x == (s || z). You say it kwontized

Rule of Three: advice on writing a PhD thesis
PhD students sometimes get the same bad advice on writing their thesis. I call this advice the Rule of Three . Typically, they get told that their thesis:
- Will take 3 months to write
- Should have 3 results chapters
- Should be 300 pages
These bits of advice have one thing in common: they are all wrong.
- If you have been organised (see below), it should not take 3 months to write a PhD thesis. It certainly shouldn’t involve leaving the lab 3 months before your hand-in date to write up.
- Theses can have one results chapter or they can have more. How many chapters depends on your project, and your results. Trying to make three results chapters out of one chapter ends up in a weak or overlong thesis.
- A thesis is like a piece of string and it will be as long as it needs to be. Aim for brevity and not producing a magnus opus (see below).
Disclaimer: what follows is some different advice. As with all “advice”, your mileage will vary. It is written for the people in my lab but likely applies to UK PhD students doing biomedical research.
Rule 1: aim for a thesis that is good enough
Who will read your thesis? Two people. Your examiners. OK, some parts – such as the Methods section – will be useful to future lab members (although with electronic lab notebooks this function is becoming redundant). Maybe your thesis will be downloaded by someone from the repository, but essentially, it will only be read by your examiners.
How long does an examiner spend reading your thesis? A few hours. One day maximum. They simply have no more time. Do you really want to spend three months of your life writing something that will be read for just a few hours by two people?
It’s for these reasons that spending too much effort writing a perfect thesis is a waste of time. It just needs to be good enough.
As well as being just good enough, it only needs to be long enough . A big mistake students make is to produce a really long thesis because they think that that is what theses should be (rule of 3). What happens is the examiner will receive the thesis, look at how many pages there are, subtract the bibliography, and their heart will sink if it is too long.
You might now be wondering: is writing a thesis a waste of time?
No, because you have to do it to get your PhD.
No, because you learn important writing skills. You also learn how to assemble a large document (it’s often how students learn to use Word properly or up their LaTeX game). It’s good training for writing papers and other technical documents down the line. Employers know this when they hire you.
But that is about it. So you just need to write something that is good enough to pass.
Rule 2: prioritise papers and the thesis will follow
Papers are the priority. They are more useful to you and to your PI. But this advice isn’t motivated by self-interest. If you go into the viva and the work in your thesis is already peer reviewed and published, it’s harder for the examiners to criticise it. At least, they will not approach your thesis with the question: is this work publishable? This is one criteria for passing your PhD, so demonstrating that it is publishable means you are (almost) there.
This was the one bit of advice I received when doing my PhD and it is still true today. OK, it is harder these days to get a first author paper published before you submit your thesis. However a preprint on bioRxiv before you begin writing will help you to prepare your thesis and will still tick the publishable box.
How long should it take to write your thesis?
There is tension here because you are at your most useful in the lab as you near the end of your PhD. One week of labwork now is worth one month (or more) earlier in your PhD. You are most valuable to your lab/PI/science/career at this point and keeping working in the lab will yield more rewards. But it won’t get your thesis written.
The first bit of writing is busywork and can be done around lab work. “Deep writing” and reading does need time away for most students.
If you have only collected data in the lab and not analysed it, if you’ve not presented your work very often, if you are disorganised… yes, it will take you a full three months to write your thesis.
All the folks in my lab are encouraged to get figures ready, analyse as they go and they also give regular talks. It should not take anyone in this position three months away from the lab to write their thesis.
Agreeing a timeline with your PI for when you begin writing is really important. Regular deadlines and a commitment to timely feedback from your supervisor make thesis writing easier. The discussion needs to be based on facts though. Often students want to budget a lot of time to writing, because of the rule of 3 or because they believe they are “bad at writing”. It helps to see some evidence. Writing draft chapters earlier in the PhD – which is a requirement at some universities – can reveal difficulties and weaknesses.
Reality check
If you hear the rule of 3 from everyone and your supervisor is giving you different advice. It might be time for a reality check. Have a look at past theses from the lab. How long were they? How many chapters? Information is good.
You can see that all theses are fewer than 300 pages in length, many substantially so. Four have three chapters and two have two. Although looking closer, two of the theses with three chapters use a results chapter as an expanded methods chapter.
Ultimately, the thesis is your work but you will get input from your supervisor. Regardless of what is written here or how many people tell you about the rule of 3, your supervisor will have their own ideas about how your thesis should be. Agreeing a sensible plan with them is the way to get started productively.
Getting started
This is not a comprehensive guide but in order to write a good enough thesis, you first need a plan.
- Make a figure list. This should be every single figure you can think of. You can cross off ones you don’t need later if they don’t fit or are insignificant.
- Plan the narrative. There is usually more than one way to put together the figures to make a thesis. Be prepared for this to change after you start writing! Sometimes the writing process reveals ways in which the narrative should be rearranged.
- How many results chapters? Start with the idea that you will have one. Does it need dividing? If yes, then what are the titles of the two chapters? If you have difficulty titling them you may need to split to a 3rd.
Now you have a plan. It’s time to get going.
Set some goals – but make them small. Having a goal of “I am going to complete my thesis” is too demoralising. You need to feel like you are making progress constantly to stay motivated. Break it down into smaller chunks. “I will finish this chapter by next Friday”. “I will write the cloning section this morning and then go for a walk”.
Write the materials and methods first . It’s the easiest bit to write because it is all technical writing with little wordcraft required. You can fit it around labwork. In fact, it is easier to write whilst in the lab because you can look up all the stuff you need. Importantly, it gets over the “blank page syndrome”.
Next get your figures together . This should already be done if you have been organised.
Then write the figure legends . You already have the title for each figure from your plan. All you need to do is describe each panel. Again, quite low energy writing required for this task.
Now write the results sections ! This is the same way that we put papers together. The results parts of the thesis are more extended but in principle you will guide the reader though the figures that you’ve made. Remember, you already have the legends written. So you are already partly on your way.
Time to regroup . At this point you can refine your plan for the introduction and check the rest of your plan still makes sense. Now is the time for some deep writing and reading.
The post title comes from “Rule of Three” by The Lemonheads.
- Share on twitter
- Share on facebook
10 tips for writing a PhD thesis
Ingrid curl shares simple rules for keeping your work clear and jargon-free.
- Share on linkedin
- Share on mail

Writing up a PhD can often take place in a frenzy of activity in the last few months of your degree study, after years of hard work. But there are some steps that you can take to increase your chances of success.
- Do not be daunted by the task of “writing up”. Work on the text as your PhD takes shape, remember that all writers need editing, and help yourself by using these basic tips to make life easier. Read what great writers say about how to write before you start, and take their advice to heart. There is no dark art to clear, concise work; it is mostly a result of editing, and editing again. Above all, keep Elmore Leonard’s advice in mind: “If it reads like writing…rewrite it.”
- Plan the structure of your thesis carefully with your supervisor. Create rough drafts as you go so that you can refine them as you become more focused on the write-up. Much of writing comprises rewriting so be prepared to rework each chapter many times. Even Ernest Hemingway said: “The first draft of everything is shit.”
- Academic writing does not have to be dry. Inject some flair into your work. Read advice on writing and remember George Orwell’s words in Why I Write : “Never use the passive where you can use the active”; and Mark Twain’s on adjectives: “When you catch an adjective, kill it.” If you prefer, Stephen King said: “The road to hell is paved with adverbs.”
- Do not write up in chronological order. Work on each chapter while it is fresh in your mind or pertinent to what you are doing at that moment, but come back to it all later and work it up into a consistent, coherent piece, restructuring sections where necessary.
- Think carefully about your writing. Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense. Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency. If you are too involved with the text to be able to take a step back and do this, then ask a friend or colleague to read it with a critical eye. Remember Hemingway’s advice: “Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.” Clarity is key.
- Most universities use a preferred style of references. Make sure you know what this is and stick to it. One of the most common errors in academic writing is to cite papers in the text that do not then appear in the bibliography. All references in your thesis need to be cross-checked with the bibliography before submission. Using a database during your research can save a great deal of time in the writing-up process. Helpful software includes EndNote or Paperpile. Managing your bibliography from day one may seem obsessive but it will save you a great deal of time and stress by the end of the PhD process.
- Use a house style. Professional publications such as Times Higher Education use a house style guide to ensure consistency in spelling. For example, do not use both -ise spellings and -ize spellings, stick to British spelling and be consistent when referring to organisations or bodies. Because dictionaries vary in their use of hyphenation, use one dictionary and stick to it throughout the writing process. If you consult the New Oxford Dictionary for Writers and Editors , you will note the extraordinary number of words with alternative spellings. It can also be a very useful guide to preferred spellings, use of italicisation and foreign phrases.
- Take care when quoting from other sources. Ensure you note whether the italic emphasis is in the original and take careful notes when you are collecting quotes for your thesis. Transcribe them accurately to save work later and keep original spellings (even if they differ from your chosen style) to ensure fidelity to your source.
- Think about plagiarism. If you are quoting from works, quote from them accurately and paraphrase where necessary for your argument. This is where careful note-taking and use of references is invaluable and will help you to avoid even inadvertently plagiarising another work.
- Remember that your thesis is your chance to present your work in the best possible light. Consider your opening paragraphs, entice your reader with your writing and above all be clear about your hypothesis and your conclusion. Append material where it adds value but not where it merely bulks out your work. Consider your reader at all times. This is your chance to showcase your work.
If you stick to these simple rules, your writing will be clear and jargon-free. Above all, take to heart Orwell’s advice: “Never use a foreign phrase, a scientific word, or a jargon word if you can think of an everyday English equivalent.”
Ingrid Curl is associate editor of Times Higher Education , and a former PhD student.
Register to continue
Why register?
- Registration is free and only takes a moment
- Once registered, you can read 3 articles a month
- Sign up for our newsletter
Or subscribe for unlimited access to:
- Unlimited access to news, views, insights & reviews
- Digital editions
- Digital access to THE’s university and college rankings analysis
Already registered or a current subscriber? Login
Related articles

