- GET INVOLVED

COVID-19 pandemic
Covid-19 pandemic response.
Humanity needs leadership and solidarity to defeat the coronavirus
The coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic is the defining global health crisis of our time and the greatest challenge we have faced since World War Two. Since its emergence in Asia late last year, the virus has spread to most of the countries.
Nepal, a landlocked country aspiring to graduate from a Least Developed Country status, stands highly vulnerable to the unfolding COVID-19 pandemic. Heedful of its vulnerabilities, the Government of Nepal has enforced a nationwide lockdown and activated its federal, provincial and local level mechanisms to respond to the crisis. While there is an urgent need to strengthen the existing health system to handle the situation in case of any sudden surge of outbreak, standardize the quarantine facilities and provide immediate relief to the most-affected, equally important is to help the country mitigate the socio-economic impacts and prepare for a longer-term recovery.
The secondary impact of the global pandemic is huge and it is already taking a serious toll on an economy that relies heavily on remittances, imports fueled by remittances, informal labor, and tourism revenues.
UNDP is working with the Government of Nepal and the UN Country Team to support the country's preparedness to face the mounting public health emergency, respond to the socio-economic impact of the protracted lockdown on the most vulnerable, and support longer-term recovery measures.
The fact that Nepal’s economy is largely dependent on remittance (25% of GDP), tourism (8% of GDP), agriculture (26% of GDP) and imports of essential items and supplies from outside has made the poor households and the often unskilled workers, including returnee migrants, particularly vulnerable to income losses.
Given that most of these people are outside the official social safety net, they are likely to bear the brunt of the sudden halt or slowdown of economic activities in Nepal.
UNDP response
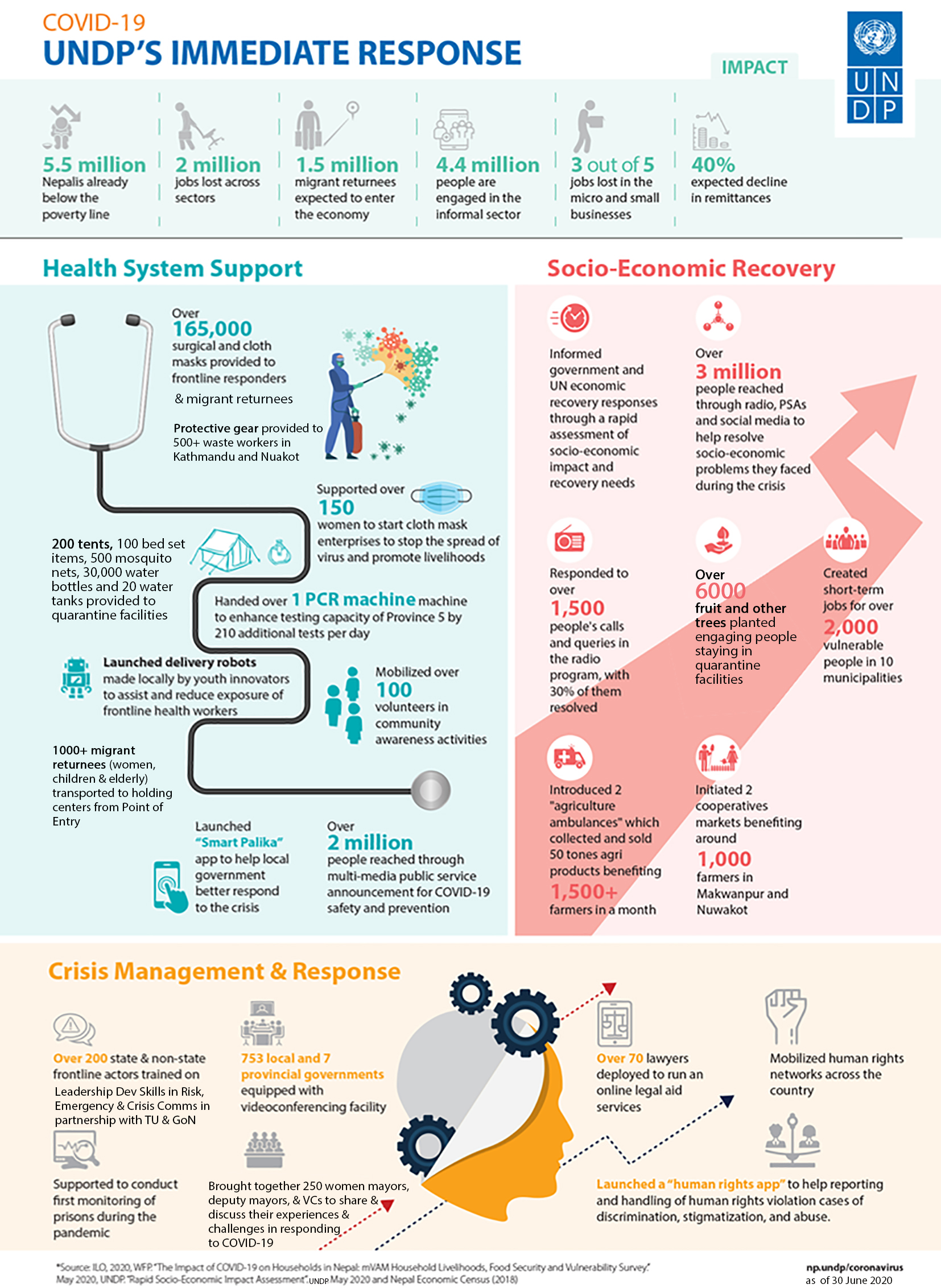
As part of the UN family and in close coordination with the World Health Organization (WHO), UNDP is responding to requests from national and sub-national governments to help them prepare for, respond to and recover from the COVID-19 pandemic, focusing particularly on the most vulnerable and where they are found. While needs assessments are being drawn, our short and medium-term response will mainly translate in activities that focus on the three major areas: Health System Suppor, Socio-economic Recovery and Crisis Management and Response .
“We are already hard at work, together with our UN family and other partners, on three immediate priorities : supporting the health response including the procurement and supply of essential health products, under WHO’s leadership, strengthening crisis management and response, and addressing critical social and economic impacts.” UNDP Administrator, Achim Steiner
Health system support
Complementing the work of the specialized agencies to bolster health systems management and capacity, UNDP is supporting the provincial and local governments to strengthen their health systems , including by providing much-needed medical supplies, assessment of quarantine facilities and public awareness on COVID-19. The major activites are as follows:
- Enhancing public awareness on COVID19 thorugh communications (PSAs , Community level activities)
- Management of quarantine facilities through monitoring and assessment and logistics support
- Strengthening health support system
- Launched delivery robots to help frontline healthworkers

UNDP provides 400 oxygen concentrators to Nepal on June 11 2021
Socio-Economic Recovery
UNDP is using its extensive experience of working on early recovery, livelihood support and job creation by mobilizing cooperatives, developing enterprises and community infrastructures. Some of the key activites are as follows:
- Rapid assessment of socio-economic impact and recovery needs
- Short-term employment programme and livelihood recovery for the most vulnerable
- Support to local farmers for supply and delivery of their produces
- Green initiatives supporting livelihood
- Promoting women entreprenuers in local mask making
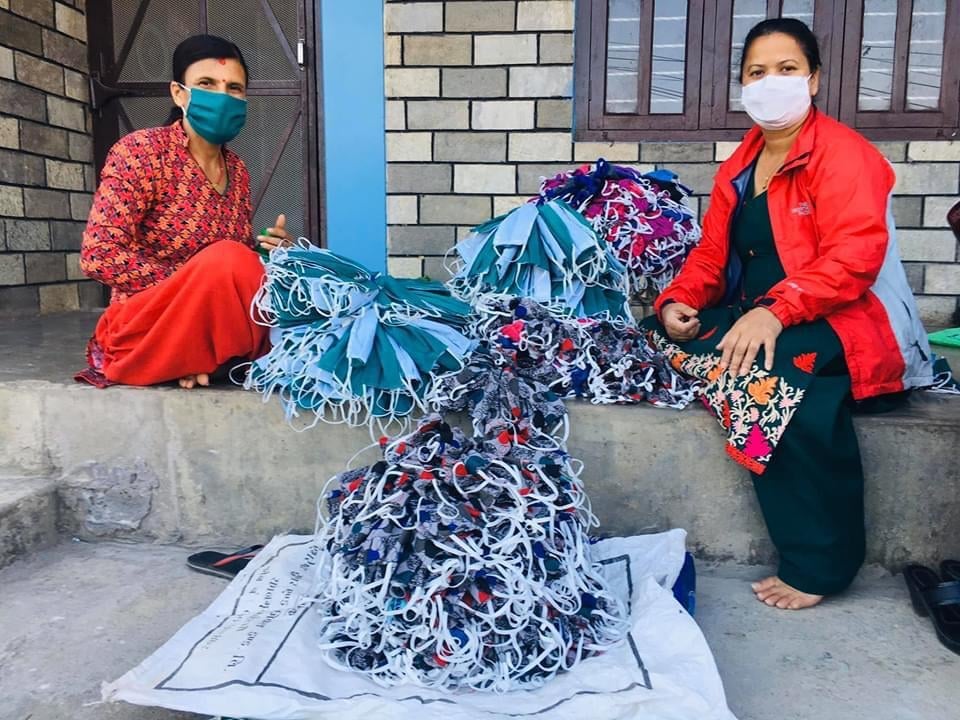

Women in Pokhara are on the frontline of mask production during the COVID-19 pandemic. This has helped address the problems of shortage and possible black marketing of masks, while also giving them a decent living amidst the crisis.
Crisis management and response
UNDP will also focus on enhancing crisis response and management capacities at the sub-national level, which include communication support and skill transfer to provincial governments and municipalities. Here are some of the key activites:
- Support the overall UN wide Preparedness and Response Plan and co-lead the Socio-Economic Recovery Cluster
- Communications support to provincial and local governments
- Live phone-in radio program aimed at helping connect people with government authorities and inform policies
- Crisis Communications training to representatives of local governments and other actors

Radio journalists at work. The Association of Community Radio Broadcasters (ACORAB) in Nepal and Community Information Network (CIN), with the support of UNDP, have launched a live phone-in radio program, which aims to help local governments address socio-economic issues/problems faced by the vulnerable people during the COVID-19 lockdown. Photo: CIN
REVIEW article
Combating the covid-19 pandemic: experiences of the first wave from nepal.

