
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light
These NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts to help students while preparing for their exams.
Light NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15
Class 7 science chapter 15 light textbook exercise questions and answers.
Question 1. Fill in the blanks: a. An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called ……………….. b. Image formed by a convex ……………….. is always virtual and smaller in size. c. An image formed by a ……………….. mirror is always of the same size as that of the object. d. An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a ……………….. image. e. An image formed by a concave ……………….. cannot be obtained on a screen. Answer: a. virtual b. mirror c. plane d. real e. lens
Question 2. Mark “T” if the statement is true and “F” if it is false. a. We can obtain an enlarged and erect image by a convex mirror. b. A concave lens always forms a virtual image. c. We can obtain a real, enlarged and inverted image by a concave mirror. d. A real image cannot be obtained on screen. e. A concave mirror always forms a real image. Answer: a. False b. True c. True d. False e. False
Question 3. Match the items given in Column I with one or more item of Column II.
Answer: 1. (e), 2. (b) 3. (a), 4. (c), 5. (f)
Question 4. State the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror. Answer: Characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror are:
- The image formed is virtual.
- The image is laterally inverted.
- It is of the same size as the object.
- The image is situated at the same distance from the mirror as the object.
- The image is erect.
Question 5. Find out the letters of English alphabet or any other language known to you in which the image formed in plane mirror appears exactly like the letter itself. Discuss your findings. Answer: A, H, I, M, O, T, U, V, W, X, Y are the letters of English alphabet in which the image formed in a plane mirror appears exactly like the letter itself.
Question 6. What is a virtual image? Give one situation where a virtual image is formed. Answer: A virtual image is an image that cannot be obtained or formed on a screen. The image formed in plane mirror cannot be obtained on a screen because this is a virtual image.
Question 7. State two differences between a convex and a concave lens. Answer: Difference between convex lens and a concave lens are:
Question 8. Give one use each of a concave and a convex mirror. Answer: Convex mirrors are used in roads and large buildings to allow people to see what is around the bend. Concave mirrors are used in reflecting telescopes and also as a magnification tool.
Question 9. Which type of mirror can form a real image? Answer: A concave mirror can form a real image of an object. The nature of the image depends on the distance of the object from the concave mirror.
Question 10. Which type of lens forms always a virtual image? Answer: A concave lens always forms a virtual image of an object.
Choose the correct option in questions 11-13.
Question 11. A virtual image larger than the object can be produced by a a. concave lens b. concave mirror c. convex mirror d. plane mirror Answer: c. concave mirror.
Question 12. David is observing his image in a plane mirror. The distance between the mirror and his image is 4 m. If he moves 1 m towards the mirror, then the distance between David and his image will be a. 3 m b. 5 m c. 6 m d. 8 m Answer: c. 6 m
Question 13. The rearview mirror of a car is a plane mirror. A driver is reversing his car at a speed of 2 m/s. The driver sees in his rearview mirror, the image of a truck parked behind the car. The speed at which the image of the truck appears to approach the driver will be a. 1 m/s b. 2 m/s c. 4 m/s d. 8 m/s Answer: c. 4 m/s
NCERT Extended Learning Activities and Projects
Question 1. Play with a mirror. Write your name with a sketch pen on a thin sheet of paper, polythene or glass. Read your name on the sheet while standing in front of a plane mirror. Now look at your image in the mirror. Hint: Do it yourself.

Question 3. Make a rainbow. Try to make your own rainbow: You can try this project in the morning or in the evening. Stand with your back towards the sun. Take a hosepipe or a water pipe used in the garden. Make a fine spray in front of you. You can see different colours of rainbow in the spray. Hint: Do it yourself.
Question 4. Visit a laughing gallery in some science centre or a science park or a village mela. You will find some large mirrors there. You can see your distorted and funny images in these mirrors. Try to find out the kind of mirror used there. Hint: Spherical mirrors are used to form funny images. This is because normal plane mirrors produce a perfect image whereas we need distorted, funny images which can be only produced by curved mirrors.
Question 5. Visit a nearby hospital. You can also visit the clinic of an ENT specialist or a dentist. Request the doctor to show you the mirror used for examination of ear, nose, throat and teeth. Can you recognise the kind of mirror used in these instruments? Hint: Concave mirrors are used by dentists because at a short range, the concave mirror produces magnified, upright images of face. By these mirrors, dentists can examine the patient more easily.
Question 6. Roleplay: Here is a game that a group of children can play. One child will be chosen to act as object and other will act as the image of the object. The object and the image will sit opposite to each other. The object will make movements, such as raising a hand, touching an ear, etc. The image will have to make the correct movement following the movement of the object. The rest of the group will watch the movements of the image. If the image fails to make the correct movement, she/he will be retired. Another child will take her/ his place and the game will continue. A scoring scheme can be introduced. The group that scores the maximum will be declared the winner. Hint: Do it yourself.
Objective: To show that the image formed in a plane mirror is erect and virtual. Materials Required: A large-sized plane mirror and a candle. Procedure:
- Place a lighted candle in front of a plane mirror. Try to see the flame of the candle in the mirror. It appears as if similar candle is placed behind the mirror.
- The candle, which appears behind the mirror, is the image of the candle formed by the mirror. The candle itself is the object.
- Now move the candle to different positions in front of the mirror. Observe the image in each case.
- Now place a vertical screen behind the mirror. Try to obtain the image of the candle on this screen. The image of the candle cannot be obtained on the screen.
- Now place the screen in front of the mirror. The image of the candle cannot be obtained on the screen in this case also.

Objective: To show that the image formed in a plane mirror is laterally inverted. Materials Required: A large size plane mirror. Procedure:
- Stand in front of a big plane mirror and observe your image in the mirror.
- Lift your right hand, then the image lifts its left hand.
- Now lift your left hand and then the image appears to lift its right hand.

Observations: When you see yourself in the plane mirror, your right side part of the body becomes left and left side part of the body become right. Conclusion: When an object is placed in front of a plane mirror, the lateral sides of the object are changed and this is called lateral inversion.

Uses of Concave Mirror:
- Concave mirror is used by dentists to focus a beam of light to see inside a patient’s mouth or ears.
- Concave mirror is used in solar furnaces, because rays of sunlight converge at a point once they reflect from the concave mirror, generating heat.
- Concave mirror is used as barber’s mirror because it shows a larger image when object is too close to the mirror. It helps in getting a closer shave.
- It is also used in reflectors of torches and headlights of vehicles.
Objective: To show that a concave mirror forms a real image of the sun. Materials Required: A concave mirror and a sheet of paper. Procedure:
- Take a concave mirror.
- Hold it facing the sun.
- Try to get the light reflected by the mirror on a sheet of paper.
- Adjust the distance of the paper until you get a sharp bright spot on it.
- Hold the mirror and the sheet of paper steady for a few minutes.

ii. Convex Mirror: It is a spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outwards. In case of convex mirror, the image is always erect, virtual and smaller than the object.
Uses of Convex Mirror:
- Convex mirror is used in rear view mirrors of vehicles, as it shows smaller images from a bigger field of view.
- Convex mirror is also used on hairpin bends of roads to see the vehicles coming from the other side of the bend.
Objective: To study the images formed by a convex mirror. Materials Required: Convex mirror, mirror stand, candle and white paper screen. Procedure:
- Mount a convex mirror on a mirror stand and place it on a table.
- Place a screen made from white paper at a distance in front of it.
- Place a lighted candle in between the mirror and the screen.
- Move the screen to see if any image is formed on it. No image is seen on the screen.
- Now look into the convex mirror. An erect and smaller image is seen in the mirror.
- Slowly move the candle away from the mirror and keep observing the nature of the image formed in the mirror.
Observation: In convex mirror, the images of candle are smaller and erect at all distances. Conclusion: Convex mirror always forms erect and small-sized images.
Lens: A lens is a part of a reflecting material like glass or plastic but transparent from both sides. Lenses are unlike mirrors that have a reflecting surface only on one side. Depending upon its shape, a lens can be categorised as follows: i. Convex lens: This lens is thinner at the edges and thicker in the centre. It is a converging lens as it converges light rays. It can form real, inverted and diminished image. When the object is placed very close to the lens, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified.
A magnifying glass is a convex lens which is used to make small things look bigger by producing their magnified (enlarged) images.

Uses of Lenses: Lenses are used in microscopes, telescopes and cameras. They are used in astronomical telescopes. They are also used in reading glasses.
Components of White Light: The white light or sunlight is composed of seven colours. These colours in order are VIBGYOR (Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red). When white light passes through a glass prism, it breaks down into its component colours. This is the reason why rainbows show all the colours of the white light. Several phenomena explain that sunlight or white light is composed of seven colours.
Objective: To show that the sunlight consists of seven colours. Materials Required: A glass prism and a white sheet of paper. Procedure:
- Take a glass prism
- Allow a narrow beam of sunlight through a small hole in the window of a dark room to fall on one face of the prism.
- Let the light coming out of the other face of the prism fall on a white sheet of paper.

Observation: When the light coming out of the other face of the prism falls on a white sheet then a band of seven colours appear on the screen. Conclusion: When a beam of white light is passed through a glass prism, then the white light splits to form a band of seven colours on a white screen. Hence, sunlight is made up of seven colours.
i. Dispersion of light: The splitting up of white light into seven colours on passing through a transparent medium, like a glass prism, is called dispersion of light. The formation of spectrum of seven colours on the other side of the prism shows that white light is a mixture of seven colours.
ii. Rainbow: The rainbow is an arch of seven colours in the sky. The rainbow is produced by the dispersion of sunlight by tiny rain drops suspended in the atmosphere that behave like minute prisms.

Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light Additional Important Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is light? Answer: Light is a form of energy which helps us in getting the vision.
Question 2. How many colours are there in the visible spectrum? Answer: Seven.
Question 3. Which types of images can be formed on a cinema screen? Answer: Real images.
Question 4. Is the image of an object in a plane mirror virtual or real? Answer: Virtual.
Question 5. Define the image of an object. Answer: Due to the reflection of light, the impression of an object formed in a mirror is called the image of the object.
Question 6. What is virtual image? Answer: The image that cannot be captured on a screen is called a virtual image.
Question 7. What is real image? Answer: Image that can be captured on a screen is known as real image.
Question 8. Give an example of real image. Answer: In a camera, images are real and can be captured on the negative, which acts as a screen.
Question 9. What happens when light rays are incident on a concave lens? Answer: When light rays are incident on a concave lens, they bend outwards from the lens or diverge.
Question 10. How is a rainbow formed in the sky? Answer: A rainbow is formed by the dispersion of the sun’s rays through raindrops into seven colours.
Question 11. What is VIBGYOR? Answer: It represents the order of seven colours in the rainbow, i.e., violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red.
Question 12. What happens when light falls on a polished or a shiny surface? Answer: When light falls on a polished or a shiny surface, it gets reflected.
Question 13. What makes things visible to us? Answer: Objects are visible only when light reflected from them reaches our eyes.
Question 14. What is reflection of light? Answer: Bouncing back of a light ray after hitting any surface is known as reflection of light.
Question 15. Why we are not able to see the candle flame through a bent pipe? Answer: We are not able to see the candle flame through a bent pipe because light travels along straight lines.
Question 16. How can we change the path of light? Answer: We can change the path of light by keeping any shiny or polished or reflecting material in the path of the light beam.
Question 17. What type of image does the outer side of a spoon show? Answer: The outer surface of a spoon acts like a convex mirror.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 2. State any two uses each of concave mirror and convex mirrors. Answer: Concave mirrors:
- Concave mirrors are used as reflectors in torches, headlights of vehicles.
- Concave mirrors are used by the dentist to see an enlarged image of teeth.
Convex mirrors:
- Convex mirrors are used as rearview mirrors or side-view mirrors in automobiles such as cars, scooter, trucks, buses, etc., to see the traffic coming from behind.
- Convex mirrors are used as staircase mirrors on the double-decker buses.
Question 3. Why is a concave mirror called a converging mirror and a convex mirror called a diverging mirror? Answer: Concave mirror is called a converging mirror because it converges the parallel rays of light that fall on the mirror at a point called focus. Convex mirror is called a diverging mirror because parallel rays of light falling on it diverge after reflection.
Question 4. Distinguish between concave mirror and convex mirror. Answer:
Question 5. Why is convex mirror used as side mirror in scooters? Answer: We can recognise that the mirrors used as side mirror in scooters are convex mirrors. Convex mirror can form erect images of object spread over large area, so helps the drivers to see the traffic behind them.
Question 6. What is the difference between a virtual image and a real image? Answer: The following are the main differences between a real image and a virtual image.
- A real image can be obtained on a screen whereas a virtual image cannot be obtained on a screen.
- A real image is always inverted whereas a virtual image is always erect.
- A real image is formed when the rays of light, after reflection, actually meet at some point whereas a virtual image is formed when the rays of light, after reflection, appear to meet at a point but do not actually meet.
Question 7. Why do we need a shiny surface for reflection? Answer: The extent of reflection depends upon the shine and smoothness of the surface. More the shine and smoothness of the surface, more will be the reflection. That is why, mirrors reflect most of the light falling on them. Hence, for reflection, shiny surfaces are required.
Question 8. Give the characteristics of images formed by convex and concave lenses. Answer:
- Convex lens: A convex lens can form real and inverted image. When the object is placed very close to the lens, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified.
- Concave lens: A concave lens always forms erect, virtual and smaller image than the object.

Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. a. What is a lens? Name the two types of lenses. Name any five things which use lenses. b. What kind of lens is used as a magnifying glass? c. Which type of reflector is used in car headlights for producing a parallel beam of light? Answer: a. A lens is a piece of any transparent material bound by two curved surfaces or by one curved and one plane surface. When light rays pass through a lens, they bend and change their direction. The two types of lenses are:
- convex lens, and
- concave lens.
The five things which use lenses are: Spectacles, cameras, microscopes, telescopes and film projectors. b. Convex lens is used as a magnifying glass. c. Concave mirrors are used in vehicle headlights to send parallel rays because it allows the light rays to be focused as a single beam and give more power to the light that makes it more efficient for seeing and to be seen by others.

Picture-Based Questions

NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Heat
- Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
- Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals of Climate
- Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Soil
- Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
- Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- Class 7 Science Chapter 14 Electric Current and its Effects
- Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light
- Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
- Class 7 Science Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
- Class 7 Science Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
CBSE Class Notes Online – Classnotes123
CBSE Class Notes, Worksheets, Question Answers, Diagrams , Definitions , Diffrence between , Maths Concepts, Science Facts Online – Classnotes123
Class 7 Science -Chapter 15 – Light- Detailed Notes

Table of Contents
Introduction to Light
Definition of light.
Light is a form of energy that enables us to see our surroundings. It is a type of radiation that our eyes can detect. Light is characterised by its ability to illuminate objects and environments, making them visible to the human eye. It plays a crucial role in visual perception.
How Light Travels?
Straight line movement – experiment with pipes.

- Concept- Light travels in a straight line.
- Experiment- This concept can be illustrated using a simple experiment involving a candle and two pipes—one straight and one bent. When you try to see the flame of a candle through a straight pipe, you can see the flame clearly. However, if you replace the straight pipe with a bent one, you can no longer see the flame. This change occurs because the bent pipe obstructs the straight path of light, demonstrating that light travels in a straight line.
Also Check – What is Light? An Easy-to-Understand Guide
Interaction of Light with Different Materials

- Transparent Objects- These are materials through which light can pass completely. For example, glass is transparent because it allows almost all light to pass through, making objects on the other side visible.
- Translucent Objects- These materials allow light to pass through them, but not completely. Butter paper is an example of a translucent object, as it lets some light pass through, making objects behind it partially visible.
- Opaque Objects- These are objects through which no light can pass. Typical examples include a table or a book. Since light cannot pass through these objects, they completely block the view of anything behind them.
Also Check – Chapter 11- A Detailed Guide to the Light Activities for Class 7 Students
Basic Principles of Reflection
Reflection of light is a fundamental optical phenomenon where light, upon contacting a surface, is either absorbed or thrown back. This section delves into the basic principles of how reflection occurs and its various aspects.
Definition of Reflection
Reflection of light can be described as the process where light hitting an object is not absorbed but rather thrown back from the surface.Nature of Reflection – When light reflects, it changes its path. This alteration in the path of light is what we observe as reflection.
Also Check – Activity – Reflection of Light from a Plane Mirror
How Reflection Occurs
The occurrence of reflection, a fundamental optical phenomenon, can be explained by understanding how light interacts with different surfaces.

Interaction with Surfaces
- Surface Characteristics- The nature of the surface that light encounters plays a crucial role in determining how reflection occurs.
- Plane Mirrors- These have a flat surface and reflect light in a manner that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
- Curved Mirrors- These can either bulge inwards (concave) or outwards (convex), affecting how light is reflected and the nature of the image formed.
Also Check – What is Light Reflection? A Simple Guide to Understanding Reflections
Absorption vs. Reflection
- Dual Behaviour – When light hits an object, it may be absorbed or reflected back. This behaviour depends on the material’s properties and the surface texture.
- Absorption- If the surface is rough or dark-coloured, more light is absorbed, and less is reflected. This absorption can lead to heat generation in some materials.
- Reflection- A highly polished or light-coloured surface reflects more light, leading to the formation of images. The proportion of reflected light dictates the clarity and nature of the image formed.
Transmission of Light
- Transmission in Reflection- Apart from absorption and reflection, transmission is another behaviour exhibited by light when it encounters a surface.
- Through Transparent Materials- In materials like glass or clear plastic, light is transmitted, allowing it to pass through with minimal absorption or reflection.
- Role in Optics- The transmission of light is crucial in optics, as it allows for the creation of lenses, windows, and other devices that rely on allowing light to pass through them.
Formation of Images
Image Formation- One of the most observable effects of reflection is the formation of images.
- When light rays from an object strike a mirror, they are reflected back, and an image is formed.
- This image can either be a real image (formed by the actual convergence of light rays) or a virtual image (formed by the apparent convergence of diverging light rays).
Also Check – NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 -Light
Laws of Reflection

Incident Ray
Definition- The incident ray is the beam of light that approaches and strikes a reflecting surface.
Characteristics-
- It originates from a light source and travels towards the reflecting surface.
- The point where this ray hits the surface is known as the point of incidence.
Reflected Ray
Definition- The reflected ray is the beam of light that bounces off the reflecting surface.
- After striking the surface, the light ray is reflected away.
- The path of the reflected ray depends on the nature of the surface (smooth, rough) and the angle of incidence.
Definition- The normal is an imaginary line drawn perpendicular to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence.
Role in Reflection-
- It is a reference line used to measure the angles of incidence and reflection.
- The normal is crucial in determining how light is reflected off a surface.
Angle of Incidence and Reflection
- It is the angle between the incident ray and the normal.
- Measured from the normal to the direction of the incoming ray.
- This is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal.
- Measured from the normal to the direction of the outgoing ray.
- States that the angle of incidence (∠i) is always equal to the angle of reflection (∠r) (∠i = ∠r).
- This law applies irrespective of the angle at which light hits the surface.
Additional Details
- Same Plane Principle- The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane. This means they are all in a flat, two-dimensional surface extended in space.
- Surface Texture- The laws of reflection apply to both smooth and rough surfaces, but the quality of the reflected ray differs. Smooth surfaces like mirrors produce clear and well-defined reflections, whereas rough surfaces scatter the light in multiple directions.
What is an Image?
Formation of an image.
- An image is formed when light rays after reflection from a mirror seem to originate from a certain point.
- This point could be either actual or apparent, depending on the type of image formed.
- For instance, when we look at our face in the mirror, the image appears to be situated behind the mirror, where the reflected light rays seem to come from.
Types of Images
Real image-.