How to submit a PhD thesis
The final few months of a PhD can often be the hardest, so here are a few tips from a doctoral candidate who recently submitted her thesis

Black vice-chancellor eyes new generation of minority researchers
David Mba creates fully funded PhD studentships after taking reins at Birmingham City University

Renaming postdocs and PhD students would boost respect, pay, progression
What other industry would deem those with so much prior training to still be mere trainees? Let’s call them what they are – researchers, says Michele Nardin

Academic careers recommended by just one in six postdocs: survey
Teachers fret about workloads and researchers about job security in ‘rare sport’ of academia

Engineering and physics PhD numbers to fall despite extra funding
Improved settlement for UK’s ‘biggest-ever’ doctoral training investment will deliver fewer funded PhD places than in previous years, UKRI confirms
Featured jobs
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Finishing your PhD thesis: 15 top tips from those in the know
Trying to complete a PhD thesis in time for the October deadline? We share some advice on getting over that final hurdle
- The key to a successful PhD thesis? Write in your own voice
Many PhD students are now in the final throes of writing their thesis. Turning years of research into a single, coherent piece of work can be tough, so we asked for tips from supervisors and recent PhD graduates. We were inundated with tweets and emails – and @AcademiaObscura helpfully created a Storify of the tweets. Below is a selection of the best tips.
1) Make sure you meet the PhD requirements for your institution “PhD students and their supervisors often presume things without checking. One supervisor told his student that a PhD was about 300 pages long so he wrote 300 pages. Unfortunately the supervisor had meant double-spaced, and the student had written single-spaced. Getting rid of 40,000 extra words with two weeks to go is not recommended.” ( Hannah Farrimond, lecturer in medical sociology, Exeter University)
2) Keep perspective “Everyone wants their thesis to be amazing, their magnum opus. But your most important work will come later. Think of your PhD as an apprenticeship. Your peers are unlikely to read your thesis and judge you on it. They are more likely to read any papers (articles, chapters, books) that result from it.” ( Dean D’Souza, PhD in cognitive neuroscience, Birkbeck, University of London)
3) Write the introduction last “Writing the introduction and conclusion together will help to tie up the thesis together, so save it for the end.” ( Ashish Jaiswal, PhD in business education, University of Oxford)
4) Use apps “ Trello is a project management tool (available as a smartphone app) which allows you to create ‘boards’ on which to pin all of your outstanding tasks, deadlines, and ideas. It allows you to make checklists too so you know that all of your important stuff is listed and to-hand, meaning you can focus on one thing at a time. It’s satisfying to move notes into the ‘done’ column too.” ( Lucy Irving, PhD in psychology, Middlesex University)
5) Address the unanswered questions “There will always be unanswered questions – don’t try to ignore or, even worse, obfuscate them. On the contrary, actively draw attention to them; identify them in your conclusion as areas for further investigation. Your PhD viva will go badly if you’ve attempted to disregard or evade the unresolved issues that your thesis has inevitably opened up.” ( Michael Perfect, PhD in English literature, University of Cambridge)
6) Buy your own laser printer “A basic monochrome laser printer that can print duplex (two-sided) can be bought online for less than £100, with off-brand replacement toners available for about £30 a pop. Repeatedly reprinting and editing draft thesis chapters has two very helpful functions. Firstly, it takes your work off the screen and onto paper, which is usually easier to proof. Secondly, it gives you a legitimate excuse to get away from your desk.” ( James Brown, PhD in architectural education, Queen’s University Belfast)
7) Checking is important “On days when your brain is too tired to write, check quotations, bibliography etc so you’re still making progress.” ( Julia Wright, professor of English at Dalhousie University, Canada)
8) Get feedback on the whole thesis “We often get feedback on individual chapters but plan to get feedback from your supervisor on the PhD as a whole to make sure it all hangs together nicely.” ( Mel Rohse, PhD in peace studies, University of Bradford)
9) Make sure you know when it will end “Sometimes supervisors use optimistic words such as ‘You are nearly there!’ Ask them to be specific. Are you three months away, or do you have six months’ worth of work? Or is it just a month’s load?” ( Rifat Mahbub, PhD in women’s studies, University of York)
10) Prepare for the viva “Don’t just focus on the thesis – the viva is very important too and examiners’ opinions can change following a successful viva. Remember that you are the expert in your specific field, not the examiners, and ask your supervisor to arrange a mock viva if practically possible.” ( Christine Jones , head of school of Welsh and bilingual studies, University of Wales Trinity St David)
11) Develop your own style “Take into account everything your supervisor has said, attend to their suggestions about revisions to your work but also be true to your own style of writing. What I found constructive was paying attention to the work of novelists I enjoy reading. It may seem that their style has nothing to do with your own field of research, but this does not matter. You can still absorb something of how they write and what makes it effective, compelling and believable.” ( Sarah Skyrme, PhD in sociology, Newcastle University)
12) Remember that more is not always better “A PhD thesis is not a race to the highest page count; don’t waste time padding.” ( Francis Woodhouse, PhD in mathematical biology, University of Cambridge)
13) Get a buddy “Find a colleague, your partner, a friend who is willing to support you. Share with them your milestones and goals, and agree to be accountable to them. This doesn’t mean they get to hassle or nag you, it just means someone else knows what you’re up to, and can help to check if your planning is realistic and achievable.” ( Cassandra Steer, PhD in criminology, University of Amsterdam)
14) Don’t pursue perfectionism “Remember that a PhD doesn’t have to be a masterpiece. Nothing more self-crippling than perfectionism.” ( Nathan Waddell, lecturer in modernist literature, Nottingham University )
15) Look after yourself “Go outside. Work outside if you can. Fresh air, trees and sunshine do wonders for what’s left of your sanity.” ( Helen Coverdale, PhD in law, LSE)
Do you have any tips to add? Share your advice in the comments below.
Join the higher education network for more comment, analysis and job opportunities , direct to your inbox. Follow us on Twitter @gdnhighered.
- Universities
- Early career researchers
- Impact of research
- Higher education
Comments (…)
Most viewed.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
PhD Thesis First Draft: 8 Practical Writing Tips for PhD Students

