

Compilation of long essay questions.
- Explain the structure of bacterial cell with the aid of a neatly labelled diagram. Also mention the roles of these structures and methods of their detection.
- Define sterilization. Classify various methods of sterilization with suitable examples.
- Define disinfection. Classify various methods of disinfection with suitable examples.
- What are culture media. Classify the types of culture media with examples and their uses.
- Describe the various methods of horizontal gene transfer among bacteria and mention their significance.
- Enlist the virulence factors of Staphylococcus aureus. Describe the various conditions caused by this bacterium along with their laboratory diagnosis.
- Classify Streptococci. Describe the virulence factors of Streptococcus pyogenes along with the lesions produced and the laboratory diagnosis.
- Enumerate the pyogenic bacteria. Describe the procedure involved in the diagnosis of any suppurative infection.
- What is pyogenic meningitis? Enlist the various etiological agents and describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of Neisseria meningitis.
- Which are the bacterial STDs? Write the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of gonorrhoea.
- Name the infections produced by pneumococcus. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of pneumococal pneumonia.
- Classify Mycobacteria. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Enlist the bacterial zoonotic diseases. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of anthrax.
- Define Pyrexia of Unknown Origin. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of brucellosis.
- Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of diphtheria.
- Classify Clostridia. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of gas gangrene.
- Classify the non-sporing anaerobes. Describe the various infections produced by them and the strategies adopted to culture them.
- Classify Enterobacteriaceae. Mention the various infections produced by Escherichia coli. Describe the laboratory diagnosis and treatment of acute cystitis.
- Name the bacteria capable of causing dysentery. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of bacillary dysentery.
- Describe the etiology, pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of enteric fever.
- Enumerate the bacteria causing gastroenteritis. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of cholera.
- What is meant by nosocomial infection? Which are common nosocomial pathogens? Describe the various infections produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Name the bacterial etiolgical agents of food-poisoning. Describe the strategy involved in diagnosing outbreaks of food-poisoning.
- Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of plague.
- Describe the pathogenesis, classification, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment of leprosy.
- Name the bacterial STDs. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment of syphilis.
- Classify treponemes. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment of leptospirosis.
- Classify Rickettsiae. Describe the etiology, pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of spotted fevers.
- Classify Chlamydia. Describe the various infections produced by C. trachomatis along with its laboratory diagnosis and treatment.
- Classify fungi and their diseases. Describe the procedures involved in laboratory diagnosis of mycoses.
- What are dermatophytes? Enlist the various dermatophytic infections along with their etiological agents. Describe the process of laboratory diagnosis and treatment.
- Name the sub-cutaneous fungal infections along with their etiological agent. Describe the pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of eumycotic mycetoma.
- Name the systemic fungal infections along with their etiological agent. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of histoplasmosis.
- Enumerate the opportunistic fungal infections along with their etiological agent. Describe the pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of candidiasis.
- Classify viruses. Describe the strategies adopted in the laboratory diagnosis of viral infections.
- Classify Herpes viruses. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment of HSV infections.
- Name the viruses causing hepatitis. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, prophylaxis and treatment of HBV infection.
- Classify arboviruses. Describe the pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of dengue.
- Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, and prophylaxis of rabies.
- Enlist the oncogenic viruses. Describe the mechanism of oncogenic transformation.
- Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment of HIV infection.
- Name the virus transmitted parenterally. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment of HCV.
- Name the sexually transmitted viral infections and their etiological agents. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment of papilloma virus.
- Enlist the viruses causing respiratory tract infections. Describe the pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of influenza.
- Name the viral diseases of childhood. Describe the etiology, pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and prophylaxis of measles.
- Name the opportunistic viral diseases. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of CMV infections.
- Classify Picornaviridae. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and prophylaxis of polio.
- Enumerate the nematodes infesting intestine. Describe the life cycle, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of roundworm/hookworm/pinworm.
- Classify tapeworms. Describe the life cycle, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of conditions produced by tapeworm.
- Describe the life cycle, pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of entamoeba infection.
- Describe the etiology, life cycle, pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of toxoplasmosis.
- Name the parasites causing infections in the immunocompromised. Describe the pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of Cryptosporidium.
- Name the species of Plasmodium and differentiate their features. Describe the life cycle, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of malaria.
- Name the filarial nematodes. Describe the life cycle, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of bancroftian filariasis.
- Name the parasites causing infection of the nervous system. Describe the life cycle, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of Acanthamoeba infection.
- Classify antigen-antibody reactions. Describe the various types of agglutination/precipitation reactions along with examples.