- Formed by the actual convergence of light rays after reflection.
- Can be obtained on a screen, like the image formed on a cinema screen.
- Occurs when light rays coming from an object meet at a point after reflection from the mirror.
Also Check – Activity-Forming Images with a Concave Mirror
Virtual Image-

- Created by the apparent convergence of diverging light rays after reflection.
- Cannot be displayed on a screen, as the light rays do not actually pass through or get received on the screen.
- An example is the image formed by a plane mirror, where light rays appear to meet after reflection.
Plane Mirrors and Image Formation

The image formed by a plane mirror has specific characteristics-
- It is always a virtual image, meaning it cannot be projected onto a screen.
- The image appears erect and is of the same size as the object.
- It is located at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
- An observer can only see a reflection in a plane mirror if within its range of visibility. To view one’s entire image, the mirror must be at least half the height of the observer.
Lateral Inversion
- Lateral inversion is a phenomenon observed in plane mirrors where the right side of an object appears as the left side in its image, and vice versa.
- Recognizing lateral inversion is essential in understanding how images are formed in plane mirrors and why they appear reversed. This knowledge is crucial in areas like design, signage, and even emergency services.
Common Examples and Applications

- Text on Ambulances: A practical application of lateral inversion is seen in how the word “AMBULANCE” is written in reverse. When viewed in a rearview mirror, the inverted text appears correctly, enabling drivers to recognize the emergency vehicle and respond accordingly.
Also Check – Activity- Observing Lateral Inversion in a Plane Mirror
Practical Demonstration with Right or Left Hand Experiment

- Right Hand Lifted: If you lift your right hand, your image in the mirror appears to lift its left hand.
- Left Hand Lifted: Conversely, if you lift your left hand, the image seems to lift its right hand.
- Observation: This experiment shows that while the top and bottom of the candle (or any object) remain the same in the image (erect image), the sides are reversed. This side inversion is a clear demonstration of lateral inversion.
Spherical Mirrors
Spherical mirrors, also known as curved mirrors, are mirrors with the shape of a piece cut out of a spherical surface. They are classified into two types- concave and convex mirrors.
Concave Mirrors
Characteristics of image.

- Concave mirrors can form real, inverted, and magnified images.
- When the object is placed very close to the mirror, the image formed is erect and virtual, instead of real and inverted.
- The nature of the image (real or virtual, erect or inverted, magnified or diminished) depends on the distance of the object from the mirror.
Practical Uses
- Medical Applications- Used by doctors and dentists to get enlarged images of ears, eyes, teeth, etc., for better examination.
- Optical Devices- Employed in devices like telescopes for their ability to magnify distant objects.
- Everyday Objects- Shaving mirrors and satellite dishes use concave mirrors for their reflective properties.
- Automotive and Lighting- Used in headlights of vehicles and torches to focus light into a strong, straight beam.
Convex Mirrors

- Convex mirrors form images that are always virtual, erect, and diminished (smaller than the object).
- These characteristics hold true regardless of the distance of the object from the mirror.
- The image appears to be located behind the mirror, and while it’s smaller than the object, it provides a wider field of view.
- Vehicle Mirrors- Widely used in vehicles as rear view and side view mirrors for their ability to provide a broad view, aiding in driving safety.
- Security and Surveillance- Large convex mirrors are used in shops, road corners, and near ATMs for security purposes, allowing a wider area to be monitored.
- Architectural Design- Employed in architectural designs for creating visual effects and enhancing the perception of space.
Dispersion of Light
Composition of white light.
- Nature of White Light- Although sunlight or white light appears colourless, it is composed of seven different colours. These colours are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red.
- Observation- This composition becomes evident when white light is passed through certain objects like a triangular prism or when it reflects off surfaces like a compact disc (CD), displaying all seven colours.
Dispersion Through a Prism

Formation of Spectrum
- Discovery by Newton- In 1665 , Sir Isaac Newton discovered that white light is a mixture of seven different colours. He demonstrated this by passing a beam of white light through a glass prism.
- Spectrum Formation- When white light passes through a prism, it splits into its constituent colours, forming a band known as a spectrum. The spectrum displays the colours red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet in order.
- Explanation- This splitting occurs because different colours of light bend by different amounts when they pass through the prism. Violet light bends the most, while red light bends the least.
Natural Phenomena – Rainbows

- Formation of Rainbows- Rainbows are a natural manifestation of light dispersion. They occur when sunlight is dispersed by tiny raindrops suspended in the atmosphere.
- Appearance- In a rainbow, the colours appear in an arc with red on the outer part and violet on the inner part, mirroring the order seen in the spectrum.
- Principle- The formation of rainbows involves both refraction (bending of light) and reflection (bouncing of light) within the raindrops, resulting in the colourful arc seen in the sky.
Also Check – Refraction of Light- A Comprehensive Guide for Students
Types of Reflection
Reflection of light can vary based on the surface characteristics of the reflecting object. There are mainly two types of reflection- diffused (or irregular) reflection and regular reflection.

Diffused (Irregular) Reflection
- Occurrence- This type of reflection occurs with irregular or rough surfaces.
- Light rays falling on such a surface are reflected back in various directions irregularly.
- There is no uniformity or order in the direction of the reflected rays.
- As a result, the image formed is usually not clear or distinct.
- Examples- Surfaces like walls, wooden objects, or unpolished metals exhibit diffused reflection.
Regular Reflection
- Occurrence- Regular reflection takes place on smooth and shiny surfaces.
- Light rays that fall on these surfaces are reflected back uniformly in a specific direction.
- The reflected rays are parallel to each other.
- This leads to the formation of clear and well-defined images.
- Examples- Mirrors, polished metals, and still water surfaces are common examples of surfaces exhibiting regular reflection.
Also Check – Laws of Refraction- A High School Student’s Comprehensive Guide
Differences between Diffused (Irregular) Reflection and Regular Reflection
- Image Formation- I n regular reflection, due to the orderly reflection of rays, clear images are formed. In diffused reflection, the scattered rays do not form a clear image.
- Surface Texture- Regular reflection is characteristic of smooth surfaces, whereas diffused reflection is more common with rough, textured surfaces.
- Applications- Regular reflection is utilised in mirrors for clear image formation, while diffused reflection is often experienced in everyday objects and surfaces around us.
Applications of Spherical Mirrors and Lenses in Everyday Life and Technology
Spherical mirrors in daily life.
- Satellite Dishes- Used to gather signals and reflect them to a specific point, concave mirrors are essential in satellite dishes for signal reception.
- Medical and Dental Uses- Doctors and dentists use concave mirrors to get enlarged images of ears, eyes, teeth, etc., for better examination and treatment.
- Personal Care- Shaving mirrors often use concave mirrors because they provide an enlarged view, making it easier to see details of the face.
- Automotive and Lighting- Headlights of cars and torches often contain concave mirrors to focus and direct light into a strong, straight beam, enhancing visibility.
- Vehicle Mirrors- Convex mirrors are used in rearview mirrors of vehicles because they provide a wider field of view, which is crucial for driving safety.
- Security and Surveillance- In places like ATMs, convex mirrors are installed to allow users to detect if anyone is watching from behind, enhancing security.
Uses of Lenses in Various Devices
Convex lenses (converging lenses).
Convex lenses are curved outward, thicker in the centre, and narrower at the edges.
Applications
- Magnifying Glasses- Utilised for enlarging the appearance of objects, making them essential in magnifying glasses.
- Optical Instruments- Used in cameras, microscopes, telescopes, and binoculars for their ability to focus light and create clear images of distant or small objects.
Also Check – Convex Lenses- Principles, Applications, and Insights
Concave Lenses (Diverging Lenses)
Concave lenses are curved inwards, with wider edges and a thinner centre.
- Peepholes- Employed in peepholes of doors, especially in hotels, to provide a wide view of the outside while maintaining privacy.
- Corrective Eyewear- Used in spectacles for correcting certain types of vision problems, like nearsightedness, by diverging light rays before they enter the eye.
Also Check – Difference Between a Convex and Concave Lens
Additional Concepts
Visibility range in plane mirrors.
- Definition- The visibility range refers to the area within which an observer can see a reflection in a plane mirror.
- Key Aspect- For a person to see their entire image in a plane mirror, the mirror must be at least half the height of the observer. This is because the image in a plane mirror is always of the same size as the object and appears to be at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
- Implication- This concept is crucial in designing mirrors for various purposes, ensuring that they are appropriately sized for the intended use, like in dressing rooms or bathrooms
Also Check NCERT Exemplar Solutions- Class 7 Science- Chapter 15- Light
Also Check Chapter 15- Light Class 7 science- Very Short Question and Answers
Also Check Chapter 15- Light Class 7 science- Question and Answers
Also Check Chapter 15- Light Class 7 science- Question and Answer (True or False)
Also Check Chapter 15- Light Class 7 science- Question and Answer (Fill in the Blanks)
Also Check NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 -Light
Also Check Class 7 Science -Chapter 15- Light- Definition and Explanation of Important Keywords
Also Check Chapter 11- A Detailed Guide to the Light Activities for Class 7 Students
Also Check – Rapid Revision – Class 7 Science -Chapter 15- Light- Complete Notes
Related Posts
Chapter 11 – light – 5 worksheets with answer key.
December 26, 2023 January 12, 2024
NCERT Exemplar Solutions- Class 7 Science- Chapter 15- Light
December 5, 2023 December 13, 2023
Chapter 15- Light Class 7 science- Very Short Question and Answers
December 4, 2023 December 13, 2023
About Jaishree Gorane
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Light Assignment Worksheet for Class 7 PDF with Answers
In Class 7 Science there is a chapter “Light Assignment”, it is a crucial lesson for the students as they get to know all the basic topics of Light Assignment. Since it is an important lesson, students should take Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7 to better develop an understanding of the concepts explained.
It is very important for Class 7 students to practise questions of the chapter Light Assignment because it will help them create their own exam strategy to score well in the upcoming final examination.
In addition to that, Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7 has quite interactive and creative tasks which boosts student’s creativity level.
Light Assignment Worksheet With Solutions
The questions in the chapter Light Assignment worksheet for Class 7 are provided with solutions. Through these solutions, students can easily solve all their doubts. By clearing the doubts of Light Assignment, students can build a strong foundation. Accordingly students can also score good marks in questions related to the chapter Light Assignment. The subject matter experts at Selfstudys has prepared Light Assignment Worksheet With Solutions in a way that helps students answer all types of questions regardless of its difficulty.
Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7 PDF
Class 7 students can easily download the Portable Document Format (PDF) of Light Assignment worksheet with the help of Selfstudys website. This can help Class 7 students to understand all the topics and concepts of the chapter Light Assignment which will help students increase their self-confidence level. A perfect level of self- confidence can easily decrease students' level of stress to prepare for the chapter Light Assignment.

