
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Last modified on: 10 months ago
- Reading Time: 6 Minutes
Here we are providing case study questions for CBSE Class 8 science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management.
Case Study Questions
Question 1:
A boy named Yash from Gwalior who studies in 8th standard is very fond of plants. He has a small garden in the backyard. Where he’s planted many small plants and takes good care of them. He regularly waters all the plants and uses fertilizers on them to keep them healthy. One day, a small announcement was made in school. In summer vacations, every student needs to do a project according to his/her own interest. Yash decided to grow a plant during summers and present it in front of the whole class as his project. Yash decided to grow peas. So he went to the market and bought the best quality seeds, sand and fertilizers. He came back home, went to the backyard and planted the seed. Started taking good care of it. But as day passed he began to realise that the seeds he planted are getting worse. The plant was unhealthy and very poor in quality. He tried everything but was unable to figure out the solution.
(i) Rabi crops are grown in which period? (a) February to June (b) October to March (c) June to November (d) December to January
(ii) Which system is used for irrigation? (a) Water (b) Sprinkler System (c) Drip System (d) Both b and c
(iii) Why Yash’s crops were grown unhealthy?
(iv) What are the disadvantages of fertilisers?
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
A to Z Classes
Cbse, ncert and icse solution online, class 8 science case study question, case study question class 8 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 8 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 8 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 8 Science.
There are total 18 chapter Crop Production and Management, Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
, Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, Materials: Metals and Non-Metals, Coal and Petroleum, Combustion and Flame, Conservation of Plants and Animals, Cell – Structure and Functions, Reproduction in Animals, Reaching the Age of Adolescence, Force and Pressure, Friction, Sound, Chemical Effects of Electric Current, Some Natural Phenomena, Light, Stars and the Solar System, Pollution of Air and Water
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.
CBSE Class 8 Science Case Study Question
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Case Study Question
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case Study Question
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Case Study Question
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Question
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum Case Study Question
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame Case Study Question
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals Case Study Question
- Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions Case Study Question
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals Case Study Question
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence Case Study Question
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure Case Study Question
- Chapter 12 Friction Case Study Question
- Chapter 13 Sound Case Study Question
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current Case Study Question
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Case Study Question
- Chapter 16 Light Case Study Question
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System Case Study Question
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water Case Study Question
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes
- Crop Production and Management Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 1
Last Updated on April 5, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 8 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 8 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 8 science chapter 1 Crop Production and Management.
Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Crop Production and Management
Question 1: A boy named Yash from Gwalior who studies in 8th standard is very fond of plants. He has a small garden in the backyard. Where he’s planted many small plants and takes good care of them. He regularly waters all the plants and uses fertilizers on them to keep them healthy. One day, a small announcement was made in school. In summer vacations, every student needs to do a project according to his/her own interest. Yash decided to grow a plant during summers and present it in front of the whole class as his project. Yash decided to grow peas. So he went to the market and bought the best quality seeds, sand and fertilizers. He came back home, went to the backyard and planted the seed. Started taking good care of it. But as day passed he began to realise that the seeds he planted are getting worse. The plant was unhealthy and very poor in quality. He tried everything but was unable to figure out the solution.
Q.1. Rabi crops are grown in which period? (a) February to June (b) October to March (c) June to November (d) December to January
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: Rabi crops are grown in winters from October to March and harvested in spring. They require warm climate for germination of seeds and cold climate to grow. Wheat, pea, barley are the examples of rabi crops.
Also read: Crop Production and Management Assertion Reason Questions Class 8 Science
Q.2. Which system is used for irrigation? (a) Water (b) Sprinkler System (c) Drip System (d) Both b and c
Ans. Option (d) is correct. Explanation: Sprinkler system- It is the modern method of irrigation. In this system water passes through a pipe generally by pumping to watering a farm. In this, water is split into tiny drops that falls to the farms. Drip System- It is also a method of modern irrigation. In this system, water falls drop by drop near the roots. it is a type of micro-irrigation which helps to save water.
Q.3. Why Yash’s crops were grown unhealthy?
Ans. Peas are the Rabi Crops which grows in winters i.e. from October to march and requires low temp at the seedling stage.
Q.4. What are the disadvantages of fertilisers?
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. The disadvantages of fertilisers are – (i) Fertilisers change the nature of the soil and reduce its fertility. (ii) Inadequate use of fertilisers can lead to pollution.
- Sound Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10
- Friction Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 9
- Force and Pressure Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 8
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 7
- Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
- Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 5
- Combustion and Flame Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 4
Coal and Petroleum Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
Microorganisms: friend and foe class 8 case study questions science chapter 2, topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Knowing types of crops.
- Learning various agricultural practices involved in crop production.
- Discussing the irrigation methods used in agriculture.
- Knowing how to protect crops from pests.
- Discussing harvesting of crops and storage of grains.
- Knowing about animal husbandry.
Living organisms need food for their growth and survival. You know that plants can prepare their own food. Animals obtain their food from plants and other animals.
We, human beings also depend on plants for our food. In order to provide food for the increasing population, we need to increase the production of the food we obtain. For this purpose, regular production, proper management and distribution of food are necessary.
This chapter deals with how various agricultural practices are useful to obtain food on large scale. So based on this the above topic list is provided.

Related Posts
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 8th Standard CBSE all question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 8th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place.
8th Standard CBSE Subjects
8th standard cbse study materials.


Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

Latest CBSE 8th Standard CBSE Study Material Updates
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Important Extra Questions
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Important Questions of Crop Production and Management. The sets of Important Questions include Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Extra Questions, intext Questions, Questions based on Keywords and other Exams questions for 2024-25. Using these Important Extra Questions students can practice for their school exams and Class tests.
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Important Questions from NCERT Textbook is given below with answers. There are Extra Questions taken from the entire chapter 1 of Class 8 Science. After reading the NCERT Books, if a student go through these questions, the chapter will be prepared for school exams or final exams.
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Important Questions Set – 1
What do you mean by production and management.
Anything which is produced or create with the help of people or machine, called “production”. To controlling or organizing any system or thing is called “management”. Production and management deals with a set of activities that embrace planning, coordination, supervision, control and decision-making activities which contribute the growth of people and country.
What are the necessary element or steps to provide food for a large population?
In order to provide food for a large population— regular production, proper management and distribution of food is necessary.
“Despite this diversity two broad cropping patterns can be identified”. What are the diversity?
India is a vast country. The climatic conditions like temperature, humidity and rainfall vary from one region to another. Although these are referred as diversity.
When plants of the same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. For example, crop of wheat means that all the plants grown in a field are that of wheat. Crops are of different types like cereals, vegetables and fruits etc.
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Important Questions Set – 2
What is the first step before growing a crop into the soil why it is so important.
The preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop. One of the most important tasks in agriculture is to turn the soil and loosen as preparation of soil. This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. The loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep into the soil. The loosened soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil. These organisms are friends of the farmer since they further turn and loosen the soil and add humus to it. Since only a few centimeters of the top layer of soil supports plant growth, turning and loosening of soil brings the nutrient-rich soil to the top so that plants can use these nutrients. Thus, turning and loosening of soil is very important for cultivation of crops.
“Before sowing the seeds it is necessary to break soil to the size of grains to get better yield”. Which type of tools are used for this purpose? Explain the construction of these tools.
This is done with the help of various tools. The main tools used for this purpose are the plough, hoe and cultivator. Plough: This is being used since ancient times for tilling the soil, adding fertilisers to the crop, removing the weeds, scraping of soil, etc. This implement is made of wood and is drawn by a pair of bulls or other animals (horses, camels, etc.). It contains a strong triangular iron strip called ploughshare. The main part of the plough is a long log of wood which is called a plough-shaft. There is a handle at one end of the shaft. The other end is attached to a beam which is placed on the bulls’ necks. One pair of bulls and a man can easily operate the plough. The indigenous wooden plough is increasingly being replaced by iron ploughs nowadays. Hoe: It is a simple tool which is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil. It has a long rod of wood or iron. A strong, broad and bent plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and works like a blade. It is pulled by animals. Cultivator: Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor driven cultivator. The use of cultivator saves labour and time.
With the help of an activity, say how seeds are selected by the farmers?
Take a beaker and fill half of it with water. Put a handful of wheat seeds and stir well. Wait for some time. There are some seeds which float on water. And there are heavier seeds also which sink in water. Damaged seeds become hollow and are thus lighter. Therefore, they float on water. This is a good method for separating good, healthy seeds from the damaged ones.
Agricultural Practices
Cultivation of crops involves several activities undertaken by farmers over a period of time. These activities or tasks are referred to as agricultural practices. These activities are listed below. (i) Preparation of soil, (ii) Sowing, (iii) Adding manure and fertilisers, (iv) Irrigation, (v) Protecting from weeds, (vi) Harvesting and (vii) Storage.
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Important Questions Set – 3
How can we make manure.
Manure is an organic substance obtained from the decomposition of plant or animal wastes. Farmers dump plant and animal waste in pits at open places and allow it to decompose. The decomposition is caused by some microorganisms. The decomposed matter is used as organic manure.
Discuss the process of manuring.
Process of manuring: Soil supplies mineral nutrients to the crop. These nutrients are essential for the growth of plants. In certain areas, farmers grow crop after crop in the same field. The field is never left uncultivated or fallow. Continuous growing of crops makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients. Thus, improper or insufficient manuring results in weak plants Therefore, farmers have to add manure to the fields to replenish the soil with nutrients. This process is called manuring.
“But excessive use of fertilizers has made the soil less fertile”. Explain the statement.
Fertilisers are chemical substances which are rich in a particular nutrient. Fertilisers are produced in factories. Some examples of fertilisers are— urea, ammonium sulphate, super phosphate, potash, NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium). The use of fertilisers has helped farmers to get better yield of crops such as wheat, paddy and maize. But excessive use of fertilisers has made the soil less fertile. Fertilisers have also become a source of water pollution. Therefore, in order to maintain the fertility of the soil, we have to substitute fertilisers by organic manure or leave the field uncultivated (fallow) in between two crops. Therefore, the use of manure improves soil texture as well as its water retaining capacity. It replenishes the soil with all the nutrients.