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of an IgG molecule. Describe the properties of all the classes of immunoglobulins.
- Describe the cells of the reticuloendothelial system. Describe their role in innate immunity.
- Classify immunity. Describe the various mechanism of innate/acquired immunity.
- Classify hypersensitivity reactions. Describe the mechanism of action of Immediate/Delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
- What is autoimmunity. Describe the pathogenesis of various autoimmune disorders and tests employed to detect them.
- What are immunodeficiency disorders? Describe briefly the various T-cell/B-cell related immunodeficiencies.
- What is the basis of humoral/cell-mediated immune response? Describe the process with an illustration.
- Classify vaccines. Write notes on various vaccines administered as per national immunization programme.
- Draw the two common complement activation pathways and describe the importance of complement in health and disease.
Compilation of short essay questions.
- Contributions of Louis Pasteur
- Contributions of Robert Koch
- Koch’s postulates
- Nobel Prize winners related to microbiology
- Morphological forms of bacteria
- Bacterial spore
- Bacterial cell wall
- Bacterial capsule
- Intracytoplasmic inclusions
- Differences between endotoxin and exotoxin
- Bacteriocine
- Darkground staining
- Negative staining
- Phase-contrast microscope
- Electron microscope
- Differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes
- Antiseptics
- Quaternary ammonium compounds
- Chemisterilants
- Hot air oven
- Tyndallization
- Inspissation
- Pasteurization
- Surface-active agents
- Sterilization controls
- Selective media
- Enriched media
- McConkey’s agar
- Anaerobic culture media
- Biphasic media
- Transport media
- Bacterial growth curve
- Conjugation
- Transduction
- Transposons/jumping genes
- Polymerase Chain Reaction
- String test
- Phage typing
- Biological safety cabinets
- Staphylococcal toxins
- Superantigen
- Toxic Shock Syndrome
- Coagulase test
- Catalase test
- Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
- Coagulase Negative Staphylococci
- Flesh eating bacteria
- Enterococci
- Viridans Streptococci
- Quellung reaction
- C-Reaction Protein (CRP)
- Pneumococcal vaccine
- Meningococcal vaccine
- Oxidase test
- Non-gonoccal urethritis (NGU)/ Non-specific urethritis
- Elek’s test
- Lysogenic conversion
- Diphtheroids
- Toxigenicity tests for Corynebactium diphtheria
- DPT vaccine
- Malignant pustule
- Hide Porter’s disease
- Nagler reaction
- Litmus milk test/Stormy clot
- Toxins of Clostridium perfringens
- Antibiotic associated pseudomembranous colitis
- Bacterioides
- Actinomycosis
- Bacterial vaginosis
- McIntosh Filde’s Jar/GasPak system
- Bacterial normal flora
- Traveler’s diarrhea
- ETEC/EIEC/EHEC/EPEC
- Presumptive coliform count
- Diarrheagenic E. coli
- Serodiagnosis of typhoid fever/Widal test
- Halophilic Vibrios
- Kanagawa phenomenon
- Bacterial pigments
- Cat scratch disease
- Rat bite fever
- X and V factor
- Satellitism
- HACEK bacteria
- Acellular pertussis vaccine
- Drug resistance in M. tuberculosis/MDR-TB/XDR-TB
- Acid Fast Staining
- BCG vaccine
- Tuberculin test
- Lepromin test
- RNTCP guidelines on diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis
- Extrapulmonary tuberculosis
- VDRL/RPR test
- Specific Treponemal tests
- Non-venereal Treponematosis
- Lyme’s disease
- Vincent’s angina/Fusospirochetosis
- Ludwig’s angina
- Helicobacter pylori
- Weil-Felix test
- Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)
- Bacterial infections of the eye
- Antifungal drugs
- Mycetism/Mycotoxicosis
- Fungal culture media
- Dermatophytes
- Candidiasis
- Cryptococcosis
- Dimorphic fungi
- Aspergillosis
- Id reaction
- Dematiaceous fungi
- Rhinosporidiosis
- Sporotrichosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Fungal spores
- Viral replication
- Cultivation of viruses
- Viral morphology
- Inclusion bodies
- Cell culture/Tissue culture
- Bacteriophage
- Viral vaccines
- Cytopathic effect
- Oncogenesis
- Burkitts’ lymphoma
- Viral latency
- Prion diseases
- Delta virus
- Immune response to Hepatitis virus
- Rabies vaccines
- Ebola virus
- Dengue shock syndrome
- Diarrheal viruses
- Antiviral drugs
- Molluscum contagiosum
- HIV post-exposure prophylaxis
- Swine flue/Bird flu
- Chikungunya virus
- Emerging viral diseases
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Varicella-zoster
- B-cell/T-cell
- MHC restriction
- HLA system/typing
- IgG/IgM/IgA/IgE
- Monoclonal antibody
- Immunofluorescence
- Immunodiffusion
- Heterophile tests
- Western Blot
- Southern Blot
- Abnormal immunoglobulins
- Class switching
- Lectin pathway
- Properdin pathway
- Host vs Graft reaction
- Graft vs Host reaction
- Immunological surveillance
- DiGeorge’s syndrome
- Anaphylaxis
- NK cells/LGLs
- Complement deficiencies
- Coomb’s test
- Frequently asked questions in Viva
- Applied microbiology: clinical cases
- Online identification of bacteria
- PPT slides for online self-study
- Ready made notes
What's new?