How to Download Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7?
To look through the questions included in Light Assignment worksheet Class 7, students can follow the given steps. These steps are the easiest one that one can follow to download Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7.
- Open the Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards the CBSE which can be seen in the navigation bar.
- A drop down menu will appear, select KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheet.
- A new page will appear, Class 7 from the list of classes.
- Click Science from the list of subjects.
- Again a new page will appear, now select Light Assignment Worksheet from the list of chapters.
Features of Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7
Before solving questions from Light Assignment worksheet Class 7, students should understand what makes Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7 PDF special. Features of the worksheet are discussed below:
- All Concepts are Covered: In Light Assignment worksheet Class 7, all concepts and topics are covered in an elaborate manner in the questions format. Through this elaboration, students can understand all the topics of the chapter Earth in a better way.
- Explained in an Easy Language: Answers of Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7 is explained in an easy language which helps students easily understand the process of answering questions.
- Varieties of Questions are Included: In the Class 7 Light Assignment worksheet, varieties of questions are included. Through this students can solve all kinds of questions of the chapter Light Assignment.
- Eye Catching Format: Light Assignment Worksheet of Class 7 is considered to be an eye catching one. This eye-catching format can attract many students to solve the questions of the chapter Light Assignment.
- Solutions are Provided: For all the questions in the worksheet of Class 7 Light Assignment, solutions are provided. Through the solutions, Class 7 students will be able to solve challenging questions which will help them develop a critical thinking capability.
- According to the Class 7 Syllabus: The questions in Class 7 Science Light Assignment Worksheet are as per the Class 7 Syllabus and prescribed NCERT books. With the help of this, kids will be able to make their foundational understanding stronger.
How to Know If You're Ready for Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7?
First of all Class 7 students need to complete the chapter Light Assignment from the main Science book. After covering all the topics, definitions and concepts from the chapter, students are totally ready to solve the questions from Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7. Solving the questions from the Class 7 worksheet can help students to increase their conceptual understanding of Light Assignment.
What Is Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7 and How to Use It?
Light Assignment worksheet Class 7 is mainly given to students to practise a variety of questions. After practising questions from Light Assignment worksheet, students can also look through the answers. Answers for all questions can help students to improve their practising skills. These skills can help Class 7 students to increase their level of understanding.
Parents are advised to tell their Class 7rd kids to begin solving Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7 the moment they finish their study of the chapter. Doing this, will help students brush up their all learning as well as be completed for upcoming annual exams or tests.
Advantages of Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7
Solving questions from Light Assignment worksheet Class 7, students can be benefited a lot. Those important advantages are:
- Boosts Confidence Level: To solve questions from the Class 7 Light Assignment worksheet can help students to boost their confidence. A perfect level of confidence can help students to improve the study process.
- Assist the Preparation Process: Solving questions from the Class 7 Light Assignment worksheet can help students in preparing for the chapter.
- Helps in Self Evaluation: Through Light Assignment worksheet, students can easily evaluate themselves. According to the self evaluation process, students can easily improve their preparation.
- Builds a Strong Foundation: It is important for all students to solve questions from the chapter Light Assignment. Regular solving questions from the worksheet can help students to build a strong foundation for the chapter Light Assignment.
- Enhances the Learning Process: Constant solving of questions from Light Assignment Worksheet can enhance a student's learning process so that students can understand all topics easily.
- Quick Revision: By solving questions from the Class 7 Light Assignment worksheet, students can easily revise all the topics and concepts included in the chapter.
Why Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7 Is Right for You?
It is a must for students to exercise questions from Light Assignment worksheet Class 7 as perfectly right for them. With the help of Light Assignment worksheet Class 7 questions, students can increase their capability of solving questions in a different and creative manner.
Tips to Understand All Questions of Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7 in a Better Way:
Students should understand all questions of Light Assignment worksheet Class 7 in a better way. Better understanding of questions can help students to score good marks in questions which are related to the chapter Light Assignment. Those important tips are:
- Finish Off The Chapter: First and foremost tip is to finish off the chapter Light Assignment. Students need to complete each and every topic included in the lesson.
- Practise Questions: After completing the chapter Light Assignment, students need to practise questions from the Class 7 worksheet. Routine practice of questions can help students in identifying their strengths and weaknesses.
- Note Down the Mistakes: While practising questions, it is very important that students note down their mistakes. Noting down the mistakes is very important as accordingly students can improve their preparation strategies.
- Correction of Mistakes: After noting down the mistakes, it is a must to correct all the mistakes made. Correction of mistakes can help students to solve worksheet questions in a better way.
- Maintain a Positive Attitude: While solving questions from the Class 7 Light Assignment worksheet, students need to maintain a positive attitude. A positive attitude can help students to remove stress and anxiety while preparing for the chapter Light Assignment.
- Remain Focused: To understand questions of Light Assignment worksheet, students need to remain focused while preparing for it.
Why Should Students Start Solving Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7 From the PDF?
Light Assignment Class 7 Worksheet is provided in the PDF so that students don’t need to search for them here and there. By solving the questions from Light Assignment worksheet Class 7, students can understand the chapter in a fine way. Routine solving of questions from the Class 7 Science Worksheet can help students increase their comprehension skills. Comprehension skills will help in performing outstanding in the final examination.
What are Included in Light Assignment Worksheet Class 7?
In Light Assignment worksheet Class 7, questions from the chapter are included. After solving questions of the chapter Light Assignment, students can also go through the answers included in the worksheet. Answers to these questions of Light Assignment are explained in a detailed manner. As it can also help teachers to make students understand in a better and elaborate way. Through this students can easily identify their skills and flaws for the Science chapter Light Assignment.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7
- Class 7 Science
- Chapter 15 Light
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light are important for students to understand the concepts involved in Light and its phenomenon. This NCERT exemplar has answers to different kinds of questions, including fill in the blanks, matching the following questions, multiple-choice questions, and short and long answer questions based on topics, such as light paths, prisms and dispersion of light and uses of different mirrors.
NCERT Exemplar will help you gain in-depth knowledge of the concepts involved in Science and Maths subjects. These exemplar solutions are prepared by experienced teachers, which makes them the most reliable study material.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science given here has answers and explanations to 8 multiple-choice questions, 3 very short answer questions, 10 short answer questions and 3 long answer questions.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 – Light

Importance of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light covers questions on nature and different phenomena of light, image formation by plane mirrors, spherical mirrors, and their image formation, and questions on experiments associated with the phenomena of light.
Topics Covered in NCERT Exemplar solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light
15.1 – Light Travels Along a Straight Line
Ex 15.2 – Reflection of Light
Ex 15.3 – Right or Left!
15.4 – Playing with Spherical Mirrors
15.5 – Images Formed by Lenses
15.6 – Sunlight – White or Coloured?
Access Answers to NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 – Light
Multiple-choice questions.
1. Boojho and Paheli were given one mirror each by their teacher. Boojho found his image to be erect and of the same size, whereas Paheli found her image erect and smaller in size. This means that the mirrors of Boojho and Paheli are, respectively
(a) plane mirror and concave mirror.
(b) concave mirror and convex mirror.
(c) plane mirror and convex mirror.
(d) convex mirror and plane mirror.
The answer is (c) plane mirror and convex mirror.
Explanation:
The plane mirror always forms an image of the same size and erected image. Convex mirror forms erected and smaller image.
2. Which of the following can be used to form a real image?
(a) Concave mirror only.
(b) Plane mirror only.
(c) Convex mirror only.
(d) Both concave and convex mirrors
Soln: (a) concave mirror only
A concave mirror alone can produce a real image. Plane mirror & convex mirror form a virtual image of an object at all times.
3. If an object is placed at a distance of 0.5 m in front of a plane mirror, the distance between the object and the image formed by the mirror will be
The answer is (b) 1 m
The image formed by a plane mirror is at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. Therefore, the distance between object and image is given by the distance between object and mirror + distance between mirror and image = 0.5 m+ 0.5 m = 1 m
4. You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object, you can use either
(a) concave mirror or convex mirror.
(b) concave mirror or convex lens.
(c) concave mirror or concave lens.
(d) concave lens or convex lens.
Concave mirror and convex lens form enlarged images whereas convex mirror and concave lens form diminished images.
5. A rainbow can be seen in the sky
(a) when the sun is in front of you.
(b) when the sun is behind you.
(c) when the sun is overhead.
(d) only at the time of sunrise.
The answer is (b) when the sun is behind you.
Rainbow is formed after rain and when the sunlight is low. A rainbow appears when is your back is towards the sun.
6. An erect and enlarged image can be formed by
(a) only a convex mirror.
(b) only a concave mirror.
(c) only a plane mirror.
(d) both convex and concave mirrors
The answer is (b) only a concave mirror.
The concave mirror always formed a virtual image which is erected and enlarged in size whereas convex mirror forms diminished and erected image.
7. You are provided with a convex mirror, a concave mirror, a convex lens and a concave lens. You can get an inverted image from
(a) both the concave lens and convex lens.
(b) both concave mirror and convex mirror.
(c) both concave mirror and convex lens.
(d) both convex mirror and concave lens.
The answer is (c) both concave mirror and convex lens.
Concave mirror and convex lens can only form a real and inverted image of an object. As a convex mirror and concave lens always form a virtual and erect image of an object.
8. An image formed by a lens is erect. Such an image could be formed by a
(a) convex lens provided the image is smaller than the object.
(b) concave lens provided the image is smaller than the object.
(c) concave lens provided the image is larger than the object.
(d) concave lens provided the image is of the same size.
The answer is (b) concave lens provided the image is smaller than the object.
Virtual, erect and diminished image of an object is formed by a concave lens. Convex lens forms magnified, erect and virtual image.
Very Short Answer Questions
9. The image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size for an object kept at different positions in front of it. Identify the nature of the lens.
The answer is Concave lens
10. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The inner surface of a steel spoon acts as a ___________ mirror. (b) The outer surface of a flat steel plate acts as a ___________ mirror. (c) The outer shining surface of a round bottom steel bowl acts as a __________ mirror. (d) The inner surface of the reflector of a torch acts as a __________ mirror.
(a) The inner surface of a steel spoon acts as a concave mirror. (b) The outer surface of a flat steel plate acts as a plane mirror. (c) The outer shining surface of a round bottom steel bowl acts as a convex mirror. (d) The inner surface of the reflector of a torch acts as a concave mirror.
11. State whether the following statements are True or False.
(a) A concave lens can be used to produce an enlarged and erect image.
(b) A convex lens always produces a real image.
(c) The sides of an object and its image formed by a concave mirror are always interchanged.
(d) An object can be seen only if it emits light.
- False- A concave lens can be used to produce a diminished and erect image.
- False- A convex lens always produces a virtual image
- False- An object can be seen if it reflects light falling on it.
Short Answer Questions
12. What type of mirror is used as a side mirror in a scooter? Why is this type of mirror chosen?
Convex mirrors are used as a side mirror in a scooter because in Convex mirrors image formed is spread over a large area. This will help the drivers to see the large area behind in the traffic.
13. Observe the figures given in Figure 15.1 carefully.

