- Utility Menu

Department of Sociology
- National Science Foundation Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant (NSF DDRI)
National Science Foundation Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant (NSF DDRI) awards are now known as American Sociological Association Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grants (ASA DDRI).
Previous NSF DDRI Grant Recipients :
2019 laura adler ; advisor: frank dobbin ; project: "pay-setting for new hires" kristina brant ; advisor: mario l. small ; project: "parental opioid addiction and kinship care" jared schachner ; advisor: robert j. sampson ; project: " skill-based sorting into neighborhoods and schools", 2018 blythe george ; advisor: william julius wilson ; project: " employment of native americans with criminal records" barbara kiviat ; advisor: frank dobbin ; project: " the moral foundations of the big data economy" amy tsang ; advisor: michele lamont ; project: " how people become urban" linda zhao ; advisor: jason beckfield ; project: " spatial inequality in birth outcomes - testing classes of proximate mechanisms", 2017 nathan wilmers ; advisor: bruce western ; project: "the role of employers in rising wage inequality" thomas wooten ; advisor: mary c. waters ; project: "the transition to college experience of low-income students", 2015 carly knight ; advisor: frank dobbin ; project: "the development of corporate personhood law in comparative perspective, 1886-2014" jasmin sandelson ; advisor: matthew desmond ; project: "unaccompanied homeless youth" chi wang ; advisor: bart bonikowski ; project: "the process and consequences of the work of 911 dispatchers", 2013 christopher muller ; advisor: bruce western ; project: "racial disparity in american incarceration, 1868-1950" kimberly e. pernell ; advisor: frank dobbin ; project: "the causes of divergent banking regulation, 1988-2006" eva rosen ; advisor: mary c. waters ; project: "post-public housing spatial concentration", 2012 jovonne bickerstaff ; advisor: orlando patterson ; project: "how attitudes and practices shape enduring relationships", 2010 nathan fosse ; advisor: michele lamont ; project: "low-income youth and perceptions of mortality" chana teeger ; advisor: mary c. waters ; project: "apartheid education and race relations", 2009 christopher bail ; advisor: michele lamont ; project: "a multi-level study of symbolic boundaries towards muslims, 2001-2007" jeffrey denis ; advisor: william julius wilson ; project: "native and non-native group interactions" jiwook jung ; advisor: frank dobbin ; project: "shareholder value and the new american workplace: investor-driven downsizing, 1980-2007" laura tach ; advisor: christopher jencks ; project: "the social consequences of neighborhood economic diversity", 2008 simone ispa-landa ; advisor: orlando patterson ; project: "urban-to-suburban racial desegregation: a natural experiment" mark pachucki ; advisor: nicholas christakis ; project: "health behaviors and social networks", 2007 lydia bean ; advisor: jason kaufman ; project: "a comparative study of political socialization in religious groups in the united states and canada" maria rendon ; advisor: mary c. waters ; project: "transition out of school and into young adulthood:the role of neighborhoods in education and work outcomes of mexican american youth" lauren rivera ; advisor: michele lamont ; project: "hiring and inequality in high prestige professions", 2006 elisabeth jacobs ; advisor: christopher jencks ; project: "the perception and management of family economic risk" zoua vang ; advisor: mary c. waters ; project: "spatial assimilation or residential segregation a comparative study of racial and ethnic minority residential patterns in ireland and the u.s.", 2004 jal mehta ; advisor: christopher jencks ; project: "the transformation of american educational policy, 1980-2001" natasha warikoo ; advisor: mary c. waters ; project: "bringing culture back in: cultural assimilation and the second generation in the global city", 2003 david j. harding ; advisor: katherine newman ; project: "linking culture and structure to adolescent outcomes in poor neighborhoods" dongxiao liu ; advisor: theda skocpol ; project: "how world conferences matter: transnational influences and organizational change in two national women's movements, 2002 tomas jimenez ; advisor: mary c. waters ; project: "the effects of mexican immigration on mexican american ethnicity", 2000 irene bloemraad ; advisor: theda skocpol ; project: "the political incorporation of immigrants: citizenship and participation in the united states and canada" ziad munson ; advisor: theda skocpol ; project: "mobilization in the american pro-life movement".
- Undergraduate
- Graduate Degrees Awarded
- Program Requirements
- Ph.D.s on the Job Market
- Graduate Student Organization (GSO)
- Information for Teaching Fellows
- Graduate Student News
- Paul and Daisy Soros Fellowship for New Americans
- AAUW American Dissertation Fellowships
- AAUW International Fellowships
- ABF Doctoral Fellowships Program in Law & Inequality
- American Sociological Association Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant (ASA DDIRG)
- American Sociological Association Minority Fellowship Program
- Asia Center Winter Research Travel Grants
- Canada Graduate Scholarship (SSHRC)
- Center for American Political Studies (CAPS) Dissertation Fellowships
- Center for American Political Studies (CAPS) Seed Grant
- Center for Geographic Analysis GIS Institute
- Clifford C. Clogg Scholarship
- Cultural Exchange Fulbright
- Djokovic Science & Innovation Fellows / Richmond Fellows
- Dorothy S. Thomas Award
- Edmond J. Safra Center for Ethics Graduate Fellowships
- Fairbank Center for Chinese Studies Summer Research Grant
- Ford Foundation Predoctoral Fellowship
- Fund for Research on the Foundations of Human Behavior
- Graduate Society Merit/Term-Time Fellowships
- Graduate Society Predissertation Summer Fellowships
- Graduate Student Associates Program at the Weatherhead Center for International Affairs
- HKS Ash Center China Programs Student Research Grant
- HKS Program in Criminal Justice Policy and Management Research Grant
- Harvard IQSS Jeanne Humphrey Block Dissertation Award
- Harvard Institute for Quantitative Social Science Research Grant
- Harvard Mellon Urban Initiative Doctoral Fellowships
- Horowitz Foundation for Social Policy Grants
- Jens Aubrey Westengard Fund
- Joint Center for Housing Studies
- Korea Institute Supplementary Dissertation Research Grant
- Krupp Foundation Dissertation Research Fellowship
- Mathematica Summer Fellowship
- Minda de Gunzburg Center for European Studies at Harvard Dissertation Completion Fellowship
- Multidisciplinary Program in Inequality & Social Policy PhD Scholars
- NAEd/Spencer Dissertation Fellowships
- National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program (NSF GRFP)
- Open Gate Foundation for LGBTQ+ Research Grant
- Radcliffe Institute for Advanced Study Graduate Student Fellowship
- Rappaport Institute for Greater Boston Public Policy Summer Fellowship
- Russell Sage Foundation
- SSRC – Mellon Mays Dissertation Completion Grant
- Social Science Research Council – Mellon Mays Pre-doctoral Research Grant
- South Asia Institute Summer Research Grant
- Tobin Project Graduate Student Fellows
- WIGi Graduate Research Fellows
- WIGi Small Research Grants for Harvard Graduate Students
- Washington Center for Equitable Growth Grantees
- Weatherhead Center for International Affairs Canada Program Fellowship
- Weatherhead Center for International Affairs Pre-Dissertation Research Grant
- Graduate Resources
- Sociology Courses
American Sociological Association (ASA) Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grants (DDRIG)
- Social Sciences
- Fall Quarter (September-December)
- International Research or Work
- Research Grant
- No citizenship requirements
The National Science Foundation (NSF) has made two awards to ASA to administer the Sociology Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant (DDRIG) program. This program supports theoretically grounded empirical investigations to advance understanding of fundamental social processes. Up to 25 awards of a maximum of $16,000 will be given each year.
