

Thesis and Dissertation Guide
- Starting your Dissertation/Thesis
- Dissertation/Thesis Resources
- Books That May Help
- Literature Reviews
- Annotated Bibliography
- We Don't Have It? / Interlibrary Loan
- Online Learning Study Tips
- Search Strategy
- Advanced Search Techniques
- Kemp Library Video Tutorials
- Find Articles / Journals / Databases
- What are...
- Database Video Tutorials
- Peer Reviewed
- How to confirm and cite peer review
- Primary/Secondary Sources
- Other Types of Sources (i.e. Newspapers)
- Legal Research Resources
- Evidence Based Practice/Appraisal Resources
Google Scholar
- Website Evaluation
- Internet Searching
- Apps You Didn't Know You Needed
- Who is citing me?
- Questions After Hours
- ESU Thesis Submission
- ESU Dissertation Submission
- How to Integrate
- How to Use It
What is Google Scholar and Why Should You Care?
Google Scholar is a special division of Google that searches for academic content. It is not as robust as Google, and as such it can be harder to search. However, if you are looking for a specific article it is a fantastic resource for finding out if you can access it through your library or if it's available for free.
Below are a few videos on how to use Google Scholar (you can skip the intros if you want) that will show you tips and tricks on how to best use Google Scholar.

Did you know that you can use Google Scholar in addition to Primo to help search Kemp library materials? You just have to add us to your Google Scholar and our results will show up in your searches showing you what you have access to as an ESU community member!
- Go to Google Scholar
- Make sure you're logged into your Google Account - you'll see your initials or your icon in the top right hand corner of the screen if you're logged in.
- Click on Settings (either from the top of the Scholar home page, or from the drop-down on the right hand side of the results page).
Choose Library Links .
Type ‘East Stroudsburg University’ into the search box.
Click the boxes next to “ESU” and "Kemp Library"
Click Save .
If you have other institutions you're affilitated with, or ResearchGate, you can add them too!
Getting to Google Scholar Settings:

The Library Link Screen: Search, Select and Save!

What your search results will look like:

Add / Reorder
Databases have more sophisticated search features than Google Scholar , but if you have a one or two word topic Google Scholar can be useful. You can also try using the Advanced Search in Google Scholar (see the first video below).
However, if you're having trouble finding something specific, i.e. a specific article, try Google Scholar. For example you want " Game of Thrones and Graffiti" and you don't see it in a database, search the title of the article in Google Scholar (here you'd search "Game of Thrones and Graffiti"). You may find it freely available OR discover it is available through the library, but in a database you didn't look at.
If we don't have it and you can't access it on Google Scholar, you can always request it via interlibrary loan .
"If Google Scholar isn’t turning up what you need, try an open Google search with the article title in quotes, and type the added filter “filetype:pdf”. This scours the open web for papers hosted somewhere, by someone, in PDF format. Google Books provides limited preview access to many copyrighted books. Other alternate services include SemanticScholar , Microsoft Academic , Dimensions , or GetTheResearch . Here too there are subject-specific portals like EconBiz or the Virtual Health Library , some of which offer multilingual search options." - Paragraph taken from A Wikipedia Librarian.
The other services like Microsoft Academic mentioned above are also useful when looking for freely available journal article and research! Don't forget to cite everything you use in your paper/project/presentation/etc.
Google Scholar Videos
- << Previous: Evidence Based Practice/Appraisal Resources
- Next: Website Evaluation >>
- Last Updated: Apr 29, 2024 12:07 PM
- URL: https://esu.libguides.com/thesis
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Google Scholar: the ultimate guide

What is Google Scholar?
Why is google scholar better than google for finding research papers, the google scholar search results page, the first two lines: core bibliographic information, quick full text-access options, "cited by" count and other useful links, tips for searching google scholar, 1. google scholar searches are not case sensitive, 2. use keywords instead of full sentences, 3. use quotes to search for an exact match, 3. add the year to the search phrase to get articles published in a particular year, 4. use the side bar controls to adjust your search result, 5. use boolean operator to better control your searches, google scholar advanced search interface, customizing search preferences and options, using the "my library" feature in google scholar, the scope and limitations of google scholar, alternatives to google scholar, country-specific google scholar sites, frequently asked questions about google scholar, related articles.
Google Scholar (GS) is a free academic search engine that can be thought of as the academic version of Google. Rather than searching all of the indexed information on the web, it searches repositories of:
- universities
- scholarly websites
This is generally a smaller subset of the pool that Google searches. It's all done automatically, but most of the search results tend to be reliable scholarly sources.
However, Google is typically less careful about what it includes in search results than more curated, subscription-based academic databases like Scopus and Web of Science . As a result, it is important to take some time to assess the credibility of the resources linked through Google Scholar.
➡️ Take a look at our guide on the best academic databases .
One advantage of using Google Scholar is that the interface is comforting and familiar to anyone who uses Google. This lowers the learning curve of finding scholarly information .
There are a number of useful differences from a regular Google search. Google Scholar allows you to:
- copy a formatted citation in different styles including MLA and APA
- export bibliographic data (BibTeX, RIS) to use with reference management software
- explore other works have cited the listed work
- easily find full text versions of the article
Although it is free to search in Google Scholar, most of the content is not freely available. Google does its best to find copies of restricted articles in public repositories. If you are at an academic or research institution, you can also set up a library connection that allows you to see items that are available through your institution.
The Google Scholar results page differs from the Google results page in a few key ways. The search result page is, however, different and it is worth being familiar with the different pieces of information that are shown. Let's have a look at the results for the search term "machine learning.”
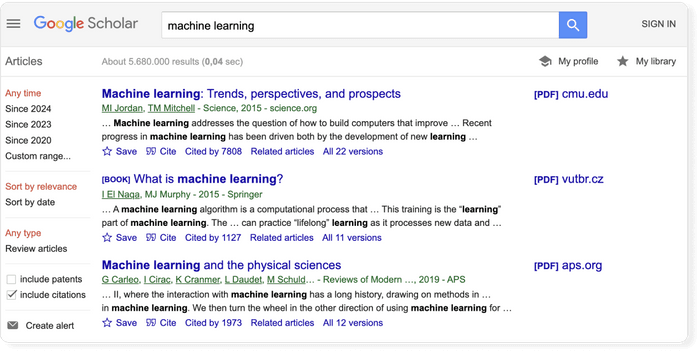
- The first line of each result provides the title of the document (e.g. of an article, book, chapter, or report).
- The second line provides the bibliographic information about the document, in order: the author(s), the journal or book it appears in, the year of publication, and the publisher.
Clicking on the title link will bring you to the publisher’s page where you may be able to access more information about the document. This includes the abstract and options to download the PDF.