Manure and Fertilizers
Manure is an organic substance obtained from the decomposition of plant or animal wastes. Fertilisers are chemical substances which are rich in a particular nutrient.
The substances which are added to the soil in the form of nutrients for the healthy growth of plants are called manure or fertilisers.
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Important Questions Set – 4
Write the difference between fertilizers and manure..
Fertiliser: A fertiliser is an organic salt. A fertiliser is prepared in factories. A fertiliser does not provide any humans to the soil. Fertilisers are very rich in plants nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. In the other hand: Manure: Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung. Human waste and plant residues. Manual can be prepared in the fields. Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients.
“The organic manure is considered better than fertilizers”. Discuss, why?
The organic manure is considered better than fertilisers. This is because: (i) It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil. (ii) It makes the soil porous due to which exchange of gases becomes easy. (iii) It increases the number of friendly microbes. (iv) It improves the texture of the soil.
What is the role of water in crop production?
All living beings need water to live. Water is important for proper growth and development of flowers, fruits and seeds of plants. Water is absorbed by the plant roots. Along with water, minerals and fertilisers are also absorbed. Plants contain nearly 90% water. Water is essential because germination of seeds does not take place under dry conditions. Nutrients dissolved in water get transported to each part of the plant. To maintain the moisture of the soil for healthy crop growth, fields have to be watered regularly. The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called “irrigation”. The time and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season.
Weeds and its Removal
In a field many other undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds.
The removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light. Thus, they affect the growth of the crop. Some weeds interfere even in harvesting and may be poisonous for animals and human beings.
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Important Questions Set – 5
Why does storage of crop grains consider as an important task for farmers.
Storage of produce is an important task. If the crop grains are to be kept for longer time, they should be safe from moisture, insects, rats and microorganisms. The fresh crop has more moisture. If freshly harvested grains (seeds) are stored without drying, they may get spoilt or attacked by organisms, losing their germination capacity. Hence, before storing them, the grains are properly dried in the sun to reduce the moisture in them. This prevents the attack by insect pests, bacteria and fungi. Generally, farmers store grains in jute bags or metallic bins. However, large scale storage of grains is done in silos and granaries to protect them from pests like rats and insects. Dried neem leaves are used for storing food grains at home. For storing large quantities of grains in big go-downs, specific chemical treatments are required to protect them from pests and microorganisms.
Paheli wants to practice crop rotation in her field. Suggest a “Rabi crop” and “Kharif crop”. Which will replenish her filled with nitrogen. Which crop replenishes nitrogen and why?
Rabi crops are wheat, pea, mustard while kharif crops are maize, paddy (rice), or soya-bean. These are grown in different seasons and therefore, can very well be rotated alternatively. Pea and soya-bean are leguminous plants which harbour bacteria, i.e. rhizobium in their nodules, thus help in fixing nitrogen. These nitrogen fixing plants can replenish nitrogen in the field and hence, Paheli can easily practice crop rotation.
Explain, how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Soil supplies minerals and nutrients to the crop. These nutrients are essential for the growth of plants. Continuous growing of crops in the same field makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients. This makes the soil infertile. And then, to replenish the soil with nutrients farmers need to add manures to the soil.
Organic Food
The crops that are cultivated using organic substances like manures etc. and prohibit the use of harmful chemical substances like fertilisers, pesticides, weedicides, etc. are called ORGANIC FOOD.
Download NCERT Books and Offline Apps 2024-25 based on new CBSE Syllabus. Ask your doubts related to NIOS or CBSE Board and share your knowledge with your friends and other users through Discussion Forum.
Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Important Questions »
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Home » NCERT Solutions » NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Technology is advancing at a fast pace and it’s important to keep pace with the changing technology. Science helps the students to develop life skills, observe, understand the natural world and ask questions. It is necessary to understand the concepts of science at an early stage. The Central Board of Secondary Education has taken various measures to help the students develop their technical skills to achieve success in this field.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science are exclusive and vital tools for Science. Experts in Science have developed them with their years of experience. To access NCERT Science book class 8 solutions , you can check out the Extramarks website.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter-Wise List
The NCERT Science book class 8 solutions have been provided below:
NCERT Class 8 Science Solutions – Your Ultimate Guide & Mentor
Middle school is a crucial phase for students who wish to pursue science in higher classes, and thus, it becomes imperative to grasp the fundamental concepts of science at this level. Instead of racking your brain for the right mentor, just imagine getting all the questions and answers of your textbook at one place, at your doorstep. How cool would that be? On the official website of Extramarks, you can get all the NCERT solutions for class 8th Science which will help you prepare for the science examination. Given below are the core contents of each chapter of Class 8 Science.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
Chapter 1: Crop Production and Management
1.1: Agricultural Practices
1.2: Basic Practices of Crop Production
1.3: Preparation of Soil
1.4: Sowing
1.5 Adding Manure and Fertilisers
1.6: Irrigation
1.7: Protection from Weeds
1.8: Harvesting
1.9: Storage
1.10: Food from Animals
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
Chapter 2: Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
2.1: Microorganisms
2.2: Where do Microorganisms Live?
2.3: Microorganisms and Us
2.4: Harmful Microorganisms
2.5: Food Preservation
2.6: Nitrogen Fixation
2.7: Nitrogen cycle
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
Chapter 3: Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
3.1: What are Synthetic Fibres?
3.2: Types of Synthetic Fibres
3.3: Characteristics of Synthetic Fibres
3.4: Plastics
3.5: Plastics as Materials of Choice
3.6: Plastics and the Environment
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
Chapter 4: Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
4.1: Physical Properties of Metals and Non-metals
4.2: Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-metals
4.3: Uses of Metals and Non-metals
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
Chapter 5: Coal and Petroleum
5.2: Petroleum
5.3: Natural Gas
5.4: Some Natural Resources are Limited
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
Chapter 6: Combustion and Flame
6.1: What is Combustion?
6.2: How Do We Control Fire?
6.3 Types of Combustion
6.5: Structure of a Flame
6.6: What is a Fuel?
6.7: Fuel Efficiency
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
Chapter 7: Conservation of Plants and Animals
7.1: Deforestation and Its Causes
7.2: Consequences of Deforestation
7.3: Conservation of Forest and Wildlife
7.4: Biosphere Reserve
7.5: Flora and Fauna
7.6: Endemic Species
7.7: Wildlife Sanctuary
7.8: National Park
7.9: Red Data Book
7.10: Migration
7.11: Recycling of Paper
7.12: Reforestation
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
Chapter 8: Cell – Structure and Functions
8.1: Discovery of the Cell
8.2: The Cell
8.3: Organisms show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
8.4: Cell Structure and Function
8.5: Parts of the Cell
8.6: Comparison of Plants and Animals Cells
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
Chapter 9: Reproduction in Animals
9.1: Modes of Reproduction
9.2: Sexual Reproduction
9.3: Asexual Reproduction
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
Chapter 10: Reaching The Age of Adolescence
10.1: Adolescence and Puberty
10.2: Changes at Puberty
10.3: Secondary Sexual Characters
10.4: Role of Hormones in Initiating Reproductive Function
10.5: Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans
10.6: How is the Sex of the Baby Determined?
10.7: Hormones other than Sex Hormones
10.8: Role of Hormones in Completing the Life History of Insects and Frogs
10.9: Reproductive Health
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
Chapter 11: Force And Pressure
11.1: Force: A push or a Pull
11.2: Forces are due to an Interaction
11.3: Exploring Forces
11.4: A Force can Change the State of Motion
11.5: Force can Change the Shape of an object
11.6: Contact Forces
11.7: Non-contact Forces
11.8: Pressure
11.9: Pressure Exerted by Liquids and Gases
11.10: Atmospheric Pressure
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 12 Friction
Chapter 12: Friction
12.1: Force of Friction
12.2: Factors affecting Friction
12.3: Friction: A Necessary Evil
12.4: Increasing and Reducing Friction
12.5: Wheels Reduce Friction
12.6: Fluid Friction
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound
Chapter 13: Sound
13.1: Sound is Produced by Vibrating Bodies
13.2: Sound Produced by Humans
13.3: Sounds Needs a Medium for Propagation
13.4: We Hear Sound through Our Ears
13.5: Aptitude, Time Period and Frequency of a vibration
13.6: Audible and Inaudible Sounds
13.7: Noise and Music
13.8: Noise Pollution
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
Chapter 14: Chemical Effects Of Electric Current
14.1: Do Liquids Conduct Electricity?
14.2: Chemical Effects Of Electric Current
14.3: Electroplating
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
Chapter 15: Some Natural Phenomena
15.1: Lightning
15.2: Charging by Rubbing
15.3: Types of Charges and Their Interaction
15.4: Transfer of Charge
15.5: The Story of Lightning
15.6: Lightning Safety
15.7: Earthquakes
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
Chapter 16: Light
16.1: What makes Things Visible
16.2: Laws of Reflection
16.3: Regular and Diffused Reflection
16.4: Reflected Light Can be Reflected Again
16.5: Multiple Images
16.6: Sunlight – White or Coloured
16.7: What is inside Our Eyes?
16.8: Care of the Eyes
16.9: Visually Impaired Persons Can Read and Write
16.10: What is the Braille System?
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System
Chapter 17: Stars And The Solar System
17.1: The Moon
17.2: The Stars
17.3: Constellations
17.4: The Solar System
17.5 : Some Other Members of the Solar System
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
Chapter 18: Pollution of Air and Water
18.1: Air Pollution
18.2: How does Air Get Polluted?
18.3: Case Study- The Taj Mahal
18.4: Greenhouse Effect
18.5: What can be done?
