe Anna McGill.

RISK ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

PwC experience: Tatarstan Denis Derevyankin Kazan PwC office leader
Jul 30, 2014
140 likes | 344 Views
www.pwc . ru. PwC experience: Tatarstan Denis Derevyankin Kazan PwC office leader. Content. Introduction PwC experience: what is Tatarstan for our business? Some hints about Tatarstan. Personal Introduction. Kazan PwC office leader Experience in the profession near 10 years
Share Presentation
- size office
- real life example
- small rent cost
- nearby regions
- informal rules

Presentation Transcript
www.pwc.ru PwC experience: TatarstanDenis DerevyankinKazan PwC office leader
Content Introduction PwC experience: what is Tatarstanfor our business? Some hints about Tatarstan
Personal Introduction • Kazan PwC office leader • Experience in the profession near 10 years • Work area – whole Russia, from St-Petersburg to Okhotsk • Clients – international, local, public, private • 2 years in Kazan with family Denis Derevyankin
Office Introduction • We opened in 2007 • Office in Kazan was 4th operational office in Russia for PwC after Moscow and Saint-Petersburg • With near 120 employees it’s third-size office in Russia • Practice is focused on development of one region, but provide wide range of services • Top companies of Tatarstan are serviced by PwC We are here
PwC experience: what is Tatarstan for our business? • There are many questions, when you enter other region: • Is it administratively easy? • Are there any perspectives in the region? • Is cost of enter less than forecasted benefits? • Will you be able to react to market quicker? • Do you understand formal and informal rules? • Is there your favorite restaurant in the city? Why?
PwC experience: what is Tatarstan for our business?
PwC experience: what is Tatarstan for our business? • Real life example of benefits of the region used by PwC: • We put Shared Service Center (for Audit services) in Tatarstan • It’s internal department, the main goal of which is supporting of audit teams in Russia by providing standardized services • Current plan - audit time transfer to SSC is almost 30% of all our time cost in Assurance Russia • Why do we such investment to Tatarstan? What does differentiate?
PwC experience: what is Tatarstan for our business? • Regional benefits utilized in creation of SSC: • Mix of industry-specific educated students (center of education in Volga region) with less staff cost (average salary and internal training supportive expenses is less on 20% in comparing with Moscow) • Small rent cost (sq.m. in Kazan office is in 10 times cheaper for us than in Moscow) • Sufficient IT infrastructure, because work of SSC depends significantly on network quality • Life cost is 30-50% less (vs Moscow) for management, that let us transfer top-level specialists on start-up stage from other regions What does differentiate?
Some hints about Tatarstan • Geographical location • Transportation corridors • Ports • Transportation pipes • Airports Tatarstan is one of Russia’s most economically developed regions. It is located in the centre of a large industrial region, 800 kilometres east of Moscow, at the confluence of the Volga and Kama rivers. What is else?
Some hints about Tatarstan Area: 67,836.2 sq. km Population: 3.8 million people Tatarstan stretches 290 km from North to South and 460 km from West to East Tatarstan has a moderately continental climate. Official languages are Tatar and Russian. Predominant religions are Islam and Orthodox Christianity 75.4% of Tatarstan’s residents live in urban areas. The capital is Kazan (area: 614.2 sq. km; population: 1.161 million people) What is else?
Some hints about Tatarstan What is else?
Some hints about Tatarstan • The main reasons to invest to Tatarstan: • Existing market in the region and nearby regions (>1 mln cities); potential demand growth • Low payroll expenses (salaries and related) • Government support for big projects • Existence of “brown-field” capacity • Openness of government What is else?
- More by User

Office Politics and Gossiping
Office Politics and Gossiping Cynthia Gordon School-to-Work Coordinator International Finance and Career High School Office Politics Office (Work) Politics Defined Detriments of Office Politics Benefits of Office Politics Five Rules Concerning Office Politics
2.08k views • 18 slides