- New web design
- New additions in PPT slides
- SOP and techniques
- HTML5 compatible slides
- Compatible with many devices
Other links
- Microbiology Blog
- My travel blogs
- My random blogs
- Wiki contributions
Connect with me
Multiple Choice
Which of the following foods is NOT made by fermentation?
- orange juice
Who is considered the “father of Western medicine”?
- Marcus Terentius Varro
- Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
- Hippocrates
Who was the first to observe “animalcules” under the microscope?
- Ötzi the Iceman
- Robert Koch
Who proposed that swamps might harbor tiny, disease-causing animals too small to see?
- Louis Pasteur
Which of the following was NOT a kingdom in Linnaeus’s taxonomy?
Which of the following is a correct usage of binomial nomenclature?
- Homo Sapiens
- homo sapiens
- Homo sapiens
Which scientist proposed adding a kingdom for protists?
- Carolus Linnaeus
- Robert Whittaker
- Ernst Haeckel
Which of the following is NOT a domain in Woese and Fox’s phylogenetic tree?
Which of the following is the standard resource for identifying bacteria?
- Systema Naturae
- Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology
- Woese and Fox’s phylogenetic tree
- Haeckel’s General Morphology of Organisms
Which of the following types of microorganisms is photosynthetic?
Which of the following is a prokaryotic microorganism?
- cyanobacterium
Which of the following is acellular?
Which of the following is a type of fungal microorganism?
Which of the following is not a subfield of microbiology?
- bacteriology
- clinical microbiology
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Nina Parker, Mark Schneegurt, Anh-Hue Thi Tu, Philip Lister, Brian M. Forster
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Microbiology
- Publication date: Nov 1, 2016
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-multiple-choice
© Jan 10, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
POTENTIAL EXAM QUESTIONS IN A MICROBIOLOGY COURSE
Professor Katherine Mcmahon (Microbiology 425, Environmental microbiology)
The questions below are all fair game for the final exam. I will select roughly half of the content for the actual exam. The actual exam will also include 5-8 multiple choice questions (not listed here).
For guidance on how much detail to provide in your answer, I am listing the approximate number of lines I would expect you to use on the actual exam, to answer the question. The last page of this document has line numbers to use for calibration purposes.
1. Imagine that after graduation you secure a job at an environmental remediation firm as the resident (micro)biologist, mainly because you took Microbiology 425 and have expertise in environmental microbiology. They hire you to advise a team of ecologists, engineers, and chemists on a range of pollution cleanup and mitigation projects. The first big project you are assigned to is an oil spill that just occurred because an oil tanker sank in Puget Sound, Washington.
a. The engineers propose spraying a chemical dispersant called Corexit on the oil slick because they read about its use for the Deep Water Horizon spill cleanup. The ecologists disagree because they think it is too toxic to wildlife.
i. Explain to both the engineer and the ecologist the purpose of the dispersant (6 lines).
ii. The team wants your advice on whether the dispersant will actually work and to provide evidence from past studies about its effect on microbial processes. Outline the technical report you would provide to them. (20 lines)
iii. Specifically, the team wants to know whether the oil and dispersant degradation rates will be comparable to those reported for the Deep Water Horizon spill. Compare and contrast the conditions at the location of the current spill vs the DWH, in order to answer their question. Focus on conditions that are relevant to the microbes. (15 lines)
b. You are given a large research budget to study the effects of the oil spill on the microbial communities in Puget Sound. Outline THREE datasets that you would collect and briefly describe how you would collect them. (30 lines)
c. Describe the results you would expect to obtain from your studies. Specifically, which organisms do you expect to be enriched in water affected by the spill? (10 lines)
d. Identify at least three genes or pathways you would expect to find enriched in Puget Sound after the spill. (6 lines)
e. One of the ecologists asks whether the team should expect to find a lot of Methylomonas in the water, since he read that this genus was enriched after the DWH spill. Answer her question and explain your answer. (10 lines)
f. One of the engineers asks why oil spills cause dissolved oxygen depletion. She learned about biological oxygen demand in her class on wastewater treatment but doesn’t understand why oil would have the same effect as sewage. Explain the mechanism of hydrocarbon-mediated DO depletion to her. (15 lines)
2. Imagine that you just joined the laboratory of a famous oceanographer who up until recently has not employed many of the more modern molecular techniques to the study of marine microbes. Thus, she is unfamiliar with the strengths and limitations of various molecular methods. She is funding you as a PhD student to study the role of polyamines in the ocean because a recent analysis of metagenomic data showed that genes encoding polyamine transporters were abundant in many marine samples. While doing some background reading, you learn that polyamines are found in marine phytoplankton.