To the far right of the entry are more direct options for obtaining the full text of the document. In this example, Google has also located a publicly available PDF of the document hosted at umich.edu . Note, that it's not guaranteed that it is the version of the article that was finally published in the journal.
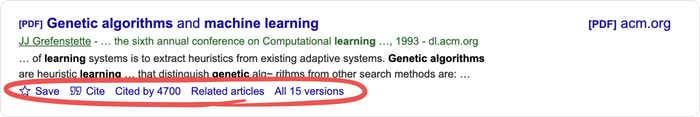
Below the text snippet/abstract you can find a number of useful links.
- Cited by : the cited by link will show other articles that have cited this resource. That is a super useful feature that can help you in many ways. First, it is a good way to track the more recent research that has referenced this article, and second the fact that other researches cited this document lends greater credibility to it. But be aware that there is a lag in publication type. Therefore, an article published in 2017 will not have an extensive number of cited by results. It takes a minimum of 6 months for most articles to get published, so even if an article was using the source, the more recent article has not been published yet.
- Versions : this link will display other versions of the article or other databases where the article may be found, some of which may offer free access to the article.
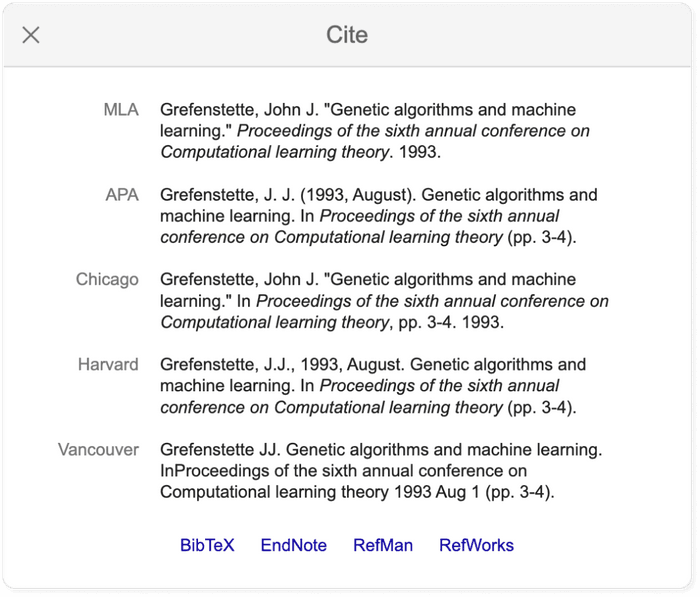
- Quotation mark icon : this will display a popup with commonly used citation formats such as MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard, and Vancouver that may be copied and pasted. Note, however, that the Google Scholar citation data is sometimes incomplete and so it is often a good idea to check this data at the source. The "cite" popup also includes links for exporting the citation data as BibTeX or RIS files that any major reference manager can import.
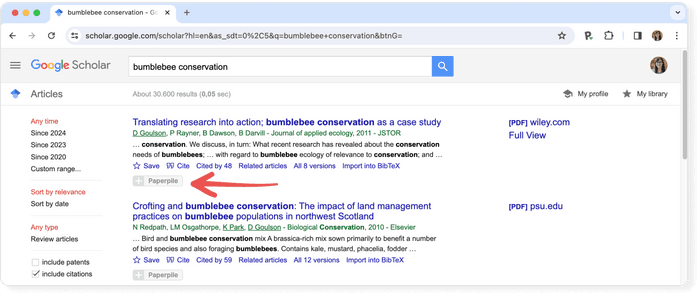
Pro tip: Use a reference manager like Paperpile to keep track of all your sources. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular academic research engines and databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons and later cite them in thousands of citation styles:
Although Google Scholar limits each search to a maximum of 1,000 results , it's still too much to explore, and you need an effective way of locating the relevant articles. Here’s a list of pro tips that will help you save time and search more effectively.
You don’t need to worry about case sensitivity when you’re using Google scholar. In other words, a search for "Machine Learning" will produce the same results as a search for "machine learning.”
Let's say your research topic is about self driving cars. For a regular Google search we might enter something like " what is the current state of the technology used for self driving cars ". In Google Scholar, you will see less than ideal results for this query .
The trick is to build a list of keywords and perform searches for them like self-driving cars, autonomous vehicles, or driverless cars. Google Scholar will assist you on that: if you start typing in the search field you will see related queries suggested by Scholar!
If you put your search phrase into quotes you can search for exact matches of that phrase in the title and the body text of the document. Without quotes, Google Scholar will treat each word separately.
This means that if you search national parks , the words will not necessarily appear together. Grouped words and exact phrases should be enclosed in quotation marks.
A search using “self-driving cars 2015,” for example, will return articles or books published in 2015.
Using the options in the left hand panel you can further restrict the search results by limiting the years covered by the search, the inclusion or exclude of patents, and you can sort the results by relevance or by date.
Searches are not case sensitive, however, there are a number of Boolean operators you can use to control the search and these must be capitalized.
- AND requires both of the words or phrases on either side to be somewhere in the record.
- NOT can be placed in front of a word or phrases to exclude results which include them.
- OR will give equal weight to results which match just one of the words or phrases on either side.
➡️ Read more about how to efficiently search online databases for academic research .
In case you got overwhelmed by the above options, here’s some illustrative examples:
Tip: Use the advanced search features in Google Scholar to narrow down your search results.
You can gain even more fine-grained control over your search by using the advanced search feature. This feature is available by clicking on the hamburger menu in the upper left and selecting the "Advanced search" menu item.

Adjusting the Google Scholar settings is not necessary for getting good results, but offers some additional customization, including the ability to enable the above-mentioned library integrations.
The settings menu is found in the hamburger menu located in the top left of the Google Scholar page. The settings are divided into five sections:
- Collections to search: by default Google scholar searches articles and includes patents, but this default can be changed if you are not interested in patents or if you wish to search case law instead.
- Bibliographic manager: you can export relevant citation data via the “Bibliography manager” subsection.
- Languages: if you wish for results to return only articles written in a specific subset of languages, you can define that here.
- Library links: as noted, Google Scholar allows you to get the Full Text of articles through your institution’s subscriptions, where available. Search for, and add, your institution here to have the relevant link included in your search results.
- Button: the Scholar Button is a Chrome extension which adds a dropdown search box to your toolbar. This allows you to search Google Scholar from any website. Moreover, if you have any text selected on the page and then click the button it will display results from a search on those words when clicked.
When signed in, Google Scholar adds some simple tools for keeping track of and organizing the articles you find. These can be useful if you are not using a full academic reference manager.
All the search results include a “save” button at the end of the bottom row of links, clicking this will add it to your "My Library".
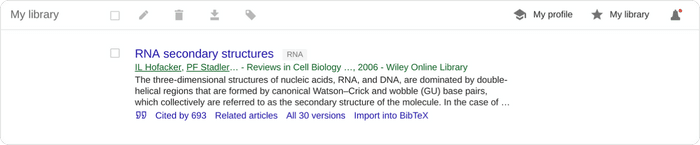
To help you provide some structure, you can create and apply labels to the items in your library. Appended labels will appear at the end of the article titles. For example, the following article has been assigned a “RNA” label:
Within your Google Scholar library, you can also edit the metadata associated with titles. This will often be necessary as Google Scholar citation data is often faulty.
There is no official statement about how big the Scholar search index is, but unofficial estimates are in the range of about 160 million , and it is supposed to continue to grow by several million each year.
Yet, Google Scholar does not return all resources that you may get in search at you local library catalog. For example, a library database could return podcasts, videos, articles, statistics, or special collections. For now, Google Scholar has only the following publication types:
- Journal articles : articles published in journals. It's a mixture of articles from peer reviewed journals, predatory journals and pre-print archives.
- Books : links to the Google limited version of the text, when possible.
- Book chapters : chapters within a book, sometimes they are also electronically available.
- Book reviews : reviews of books, but it is not always apparent that it is a review from the search result.
- Conference proceedings : papers written as part of a conference, typically used as part of presentation at the conference.
- Court opinions .
- Patents : Google Scholar only searches patents if the option is selected in the search settings described above.
The information in Google Scholar is not cataloged by professionals. The quality of the metadata will depend heavily on the source that Google Scholar is pulling the information from. This is a much different process to how information is collected and indexed in scholarly databases such as Scopus or Web of Science .
➡️ Visit our list of the best academic databases .
Google Scholar is by far the most frequently used academic search engine , but it is not the only one. Other academic search engines include:
- Science.gov
- Semantic Scholar
- scholar.google.fr : Sur les épaules d'un géant
- scholar.google.es (Google Académico): A hombros de gigantes
- scholar.google.pt (Google Académico): Sobre os ombros de gigantes
- scholar.google.de : Auf den Schultern von Riesen
➡️ Once you’ve found some research, it’s time to read it. Take a look at our guide on how to read a scientific paper .
No. Google Scholar is a bibliographic search engine rather than a bibliographic database. In order to qualify as a database Google Scholar would need to have stable identifiers for its records.
No. Google Scholar is an academic search engine, but the records found in Google Scholar are scholarly sources.
No. Google Scholar collects research papers from all over the web, including grey literature and non-peer reviewed papers and reports.
Google Scholar does not provide any full text content itself, but links to the full text article on the publisher page, which can either be open access or paywalled content. Google Scholar tries to provide links to free versions, when possible.
The easiest way to access Google scholar is by using The Google Scholar Button. This is a browser extension that allows you easily access Google Scholar from any web page. You can install it from the Chrome Webstore .


