Unit 2 Family Materials
Fractions as quotients and fraction multiplication.
In this unit, students solve problems involving division of whole numbers with answers that are fractions (which could be in the form of mixed numbers). They develop an understanding of fractions as the division of the numerator by the denominator, that is \(a \div b = \frac{a}{b}\) . They then solve problems that involve the multiplication of a whole number by a fraction or mixed number.

Section A: Fractions as Quotients
In this section, students learn that fractions are quotients and can be interpreted as division of the numerator by the denominator. Students draw and analyze tape diagrams that represent sharing situations. Through the context of first sharing 1, then sharing more than 1, then sharing a number of things with increasingly more people, students notice patterns and begin to understand that in general \(\frac{a}{b} = a \div b\) . For example, students use the diagram below to show 4 objects being shared equally by 3 people, or \(4 \div 3\) , which can also be written as a fraction, \(\frac{4}{3}\) .

Section B: Fractions of Whole Numbers
In this section, students make connections between multiplication and division and use visual representations that can show both operations. For example, the diagram above can also represent 4 groups of \(\frac{1}{3}\) , or \(4 \times \frac{1}{3}\) . Students discover ways of finding the product of a fraction and whole number that make sense to them and connect the product to the context and diagrams. They multiply a whole number by a fraction, \(\frac{a}{b} \times q\) .
Section C: Area and Fractional Side Lengths
In this section, students use what they know about the area of rectangles with whole number side lengths to find the area of rectangles that have one whole number side length and one fractional side length.
The expression \(6 \times 1\) represents the area of a rectangle that is 6 units by 1 unit.
In the same way, \(6 \times \frac{2}{3}\) represents the area of a rectangle that is 6 units by \(\frac{2}{3}\) unit.
In addition, students see that the expressions \(6\times\frac{2}{3}\) , \(6\times2\times\frac{1}{3}\) , and \(12\times\frac{1}{3}\) can all represent the area of this same diagram.
Students analyze diagrams where one side length is a mixed number, for example a rectangle that is 2 by \(3\frac{2}{5}\) . They decompose the shaded region to show the whole units and the fractional units.
To find the area represented by this diagram, students may see two rectangles: a rectangle that is 2 units by 3 units and a rectangle that is 2 units by \(\frac{2}{5}\) unit. While they may recognize that the area can be represented as \(2 \times 3\frac{2}{5}\) , students who see the decomposed rectangle may write \((2 \times 3) + (2 \times \frac{2}{5})\) to find the area.
Try it at home!
Near the end of the unit, ask your student the following questions:
Write as many expressions as you can that represent this diagram:
Questions that may be helpful as they work:
- How are the two problems similar? How are they different?
- How does your expression represent the diagram?
- How did you break up the rectangle to help you solve for the entire area?
- What are the side lengths of the rectangle?
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Everyday Math Grade 5 Answers Unit 2 Whole Number Place Value and Operations
Everyday mathematics 5th grade answer key unit 2 whole number place value and operations, everyday mathematics grade 5 home link 2.1 answers.
Solving Place-Value Riddles Solve the number riddles. Question 1. I have 5 digits. My 5 is worth 50,000. My 8 is worth 8,000. One of my 6s is worth 60. The other is worth 10 times as much. My other digit is a 0. What number am I? Answer: The number is 58,660 Explanation: Here I have 5 digits number. My 5 is worth 50,000 ; Ten thousand place. My 8 is worth 8,000 ; Thousands place. One of my 6s worth is 60. The number is written as 66; Tens place. My other digit is 0. 0 is in ones place. By adding the above numbers we got the 5 digit number. The number is 58,660.
Question 2. I have 5 digits. My 9 is worth 9 ∗ 10,000. My 2 is worth 2 thousand. One of my 7s is worth 70. The other is worth 10 times as much. My other digit is a 6. What number am I? Answer: The number is 92,776 Explanation: Here I have 5 digits number. My 9 is worth 9 ∗ 10,000 = 90,000; Ten thousand place. My 2 is worth 2,000; Thousands place. One of my 7s worth is 70. The number is written as 77; Tens place. My other digit is 6. 6 is in ones place. By adding the above numbers we got the 5 digit number. The number is 92,776.
Question 3. I have 4 digits. My 7 is worth 7 ∗ 1,000. My 2 is worth 200. One of my 4s is worth 40. The other is worth \(\frac{1}{10}\) as much. What number am I? Answer: The number is 7,244 Explanation: I have 4 digits number. My 7 is worth 7 ∗ 1,000 = 7,000; Thousands place. My 2 is worth 200. Hundreds place. One of my 4s is worth 40. The number is written as 44; tens place. By adding the above numbers we got the 4 digit number. The number is 7,244.