- 1 Faculty of Science, Nepal Academy of Science and Technology, Lalitpur, Nepal
- 2 Nepal Environment and Development Consultant Pvt. Ltd., Kathmandu, Nepal
- 3 Central Department of Environmental Science, Institute of Science and Technology, Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Nepal
- 4 Nepal Development Society, Bharatpur, Nepal
- 5 Kantipur Dental College Teaching Hospital and Research Center, Kathmandu University, Kathmandu, Nepal
- 6 National Disaster Risk Reduction Centre, Kathmandu, Nepal
- 7 Little Buddha College of Health Sciences, Kathmandu, Nepal
Unprecedented and unforeseen highly infectious Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a significant public health concern for most of the countries worldwide, including Nepal, and it is spreading rapidly. Undoubtedly, every nation has taken maximum initiative measures to break the transmission chain of the virus. This review presents a retrospective analysis of the COVID-19 pandemic in Nepal, analyzing the actions taken by the Government of Nepal (GoN) to inform future decisions. Data used in this article were extracted from relevant reports and websites of the Ministry of Health and Population (MoHP) of Nepal and the WHO. As of January 22, 2021, the highest numbers of cases were reported in the megacity of the hilly region, Kathmandu district (population = 1,744,240), and Bagmati province. The cured and death rates of the disease among the tested population are ~98.00 and ~0.74%, respectively. Higher numbers of infected cases were observed in the age group 21–30, with an overall male to female death ratio of 2.33. With suggestions and recommendations from high-level coordination committees and experts, GoN has enacted several measures: promoting universal personal protection, physical distancing, localized lockdowns, travel restrictions, isolation, and selective quarantine. In addition, GoN formulated and distributed several guidelines/protocols for managing COVID-19 patients and vaccination programs. Despite robust preventive efforts by GoN, pandemic scenario in Nepal is, yet, to be controlled completely. This review could be helpful for the current and future effective outbreak preparedness, responses, and management of the pandemic situations and prepare necessary strategies, especially in countries with similar socio-cultural and economic status.
Introduction
The unanticipated outbreak of the novel coronavirus was first reported in Wuhan, China, in December 2019; it transmits from human to human via droplets and aerosol ( 1 ). The WHO declared Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) on January 30, 2020, and a pandemic on March 11, 2020 ( 2 ). As a result, countries worldwide adopted various mitigative measures ( 3 , 4 ) and eradication strategies ( 5 ), aiming to reduce potentially enormous damage and reach zero cases, respectively. However, significant gaps in advance preparedness and the implementation of response plans resulted in the rapid spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) globally with 219 nations reporting it as of January 22, 2021 1 ( 6 ).
The Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal is a landlocked country in South Asia bordered by India in the south, east, and west, and China in the north. Its population, gross domestic product (GDP), and human development index (HDI) are 29.24 million 2 , 30.64 billion 3 , and 0.579 4 , respectively. The constitution of Nepal (2015) consists of a three-tier (federal, province, and local) governmental system. Each tier has the constitutional power to enact laws and mobilize its resources. In Nepal, the first case of COVID-19 was reported on January 23, 2020, in a 32-year-old Nepalese man who returned from Wuhan, China. Two months after the first case, the second case was diagnosed through domestic testing on March 23 in a returnee from France ( 7 ). Subsequently, the Government of Nepal (GoN) imposed early interventions approved by the WHO, including a travel ban and the Indo-Nepal and China-Nepal borders closure 5 . ( 8 ) to delay the possible onset of the detrimental effects of the outbreak across the country.
This review presents a 1-year (up to January 22, 2021) scenario of COVID-19 in Nepal, reviews the strategies employed by the GoN to control COVID-19, and provides suggestions for the prevention and control of current and future pandemics. Federal, provincial, and district-level daily cases of COVID-19 [confirmed by real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), cured, and death] in Nepal from January 23, 2020, to January 22, 2021, were obtained from the Ministry of Health and Population (MoHP), GoN 6 . Searches using the website of MoHP of Nepal, PubMed, the WHO, the worldometer official website, and Google were conducted to gather the information on the number of deaths, cured, and confirmed cases of COVID-19 and reports describing the approach taken by the government to contain COVID-19 in Nepal. The search terms included “COVID-19 in Nepal” and “Prevention and management of COVID-19 in Nepal.” Data used in this article were extracted from relevant documents and websites. The figures were constructed by using Origin 2016 and GIS 10.4.1. We did not consult any databases that are privately owned or inaccessible to the public.
Epidemic Status of COVID-19 in Nepal
The MoHP of Nepal confirmed the first and second cases of COVID-19, respectively, in January and March, in an interval of 2 months 1 ( 9 ). As of January 22, 2021, 268,948 COVID-19 positive cases were reported, with 263,546 recovered, and 1,986 death cases 6 . This data showed nearly 0.74% death and about 98% recovery rate in Nepal. The case fatality rate (CFR) was 0.5% up to March 30 in Nepal ( 9 ). The CFR in the USA, Brazil, and Russia is similar (~2%), whereas in the South Asian Association of Regional Cooperation (SAARC) countries, the CFR varied from ~0.09 to ~4.7 % ( Table 1 ). In total, 2,035,301 qRT-PCR tests were performed in Nepal, indicating about 13.47% current prevalence of COVID-19 among the qRT-PCR tested population as compared with 2.5% as of March 31, 2020 2 . As of reviewing, the prevalence of COVID-19 among the qRT-PCR tested population is higher than the neighboring countries, China (~0.055%) and India (~0.099%) ( Table 1 ). In addition, up to the third quarter of 2020, <1% of the confirmed COVID-19 cases were symptomatic across all age groups, while the proportion of symptomatic cases progressively increased beyond 55 years of age from 1.3 to 9% 7 , 8 . Unlike Nepal, higher symptomatic cases were reported from other parts of the world during the same period ( 10 ). Understandably, the scenario of the proportion of symptomatic to asymptomatic cases remains to vary between countries and care facilities. Few possible reasons for low symptomatic cases reported in the Nepalese population may be poor health-seeking behavior and utilization of tertiary health care services ( 11 ) for mild symptomatic cases, home isolation without a diagnosis, and a high rate of self-medication practices ( 12 ).
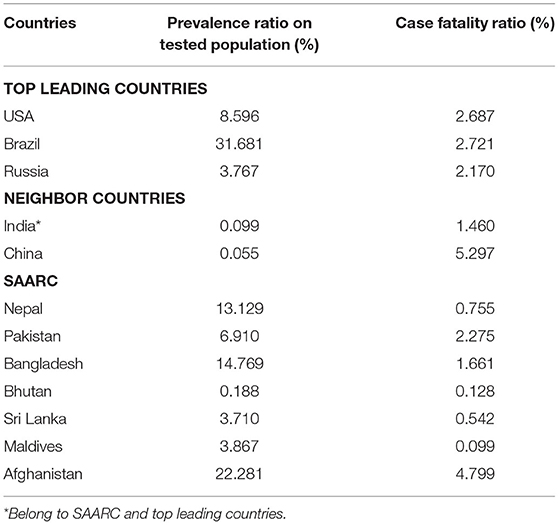
Table 1 . Prevalence and case fatality ratio (CFR) of COVID-19 of top leading countries, neighbor countries of Nepal, and SAARC as of Jan 28, 2021.
Among the provinces, Bagmati province ( n = 144,278) has the highest number of confirmed cases in Nepal, followed by province no. 1 ( n = 30,422) and Lumbini ( n = 30,308) ( Figure 1A ). As depicted in Table 2 , the confirmed cases of COVID-19 are distributed throughout the country in all the administrative districts. The total number of confirmed cases is highest in the Kathmandu district ( n = 103,523) followed by Lalitpur ( n = 16,106), Morang ( n = 13,236), and Rupandehi ( n = 9,708) districts and lowest in Manang ( n = 20), Mugu ( n = 37), Mustang ( n = 43), and Humla ( n = 44) districts ( Table 2 ).
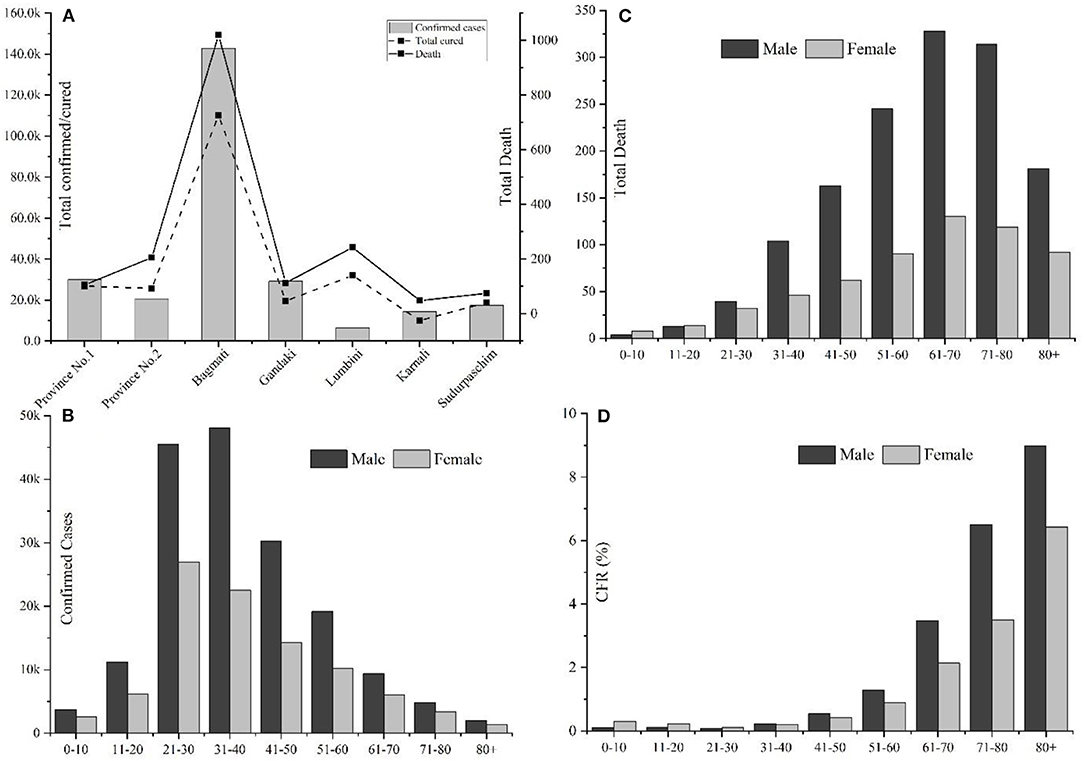
Figure 1 . Overview of COVID-19 cases in Nepal up to January 22, 2021. (A) Province-wise distribution of total confirmed cases, recovery, and deaths; (B) Gender, age-wise distribution of COVID-19 confirmed cases; (C) Gender-age wise distribution of COVID-19 death cases; and (D) Age and gender-wise case fatality rate (CFR) in Nepal.
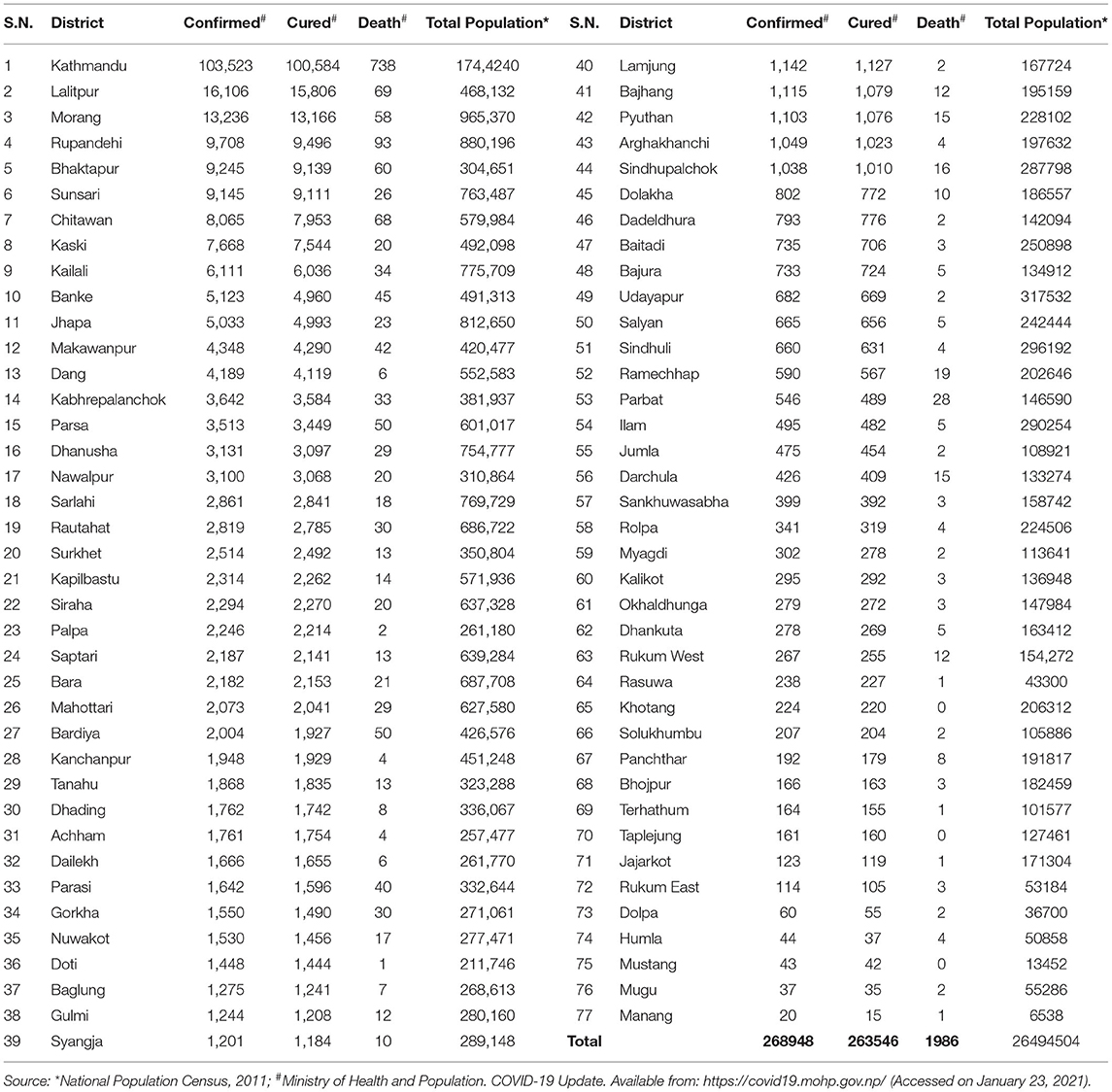
Table 2 . District wise distribution of confirmed cases, recoveries, and deaths due to COVID-19 and total population in Nepal.
Among 268,948 confirmed cases, 174,193 were males, and 94,755 were females, with a male-to-female sex ratio of 1.85. The largest number of infected cases was reported in the age group 21–30 years (26.92%, n = 72,396), followed by the age group of 31–40 years (26.26%, n = 70,648) ( Figure 1B ); however, the number of death cases was higher in the age group 61–70 (23%, n = 458) ( Figure 1C ). A higher death trend in old age is also observed in Europe, America, and Asian countries ( 13 , 14 ). Overall, male death was ~2.33 times the death rate of females. Reports have indicated that men are at greater risk of around two time of acquiring severe outcomes of COVID-19, including hospitalizations, intensive care unit (ICU) admissions, and deaths ( 15 ). The enhanced susceptibility of males for COVID-19 associated adverse events may be correlated with the hormonal and immunological differences between males and females ( 15 , 16 ). Among a total of 1,986 fatal cases (Male: n = 1,391; female: n = 595), over half ( n = 1,166) were observed in senior adults (≥60 years). One early study among the Nepalese children suggested that male children were more commonly infected than female children ( 17 ).
Among 1,986 fatal cases (mean age: 66.15 years), 623 (31.37%), 721 (36.30%), and 642 (32.32%) were with no report of comorbidities, with single comorbidities, and with multiple comorbidities, respectively. In cases with single comorbidities, the highest incidence was reported in respiratory disease ( n = 184) followed by hypertension ( n = 117), renal disease ( n = 107), diabetes ( n = 77), liver disease ( n = 44), and cardiovascular disease ( n = 36) ( Figure 2 ). Similar results are reported from other parts of the world ( 18 ). The detailed epidemiological trend analysis of COVID-19 in Nepal is shown in Figure 3 .
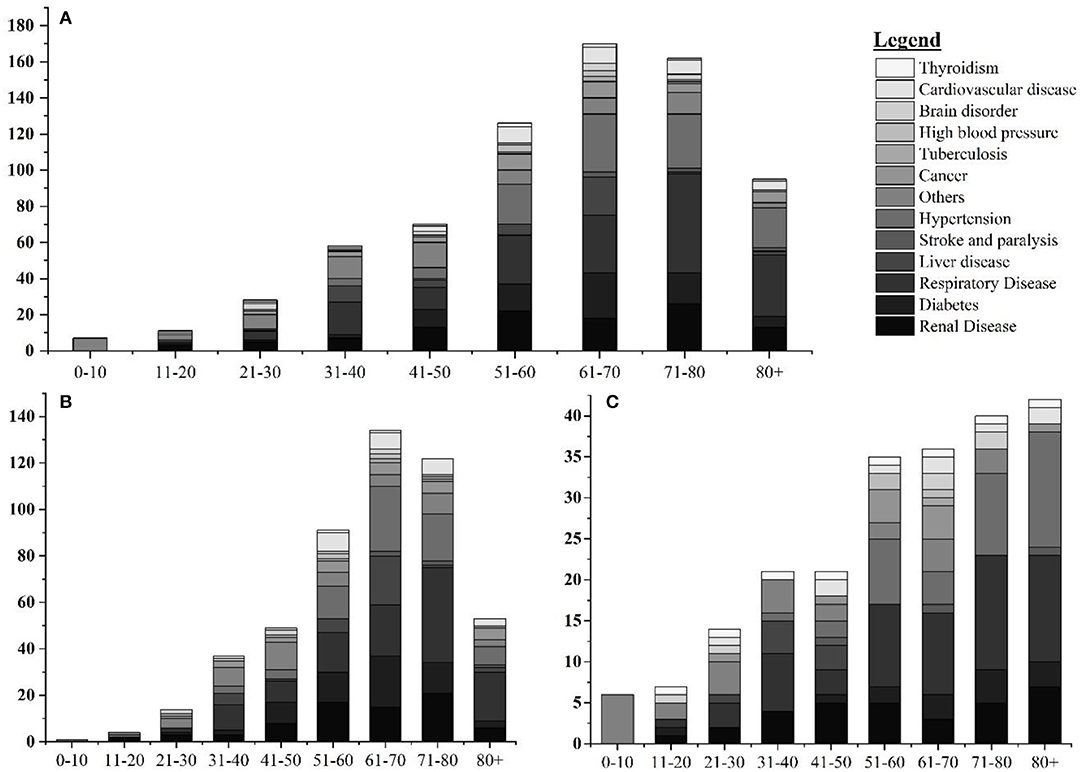
Figure 2 . Age and gender-wise distribution fatal cases with single comorbidities. (A) Age-wise distribution of leading single comorbidities among COVID-19 deaths; (B) age-wise distribution of leading single comorbidities among COVID-19 deaths in Nepal in male; and (C) age-wise distribution of leading single comorbidities among COVID-19 deaths in Nepal in female.
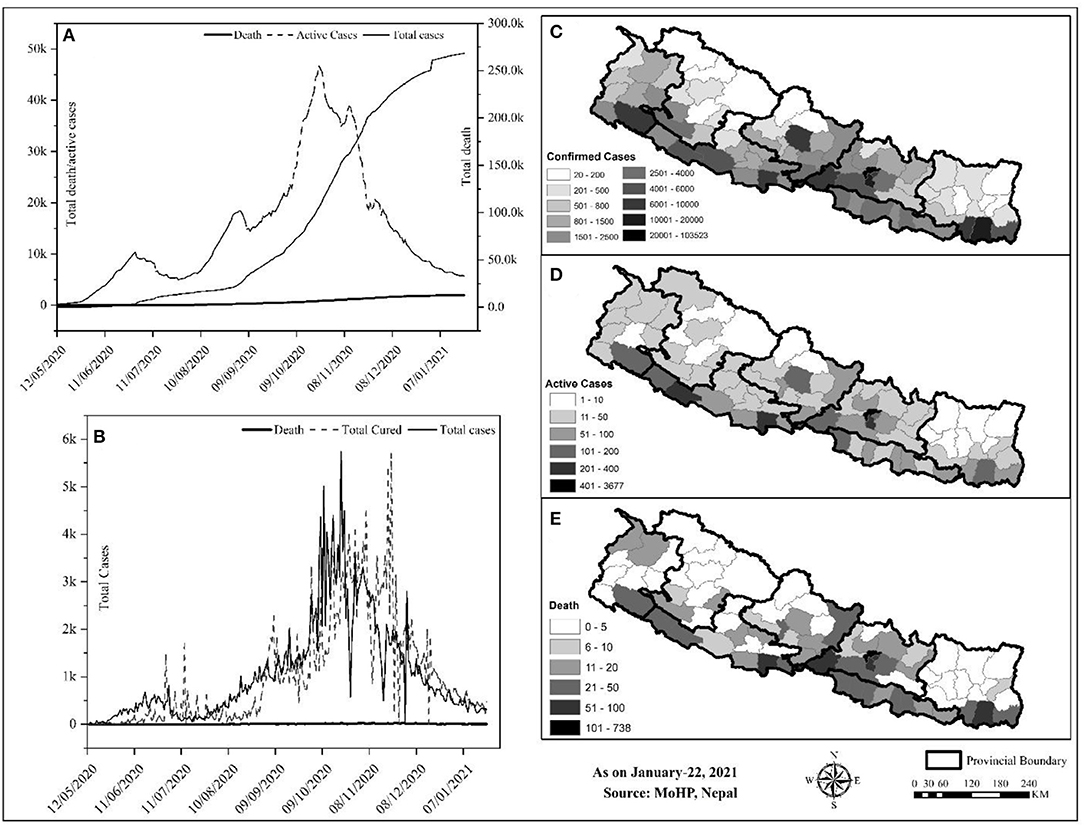
Figure 3 . Trend and spatial distribution of COVID-19 cases in Nepal. (A) Cumulative trend analysis of COVID-19 cases, (B) daily case wise trend analysis of COVID-19, (C–E) spatial distribution of infected, recovered, and death cases.
Geographically, Nepal is divided into three distinct ecological zones, mountain, hilly, and low-plain land from north to south. Politically, Nepal is divided into 7 provinces, 77 districts, and 753 local bodies. There were multiple peaks of active cases of COVID-19 in Nepal: active cases rapidly increased from early May to early July 2020, then increased slowly up to late July and increased at a higher rate again up to the end of December, and then decreased sharply ( Figure 3A ). The spatial distribution of COVID-19 confirmed cases, recovery, and deaths were compared ( Figures 3B–D ). Approximately, 64.84% of the total confirmed cases were reported from the hill regions, with single megacity Kathmandu contributing nearly half, 33.31% of lowland-plain areas, and 1.85% of Himalayan regions. The reported cases in the megacities are relatively higher than in the other regions. The higher number of cases in megacities may be correlated with dense populations in these areas ( 8 ). In the earlier months, the testing facilities and contact tracing were limited only to few districts, including the capital, Kathmandu, which gradually became available in other parts of the country. However, the testing frequency and testing facilities are still not homogeneous due to the lack of required technical resources and professional workforces ( 19 ) 9 .
The Response of Nepal Government to COVID-19
Nepal has adopted many readiness and response-related initiatives at the federal, provincial, and local government levels to fight against COVID-19. Initially, the government had set health desks and allocated spaces for quarantine purposes at the international airport and at the borders, crossing points of entry (PoE) with India and China 10 , to withstand the influx of many possible infected individuals from India and other countries. The open border and the politico-religious relationship with India and migrant workers returning from the Middle East, and other countries were a source of rapid transmission to Nepal 10 , 11 . The Nepal-China official border crossing points have remained closed since January 21, 2020. On March 24, 2020, the GoN imposed a complete “lockdown” of the country up to July 21, 2020. As part of the lockdown, businesses were closed, the restriction was imposed on movement within the country, workplaces were closed, travel was banned, and air transportation was halted 11 , 12 . In addition, for COVID-19 preparedness and response, the GoN developed a quarantine procedure and issued an international travel advisory notice. Closing the border was critical as Nepal and India share open borders across which citizens travel freely for business and work.
The GoN underestimated both the short and long-term impacts of border closure 11 . Around 2.8 million Nepali migrant workers work in India. Though the GoN discussed holding these workers in India with its Indian counterpart 13 , this plan did not materialize. Nepal has 1,690 km-long open borders with India, which could not keep migrant workers long despite the restrictions implemented by both governments 12 . As a consequence, the majority of COVID-19 cases were in the districts along the Indo-Nepal border. The decision of the government to lockdown the country from March 10, 2020, without sufficient preparation pushed daily wage laborers in urban areas to lose their jobs, and, hence, they were trapped without food or money. Ultimately, after a couple of days of lockdown, both migrant workers and daily wage laborers started walking the long way home due to the economic crisis.
As per the cabinet decision on March 25, 2020, Nepal established a COVID-19 response fund, developed a relief package 13 , and distributed relief to families in need through a “one door policy” 13 designed to reduce the COVID-19 impact; however, there were several gaps: the selection of families was unfair, GoN delayed the procurement of relief, relief packages did not include cash, and relief materials were inadequate and substandard 14 , 15 . The government has not adequately taken into account the impact of COVID-19 on the socio-economic sector. For instance, people participated in meetings, rallies, political demonstrations, and protests, where the virus could quickly spread among a large group of people. The government has, yet, to develop a stimulus package for social and economic recovery at the micro and macro levels. As the government has allocated $788 million for the health sector for the fiscal year (July–June 2020), a budget of 32% larger than the previous fiscal year, it should address the COVID-19 impact on the socio-economic front 16 . There is an opportunity to integrate all fragmented social protection schemes to strengthen socio-economic conditions and to emphasize more tremendous efforts, capacities, and resources to cope with the likely impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic 16 .
In addition, a minimal standard of quarantine as per the “Quarantine Operation and Management Protocol” (2076 B.S.) and “Standards for Home Quarantine” were imposed for all provinces 16 , 17 . The Sukraraj Infectious and Tropical Disease Hospital (SITDH) in Teku, Kathmandu, was designated by GoN as the primary hospital for COVID-19 cases along with Patan Hospital, the Armed Police Forces Hospital, in the Kathmandu Valley, followed by twenty-four hubs, and four satellite hospitals across the country 18 . Similarly, MoHP updated the National Public Health Laboratory (NPHL) capacity for confirmatory laboratory diagnosis of the COVID-19 from January 27, 2020, followed by the regional laboratory. The interim guideline for the establishing and operating of molecular laboratories for COVID-19 testing in Nepal was imposed to make uniformity in the test results 14 . Furthermore, the NPHL organized the training of trainers for laboratory staff in collaboration with the Medical Laboratory Association of Nepal 19 Ministry of Health and Population established two hotline numbers (1115 and 1133) to address public concerns, and prepared and disseminated regular press briefings, and improved its websites to channel appropriate information to the public. Besides, MoHP also conveyed decisions, notices, and situation updates periodically through its websites. Further, the Health Emergency Operation Centre (HEOC) of MoHP launched a “Viber communication group” to circulate updates on COVID-19 11, 13 . Early testing and timely contact tracing are crucial restrictive policies to control the spreading of the SARS-CoV-2 virus ( 20 , 21 ); however, in the earlier days of the pandemic, Nepal could not perform enough diagnostic tests and timely contact tracing; it resulted in a crucial time lag in identifying and isolating COVID-19 patients and caused delays in the ability of government to respond to the pandemic adequately. To alert and improve the testing and tracing response of the government, youth-led protests were carried out in different parts of the country 20 . Health Sector Emergency Response Plan was implemented in May 2020, focusing on the COVID-19 pandemic. This plan intends to prepare and strengthen the health system response capable of minimizing the adverse impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Government of Nepal devised a comprehensive plan on March 27, 2020, for quarantining people who arrived in Nepal from COVID-19 affected countries. The GoN had initially airlifted 175 Nepalese from six cities across Hubei Province of China on February 15, 2020, followed by Middle East countries, Australia, and so on 13 .
Ministry of Health and Population engaged in developing, endorsing, improving, and disseminating contextualized technical guidelines, standard operating procedures (SOPs), tools, and training in all other critical aspects of the response to COVID-19, for instance, surveillance, case investigation, laboratory testing, contact tracing, case detection, isolation and management, infection prevention and control, empowering health and community volunteers, media communication and community engagement, rational use of personal protective equipment (PPE), requirements of drugs and equipment for case management and public health interventions, and continuity of essentials services 13 ( 15 ). The major contextualized technical guidelines, SOPs, tools, and training materials developed by GoN to respond to COVID-19 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 were listed in Table 3 .