18.6: Water Pollution
18.7: How does Water Get Polluted?
18.8: What is Potable Water and How is Water Purified?
18.9: What Can be Done?
Why is Extramarks the Best Class 8 Science Solution Provider?
Extramarks give you a competitive edge and help you comprehend scientific concepts by providing the best NCERT Science class 8 solutions. After a crucial analysis of the chapters, the subject matter experts have prepared these solutions to give the students 100% authentic and complete guidance. Besides this, it also offers NCERT solutions class 11, & NCERT solutions class 12 for all the subjects in every stream.
Extramarks focus on providing complete learning solutions, and the same goes for NCERT science class 8. We have updated answers according to the latest CBSE class 8 science syllabus, which will also prepare the students to crack competitive exams JEE Main/Advanced, VITEEE, and other exams.
Why are NCERT Science Solutions important for Class 8 students?
Middle school Science comprises Physics, Chemistry, and Biology and often gets pretty tough to understand because CBSE, through its NCERT curriculum, has set a high standard. With working parents and the absence of proper guidance, in this scenario , NCERT solutions for class 8th science become a vital tool that comes in handy to the students of class 8.
Being an average student, is it possible to get a high score in the CBSE Class 8 Science exam?
Some tips which can be followed to score well in CBSE class 8 Science question paper are given below:
- Class 8 Science requires lots of practice and learning from day one, so create a proper study plan and stick to it.
- Solve as many sample papers as possible. Previous year questions can also be used for further practice.
- Follow the Solutions of NCERT Science class 8, which you can find on the official website of Extramarks
- Revise thoroughly and take frequent self-tests to assess yourself.
- Practicing the diagrams repeatedly will improve your score and confidence level.
- NCERT Solutions can be your best guide and mentor to boost your performance in all subjects not just Science.
Why should you refer to Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions? How is it different?
Some of the benefits of referring to class 8 Science NCERT solutions are given below:
- The answers provided are concise and to the point
- The Subject matter experts with years of teaching experience have updated and cross-checked the solutions.
- The solutions have been simplified without any repetition, making it easier for the students to understand and grasp the concepts quickly and easily.
- The solutions help the students in cracking the examination with excellent results.
- The NCERT Science Solutions can be found at the Extramarks website to help the students download Solutions free of cost and make the most of it.

Salient Features of Extramarks’ NCERT Science Solutions Class 8
Some salient features of Extramarks NCERT Science Solutions Class 8 are given below:
- It assists the students of class 8 to prepare well for their science examination. It is a suitable revision material
- It provides in-depth knowledge of the subject to increase your confidence level while writing your exam
- It is a quick resource for learning written in simple English to ensure that all the students can understand it
- It helps quickly grasp all the ideas and concepts related to Physics, Chemistry, and Biology
- The NCERT Solutions by Extramarks strives to reach out to each and every learner right from the foundation level to the Secondary level to excel in life.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter-wise List
Chapter 1 - crop production and management.

Chapter 2 - Microorganisms : Friend and Foe
Chapter 3 - synthetic fibres and plastics, chapter 4 - materials : metals and non-metals, chapter 5 - coal and petroleum, chapter 6 - combustion and flame, chapter 7 - conservation of plants and animals, chapter 8 - cell - structure and functions, chapter 9 - reproduction in animals, chapter 10 - reaching the age of adolescence, chapter 11 - force and pressure, chapter 12 - friction, chapter 13 - sound, chapter 14 - chemical effects of electric current, chapter 15 - some natural phenomena, chapter 16 - light, chapter 17 - stars and the solar system, chapter 18 - pollution of air and water, ncert solutions for class 8 science in hindi, chapter 1- crop production and management in hindi, chapter 2 - microorganisms : friend and foe in hindi, chapter 3 - synthetic fibres and plastics in hindi, chapter 4 - materials : metals and non-metals in hindi, chapter 5 - coal and petroleum in hindi, chapter 6 - combustion and flame in hindi, chapter 7 - conservation of plants and animals in hindi, chapter 8 - cell structure and functions in hindi, chapter 9 - reproduction in animals in hindi, chapter 10 - reaching the age of adolescence in hindi, chapter 11 - force and pressure in hindi, chapter 12 - friction in hindi, chapter 13- sound in hindi, chapter 14 - chemical effects of electric current in hindi, chapter 15 - some natural phenomena in hindi, chapter 16- light in hindi, chapter 17 - stars and the solar system in hindi, chapter 18 - pollution of air and water in hindi, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. what are the advantages of ncert solutions for class 8th science.
The advantages are as follows:
- The NCERT Solutions uses the latest and updated NCERT curriculum for the CBSE Class 8 Science subject.
- Yet another important reason is that one can easily crack competitive examinations after practising solutions because it has problems that are tweaked and students get enough practise during the entire semester.
- NCERT Science Class 8 solutions help in quick revision.
2. How many chapters are there in the CBSE class 8 Science book?
The Class 8 Science books follow the latest CBSE guidelines and it has a total of 18 chapters that deal with the three branches of science: Physics, Chemistry, and Biology.
NCERT Solutions Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers is provided here. We prepared these extra questions based on the latest NCERT Class 8 Science Book. CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Extra Questions will help you to properly understand a particular concept of the chapter.
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Extra Questions
Very short answer type question.
Question 1: Give few examples of weedicides.
Answer: 2, 4-D
Question 2: Name the bacteria which fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Answer: Rhizobium bacteria
Question 3: What is called weeding?
Answer: The removal of weeds is called weeding.
Question 4: Name the tool used for tilling of soil.
Answer: Tilling of soil is done by using a plough.
Question 5: How are crumbs broken?
Answer: Crumbs are broken with the help of plank.
Question 6: Write 2 natural methods of replenishing the soil with nutrients.
Answer: i. Use of manure ii. Crop rotation
Question 7: How is levelling of soil done?
Answer: The levelling of soil is done with the help of a leveller.
Question 8: What are the two ways of sowing the seeds?
Answer: Seeds can be sown manually or by seed drills.
Question 9: How is ploughing done nowadays?
Answer: Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor driven cultivator.
Question 10: What is sowing?
Answer: Sowing is the process of planting seeds in the soil.
Question 11: Name two categories of crops based on season.
Answer: Two categories of crop based on season are kharif and rabi crops.
Question 12: What is threshing?
Answer: Separation of the grains from the chaff is called threshing.
Question 13: How are grains stored at home?
Answer: Dried neem leaves are used for storing food grains at home.
Question 14: What are called crumbs?
Answer: The ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs.
Question 15: Why is it important to level the field after ploughing?
Answer: The field is levelled for sowing as well as for irrigation purposes.
Question 16: What are good quality seeds?
Answer: Good quality seeds are clean and healthy seeds of a good variety.
Question 17: Give some examples of Rabi crop?
Answer: Examples of rabi crops are wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed.
Question 18: What is harvesting?
Answer: Harvesting is the cutting of the mature crop manually or by machines.
Question 19: Name the two modern methods of irrigation that help us to use water economically.
Answer: Sprinkler System and Drip system
Question 20: Why can paddy not be grown in the winter season?
Answer: Paddy requires a lot of water. Therefore, it is grown only in the rainy season.
Question 21: Why proper storage of crop products is important?
Answer: Proper storage of crop products is important to prevent them from spoilage.
Question 22: Give some examples of Kharif crop.
Ans. Examples of Kharif crops are Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton, etc.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1: What are the benefits of eating fish?
Answer: Fish is good for health. We get cod liver oil from fish which is rich in vitamin D.
Question 2: How do fertilisers help farmers?
Answer: The use of fertilisers has helped farmers to get better yield of crops such as wheat, paddy and maize.
Question 3: How are crops categorised in India?
Answer: In India, crops can be broadly categorised into two types based on seasons – rabi and kharif crops.
Question 4: How is harvesting done in India?
Answer: Harvesting in our country is either done manually by sickle or by a machine called harvester.
Question 5: What is winnowing?
Answer: After threshing, grains are separated from chaff with help of wind. This process is called winnowing.
Question 6: List some festivals that are associated with the harvest season.
Answer: Special festivals associated with the harvest season are Pongal, Baisakhi, Holi, Diwali, Nabanya and Bihu.
Question 7: What is crop rotation?
Answer: Crop rotation is a method of replenishing the soil with nutrients by growing different crops alternately.
Question 8: Why should excessive supply of water to plants be avoided?
Answer: Excessive supply of water to plants should be avoided because roots get damaged and the plants die.
Question 9: Why some seeds float on water?
Answer: Damaged seeds become hollow and are thus lighter. Therefore, they float on water.
Question 10: Why does farmer rotate crops in the field?
Answer: Farmer rotates crops in the field because crop rotation helps in the replenishment of the soil nutrients.
Question 11: What are the different sources of irrigation?
Answer: Sources of irrigation: The sources of irrigation are— wells, tube-wells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals.
Question 12: What is the right time to spray weedicides?
Answer: The weedicides are sprayed during the vegetative growth of weeds before flowering and seed formation.
Question 13: How is threshing carried out?
Answer: Threshing is carried out with the help of a machine called ‘combine’ which is in fact a combined harvester and thresher.
Question 14: What are the advantages of using manure in crop fields?
Answer: The use of manure improves soil texture as well as its water retaining capacity. It replenishes the soil with all the nutrients.
Question 15: In summer, the frequency of watering is higher. Why is it so?
Answer: In summer, the frequency of watering is higher due to the increased rate of evaporation of water from the soil and the leaves.
Question 16: Why does the loosening of soil allow the roots to breathe easily?
Answer: Loosening of soil allow the roots to breathe easily because air fill up the spaces between the soil particles and provides airy soil to the roots.
Question 17: How are grains stored in godowns?
Answer: For storing large quantities of grains in big godowns, specific chemical treatments are required to protect them from pests and microorganisms.
Question 18: Is it a good practice to burn the stubs left in the field? Give reasons.