Question 4. I have 6 digits. One of my 3s is worth 300,000. The other is worth \(\frac{1}{10}\) as much. My 6 is worth 600. The rest of my digits are zeros. What number am I? Answer: The number is 330,600 Explanation: I have 6 digits number. My 3s is worth 300,000; The number is written as 330,000. My 6 is worth 600; Hundreds place. The rest of my digits are zeroes. By adding the above numbers we got the 6 digit number. The number is 330,600.
Question 5. I have 5 digits. My 4s are worth 4 [10,000s] and 4 ∗ 10. One of my 3s is worth 3,000. The other is worth \(\frac{1}{10}\) as much. My other digit is a 2. What number am I? Answer: The number is 43,342 Explanation: I have 5 digits number. My 4s is worth 4[10,000s]=40,000; and 4 ∗ 10= 40. My 3s is worth 3,000. The number is written as 3,300. The other digit is 2. keep 2 in ones place. By adding the above numbers we got the 5 digit number. The number is 43,342.
Question 6. I am the largest 7-digit number you can write with the digits 3, 6, 9, 4, 0, 8, and 2. What number am I? Answer: The largest 7-digit number with the above digits is 9,864,320 Explanation: We can write the largest seven digits number with the above digits. Write the above numbers in descending order. The largest seven digit number is 9,864,320.
Practice Solve. Question 7. 4 ∗ (3 + 2) = _______ Answer: 4 ∗(3 + 2) = 20 4 ∗ (5) = 20 Explanation: In the above expression we can observe two arithmetic operations. One is multiplication and other one is addition. First we have to perform addition operation and then multiplication operation. An addition sentence is a mathematical expression that shows two or more values added together. First add three and two then we got five. Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Then multiply four and five then we got 20.
Question 8. 100 – [(\(\frac{25}{5}\)) ∗ 10] = ________ Answer: 100 – [(25/5) ∗ 10] = 50 100 – [(5) ∗ 10] = 50 100 -[50] = 50 Explanation: In the above expression we can observe three arithmetic operations. One is subtraction, division, and multiplication. First we have to perform division operation and then we have to perform multiplication operation and then subtraction operation. The division is a method of distributing a group of things into equal parts. It is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, which gives a fair result of sharing. The division is an operation inverse of multiplication. First divide 25/5 which is equal to the five. Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Second multiply 5 with 10 then we got 50. Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. Third Subtract the result 50 from 100 then we got 50.
Question 9. {(\(\frac{24}{6}\)) + (\(\frac{36}{6}\))} + 2 = ________ Answer: {(24/6) + (36/6)} + 2 = 12 {(4) + (6)} + 2 = 12 {10} + 2 = 12 Explanation: In the above expression we can observe two arithmetic operations. One is division, and other is addition. First we have to perform division operation and then addition operation. The division is a method of distributing a group of things into equal parts. It is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, which gives a fair result of sharing. The division is an operation inverse of multiplication. First divide 24/6 then we got four; and also divide 36/6 which is equal to the six. An addition sentence is a mathematical expression that shows two or more values added together. After completion of division operation perform addition operation. First add four and six then we got ten. Then add ten with two which results twelve.
Question 10. (3 ∗ 5) – (2 ∗ 5) = _________ Answer: (3 ∗ 5) – (2 ∗ 5)= 5 (15) – (10) = 5 Explanation: In the above expression we can observe two arithmetic operations. One is Multiplication, and other is Subtraction. First we have to perform multiplication operation and then subtraction operation. Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. First multiply these two numbers 3 and 5 then we got 15. Second multiply these two numbers 2 and 5 then we got 10. Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract 10 from 15 then we got 5.
Question 11. (3 ∗ 7) + (2 ∗ 5) = _______ Answer: (3 ∗ 7) + (2 ∗ 5) = 31 (21) + (10) = 31 Explanation: In the above expression we can observe two arithmetic operations. One is Multiplication, and other is addition. First we have to perform multiplication operation and then addition operation. Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. First multiply these two numbers 3 and 7 then we got 21. Second multiply these two numbers 2 and 5 then we got 10. An addition sentence is a mathematical expression that shows two or more values added together. ADD the two numbers 21 and 10 then we got 31.
Question 12. (\(\frac{56}{7}\)) ∗ (\(\frac{42}{7}\)) = _________ Answer: ([56/7] ∗ ([42/7]) = 48 ([8] ∗ ([6]) = 48 Explanation: In the above expression we can observe two arithmetic operations. One is division, and other is multiplication. First we have to perform division operation and then we have to perform multiplication operation. The division is a method of distributing a group of things into equal parts. It is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, which gives a fair result of sharing. The division is an operation inverse of multiplication. First divide 56/7 which is equal to the 8. Second divide 42/7 then we got 6. Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiply these two numbers 8 and 6 then we got 48.
Everyday Math Grade 5 Home Link 2.2 Answer Key
Evaluating Expressions with Exponential Notation Write each number in standard notation. Question 1. 10 6 _________ Answer: 10 1 =10 10 2 = 100 10 3 = 1,000 10 4 = 10,000 10 5 = 1,00,000 10 6 = 1,000,000 Explanation: Standard notation is also known as scientific notation where a large number is written in the form of power of 10. The number 1,000,000 is written as 10 6 .