Table 3 . Major contextualized technical guidelines, standard operating protocols, tools, and training materials developed by the Government of Nepal (GoN) to respond to COVID-19.
Ministry of Health and Population and supporting organizations, such as United Nations Development Program (UNDP), UNICEF, and World Vision managed crucial supplies of PPE, facemasks, gloves, and sanitizers to ensure the protection of frontline workers and supporting staffs 13 , 30 , 31 , 32 . The frontline media of the nation increased online awareness programs via the involvement of celebrities, doctors, and experts of microbiology and infectious diseases on physical distancing and the importance and use of masks and sanitizers to prevent the COVID-19 contagion. In addition, camping programs were launched by the involvement of youth volunteers of the community in central Nepal 33 .
Government of Nepal received funds from the World Bank ($29 million), the United States of America ($1.8 million), and Germany ($1.22 million) to keep people protected from COVID-19 through health systems preparedness, emergency response, and research. In addition, support from UNICEF and countries, including China, India, and the USA, in the form of emergency medical supplies and equipment were received within January 2020 to March 2020. Private companies, corporate houses, business organizations, and individuals have also contributed to the prevention, control, and treatment fund of coronavirus ($13.8 million), established by GoN to cope with COVID-19. The Prime Minister Relief Fund is also expected to be utilized. The GoN allowed international NGOs to divert 20% of their program budget to COVID-19 preparedness and response; for instance, the Social Welfare Council has allocated $226 million 31 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 .
The GoN has formed a committee to coordinate the preparedness and response efforts, including the MoHP, Ministry of Home Affairs, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Culture, Tourism and Civil Aviation, Ministry of Urban Development, Nepal Army, Nepal Police, and Armed Police Force. The Humanitarian Country Team (HCT) includes the Red Cross Movement and civil society organizations (national and international NGOs). Under the joint leadership of the office of Resident Coordinator and the WHO, the HCT has initiated contingency planning and preparedness interventions, including the dissemination of communications materials to raise community-level awareness across the country 21 . The clusters led by the GoN and co-led by the International Astronomical Search Collaboration (IASC) cluster leads and partners are working on finalizing contingency plans, which will be consolidated into an overall joint approach with the Government and its international partners. The UN activated the provincial focal point agency system to support coordination between the international community and the GoN at the provincial level 21 .
However, despite these robust efforts implemented by GoN, few lapses existed. Examples are the following: issues of inconsistent implementation of immigration policies usually at Indo-Nepal borders 38 , 39 , 40 , shortage and misuse of crucial protective suits and other supplies in hospitals, the ease and the end of lockdown, lack of poor infrastructure facilities, and continuous spread of COVID-19 across the country ( 19 ). The GoN decided to lift the lockdown effective from July 22, 2020, completely; however, the socio-administrative and health measures with the potential for high-intensity transmission (colleges, seminars, training, workshops, cinema halls, party palaces, dance bars, swimming pools, religious places, etc.) remained closed until the following directive as of September 1, 2020. Long route bus services and domestic and international passenger flights were halted until August 1, 2020 41 . A high-level committee at the MoHP has requested all satellite hospitals (public, private, and others) to allocate 20% of their beds for COVID-19 cases. The respective hub hospitals coordinate with the HEOC and satellite hospitals to manage COVID-19 cases 42 . After lifting lockdown for 3 weeks, the federal government has given authority to local administrations to decide on restrictions and lockdown measures as COVID-19 cases continue to rise. In addition, the authority to impose necessary restrictions if COVID-19 active cases surpass the threshold of 200 was given to the Chief District Officer (CDO) 43 . Since March 2020, all the central hospitals, provincial hospitals, medical colleges, academic institutions, and hub-hospitals were designated to provide treatment care for COVID-19 cases. At this stage of operation, the major challenges for the COVID-19 response were managing quarantine facilities, lack of enough human resources, having limited laboratories for testing, and availability of limited stock of medical supplies, including PPEs 14 . To the best of our knowledge, this pandemic is the most extensive public health emergency the GoN faced in its recent history.
There is no doubt that GoN has taken major initiatives to fight the COVID-19 pandemic. The MoHP, together with associated national and international organizations are closely monitoring and evaluating the signs of outbreaks, challenges, and enforcing the plan and strategies to mitigate the possible impact; however, many challenges and difficulties, such as management of testing, hospital beds, and ventilators, quarantine centers, frontline staffs, movement of people during the lockdown, are yet to be solved 18 , 30 , 38 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 . Therefore, in the opinion of the authors, we recommend some steps to be implemented as soon as possible to mitigate and lessen the impacts of COVID-19 ( Table 4 ).
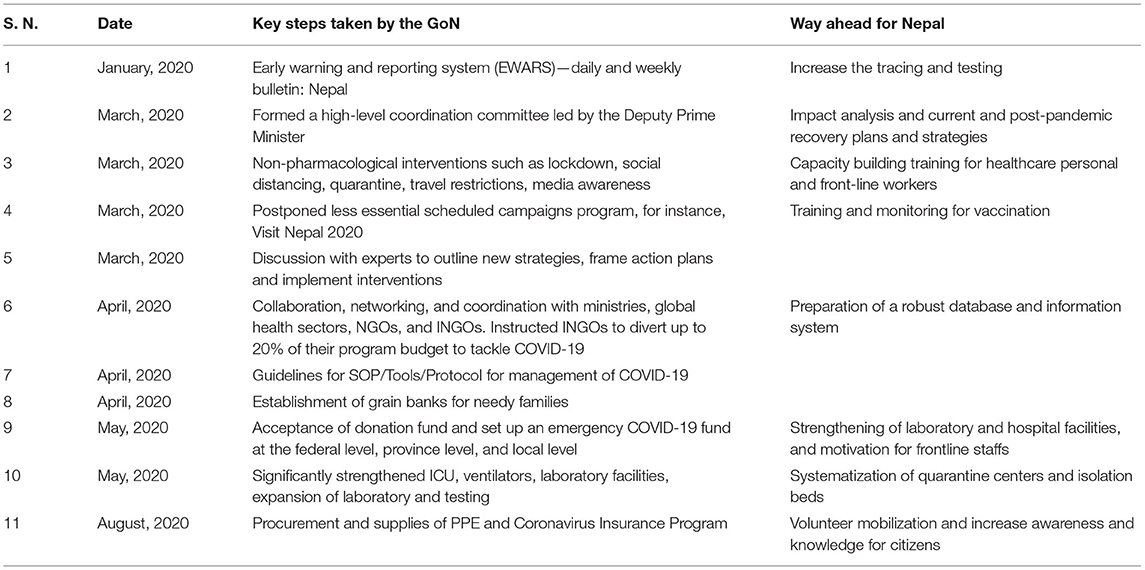
Table 4 . Major steps taken by GoN and way forward in the response to COVID-19 outbreak.
To strengthen its coordination mechanism, the government formed a team to monitor conditions and measures applied to control the outbreak; a COVID-19 coordination committee 11 to coordinate the overall response, and a COVID-19 crisis management center 14 to coordinate daily operations; however, these teams and committees did not function efficiently because roles and authorities were not delegated to ministries and government. A new institution was created, instead of using the National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Authority (NDRRMA) 48 , which enhanced additional confusion. The MoHP is responsible for overall policy formulation, planning, organization, and coordination of the health sector at federal, provincial, district, and community levels during the COVID-19 pandemic situation. Allegedly, there is an opportunity to strengthen coordination among the tiers of governments by following protocols and guidance for effective preparedness and response. For example, some quarantine centers were so poorly run that, in turn, could potentially develop into breeding grounds for the COVID-19 transmission 15 .
Finally, this study only focuses on analyzing COVID-19 data extracted from the MoHP database for 1 year. Furthermore, we did not quantify the effectiveness of the strategies of GoN and the role of non-governmental organizations and authorities to combat COVID-19 in Nepal.
This study provides an insight into the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic from the Nepalese context for the period of first-wave from January 2020 to January 2021. Despite the several initiatives taken by the GoN, the current scenario of COVID-19 in Nepal is yet to be controlled in terms of infections and mortality. A total of 268,948 confirmed cases and 1,986 deaths were reported in one year period. The maximum number of cases were reported from Bagmati province ( n = 144,278), all of the 77 districts were affected. The cases showing highly COVID-specific symptoms were low (<1%) in comparison with the reports across the globe ( 10 ), which may be because the average age of the Nepalese population is younger than many of the highly affected European countries. The other reasons may be differences in demographic characteristics, sampling bias, healthcare coverage, testing availability, and inconsistencies relating to the reporting of the data included in the current study. Both the number of infections and deaths are higher in males than in females. Despite the age, testing and positivity, hospital capacity and hospital admission criterion, demographics, and HDI index, the overall case fatality was reported to be less than in some other developed countries ( Table 1 ). Consistent with reports from other countries ( 22 , 23 ), the death rate is higher in the old age group ( Figure 1 ). Spatial distribution displayed the cases, which are majorly distributed in megacities compared with the other regions of the country.
Based on this assessment, in addition to the WHO COVID-19 infection prevention and control guidance 49 , some recommendations, such as massive contact tracing, improving bed capacity in health care settings and rapid test, proper management of isolation and quarantine facilities, and advocacy for vaccines, may be helpful for planning strategies and address the gaps to combat against the COVID-19. Notably, the recommendations provided could benefit the governmental bodies and concerned authorities to take the appropriate decisions and comprehensively assess the further spread of the virus and effective public health measures in the different provinces and districts in Nepal. In this review, we have summarized the ongoing experiences in reducing the spread of COVID-19 in Nepal. The Nepalese response is characterized by nationwide lockdown, social distancing, rapid response, a multi-sectoral approach in testing and tracing, and supported by a public health response. Overall, the broader applicability of these experiences is subject to combat the COVID-19 impacts in different socio-political environments within and across the country in the days to come.
Author Contributions
BB: Conceptualization, writing, and original draft preparation. KB, BB, and AG: data curation. BB, RP, TB, SD, NP, and DG: writing, review, and editing. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
KB and AG were employed by Nepal Environment and Development Consultant Pvt. Ltd., in Kathmandu, Nepal.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Ministry of Health and Population (MoHP), Government of Nepal, for supporting data in this research. We are thankful to the reviewers for their meticulous comments and suggestions, which helped to improve the manuscript.
1. ^ Worldometer. COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic . (2020). Available online at: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed January 15, 2021).
2. ^ Worldometer. Nepal Population . (2020). Available online at: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/nepal-population/ (accessed January 15, 2021).
3. ^ Trading Economics. Nepal GDP . (2020). Available online at: https://tradingeconomics.com/nepal/gdp (accessed January 15, 2021).
4. ^ UNDP. Human Development Reports . (2020). Available online at: http://hdr.undp.org/en/countries/profiles/NPL (accessed January 15, 2021).
5. ^ World Health Organization. COVID-19 Nepal: Preparedness and Response Plan (NPRP) . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/covid-19-nepal-preparedness-and-response-plan-(nprp)-draft-april-9.pdf?sfvrsn=808a970a_2 (accessed January 15, 2021).
6. ^ Ministry of Health and Population. COVID-19 Update . (2020). Available online at: https://covid19.mohp.gov.np/ (accessed January 15, 2021).
7. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-19 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/19-who-nepal-sitrep-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=c9fe7309_2 (accessed January 15, 2021).
8. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-22 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/22-who-nepal-sitrep-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=df7c946a_2 (accessed January 15, 2021).
9. ^ World Health Organization. (2020). WHO Nepal Situation Updates-16 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/16–who-nepal–sitrep-covid-19-07082020-final.pdf?sfvrsn=53c5360f_2 (accessed January 15, 2021).
10. ^ Bhattarai, KD. South Asian Voices: COVID-19 and Nepal's Migration Crisis . Available online at: https://southasianvoices.org/covid-19-and-nepals-migration-crisis/ (accessed January 15, 2021).
11. ^ GRADA WORLD Nepal: Government announces nationwide lockdown from March 24–31/update . Available online at: https://www.garda.com/crisis24/news-alerts/326601/nepal-government-announces-nationwide-lockdown-from-march-24-31-update-4 (accessed January 15, 2021).
12. ^ Gautam D. NDRC. Nepal's Readiness and Response to COVID-19 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.preventionweb.net/files/71274_71274nepalsreadinessandresponsetopa.pdf (accessed January 15, 2021).
13. ^ Building Back Better (BBB) from COVID-19: World Vision Policy Brief on Building Back Better from COVID-19 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.wvi.org/sites/default/files/202005/World%20Vision%20Policy%20Brief%20on%20Building%20Back%20Better_25%20May%202020.pdf (accessed January 15, 2021).
14. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-1 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/who-nepal–sitrep-covid-19-20apr2020.pdf?sfvrsn=c788bf96_2 (accessed January 15, 2021).
15. ^ GoN MoHP. Health Sector Emergency Response Plan COVID-19 Pandemic 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/health-sector-emergency-response-plan-covid-19-endorsed-may-2020.pdf?sfvrsn=ef831f44_2 (accessed January 15, 2021).
16. ^ Gautam, D. The COVID-19 Crisis in Nepal: Coping Crackdown Challenges. National Disaster Risk Reduction Centre, Kathmandu, Nepal. Issue 3, 2020 . Available online at: https://www.alnap.org/help-library/the-covid-19-crisis-in-nepal-coping-crackdown-challenges (accessed January 30, 2021).
17. ^ Gautam, D. Fear of COVID-19 Overshadowing Climate-Induced Disaster Risk Management . Available online at: https://www.spotlightnepal.com/2020/05/08/fear-covid-19-overshadowing-climate-induced-disaster-risk-management/ (accessed January 30, 2021).
18. ^ Pradhan TR. The Kathmandu Post. Nepal Goes Under Lockdown for a Week Starting 6am Tuesday . Available online at: https://kathmandupost.com/national/2020/03/23/nepal-goes-under-lockdown-for-a-week-starting-6am-tuesday (accessed January 30, 2021).
19. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-3 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/who-nepal–situpdate-3-covid-19-06052020.pdf?sfvrsn=714d14c4_2 (accessed January 30, 2021).
20. ^ Jha IC. The Rising Nepal. MoHP Sets Forth Standards for Home Quarantine . Available online at: https://risingnepaldaily.com/featured/mohp-sets-forth-standards-for-home-quarantine (accessed January 30, 2021).
21. ^ The Kathmandu Post. Youth-Led Protests Against the Government's Handling of Covid-19 Spread to Major Cities . (2020). Available online at: https://kathmandupost.com/national/2020/06/12/youth-led-protests-against-the-government-s-handling-of-covid-19-spread-to-major-cities (accessed January 30, 2021).
22. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-2 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/who-nepal–sitrep-covid-19-29apr2020.pdf?sfvrsn=dac001bf_2 (accessed January 30, 2021).
23. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-4 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/who-nepal–situpdate-4-13052020.pdf?sfvrsn=630b68ea_6 (accessed January 30, 2021).
24. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-18 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/18-who-nepal-sitrep-covid-19-23082020.pdf?sfvrsn=6fb20500_2 (accessed February 5, 2021).
25. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-5 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/5-who-nepal–situpdate-covid-19-20052020-final.pdf?sfvrsn=7552c8ba_4 (accessed February 5, 2021).
26. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-7 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/7-who-nepal–situpdate-covid-19-03062020-final.pdf?sfvrsn=87f582d6_2 (accessed February 5, 2021).
27. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-8 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/8-who-nepal–situpdate-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=ce5ecb07_2 (accessed February 5, 2021).
28. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-10 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/10-who-nepal–situpdate-covid-19-24062020.pdf?sfvrsn=c7f99a61_8 (accessed February 5, 2021).
29. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-13 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/13–who-nepal–situpdate-covid-19-17072020-v4.pdf?sfvrsn=fc0f19cc_2 (accessed February 5, 2021).
30. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-17 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/17-who-nepal-sitrep-covid-19-15082020.pdf?sfvrsn=68a53b32_2 (accessed February 10, 2021).
31. ^ UN. Nepal Information Platform, COVID-19 Nepal: Preparedness and Response Plan . Available online at: http://un.org.np/reports/covid-19-nepal-preparedness-and-response-plan (accessed February 10, 2021).
32. ^ UNICEF for Every Child, Supporting COVID-19 Readiness and Response in the West of Nepal . Available online at: https://www.unicef.org/nepal/stories/supporting-covid-19-readiness-and-response-west-nepal (accessed February 10, 2021).
33. ^ UNDP. Enhancing Public Awareness on COVID-19 Through Communications . Available online at: https://www.np.undp.org/content/nepal/en/home/presscenter/articles/2020/Enhancing-public-awareness-of-COVID-19-through-communications.html (accessed February 10, 2021).
34. ^ The World Bank. The Government of Nepal and the World Bank sign $29 Million Financing Agreement for Nepal's COVID-19 (Coronavirus) Response . Available online at: https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2020/04/03/world-bank-fast-tracks-29-million-for-nepal-covid-19-coronavirus-response (accessed February 10, 2021).
35. ^ Khatri PP. The Rising Nepal. Govt Receives Over Rs 1.59 Bln In Anti-COVID-19 Fund . Available online at: https://risingnepaldaily.com/main-news/govt-receives-over-rs-159-bln-in-anti-covid-19-fund (accessed February 10, 2021).
36. ^ Dahal A. Govt Does U-Turn to Let NGOs Hand Out Medical Supplies, Food, Cash directly . Available online at: https://myrepublica.nagariknetwork.com/news/govt-does-u-turn-to-let-ingos-hand-out-medical-supplies-food-cash-directly/ (accessed February 10, 2021).
37. ^ Rijal A. The Rising Nepal. China Gives Anti-Corona Medical Aid . Available online at: https://risingnepaldaily.com/main-news/china-gives-anti-corona-medical-aid (accessed February 10, 2021).
38. ^ Nepali Sansar. Nepal Receives 23 Tons ‘COVID-19 Medical Equip' As Gifts from India . (2020). Available online at: https://www.nepalisansar.com/coronavirus/nepal-receives-23-tons-covid-19-medical-equip-as-gifts-from-india/ (accessed February 10, 2021).
39. ^ Koirala S, Bhattarai, S. My Republica. Protect Frontline Healthcare Workers . Available online at: https://myrepublica.nagariknetwork.com/news/protect-frontline-healthcare-workers/ (accessed February 10, 2021).
40. ^ Halder R. Lockdowns and national borders: How to manage the Nepal-India border crossing during COVID-19 . Available online at: https://blogs.lse.ac.uk/southasia/2020/05/19/lockdowns-and-national-borders-how-to-manage-the-nepal-india-border-crossing-during-covid-19/ (accessed February 10, 2021).
41. ^ Raturi K. How Is Nepal Tackling COVID Crisis & Reverse Migration of Workers? Available online at: https://www.thequint.com/voices/opinion/india-nepal-border-coronavirus-pandemic-migrant-workers-exodus-reverse-migration-unemployment (accessed February 10, 2021).
42. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-14 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/14–who-nepal–sitrep-covid-19-26072020.pdf?sfvrsn=65868c9e_2 (accessed February 10, 2021).
43. ^ World Health Organization. WHO Nepal Situation Updates-19 on COVID-19, 2020 . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/19-who-nepal-sitrep-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=c9fe7309_2 (accessed February 10, 2021).
44. ^ Prasain S, Pradhan TR. The Kathmandu Post . Available online at: https://kathmandupost.com/politics/2020/08/12/nepal-braces-for-a-return-to-locked-down-life-as-rise-in-covid-19-cases-rings-alarm-bells (accessed February 10, 2021).
45. ^ NHPL. Information regarding Novel Corona Virus . (2020). Available online at: https://www.nphl.gov.np/page/ncov-related-lab-information (accessed February 10, 2021).
46. ^ NHRC. Assessment of Health-related Country Preparedness and Readiness of Nepal for Responding to COVID-19 Pandemic Preparedness and Readiness of Government of Nepal Designated COVID Hospitals . (2020). Available online at: http://nhrc.gov.np/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Fact-sheet-Preparedness-and-Readiness-of-Government-of-Nepal-Designated-COVID-Hospitals.pdf (accessed February 10, 2021).
47. ^ Koirala S. Comprehensive response to COVID 19 in Nepal . Available online at: https://en.setopati.com/blog/152612 (accessed February 10, 2021).
48. ^ National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Authority, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of Nepal . Available online at: https://covid19.ndrrma.gov.np/ (accessed February 10, 2021).
49. ^ World Health Organization. Infection Prevention and Control Guidance - (COVID-19) . (2021). Available online at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public (accessed February 10, 2021).
1. Jayaweera M, Perera H, Gunawardana B, Manatunge J. Transmission of COVID-19 virus by droplets and aerosols: a critical review on the unresolved dichotomy. Environ Res. (2020) 188:109819. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109819
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Zheng J. SARS-CoV-2: an emerging coronavirus that causes a global threat. Int J Biol Sci. (2020) 16:1678–85. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.45053
3. Islam N, Sharp SJ, Chowell G. Physical distancing interventions and incidence of coronavirus disease 2019: natural experiment in 149 countries. BMJ. (2020) 370:27–43. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2743
4. Gupta A, Singla M, Bhatia H, Sharma V. Lockdown-the only solution to defeat COVID-19. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. (2020) 6:1–2. doi: 10.1007/s13410-020-00826-3
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
5. Lu G, Razum O, Jahn A, Zhang Y, Sutton B, Sridhar D, et al. COVID-19 in Germany and China: mitigation versus elimination strategy. Glob. Health Action . (2021). 14:1875601. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2021.1875601
6. The Lancet. COVID-19: too little, too late. Lancet . (2020) 395:P755. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30522-5
7. Bastola A, Sah R, Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Lal BK, Jha R, Ojha HC, et al. The first 2019 novel coronavirus case in Nepal. Lancet Infect Dis. (2020) 20:279–80. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30067-0
8. Dhakal S, Karki S. Early epidemiological features of COVID-19 in Nepal and public health response. Front. Med. (2020) 7:524. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00524
9. Panthee B, Dhungana S, Panthee N, Paudel A, Gyawali S, Panthee S. COVID-19: the current situation in Nepal. New Microbes New Infect. (2020) 37:100737. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2020.100737
10. Oran DP, Topol EJ. The proportion of SARS-CoV-2 infections that are asymptomatic: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. (2021) 174:655–62. doi: 10.7326/M20-6976
11. Bhattarai S, Parajuli SB, Rayamajhi RB, Paudel IS, Jha N. Clinical health seeking behavior and utilization of health care services in eastern hilly region of Nepal. J Coll Med. Sci Nepal . (2015). 11:8–16. doi: 10.3126/jcmsn.v11i2.13669
12. Paudel S, Aryal B. Exploration of self-medication practice in Pokhara valley of Nepal. BMC Public Health. (2020) 20:714. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-08860-w
13. Ioannidis JPA, Axfors C. Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG. Population-level COVID-19 mortality risk for non-elderly individuals overall and for non-elderly individuals without underlying diseases in pandemic epicenters. Environ Res . (2020) 188:109890. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109890
14. Cortis D. On determining the age distribution of COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Publ. Health. (2020) 8:202. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00202
15. Gebhard C, Regitz-Zagrosek V, Neuhauser HK, Morgan R, Klein SL. Impact of sex and gender on COVID-19 outcomes in Europe. Biol Sex Differ. (2020) 11:29. doi: 10.1186/s13293-020-00304-9
16. Sharma G, Volgman AS, Michos ED. Sex differences in mortality from COVID-19 pandemic: are men vulnerable and women protected? JACC Case Rep. (2020) 2:1407–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.04.027
17. Sharma AK, Chapagain RH, Bista KP, Bohara R, Chand B, Chaudhary NK, et al. Epidemiological and clinical profile of COVID-19 in Nepali children: an initial experience. J Nepal Paediatr Soc. (2020) 40:202–9. doi: 10.3126/jnps.v40i3.32438
18. Piryani RM, Piryani S, Shah JN. Nepal's response to contain COVID-19 infection. J Nepal Health Res Counc. (2020) 18:128–34. doi: 10.33314/jnhrc.v18i1.2608
19. Rayamajhee B, Pokhrel A, Syangtan G. How well the government of nepal is responding to COVID-19? An experience from a resource-limited country to confront unprecedented pandemic. Front Public Health. (2021) 9:597808. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.597808
20. Kretzschmar ME, Rozhnova G, Bootsma MC, van Boven M, van de Wijgert JH, Bonten MJ. Impact of delays on effectiveness of contact tracing strategies for COVID-19: a modelling study. Lancet Public Health. (2020) 5:e452–9. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30157-221
21. Contreras S, Biron-Lattes JP, Villavicencio HA, Medina-Ortiz D, Llanovarced-Kawles N, Olivera-Nappa Á. Statistically-based methodology for revealing real contagion trends and correcting delay-induced errors in the assessment of COVID-19 pandemic. Chaos Solit Fract . (2020). 139:110087. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110087
22. Levin AT, Hanage WP, Owusu-Boaitey N, Cochran KB, Walsh SP, Meyerowitz-Katz G. Assessing the age specificity of infection fatality rates for COVID-19: systematic review, meta-analysis, and public policy implications. Eur J Epidemiol. (2020) 35:1123–38. doi: 10.1007/s10654-020-00698-1
23. O'Driscoll M, Dos Santos GR, Wang L, Cummings DA, Azman AS, Paireau J, et al. Age-specific mortality and immunity patterns of SARS-CoV-2. Nature . (2021). 590:140–5. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2918-0
Keywords: COVID-19, pandemic, preparedness, response, spatial distribution, public health, Nepal
Citation: Basnet BB, Bishwakarma K, Pant RR, Dhakal S, Pandey N, Gautam D, Ghimire A and Basnet TB (2021) Combating the COVID-19 Pandemic: Experiences of the First Wave From Nepal. Front. Public Health 9:613402. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.613402
Received: 05 October 2020; Accepted: 11 June 2021; Published: 12 July 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Basnet, Bishwakarma, Pant, Dhakal, Pandey, Gautam, Ghimire and Basnet. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Til Bahadur Basnet, ddst19basnet@hotmail.com
† These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- News & Views
- Twin crises in Nepal:...
Twin crises in Nepal: covid-19 and climate change
- Related content
- Peer review
- Basu Dev Pandey , doctor and professor 1 2 ,
- Kouichi Morita , professor 3 ,
- Anthony Costello , professor of global health and sustainable development 4
- 1 Everest International Clinic and Research Center, Kathmandu, Nepal,
- 2 Department of Molecular Epidemiology, Institute of Tropical Medicine, Nagasaki University, Japan
- 3 Department of Virology, Institute of Tropical Medicine, Nagasaki University, Japan
- 4 University College London, UK
Nepal has been on the frontline of both the covid-19 pandemic and climate change, and in both crises the response by the international community and Nepal’s government has been marked by a failure to prepare or to invest proactively in strong prevention measures.
The first case of covid-19 in Nepal was reported in January 2020 and the country’s modest first wave peaked in late October 2020 with a case fatality rate of less than 1%. 1 2 As cases fell steadily in January 2021, the government relaxed—a response that would turn out to be premature.
Throughout spring 2021, hundreds of thousands of people assembled on the streets in party political activities to prepare for the May election, adding to the number of people already joining gatherings for seasonal weddings and religious festivals. Meanwhile, in March 2021 the new delta variant, considered more infectious and virulent by the World Health Organization (WHO), was contributing to surging case numbers in India. 3 In April, at a time when cases in India were steadily rising, an estimated 50 000 Nepali pilgrims went to northern India for Kumbh Mela, a Hindu festival participated in by millions of people. 4 While there, many of the pilgrims caught covid-19.
Thousands of migrant workers also crossed over into Nepal from India, bringing the Delta strain with them, where it spread rapidly through the populous Kathmandu valley. 5 In Kathmandu, the hallways and courtyards of hospitals became crowded with patients competing to get a bed linked to an oxygen supply. Many patients were turned away due to lack of oxygen, ICU beds, and ventilators. Nepal’s president called a state of health emergency and 75 out of 77 districts had imposed a lockdown by 23 May. Nepal’s Ministry of Health and Population (MoHP) reported the country’s highest number of daily deaths (246) so far on 19 May 2021. 6
Restrictions were lifted as cases fell in July 2021 but the number of deaths surged again in August with a test positivity rate of 24% and more than 2500 cases recorded per day. 7 Many people in Nepal’s scattered rural population lack access to tests and deaths go unrecorded—a situation that is little different from India, where estimates suggest there were as many as 3.4-4.9 million excess deaths from the pandemic’s start to June 2021, numbers that are around 10-fold higher than official reports. 8 Hospitals and ICUs were full again during this period, including many severe cases in children. This wave hit the country so hard because communities were unprepared, the government had a false sense of security, residents relaxed social distancing, and authorities allowed religious festivals and political gatherings to go ahead as normal. The country still faces shortages of oxygen, ventilators, and other intensive care equipment.
Vaccines could have helped to relieve this pressure on Nepal’s hospitals, but the country has been beset by difficulties in obtaining them. At the end of March 2021, at a crucial point in the pandemic, India banned exports of AstraZeneca jabs until 2022. 9 This included one million doses already purchased by Nepal. By 11 December 2021, just 30% of the population had received two doses of the vaccine. 10 Nepal was not in a strong position then as the new omicron variant emerged and began to spread globally. First reported in Nepal by its MoHP in late December 2021, the omicron variant peaked with more than 10 000 daily cases on 18 January 2022. 11 12 More than 600 healthcare workers at the five biggest public hospitals in Kathmandu were infected and their absence added to the strain on the health system. 12 The number of daily deaths was much lower in the third wave (32 at its peak compared with 246 in the second wave) and cases dropped quickly to 2.9 per 100 000 population at the national level by the first week of March. 13 14 15 As before, the India-Nepal border was without strict screening, social distancing restrictions were relaxed, and compliance with public health protocols was often poor, all contributing to this third wave. But the introduction of covid-19 vaccination undoubtedly helped to reduce hospitalisations and mortality.
Against the backdrop of the covid-19 pandemic, another crisis unfolded. The annual monsoon season beginning in June 2021 brought flooding and landslides like never before across many of Nepal’s districts. Major rivers and streams swelled dangerously, and people lost their lives. After 200 mm of rain fell in six days up to 14 June, floods from the Melamchi river alone swept away 13 suspension bridges, seven motor bridges, and numerous stretches of road, destroying 337 houses, 259 enterprises, and thousands of acres of rice paddies. 16 The risk of flooding grows as glaciers in the Himalayas melt as a result of both rising temperatures and the proliferation of black carbon deposits from industry, vehicles, and cooking. 17
The government was overwhelmed, lacking as they do comprehensive plans for monsoon flooding. They mobilised the army and the Red Cross to assist communities, and arranged safe areas, drinking water, and food supplies. But they have no early warning systems, no anticipatory plans in place, and poor communication with many officials in local municipalities. A flood warning via Twitter was only sent out on 16 June—two days after dangerous flooding was first reported. 18 The country’s disaster budgets are tiny and procurement law does not allow relief materials and equipment to be bought in advance—only after disaster strikes subject to government approval. 19 Policies that build resilience against climate related disasters should be a top priority for the government because, while the pandemic may recede, the impacts of climate change will only worsen.
The latest reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change have been red alerts for the world, describing climate change as widespread, rapid, and intensifying. 20 The mountain ranges of South Asia contain almost 55 000 glaciers that store more freshwater than anywhere but the North and South Poles. A World Bank report estimates that global black carbon emissions could be cut in half with policies that are currently economically and technically feasible, allied with the cuts in carbon emissions set out in the Paris Agreement. 21 Without urgent action, glacier melt will threaten hundreds of millions of people in Nepal, Afghanistan, India, Pakistan, China, and beyond.
As a low income country, Nepal deserves much greater international support through the Covax scheme to provide vaccines, diagnostics, and treatments, and for climate resilience through the “loss and damage” funds agreed at the COP26 summit in Glasgow. At the same time, Nepal’s government could have done far more to mobilise preventive and responsive measures for these twin crises; making sure the country is better prepared for the next one must be a priority.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; not peer reviewed.
- ↵ Bastola A, Sah R, Rodriguez-Morales A J, Kumar Lal B, et al. The first 2019 novel coronavirus case in Nepal. Lancet Infectious Diseases. 20:3:279 - 280. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30067-0 OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- ↵ Ministry of Health and Population, Government of Nepal. Nepal: Covid 19 Response Situation Report No.XXXVI. Dec 14 2020. https://reliefweb.int/report/nepal/nepal-covid-19-response-situation-report-noxxxvi-14-december-2020
- ↵ Sharma G. Covid infections surge in Nepal fuelled by mutant strains in India. Reuters. 26 Apr 2021. https://www.reuters.com/world/china/covid-19-infections-surge-nepal-fueled-by-mutant-strains-india-2021-04-26/
- ↵ Pandey g. India Covid: Kumbh Mela pilgrims turn into super-spreaders. BBC News. 10 May 2021. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-57005563
- Weissenbach B
- ↵ Nepal reports 242 new COVID cases, 1 death on Sunday. Nepal News Nationwide. 12 Dec 2021. https://www.nepalnews.com/s/nation/nepal-reports-242-new-covid-cases-1-death-on-sunday
- ↵ Update S. #68: Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). WHO Country Office for Nepal. Reporting Date: 27 July – 2 August 2021. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/nepal-documents/novel-coronavirus/who-nepal-sitrep/-68_weekly-who-nepal-situation-updates.pdf?sfvrsn=bb521cc0_5
- ↵ Anand A, Sandefur J, Subramanian A. Three New Estimates of India’s All-Cause Excess Mortality during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Centre for Global Development Working Paper. 20 Jul 2021. https://www.cgdev.org/publication/three-new-estimates-indias-all-cause-excess-mortality-during-covid-19-pandemic
- ↵ Gettleman J, Schmall E, Mashal M. India Cuts Back on Vaccine Exports as Infections Surge at Home. The New York Times. 25 Mar 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/03/25/world/asia/india-covid-vaccine-astrazeneca.html
- ↵ Poudel A. Nepal receives 1 965 600 doses of Moderna vaccine from COVAX. The Kathmandu Post. 12 Dec 2021. https://kathmandupost.com/health/2021/12/12/nepal-receives-1-965-600-doses-of-moderna-vaccine-from-covax
- ↵ Poudel A. Nepal reports new Omicron case. The Kathmandu Post. 22 Dec 2021. https://kathmandupost.com/health/2021/12/22/nepal-reports-new-omicron-case-third-to-date
- ↵ Nepal faces new omicron-fueled coronavirus surge. Deutsche Welle. 19 Jan 2022. https://www.dw.com/en/nepal-faces-new-omicron-fueled-coronavirus-surge/a-60481393
- ↵ Omicron: Nepal makes quarantine mandatory for travellers arriving from 67 countries. The Times of India. 18 Dec 2021. https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/articleshow/88352043.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
- ↵ Nepal Covid-19 tally: 3,540 new cases, 6,359 recoveries, 32 deaths in 24 hours. Onlinekhabar. 30 Jan 2022. https://english.onlinekhabar.com/nepal-covid-19-tally-3540-new-cases-6359-recoveries-32-deaths-in-24-hours.html
- ↵ World Health Organization Regional Office for South East Asia. COVID-19 Weekly Situation Report: Week #09 (03 March – 09 March 2022). 11 Mar 2022. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/searo/whe/coronavirus19/sear-weekly-reports/searo-weekly-situation-report-9-2022.pdf?sfvrsn=f712043a_7
- ↵ Maharjan SB, Steiner JF, Bhakta Shrestha A, et al. The Melamchi flood disaster: Cascading hazard and the need for multihazard risk management. Disaster Task Force, ICIMOD. 4 Aug 2021. https://www.icimod.org/article/the-melamchi-flood-disaster/
- ↵ Mandal CK. Black carbon speeding up melting of glaciers, posing water scarcity threat to millions, report finds. The Kathmandu Post. 5 Jun 2021. https://kathmandupost.com/climate-environment/2021/06/05/black-carbon-speeding-up-melting-of-glaciers-posing-water-scarcity-threat-to-millions-report-finds
- ↵ Nepal Flood Alert. Twitter. 16 Jun 2021. https://twitter.com/DHM_FloodEWS/status/1405005910997540864
- ↵ Public Procurement Monitoring Office, Government Of Nepal. The Public Procurement Act, 2063 (2007). para 66 https://ppmo.gov.np/image/data/files/acts_and_regulations/public_procurement_act_2063.pdf
- ↵ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate change widespread, rapid, and intensifying. IPCC Report. 9 Aug 2021 https://www.ipcc.ch/2021/08/09/ar6-wg1-20210809-pr/
COVID-19: the current situation in Nepal
Affiliations.
- 1 Sustainable Study and Research Institute, Balaju, KathmanduNepal.
- 2 Patan Academy of Health Sciences, School of Nursing and Midwifery, LalitpurNepal.
- 3 Department of Psychiatry and Mental Health, Tribhuvan University Teaching HospitalKathmandu, Nepal.
- 4 Department of Cardiac Surgery, Sahid Gangalal National Heart Center, Kathmandu, Nepal.
- PMID: 32834901
- PMCID: PMC7403099
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmni.2020.100737
The recent global pandemic of novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is increasingly alarming. As of 21 June 2020, there are more than 8.7 million cases worldwide, with 460 000 deaths. Nepal is not an exception to COVID-19 and is currently facing a challenge to prevent the spread of infection. The analysis of the detected cases, severity and outcomes of the cases within a country is important to have a clear picture of where the pandemic is heading and what measures should be taken to curb the infection before it becomes uncontrollable. We collected data regarding all the cases, recoveries and deaths attributed to COVID-19 in Nepal starting from the first case on 23 January to 21 June 2020. At present, COVID-19 has spread all over Nepal, with a rapid increase in the number of new cases and deaths, which is alarming in a low-income country with an inadequate healthcare system like Nepal. Although the government implemented early school closure and lockdown, the management to contain COVID-19 does not appear to be adequate. Understanding the current situation regarding COVID-19 in Nepal is important for providing a direction towards proper management of the disease.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Nepal; local transmission; lockdown; management.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Publication types
Content Search
Nepal + 1 more
COVID-19 Response and WASH Lessons Learned in Nepal
Attachments.