The given figures show the path of light through lenses of two different types, represented by rectangular boxes A and B. What is the nature of lenses A and B?
- Convex lens
- Concave lens
14. Boojho made light from a laser torch to fall on a prism. Will he be able to observe a band of seven colours? Explain with a reason.
No, Boojho cannot observe a band of colours because laser light gives torch of only one colour.
15. State the correct sequence (1-7) of colours in the spectrum formed by the prisms A and B, shown in Figure 15.2.

16. The side mirror of a scooter got broken. The mechanic replaced it with a plane mirror. Mention any inconvenience that the driver of the scooter will face while using it?
A driver cannot see the traffic spread over the large area behind him.
17. The concave reflecting surface of a torch got rusted. What effect would this have on the beam of light from the torch?
If the concave reflecting surface of a torch got rusted, a beam of light will be diffused with lower intensity.
18. An erect and enlarged image of an object is formed on a screen. Explain how this could be possible.
An erect and enlarged image of an object is formed on a screen if the object is placed upside down between F and 2F of the lens.
19. Two different types of lenses are placed on a sheet of newspaper. How will you identify them without touching them?
The lens is a convex lens if the letters appear magnified and the lens is concave if the image appears shortened.
20. A shopkeeper wanted to fix a mirror which would give a maximum view of his shop. What type of mirror should he use? Give reason.
The shopkeeper fixes convex mirror because forms images of object spread from large areas.
21. The distance between an object and a convex lens is changing. It is noticed that the size of the image formed on a screen is decreasing. Is the object moving in a direction towards the lens or away from it?
An object is moving away from the lens.
Long Answer Questions
22. Suppose we wish to obtain the real image of a distant tree. Explain two possible ways in which we can do it.
Two possible ways in which the real image of a distant tree can be obtained are given below :
- By using a concave mirror and a screen- By using a concave mirror, a real image is formed if the distance between the mirror and the object is beyond the focus.
- By using a convex lens and a screen- In a convex lens, when the object is far away from the lens, the image is very close to the lens forming a real and inverted image.
23. It was observed that when the distance between an object and a lens decreases, the size of the image increases. What is the nature of this lens? If you keep on decreasing the distance between the object and the lens, will you still able to obtain the image on the screen? Explain.
It is a convex lens.
No, when the object is placed close to a convex lens then the image formed is virtual, which cannot be obtained on the screen.
24. You are given three mirrors of different types. How will you identify each one of them?
We can identify the mirrors by forming images of an object which are given as below:
i) Plane mirror, in the case of a plane mirror, the image will be virtual, erect and of the same size as that of an object.
ii) Concave mirror, in the case of a concave mirror, an image may be real or virtual, inverted or erect and magnified or diminished depending upon the position of the object.
iii) Convex mirror, in the case of a convex mirror, an image formed will always be virtual, erect and diminished in spite of the position of the object.
In order to make your learning easier, BYJU’S brings videos, animations, info-graphics, NCERT Solutions, sample papers, previous years’ question papers, sample papers , and notes. To get free access to all the study material we provide, log onto BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S – The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light
The image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size for an object kept at different positions in front of it. identify the nature of the lens..
The answer is concave lens.
What type of mirror is used as a side mirror in a scooter? Why is this type of mirror chosen?
Convex mirrors are used as side mirrors in a scooter because, in convex mirrors, the image formed is spread over a large area. This will help the drivers to see the large area behind in the traffic.
Boojho made light from a laser torch to fall on a prism. Will he be able to observe a band of seven colours? Explain with a reason.
No, Boojho cannot observe a band of colours because laser light gives a torch of only one colour.
The side mirror of a scooter got broken. The mechanic replaced it with a plane mirror. Mention any inconvenience that the driver of the scooter will face while using it.
The driver cannot see the traffic spread over the large area behind him.
The concave reflecting surface of a torch got rusted. What effect would this have on the beam of light from the torch?
If the concave reflecting surface of a torch got rusted, a beam of light would be diffused with lower intensity.
An erect and enlarged image of an object is formed on a screen. Explain how this could be possible.
Two different types of lenses are placed on a sheet of newspaper. how will you identify them without touching them.
The lens is a convex lens if the letters appear magnified, and the lens is concave if the image appears shortened.
A shopkeeper wants to fix a mirror which will give a maximum view of his shop. What type of mirror should he use? Give a reason.
The shopkeeper fixes a convex mirror because it forms images of objects spread from large areas.
The distance between an object and a convex lens is changing. It is noticed that the size of the image formed on a screen is decreasing. Is the object moving in a direction towards the lens or away from it?
The object is moving away from the lens.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Bihar Board
SRM University
Cg 10, 12th result 2024.
- Assam Board Result 2024
- GSEB Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result 2024
- CG Board Result 2024
- Kerala Board Result 2024
- TN Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
Chapter 15: Light (PDF) - Class 7 Science NCERT Book
Chapter 15 - light (pdf) of class 7 science ncert book is available here for download in pdf format. download now and prepare for cbse class 7 exam..

Chapter 15 Light of Class 7 Science NCERT Book (PDF) is available here for download in PDF format. Chapter 15 of Class 7 Science NCERT Books is one of the important chapters and also one of the interesting chapters. Students are advised to learn this chapter and prepare for Class 7 Science exams.
Download Chapter 15 - Light of Class 7 Science NCERT Book (PDF)
A snapshot from the chapter:

Important concepts of the chapter:
⇒ Concave lens
⇒ Concave mirror
⇒ Convex lens
⇒ Convex mirror
⇒ Erect image
⇒ Magnified image
⇒ Magnifying glass
⇒ Prism
⇒ Rainbow
⇒ Real image
⇒ Rear view mirror
⇒ Side mirror
⇒ Spherical mirror
⇒ Virtual image
Important points of the chapter:
⇒ Light travels along straight lines.
⇒ Any polished or a shining surface acts as a mirror.
⇒ An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a real image.
⇒ An image which cannot be obtained on a screen is called a virtual image.
⇒ The image formed by a plane mirror is erect. It is virtual and is of the same size as the object. The image is at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
⇒ In an image formed by a mirror, the left side of the object is seen on the right side in the image, and right side of the object appears to be on the left side in the image.
⇒ A concave mirror can form a real and inverted image. When the object is placed very close to the mirror, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified.
⇒ Image formed by a convex mirror is erect, virtual and smaller in size than the object.
⇒ A convex lens can form real and inverted image. When the object is placed very close to the lens, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified. When used to see objects magnified, the convex lens is called a magnifying glass.
⇒ A concave lens always forms erect, virtual and smaller image than the object.
⇒ White light is composed of seven colours.
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- keralaresults.nic.in Result 2024
- cgbse.nic.in Result 2024
- result.kite.kerala.gov.in Result 2024
- CGBSE 10th, 12th Result 2024
- Kerala Plus Two Result 2024
- DHSE Kerala Plus Two Result 2024
- CGBSE 10th Result 2024
- CGBSE 12th Result 2024
- NDA Result 2024
- NCERT Books
Latest Education News
[Today] IPL 2024 Points Table: Team Rankings and Net Run Rate
Purple Cap in IPL 2024: Top Players List with Most Wickets in TATA IPL
Who Won Yesterday IPL Match: RCB vs PBKS, Match 58, Check All Details and Latest Points Table
SSLC Result 2024 TN Live Updates: Tamil Nadu 10th Results Link Online at tnresults.nic.in via Registration Number and Date of Birth
Kerala 12th Result 2024: Check SAY Improvement and Revaluation Process, Fees and Other Details Here
10th Public Exam Result 2024 Tamil Nadu Releasing on May 10, Check TN SSLC Latest News and Updates Here
[LINK ACTIVE] Kerala Plus Two Result 2024 School-Wise, Link Declared: Check DHSE Results, Marks with School Code at keralaresults.nic.in
Today’s School Assembly Headlines (10 May): Stock Market Downfall, Air India Express Flight Shortage, PM Modi and Rahul Gandhi debate face-to-face, Ukraine war, Open AI and Other News in English
Orange Cap in IPL 2024: Top Players List with Most Runs in TATA IPL
Most Sixes In IPL 2024: आईपीएल में चौकों-छक्कों की रेस में कौन सबसे आगे? देखें पूरी लिस्ट
Australia's T20 World Cup Squad: वर्ल्ड कप 2024 में किसे मिला मौका कौन हुआ बाहर, यहां देखें पूरी लिस्ट
[चेक] Most Runs In IPL 2024: दिलचस्प हो गयी है Orange Cap की रेस, Virat टॉप पर
[जिलेवार] CGBSE 12th Toppers 2024 OUT: महक रही अव्वल, यहां देखें 12वीं के मेधावी छात्रों के नाम और उनके अंक
TN SSLC Result 2024 Official Date & Time Announced: Check Tamil Nadu Class 10th Notice and Link at dge.tn.gov.in
Accept The Challenge To Find The SNOWMAN Hidden In This IQ Test Puzzle. 11 Seconds Left!
(डायरेक्ट रिजल्ट) CG Board 10th, 12th Result 2024 Link, Roll Number: नतीजे जारी, एक क्लिक में देखें अपना परिणाम और मार्कशीट
SSC GD Result 2024 Live: Constable Results on ssc.gov.in; Check Expected Cut Off, Merit List Date, Marking Scheme
NCERT Book for Class 9 Maths PDF (2024-25)
TN Board Result 2024 விளைவாக: Tamil Nadu 10th Result at tnresults.nic.in and dge.tn.gov.in
TN 10th Result 2024 விளைவாக: Tamil Nadu SSLC Result Online at tnresults.nic.in and dge.tn.gov.in
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Light
- 7th June 2023
NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Light is provided here to help students in understanding the topic thoroughly. All these solutions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation. Class 7 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 11 includes all the textbook exercise questions and answers. These solutions will help students complete their assignments & homework.
Class 7 Science Light Questions and Answers
Exercise Questions
Question 1: Fill in the blanks:
(a) An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called ___________ . (b) Image formed by a convex is __________ always virtual and smaller in size. (c) An image formed by a __________ mirror is always of the same size as that of the object. (d) An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a __________ image. (e) An image formed by a concave __________ cannot be obtained on a screen.
Answer: (a) virtual image (b) mirror (c) plane (d) real (e) lens
Question 2: Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(a) We can obtain an enlarged and erect image by a convex mirror. (T/F) (b) A concave lens always form a virtual image. (T/F) (c) We can obtain a real, enlarged and inverted image by a concave mirror. (T/F) (d) A real image cannot be obtained on a screen. (T/F) (e) A concave mirror always form a real image. (T/F)
Answer. (a) False (b) True (c) True (d) False (e) False
Question 3: Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II
Question 4 . State the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
Answer: Characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror: (i) The image formed is virtual (ii) The image is laterally inverted. (iii) It is of the same size as the object. (iv) The image is situated at the same distance from the mirror as the object. (v) The image is erected.
Question 5. Find out the letters of English alphabet or any other language known to you in which the image formed in a plane mirror appears exactly like the letter itself. Discuss your findings.
Answer: If the letters of English alphabet A, H, I, M, O, T, U, V, W, X, Y are kept in front of a plane mirror, then they would form images which exactly look like the original letters of the alphabet. These letters are vertically symmetric. For example, if we divide letters A and U in the middle, then we would find that the right halves are equivalent to the left halves of the letters. Hence, even if the image interchanges sidewise, it will appear same as the letter
Question 6. What is a virtual image? Give one situation where a virtual image is formed.
Answer: The image which cannot be taken on a screen is called virtual image. When some object is placed very close to the concave mirror we don’t get any image on the white screen placed behind the mirror. Such image is called virtual image.
Question 7. State two differences between a convex and a concave lens.
Question 8. Give one use each of a concave and a convex mirror.
Answer: Concave mirrors can form enlarged image of the object. Therefore, they are used by the dentist to see the enlarged image of the patient’s teeth.
Convex mirror forms diminished and upright image of the object. It is used as a side view mirror of the car because it enables the driver to view objects spread over a large area behind him/her.
Question 9. Which type of mirror can form a real image?
Answer: Concave mirror can form a real image.
Question 10. Which type of lens forms always a virtual image?
Answer: Concave lens always forms a virtual image.
Choose the correct option in Questions 11-13:
Question 11. A virtual image larger than the object can be produced by a
(i) concave lens (ii) concave mirror (iii) convex mirror (iv) plane mirror
Answer: (ii) concave mirror
Question 12. David is observing his image in a plane mirror. Die distance between the mirror and his image is 4 m. If he moves 1 m towards the mirror, then the distance between David and his image will be
(i) 3 m (ii) 5 m (iii) 6 m (iv) 8 m
Answer: (iii) 6 m
In the case of a plane mirror, the distance between the object and the mirror (d 1 ) is same as the distance between the image and the mirror (d 2 ).
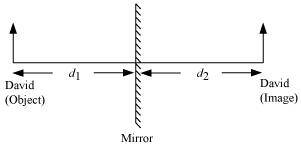
Given, Distance between the mirror and David’s image, d 2 = 4 m Therefore, d 1 = d 2 = 4 m If David moves 1 m towards the mirror, then d 1 = 4 − 1 = 3 m Again, d 1 = d 2 = 3 m Therefore, the distance between David and his image is d 1 + d 2 = 3 + 3 = 6 m.
Question 13. The rear view mirror of a car is a plane mirror. A driver is reversing his car at a speed of 2 m/s. The driver sees in his rear mew mirror the image of a truck parked behind his car. The speed at which the image of the truck appears to approach the driver will be
(i) 1 m/s (ii) 2 m/s (iii) 4 m/s (iv) 8 m/s
Answer: (ii) 4 m/s
The speed of the car is 2 m/s which means the car is approaching the truck with a speed of 2 m per second. The distance between the car and truck will decrease at a double rate. This is because the image of the truck will travel a distance twice the distance travelled by the car in equal time. Hence, the image of the truck will appear to approach the driver with the speed of 2 ×2 = 4 m/s.
Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Light provided by CBSE Path help students to clear their doubts and to obtain good marks in the exams. All the solutions provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum.
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Post Comment
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Light
- Textbook Solutions

