- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 14 December 2021

Bullying at school and mental health problems among adolescents: a repeated cross-sectional study
- Håkan Källmén 1 &
- Mats Hallgren ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0599-2403 2
Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health volume 15 , Article number: 74 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
96k Accesses
13 Citations
37 Altmetric
Metrics details
To examine recent trends in bullying and mental health problems among adolescents and the association between them.
A questionnaire measuring mental health problems, bullying at school, socio-economic status, and the school environment was distributed to all secondary school students aged 15 (school-year 9) and 18 (school-year 11) in Stockholm during 2014, 2018, and 2020 (n = 32,722). Associations between bullying and mental health problems were assessed using logistic regression analyses adjusting for relevant demographic, socio-economic, and school-related factors.
The prevalence of bullying remained stable and was highest among girls in year 9; range = 4.9% to 16.9%. Mental health problems increased; range = + 1.2% (year 9 boys) to + 4.6% (year 11 girls) and were consistently higher among girls (17.2% in year 11, 2020). In adjusted models, having been bullied was detrimentally associated with mental health (OR = 2.57 [2.24–2.96]). Reports of mental health problems were four times higher among boys who had been bullied compared to those not bullied. The corresponding figure for girls was 2.4 times higher.
Conclusions
Exposure to bullying at school was associated with higher odds of mental health problems. Boys appear to be more vulnerable to the deleterious effects of bullying than girls.
Introduction
Bullying involves repeated hurtful actions between peers where an imbalance of power exists [ 1 ]. Arseneault et al. [ 2 ] conducted a review of the mental health consequences of bullying for children and adolescents and found that bullying is associated with severe symptoms of mental health problems, including self-harm and suicidality. Bullying was shown to have detrimental effects that persist into late adolescence and contribute independently to mental health problems. Updated reviews have presented evidence indicating that bullying is causative of mental illness in many adolescents [ 3 , 4 ].
There are indications that mental health problems are increasing among adolescents in some Nordic countries. Hagquist et al. [ 5 ] examined trends in mental health among Scandinavian adolescents (n = 116, 531) aged 11–15 years between 1993 and 2014. Mental health problems were operationalized as difficulty concentrating, sleep disorders, headache, stomach pain, feeling tense, sad and/or dizzy. The study revealed increasing rates of adolescent mental health problems in all four counties (Finland, Sweden, Norway, and Denmark), with Sweden experiencing the sharpest increase among older adolescents, particularly girls. Worsening adolescent mental health has also been reported in the United Kingdom. A study of 28,100 school-aged adolescents in England found that two out of five young people scored above thresholds for emotional problems, conduct problems or hyperactivity [ 6 ]. Female gender, deprivation, high needs status (educational/social), ethnic background, and older age were all associated with higher odds of experiencing mental health difficulties.
Bullying is shown to increase the risk of poor mental health and may partly explain these detrimental changes. Le et al. [ 7 ] reported an inverse association between bullying and mental health among 11–16-year-olds in Vietnam. They also found that poor mental health can make some children and adolescents more vulnerable to bullying at school. Bayer et al. [ 8 ] examined links between bullying at school and mental health among 8–9-year-old children in Australia. Those who experienced bullying more than once a week had poorer mental health than children who experienced bullying less frequently. Friendships moderated this association, such that children with more friends experienced fewer mental health problems (protective effect). Hysing et al. [ 9 ] investigated the association between experiences of bullying (as a victim or perpetrator) and mental health, sleep disorders, and school performance among 16–19 year olds from Norway (n = 10,200). Participants were categorized as victims, bullies, or bully-victims (that is, victims who also bullied others). All three categories were associated with worse mental health, school performance, and sleeping difficulties. Those who had been bullied also reported more emotional problems, while those who bullied others reported more conduct disorders [ 9 ].
As most adolescents spend a considerable amount of time at school, the school environment has been a major focus of mental health research [ 10 , 11 ]. In a recent review, Saminathen et al. [ 12 ] concluded that school is a potential protective factor against mental health problems, as it provides a socially supportive context and prepares students for higher education and employment. However, it may also be the primary setting for protracted bullying and stress [ 13 ]. Another factor associated with adolescent mental health is parental socio-economic status (SES) [ 14 ]. A systematic review indicated that lower parental SES is associated with poorer adolescent mental health [ 15 ]. However, no previous studies have examined whether SES modifies or attenuates the association between bullying and mental health. Similarly, it remains unclear whether school related factors, such as school grades and the school environment, influence the relationship between bullying and mental health. This information could help to identify those adolescents most at risk of harm from bullying.
To address these issues, we investigated the prevalence of bullying at school and mental health problems among Swedish adolescents aged 15–18 years between 2014 and 2020 using a population-based school survey. We also examined associations between bullying at school and mental health problems adjusting for relevant demographic, socioeconomic, and school-related factors. We hypothesized that: (1) bullying and adolescent mental health problems have increased over time; (2) There is an association between bullying victimization and mental health, so that mental health problems are more prevalent among those who have been victims of bullying; and (3) that school-related factors would attenuate the association between bullying and mental health.
Participants
The Stockholm school survey is completed every other year by students in lower secondary school (year 9—compulsory) and upper secondary school (year 11). The survey is mandatory for public schools, but voluntary for private schools. The purpose of the survey is to help inform decision making by local authorities that will ultimately improve students’ wellbeing. The questions relate to life circumstances, including SES, schoolwork, bullying, drug use, health, and crime. Non-completers are those who were absent from school when the survey was completed (< 5%). Response rates vary from year to year but are typically around 75%. For the current study data were available for 2014, 2018 and 2020. In 2014; 5235 boys and 5761 girls responded, in 2018; 5017 boys and 5211 girls responded, and in 2020; 5633 boys and 5865 girls responded (total n = 32,722). Data for the exposure variable, bullied at school, were missing for 4159 students, leaving 28,563 participants in the crude model. The fully adjusted model (described below) included 15,985 participants. The mean age in grade 9 was 15.3 years (SD = 0.51) and in grade 11, 17.3 years (SD = 0.61). As the data are completely anonymous, the study was exempt from ethical approval according to an earlier decision from the Ethical Review Board in Stockholm (2010-241 31-5). Details of the survey are available via a website [ 16 ], and are described in a previous paper [ 17 ].
Students completed the questionnaire during a school lesson, placed it in a sealed envelope and handed it to their teacher. Student were permitted the entire lesson (about 40 min) to complete the questionnaire and were informed that participation was voluntary (and that they were free to cancel their participation at any time without consequences). Students were also informed that the Origo Group was responsible for collection of the data on behalf of the City of Stockholm.
Study outcome
Mental health problems were assessed by using a modified version of the Psychosomatic Problem Scale [ 18 ] shown to be appropriate for children and adolescents and invariant across gender and years. The scale was later modified [ 19 ]. In the modified version, items about difficulty concentrating and feeling giddy were deleted and an item about ‘life being great to live’ was added. Seven different symptoms or problems, such as headaches, depression, feeling fear, stomach problems, difficulty sleeping, believing it’s great to live (coded negatively as seldom or rarely) and poor appetite were used. Students who responded (on a 5-point scale) that any of these problems typically occurs ‘at least once a week’ were considered as having indicators of a mental health problem. Cronbach alpha was 0.69 across the whole sample. Adding these problem areas, a total index was created from 0 to 7 mental health symptoms. Those who scored between 0 and 4 points on the total symptoms index were considered to have a low indication of mental health problems (coded as 0); those who scored between 5 and 7 symptoms were considered as likely having mental health problems (coded as 1).
Primary exposure
Experiences of bullying were measured by the following two questions: Have you felt bullied or harassed during the past school year? Have you been involved in bullying or harassing other students during this school year? Alternatives for the first question were: yes or no with several options describing how the bullying had taken place (if yes). Alternatives indicating emotional bullying were feelings of being mocked, ridiculed, socially excluded, or teased. Alternatives indicating physical bullying were being beaten, kicked, forced to do something against their will, robbed, or locked away somewhere. The response alternatives for the second question gave an estimation of how often the respondent had participated in bullying others (from once to several times a week). Combining the answers to these two questions, five different categories of bullying were identified: (1) never been bullied and never bully others; (2) victims of emotional (verbal) bullying who have never bullied others; (3) victims of physical bullying who have never bullied others; (4) victims of bullying who have also bullied others; and (5) perpetrators of bullying, but not victims. As the number of positive cases in the last three categories was low (range = 3–15 cases) bully categories 2–4 were combined into one primary exposure variable: ‘bullied at school’.
Assessment year was operationalized as the year when data was collected: 2014, 2018, and 2020. Age was operationalized as school grade 9 (15–16 years) or 11 (17–18 years). Gender was self-reported (boy or girl). The school situation To assess experiences of the school situation, students responded to 18 statements about well-being in school, participation in important school matters, perceptions of their teachers, and teaching quality. Responses were given on a four-point Likert scale ranging from ‘do not agree at all’ to ‘fully agree’. To reduce the 18-items down to their essential factors, we performed a principal axis factor analysis. Results showed that the 18 statements formed five factors which, according to the Kaiser criterion (eigen values > 1) explained 56% of the covariance in the student’s experience of the school situation. The five factors identified were: (1) Participation in school; (2) Interesting and meaningful work; (3) Feeling well at school; (4) Structured school lessons; and (5) Praise for achievements. For each factor, an index was created that was dichotomised (poor versus good circumstance) using the median-split and dummy coded with ‘good circumstance’ as reference. A description of the items included in each factor is available as Additional file 1 . Socio-economic status (SES) was assessed with three questions about the education level of the student’s mother and father (dichotomized as university degree versus not), and the amount of spending money the student typically received for entertainment each month (> SEK 1000 [approximately $120] versus less). Higher parental education and more spending money were used as reference categories. School grades in Swedish, English, and mathematics were measured separately on a 7-point scale and dichotomized as high (grades A, B, and C) versus low (grades D, E, and F). High school grades were used as the reference category.
Statistical analyses
The prevalence of mental health problems and bullying at school are presented using descriptive statistics, stratified by survey year (2014, 2018, 2020), gender, and school year (9 versus 11). As noted, we reduced the 18-item questionnaire assessing school function down to five essential factors by conducting a principal axis factor analysis (see Additional file 1 ). We then calculated the association between bullying at school (defined above) and mental health problems using multivariable logistic regression. Results are presented as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (Cis). To assess the contribution of SES and school-related factors to this association, three models are presented: Crude, Model 1 adjusted for demographic factors: age, gender, and assessment year; Model 2 adjusted for Model 1 plus SES (parental education and student spending money), and Model 3 adjusted for Model 2 plus school-related factors (school grades and the five factors identified in the principal factor analysis). These covariates were entered into the regression models in three blocks, where the final model represents the fully adjusted analyses. In all models, the category ‘not bullied at school’ was used as the reference. Pseudo R-square was calculated to estimate what proportion of the variance in mental health problems was explained by each model. Unlike the R-square statistic derived from linear regression, the Pseudo R-square statistic derived from logistic regression gives an indicator of the explained variance, as opposed to an exact estimate, and is considered informative in identifying the relative contribution of each model to the outcome [ 20 ]. All analyses were performed using SPSS v. 26.0.
Prevalence of bullying at school and mental health problems
Estimates of the prevalence of bullying at school and mental health problems across the 12 strata of data (3 years × 2 school grades × 2 genders) are shown in Table 1 . The prevalence of bullying at school increased minimally (< 1%) between 2014 and 2020, except among girls in grade 11 (2.5% increase). Mental health problems increased between 2014 and 2020 (range = 1.2% [boys in year 11] to 4.6% [girls in year 11]); were three to four times more prevalent among girls (range = 11.6% to 17.2%) compared to boys (range = 2.6% to 4.9%); and were more prevalent among older adolescents compared to younger adolescents (range = 1% to 3.1% higher). Pooling all data, reports of mental health problems were four times more prevalent among boys who had been victims of bullying compared to those who reported no experiences with bullying. The corresponding figure for girls was two and a half times as prevalent.
Associations between bullying at school and mental health problems
Table 2 shows the association between bullying at school and mental health problems after adjustment for relevant covariates. Demographic factors, including female gender (OR = 3.87; CI 3.48–4.29), older age (OR = 1.38, CI 1.26–1.50), and more recent assessment year (OR = 1.18, CI 1.13–1.25) were associated with higher odds of mental health problems. In Model 2, none of the included SES variables (parental education and student spending money) were associated with mental health problems. In Model 3 (fully adjusted), the following school-related factors were associated with higher odds of mental health problems: lower grades in Swedish (OR = 1.42, CI 1.22–1.67); uninteresting or meaningless schoolwork (OR = 2.44, CI 2.13–2.78); feeling unwell at school (OR = 1.64, CI 1.34–1.85); unstructured school lessons (OR = 1.31, CI = 1.16–1.47); and no praise for achievements (OR = 1.19, CI 1.06–1.34). After adjustment for all covariates, being bullied at school remained associated with higher odds of mental health problems (OR = 2.57; CI 2.24–2.96). Demographic and school-related factors explained 12% and 6% of the variance in mental health problems, respectively (Pseudo R-Square). The inclusion of socioeconomic factors did not alter the variance explained.
Our findings indicate that mental health problems increased among Swedish adolescents between 2014 and 2020, while the prevalence of bullying at school remained stable (< 1% increase), except among girls in year 11, where the prevalence increased by 2.5%. As previously reported [ 5 , 6 ], mental health problems were more common among girls and older adolescents. These findings align with previous studies showing that adolescents who are bullied at school are more likely to experience mental health problems compared to those who are not bullied [ 3 , 4 , 9 ]. This detrimental relationship was observed after adjustment for school-related factors shown to be associated with adolescent mental health [ 10 ].
A novel finding was that boys who had been bullied at school reported a four-times higher prevalence of mental health problems compared to non-bullied boys. The corresponding figure for girls was 2.5 times higher for those who were bullied compared to non-bullied girls, which could indicate that boys are more vulnerable to the deleterious effects of bullying than girls. Alternatively, it may indicate that boys are (on average) bullied more frequently or more intensely than girls, leading to worse mental health. Social support could also play a role; adolescent girls often have stronger social networks than boys and could be more inclined to voice concerns about bullying to significant others, who in turn may offer supports which are protective [ 21 ]. Related studies partly confirm this speculative explanation. An Estonian study involving 2048 children and adolescents aged 10–16 years found that, compared to girls, boys who had been bullied were more likely to report severe distress, measured by poor mental health and feelings of hopelessness [ 22 ].