• As of 5 October, there have been 89,263 positive cases, 65,202 recoveries, and 554 deaths across the country.
• UNICEF reached 3.15 million people through WASH promotional and behavioral-change communications activities. A total of 125,700 people benefitted from the installation of 559 contactless handwashing stations.
• The influx of around 3,000 to 5,000 people per day returning from India per point of entry, created additional emergency needs at the border for WASH services.
• In addition to the timely and sufficient coverage of PPE for frontline workers, a strategy to provide psychosocial support was critical to ensure the continuity of WASH services.
The COVID-19 pandemic spread to Nepal when its index case in Kathmandu was confirmed on 9 January 2020. As of 5 October, there have been 89,263 positive cases, 65,202 recoveries, and 554 deaths across the country. The disease has been detected in all provinces and districts of the country, with Province No. 2 and Kathmandu valley being the worst-hit area. A country-wide lockdown came into effect on 24 March 2020 and ended on 21 July 2020. Schools have been closed since March 2020 while a significant number of quarantine and isolation centers were hosted in schools with minimum preparedness to cater to such a large population. UNICEF’s WASH response included: support in assessments; the provision of WASH supplies and facilities in Health Care Facilities (HCFs), quarantine centers, isolation centers, and points of entry; community, handwashing promotion; innovation in handwashing stations as well as capacity building to government and various stakeholders on WASH and Infection Prevention and Control (IPC).
Related Content
Nepal 2024 ifrc network country plan (upl-2024-maanp001), nepal annual country report 2023 - country strategic plan 2019 - 2023, nepal: dengue response - dref final report (mdrnp014), progress and lessons learned - dengue prevention and control dref (june to december 2023).