UChicago doctoral candidates should consult the SSRC DDRIG toolkit for program dates, timelines and other institutional support.
Eligible Research
Topics can include, but will not be limited to, organizations and organizational behavior, health and medicine, crime and deviance, inequality and stratification, population dynamics, social movements, social groups, labor force participation, stratification and mobility, family, social networks, socialization, gender, race, ethnicity, and the sociology of science and technology. Projects that explore new methodologies, including but not limited to computational sociology, big data, large scale modeling, and innovative use of emerging technologies, will also be welcomed.
Grant funds can be used for costs directly associated with conducting research, such as dataset acquisition, statistical or methodological training, equipment, payments to research subjects or research assistants, data transcription, and costs associated with conducting archival research or field work. Living expenses, including dependent care, are also allowed, as are travel expenses to attend professional meetings, including the ASA Annual Meeting. Indirect costs are not permitted.
Eligibility
Doctoral students attending PhD-granting institutions of higher education accredited in, and having a campus located in, the United States, are eligible to apply. Proposals must be submitted by a research scholar with support from a research sponsor. The research scholar is the doctoral student whose dissertation research will be supported and should be the one to submit the application. Doctoral students who have previously received an NSF-funded DDRIG, whether administered directly by NSF (such as the DRMS DDRIG), by ASA, or by another organization (such as the APSA DDRIG or ASU LSDG), are ineligible to apply for additional funding through this program.
Fellowship Website:
Your information has been submitted. Thanks!
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS. A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

NSF 101: Graduate and postdoctoral researcher funding opportunities
The U.S. National Science Foundation supports research opportunities and provides stipends for graduate students and postdoctoral fellows and scholars.
There are multiple ways to find these programs, including the funding search on NSF’s website and the NSF Education & Training Application , which is growing its list of opportunities for graduate students and postdoctoral scholars.
To help begin your search, opportunities for graduate students and postdoctoral researchers are listed below. The principal investigator, or PI (a researcher who oversees a project), is often listed on these grants, along with their graduate students or postdoctoral researchers.
Graduate Student
While funding for graduate students is often included in a PI’s research proposal, the following opportunities are also available for early career researchers.
- Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Awards/Grants (DDRI/DDRIG) These programs help fund doctoral research in a variety of fields to help provide for items not already available at the academic institution. The funding provided cannot be used for items such as, but not limited to, tuition, stipends, textbooks or journals. The monetary amount listed in each DDRI/ DDRIG section does not include indirect cost associated with the project. The doctoral student should be listed as a co-PI on the grants with their advisor listed as the primary PI.
Archaeology Program- DDRIG : This program supports doctoral laboratory and field research on archaeologically relevant topics, with the goal of increasing anthropologically focused understanding of the past. Awards provide funding up to $25,000 per awardee.
Arctic Science Section DDRIG : The Arctic Sciences Section offers opportunities for DDRI proposals in the following programs: Arctic Social Sciences supports research in any field of social science. Arctic System Science supports projects that address the relationships among physical, chemical, biological, geological, ecological, social, cultural and/or economic processes to advance our understanding of the Arctic system. Arctic Observing Network supports projects focused on scientific and community-based- observations; development of in situ or remote sensors and automated systems; design and optimization of coordinated and scalable observation networks; and management of Arctic Observation Network data, data accessibility and data discovery. Awards provide funding up to $40,000 for a maximum of 3 years.
Biological Anthropology Program- DDRIG : This program supports research on human and non-human primate adaptation, variation and evolution. Awards provide funding up to $25,000 for up to two years.
Cultural Anthropology Program- DDRIG : This program supports research that is focused on cultural anthropology research, including topics such as: Sociocultural drivers of anthropogenic processes (i.e., deforestation, urbanization); resilience and robustness of sociocultural systems; scientific principles underlying altruism, conflict, cooperation, and variations in culture and behaviors; economy, culture migration and globalization; kinship and family norms. Awards provide funding for up to $25,000 for up to two years.
Decision, Risk and Management Science DDRIG : This program supports research on decision, risk and management sciences. This includes research in the areas of judgement and decision making; decision analysis and decision aids, risk analysis; perception and communication; societal and public-policy decision making; and management science and organizational design. Awards are for a maximum of 12 months.
Economics DDRIG :This program provides funding for research focused on improving the understanding of the U.S. and global economy from macroscale to microscale, including all field of economics such as macroeconomics, microeconomics, econometrics, economic theory, behavioral economics and empirical economics.
Human-Environment and Geographical Sciences Program- DDRI : This program supports basic scientific research about the nature, causes and/or consequences of the spatial distribution of human activity and/or environmental processes across a range of scales. The program welcomes proposals for empirically grounded, theoretically engaged, and methodologically sophisticated, generalizable research in all sub-fields of geographical and spatial sciences. Awards may not exceed $20,000 in direct costs.
Linguistics Program- DDRI : This program supports research on human language, including syntax, linguistic semantics and pragmatics, morphology, phonetics, and phonology of individual languages or in general. Awards provide up to $12,000 for a maximum of two years.
Dynamic Language Infrastructure- DDRI : This program supports research on building dynamic language infrastructure, which includes describing languages; digitizing and preserving languages; and developing standards and databases for analyzing languages. Provides funding up to $15,000 for up to two years.
Graduate Research Fellowship Program This fellowship supports full-time master's or doctoral students earning their degree in a research-based program focused on STEM or STEM education. Students are the primary submitter for the fellowship. Fellows will be awarded a $37,000 stipend and $12,000 cost-of-education allowance for three years of the five-year fellowship. For tips on applying, see our previous NSF 101 article on the fellowship program .
Non-Academic Research Internships for Graduate Students (INTERN) Supplemental Funding Opportunity This supplemental funding opportunity is for graduate students funded by active NSF grants. PIs may submit for up to an additional six months of funding to allow students to participate in research internship activities and training opportunities in non-academic settings, such as the following: for-profit industry research; start-up businesses; government agencies and national laboratories; museums, science centers, and other informal learning settings; policy think tanks; and non-profit institutions. Students must have completed at least one academic year of their program. This funding request may not exceed $55,000 per student for each six-month period. A student may only receive this opportunity twice. In addition to the general INTERN opportunity, there are two topic-specific INTERN opportunities:
Non-Academic Research Internships for Graduate Students in Geothermal Energy Supplemental Funding Opportunity : This opportunity is provided by NSF in partnership with the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. It maintains the same funding levels and requirements as the general INTERN program; however, funding may only be used for gaining knowledge, skills, training and experience in geothermal energy and technology.
- Research Internships for Graduate Students at Air Force Research Laboratory Supplemental Funding Opportunity : This funding opportunity is for students supported on an active NSF grant to intern at a Air Force Research Laboratory facility. AFRL has several potential technology directorates available for students at locations across the U.S.: Aerospace Systems (Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio), Information (Rome, New York), Materials and Manufacturing (Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio), Directed Energy (Kirtland Air Force Base, New Mexico), Munitions (Eglin Air Force Base, Florida), Sensors (Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio), Space Vehicles (Kirtland Air Force Base, New Mexico), 711th Human Performance Wing Training (Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio).
Mathematical Sciences Graduate Internship This summer internship is for doctoral students in mathematical sciences through a partnership between NSF and Oak Ridge Institute for Science and E ducation. It provides students who are interested in academic and non-academic careers with the opportunity to learn how advanced mathematics and statistical techniques can be applied to real-world problems. Participants in the internship will receive a stipend of $1,200 per week during the 10-week internship. In addition, there is travel reimbursement for up to $2,000 for those who live more than 50 miles away from their hosting site.