Many early career researchers will agree that the most difficult step in writing a PhD thesis is getting started. Students often find themselves mentally unprepared to take on this challenge as most formal training revolves around conducting research with little focus on how to write a PhD thesis. Uncertainty about the guidelines for PhD thesis writing and how to present their study in an engaging, impactful way often results in procrastination, self-doubt, and anxiety among otherwise confident researchers. The fact is students need to write a PhD thesis to complete their doctoral degree, and as ironic as it seems, the only remedy to this inertia is to meet this challenge head-on.
This article provides young researchers with practical tips to help them deliver a successful first draft when writing a PhD thesis.
- Create an outline and structure: A good way to start writing a PhD thesis is to first create a draft outline or structure of your thesis. Like journal articles, a PhD thesis must have an introduction that presents the key points of your study in a compelling way, a body section that contains the main aspects of your research along with supporting data and evidence, and a conclusion that summarizes the thesis and provides additional insights or suggestions for further research. This first step is important because once you have the right structure in place, summarizing your thesis can happen more easily.
- Adhere to university or institutional guidelines: A common mistake that many students make while creating an outline and structure is not keeping in mind the guidelines for PhD thesis writing set by your university or institute. It’s important to adhere to the university or institute’s guidelines, for example the preferred structure or style of references, when writing a PhD thesis. Be sure to check with your supervisor to ensure that the word count, structure, citation style and other key elements of your thesis meet the recommended guidelines for PhD thesis writing.
- Use active voice and avoid grammatical and spelling errors: It is important to focus on using simple language that’s free of complicated jargon when writing a PhD thesis. To ensure better readability, use active voice instead of passive voice and avoid long winding sentences. Be aware of and avoid spelling and grammar errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement, and parallelism in your work. You can use AI tools like Paperpal for Word , which offers real-time suggestions to help you improve your language right from the first draft itself.
- Maintain consistency in your writing style: One of the most useful writing tips for PhD students is referring to the preferred style guide to ensure consistency in spellings, proper punctuation, correct hyphenation, and the right use of technical terms and phrases. Also check for consistency when it comes mentioning organizations and institutions, affiliations, references, legends and other key elements when writing a PhD thesis.
- Be careful when citing or quoting text: With the sheer quantum of research reading required when writing a PhD thesis, it can be difficult to keep track of sources of information. It is also quite possible for students to inadvertently introduce plagiarism in their writing by using chunks of well-written text as is or quoting information without citing it correctly. So be sure to properly cite any sources of data that you’re using in your thesis, including text, images and figures to avoid any ethical misconduct.
- Set a target deadline for completion : Another top writing tip for PhD students is to set a delivery date and stay committed to it. You can also share this goal with a broader set of people (peers, supervisor, friends, etc.), who will act as catalysts on the journey of writing your PhD thesis first draft and in the time you’ve set for yourself. It is critical however that the final deadline be realistic and take into account challenges that may come in the way of you achieving your goals.
Write your PhD thesis confidently with Paperpal’s AI writing assistant
- Take time to make revisions and proofread before submission: This is one of the most important writing tips for PhD students, but one that often takes the back seat. Remember that no matter how clear your first draft seems about your research findings, argumentation and flow, there will always be room for improvement and especially to your first draft. Once you’re done with your first draft, be sure to revisit each chapter and make the necessary edits before sharing it ahead with your mentor for feedback. When planning your work, make sure to factor in ample time for editing and proofreading, so that all the work you put into writing a PhD thesis is polished before submission.
- Remember it’s a first draft and not the final version: If you’re getting stuck with your writing, move on and start work on a different section; you don’t need to write in chronological order as long as you follow the structure you’ve created for yourself. Remember the cardinal rule when wondering how to write a PhD thesis – No one gets it right in the first draft itself. Capture your thoughts and findings as clearly and engagingly as possible in your first draft, don’t waste too much time striving for perfection at this stage. You can always fine-tune your writing and repeat this process as you go along, which can help you reach your writing goals faster.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Good Writing Habits: 7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing
- How to Make Your Thesis Supervision Work for You
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- PhD Dissertation Outline: Creating a Roadmap to Success
Dangling Modifiers and How to Avoid Them in Your Writing
How to write a research paper outline: simple steps for researchers, you may also like, ai in education: it’s time to change the..., publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., 8 most effective ways to increase motivation for..., how to make your thesis supervision work for..., how to write a conclusion for research papers..., ethical research practices for research with human subjects, 5 reasons for rejection after peer review, what is peer review: importance and types of....
ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
How to generate, capture, and collect ideas to realize creative projects., how to write a dissertation thesis in a month: outlines, outlines, outlines.
2010-05-23 Daniel Circus Ponies Notebook , Doing Science , Learning to do Science , Science , Scrivener , Tools , Writing 41
“Writing a book is an adventure: to begin with it is a toy and amusement; then it becomes a master, and than it becomes a tyrant; and the last phase is just as you are about to be reconciled to your servitude – you kill the monster and fling him to the public.” Winston Churchill
Last year I took a vacation for a month to write my dissertation thesis. And it took me that one month to come up with the first draft, which made it into the final version with only minor alterations (but a lot of error checking ). While the lack of major alterations might be in part due to my academic advisers (and my) wish to finish the work as soon as possible, I think the major part of this is due to the way it was written, or rather structured.
Doing a dissertation thesis is a major project, the writing itself is a different but not less complicated animal. I think it is a mistake to start writing in sentences unless you know the structure and the content. Once you write sentences, they stick together and are hard to change. And I think it is nearly impossible to write a 200+ pages work if you do not structure it beforehand, and there is a great way to do so: Outlines.
Most people know outlines from school. Many teachers try to give this valuable hint for exams. Plan what you write before you start writing. An outline for a dissertation is similar, but not quite the same. For one thing, it is much more detailed .
How detailed? Well, everything you want to write later should be included in it, without the actual sentences. Metaphorically it should contain the bones of the text, the whole skeleton, and hints for everything else. This means
- the order you want to write the different pieces of information that make your theory
- the notes you made about your studies, the design, the participants, the instruments, the procedure
- the results of any statistical analysis you made
- the ideas for and the issues you want to raise in the discussion
It also includes any notes you do not want to forget and any ideas, e.g., for further studies even if you cannot realize them (a valuable hint from my informal academic adviser: you will have ideas of things you want to realize but you cannot realize everything, so make notes and raise these points in “future work”).
Given that the outline only contains the information, but not the sentences, it is easily changeable. And once you get in the flow of adding flesh to the bones, you can write really fast. An additional benefit of using outlines: I used the same outline as a basis for the articles I wrote about my dissertation. The outline also allows you to focus only on the relevant part by using the hierarchical structure: You can arrange the information similar to the structure you use for your PhD thesis and simply fold in the parts you do not need at the moment. This way, thousands of lines of text become easily manageable. For example, you can fold the parts between the introduction and the discussion to write parts of the discussion while simulateneously seeing parts of the introduction. Sure, you could do something similar with Word’s “split view”, but not as easy and with this focus on the parts you want to see.
Personally, my outline for my dissertation was a 66.5 MB Circus Ponies Notebook file, containing 333,215 words (> 2.2 million characters, equivalent of about 1305 pages). I made sure to write down everything I did, the results of any analysis, etc. It was more or less structured in the way I wanted to write my dissertation. With this outline next to my writing program ( Scrivener ), it was possible to come up with a good first draft within a month. Why? Because I first read the whole outline, taking care to move the information that did not fit where it was to the correct place, then sorted each sub-point (e.g,, theory, results of Study 1) in the correct order, and then used this sorted outline that contained all the information I needed to write it as a guideline to write that chapter. Given that the sources were marked in the outline (see Academic Workflow ) I did not have to check other sources for the actual writing. I didn’t even have to re-check statistical printouts — it was all in that one huge outline (and then in a smaller one that dealt only with the chapter).
I created the outline before I started to write, during the last year of my PhD. But thinking back, it would have been much easier to create the outline during the whole PhD thesis time, as soon as the topic and the first experiments were decided. Noting the decisions (and the reasons for doing so), the results, etc. while planning and doing the studies would have made it much easier in the end, but it also worked this way.
So, I can only highly recommend creating a detailed outline prior to writing and using it for the writing process. It makes an insanely complex work manageable. 🙂
- Circus_Ponies_Notebook
- conveying_ideas
- infrastructure
15 Comments
I received a question regarding the transfer of notes from other programs to Circus Ponies Notebook:
Hi Daniel! My name is Chris and I´m working on my dissertation manuscript for my MD at the moment. I´m using Scrivener for writing, Bookends as BibRef tool for Scrivener and Papers for getting and sorting my papers. Yet, I´ve done a lot of work, writing on my self and using associated project scripts of my Institute. My question is, how can I import the manuscript´s status quo of Outline, BibRef and Content into CPN for not losing so much time by starting again from the beginning… Thx a lot, Chris
Hmmm, if I understand the question correctly you are currently using three different programs for writing your dissertation (Bookends, Scrivener and Papers) and now you want to create an outline in CPN … good question … hmm, first, do you really want to take a step back? An outline makes sense to organize the material you have in a red thread and collect all information in one place that you can use (with Scrivener) to write you dissertation in one go. At the moment, you already have written text … hmmm …
Okay, it’s difficult to say (will be influenced by a lot of factors I don’t know, like the rules of your field for dissertations, the time you have left, your goals, your working habits, etc. pp.) and I wouldn’t bet my dissertation on it, but I would probably go alone the lines of this:
1. What is the problem? Do I have problems making a coherent package out of my material? In this case, going back to an outline might be one way to solve it. If, however, I’m just not motivated to write, I don’t want to finish it or I’m looking for some other thing to do, I’d grind my teeth and punch through writing the way I did before.
2. If it’s the first case and now I have to put my material in one CPN file, I’d create one outlining page, start with the sections of the dissertation (title page, abstract, introduction …), highlight them, and then manually copy the text I have already written into this outline. The reason is that if the structure is a problem (it usually is), you need little cells of text (one argument per cell) that you can organize hierarchically and move really easily. You can try to automate it by copying your whole text first (depending on the fonts you have used, e.g., for formulas or the importance of formatting you have already used by compiling a draft from Scrivener and using this as a starting point), then paste it into a pure text editor (like TextWrangler) and then copy it onto the notebook page with “Edit – Paste – Paste Text as Outline” to avoid switching between two applications, but the division into cells you’ll have to do yourself.
3. While pasting I would use the situation to make notes (using a cell on its own with text in another color). You might have some ideas what to do and what you still need to check, use that moment.
x. optional: If I need the references as keywords (only if you want to write what they have said as text and keep the reference in the margin) I’d copy all references (only author and year or however they are cited in the text in your discipline, mind the Miller 1999a, Miller 1999b, etc. if one author has published multiple papers in one year) at the end of the outline, and then — for each reference — highlight it in the text (not the cell) and make a keyword out of it (assign as keyword). This way CPN already knows the keywords and I can assign them to the margins easily (you have to leave at least one occurrence of the keyword in the file, so give the references a top cell like “refs” and fold this in and keep it at the end of the outline where it doesn’t bug you. But this is a large step backwards in the process, as I would tag cells with only one reference. This means splitting up/copying sentences if you refer to multiple sources.
4. Then I’d resort the cells in a fitting order. I’d make sure that the whole structure has a hierarchical order and let’s me easily see the gist of the different sections (summaries in the higher cells). I’d make sure that the whole picture is coherent and invest work in the parts that aren’t. Perhaps changing the structure, perhaps hitting literature again.
5. Once I’m sure I have a coherent work that is “enough” to get me the grad I need (for me: “magna cum laude” to stay in research, which luckily worked out) and after checking with my supervisor, I’d write the whole text (I can recommend taking a month off and copying the text sectionwise into a new CPN file and then checking the order again. If you stumble during writing it’s often the order/structure that’s a problem. Try to catch this first.)
6. While writing I’d put the text citations into the text (or use the Reference Manager that you have assigned to Scrivener). After writing the text, if I did the references manually, I’d put in the references at the end of the document.
But like said, I’d only do this if structure really is a problem. CPN is great for making an outline that really deserves the name — that contains all the information in one huge structure you need to write. A good outline (yup, like said, this means manual work) allows you to see the structure on the higher levels, allowing you to fold in the sublevels and concentrate on whether your arguments make sense. This is often lost in the text.
One important aspect: Keep your papers (with notes regarding the papers) sorted the way you did it (if it works for you). The dissertation is a project that will be finished. The outline you create for writing it can be used as a starting point for articles and future work, but one day you’ll have to go back to the place you have sorted your papers in. I have tried using CPN for organizing papers I read and while some aspects worked really well (like tagging each cell with the reference) it got slow fast. I switched to a Wiki (and highly automated some functions with Javascript/PHP, i.e., Ferret) to make it usable. Currently I have over 1000 papers/books/whatever in my literature section — DokuWiki can handle it, CPN would probably have been slow as hell. So, whatever you do, use CPN’s outline function to get the structure in order and get all your material for this project in one place if you need to, but keep your literature in a separate collection.
I hope this answers your question.
Best regards
This is the third often read posting I have in my blog. I think (and am pretty certain) that outlines, especially using Circus Ponies Notebook, helped me — or rather enabled me — to finish not only my diploma thesis but also my dissertation thesis, not only in a month but ever . I’m curious, what are your experiences? Did it work for you? If now, why? If you found another solution, what worked for you? It would be nice to hear a comment from you if you have read this posting. 🙂
Very useful. Concerning your most recent comment: I think it’s the third most read article in your blog because it’s the number 1 google search result for : how to write a dissertation thesis in 1 month –> which brought me here.. Add millions of other lazy bastards who work at the last minute and voila!
thank you for the comment — I didn’t know that Google liked this posting that much, cool 🙂
Best regards (and good luck for your thesis)
PS: The writing took one month, the preparation for the writing phase took a little longer. 😉
I commend your spirit and your nice expressions. I do really enjoy every single word you wrote. I’m working right now on my thesis and I’m totally frustrated, bored, don’t know how to finish it and how to manage my time. What you wrote made me think that writing a thesis is not so hard but it needs time, outlining and most important optimism!
Thanks for sharing this with us.
Thank you for the positive feedback 🙂
I think it’s quite normal to feel this way when doing a dissertation thesis — there are many crises (e.g., Dissertation Crises , or Dissertation Crisis — Past the Mountain ) and while a dissertation is (supposed to be) difficult, it’s good to keep it in perspective. For example:
“A PhD is a stepping stone into a research career. All you need to do is to demonstrate your capacity for independent, critical thinking. That’s all you need to do. A PhD is three years of solid work, not a Nobel Prize” Maths–Eng/Female/18, in Mullins & Kiley, 2002
“Das Kapital wasn’t Marx’s thesis: and my PhD thesis doesn’t have to be my life’s work. It’s a training ground.” catspyjamas on phinished.org
“The only good dissertation is a DONE dissertation.” Capella faculty quote
So, if you are stuck, perhaps creating an outline will help. And like Churchill said, “If you’re going through hell, keep going.” I wish you the best 🙂
Hi Daniel. I read your story about your thesis writing and understood you write about 333000 words in just one month,how did you do that?I am a PhD student in engineering really struggling with my writing up, I almost have not written anything because of my depression problems. I have about a month and half to submit, I have no limit but want to write at least 100 pages except the bibliography and appendices. I appreciate if you advice me how to do it.many thanks Hannah
Mai I mention here that I do have outlines and kind of know the structure of thesis writing.
Hoi Hannah,
nope, writing 333k words in a month would be a feat beyond me. 😉 I created the outline during my dissertation prior to sitting down to write the thesis. What I did write in that month was the dissertation thesis itself which was 250 pages long and had about 71000 words. I did not use all the material I had in my outline and the hierarchical structure made it possible (and fairly easy) to select among the material I wanted to use.
Regarding your case — difficult. If you have a depression (in the clinical term, not in the colloquial meaning), then this should probably be a priority (and not my field of expertise, that’s something for the local health service). Regarding the writing — personally it helped me a lot to use the outliner to create a content outline . This goes beyond the structure — it externalizes all what you want to write and allows you to resort the content in the structure that fits best, without starting to write sentences that stick together. Then you can focus on the criteria on scientific writing (e.g., Alley’s criteria, see here or the other postings in that series ). However, there is a huge risk here if you have a deadline looming: It stays pre-text for a long time. For me writing the thesis from the content outline was quick (I can type with 10 fingers and am reasonably fast), but it was easy for me to sort the material and I had no looming deadline. So, using the same strategy might be a way that might work, but nobody can guarantee success.
All the best
Well i completed my thesis in few weeks, but i adopted a unique method, I had the draft out sourced and when i got it back i made my own changes to it and it was ready. I used [URL REMOVED] They were right on money and topic
Normally such a comment would be sorted into the spam folder, but after removing the I’ve approved it to make a point. Outsourcing is not a unique method — it’s unfortunately common with some people who think they can buy an academic degree. Well, some are paying for college and some will pay for others to do their work later, so why not for the thesis too? Well, because it’s plagiarism. Unless you stated that you used a ghostwriting service in your thesis — which I doubt that you did, because any university worth the name would not accept that work as yours — you lied about who did the work. And the academic work should be your own. Not only did you not learn the necessary skills — nope, seeing the result is easy, doing it on your own is something completely different — you betrayed yourself of the chance to do a difficult high-level piece of work. Something like this is frequently a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity and you blew it. The funny thing, I am willing to bet that in the future — give it 5 to 10 years — some hackers or whistleblowers will make the customers of these ‘services’ public. Or Google/Plagiarism software will improve so much that it will detect these kinds of plagiarisms. And then a lot of people who thought they could buy their title, or a huge chunk of the work necessary will lose it. So, congratulations, you not only blew an academic adventure that you could have had with the right mindset, you also put a time bomb in your CV. Tick-tock-tick-tock … have fun.
Love, love, love your comment to Jenni. Writing my dissertation is proving to be extremely hard but mainly because I want it to be the best possible representation of my body of knowledge. The idea of outsourcing a dissertation is ridiculous. Sooner or later the truth will come out. If Jenni had her “own details” to begin with, she should have used them to produce her own work!
Thank you, I doubt that it will change anything given that “she” seems to be the companies ad/spam person (received another spam message disguised as “PhD student testimonial”), but perhaps other readers will think twice on “outsourcing” the work. 🙂
Thank you, very useful, informative articles. I only have one question is how to write an essay on a topic that you do not know and do not lose face? How to write a good informative article in a short period of time and not to make mistakes? In internet many articles which give different advice, such as, this article https://thesiswhisperer.com/2011/03/24/how-to-write-1000-words-a-day-and-not-go-bat-shit-crazy/ , but they can not really help me and answer my questions. I study at the Institute and I need in a short time write a good dissertation. Now I do not know what to do … looking for a different article in internet about thesis writing. There I found this article http://phdify.com/blog/how-many-chapters-in-a-dissertation on how to write a dissertation, but it do not tell me how to write a dissertation 2 months. Can you give me some good advice?
Hoi Jenifer,
the only (honest) advice I can give you is to talk to your advisor. They (and the committee) are the ones determining what is necessary for your dissertation. I am recommending this because it seems to me that the problem is not how to write a certain amount of words, or how to write a thesis in a certain amount of time, but because I think there is some confusion about what the dissertation is about. And I might be wrong here! I think for most writing tips to work you have to be clear about what your contribution in your thesis is — and for that you need discussions with your supervisor. Once that is determined, you can do an outline (as I would recommend) or use Mewburn’s tips.
(And as for outlines — yup, I think there are great, but they will not work for everyone. They are an option you should know about. And while I did write my thesis in a month — the first and nearly final draft that is — I did it with an outline I had created during nearly three years of studying.)
26 Trackbacks / Pingbacks
- The mobile Scientist » Blog Archive » Apple iBooks 2 and Apple iBooks Author - Psychology & Technology in Mobile Media
- Organizing Creativity & Crisis of the Dissertation « The Returning Researcher
- How to Write a Dissertation Thesis in a Month: Outlines, Outlines, Outlines | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY | Hùng Trang @ Thailand
- Workshop: Scientific Work — Reading & Using Literature | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Workshop: Scientific Work — Possible Academic Literature Workflow | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Scrivener — A perfect program for dissertation writing | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Circus Ponies Notebook: The Best Tool for Structuring Creative Writing Projects (esp. Research Projects) | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Curio | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Writing Articles with a Mind Map | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- How to create a content outline in Circus Ponies Notebook | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Visually developing ideas in Keynote | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Another academic workflow visualization | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Non-Destructive Graffiti | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Dealing With the Plagiarism Plague Among Students | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Writing | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Workshop: Scientific Work — Writing #2 Knowing What To Write | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Perhaps I need a question section … | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Workshop: Scientific Work — Topic Notebooks | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Master’s Projects & Theses: Tips & Tools for Your Winter Break! | Journalism Library Blog
- Outsourcing a Thesis | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- A Critical Look at Scientific Writing Courses | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Beware of a (wo)man of one book | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Circus Ponies Notebook 4 | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- How to Write a Dissertation in One Month
- Configuring Scrivener (Make Scrivener grey — and get that icon back) | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
- Winter Break: Some Project and Thesis Tips! – Libraries Spotlight BLOG
Comments are closed.
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
How to Write a Research Paper in a Month?
How to write a research paper in a month: a step-by-step guide with timeline.