How to Write a Research Paper: Thesis Statement
- Anatomy of a Research Paper
- Developing a Research Focus
- Background Research Tips
- Searching Tips
- Scholarly Journals vs. Popular Journals
- Thesis Statement
- Annotated Bibliography
- Citing Sources
- Evaluating Sources
- Literature Review
- Academic Integrity
- Scholarship as Conversation
- Understanding Fake News
- Data, Information, Knowledge
What is a Thesis Statement?
What is a Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a concise statement of an academic work's main point. The thesis statement should identify both what the paper is about (the topic) and what you are saying about it. Your thesis statement should be as specific as possible. For a short essay, the length of your thesis statement should be one or two sentences. If you are writing a dissertation or book, your thesis statement should be about a paragraph in length. A thesis should avoid saying "This paper is about..." Your thesis statement should be as specific as possible.
A basic pattern to follow is "An analysis of (insert topic here) will show that (point one), (point two), and (point three)." Keep in mind this is only an example, there is no one-size-fits-all formula.
Who Needs a Thesis Statement?
All academic writing, from a short essay to a dissertation or a monograph, should have an identifiable thesis statement somewhere in it. The longer or more complicated an academic work is, the easier is becomes to get bogged down in details and lose sight of the overall argument, and the more important it is to clearly state the central point.
Where Should I Put My Thesis Statement?
Thesis statements are most commonly located near the beginning of the academic work, usually towards the end of the introduction. This strategic placement allows the reader to quickly understand specifically what the essay is about and be able to follow the arguments as they are presented.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements: Purdue Owl
This resource from Purdue University's Online Writing Lab (OWL) provides tips for creating a thesis statement and examples of different types of thesis statements.
- << Previous: Scholarly Journals vs. Popular Journals
- Next: Annotated Bibliography >>
- Last Updated: Apr 4, 2024 5:51 PM
- URL: https://libguide.umary.edu/researchpaper

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
What is a thesis statement?

A thesis statement is an essential component of ALL academic and research writing.
A thesis statement:
- occurs early in a piece of written work (introduction)
- tells the reader what the purpose and scope of the work will be
- provides more than a mere description of the topic
- puts a ‘wager’ (i.e. a bet) on the topic by telling us what the significance of the research will be
- defines what will be investigated and what they think will be found (note, it’s OK if the hypothesis is disproven once the data is in)
Descriptive thesis statements
Beware thesis statements that are too descriptive because they “do not investigate anything, critique anything, or analyze anything […] they also do not invite support and argument from outside of the central text” ( UW Expository Writing Program, 2007, p. 2). The problem with thesis statements that are merely descriptive is that they lack a ‘stance’ or an argument. They are therefore difficult to support with evidence and to build an argument for.
The examples below would not make good thesis statements because they are too descriptive.
a) Shakespeare was a famous playwright during the Elizabethan era. He wrote numerous plays and poems.
b) Almost one in two marriages in Australia end in divorce. That means the divorce rate is almost 50%.
c) Covid-19 was a virus that caused an epidemic in the early 2020’s.
Check your understanding
Where is the thesis statement in the passage below?
My intention was to investigate and portray Antarctica through my own and others’ personal experiences, through historical examples of jewellery and souvenirs and through experimentation in the studio-based manufacture of new jewellery and souvenirs [e] . The objects produced through this research would reference the valued jewellery and souvenirs now displayed in museums as historical artefacts which were once personal mementos [f] . I was particularly interested in the potential of these objects to represent personal narratives and experiences of the past [g] . In this research project I have explored some of the ways in which I can make objects, specifically jewellery and souvenirs that draw on this rich heritage to present Antarctica in an innovative way [h] .
Excerpt from Kirsten Haydon’s dissertation Antarctic landscapes in the souvenir and jewellery (used with permission)
Research and Writing Skills for Academic and Graduate Researchers Copyright © 2022 by RMIT University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Research Essentials
- Develop a Question
- Identify Keywords
- Search Tips
- Too Few/Many Results?
- Use Sources
- Scholarly vs Popular
What Is a Thesis?
Crafting a thesis.
- Cite Sources
- Find Articles
- Primary Sources
More Resources
- How to Write a Thesis Statement IU Writing Tutorial Services
- Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements Purdue OWL
A thesis is the main point or argument of an information source. (Many, but not all, writing assignments, require a thesis.) Thesis are often answer your research question. Note that it does not have to be the only answer to your research question, a strong thesis question gives a reasonable answer. Below are some characteristics of a strong thesis.
A strong thesis is:
- Arguable: Can be supported by evidence and analysis, and can be disagreed with.
- Unique: Says something new and interesting.
- Concise and clear: Explained as simply as possible, but not at the expense of clarity.
- Unified: All parts are clearly connected.
- Focused and specific: Can be adequately and convincingly argued within the the paper, scope is not overly broad.
- Significant: Has importance to readers, answers the question "so what?"
Reading previous research is vital to developing a strong thesis. By reading what others have to say about, you'll learn what interests you, and develop interesting questions with interesting answers. Exploring broadly can help you refine your central point.
Conduct Background Research
A strong thesis is specific and unique, so you first need knowledge of the general research topic. Background research will help you narrow your research focus by answering the obvious questions with established answers; it will also help contextualize your argument in relation to other research.
Narrow the Research Topic
Ask questions as you review sources:
- What aspect(s) of the topic interest you most?
- Are there disagreements between different papers and authors?
- What questions or concerns does the topic raise for you? Example of a general research topic: Climate change and carbon emissions Example of more narrow topic: U.S. government policies on carbon emissions
Formulate and explore a relevant research question
Before committing yourself to a single viewpoint, formulate a specific question to explore. Consider different perspectives on the issue, and find sources that represent these varying views. Reflect on strengths and weaknesses in the sources' arguments. Consider sources that challenge these viewpoints.
Example: What role does and should the U.S. government play in regulating carbon emissions?
Develop a working thesis
- A working thesis has a clear focus but is not yet be fully formed. It is a good foundation for further developing a more refined argument. Example: The U.S. government has the responsibility to help reduce carbon emissions through public policy and regulation. This thesis has a clear focus but leaves some major questions unanswered. For example, why is regulation of carbon emissions important? Why should the government be held accountable for such regulation?
Continue research on the more focused topic
Is the topic:
- broad enough to yield sufficient sources and supporting evidence?
- narrow enough for in-depth and focused research?
- original enough to offer a new and meaningful perspective that will interest readers?
Fine-tune the thesis
Your thesis will probably evolve as you gather sources and ideas. If your research focus changes, you may need to re-evaluate your search strategy and to conduct additional research. This is usually a good sign of the careful thought you are putting into your work!
Example: Because climate change, which is exacerbated by high carbon emissions, adversely affects almost all citizens, the U.S. government has the responsibility to help reduce carbon emissions through public policy and regulation.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs Popular
- Next: Cite Sources >>
- Last Updated: Nov 13, 2023 10:40 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.indiana.edu/essentials
Social media
- Instagram for Herman B Wells Library
- Facebook for IU Libraries
Additional resources
Featured databases.
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) OneSearch@IU
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Academic Search (EBSCO)
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) ERIC (EBSCO)
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Nexis Uni
- Resource available without restriction HathiTrust Digital Library
- Databases A-Z
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Google Scholar
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) JSTOR
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Web of Science
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Scopus
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) WorldCat
IU Libraries
- Diversity Resources
- About IU Libraries
- Alumni & Friends
- Departments & Staff
- Jobs & Libraries HR
- Intranet (Staff)
- IUL site admin
Writing a Postgraduate or Doctoral Thesis: A Step-by-Step Approach
- First Online: 01 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Usha Y. Nayak 4 ,
- Praveen Hoogar 5 ,
- Srinivas Mutalik 4 &
- N. Udupa 6
770 Accesses
1 Citations
A key characteristic looked after by postgraduate or doctoral students is how they communicate and defend their knowledge. Many candidates believe that there is insufficient instruction on constructing strong arguments. The thesis writing procedure must be meticulously followed to achieve outstanding results. It should be well organized, simple to read, and provide detailed explanations of the core research concepts. Each section in a thesis should be carefully written to make sure that it transitions logically from one to the next in a smooth way and is free of any unclear, cluttered, or redundant elements that make it difficult for the reader to understand what is being tried to convey. In this regard, students must acquire the information and skills to successfully create a strong and effective thesis. A step-by-step description of the thesis/dissertation writing process is provided in this chapter.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Carter S, Guerin C, Aitchison C (2020) Doctoral writing: practices, processes and pleasures. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1808-9
Book Google Scholar
Odena O, Burgess H (2017) How doctoral students and graduates describe facilitating experiences and strategies for their thesis writing learning process: a qualitative approach. Stud High Educ 42:572–590. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2015.1063598
Article Google Scholar
Stefan R (2022) How to write a good PhD thesis and survive the viva, pp 1–33. http://people.kmi.open.ac.uk/stefan/thesis-writing.pdf
Google Scholar
Barrett D, Rodriguez A, Smith J (2021) Producing a successful PhD thesis. Evid Based Nurs 24:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2020-103376
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Murray R, Newton M (2009) Writing retreat as structured intervention: margin or mainstream? High Educ Res Dev 28:541–553. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360903154126
Thompson P (2012) Thesis and dissertation writing. In: Paltridge B, Starfield S (eds) The handbook of english for specific purposes. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Hoboken, NJ, pp 283–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118339855.ch15
Chapter Google Scholar
Faryadi Q (2018) PhD thesis writing process: a systematic approach—how to write your introduction. Creat Educ 09:2534–2545. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2018.915192
Faryadi Q (2019) PhD thesis writing process: a systematic approach—how to write your methodology, results and conclusion. Creat Educ 10:766–783. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2019.104057
Fisher CM, Colin M, Buglear J (2010) Researching and writing a dissertation: an essential guide for business students, 3rd edn. Financial Times/Prentice Hall, Harlow, pp 133–164
Ahmad HR (2016) How to write a doctoral thesis. Pak J Med Sci 32:270–273. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.322.10181
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gosling P, Noordam LD (2011) Mastering your PhD, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 12–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15847-6
Cunningham SJ (2004) How to write a thesis. J Orthod 31:144–148. https://doi.org/10.1179/146531204225020445
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Azadeh F, Vaez R (2013) The accuracy of references in PhD theses: a case study. Health Info Libr J 30:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/hir.12026
Williams RB (2011) Citation systems in the biosciences: a history, classification and descriptive terminology. J Doc 67:995–1014. https://doi.org/10.1108/00220411111183564
Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P, Kashfi K, Ghasemi A (2020) The principles of biomedical scientific writing: citation. Int J Endocrinol Metab 18:e102622. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijem.102622
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yaseen NY, Salman HD (2013) Writing scientific thesis/dissertation in biology field: knowledge in reference style writing. Iraqi J Cancer Med Genet 6:5–12
Gorraiz J, Melero-Fuentes D, Gumpenberger C, Valderrama-Zurián J-C (2016) Availability of digital object identifiers (DOIs) in web of science and scopus. J Informet 10:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2015.11.008
Khedmatgozar HR, Alipour-Hafezi M, Hanafizadeh P (2015) Digital identifier systems: comparative evaluation. Iran J Inf Process Manag 30:529–552
Kaur S, Dhindsa KS (2017) Comparative study of citation and reference management tools: mendeley, zotero and read cube. In: Sheikh R, Mishra DKJS (eds) Proceeding of 2016 International conference on ICT in business industry & government (ICTBIG). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Piscataway, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTBIG.2016.7892715
Kratochvíl J (2017) Comparison of the accuracy of bibliographical references generated for medical citation styles by endnote, mendeley, refworks and zotero. J Acad Librariansh 43:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2016.09.001
Zhang Y (2012) Comparison of select reference management tools. Med Ref Serv Q 31:45–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/02763869.2012.641841
Hupe M (2019) EndNote X9. J Electron Resour Med Libr 16:117–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/15424065.2019.1691963
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Pharmaceutics, Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Usha Y. Nayak & Srinivas Mutalik
Centre for Bio Cultural Studies, Directorate of Research, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Praveen Hoogar
Shri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara University, Dharwad, Karnataka, India
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to N. Udupa .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Retired Senior Expert Pharmacologist at the Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology, and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Gowraganahalli Jagadeesh
Professor & Director, Research Training and Publications, The Office of Research and Development, Periyar Maniammai Institute of Science & Technology (Deemed to be University), Vallam, Tamil Nadu, India
Pitchai Balakumar
Division Cardiology & Nephrology, Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Fortunato Senatore
Ethics declarations
No conflict of interest exists.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Nayak, U.Y., Hoogar, P., Mutalik, S., Udupa, N. (2023). Writing a Postgraduate or Doctoral Thesis: A Step-by-Step Approach. In: Jagadeesh, G., Balakumar, P., Senatore, F. (eds) The Quintessence of Basic and Clinical Research and Scientific Publishing. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_48
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_48
Published : 01 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-1283-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-1284-1
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Research Tutorial
- Library Research Tutorial