Question 2. 3 ∗ 10 6 __________ Answer: 3 ∗ 10 6 = 3,000,000 3 ∗ 1,000,000 = 3,000,000 Explanation: Standard notation is also known as scientific notation where a large number is written in the form of power of 10. The number 1,000,000 is written as 10 6 . Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiply 3 with 1,000,000 then we got 3,000,000.
Question 3. 10 3 __________ Answer: 10 3 = 1,000 Explanation: Standard notation is also known as scientific notation where a large number is written in the form of power of 10. The number 1,000 is written as 10 3 .
Question 4. 24 ∗ 10 3 __________ Answer: 24 ∗ 10 3 = 24,000 Explanation: Standard notation is also known as scientific notation where a large number is written in the form of power of 10. The number 1,000 is written as 10 3 . Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiply 24 with 1,000 then we got 24,000.
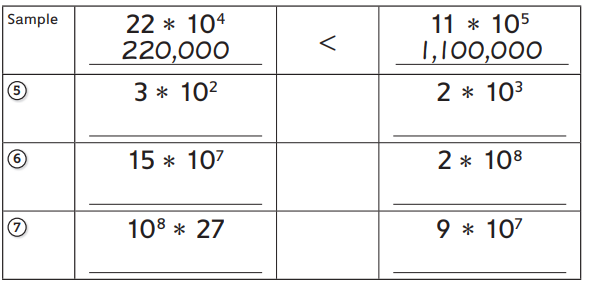
Question 9. How much will Jackie pay for shipping? $ __________ Answer: Charges to ship the box of hockey is $26. Explanation: Charges to ship a box having volume = $20 up to 10 cubic feet. Since this box has the volume = 16 Cubic feet. So charges to 10 cubic feet will be $20. Remaining volume of the box = 16 – 10 = 6 cubic feet. Now charges for rest volume = $1 x 6 =$6. Total charges= $20 +$6 = $26. Therefore charges to ship the box of hockey is $26.
Everyday Mathematics Grade 5 Home Link 2.3 Answers
Solving Problems Using Powers of 10
Use estimation to solve. Renee is in charge of the school carnival for 380 students. She has 47 boxes of prizes. Each box has 22 prizes. She wants to make sure she has enough prizes for each student to win 2 prizes. Question 1. Does Renee have enough prizes? Explain how you solved the problem. Answer: Yes Renee have enough prizes for each student to win 2 prizes. Explanation: To estimate the number of prizes Renee has, I rounded 47 boxes of prizes to 50 and 22 prizes to 20. I multiplied 50 and 20 to get 1,000. If each student wins 2 prizes, that is 380 x 2. I can round 380 students to 400 students. Multiply 400 x 2 = 800. Here Renee needs only 800 prizes. So she has enough prizes for each student to win 2 prizes.
Question 2. Does Renee have enough prizes for each student to win 3 prizes? Explain. Answer: No, Renee doesn’t have enough prizes for each student to win 3 prizes. Explanation: If each student wins 3 prizes, Renee needs 380 x 3 prizes. If i rounded 380 to 400, then 400 x 3 = 1,200 prizes. Renee only has about 1,000 prizes. So she doesn’t have enough prizes for each student to win 3 prizes.
Practice Write each number in standard notation. Question 3. 42 ∗ 10 6 _________ Answer: 42 ∗ 10 6 42 ∗ 1,000,000 42,000,000 Explanation: Standard notation is also known as scientific notation where a large number is written in the form of power of 10. The number 1,000,000 is written as 10 3 . Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiply these two numbers 42 ∗ 1,000,000 then we got 42,000,000.
Question 4. 8 ∗ 10 1 ___________ Answer: 8 ∗ 10 1 8 ∗ 10 80 Explanation: Standard notation is also known as scientific notation where a large number is written in the form of power of 10. The number 10 is written as 10 1 . Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiply these two numbers 8 ∗ 10 then we got 80.
Write each number in exponential notation. Question 5. 30,000 _________ Answer: 30,000 = 3 ∗ 10 4 Explanation: Standard notation is also known as scientific notation where a large number is written in the form of power of 10. The number 10,000 is written as 10 4 . Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiply these two numbers 3 ∗ 10,000 then we got 30,000.
Question 6. 70,000,000 ________ Answer: 70,000,000 = 7 ∗ 10 7 Explanation: Standard notation is also known as scientific notation where a large number is written in the form of power of 10. The number 10,000,000 is written as 10 7 . Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiply these two numbers 7 ∗ 10,000,000 then we got 70,000,000.
