
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

17.3 Organizing Persuasive Speeches
Learning objectives.
- Understand three common organizational patterns for persuasive speeches.
- Explain the steps utilized in Monroe’s motivated sequence.
- Explain the parts of a problem-cause-solution speech.
- Explain the process utilized in a comparative advantage persuasive speech.

Steven Lilley – Engaged – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Previously in this text we discussed general guidelines for organizing speeches. In this section, we are going to look at three organizational patterns ideally suited for persuasive speeches: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantages.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
One of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches is Alan H. Monroe’s motivated sequence. The purpose of Monroe’s motivated sequence is to help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole” (German et al., 2010).
While Monroe’s motivated sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. In the only study conducted experimentally examining Monroe’s motivated sequence, the researchers did not find the method more persuasive, but did note that audience members found the pattern more organized than other methods (Micciche, Pryor, & Butler, 2000). We wanted to add this sidenote because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is a kind of magic persuasive bullet; the research simply doesn’t support this notion. At the same time, research does support that organized messages are perceived as more persuasive as a whole, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
Table 17.1 “Monroe’s Motivated Sequence” lists the basic steps of Monroe’s motivated sequence and the subsequent reaction a speaker desires from his or her audience.
Table 17.1 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
The first step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the attention step , in which a speaker attempts to get the audience’s attention. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. As previously discussed in Chapter 9 “Introductions Matter: How to Begin a Speech Effectively” , a strong attention getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic.
In the need step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.
Satisfaction
In the third step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the satisfaction step , the speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. Within this step, Monroe (1935) proposed a five-step plan for satisfying a need:
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is.
Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution.
Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem.
Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience.
Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker respond to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
Visualization
The next step of Monroe’s motivated sequence is the visualization step , in which you ask the audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. In essence, the visualization stage is where a speaker can show the audience why accepting a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior can positively affect the future. When helping people to picture the future, the more concrete your visualization is, the easier it will be for your audience to see the possible future and be persuaded by it. You also need to make sure that you clearly show how accepting your solution will directly benefit your audience.
According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast (Monroe, 1935). The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization can include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
The final step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the action step , in which a speaker asks an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. For understanding purposes, we break action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
Now that we’ve walked through Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
Main Points:
- Attention: Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
- Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
- Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
- Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
- Action: In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively.
Table 17.2 “Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist” also contains a simple checklist to help you make sure you hit all the important components of Monroe’s motivated sequence.
Table 17.2 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing a persuasive speech is the problem-cause-solution format. In this specific format, you discuss what a problem is, what you believe is causing the problem, and then what the solution should be to correct the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that our campus should adopt a zero-tolerance policy for hate speech.
- Demonstrate that there is distrust among different groups on campus that has led to unnecessary confrontations and violence.
- Show that the confrontations and violence are a result of hate speech that occurred prior to the events.
- Explain how instituting a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy against hate speech could stop the unnecessary confrontations and violence.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have shown the problem, you then explain to your audience that the cause of the unnecessary confrontations and violence is prior incidents of hate speech. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence. Again, this method of organizing a speech is as simple as its name: problem-cause-solution.
Comparative Advantages
The final method for organizing a persuasive speech is called the comparative advantages speech format. The goal of this speech is to compare items side-by-side and show why one of them is more advantageous than the other. For example, let’s say that you’re giving a speech on which e-book reader is better: Amazon.com’s Kindle or Barnes and Nobles’ Nook. Here’s how you could organize this speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the Nook is more advantageous than the Kindle.
- The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not.
- The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and noninteractive.
- The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
As you can see from this speech’s organization, the simple goal of this speech is to show why one thing has more positives than something else. Obviously, when you are demonstrating comparative advantages, the items you are comparing need to be functional equivalents—or, as the saying goes, you cannot compare apples to oranges.
Key Takeaways
- There are three common patterns that persuaders can utilize to help organize their speeches effectively: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantage. Each of these patterns can effectively help a speaker think through his or her thoughts and organize them in a manner that will be more likely to persuade an audience.
- Alan H. Monroe’s (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience’s attention. In the second stage, the speaker shows an audience that a need exists. In the third stage, the speaker shows how his or her persuasive proposal could satisfy the need. The fourth stage shows how the future could be if the persuasive proposal is or is not adopted. Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker’s persuasive proposal.
- The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem. Lastly, the speaker proposes a solution to the problem that corrects the underlying causes.
- The comparative advantages speech format is utilized when a speaker is comparing two or more things or ideas and shows why one of the things or ideas has more advantages than the other(s).
- Create a speech using Monroe’s motivated sequence to persuade people to recycle.
- Create a speech using the problem-cause-solution method for a problem you see on your college or university campus.
- Create a comparative advantages speech comparing two brands of toothpaste.
German, K. M., Gronbeck, B. E., Ehninger, D., & Monroe, A. H. (2010). Principles of public speaking (17th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 236.
Micciche, T., Pryor, B., & Butler, J. (2000). A test of Monroe’s motivated sequence for its effects on ratings of message organization and attitude change. Psychological Reports, 86 , 1135–1138.
Monroe, A. H. (1935). Principles and types of speech . Chicago, IL: Scott Foresman.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Persuasive Techniques Quiz - How well do you know them?
Leaderboard, visual style, switch template.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter Sixteen – Speaking to Persuade
On the first day of class, your instructor provided you a “lay of the land.” They introduced you to course documents, the syllabus, and reading materials.
“It’s important that you read your textbook,” they likely shared. “The material will allow you to dive deeper into the course material and, even if you don’t initially realize its importance, the reading material will build throughout the semester. The time spent reading will be worth it because without that knowledge, it will be difficult to complete assignments and receive full credit. The time spent reading will benefit you after you leave for the semester, too, and you’ll have critical thinking skills that will permeate your life out of the classroom.” Sound familiar?
This is persuasion. Your instructor is persuading you that reading the textbook is a good idea—that it’s an action you should take throughout the semester. As an audience member, you get to weigh the potential benefits of reading the textbook in relation to the consequences. But if your instructor has succeeded in their persuasive attempt, you will read the book because they have done a good job of helping you to conclude in favor of their perspective.
Your instructor may have even gone a step further, introducing themselves and including their credentials, such as degrees earned, courses taught, years of teaching, books published, etc. That sounds like what Aristotle called ethos , right? This is another key to persuasion, which we will discuss further in Chapter 17.
Persuasion is everywhere. We are constantly inundated with ideas, perspectives, politics, and products that are requesting our attention. Persuasion is often positively paired with ideas of encouragement, influence, urging, or logic. Your instructors, for example, are passionate about the subject position and want you to succeed in the class. Sadly, persuasion can also be experienced as manipulation, force, lack of choice, or inducement. You might get suspicious if you think someone is trying to persuade you. You might not appreciate someone telling you to change your viewpoints.
In this chapter, we explore persuasive speaking and work through best practices in persuasion. Because persuasion is everywhere, being critical and aware of persuasive techniques will allow you to both ethically persuade audiences and evaluate arguments when others attempt to persuade you. We’ll start with the basics by answering the question, “what is persuasion?”
Introducing Persuasive Speaking
Persuasion is “the process of creating, reinforcing, or changing people’s beliefs or actions” (Lucas, 2015, p. 306). Persuasion is important in all communication processes and contexts—interpersonal, professional, digital—and it’s something that you do every day. Convincing a friend to go see the latest movie instead of staying in to watch TV; giving your instructor a reason to give you an extension on an assignment; writing a cover letter and resume and going through an interview for a job—all of these and so many more are examples of persuasion. In fact, it is hard to think of life without the everyday give-and-take of persuasion. In each example listed, Lucas’s definition of persuasion is being implemented: you are asking a person or group to agree with your main idea.
When using persuasion in a public speech, the goal is to create, change, or reinforce a belief or action by addressing community problems or controversies. Remember that public speaking is a long-standing type of civic engagement; when we publicly speak, we are participating in democratic deliberation. Deliberatio n , or the process of discussing feasible choices that address community problems, is important in resolving community concerns because it allows all perspectives to be considered. Persuasive speaking means addressing a public controversy and advocating for a perspective that the speaker hopes the audience will adopt. If the issue isn’t publicly controversial – if everyone agrees or if there are not multiple perspectives – you are not persuading. You’re informing.
So, what’s a public controversy? Public controversies are community disputes that affect a large number of people. Because they involve a large number of people, public controversies often have multiple perspectives, leading to public deliberation and debate to resolve each dispute.
We experience public controversies daily. Through our social media feeds, we continuously scroll past shared articles, comments, or posts that provide different perspectives on community problems and potential solutions. You might, for example, join your local neighborhood (or dorm) Facebook group where neighbors share information and collaborate on solutions to specific problems facing the community. Each problem has consequences for different neighbors, and Facebook allows a space to deliberate and organize to address community priorities. They are controversial, however, because not all neighbors agree what which problems should be solved first or what those solutions are.
Sadly, there is no shortage of public controversies, and advocating for solutions to key community problems can feel overwhelming.
“How do I figure out one controversy to speak out about?” you may wonder.
Identify public controversies by listening and engaging with your community. What issues are affecting them? What are priorities? Once you’re able to locate a key community dispute, ask yourself:
- What is it? What is the problem? Are there more than 1? Is this the key problem or are there other hidden issues?
- What is the impact? What will happen if the problem is not resolved?
- Who’s affected? Who’s being affected or implicated by this problem? Who are the audiences or stakeholders affected? Are the stakeholders a part of my formal audience?
- What can solve it? Are there suggested solutions?
Controversies arise when a community experiences a problem, so your job is to decipher the breadth and depth of that problem. It’s impossible to address all issues in one speech, so researching and prioritizing are key to identifying what advocacy you find most urgent. For any controversy that you can address in a persuasive speech, keep context and power in mind.
Your public speaking context always informs what’s possible to accomplish during a speech. Remember, the public speaking context refers to both the physical space and cultural context.