Other studies suggest that heritable traits, such as the tendency to internalize problems and having low self-esteem are associated with being a bully-victim [ 23 ]. Genetics are understood to explain a large proportion of bullying-related behaviors among adolescents. A study from the Netherlands involving 8215 primary school children found that genetics explained approximately 65% of the risk of being a bully-victim [ 24 ]. This proportion was similar for boys and girls. Higher than average body mass index (BMI) is another recognized risk factor [ 25 ]. A recent Australian trial involving 13 schools and 1087 students (mean age = 13 years) targeted adolescents with high-risk personality traits (hopelessness, anxiety sensitivity, impulsivity, sensation seeking) to reduce bullying at school; both as victims and perpetrators [ 26 ]. There was no significant intervention effect for bullying victimization or perpetration in the total sample. In a secondary analysis, compared to the control schools, intervention school students showed greater reductions in victimization, suicidal ideation, and emotional symptoms. These findings potentially support targeting high-risk personality traits in bullying prevention [ 26 ].
The relative stability of bullying at school between 2014 and 2020 suggests that other factors may better explain the increase in mental health problems seen here. Many factors could be contributing to these changes, including the increasingly competitive labour market, higher demands for education, and the rapid expansion of social media [ 19 , 27 , 28 ]. A recent Swedish study involving 29,199 students aged between 11 and 16 years found that the effects of school stress on psychosomatic symptoms have become stronger over time (1993–2017) and have increased more among girls than among boys [ 10 ]. Research is needed examining possible gender differences in perceived school stress and how these differences moderate associations between bullying and mental health.
Strengths and limitations
Strengths of the current study include the large participant sample from diverse schools; public and private, theoretical and practical orientations. The survey included items measuring diverse aspects of the school environment; factors previously linked to adolescent mental health but rarely included as covariates in studies of bullying and mental health. Some limitations are also acknowledged. These data are cross-sectional which means that the direction of the associations cannot be determined. Moreover, all the variables measured were self-reported. Previous studies indicate that students tend to under-report bullying and mental health problems [ 29 ]; thus, our results may underestimate the prevalence of these behaviors.
In conclusion, consistent with our stated hypotheses, we observed an increase in self-reported mental health problems among Swedish adolescents, and a detrimental association between bullying at school and mental health problems. Although bullying at school does not appear to be the primary explanation for these changes, bullying was detrimentally associated with mental health after adjustment for relevant demographic, socio-economic, and school-related factors, confirming our third hypothesis. The finding that boys are potentially more vulnerable than girls to the deleterious effects of bullying should be replicated in future studies, and the mechanisms investigated. Future studies should examine the longitudinal association between bullying and mental health, including which factors mediate/moderate this relationship. Epigenetic studies are also required to better understand the complex interaction between environmental and biological risk factors for adolescent mental health [ 24 ].
Availability of data and materials
Data requests will be considered on a case-by-case basis; please email the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Olweus D. School bullying: development and some important challenges. Ann Rev Clin Psychol. 2013;9(9):751–80. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185516 .
Article Google Scholar
Arseneault L, Bowes L, Shakoor S. Bullying victimization in youths and mental health problems: “Much ado about nothing”? Psychol Med. 2010;40(5):717–29. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291709991383 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Arseneault L. The long-term impact of bullying victimization on mental health. World Psychiatry. 2017;16(1):27–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20399 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Moore SE, Norman RE, Suetani S, Thomas HJ, Sly PD, Scott JG. Consequences of bullying victimization in childhood and adolescence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Psychiatry. 2017;7(1):60–76. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v7.i1.60 .
Hagquist C, Due P, Torsheim T, Valimaa R. Cross-country comparisons of trends in adolescent psychosomatic symptoms—a Rasch analysis of HBSC data from four Nordic countries. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2019;17(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-019-1097-x .
Deighton J, Lereya ST, Casey P, Patalay P, Humphrey N, Wolpert M. Prevalence of mental health problems in schools: poverty and other risk factors among 28 000 adolescents in England. Br J Psychiatry. 2019;215(3):565–7. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2019.19 .
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Le HTH, Tran N, Campbell MA, Gatton ML, Nguyen HT, Dunne MP. Mental health problems both precede and follow bullying among adolescents and the effects differ by gender: a cross-lagged panel analysis of school-based longitudinal data in Vietnam. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13033-019-0291-x .
Bayer JK, Mundy L, Stokes I, Hearps S, Allen N, Patton G. Bullying, mental health and friendship in Australian primary school children. Child Adolesc Ment Health. 2018;23(4):334–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/camh.12261 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hysing M, Askeland KG, La Greca AM, Solberg ME, Breivik K, Sivertsen B. Bullying involvement in adolescence: implications for sleep, mental health, and academic outcomes. J Interpers Violence. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260519853409 .
Hogberg B, Strandh M, Hagquist C. Gender and secular trends in adolescent mental health over 24 years—the role of school-related stress. Soc Sci Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.112890 .
Kidger J, Araya R, Donovan J, Gunnell D. The effect of the school environment on the emotional health of adolescents: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2012;129(5):925–49. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-2248 .
Saminathen MG, Låftman SB, Modin B. En fungerande skola för alla: skolmiljön som skyddsfaktor för ungas psykiska välbefinnande. [A functioning school for all: the school environment as a protective factor for young people’s mental well-being]. Socialmedicinsk tidskrift [Soc Med]. 2020;97(5–6):804–16.
Google Scholar
Bibou-Nakou I, Tsiantis J, Assimopoulos H, Chatzilambou P, Giannakopoulou D. School factors related to bullying: a qualitative study of early adolescent students. Soc Psychol Educ. 2012;15(2):125–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-012-9179-1 .
Vukojevic M, Zovko A, Talic I, Tanovic M, Resic B, Vrdoljak I, Splavski B. Parental socioeconomic status as a predictor of physical and mental health outcomes in children—literature review. Acta Clin Croat. 2017;56(4):742–8. https://doi.org/10.20471/acc.2017.56.04.23 .
Reiss F. Socioeconomic inequalities and mental health problems in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Soc Sci Med. 2013;90:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.04.026 .
Stockholm City. Stockholmsenkät (The Stockholm Student Survey). 2021. https://start.stockholm/aktuellt/nyheter/2020/09/presstraff-stockholmsenkaten-2020/ . Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
Zeebari Z, Lundin A, Dickman PW, Hallgren M. Are changes in alcohol consumption among swedish youth really occurring “in concert”? A new perspective using quantile regression. Alc Alcohol. 2017;52(4):487–95. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agx020 .
Hagquist C. Psychometric properties of the PsychoSomatic Problems Scale: a Rasch analysis on adolescent data. Social Indicat Res. 2008;86(3):511–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-007-9186-3 .
Hagquist C. Ungas psykiska hälsa i Sverige–komplexa trender och stora kunskapsluckor [Young people’s mental health in Sweden—complex trends and large knowledge gaps]. Socialmedicinsk tidskrift [Soc Med]. 2013;90(5):671–83.
Wu W, West SG. Detecting misspecification in mean structures for growth curve models: performance of pseudo R(2)s and concordance correlation coefficients. Struct Equ Model. 2013;20(3):455–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705511.2013.797829 .
Holt MK, Espelage DL. Perceived social support among bullies, victims, and bully-victims. J Youth Adolscence. 2007;36(8):984–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-006-9153-3 .
Mark L, Varnik A, Sisask M. Who suffers most from being involved in bullying-bully, victim, or bully-victim? J Sch Health. 2019;89(2):136–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/josh.12720 .
Tsaousis I. The relationship of self-esteem to bullying perpetration and peer victimization among schoolchildren and adolescents: a meta-analytic review. Aggress Violent Behav. 2016;31:186–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2016.09.005 .
Veldkamp SAM, Boomsma DI, de Zeeuw EL, van Beijsterveldt CEM, Bartels M, Dolan CV, van Bergen E. Genetic and environmental influences on different forms of bullying perpetration, bullying victimization, and their co-occurrence. Behav Genet. 2019;49(5):432–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-019-09968-5 .
Janssen I, Craig WM, Boyce WF, Pickett W. Associations between overweight and obesity with bullying behaviors in school-aged children. Pediatrics. 2004;113(5):1187–94. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.113.5.1187 .
Kelly EV, Newton NC, Stapinski LA, Conrod PJ, Barrett EL, Champion KE, Teesson M. A novel approach to tackling bullying in schools: personality-targeted intervention for adolescent victims and bullies in Australia. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020;59(4):508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2019.04.010 .
Gunnell D, Kidger J, Elvidge H. Adolescent mental health in crisis. BMJ. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k2608 .
O’Reilly M, Dogra N, Whiteman N, Hughes J, Eruyar S, Reilly P. Is social media bad for mental health and wellbeing? Exploring the perspectives of adolescents. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;23:601–13.
Unnever JD, Cornell DG. Middle school victims of bullying: who reports being bullied? Aggr Behav. 2004;30(5):373–88. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.20030 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the Department for Social Affairs, Stockholm, for permission to use data from the Stockholm School Survey.
Open access funding provided by Karolinska Institute. None to declare.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Stockholm Prevents Alcohol and Drug Problems (STAD), Center for Addiction Research and Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Solna, Sweden
Håkan Källmén
Epidemiology of Psychiatric Conditions, Substance Use and Social Environment (EPiCSS), Department of Global Public Health, Karolinska Institutet, Level 6, Solnavägen 1e, Solna, Sweden
Mats Hallgren
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
HK conceived the study and analyzed the data (with input from MH). HK and MH interpreted the data and jointly wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mats Hallgren .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
As the data are completely anonymous, the study was exempt from ethical approval according to an earlier decision from the Ethical Review Board in Stockholm (2010-241 31-5).
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Principal factor analysis description.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Källmén, H., Hallgren, M. Bullying at school and mental health problems among adolescents: a repeated cross-sectional study. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health 15 , 74 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-021-00425-y
Download citation
Received : 05 October 2021
Accepted : 23 November 2021
Published : 14 December 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-021-00425-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mental health
- Adolescents
- School-related factors
- Gender differences
Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health
ISSN: 1753-2000
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Understanding alternative bullying perspectives through research engagement with young people.

- School of Education and Social Care, Faculty of Health, Education, Medicine and Social Care, Anglia Ruskin University, Chelmsford, United Kingdom
Bullying research has traditionally been dominated by largescale cohort studies focusing on the personality traits of bullies and victims. These studies focus on bullying prevalence, risk and protective factors, and negative outcomes. A limitation of this approach is that it does not explain why bullying happens. Qualitative research can help shed light on these factors. This paper discusses the findings from four mainly qualitative research projects including a systematic review and three empirical studies involving young people to various degrees within the research process as respondents, co-researchers and commissioners of research. Much quantitative research suggests that young people are a homogenous group and through the use of surveys and other large scale methods, generalizations can be drawn about how bullying is understood and how it can be dealt with. Findings from the studies presented in this paper, add to our understanding that young people appear particularly concerned about the role of wider contextual and relational factors in deciding if bullying has happened. These studies underscore the relational aspects of definitions of bullying and, how the dynamics of young people’s friendships can shift what is understood as bullying or not. Moreover, to appreciate the relational and social contexts underpinning bullying behaviors, adults and young people need to work together on bullying agendas and engage with multiple definitions, effects and forms of support. Qualitative methodologies, in particular participatory research opens up the complexities of young lives and enables these insights to come to the fore. Through this approach, effective supports can be designed based on what young people want and need rather than those interpreted as supportive through adult understanding.
Introduction
Research on school bullying has developed rapidly since the 1970s. Originating in social and psychological research in Norway, Sweden, and Finland, this body of research largely focusses on individualized personality traits of perpetrators and victims ( Olweus, 1995 ). Global interest in this phenomenon subsequently spread and bullying research began in the United Kingdom, Australia, and the United States ( Griffin and Gross, 2004 ). Usually quantitative in nature, many studies examine bullying prevalence, risk and protective factors, and negative outcomes ( Patton et al., 2017 ). Whilst quantitative research collates key demographic information to show variations in bullying behaviors and tendencies, this dominant bullying literature fails to explain why bullying happens. Nor does it attempt to understand the wider social contexts in which bullying occurs. Qualitative research on the other hand, in particular participatory research, can help shed light on these factors by highlighting the complexities of the contextual and relational aspects of bullying and the particular challenges associated with addressing it. Patton et al. (2017) in their systematic review of qualitative methods used in bullying research, found that the use of such methods can enhance academic and practitioner understanding of bullying.
In this paper, I draw on four bullying studies; one systematic review of both quantitative and qualitative research ( O’Brien, 2009 ) and three empirical qualitative studies ( O’Brien and Moules, 2010 ; O’Brien, 2016 , 2017 ) (see Table 1 below). I discuss how participatory research methodologies, to varying degrees, were used to facilitate bullying knowledge production among teams of young people and adults. Young people in these presented studies were consequently involved in the research process along a continuum of involvement ( Bragg and Fielding, 2005 ). To the far left of the continuum, young people involved in research are referred to as “active respondents” and their data informs teacher practice. To the middle of the continuum sit “students as co-researchers” who work with teachers to explore an issue which has been identified by that teacher. Finally to the right, sit “students as researchers” who conduct their own research with support from teachers. Moving from left to right of the continuum shows a shift in power dynamics between young people and adults where a partnership develops. Young people are therefore recognized as equal to adults in terms of what they can bring to the project from their own unique perspective, that of being a young person now.