Table of contents
Step 1: choose an engaging topic (days 1-2):, step 2: perform in-depth research (days 3-8):, step 3: develop a solid thesis statement (day 9):, step 4: create an outline (days 10-11):, step 5: write the first draft (days 12-23):, step 6: revise and edit (days 24-25):, step 7: seek feedback and revise again (days 26-27):, step 8: proofread and finalize (days 28-29):, step 9: write the abstract and introduction (day 30):, 10 tips to write a research paper in a month.
Writing a research paper is one of the challenging tasks in research, but with proper planning and organization, it can be accomplished within a month. While the timeline may seem tight, this article will guide you through a step-by-step procedure to efficiently write a research paper in just 30 days. By following this timeline strictly, one can successfully navigate through the research process and produce a high-quality paper .
Learn how to write a research paper in just one month with our comprehensive step-by-step guide. This timeline-based approach will help you manage your time effectively and achieve efficient results. Discover research tips, writing techniques, and valuable strategies to stay organized throughout the process. Enhance your research productivity and successfully complete your paper within the given deadline.
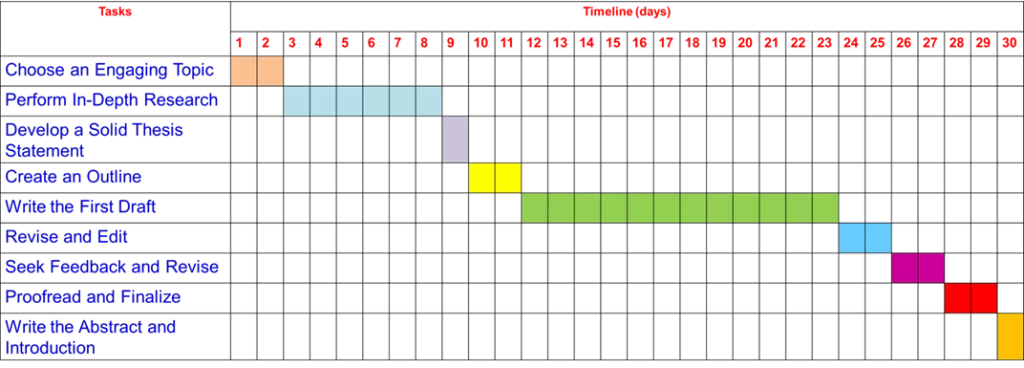
- Selecting an intriguing and research-worthy topic is the first crucial step.
- Spend some time brainstorming ideas, exploring academic journals, and consulting your professor or advisor.
- Ensure your topic is specific, manageable, and aligns with your field of study.
- Dedicate a significant portion of time to conducting thorough research.
- Utilize academic databases, online libraries, and reputable sources to gather relevant information.
- Make sure to take detailed notes and organize your sources using a citation management tool such as EndNote or Zotero.
Top 5 Free Reference Management Software for Research
- Based on your research, craft a clear and concise thesis statement that summarizes the main argument or focus of your paper.
- Your thesis statement should be specific and supportable with evidence from your research.
- Construct a well-organized outline that serves as a roadmap for your paper .
- Divide your research into sections and sub-sections, ensuring a logical flow of ideas.
- This step will help you maintain coherence throughout the writing process.
- Begin writing your paper based on the outline you created.
- Aim to complete a specific number of pages or sections each day, keeping in mind the deadline.
- Focus on expressing your ideas and arguments clearly, avoiding perfectionism during this initial draft.
- Once the first draft is complete, take a break for a day to gain a fresh perspective.
- Return to your paper and start revising it critically.
- Pay attention to sentence structure, grammar , and clarity.
- Eliminate any unnecessary information and ensure that your arguments are supported by evidence.
- Share your paper with peers , professors, and experts to obtain valuable feedback.
- Consider their suggestions and incorporate necessary changes into your paper.
- This step helps improve the overall quality of your work and ensures it meets the required standards.
- Proofread your paper meticulously, checking for spelling errors, typos, and formatting inconsistencies.
- Ensure that your paper adheres to the specified citation style (APA, MLA, etc.).
- Verify that your references are accurately cited and cross-checked with your citation management tool.
- Craft a concise abstract that summarizes the key points of your paper.
- Then, write an engaging introduction that introduces the topic, provides background information, and presents your thesis statement.
- These sections should capture the reader’s attention and provide a clear context for your research.
- Finally, submit the paper to a reputed journal.
- Plan your time: Create a realistic timeline that outlines the tasks you need to complete at each stage of the research paper writing process.
- Select a focused topic: Choose a research topic that is manageable and aligns with your interests and available resources.
- Conduct efficient research: Utilize online databases, academic journals, and credible sources to gather relevant information quickly. Take organized notes to streamline your writing process.
- Develop a strong thesis statement: Formulate a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or objective of your research paper.
- Create an outline: Structure your research paper by creating a detailed outline that includes the introduction, main body paragraphs, and conclusion. This will help you maintain a logical flow throughout your writing.
- Break it down into smaller tasks: Divide your research paper into smaller, manageable tasks such as literature review, data analysis, and drafting different sections. This approach will make the writing process less overwhelming.
- Stay focused and organized: Maintain a distraction-free work environment, organize your research materials, and keep track of your sources to save time when citing references.
- Write regularly: Set aside dedicated time each day for writing. Even if it’s just a small portion of your paper, consistent progress will help you stay on track.
- Edit and revise: Allocate time for editing and proofreading your research paper. Check for clarity, coherence, grammar, and spelling errors to ensure a polished final product.
- Seek feedback: Share your draft with peers, professors, or writing centers for valuable feedback. Incorporate suggestions and refine your paper further for a well-rounded research outcome.
By following these tips, you can effectively write a research paper within a month while maintaining a high standard of quality and academic integrity.
Conclusion:
Writing a research paper within a month is an achievable goal if you follow a systematic approach. By allocating time to each stage of the process, from topic selection to final proofreading, you can efficiently complete a well-researched and well-written paper. Always stay focused, organize your thoughts, seek feedback, and revise your work. With determination and proper planning, you can produce a high-quality research paper that contributes to your field of study. Happy researching!