The physical context will influence how much information you can provide to your audience. In other words, “Do I have time to talk about this issue?” “What is the most essential information to cover in a limited timeframe?” The broader cultural context can help you in situating your advocacy alongside other community conversations. What else is happening? Have other communities experienced this problem?
As persuasive speakers, you are attempting to influence an audience. What you select and how you present that information will alter how audiences understand the world, and that’s a pretty powerful thought. When you select an advocacy that addresses a public controversy, you are asking the audience to trust your perspective. To uphold that trust, it’s key to examine who is empowered or disempowered by our perspective.
When you’re considering a position toward a public controversy, you might ask, who’s empowered or disempowered by this problem? Who’s left out of the research? How are communities being represented? What am I assuming about those communities? Who is affected by my advocacy?
We can be well-meaning in our advocacies, especially when we select a persuasive insight based on our own experience. We become passionate about issues that we have seen, and that’s OK! Such passion can also, however, mean that we represent information in ways that are stereotypical or lead to the disempowerment of others.
If your city, for example, is deciding where to place a landfill, you may advocate against the plant being placed in your neighborhood. That advocacy, on face, makes sense!
“This will reduce our property values and just be plain stinky,” you might argue.
When we think about the issue reflexively and with power in mind, however, we may find that landfills are much more likely to be placed in neighborhoods that are predominant people of color (Massey, 2004). Advocating against placing the plant in your home may inadvertently mean the plant is placed in more vulnerable neighborhoods. Those neighbors become disempowered in your attempt to empower your own community.
In this example, practicing reflexivity might include asking: What are the potential solutions? What options do I have to avoid disempowering groups? Using sound research skills, considering other alternatives or perspectives, and listening can be mechanisms to answer these inquiries
There are no easy answers, but we are confident that you can select advocacies that are meaningful and worthwhile.
Formulating Persuasive Propositions
Once you feel comfortable and confident about a controversial issue that is ethical, timely and contextually relevant, you will need to identify what type of persuasive proposition that you’ll use in your speech. There are three types of persuasive propositions: propositions of fact, value, or policy. Each type will require different approaches and may have different persuasive outcomes for your audience.
Propositions of Fact
Propositions of fact answer the question, “is this true?” Speeches with this type of proposition attempt to establish the truth of a statement. There is not a sense of what is morally right and wrong or what should be done about the issue, only that a statement is supported by evidence or not. Imagine these questions as true or false.
These propositions are not facts like “the chemical symbol for water is H20” or “Barack Obama won the presidency in 2008.” Propositions or claims of fact are advocacies with evidence on different sides and/or spark disagreement. Imagine that you are a lawyer in the courtroom arguing if something is true or false, with evidence. Some examples of propositions of fact are:
- Converting to solar energy can save homeowners money.
- John F. Kennedy was assassinated by Lee Harvey Oswald working alone.
- Coal exacerbates global warming.
- Climate change has been caused by human activity.
- Granting tuition tax credits to the parents of children who attend private schools will perpetuate educational inequity.
- Watching violence on television causes violent behavior in children.
- William Shakespeare did not write most of the plays attributed to him.
- John Doe committed the crime of which he is accused.
Notice that no values—good or bad—are explicitly mentioned. The point of these propositions is to prove with evidence the truth of a statement, not its inherent value. Your goal is to persuade the audience to update their understanding or belief about the topic in question. Because you are likely not asking the audience to overtly act, it’s necessary to embed arguments that highlight how or why this factual information is meaningful for them or how the factual statement resolves a public controversy.
Propositions of fact are meaningful persuasive claims when new evidence or scientific observations arise that your audience may not know. Facts, statistics, definitions, or expert testimony are common evidence types for these propositions.
Propositions of Value
Propositions of value argue that something is good/bad or right/wrong. When the proposition has a word such as good, bad, best, worst, just, unjust, ethical, unethical, moral, immoral, advantageous or disadvantageous, it is a proposition of value. Some examples include:
- Hybrid cars are the best form of automobile transportation available today.
- Homeschooling is more beneficial for children than traditional schooling.
- The War in Iraq was not justified.
- The United States is not the greatest country on earth.
- Capital punishment is morally wrong.
- White supremacy is wrong.
- Running is the best form of exercise.
- A vegan diet is the healthiest one for adults.
Communication is a key vehicle in understanding values because communication is how communities collectively determine what is right or wrong. Because values are culturally situated and not universal, as a speaker, you must ground and describe what value or moral judgement you’re utilizing. If a war is unjustified, what makes a war “just” or “justified” in the first place? What makes a form of transportation “best” or “better” than another? Isn’t that a matter of personal approach? For different people, “best” might mean “safest,” “least expensive,” “most environmentally responsible,” “most stylish,” “powerful,” or “prestigious.”
Effective propositions of value rely on shared beliefs held by your audience. Developing confidence about your audience will allow you to determine what value systems they rely on and how your proposition relies on similar belief systems. We’ll talk more about appealing to your audience below.

Propositions of Policy
Policy propositions identify a solution to correct the problem. These propositions call for a change in policy (including those in a government, community, or school) or call for the audience to adopt a certain behavior.
Speeches with propositions of policy try to instigate the audience to act immediately, in the long-term, or alter their perspective on an issue. A few examples include:
- Our state should require mandatory recertification of lawyers every ten years.
- The federal government should act to ensure clean water standards for all citizens.
- The state of Georgia should require drivers over the age of 75 to take a vision test and present a certificate of good health from a doctor before renewing their licenses.
- Wyeth Daniels should be the next governor of the state.
- The Supreme Court should rule that migrant detention centers are unconstitutional.
These propositions are easy to identify because they almost always have the word “should” in them.
Many policy propositions advocate for a solution through a specific organization or government agency. In the examples above, the federal government, the state, and the Supreme Court are all listed as relevant actors to resolve the problem.
Alternatively, you could advocate for your audience to make specific behavioral changes that lead to solutions. If you’re addressing the consequences of climate change in your local community, do solutions require government or non-profit action? Could your audience make in-roads to reducing the negative effects of climate change alone? Thorough research will assist you in determining what actors – organizations or your audience—are best suited to implement your policy solution.
Policy propositions commonly embed a specific call-to-action. What should the audience do if they are persuading by your perspective? What actions can and should they take that can support your policy proposition? This can include “call your senator” (though more specificity is often helpful), but your call-to-action should be crafted with audience adaptation and information in mind.

Burns Library, Boston College – Maya Angelou – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Organizing Persuasive Propositions
Organization plays a key role in comprehending an argument. While we have previously discussed organization, in this section, we discuss organizing persuasive speeches with a focus on propositions of policy.
Once you’ve identified your main argument, ask, “what organizational pattern best suits my argument?”
For propositions of fact or value, you might select a categorical organization. Essentially that means that you will have two to four discrete, separate arguments in support of the proposition. For example:
Proposition of Fact: Converting to solar energy can save homeowners money.
- Solar energy reduces power bills.
- Solar energy requires less money for maintenance.
- Solar energy works when the power grid goes down.
For propositions of policy, the problem-solution organization pattern is commonly used. We do not typically feel any motivation to change unless we are convinced that some harm, problem, need, or deficiency exists, and even more, that it affects us personally. As the saying goes, “If it ain’t broke, why fix it?” In a problem-solution pattern, you can spend ample and organized time outlining the consequences to inaction, i.e. the problem.
Although a simple problem-solution organization is permissible for a speech of actuation, you will probably do well to utilize the more detailed format called Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
This format, designed by Alan Monroe (1951), is based on John Dewey’s reflective thinking process to consider audience listening patterns. This is one of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches. The purpose of Monroe’s motivated sequence is to help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole” (German et al., 2010). Each step is described below and fully developed following:
- Attention . This is the introduction, where the speaker brings attention to the importance of the topic as well as their own credibility and connection to the topic. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. As previously discussed, a strong attention getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic.
- Need. Here the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. It is important to make the audience see the severity of the problem, and how it affects them, their family, or their community. The harm or need can be physical, financial, emotional, educational, or social. It will have to be supported by evidence. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is.
Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution.
Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem.
Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience.
Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker respond to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
- Visualization. According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast (Monroe, 1935). The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization could include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
- Action . In the action step, the goal is to give specific steps for the audience to take as soon as possible to move toward solving the problem. Whereas the satisfaction step explains the solution overall, the action step gives concrete ways to begin making the solution happen. For understanding purposes, we break action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
The more concrete you can make the action step, the better. Research shows that people are more likely to act if they know how accessible the action can be. For example, if you want students to be vaccinated against the chicken pox virus (after establishing that it is a key public controversy), you can give them directions to and hours for a clinic or health center where vaccinations at a free or discounted price can be obtained.
Now that we have discussed Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
Introduction (Attention): Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
Main Points:
- Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
- Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
- Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
Conclusion (Action): In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively.
While Monroe’s motivated sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. We add this sidenote because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is some kind of magic persuasive bullet. At the same time, research does support organized messages being perceived as more persuasive, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing a persuasive speech is the problem-cause-solution format. In this specific format, you discuss what a problem is, what you believe is causing the problem, and then what the solution should be to correct the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that our campus should adopt a zero-tolerance policy for hate speech.
- Demonstrate that there is distrust among different groups on campus that has led to unnecessary confrontations and violence.
- Show that the confrontations and violence are a result of hate speech that occurred prior to the events.
- Explain how instituting a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy against hate speech could stop the unnecessary confrontations and violence.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have shown the problem, you then explain to your audience that the cause of the unnecessary confrontations and violence is prior incidents of hate speech. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence. Again, this method of organizing a speech is as simple as its name: problem-cause-solution.
Comparative Advantages
The final method for organizing a persuasive speech is called the comparative advantages speech format. The goal of this speech is to compare items side-by-side and show why one of them is more advantageous than the other. For example, let’s say that you’re giving a speech on which e-book reader is better: Amazon.com’s Kindle or Barnes and Nobles’ Nook. Here’s how you could organize this speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the Nook is more advantageous than the Kindle.
- The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not.
- The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and noninteractive.