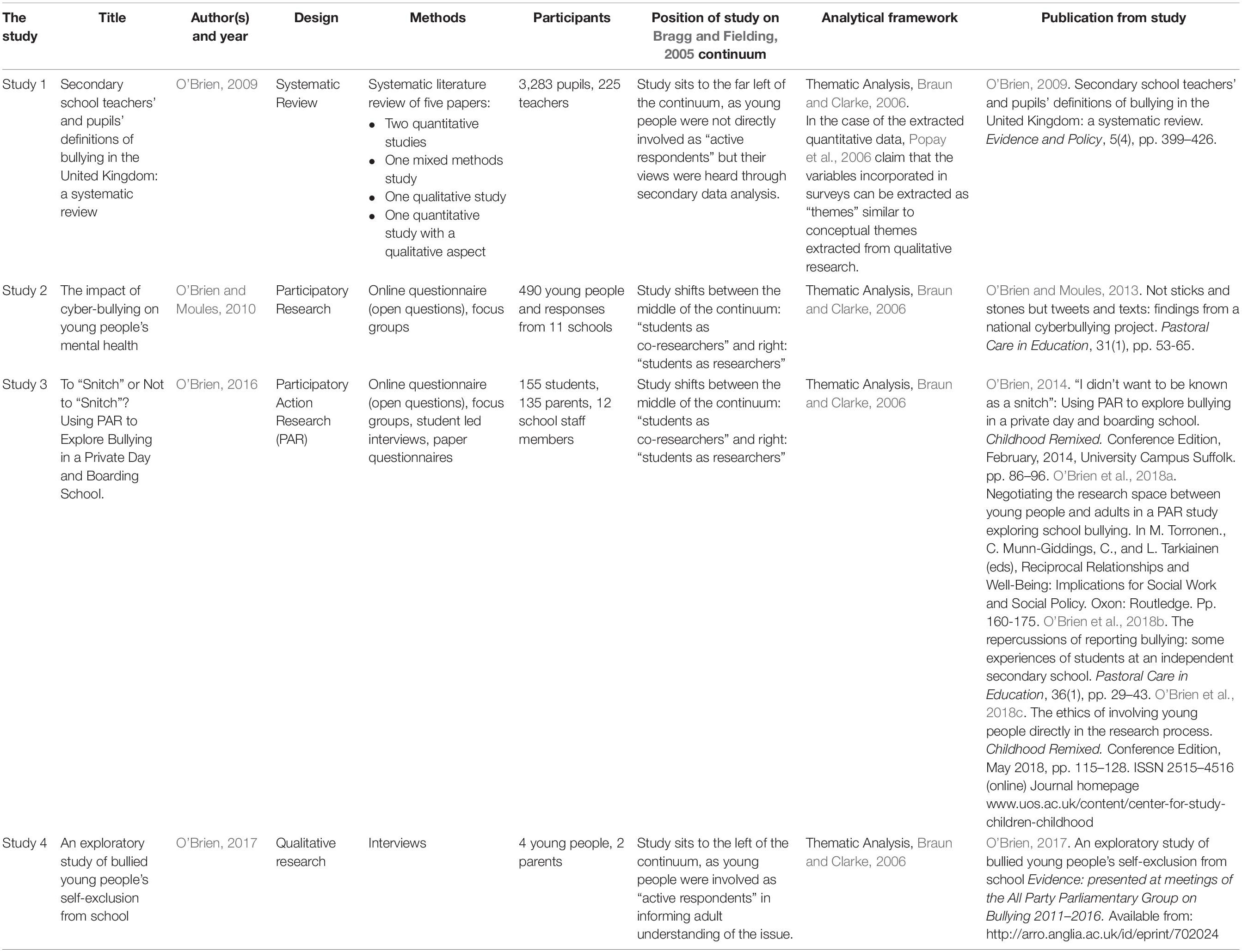
Table 1. The studies.
In this paper, I advocate for the active involvement of young people in the research process in order to enhance bullying knowledge. Traditional quantitative studies have a tendency to homogenize young people by suggesting similarity in thinking about what constitutes bullying. However, qualitative studies have demonstrated that regardless of variables, young people understand bullying in different ways so there is a need for further research that starts from these perspectives and focusses on issues that young people deem important. Consequently, participatory research allows for the stories of the collective to emerge without losing the stories of the individual, a task not enabled through quantitative approaches.

What Is Bullying?
Researching school bullying has been problematic and is partly related to the difficulty in defining it ( Espelage, 2018 ). Broadly speaking, bullying is recognized as aggressive, repeated, intentional behavior involving an imbalance of power aimed toward an individual or group of individuals who cannot easily defend themselves ( Vaillancourt et al., 2008 ). In more recent times, “traditional” bullying behaviors have been extended to include cyber-bullying, involving the use of the internet and mobile-phones ( Espelage, 2018 ). Disagreements have been noted in the literature about how bullying is defined by researchers linked to subject discipline and culture. Some researchers for example, disagree about the inclusion or not of repetition in definitions ( Griffin and Gross, 2004 ) and these disagreements have had an impact on interpreting findings and prevalence rates. However, evidence further suggests that young people also view bullying in different ways ( Guerin and Hennessy, 2002 ; Cuadrado-Gordillo, 2012 ; Eriksen, 2018 ). Vaillancourt et al. (2008) explored differences between researchers and young people’s definitions of bullying, and found that children’s definitions were usually spontaneous, and did not always encompass the elements of repetition, power imbalance and intent. They concluded, that children need to be provided with a bullying definition so similarities and comparisons can be drawn. In contrast, Huang and Cornell (2015) found no evidence that the inclusion of a definition effected prevalence rates. Their findings, they suggest, indicate that young people use their own perceptions of bullying when answering self-report questionnaires and they are not influenced by an imposed definition.
Nevertheless, differences in children and young people’s bullying definitions are evident in the research literature and have been explained by recourse to age and stage of development ( Smith et al., 2002 ) and their assumed lack of understanding about what constitutes bullying ( Boulton and Flemington, 1996 ). Naylor et al. (2001) for example, found that younger children think similarly in their definitions of bullying, while Smith et al. (2002) found that 8 year olds did not distinguish as clearly between different forms of behavioral aggression as 14 year olds. Methodological limitations associated with understanding bullying have been identified by Forsberg et al. (2018) and Maunder and Crafter (2018) . These authors postulate that quantitative approaches, although providing crucial insights in understanding bullying, are reliant on pre-defined variables, which can shield some of the complexities that qualitative designs can unravel, as individual experiences of bullying are brought to the fore. Indeed, La Fontaine (1991) suggests that unlike standard self-report questionnaires and other quantitative methods used to collect bullying data, analyzing qualitative data such as those collected from a helpline, enables the voice of young people to be heard and consequently empowers adults to understand bullying on their terms rather than relying solely on interpretations and perceptions of adults. Moore and Maclean (2012) collected survey, as well as interview and focus group data, on victimization occurring on the journey to and from school. They found that what young people determined as victimization varied and was influenced by a multifaceted array of circumstances, some of which adults were unaware of. Context for example, played an important role where certain behaviors in one situation could be regarded as victimization while in another they were not. Specific behaviors including ignoring an individual was particularly hurtful and supporting a friend who was the subject of victimization could lead to their own victimization.
Lee (2006) suggests that some bullying research does not reflect individual experiences, and are thus difficult for participants to relate to. Canty et al. (2016) reiterates this and suggests that when researchers provide young people with bullying definitions in which to position their own experiences, this can mask some of the complexities that the research intends to uncover. Such approaches result in an oversight into the socially constructed and individual experiences of bullying ( Eriksen, 2018 ). Griffin and Gross (2004) further argue that when researchers use vague or ambiguous definitions an “overclassification of children as bullies or victims” (p. 381) ensues. Consequently, quantitative research does not consider children as reliable in interpreting their own lived experiences and therefore some of the interactions they consider as bullying, that do not fit within the conventional definitions, are concealed. This approach favors the adult definition of bullying regarding it as “more reliable” than the definitions of children and young people Canty et al. (2016) . The perceived “seriousness” of bullying has also been explored. Overall, young people and adults are more likely to consider direct bullying (face-to-face actions including hitting, threatening and calling names) as “more serious” than indirect bullying (rumor spreading, social exclusion, forcing others to do something they do not want to do) ( Maunder et al., 2010 ; Skrzypiec et al., 2011 ). This perception of “seriousness,” alongside ambiguous definitions of bullying, has further implications for reporting it. Despite the advice given to young people to report incidents of school bullying ( Moore and Maclean, 2012 ), the literature suggests that many are reluctant to do so ( deLara, 2012 ; Moore and Maclean, 2012 ).
Several factors have been highlighted as to why young people are reluctant to report bullying ( Black et al., 2010 ). deLara (2012) , found apprehension in reporting bullying to teachers due to the fear that they will either not do enough or too much and inadvertently make the situation worse, or fear that teachers will not believe young people. Research also shows that young people are reluctant to tell their parents about bullying due to perceived over-reaction and fear that the bullying will be reported to their school ( deLara, 2012 ; Moore and Maclean, 2012 ). Oliver and Candappa (2007) suggest that young people are more likely to confide in their friends than adults (see also Moore and Maclean, 2012 ; Allen, 2014 ). However, if young people believe they are being bullied, but are unable to recognize their experiences within a predefined definition of bullying, this is likely to impact on their ability to report it.
Research from psychology, sociology, education and other disciplines, utilizing both quantitative and qualitative approaches, have enabled the generation of bullying knowledge to date. However, in order to understand why bullying happens and how it is influenced by wider social constructs there is a need for further qualitative studies, which hear directly from children and young people themselves. The next section of this paper discusses the theoretical underpinnings of this paper, which recognizes that young people are active agents in generating new bullying knowledge alongside adults.
Theoretical Underpinnings – Hearing From Children and Young People
The sociology of childhood ( James, 2007 ; Tisdall and Punch, 2012 ) and children’s rights agenda more broadly ( United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child, 1989 ) have offered new understandings and methods for research which recognize children and young people as active agents and experts on their own lives. From this perspective, research is conducted with rather than on children and young people ( Kellett, 2010 ).
Participatory methodologies have proven particularly useful for involving young people in research as co-researchers (see for example O’Brien and Moules, 2007 ; Stoudt, 2009 ; Kellett, 2010 ; Spears et al., 2016 ). This process of enquiry actively involves those normally being studied in research activities. Previously, “traditional” researchers devalued the experiences of research participants arguing that due to their distance from them, they themselves are better equipped to interpret these experiences ( Beresford, 2006 ). However, Beresford (2006) suggests that the shorter the distance between direct experience and interpretation, the less distorted and inaccurate the resulting knowledge is likely to be. Jones (2004) further advocates that when young people’s voices are absent from research about them the research is incomplete. Certainly Spears et al. (2016) , adopted this approach in their study with the Young and Well Cooperative Research Centre (CRC) in Australia. Young people played an active role within a multidisciplinary team alongside researchers, practitioners and policymakers to co-create and co-evaluate the learning from four marketing campaigns for youth wellbeing through participatory research. Through this methodological approach, findings show that young people were able to reconceptualize mental health and wellbeing from their own perspectives as well as share their lived experiences with others ( Spears et al., 2016 ). Bland and Atweh (2007) , Ozer and Wright (2012) , highlight the benefits afforded to young people through this process, including participating in dialog with decision-makers and bringing aspects of teaching and learning to their attention.
Against this background, data presented for this paper represents findings from four studies underpinned by the ethos that bullying is socially constructed and is best understood by exploring the context to which it occurs ( Schott and Sondergaard, 2014 ; Eriksen, 2018 ). This socially constructed view focusses on the evolving positions within young people’s groups, and argues that within a bullying situation sometimes a young person is the bully, sometimes the victim and sometimes the bystander/witness, which contrasts the traditional view of bullying ( Schott and Sondergaard, 2014 ). The focus therefore is on group relationships and dynamics. For that reason, Horton (2011) proposes that if bullying is an extensive problem including many young people, then focusing entirely on personality traits will not generate new bullying knowledge and will be problematic in terms of interventions. It is important to acknowledge that this change in focus and view of bullying and how it is manifested in groups, does not negate the individual experiences of bullying rather the focus shifts to the process of being accepted, or not, by the group ( Schott and Sondergaard, 2014 ).
The Studies
This section provides a broad overview of the four included studies underpinned by participatory methodologies. Table 1 presents the details of each study. Young people were involved in the research process as respondents, co-researchers and commissioners of research, along a continuum as identified by Bragg and Fielding (2005) . This ranged from “active respondents” to the left of the continuum, “students as co-researchers” in the middle and “students as researchers” to the right of the continuum. Young people were therefore recognized as equal to adults in terms of what they can bring to the project from their own unique perspectives ( Bradbury-Jones et al., 2018 ).
A key finding from study one ( O’Brien, 2009 ) was the lack of voice afforded to young people through the research process and can be seen to reflect the far left of Bragg and Fielding (2005) continuum, as young people were not directly involved as “active respondents” but their views were included in secondary data analysis and informed the studies that followed. For example, the quantitative studies used an agreed academic definition of bullying which may or may not have influenced how young participants defined bullying within the studies. On the other hand, the qualitative study involved a group of students in deciding which questions to ask of the research participants and in interpreting the findings.
In contrast, study two ( O’Brien and Moules, 2010 ) was commissioned and led by a group of young people called PEAR (Public health, Education, Awareness, Researchers), who were established to advise on public health research in England. PEAR members were based in two large English cities and comprised 20 young people aged between 13 and 20 years. The premise of the study was that PEAR members wanted to commission research into cyber bullying and the effects this has on mental health from the perspectives of young people rather than adult perspectives. This project was innovative as young people commissioned the research and participated as researchers ( Davey, 2011 ) and can be seen to reflect the middle “students as co-researchers” as well as moving toward to right “students as researchers” of Bragg and Fielding (2005) continuum. Although the young people did not carry out the day-to-day work on the project, they were responsible for leading and shaping it. More importantly, the research topic and focus were decided with young people and adults together.
Study three ( O’Brien, 2016 ) involved five self-selecting students from an independent day and boarding school who worked with me to answer this question: What do young people in this independent day and boarding school view as the core issue of bullying in the school and how do they want to address this? These students called themselves R4U (Research for You) with the slogan researching for life without fear . Three cycles of Participatory Action Research (PAR) ensued, where decision making about direction of the research, including methods, analysis and dissemination of findings were made by the research team. As current students of the school, R4U had a unique “insider knowledge” that complemented my position as the “academic researcher.” By working together to generate understanding about bullying at the school, the findings thus reflected this diversity in knowledge. As the project evolved so too did the involvement of the young researchers and my knowledge as the “outsider” (see O’Brien et al., 2018a for further details). Similar to study two, this project is situated between the middle: “students as co-researchers” and the right: “students as researchers” of Bragg and Fielding (2005) continuum.