- accelerated academic writing
- deadline-driven writing
- effective research
- efficient writing
- fast research paper
- quick research paper
- Research Methodology
- research organization
- Research Paper Writing
- research planning
- research process
- research productivity
- research strategies
- research tips and tricks
- Scopus Journals
- time management tips
- time-bound research paper
- writing hacks
- writing process
- writing techniques
42 Digital Signal Processing Project Ideas to Explore
What is a research design importance and types, z-library is legal you can download 70,000,000+ scientific articles for free, email subscription.

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
WhatsApp Channel
Join iLovePhD WhatsApp Channel Now!
Contact us: [email protected]
Copyright © 2019-2024 - iLovePhD
- Artificial intelligence
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.10(12); 2014 Dec

Ten Simple Rules for Finishing Your PhD
Jacopo marino.
1 Department of Chemistry, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Melanie I. Stefan
2 Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America
Sarah Blackford
3 Society for Experimental Biology (SEB), Lancaster University, Lancaster, United Kingdom
Introduction
After years of research and with completion in sight, the final year of the PhD often represents the most challenging time of a student's career, in which the ultimate reward is the PhD honor itself. A large investment in time, energy, and motivation is needed, with many tasks to be completed; concluding experiments must be carried out, results interpreted, and a research story mapped out in preparation for writing the final thesis. All the while, administrative obligations need attention (e.g., university credits and mandatory documents), papers may need to be published, students mentored, and due consideration paid to planning for the next career move. Without some form of strategic action plan and the employment of project management skills, students run the risk of becoming overwhelmed and run down or of not meeting their final deadlines. Personal time management and stress resilience are competences that can be developed and honed during this final period of the PhD.
Here, we present ten simple rules on how to deal with time issues and conflict situations when facing the last year of a PhD in science. The rules focus on defining research goals in advance and designing a plan of action. Moreover, we discuss the importance of managing relationships with supervisors and colleagues, as well as early career planning.
Rule 1: Plan Your Last Year in Advance
Preparing a plan of action for the final year of your PhD is vital. Ideally, devised and agreed upon with your supervisor, a plan will help to optimize the time left and reduce feelings of being overwhelmed. Individuals plan in different ways; some prefer to work towards their goals in a stepwise linear fashion, whilst others are more comfortable flitting from task to task until all the jobs are done. There is no definitive way to plan, so find out what works best for you. You may decide to map out a timeline, or perhaps a mind-map is your preferred planning style. Whichever method you use, it's important that you adhere to your plan whilst allowing for some flexibility (but not distraction or procrastination).
Your time frame will vary according to the organization of your graduate school, your supervisor or advisory committee, and even your graduation date, but one year before submission of your doctoral thesis is the time when you should decide on how best to invest the last months of your research and associated activities. Having a plan of action will help to avoid time wasting, e.g., being distracted by superfluous experiments that might be interesting but are not necessary. Furthermore, from a psychological point of view, referring to a concrete plan can make you feel more secure and in control. Ideally, the supervisor and PhD student should both agree on the overall plan (with provision for the unexpected, e.g., technical issues), with intermittent reviews every few weeks to check that progress is being made. Your supervisor should also be able to advise you on the organization and writing of your thesis—for example, its structure—and the number and length of chapters to include.