Answer: No, it is not a good practice to burn the stubs left in the field because it causes pollution. It may also catch fire and damage the crops lying in the fields.
Question 19: How weeds are removed manually?
Answer: The manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time. This is done with the help of a khurpi.
Question 20: What are the harmful effects of using fertilisers?
Answer: Harmful effects of using fertilisers
- Excessive use of fertilizers has made the soil less fertile.
- Fertilizers have also become a source of water pollution.
Question 21: What do you understand by agricultural practices?
Answer: Cultivation of crops involves several activities undertaken by farmers over a period of time. These activities or tasks are referred to as agricultural practices.
Question 22: What is animal husbandry?
Answer: Animals reared at home or in farms, have to be provided with proper food, shelter and care. When this is done on a large scale, it is called animal husbandry.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1: What precautions should be taken while spraying weedicides and why?
Answer: Spraying of weedicides may affect the health of farmers. So they should use these chemicals very carefully. They should cover their nose and mouth with a piece of cloth during spraying of these chemicals.
Question 2: Explain in detail the structure and use of hoe.
Answer: It is a simple tool which is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil. It has a long rod of wood or iron. A strong, broad and bent plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and works like a blade. It is pulled by animals.
Question 3: What are fertilisers? Give some examples.
Answer: Fertilisers are chemical substances which are rich in a particular nutrient. Some examples of fertilisers are— urea, ammonium sulphate, super phosphate, potash, NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium).
Question 4: Why appropriate distance between the seeds is important?
Answer: An appropriate distance between the seeds is important to avoid overcrowding of plants. This allows plants to get sufficient sunlight, nutrients and water from the soil.
Question 5: Why earthworms and microbes are called friends of farmer?
Answer: The loosened soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil. These organisms are friends of the farmer since they further turn and loosen the soil and add humus to it.
Question 6: What are kharif crops?
Answer: The crops which are sown in the rainy season are called kharif crops. The rainy season in India is generally from June to September. Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton, etc., are kharif crops.
Question 7: What are rabi crops?
Answer: The crops grown in the winter season are called rabi crops. Their time period is generally from October to March. Examples of rabi crops are wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed.
Question 8: Why do farmers add manure to the soil?
Answer: Continuous growing of crops makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients. Therefore, farmers have to add manure to the fields to replenish the soil with nutrients.
Question 9: What will happen if field is not ploughed before sowing the seeds?
Answer: Disadvantage of not ploughing the field are:
- Seeds cannot be sown at proper depth.
- Water and air holding capacity of soil will be poor.
Question 10: What is called a crop?
Answer: When plants of the same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. For example, crop of wheat means that all the plants grown in a field are that of wheat.
Question 11: What is seed drill?
Answer: This tool sows the seeds uniformly at proper distances and depths. It ensures that seeds get covered by the soil after sowing. This prevents damage caused by birds. Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour.
Question 12: Why traditional methods of irrigation are cheaper, but less efficient?
Answer: The water available in wells, lakes and canals is lifted up by different methods in different regions, for taking it to the fields. Cattle or human labour is used in these methods. So, these methods are cheaper, but less efficient.
Question 13: How can we separate good, healthy seeds from the damaged ones?
Answer: Take a beaker and fill half of it with water. Put a handful of wheat seeds and stir well. Wait for some time. Are there seeds which float on water? Seeds that float on water are the damaged ones. Damaged seeds become hollow and are thus lighter. Therefore, they float on water.
Question 14: What are the advantages of drip system of irrigation?
Answer: Advantages of drip system of irrigation are:
- It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees.
- The system provides water to plants drop by drop. Water is not wasted at all.
- It is a boon in regions where availability of water is poor.
Question 15: How is turning and loosening of soil important for cultivation of crops?
Answer: Since only a few centimetres of the top layer of soil supports plant growth, turning and loosening of soil brings the nutrient-rich soil to the top so that plants can use these nutrients. Thus, turning and loosening of soil is very important for cultivation of crops.
Question 16: Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer: Continuous plantation of crops in a field makes the soil deficient in certain nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc. These nutrients are essential for the growth of plants. As such soil does not get time to replenish the lost nutrients, the crop yield decreases automatically.
Question 17: What are the traditional methods of irrigation?
Answer: The various traditional ways are:
- moat (pulley-system)
- dhekli, and
- rahat (Lever system)
Question 18: Why it is necessary to remove weeds? Or Why is weeding necessary?
Answer: The removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light. Thus, they affect the growth of the crop. Some weeds interfere even in harvesting and may be poisonous for animals and human beings.
Question 19: What is manure and how is it prepared? Or How is organic manure obtained?
Answer: Manure is an organic substance obtained from the decomposition of plant or animal wastes. Farmers dump plant and animal waste in pits at open places and allow it to decompose. The decomposition is caused by some microorganisms. The decomposed matter is used as organic manure.
Question 20: Why is water essential for plant? Discuss.
Answer: Water is essential because germination of seeds does not take place under dry conditions. Nutrients dissolved in water get transported to each part of the plant. Water also protects the crop from both frost and hot air currents. To maintain the moisture of the soil for healthy crop growth, fields have to be watered regularly.
Question 21: What are the characteristics of good quality seeds?
Answer: Following are the characteristics of a good quality seed:
- It should be clean.
- It should be healthy and of good variety.
- It should have high yield.
- It should be disease resistant.
Question 22: Why is it necessary to dry the harvested food grains before storage?
Answer: The fresh crop has more moisture. If freshly harvested grains (seeds) are stored without drying, they may get spoilt or attacked by organisms, losing their germination capacity. Hence, before storing them, the grains are properly dried in the sun to reduce the moisture in them. This prevents the attack by insect pests, bacteria and fungi.
Question 23: Why drilling is the best method for sowing of seeds? Or Explain the method used these days to sow seeds.
Answer: Nowadays the seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. Seed drill sows the seeds uniformly at proper distances and depths. It ensures that seeds get covered by the soil after sowing. This prevents damage caused by birds. Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour. Hence, it is considered as the best method for sowing of seeds.
Question 24: What are the advantages of sprinkler system of irrigation?
Answer: Advantages of sprinkler system of irrigation
- This system is more useful on the uneven land where sufficient water is not available.
- Water gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining.
- Sprinkler is very useful for sandy soil.
- Water is also distributed more evenly across crops helping to avoid wastage.
Question 25: What are the steps involved in agricultural practices?
Answer: Steps involved in agricultural practices are:
- Preparation of soil
- Adding manure and fertilisers
- Protecting from weeds
Question 26: Why organic manure is considered better than fertilisers? Or What are the advantages of organic manure?
Answer: The organic manure is considered better than fertilisers. This is because
- It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.
- It makes the soil porous due to which exchange of gases becomes easy.
- It increases the number of friendly microbes.
- It improves the texture of the soil.
Question 27: If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer: Wheat is a rabi crop and grown in the winter season. Their time period is generally from October to March. It needs a cool, dry, and clear climate for better growth and yield. Kharif season is generally from June to September. Kharif crops require a huge amount of water and hot weather to grow. If wheat is grown in Kharif season it will be affected adversely as hot and humid climate is not ideal for the cultivation of wheat.
Question 25: Name the three tools used for ploughing. Write function of each.
Answer: Tools used for ploughing are:
Plough: This is being used since ancient times for tilling the soil, adding fertilisers to the crop, removing the weeds, scraping of soil, etc.
Hoe: It is a simple tool that is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil.
Cultivator: Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor driven cultivator. The use of cultivators saves labour and time.
Question 26: Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer: Difference between fertilisers and manure
Question 27: How a plough works?
Answer: Plough is used for tilling the soil, adding fertilisers to the crop, removing the weeds, scraping of soil, etc. This implement is made of wood and is drawn by a pair of bulls or other animals (horses, camels, etc.). It contains a strong triangular iron strip called ploughshare. The main part of the plough is a long log of wood which is called a ploughshaft. There is a handle at one end of the shaft. The other end is attached to a beam which is placed on the bulls’ necks. One pair of bulls and a man can easily operate the plough.
Question 28: What are weeds? How can we control them?
Answer: In a field many other undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds. Weeds can be controlled in the following ways:
- Tilling before sowing of crops helps in uprooting and killing of weeds.
- The manual removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time. This is done with the help of a khurpi. A seed drill is also used to uproot weeds.
- Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides, like 2,4-D. These are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds.
Question 28: What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer: The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation.
Sprinkler System: This system is more useful on the uneven land where sufficient water is not available. The perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. When water is allowed to flow through the main pipe under pressure with the help of a pump, it escapes from the rotating nozzles. It gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining. Sprinkler is very useful for sandy soil.
Drip system: In this system, the water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. So, it is called drip system. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees. The system provides water to plants drop by drop. Water is not wasted at all.
Question 29: Why is tilling of soil important? Or Why is turning and loosening of soil important? Or Give any three advantages of ploughing.
Answer: Importance of tilling are as follows:
- This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. The loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep into the soil.
- The loosened soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil. They further turn and loosen the soil and add humus to it.
- This brings the nutrient-rich soil to the top so that plants can use these nutrients.
Question 30: Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil (b) Sowing (c) Weeding (d) Threshing
Answer: (a) Preparation of soil
- The preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop.
- One of the most important tasks in agriculture is to turn the soil and loosen it. This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing. This is done by using a plough.
- The ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs. It is necessary to break these crumbs with a plank.
- The field is levelled for sowing as well as for irrigation purposes. The levelling of soil is done with the help of a leveller.
- Sometimes, manure is added to the soil before tilling. This helps in proper mixing of manure with soil. The soil is watered before sowing.
(b) Sowing
- Sowing is the most important part of crop production. Before sowing, good quality seeds are selected.
- The tool used traditionally for sowing seeds is shaped like a funnel. The seeds are filled into the funnel, passed down through two or three pipes having sharp ends. These ends pierce into the soil and place seeds there.