- Emergency information
- Increase Font Size
- Decrease Font Size

Nepali (नेपाली)

- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Main Registration
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- GATE 2024 Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- DDU Entrance Exam
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET PG Admit Card 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Application Form 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET PG Courses 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
Covid 19 Essay in English
Essay on Covid -19: In a very short amount of time, coronavirus has spread globally. It has had an enormous impact on people's lives, economy, and societies all around the world, affecting every country. Governments have had to take severe measures to try and contain the pandemic. The virus has altered our way of life in many ways, including its effects on our health and our economy. Here are a few sample essays on ‘CoronaVirus’.
100 Words Essay on Covid 19
200 words essay on covid 19, 500 words essay on covid 19.

COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very short period of time. It has affected lives, economies and societies across the world, leaving no country untouched. The virus has caused governments to take drastic measures to try and contain it. From health implications to economic and social ramifications, COVID-19 impacted every part of our lives. It has been more than 2 years since the pandemic hit and the world is still recovering from its effects.
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, the world has been impacted in a number of ways. For one, the global economy has taken a hit as businesses have been forced to close their doors. This has led to widespread job losses and an increase in poverty levels around the world. Additionally, countries have had to impose strict travel restrictions in an attempt to contain the virus, which has resulted in a decrease in tourism and international trade. Furthermore, the pandemic has put immense pressure on healthcare systems globally, as hospitals have been overwhelmed with patients suffering from the virus. Lastly, the outbreak has led to a general feeling of anxiety and uncertainty, as people are fearful of contracting the disease.
My Experience of COVID-19
I still remember how abruptly colleges and schools shut down in March 2020. I was a college student at that time and I was under the impression that everything would go back to normal in a few weeks. I could not have been more wrong. The situation only got worse every week and the government had to impose a lockdown. There were so many restrictions in place. For example, we had to wear face masks whenever we left the house, and we could only go out for essential errands. Restaurants and shops were only allowed to operate at take-out capacity, and many businesses were shut down.
In the current scenario, coronavirus is dominating all aspects of our lives. The coronavirus pandemic has wreaked havoc upon people’s lives, altering the way we live and work in a very short amount of time. It has revolutionised how we think about health care, education, and even social interaction. This virus has had long-term implications on our society, including its impact on mental health, economic stability, and global politics. But we as individuals can help to mitigate these effects by taking personal responsibility to protect themselves and those around them from infection.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Education
The outbreak of coronavirus has had a significant impact on education systems around the world. In China, where the virus originated, all schools and universities were closed for several weeks in an effort to contain the spread of the disease. Many other countries have followed suit, either closing schools altogether or suspending classes for a period of time.
This has resulted in a major disruption to the education of millions of students. Some have been able to continue their studies online, but many have not had access to the internet or have not been able to afford the costs associated with it. This has led to a widening of the digital divide between those who can afford to continue their education online and those who cannot.
The closure of schools has also had a negative impact on the mental health of many students. With no face-to-face contact with friends and teachers, some students have felt isolated and anxious. This has been compounded by the worry and uncertainty surrounding the virus itself.
The situation with coronavirus has improved and schools have been reopened but students are still catching up with the gap of 2 years that the pandemic created. In the meantime, governments and educational institutions are working together to find ways to support students and ensure that they are able to continue their education despite these difficult circumstances.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Economy
The outbreak of the coronavirus has had a significant impact on the global economy. The virus, which originated in China, has spread to over two hundred countries, resulting in widespread panic and a decrease in global trade. As a result of the outbreak, many businesses have been forced to close their doors, leading to a rise in unemployment. In addition, the stock market has taken a severe hit.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Health
The effects that coronavirus has on one's health are still being studied and researched as the virus continues to spread throughout the world. However, some of the potential effects on health that have been observed thus far include respiratory problems, fever, and coughing. In severe cases, pneumonia, kidney failure, and death can occur. It is important for people who think they may have been exposed to the virus to seek medical attention immediately so that they can be treated properly and avoid any serious complications. There is no specific cure or treatment for coronavirus at this time, but there are ways to help ease symptoms and prevent the virus from spreading.
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
GIS officer work on various GIS software to conduct a study and gather spatial and non-spatial information. GIS experts update the GIS data and maintain it. The databases include aerial or satellite imagery, latitudinal and longitudinal coordinates, and manually digitized images of maps. In a career as GIS expert, one is responsible for creating online and mobile maps.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Database Architect
If you are intrigued by the programming world and are interested in developing communications networks then a career as database architect may be a good option for you. Data architect roles and responsibilities include building design models for data communication networks. Wide Area Networks (WANs), local area networks (LANs), and intranets are included in the database networks. It is expected that database architects will have in-depth knowledge of a company's business to develop a network to fulfil the requirements of the organisation. Stay tuned as we look at the larger picture and give you more information on what is db architecture, why you should pursue database architecture, what to expect from such a degree and what your job opportunities will be after graduation. Here, we will be discussing how to become a data architect. Students can visit NIT Trichy , IIT Kharagpur , JMI New Delhi .
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.
Finance Executive
Product manager.
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Operations Manager
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Stock Analyst
Individuals who opt for a career as a stock analyst examine the company's investments makes decisions and keep track of financial securities. The nature of such investments will differ from one business to the next. Individuals in the stock analyst career use data mining to forecast a company's profits and revenues, advise clients on whether to buy or sell, participate in seminars, and discussing financial matters with executives and evaluate annual reports.
A Researcher is a professional who is responsible for collecting data and information by reviewing the literature and conducting experiments and surveys. He or she uses various methodological processes to provide accurate data and information that is utilised by academicians and other industry professionals. Here, we will discuss what is a researcher, the researcher's salary, types of researchers.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.

Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Safety Manager
A Safety Manager is a professional responsible for employee’s safety at work. He or she plans, implements and oversees the company’s employee safety. A Safety Manager ensures compliance and adherence to Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) guidelines.
Conservation Architect
A Conservation Architect is a professional responsible for conserving and restoring buildings or monuments having a historic value. He or she applies techniques to document and stabilise the object’s state without any further damage. A Conservation Architect restores the monuments and heritage buildings to bring them back to their original state.
Structural Engineer
A Structural Engineer designs buildings, bridges, and other related structures. He or she analyzes the structures and makes sure the structures are strong enough to be used by the people. A career as a Structural Engineer requires working in the construction process. It comes under the civil engineering discipline. A Structure Engineer creates structural models with the help of computer-aided design software.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Field Surveyor
Are you searching for a Field Surveyor Job Description? A Field Surveyor is a professional responsible for conducting field surveys for various places or geographical conditions. He or she collects the required data and information as per the instructions given by senior officials.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Pathologist
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Veterinary Doctor
Speech therapist, gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Are you searching for an ‘Anatomist job description’? An Anatomist is a research professional who applies the laws of biological science to determine the ability of bodies of various living organisms including animals and humans to regenerate the damaged or destroyed organs. If you want to know what does an anatomist do, then read the entire article, where we will answer all your questions.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Photographer
Photography is considered both a science and an art, an artistic means of expression in which the camera replaces the pen. In a career as a photographer, an individual is hired to capture the moments of public and private events, such as press conferences or weddings, or may also work inside a studio, where people go to get their picture clicked. Photography is divided into many streams each generating numerous career opportunities in photography. With the boom in advertising, media, and the fashion industry, photography has emerged as a lucrative and thrilling career option for many Indian youths.
An individual who is pursuing a career as a producer is responsible for managing the business aspects of production. They are involved in each aspect of production from its inception to deception. Famous movie producers review the script, recommend changes and visualise the story.
They are responsible for overseeing the finance involved in the project and distributing the film for broadcasting on various platforms. A career as a producer is quite fulfilling as well as exhaustive in terms of playing different roles in order for a production to be successful. Famous movie producers are responsible for hiring creative and technical personnel on contract basis.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Individuals who opt for a career as a reporter may often be at work on national holidays and festivities. He or she pitches various story ideas and covers news stories in risky situations. Students can pursue a BMC (Bachelor of Mass Communication) , B.M.M. (Bachelor of Mass Media) , or MAJMC (MA in Journalism and Mass Communication) to become a reporter. While we sit at home reporters travel to locations to collect information that carries a news value.
Corporate Executive
Are you searching for a Corporate Executive job description? A Corporate Executive role comes with administrative duties. He or she provides support to the leadership of the organisation. A Corporate Executive fulfils the business purpose and ensures its financial stability. In this article, we are going to discuss how to become corporate executive.
Multimedia Specialist
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Process Development Engineer
The Process Development Engineers design, implement, manufacture, mine, and other production systems using technical knowledge and expertise in the industry. They use computer modeling software to test technologies and machinery. An individual who is opting career as Process Development Engineer is responsible for developing cost-effective and efficient processes. They also monitor the production process and ensure it functions smoothly and efficiently.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
Information Security Manager
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
ITSM Manager
Automation test engineer.
An Automation Test Engineer job involves executing automated test scripts. He or she identifies the project’s problems and troubleshoots them. The role involves documenting the defect using management tools. He or she works with the application team in order to resolve any issues arising during the testing process.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

SAT® | CollegeBoard
Registeration closing on 19th Apr for SAT® | One Test-Many Universities | 90% discount on registrations fee | Free Practice | Multiple Attempts | no penalty for guessing

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Thinking of Studying Abroad? Think the TOEFL® test. Register now & Save 10% on English Proficiency Tests with Gift Cards

Resonance Coaching
Enroll in Resonance Coaching for success in JEE/NEET exams

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications
We Appeared in
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
NPR in Turmoil After It Is Accused of Liberal Bias
An essay from an editor at the broadcaster has generated a firestorm of criticism about the network on social media, especially among conservatives.

By Benjamin Mullin and Katie Robertson
NPR is facing both internal tumult and a fusillade of attacks by prominent conservatives this week after a senior editor publicly claimed the broadcaster had allowed liberal bias to affect its coverage, risking its trust with audiences.
Uri Berliner, a senior business editor who has worked at NPR for 25 years, wrote in an essay published Tuesday by The Free Press, a popular Substack publication, that “people at every level of NPR have comfortably coalesced around the progressive worldview.”
Mr. Berliner, a Peabody Award-winning journalist, castigated NPR for what he said was a litany of journalistic missteps around coverage of several major news events, including the origins of Covid-19 and the war in Gaza. He also said the internal culture at NPR had placed race and identity as “paramount in nearly every aspect of the workplace.”
Mr. Berliner’s essay has ignited a firestorm of criticism of NPR on social media, especially among conservatives who have long accused the network of political bias in its reporting. Former President Donald J. Trump took to his social media platform, Truth Social, to argue that NPR’s government funding should be rescinded, an argument he has made in the past.
NPR has forcefully pushed back on Mr. Berliner’s accusations and the criticism.
“We’re proud to stand behind the exceptional work that our desks and shows do to cover a wide range of challenging stories,” Edith Chapin, the organization’s editor in chief, said in an email to staff on Tuesday. “We believe that inclusion — among our staff, with our sourcing, and in our overall coverage — is critical to telling the nuanced stories of this country and our world.” Some other NPR journalists also criticized the essay publicly, including Eric Deggans, its TV critic, who faulted Mr. Berliner for not giving NPR an opportunity to comment on the piece.
In an interview on Thursday, Mr. Berliner expressed no regrets about publishing the essay, saying he loved NPR and hoped to make it better by airing criticisms that have gone unheeded by leaders for years. He called NPR a “national trust” that people rely on for fair reporting and superb storytelling.
“I decided to go out and publish it in hopes that something would change, and that we get a broader conversation going about how the news is covered,” Mr. Berliner said.
He said he had not been disciplined by managers, though he said he had received a note from his supervisor reminding him that NPR requires employees to clear speaking appearances and media requests with standards and media relations. He said he didn’t run his remarks to The New York Times by network spokespeople.
When the hosts of NPR’s biggest shows, including “Morning Edition” and “All Things Considered,” convened on Wednesday afternoon for a long-scheduled meet-and-greet with the network’s new chief executive, Katherine Maher , conversation soon turned to Mr. Berliner’s essay, according to two people with knowledge of the meeting. During the lunch, Ms. Chapin told the hosts that she didn’t want Mr. Berliner to become a “martyr,” the people said.
Mr. Berliner’s essay also sent critical Slack messages whizzing through some of the same employee affinity groups focused on racial and sexual identity that he cited in his essay. In one group, several staff members disputed Mr. Berliner’s points about a lack of ideological diversity and said efforts to recruit more people of color would make NPR’s journalism better.
On Wednesday, staff members from “Morning Edition” convened to discuss the fallout from Mr. Berliner’s essay. During the meeting, an NPR producer took issue with Mr. Berliner’s argument for why NPR’s listenership has fallen off, describing a variety of factors that have contributed to the change.
Mr. Berliner’s remarks prompted vehement pushback from several news executives. Tony Cavin, NPR’s managing editor of standards and practices, said in an interview that he rejected all of Mr. Berliner’s claims of unfairness, adding that his remarks would probably make it harder for NPR journalists to do their jobs.
“The next time one of our people calls up a Republican congressman or something and tries to get an answer from them, they may well say, ‘Oh, I read these stories, you guys aren’t fair, so I’m not going to talk to you,’” Mr. Cavin said.
Some journalists have defended Mr. Berliner’s essay. Jeffrey A. Dvorkin, NPR’s former ombudsman, said Mr. Berliner was “not wrong” on social media. Chuck Holmes, a former managing editor at NPR, called Mr. Berliner’s essay “brave” on Facebook.
Mr. Berliner’s criticism was the latest salvo within NPR, which is no stranger to internal division. In October, Mr. Berliner took part in a lengthy debate over whether NPR should defer to language proposed by the Arab and Middle Eastern Journalists Association while covering the conflict in Gaza.
“We don’t need to rely on an advocacy group’s guidance,” Mr. Berliner wrote, according to a copy of the email exchange viewed by The Times. “Our job is to seek out the facts and report them.” The debate didn’t change NPR’s language guidance, which is made by editors who weren’t part of the discussion. And in a statement on Thursday, the Arab and Middle Eastern Journalists Association said it is a professional association for journalists, not a political advocacy group.
Mr. Berliner’s public criticism has highlighted broader concerns within NPR about the public broadcaster’s mission amid continued financial struggles. Last year, NPR cut 10 percent of its staff and canceled four podcasts, including the popular “Invisibilia,” as it tried to make up for a $30 million budget shortfall. Listeners have drifted away from traditional radio to podcasts, and the advertising market has been unsteady.
In his essay, Mr. Berliner laid some of the blame at the feet of NPR’s former chief executive, John Lansing, who said he was retiring at the end of last year after four years in the role. He was replaced by Ms. Maher, who started on March 25.
During a meeting with employees in her first week, Ms. Maher was asked what she thought about decisions to give a platform to political figures like Ronna McDaniel, the former Republican Party chair whose position as a political analyst at NBC News became untenable after an on-air revolt from hosts who criticized her efforts to undermine the 2020 election.
“I think that this conversation has been one that does not have an easy answer,” Ms. Maher responded.
Benjamin Mullin reports on the major companies behind news and entertainment. Contact Ben securely on Signal at +1 530-961-3223 or email at [email protected] . More about Benjamin Mullin
Katie Robertson covers the media industry for The Times. Email: [email protected] More about Katie Robertson

NPR editor rebukes own outlet's coverage of Hunter Biden laptop, COVID lab leak and Russiagate
N PR editor Uri Berliner issued a lengthy rebuke of NPR's media coverage of major news stories over the last few years, such as the Hunter Biden laptop and the COVID lab leak theory, and called out the outlet's "efforts to damage" Trump's presidency.
Berliner, a senior business editor at the outlet, wrote in an essay for The Free Press that NPR's coverage veered off the deep end when Trump was elected in 2016. He cited its coverage of Russiagate first, and said NPR "hitched our wagon" to Rep. Adam Schiff, D-Calif., who peddled Trump-Russia collusion claims for years.
"Schiff, who was the top Democrat on the House Intelligence Committee, became NPR’s guiding hand, its ever-present muse. By my count, NPR hosts interviewed Schiff 25 times about Trump and Russia. During many of those conversations, Schiff alluded to purported evidence of collusion. The Schiff talking points became the drumbeat of NPR news reports," Berliner wrote.
After the Robert Mueller report found "no credible evidence of collusion," he wrote, the Trump-Russia story disappeared from NPR's coverage. Berliner argued the outlet pretended like it never happened.
BEFORE THE DURHAM REPORT, TV NETWORKS ALLOWED RUSSIAGATE BOOSTER ADAM SCHIFF TO CLAIM ‘EVIDENCE’ OF COLLUSION
Berliner also pointed to NPR's decision to turn a "blind eye" to the Hunter Biden laptop story in 2020.
READ ON THE FOX NEWS APP
"The laptop was newsworthy. But the timeless journalistic instinct of following a hot story lead was being squelched. During a meeting with colleagues, I listened as one of NPR’s best and most fair-minded journalists said it was good we weren’t following the laptop story because it could help Trump," he wrote.
When the New York Post first reported on Hunter Biden's laptop in 2020, NPR infamously issued a statement as to why it wasn't covering the story. At the time, a popular narrative in liberal media was the laptop was a possible Russian disinformation operation , but its contents were later verified by multiple outlets that previously cast aspersions on it.
"We don’t want to waste our time on stories that are not really stories, and we don’t want to waste the listeners’ and readers’ time on stories that are just pure distractions," NPR's statement said.
NPR UNDER FIRE FOR CLAIMING HUNTER BIDEN LAPTOP STORY WAS 'DISCREDITED' BY US INTELLIGENCE, MEDIA
"But it wasn’t a pure distraction, or a product of Russian disinformation, as dozens of former and current intelligence officials suggested. The laptop did belong to Hunter Biden. Its contents revealed his connection to the corrupt world of multimillion-dollar influence peddling and its possible implications for his father," Berliner continued.
Berliner also pointed to NPR's coverage of the COVID-19 lab leak theory, which he said the outlet was supposed to ignore. Similar to the Biden laptop story, the notion the virus may have leaked from a Wuhan virology lab was dismissed as right-wing claptrap before ultimately being accepted as at least a plausible theory in mainstream media.
"Over the course of the pandemic, a number of investigative journalists made compelling, if not conclusive, cases for the lab leak. But at NPR, we weren’t about to swivel or even tiptoe away from the insistence with which we backed the natural origin story," he said.
Berliner said one of his colleagues on the Science team was asked why they were so dismissive of the theory and said his response was "odd."
"The colleague compared it to the Bush administration’s unfounded argument that Iraq possessed weapons of mass destruction, apparently meaning we won’t get fooled again. But these two events were not even remotely related. Again, politics were blotting out the curiosity and independence that ought to have been driving our work," he wrote.
The pandemic's true origins remain unknown, with many experts still pointing to a natural, zoonotic origin as its most likely cause.
NPR didn't respond to a request for comment.
Original article source: NPR editor rebukes own outlet's coverage of Hunter Biden laptop, COVID lab leak and Russiagate


Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

Explain the concept of mRNA vaccines, outlining their potential benefits in preventing infectious diseases like COVID-19, and discuss their limitations and challenges.
Topic: Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, Nano-technology, biotechnology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
4. Explain the concept of mRNA vaccines, outlining their potential benefits in preventing infectious diseases like COVID-19, and discuss their limitations and challenges. (250 words)
Difficulty level: Moderate
Reference: Insights on India
Why the question: The question is part of the static syllabus of General studies paper – 3 and mentioned as part of Mission-2024 Secure timetable. Key Demand of the question: To write about mRNA vaccines, their potential benefits and challenges and limitations associated with their use. Directive word: Discuss – This is an all-encompassing directive – you must debate on paper by going through the details of the issues concerned by examining each one of them. You must give reasons for both for and against arguments. Structure of the answer: Introduction: Begin by introducing the concept of mRNA vaccines and their relevance, especially in the context of recent vaccine developments. Body: Firstly, explain the fundamental concept of mRNA vaccines, including how they work to stimulate an immune response. Next, write about the advantages of mRNA vaccines, such as their rapid development potential, versatility against various pathogens, and effectiveness in preventing infectious diseases. Highlight their role in addressing public health emergencies, like the COVID-19 pandemic, through quick vaccine development. Next, write about the limitations associated with mRNA vaccines, such as the need for ultra-cold storage, potential short-term side effects, and the relatively recent nature of this technology. Conclusion: Conclude by writing a way forward.