NSF Research Traineeship Program Graduate students can apply for this traineeship through their institutions, if available. These topics can range across the scientific spectrum. Current projects can be found by state .
Research Experiences for Graduate Students Supplemental Funding These awards provide additional funding for graduate students with mentors who have an active NSF grant. Currently funding is available through the following programs:
Cultural Anthropology provides up to $6,000 per student for research activities.
Human Environment and Geographical Sciences at Minority Serving Institutions and Community Colleges provides up to $7,000 per student for research activities.
Postdoctoral Scholars
Astronomy and Astrophysics Postdoctoral Fellowship This fellowship supports research investigating a field within astronomy or astrophysics for up to three years. The stipend is $75,000, with a fellowship allowance (i.e., expenses for conducting and publishing research, fringe benefits) of $35,000.
Atmospheric and Geospace Sciences Postdoctoral Fellowship This fellowship supports postdoctoral fellows in atmospheric or geospace sciences. Atmospheric science includes topics such as atmospheric chemistry; climate and large-scale dynamics; paleoclimate climate; and physical and dynamic meteorology. Geospace science focuses on aeronomy, magnetospheric physics and solar terrestrial research. This fellowship provides up to 24 months of support. The stipend is $70,000 per year, with a fellowship allowance of $30,000.
Earth Science Postdoctoral Fellowship This program supports the study of structure, composition and evolution, the life it supports and the processes that govern the formation and behavior of Earth’s materials. Researchers are supported for up to two years at the institution of their choice, including institutions abroad. The stipend is $65,000 per year, with a fellowship allowance of $25,000 per year.
Mathematical and Physical Sciences Ascending Postdoctoral Research Fellowships
This program supports postdoctoral fellows performing impactful research while broadening the participation of members of groups that are historically excluded and currently underrepresented in mathematical and physical sciences. This fellowship can last between one and three years. The stipend is up to $70,000 per year, with a fellowship allowance of $30,000 per year.
Mathematical Sciences Postdoctoral Research Fellowships This fellowship has two options:
- The Research Fellowship provides full-time support for any 18 months within a three-year academic period.
- The Research Instructorship provides a combination of full-time and half-time support over a period of three academic years, which allows the fellow to gain teaching experience. Both options receive up to $190,000 over the fellowship period. The full-time stipend is $5,833 per month and the part-time stipend is $2,917 per month. In addition, the fellow will receive $50,000 in two lump sums ($30,000 in the first year and $20,000 in the second year) for fellowship expenses.
Ocean Sciences Postdoctoral Research Fellowships This fellowship supports research in topic areas such as: biological oceanography, chemical oceanography, physical oceanography, marine geology and geophysics, ocean science and technology. This two-year fellowship with a stipend of $67,800 for the first year and $70,000 for the second year, with a fellowship allowance of $15,000 per year.
Office of Polar Programs Postdoctoral Research Fellowships This fellowship supports postdoctoral research in any field of Arctic or Antarctic science. This two-years fellowship, with a stipend of $67,800 for the first year and $70,000 for the second year, with fellowship expenses of $15,000 per year.
Postdoctoral Research Fellowship in Biology The Directorate of Biology offers a fellowship for postdoctoral researchers in one of three areas:
- Broadening Participation of Groups Underrepresented in Biology. This area requires a research and training plan that is within the scope of the Directorate for Biology and that enhances diversity within the field.
- Integrative Research Investigating the Rules of Life Governing Interaction between Genomes, Environment and Phenotypes. This area aims to understand higher-order structures and functions of biological systems. Research should use a combination of computational, observational, experimental or conceptual approaches.
- Plant Genome Postdoctoral Research Fellowships. This area has a broad scope and supports postdoctoral training and research at the frontier of plant biology and of broad societal impact. Highly competitive proposals will describe interdisciplinary training and research on a genome wide scale. The fellowships are for 36 months and have a stipend of $60,000 per year, with a research and training allowance of $20,000 per year.
SBE Postdoctoral Research Fellowships This fellowship supports postdoctoral research in the social, behavioral and economic sciences and/or activities that broaden the participation of underrepresented groups in these fields. Funding is up to two years and has two tracks available:
- Fundamental Research in the SBE Sciences. This track supports research focused on human behavior, interaction, social and economic systems.
- Broadening Participation in SBE Sciences. This track aims to increase the diversity of post-doctoral researchers in the social, behavioral and economic sciences. In addition to the research proposal, these applications should also answer the question: “How will this fellowship help broaden or inform efforts to broaden the participation of underrepresented groups in the United States?” The stipend for this program is $65,000 per year (paid in quarterly installments) and the research and training allowance is $15,000 per year.
SBIR Innovative Postdoctoral Entrepreneurial Research Fellowship This fellowship supports postdoctoral researchers at start-up companies through the Small Business Innovation Research program. By recruiting, training, mentoring, matching and funding these early-career scientists, this fellowship addresses the need of doctoral-level expertise at small, high-tech businesses. The base stipend is $78,000 per year with optional individual health and life insurance, relocation assistance (company dependent), professional conference travel allowance, and professional development funds.
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics Education Individual Postdoctoral Research Fellowship This fellowship is for postdoctoral researchers to enhance their research knowledge, skills, and practices of STEM education research. If the fellowship is granted, the fellow is expected to remain affiliated with the host organization and PI sponsoring them. The fellowship can last up to two years with an annual stipend of $70,000, with fellowship expenses of $15,000.
Multilevel
CyberCorps® Scholarship for Service This program is for students earning their associates, bachelor's, master's or doctoral degree in cybersecurity. A stipulation of the program is that the recipients must work after graduation in a cybersecurity mission of the federal, state, local or tribal government for an equal amount of time as the scholarship's duration. It will provide full tuition and fees plus a stipend of $27,000 per academic year for undergraduates and a stipend of $37,000 per academic year for graduate students, in addition to a professional allowance of $6,000 for all levels.
NSF-NIST Interaction in Basic and Applied Scientific Research This supplemental funding request is for NSF-supported researchers to collaborate with researchers at a National Institute of Standards and Technology facility. It can be used for travel expenses and per diem associated with on-site work at NIST. It is available for NSF-supported PIs, co-PIs, postdoctoral scholars, graduate and undergraduate students and other personnel associated with the research. PIs should contact their NSF program director for their award before applying.
This extensive list shows the ways in which NSF helps train the next generation of STEM researchers. If you are interested in learning more about any of these programs, reach out to contacts listed on the award webpages.
If you are interested in awards for high school students, undergraduates and post-baccalaureate scholars, check out our previous NSF101 for more information!
About the Author
Related stories.