- Nowadays the seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. This tool sows the seeds uniformly at proper distances and depths. It ensures that seeds get covered by the soil after sowing. This prevents damage caused by birds. Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour.
(c) Weeding
- The removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light.
- Farmers adopt many ways to remove weeds and control their growth. Tilling before sowing of crops helps in uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil.
- The best time for the removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds.
- The manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time. This is done with the help of a khurpi. A seed drill is also used to uproot weeds.
(d) Threshing
In the harvested crop, the grain seeds need to be separated from the chaff. This process is called threshing. This is carried out with the help of a machine called ‘combine’ which is in fact a combined harvester and thresher.
At Study Path, you can also learn more about Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management by accessing the free exhaustive list of study materials and resources related to the chapter such as NCERT Solutions, Notes, Important Questions, and MCQ.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answers

CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter wise Important Questions - Free PDF Download
Class 8 Science is a very crucial subject that needs proper attention from the students. Preparing all the chapters in this subject will help students to boost their overall scores in the exams. This is where students will need the assistance of Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answers PDF for all chapters. Apart from the exercises, these important questions can boost the preparation of the students. The experts have solved all these questions to assist in preparing this subject properly.
If you are currently studying in Class 8 , consider it one of your school life milestones as you start entering into in-depth studies related to Science. You need to solve Class 8 Science’s important questions apart from studying the Science book in such a scenario. You can expect your syllabus to comprise different aspects of scientific studies. The question papers with the solution can be the best support for those who are weak in Science or fear facing the challenge of learning complicated concepts of higher-level Science. The NCERT Class 8 Science important questions and their CBSE solutions can act as the students’ study materials.
You can also download NCERT Solution for Class 8 Science and Class 8 Maths to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Note: ➤ Predict your NEET rank effortlessly with our NEET Rank Predictor 2024 !
Download CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answers 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions for chapter-wise PDF for other chapters:
Chapterwise Important Questions for CBSE Class 8 Science
Class 8 Science: Chapter-wise Important Questions
Chapters included in class 8 science ncert book.
As a student, you must know about the chapters included in the Science book of Class 8 NCERT Science book . Moreover, the relevance of some chapters in their everyday life is given here in brief:
Microorganisms: While studying the chapter on microorganisms, you will acquire knowledge regarding life under a microscope. Moreover, here you will understand which are friendly to us and the ones which are not.
Materials and Their Nature: The chapter dealing with materials and their nature is covered in one of the chapters of the Science book. You can read the book and refer to the study materials of Vedantu to understand all about the matter in detail.
Light: A chapter in the Science book for Class 8 deals with the concepts of light. You can understand how light travels and how you can split and converge white light. In the Science book, you can also find the basic experiments that you can do with light. The NCERT Class 8 Science important questions with answers come from this chapter.
Coal and Petroleum: While studying the chapter coal and petroleum, you can know about the mines and get a clear picture of how a mine works. Moreover, you can also know the places in India where the mines are found. The information about the revenue earned by the country from the coal mines is also mentioned in the chapter.
Sound: Sound is another most important chapter which you can study in detail with the NCERT Science book of Class 8. There are different experiments that you can know about from the book. Expect to learn the numerics related to the chapter also.
So, it is clear that the Science book of Class 8 has a combination of the chapters that belong to its main streams like Chemistry, Physics, and Biology.
Solved Examples
Q1. What is the Difference Between a Virus from Other Organisms?
Answer: The main difference between all other microorganisms from a virus is that it grows inside a host cell. All other unicellular organisms grow independently.
Q2. What are the Types of Reproductions that Occur in Living Organisms?
Answer: In all living organisms, there are two types of reproduction such as asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction mainly happens in lower class organisms, where the higher ones reproduce sexually.
Significance of CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answers PDF
There are 18 chapters included in the Class 8 Science syllabus that covers vivid topics related to pollution, astronomy, light, natural phenomena, sound, force, friction, etc. These chapters need the highest attention from the students to complete preparing the syllabus. To reinforce the concepts and scientific principles, students can use the Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answers for all chapters.
Class 8 Science Term 2 Important Questions with Solutions have been compiled by following the latest CBSE syllabus to cover all the essential topics in the chapters. These questions are formulated by following the question patterns and formats of the CBSE board . In fact, the solutions are framed in a more straightforward tone so that students can easily comprehend the context behind the questions and can relate to the answers.
These Important Questions for the Class 8 Science Board Exam can be used as an evaluation tool by the students. They can solve the questions once the chapters are completed and compare their answers to the solutions. This way, they can spot the gaps in the preparations and focus on the important sections of the chapters further.
Advantages of CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answers for Board Exam
The questions have been compiled for individual chapters. Hence, the list contains separate files dedicated to all the chapters. It will become easier for the students to find the files and add them to their practice sessions.
The solutions provided with the questions are framed in a comprehensive way so that students can memorize them easily and recall them during the exams to score more.
Resolving doubts will be much easier when you have the Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answers PDF in your hands. Refer to the solutions and clarify your queries instantly to proceed with your preparation.
Follow the standard answering format of the solutions to keep your answers at par with the CBSE Class 8 standards and score more.
CBSE Class 8 Science Study Materials
Other cbse class 8 important questions related links.
The Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answers provided by Vedantu offer valuable insights in simple language. These resources aim to enhance understanding and retention of key scientific concepts among students. By presenting essential questions and providing clear, concise answers, Vedantu helps learners grasp fundamental principles effectively. The emphasis on simplicity ensures that students can easily comprehend complex topics, fostering a strong foundation in science.
Get the free PDF version of these questions and solutions for all the chapters. Practice answering these questions and develop your concepts better. Learn how to attempt to answer such fundamental questions by following the solutions and gaining confidence to stay ahead of the competition.

FAQs on Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answers
1. What is the relevance of practising extra questions of Class 8 Science?
Ans: You can enjoy a lot of perks while solving more questions that are generally available on the Vedantu website. It can help you write different answers for a common question as per the right concept that can fetch good marks. The best you can do is consult with the experts of Vedantu and go through the papers available on their site. Moreover, the Vedantu question papers can help you to revise a chapter after completion. Mostly, you can enhance the language and presentation style of the answers while solving the papers. Make sure to draw the diagrams wherever needed as it can boost up the chances of getting marks.
2. Why is it important to find CBSE question papers for preparing a Science chapter, and where can we get them?
Ans: You should always get the CBSE question papers for solving as it can help you know the examination pattern. So, you can get questions in a familiar language while facing the examination. You can visit the site of Vedantu and get all the question papers. There are links where you can click and see the questions based on years. Remember to pick up random question papers from the Vedantu site and solve it multiple times in the intervals of short periods. Access to the question papers is free and you can easily download the pdf versions from the site.
3. What are the chapters included in the NCERT book of Class 8 Science?
Ans: The NCERT book of Class 8 Science consists of the following chapters:
Chapter 1–Crop Production and Management
Chapter 2 –Microorganisms: Friend or Foe
Chapter 3–Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
Chapter 4–Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
Chapter 5–Coal and Petroleum
Chapter 6–Combustion and Flame
Chapter 7–Conservation of Animals and Plants
Chapter 8 - Cell- Functions and Structure
Chapter 9–Reproduction in Animals
Chapter 10–Reaching the Age of Adolescence
Chapter 11–Force and Pressure
Chapter 12–Friction
Chapter 13–Sound
Chapter 14–Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentChapter 15–Some Natural Phenomena
Chapter 16 - Light
Chapter 17–Star and The Solar System
Chapter 18–Pollution of Water and Air
4. How can I develop the best study plan for Class 8 Science?
Ans: To develop the best study plan for Class 8 Science obey the given points:
Managing time is very important. Therefore, create a timetable so that you can focus on every chapter.
Use the NCERT book for reading the chapters as the content of the book is prepared by professionals.
Take the help of Vedantu’s website for downloading the important questions of all the chapters.
Work out on the sample papers and previous years question papers to have a strong grip on the topics.
5. What is the method that students follow to download the important questions of Class 8 Science?
Ans: Beneath are the steps that will be helpful in downloading the important questions of Class 8 Science:
Visit the link of Important Questions for CBSE Class 8 Science, Chapter wise Solutions - Free PDF Download.
As the link will open, the official page of Vedantu will appear on the screen of your device.
This official page will provide you with the list of the chapters of Class 8 Science.
Select the chapter you want to download for the important questions.
Then hit on the “Download PDF” option.
The important questions will get downloaded in PDF format.
6. What are the benefits of downloading and studying important questions of Class 8 Science from Vedantu?
Ans: The perks of studying or downloading important questions of Class 8 Science from Vedantu are:
The content is prepared by the subject matter experts.
Important questions of all the chapters are available.
These problems are based on the NCERT syllabus.
Vedantu allows you to study offline by giving the option to download the important questions.
These important questions are available in the form of PDF files. These solutions are available at free of cost on Vedantu(vedantu.com) and mobile app.
Vedantu also allows you to ask your doubts through online chat.
7. How to achieve good results in Class 8 Science?
Ans: Below are the points which will help students in getting a good result in Class 8 Science:
To start with your preparation, first know about your syllabus.
Study every chapter from the NCERT book.
Make use of mock tests and previous years sample papers to get a hint about the exam pattern.
Have a habit of writing. This will improve your writing speed and help you to learn things faster.
While giving the exam, try to solve those questions first whose answer you know.
8. What is the most important chapter in science class 8?
Cell Structure and Function: This lays the groundwork for understanding living organisms.
Chemical Reactions and Equations: Understanding chemical reactions is crucial for various scientific concepts.
Light: This chapter forms the basis for understanding optics and other phenomena.
9. How to get 100 marks in science class 8?
While aiming for a perfect score is commendable, the focus should be on thorough understanding rather than just marks. However, here are some tips that might help:
Grasp concepts deeply: Don't just memorize facts, strive to understand the "why" behind them.