Everyday Math Grade 5 Home Link 2.4 Answer Key
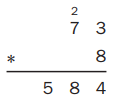
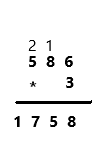
U.S. Traditional Multiplication Family Note Today your child began learning a multiplication strategy called U.S. traditional multiplication. This strategy may be familiar to you, as it is the multiplication strategy that many adults learned when they were in school. Your child will be learning to use U.S. traditional multiplication with larger and larger numbers over the next week or two. U.S. traditional multiplication is often challenging for students to learn. Do not expect your child to use it easily right away. There will be plenty of opportunities for practice throughout the school year. As your child uses U.S. traditional multiplication to solve the problems below, encourage him or her to check the answers by solving the problems in another way or using an estimate.
Practice Write each number in expanded form. Question 3. 397 _____________ Answer: The expanded form of 397 = 300 + 90 + 7 Explanation: The expanded form of the numbers helps to determine the place value of each digit in the given number. It means that the expansion of numbers is based on the place value. The expanded form splits the number, and it represents the number in units, tens, hundreds and thousands form. The Expanded form of 397 = 300 + 90 + 7.
Question 4. 1,268 ____________ Answer: The expanded form of 1,268 = 1 ∗ 1000 + 2 ∗ 100 + 6 ∗ 10 + 8 ∗ 1 Explanation: The expanded form of the numbers helps to determine the place value of each digit in the given number. It means that the expansion of numbers is based on the place value. The expanded form splits the number, and it represents the number in units, tens, hundreds and thousands form. The Expanded form of 1,268 = 1 ∗ 1000 + 2 ∗ 100 + 6 ∗ 10 + 8 ∗ 1.
Question 5. 4,082 ____________ Answer: The expanded form of 4,082 = 4000 + 80 + 2 Explanation: The expanded form of the numbers helps to determine the place value of each digit in the given number. It means that the expansion of numbers is based on the place value. The expanded form splits the number, and it represents the number in units, tens, hundreds and thousands form. The Expanded form of 4,082 = 4000 + 80 + 2.
Question 6. 29,141 __________ Answer: The expanded form of 29,141 = (2 ∗10 4 ) + (9 ∗ 10 3 ) +(1 ∗ 10 2 ) + (4 ∗ 10 1 ) + (1 ∗ 10 0 ) Explanation: The expanded form of the numbers helps to determine the place value of each digit in the given number. It means that the expansion of numbers is based on the place value. The expanded form splits the number, and it represents the number in units, tens, hundreds and thousands form. The Expanded form of 29,141 = (2 ∗10 4 ) + (9 ∗ 10 3 ) +(1 ∗ 10 2 ) + (4 ∗ 10 1 ) + (1 ∗ 10 0 ).
Everyday Mathematics Grade 5 Home Link 2.5 Answers
Multiplication Top-It: Larger Numbers Make a set of number cards by writing the numbers 0–9on slips of paper or index cards. Make four of each number card. You can also use the 2–9 cards and the aces from a deck of regular playing cards. Explain the rules of Multiplication Top-It: Larger Numbers to someone at home.
Multiplication Top-It: Larger Numbers 1. Each player draws 4 cards. Use 3 of the cards to make a 3-digit number. Use the other card to make a 1-digit number. 2. Multiply the numbers. Compare your product to the other player’s product. The player with the larger product takes all the cards. 3. Keep playing until you run out of cards. The player with more cards wins the game. To play by yourself: Keep the cards if your product is more than 1,000. Discard the cards if your product is less than 1,000. If you have more than 20 cards at the end of the game, you win.
Practice Write each power of 10 using exponential notation. Question 3. 100 = __________ Answer: 100 = 10 2 Explanation: It is the shortest way of expressing a large number. It is also known as the Scientific Notation. The number 100 can be written as power of 10. The exponential notation of 100 is 10 2 .
Question 4. 10,000 = __________ Answer: 10,000 = 10 4 Explanation: It is the shortest way of expressing a large number. It is also known as the Scientific Notation. The number 10,000 can be written as power of 10. The exponential notation of 10,000 is 10 4 .
Question 5. 100,000,000 = __________ Answer: 100,000,000 = 10 8 Explanation: It is the shortest way of expressing a large number. It is also known as the Scientific Notation. The number 100,000,000 can be written as power of 10. The exponential notation of 100,000,000 = 10 8 .
Question 6. 1,000 = __________ Answer: 1,000 = 10 3 Explanation: It is the shortest way of expressing a large number. It is also known as the Scientific Notation. The number 1,000 can be written as power of 10. The exponential notation of 1,000 = 10 3 .

Everyday Math Grade 5 Home Link 2.6 Answer Key
Converting Units Ask someone at home to help you find the following:
- a 1-cup measuring cup or a coffee mug
- a large bowl
- a stopwatch or clock
- a 12-inch ruler or tape measure
- a food package with a weight given in pounds

b. Convert your measurement to fluid ounces. _________ fluid ounces Answer: 1 cup = 8 fluid ounces. 3 cups = 24 fluid ounces. Explanation: In the above image we can observe 1 cup = 8 fluid ounces. The larger bowl takes 3 cups of water to fill the bowl. The process of adding a number to itself a certain number of times is called as multiplication. Multiply 1 x 3 = 3 cups; which is equal to 24 fluid ounces.