- The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
As you can see from this speech’s organization, the simple goal of this speech is to show why one thing has more positives than something else. Obviously, when you are demonstrating comparative advantages, the items you are comparing need to be functional equivalents—or, as the saying goes, you cannot compare apples to oranges.
Before we continue with the potential barriers to persuasive speaking, consider this TEDEd talk: How to Use Rhetoric to Get What You Want .
Barriers to Effective Persuasi ve Speaking
Persuasive speaking can provide opportunities to advocate for important community solutions. But persuasion is really difficult, and there are often barriers to effectively persuading our audience to change their beliefs or act in a new way.
Persuasion is hard because we have a bias against change. As much as we hear statements like “The only constant is change” or “Variety is the spice of life,” the evidence from research and from our personal experience shows that, in reality, we do not like change. Recent risk aversion research, for example, found that humans are concerned more with what we lose than what we gain. Change is often seen as a loss of something rather than a gain of something else, and that’s stressful. We do not generally embrace things that bring us stress.
Given our aversion to change, audiences often go out of their way to protect their beliefs, attitudes, and values. We (as audience members) selectively expose ourselves to messages that we already agree with, rather than those that confront or challenge us. This selective exposure is especially seen in choices of mass media that individuals listen to, watch, and read. Not only do we selectively expose ourselves to information, but we also selectively attend to, perceive, and recall information that supports our existing viewpoints (referred to a s elective recall ).
This principle led Leon Festinger (1957) to form the theory of cognitive dissonance , which states, among other ideas, that when we are confronted with conflicting information or viewpoints, we reach a state of dissonance, or tension between ideas and beliefs. It often occurs when we’re presented information that’s out of line with our values or experiences. This state can be very uncomfortable, and we will do things to get rid of the dissonance and maintain “consonance.” We don’t want to accept that our beliefs may be wrong or inconsistent; we want to remain harmonious.
In a sense, not changing can outweigh very logical reasons to change. For example, you probably know a friend who will not wear a seatbelt in a car. You can say to your friend, “Don’t you know that the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (2009) says, and I quote, ‘1,652 lives could be saved, and 22,372 serious injuries avoided each year on America’s roadways if seat belt use rates rose to 90 percent in every state’?” What will your friend probably say, even though you have cited a credible source?
They will come up with some reason for not wearing it, even something as dramatic as “I knew a guy who had a cousin who was in an accident and the cop said he died because he was wearing his seatbelt.” They may even say, “Well I am a good driver, so you only need seat belts if you’re driving poorly.” You may have had this conversation, or one like it. Their argument may be less dramatic, such as “I don’t like how it feels” or “I don’t like the government telling me what to do in my car.” For your friend, the argument for wearing a seat belt is not as strong as the argument against it, at least at this moment. Ideally, at least for a public speaker, the dissonance is relieved or resolved by being persuaded (changed) to a new belief, attitude, or behavior.
So, what is a speaker to do to overcome these barriers? We suggest making reasonable requests, articulating the benefits or consequences, and answering oppositional arguments.
Make Reasonable Requests
Setting reasonable persuasive goals is the first way to meet audience resistance. Since we resist change, we do not make many large or major changes in our lives. We do, however, make smaller, concrete, step-by-step or incremental changes every day. Over time these small shifts can eventually result in a significant amount of persuasion. Aim small, especially within a time constraint, and work to find future room to build.
Focus on Benefits and Consequences
When problems aren’t resolved, there are consequences. When problems are resolved, there are positive benefits for the community. Because you are asking the audience to change something, they must view the benefits of acting as worth the stress of the change. A speaker should be able to engage the audience at the level of needs, wants, and values as well as logic and evidence.
Identify the benefits, advantages, or improvements that would happen for the audience members who enacted your advocacy. If you do good audience analysis, you know that audiences are asking, “What’s in it for me?” “Why do I need this?”
Alternatively, you could outline the short and long-term consequences of inaction and detail how the problem would negatively affect the audience and/or their community. In other words, you’re identifying what would occur if the audience did nothing, if they choose not to act. Using Monroe’s Motivated Sequences can assist in organizing these arguments.
Answer Oppositional Arguments
During a persuasive speech, audience members are holding a mental dialogue, and they are thinking through rebuttals or oppositional arguments to your advocacy. These mental dialogues could be called the “yeah-buts”—the audience members are saying in their minds, “Yeah, I see what you are arguing, but—”. Reservations can be very strong, since, again, our human bias is to be loss averse and not to change our actions or beliefs.
If you’re advocating a claim that humans are the primary cause of climate change, your audience may think, “yeah, but these consequences won’t happen for a long time,” or “yeah, but we have time to resolve these problems.”
As a speaker, address these! Refute the arguments that may prohibit your audience from changing.
It’s common to call oppositional arguments “misconceptions,” “myths,” or “mistaken ideas” that are widely held about the proposition. You may answer oppositional arguments around climate change by saying, “One common misconception about climate change is that we won’t see the negative impacts for decades. A recent study determined that consequences are already upon us.”
After acknowledging oppositional arguments and seeking to refute or rebut the reservations, you must also provide evidence for your refutation. Ultimately, this will show your audience that you are aware of both sides of the issue you are presenting and make you a more credible speaker.
Additionally, keep in mind that you may be asking your audience for passive agreement or immediate action. Each is described below.
Gain Passive Agreement
When we attempt to gain the passive agreement of our audiences, our goal is to get our audiences to agree with what we are saying and our specific policy without asking the audience to do anything to enact the policy. For example, maybe your speech is on why the Federal Communications Commission should regulate violence on television like it does foul language (i.e., no violence until after 9 p.m.). Your goal as a speaker is to get your audience to agree that it is in our best interest as a society to prevent violence from being shown on television before 9 p.m., but you are not seeking to have your audience run out and call their senators or congressmen or even sign a petition. Often the first step in larger political change is simply getting a massive number of people to agree with your policy perspective.
Let’s look at a few more passive agreement claims:
- Racial profiling of individuals suspected of belonging to known terrorist groups is a way to make America safer.
- Requiring American citizens to “show their papers” is a violation of democracy and resembles tactics of Nazi Germany and communist Russia.
- Colleges and universities should voluntarily implement a standardized testing program to ensure student learning outcomes are similar across different institutions.
In each of these claims, the goal is to sway one’s audience to a specific attitude, value, or belief, but not necessarily to get the audience to enact any specific behaviors.
Gain Immediate Action
The alternative to passive agreement is immediate action, or persuading your audience to start engaging in a specific behavior. Many passive agreement topics can become immediate action-oriented topics as soon as you tell your audience what behavior they should engage in (e.g., sign a petition, call a senator, vote). While it is much easier to elicit passive agreement than to get people to do something, you should always try to get your audience to act and do so quickly. A common mistake that speakers make is telling people to enact a behavior that will occur in the future. The longer it takes for people to engage in the action you desire, the less likely it is that your audience will engage in that behavior.
Here are some examples of good claims with immediate calls to action:
- College students should eat more fruit, so I am encouraging everyone to eat the apple I have provided you and start getting more fruit in your diet.
- Teaching a child to read is one way to ensure that the next generation will be stronger than those that have come before us, so please sign up right now to volunteer one hour a week to help teach a child to read.
- The United States should reduce its nuclear arsenal by 20 percent over the next five years. Please sign the letter provided encouraging the president to take this necessary step for global peace. Once you’ve signed the letter, hand it to me, and I’ll fax it to the White House today.
Each of these three examples starts with a basic claim and then tags on an immediate call to action. Remember, the faster you can get people to engage in a behavior the more likely they actually will.
- Lucas, S. E. (2019). The Art of Public Speaking ( 13th edition) Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill.
- German, K. M., Gronbeck, B. E., Ehninger, D., & Monroe, A. H. (2010). Principles of public speaking (17th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 236.
- Micciche, T., Pryor, B., & Butler, J. (2000). A test of Monroe’s motivated sequence for its effects on ratings of message organization and attitude change. Psychological Reports, 86 , 1135–1138.
- Monroe, A. H. (1935). Principles and types of speech . Chicago, IL: Scott Foresman.
- https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-stretching-his-legs-9623853/
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
- This chapter adapted from Stand up, Speak out. Stand up, Speak out by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted, and Speak out, Call in. Speak Out, Call In: Public Speaking as Advocacy by Meggie Mapes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Principles of Public Speaking Copyright © 2022 by Katie Gruber is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Quiz 16: Speaking to Persuade
Access For Free
Audience analysis and adaptation are usually more demanding in persuasive speaking than in speaking to inform.
When trying to persuade a hostile audience, you should usually be wary oeven mentioning the audience's objections to your point oview.
Research indicates that audiences often engage in a mental give-and-take with the speaker as they listen to a persuasive speech.
When trying to persuade listeners that are skeptical about your position, you need to deal directly with the reasons for their skepticism.
When speaking to persuade, you need to think oyour speech as a kind omental dialogue with your audience.
As your textbook explains, when faced with an audience that strongly opposes your point oview, you can consider your persuasive speech a success iit leads even a few listeners to reexamine their views.
Your success in a persuasive speech will usually depend on how well you adapt to the attitudes, beliefs, and values oyour audience.
Even though a persuasive speaker's goal is to influence the audience's beliefs or actions, she or he still has an ethical obligation to present evidence fairly and accurately.
Oall the kinds opublic speaking, persuasion is the most complex and the most challenging.
No matter how carefully prepared or skillfully delivered a persuasive speech is, it may be impossible to change the minds osome oyour listeners.
When speaking to persuade, you should try to anticipate places where the audience might object and then answer the objections in your speech.
One way for a persuasive speaker to uphold the ethical obligations ospeechmaking is to learn about all sides oan issue.
Because everyone knows that a persuasive speaker's goal is to influence the audience's beliefs or actions, questions oethics are less important in persuasive speaking than in other kinds ospeaking.
The target audience is that portion othe whole audience that the speaker most wants to persuade.
As your textbook explains, persuasion takes place only ithe audience is strongly in favor othe speaker's position by the end othe speech.