5 NSF projects transforming how researchers understand plastic waste

NSF 101: The NSF brand identity

Exploring the science of the sun during the eclipse

- find/post job
- annual meeting
- Governing Documents
- Strategic Plan
- APSA Public Statements and Letters
- Staff Directory
- APSA Annual Fund
- Ways to Make a Contribution
- Join the APSA Legacy Society
- Support the Ralph J. Bunche Fund
- APSA Relief Fund
- APSA Membership
- Individual Membership Benefits
- Individual Membership Forms
- Individual Membership FAQs
- Past Member Spotlights
- Trial Membership
- Departmental Membership FAQs
- Departmental Sponsored Student Membership
- Institutional Subscription
- Interdisciplinary Membership FAQ's
- Student Benefits
- Section Awards
- Organized Section FAQ's
- For Section Officers and Organizers
- Committee On Organized Sections
- Section Dues
- Related Groups
- Partner Associations
- Annual Meeting & Exhibition
- Webinar Archive
- APSA Virtual Research Meeting
- Teaching & Learning Conference
- Past APSA Conferences
- Exhibits and Sponsorships
- Conferences In The Profession
- APSA Publications
- Call for Editors
- APSR Submission Guidelines
- Appeals Process
- Peer Review Policy
- APSR Editorial Board
- About the Editors
- Editorial Reports
- Perspectives Submission Guidelines
- Submission Guidelines
- Guidelines for Proposals: Symposia and Spotlights
- Calls for Papers
- Journal of Political Science Education
- Political Science Today
- Political Science Internships
- Navigating Political Science
- Style Manual
- Strategies for Navigating Graduate School and Beyond
- Publications Permissions
- Ithiel de Sola Pool Lectures
- James Madison Lectures
- John Gaus Lectures
- Benjamin E. Lippincott Lectures
- Johan Skytte Lectures
- APSA Preprints
- Publishing Resources
- Publishing FAQs
- Student Resources
- Academic Careers
- Applied Careers
- Professional Development
- Jobs At APSA
- Executive Director (Job Ad)
- Internship Resources
- Graduate Student Connection
- Graduate Student Questions
- Student Journals
- Institutions Granting Ph.D.s in Political Science
- Political Science Organizations
- Resources for Teaching and Learning
- Resources for Community College Faculty
- Pedagogy Workshops
- APSA Travel Grants
- Other Grants, Fellowships and Awards in the Discipline
- Chart of the Month
- Tools and Datasets
- Caucuses in Political Science
- Related Group Officer Resources
- Sexual Harassment
- Political Science Associations
- Resources for Coronavirus Response
- Travel Advisory Resources
- Resources for Addressing Anti-Asian Hate and Violence
- Resources for Addressing Antisemitism, Islamophobia, and Anti-Arab Racism
- Juneteenth Resources
- Merze Tate - Elinor Ostrom Outstanding Book Award
- APSA Best Poster Award
- APSA Community College Faculty Award
- APSA Distinguished Award for Civic and Community Engagement
- APSA Distinguished Teaching Award
- APSA-IPSA Theodore J. Lowi Award
- APSA-PSA International Partnerships Award
- Barbara Sinclair Lecture
- Benjamin E. Lippincott Award
- Carey McWilliams Award
- Charles Merriam Award
- APSA Award for Teaching Innovation
- E.E. Schattschneider Award
- Edward S. Corwin Award
- Frank J. Goodnow Award
- Franklin L. Burdette/Pi Sigma Alpha Award
- Gabriel A. Almond Award
- Gladys M. Kammerer Award
- Hanes Walton, Jr. Award
- Harold D. Lasswell Award
- Heinz I. Eulau Award
- Hubert H. Humphrey Award
- Ithiel de Sola Pool Award
- James Madison Award
- John Gaus Award
- Kenneth Sherrill Prize
- Leo Strauss Award
- Leonard D. White Award
- Merze Tate Award
- Michael Brintnall Teaching and Learning Award
- Ralph J. Bunche Award
- Robert A. Dahl Award
- Victoria Schuck Award
- William Anderson Award
- Prospective Fellow Resources
- The Fellowship Experience
- Fellowship FAQs
- Our Fellows
- CFP Alumni Resources
- Partner Organizations and Resources
- History of Congressional Fellowship Program
- Applicants and Eligibility
- Application Materials and Format
- Grantee Resources
- 2023 DDRI Grantees
- 2020 DDRI Grantees
- 2021 DDRI Grantees
- 2022 DDRI Grantees
- TLC at APSA
- Departmental Services
- For the Media
- For the Public
- Tool and Tips for Engagement
- Communications Training Workshops
- Resources for Public Engagement
- Asia Workshops
- MENA Workshop
- International Conference Panels Travel Grant
- National Science Foundation
- National Endowment for the Humanities
- International Education
- Letters & Statements
- Member Action
- APSA Educate: Online Teaching Library
- Undergraduate Research Week
- Joint International Teaching Conference
- Virtual Teaching Workshops
- Informational Resources on the Middle East, Israel, and Palestine
- Online Syllabi Collections
- Teaching Awards & Recognition
- APSA Webinars
- RAISE the Vote
- Background and History of Diversity and Inclusion Programs
- Resources for Diversity and Inclusion
- How to Apply
- About the RBSI Program
- Current RBSI Scholars
- RBSI 30th Anniversary
- Alumni Reflections
- About Dr. Ralph J. Bunche
- Donate: RBSI Endowment Fund
- APSA RBSI Advisory Committee
- Spring DFP Application
- Fall DFP Application
- Past DFP Fellows
- 2023 Fujii DFP Travel Grant Recipients
- Current DFP Fellows
- Find an APSA Mentor
- Become an APSA Mentor
- Apply to Be a Mentee
- Mentor Resources
- Mentoring FAQs
- DSRP Recruiting Departments
- 2023-2024 DSRP Recruiting Departments
- Advancing Research Grants- Early Career Scholars
- Advancing Research Grants- Indigenous Politics
- Guidelines for Grants
- Current FLS Recipients
- 2021 FLS Recipients
- Adaljiza Sosa-Riddell Mentor Award
- Status of Blacks in the Profession Committee
- Status of Women in the Profession Committee
- Committee on the Status of Community Colleges in the Profession
- 2022 First Generation Scholar Travel and Accessibility Grant Recipients
- 2023 First Generation Scholar Travel and Accessibility Grant Recipients
- Committee on the Status of Graduate Students in the Profession
- Committee on the Status of Contingent Faculty in the Profession
- Status of Asian Pacific Americans in the Profession Committee
- Status of Lesbians, Gays, Bisexuals, and Transgender Individuals in the Profession
- Status of Disability in the Profession
- Diversity and Inclusion FAQs

The National Science Foundation (NSF) has made two awards to APSA to administer the Political Science Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant (DDRIG) program. The NSF awarded APSA $1,410,000 to administer the DDRIG program from 2020 to 2023, and they renewed this award to continue its administration from 2023 to 2026.
"APSA is excited to support the advancement of knowledge of citizenship, government, and politics by providing funding for highly promising doctoral dissertation research. The program also plans to draw upon APSA’s networks and programming to promote diversity and representation throughout the recruitment, selection, and support of awardees."
– Steven Rathgeb Smith, Executive Director of APSA
The Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant project provides support to enhance and improve the conduct of doctoral dissertation research in political science. Awards will support basic research which is theoretically derived and empirically oriented. The APSA Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant program will award between twenty and twenty-five grants yearly of between $10,000 and $15,000 to support doctoral dissertation research that advances knowledge and understanding of citizenship, government, and politics. The 2024 cycle of APSA Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grants opens April 1, 2024 and closes June 15, 2024.
The program will also connect awardees to APSA’s extensive professional development and public engagement networks and resources, to amplify the effect of the award on the awardee’s career and on the impact of their work as they explore solutions to a wide range of institutional, political, and social challenges. In addition, it will support the advancement of national health, prosperity, and welfare, by supporting projects that identify ways to use knowledge of citizenship, government, and politics to benefit society. The APSA Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grants was funded under NSF award number 2000500 and under NSF award number 2317099 .