Class 7 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter 15 Light
Download Free PDF of NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter - 15 Light solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter - 15 Light exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
You can also Download NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science to help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science(Physics) Chapter 15 - Light
Multiple choice questions.
1. Boojho and Paheli were given one mirror each by their teacher. Boojho found his image to be erect and of the same size whereas Paheli found her image erect and smaller in size. This means that the mirrors of Boojho and Paheli are, respectively
a) Plane mirror and concave mirror.
b) Concave mirror and convex mirror.
c) Plane mirror and convex mirror.
d) Convex mirror and plane mirror.
Ans: The correct answer is option (c), Plane mirror and convex mirror. Plane mirror always forms an image of equal size, an erected image and convex mirror always forms an image erect and smaller in size.
2. Which of the following can be used to form a real image?
a) Concave mirror only.
b) Plane mirror only.
c) Convex mirror only.
d) Both concave and convex mirrors.
Ans: The correct answer is option (b), plane mirror. Plane mirror always forms an erect image of equal size.
3. If an object is placed at a distance of 0.5 m in front of a plane mirror, the distance between the object and the image formed by the mirror will be
Ans: The correct answer is option (b), 1 m.
The image formed or created by a plane mirror is at equal distance behind the plane mirror as the object is in front of it. So, now
The distance of object from plane mirror = 0.5 m
Then the distance of image from plane mirror = 0.5 m
Total distance between object and plane mirror = 0.5+0.5=1m
4. You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a Concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
a) Concave mirror or convex mirror.
b) Concave mirror or convex lens.
c) Concave mirror or concave lens.
d) Concave lens or convex lens.
Ans: The correct answer is option (b), Concave mirror or convex lens. Enlarged images are formed by only a concave mirror or convex lens.
5. A rainbow can be seen in the sky
a) When the sun is in front of you.
b) When the sun is behind you.
c) When the sun is overhead.
d) Only at the time of sun rise.
Ans: The correct answer is option (b), when the sun is behind you. When the sun is behind you and the light is low, you can easily see rainbows during the rainy season.
6. An erect and enlarged image can be formed by
a) Only a convex mirror.
b) Only a concave mirror.
c) Only a plane mirror.
d) Both convex and concave mirrors.
Ans: The correct answer is option (b), only a concave mirror. Concave mirror forms a virtual, erect and enlarged image.
7. You are provided with a convex mirror, a concave mirror, a convex lens and a concave lens. You can get an inverted image from
a) Both concave lens and convex lens.
b) Both concave mirror and convex mirror.
c) Both concave mirror and convex lens.
d) Both convex mirror and concave lens.
Ans: The correct answer is option (c), both concave mirror and convex lens. Both concave mirror and convex lens can form inverted and real images of an object.
8. An image formed by a lens is erect. Such an image could be formed by a
a) Convex lens provided the image is smaller than object.
b) Concave lens provided the image is smaller than object.
c) Concave lens provided the image is larger than object.
d) Concave lens provided the image is of the same size.
Ans: The correct answer is option (b), Concave lens provided the image is smaller than object. The image of an object created by a concave lens is erect, virtual, and diminished.
Very Short Answer Questions
9. The image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size for an object kept at different positions in front of it. Identify the nature of the lens.
Ans: The lens is a “Concave lens”.
10. Fill in the blanks:
a) The inner surface of a steel spoon acts as a ___________ mirror.
Ans: Concave
b) The outer surface of a flat steel plate acts as a ___________ mirror.
c) The outer shining surface of a round bottom steel bowl acts as a __________ mirror.
Ans: Convex
d) The inner surface of the reflector of a torch acts as a __________ mirror.
11. State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) A concave lens can be used to produce an enlarged and erect image.
Ans: The given statement is false. A concave lens can only form an erect, diminished and virtual image of an object.
(b) A convex lens always produces a real image.
Ans: The given statement is false. A convex lens can form an inverted, diminished and real image of an object.
(c) The sides of an object and its image formed by a concave mirror are always interchanged.
Ans: The given statement is true.
(d) An object can be seen only if it emits light.
Ans: The given statement is false. Only if an object reflects light falling on it can it be seen.
Short Answer Questions
12. What type of mirror is used as a side mirror in a scooter? Why is this type of mirror chosen?
Ans: Convex mirrors are used as side mirrors on scooters. The convex mirror forms a diminished image of an object which is helpful for the driver to cover a wide area of view.
13. Observe the figures given as Figure 15.1 carefully
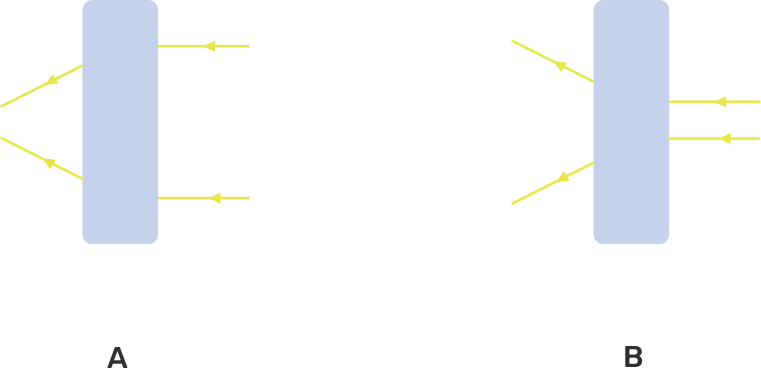
The given figures show the path of light through lenses of two different types, represented by rectangular boxes A and B. What is the nature of lenses A and B?
Ans: Lens A = Light rays are converging in the direction of point. So, this is a convex lens.
Lens B = Light rays are diverging from the direction of point. So, this is a concave lens.
14. Boojho made light from a laser torch to fall on a prism. Will he be able to observe a band of seven colours? Explain with a reason.
Ans: The laser light is made up of a particular colour. Thus, he will not be able to observe the band of all seven colours. They will only be observed, when white colour passes through the prism and dispersion takes place.
15. State the correct sequence (1-7) of colours in the spectrum formed by the prisms A and B, shown in Figure 15.2.
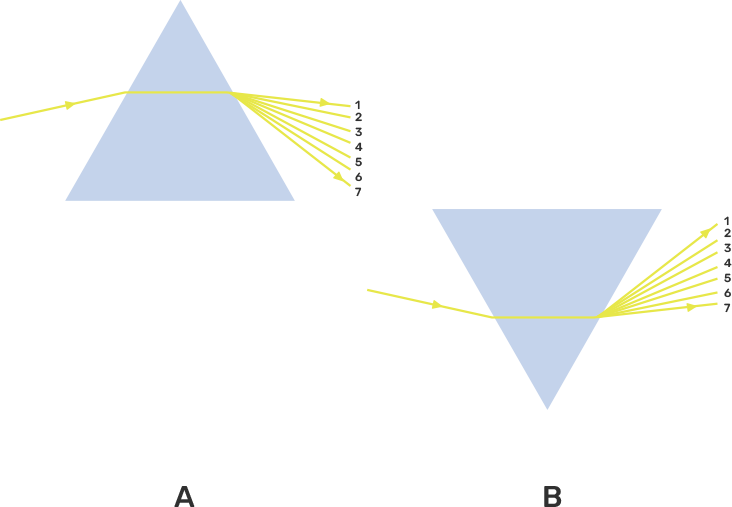
Ans: In figure A and figure B
16. The side mirror of a scooter got broken. The mechanic replaced it with a plane mirror. Mention any inconvenience that the driver of the scooter will face while using it?
Ans: A convex mirror is used as a side mirror on a scooter.
Inconveniences are
i) Less area visible on a plane mirror as compared to a convex mirror.
ii) Traffic behind the vehicle is hidden.
17. The concave reflecting surface of a torch got rusted. What effect would this have on the beam of light from the torch?
Ans: The torch will produce a dim and diffused beam with a lower intensity. Due to this, the object will not be clearly visible.
18. An erect and enlarged image of an object is formed on a screen. Explain how this could be possible.
Ans: If the object is placed upside down between F (focus) and 2F (centre of curvature) of the convex lens. An erect and enlarged image of an object is created as a result.
19. Two different types of lenses are placed on a sheet of newspaper. How will you identify them without touching?
Ans: If the letters of newspaper appear magnified, the placed lens is convex lens. If the letters of newspaper appear shortened, the placed lens is concave lens.
20. A shopkeeper wanted to fix a mirror which will give a maximum view of his shop. What type of mirror should he use? Give a reason.
Ans: A shopkeeper will fix a convex mirror. The convex mirror may create images of an object that are spread out across a broad area.
21. The distance between an object and a convex lens is changing. It is noticed that the size of the image formed on a screen is decreasing. Is the object moving in a direction towards the lens or away from it?
Ans: According to the question, the object is moving away from the lens.
In convex, the size of the image formed on screen will increase if an object is moved in the direction of that lens.
Long Answer Questions
22. Suppose we wish to obtain the real image of a distant tree. Explain two possible ways in which we can do it.
Ans: Two possible ways are
1. With the help of a “concave mirror” and screen, we can obtain the real image of a distant tree. “A concave mirror forms a real image of an object at its focus”. So, the real image of a distant tree will be formed.
2. With the help of a “convex lens” and screen, we can obtain the real image of a distant tree. “A convex lens forms a real image of an object at its focus”. So, the real image of a distant tree will be formed.
23. It was observed that when the distance between an object and a lens decreases, the size of the image increases. What is the nature of this lens? If you keep on decreasing the distance between the object and the lens, will you still able to obtain the image on the screen? Explain.
Ans: Nature of the asked lens is “Convex Lens”. When we place an object close to a convex lens, then the formed image will be Virtual. This image cannot be obtained on screen.
24. You are given three mirrors of different types. How will you identify each one of them?
Ans: By forming images of an object, you can identify all three mirrors:
i) Plane Mirror: The formed image of an object by the mirror is erect, virtual and of the same size (of that object).
ii) Concave Mirror: The formed image of an object by the mirror is inverted, virtual and diminished (according to the position of an object).
iii) Convex Mirror: The formed image of an object by the mirror is erect, virtual and diminished (according to the position of an object).
About Light - Class 7 Science Chapter 15
Light is simply energy travelling from one place to another, and it does not require any medium to travel and can travel in space, Unlike sound.
Light is a fascinating topic for young minds, which lets them think about their limits. This chapter, named Light, provides a proper explanation of various concepts on the light.

FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Light
1. What are the most important topics covered in Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light?
This chapter teaches the students about the various concepts of light and how it undergoes different changes under different conditions. The major topics from this chapter, named LIGHT, are listed down here:
The Path of Light
Definition of Reflection and laws on Reflection
Visibility Range
Different Types of mirrors - plane mirrors, spherical mirrors, concave mirrors, and convex mirrors
Lateral Inversion
Formation of the images through spherical mirrors
Various types of Lenses
Images formed via lenses
Dispersion of light via the prism
The student can prepare these topics via the NCERT exemplar solutions provided on Vedantu.
2. What are the Different Types of Spherical Mirrors and their uses?
There are only two types of spherical mirrors in existence. These two types of mirrors are -
Concave Mirrors - Spherical mirrors, which are curved inwards like a spoon are called Concave mirrors. Concave mirrors Enlarge the forming images and are commonly used by dentists, and also used as shaving mirrors.
Convex Mirrors - These spherical mirrors bulge out and make the reflected image smaller. Convex mirrors are typically used as rear view mirrors in vehicles and also as security mirrors.
3. What is the Dispersion of Light?
Splitting of the white light, such as Sunlight, into its seven components colours (VIBGYOR) of light, after passing through a transparent medium is called dispersion of light. In 1665, Newton, while conducting his experiments with a prism, found out that the visible white light is a combination of seven Lights of different colours. These seven colours are Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red (Termed as VIBGYOR). We can also mix these 7 component colours to get the form of the white light again.
4. What is the difference between Real and Virtual Images?
Real images are those images that can be obtained on a screen but it is impossible to obtain a virtual image on any screen. Virtual images appear as they are formed on the other side of mirrors. In the typical plane mirrors present in our houses, one can see that the image appears to be formed on the other side of the mirror. A real image can be projected on other surfaces or screens, one example of it will be the image formed on a cinema screen by the projector.
5. What is the difference between images formed by different kinds of Mirrors?
There are three types of mirrors, which are different types of images. The properties of images formed by different images are listed below.
Plane Mirrors: The images formed are virtual, erect, and laterally inverted. The images formed are of the same size as the objects.
Concave Mirrors: Both virtual and real can be formed by Concave mirrors, it depends on the distance at which the object is placed. If the object is very close to the mirror, then a virtual and magnified image is formed. And Vice-versa, if the object is away from the mirror.
Convex mirror: Convex mirrors always form virtual and erect images. But unlike a Plane mirror, the size of the image formed is reduced significantly.
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students
MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light with Answers
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science with Answers on a daily basis and score well in exams. Refer to the Light Class 7 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
Light Class 7 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option.
Question 1. Which one of the following shows lateral inversion? (a) Plane mirror (b) Concave mirror (c) Convex mirror (d) Convex lens
Answer: (a) Plane mirror
Question 2. Which of the following is used as a side view mirror? (a) Plane mirror (b) Concave mirror (c) Convex mirror (d) Convex lens
Answer: (c) Convex mirror
Question 3. The path of the light is (a) always a straight line (b) a curved line (c) a zig-zag line (d) depends on the medium
Answer: (a) always a straight line
Question 4. White light is composed of (a) three colours (b) seven colours (c) five colours (d) eight colours
Answer: (b) seven colours
Question 5. A virtual image (a) can be formed on the screen (b) cannot be formed on the screen (c) is formed only by the plane mirror (d) is formed only by the convex mirror
Answer: (b) cannot be formed on the screen
Question 6. The image formed by spherical mirror is virtual. The mirror will be (a) concave (b) convex (c) either concave or convex (d) none of these
Answer: (c) either concave or convex
Question 7. The coloured band of light obtained by dispersion of light is called (a) image (b) spectrum (c) convergence (d) scattering
Answer: (b) spectrum
Question 8. We can get an inverted image from (a) both concave lens and convex lens. (b) both concave mirror and convex mirror. (c) both concave mirror and convex lens. (d) both convex mirror and concave lens.
Answer: (c) both concave mirror and convex lens.
Question 9. A convex lens is (a) thick at centre (b) thin at the centre (c) thick at edges (d) hollow at the centre
Answer: (a) thick at centre
Question 10. The image that can not be obtained on a screen is called (a) real image (b) virtual image (c) diminished image (d) none of these
Answer: (b) virtual image
Question 11. A ray of light falling on a mirror is a (a) reflected ray (b) normal (c) deflection (d) incident ray
Answer: (d) incident ray
Question 12. The image of an object formed by a plane the mirror is (a) virtual (b) real (c) diminished (d) upside-down
Answer: (a) virtual
Question 13. A diverging mirror is (a) a plane mirror (b) a convex mirror (c) a concave mirror (d) a shaving mirror
Answer: (b) a convex mirror
Question 14. If the image formed is always virtual, the mirror can be (a) concave or convex (b) concave or plane (c) convex or plane (d) only convex
Answer: (c) convex or plane
Question 15. Which of the following mirrors can form a real image of an object? (a) Convex (b) Concave (c) Plane (d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer: (b) Concave
Question 16. The splitting up of white light into seven colours on passing through a glass prism is called (a) refraction (b) deflection (c) dispersion (d) scattering
Answer: (c) dispersion
Question 17. If you are standing 2 m away from a plane mirror, the distance between you and your image is (a) 2 m (b) 4 m (c) 6 m (d) 8 m
Answer: (b) 4 m
Question 18. A spherical mirror having reflecting surface curved outward is a (a) plane mirror (b) concave mirror (c) convex mirror (d) either concave or convex
Answer: (c) convex mirror
Question 19. A plane mirror produces a (a) virtual and erect image (b) virtual and inverted image (c) real and erect image (d) real and inverted image
Answer: (a) virtual and erect image
Question 20. A diverging mirror is (a) a plane mirror (b) a convex mirror (c) a concave mirror (d) none of the above
Fill in the blanks with suitable word/s.
Question 1. An image can be obtained on a screen is called a …………….
Answer: real
Question 2. An image formed by ……………. lens cannot be obtained on a screen.
Answer: concave
Question 3. light deviates the least, while ……………. light deviates the more.
Answer: Red, violet
Question 4. The outer surface of a flat steel plate acts as a ……………. mirror.
Answer: plane
Question 5. The inner surface of the reflector of a torch acts as a ……………. mirror.
Question 6. A ……………. is a piece of any transparent material bound by two curved surfaces or by one curved and one plane surface.
Answer: lens
Question 7. Convex mirrors are used as ……………. mirrors.
Answer: rear view
Question 8. The image formed by a plane mirror is …………….
Answer: virtual
Question 9. The change of sides of an object and its mirror image is called …………….
Answer: lateral inversion
Question 10. The ray of light which falls on the smooth polished surface is called ……………. ray of light.
Answer: incident
Question 11. Light travels in a …………………….. line.
Answer: straight
Question 12. There are …………………….. types of spherical mirrors.
Answer: two
Question 13. The change in the direction of light by a mirror is called …………………….. of light.
Answer: reflection
Question 14. The image formed in a plane mirror is …………………….. inverted.
Answer: laterally
Question 15. If the image formed is always virtual, the mirror can be ……………………..
Answer: convex or plane
Question 16. Convex mirror is …………………….. in the middle than at the edges whereas concave lens is …………………….. in the middle than at the edges.
Answer: thicker, thinner
Question 17. The rear view mirror/side mirror in automobiles is a …………………….. mirror.
Answer: convex
Question 18. …………………….. lens is called a converging lens.
Answer: Convex
True or False
Question 1. The image formed by a convex mirror is erect.
Answer: False
Question 2. The image formed by a concave mirror is formed on the screen.
Answer: True
Question 3. The image formed by a plane mirror is real.
Question 4. The change of sides of an object and its mirror image is called lateral inversion.
Question 5. The image formed by plane mirror is erect.
Question 6. When the reflecting surface of the spherical mirror is curved inwards, it is called concave mirror.
Question 7. A concave mirror forms a virtual and erect image.
Question 8. Any polished or shining surface acts as a mirror.
Question 9. A convex mirror always forms a real image.
Question 10. The concave mirror is converging.
Question 11. Light is a form of energy.
Answer: (c) Water
Question 12. Light travels at the same speed in all media.
Question 13. The image formed by a plane mirror is erect, virtual and laterally inverted.
Question 14. A concave lens always forms a virtual image.
Question 15. White light is composed of seven different colours.
Question 16. Image formed by a plane mirror is usually real.
Match the items given in column I suitably with those given in column II.
Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 7 Science Light MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, feel free to reach us so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.