Moving listeners from being strongly opposed to a speaker's position to being only moderately opposed would be a sign oa successful persuasive speech.
Persuasive speakers should aim to construct speeches that are both convincing and ethically sound.
Persuasion is a psychological process in which listeners engage in a mental dialogue with the speaker.
Audience analysis and adaptation are usually less challenging in persuasive speaking than in speaking to inform.
Persuasion is the process ocreating, reinforcing, or changing people's beliefs or actions.
showing 1 - 20 of 185
Related Quizzes
Speaking in Public
103 Questions
Ethics and Public Speaking
102 Questions
91 Questions
Giving Your First Speech
50 Questions
Selecting a Topic and a Purpose
137 Questions
Analyzing the Audience
135 Questions
Gathering Materials
97 Questions
Supporting Your Ideas
153 Questions
Organizing the Body Othe Speech
170 Questions
Beginning and Ending the Speech
125 Questions
Outlining the Speech
92 Questions
Using Language
134 Questions
Using Visual Aids
149 Questions
Speaking to Inform
110 Questions
Methods Opersuasion
287 Questions
Speaking on Special Occasions
90 Questions
Speaking in Small Groups
136 Questions
Public Speaking and Communication Skills
172 Questions
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10 Chapter 10: Persuasive Speaking
Amy Fara Edwards and Marcia Fulkerson, Oxnard College
Victoria Leonard, Lauren Rome, and Tammera Stokes Rice, College of the Canyons
Adapted by Jamie C. Votraw, Professor of Communication Studies, Florida SouthWestern State College

Figure 10.1: Abubaccar Tambadou 1
Introduction
The American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) was founded on April 10, 1866. You may be familiar with their television commercials. They start with images of neglected and lonely-looking cats and dogs while the screen text says: “Every hour… an animal is beaten or abused. They suffer… alone and terrified…” Cue the sad song and the request for donations on the screen. This commercial causes audiences to run for the television remote because they can’t bear to see those images! Yet it is a very persuasive commercial and has proven to be very successful for this organization. According to the ASPCA website, they have raised $30 million since 2006, and their membership has grown to over 1.2 million people. The audience’s reaction to this commercial showcases how persuasion works! In this chapter, we will define persuasive speaking and examine the strategies used to create powerful persuasive speeches.

Figure 10.2: Caged Dogs 2
Defining Persuasive Speaking
Persuasion is the process of creating, reinforcing, or changing people’s beliefs or actions. It is not manipulation, however! The speaker’s intention should be clear to the audience in an ethical way and accomplished through the ethical use of methods of persuasion. When speaking to persuade, the speaker works as an advocate. In contrast to informative speaking, persuasive speakers argue in support of a position and work to convince the audience to support or do something.
As you learned in chapter five on audience analysis, you must continue to consider the psychological characteristics of the audience. You will discover in this chapter the attitudes, beliefs, and values of the audience become particularly relevant in the persuasive speechmaking process. A key element of persuasion is the speaker’s intent. You must intend to create, reinforce, and/or change people’s beliefs or actions in an ethical way.
Types of Persuasive Speeches
There are three types of persuasive speech propositions. A proposition , or speech claim , is a statement you want your audience to support. To gain the support of our audience, we use evidence and reasoning to support our claims. Persuasive speech propositions fall into one of three categories, including questions of fact, questions of value, and questions of policy. Determining the type of persuasive propositions your speech deals with will help you determine what forms of argument and reasoning are necessary to effectively advocate for your position.
Questions of Fact
A question of fact determines whether something is true or untrue, does or does not exist, or did or did not happen. Questions of fact are based on research, and you may find research that supports competing sides of an argument! You may even find that you change your mind about a subject when researching. Ultimately, you will take a stance and rely on credible evidence to support your position, ethically.
Today there are many hotly contested propositions of fact: humans have walked on the moon, the Earth is flat, Earth’s climate is changing due to human action, we have encountered sentient alien life forms, life exists on Mars, and so on.
Here is an example of a question of fact:
Recreational marijuana does not lead to hard drug use.
Recreational marijuana does lead to hard drug use.

Questions of Value
A question of value determines whether something is good or bad, moral or immoral, just or unjust, fair or unfair. You will have to take a definitive stance on which side you’re arguing. For this proposition, your opinion alone is not enough; you must have evidence and reasoning. An ethical speaker will acknowledge all sides of the argument, and to better argue their point, the speaker will convince the audience why their position is the “best” position.
Here is an example of a question of value:
Recreational marijuana use is immoral .
Recreational marijuana use is moral .
Questions of Policy
A question of policy advances a specific course of action based on facts and values. You are telling the audience what you believe should be done and/or you are asking your audience to act in a particular way to make a change. Whether it is stated or implied, all policy speeches focus on values. To be the most persuasive and get your audience to act, you must determine their beliefs, which will help you organize and argue your proposition.
Persuasive speeches on questions of policy must address three elements: need, plan, and practicality . First, the speaker must demonstrate there is a need for change (i.e., there is a problem). Next, the speaker offers the audience a plan (i.e., the policy solution) to address the problem. Lastly, the speaker shows the audience that the solution is practical . This requires that the speaker demonstrate how their proposed plan will address the identified problem without creating new problems.
Consider the topic of car accidents. A persuasive speech on a question of policy might focus on reducing the number of car accidents on a Florida highway. First, the speaker could use evidence from their research to demonstrate there is a need for change (e.g., statistics showing a higher-than-average rate of accidents). Then, the speaker would offer their plan to address the problem. Imagine their proposed plan was to permanently shut down all Florida highways. Would this plan solve the problem and reduce the number of accidents on Florida highways? Well, yes. But is it practical? No. Will it create new problems? Yes – side roads will be congested, people will miss work, kids will miss school, emergency response teams will be slowed, and tourism will decrease. The speaker could not offer such a plan and demonstrate that it is practical. Alternatively, maybe the speaker advocates for a speed reduction in a particularly problematic stretch of highway or convinces the audience to support increasing the number of highway patrol cars.
Here is an example of a question of policy:
Recreational marijuana use should be legal in all 50 states.
Recreational marijuana use should not be legal in all 50 states.
Persuasive Speech Organizational Patterns
There are several methods of organizing persuasive speeches. Remember, you must use an organizational pattern to outline your speech (think back to chapter eight). Some professors will specify a specific pattern to use for your assignment. Otherwise, the organizational pattern you select should be based on your speech content. What pattern is most logical based on your main points and the goal of your speech? This section will explain five common formats of persuasive outlines: Problem-Solution, Problem-Cause-Solution, Comparative Advantages, Monroe’s Motivated Sequence, and Claim to Proof.
Problem-Solution Pattern
Sometimes it is necessary to share a problem and a solution with an audience. In cases like these, the problem-solution organizational pattern is an appropriate way to arrange the main points of a speech. It’s important to reflect on what is of interest to you, but also what is critical to engage your audience. This pattern is used intentionally because, for most problems in society, the audience is unaware of their severity. Problems can exist at a local, state, national, or global level.
For example, the nation has recently become much more aware of the problem of human sex trafficking. Although the US has been aware of this global issue for some time, many communities are finally learning this problem is occurring in their own backyards. Colleges and universities have become engaged in the fight. Student clubs and organizations are getting involved and bringing awareness to this problem. Everyday citizens are using social media to warn friends and followers of sex-trafficking tricks to look out for.
Let’s look at how you might organize a problem-solution speech centered on this topic. In the body of this speech, there would be two main points; a problem and a solution. This pattern is used for speeches on questions of policy.
Topic: Human Sex Trafficking
General Purpose: To persuade
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to support increased legal penalties for sex traffickers.
Thesis (Central Idea): Human sex trafficking is a global challenge with local implications, but it can be addressed through multi-pronged efforts from governments and non-profits.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will define and explain the extent of the problem of sex trafficking within our community while examining the effects this has on the victims. Then, I will offer possible solutions to take the predators off the streets and allow the victims to reclaim their lives and autonomy.
- The problem of human sex trafficking is best understood by looking at the severity of the problem, the methods by which traffickers kidnap or lure their victims, and its impact on the victim.
- The problem of human sex trafficking can be solved by working with local law enforcement, changing the laws currently in place for prosecuting the traffickers and pimps, and raising funds to help agencies rescue and restore victims.
Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
To review the problem-solution pattern, recall that the main points do not explain the cause of the problem, and in some cases, the cause is not necessary to explain. For example, in discussing the problem of teenage pregnancy, most audiences will not need to be informed about what causes someone to get pregnant. However, there are topics where discussing the cause is imperative to understanding the solution. The Problem-Cause-Solution organizational pattern adds a main point between the problem and solution by discussing the cause of the problem. In the body of the speech, there will be three main points: the problem, the cause, and finally, the solution. This pattern is also used for speeches dealing with questions of policy. One of the reasons you might consider this pattern is when an audience is not familiar with the cause. For example, if gang activity is on the rise in the community you live in, you might need to explain what causes an individual to join a gang in the first place. By explaining the causes of a problem, an audience might be more likely to accept the solution(s) you’ve proposed. Let’s look at an example of a speech on gangs.
Topic: The Rise of Gangs in Miami-Dade County
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to urge their school boards to include gang education in the curriculum.
Thesis (Central Idea): The uptick in gang affiliation and gang violence in Miami-Dade County is problematic, but if we explore the causes of the problem, we can make headway toward solutions.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will explain the growing problem of gang affiliation and violence in Miami-Dade County. Then, I will discuss what causes an individual to join a gang. Finally, I will offer possible solutions to curtail this problem and get gangs off the streets of our community.
- The problem of gang affiliation and violence is growing rapidly, leading to tragic consequences for both gang members and their families.
- The causes of the proliferation of gangs can be best explained by feeling disconnected from others, a need to fit in, and a lack of supervision after school hours.
- The problem of the rise in gangs can be solved, or minimized, by offering after-school programs for youth, education about the consequences of joining a gang, and parent education programs offered at all secondary education levels.