Advancing diversity and inclusion in the profession is a key priority of the association and the APSA Strategic Plan . As such, APSA is committed to identifying and supporting especially promising doctoral dissertation research, particularly research by scholars from groups, institutions, and geographic areas that are underrepresented in political science. The APSA Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grants Program is dedicated to recruiting diverse applicant and reviewer pools to fund doctoral students from diverse groups and institutions, and ultimately support increased participation of women and underrepresented minorities in political science research.
For more information, contact [email protected] .
All proposals for APSA Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grants must include the following:
These frequently asked questions will be helpful to PhD students who are considering applying for the APSA Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant.
Message Title goes here
Select the company to represent.
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS. A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Search Awards
- Recent Awards
- Presidential and Honorary Awards
- About Awards
- How to Manage Your Award
- Grant General Conditions
- Cooperative Agreement Conditions
- Special Conditions
- Federal Demonstration Partnership
- Policy Office Website
Please report errors in award information by writing to: [email protected] .
Finished Papers
Customer Reviews
receive 15% off
The shortest time frame in which our writers can complete your order is 6 hours. Length and the complexity of your "write my essay" order are determining factors. If you have a lengthy task, place your order in advance + you get a discount!
To describe something in great detail to the readers, the writers will do my essay to appeal to the senses of the readers and try their best to give them a live experience of the given subject.

Looking for something more advanced and urgent? Then opt-in for an advanced essay writer who’ll bring in more depth to your research and be able to fulfill the task within a limited period of time. In college, there are always assignments that are a bit more complicated and time-taking, even when it’s a common essay. Also, in search for an above-average essay writing quality, more means better, whereas content brought by a native English speaker is always a smarter choice. So, if your budget affords, go for one of the top 30 writers on our platform. The writing quality and finesse won’t disappoint you!
Premium essay writers
Essay writing help from a premium expert is something everyone has to try! It won’t be cheap but money isn’t the reason why students in the U.S. seek the services of premium writers. The main reason is that the writing quality premium writers produce is figuratively out of this world. An admission essay, for example, from a premium writer will definitely get you into any college despite the toughness of the competition. Coursework, for example, written by premium essay writers will help you secure a positive course grade and foster your GPA.
Alexander Freeman

Getting an essay writing help in less than 60 seconds
We use cookies to make your user experience better. By staying on our website, you fully accept it. Learn more .
THE MANY SINS OF MOSCOW�S NEW ST. ANDREWS COLLEGE
by Nick Gier
For a full accreditation report on NSA see this link . For articles on the Wilson Saga click this link .
In April 2000, I gave a talk to the students and faculty of New St. Andrews College (NSA), a small Calvinist college established in Moscow in 1994. At that time I congratulated Douglas Wilson, founder of the college, on the success of both NSA and his K-12 Logos School. Wilson appeared to enjoy a story I told about him as a student in the philosophy department, and it got a good laugh from the audience. I also announced that I was prepared to help NSA students with their senior theses. In the previous year I had spent about 60 hours helping a bright NSA student with a thesis on Buddhism.
In December 2002, I invited NSA faculty and students to the regional meeting of the American Academy of Religion. It was held in Moscow in May 2003, and 40 percent of the papers were presented by faculty from conservative Christian colleges. NSA president Roy Atwood defended their absence by saying that they �had better things to do.�
Wilson wrote an article �Why Evangelical Colleges Are Not� in Chronicles (September, 1998), the journal of the far right Rockford Institute. The hostility displayed against reputable evangelical colleges in this article not only shows blatant disrespect for these fine schools, but it manifests shameful disregard for the entire academic enterprise.
In a letter to the Moscow-Pullman Daily News on May 23, 2003, Atwood wrote that his college was an accredited institution. At a legal hearing before the Latah County Commissioners in April 2003, the NSA attorney also testified that NSA was accredited. The problem, however, is that NSA did not receive its accreditation until November 29, 2005.
In October, 2003, the community learned of the existence of Wilson�s booklet on slavery in the Antebellum South in which he stated that �there has never been a multi-racial society which has existed with such mutual intimacy and harmony in the history of the world" (p. 24). It was later discovered that 20 percent of this text was lifted from another book. When two UI history professors wrote a paper criticizing Wilson, his reaction was to write Governor Kempthorne and request that the professors be disciplined.
Only recently did I learn that NSA faculty celebrated April Fools of 1999 by stealing letterhead from the UI provost�s office to distribute an announcement of visiting feminist scholars who would give their presentations topless. There is nothing wrong with a good joke, but one usually tries to avoid criminal activity in pulling stunts such as this. Recently Wilson defended this action in his blog: �By the time you receive this, our local police will probably have forgotten all about it, so a little bragging is now safe. . . . [My son-in-law], . . . encouraged by some winks and nudges from me, . . . made up a flyer which announced a topless and proud lecture series by topless feminist scholars.�
An important academic virtue is �collegiality,� which consists of respect for, and cooperation with, all members of the academic community. I believe that we can conclude from NSA�s actions that it has not been a very good academic citizen. The supreme irony is that 9 of the15 NSA faculty have, or are expecting, 13 UI degrees.
The following are some more disturbing NSA facts:
Only 27 percent of the college�s faculty have PhDs. NSA has the resources to hire PhDs, but evidently chooses not to do so. Their less than prestigious accrediting agency requires that only one third of the faculty have the doctorate.
Two of the college�s senior fellows, presumably equivalent to full professors, do not have PhDs. Generally, a PhD is required at the lowest rank of assistant professor.
Although full resumes are not available on NSA�s website, it appears that a majority of the faculty�s published books are from Canon Press, Wilson�s own creation and the publisher of the infamous slavery booklet.
Of special concern is the fact that Wilson�s brother, his son, and his son-in-law are on the college�s faculty.
Steve Wilkins and George Grant are regular speakers at Wilson�s annual conferences in Moscow. Grant has a mail order doctorate and Wilkins is a conservative Calvinist minister from Louisiana. Wilkins is a founding director of the League of the South, which has been declared a hate group by the Southern Poverty Law Center. The Confederate flag used to hang in Wilson�s office and Logos School displayed it at its social functions.
When a Moscow journalist interviewed Wilson, Grant, and Wilkins in February, 2004, they each proudly affirmed their belief that only propertied males should vote. Always the jokester, Wilson said that democracy was just like two coyotes and a lamb voting on what to have for lunch.
There are well qualified students at NSA and some competent faculty, just as there are good, decent people who attend Wilson�s 800-member Christ Church. One can usually spot these people because they frequently speak of Wilson�s goal of achieving �truth, goodness, and beauty.� These fine folks need to be reminded that their leaders have not always told the truth, that condoning slavery is not good, and that calling for the execution of homosexuals is just plain ugly.
- Preplanned tours
- Daytrips out of Moscow
- Themed tours
- Customized tours
- St. Petersburg
Theatres in Moscow
Cultural life of Moscow city is various and rich! Operas, ballets, symphonic concerts... Russian composers have created some of the most beautiful classical music. Russian classical music is very popular in Moscow. It is performed in many beautiful historical venues. Do not forget to include a visit to a concert hall in your itinerary when you are planning your stay in Moscow! And do it in advance.
There are almost no restrictions on dress code in Russian theatres. Visitors may wear jeans and sports shoes, they may have a backpack with them. Only shorts are not allowed.
A typical feature of Russian theatre – visitors are bringing a lot of flowers which they present to their favorite performers after the show.
Here are some practical advices where to go and how to buy tickets.