Question 2. a. Time or estimate how long it takes you to walk around your block in minutes. _________ minutes Answer: It takes 15 minutes to walk around my block. Explanation: To walk around my block it takes 15 minutes to complete one round.
b. Convert your measurement to seconds. _________ seconds Answer: 1 minute = 60 seconds 15 minutes = 900 seconds Explanation: It takes 15 minutes to walk around our block. we have to convert minutes into seconds. 1 minute = 60 seconds. The process of adding a number to itself a certain number of times is called as multiplication. Multiply 1 x 15 = 15 minutes; which is equal to 900 seconds.
Question 3. a. Measure the length of your bed to the nearest foot. _________ feet Answer: The length of my bed is 3 feet. Explanation: Measuring the length of my bed is 3 feet long.
b. Convert your measurement to inches. _________ inches Answer: 1 foot = 12 inches. 3 foot = 36 inches. Explanation: Measuring the length of my bed is 3 feet long. Convert the measurement into inches. The process of adding a number to itself a certain number of times is called as multiplication. Multiply 1 x 3 = 3 foot; which is equal to 36 inches.
Question 4. a. Record the weight on the food package in pounds. _________ pounds Answer: The weight on the food package is 5 pounds. Explanation: Measuring the weight on the food package is 5 pounds.
b. Convert the weight to ounces. _________ ounces Answer: 1 pound = 16 ounces. 5 pounds = 80 ounces. Explanation: The weight on the food package is 5 pounds. The process of adding a number to itself a certain number of times is called as multiplication. Multiply 1 x 5 = 5 pounds; which is equal to 80 ounces.
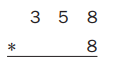
Everyday Mathematics Grade 5 Home Link 2.7 Answers
Estimating and Multiplying Make an estimate for each multiplication problem. Write a number sentence to show how you estimated. Then solve ONLY the problems that have answers that are more than 1,000. Use your estimates to help you decide which problems to solve.
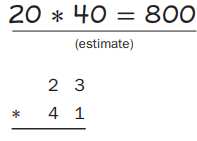
Practice Solve. Question 7. a. 7 ∗ 10,000 = ________ b. 7 ∗ 10 4 = ________ Answer: a. 7 ∗ 10,000 = 70,000 b. 7 ∗ 10 4 = 70,000 Explanation: Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiplication is one of the basic arithmetic operations. a. By multiplying these two numbers we got 7 ∗ 10,000 = 70,000. b. By multiplying these two numbers we got 7 ∗ 10 4 = 70,000.
Question 8. a. 2 ∗ 400 = ________ b. 2 ∗ 4 ∗ 10 2 = ________ Answer: a. 2 ∗ 400 = 800 b. 2 ∗ 4 ∗ 10 2 = 8 ∗ 10 2 = 800 Explanation: Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiplication is one of the basic arithmetic operations. a. By multiplying these two numbers we got 2 ∗ 400 = 800. b. By multiplying these three numbers we got 2 ∗ 4 ∗ 10 2 = 8 ∗ 10 2 = 800.
Question 9. a. 6,000 ∗ 300 = ________ b. 6 ∗ 10 3 ∗ 3 ∗ 10 2 = ________ Answer: a. 6,000 ∗ 300 = 1,800,000 b. 6 ∗ 10 3 ∗ 3 ∗ 10 2 = 18 ∗ 10 5 = 1,800,000 Explanation: Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiplication is one of the basic arithmetic operations. a. By multiplying these two numbers we got 6,000 ∗ 300 =1,800,000. b. By multiplying these four numbers we got 6 ∗ 10 3 ∗ 3 ∗ 10 2 = 18 ∗ 10 5 = 1,800,000.
Everyday Math Grade 5 Home Link 2.8 Answer Key
Choosing Multiplication Strategies

Question 4. The distance from Chicago, Illinois, to Boston , Massachusetts, by plane is 851 miles. A pilot flew from Chicago to Boston 37 times in one year. How many miles was that? Estimate: ___________ Answer: ________ miles Answer: Estimate : 850 ∗ 40 = 34,000 The distance for Chicago to Boston = 851 miles. A pilot flew from Chicago to Boston 37 times in one year. So, 851 ∗ 37 = 31,487 miles Explanation: The distance from Chicago, Illinois, to Boston , Massachusetts, by plane is 851 miles. A pilot flew from Chicago to Boston 37 times in one year. So we have to multiply 851 miles with 37 times in one year. Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. So, 851 ∗ 37 = 31,487 miles.