Practice consistently: Regularly solve problems, answer practice questions, and revise concepts.
Pay attention in class: Actively participate, ask questions, and clarify doubts with your teacher.
Manage time effectively: Create a study plan, schedule revisions, and avoid last-minute cramming.
10. Class 8 is very important?
Class 8 acts as a bridge between the foundational concepts learned in earlier grades and the more complex topics introduced in higher classes. It's crucial for building a strong foundation in Science and other subjects.
11. How to top in science exam class 8?
While "topping" isn't the only measure of success, here are some strategies:
Follow the tips mentioned above to get high marks.
Focus on understanding the exam format and marking scheme.
Practice mock tests and previous year papers to manage time and get familiar with the question pattern.
Seek help from teachers or tutors if you face any difficulties.
Important Questions for CBSE Class 8
Cbse class 8 study materials, home tuitions in india.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
CBSE Class 8th Science Value Based Questions PDF Download
Free pdf download.
SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
CBSE Class 8th Science Value Based Questions are the easiest questions which you see in your question paper and the scoring one all student who attempt it surely get they are just little bit difficult and examine your basic knowledge regarding the particular chapter. Science Value Based Questions for Class 8th are available here at Free of cost. These questions are expected to be asked in the Class 8th board examination. These Science Value Based Questions are from complete CBSE Syllabus.
CBSE Class 8th Science Value Based Questions

Most of these Science Value Based Questions are quite easy and students need only a basic knowledge of the chapter to answer these questions. Download CBSE Science Value Based Questions for board examinations. These Science Value Based Questions are prepared by Directorate of Education, Delhi.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions Class 8th PDF
The purpose of the Science Value Based Questions is to make students aware of how basic values are needed in the analysis of different situations and how students require to recognize those values in their daily lives. Some questions are subject related. But even if they are not, that one-minute awareness of what we write about value without any specific preparation is a good step indeed.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions for Class 8th download here in PDF format. The most CBSE Science Value Based Questions for annual examination are given here for free of cost. The additional questions for practice the Class 8th exam are collected from various sources. It covers questions asked in previous year examinations.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions for Class 8th Free PDF
Class 8th books have many questions. These questions are regularly asked in exams in one or other way. Practising such most CBSE Science Value Based Questions certainly help students to obtain good marks in the examinations.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 8 Science Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
Case study questions class 8 science chapter 2 microorganisms: friend and foe.
CBSE Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Microorganisms: Friend and Foe. Important Case Study Questions for Class 8 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 8 Science Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
Case study 1.
You have seen several kinds ofplants and animals. However,there are other living organismsaround us which we normally cannotsee. These are called microorganismsor microbes. For example, you mighthave observed that during the rainyseason moist bread gets spoilt and itssurface gets covered with greyish whitepatches. Observe these patches througha magnifying glass. You will see tiny,black rounded structures. Do you knowwhat these structures are and where dothese come from? Waterand soil are full of tiny organisms,though not all of them fall into thecategoryofmicrobes.Thesemicroorganisms or microbes are sosmall in size that they cannot be seenwith the unaided eye. Some of these,such as the fungus that grows on bread,can be seen with a magnifying glass.Others cannot be seen without the helpof a microscope. That is why these arecalled microorganisms or microbes.Microorganisms are classified intofour major groups. These groups arebacteria, fungi, protozoa and somealgae. Viruses are also microscopic but aredifferent from other microorganisms.They, however, reproduce only inside thecells of the host organism, which may bea bacterium, plant or animal. Commonailments like cold, influenza (flu) andmost coughs are caused by viruses.Serious diseases like polio and chickenpox are also caused by viruses.Diseases like dysentery and malariaare caused by protozoa(protozoans)whereas typhoid and tuberculosis (TB)are bacterial diseases.You have learnt about some ofthese microorganisms in Classes VIand VII.Microorganisms may be single-celledlike bacteria, some algae and protozoa,or multicellular, such as many algae andfungi. They live in all types of environments, ranging from ice coldclimate to hot springs; and deserts tomarshy lands. They are also foundinside the bodies of animals includinghumans. Some microorganismsgrow on other organisms while othersexist freely.
Que. 1) ……………………………………………………………………………. only reproduce inside the cells of host organisms like bacteria, plants or animals.
(a) Microbes
(b) Viruses
(d) Bacillus
Que. 2) Which among the following is an example of disease caused by bacteria?
(b) Malaria
(c) Tuberculosis
(d) Covid 19
Que. 3) During rainy season moist bread gets spoilt and are covered with greyish white patches. What are these greyish white patches?
(a) Bacteria
Que. 4) Define microorganisms and state its major groups of classification.
Que. 5) Explain in detail where are microorganisms commonly found.
Que. 1) (b) Viruses
Que. 2) (c) Tuberculosis
Que. 3) (d) Fungus
Que. 4) Answer: Microorganisms are tiny living organisms that cannot be seen with our naked eyes. Microorganisms are classified into four major groups namely bacteria, fungi, protozoa and some algae.
Que. 5) Answer: Microorganisms are present in all types of environments ranging from ice cold climate to hot springs, deserts and marshy lands. They can also be seen inside the bodies of animals. Some microorganisms exist freely and some grow on other organisms.
Case study 2
Microorganisms are used for variouspurposes. They are used in thepreparation of curd, bread and cake.Microorganisms have been used forthe production of alcohol since ages.They are also used in cleaning upof the environment. For example, theorganic wastes (vegetable peels, remainsof animals, faeces, etc.) are brokendown into harmless and usablesubstances by bacteria. Recall thatbacteria are also used in thepreparation of medicines. In agriculturethey are used to increase soil fertilityby fixing nitrogen.You have learnt in Class VII that milk isturned into curd by bacteria.Curd contains several micro-organisms. Of these, the bacterium,Lactobacillus promotes the formationof curd. It multiplies in milk andconverts it into curd. Bacteria are alsoinvolved in the making of cheese,pickles and many other food items. Animportant ingredient of rava (sooji )idlis and bhaturas is curd. Can youguess why? Bacteria and yeast are alsohelpful for fermentation of rice idlisand dosa batter. Kneading of Yeast and sugar into the flour causes the flour to rise and double in size. Yeast reproduces rapidly andproduces carbon dioxide duringrespiration. Bubbles of the gas fill thedough and increase its volume.This is the basis of the use of yeast inthe baking industry for making breads,pastries and cakes.Commercial Use of Microorganisms:Microorganisms are used for the large-scale production of alcohol, wine and acetic acid(vinegar).
Yeast is used for commercialproduction of alcohol and wine. For this purpose, yeast is grown on natural sugarspresent in grains like barley, wheat, rice,crushed fruit juices, etc. Adding a spoon full of yeast powder into sugar solution gives out a characteristic smell after few hours.This is the smell of alcohol as sugarhas been converted into alcohol by yeast.This process of conversion of sugar intoalcohol is known as fermentation.Louis Pasteurdiscoveredfermentationin 1857.
Que. 1) In the process of fermentation the sugar is converted into …………………………………………………………………………………………. .
(a) Vinegar
(d) Alcohol
Que. 2) Name the bacterium which when added to milk, multiplies in it and converts milk into curd?
(a) Lactobacillus
(b) Streptococcus
(c) Salmonella
Que. 3) Louis Pasteur a French chemist in 1857 discovered the process of ……………………………………………………………………………………. ?
(a) Fermentation
(b) Pollination
(c) Saturation
(d) Composting
Que. 4) Explain the process of doubling of flour after addition of yeast into it.
Que. 5) Name some of the common uses of microorganisms.
Que. 1) (d) Alcohol
Que. 2) (a) Lactobacillus
Que. 3) (a) Fermentation
Que. 4) Answer: After adding yeast and sugar into the flour, the yeast reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of gas fill the dough and hence the volume of dough is doubled in size.
Que. 5) Answer: Microorganisms are useful in various purposes like in the preparation of curd, bread and cake. It is used in the production of alcohol as well as medicines. These are also used to increase the fertility of soil.
Case study 3
Whenever you fall ill the doctor may give you some antibiotic tablets, capsules or injections such as of penicillin. The source of these medicines is microorganisms. These medicines kill or stop the growth of the disease-causing microorganisms. Such medicines are called antibiotics. These days a number of antibiotics are being produced from bacteria and fungi. Streptomycin, tetracycline and erythromycin are some of thecommonly known antibiotics which are made from fungi and bacteria. The antibiotics are manufactured by growing specific microorganisms and are used to cure a variety of diseases. Antibiotics are even mixed with the feed of livestock and poultry to check microbial infection in animals. They are also used to control many plant diseases.In 1929, Alexander Fleming was working on a culture of disease- causing bacteria. Suddenly he found the spores of a little green mould in one of his culture plates. He observed that the presence of mould prevented the growth of bacteria. In fact, it also killed many of these bacteria. From this the mould penicillin was prepared.When a disease-carrying microbe enters our body, the body produces antibodies to fight the invader. The body also remembers how to fight the microbe if it enters again. If dead or weakened microbes are introduced into a healthy body, the body fights and kills the invading bacteria by producing suitable antibodies. The antibodies remain in the body and we are protected from the disease-causing microbes for ever. This is how a vaccine works. Several diseases, including cholera, tuberculosis, smallpox and hepatitis can be prevented by vaccination.Edward Jenner discovered the vaccine for small- pox in 1798.In your childhood, you must have been given injections to protect yourself against several diseases. Can you prepare a list of these diseases? You may take help from your parents.
It is essential to protect all children against these diseases. Necessary vaccines are available in the nearby hospitals. You might have seen the advertisement on TV and newspapers regarding protection of children against polio under the Pulse Polio Programme. Polio drops given to children are actually a vaccine. A worldwide campaign against smallpox has finally led to its eradication from most parts of the world. These days vaccines are made on a large scale from microorganisms to protect humans and other animals from several diseases.