Rule 2: Make Your Priorities Clear
Select the activities you want to include in your plan. What are your priorities? They are likely to include experiments that will give the thesis a conclusion or that may be necessary to publish a final paper. Mandatory administrative tasks will also need attention, and allowing time to prepare for your next career move will give you the best chance of a seamless and successful transition post-PhD. As a final year PhD candidate, you are likely to have acquired high-level competencies comparable to those of a junior postdoctoral researcher, in which case your supervisor may offer you responsibility for new projects or graduate students. Saying no to him/her can be difficult for various reasons, e.g., fear of potentially creating conflict in your relationship or causing a negative reaction or of perhaps losing the opportunity to be included in future research activities and publications. It can also be difficult to let go of a topic or project to which you are wedded or to miss out on the opportunity to help train the next generation of scientists. In such situations, referring back to your plan (Rule 1), previously agreed upon with your supervisor, should help to remind you both of your priorities and deadlines, making negotiation easier. However, should any conflict of opinion arise between you, bear in mind that finding a mutually agreeable solution is the best way forward. You can take advice from a mentor or refer to the many publications that provide approaches and tactics for effective negotiation. If the relationship between you and your supervisor is more complicated and cannot be resolved by a discussion, you may need to turn to your graduate school, your academic committee, or other senior managers in your institution, who can act to mediate the situation.
Rule 3: “The Truth Can Wait”
A research project is never really finished, so do not try to do everything before submitting. In fact, the perfect doctoral thesis does not exist; there are students with good research projects and many publications and others with more difficult and testing challenges who are still waiting for their first paper. If the project is ambitious, it might take several years to reach the final goal, and thus the thesis might only be a small part of the whole story. If the project is going well, it will open up new research questions and future directions, some of which will be beyond the scope of a PhD. At some point, you need to decide that what you have is enough for a PhD and start writing (a strategy we heard described at a dissertation-writing seminar in Cambridge as “the truth can wait”; it helps to write this on a post-it note and stick it on your computer!). Starting to write the thesis is not easy when there is a sense that more could be done to accumulate more data and a fuller story; a common mistake is to go back to the lab instead of getting started with the results chapters of the thesis. To postpone writing will cause delays and not necessarily improve the thesis whilst increasing the prospect of unfulfilled and extended deadlines. Thus, once the experiments that you have agreed on have been completed, it is really important to start writing with the data in hand.
Rule 4: Enlist Support
Finalizing experiments and writing the thesis (and even papers), as well as considering your next career transition, can be stressful and even isolating. It is a contrast to the relatively more relaxed earlier years of the PhD experience, and the writing process does not come naturally to everyone. The prospect of facing these stresses alone can make the experience even harder to bear, so it is advisable to communicate with and find support in those you trust and respect. Relying on such people during this period can help to ease the strain and enable you to achieve your final aims so that you arrive at your PhD graduation with your sanity still intact! Talking about personal feelings with selected colleagues usually helps you to realize that you are not alone, whatever difficulties and challenges you might be experiencing with your research project, supervisor, or coworkers. Sharing uncertainties and talking through issues can be constructive, helping you to understand the strategies other people use to cope with similar problems. As well as colleagues, it can also help to talk to friends and family, even though they won't be as au fait with the highly particular challenges you are experiencing. You can share your feelings and anxieties with them, but they can also act as a welcome distraction to help you to relax and take a break from thinking about the stresses of your PhD.
Support and advice can also come in the shape of courses, books, blogs, mentoring, etc. There is much published on the subject of how to write a thesis [1] . Furthermore, graduate schools, such as those in which we are based, usually offer courses to help PhD candidates improve their personal and professional skills. For example, the University of Zurich organizes courses on, amongst others, time and self-management skills, managing conflict, and academic writing and publishing [2] . The Graduate School of Arts and Sciences at Harvard lists workshops and resources offered across the university on topics such as scientific writing, time management, and overcoming procrastination. In addition to relying on your supervisor, postdoctoral researchers in your group or department (or even friendly collaborators) may agree to read chapters of your thesis and comment on aspects such as content, logical flow of ideas, and the overall structure. At a later stage, you may want to engage someone to check your grammar, spelling, and reference style (this can be especially important if you are not writing in your native language). If your PhD defense includes a presentation, try to practice beforehand, preferably in front of some of your peers, and include asking for feedback and possible questions that may come up. This should make you feel more prepared and confident.
Rule 5: Get Familiar with the Software
Being familiar with software for both writing and making figures will facilitate the creation of your thesis. One of the most effective tools with which to produce a scientific document is LaTeX ( www.latex-project.org ). This software, freely available, is not as immediately understandable as other text editors, but the advantages are greater: it offers a professional layout similar to published books, it makes the insertion and management of figures easier as their position in the file does not depend on text editing, and it allows for easy typesetting of mathematical equations and referencing of articles from a bibliography database. Moreover, the text file size does not increase while inserting figures, making its handling easier. An example LaTeX package for typesetting dissertations is “classicthesis”, written by André Miede ( http://www.miede.de/index.php?page=classicthesis ). Although advantageous, LaTeX can also present disadvantages. In contrast to commonly used text editors (e.g., Microsoft Word), it does not make it easy to track changes in the manuscript, often a preferred way for supervisors to correct theses in an electronic form. Therefore, we suggest you discuss the preferred software with your supervisor when you agree upon your plan (Rule 1).
A professional design software can also speed up the creation of figures for your thesis, which can be further used for your final PhD presentation, so check whether your institution provides an introductory course to some of these software packages. Taking a one-day class can save you a lot of time later. Organize your bibliography; many excellent reference managers exist that allow you to catalogue and annotate the papers you have read and integrate them seamlessly with text processing software (e.g., Endnote or the freely available Mendeley and Readcube). Choose one that fits your needs and check whether your university provides institutional licenses (and be disciplined about adding each paper you read to it!).
Consider using version control software. This allows you to keep a log of all the changes you make to a file or directory and makes it easy to recover a previous version if something goes wrong or to merge two versions of a file. This is often used in software projects to produce, document, and improve computer code, but it can also be useful when working on a long text document, such as a dissertation. Commonly used free version control systems include git/GitHub [git, github], Subversion [svn], and Bazaar [bzr] (see Table 1 ).
Most important of all is to have a backup strategy. A hard-drive crash at the wrong moment can set your work back by weeks and jeopardize the timely completion of your thesis. Institutions or departments will often have a backup system employees can make use of. This may require you to install a specific piece of software on your computer that backs up your data at regular intervals or to save your file on an institute server. Contact the information technology (IT) department at your institute to learn about your options.
Rule 6: Know Your University's Procedures and Regulations
During the course of your PhD, you will have been acquiring project management skills, such as organizing your time and resources, reviewing progress, and meeting deadlines. In order to avoid last-minute surprises, you can capitalize on and develop these skills during the final year of your PhD. Prepare a list of all the documents and certificates that you will need, even before you start writing; it will be of critical importance to include this information in your plan and priorities (Rules 1 and 2). Having a good working relationship with someone who can help you to navigate a bureaucratic process will usually be an asset and will ensure you are familiar and aware of all the rules. Considering the amount of documents and certificates that are needed for handing in a thesis, it is advantageous to introduce yourself to the institute secretary or human resources manager, as well as any other staff who can help you to deal with the administrative side of the process. Don't rely on previous documents, which may have been revised since the last person in your group graduated. Be aware of all the necessary institutional administrative requirements (e.g., credit points, research seminar attendance, publications, etc.), as well as the faculty criteria, including deadlines (as well the date of the graduation ceremony), thesis copy numbers and format, font size, binding, and supporting documents. Take time to go through the list of documents and start collecting them in a folder. Get the formatting right early on, e.g., by using a dedicated template file. With your documents in order, you are bound to feel you have the situation more under control, which can help to reduce stress and enable you to focus more closely on writing your thesis.
Rule 7: Exploit Synergies
You are doing a lot of work for your thesis, so use it to your advantage. The literature review in your introduction can also be used to write and publish a future review article, an idea that might also be welcomed by your supervisor. If you are intending to write a grant proposal for a postdoctoral fellowship on a similar research topic, you can use some of the thesis introduction and future directions as a basis for your research plan. If you are keen to gain teaching experience, you could propose a short course on your specialty area. For instance, at Harvard Medical School, senior graduate students and postdoctoral researchers can be involved in lecturing on short, specialized “nanocourses” [3] . You may also be able to deliver a specialized lecture within a class your supervisor is teaching or, ideally after you have completed the PhD, teach at a workshop or summer school.
Take advantage of opportunities to deliver a talk as an invited speaker at a conference or at another institute, for example, if you are visiting a research group or investigating possible postdoctoral options. This will give you the chance to practice your defense presentation in front of an unfamiliar audience and, at the same time, allow a potential future supervisor and colleagues to gain a more complete picture of your research interests, skills, and personality.
Rule 8: Pay Attention to Your Career
It is not always easy to decide on which career path to follow after your PhD. You have been trained primarily towards an academic research career, and so many PhD graduates choose to continue on with a postdoctoral position as their first career destination. This is perfectly acceptable, and many industrial employers look upon early-career postdoctorals favorably. However, it is worth bearing in mind that permanent tenured positions are hard to secure nowadays and competition is tough, with less than 5% of those who complete a PhD ultimately realizing an academic career [4] . For those who are determined to have an academic career, a strategic research plan is crucial; for those who are unsure, a viable alternative career plan is equally important.
Knowledge of your professional and personal skills and capabilities, personality, values, and interests, as well as how to map them onto the job market and sell them to employers, will help you to make effective career decisions and a successful transition to your next job. In addition, factors such as your personal situation and priorities, mobility, and preferred work–life balance all need to be taken into consideration before entering the complicated world of the job market. Be ready to make compromises either in your work or personal life, depending on your priorities. Take advantage of courses and professional career guidance and coaching while you are still at university, as they are usually offered free of charge. Along with books and websites, face-to-face career support can help raise your self-awareness and knowledge of the job market so you can start to decide which types of career may best suit you. Blackford's book and blog [4] contain useful material on career planning for bioscientists, with concrete examples of different career paths within and outside of academia, and further information and resources. In addition, the Science Careers portal offers an online tool [5] to create an individual development plan and explore your career options based on your skills, interests, and values. Also, take advantage of dedicated career job boards associated with specialist websites, such as that of the International Society for Computational Biology [6] .
How soon should you start job seeking? Finding a job whilst writing up your thesis can seem like an attractive prospect, but it's important to consider that applying for jobs can easily take up as much time as working a full-time job. Then, if you do secure a job, the time left for writing up your thesis, completing experiments, and wrapping up your lab work will be seriously limited. It is exceedingly hard to write a doctoral thesis in the evenings after work or on the weekends, so in case you are offered a job before you have finished the PhD, consider seriously how this might affect your work and life. On the other hand, finishing a PhD when scholarship money has been seriously reduced (or has run out) comes with a different set of challenges. Many students need to tap into their savings (if indeed they have any), drastically reduce their spending, and move out of their accommodation. Losing employment at the university can also affect health insurance, social security, and visa status. Finishing up a PhD under these additional constraints and pressures can be extremely challenging, both logistically and psychologically. To ensure that you can concentrate all your time on (and get paid for) finishing your PhD, start planning ahead one year earlier. Be aware of your university's regulations, talk to your supervisor about the funding situation (is it possible for you stay on as a postdoctoral researcher for a short period?), and know what you need to do in order to finish on time (Rule 1).
Rule 9: Network
Unofficial statistics tell us that only around 30% of jobs are advertised, so to enhance your employment prospects you would be well advised to network in order to access the hidden job market. During the final year of your PhD, and even earlier, you can build up and extend your network so that your chances of finding the job of your choice are optimized. If you are looking for research positions, your supervisor might have contacts or know about positions available in academia or industry. Reviewing your personal network further will reveal it consists of colleagues, friends, and family. You may also have a wider network of collaborators (research and industry), people associated with your research whom you have met during the course of your PhD, as well as many others. Conferences, seminars, informal gatherings, and learned societies are great places to meet the academic community face to face or to broaden your horizons. Job fairs are held at universities and sometimes during conferences, where experts from industry look for potential employees as well as sometimes provide informal advice on your curriculum vitae (CV). Try to exploit these opportunities if they come your way.
A relatively recent, and highly democratic, addition to the networking system is social media, through which it is possible to meet people online from all over the world and from all walks of life. More and more professors, researchers, students, policy makers, science “celebrities”, science communicators, industry personnel, and professionals have a presence on social media, using it primarily for work-related purposes. Researchgate, LinkedIn, and Twitter are probably the most useful platforms for networking with academia, business, and the wider world, respectively. Your online profile should be fully completed and reflect your expertise, achievements, and personality. Used to greatest effect, social media will give you access to information, jobs, and influential people—its importance to you as a PhD student cannot be overestimated.
Rule 10: Leave on Good Terms
Wrap up the work in your lab, especially if you are leaving the institute. This includes any required training of new personnel in the methods and techniques you use, having lab notes in order, making it easy for other lab members to access your protocols and data, organizing and labelling your reagents and equipment, and documenting your computer code. If someone is taking over an unfinished project from you, take time to hand it over. Discuss with your supervisor to find a solution for who will do the final experiments, how to proceed with the writing of journal manuscripts, and what should be the order of authorship. If you have started a project that you want to take with you to your new lab, discuss with your supervisor how to handle possible future publications and how to agree on material transfer. If your work resulted in patents or patentable innovations, make sure you are clear about regulations concerning patents and intellectual property, both at your PhD institution and at the institution to which you are moving. Stay in touch with your former colleagues and cultivate the contacts you have made in graduate school; they are sure to be useful during the course of your career.
Acknowledgments
Jacopo Marino is grateful to colleagues from the University of Zurich for the everyday discussions that have inspired this manuscript. Melanie I. Stefan is likewise grateful for discussions on the topic with fellow predocs (and sympathetic postdocs) at the European Bioinformatics Institute. She would also like to acknowledge advice and support from Nicolas Le Novère and Susan Jones, which helped her navigate her PhD and graduate in a timely manner. She has since learnt a lot from discussions with colleagues at the California Institute of Technology, the University of Tokyo, and Harvard Medical School.
Funding Statement
The authors have received no specific funding for this article.