What Is a Thesis Statement?
- Topic Development
- Improve Your Research Question
- Good and Bad Research Questions
- Video Review
- Sources for Background Reading
- What about Wikipedia?
- Related Terms
- Subject Terms
- Boolean Searching
- Advanced Searching Techniques
- Definition of "Scholarly"
- Subject Guides
- Individual Databases
- Open Access Resources
- Google Scholar
- Library Catalog
- Evaluation of Sources
- Academic Writing
- Writing Resources
- Citing Sources
- Citation Formats
- Citation Resources
- Academic Integrity
- Research on the Job
Your instructor may ask you to provide a thesis statement, rather than a research question. The main difference between a thesis statement and a research question is that a thesis statement makes a claim upfront that you will attempt to validate in your paper. A thesis statement:
- States your position on a topic
- Is not always required when writing a research paper
- Is often your research question reworded as a statement with a position
For more information on writing thesis statements, see UMGC's Online Guide to Writing and Research: Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea .
- << Previous: 1. Research Question
- Next: Topic Development >>
- Last Updated: Nov 9, 2023 10:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.umgc.edu/research-tutorial
University Library, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign

How to Find Dissertations and Theses
- Finding Dissertations and Theses
- University of Illinois Dissertations
Google Scholar
Proquest dissertations and theses, non-u.s. dissertations.
- Dissertation Tracking
Ask a Librarian