Que. 1) Which among the following scientist discovered the vaccine for Small pox in 1798?
(a) Edward Jenner
(b) Alexander Fleming
(c) Carl Linnaeus
(d) Rosalind Franklin
Que. 2) When a disease carrying microbe enters our body, the body produces ……………………………………………………………………………… to fight against it.
(a) Soldiers
(b) Antibodies
(c) Viruses
(d) Bacteria
Que. 3) In which year did Alexander Fleming a Scottish Physician discover penicillin?
Que. 4) Define antibiotics and give their uses.
Que. 5) Name some of the diseases that can be prevented by taking vaccination.
Que. 1) (a) Edward Jenner
Que. 2) (b) Antibodies
Que. 3) (d) 1929
Que. 4) Answer: Antibiotics are medicines produced from microorganisms that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms. Some common examples include Streptomycin, Tetracycline and erythromycin. They are used to cure a variety of human and plant diseases and also to check microbial infection in animals.
Que. 5) Answer: Some diseases that can be prevented by taking vaccination are Cholera, tuberculosis, smallpox, and hepatitis.
Case study 4
Microorganisms are harmful in manyways. Some of the microorganismscause diseases in human beings, plantsand animals. Such disease-causing microorganisms are called pathogens.Some microorganisms spoil food,clothing and leather. Let us study moreabout their harmful activities.Pathogens enter our body through theair we breathe, the water we drink orthe food we eat. They can also gettransmitted by direct contact with aninfected person or carried by an animal.Microbial diseases that can spread froman infected person to a healthy personthrough air, water, food or physicalcontact are called communicablediseases. Examples of such diseasesinclude cholera, common cold, chickenpox and tuberculosis.When a person suffering fromcommon cold sneezes, fine droplets ofmoisture carrying thousands of virusesare spread in the air. The virus may enterthe body of a healthy person whilebreathing and cause infection.There are some insects and animalswhich act as carriers of disease-causing microbes. Housefly is one suchcarrier. The flies sit on the garbage andanimal excreta. Pathogens stick to theirbodies. When these flies sit on uncoveredfood, they may transfer the pathogens.Whoever eats the contaminated food islikely to get sick. So, it is advisable toalways keep food covered. Avoidconsuming uncovered items of food.Another example of a carrier is thefemale Anopheles mosquito,which carries the parasite of malaria(Plasmodium). Female Aedes mosquitoacts as carrier of dengue virus.How can we control the spread of malariaor dengue?All mosquitoes breed in water. Hence,one should not let water collectanywhere, in coolers, tyres, flower pot,etc. By keeping the surroundings cleanand dry we can prevent mosquitoes frombreeding. Try to make a list of measureswhich help to avoid the spread ofmalaria.Several microorganisms not only causediseases in humans and plants, but alsoin other animals. For example, anthraxis a dangerous human and cattledisease caused by a bacterium. Footand mouth disease of cattle is causedby a virus.RobertKöch(1876)discovered the bacterium(Bacillus anthracis) whichcauses anthrax disease.Severalmicroorganismscausediseases in plants like wheat, rice, potato,sugarcane, orange, apple and others.The diseases reduce the yield of crops. They can be controlled by theuse of certain chemicals which kill themicrobes.
Que. 1) Disease causing microorganisms are called as …………………………………………………………………………………………. .
(a) Antibodies
(b) Macrophages
(c) Pathogens
(d) Eosinophils
Que. 2) Which among the following insect acts as the carrier of dengue virus?
(a) Female Anopheles
(b) Female Aedes
(c) Female Culex
(d) Ochlerotatus
Que. 3) Robert Koch in 1876 discovered the bacterium (Bacillus anthracis) which causes …………………………………………………………………………………….. disease.
(a) Anthrax
(c) Chikungunya
(d) Cholera
Que. 4) Define the term “communicable diseases” with some examples.
Que. 5) How can we control the spread of diseases caused by mosquitoes?
Que. 1) (c) Pathogens
Que. 2) (b) Female Aedes
Que. 3) (a) Anthrax
Que. 4) Answer: Microbial diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person through air, water, food or physical contact are called communicable diseases. Cholera, common cold, chicken pox, and tuberculosis are some of the examples.
Que. 5) Answer: Breeding of mosquitoes occur in water. Therefore, by not letting water to collect in our surroundings like in coolers, tyres, flower pot, etc and keeping the surrounding clean and dry, we can control the spread of such diseases.
Case study 5
How do we preserve cooked foodat home? You know that bread leftunused under moist conditions isattacked by fungus. Microorganismsspoil our food. Spoiled food emits badsmell and has a bad taste and changedcolour. Is spoiling of food a chemicalreaction?Paheli bought some mangoes but shecould not eat them for a few days. Latershe found that they were spoilt androtten. But she knows that the mango picklesthat her grandmother makes does notspoil for a long time. She is confused.Let us study the common methodsof preserving food in our homes. Wehave to save it from the attack ofmicroorganisms.Chemical Method:Salts and edible oils are the commonchemicals generally used to check thegrowth of microorganisms. Therefore, they are called preservatives. We addsalt or acid preservatives to pickles toprevent the attack of microbes. Sodiumbenzoate and sodium metabisulphite arecommon preservatives. These are alsoused in jams and squashes to checktheir spoilage.Preservation by Common Salt:Common salt has been used to preservemeat and fish for ages. Meat and fishare covered with dry salt to checkthe growth of bacteria. Salting is alsoused to preserve amla, raw mangoes,tamarind, etc.Preservation by Sugar:Jams, jellies and squashes are preservedby sugar. Sugar reduces the moisturecontent which inhibits the growth ofbacteria which spoil food.Preservation by Oil and Vinegar:Use of oil and vinegar prevents spoilageof pickles because bacteria cannot livein such an environment. Vegetables,fruits, fish and meat are often preservedby this method.Heat and Cold Treatments: You must have observed your motherboiling milk before it is stored or used.Boiling kills many microorganisms.Similarly, we keep our food in the refrigerator. Low temperature inhibits the growth of microbes.Pasteurised milk can be consumed without boiling as it is free from harmful microbes.
The milk is heated to about 700C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. By doing so, it prevents the growth of microbes. This process was discovered by Louis Pasteur. It is called pasteurisation. Storage and Packing: These days dry fruits and even vegetables are sold in sealed air tight packets to prevent the attack of microbes.
Que. 1) Which of the following is NOT an example of chemical method of preservation?
(b) Heating
(c) Sodium Benzoate
(d) Sodium Metabisulphite
Que. 2) ………………………………………………………………………………. of milk before storing is done to kill many microorganisms.
(b) Distilling
(d) Boiling
Que. 3) Pasteurisation technique was discovered by which of the following scientist?
(a) Louis Pasteur
(b) Fanny Hesse
(c) Ronald Ross
(d) Harold Ginsberg
Que. 4) Explain the process of Pasteurization in detail.
Que. 5) Name some of the common methods of food preservation at your home.
Que. 1) (b) Heating
Que. 2) (d) Boiling
Que. 3) (a) Louis Pasteur
Que. 4)Answer: In the pasteurisation process the milk is heated to about 700°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. This process prevents the growth of microbes.
Que. 5) Answer: Some common methods of preservation include: Adding common salt to pickles, meat and fish. Using sugar as well as oil and vinegar are also some of the preservation methods.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
West bengal board class 9 english solution chapter 8 his first flight, sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 6b the smile of the terek sandpiper solution, amader poribesh class 4 solutions chapter 4 abohawa o basosthan, sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 6d i’m climbing a mountain solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
- CBSE Notes For Class 8
- Class 8 Science Notes
- Chapter 1: Crop Production And Management
Crop Production And Management Class 8 Notes
Plants of the same kind that are grown and cultivated as a source of food in a large cultivable land is called a crop.
To know more about Crops, visit here .
Types of Crops
Crops, which are grown in the winter season (from October to March) are called Rabi crops. The crops, which are sown in the rainy season (from July to October) are called Kharif crops.
For more information on Food Production and Management, watch the below video

Preparation of Soil
- Preparation of soil is the first step in cultivating crops for food production.
- The soil is prepared for sowing the seeds of the crop.
- This is carried out using various processes and tools.
To know more about Agriculture Soil Formation and Preparation, visit here .
For more information on Farming, watch the below video
Tilling or Ploughing
The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing and is done by using a plough.
- A plough is a device that is used by farmers for different purposes, such as adding fertilizers, tilling and loosening the soil.
- It is also used for adding fertilizers to the soil, removing weeds, scraping of soil, etc.
- The ploughshare is the triangular iron strip.
- A ploughshaft is the main part of the plough, which is made using a log of wood.
- The other end of the shaft has a handle.
- The other end is attached to a beam which is placed on the bull’s neck.
- A wooden, traditional plough can be operated by a pair of ox and a man.
- Nowadays, these wooden ploughs are being replaced by iron ploughs.
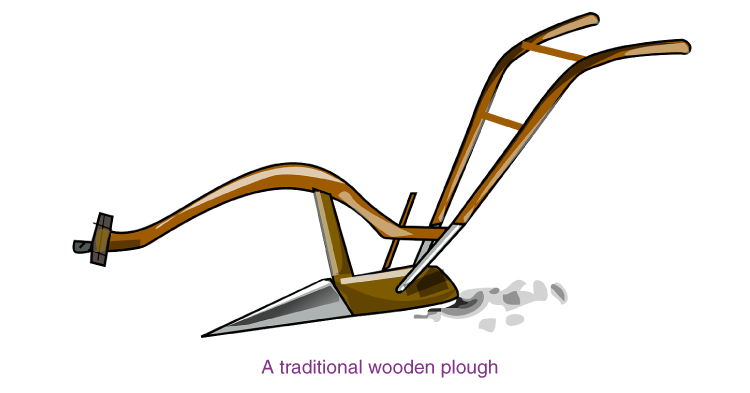
- A cultivator is attached to the tractor and helps in loosening soil.