PREGINET: Advancing Research and Education Networking in the Philippines Denis F. Villorente [email protected]
PREGINET: Advancing Research and Education Networking in the Philippines Denis F. Villorente [email protected] 1 st International Workshop on Networking Technologies December 17-18, 2003 Bangkok, Thailand History
994 views • 17 slides

Integrating ColdFusion with Microsoft Office
Integrating ColdFusion with Microsoft Office Samuel Neff November 19-21, 2003 About the Presenter Samuel Neff ([email protected]) Senior Software Engineer at B-Line Express Team Macromedia Volunteer for CF Before CF, three years specific experience in Office dev
1.3k views • 38 slides

Servant Leadership
Servant Leadership So many people are suffering for want of good leader throughout the whole world. Morning Talk -- April 25, 1977, Bombay Leader means authority. His instruction is followed, and actually it happens. That is leader. December 16, 1973, Los Angeles
1.85k views • 87 slides

Pod Leader Information
Pod Leader Information. Kayak for a Cause IX July 25, 2009. Updated 7/09 [email protected] and [email protected]. What Makes a Great Pod? Good Leadership. Congratulations on becoming a pod leader!
969 views • 29 slides

Developing the Leader Within You
Developing the Leader Within You. Dr. John C. Maxwell. The key to success in an endeavor is the ability to lead others successfully. Leadership can be taught. Leadership is not an exclusive club for those who were “born with it.”. The Leading Leader. Is born with leadership qualities
11.46k views • 69 slides

Skillful Leader II
Skillful Leader II. PA Rounds Walk Jan 2010. MAKING THE SHIFT TO. Skillful Leader II. LEARNING-FOCUSED AND COMMUNITY-FOCUSED SUPERVISION. Skillful Leader II. CONTENT RIGOR. TEACHER ACTIONS. Traditional Balance of Attention. Student Performance. Skillful Leader II.
1.44k views • 67 slides

[email protected]
A Strong Programming Model Bridging Distributed and Multi-Core Computing. [email protected]. Background: INRIA, Univ. Nice, OASIS Team Programming : Parallel Programming Models: Asynchronous Active Objects, Futures, Typed Groups High-Level Abstractions (OO SPMD, Comp., Skeleton)
1.21k views • 106 slides

Gothic: St.-Denis and the First Cathedrals
Gothic: St.-Denis and the First Cathedrals. Basilica of St.-Denis, Paris, apse and triforium of the choir, 1231 . French Gothic. English Gothic. German Gothic. Spanish Gothic. Italian Gothic. Conventional ways of classifying Gothic architecture. French Gothic: classic balance.
1.22k views • 42 slides

Quiz – Modern U.S.
Quiz – Modern U.S. . Attitude of Americans toward European affairs in the 1930s. isolationism. Official policy of the United States toward European conflicts in the 1930s. neutrality. Leader of fascist Italy. Mussolini. Leader of Nazi Germany. Hitler. Military leader of Japan during WWII.
1.25k views • 108 slides

Troop xx Junior Leader Training
Troop xx Junior Leader Training. <name>, Scoutmaster <name>, Senior Patrol Leader. <location> <date>. Introduction . Purpose: To give YOU the resources YOU need to do YOUR job Evidence: Upon completion, YOU will wear the “Trained” emblem
1.09k views • 89 slides

Experience eBuy : Version 8
Experience eBuy : Version 8. 8. 8. Experience eBuy: Version. Peter A. Bastone Office of Acquisition Management (QVOD) May 15 th - 17 th 2012 . My Background. FAS CIO Experience Advantage/e-Buy Development/Requirements Categorization and Product Data Business stats and reporting
793 views • 65 slides

Experience eBuy : Version 8. 8. 8. Experience eBuy: Version. Peter A. Bastone Office of Acquisition Management (QVOD) May 15 th - 17 th 2012. My Background. FAS CIO Experience Advantage/e-Buy Development/Requirements Categorization and Product Data Business stats and reporting
776 views • 65 slides