Google Scholar searches specifically for scholarly materials, including Open Access (freely available) dissertations and theses. Many institutions make their dissertations publicly available, making Google Scholar a great place to search.
See the Library's guide on Google for Academic Research for more information.
If the Library does not have a copy of a dissertation or a theses, use ProQuest Dissertations and Theses to obtain a citation for the dissertation. Most American and Canadian universities are represented in this database, as well as selected British and European universities. Dissertations completed at many major U.S. universities during the past 10 years (and sometimes earlier) are available as full-text downloads.
If full text is not available, you can request a dissertation through interlibrary loan.
- ProQuest Dissertations and Theses This link opens in a new window PQDT is a collection of citations to dissertations and theses worldwide from 1861 to the present day. Full-text is available for most of the dissertations added since 1997 and some of the older graduate works. PQDT is also the official digital dissertations archive for the Library of Congress. Also included are the citations to British and Irish dissertations and theses (PQDT: UK & Ireland) since 1761 and abstracts for content since 1986. Note: UIUC masters theses are not in PQDT. They are only found in IDEALS or in the library catalog .
A note on terminology for dissertations and theses: these words are used differently depending on the country (at least in the English speaking world). In the US, dissertations are for doctoral work while a thesis can be a for a bachelor’s or master’s degree. However, it’s often flipped in Europe, e.g., a master’s dissertation and a doctoral thesis.
- The DART-Europe E-theses Portal DART-Europe is a partnership of research libraries in Europe who are working together to improve access to European theses. Several hundred universities link their digital repositories to DART-Europe and link to full text theses.
- EThOS: e-theses online service A project by the British Library Board to provide access to all dissertations from institutions in the UK. This website indexes the dissertations and provides links to full text where available and provide assistance to institutions digitizing dissertations. If available, full text dissertations are free to download.
- Foreign Dissertations at the Center for Research Libraries Try here when looking for a dissertation outside of the United States and Canada. CRL acquires hundreds of non-US, non-Canadian doctoral dissertations a year to add to its 800,000+ collection of dissertations. Acquisitions are primarily through the demand purchase program . Because the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign is a member of CRL, loans to the U of I community are provided free of charge - just fill out a standard interlibrary loan request and put "Item held by CRL" in the notes field.
- Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations This directory provides links to country-specific and international online libraries of electronic theses and dissertations. Many items, including those dating back to the early 1900s, are available in full text for free. For those not available in full text, fill out an interlibrary loan request.
- Theses Canada Portal A searchable catalog of all Canadian theses published since 1965, many of which are available in full-text electronic versions which can be downloaded free by students, scholars, and the public. You can also access and search for free full text electronic versions of Canadian theses and dissertations that were published from the beginning of 1998 to August 31, 2002.
- << Previous: University of Illinois Dissertations
- Next: Dissertation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024 2:48 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.illinois.edu/finddissertationstheses

Searching for Resources - Skills Guide
- Planning & doing your search
- Phrase searching and Truncation
- Using Wildcards
- Proximity and nested searching
- Are you doing your Dissertation or Thesis?
- Google & Google Scholar
- Screening your results
- Video Playlist
- Downloadable Resources
Using Google effectively
- Intermediate
- Linking Google Scholar to Derby Library's full-text resources This guide details the step-by-step process to linking Google Scholar to Derby Library's E-Journals Finder and ProQuest Fulltext collections. It won't be able to link to all of our full-text resources, but a considerable number should show a link when you search. [PDF 602KB]
- Using Google - Scholar keyword search Brief collection of slides looking at using Google Scholar to search for items containing some of your key topic terms [.pptx 2.8MB]
- Using Google - Reverse Image Search Brief collection of slides covering how--and why--you'd use Google Images' Reverse Image search option [.pptx 3.7MB]
- Using Google - Setting up alerts Brief collection of slides showing how to set up alerts via Google to keep you up to date with topics of interest [.pptx 2.8 MB]
- Google Tools and Tips A page of punctuation symbols, search operators and some tips and tricks which can be used in Google to do more strategic searching [.docx 32KB]
- Using Google - Scholar Citation Search Brief collection of slides showing how--and why--you'd do a citation search in Google Scholar. [.pptx 2.7MB]
- Using Google - Advanced Google Search Brief collection of slides covering the advanced search in Google and how to make the search engine work harder for you [.pptx 2.8MB]
- << Previous: Are you doing your Dissertation or Thesis?
- Next: Screening your results >>
- Last Updated: Aug 23, 2023 3:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.derby.ac.uk/searching