Study four ( O’Brien, 2017 ) was small-scale and involved interviewing four young people who were receiving support from a charity providing therapeutic and educational support to young people who self-exclude from school due to anxiety, as a result of bullying. Self-exclusion, for the purposes of this study, means that a young person has made a decision not to go to school. It is different from “being excluded” or “truanting” because these young people do not feel safe at school and are therefore too anxious to attend. Little is known about the experiences of young people who self-exclude due to bullying and this study helped to unravel some of these issues. This study reflects the left of Bragg and Fielding (2005) continuum where the young people were involved as “active respondents” in informing adult understanding of the issue.
A variety of research methods were used across the four studies including questionnaires, interviews and focus groups (see Table 1 for more details). In studies two and three, young researchers were fundamental in deciding the types of questions to be asked, where they were asked and who we asked. In study three the young researchers conducted their own peer-led interviews. The diversity of methods used across the studies are a strength for this paper. An over-reliance on one method is not portrayed and the methods used reflected the requirements of the individual studies.
Informed Consent
Voluntary positive agreement to participate in research is referred to as “consent” while “assent,” refers to a person’s compliance to participate ( Coyne, 2010 ). The difference in these terms are normally used to distinguish the “legal competency of children over and under 16 years in relation to research.” ( Coyne, 2010 , 228). In England, children have a legal right to consent so therefore assent is non-applicable ( Coyne, 2010 ). However, there are still tensions surrounding the ability of children and young people under the age of 18 years to consent in research which are related to their vulnerability, age and stage of development ( Lambert and Glacken, 2011 ). The research in the three empirical studies (two, three and four) started from the premise that all young participants were competent to consent to participate and took the approach of Coyne (2010) who argues that parental/carer consent is not always necessary in social research. University Research Ethics Committees (RECs) are nonetheless usually unfamiliar with the theoretical underpinnings that children are viewed as social actors and generally able to consent for themselves ( Lambert and Glacken, 2011 ; Fox, 2013 ; Parsons et al., 2015 ).
In order to ensure the young people in these reported studies were fully informed of the intentions of each project and to adhere to ethical principles, age appropriate participant information sheets were provided to all participants detailing each study’s requirements. Young people were then asked to provide their own consent by signing a consent form, any questions they had about the studies were discussed. Information sheets were made available to parents in studies three and four. In study two, the parents of young people participating in the focus groups were informed of the study through the organizations used to recruit the young people. My full contact details were provided on these sheets so parents/carers could address any queries they had about the project if they wished. When young people participated in the online questionnaire (study two) we did not know who they were so could not provide separate information to parents. Consequently, all participants were given the opportunity to participate in the research without the consent of their parents/carers unless they were deemed incompetent to consent. In this case the onus was on the adult (parent or carer for example) to prove incompetency ( Alderson, 2007 ). Favorable ethical approval, including approval for the above consent procedures, was granted by the Faculty Research Ethics Committee at Anglia Ruskin University.
In the next section I provide a synthesis of the findings across the four studies before discussing how participatory research with young people can offer new understandings of bullying and its impacts on young people.
Although each study was designed to answer specific bullying research questions, the following key themes cut across all four studies 1 :
• Bullying definitions
◦ Behaviors
• Impact of bullying on victim
• Reporting bullying
Bullying Definitions
Young people had various understandings about what they considered bullying to be. Overall, participants agreed that aggressive direct behaviors, mainly focusing on physical aggression, constituted bullying:
“…if someone is physically hurt then that is bullying straight away.” (Female, study 3).
“I think [cyber-bullying is] not as bad because with verbal or physical, you are more likely to come in contact with your attacker regularly, and that can be disturbing. However, with cyber-bullying it is virtual so you can find ways to avoid the person.” (Female, study 2).
Name-calling was an ambiguous concept, young people generally believed that in isolation name-calling might not be bullying behavior or it could be interpreted as “joking” or “banter”:
“I never really see any, a bit of name calling and taking the mick but nothing ever serious.” (Male, study 3).
The concept of “banter” or “joking” was explored in study three as a result of the participatory design. Young people suggested “banter” involves:
“…a personal joke or group banter has no intention to harm another, it is merely playful jokes.” (Female, study 3).
However, underpinning this understanding of “banter” was the importance of intentionality:
“Banter saying things bad as a joke and everyone knows it is a joke.” (Male, study 3).
“Banter” was thus contentious when perception and reception were ambiguous. In some cases, “banter” was considered “normal behavior”:
“…we’ve just been joking about, but it’s never been anything harsh it’s just been like having a joke…” (Male, study 3).
The same view was evident in relation to cyber-bullying. Some participants were rather dismissive of this approach suggesting that it did not exist:
“I don’t really think it exists. If you’re being cyber-“bullied” then there is something wrong with you- it is insanely easy to avoid, by blocking people and so on. Perhaps it consists of people insulting you online?” (Male, study 2).
When young people considered additional factors added to name calling such as the type of name-calling, or aspects of repetition or intention, then a different view was apparent.
“…but it has to be constant it can’t be a single time because that always happens.” (Male, study 3).
Likewise with words used on social media, young people considered intentionality in their consideration of whether particular behaviors were bullying, highlighting important nuances in how bullying is conceptualized:
“Some people they don’t want to sound cruel but because maybe if you don’t put a smiley face on it, it might seem cruel when sometimes you don’t mean it.” (Female, study 2).
Study one also found that young people were more likely to discuss sexist or racist bullying in interviews or focus groups but this information was scarce in the questionnaire data. This is possibly as a result of how the questions were framed and the researchers’ perspectives informing the questions.
Evident across the four studies was the understanding young people had about the effects of continuous name-calling on victims:
“…you can take one comment, you can just like almost brush it off, but if you keep on being bullied and bullied and bullied then you might kind of think, hang on a minute, they’ve taken it a step too far, like it’s actually become more personal, whereas just like a cheeky comment between friends it’s become something that’s more serious and more personal and more annoying or hurtful to someone.” (Female, study 3).
“Cyber-bullying is basically still verbal bullying and is definitely psychological bullying. Any bullying is psychological though, really. And any bullying is going to be harmful.” (Female, study 2).
Aspects of indirect bullying (social exclusion) were features of studies one and three. For the most part, the research reviewed in study one found that as young people got older they were less likely to consider characteristics of social exclusion in their definitions of bullying. In study three, when discussing the school’s anti-bullying policy, study participants raised questions about “ isolating a student from a friendship group .” Some contested this statement as a form of bullying:
“…. there is avoiding, as in, not actively playing a role in trying to be friends which I don’t really see as bullying I see this as just not getting someone to join your friendship group. Whereas if you were actually leaving him out and rejecting him if he tries to be friends then I think I would see that as malicious and bullying.” (Male, study 3).
“Isolating a student from a friendship group – I believe there are various reasons for which a student can be isolated from a group – including by choice.” (Female, study 3).
Cyber-bullying was explored in detail in study two but less so in the other three studies. Most study two participants considered that cyber-bullying was just as harmful, or in some cases worse than, ‘traditional’ bullying due to the use of similar forms of “harassment,” “antagonizing,” “tormenting,” and ‘threatening’ through online platforms. Some young people believed that the physical distance between the victim and the bully is an important aspect of cyber-bullying:
“I think it’s worse because people find it easier to abuse someone when not face to face.” (Male, study 2).
“I think it could be worse, because lots of other people can get involved, whereas when it’s physical bullying it’s normally just between one or two or a smaller group, things could escalate too because especially Facebook, they’ve got potential to escalate.” (Female, study 2).
Other participants in study two spoke about bullying at school which transfers to an online platform highlighting no “escape” for some. In addition, it was made clearer that some young people considered distancing in relation to bullying and how this influences perceptions of severity:
“…when there’s an argument it can continue when you’re not at school or whatever and they can continue it over Facebook and everyone can see it then other people get involved.” (Female, study 2).
“I was cyber-bullied on Facebook, because someone put several hurtful comments in response to my status updates and profile pictures. This actually was extended into school by the bully…” (Male, study 2).
Impact of Bullying on Victim
Although bullying behaviors were a primary consideration of young people’s understanding of bullying, many considered the consequences associated with bullying and in particular, the impact on mental health. In these examples, the specifics of the bullying event were irrelevant to young people and the focus was on how the behavior was received by the recipient.
In study two, young people divulged how cyber-bullying had adversely affected their ability to go to school and to socialize outside school. Indeed some young people reported the affects it had on their confidence and self-esteem:
“I developed anorexia nervosa. Although not the single cause of my illness, bullying greatly contributed to my low self-esteem which led to becoming ill.” (Female, study 2).
“It hurts people’s feelings and can even lead to committing suicide….” (Female, study 2).
Across the studies, young people who had been bullied themselves shared their individual experiences:
“….you feel insecure and it just builds up and builds up and then in the end you have no self-confidence.” (Female, study 2).
“…it was an everyday thing I just couldn’t take it and it was causing me a lot of anxiety.” (Male, study 4).
“I am different to everyone in my class …. I couldn’t take it no more I was upset all the time and it made me feel anxious and I wasn’t sleeping but spent all my time in bed being sad and unhappy.” (Male, study 4).
Young people who had not experienced bullying themselves agreed that the impact it had on a person was a large determiner of whether bullying had happened:
“When your self-confidence is severely affected and you become shy. Also when you start believing what the bullies are saying about you and start to doubt yourself.” (Female, study 3).
“…it makes the victim feel bad about themselves which mostly leads to depression and sadness.” (Male, study 2).
Further evidence around the impact of bullying was apparent in the data in terms of how relational aspects can affect perceived severity. In the case of cyber-bullying, young people suggested a sense of detachment because the bullying takes place online. Consequently, as the relational element is removed bullying becomes easier to execute:
“…because people don’t have to face them over a computer so it’s so much easier. It’s so much quicker as well cos on something like Facebook it’s not just you, you can get everyone on Facebook to help you bully that person.” (Female, study 2).
“Due to technology being cheaper, it is easier for young people to bully people in this way because they don’t believe they can be tracked.” (Male, study 2).
“The effects are the same and often the bullying can be worse as the perpetrator is unknown or can disguise their identity. Away from the eyes of teachers etc., more can be done without anyone knowing.” (Female, study 2).
Relational aspects of bullying were further highlighted with regards to how “banter” was understood, particularly with in-group bullying and how the same example can either be seen as “banter” or bullying depending on the nature of the relationship:
“…we’ve just been joking about, but it’s never been anything harsh it’s just been like having a joke. well, I haven’t done it but I’ve been in a crowd where people do it, so I don’t want to get involved just in case it started an argument.” (Female, study 3).
“But it also depends…who your groups with, for example, if I spoke to my friends from [School]… I wouldn’t like use taboo language with them because to them it may seem inappropriate and probably a bit shocked, but if I was with my friends outside of school we use taboo language, we’ll be ourselves and we’ll be comfortable with it, and if a stranger walked past and heard us obviously they’d be thinking that we’re being bullied ourselves.” (Female, study 3).
Furthermore, how individuals are perceived by others tended to influence whether they were believed or not. In study four for example, participants suggested that who the bullies were within the school might have impacted how complaints were acted upon by school officials:
“When I went to the school about it, the students said I had attacked them – all eight of them! I just realized that no one believes me….” (Female, study 4).
While in study three, a characteristic of bullying was the influence the aggressor has over the victim:
“When the victim starts to feel in danger or start to fear the other person. Consequently he or she tries to avoid the bad guy (or girl!)” (Male, study 3).
These relational and contextual issues also influenced a young person’s ability to report bullying.
Reporting Bullying
Young people were more likely to report bullying when they considered it was ‘serious’ enough. Just under half of participants in study two sought emotional/practical support if they worried about, or were affected by cyber-bullying, with most talking to their parents. In study three, young people were less likely to seek support but when they did, most went to their teachers. In study four, all participants reported bullying in school where they did not feel supported.
Fear of making the bullying worse was captured across the studies as a reason for not reporting it:
“I’m scared that if I tell then the bullying will still go on and they will do more.” (Female, study 3).
“The bully might bully you if he finds out.” (Male, study 3).
Being able to deal with the incident themselves was also a reason for non-reporting:
“…it’s embarrassing and not necessary, my friends help me through it, adults never seem to understand.” (Female, study 2).
“I don’t tend to talk to anyone about it, I just keep it to myself and obviously that’s the worst thing you should ever do, you should never keep it to yourself, because I regret keeping it to myself to be honest….” (Female, study 3).
“…but I think I’d deal with it myself ‘cos. I was quite insecure but now I’m quite secure with myself, so I’ll sort it out myself. I think it’s just over time I’ve just sort of hardened to it.” (Male, study 3).
Most young people seeking support for bullying said they spoke to an adult but the helpfulness of this support varied. This finding is important for understanding relationships between young people and adults. Those who felt supported by their teachers for example, suggested that they took the time to listen and understood what they were telling them. They also reassured young people who in turn believed that the adult they confided in would know what to do:
“So I think the best teacher to talk to is [Miss A] and even though people are scared of her I would recommend it, because she’s a good listener and she can sense when you don’t want to talk about something, whereas the other teachers force it out of you.” (Female, study 3).
“My school has had assemblies about cyber-bullying and ways you can stop it or you can report it anonymously…. you can write your name or you can’t, it’s all up to YOU.” (Male, study 2).
Others however had a negative experience of reporting bullying and a number of reasons were provided as to why. Firstly, young people stated that adults did not believe them which made the bullying worse on some level:
“I went to the teachers a couple of times but, no, I don’t think they could do anything. I did sort of go three times and it still kept on going, so I just had to sort of deal with it and I sort of took it on the cheek….” (Male, study 3).
Secondly, young people suggested that adults did not always listen to their concerns, or in some cases did not take their concerns seriously enough:
“…I had had a really bad day with the girls so I came out and I explained all this to my head of year and how it was affecting me but instead of supporting me he put me straight into isolation.” (Male, study 4).
“I could understand them thinking I maybe got the wrong end of the stick with one incident but this was 18 months of me constantly reporting different incidents.” (Female, study 4).
“If cyber-bullying is brought to our school’s attention, usually, they expect printed proof of the situation and will take it into their own hand depending on its seriousness. However this is usually a couple of detentions. And it’s just not enough.” (Female, study 2).