Let’s revisit the human sex trafficking topic from above. Instead of using only a problem-solution pattern, the example that follows adds “cause” to their main points.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will define and explain the extent of the problem of sex trafficking within our community while examining the effects this has on the victims. Second, I will discuss the main causes of the problem. Finally, I will offer possible solutions to take the predators off the streets and allow the victims to reclaim their lives.
- The cause of the problem can be recognized by the monetary value of sex slavery.
- The problem of human sex trafficking can be solved by working with local law enforcement, changing the current laws for prosecuting traffickers, and raising funds to help agencies rescue and restore victims.
Comparative Advantages
Sometimes your speech will showcase a problem, but there are multiple potential solutions for the audience to consider. In cases like these, the comparative advantages organizational pattern is an appropriate way to structure the speech. This pattern is commonly used when there is a problem, but the audience (or the public) cannot agree on the best solution. When your goal is to convince the audience that your solution is the best among the options, this organizational pattern should be used.
Consider the hot topic of student loan debt cancellation. There is a rather large divide among the public about whether or not student loans should be canceled or forgiven by the federal government. Once again, audience factors come into play as attitudes and values on the topic vary greatly across various political ideologies, age demographics, socioeconomic statuses, educational levels, and more.
Let’s look at how you might organize a speech on this topic. In the body of this speech, one main point is the problem, and the other main points will depend on the number of possible solutions.
Topic: Federal Student Loan Debt Cancellation
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to support the government cancellation of $10,000 in federal student loan debt.
Thesis (Central Idea): Student loans are the largest financial hurdle faced by multiple generations, and debt cancellation could provide needed relief to struggling individuals and families.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will define and explain the extent of the student loan debt problem in the United States. Then, I will offer possible solutions and convince you that the best solution is a debt cancellation of $10,000.
- Student loan debt is the second greatest source of financial debt in the United States and several solutions have been proposed to address the problem created by unusually high levels of educational debt.
- The first proposed solution is no debt cancellation. This policy solution would not address the problem.
- The second proposed solution is $10,000 of debt cancellation. This is a moderate cancellation that would alleviate some of the financial burden faced by low-income and middle-class citizens without creating vast government setbacks.
- The third proposed solution is full debt cancellation. While this would help many individuals, the financial setback for the nation would be too grave.
- As you can see, there are many options for addressing the student loan debt problem. However, the best solution is the cancellation of $10,000.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Format
Alan H. Monroe, a Purdue University professor, used the psychology of persuasion to develop an outline for making speeches that will deliver results and wrote about it in his book Monroe’s Principles of Speech (1951). It is now known as Monroe’s Motivated Sequence . This is a well-used and time-proven method to organize persuasive speeches for maximum impact. It is most often used for speeches dealing with questions of policy. You can use it for various situations to create and arrange the components of any persuasive message. The five steps are explained below and should be followed explicitly and in order to have the greatest impact on the audience.
Step One: Attention
In this step, you must get the attention of the audience. The speaker brings attention to the importance of the topic as well as their own credibility and connection to the topic. This step of the sequence should be completed in your introduction like in other speeches you have delivered in class. Review chapter 9 for some commonly used attention-grabber strategies.
Step Two: Need
In this step, you will establish the need; you must define the problem and build a case for its importance. Later in this chapter, you will find that audiences seek logic in their arguments, so the speaker should address the underlying causes and the external effects of a problem. It is important to make the audience see the severity of the problem, and how it affects them, their families, and/or their community. The harm , or problem that needs changing, can be physical, financial, psychological, legal, emotional, educational, social, or a combination thereof. It must be supported by evidence. Ultimately, in this step, you outline and showcase that there is a true problem that needs the audience’s immediate attention. For example, it is not enough to say “pollution is a problem in Florida,” you must demonstrate it with evidence that showcases that pollution is a problem. For example, agricultural runoff is said to cause dangerous algal blooms on Florida’s beaches. You could show this to your audience with research reports, pictures, expert testimony, etc.
Step Three: Satisfaction
In this step, the need must be “satisfied” with a solution. As the speaker, this is when you present the solution and describe it, but you must also defend that it works and will address the causes and symptoms of the problem. Do you recall “need, plan, and practicality”? This step involves the plan and practicality elements. This is not the section where you provide specific steps for the audience to follow. Rather, this is the section where you describe “the business” of the solution. For example, you might want to change the voting age in the United States. You would not explain how to do it here; you would explain the plan – what the new law would be – and its practicality – how that new law satisfies the problem of people not voting. Satisfy the need!
Step Four: Visualization
In this step, your arguments must look to the future either positively or negatively, or both. If positive, the benefits of enacting or choosing your proposed solution are explained. If negative, the disadvantages of not doing anything to solve the problem are explained. The purpose of visualization is to motivate the audience by revealing future benefits or using possible fear appeals by showing future harms if no changes are enacted. Ultimately, the audience must visualize a world where your solution solves the problem. What does this new world look like? If you can help the audience picture their role in this new world, you should be able to get them to act. Describe a future where they fail to act, and the problem persists or is exacerbated. Or, help them visualize a world where their adherence to the steps you outlined in your speech remediates the problem.
Step Five: Action
In the final step of Monroe’s Motivated Sequence, we tell the audience exactly what needs to be done by them . Not a general “we should lower the voting age” statement, but rather, the exact steps for the people sitting in front of you to take. If you really want to move the audience to action, this step should be a full main point within the body of the speech and should outline exactly what you need them to do. It isn’t enough to say “now, go vote!” You need to tell them where to click, who to write, how much to donate, and how to share the information with others in their orbit. In the action step, the goal is to give specific steps for the audience to take, as soon as possible, to move toward solving the problem. So, while the satisfaction step explains the solution overall, the action section gives concrete ways to begin making the solution happen. The more straightforward and concrete you can make the action step, the better. People are more likely to act if they know how accessible the action can be. For example, if you want your audience to be vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus (HBV), you can give them directions to a clinic where vaccinations are offered and the hours of that location. Do not leave anything to chance. Tell them what to do. If you have effectively convinced them of the need/problem, you will get them to act, which is your overall goal.
Claim-to-Proof Pattern
A claim-to-proof pattern provides the audience with reasons to accept your speech proposition (Mudd & Sillars, 1962). State your claim (your thesis) and then prove your point with reasons (main points). The proposition is presented at the beginning of the speech, and in the preview, tells the audience how many reasons will be provided for the claim. Do not reveal too much information until you get to that point in your speech. We all hear stories on the news about someone killed by a handgun, but it is not every day that it affects us directly, or that we know someone who is affected by it. One student told a story of a cousin who was killed in a drive-by shooting, and he was not even a member of a gang.
Here is how the setup for this speech would look:
Thesis and Policy Claim: Handgun ownership in America continues to be a controversial subject, and I believe that private ownership of handguns should have limitations.
Preview: I will provide three reasons why handgun ownership should be limited.
When presenting the reasons for accepting the claim, it is important to consider the use of primacy-recency . If the audience is against your claim, put your most important argument first. For this example, the audience believes in no background checks for gun ownership. As a result, this is how the main points may be written to try and capture the audience who disagrees with your position. We want to get their attention quickly and hold it throughout the speech. You will also need to support these main points. Here is an example:
- The first reason background checks should be mandatory is that when firearms are too easily accessed by criminals, more gun violence occurs.
- A second reason why background checks should be mandatory is that they would lower firearm trafficking.
Moving forward, the speaker would select one or two other reasons to bring into the speech and support them with evidence. The decision on how many main points to have will depend on how much time you have for this speech, and how much research you can find on the topic. If this is a pattern your instructor allows, speak with them about sample outlines. This pattern can be used for fact, value, or policy speeches.
Methods of Persuasion
The three methods of persuasion were first identified by Aristotle, a Greek philosopher in the time of Ancient Greece. In his teachings and book, Rhetoric, he advised that a speaker could persuade their audience using three different methods: Ethos (persuasion through credibility), Pathos (persuasion through emotion), and Logos (persuasion through logic). In fact, he said these are the three methods of persuasion a speaker must rely on.

Figure 10.3: Aristotle 3
By definition, ethos is the influence of a speaker’s credibility, which includes character, competence, and charisma. Remember in earlier chapters when we learned about credibility? Well, it plays a role here, too. The more credible or believable you are, the stronger your ethos. If you can make an audience see you believe in what you say and have knowledge about what you say, they are more likely to believe you and, therefore, be more persuaded by you. If your arguments are made based on credibility and expertise, then you may be able to change someone’s mind or move them to action. Let’s look at some examples.
If you are considering joining the U.S. Air Force, do you think someone in a military uniform would be more persuasive than someone who was not in uniform? Do you think a firefighter in uniform could get you to make your house more fire-safe than someone who was not in uniform? Their uniform contributes to their ethos. Remember, credibility comes from audience perceptions – how they perceive you as the speaker. You may automatically know they understand fire safety without even opening their mouths to speak. If their arguments are as strong as the uniform, you may have already started putting your fire emergency kit together! Ultimately, we tend to believe in people in powerful positions. We often obey authority figures because that’s what we have been taught to do. In this case, it works to help us persuade an audience.
Advertising campaigns also use ethos well. Think about how many celebrities sell you products. Whose faces do you regularly see? Taylor Swift, Kerry Washington, Kylie Jenner, Jennifer Aniston? Do they pick better cosmetics than the average woman, or are they using their celebrity influence to persuade you to buy? If you walk into a store to purchase makeup and remember which ones are Kylie Jenner’s favorite makeup, are you more likely to purchase it? Pop culture has power, which is why you see so many celebrities selling products on social media. Now, Kylie may not want to join you in class for your speech (sorry!), so you will have to be creative with ethos and incorporate experts through your research and evidence. For example, you need to cite sources if you want people to get a flu shot, using a doctor’s opinion or a nurse’s opinion is critical to get people to make an appointment to get the shot. You might notice that even your doctor shares data from research when discussing your healthcare. Similarly, y ou have to be credible. You need to become an authority on your topic, show them the evidence, and persuade them using your character and charisma.