Navigating the First Three Months of your PhD
The decision to undertake a PhD program is a long-term commitment that requires substantial planning. The source of funding, area of specialization and the intended outcome are often in focus at the start. Navigating through a PhD is frequently compared to a journey in an unchartered territory , compelling clear direction during the first three months. Rational thinking and resourcefulness will enable smooth progression from one semester to the next and completion of your study in a pre-decided timeframe.
Read Before you Begin
The PhD experience sets a steep learning curve and the best way to engage academically is to start by reading. Read the background literature, maintain information flow in the field of specialization and gradually form your opinion or overview. To narrow down the area of research, start reading previously published information in the field, available via digital repositories . Preferably, start with the thesis and research publications of a preceding PhD researcher from your own group. Do not be overwhelmed by previous publications, however, as you will have a timeline to accomplish the tasks logically. A strong support network and reliable supervision is crucial to ensure long-term stability in PhD and in academic career. After substantial reading in the first few weeks, meet your supervisor to organize a three-month plan for your PhD research. Keep the initial research structure simple and open-ended for improvement based on feedback. Outline a basic plan of work, based on the literature you reviewed. Share your independent opinion matters too. Free templates and planners are available on several websites to aid a constructive research flow, use them to think well.
Write your opinion
Academic writing that follows substantial reading on and related to the area of interest, defines the PhD research process. A literature review of research, based on the journal articles you read and the concepts noted, will complement the initial reading. The literature review is usually short but informative, well researched and supported with citations for accuracy. Get acquainted with referencing software such as EndNote and Mendeley . Depending on the research program, the literature review may be publishable in a journal aligned to your research field. Verify eligibility for this with your supervisor, or express your interest to publish, and then follow-through with the journal guidelines. Guidelines for authors are available on the journal’s website, detailing requirements for academic writing; adhere to them from the start. At first, the academic research writing process will be daunting and will require many revisions. For clarity, keep a folder of drafts, to file major revisions and then write regularly on a daily basis . Alternatively, maintain an external writing platform, communicate your research and incrementally post your opinion. You would be surprised by the level of clarity the routine would present to your thinking process over time.
Think before you proceed
As a graduate PhD researcher, you will bear much responsibility for your research work and writing. Be aware of the impact you have on the study outlined, take time to think through your research ideas and proposed methods. Ensure the work outlined for the first three months is reproducible, based on previous publications to avoid wasting research funds. Collaborate with your peers and other researchers prior to ordering equipment and reagents for your work. At the start of a project, the outlook will be overwhelming when viewing the bigger picture alone. Set aside time to think through the proposed work before you actually conduct it. Most labs have an ordering system and an invoice procedure. Become familiar with these before placing your first order. Plenty of online resources that facilitate workflow in research are now available, including web-based lab inventories to online research assistance . It is never too early to improve your research experience. The overall outcome would make for an interesting thesis publication of your own, so think first and work accordingly.
Optimize and repeat
In the first three months of your PhD, you will most likely realize the intensity of experimental work. Bear in mind that even with adequate supervision support, you remain the researcher solely responsible for your own work. So do not be afraid to enjoy the research process as your own ideas unfold into practice. Read extensively before you begin the work. Make notes and write a short literature review to recap your opinion on the area of interest. Later when you complete the first experiments, read supporting literature again to validate any unexpected results. Ensure reproducibility of research protocols by conducting repeatable experiments in lab. Use resources constructively, even procrastinate productively with science networking , research updates and by co-creating/viewing interesting PhD documentaries online. Outreach efforts on broad platforms via writing or speech can contribute to career progression as a PhD researcher. Overall, the first three months are a preview to the long-term PhD process. The preview is a timeline of reading, writing, thinking and repeating the process with innovation, for an optimized, long-term outcome.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- PhDs & Postdocs
Whichever Universe, It’s Not So STRANGE to Be a DOCTOR of Philosophy! (It’s a Superpower, Indeed!)
“PhDs, Assemble!” Donned as a badge of honor, the “Doctor” as a prefix to your…

- Career Corner
How to Write an Exceptional Research Scholarship Motivation Letter
Haven’t heard from the scholarship committee yet? Another email of rejection? Numerous drafts, constant search…

6 Effective Tips on How to Ace Your PhD Qualifying Exam
It’s probably not your first day at the university and you are still exploring the…

Top 12 Potential PhD Viva Questions and How to Answer Them
Breathed a sigh of relief after submitting the PhD thesis you’ve burnt the midnight oil…

How to Write a Data Management Plan During Grant Application
Along with other essential requisites of a grant application, funders are increasingly mandating applicants to…
Whichever Universe, It’s Not So STRANGE to Be a DOCTOR of Philosophy! (It’s a…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

How to Write a PhD Thesis in Three Months
How much time does it take to complete writing a thesis? A year or two? Right, it might take your entire last year to complete one. From deciding the topic, conducting the research and asking for PhD Thesis Statistics Help from your seniors or professors to writing down your thesis, takes a lot of time, energy and hardwork.
What if we say that you can write your thesis in just three months? You might get shocked and many questions must have started running in your mind, isn’t it? But, yes you can definitely complete writing your PhD thesis in three months. There are two ways to achieve this goal. First, reaching out to PhD Thesis Writing Services and ask for assistance and the second way is just you need to follow the steps listed in this article.
The goal might look easy after reading the entire article, but it all depends on how dedicated and how you can take help of your colleagues in topic deciding or Phd Thesis Statistics Help.
Do not try to steer through a jungle of challenges.
Restrict yourself, frame a boundary and be determined. Determine the steps you will take to gather data and prepare a draft of the thesis within 5-6weeks. For this, deadlines should be set up, sticking to those deadlines will be beneficial. And the most important thing, you need to take care of is avoiding stuff which might set you back from achieving your deadlines such as social media.
Here’s what you need to do, to achieve your goal
Follow this steps to complete your Thesis Writing in Three Months
- Step #1: Don't doubt your abilities, tell yourself you can do this. Your perception and opinion might not match with your near ones. Therefore, it is recommended not to share with your near ones,because you might get a feeling of peer pressure. You don't need any approval or feedback from anyone, just focus on your goal.
Step #2: Prepare a short to do list of a paper. Jot down tasks you are going to do in the entire day. Work for an hour and take a 15mins break. If you are working 6hours in a day, plan your tasks accordingly in that to-do list. And stick to that strictly, there should be no exceptions.
- Step #3: Hang a bit note on your calendar of the writing task beginning date. Be excited and determined for the date to arrive and focus on your goal accomplishment.
Step #4: Give sufficient time to topic selection. The accomplishment of your three months writing task depends majorly on this. To find out a topic quickly, sit and have a brainstorming session with yourself or people into research for a week, you might also connect to a few PhD Thesis Writing Services who will help you get a topic of your interest. If you fail in choosing your topic in the alloted time, the result may be delayed as well.
- Step #5: Given below are some points which should be present in your outline that you’ll prepare. If you have something more to add, add it.
- You must be having some ideas and points related to your thesis, note it down.
Create a frame of your supporting paragraphs and arguments.
- Take snaps of your bibliography and sources, let digital applications do some work (wasting time in writing them down is not acceptable at this moment).
There must be few areas of your research that you definitely don’t want to miss out, list down those ‘must’ cover areas of your research.
- Analytical findings and final conclusions should also be written down, it is always advisable to go for a PhD Thesis Statistics Help rather than taking time to conduct the analytics part.
And lastly, while doing all this list down various other ideas that cross your mind.
Once you are done preparing the outline, you are almost there. Hardly 15-20 days away from your writing down thesis task. This step might help you cover up your speed and help you give time to things which might have taken more time than the deadline. But you still can’t rest. Writing part should occupy half of your day until completed.
Step #6: The best way to complete your thesis writing work in three months is to have your data in digital form. It makes referring and using the data quite simple and easy. You can jump on the piece of data you require at that moment. You don't have to search for it. For this purpose research needs to be carried out well in advance, once you have the data in hand your writing work becomes much easier.
Step #7: At some point of time, being a human you might feel like having a walk along a beachside, grab some coffee and chill out with friends and family. You can surely do that, provided you have been loyal to your work till date, and have completed every task as per your outline and deadlines. If you are strictly following your outline you are 50% done with your task. Feel free to reward yourself.
Step #8: Time alloted to writing your thesis must be followed. Dedicate the last 12-15 days to writing your thesis and you are almost through.
Step #9: Appoint an eminent Phd Thesis Statistics Help Professional, to have a thorough check of your analytics.
Step #10: Finally hire an esteemed PhD Thesis Writing Services and go for an editing, and then submit it after the changes made. Sit back, relax and pat yourself on the back. You have completed your thesis in just three months.
For any PhD Thesis Writing Services help: Contact us.