Finally, some young people suggested that teachers did not always know what to do when bullying concerns were raised and consequently punished those making the complaint:
“I think I would have offered support instead of punishment to someone who was suffering with anxiety. I wouldn’t have seen anxiety as bad behavior I think that’s quite ignorant but they saw it as bad behavior.” (Male, study 4).
It is worth reiterating, that the majority of young people across the studies did not report bullying to anybody , which further underscores the contextual issues underpinning bullying and its role in enabling or disabling bullying behaviors. Some considered it was “pointless” reporting the bullying and others feared the situation would be made worse if they did:
“My school hide and say that bullying doesn’t go on cos they don’t wanna look bad for Ofsted.” (Male, study 2).
“My school is oblivious to anything that happens, many things against school rules happen beneath their eyes but they either refuse to acknowledge it or are just not paying attention so we must suffer.” (Female, study 2).
“That’s why I find that when you get bullied you’re scared of telling because either, in most cases the teacher will – oh yeah, yeah, don’t worry, we’ll sort it out and then they don’t tend to, and then they get bullied more for it.” (Female, study 3).
Young people were concerned that reporting bullying would have a negative impact on their friendship groups. Some were anxious about disrupting the status quo within:
“I think everyone would talk about me behind my back and say I was mean and everyone would hate me.” (Female, study 3).
Others expressed concern about the potential vulnerability they were likely to experience if they raised concerns of bullying:
“I was worried it might affect my other friendships.”(Boy, study 2).
“I’m scared that if I tell, then the bullying will still go on and they will do more.” (Female, study 3).
“….because they might tell off the bullies and then the bullies will like get back at you.” (Female, study 3).
These findings underscore the importance of contextual and relational factors in understanding bullying from the perspectives of young people and how these factors influence a young person’s ability or willingness to report bullying.
Finally one young person who had self-excluded from school due to severe bullying suggested that schools:
“…need to be looking out for their students’ mental wellbeing – not only be there to teach them but to support and mentor them. Keep them safe really… I missed out on about three years of socializing outside of school because I just couldn’t do it. I think it’s important that students are encouraged to stand up for each other.” (Female, study 4).
The studies presented in this paper illustrate the multitude of perceptions underpinning young people’s understandings of what constitutes bullying, both in terms of the behavior and also the impact that this behavior has on an individual. In turn, the ambiguity of what constitutes bullying had an impact on a young person’s ability to seek support. Discrepancies in bullying perceptions within and between young people’s groups are shown, highlighting the fluid and changing roles that occur within a bullying situation. Findings from quantitative studies have demonstrated the differing perceptions of bullying by adults and young people (see for example Smith et al., 2002 ; Vaillancourt et al., 2008 ; Maunder et al., 2010 ; Cuadrado-Gordillo, 2012 ). However, by combining findings from participatory research, new understandings of the relational and contextual factors important to young people come to the fore.
Young people participating in these four studies had unique knowledge and experiences of bullying and the social interactions of other young people in their schools and wider friendship groups. The underpinning participatory design enabled me to work alongside young people to analyze and understand their unique perspectives of bullying in more detail. The research teams were therefore able to construct meaning together, based not entirely on our own assumptions and ideologies, but including the viewpoint of the wider research participant group ( Thomson and Gunter, 2008 ). Together, through the process of co-constructing bullying knowledge, we were able to build on what is already known in this field and contribute to the view that bullying is socially constructed through the experiences of young people and the groups they occupy ( Schott and Sondergaard, 2014 ).
With regards to understanding what bullying is, the findings from these studies corroborate those of the wider literature from both paradigms of inquiry (for example Naylor et al., 2001 ; Canty et al., 2016 ); that being the discrepancies in definitions between adults and young people and also between young people themselves. Yet, findings here suggest that young people’s bullying definitions are contextually and relationally contingent. With the exception of physical bullying, young people did not differentiate between direct or indirect behaviors, instead they tended to agree that other contextual and relational factors played a role in deciding if particular behaviors were bullying (or not). The participatory research design enabled reflection and further investigation of the ideas that were particularly important to young people such as repetition and intentionality. Repetition was generally seen as being indicative of bullying being “serious,” and therefore more likely to be reported, and without repetition, a level of normality was perceived. This finding contradicts some work on bullying definitions, Cuadrado-Gordillo (2012) for example found that regardless of the role played by young people in a bullying episode (victim, aggressor or witness), the criteria of ‘repetition’ was not important in how they defined bullying.
Relational factors underpinning young people’s perception of bullying and indeed it’s “seriousness” were further reflected in their willingness or otherwise to report it. Fear of disrupting the status quo of the wider friendship group, potentially leading to their own exclusion from the group, was raised as a concern by young people. Some were concerned their friends would not support them if they reported bullying, while others feared further retaliation as a result. Friendship groups have been identified as a source of support for those who have experienced bullying and as a protective factor against further bullying ( Allen, 2014 ). Although participants did not suggest their friendship groups are unsupportive it is possible that group dynamics underscore seeking (or not) support for bullying. Other literature has described such practices as evidence of a power imbalance ( Olweus, 1995 ; Cuadrado-Gordillo, 2012 ) but young people in these studies did not describe these unequal relationships in this way and instead focused on the outcomes and impacts of bullying. Indeed Cuadrado-Gordillo (2012) also found that young people in their quantitative study did not consider “power imbalance” in their understanding of bullying and were more likely to consider intention. This paper, however, underscores the relational aspects of definitions of bullying and, how the dynamics of young people’s friendships can shift what is understood as bullying or not. Without such nuances, some behaviors may be overlooked as bullying, whereas other more obvious behaviors draw further attention. This paper also shows that contextual issues such as support structures can shift how young people see bullying. Contextual factors were evident across the four studies through the recognition of bullying being enabled or disabled by institutional factors, including a school’s ability to respond appropriately to bullying concerns. Young people suggested that schools could be influenced by bullies, perceiving them as non-threatening and consequently not dealing appropriately with the situation. Indeed some young people reported that their schools placed the onus on them as victims to change, consequently placing the “blame” on victims instead. These findings raise questions about who young people feel able to confide in about bullying as well as issues around training and teacher preparedness to deal with bullying in schools. Evidenced in these four studies, is that young people feel somewhat disconnected from adults when they have bullying concerns. Those who did report bullying, identified particular individuals they trusted and knew would support them. Novick and Isaacs (2010) identified teachers who young people felt comfortable in approaching to report bullying and described them as “most active, engaged and responsive.” (p. 291). The bullying literature suggests that as young people get older they are more likely to confide in friends than adults ( Moore and Maclean, 2012 ; Allen, 2014 ). However, findings from this paper indicate that although fewer young people reported bullying, those who did confided in an adult. Young people have identified that a variety of supports are required to tackle bullying and that adults need to listen and work with them so nuanced bullying behaviors are not recognized as “normal” behaviors. Within the data presented in this paper, “banter” was portrayed as “normal” behavior. Young people did not specify what behaviors they regarded as “banter,” but suggested that when banter is repeated and intentional the lines are blurred about what is bullying and what is banter.
Exploring bullying nuances in this paper, was enhanced by the involvement of young people in the research process who had a unique “insider” perspective about what it is like to be a young person now and how bullying is currently affecting young people. In studies one and four, young people were “active respondents” ( Bragg and Fielding, 2005 ) and provided adults with their own unique perspectives on bullying. It could be argued that study one did not involve the participation of young people. However, this study informed the basis of the subsequent studies due to the discrepancies noted in the literature about how bullying is understood between adults and young people, as well as the lack of young people’s voice and opportunity to participate in the reviewed research. Accordingly, young people’s data as “active respondents” informed adult understanding and led to future work involving more active research engagement from other young people. Participation in study four provided an opportunity for young people to contribute to future participatory research based on lived experiences as well as informing policy makers of the effects bullying has on the lives of young people ( O’Brien, 2017 ). In studies two and three, young people were involved further along Bragg and Fielding (2005) continuum as “co-researchers” and “students as researchers” with these roles shifting and moving dependent on the context of the project at the time ( O’Brien et al., 2018a ). These young researchers brought unique knowledge to the projects ( Bradbury-Jones et al., 2018 ) that could not be accessed elsewhere. Perspectives offered by the young researchers supported adults in understanding more about traditional and cyber-bullying from their perspectives. Furthermore, this knowledge can be added to other, quantitative studies to further understand why bullying happens alongside bullying prevalence, risk and protective factors, and negative outcomes.
Findings from the four studies offer an alternative perspective to how bullying is understood by young people. Complexities in defining bullying have been further uncovered as understanding is informed by individual factors, as well as wider social and relational contexts ( Horton, 2011 ; Schott and Sondergaard, 2014 ). This has implications for the type of support young people require. This paper highlights how definitions of bullying shift in response to relational and contextual aspects deemed important to young people. Because of this, further nuances were uncovered through the research process itself as the respective studies showed discrepancies in bullying perceptions within and between young people’s groups.
These understandings can act as a starting point for young people and adults to collaborate in research which seeks to understand bullying and the context to which it occurs. Furthermore, such collaborations enable adults to theorize and understand the complexities associated with bullying from the perspective of those at the center. There is a need for additional participatory research projects involving such collaborations where adults and young people can learn from each other as well as combining findings from different methodologies to enable a more comprehensive picture of the issues for young people to emerge. Further research is needed to unravel the complexities of bullying among and between young people, specifically in relation to the contextual and relational factors underscoring perceptions of bullying.
Data Availability
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this manuscript will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation, to any qualified researcher.
Ethics Statement
Ethical approval was granted for all four studies from the Faculty of Health, Education, Medicine and Social Care at the Anglia Ruskin University. The research was conducted on the premise of Gillick competency meaning that young people (in these studies over the age of 12 years) could consent for themselves to participate. Parents/carers were aware the study was happening and received information sheets explaining the process.
Author Contributions
The author confirms being the sole contributor of this work and has approved it for publication.
These four studies were conducted at the Anglia Ruskin University. Study one was part of a wider masters degree funded by the Anglia Ruskin University, Study two was funded by a group of young people convened by the National Children’s Bureau with funding from the Wellcome Trust (United Kingdom). Study three was a wider Doctoral study funded by the Anglia Ruskin University and Study four was also funded by the Anglia Ruskin University.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Dr. Grace Spencer, Ruskin Fellow at the Anglia Ruskin University for providing the critical read of this manuscript and offering constructive feedback. I would also like to thank the two independent reviewers for their feedback on the drafts of this manuscript.
- ^ These findings focus on perceptions and data from the young people in the four studies. For a full discussion on adult perceptions please refer to the individual studies.
Alderson, P. (2007). Competent children? Minors’ consent to health care treatment and research. Soc. Sci. Med. 65, 2272–2283. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.08.005
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Allen, M. (2014). Local Action on Health Inequalities: Building Children and Young People’s Resilience in Schools , London: Public Health England.
Google Scholar
Beresford, P. (2006). Making the connections with direct experience: from the western front to user-controlled research. Educ. Action Res. 14, 161–170.
Black, S., Weinles, D., and Washington, E. (2010). Victim strategies to stop bullying. Youth Violence Juv. Justice 8, 138–147. doi: 10.1177/1541204009349401
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Bland, D., and Atweh, B. (2007). Students as researchers: engaging students’ voices in PAR. Educ. Action Res. 15, 337–349. doi: 10.1080/09650790701514259
Boulton, M. J., and Flemington, I. (1996). The effects of a short video intervention on secondary school Pupils’ involvement in definitions of and attitudes towards bullying. Sch. Psychol. Int. 17, 331–345. doi: 10.1177/0143034396174003
Bradbury-Jones, C., Isham, L., and Taylor, J. (2018). The complexities and contradictions in participatory research with vulnerable children and young people: a qualitative systematic review. Soc. Sci. Med. 215, 80–91. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2018.08.038
Bragg, S., and Fielding, M. (2005). “It’s an equal thing. It’s about achieving together: student voices and the possibility of a radical collegiality,” in Improving Schools Through Collaborative Enquiry , eds H. Street, and J. Temperley, (London: Continuum), 105–135.
Braun, V., and Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in Psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 3, 77–101.
Canty, J., Stubbe, M., Steers, D., and Collings, S. (2016). The trouble with bullying–deconstructing the conventional definition of bullying for a child-centred investigation into Children’s use of social media. Child. Soc. 30, 48–58. doi: 10.1111/chso.12103
Coyne, I. (2010). Research with children and young people: the issue of parental (proxy) consent. Child. Soc. 24, 227–237.
Cuadrado-Gordillo, I. (2012). Repetition, power imbalance, and intentionality: do these criteria conform to teenagers’ perception of bullying? A role-based analysis. J. Interpers. Violence 27, 1889–1910. doi: 10.1177/0886260511431436
Davey, C. (2011). Evaluation of the PEAR Project. London: National Children’s Bureau.
deLara, E. W. (2012). Why adolescents Don’t disclose incidents of bullying and harassment. J. Sch. Violence 11, 288–305. doi: 10.1080/15388220.2012.705931
Eriksen, I. M. (2018). The power of the word: students’ and school staff’s use of the established bullying definition. Educ. Res. 60, 157–170. doi: 10.1080/00131881.2018.1454263
Espelage, D. L. (2018). Understanding the complexity of school bully involvement. Chautauqua J. 2:20.
Forsberg, C., Wood, L., Smith, J., Varjas, K., Meyers, J., Jungert, T., et al. (2018). Students’ views of factors affecting their bystander behaviors in response to school bullying: a cross-collaborative conceptual qualitative analysis. Res. Pap. Educ. 33, 127–142. doi: 10.1080/02671522.2016.1271001
Fox, R. (2013). Resisting participation: critiquing participatory research methodologies with young people. J. Youth Stud. 16, 986–999. doi: 10.1080/13676261.2013.815698
Griffin, R. S., and Gross, A. M. (2004). Childhood bullying: current empirical findings and future directions for research. Aggr. Violent Behav. 9, 379–400. doi: 10.1016/s1359-1789(03)00033-8
Guerin, S., and Hennessy, E. (2002). Pupils’ definitions of bullying. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 17, 249–261. doi: 10.1007/bf03173535
Horton, P. (2011). School bullying and social and moral orders. Child. Soc. 25, 268–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1099-0860.2011.00377.x
Huang, F. L., and Cornell, D. G. (2015). The impact of definition and question order on the prevalence of bullying victimization using student self-reports. Psychol. Assess. 27:1484. doi: 10.1037/pas0000149
James, A. (2007). Giving voice to children’s voices: practices and problems, pitfalls and potentials. Am. Anthropol. 109, 261–272. doi: 10.1525/aa.2007.109.2.261
Jones, A. (2004). “Involving children and yong people as researchers,” in Doing Research with Children and Young People , eds S. Fraser, V. Lewis, S. Ding, M. Kellett, and C. Robinson, (London: Sage Publications), 113–130.