Question 5. It takes 246 floor tiles to cover the floor of a classroom. There are 31 same-size classrooms in the school. How many floor tiles does it take to cover all the classroom floors? Estimate: ___________ Answer: ________ miles Answer: Estimate : 250 ∗ 30 = 7,500 The floor of a classroom covers 246 floor tiles. There are 31 same-size classrooms in the school. So, 246 ∗ 31 = 7,626 Explanation: The floor of a classroom covers 246 floor tiles. There are 31 same-size classrooms in the school. So we have to multiply 246 floor tiles with 31 same size classroom in the school. Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. So, 246 ∗ 31 = 7,626. Question 6. Explain to someone at home which strategy you used to solve each problem and why. Answer: Here I used U.S traditional multiplication Strategy to solve the problems.
Practice Solve. Question 7. a. 5 ∗ 300,000 = ________ b. 5 ∗ 3 ∗ 10 5 =____________ Answer: a. 5 ∗ 300,000 = 1,500,000 b. 5 ∗ 3 ∗ 10 5 = 15 ∗ 10 5 = 1,500,000 Explanation: Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiplication is one of the basic arithmetic operations. a. By multiplying these two numbers we got 5 ∗ 300,000 = 1,500,000. b. By multiplying these three numbers we got 5 ∗ 3 ∗ 10 5 = 15 ∗ 10 5 = 1,500,000.
Question 8. a. 40 ∗ 6,000 = _________ b. 4 ∗ 10 ∗ 6 ∗ 10 3 = _________ Answer: a. 40 ∗ 6,000 = 240,000 b. 4 ∗ 10 ∗ 6 ∗ 10 3 = 24 ∗ 10 4 = 240,000 Explanation: Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiplication is one of the basic arithmetic operations. a. By multiplying these two numbers we got 40 ∗ 6,000 = 240,000. b. By multiplying these four numbers we got 4 ∗ 10 ∗ 6 ∗ 10 3 = 24 ∗ 10 4 = 240,000.
Question 9. a. 20,000 ∗ 700 = _________ b. 2 ∗10 4 ∗ 7 ∗ 10 2 = __________ Answer: a. 20,000 ∗ 700 = 14,000,000 b. 2 ∗ 10 4 ∗ 7 ∗ 10 2 = 14 ∗ 10 6 = 14,000,000 Explanation: Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiplication is one of the basic arithmetic operations. a. By multiplying these two numbers we got 20,000 ∗ 700 = 14,000,000. b. By multiplying these four numbers we got 2 ∗ 10 4 ∗ 7 ∗ 10 2 = 14 ∗ 10 6 = 14,000,000.
Everyday Mathematics Grade 5 Home Link 2.9 Answers
Using Multiples of 10 to Estimate Question 1. Estimate about how many meters Martin swims in June if he swims about 200 meters per day. There are 30 days in June. Show how you made your estimate. About ________ meters Answer: He swims about 200 meters per day. There are 30 days in June. So 200 ∗ 30 = 6,000 meters. About 6,000 meters. Explanation: Martin swims about 200 meters per day. There are 30 days in June. So multiply 200 meters and 30 days. Multiplication of two numbers is the repeated addition of one number to the number of times equal to the other number. Multiplication is one of the basic arithmetic operations. So 200 ∗ 30 = 6,000 meters.
Question 2. Estimate how many days it would take Martin to swim 60,000 meters. Show how you made your estimate. About ________ days Answer: Martin swim 60,000 meters. We have to calculate the days. If he swim 200 meters per day. Then 200 ∗ 300 = 60,000 meters. About 300 days. Explanation: Martin swim 60,000 meters. We have to calculate the days. If he swim 200 meters per day. Then 200 ∗ 300 = 60,000 meters. Martin takes about 300 days to swim 60,000 meters.
Everyday Math Grade 5 Home Link 2.10 Answer Key
Mental Division Practice Use multiplication and division facts to solve the following problems mentally. Remember: Write an equivalent name for the dividend by breaking it into smaller parts that are easier to divide. Example: 72 divided by 4
- Write some multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40
- Write an equivalent name by breaking 72 into smaller numbers that are multiples of 4. Equivalent name for 72: 40 + 32
- Use the equivalent name to divide mentally. Ask yourself: How many 4s are in 40? (10) How many 4s are in 32? (8) Think: How many total 4s are in 72? (10 [4s] + 8 [4s] = 18 [4s], so 72 ÷ 4 = 18)
Question 1. 57 ÷ 3 → ? Multiples of 3: __________ Equivalent name for 57: __________ 57 ÷ 3 → __________ Answer: Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 Equivalent name for 57: 30 + 27 57 ÷ 3 → 19 Explanation: 1. First write some multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 2. Then write an equivalent name by breaking 57 into smaller numbers that are multiples of 3. 3. Equivalent name for 57: 30 + 27 4. Use the equivalent name to divide mentally. First we have to check how many 3s are in 30 and how many 3s are in 27. There are (10) 3s in 30 and (9) 3s in 27. 5. Then check how many total 3s are in 57. There are 10[3s] +9[3s] = 19[3s]. So 57 ÷ 3 = 19.