a. The PI asks you to analyze some unassembled metagenomes and tell her which of the major heterotrophic marine bacteria have polyamine transporters in their genomes. You know this is not possible to do without gathering additional data. Explain why this is the case. (8 lines)
b. Propose a workflow that could be used to generate the information your PI is seeking, assuming no budgetary constraints. (15 lines)
c. Now that you know which marine bacteria carry polyamine transporter genes, your PI wants to know which of these bacteria are actively using polyamines, in water off the coast of Georgia. Propose a workflow that could be used to generate the information your PI is seeking. (15 lines)
d. Now imagine that a new undergraduate researcher joins the lab. He has never taken a course in environmental microbiology or marine microbiology. The PI asks you to explain the concept of the Microbial Loop to this new lab member. Outline how you would do this, using the polyamines as an illustrative example. Feel free to draw a diagram if you think it would help. (12 lines)
3. The nitrogen cycle in freshwater lakes is complex. In temperate eutrophic lakes such as Lake Mendota, which thermally stratify during the summer, ammonium accumulates to high concentrations in the hypolimnion. When the lake turns over and mixes in the fall, the ammonium is distributed throughout the water column and persists at concentrations ~ 1 mg-N/L until ice forms. During the winter under the ice, much of the ammonium is gradually converted to nitrate.
a. Identify the individual steps in the conversion of ammonium to nitrate. Write the balanced reactions. (6 lines)
b. Nitrite concentrations under the ice rarely rise above 20 uM. Predict which groups of nitrite oxidizing bacteria would be found under the ice in the winter: Nitrospira or Nitrobacter. Justify your answer. (8 lines)
c. The dissolved oxygen concentrations under the ice tend to be high when the ice forms, but they become depleted during winter leading up to the spring thaw (but not to the point of “hypoxia”). Outline the processes that are leading to this oxygen consumption in the context of the carbon cycle under the ice. Compare and contrast this with what is happening in such lakes during the summer. (15 lines)
- Intro to Microbiology [ Test Questions only or all Intro to Microbiology materials ]
- History of Microbiology [ Test Questions only or all History of Microbiology materials ]
- Chemistry of Microbiology
- Bacterial Cell Wall & Differential Staining
- Prokaryote Cell Structure & Function [ Test Questions only or all materials ]
- Eukaryote Cell Structure & Function [ Test Questions only or all materials ]
- DNA Replication [ Test Questions only or all DNA Replication materials ]
- DNA Transcription & Translation [ Test Questions only or all materials ]
- Microbial Genetics [ Test Questions only or all Microbial Genetics materials ]
- Biological Classification [ Test Questions only or all Biological Classification materials ]
- Meet the Microbes: Prokaryotes [ Test Questions only or all all materials ]
- Meet the Microbes: Eukaryotes [ Test Questions only or all materialsl ]
- Virus Structure [ Test Questions only or all Virus Structure materials ]
- Virus Life Cycle [ Test Questions only or all Virus Life Cycle materials ]
- Meet the Microbes: Viruses [ Test Questions only or all Meet the Viruses materials ]
- Microbial Growth [ Test Questions only or all Microbial Growth materials ]
- Microbial Metabolism [ Test Questions only or all the Microbial Metabolism materials ]
- Specialized Bacterial Growth Media [ Test questions only or all materials ]
- Nonspecific / Innate Immunity [ Test Questions only or all Innate Immunity materials ]
- Specific / Acquired Immunity [ Test Questions only or all Acquired Immunity materials ]

- Online Practice Tests
Microbiology Practice Questions
1. which of the following structures contains genes for enzymes and antibiotic resistance.