Finally, ethos also relates to ethics. The audience needs to trust you and your speech needs to be truthful. Most importantly, this means ethical persuasion occurs through ethical methods – you should not trick your audience into agreeing with you. It also means your own personal involvement is important and the topic should be something you are either personally connected to or passionate about. For example, if you ask the audience to adopt a puppy from a rescue, will your ethos be strong if you bought your puppy from a pet store or breeder? How about asking your audience to donate to a charity; have you supported them yourself? Will the audience want to donate if you haven’t ever donated? How will you prove your support? Think about your own role in the speech while you are also thinking about the evidence you provide.
The second appeal you should include in your speech is pathos , an emotional appeal . By definition, pathos appeals evoke strong feelings or emotions like anger, joy, desire, and love. The goal of pathos is to get people to feel something and, therefore, be moved to change their minds or to act. You want your arguments to arouse empathy, sympathy, and/or compassion. So, for persuasive speeches, you can use emotional visual aids or thoughtful stories to get the audience’s attention and hook them in. If you want someone to donate to a local women’s shelter organization to help the women further their education at the local community college, you might share a real story of a woman you met who stayed at the local shelter before earning her degree with the help of the organization. We see a lot of advertisement campaigns rely on this. They show injured military veterans to get you to donate to the Wounded Warriors Project , or they show you injured animals to get you to donate to animal shelters. Are you thinking about how your own topic is emotional yet? We hope so!
In addition, we all know that emotions are complex. So, you can’t just tell a sad story or yell out a bad word to shock them and think they will be persuaded. You must ensure the emotions you engage relate directly to the speech and the audience. Be aware that negative emotions can backfire, so make sure you understand the audience, so you will know what will work best. Don’t just yell at people that they need to brush their teeth for two minutes or show a picture of gross teeth; make them see the benefits of brushing for two minutes by showing beautiful teeth too.
Emotional appeals also need to be ethical and incorporated responsibly. Consider a persuasive speech on distracted driving. If your audience is high school or college students, they may be mature enough to see an emotional video or photo depicting the devastating consequences of distracted driving. If you’re teaching an elementary school class about car safety (e.g., keeping your seatbelt on, not throwing toys, etc.), it would be highly inappropriate to scare them into compliance by showing a devastating video of a car accident. As an ethical public speaker, it is your job to use emotional appeals responsibly.
One way to do this is to connect to the theory by Abraham Maslow, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, which states that our actions are motivated by basic (physiological and safety), psychological (belongingness, love, and esteem), and self-fulfillment needs (self-actualization). To persuade, we have to connect what we say to the audience’s real lives. Here is a visual of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Pyramid:
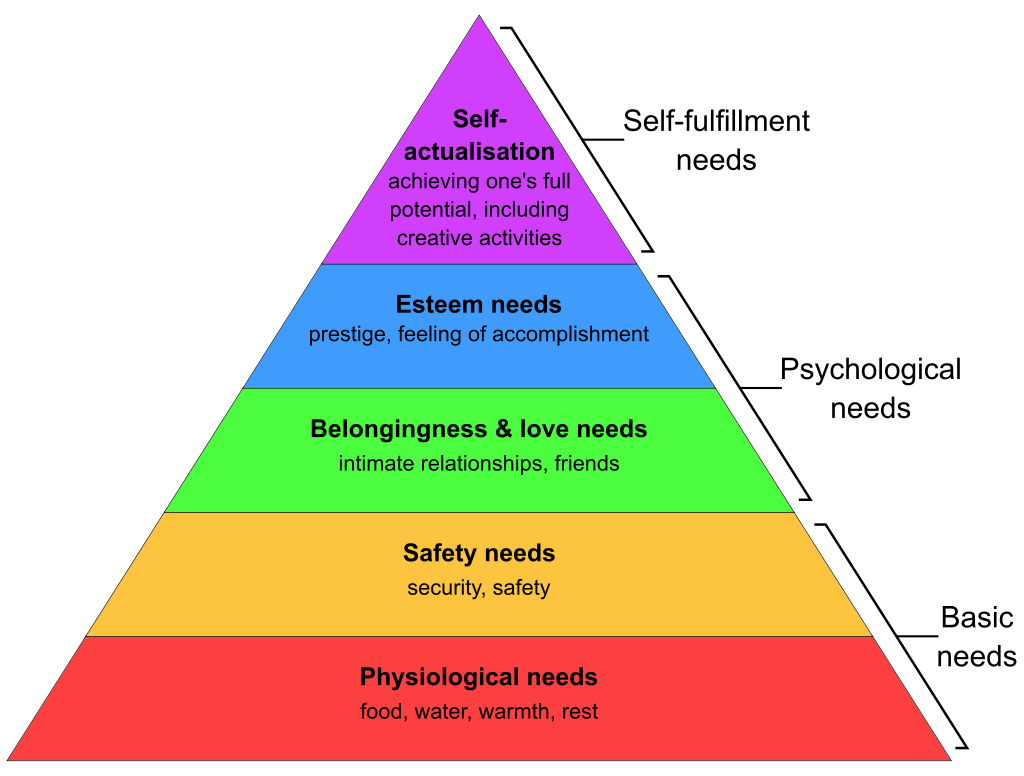
Figure 10.4: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 4
Notice the pyramid is largest at the base because our basic needs are the first that must be met. Ever been so hungry you can’t think of anything except when and what you will eat? (Hangry anyone?) Well, you can’t easily persuade people if they are only thinking about food. It doesn’t mean you need to bring snacks to your speech class on the day of your speech (albeit, this might be relevant to a food demonstration speech). Can you think about other ways pathos connects to this pyramid? How about safety and security needs, the second level on the hierarchy? Maybe your speech is about persuading people to purchase more car insurance. You might argue they need more insurance so they can feel safer on the road. Or maybe your family should put in a camera doorbell to make sure the home is safe. Are you seeing how we can use arguments that connect to emotions and needs simultaneously?
The third level in Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, love and belongingness, is about the need to feel connected to others. This need level is related to the groups of people we spend time with like friends and family. This also relates to the feeling of being “left out” or isolated from others. If we can use arguments that connect us to other humans, emotionally or physically, we will appeal to more of the audience. If your topic is about becoming more involved in the church or temple, you might highlight the social groups one may join if they connect to the church or temple. If your topic is on trying to persuade people to do a walk for charity, you might showcase how doing the event with your friends and family becomes a way of raising money for the charity and carving out time with, or supporting, the people you love. For this need, your pathos will be focused on connection. You want your audience to feel like they belong in order for them to be persuaded. People are more likely to follow through on their commitments if their friends and family do it. We know that if our friends go to the party, we are more likely to go, so we don’t have FOMO (fear of missing out). The same is true for donating money; if your friends have donated to a charity, you might want to be “in” the group, so you would donate also.
Finally, we will end this pathos section with an example that connects Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to pathos. Maybe your speech is to convince people to remove the Instagram app from their phones, so they are less distracted from their life. You could argue staying away from social media means you won’t be threatened online (safety), you will spend more real-time with your friends (belongingness), and you will devote more time to writing your speech outlines (esteem and achievement). Therefore, you can use Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs as a roadmap for finding key needs that relate to your proposition which helps you incorporate emotional appeals.
The third and final appeal Aristotle described is logos , which, by definition, is the use of logical and organized arguments that stem from credible evidence supporting your proposition. When the arguments in your speech are based on logic, you are utilizing logos. You need experts in your corner to persuade; you need to provide true, raw evidence for someone to be convinced. You can’t just tell them something is good or bad for them, you have to show it through logic. You might like to buy that product, but how much does it cost? When you provide the dollar amount, you provide some logos for someone to decide if they can and want to purchase that product. How much should I donate to that charity? Provide a dollar amount reasonable for the given audience, and you will more likely persuade them. If you asked a room full of students to donate $500.00 to a charity, it isn’t logical. If you asked them to donate $10.00 instead of buying lattes for two days, you might actually persuade them.
So, it is obvious that sources are a part of logos, but so is your own honest involvement with the topics. If you want people to vote, you need to prove voting matters and make logical appeals to vote. We all know many people say, “my vote doesn’t count.” Your speech needs to logically prove that all votes count, and you need to showcase that you always vote in the local and national elections. In this example, we bring together your ethos and your pathos to sell us on the logos. All three appeals together help you make your case. Audiences are not only persuaded by experts, or by emotions, they want it all to make sense! Don’t make up a story to “make it fit”. Instead, find a real story that is truthful, emotional, and one your audience can relate to make your speech logical from beginning to end and, therefore, persuasive.
Reasoning and Fallacies in Your Speech
In this chapter, we have provided you with several important concepts in the persuasive speech process, including patterns of organization and methods of persuasion. Now, we want to make sure your speech content is clear and includes strong and appropriate arguments. You have done extensive research to support the claims you will make in your speech, but we want to help you ensure that your arguments aren’t flawed. Thus, we will now look at different forms of reasoning and fallacies (or errors) to avoid in your logic.
Thus far, you have read how Aristotle’s proofs can and should be used in a persuasive speech. But, you might wonder how that influences the approach you take in writing your speech outline. You already know your research needs to be credible, and one way to do this is through research. Let’s now put this all together by explaining how reasoning is used in a speech, as well as the fallacies, or errors in reasoning, that often occur when speechwriting.
You may have seen graduation requirements include the category of critical thinking, which is the ability to think about what information you are given and make sense of it to draw conclusions. Today, colleges, universities, and employers are seeking individuals who have these critical thinking skills. Critical thinking can include abilities like problem-solving or decision-making. How did you decide on which college to start your higher educational journey? Was it a decision based on finances, being close to home, or work? This decision involved critical thinking. Even if you had an emotional investment in this decision (pathos), you still needed to use logic, or logos, in your thought process. Reasoning is the process of constructing arguments in a logical way. The use of evidence, also known as data , is what we use to prove our claims. We have two basic and important approaches for how we come to believe something is true. These are known as induction and deduction. Let us explain.