The Bolshoi Theatre
The Bolshoi Theatre is the oldest, the most famous and popular opera and ballet theatre in Russia. The word “Bolshoi” means “big” in Russian. You can buy a ticket online in advance, 2-3 months before the date of performance on the official website . Prices for famous ballets are high: 6-8 thousand rubles for a seat in stalls. Tickets to operas are cheaper: you can get a good seat for 4-5 thousand rubles. Tickets are cheaper for daytime performances and performances on the New Stage. The New Stage is situated in the light-green building to the left of the Bolshoi's main building. The quality of operas and ballets shown on the New Stage is excellent too. However, you should pay attention that many seats of the Bolshoi’s Old and New Stages have limited visibility . If you want to see the Bolshoi’s Old Stage but all tickets are sold out, you can order a tour of the theatre. You can book such a tour on the official website.
If you want, following Russian tradition, to give flowers to the performers at the end of the show, in the Bolshoi flowers should be presented via special staff who collects these flowers in advance.
In August the Bolshoi is closed.
The Stanislavsky and Nemirovich-Danchenko Music Theatre
This theatre is noteworthy. On one hand, it offers brilliant classical opera and ballet performances. On the other hand, it is an experimental venue for modern artists. You can check the program and buy tickets online here http://stanmus.com/ . If you are opera lover, get a ticket to see superstar Hibla Gerzmava . The theatre has a very beautiful historic building and a stage with a good view from every seat. Tickets are twice cheaper than in the Bolshoi.
The Novaya Opera
“Novaya” means “New” in Russian. This opera house was founded in 1991 by a famous conductor Eugene Kolobov. Its repertoire has several directions: Russian and Western classics, original shows and divertissements, and operas of the 20th and 21st centuries. It is very popular with Muscovites for excellent quality of performances, a comfortable hall, a beautiful Art Nouveau building and a historic park Hermitage, which is situated right next to it. You can buy tickets online here http://www.novayaopera.ru/en .
Galina Vishnevskaya Opera Center
The Opera Center has become one of the best theatrical venues in Moscow. It was founded in 2002 by great diva Galina Vishnevskaya. Nowadays its artistic director is Olga Rostropovich, daughter of Galina Vishnevskaya and her husband Mstislav Rostropovich, great cellist and conductor. Not only best young opera singers perform here, but also world music stars do; chamber and symphonic concerts, theatrical productions and musical festivals take place here. You can see what is on the program here http://opera-centre.ru/theatre . Unfortunately “booking tickets online” is available in Russian only. If you need help, you can contact us at and we can book a ticket for you.
Tchaikovsky Concert Hall and The Great Hall of Moscow Conservatory
These are two major concert halls for symphonic music in Moscow. Both feature excellent acoustics, impressive interior, various repertoire and best performers. You can check the program here http://meloman.ru/calendar/ . You need just to switch to English. Booking tickets online is available only for owners of Russian, Ukrainian and Belorussian phone numbers. If you need help, you can contact us and we can book a ticket for you.
Moscow International Performing Arts Center (MIPAC)
This modern and elegant concert hall houses performances of national and foreign symphony orchestras, chamber ensembles, solo instrumentalists, opera singers, ballet dancers, theatre companies, jazz bands, variety and traditional ensembles. Actually, it has three concert halls placed on three different levels and having separate entrances. The President of MIPAC is People’s Artist of the USSR Vladimir Spivakov, conductor of “Virtuosy Moskvy” orchestra. You can see pictures of the concert halls here http://www.mmdm.ru/en/content/halls . The program is impressive in its variety but is not translated into English. You can contact us at and we can find a performance for you.
Communities of microorganisms and invertebrates in soil-like bodies of soccer fields in Moscow oblast
- Soil Biology
- Published: 06 November 2014
- Volume 47 , pages 1107–1115, ( 2014 )
Cite this article

- O. V. Kutovaya 1 ,
- I. V. Zamotaev 2 &
- V. P. Belobrov 1
75 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Artificially created soil-like technogenic formations (STFs) of soccer fields are developed under combined action of intense technogenic and natural factors and processes, which cannot but affect the structure and biological activity of their microbial communities and mesofauna. The microflora of the STFs is very similar to the microflora of the background soddy-podzolic soils of Moscow oblast with respect to the composition of the physiological groups of microorganisms. However, they are drastically different in their quantitative characteristics. The numbers of all the trophic groups of microorganisms, except for the microscopic fungi, in the STFs are much higher than those in the zonal soils. An increased biological activity of the STFs is due to regular watering, heating, application of sand and mineral fertilizers, and technogenic turbation processes. The mesofauna of the STFs is represented by several ecological groups of earthworms, including soildwelling (endogeic) earthworms ( Aporrectodea caliginosa ), epigeic earthworms dwelling at the soil-litter interface ( Lumbricus rubellus ), and litter-dwelling earthworms ( Eisenia foetida ).
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
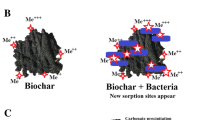
The mechanisms of biochar interactions with microorganisms in soil
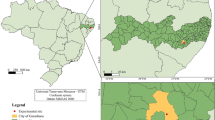
Litter Deposition and Decomposition in a Tropical Grass-Legume Silvopastoral System
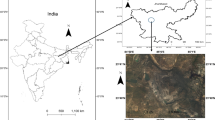
Reclamation of coal mine spoil and its effect on Technosol quality and carbon sequestration: a case study from India
G. G. Abramashvili, Sports Lawns. Methodological Guidelines for Employees of Stadiums and Sports Bases Exploiting Soccer Fields (Sovetskii sport, Moscow, 1988) [in Russian].
Google Scholar
A. L. Aleksandrovskii and E. I. Aleksandrovskaya, Soil Evolution and the Geographic Environment (Nauka, Moscow, 2005) [in Russian].
V. N. Bashkin and N. S. Kasimov, Biogeochemistry (Nauchn. mir, Moscow, 2004) [in Russian].
O. S. Bezuglova, S. N. Gorbov, A. V. Gorovtsov, et al., “Agrochemical and microbiological properties of constructozems of golf courses and their impact on the state of the lawns,” Probl. Agrokhim. Ekolog., No. 4, 14–17 (2012).
O. S. Bezuglova, S. N. Gorbov, I. V. Morozov, and D. G. Nevidomskaya, Urbopedology: A Textbook (Izd. Yuzhn. Fed. Univ., Rostov-on-Don, 2012) [in Russian].
V. P. Belobrov and I. V. Zamotaev, Soils and Green Lawns of Sports and Technical Constructions (GEOS, Moscow, 2007) [in Russian].
V. P. Belobrov, I. V. Zamotaev, and A. Yu. Kulenkamp, “Pedogenic and technogenic processes in artificial recreation landscapes of Russia,” Dokl. RASKhN, No. 2, 35–38 (2002).
V. A. Bol’shakov, V. P. Belobrov, and L. L. Shishov, Terms, Their Concise Definitions, and Reference Materials on General and Soil Ecology and on the Geography and Classification of Soils (Pochven. Inst. im. V.V. Dokuchaeva RASKhN, Moscow, 2004) [in Russian].
B. A. Byzov, Zoomicrobial Interactions in Soils (GEOS, Moscow, 2005) [in Russian].
E. S. Vasilenko, I. S. Prokhorov, and A. Yu. Sementsov, “Microbiological processes upon the construction of artificial soils,” Agrokhim. Vestn., No. 5, 20–24 (2006).
T. S. Vsevolodova-Perel’, Earthworms of Russian Fauna: Cadaster and Determinative Guide (Nauka, Moscow, 1997) [in Russian].
M. I. Gerasimova, M. N. Stroganova, N. V. Mozharova, and T. V. Prokof’eva, Anthropogenic Soils (Genesis, Geography, and Reclamation) (Izd. Mosk. Gos. Univ., Moscow, 2003) [in Russian].