- Plasma Membrane
2. Which of the following is the most important structure related to microbial attachment to cells?
- Peptidoglycan
3. Which of the following is not a gram-negative bug?
- Clostridium perfringens
- Vibrio cholerae
- Escherichia coli
- Bordetella pertussis
4. Which of the following is not true related to endotoxins?
- Endotoxins are secreted from cells.
- Can be linked to Meningococcemia
- Produced by gram negative microorganisms
- Can cause fever
5. Which of the following microorganisms stain well?
- Legionella pneumophila
- Treponema
6. Which of the following microorganisms are not matched correctly with the appropriate isolation media?
- Fungi – Sabourand’s agar
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae – Pink colonies media
- Haemophilus influenzae – Chocolate agar
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis – Lowenstein-Jensen agar
7. Which of the following diseases and bacteria are matched up incorrectly?
- Cellulitis – Pasteurella multocida
- Tularemia – Francisella tularensis
- Gastritis – Heliobacter pylori
- Lyme disease – Yersinia pestis
8. Which of the following diseases and bacteria are matched up incorrectly?
- Treponema pallidum – Syphilis
- Tinea nigra – Cladosporium werneckii
- Borrelia burgdorferi – Lyme disease
- Yersinia enterocolitica – Diptheria
9. Which of the following is not true concerning Staphylococcus aureus?
- S. aureus is related to inflammation.
- S. aureus can cause pneumonia
- S. aureus can lead to acute bacterial endocarditis
- S. aureus does not make coagulase
10. Which of the following signs and symptoms is not linked to Haemophilus influenzae?
- Otitis media
11. The Tsetse fly is a transmission factor for which of the following organisms?
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Trypanosoma gambiense
- Entamoeba histolytica
12. The Ixodes tick is a transmission factor for which of the following organisms?
- Leishmania donovani
- Giardia lamblia
13. Chagas’ disease is commonly treated with Nifurtimox and is linked to the ____ microorganism.
- Schistosoma
- Wucheria bancrofti
- Trypanosoma cruzi
14. Which of the following is not fungal related?
- Cryptococcus neoformans
- Candida albicans
- Tinea nigra

15. Which of the following is not a DNA virus?
- Adenovirus
- Calicivirus
16. Which of the following is not a RNA virus?
- Orthomyxovirus
- Deltavirus
- Herpesvirus
17. Which of the following viruses is not a double strand linear DNA virus?
- Papovavirus
18. Which of the following viruses is not a single strand linear RNA virus?
- Retrovirus
- Bunyavirus
- Picornavirus
19. The Tzanck test is not used on which of the following viruses?
20. which of the following microorganisms has not been linked to uti’s.
- Pseudomonas
- Klebsiella
- Haemophilus
1. A 2. D 3. A 4. A 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. D 9. D 10. C 11. B 12. C 13. D 14. D 15. B 16. D 17. B 18. C 19. C 20. D
- Create A Quiz
- Relationship
- Personality
- Harry Potter
- Online Exam
- Entertainment
- Training Maker
- Survey Maker
- Brain Games
- ProProfs.com
Microbiology Quizzes, Questions & Answers
Top trending quizzes.
Popular Topics
Recent quizzes.
« Previous 1 2 3 4 5 6 Next »
Popular Quizzes
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
- Document library
Medical Microbiology Part 2 - Essay sample questions

Designing Effective Assignments
Potential Exam Questions in a Microbiology Course
Professor Katherine McMahon - Microbiology 425: Environmental Microbiology
The questions below are all fair game for the final exam. I will select roughly half of the content for the actual exam. The actual exam will also include 5-8 multiple choice questions (not listed here).
For guidance on how much detail to provide in your answer, I am listing the approximate number of lines I would expect you to use on the actual exam, to answer the question. The last page of this document has line numbers to use for calibration purposes.
1. Imagine that after graduation you secure a job at an environmental remediation firm as the resident (micro)biologist, mainly because you took Microbiology 425 and have expertise in environmental microbiology. They hire you to advise a team of ecologists, engineers, and chemists on a range of pollution cleanup and mitigation projects. The first big project you are assigned to is an oil spill that just occurred because an oil tanker sank in Puget Sound, Washington.
a. The engineers propose spraying a chemical dispersant called Corexit on the oil slick because they read about its use for the Deep Water Horizon spill cleanup. The ecologists disagree because they think it is too toxic to wildlife.
i. Explain to both the engineer and the ecologist the purpose of the dispersant (6 lines).