Question 2. 96 ÷ 8 → ? Multiples of 8: __________ Equivalent name for 96: __________ 96 ÷ 8 → __________ Answer: Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80 Equivalent name for 96: 80 + 16 96 ÷ 8 → 12 Explanation: 1. First write some multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80 2. Then write an equivalent name by breaking 96 into smaller numbers that are multiples of 8. 3. Equivalent name for 96: 80 + 16 4. Use the equivalent name to divide mentally. First we have to check how many 8s are in 80 and how many 8s are in 16. There are (10) 8s in 80 and (2) 8s in 16. 5. Then check how many total 8s are in 96. There are 10[8s] +2[8s] = 12[3s]. So 96 ÷ 8 = 12.
Everyday Mathematics Grade 5 Home Link 2.11 Answers
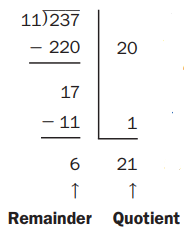
Question 1. You could have started solving the example problem by taking away 110 from 237. If this was your first step, what would have been the first partial quotient, and why? Answer: 10 is the first partial quotient, because there are 10 [11s] in 110. Explanation: The division is a method of distributing a group of things into equal parts. It is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic. In the example problem, if we are taking away 110 from 237 then 10 is the first partial quotient, because there are 10 [11s] in 110.
Everyday Math Grade 5 Home Link 2.12 Answer Key
Division with Multiples Here is how to use partial-quotients division with a list of multiples to solve \(\frac{2106}{19}\). First, list some multiples of 19: 100 ∗ 19 = 1,900 50 ∗ 19 = 950 20 ∗ 19 = 380 10 ∗ 19 = 190 5 ∗ 19 = 95
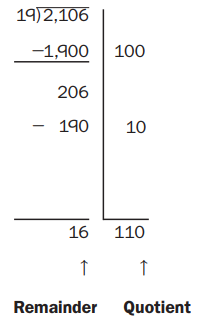
Complete the list of multiples below. Then use it to help you solve \(\frac{1954}{18}\). Question 1. 100 ∗ __________ = ___________ 50 ∗ __________ = __________ 20 ∗ __________ = __________ 10 ∗ __________ = __________ 5 ∗ __________ = __________ 2 ∗ __________ = __________ Answer: 100 ∗ 18 = 1,800 50 ∗ 18 = 900 20 ∗ 18 = 360 10 ∗ 18 = 180 5 ∗ 18 = 90 2 ∗ 18 = 36 Explanation: A multiple of a number is a number that is the product of a given number and some other natural number. Multiples can be observed in a multiplication table. Multiples of 18 are 100 ∗ 18 = 1,800, 50 ∗ 18 = 900, 20 ∗ 18 = 360, 10 ∗ 18 = 180,5 ∗ 18 = 90, 2 ∗ 18 = 36
Everyday Mathematics Grade 5 Home Link 2.13 Answers
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Unit 2: Linear Funcöons Homework 5: Solving Systems of Equations ... ** This is a 2-page document! ** Directions: Solve each system of equaäons by elimination. Clearly identify your soluton. ... 8y+26 -3 = 46) 6. 8. 14x+7y=-7 l.ÐI.þ Gina Wilson (All 2015 . Title: Unit 2 - Linear Functions & Systems Author: Amanda Appel Created Date: 9/1 ...
Unit 5: Systems of Equations & Inequalities Homework 1: Solving Systems by Graphing ** This is a 2-page document! ** Solve each system of equations by graphing. Clearly identify your solution. -16 — 6y = 30 9x + = 12 +4 v = —12 O Gina Wilson (All Things Algebra', LLC), 2012-2016
Homework 5-2 Divide. 1 39 2,886 _ 5 28 _ 2,520 2 81 _ 7,533 6 33 _ 1,287 3 68 4,967 _ 7 46 _ 1,426 4 72 _ 4,968 8 55 _ 990 Solve. 9 The lunchroom has enough seats for 168 students. Each class has 24 students. How many classes can eat in the lunchroom at the same time? 10 Mrs. Randall bought tickets to the art museum for all the
Unit 2: Functions & Their Graphs Homework 5: Average Rate of Change ** This is a 2-page document! ** Directions: Given the function below, find the average rate of change on each interval. fix) fix) 2 3 4 - co 13) 1b Round your 0] 7] 0] 2 (00) Directions: Find the average rate of change of each function on the given interval.
Unit 5: Polynomial Functons Homework 1: Monomials & Polynomials Direcäons: Simplify the monomials below. Final answers should positive only. 1. Subtract -3n2 from -7n2 C-1nÒ-G3nZ) two monomials with a product of 3. (—4a3b2)2 • (3a2b) 15? y -6x7y (3xy)2 8. The side length of a cu can be repræented by the expression 215. If the side length is
Unit 5 - Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities. This unit begins by ensuring that students understand that solutions to equations are points that make the equation true, while solutions to systems make all equations (or inequalities) true. Graphical and substitution methods for solving systems are reviewed before the development of the ...