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.7(9); 2021 Sep

Education system of Nepal: impacts and future perspectives of COVID-19 pandemic
Khadka bahadur pal.
a Department of Chemistry, Tri-Chandra Multiple Campus, Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Nepal
Buddha Bahadur Basnet
b Faculty of Sciences, Nepal Academy of Science and Technology, Khumaltar, Lalitpur, Nepal
Ramesh Raj Pant
c Central Department of Environmental Science, Institute of Science and Technology, Tribhuvan University, Nepal
Kiran Bishwakarma
d Key Laboratory of Tibetan Environment Changes and Land Surface Processes, Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
e University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Kopila Kafle
Namraj dhami.
f Pokhara University, Pokhara 30, Gandaki 33700, Nepal
Motee Lal Sharma
g Central Department of Chemistry, Institute of Science and Technology, Tribhuvan University, Nepal
Lal B. Thapa
h Central Department of Botany, Institute of Science and Technology, Tribhuvan University, Nepal
Binod Bhattarai
i University Grants Commission, Sanothimi, Bhaktapur, Nepal
Youb Raj Bhatta
Associated data.
All data are available described in the article.
The academic sectors are badly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic globally. The studies regarding the implications of COVID-19 in education in Nepal were minimal, thus, this paper aims to highlight the impacts of the pandemic on the education sector of Nepal. It is revealed that the Nepalese academia has been facing problems due to lack of adequate and appropriate sustainable infrastructure for the online system, including skilled human resources. In addition, limited internet facilities in remote and rural areas were the other challenging tasks for virtual academic activities. Therefore, the concerned stakeholders should provide necessary services and appropriate strategies for virtual means of the education system to compensate the repercussion caused by the pandemic. This study could be helpful to identify the critical needs emerged due to the pandemic at present and in future and also contribute to adopt appropriate policy for the revival of educational institutions.
COVID-19; Pandemic; Virtual education; Online education, Nepal.
1. Introduction
The year 2020 was started with the terror of the COVID-19 and witnessed the indelible imprints of the pandemic on the global community ( WHO, 2020 ). The global health emergency due to COVID-19 was declared by the World Health Organization (WHO) on 30 th January 2020. Subsequently, it was declared a pandemic after more than 118,000 infected population by COVID-19 from 114 countries with 4,291 deaths up to 11 th March 2020. Globally, up to 6 th August 2021, there have been over 200 million confirmed cases, including the deaths over 42 million ( WHO, 2021 ).
WHO recommended the countries across the world to take precautionary measures to break the transmission chain of the coronavirus ( Barkur and Vibha Kamath, 2020 ). Among the different prevention strategies, the lockdown was considered as one of the best approaches for interrupting transmission, which was widely adopted by the global community ( Flaxman et al., 2020 ). Therefore, many of the countries in the world imposed lockdown throughout the national and regional levels. In the same line, the Government of Nepal (GoN) also announced the first lockdown on 24 th March 2020 and continued for about six months ( Basnet et al., 2021a , 2021b ). Besides the lockdown, effective tracking, tracing, quarantine, social distancing, and hygienic behaviours of some countries such as China controlled the disease spread successfully ( Basnet et al., 2021c ). However, the lockdown has not been sufficient in many countries ( Zhu et al., 2020 ).
The lockdown imposed noxious impacts affecting the psycho-sociological and livelihoods of people. On one side, the new cases of the virus around the globe are increasing and on the other side, the commencement of lockdown has affected a more significant number of sectors, including academia ( Dawadi et al., 2020 ). Importantly, the academia victimized severely from the lockdowns owing to the COVID-19 pandemic. Most academic institutions such as schools, colleges, and universities remained closed during the lockdown period. Still, the academic activities have not been resumed fully as usual with face-to-face instructions.
The pandemic challenges in the education systems have been the greatest ever faced by the world community ( Azzi-Huck and Shmis, 2020 ). According to the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), the closures of academic institutions have impacted more than 1.5 billion students and youth across the globe directly/indirectly ( UNESCO, 2020 ). The COVID-19 pandemic has changed the world, creating the need for new actions from society, including universities and academia ( Alvarez-Risco et al., 2021 ). Cease of the physical presence of students and teachers in the classroom for teaching and learning have switched the academic institutions to online teaching and virtual education. The educational institutions faced an economic crisis due to less number enrollment of students, delay in fee collection, and the management of alternate methods for teaching and learning. The institutions tried to adopt the alternate methods for teaching and learning such as online or virtual methods which are not likely to provide the quality of education as delivered in the classroom ( Panthee et al., 2020 ; Viner et al., 2020 ). Such challenges of the COVID-19 to the education sector especially in the developing countries like Nepal are the severer than the developed countries as the former countries have limited facilities of online systems (e.g., internet, devices, and skilled human resources) ( Poudel and Subedi, 2020 ). In the case of Nepal, the academic institutions remained closed for a long time during the lockdown, and some of them started to manage alternate ways of teaching with the prolongation of lockdown. The government institutions were affected mainly in two ways: firstly, they were turned into quarantine stations, and secondly, there were limited facilities including internet access, computer devices, and a skilled workforce. After the lockdown, the government of Nepal has given authority to the local governments to decide on resuming the academic institutions as usual, and many of the institutions are partially or fully reopened, but the health experts have warned that this decision has increased the risk of the virus transmission ( Poudel and Subedi, 2020 ).
The number of darks sides of the COVID-19 pandemic has given opportunities to the researchers to explore new avenues of cure and treatments and other several facts related to the disease. Many of the researchers have engaged in analyzing the consequences of this pandemic, focusing on different sectors such as environment, agriculture, business, tourism, economy, and education, etc ( Pant et al., 2021 ; Azzi-Huck and Shmis, 2020 ; Barkur and Vibha Kamath, 2020 ; Flaxman et al., 2020 ; IAU, 2020 ). Such analysis, findings, and recommendations have contributed to the nations making policies and strategies to combat future pandemics. However, it has been felt that the studies regarding the implications of COVID-19 in the education sector are minimal. In the context of Nepal, the publications related to the facts are almost naught. Thus, this paper aims to highlight the impacts of COVID-19 on the education sector of Nepal.
This study is based on both primary and secondary data. The electronic databases through Google Scholar, Science Direct, and published reports of national and international organizations were the secondary sources of information on COVID-19. A manual search was conducted to search related articles to gather relevant literature ( Kapasia et al., 2020 ). A survey was also conducted by preparing a short questionnaire (open-ended) to collect primary data. The questionnaire was formatted to collect information on the impacts of COVID-19 in academic institutions. Altogether 35 academic institution heads [10 government schools, 10 private boarding schools, 5 Council for Technical Education and Vocational Training (CTEVT) institutions, 5 university constituent campuses, and 5 university-affiliated campuses] were requested to respond to the questionnaire. Authorities of the Federal GoN, Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, provincial and local governments, and universities were consulted as the key informants. The questionnaire was validated with the help of a review by two experts from medical sciences and two experts from the education sector in Nepal. In addition, before the review, the questionnaire was subjected to purposive sampling of 10 respondents from the Kathmandu valley for the pilot test.
3. Education system in Nepal
In Nepal, the school-level education comprises the primary level (1–8) and secondary level (9–12). There are a total of 35,055 schools in Nepal, of which 27,728 are public schools (community schools), 6,206 private schools, and 1,121 religious schools (Muslim religious schools, Gumbas/Vihar , and Hindu A shrams schools) ( DoE 2018 , Figure 1 ). Thus, there are 7,214,525 students enrolled in school level (grade 1–12) in the year 2018/19. Out of the total enrolment, 77% of students are at the primary level and 23% at the secondary level. Meanwhile, 4,124,478; 1,368,620; and 62,281 students were enrolled in public, private, and religious schools at the primary level, respectively. Similarly, 1,152,674; 294,732; and 610 students were enrolled in public, private, and religious schools at the secondary level, respectively ( DoE 2018 ).

Students enrollment in public, private and religious schools in Nepal ( DoE 2018 ).
The education imparted after the secondary level is considered higher education (tertiary education) in Nepal. According to a report of the University Grants Commission (UGC), Nepal, there are 11 universities and six autonomous medical academies that offer higher education in Nepal ( UGC, 2020 , Table 1 ). Higher education is offered at the universities, of which the Tribhuvan University (TU) is the oldest and largest one. The universities in Nepal currently provide courses on sciences and technology; education; management; social sciences and humanities; law; engineering; forestry; medicine; agriculture and animal sciences; Ayurved; Sanskrit, etc. These academic programs run based on annual and semester systems at bachelor, master, MPhil, and PhD levels. Depending upon the nature of the courses, the time duration allocated to accomplish the programs varies with universities. For example, the bachelors, masters, MPhil, and PhD courses require 3–4, 2, 1.5, and 3 years, respectively, in most of the academic institutions in Nepal. The academic, research, and administrative activities are governed by the rules and regulations of the concerned institutions.
Table 1
Status of students and Universities in Nepal (2017) ( UGC, 2020 ).
Under the umbrella of Higher education in Nepal, 1,425 campuses and 423,996 students enrolled in different academic programs ( UGC, 2020 ). According to the office of planning directorate (TU), it has 1,124 campuses (62 constituents and 1,062 affiliated campuses). Open and distance learning programs have been adopted by the National Open University (NOU). The NOU programs are designed for e-based learning for interested students. The relevance and need for such open and distance learning programs markedly increased under the context of pandemic situations. Regarding the enrollment percentage, the TU has the highest i.e., 79.04 % while Pokhara University, Purbanchal University, and Kathmandu University have the enrollment 6.94 %, 6.16 %, and 4.23% students, respectively ( UGC, 2020 ). Among the enrolled students, 78.6% and 21.4% were enrolled in general and technical programs, respectively. The students in management; education; and humanities and social sciences were 46.78%, 17.88%, and 13.20%, respectively. There are 7.11% of students in science and technology, and only 6.08% and 6.55% of students are in medicine and engineering, respectively ( Figure 2 ).

Current scenario of students distributions in different faculties at higher education level ( UGC, 2020 ).
The provincial-level distribution of students in tertiary education revealed that >50% of students are concentrated in the Bagmati Province only while the least number of students (3.31%) are studying in the Karnali Province. The dominancy order of number of students is Bagmati Province > Lumbini Province > Province no. 1 > Gandaki Province > Province no. 2 > Sudurpaschim Province > Province no. 1 > Karnali Province ( Figure 3 ). The share of student enrollment in the community campuses is 30.29%, whereas constituent campuses and private campuses have received 32.41% and 37.30%, respectively ( UGC, 2020 ). The data shows that private campuses have relatively higher number of students enrolled in Nepal.