ii. The team wants your advice on whether the dispersant will actually work and to provide evidence from past studies about its effect on microbial processes. Outline the technical report you would provide to them. (20 lines)
iii. Specifically, the team wants to know whether the oil and dispersant degradation rates will be comparable to those reported for the Deep Water Horizon spill. Compare and contrast the conditions at the location of the current spill vs the DWH, in order to answer their question. Focus on conditions that are relevant to the microbes. (15 lines)
b. You are given a large research budget to study the effects of the oil spill on the microbial communities in Puget Sound. Outline THREE datasets that you would collect and briefly describe how you would collect them. (30 lines)
c. Describe the results you would expect to obtain from your studies. Specifically, which organisms do you expect to be enriched in water affected by the spill? (10 lines)
d. Identify at least three genes or pathways you would expect to find enriched in Puget Sound after the spill. (6 lines)
e. One of the ecologists asks whether the team should expect to find a lot of Methylomonas in the water, since he read that this genus was enriched after the DWH spill. Answer her question and explain your answer. (10 lines)
f. One of the engineers asks why oil spills cause dissolved oxygen depletion. She learned about biological oxygen demand in her class on wastewater treatment but doesn’t understand why oil would have the same effect as sewage. Explain the mechanism of hydrocarbon-mediated DO depletion to her. (15 lines)
2. Imagine that you just joined the laboratory of a famous oceanographer who up until recently has not employed many of the more modern molecular techniques to the study of marine microbes. Thus, she is unfamiliar with the strengths and limitations of various molecular methods. She is funding you as a PhD student to study the role of polyamines in the ocean because a recent analysis of metagenomic data showed that genes encoding polyamine transporters were abundant in many marine samples. While doing some background reading, you learn that polyamines are found in marine phytoplankton.
a. The PI asks you to analyze some unassembled metagenomes and tell her which of the major heterotrophic marine bacteria have polyamine transporters in their genomes. You know this is not possible to do without gathering additional data. Explain why this is the case. (8 lines)
b. Propose a workflow that could be used to generate the information your PI is seeking, assuming no budgetary constraints. (15 lines)
c. Now that you know which marine bacteria carry polyamine transporter genes, your PI wants to know which of these bacteria are actively using polyamines, in water off the coast of Georgia. Propose a workflow that could be used to generate the information your PI is seeking. (15 lines)
d. Now imagine that a new undergraduate researcher joins the lab. He has never taken a course in environmental microbiology or marine microbiology. The PI asks you to explain the concept of the Microbial Loop to this new lab member. Outline how you would do this, using the polyamines as an illustrative example. Feel free to draw a diagram if you think it would help. (12 lines)
3. The nitrogen cycle in freshwater lakes is complex. In temperate eutrophic lakes such as Lake Mendota, which thermally stratify during the summer, ammonium accumulates to high concentrations in the hypolimnion. When the lake turns over and mixes in the fall, the ammonium is distributed throughout the water column and persists at concentrations ~ 1 mg-N/L until ice forms. During the winter under the ice, much of the ammonium is gradually converted to nitrate.
a. Identify the individual steps in the conversion of ammonium to nitrate. Write the balanced reactions. (6 lines)
b. Nitrite concentrations under the ice rarely rise above 20 uM. Predict which groups of nitrite oxidizing bacteria would be found under the ice in the winter: Nitrospira or Nitrobacter . Justify your answer. (8 lines)
c. The dissolved oxygen concentrations under the ice tend to be high when the ice forms, but they become depleted during winter leading up to the spring thaw (but not to the point of “hypoxia”). Outline the processes that are leading to this oxygen consumption in the context of the carbon cycle under the ice. Compare and contrast this with what is happening in such lakes during the summer. (15 lines)
UW-Madison WAC Sourcebook 2020 Copyright © by Professor Katherine McMahon - Microbiology 425: Environmental Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book

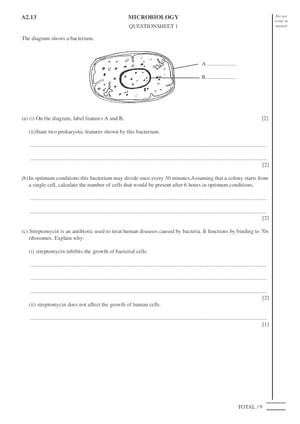
Microbiology Questions - A-Level
Description, download type.
.PDF (pdf) 431.145 KB
Publication Date
January 2010
Copyright Disclaimer
The materials published on this website are protected by the Copyright Act of 1988. No part of our online resources may be reproduced or reused for any commercial purpose, or transmitted, in any other form or by any other means, without the prior permission of Curriculum Press Ltd.
Similar Resources
What our customers say.
Find exactly what you’re looking for.
- Popular Searches
- A Level Media Studies
- A Level Sociology
Work with us
Get in touch.