Kellett, M. (2010). Small shoes, Big Steps! Empowering children as active researchers. Am. J. Commun. Psychol. 46, 195–203. doi: 10.1007/s10464-010-9324-y
La Fontaine, J. (1991). Bullying: The Child’s View – an Analysis of Telephone Calls to ChildLIne about Bullying. London: Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation.
Lambert, V., and Glacken, M. (2011). Engaging with children in research: theoretical and practical implications of negotiating informed consent/assent. Nurs. Ethics 18, 781–801. doi: 10.1177/0969733011401122
Lee, C. (2006). Exploring teachers’ definitions of bullying. Emot. Behav. Diffic. 11, 61–75. doi: 10.1080/13632750500393342
Maunder, R. E., and Crafter, S. (2018). School bullying from a sociocultural perspective. Aggr. Violent Behav. 38, 13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.avb.2017.10.010
Maunder, R. E., Harrop, A., and Tattersall, A. J. (2010). Pupil and staff perceptions of bullying in secondary schools: comparing behavioural definitions and their perceived seriousness. Educ. Res. 52, 263–282. doi: 10.1080/00131881.2010.504062
Moore, S., and Maclean, R. (2012). Victimization, friendship and resilience: crossing the land in-between. Pastor. Care Educ. 30, 147–163. doi: 10.1080/02643944.2012.679956
Naylor, P., Cowie, H., and del Rey, R. (2001). Coping strategies of secondary school children in response to being bullied. Child Psychol. Psychiatry Rev. 6, 114–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02137.x
Novick, R. M., and Isaacs, J. (2010). Telling is compelling: the impact of students reports of bullying on teacher intervention. Educ. Psychol. 30, 283–296. doi: 10.1080/01443410903573123
O’Brien, N. (2009). Secondary school teachers’ and pupils’ definitions of bullying in the UK: a systematic review. Evid. Policy 5, 399–426.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
O’Brien, N. (2014). “I Didn’t Want to be Known as a Snitch”: Using PAR to Explore Bullying in a Private day and Boarding School. Childhood Remixed. Conference Edition. Suffolk: University Campus Suffolk, 86–96.
O’Brien, N. (2016). To ‘Snitch’ or Not to ‘Snitch’? Using PAR to Explore Bullying in a Private Day and Boarding School. Available at: http://arro.anglia.ac.uk/700970/ (accessed September 20, 2018).
O’Brien, N. (2017). An Exploratory Study of Bullied Young People’s Self-Exclusion from School. Evidence: Presented at Meetings of the All Party Parliamentary Group on Bullying 2011-2016. Project Report. All Party Parliamentary Group on Bullying. Available at: http://arro.anglia.ac.uk/id/eprint/702024 (accessed September 20, 2018).
O’Brien, N., and Moules, T. (2007). So round the spiral again: a reflective participatory research project with children and young people. Educ. Action Res. J. 15, 385–402. doi: 10.1080/09650790701514382
O’Brien, N., and Moules, T. (2010). The Impact of Cyber-Bullying on Young People’s Mental Health. Project Report. Chelmsford: Anglia Ruskin University.
O’Brien, N., and Moules, T. (2013). Not sticks and stones but tweets and texts: findings from a national cyberbullying project. Pastor. Care Educ. 31, 53–65. doi: 10.1080/02643944.2012.747553
O’Brien, N., Moules, T., and Munn-Giddings, C. (2018a). “Negotiating the research space between young people and adults in a PAR study exploring school bullying,” in Reciprocal Relationships and Well-Being: Implications for Social Work and Social Policy , eds M. Torronen, C. Munn-Giddings, and L. Tarkiainen, (Oxon: Routledge), 160–175. doi: 10.4324/9781315628363-11
O’Brien, N., Munn-Giddings, C., and Moules, T. (2018b). The repercussions of reporting bullying: some experiences of students at an independent secondary school. Pastor. Care Educ. 36, 29–43. doi: 10.1080/02643944.2017.1422004
O’Brien, N., Munn-Giddings, C., and Moules, T. (2018c). The Ethics of Involving Young People Directly in the Research Process. Childhood Remixed. Conference Edition , 115–128. Available at: www.uos.ac.uk/content/centre-for-study-children-childhood (accessed May 2018).
Oliver, C., and Candappa, M. (2007). Bullying and the politics of ‘telling’. Oxford Rev. Educ. 33, 71–86. doi: 10.1080/03054980601094594
Olweus, D. (1995). Bullying or peer abuse at school: facts and intervention. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 4, 196–200. doi: 10.1111/1467-8721.ep10772640
Ozer, E. J., and Wright, D. (2012). Beyond school spirit: the effects of youth-led participatory action research in two urban high schools. J. Res. Adolesc. 22, 267–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-7795.2012.00780.x
Parsons, S., Abbott, C., McKnight, L., and Davies, C. (2015). High risk yet invisible: conflicting narratives on social research involving children and young people, and the role of research ethics committees. Br. Educ. Res. J. 41, 709–729. doi: 10.1002/berj.3160
Patton, D. U., Hong, J. S., Patel, S., and Kral, M. J. (2017). A systematic review of research strategies used in qualitative studies on school bullying and victimization. Trauma Violence Abuse 18, 3–16. doi: 10.1177/1524838015588502
Popay, J., Roberts, H., Sowden, A., Petticrew, M., Arai, L., Rodgers, M., et al. (2006). Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. Eur. Soc. Res. Council Methods Program. doi: 10.13140/2.1.1018.4643
Schott, R. M., and Sondergaard, D. M. (2014). “Introduction: new approaches to school bullying,” in School Bullying: New Theories in Context , eds R. M. Schott, and D. M. Sondergaard, (Massachusetts, MA: Cambridge University Press), 1–17.
Skrzypiec, G., Slee, P., Murray-Harvey, R., and Pereira, B. (2011). School bullying by one or more ways: does it matter and how do students cope? Sch. Psychol. Int. 32, 288–311. doi: 10.1177/0143034311402308
Smith, P. K., Cowie, H., Olafsson, R. F., and Liefooghe, A. P. D. (2002). Definitions of bullying: a comparison of terms used, and age and gender differences, in a fourteen-country international comparison. Child Dev. 73, 1119–1133. doi: 10.1111/1467-8624.00461
Spears, B., Taddeo, C., Collin, P., Swist, T., Razzell, M., Borbone, V., et al. (2016). Safe and Well Online: Learnings from Four Social Marketing Campaigns for Youth Wellbeing. Available at: https://researchdirect.westernsydney.edu.au/islandora/object/uws:36405/datastream/PDF/view (accessed July 1, 2019).
Stoudt, B. G. (2009). The role of language & discourse in the investigation of privilege: using participatory action research to discuss theory. Dev. Methodol. Interrupt. Power Urban Rev. 41, 7–28.
Thomson, P., and Gunter, H. (2008). Researching Bullying with students: a lens on everyday life in an ‘innovative school’. Int. J. Inclusive Educ. 12, 185–200. doi: 10.1080/13603110600855713
Tisdall, E. K. M., and Punch, S. (2012). Not so ‘new’? Looking critically at childhood studies. Child. Geogr. 10, 249–264. doi: 10.1080/14733285.2012.693376
United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (1989). Available at: http://www.unicef.org.uk/Documents/Publication-pdfs/UNCRC_PRESS2009 10web.pdf (accessed January 19, 2014).
Vaillancourt, T., McDougall, P., Hymel, S., Krygsman, A., Miller, J., Stiver, K., et al. (2008). Bullying: are researchers and children/youth talking about the same thing? Int. J. Behav. Dev. 32, 486–495. doi: 10.1177/0165025408095553
Keywords : bullying, young people, participatory research, social constructionism, young people as researchers, collaboration, bullying supports
Citation: O’Brien N (2019) Understanding Alternative Bullying Perspectives Through Research Engagement With Young People. Front. Psychol. 10:1984. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01984
Received: 28 February 2019; Accepted: 13 August 2019; Published: 28 August 2019.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2019 O’Brien. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Niamh O’Brien, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Qualitative Methods in School Bullying and Cyberbullying Research: An Introduction to the Special Issue
- Published: 12 August 2022
- Volume 4 , pages 175–179, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Paul Horton 1 &
- Selma Therese Lyng 2
9425 Accesses
12 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
School bullying research has a long history, stretching all the way back to a questionnaire study undertaken in the USA in the late 1800s (Burk, 1897 ). However, systematic school bullying research began in earnest in Scandinavia in the early 1970s with the work of Heinemann ( 1972 ) and Olweus ( 1978 ). Highlighting the extent to which research on bullying has grown exponentially since then, Smith et al. ( 2021 ) found that there were only 83 articles with the term “bully” in the title or abstract published in the Web of Science database prior to 1989. The numbers of articles found in the following decades were 458 (1990–1999), 1,996 (2000–2009), and 9,333 (2010–2019). Considering cyberbullying more specifically, Smith and Berkkun ( 2017 , cited in Smith et al., 2021 ) conducted a search of Web of Science with the terms “cyber* and bully*; cyber and victim*; electronic bullying; Internet bullying; and online harassment” until the year 2015 and found that while there were no articles published prior to 2000, 538 articles were published between 2000 and 2015, with the number of articles increasing every year (p. 49).
Numerous authors have pointed out that research into school bullying and cyberbullying has predominantly been conducted using quantitative methods, with much less use of qualitative or mixed methods (Hong & Espelage, 2012 ; Hutson, 2018 ; Maran & Begotti, 2021 ; Smith et al., 2021 ). In their recent analysis of articles published between 1976 and 2019 (in WoS, with the search terms “bully*; victim*; cyberbullying; electronic bullying; internet bullying; and online harassment”), Smith et al. ( 2021 , pp. 50–51) found that of the empirical articles selected, more than three-quarters (76.3%) were based on quantitative data, 15.4% were based on a combination of quantitative and qualitative data, and less than one-tenth (8.4%) were based on qualitative data alone. What is more, they found that the proportion of articles based on qualitative or mixed methods has been decreasing over the past 15 years (Smith et al., 2021 ). While the search criteria excluded certain types of qualitative studies (e.g., those published in books, doctoral theses, and non-English languages), this nonetheless highlights the extent to which qualitative research findings risk being overlooked in the vast sea of quantitative research.
School bullying and cyberbullying are complex phenomena, and a range of methodological approaches is thus needed to understand their complexity (Pellegrini & Bartini, 2000 ; Thornberg, 2011 ). Indeed, over-relying on quantitative methods limits understanding of the contexts and experiences of bullying (Hong & Espelage, 2012 ; Patton et al., 2017 ). Qualitative methods are particularly useful for better understanding the social contexts, processes, interactions, experiences, motivations, and perspectives of those involved (Hutson, 2018 ; Patton et al., 2017 ; Thornberg, 2011 ; Torrance, 2000 ).
Smith et al. ( 2021 ) suggest that the “continued emphasis on quantitative studies may be due to increasingly sophisticated methods such as structural equation modeling … network analysis … time trend analyses … latent profile analyses … and multi-polygenic score approaches” (p. 56). However, the authors make no mention of the range or sophistication of methods used in qualitative studies. Although there are still proportionately few qualitative studies of school bullying and cyberbullying in relation to quantitative studies, and this gap appears to be increasing, qualitative studies have utilized a range of qualitative data collection methods. These methods have included but are not limited to ethnographic fieldwork and participant observations (e.g., Eriksen & Lyng, 2018 ; Gumpel et al., 2014 ; Horton, 2019 ), digital ethnography (e.g., Rachoene & Oyedemi, 2015 ; Sylwander, 2019 ), meta-ethnography (e.g., Dennehy et al., 2020 ; Moretti & Herkovits, 2021 ), focus group interviews (e.g., Odenbring, 2022 ; Oliver & Candappa, 2007 ; Ybarra et al., 2019 ), semi-structured group and individual interviews (e.g., Forsberg & Thornberg, 2016 ; Lyng, 2018 ; Mishna et al., 2005 ; Varjas et al., 2013 ), vignettes (e.g., Jennifer & Cowie, 2012 ; Khanolainen & Semenova, 2020 ; Strindberg et al., 2020 ), memory work (e.g., Johnson et al., 2014 ; Malaby, 2009 ), literature studies (e.g., Lopez-Ropero, 2012 ; Wiseman et al., 2019 ), photo elicitation (e.g., Ganbaatar et al., 2021 ; Newman et al., 2006 ; Walton & Niblett, 2013 ), photostory method (e.g., Skrzypiec et al., 2015 ), and other visual works produced by children and young people (e.g., Bosacki et al., 2006 ; Gillies-Rezo & Bosacki, 2003 ).
This body of research has also included a variety of qualitative data analysis methods, such as grounded theory (e.g., Allen, 2015 ; Bjereld, 2018 ; Thornberg, 2018 ), thematic analysis (e.g., Cunningham et al., 2016 ; Forsberg & Horton, 2022 ), content analysis (e.g., Temko, 2019 ; Wiseman & Jones, 2018 ), conversation analysis (e.g., Evaldsson & Svahn, 2012 ; Tholander, 2019 ), narrative analysis (e.g., Haines-Saah et al., 2018 ), interpretative phenomenological analysis (e.g., Hutchinson, 2012 ; Tholander et al., 2020 ), various forms of discourse analysis (e.g., Ellwood & Davies, 2010 ; Hepburn, 1997 ; Ringrose & Renold, 2010 ), including discursive psychological analysis (e.g., Clarke et al., 2004 ), and critical discourse analysis (e.g., Barrett & Bound, 2015 ; Bethune & Gonick, 2017 ; Horton, 2021 ), as well as theoretically informed analyses from an array of research traditions (e.g., Davies, 2011 ; Jacobson, 2010 ; Søndergaard, 2012 ; Walton, 2005 ).