Inductive Reasoning
You have probably used inductive reasoning in your life without even knowing it! Inductive reasoning is a type of reasoning in which examples or specific instances are used to provide strong evidence for (though not absolute proof of) the truth of the conclusion (Garcia, 2022). In other words, you are led to a conclusion through your “proof”. With inductive reasoning, we are exposed to several different examples of a situation, and from those examples, we conclude a general truth because there is no theory to test. Think of it this way: you first make an observation, then, observe a pattern, and finally, develop a theory or general conclusion.
For instance, you visit your local grocery store daily to pick up necessary items. You notice that on Sunday, two weeks ago, all the clerks in the store were wearing football jerseys. Again, last Sunday, the clerks wore their football jerseys. Today, also a Sunday, they’re wearing them again. From just these three observations, you may conclude that on Sundays, these supermarket employees wear football jerseys to support their favorite teams. Can you conclude that this pattern holds indefinitely? Perhaps not; the phenomenon may only take place during football season. Hypotheses typically need much testing before confirmation. However, it seems likely that if you return next Sunday wearing a football jersey, you will fit right in.
In another example, imagine you ate an avocado, and soon afterward, the inside of your mouth swelled. Now imagine a few weeks later you ate another avocado and again the inside of your mouth swelled. The following month, you ate yet another avocado, and you had the same reaction as the last two times. You are aware that swelling on the inside of your mouth can be a sign of an allergy to avocados. Using induction, you conclude, more likely than not, you are allergic to avocados.
Data (evidence): After I ate an avocado, the inside of my mouth was swollen (1st time).
Data (evidence): After I ate an avocado, the inside of my mouth was swollen (2nd time).
Data (evidence): I ate an avocado, and the inside of my mouth was swollen (3rd time).
Additional Information: Swollen lips can be a sign of a food allergy.
Conclusion: Likely, I am allergic to avocados.
Inductive reasoning can never lead to absolute certainty. Instead, induction allows you to say, given the examples provided for support, the conclusion is most likely true. Because of the limitations of inductive reasoning, a conclusion will be more credible if multiple lines of reasoning are presented in its support. This is how inductive reasoning works. Now, let’s examine four common methods of inductive reasoning to help you think critically about your persuasive speech.
An analogy allows you to draw conclusions about an object or phenomenon based on similarities to something else (Garcia, 2022). Sometimes the easiest way to understand reasoning is to start with a simple analogy. An avid DIY enthusiast may love to paint -walls, furniture, and objects. To paint well, you need to think about what materials you will need, a knowledge of the specific steps to paint, and the knowledge of how to use an approach to painting so that your paint doesn’t run and your project comes out perfectly! Let’s examine how this example works as an analogy.
Analogies can be figurative or literal. A figurative analogy compares two things that share a common feature, but are still different in many ways. For example, we could say that painting is like baking; they both involve making sure that you have the correct supplies and follow a specific procedure. There are similarities in these features, but there are profound differences. However, a literal analogy is where the two things under comparison have sufficient or significant similarities to be compared fairly (Garcia, 2022). A literal analogy might compare different modalities at the school where your authors teach. If we claim that you should choose Florida SouthWestern State College’s face-to-face courses rather than enrolling in online courses , we could make literal comparisons of the courses offered, available student services, or the classroom atmosphere, for instance.
If we use the more literal analogy of where you choose to go to college, we are using an analogy of two similar “things,” and hopefully, this makes your analogy carry more weight. What this form of reasoning does is lead your audience to a conclusion. When we address fallacies later in this chapter, you will see that comparing two things that are not similar enough could lead you might make an error, or what we call a false analogy fallacy.
Generalization
Another effective form of reasoning is through the use of generalizations. Generalization is a form of inductive reasoning that draws conclusions based on recurring patterns or repeated observations (Garcia, 2022), observing multiple examples and looking for commonalities in those examples to make a broad statement about them. For example, if I tried four different types of keto bread (the new craze), and found that each of them tasted like Styrofoam , I could generalize and say all keto bread is NOT tasty! Or, if in your college experience, you had two professors that you perceived as “bad professors,” you might take a big leap and say that all professors at your campus are “bad.” As you will see later in the discussion on fallacies, this type of reasoning can get us into trouble if we draw a conclusion without sufficient evidence, also known as a hasty generalization. Have you ever drawn a conclusion about a person or group of people after only one or two experiences with them? Have you ever decided you disliked a pizza place because you didn’t like the pizza the first time you tried it? Sometimes, we even do this in our real lives.
Causal Reasoning
Causal reasoning is a form of inductive reasoning that seeks to make cause-effect connections (Garcia, 2022). We don’t typically give this a lot of thought. In the city where one of your authors lives, there are periodic street closures with cones up or signs to redirect drivers. The past several times this has happened, it has been because there was a community 5K run. It is easy to understand why each time I see cones I assume there is a 5K event. However, there could be a completely different cause that I didn’t even think about. The cones could be there due to a major accident or road work.
Reasoning from Sign
Reasoning from sign is a form of inductive reasoning in which conclusions are drawn about phenomena based on events that precede or co-exist with (but do not cause) a subsequent event (Garcia, 2022). In Southern California, a part of the country with some of the worst droughts, one may successfully predict when summer is coming. The lawn begins to die, and the beautiful gardens go limp. All of this occurs before the temperature reaches 113 degrees and before the calendar changes from spring to summer. Based on this observation, there are signs that summer has arrived.
Like many forms of reasoning, it is easy to confuse “reasoning from sign” with “causal reasoning.” Remember, that for this form of reasoning, we looked at an event that preceded another, or co-existed, not an event that occurred later. IF the weather turned to 113 degrees, and then the grass and flowers began to die, then it could be causal.
Deductive Reasoning
The second type of reasoning is known as deductive reasoning , or deduction, which is a conclusion based on the combination of multiple premises that are generally assumed to be true (Garcia, 2022). Whereas with inductive reasoning, we were led to a conclusion, deductive reasoning starts with the overall statement and then identifies examples that support it to reach the conclusion.
Deductive reasoning is built on two statements whose logical relationship should lead to a third statement that is an unquestionably correct conclusion, as in the following example:
Grocery store employees wear football jerseys on Sundays.
Today is Sunday.
Grocery store employees will be wearing football jerseys today.
Suppose the first statement is true (Grocery store employees wear football jerseys on Sundays) and the second statement is true (Today is Sunday). In that case, the conclusion (Grocery store employees will be wearing football jerseys today) is reasonably expected. If a group must have a certain quality, and an individual is a member of that group, then the individual must have that quality.
Unlike inductive reasoning, deductive reasoning allows for certainty as long as certain rules are followed.
Fallacies in Reasoning
As you might recall from our discussion, we alluded to several fallacies. Fallacies are errors in reasoning logic or making a mistake when constructing an inductive or deductive argument. There are dozens of fallacies we could discuss here, but we will highlight those we find to be the most common. Our goal is to help you think through the process of writing your persuasive speech so that it is based on sound reasoning with no fallacies in your arguments.
Table 10.1 describes fifteen fallacies that can be avoided once you understand how to identify them.
Table 10.1: Fallacies
In this chapter, you can feel confident that you have learned what you need to know to complete an effective persuasive speech. We have defined persuasion, explained speech propositions and patterns, and offered strategies to persuade, including ways to use logic. We also helped you learn more about inductive and deductive reasoning, and all of the various ways these methods help you construct your speeches. Finally, we provided you with the most common fallacies that could trip you up if you aren’t careful. The goal is to be clear, logical, and persuasive! Motivate your audience. Hey, have you been persuaded to start your speech outline yet? We hope so!
Reflection Questions
- What is the difference between propositions of fact, value, and policy?
- How will you determine which pattern of organization to use for your persuasive speech?
- How might you use ethos, pathos, and logos effectively in your speech? How can you write these three proofs into your content?
- What form(s) of reasoning will you use in your speech? How can you ensure you are not using any fallacies?
Appeal to Novelty
Appeal to Tradition
Circular Reasoning
Claim-to-Proof
Critical Thinking
Emotional Appeal
False Analogy
False Cause
Figurative Analogy
Hasty Generalization
Literal Analogy
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
Non-Sequitur
Primacy-recency
Problem-Cause-Solution
Problem-Solution
Proposition
Question of Fact
Question of Policy
Question of Value
Red Herring
Slippery Slope
Sweeping Generalization
Two Wrongs Make a Right
Garcia, A. R. (2022). Inductive and Deductive Reasoning. Retrieved May 5, 2022, from https://englishcomposition.org/advanced-writing/inductive-and-deductive-reasoning/.
Monroe, A. H. (1949). Principles and types of speech . Glenview, IL: Scott, Foresman and Company.
Mudd, C. S. & Sillars, M.O. (1962), Speech; content and communication. San Francisco, CA: Chandler Publishing Company.
Introduction to Public Speaking Copyright © by Jamie C. Votraw, M.A.; Katharine O'Connor, Ph.D.; and William F. Kelvin, Ph.D. is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Persuasive Writing Quiz Questions And Answers

Check out this amazing 'persuasive writing quiz' that we've created just for you! Persuasive writing is a form of writing where the writer uses words to convince the reader that the writer's opinion or idea is correct in regard to an issue. In this quiz, we'll test your knowledge, asking you to identify attributes of persuasive writing. You'll be asked a few questions, and you have to choose the best answer for each of them. So, are you ready? Let's start then… Good luck!

Upgrade and get a lot more done!
What is the purpose of persuasive writing?
To persuade
To tell a story
To tell 'how-to'
Rate this question:
What is the sentence that tells the main idea or point of view of the whole essay?
Topic sentence
Funky paragraphs
Thesis statement
What are the components of a persuasive essay?
Argument, Details, Thesis
Topic sentence, Details, Concluding Sentence
Introduction, Thesis Statement, Body Paragraphs, Conclusion
How many body paragraphs do you need, at least, in a persuasive essay?
Which two paragraphs are the most similar.
Introduction and Conclusion
None of the paragraphs are similar.