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.1 Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement
Learning objectives.
- Develop a strong, clear thesis statement with the proper elements.
- Revise your thesis statement.
Have you ever known a person who was not very good at telling stories? You probably had trouble following his train of thought as he jumped around from point to point, either being too brief in places that needed further explanation or providing too many details on a meaningless element. Maybe he told the end of the story first, then moved to the beginning and later added details to the middle. His ideas were probably scattered, and the story did not flow very well. When the story was over, you probably had many questions.
Just as a personal anecdote can be a disorganized mess, an essay can fall into the same trap of being out of order and confusing. That is why writers need a thesis statement to provide a specific focus for their essay and to organize what they are about to discuss in the body.
Just like a topic sentence summarizes a single paragraph, the thesis statement summarizes an entire essay. It tells the reader the point you want to make in your essay, while the essay itself supports that point. It is like a signpost that signals the essay’s destination. You should form your thesis before you begin to organize an essay, but you may find that it needs revision as the essay develops.
Elements of a Thesis Statement
For every essay you write, you must focus on a central idea. This idea stems from a topic you have chosen or been assigned or from a question your teacher has asked. It is not enough merely to discuss a general topic or simply answer a question with a yes or no. You have to form a specific opinion, and then articulate that into a controlling idea —the main idea upon which you build your thesis.
Remember that a thesis is not the topic itself, but rather your interpretation of the question or subject. For whatever topic your professor gives you, you must ask yourself, “What do I want to say about it?” Asking and then answering this question is vital to forming a thesis that is precise, forceful and confident.
A thesis is one sentence long and appears toward the end of your introduction. It is specific and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how you will organize your information. Remember that a thesis statement does not summarize an issue but rather dissects it.
A Strong Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement contains the following qualities.
Specificity. A thesis statement must concentrate on a specific area of a general topic. As you may recall, the creation of a thesis statement begins when you choose a broad subject and then narrow down its parts until you pinpoint a specific aspect of that topic. For example, health care is a broad topic, but a proper thesis statement would focus on a specific area of that topic, such as options for individuals without health care coverage.
Precision. A strong thesis statement must be precise enough to allow for a coherent argument and to remain focused on the topic. If the specific topic is options for individuals without health care coverage, then your precise thesis statement must make an exact claim about it, such as that limited options exist for those who are uninsured by their employers. You must further pinpoint what you are going to discuss regarding these limited effects, such as whom they affect and what the cause is.
Ability to be argued. A thesis statement must present a relevant and specific argument. A factual statement often is not considered arguable. Be sure your thesis statement contains a point of view that can be supported with evidence.
Ability to be demonstrated. For any claim you make in your thesis, you must be able to provide reasons and examples for your opinion. You can rely on personal observations in order to do this, or you can consult outside sources to demonstrate that what you assert is valid. A worthy argument is backed by examples and details.
Forcefulness. A thesis statement that is forceful shows readers that you are, in fact, making an argument. The tone is assertive and takes a stance that others might oppose.
Confidence. In addition to using force in your thesis statement, you must also use confidence in your claim. Phrases such as I feel or I believe actually weaken the readers’ sense of your confidence because these phrases imply that you are the only person who feels the way you do. In other words, your stance has insufficient backing. Taking an authoritative stance on the matter persuades your readers to have faith in your argument and open their minds to what you have to say.
Even in a personal essay that allows the use of first person, your thesis should not contain phrases such as in my opinion or I believe . These statements reduce your credibility and weaken your argument. Your opinion is more convincing when you use a firm attitude.
On a separate sheet of paper, write a thesis statement for each of the following topics. Remember to make each statement specific, precise, demonstrable, forceful and confident.
- Texting while driving
- The legal drinking age in the United States
- Steroid use among professional athletes
Examples of Appropriate Thesis Statements
Each of the following thesis statements meets several of the following requirements:
- Specificity
- Ability to be argued
- Ability to be demonstrated
- Forcefulness
- The societal and personal struggles of Troy Maxon in the play Fences symbolize the challenge of black males who lived through segregation and integration in the United States.
- Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration.
- Shakespeare’s use of dramatic irony in Romeo and Juliet spoils the outcome for the audience and weakens the plot.
- J. D. Salinger’s character in Catcher in the Rye , Holden Caulfield, is a confused rebel who voices his disgust with phonies, yet in an effort to protect himself, he acts like a phony on many occasions.
- Compared to an absolute divorce, no-fault divorce is less expensive, promotes fairer settlements, and reflects a more realistic view of the causes for marital breakdown.
- Exposing children from an early age to the dangers of drug abuse is a sure method of preventing future drug addicts.
- In today’s crumbling job market, a high school diploma is not significant enough education to land a stable, lucrative job.
You can find thesis statements in many places, such as in the news; in the opinions of friends, coworkers or teachers; and even in songs you hear on the radio. Become aware of thesis statements in everyday life by paying attention to people’s opinions and their reasons for those opinions. Pay attention to your own everyday thesis statements as well, as these can become material for future essays.
Now that you have read about the contents of a good thesis statement and have seen examples, take a look at the pitfalls to avoid when composing your own thesis:
A thesis is weak when it is simply a declaration of your subject or a description of what you will discuss in your essay.
Weak thesis statement: My paper will explain why imagination is more important than knowledge.
A thesis is weak when it makes an unreasonable or outrageous claim or insults the opposing side.
Weak thesis statement: Religious radicals across America are trying to legislate their Puritanical beliefs by banning required high school books.
A thesis is weak when it contains an obvious fact or something that no one can disagree with or provides a dead end.
Weak thesis statement: Advertising companies use sex to sell their products.
A thesis is weak when the statement is too broad.
Weak thesis statement: The life of Abraham Lincoln was long and challenging.
Read the following thesis statements. On a separate piece of paper, identify each as weak or strong. For those that are weak, list the reasons why. Then revise the weak statements so that they conform to the requirements of a strong thesis.
- The subject of this paper is my experience with ferrets as pets.
- The government must expand its funding for research on renewable energy resources in order to prepare for the impending end of oil.
- Edgar Allan Poe was a poet who lived in Baltimore during the nineteenth century.
- In this essay, I will give you lots of reasons why slot machines should not be legalized in Baltimore.
- Despite his promises during his campaign, President Kennedy took few executive measures to support civil rights legislation.
- Because many children’s toys have potential safety hazards that could lead to injury, it is clear that not all children’s toys are safe.
- My experience with young children has taught me that I want to be a disciplinary parent because I believe that a child without discipline can be a parent’s worst nightmare.
Writing at Work
Often in your career, you will need to ask your boss for something through an e-mail. Just as a thesis statement organizes an essay, it can also organize your e-mail request. While your e-mail will be shorter than an essay, using a thesis statement in your first paragraph quickly lets your boss know what you are asking for, why it is necessary, and what the benefits are. In short body paragraphs, you can provide the essential information needed to expand upon your request.
Thesis Statement Revision
Your thesis will probably change as you write, so you will need to modify it to reflect exactly what you have discussed in your essay. Remember from Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” that your thesis statement begins as a working thesis statement , an indefinite statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process for the purpose of planning and guiding your writing.
Working thesis statements often become stronger as you gather information and form new opinions and reasons for those opinions. Revision helps you strengthen your thesis so that it matches what you have expressed in the body of the paper.
The best way to revise your thesis statement is to ask questions about it and then examine the answers to those questions. By challenging your own ideas and forming definite reasons for those ideas, you grow closer to a more precise point of view, which you can then incorporate into your thesis statement.
Ways to Revise Your Thesis
You can cut down on irrelevant aspects and revise your thesis by taking the following steps:
1. Pinpoint and replace all nonspecific words, such as people , everything , society , or life , with more precise words in order to reduce any vagueness.
Working thesis: Young people have to work hard to succeed in life.
Revised thesis: Recent college graduates must have discipline and persistence in order to find and maintain a stable job in which they can use and be appreciated for their talents.
The revised thesis makes a more specific statement about success and what it means to work hard. The original includes too broad a range of people and does not define exactly what success entails. By replacing those general words like people and work hard , the writer can better focus his or her research and gain more direction in his or her writing.
2. Clarify ideas that need explanation by asking yourself questions that narrow your thesis.
Working thesis: The welfare system is a joke.
Revised thesis: The welfare system keeps a socioeconomic class from gaining employment by alluring members of that class with unearned income, instead of programs to improve their education and skill sets.
A joke means many things to many people. Readers bring all sorts of backgrounds and perspectives to the reading process and would need clarification for a word so vague. This expression may also be too informal for the selected audience. By asking questions, the writer can devise a more precise and appropriate explanation for joke . The writer should ask himself or herself questions similar to the 5WH questions. (See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information on the 5WH questions.) By incorporating the answers to these questions into a thesis statement, the writer more accurately defines his or her stance, which will better guide the writing of the essay.
3. Replace any linking verbs with action verbs. Linking verbs are forms of the verb to be , a verb that simply states that a situation exists.
Working thesis: Kansas City schoolteachers are not paid enough.
Revised thesis: The Kansas City legislature cannot afford to pay its educators, resulting in job cuts and resignations in a district that sorely needs highly qualified and dedicated teachers.
The linking verb in this working thesis statement is the word are . Linking verbs often make thesis statements weak because they do not express action. Rather, they connect words and phrases to the second half of the sentence. Readers might wonder, “Why are they not paid enough?” But this statement does not compel them to ask many more questions. The writer should ask himself or herself questions in order to replace the linking verb with an action verb, thus forming a stronger thesis statement, one that takes a more definitive stance on the issue:
- Who is not paying the teachers enough?
- What is considered “enough”?
- What is the problem?
- What are the results
4. Omit any general claims that are hard to support.
Working thesis: Today’s teenage girls are too sexualized.
Revised thesis: Teenage girls who are captivated by the sexual images on MTV are conditioned to believe that a woman’s worth depends on her sensuality, a feeling that harms their self-esteem and behavior.
It is true that some young women in today’s society are more sexualized than in the past, but that is not true for all girls. Many girls have strict parents, dress appropriately, and do not engage in sexual activity while in middle school and high school. The writer of this thesis should ask the following questions:
- Which teenage girls?
- What constitutes “too” sexualized?
- Why are they behaving that way?
- Where does this behavior show up?
- What are the repercussions?
In the first section of Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , you determined your purpose for writing and your audience. You then completed a freewriting exercise about an event you recently experienced and chose a general topic to write about. Using that general topic, you then narrowed it down by answering the 5WH questions. After you answered these questions, you chose one of the three methods of prewriting and gathered possible supporting points for your working thesis statement.
Now, on a separate sheet of paper, write down your working thesis statement. Identify any weaknesses in this sentence and revise the statement to reflect the elements of a strong thesis statement. Make sure it is specific, precise, arguable, demonstrable, forceful, and confident.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
In your career you may have to write a project proposal that focuses on a particular problem in your company, such as reinforcing the tardiness policy. The proposal would aim to fix the problem; using a thesis statement would clearly state the boundaries of the problem and tell the goals of the project. After writing the proposal, you may find that the thesis needs revision to reflect exactly what is expressed in the body. Using the techniques from this chapter would apply to revising that thesis.
Key Takeaways
- Proper essays require a thesis statement to provide a specific focus and suggest how the essay will be organized.
- A thesis statement is your interpretation of the subject, not the topic itself.
- A strong thesis is specific, precise, forceful, confident, and is able to be demonstrated.
- A strong thesis challenges readers with a point of view that can be debated and can be supported with evidence.
- A weak thesis is simply a declaration of your topic or contains an obvious fact that cannot be argued.
- Depending on your topic, it may or may not be appropriate to use first person point of view.
- Revise your thesis by ensuring all words are specific, all ideas are exact, and all verbs express action.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Training videos | Faqs