M. S. Gilyarov, “Dwelling conditions for invertebrates of different size groups in soil,” in Methods of Soil Zoology (Nauka, Moscow, 1975), pp. 7–12 [in Russian].
M. A. Glazovskaya, “Biotic and abiotic factors in the organization of soil biota and morphogenesis of soils,” in Soil Science: History, Sociology, and Methodology , Ed. by V. N. Kudeyarov and I. V. Ivanov (Nauka, Moscow, 2005), pp. 243–257 [in Russian].
M. I. Gol’din and K. Ya. Lyal’chenko, A Soccer Field. Construction and Exploitation (Fizkul’tura i sport, Moscow, 1971) [in Russian].
I. L. Gol’dfarb, Extended Abstract of Candidate’s Dissertation in Geography (Moscow, 2005).
I. S. Goryachkina, A. A. Rakhleeva, M. N. Stroganova, and A. V. Rappoport, “Soil mesofauna of botanical gardens (by the example of Moscow and Saint Petersburg),” Vestn. Mosk Univ., Ser. 17: Pochvoved., No. 4, 33–40 (2003).
T. G. Dobrovol’skaya, A. V. Golovchenko, T. A. Pankratov, L. V. Lysak, D. G. Zvyagintsev, “Assessment of the bacterial diversity in soils: evolution of approaches and methods,” Eur. Soil Sci. 42 (10), 1138–1147 (2009).
Article Google Scholar
I. V. Zamotaev, Extended Abstract of Doctoral Dissertation in Geography (Moscow, 2009).
I. V. Zamotaev, “Factors of soil formation on soccer fields,” Vestn. MGPU, No. 3, 15–32 (2008).
I. V. Zamotaev and V. P. Belobrov, “Technopedogenesis on artificially formed substrates of soccer fields,” Ekolog. Planirov. Upravlen., No. 3(4), 48–63 (2007).
I. V. Zamotaev, V. P. Belobrov, V. T. Dmitrieva, and D. L. Shevelev, Technopedogenesis on Soccer Fields of Russia (Media-PRESS, Moscow, 2012) [in Russian].
I. V. Zamotaev and D. L. Shevelev, “Sports technogenesis as a factor of soil formation,” Probl. Region. Ekolog., No. 6, 268–274 (2009).
D. G. Zvyagintsev, T. G. Dobrovol’skaya, I. P. Bab’eva, G. M. Zenova, L. V. Lysak, “The role of microorganisms in the biogeocenotic functions of soils,” in The Structural-Functional Role of Soils in the Biosphere (GEOS, Moscow, 1999) [in Russian].
F. A. Ivannikov, Extended Abstract of Candidate’s Dissertation in Biology (Moscow, 2012).
A. E. Ivanova, I. S. Sukhanova, and O. E. Marfenina, “Ecotrophic groups of fungi in urban soils of different ages,” Materials of the V All-Russia Soil Sci. Congr. (Rostov-on-Don, 2008), p. 436 [in Russian].
T. K. Il’ina and O. M. Fomina, USSR Inventor’s Certificate No. 1, 3328.
N. A. Karavaeva, “Agrogenic soils: environmental conditions, properties, and processes,” Eur. Soil Sci. 38 (12), 1355–1365 (2005).
N. A. Karavaeva, “Soil climate in the boreal zonal series of natural and agrolandscapes,” in Multifaceted Geography: The Development of Ideas of Innokentii Petrovich Gerasimov (on the Centennial Anniversary of the Birth) (KMK, Moscow, 2005), pp. 195–222 [in Russian].
Classification and Diagnostic System of Russian Soils (Oikumena, Smolensk, 2004) [in Russian].
O. V. Kutovaya, Extended Abstract of Candidate’s Dissertation in Agriculture (Moscow, 2012).
O. V. Kutovaya, “Transformation of the structure of microbial communities in soddy-podzolic soils under the impact of earthworms,” Agrokhim. Vestn., No. 2, 13–14 (2008).
O. V. Kutovaya, “Characterization of humic substances in agrosoddy-podzolic soils and earthworm coprolites,” Byull. Pochv. Inst. im. V.V. Docuchaeva, No. 69, 46–59 (2011).
L. V. Lysak, Extended Abstract of Doctoral Dissertation in Biology (Moscow, 2010).
L. V. Lysak, N. N. Sidorenko, O. E. Marfenina, and D. G. Zvyagintsev, “Microbial complexes in urban soils,” Eur. Soil Sci. 33 (1), 70–75 (2000).
V. G. Matveeva and T. S. Perel’, “Earthworms of the Lumbricidae family in Moscow oblast,” in Soil Invertebrates of Moscow Oblast (Nauka, Moscow, 1982), pp. 133–143 [in Russian].
A Practicum on Microbiology , Ed. by N. S. Egorov (Izd. Mosk. Gos. Univ., Moscow, 1976) [in Russian].
I. S. Prokhorov, Extended Abstract of Candidate’s Dissertation in Agriculture (Moscow, 2006).
A. V. Rappoport, A. S. Myasoedov, and L. V. Lysak, “Biological activity of some urbanozems and kulturozems in Moscow,” in Outlooks for the Development of Soil Biology (MAKS-Press, Moscow, 2001), pp. 279–282 [in Russian].
O. B. Rumyantsev, Soccer Field. Recommendations on Maintenance of Natural Soddy Soccer Fields (PFL Rossii, Moscow, 1999) [in Russian].
I. N. Skvortsova, A. V. Rappoport, T. V. Prokof’eva, and A. E. Andreeva, “Biological properties of soils in the Moscow State University botanical garden: the branch on Prospekt Mira,” Eur. Soil Sci. 39 (7), 771–778 (2006).
A. V. Smagin, Theory and Practice of Soil Construction (Izd. Mosk. Gos. Univ., Moscow, 2012) [in Russian].
N. P. Sorokina, Large-Scale Soil Maps and Their Applications. Methodological Recommendations (Pochv. inst. im. V.V. Dokuchaeva VASKhNIL, Moscow, 1977) [in Russian].
A. L. Stepanov, N. A. Manucharova, A. V. Smagin, A. S. Kurbatova, A. D. Myagkova, V. N. Bashkin, “Characterization of the biological activity of the microbial complex in urban soils,” Eur. Soil Sci. 38 (8), 864–869 (2005).
M. N. Stroganova, Extended Abstract of Doctoral Dissertation in Biology (Moscow, 1998).
E. Z. Tepper, V. K. Shil’nikova, and G. I. Pereverzeva, A Practicum on Microbiology (Drofa, Moscow, 2005) [in Russian].
D. L. Shevelev, Extended Abstract of Candidate’s Dissertation in Geography (Moscow, 2011).
Bauen mit Gruen: die Bauuund Vegetationstechnik des Landschafts und Sportplatzbaus (Parey, Berlin-Hamburg, 1989).
Grundsaetze zur Functions und Umweltgerechten Pflege von Rasensportflaechen. Teil II. Wassersparende Massnahmen , (Bundesinstitut fuer Sportwissenschaft, Hoffman, Schorndor, 1994)
Grundsaetze zur Functions und Umweltgerechten Pflege von Rasensportflaechen. Teil III. Unerwuenschte Pflanzenarten auf Rasensportflaechen , (Bundesinstitut fuer Sportwissenschaft, Verl.-Gmbh, Koeln, 1995).