- © 2024 Curriculum Press
- | Terms & Conditions
- | Privacy & Cookies |
- Website MadeByShape
Privacy notice
This site makes use of cookies . If you continue we'll assume you are happy to receive them.
- Read our cookie policy

Dedicated to excellence in biomedical science
- Specialist Advisory Panels
- Annual Report
- Chief Executive's biography
- Equity, Diversity and Inclusion
- Discussion groups
- IBMS library
- Media and press
- President's welcome
- Member benefits
- Applicants with overseas qualifications
- Help & FAQs
- Code of Conduct
- Professional indemnity cover
- IBMS Additions discount scheme
- Legal helpline
- Membership number login
- Request promotional items
- Update your details
- Laboratory Transformation and Improvement Program
- What is CPD?
- Science reading
- Choose IBMS Accredited
- Affiliated university societies
- President's Prize
- Certificate of Achievement
- Certificate of Competence by Equivalence
- Certificate of Attainment - Clinical Scientist
- Registration Training Portfolio
- Laboratory Training Approval
- Non-accredited degree assessment
- Return to practice
- Standards of Proficiency Updates 2023
- IBMS Mentoring Scheme
- Professional guidance
- Sample Journey videos
- SUPERLAB comics
- Resource hub
- IBMS qualifications resources
Past papers
- Activities for Children
- Biomedical Science Day
- Discover Biomedical Science
- Harvey's Lab Tours
- Membership publications
- Public engagement
A list of past papers for IBMS DEP and IBMS HSD
IBMS Diploma of Expert Practice
DEP Immunocytochemistry
DEP 2023 Immunocytochemistry Papers 1 and 2
DEP 2022 Immunocytochemistry Papers 1 and 2
DEP Histological Dissection
DEP 2023 Histological Dissection Papers 1 and 2
DEP 2022 Histological Dissection Papers 1 and 2
IBMS Higher Specialist Diploma
Cellular Pathology
HSD September 2023 Cellular Pathology
HSD September 2022 Cellular Pathology
Clinical Chemistry
HSD September 2023 Clinical Chemistry
HSD September 2022 Clinical Chemistry
Cytopathology
HSD September 2021 Cytopathology
Generic Paper
HSD September 2023 Generic Paper
HSD September 2022 Generic Paper
Haematology
HSD September 2023 - Haematology
HSD September 2022 - Haematology
HSD September 2022 - Immunology
Leadership and Management
HSD September 2023 Leadership and Management
HSD September 2022 Leadership and Management
Medical Microbiology
HSD September 2023 Medical Microbiology
HSD September 2022 Medical Microbiology
Transfusion Science
HSD September 2023 Transfusion Science
HSD September 2022 Transfusion Science
HSD September 2022 Virology
Share this page:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
General Microbiology Biol 4501 8 ESSAY QUESTIONS Answer all parts of the following questions completely. 1. (A) Diagram a Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial cell wall. (B) Demonstrate the differences in the chemical structure of these two types of bacterial cell walls. (C) Where and when does penicillin affect bacterial cells?
Microbiology Exam #1 Essay Questions. Hans and Zacharias Janssen's contributions to the development of microscopes. greatly contributed to the development of the microscope. In fact, he is recognized as its original founder around the 1590's. He was a Dutch spectacle maker, so he had proper experience with lenses.
Name the filarial nematodes. Describe the life cycle, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of bancroftian filariasis. Name the parasites causing infection of the nervous system. Describe the life cycle, laboratory diagnosis and treatment of Acanthamoeba infection. Classify antigen-antibody reactions.
Microbiology Exam 2 Essay Questions. 1. Describe the anatomy and functions of the following prokaryotic cell structures: Gram positive cell wall, capsule, phycobilisome, pilus. Click the card to flip 👆. Gram positive cell walls have a thick layer of peptidoglycan that can make up to 50% of the cell's dry weight, lying outside the plasma ...
Microbiology Exam 1 Essay Questions. #2 Describe the three kingdoms in Whittaker's system which contain at least some single-celled organisms. Include common characteristics that organisms within a kingdom share and one example from each kingdom of the importance of that group of organisms to humans. Whittaker's 5- kingdom system was based on ...
Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following foods is NOT made by fermentation? 2. Who is considered the "father of Western medicine"? 3. Who was the first to observe "animalcules" under the microscope? 4. Who proposed that swamps might harbor tiny, disease-causing animals too small to see?
1. Imagine that after graduation you secure a job at an environmental remediation firm as the resident (micro)biologist, mainly because you took Microbiology 425 and have expertise in environmental microbiology. They hire you to advise a team of ecologists, engineers, and chemists on a range of pollution cleanup and mitigation projects.