Standards Alignment - Powered by EdGate. Table of Contents for Common Core Algebra I. Unit 1 - The Building Blocks of Algebra. Unit 2 - Linear Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities. Unit 3 - Functions. Unit 4 - Linear Functions and Arithmetic Sequences. Unit 5 - Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities.
Unit 3 Vocabulary - 6th Grade. Teacher 20 terms. SpectacularMrsHouser. Preview. Unit 2B Vocabulary - 6th Grade. Teacher 22 terms. Vickie_White4 ... you must break into seperate cases (case 1 and 2) Solving absolute value equations: Case 1. rewrite problem without absolute value and solve. Solving absolute value equations: Case 2. rewritw ...
1. Sort to line up the variable and equal signs. 2. Multiply one or both equations by a constant to create the additive inverse of the variable. 3. add or subtract one equation eliminate one of the variables. 4. Solve for variables that remain. 5. substitute new value back into the equation to get the other variable. 6.
Unit 5 Homework 2 Answer Key.pdf - Doc Preview. Pages 2. Total views 100+ University of Illinois, Chicago. MATH. MATH Pure Math. magjohn. 1/15/2020. View full document. Students also studied. Unit 9 Homework 3 Answer Key.pdf. University of Illinois, Chicago. MATH Pure Math. Homework 5 Answer Key.pdf.
HW #3. 33. For f(x), D: -2 £ x £ 5 and R: -3 £ y £ 3 For f-1(x), D: -3 £ x £ 3 and R: -2 £ y £ 5 34a. L(x) = x2 - 1 and R(x) = 3(x + 2) 34b. 30 34c. order does matter - show by substituting numbers; output is 224 if x = 3 for L(R(x)) 35a. the system has no solution 35b. the graphs do not intersect because they are parallel lines 37a ...
Topic 1: Quadratic Expressions and Equations • Solve quadratic equations by inspection, taking square roots, completing the square, the quadratic formula, and factoring, as appropriate to the initial form of the equation. (cK-12 Flexbook Unit 2 Topic 1 SLT 1) • Identify zeros of quadratic functions when suitable factorizations are available, and use the zeros to construct a rough graph ...
Grade 5 Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8. Unit 2 Family Materials. Fractions as Quotients and Fraction Multiplication. Fractions as Quotients and Fraction Multiplication. In this unit, students solve problems involving division of whole numbers with answers that are fractions (which could be in the form of mixed numbers).
Deductive Reasoning
Increased , -bqet-her MULTIPLICATION , Date: Class: SUBTRACTION Itss -Hun S(.Lbfrac+tÅ. decreased b9 DIVISON divided sc and Watch out for subtraction! Phrases like indicate that you need to reverse the order! Directions: Translate each expression. Words "five more than a numbed' "the quotient of a number and -2" "twice a number" "a number ...
Unit 2: Homework In Lessons 1-10, homework focuses on research reading, determining the meaning of unfamiliar words using context, common affixes and roots, and reference materials. Students also write paragraphs about character reactions to threats to human rights in Esperanza Rising, and answer questions about what happened in each chapter.
Question: Review Unit 2: Algebraic Expressions 5. Write an expression that represents the perimeter of the figure shown below. Simplify completely. Show your work lla Sa 36 6. Let B represent the bill for dinner at your favorite restaurant. Write an algebraic expression to represent the total amount paid for dimer if you decide to leave a 15% ...
Standards Alignment - Powered by EdGate. Table of Contents and Standards Alignment for Common Core Algebra II. Unit 1 - Algebraic Essentials Review. Unit 2 - Functions as the Cornerstones of Algebra II. Unit 3 - Linear Functions, Equations, and Their Algebra. Unit 4 - Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Unit 5 - Sequences and Series.
Unit 2: Algebraic Expressions Homework 1 1: Adding & Subtracting Polynomials -1 +17a 6. k -17-2k3 +14k2 4. 3p+2p —16p 2. +25-2w — 2..VXJ +2.5 5. —6 + 8m2 —4m + 9m Directions: Find each sum/difference. Write all answers in standard form. 7. ... Unit 2 - Algebraic Expressions Key
true way asl Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
LESSON/HOMEWORK. LESSON VIDEO. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE LESSON. EDITABLE KEY. Lesson 2 Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences. LESSON/HOMEWORK. LESSON VIDEO. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE LESSON. ... Unit 5 - Mid-Unit Quiz (After Lesson #3) - Form D ASSESSMENT. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE ASSESSMENT. EDITABLE KEY.
Add the 2 ten from the first step 54 tens + 2 tens = 56 tens, or 5 hundreds and 6 tens. Multiply the ones 3 ∗ 3 ones = 9 ones. Write 9 in tens place below the 6. Then multiply the tens 3 ∗ 6 = 18 tens or 1 thousand and 8 hundreds. Keep the 8 below the 5 in hundreds place and 1 in thousands place.