Grundsaetze zur Functions und Umweltgerechten Pflege von Rasensportflaechen. Teil IY. Pflanzenkrankheiten und Schaedlinge (Bundesinstitut fuer Sportwissen-schaft, Sport und Buch Strauss, Koeln, 1995).
C. G. Matthias, Praxis des Sportplatzbaus. Fehleraufdeckung und Vermeidung (Renningen-Malmsheim, 2002).
J. Puhalla, J. Krans, and J. Goatley, Sports Fields: Design, Construction, Maintenance , (J. Wiley & Sons, 2010).
Sportrasenpflege (DEULA Rheinland Kempen, 2006)..
Urbaner Bodenschutz. Arbeitkreis Stadtboeden der Deutschen Bodenkundlichen Gesellschaft (Hrsg.) (Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, 1996).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Dokuchaev Soil Science Institute, per. Pyzhevskii 7, Moscow, 119017, Russia
O. V. Kutovaya & V. P. Belobrov
Institute of Geography of the Russian Academy of Sciences, per. Staromonetnyi 29, Moscow, 119017, Russia
I. V. Zamotaev
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to O. V. Kutovaya .
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.V. Kutovaya, I.V. Zamotaev, V.P. Belobrov, 2014, published in Pochvovedenie, 2014, No. 11, pp. 1315–1324.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kutovaya, O.V., Zamotaev, I.V. & Belobrov, V.P. Communities of microorganisms and invertebrates in soil-like bodies of soccer fields in Moscow oblast. Eurasian Soil Sc. 47 , 1107–1115 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229314110052
Download citation
Received : 25 February 2014
Published : 06 November 2014
Issue Date : November 2014
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229314110052
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- artificially constructed soil-like technogenic formations
- soccer fields
- biological activity
- microorganisms
- soil biological processes
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Synopsis. The Sociology Program supports basic research on all forms of human social organization — societies, institutions, groups and demography — and processes of individual and institutional change. The program encourages theoretically focused empirical investigations aimed at improving the explanation of fundamental social processes.
National Science Foundation Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant (NSF DDRI) awards recommended by Sociology will not exceed $16,000, a total that includes both allowable direct costs and appropriate indirect costs over the duration of the award. Project budgets should be developed at scales appropriate for the work to be conducted and may only include costs directly associated with ...
NSF's mission is to advance the progress of science, a mission accomplished by funding proposals for research and education made by scientists, engineers, and educators from across the country. An official website of the United States government. Here's how you know.
The National Science Foundation (NSF) has made two awards to ASA to administer the Sociology Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant (DDRIG) program. This program supports theoretically grounded empirical investigations to advance understanding of fundamental social processes. Up to 25 awards of a maximum of $16,000 will be given each ...
Some of NSF's programs offer grants to doctoral students, allowing them to undertake significant data-gathering projects and conduct field research in settings away from their campus. The award amounts of these grants vary across programs but typically fall between $15,000 to $40,000 (excluding indirect costs).
NSF Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant Program Holly M. Hapke, PhD Director of Research Development ... University of California, Irvine. Objectives: •Introduce participants to the NSF DDRI(G) funding opportunity; •Explain NSF's mission, organizational structure, and merit review process; ... •Sociology -October 15 ...
Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Awards/Grants (DDRI/DDRIG) These programs help fund doctoral research in a variety of fields to help provide for items not already available at the academic institution. The funding provided cannot be used for items such as, but not limited to, tuition, stipends, textbooks or journals.
ASA is grateful to the National Science Foundation for its support of this program. ... Intellectual Merit should describe the potential of the project to advance sociology substantively and or methodologically by describing how the project fits within and extends the existing literature. ... ASA Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant ...
(Note that NSF will not recommend a DDRIG solely for sharing research results at conferences.) Programs and Due Dates. Many programs in the seven NSF directorates accept doctoral dissertation improvement grant proposals. Requirements vary across programs, so applicants are advised to consult the relevant program's solicitation and instructions.
Doctoral Dissertation Improvement Grant: Establishment of Long Term Group Interaction Relationships. NSF Org: BCS Division Of Behavioral and Cognitive Sci: Recipient: ... Primary Program Source: 01002324DB NSF RESEARCH & RELATED ACTIVIT: Program Reference Code(s): 1391, 9179: Program Element Code(s): 760600: Award Agency Code: 4900: Fund Agency ...
The National Science Foundation Information Center may be reached at (703) 292-5111. The National Science Foundation promotes and advances scientific progress in the United States by competitively awarding grants and cooperative agreements for research and education in the sciences, mathematics, and engineering.
The National Science Foundation (NSF) has made two awards to APSA to administer the Political Science Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grant (DDRIG) program. The NSF awarded APSA $1,410,000 to administer the DDRIG program from 2020 to 2023, and they renewed this award to continue its administration from 2023 to 2026.
Doctoral Dissertation Improvement Grant: Political Economy And Subsistence Linkages. NSF Org: BCS Division Of Behavioral and Cognitive Sci: Recipient: ... Primary Program Source: 01001415DB NSF RESEARCH & RELATED ACTIVIT: Program Reference Code(s): 1391: Program Element Code(s): 139100: Award Agency Code: 4900: Fund Agency Code:
The APSA Dissertation Improvement Grant project will support doctoral dissertation research in political science to enhance and improve the conduct of doctoral dissertation projects. The program will be executed by APSA staff and supervised by the APSA Executive Director. The APSA Dissertation Improvement Grant program will award up to twenty ...
ABSTRACT This doctoral dissertation research improvement grant supports a project on the use of big data science methods in genomics. Much of the research in genomics involves the use such methods; that is to say, they require data from thousands of participants in order to detect subtle relationships between genes and health outcomes.
Nsf Sociology Dissertation Improvement Grant, Objective Essay Topics, Blood Advances Cover Letter, Essay About Terrorism, Sample Resume Achievements Administrative Assistant, Graphic Designer Resume Doc, Curriculum Vitae De Una Recepcionista 741 Orders prepared ...
Indirect Costs: Please note an important change to the treatment of indirect costs that was incorporated into the SBE Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grants (SBE DDRIG) program solicitation (NSF 11-547). NSF's long-standing policy regarding the reimbursement of administrative costs is full reimbursement of indirect costs, based on ...
Nsf Sociology Dissertation Improvement Grant - 4.9/5. 580 . Finished Papers. Legal. Login. 4423 Orders prepared. We Make It Better. Nsf Sociology Dissertation Improvement Grant: Review Category. 15 Customer reviews. Paperwork. Customer support. Customer support. ID 15031 ...
The Confederate flag used to hang in Wilson's office and Logos School displayed it at its social functions. When a Moscow journalist interviewed Wilson, Grant, and Wilkins in February, 2004, they each proudly affirmed their belief that only propertied males should vote. Always the jokester, Wilson said that democracy was just like two coyotes ...
Galina Vishnevskaya Opera Center. The Opera Center has become one of the best theatrical venues in Moscow. It was founded in 2002 by great diva Galina Vishnevskaya. Nowadays its artistic director is Olga Rostropovich, daughter of Galina Vishnevskaya and her husband Mstislav Rostropovich, great cellist and conductor.
Elektrostal is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located 58 kilometers east of Moscow. Elektrostal has about 158,000 residents. Mapcarta, the open map.
Artificially created soil-like technogenic formations (STFs) of soccer fields are developed under combined action of intense technogenic and natural factors and processes, which cannot but affect the structure and biological activity of their microbial communities and mesofauna. The microflora of the STFs is very similar to the microflora of the background soddy-podzolic soils of Moscow oblast ...