Provincial status of students at higher education level ( UGC, 2020 ).
Regarding the academic institutions' student evaluation and monitoring system, schools and universities have different provisions in Nepal. There is an annual examination system with midterm and internal evaluations for the basic level students under the direct supervision of respective schools and local governments. Furthermore, students are evaluated by annual examinations for the school level, including internal and midterm evaluations by the respective schools and the local government. However, the final examination of grade XII is provisioned to be examined by the National Education Board (NEB). In tertiary education, both the internal evaluations and final examinations are held at the end of each semester or year. Tribhuvan University has reintroduced the semester systems from 2012 onwards, and students are evaluated internally (40%) by the respective campuses/departments and externally (60%) by the concerned office of the dean under the Office of the Controller of the Examinations ( TU, 2012 ). The Council for Technical Education and Vocational Training (CTEVT) has adopted semester systems from the beginning of all programs ( DoE, 2018 ). Notably, most of the school and tertiary level examinations are held in a conventional system with physical presence and there was no application of virtual means of teaching and learning.
4. Appraisal of COVID-19 impacts in Nepalese education system
Regarding the recent gloom and doom scenario created by the COVID-19 pandemic in academia, many countries have tried to adopt various virtual media for learning and teaching activities. The COVID-19 lockdown was implemented at the end of the academic session (March, 2020), which directly hindered both school and university academic calendars in Nepal. The nationwide lockdown immediately impacted the pre-scheduled examinations of the grade 10 to 12. In addition, the scheduled semester examinations of many universities had been postponed. As the lockdown prolonged, almost all the academic activities, including examinations halted. It has directly affected the teaching-learning activities of nearly 8,796,624 students belonging to pre-primary (11%), primary (28%), secondary (39%), and tertiary (5%) levels nationwide, as estimated by UNESCO ( Dawadi et al., 2020 ). The questionnaire survey and key informant interviews in this study have highlighted the several aspects of impacts of COVID-19 lockdown on academia in Nepal.
The impacts of COVID-19 on academia has directly affected the students, teachers, and parents. The challenges and impacts of the pandemic highlighted by the respondents were cancellation of board exams, irregularity in learning and skills development, assessments, restriction to study abroad, disrupted the enrollment cycle, inequality in access to education, anxiety to start schools and universities, etc. In higher education, laboratory-based research and field works are greatly hindered. In addition, there may also be decreased funding to continue or undertake new research and innovative activities in the universities in Nepal ( Michael and Murphy, 2020 ).
The lockdown has reduced the enrollment of students and increased the risk of dropout rate. In addition, it has created the obligation for the academic institutions to switch on the virtual media to maintain the pre-announced academic calendars. A transition phase of the traditionaleducational system to the digital system appeared and the Nepalese academia started partially or fully digital system with prolongation of the lockdown. The academic institutions became engagged on transformations in policy formulation, infrastructure development, searching appropriate online methods of teaching, and conducting assessments. As there was a lack of proper planning and educational guidelines previously for online teaching and learning, most of the universities and schools could not run any online models of pedagogical approaches in the initial phase ( MWU, 2020 ).
A handful number of colleges and schools launched online classes in urban areas. The majority of the respondents highlighted that comparing to the physical classes, the online methods are relatively less effective due to more absenteeism and irregularities of the students. It has been estimated that only 9% of the total students from Nepal are getting online classes, and >90% of the students from rural and urban areas are still out of such virtual courses. Currently, 12% of schools and 56% of households have internet facilities, while 51% of students are using media such as radio and TV ( Dawadi et al., 2020 ). It shows that the remaining 44% of students are unlikely to regularly access online or other media, which could be one of the serious concerns for the policymakers of the academic sectors ( Marahatta et al., 2020 ).
Meanwhile, the greatly impacted sector by the COVID-19 pandemic is the research activities in higher education, according to the respondents. The research activities such as field researches had been postponed, and the laboratory research activities remained suspended by the universities. According to the informants, the numbers of chemical reagents and enzymes prepared for upcoming experiments basically in the laboratory based research were worthless due to the closer of the laboratories for an extended period. Master and PhD level dissertations were delayed, and the time-bound research grants and scholarships were cancelled. In such a situation, academia and the policymakers were in dilemmas to design a clear roadmap about the commencement of academic activities. Limited internet facilities, computer devices, and lack of skilled human resources hindered running virtual classes and other activities. It was a challenging to connect the studnets from the rural and remote areas of Nepal in the online classes. The virtual courses are even more challenging for those learners who are differently able students which is consistent around the globe ( Manzoor, 2020 ; Chalise and Dhungana, 2020 ). Notably, the closures of academic institutions have resulted in multi-faceted implications such as disrupting completion of the syllabus on time, the regular cycle of academic intakes, semester end examinations required for graduation.
Despite the pandemic situation, there were some positive impacts on academia at the same time. It had allowed reshaping the of pedagogical strategies and adapt to innovative e-learning techniques. Schools and universities decided to introduce a digital education system. Several platforms, such as Zoom, Google Meet, Microsoft Teams, and Social Media including Viber, WhatsApp, Facebook, were given priority by the academia to run the academic activities online. For instance, with the help of Microsoft Teams, TU initiated its virtual academic activities with 500,000 users (teachers and students) ( TU, 2020 ). In the history of Nepalese academia, this was one of the most outstanding achievements for the paradigm shift of the conventional pedagogical approaches. The learners and education provider institutions used media such as television, radio networks, YouTube, and other social media. Interestingly, the literacy and expertise on computers, apps, and virtual platforms have improved at the grass-root level. The universities conducted training for teachers and students for the online system of joining in academic activities.
The schools and higher education institutions expanded ICT infrastructures to support ICT associated teaching/learning. Most of the institutions have also prepared their guideline for facilitating online classes and assessment systems under the direction of the GoN and the University Grants Commission (UGC). Academic institutions have also initiated collaborations with local to national media such as Radios, FMs, and TVs. The virtual media have significant positive impacts on providing educational content and lives call with teachers in support of students ( Hiltz and Wellman, 1997 ). As the cases of COVID-19 are still increasing globally, the public policies significantly, the academic policies should be revised and strictly follow with the epidemiological alerts ( Yáñez et al., 2020 ). Precisely, the COVID-19 situation compelled all the academic institutions and stakeholders for redesigning and reconsidering their teaching-learning and research approaches.
5. Future perspectives and conclusion
The schools and HEIs in Nepal have limited digital services, including electronic libraries, relevant online scientific publications, and other resources. The major challenge for the institutions was conducting assessments and exams online. In the context of Nepal, many children from low-income families and disadvantaged groups do not afford even the necessities of learning, such as textbooks, notebooks, and other required stationaries. Modern digital devices, including smartphones, iPad, iPods, laptops, computers, the internet, etc., are far from their expectations ( UNESCO and IESALC, 2020 ). On the other side, the people in the remote and rural areas are deprived of online access due to limited internet facilities. In this context, providing equal opportunity for virtual learning to all groups of people and all parts of the country has become challenging. Therefore, the federal, provincial, and local governments are urged to switch their strategies and programs towards modern virtual education systems. For this purpose, different programs for enhancing the capacities of human resources, students, institution authorities, management, and parents are recommended. It is essential to understand the behaviour of learners about online and face-to-face academic activities to ensure the best academic outcomes ( Alvarez-Risco et al., 2020b ).
Due to the lack of adequate and appropriate sustainable infrastructure in Nepalese academia for the online system, developing such infrastructure is indispensable. The infrastructures for virtual education (internet facilities and digital devices) should be affordable to institutions of remote and rural areas. Especially the poor and disadvantaged groups should be prioritized, clustered, and trained in low/no cost by the government. The international and national organizations anduniversity graduates could be mobilized as volunteers to teach in rural areas. The school education boards and universities should prioritize to revise their curricula including internship or community services for their students to share the knowledge and expertise to the needy people in rural and remote areas in Nepal. The institutions should consider adjustments in terms of accessibility, infrastructure, and equipment from a long term perspective.
Additionally, within traditional pedagogical approaches, the blended modes of education system could be implemented to improve the quality of education at an affordable cost with limited trained human resources. The activities such as homework assignments, open-book exams, home take exams, quizzes, or small projects can be considered as the options of conventional paper-based examinations. Moreover, some modes of communication such as chat channels and discussion groups in social media could also benefit to the learners. There is limited preparedness to cope with such pandemic in Nepal, thus, there must be cooperation and coordination among the different sectors to combat the impacts of COVID-19. There could be a multifactorial fight during the pandemic to increase health literacy, develop better detection tools, and enable action by local, provincial and federal governments ( Alvarez-Risco et al., 2020c ). Continuous awareness and sensitization about the risks of COVID-19 also play a vital role to reduce the havoc created by the pandemic ( Quispe-Cañari et al., 2021 ).
Overall, this study comprises the education system in Nepal and COVID-19 imprints in the school and university education in Nepal. Also, we have tried to highlight the pros and cons of the pandemic on academia during the lockdown and suggested the possible way forwards. In this context, the concerned stakeholders should provide necessary services and develop appropriate strategies for virtual means of the education system to compensate for the repercussion caused by COVID-19 lockdown. Sustainable solutions are essential to manage the crisis and build a resilient education system in the long run. Thus, the insights from this study could be helpful to cope with the problem due to the pandemic and contribute to adopting an appropriate policy for the revival of educational institutions. Also, the present work contributes to the necessary way forward to tackle the crisis in academia in Nepal in the future.
Declarations
Author contribution statement.
All authors listed have significantly contributed to the development and the writing of this article.
Funding statement
This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency.
Data availability statement
Declaration of interests statement.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Not applicable.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MoEST), Department of Education (DoE), GoN and University Grants Commission (UGC), Nepal for supporting data in this research.
- Alvarez-Risco A., Mejia C.R., Delgado-Zegarra J., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Arce-Esquivel A.A., Valladares-Garrido M.J., The Peru approach against the COVID-19 infodemic: insights and strategies. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020; 103 (2):583–586. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alvarez-Risco A., Estrada-Merino A., de las Mercedes Anderson-Seminario M., Mlodzianowska S., García-Ibarra V., Villagomez-Buele C., Carvache-Franco M. ITSE; 2020. Multitasking Behaviour in Online Classrooms and Academic Performance: the Case of university Students in Ecuador during COVID-19 Outbreak. [ Google Scholar ]
- Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Rosen M.A., García-Ibarra V., Maycotte-Felkel S., Martínez-Toro G.M. Expectations and interests of university students in covid-19 times about sustainable development goals: evidence from Colombia, Ecuador, Mexico, and Peru. Sustainability. 2021; 13 (6):3306. [ Google Scholar ]
- Azzi-Huck K., Shmis T. 2020. Managing the Impact of COVID-19 on Education Systems Worldwide: How Countries Are Preparing, Copying, and Planning for Recovery. https://blogs.worldbank.org/education/managing-impact-COVID-19-education-systems-around-world-how-countries-are-preparing [ Google Scholar ]
- Barkur G., Vibha Kamath G.B. Sentiment analysis of nationwide lockdown due to COVID 19 outbreak: evidence from India. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2020; 51 :102089. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Basnet B.B., Bishwakarma K., Pant R.R., Dhakal S., Pandey N., Gautam D., Ghimire A., Basnet T.B. Combating the COVID-19 pandemic: experiences of the first wave from Nepal. Front. Public Health. 2021; 12 (9):613402. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Basnet B.B., Pant R.R., Bishwakarma K., Paudel S., Pandey N., Adhikari S.K., Ranabhat K., Ghimire A. A year trend analysis and spatial distribution of COVID-19 cases in Nepal. Asia Pac. J. Publ. Health. 2021 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Basnet B.B., Basnet R., Panday R. Prospects for controlling future pandemics of SARS in highlights of SARS-CoV-2. VirusDis. 2021 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chalise H.N., Dhungana H.N. Fears of COVID-19 catastrophe as Nepal reports death from new Coronavirus. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Disabil. 2020; 6 :47. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dawadi S., Giri R., Simkhada P. Sage submissions; 2020. Impact of COVID-19 on the Education Sector in Nepal- Challenges and Coping Strategies. [ Google Scholar ]
- Department of Education . 2018. Flash Report I (2017-2018), Sanothimi, Bhaktapur, Nepal. https://www.doe.gov.np/assets/uploads/files/cbe2b2b1ae68bb5bdaa93299343e5c28.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Flaxman S., Mishra S., Gandy A., Unwin H.J.T., Mellan T.A., Coupland H., Bhatt S. Estimating the effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions on COVID-19 in Europe. Nature. 2020 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hiltz S.R., Wellman B. Vol. 40. 1997. Asynchronous Learning Networks as a Virtual Classroom; pp. 44–49. (9) [ Google Scholar ]
- International Association of Universities . 2020. The Impact of COVID-19 on Higher Education Worldwide Resources for Higher Education Institutions. https://www.iau-aiu.net/IMG/pdf/COVID-19_and_he_resources.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Kapasia N., Paul P., Roy A., Saha J., Zaveri A., Mallick R., Barman B., Das P., Chouhan P. Impact of lockdown on learning status of undergraduate and postgraduate students during COVID-19 pandemic in West Bengal, India. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020; 116 :105194. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Manzoor A. 2020. Online Teaching and Challenges of COVID-19 for Inclusion of PWDs in Higher Education. https://dailytimes.com.pk/595888/online-teaching-and-challenges-of-covid-19-for-inclusion-of-pwds-in-higher-education/ [ Google Scholar ]
- Marahatta S., Paudel S., Aryal N. COVID-19 Pandemic: what can Nepal do to curb the potential public health disaster? JKAHS. 2020; 3 (1):1–14. https://www.jkahs.org.np/jkahs/index.php/jkahs/article/view/213 [ Google Scholar ]
- Michael P., Murphy A. COVID-19 and emergency e-Learning: consequences of the securitization of higher education for post-pandemic pedagogy. Contemp. Secur. Pol. 2020; 41 (3) [ Google Scholar ]
- Mid-Western University . 2020. Digital, Virtual and Alternative Teaching-Learning and Operating Systems Policy Guidelines (2020) https://www.mwu.edu.np/mwu-dvatlosp-guideline-2020/news/ [ Google Scholar ]
- Poudel K., Subedi P. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on socioeconomic and mental health aspects in Nepal. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatr. 2020; 66 (8):748–755. 2020 12. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Panthee B., Dhungana S., Panthee N., Paudel A., Gyawali S., Panthee S. COVID-19: the current situation in Nepal. New Microbes New Infect. 2020; 37 :100737. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pant R.R., Bishwakarma K., Qaiser F.U.R., Pathak L., Jayaswal G., Sapkota B., Pal K.B., Thapa L.B., Koirala M., Rijal K., Maskey R. Imprints of COVID-19 lockdown on the surface water quality of Bagmati river basin, Nepal. J. Environ. Manang. 2021; 289 :112522. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Quispe-Cañari J.F., Fidel-Rosales E., Manrique D., Mascaró-Zan J., Huamán-Castillón K.M., Chamorro–Espinoza S.E., Mejia C.R. Self-medication practices during the COVID-19 pandemic among the adult population in Peru: a cross-sectional survey. Saudi Pharmaceut. J. 2021; 29 (1):1–11. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tribhuvan University Online Class Nirdeshika. 2020. https://neporesult.com/news_notices/tribhuwan-university-online-class-nirdeshika/ [ Google Scholar ]
- TU . B.S. Tribhuvan University; Kathmandu, Nepal: 2012. Tribhuvan University, TU semester system operational guideline - 2070. [ Google Scholar ]
- UNESCO . UNESCO; 2020. COVID-19: Impact on Education. https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse [ Google Scholar ]
- UNESCO and IESALC COVID-19 and higher education: today and tomorrow. Impact analysis, policy responses and recommendations. Isaac. 2020;(9):1–46. http://www.iesalc.unesco.org/en/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/COVID-19-EN-090420-2.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- University Grant Commission . 2020. Education Management Information System (EMIS), UGC Report on Higher Education 2017-2018. https://www.ugcnepal.edu.np/uploads/publicationsAndReports/b6ABmh.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Viner R.M., Russell S.J., Croker H., Packer J., Ward J., Stansfield C., Mytton O., Bonell C., Booy R. School closure and management practices during coronavirus outbreaks including COVID-19: a rapid systematic review. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health. 2020; 4 (5):397–404. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO . 2020. World health organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. https://www.who.int. [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO . 2021. World health organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. https://covid19.who.int/ [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yáñez J.A., Alvarez-Risco A., Delgado-Zegarra J. Covid-19 in Peru: from supervised walks for children to the first case of Kawasaki-like syndrome. BMJ. 2020; 369 :m2418. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B., Song J., Tan W. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China 2019. NEJM. 2020; 382 :723–733. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay on Coronavirus in Nepali. This essay will help students with coronavirus. It is very simple and easy essay in Nepali to understand. कोरोना भाइरसको बारे...
The COVID-19 pandemic in Nepal is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first case in Nepal was confirmed on 23 January 2020 when a 31-year-old student, who had returned to Kathmandu from Wuhan on 9 January, tested positive for the disease.
The MoHP of Nepal confirmed the first and second cases of COVID-19, respectively, in January and March, in an interval of 2 months 1 ( 9 ). As of January 22, 2021, 268,948 COVID-19 positive cases were reported, with 263,546 recovered, and 1,986 death cases 6. This data showed nearly 0.74% death and about 98% recovery rate in Nepal.
Nepal confirmed its first COVID-19 case in a returnee student from Wuhan, China, on Jan 23, 2020, after the throat swabs sent to the WHO laboratory in Hong Kong identified SARS-CoV-2. Even though this was an isolated event with no further identifiable transmission, it set into motion some of the early responses by the Government of Nepal, including setting up screening at the airport ...
COVID-19 Pandemic Response. The coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic is the defining global health crisis of our time and the greatest challenge we have faced since World War Two. Since its emergence in Asia late last year, the virus has spread to most of the countries. Nepal, a landlocked country aspiring to graduate from a Least Developed Country ...
By April 6, 2021, the total confirmed cases worldwide are 132.28 million cases and 2.87 million deaths with more than 200 countries affected, and in Nepal alone, there are 278,470 cases confirmed and 3,036 deaths. [ 1] Nepal had its first COVID-19 case on January 13, 2020. The index case was a student studying in Wuhan and had returned to Nepal ...
The search terms included "COVID-19 in Nepal" and "Prevention and management of COVID-19 in Nepal." Data used in this article were extracted from relevant documents and websites. The figures were constructed by using Origin 2016 and GIS 10.4.1. We did not consult any databases that are privately owned or inaccessible to the public.
The first COVID-19 case in Nepal was recorded on 23 January 2020. The number of cases started increasing from the third week of March 2020 and by the end of 2020 there were 260 593 cases, with 1 856 recorded fatalities.. In early 2021, Nepal's Ministry of Health and Population (MoHP) submitted the National Deployment and Vaccination Plan (NDVP), which was developed with technical support ...
Study design. A qualitative research methodology was used 21 to assess the perspective of people towards the management of COVID‐19 and vaccination in rural and urban areas of Nepal. The study was guided and presented in accordance with the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative research Checklist. 22. 2.2.
Nepal has been on the frontline of both the covid-19 pandemic and climate change, and in both crises the response by the international community and Nepal's government has been marked by a failure to prepare or to invest proactively in strong prevention measures. The first case of covid-19 in Nepal was reported in January 2020 and the country's modest first wave peaked in late October 2020 ...
May 14, 2021. A COVID-19 patient receives oxygen outside an emergency ward at a government-run hospital in Kathmandu, Nepal, Thursday, May 13, 2021. Credit: AP Photo/Niranjan Shrestha. The COVID ...
The coronavirus crisis has brought to the fore — and exacerbated — a number of the Nepali state's long-standing weaknesses. By Peter Gill and Janak Raj Sapkota. June 29, 2020. Nepali youth ...
At present, COVID-19 has spread all over Nepal, with a rapid increase in the number of new cases and deaths, which is alarming in a low-income country with an inadequate healthcare system like Nepal. Although the government implemented early school closure and lockdown, the management to contain COVID-19 does not appear to be adequate.
The Nepal Preparedness and Response Plan (NPRP) lays out the preparedness actions and key response activities to be undertaken in Nepal, based on the trends and developments of the global COVID-19 pandemic. The plan outlines two levels of interventions; one that is the preparedness that should take place at the earliest possible and that ...
The COVID-19 pandemic spread to Nepal when its index case in Kathmandu was confirmed on 9 January 2020. As of 5 October, there have been 89,263 positive cases, 65,202 recoveries, and 554 deaths ...
This paper looks at the economic condition of Nepal before the COVID-19 spread, impact of the pandemic on its economy and measures taken to deal with the situation. Nepal's Economic Health before COVID-19 . Nepal's total economy is around US$32 billion (S$44.73 billion) annually. Since 2016, the country has been rebuilding its economy.
The response to COVID-19 in Nepal has been majorly led and controlled by the federal government. All three levels of government are performing their responsibilities; however, they face various challenges in responding to COVID-19. This study aimed to critically analyze Nepal's health system in the context of the COVID-19 response.
Nepali (नेपाली) Audio. Rapid Antigen Testing (audio) 2021-11-01 00:00:00. Fact sheets. COVID-19 Glossary. 2021-07-16 00:00:00. COVID-19 Self-Isolation change. ... COVID-19 can live on surfaces for days, but simple cleaning can kill it. Covid-19 testing and antiviral information.
100 Words Essay on Covid 19. COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very ...
Impact of COVID-19 on tourism in Nepal. R. Sah, S. Sigdel, +11 authors. R. Dhakal. Published in Journal of Travel Medicine 7 July 2020. Environmental Science, Medicine, Economics. The effects of COVID-19 on the global economy have been and will be, catastrophic. However, the full global impact, in both economic and health terms, remains unknown.
The Israeli government needs to open more land routes for food and medicine today. It needs to stop killing civilians and aid workers today. It needs to start the long journey to peace today.
Uri Berliner, an editor at NPR, castigated the broadcaster for what he said was a litany of journalistic missteps in coverage of several major news events, including the origins of Covid-19 and ...
Conclusion. The nationwide lockdown in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in remarkable disturbance in every level of academic institutions in Nepal. The present online survey evaluated the learning status of Nepalese students from all academic levels during this epidemic.
An editor at NPR issued a strong rebuke of the outlet's coverage of major news stories, such as Hunter Biden's laptop, in an essay for The Free Press on Tuesday.
Topic: Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, Nano-technology, biotechnology and issues relating to intellectual property rights. 4. Explain the concept of mRNA vaccines, outlining their potential benefits in preventing infectious diseases like COVID-19, and discuss their limitations and challenges. (250 words) Difficulty level: Moderate Reference: Insights on India Why the ...
Introduction. The unprecedented spread of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused a global public health crisis. Nepal is no exception to this pandemic with overwhelming effects on its economy and healthcare system [].As of 7 th March 2022, 977567 cases and 11948 deaths had been reported in the country despite adopting operative measures like nationwide lockdown, social distancing, and ...
Seke, from Nepal, is squeezed by Nepali and Tibetan. Wakhi, from Central Asia, sits between Chinese, Persian and Russian; its speakers also usually speak Tajik with others from their home country.
The studies regarding the implications of COVID-19 in education in Nepal were minimal, thus, this paper aims to highlight the impacts of the pandemic on the education sector of Nepal. It is revealed that the Nepalese academia has been facing problems due to lack of adequate and appropriate sustainable infrastructure for the online system ...