In light of the growing volume and variety of qualitative studies during the past two decades, we invited researchers to discuss and explore methodological issues related to their qualitative school bullying and cyberbullying research. The articles included in this special issue of the International Journal of Bullying Prevention discuss different qualitative methods, reflect on strengths and limitations — possibilities and challenges, and suggest implications for future qualitative and mixed-methods research.
Included Articles
Qualitative studies — focusing on social, relational, contextual, processual, structural, and/or societal factors and mechanisms — have formed the basis for several contributions during the last two decades that have sought to expand approaches to understanding and theorizing the causes of cyber/bullying. Some have also argued the need for expanding the commonly used definition of bullying, based on Olweus ( 1993 ) (e.g., Allen, 2015 ; Ellwood & Davies, 2010 Goldsmid & Howie, 2014 ; Ringrose & Rawlings, 2015 ; Søndergaard, 2012 ; Walton, 2011 ). In the first article of the special issue, Using qualitative methods to measure and understand key features of adolescent bullying: A call to action , Natalie Spadafora, Anthony Volk, and Andrew Dane instead discuss the usefulness of qualitative methods for improving measures and bettering our understanding of three specific key definitional features of bullying. Focusing on the definition put forward by Volk et al. ( 2014 ), they discuss the definitional features of power imbalance , goal directedness (replacing “intent to harm” in order not to assume conscious awareness, and to include a wide spectrum of goals that are intentionally and strategically pursued by bullies), and harmful impact (replacing “negative actions” in order to focus on the consequences for the victim, as well as circumventing difficult issues related to “repetition” in the traditional definition).
Acknowledging that these three features are challenging to capture using quantitative methods, Spadafora, Volk, and Dane point to existing qualitative studies that shed light on the features of power imbalance, goal directedness and harmful impact in bullying interactions — and put forward suggestions for future qualitative studies. More specifically, the authors argue that qualitative methods, such as focus groups, can be used to investigate the complexity of power relations at not only individual, but also social levels. They also highlight how qualitative methods, such as diaries and autoethnography, may help researchers gain a better understanding of the motives behind bullying behavior; from the perspectives of those engaging in it. Finally, the authors demonstrate how qualitative methods, such as ethnographic fieldwork and semi-structured interviews, can provide important insights into the harmful impact of bullying and how, for example, perceived harmfulness may be connected to perceived intention.
In the second article, Understanding bullying and cyberbullying through an ecological systems framework: The value of qualitative interviewing in a mixed methods approach , Faye Mishna, Arija Birze, and Andrea Greenblatt discuss the ways in which utilizing qualitative interviewing in mixed method approaches can facilitate greater understanding of bullying and cyberbullying. Based on a longitudinal and multi-perspective mixed methods study of cyberbullying, the authors demonstrate not only how qualitative interviewing can augment quantitative findings by examining process, context and meaning for those involved, but also how qualitative interviewing can lead to new insights and new areas of research. They also show how qualitative interviewing can help to capture nuances and complexity by allowing young people to express their perspectives and elaborate on their answers to questions. In line with this, the authors also raise the importance of qualitative interviewing for providing young people with space for self-reflection and learning.
In the third article, Q methodology as an innovative addition to bullying researchers’ methodological repertoire , Adrian Lundberg and Lisa Hellström focus on Q methodology as an inherently mixed methods approach, producing quantitative data from subjective viewpoints, and thus supplementing more mainstream quantitative and qualitative approaches. The authors outline and exemplify Q methodology as a research technique, focusing on the central feature of Q sorting. The authors further discuss the contribution of Q methodology to bullying research, highlighting the potential of Q methodology to address challenges related to gaining the perspectives of hard-to-reach populations who may either be unwilling or unable to share their personal experiences of bullying. As the authors point out, the use of card sorting activities allows participants to put forward their subjective perspectives, in less-intrusive settings for data collection and without disclosing their own personal experiences. The authors also illustrate how the flexibility of Q sorting can facilitate the participation of participants with limited verbal literacy and/or cognitive function through the use of images, objects or symbols. In the final part of the paper, Lundberg and Hellström discuss implications for practice and suggest future directions for using Q methodology in bullying and cyberbullying research, particularly with hard-to-reach populations.
In the fourth article, The importance of being attentive to social processes in school bullying research: Adopting a constructivist grounded theory approach , Camilla Forsberg discusses the use of constructivist grounded theory (CGT) in her research, focusing on social structures, norms, and processes. Forsberg first outlines CGT as a theory-methods package that is well suited to meet the call for more qualitative research on participants’ experiences and the social processes involved in school bullying. Forsberg emphasizes three key focal aspects of CGT, namely focus on participants’ main concerns; focus on meaning, actions, and processes; and focus on symbolic interactionism. She then provides examples and reflections from her own ethnographic and interview-based research, from different stages of the research process. In the last part of the article, Forsberg argues that prioritizing the perspectives of participants is an ethical stance, but one which comes with a number of ethical challenges, and points to ways in which CGT is helpful in dealing with these challenges.
In the fifth article, A qualitative meta-study of youth voice and co-participatory research practices: Informing cyber/bullying research methodologies , Deborah Green, Carmel Taddeo, Deborah Price, Foteini Pasenidou, and Barbara Spears discuss how qualitative meta-studies can be used to inform research methodologies for studying school bullying and cyberbullying. Drawing on the findings of five previous qualitative studies, and with a transdisciplinary and transformative approach, the authors illustrate and exemplify how previous qualitative research can be analyzed to gain a better understanding of the studies’ collective strengths and thus consider the findings and methods beyond the original settings where the research was conducted. In doing so, the authors highlight the progression of youth voice and co-participatory research practices, the centrality of children and young people to the research process and the enabling effect of technology — and discuss challenges related to ethical issues, resource and time demands, the role of gatekeepers, and common limitations of qualitative studies on youth voice and co-participatory research practices.
Taken together, the five articles illustrate the diversity of qualitative methods used to study school bullying and cyberbullying and highlight the need for further qualitative research. We hope that readers will find the collection of articles engaging and that the special issue not only gives impetus to increased qualitative focus on the complex phenomena of school bullying and cyberbullying but also to further discussions on both methodological and analytical approaches.
Allen, K. A. (2015). “We don’t have bullying, but we have drama”: Understandings of bullying and related constructs within the school milieu of a U.S. high school. Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment , 25 (3), 159–181.
Barrett, B., & Bound, A. M. (2015). A critical discourse analysis of No Promo Homo policies in US schools. Educational Studies, 51 (4), 267–283.
Article Google Scholar
Bethune, J., & Gonick, M. (2017). Schooling the mean girl: A critical discourse analysis of teacher resource materials. Gender and Education, 29 (3), 389–404.
Bjereld, Y. (2018). The challenging process of disclosing bullying victimization: A grounded theory study from the victim’s point of view. Journal of Health Psychology, 23 (8), 1110–1118.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bosacki, S. L., Marini, Z. A., & Dane, A. V. (2006). Voices from the classroom: Pictorial and narrative representations of children’s bullying experiences. Journal of Moral Education, 35 (2), 231–245.
Burk, F. L. (1897). Teasing and Bullying. Pedagogical Seminary, 4 (3), 336–371.
Clarke, V., Kitzinger, C., & Potter, J. (2004). ‘Kids are just cruel anyway’: Lesbian and gay parents’ talk about homophobic bullying. British Journal of Social Psychology, 43 (4), 531–550.
Cunningham, C. E., Mapp, C., Rimas, H., Cunningham, S. M., Vaillancourt, T., & Marcus, M. (2016). What limits the effectiveness of antibullying programs? A thematic analysis of the perspective of students. Psychology of Violence, 6 (4), 596–606.
Davies, B. (2011). Bullies as guardians of the moral order or an ethic of truths? Children & Society, 25 , 278–286.
Dennehy, R., Meaney, S., Walsh, K. A., Sinnott, C., Cronin, M., & Arensman, E. (2020). Young people’s conceptualizations of the nature of cyberbullying: A systematic review and synthesis of qualitative research. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 51 , 101379.
Ellwood, C., & Davies, B. (2010). Violence and the moral order in contemporary schooling: A discursive analysis. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 7 (2), 85–98.
Eriksen, I. M., & Lyng, S. T. (2018). Relational aggression among boys: Blind spots and hidden dramas. Gender and Education, 30 (3), 396–409.
Evaldsson, A. -C., Svahn, J. (2012). School bullying and the micro-politics of girls’ gossip disputes. In S. Danby & M. Theobald (Eds.). Disputes in everyday life: Social and moral orders of children and young people (Sociological Studies of Children and Youth, Vol. 15) (pp. 297–323). Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing.
Forsberg, C., & Horton, P. (2022). ‘Because I am me’: School bullying and the presentation of self in everyday school life. Journal of Youth Studies, 25 (2), 136–150.
Forsberg, C., & Thornberg, R. (2016). The social ordering of belonging: Children’s perspectives on bullying. International Journal of Educational Research, 78 , 13–23.
Ganbaatar, D., Vaughan, C., Akter, S., & Bohren, M. A. (2021). Exploring the identities and experiences of young queer people in Mongolia using visual research methods. Culture, Health & Sexuality . Advance Online Publication: https://doi.org/10.1080/13691058.2021.1998631
Gillies-Rezo, S., & Bosacki, S. (2003). Invisible bruises: Kindergartners’ perceptions of bullying. International Journal of Children’s Spirituality, 8 (2), 163–177.
Goldsmid, S., & Howie, P. (2014). Bullying by definition: An examination of definitional components of bullying. Emotional and Behavioural Difficulties, 19 (2), 210–225.
Gumpel, T. P., Zioni-Koren, V., & Bekerman, Z. (2014). An ethnographic study of participant roles in school bullying. Aggressive Behavior, 40 (3), 214–228.
Haines-Saah, R. J., Hilario, C. T., Jenkins, E. K., Ng, C. K. Y., & Johnson, J. L. (2018). Understanding adolescent narratives about “bullying” through an intersectional lens: Implications for youth mental health interventions. Youth & Society, 50 (5), 636–658.
Heinemann, P. -P. (1972). Mobbning – gruppvåld bland barn och vuxna [Bullying – group violence amongst children and adults]. Stockholm: Natur och Kultur.
Hepburn, A. (1997). Discursive strategies in bullying talk. Education and Society, 15 (1), 13–31.
Hong, J. S., & Espelage, D. L. (2012). A review of mixed methods research on bullying and peer victimization in school. Educational Review, 64 (1), 115–126.
Horton, P. (2019). The bullied boy: Masculinity, embodiment, and the gendered social-ecology of Vietnamese school bullying. Gender and Education, 31 (3), 394–407.
Horton, P. (2021). Building walls: Trump election rhetoric, bullying and harassment in US schools. Confero: Essays on Education, Philosophy and Politics , 8 (1), 7–32.
Hutchinson, M. (2012). Exploring the impact of bullying on young bystanders. Educational Psychology in Practice, 28 (4), 425–442.
Hutson, E. (2018). Integrative review of qualitative research on the emotional experience of bullying victimization in youth. The Journal of School Nursing, 34 (1), 51–59.
Jacobson, R. B. (2010). A place to stand: Intersubjectivity and the desire to dominate. Studies in Philosophy and Education, 29 , 35–51.
Jennifer, D., & Cowie, H. (2012). Listening to children’s voices: Moral emotional attributions in relation to primary school bullying. Emotional and Behavioural Difficulties, 17 (3–4), 229–241.
Johnson, C. W., Singh, A. A., & Gonzalez, M. (2014). “It’s complicated”: Collective memories of transgender, queer, and questioning youth in high school. Journal of Homosexuality, 61 (3), 419–434.
Khanolainen, D., & Semenova, E. (2020). School bullying through graphic vignettes: Developing a new arts-based method to study a sensitive topic. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1–15.
Lopez-Ropero, L. (2012). ‘You are a flaw in the pattern’: Difference, autonomy and bullying in YA fiction. Children’s Literature in Education, 43 , 145–157.
Lyng, S. T. (2018). The social production of bullying: Expanding the repertoire of approaches to group dynamics. Children & Society, 32 (6), 492–502.
Malaby, M. (2009). Public and secret agents: Personal power and reflective agency in male memories of childhood violence and bullying. Gender and Education, 21 (4), 371–386.
Maran, D. A., & Begotti, T. (2021). Measurement issues relevant to qualitative studies. In P. K. Smith & J. O’Higgins Norman (Eds.). The Wiley handbook of bullying (pp. 233–249). John Wiley & Sons.
Mishna, F., Scarcello, I., Pepler, D., & Wiener, J. (2005). Teachers’ understandings of bullying. Canadian Journal of Education, 28 (4), 718–738.
Moretti, C., & Herkovits, D. (2021). Victims, perpetrators, and bystanders: A meta-ethnography of roles in cyberbullying. Cad. Saúde Pública, 37 (4), e00097120.
Newman, M., Woodcock, A., & Dunham, P. (2006). ‘Playtime in the borderlands’: Children’s representations of school, gender and bullying through photographs and interviews. Children’s Geographies, 4 (3), 289–302.
Odenbring, Y. (2022). Standing alone: Sexual minority status and victimisation in a rural lower secondary school. International Journal of Inclusive Education, 26 (5), 480–494.
Oliver, C., & Candappa, M. (2007). Bullying and the politics of ‘telling.’ Oxford Review of Education, 33 (1), 71–86.
Olweus, D. (1978). Aggression in the schools – Bullies and the whipping boys . Wiley.
Google Scholar
Olweus, D. (1993). Bullying in school: What we know and what we can do . Blackwell.
Patton, D. U., Hong, J. S., Patel, S., & Kral, M. J. (2017). A systematic review of research strategies used in qualitative studies on school bullying and victimization. Trauma, Violence, & Abuse, 18 (1), 3–16.
Pellegrini, A. D., & Bartini, M. (2000). A longitudinal study of bullying, victimization, and peer affiliation during the transition from primary school to middle school. American Educational Research Journal, 37 (3), 699–725.
Rachoene, M., & Oyedemi, T. (2015). From self-expression to social aggression: Cyberbullying culture among South African youth on Facebook. Communicatio: South African Journal for Communication Theory and Research , 41 (3), 302–319.
Ringrose, J., & Rawlings, V. (2015). Posthuman performativity, gender and ‘school bullying’: Exploring the material-discursive intra-actions of skirts, hair, sluts, and poofs. Confero: Essays on Education, Philosophy and Politics , 3 (2), 80–119.