- Cultivators are used instead of ploughs since they are faster.

For more information on Irrigation, watch the below video

- Sowing is the process of planting seeds in the soil.
- The seeds are sowed in the soil that is loosened by a cultivator or plough.
To know more about Sowing, visit here .
Quality of the Seeds
- The quality of the seed is an important factor that determines the crop yield.
- The selection of good seeds is done by putting the seeds in water.
- The dead and damaged seeds become hollow and float on water, whereas the good seeds sink.
To know more about Selection and Sowing of Seeds, visit here .
Traditional Tools
- Before the advent of modern agricultural machinery, traditional tools were used by farmers.
- These include ploughs, shovels, scythes and pickaxes.
- The traditional tool used to sow the seeds was like a funnel.
- Once seeds were put into this funnel, they would go into 2-3 tubes having sharp ends.
- The ends will pierce into the soil and place the seeds there.
- Seed drills are used for sowing with the help of tractors.
- It ensures that seeds are sown uniformly, at a particular depth and are covered by soil after sowing.
- A nursery is a place where young plants and trees are grown for planting elsewhere.
- Nursery acts as a repository of saplings.
Germination of Seeds
- Germination of the seed happens when the seed is sown in the land and watered.
- A plant starts to emerge from the seed and starts to grow.
Adding Manure and Fertilisers
Manure/fertilizers.
- Manures and fertilizers are substances that are added to the soil to increase its fertility.
- Manures are made by decomposition of organic substances, and fertilizers are made of inorganic chemicals.
Differences between Manure and Fertilizers
To know more about Manure and Fertilizer, visit here .
Disadvantages of Using Fertilizers
- Excessive use of fertiliser can cause pollution.
- It can also change the pH of the soil in certain rare cases.
Leaving the Land Fallow
- When land is left fallow for a certain period of time, the land replenishes its nutrients by itself.
- This land can be used for agriculture again.
Crop Rotation
- Crop rotation ensures that the same crop will not grow continuously and lead to the erosion of soil fertility.
- By growing crops that require different sets of nutrients, we can ensure that soil fertility is restored.
Protecting from Weeds
Weeds are undesirable plants that may grow naturally along with the crop.
- Weeds compete with the crops by absorbing all the water, nutrients, space and light.
To know more about Weeds, visit here .
- Tilling is a process done before sowing of crops that helps in uprooting and killing weeds.
Manual Removal
- Manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by uprooting them from the soil or chopping them off to ground level periodically.
- Chemicals used to kill the weeds are known as weedicides.
- They usually don’t damage the crop.
- Harvesting is the process of cutting the crop after it is mature.
Methods of Harvesting
- Harvesting is done by two methods.
- First is the manual method, where a sickle is used.
- Second is the mechanical method, where a huge machine called a harvester is used.
- Threshing is the process of loosening the grains from the chaff.
- While it can be done manually, a machine is used that separates all the grain seeds these days.

To know more about Threshing, visit here .
- Winnowing is the process that separates grain seeds from the chaff using the help of the wind.
- Due to the wind, the lighter chaff flies away, and the heavier grains fall down.
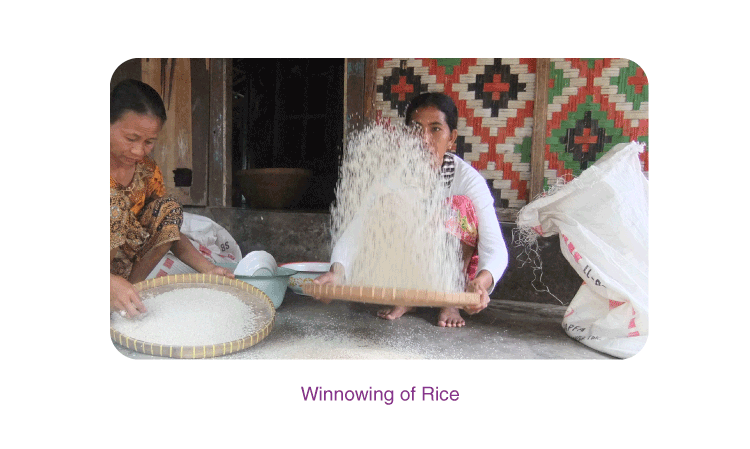

To know more about Winnowing, visit here .
- Storage of the grains is an important step in agriculture.
- After harvesting steps, the ready grains are stored in granaries or silos.
- The grains have to be stored in a dry place that does not have a rodent or fungal infestation.
- Fumigation of storage places is carried out to make it free from microbes.
- Granaries are the place where freshly obtained food grains are stored.
To know more about Storage of Grains, visit here .
Animal Husbandry
- Animal husbandry is the management and care of farm animals for milk, egg or meat.
To know more about Animal Husbandry, visit here .
At BYJU’S, learn more about crop production and management and other related topics, including class 8 Science notes .
Also Read:-
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
What are the different types of irrigation methods.
The four main types of irrigation are Surface, Sprinkler, Drip and Subsurface.
What are biofertilizers?
Biofertilizers are living microbes that enhance plant nutrition by either mobilizing or increasing nutrient availability in soils. Various microbial taxa, including beneficial bacteria and fungi are currently used as biofertilizers, as they successfully colonize the rhizosphere, rhizoplane or root interior.
What is animal husbandry?
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk or other dairy products.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Helped me a lot
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Here we are providing case study questions for CBSE Class 8 science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management. Case Study Questions Question 1: A boy named Yash from Gwalior who studies in 8th standard is very fond of plants. He has a small … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 ...
Answer Key. Que. 1) (a) Kharif. Que. 2) (d) Mustard. Que. 3) (c) Literacy. Que. 4) Answer: When plants of same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale in order to provide food for a large population, it is called a crop. Que. 5) Answer: Rabi crops are grown in winter season mainly from October to March.
CBSE Class 8 Science Case Study Question. Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Case Study Question. Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case Study Question. Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Case Study Question. Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Question.
Case Study Questions on Crop Production and Management. Questions. Question 1: A boy named Yash from Gwalior who studies in 8th standard is very fond of plants. He has a small garden in the backyard. Where he's planted many small plants and takes good care of them.
CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter-1 Important Questions - Free PDF Download. Class 8 is very important as the preparation of the board examination starts here. The concepts that you are going to learn in class 8 is going to help you to perform well in class 9 and also in the board examination. Understanding the concepts is important.
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science NCERT Textbook Questions. Question 1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks. float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation. (a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____. (b) The first step before growing crops is ...
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Free PDF Download. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management are the most important study materials for CBSE Class 8 Science. In order to get complete knowledge of the chapter Crop Production and Management, learners should solve and practise the answers provided in this NCERT Exemplar.
The first method in crop management is soil preparation. This process is done by loosening the soil with the help of a plough which helps in ploughing or tilling it. ii. Loosening of soil particles adds humus and nutrients and increases the absorption of water and manure in the soil which increases crop yields. b.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Free PDF Download . NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management guides you with the answers to the questions given in the textbook. Class 8 is an important phase in the student's life as they are introduced to many new concepts that are essential to set strong basics for the topics to be taught later in Class 9.
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions. Question 1: Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks. float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation. (a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____________.
CBSE 8th Standard CBSE all English medium question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 8th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place
This NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science contains answers of all questions asked in Chapter 1 in textbook, Science. Therefore you can refer it to solve Crop Production and Management exercise questions and learn more about the topic. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management. Class - Class 8 Subject - Science
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Important Questions from NCERT Textbook is given below with answers. There are Extra Questions taken from the entire chapter 1 of Class 8 Science. After reading the NCERT Books, if a student go through these questions, the chapter will be prepared for school exams or final exams.
Benefits of Solving Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 1. Chapter 1 of Class 8 Science is called 'Crop Production and Management'. In this chapter, we learn about various agricultural practices in cultivating crops and managing the crops produced after the complete harvesting process. There are various interesting concepts to learn ...
The NCERT Science book class 8 solutions have been provided below: Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management. Chapter 2 - Microorganisms : Friend and Foe. Chapter 3 - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics. Chapter 4 - Materials : Metals and Non-Metals. Chapter 5 - Coal and Petroleum. Chapter 6 - Combustion and Flame. Chapter 7 ...
Answer: Sowing is the process of planting seeds in the soil. Question 11: Name two categories of crops based on season. Answer: Two categories of crop based on season are kharif and rabi crops. Question 12: What is threshing? Answer: Separation of the grains from the chaff is called threshing.
Also, check CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions for chapter-wise PDF for other chapters: CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answer PDF. Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management. Chapter 2 - Microorganisms : Friend and Foe. Chapter 3 - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics. Chapter 4 - Materials : Metals and Non-Metals.
Answer: (a) Organic farming is a form of agriculture that relies on techniques such as crop rotation, green ma-nure, compost and biological pest control. (b) Advantages of organic farming are: Do not use any harmful chemicals. Crops have better taste and nutrition. Eco-friendly.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions for Class 8th download here in PDF format. The most CBSE Science Value Based Questions for annual examination are given here for free of cost. The additional questions for practice the Class 8th exam are collected from various sources. It covers questions asked in previous year examinations.
CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Science help students face the exams confidently. As the exam nears, they should complete the syllabus and start with the revision. The CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Science will help them revise the subject quickly. Here, we have compiled the important questions for all the chapters of the CBSE Class 8 Science subject.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 8 Science Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case study 1. You have seen several kinds ofplants and ...
2024 AP Exam Dates. The 2024 AP Exams will be administered in schools over two weeks in May: May 6-10 and May 13-17. AP coordinators are responsible for notifying students when and where to report for the exams. Early testing or testing at times other than those published by College Board is not permitted under any circumstances.
Various agricultural practices required for the crop production are listed in the concise crop production and management class 8 notes. The cropping pattern followed in India and a few extra questions are also discussed in the Class 8 science chapter 1 notes.