Paraphrasing Tool – Academic Rephrase Tool for Researchers
Ref-n-write’s paraphrasing tool has a powerful AI (Artificial Intelligence) module that is specifically designed for academic writing. It is very important to avoid plagiarism when it comes to academic writing. You can no longer use your own text after it is published, it should be paraphrased manually or with a good rephrase tool, otherwise it will be considered self-plagiarism . Ref-n-write has been ranked as one of the best paraphrasing tools available out there. Ref-n-write’s legacy phrase templates feature offers the ability to rephrase sentences individually, while the newly added paraphrasing tool allows the users to rephrase paragraphs with one click. These tools work hand-in-hand with the academic phrasebank and rewording tools to provide a full suite of tools for researchers. This makes Ref-n-write one of the best research tools available for students and academics. In a recent survey of rewriter tools available to students and academics to reduce plagiarism, Ref-n-write was rated as the best scholarly paraphrasing tool . Click here to see the video of paraphrasing tool in action rephrasing a paragraph.
What is a Paraphrasing Tool?
A paraphrasing tool is used to rewrite or rephrase a sentence without altering its meaning. This is accomplished by substituting any number of alternate versions for specific words, phrases, sentences, or even whole paragraphs to create a slightly different variant.
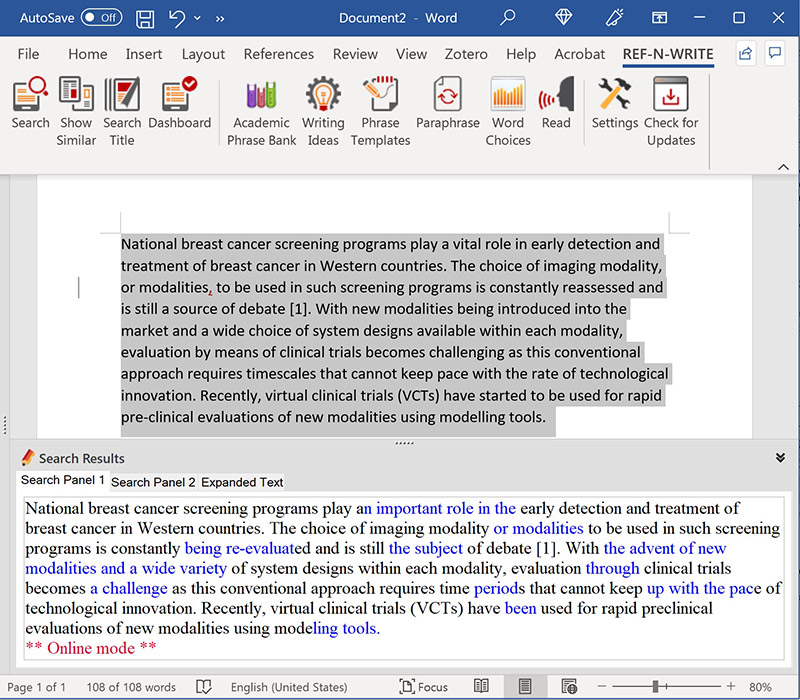
How do you use the Ref-n-Write’s Paraphrasing Tool in Word?
You have to select a passage and click the ‘Paraphrase’ button in the Ref-n-write’s button panel. Ref-n-Write will rewrite the text and display the results in the panels below. Following figure demonstrates Ref-n-Write’s paraphrasing tool in action.
Can Ref-n-write’s Paraphrasing Tool correct grammatical errors in the text?
The Ref-n-Write’s paraphrasing tool functions as a grammar checker. In addition to rephrasing and rewording the text the tool can detect and correct grammatical errors. You don't have to spend extra money on a separate grammar check as these tools can be quite expensive and you have to sign up for an annual subscription.
How do you Rephrase a Sentence?
Rephrasing a sentence follows the same process as paraphrasing, but the most important consideration is to make the sentence clearer. Rephrasing may or may not be coupled with rewording or synonym adjustments. It may only entail rearranging the original sentence as long as clarity is obtained.
Can Ref-n-write Rephrase a Sentence?
Perfectly! It is an all-in-one tool that will assist you with every aspect of academic writing. Ref-n-write makes it very easy to rephrase, reword, rewrite, paraphrase, cite and avoid plagiarism.
Is it Okay to use a Paraphrasing tool?
Yes, it is okay to use a paraphrasing tool. However, there has been much debate about whether or not using a paraphrasing tool is a good practice. Some may argue that it prevents authors and students from improving their ability to express themselves in their own words. As with any invention, these paraphrasing tools can be misused. But that doesn’t mean using them is bad. These tools provide suggestions and ideas to help the user paraphrase, but the final product is still up to the user. Only when authors, students, or users see these paraphrasing tools as a direct substitute for citation does it become a bad practice.
How do you Paraphrase Correctly?
- • Read the text to get an understanding of its message and flow.
- • Identify and highlight keywords that must not be changed to retain the text’s meaning.
- • Identify words that can be rearranged or moved without changing the meaning or flow of the text.
- • Identify words and phrases that can be changed and replace them with appropriate synonyms.
- • Double-check that you included all of the vital information in the original text.
How do you Professionally Paraphrase?
You Paraphrase professionally by following our guidelines on paraphrasing correctly and appropriately citing and referencing the source materials. A paraphrasing tool (ideally Ref-n-write) will make the process quicker and faster, increase the overall quality of your work, and provide you with a greater variety of ideas to work with.
How do you Rephrase a Paragraph?
- • Paraphrasing each sentence that makes up the paragraph.
- • Ensuring there is an adequate flow from sentence to sentence
- • Ensuring every sentence is clear
- • Ensuring the meaning of each sentence and the overall message of the whole paragraph is not altered
How can I make a Sentence Better?
It is essential that a good sentence be clear, concise, appropriately punctuated, free of grammar errors, and have a proper flow. All of the elements stated above must be improved for a sentence to be better. Effective paraphrasing may help you improve a sentence, and employing the right paraphrasing tools can help you improve a sentence even more.
Can you use the Ref-n-Write’s Paraphrasing Tool Offline?
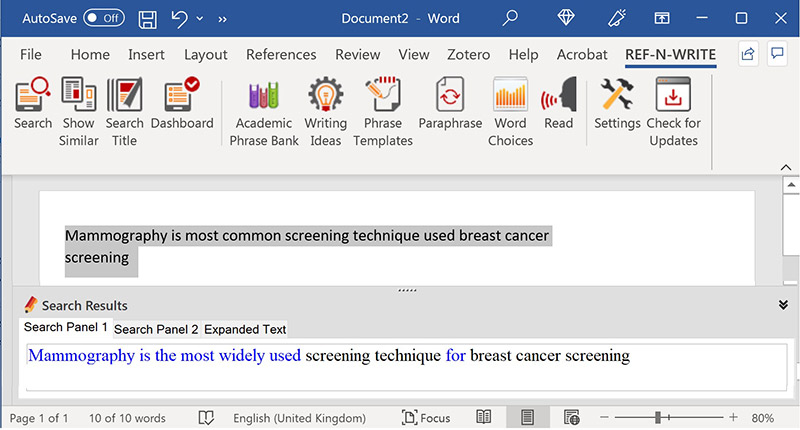
Most of the existing rephrase tools requires access to the internet. On the contrary, the Ref-n-write’s paraphrasing tool can be operated in both online and offline modes. Following images show the rephrased output of the paraphrasing tool when operating in online and offline modes. If you look at the rephrased paragraph, you will notice that the rephrased sentences are colour coded in offline mode indicating the confidence of each word replacement - green means very confident; blue means moderately confident and red means not very confident. There is no colour coding in the online mode, however the quality of rephrasing is much better in the online paraphrasing mode compared to the offline mode. It is highly recommended to use the paraphrasing tool in online mode since this is much more powerful than the offline mode.
How do you Paraphrase a file with Ref-n-Write?
Ref-n-Write allows users to paraphrase their file one passage at a time. This enables the author to learn and understand the paraphrasing process and do it without outside help in the future. Since Ref-n-write is a Microsoft Word add-in, paraphrasing can be applied directly to the document without losing the formatting.
What is the best free online paraphrasing tool?
There is no such thing as the best online paraphrasing tool. An excellent online paraphrasing tool should provide final paraphrased results that adhere to the steps recommended in our guideline to correctly paraphrasing. Ref-n-write provides a 15-day free trial period in which you can test the paraphrasing feature before charging a one-time fee.
Can I get the paraphrasing tool for free?
As the saying goes, “the great ones don’t come cheap.” Ref-n-write is the best academic paraphrasing tool available. It is a Microsoft Word add-in that is compatible with both Windows and Mac computers. If you are a scholar, student, researcher, author, or you have a job that requires a lot of writing, Ref-n-write is the best for you. Ref-n-write provides a 15-day free trial period before charging a one-time fee of around £29.99 for the full version. That is significantly less expensive than any other paraphrasing tool that charges a monthly fee. It aids in citation and allows you to import your source materials and conduct a full-text search to avoid plagiarism. Ref-n-write is the most affordable all-in-one paraphrasing tool available.
What is the difference between free and paid Paraphrasing tool?
Paraphrasing with a free or paid tool follows the same steps as mentioned above for correctly paraphrasing. However, when compared to the paid version of Ref-n-write, using a free tool has some limitations on the word count of the text being paraphrased.
Is Ref-n-write Paraphrasing Tool Safe?
Ref-n-write’s paraphrasing tools are secure and dependable. They take the security and privacy of their members seriously, and they operate in line with all relevant privacy and data protection legislation.
Is using Paraphrasing Tool Cheating?
Some may argue that employing paraphrasing tools is unethical because the information is not original and the tools do not acknowledge the original writer. Paraphrasing, on the other hand, is not plagiarism if adequately cited and referenced. Hence, utilising paraphrasing tools with correct citation and reference is not considered cheating.
Is Paraphrasing Tool Legit?
The utilisation of paraphrase tools determines their legitimacy. When used correctly, they are legal; nevertheless, when misused, they constitute plagiarism, which is illegal. True, these paraphrase tools make work easier and faster, especially when one is on a tight deadline, but they must be utilised correctly.