Ringrose, J., & Renold, E. (2010). Normative cruelties and gender deviants: The performative effects of bully discourses for girls and boys in school. British Educational Research Journal, 36 (4), 573–596.
Skrzypiec, G., Slee, P., & Sandhu, D. (2015). Using the PhotoStory method to understand the cultural context of youth victimization in the Punjab. The International Journal of Emotional Education, 7 (1), 52–68.
Smith, P., Robinson, S., & Slonje, R. (2021). The school bullying research program: Why and how it has developed. In P. K. Smith & J. O’Higgins Norman (Eds.). The Wiley handbook of bullying (pp. 42–59). John Wiley & Sons.
Smith, P. K., & Berkkun, F. (2017). How research on school bullying has developed. In C. McGuckin & L. Corcoran (Eds.), Bullying and cyberbullying: Prevalence, psychological impacts and intervention strategies (pp. 11–27). Hauppage, NY: Nova Science.
Strindberg, J., Horton, P., & Thornberg, R. (2020). The fear of being singled out: Pupils’ perspectives on victimization and bystanding in bullying situations. British Journal of Sociology of Education, 41 (7), 942–957.
Sylwander, K. R. (2019). Affective atmospheres of sexualized hate among youth online: A contribution to bullying and cyberbullying research on social atmosphere. International Journal of Bullying Prevention, 1 , 269–284.
Søndergaard, D. M. (2012). Bullying and social exclusion anxiety in schools. British Journal of Sociology of Education, 33 (3), 355–372.
Temko, E. (2019). Missing structure: A critical content analysis of the Olweus Bullying Prevention Program. Children & Society, 33 (1), 1–12.
Tholander, M. (2019). The making and unmaking of a bullying victim. Interchange, 50 , 1–23.
Tholander, M., Lindberg, A., & Svensson, D. (2020). “A freak that no one can love”: Difficult knowledge in testimonials on school bullying. Research Papers in Education, 35 (3), 359–377.
Thornberg, R. (2011). ‘She’s weird!’ – The social construction of bullying in school: A review of qualitative research. Children & Society, 25 , 258–267.
Thornberg, R. (2018). School bullying and fitting into the peer landscape: A grounded theory field study. British Journal of Sociology of Education, 39 (1), 144–158.
Torrance, D. A. (2000). Qualitative studies into bullying within special schools. British Journal of Special Education, 27 (1), 16–21.
Varjas, K., Meyers, J., Kiperman, S., & Howard, A. (2013). Technology hurts? Lesbian, gay, and bisexual youth perspectives of technology and cyberbullying. Journal of School Violence, 12 (1), 27–44.
Volk, A. A., Dane, A. V., & Marini, Z. A. (2014). What is bullying? A Theoretical Redefinition, Developmental Review, 34 (4), 327–343.
Walton, G. (2005). Bullying widespread. Journal of School Violence, 4 (1), 91–118.
Walton, G. (2011). Spinning our wheels: Reconceptualizing bullying beyond behaviour-focused Approaches. Discourse: Studies in the Cultural Politics of Education , 32 (1), 131–144.
Walton, G., & Niblett, B. (2013). Investigating the problem of bullying through photo elicitation. Journal of Youth Studies, 16 (5), 646–662.
Wiseman, A. M., & Jones, J. S. (2018). Examining depictions of bullying in children’s picturebooks: A content analysis from 1997 to 2017. Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 32 (2), 190–201.
Wiseman, A. M., Vehabovic, N., & Jones, J. S. (2019). Intersections of race and bullying in children’s literature: Transitions, racism, and counternarratives. Early Childhood Education Journal, 47 , 465–474.
Ybarra, M. L., Espelage, D. L., Valido, A., Hong, J. S., & Prescott, T. L. (2019). Perceptions of middle school youth about school bullying. Journal of Adolescence, 75 , 175–187.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the authors for sharing their work; Angela Mazzone, James O’Higgins Norman, and Sameer Hinduja for their editorial assistance; and Dorte Marie Søndergaard on the editorial board for suggesting a special issue on qualitative research in the journal.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Behavioural Sciences and Learning (IBL), Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
Paul Horton
Work Research Institute (WRI), Oslo Metropolitan University, Oslo, Norway
Selma Therese Lyng
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Paul Horton .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Horton, P., Lyng, S.T. Qualitative Methods in School Bullying and Cyberbullying Research: An Introduction to the Special Issue. Int Journal of Bullying Prevention 4 , 175–179 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42380-022-00139-5
Download citation
Published : 12 August 2022
Issue Date : September 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s42380-022-00139-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Solutions Industry Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Employee Experience Conjoint
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Bullying Survey for Students Questions + Sample Questionnaire Template
Bullying surveys are important tools for collecting data and gathering information about the prevalence and nature of bullying in educational settings. They can help schools and educators identify areas where bullying is a problem, and implement strategies and interventions to address it. Bullying surveys can be administered to students, teachers, and other school staff, and may ask questions about the frequency and severity of bullying behaviors, the types of bullying that occur (e.g., physical, verbal, cyber), and the relationships between the bully and the victim. They may also ask about the impact of bullying on individuals and the school community and the effectiveness of school policies and interventions in addressing bullying. By collecting and analyzing data from bullying surveys, K-12 Institutions and Universities can create more targeted and effective strategies to prevent and address bullying. This can lead to a safer and more positive school environment for all students, which is essential for their academic and social development.
- Desktop Created with Sketch.
- Mobile Created with Sketch.
Advantages of the running anti-bullying surveys using this survey template:
Related templates and questionnaires, course evaluation and improvement survey template, graduation exit survey template, teacher evaluation & student course evaluation survey.
- Sample Questions
- Sample Reports
- Survey Logic
- Integrations
- Professional Services
- Survey Software
- Customer Experience
- Communities
- Polls Explore the QuestionPro Poll Software - The World's leading Online Poll Maker & Creator. Create online polls, distribute them using email and multiple other options and start analyzing poll results.
- Research Edition
- Survey Templates
- Case Studies
- Coronavirus Resources
- Qualtrics Explore the list of features that QuestionPro has compared to Qualtrics and learn how you can get more, for less.
- SurveyMonkey
- VisionCritical
- Market Research Survey Software Real-time, automated and advanced market research survey software & tool to create surveys, collect data and analyze results for actionable market insights.
- Employee Survey Software Employee survey software & tool to create, send and analyze employee surveys. Get real-time analysis for employee satisfaction, engagement, work culture and map your employee experience from onboarding to exit!
- Customer Survey Software Robust, automated and easy to use customer survey software & tool to create surveys, real-time data collection and robust analytics for valuable customer insights.
- Community Survey Software Use the community survey software & tool to create and manage a robust online community for market research. Collect community feedback and insights from real-time analytics!
- Web Survey Software Powerful web survey software & tool to conduct comprehensive survey research using automated and real-time survey data collection and advanced analytics to get actionable insights.
- Mobile Survey Software Leverage the mobile survey software & tool to collect online and offline data and analyze them on the go. Create and launch smart mobile surveys!
- Business Survey Software Powerful business survey software & tool to create, send and analyze business surveys. Get actionable insights with real-time and automated survey data collection and powerful analytics!
- Enterprise Survey Software Real time, automated and robust enterprise survey software & tool to create surveys. collect data and analyze responses to get quick actionable insights.
- Email Survey Software Robust email survey software & tool to create email surveys, collect automated and real-time data and analyze results to gain valuable feedback and actionable insights!
- SMS Survey Software Use the power of SMS to send surveys to your respondents at the click of a button. SMS survey software and tool offers robust features to create, manage and deploy survey with utmost ease.
- Offline Surveys
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) Learn everything about Net Promoter Score (NPS) and the Net Promoter Question. Get a clear view on the universal Net Promoter Score Formula, how to undertake Net Promoter Score Calculation followed by a simple Net Promoter Score Example.
- Conjoint Analysis
- GDPR & EU Compliance
- Likert Scale Complete Likert Scale Questions, Examples and Surveys for 5, 7 and 9 point scales. Learn everything about Likert Scale with corresponding example for each question and survey demonstrations.
- Executive Team
- Advisory Board
- Testimonials
- In the news
QuestionPro in your language
- Encuestas Online
- Pesquisa Online
- Umfrage Software
- Сервис опросов
- برامج للمسح
- Logiciel d'enquête
Awards & certificates
The experience journal.
Find innovative ideas about Experience Management from the experts
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Cookie Settings
Creating a survey with QuestionPro is optimized for use on larger screens -
Though you're welcome to continue on your mobile screen, we'd suggest a desktop or notebook experience for optimal results.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Quantitative research designs, which have long dominated the field of bullying research (Eriksen Citation 2018), are often constructed based on researchers' understanding rather than constructing the design from the viewpoint of young people interpreting their own lived experiences (see Canty et al. Citation 2016). For example, some ...
Bullying, internationally recognized as a problematic and aggressive form of behavior, has negative effects, not only for those directly involved but for anybody and in particular children in the surrounding environment (Modin, 2012).However, one of the major concerns among researchers in the field of bullying is the type of research methods employed in the studies on bullying behavior in schools.
The goal of the current study was to further establish the reliability and validity of the Bullying Participant Behaviors Questionnaire (BPBQ), a self-report survey that allows for an examination ...
To examine recent trends in bullying and mental health problems among adolescents and the association between them. A questionnaire measuring mental health problems, bullying at school, socio-economic status, and the school environment was distributed to all secondary school students aged 15 (school-year 9) and 18 (school-year 11) in Stockholm during 2014, 2018, and 2020 (n = 32,722).
For example, the quantitative studies used an agreed academic definition of bullying which may or may not have influenced how young participants defined bullying within the studies. On the other hand, the qualitative study involved a group of students in deciding which questions to ask of the research participants and in interpreting the findings.
Participatory Action Research (PAR) empowers young people to work alongside adult researchers to determine the purpose/scope of research projects. By naming the purpose of the research, young people have the potential to transform it. Beginning with a broad question, we worked in collaboration with secondary school students (co-researchers) and staff to decide on the focal research question ...
3. Measuring bullying. Having a valid definition accompanied by a clear logic model offers a firm base from which researchers can measure bullying, but measurement is still the Achilles' heel of bullying research: the measurement of bullying does not often map onto the definition employed (Cornell, Sheras, & Cole, 2006).Researchers have used such a wide range of different measures of bullying ...
The findings of the interviews extended knowledge related to bullying and cyberbullying in the following ways, which can inform "bottom-up research and intervention efforts" (Dennehy et al., 2020, p. 10): augmenting quantitative findings, contextualizing new or rapidly evolving areas of research, capturing nuances and complexity of ...
Abstract. During the school years, bullying is one of the most common expressions of violence in the peer context. Research on bullying started more than forty years ago, when the phenomenon was defined as 'aggressive, intentional acts carried out by a group or an individual repeatedly and over time against a victim who cannot easily defend him- or herself'.
Abstract. Given the high prevalence and dramatic impact of being bullied at school, it is crucial to get more insight into how teachers can reduce bullying. So far, few instruments have measured elementary teachers' responses to bullying. This study investigated the validity of the student-reported Teachers' Responses to Bullying Questionnaire.
The open science movement has developed out of growing concerns over the scientific standard of published academic research and a perception that science is in crisis (the "replication crisis"). Bullying research sits within this scientific family and without taking a full part in discussions risks falling behind. Open science practices can inform and support a range of research goals ...
The Questionnaire on School Bullying, with its 70 'Hardly ever, Sometimes, Often, Almost always' options, reveals the phenomena of violence and harassment between pupils in everyday school life in ...
We review qualitative research on school bullying and victimization published between 2004 and 2014. Twenty-four empirical research studies using qualitative methods were reviewed. We organize the findings from these studies into (1) emic, (2) context specific, (3) iterative, (4) power relations, and (5) naturalistic inquiry.
This quantitative study endeavoured to answer the following research question: "What is the impact of bullying on the adolescent's sense of self." The researcher aimed to use the statistical analysis of the empirical study to improve the helping profession's understanding of the phenomenon. This may lead to more
Relational bullying. Even in the home, relational bullying or relational aggression can have a profound impact on family dynamics and relationships. Domestic violence and elder abuse are examples of bullying that occur within the family. It is crucial for families to address such behavior and to seek help from resources such as hotlines and ...
Bullying - Science topic. Bullying is an aggressive behavior intended to cause harm or distress. The behavior may be physical or verbal. There is typically an imbalance of power, strength, or ...
A research, of 187 undergraduate students matriculated at a large U.S. Northeastern metropolitan Roman Catholic university (Webber and Ovedovitz, 2018), found that 4.3% indicated that they were victims of cyberbullying at the university level and a total of 7.5% students acknowledged having participated in bullying at that level while A survey ...
School bullying research has a long history, stretching all the way back to a questionnaire study undertaken in the USA in the late 1800s (Burk, 1897).However, systematic school bullying research began in earnest in Scandinavia in the early 1970s with the work of Heinemann and Olweus ().Highlighting the extent to which research on bullying has grown exponentially since then, Smith et al. found ...
Bullying can occur between customers or. clients and workers, employees and employers, or employees and their peers (Brodsky, 1976). In many cases, the victims of workplace bullying abandon careers, lose friends. and family, develop physical illnesses, and in worst-case scenarios, retaliate.
Norman Raotraot Galabo. ABSTRACT: The purpose of this qualitative case study was to describe the campus bullying experiences of senior high school students in a certain. secondary school at Davao ...
Use this free bullying survey for students template to collect first-hand information about students being bullied. This sample bullying survey template designed by experts understands the reason why a student becomes a bully. Customize your questions to suit your institution to stop bullying and provide students with a healthy study environment.
The study employed the theoretical framework of Perception Theory, Symbolic Interaction Theory, and Conflict Theory. This study provides better understanding on the perceptions and experiences of cyber bullying experiences of female university students at Zayed University in the United Arab Emirates. A quantitative study with a sample size of ...
Abstract Current research on how adolescents cope with bullying is primarily quantitative, examines youth in Grades 1 through 6, and neglects to specifically assess how victims of bullying cope with being bullied. The cur-rent qualitative study explored the coping strategies of 22 rural middle- and high-school youth victimized by bul-lying.