How Hiring an Assignment Master Can Really Help You?

How To Write a PhD Thesis in One Month?

Top 5 Websites to Access Free Journal Articles and Research Papers for Your PhD Dissertation
Worried about q/a session of your phd defense here is a complete guide to handle q/a sessions effectively.

Guidelines in Writing Scope of Study Effectively

7 Things To Know About Sky Glass, Including Release Date, Specs, And Price.

Spy Gadgets that You Can Use with Ease

Internet Marketing Software That You Can Use

5 Most Beautiful Places in World to Lessen Your Academic Stress

Strategies to Improve Listening Skills

To write a thesis on the PhD level is not a joke. As we know this will have to publish on the international level, so we should have to make care about our wording, about our data and the materials which we are using in our thesis. But if we want to do any work that is not difficult, so if we want to PhD thesis in one month then we need to make some kind of techniques in order to complete this task on time. To keep your time from wasting I am going to give some techniques which will be very helpful for you. These will also save your time and also your money. In this article, we will give you some guidelines to write your PhD thesis in one month. These guidelines are given below;
1. Get sufficient information about PhD thesis
Before writing a thesis for your institution you first have a clear idea about your thesis that why it actually is. What your professor wants to ask from you. Have you got clear idea about your research? If there is any ambiguity, then you can take help from your professor as well as from a PhD thesis writing service . At the end of the day, you have clear idea about the thesis and everything relating to it.
2. Keep perspective and follow a timetable strictly
As we know that in this world everyone wants that his research should be best and it looks quite easy and simple. There will be also no ambiguity in it. As far as your researcher is concerned he wants to get a clear idea from your preface .They are not going to read your thesis as a whole. So if someone looks your thesis he should have clear view about this.
3. Write the each section by following the timetable
The introduction and conclusion are two different parts of thesis. So do not mix these two things together. If you try to mix these two things together then you will not be able to write your thesis accurately. You must write the conclusion first and try to write introduction in the end. As conclusion is the short summary of your thesis and introduction is written lengthy. So by doing this there will be no mixture of these two and one will understand quite easily.
4. Follow the timetable with the help of the technology
As we know that this is the modern era, everyone is facilitating himself from the modern science and its vast application. While writing the PhD thesis, you can also make use of some apps. So by making the use of these apps, your thesis will be no old one and there will be a reflection of the modern technique. In this way, with the help of technology, we will be able to write the PhD thesis within one month.
So these are some techniques which you can use in order to write the Thesis in one month.
About Post Author

Related Post

How to Make A Business Plan for Your College Coursework?
Recent post, top category.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
FIGURE 8. EndNote's Cite While You Write function. 2) Intermediate documents: the thesis/dissertation proposal and grant applications. Think of your thesis or dissertation proposal and any grant applications as being a big first step toward the first chapter of your final document: the introduction.
Instead of inserting "work on thesis" into your calendar, insert measurable goals like "finish Figure 1" or "write two pages of Chapter 2.". 7. Write In Very Short Bursts. Writing in several short bursts is more efficient than writing in a few, long extended periods of time. If you ever tried to write for several hours in a row, you ...
A PhD thesis is a work of original research all students are requiured to submit in order to succesfully complete their PhD. The thesis details the research that you carried out during the course of your doctoral degree and highlights the outcomes and conclusions reached. The PhD thesis is the most important part of a doctoral research degree ...
Strive to be understood and avoid unnecessary words. Be persistent and eager - Writing a doctoral thesis becomes easier if you are consistent and dedicated. All other things being equal, your attitude will ultimately determine your success. Have patience and work hard. Create work you will be proud of for a lifetime.
Rule 2: prioritise papers and the thesis will follow. Papers are the priority. They are more useful to you and to your PI. But this advice isn't motivated by self-interest. If you go into the viva and the work in your thesis is already peer reviewed and published, it's harder for the examiners to criticise it.
Think carefully about your writing. Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense. Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency.
8) Get feedback on the whole thesis. "We often get feedback on individual chapters but plan to get feedback from your supervisor on the PhD as a whole to make sure it all hangs together nicely ...
Set a target deadline for completion: Another top writing tip for PhD students is to set a delivery date and stay committed to it. You can also share this goal with a broader set of people (peers, supervisor, friends, etc.), who will act as catalysts on the journey of writing your PhD thesis first draft and in the time you've set for yourself.
Gather data and information for your study. Analyze your data. Write, write, and write some more. Ideally, aim to write for a minimum of 30 minutes a day. Defend your thesis. Finish. Completing your PhD paper on time is definitely possible. Knowing the tips and tricks of the trade can help you to get on your way towards a life in academia.
Writing. BookPDF Available. HOW TO WRITE YOUR Phd THESIS: THE EASY HANDBOOK. January 2023. Publisher: Journal of Contemporary Research in Business Administration and Economic Sciences (JCR-BAES ...
I procrastinated 3 months away and did 90% of the research and writing in about one month for my 40 page minimum master's thesis. You can see a flurry of activity on my github in the 1-1.5 weeks of writing. I'm now doing a PhD straight out of my master's. You'll be okay.
Last month, we offered suggestions on how to prepare for your thesis defence: Decide whether you need more research results, sketch out a plan for those experiments and for writing thesis chapters, and--importantly--get your supervisor's support for that plan.Now it's time to wrap things up in the lab and start writing. Writing a thesis is easier said than done, of course, and you have plenty ...
the order you want to write the different pieces of information that make your theory. the notes you made about your studies, the design, the participants, the instruments, the procedure. the results of any statistical analysis you made. the ideas for and the issues you want to raise in the discussion. It also includes any notes you do not want ...
Step 5: Write the First Draft (Days 12-23): Begin writing your paper based on the outline you created. Aim to complete a specific number of pages or sections each day, keeping in mind the deadline. Focus on expressing your ideas and arguments clearly, avoiding perfectionism during this initial draft. Step 6: Revise and Edit (Days 24-25): Once ...
7. Targets and consistency. I set myself a target of 3 months, broken down into targets for each chapter. This would give me about 3 months in reserve before the final absolute deadline. I had a daily minimum target of 500 words, which I knew I could meet even on the least productive days.
Prioritize sleep and exercise. Work smartly. Plan, reflect, and adapt. 1. Commit publicly. The first thing to do is to decide on a realistic date. The emphasis is on realistic. Make sure that you ...
Before writing one should observe each diagram for some time and make a list of observations in the form of key words. The more one has understood the information content of a figure; the better will be the fluency of writing. ... The weightage should be in favour of the PhD candidate, so that the thesis can ethically be better defended before ...
Here are two ways that I managed to do it. Write. Even when you have zero motivation. This applies especially to those who are in the situation I was in. Since the aim is to fill your content ...
Then, if you do secure a job, the time left for writing up your thesis, completing experiments, and wrapping up your lab work will be seriously limited. It is exceedingly hard to write a doctoral thesis in the evenings after work or on the weekends, so in case you are offered a job before you have finished the PhD, consider seriously how this ...
In that sense, writing your PhD outside of the designated framework is a bit like digging a well with a spoon. It can be done, but it is not too efficient. On top of that (as others have said already), at many institutions, the written thesis is only one requirement among others to be awarded a title.
After substantial reading in the first few weeks, meet your supervisor to organize a three-month plan for your PhD research. Keep the initial research structure simple and open-ended for improvement based on feedback. Outline a basic plan of work, based on the literature you reviewed. Share your independent opinion matters too.
Dedicate the last 12-15 days to writing your thesis and you are almost through. Step #9: Appoint an eminent Phd Thesis Statistics Help Professional, to have a thorough check of your analytics. Step #10: Finally hire an esteemed PhD Thesis Writing Services and go for an editing, and then submit it after the changes made.
You must write the conclusion first and try to write introduction in the end. As conclusion is the short summary of your thesis and introduction is written lengthy. So by doing this there will be no mixture of these two and one will understand quite easily. 4. Follow the timetable with the help of the technology.