Can Turnitin Detect Paraphrasing Tool?
An excellent way to avoid plagiarism scanners is by paraphrasing. Turnitin’s algorithms do not detect paraphrasing. They are primarily concerned with recognising similar language structures, grammatical patterns, and phrases. This paraphrasing tool will not be flagged as plagiarised as long as it generates unique content that exhibits little or no similarity to anything in the Turnitin database.
Is Paraphrasing Tool Plagiarism?
As previously stated, combining paraphrasing tools with proper citation and referencing is a good practice. Yes, some of these paraphrasing tools can produce 100% unique content, but the source material should be acknowledged. As a result, if proper citation is not used, a paraphrasing tool can constitute plagiarism.
Is there a Website that can Paraphrase Sentences for you?
You can try the Ref-n-write paraphrasing tool on the website, however it is recommended to install the plugin on your Microsoft Word as it offers more options and is easy to use. If you conduct a Google search, you will be presented with an unending list of websites to consider. Many of these websites reword sentences; they do not adequately rewrite them.
What is the Best Paid Paraphrasing tool?
We are possibly the best paid paraphrasing tool available. Ref-n-write does more than just paraphrase; it also assists with citation and referencing and allows you to import all of your source materials and perform a full-text search to check for similarity and text overlap. Our academic phrase bank provides you with a variety of phrases related to your topic of interest from which to choose. Ref-n-write helps you enhance your writing to suit today’s standards. Oh, and did I forget to mention that it is very affordable compared to other paid tools? We give you good value for your money.
How do you Use the Paraphrasing Tool in Word?
Microsoft Word’s Web version now includes rewrite suggestions, but it is very basic. However, this is a new function and has not yet been implemented on the PC or mobile versions. There are various paraphrasing tools available as Microsoft Word add-ins on PC, including Ref-n-write and many others. These add-ins will assist you in rewording your texts in a variety of ways.
- 1.4K Share Facebook
- 1K Share Twitter
- 1.1K Share LinkedIn
- 1.5K Share Email
Citations per year
Duplicate citations, merged citations, add co-authors co-authors, cited by view all.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
What is Google Scholar and Why Should You Care? Google Scholar is a special division of Google that searches for academic content. It is not as robust as Google, and as such it can be harder to search. However, if you are looking for a specific article it is a fantastic resource for finding out if you can access it through your library or if it ...
Google Scholar searches are not case sensitive. 2. Use keywords instead of full sentences. 3. Use quotes to search for an exact match. 3. Add the year to the search phrase to get articles published in a particular year. 4. Use the side bar controls to adjust your search result.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement is a concise statement of an academic work's main point. The thesis statement should identify both what the paper is about (the topic) and what you are saying about it. Your thesis statement should be as specific as possible. For a short essay, the length of your thesis statement should be one or two sentences.
Search Help. Get the most out of Google Scholar with some helpful tips on searches, email alerts, citation export, and more. Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar: click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
A thesis statement is an essential component of ALL academic and research writing. A thesis statement: occurs early in a piece of written work (introduction) tells the reader what the purpose and scope of the work will be. provides more than a mere description of the topic. puts a 'wager' (i.e. a bet) on the topic by telling us what the ...
A thesis is the main point or argument of an information source. (Many, but not all, writing assignments, require a thesis.) Thesis are often answer your research question. Note that it does not have to be the only answer to your research question, a strong thesis question gives a reasonable answer. Below are some characteristics of a strong ...
The kind of thesis statement you write will depend on the type of paper you are writing. Here is how to write the different kinds of thesis statements: Argumentative Thesis Statement: Making a Claim. Analytical Thesis Statement: Analyzing an Issue. Expository Thesis Statement: Explaining a Topic.
It is a place for introducing the research and its topic and the thesis. The statements, quotes, or definitions from other authors can be placed in the section, which will provide the stronghold, understanding, importance, and relevance of the study topic. ... Book Google Scholar Odena O, Burgess H (2017) How doctoral students and graduates ...
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
The main difference between a thesis statement and a research question is that a thesis statement makes a claim upfront that you will attempt to validate in your paper. A thesis statement: States your position on a topic; Is not always required when writing a research paper; Is often your research question reworded as a statement with a position
Contents Why Should I Read This Guide? . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Before the Project Begins: Basic Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
This is the liveliest part of a thesis. Its main goal is to defend the work by staging a constructive debate with the literature. The golden rule of this written debate should be that a rigid explanation looks backward and a design looks forward. The object is to derive a model out of a jig-saw puzzle of information.
A good RQ helps support a focused arguable thesis and construction of a logical argument. ... It is a predictive statement about the outcome of the research, ... [Google Scholar] 7. Jones R. Choosing a research question. Asia Pac Fam Med. 2003; 2:42-4.
Google Scholar searches specifically for scholarly materials, including Open Access (freely available) dissertations and theses. Many institutions make their dissertations publicly available, making Google Scholar a great place to search. See the Library's guide on Google for Academic Research for more information.
A Thesis Statement: Describes how you interpret the subject matter's cause, significance, and results. Is a guideline for the paper. In other words, it provides an understanding of the research topic. Directly answers the question you are asked. The thesis is not the question itself but an interpretation of it.
Linking Google Scholar to Derby Library's full-text resources. This guide details the step-by-step process to linking Google Scholar to Derby Library's E-Journals Finder and ProQuest Fulltext collections. It won't be able to link to all of our full-text resources, but a considerable number should show a link when you search. [PDF 602KB]
Weak thesis statement: The life of Abraham Lincoln was long and challenging. Exercise 2. Read the following thesis statements. On a separate piece of paper, identify each as weak or strong. For those that are weak, list the reasons why. Then revise the weak statements so that they conform to the requirements of a strong thesis.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Thesis Statements. • Definition. • A concise , specific, and arguable explanation of your paper's main argument or purpose. • Appears at or toward the end of the introduction. • Importance. • Keeps writer on topic. • Sets readers' expectations. • Answers the question.
The results show that the 612 theses and dissertations attracted 931 citations which translates to 1.52 citations per thesis on average. A total of 41.2% theses and dissertations received at least ...
Ref-n-write is the best academic paraphrasing tool available. It is a Microsoft Word add-in that is compatible with both Windows and Mac computers. If you are a scholar, student, researcher, author, or you have a job that requires a lot of writing, Ref-n-write is the best for you. Ref-n-write provides a 15-day free trial period before charging ...
378. 2014. Activation and dynamic network of the M2 muscarinic receptor. Y Miao, SE Nichols, PM Gasper, VT Metzger, JA McCammon. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 110 (27), 10982-10987. , 2013. 240. 2013. Accelerated molecular dynamics simulations of protein folding.