Denis Caromel Scientific Coordinator [email protected] Beijing, October 2007
Denis Caromel Scientific Coordinator [email protected] Beijing, October 2007. Overview of. GCM Partners. GCM: Grid Component Model GCM Being defined in the NoE CoreGRID (42 institutions) Open Source ObjectWeb Pro Active implements a preliminary version of GCM
934 views • 79 slides

Servant Leadership. So many people are suffering for want of good leader throughout the whole world. Morning Talk -- April 25, 1977, Bombay. Leader means authority. His instruction is followed, and actually it happens. That is leader. December 16, 1973, Los Angeles.
1.3k views • 87 slides

TEAM LEADER
NOVA SCOTIA GROUND SEARCH AND RESCUE ASSOCIATION. TEAM LEADER. Search Teams. Most valuable component of Search Success - desire, ability and knowledge Team Leadership key. Team Leader considerations. Responsibilities and Expectations Search Management Deal with situations
949 views • 53 slides

Erdogan's Turkey
Ahead of Sunday's referendum on broadening President Tayyip Erdogan's powers, a look back at the influential leader's time in office.
621 views • 27 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Receiver shall produce the permit to the Contractor responsible personnel for the work requested in the permit for review and verification by 15:00 hours a day before the commencement of the activity/work. As rapidly as the assessment & verification were made, the PTW Receiver shall deliver the verified allow to the HSE Permit Coordinator.
A Permit to Work (PTW) serves the primary purpose of ensuring safety in the workplace. It is a formal document that authorizes specific activities, especially those with potential risks to health and safety. The PTW helps in assessing and mitigating these risks, making sure that all necessary precautions are taken before hazardous work begins. 2.
A P.T.W system aims to ensure that proper planning and consideration is given to the risks of a particular job. The permit is a written document which authorizes certain people to carry out specific work, at a certain time and place, and which sets out the main precautions needed to complete the job safely.
A permit to work (PTW) system is a process to keep employees safe during hazardous and nonstandard operations. It involves assessing the risks, establishing a proper safety protocol based on the risks, and proper communication throughout the entire process. The PTW system is designed to mitigate environmental, health, sustainability, and safety ...
The Permit to Work System training is a comprehensive program designed to equip participants with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement and manage a robust permit to work system within their organizations. This training is essential for anyone responsible for workplace safety and controlling hazardous work activities.
The Work permit system should include a process for the display of permits, the suspension of work, and the handover of work. The display of permits ensures that everyone involved in the work is aware of the permit and its conditions. The suspension of work allows for the safe stoppage of work if necessary.
Satisfy employers' PTW and LOTO training requirements Have an additional safety training certificate for an impressive resume Certificate: You'll be able to print your digital certificate of completion from Trainovate®, once you've completed the Permit to Work and LOTO course. Course Delivery and Contents: E-learning videos/lessons Text ...
PPE e.g. by providing personal protective equipment and clothing PTW System - PI & PH Orientation Training. 25 Hierarchy of Fall Protection Controls Fall Protection hierarchy of controls for determining work at height control measures in order: 1. Eliminate the work at height e.g. by changing the work 2. Work from permanent guard rail; parapet 3.
basis of e-learning courses in physics is an important comp. ement to traditional forms of learning. Work in the on-line mode is natural for today's students. This form of education is useful and convenient, it helps to make self-study more active, allows monitoring the results, participa.
In Kazan federal university there are 12 institutes, 10 independent faculties and consisting of many different and connected high tech laboratory with university campus. The hospital affiliated with Kazan federal University provides large opportunities to the students to gain practical training. Because 30% population of Russia lives in Kazan city.
www.pwc . ru. PwC experience: Tatarstan Denis Derevyankin Kazan PwC office leader. Content. Introduction PwC experience: what is Tatarstan for our business? Some hints about Tatarstan. Personal Introduction. Kazan PwC office leader Experience in the profession near 10 years Slideshow 2635217 by...