Conclusion and Body Paragraphs
Introduction and Body Paragraphs
Which sentence in this introduction paragraph is the thesis statement? The average family spends $1500 a year on clothes for school. In this economy, that seems like a lot of money! Many people argue that students should wear uniforms to school instead of their own clothes. Wearing school uniforms not only saves families money but also reduces bullying and allows students to focus on academics instead of style. Due to the reduced costs of uniforms, the reduction of bullying, and the focus on academics, all students should be required to wear uniforms to school.
In this economy, that seems like a lot of money!
Many people argue that students should wear uniforms to school instead of their own clothes.
Wearing school uniforms saves families money.
Due to the reduced costs of uniforms, the reduction of bullying, and the focus on academics. For these reasons, all students should be required to wear uniforms to school.
Which statement BEST supports the argument that all schools should be within walking distance of students' homes?
Students can sleep later.
It gives more people jobs.
It reduces pollution and increases physical activity.
No students can use the excuse that they missed the bus.
Are love letters a form of persuasive writing?
Yes, they can be.
No, love letters never fall under the umbrella of persuasive writing.
Persuasive essay writing pieces are also known as argumentative essays. True or false?
Quiz Review Timeline +
Our quizzes are rigorously reviewed, monitored and continuously updated by our expert board to maintain accuracy, relevance, and timeliness.
- Current Version
- Feb 13, 2024 Quiz Edited by ProProfs Editorial Team Expert Reviewed by Juliette Firla
- Nov 20, 2009 Quiz Created by Emessutta
Related Topics
Featured Quizzes
Popular Topics
- APA Style Quizzes
- MLA Format Quizzes
- Paragraph Quizzes
- Pencil Quizzes
- Plagiarism Quizzes
- Report Writing Quizzes
- Romantic Fiction Writing Quizzes
- Structure And Written Expression Quizzes
- Summary Writing Quizzes
- Technical Writing Quizzes
- Typography Quizzes
- Writing Process Quizzes

Related Quizzes
Wait! Here's an interesting quiz for you.
Have an account?
Suggestions for you See more

Commas, Ellipses, & Dashes
6th - 8th , argumentative writing, academic writing, 9th - 10th , informative writing & writing process, the writing process, university - professional development , occupations, 25.1k plays, argumentative texts.

Persuasive Writing Quiz
10th - 12th grade, english, other.
15 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
What is the purpose of a thesis statement in a persuasive essay?
To present a broad topic
To present the writer's opinion about a topic
To make an announcement about something
To introduce a statement of fact
True or False. When responding to a prompt it is important to pick a side and stay on topic.
- 3. Multiple Choice Edit 30 seconds 1 pt When constructing a convincing argument you should... Only focus on one side of the issue Address the counter argument Use a very aggressive tone Ignore all of the evidence and just state your opinion.
- 4. Multiple Choice Edit 30 seconds 1 pt True or False: A thesis statement should express what you believe and why you believe it. True False
What is wrong with the following thesis? In this paper my argument will be about school uniforms.
It is an announcement
It is argumentative
There is nothing wrong with it
It is too creative
All of the following are features of a persuasive essay EXCEPT...
Clearly stated position
Use of reasonable tone
Specific and reliable examples and evidence
Broad topic sentences
- 7. Multiple Choice Edit 30 seconds 1 pt Which of the following should NOT be used as a hook in an introductory paragraph? question anecdote (short story) quote startling fact
- 8. Multiple Choice Edit 30 seconds 1 pt Use ________ to avoid repetition in your persuasive essays. recording devices antonyms evidence synonyms
What is the purpose of persuasive writing?
To show the reader all of the facts about a topic
To describe the problems to the reader
To convince the reader of the author's point of view/opinion
To tell the reader how to do something
When reading a persuasive prompt, what should you be looking for as you READ the PROMPT?
The author's point of view
Supporting details
The thesis statement
The two sides of the argument/topic
After you have determined the two sides of the topic, you should _______.
Pick your point of view or decide which side to write about
Write the body paragraphs
Research information and relevant sources
Visit the library to discuss resources with the librarian
What do you need to include in the thesis statement?
Your position on the topic
All of the supporting details
Brief facts about the entire essay
What is the purpose of providing evidence in your persuasive essay?
Giving evidence proves your point rather than just saying 'because I said so'.
Giving evidence helps you reach the word count minimum.
Giving evidence only relates to trials in court.
Giving evidence makes means you're right.
What is the purpose of a conclusion?
A conclusion summarizes what you already said, restates your thesis, and hopefully leaves your reader convinced.
A conclusion is only needed because you says so.
A conclusion introduces the topic at the beginning of the essay.
A conclusion provides evidence to support the side you chose.
What must the thesis and the whole essay include so that you can develop your paper?
Supporting points
Beyonce's twins
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone
Developing Persuasive Speeches Quiz Active TINE REWNING z 3 4 5 56:20 "After my speech, I want my audience to support a budget increase for technology in the classroom" is an example of a _ a. thesis statement b. purpose statement d. question of value c. question of fact
Gauth ai solution, super gauth ai.
purpose statement
Explanation
b. purpose statement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We have an expert-written solution to this problem! Regardless of the type of speech, it is important that your supporting materials are ________. b. credible. Questions of policy address issues of right and wrong. T. To develop the main points for a speech on a question of value, you should ___________. why is it good or bad.
a course of action adopted and pursued by an organization, government, ruler, political party, etc. To develop the main points for a speech on a question of value, you should ___________. a. relate personal narratives. b. ask "Why is this good or bad". c. include statistics.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following is a question of policy? a. "Should a graduation exam be required?" b. "Should the government provide more aid to college students?" c. "Should high school students be required to study a foreign language?" d. All of the above, Demonstrating that your ideas are practical and reasonable is especially ...
Alan H. Monroe's (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience's attention.
Persuasive Techniques - How well do you know them? - Quiz. 1) Describing words which are most commonly used to make the reader feel a specific way regarding something. a) Adverbs b) Hyperbole or exaggeration c) Adjectives d) Assonance 2) Words which modify verbs or adjectives. They are used to make the reader feel a certain way about an issue.
Multiple Choice. An informative speaker who provides a fresh perspective is able to __________. Question 8. Multiple Choice. Some difference must especially exist between the speaker's view and that of the audience when the speaker's goal is __________. Question 9. Multiple Choice. In his speech, Keegan wants to signal what is coming and warn ...
Verified Questions and Answers for Quiz 13: Persuasive Messages. Services. Discover Topics. Homeschooling Ask a Question. Login ... Speaker should use the Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM) to develop persuasive speeches because it can be used _____. Question 15. ... Quiz 6. Topic Development. 30 Questions. Quiz 7. Organizing the Speech Body ...
This is another key to persuasion, which we will discuss further in Chapter 17. Persuasion is everywhere. We are constantly inundated with ideas, perspectives, politics, and products that are requesting our attention. Persuasion is often positively paired with ideas of encouragement, influence, urging, or logic.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following is a question of policy? a. "Should a graduation exam be required?" b. "Should the government provide more aid to college students?" c. "Should high school students be required to study a foreign language?" d. All of the above, "Violence on television does not lead to violent behavior" is an example of a ...
Quiz 16: Speaking to Persuade. Access For Free. Practice Exam. Question 1. True/False. Audience analysis and adaptation are usually more demanding in persuasive speaking than in speaking to inform. Question 2. True/False. When trying to persuade a hostile audience, you should usually be wary oeven mentioning the audience's objections to your ...
Whenever you give a persuasive speech on a question of value, you need to; A) inspire your audience to follow your call for action. B) justify your value judgment against a set of standards or criteria. C) provide evidence to prove the cause of a serious social problem. D) all of the above.
Defining Persuasive Speaking. Persuasion is the process of creating, reinforcing, or changing people's beliefs or actions. It is not manipulation, however! The speaker's intention should be clear to the audience in an ethical way and accomplished through the ethical use of methods of persuasion.
Flashcards Developing Persuasive Speeches | Quizlet. Which of the following is an example of a thesis statement? Click the card to flip. b. Joining the Red Cross is a simple way to become more active in your community. Quizlet has study tools to help you learn anything. Improve your grades and reach your goals with flashcards, practice tests ...
Persuasive writing is a form of writing where the writer uses words to convince the reader that the writer's opinion or idea is correct in regard to an issue. In this quiz, we'll test your knowledge, asking you to identify attributes of persuasive writing. You'll be asked a few questions, and you have to choose the best answer for each of them.
Question 2. True/False. If you are trying to convince an audience to oppose the death penalty, and you are a very good public speaker, you should expect that they will likely be persuaded with a single speech. Question 3. True/False. You have a very difficult class and you are thinking about dropping it. You estimate that you currently have an ...
Persuasive Writing Quiz quiz for 10th grade students. Find other quizzes for English and more on Quizizz for free! ... University - Professional Development 10 Qs . Occupations 25K plays 2nd 13 Qs . Argumentative Texts 1.1K plays 5th SUPER. 20 Qs . Argumentative Writing 366 plays 8th
persuasion. trying to get people to believe something is true, right or wrong, and getting people to do something. credibility, emotional appeal, evidence, reasoning. four ways we persuade. question of fact, value, policy. three types of persuasive speeches. question of fact. convince of truth. TRUTH is NON ABSOLUTE, and the SPEAKER is a PARTISAN.
You want to present a persuasive speech on adopting a vegetarian lifestyle, and you are concerned that your class meets right after lunch. ... Quiz 6. Topic Development. 30 Questions. Quiz 7. Organizing the Speech Body. 30 Questions. Quiz 8. The Introduction and Conclusion. 30 Questions. Quiz 9. Presentational Aids. 30 Questions. Quiz 10 ...
Developing Persuasive Speeches Quiz Active TINE REWNING z 3 4 5 56:20 "After my speech, I want my audience to support a budget increase for technology in the classroom" is an example of a _ a. thesis statement b. purpose statement d. question of value c. question of fact. Asked in United States.
UNIT TEST 5. Describe the development process for a persuasive speech addressing a question of facts. Click the card to flip 👆. The development process for a persuasive speech addressing a question of facts comes from a step process: develop a thesis, generate main points, supporting materials, and final development.