FREE Microbiology Practice Test Questions. Science Prof Online offers free lecture and lab PowerPoints on a variety of science topics. You have free access to a large collection of materials used in college-level introductory microbiology courses ( 8-week & 16-week ). The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational ...
Microbiology (BIOS 313 ) 23 Documents. Students shared 23 documents in this course. University Northern Illinois University. Academic year: 2021/2022. Uploaded by: ... Micro Unit 1 Essay Questions_Answering Questions. Course: Microbiology (BIOS 313 ) 23 Documents. Students shared 23 documents in this course. University: Northern Illinois ...
Bio 215: Exam 1, Fall 2019. 100 pts total. Version 2. Directions: Write answers to the matching section and short answers on the BACK of the Scantron sheet. Put answers to multiple choice and true/false questions on the Scantron bubble sheet. PUT YOUR NAME & VERSION NUMBER ON THE SCANTRON SHEET!!! Section 1: Multiple Choice (50 pts) Each ...
Borrelia burgdorferi - Lyme disease. Yersinia enterocolitica - Diptheria. 9. Which of the following is not true concerning Staphylococcus aureus? S. aureus is related to inflammation. S. aureus can cause pneumonia. S. aureus can lead to acute bacterial endocarditis. S. aureus does not make coagulase. 10.
Question Type: Essay. ... Micro Biology 2 - This is good study material that breaks down difficult concepts for Exam 2 which; Microbiology Lab - This has material over the course of the lab including biochemical tests, dilution; Micro Biology 4 - This has good materials for the last two exams including information that breaks ...
A. direct microscopic count. B. standard plate count. C. filtration on a support membrane followed by incubation on medium. D. metabolic activity. E. most probably number. D. metabolic activity. Media counting some ingredients of unknown chemical composition are called ______ media. A. undefined. B. complex.
Microbiology Quizzes, Questions & Answers. Microbiology studies organisms that cannot be easily visible to the naked eye. It is a lucrative route into science. We suggest you take some informative microbiology trivia quizzes to enhance your knowledge. The world of microbes is a whole new different one!
The Royal College of Pathologists. 6 Alie Street. London E1 8QT. Map and directions. Tel: +44 (0) 20 7451 6700
Essay # 1. Meaning of Microbiology: Microbiology is a branch of biology that deals with microorganisms (often upto a diameter of 1000 µ ) and their effects on other living organisms. It derives its name from the union of three greek words: mikros (= small), bios (= life bearing); and logos (= study). It ia a multi-disciplinary science of ...
The questions below are all fair game for the final exam. I will select roughly half of the content for the actual exam. The actual exam will also include 5-8 multiple choice questions (not listed here). For guidance on how much detail to provide in your answer, I am listing the approximate number of lines I would expect you to use on the ...
ADVERTISEMENTS: Exam Questions and Answers on Virus. In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Definition of Viruses 2. Morphology of Virus 3. Reaction to Physical and Chemical Agents 4. Multiplication of Virus inside the Host Cell 5. Cultivation 6. Classification 7. Major Groups of DNA and RNA Viruses. Contents: Definition of Viruses Morphology of […]
1. algae. 2. protozoa. 3. fungi. 4. animals. 5. plants. What is a carbohydrate and protein complex that is an external structure of cells; this is not found in cells with cell walls; "let me sugar coat this for you"? glycocalyx. What are the 4 main functions of the glycocalyx? 1. identification tag for cell.
HSD in Med Micro - Sept 2021 Short Answer, Essay and Case Studies Papers FINAL EXAM PAPERS. Higher Specialist Diploma Medical Microbiology Examination - September 2021 Short-answer questions 60 minutes . Attempt all four questions . Instructions to candidates 1. Record your candidate number and HSD discipline on the front sheet of the answer
FSC 530 FOOD MICROBIOLOGY EXAMS. Old Exams. These exams represent a composite of the types of questions that have been asked in previous years. Please note that the sequence and depth of topics covered varies from year to year. These exams should be used only as guide for the types of questions which may be asked.
These are practice examination questions on Microbiology for A-Level Biology. ... It allows students to become insightful geographers and thus demonstrate this in their extended answers and essay writing. Chris Critchlow. ... whilst always focusing on what students need to be able to answer exam questions. 10/10 always. Well worth the ...
Frequently Asked Questions; HCPC Resources; Non-accredited degree assessment ; Return to practice; Standards of Proficiency Updates 2023; Science Council registration. ... Medical Microbiology. HSD September 2023 Medical Microbiology. HSD September 2022 Medical Microbiology. Transfusion Science.