Find your desired course
Select your favourite category and start learning..

← Chapter 14
Chapter 16 →
Chapter 15 Light
Science helpbook solutions class 7, ncert exemplar chapter 15: light.
Social Science
Notes + Important Questions
NCERT Solutions
Helpbook Solutions
Sample Papers
Assignments
Nutrition in Plants
Nutrition in Animals
Fiber to Fabric
Acids, Bases and Salts
Physical and Chemical Changes
Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
Winds Storms and Cyclones
Respiration in Organisms
Transportation in Animals and Plants
Reproduction in Plants
Motion and Time
Electric Current and Its Effects
Water A Precious Resource
Forests Our Lifeline
Wastewater Story
As Featured In
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Refunds or Cancellations
- Course Catalog
Hello there, haven’t we seen you before?
New here? Sign Up
Already have an account? Sign In
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
What marijuana reclassification means for the United States
The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration will move to reclassify marijuana as a less dangerous drug, a historic shift to generations of American drug policy that could have wide ripple effects across the country.
FILE - Marijuana plants are seen at a secured growing facility in Washington County, N.Y., May 12, 2023. The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration will move to reclassify marijuana as a less dangerous drug, a historic shift to generations of American drug policy that could have wide ripple effects across the country. (AP Photo/Hans Pennink, File)
- Copy Link copied
Budtender Rey Cruz weighs cannabis for a customer at the Marijuana Paradise on Friday, April 19, 2024, in Portland, Ore. (AP Photo/Jenny Kane)
Cloud 9 Cannabis employee Beau McQueen, right, helps a customer, Saturday, April 13, 2024, in Arlington, Wash. The shop is one of the first dispensaries to open under the Washington Liquor and Cannabis Board’s social equity program, established in efforts to remedy some of the disproportionate effects marijuana prohibition had on communities of color. (AP Photo/Lindsey Wasson)
WASHINGTON (AP) — The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration is moving toward reclassifying marijuana as a less dangerous drug. The Justice Department proposal would recognize the medical uses of cannabis , but wouldn’t legalize it for recreational use.
The proposal would move marijuana from the “Schedule I” group to the less tightly regulated “Schedule III.”
So what does that mean, and what are the implications?
WHAT HAS ACTUALLY CHANGED? WHAT HAPPENS NEXT?
Technically, nothing yet. The proposal must be reviewed by the White House Office of Management and Budget, and then undergo a public-comment period and review from an administrative judge, a potentially lengthy process.
Still, the switch is considered “paradigm-shifting, and it’s very exciting,” Vince Sliwoski, a Portland, Oregon-based cannabis and psychedelics attorney who runs well-known legal blogs on those topics, told The Associated Press when the federal Health and Human Services Department recommended the change.
“I can’t emphasize enough how big of news it is,” he said.
It came after President Joe Biden asked both HHS and the attorney general, who oversees the DEA, last year to review how marijuana was classified. Schedule I put it on par, legally, with heroin, LSD, quaaludes and ecstasy, among others.
Biden, a Democrat, supports legalizing medical marijuana for use “where appropriate, consistent with medical and scientific evidence,” White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre said Thursday. “That is why it is important for this independent review to go through.”
Cloud 9 Cannabis employee Beau McQueen, right, helps a customer, Saturday, April 13, 2024, in Arlington, Wash. (AP Photo/Lindsey Wasson)
IF MARIJUANA GETS RECLASSIFIED, WOULD IT LEGALIZE RECREATIONAL CANNABIS NATIONWIDE?
Ap audio: what marijuana reclassification means for the united states.
AP correspondent Haya Panjwani reports on a proposal for the federal government to reclassify marijuana in what would be a historic shift that could have wide ripple effects across the country.
No. Schedule III drugs — which include ketamine, anabolic steroids and some acetaminophen-codeine combinations — are still controlled substances.
They’re subject to various rules that allow for some medical uses, and for federal criminal prosecution of anyone who traffics in the drugs without permission.
No changes are expected to the medical marijuana programs now licensed in 38 states or the legal recreational cannabis markets in 23 states, but it’s unlikely they would meet the federal production, record-keeping, prescribing and other requirements for Schedule III drugs.
There haven’t been many federal prosecutions for simply possessing marijuana in recent years, even under marijuana’s current Schedule I status, but the reclassification wouldn’t have an immediate impact on people already in the criminal justice system.
“Put simple, this move from Schedule I to Schedule III is not getting people out of jail,” said David Culver, senior vice president of public affairs at the U.S. Cannabis Council.
But rescheduling in itself would have some impact, particularly on research and marijuana business taxes.
WHAT WOULD THIS MEAN FOR RESEARCH?
Because marijuana is on Schedule I, it’s been very difficult to conduct authorized clinical studies that involve administering the drug. That has created something of a Catch-22: calls for more research, but barriers to doing it. (Scientists sometimes rely instead on people’s own reports of their marijuana use.)
Marijuana plants are seen at a secured growing facility in Washington County, N.Y., May 12, 2023. (AP Photo/Hans Pennink, File)
Schedule III drugs are easier to study, though the reclassification wouldn’t immediately reverse all barriers to study.
“It’s going to be really confusing for a long time,” said Ziva Cooper, director of the University of California, Los Angeles Center for Cannabis and Cannabinoids. “When the dust has settled, I don’t know how many years from now, research will be easier.”
Among the unknowns: whether researchers will be able to study marijuana from state-licensed dispensaries and how the federal Food and Drug Administration might oversee that.
Some researchers are optimistic.
“Reducing the schedule to schedule 3 will open up the door for us to be able to conduct research with human subjects with cannabis,” said Susan Ferguson, director of University of Washington’s Addictions, Drug & Alcohol Institute in Seattle.
WHAT ABOUT TAXES (AND BANKING)?
Under the federal tax code, businesses involved in “trafficking” in marijuana or any other Schedule I or II drug can’t deduct rent, payroll or various other expenses that other businesses can write off. (Yes, at least some cannabis businesses, particularly state-licensed ones, do pay taxes to the federal government, despite its prohibition on marijuana.) Industry groups say the tax rate often ends up at 70% or more.
The deduction rule doesn’t apply to Schedule III drugs, so the proposed change would cut cannabis companies’ taxes substantially.
They say it would treat them like other industries and help them compete against illegal competitors that are frustrating licensees and officials in places such as New York .
“You’re going to make these state-legal programs stronger,” says Adam Goers, of The Cannabist Company, formerly Columbia Care. He co-chairs a coalition of corporate and other players that’s pushing for rescheduling.
It could also mean more cannabis promotion and advertising if those costs could be deducted, according to Beau Kilmer, co-director of the RAND Drug Policy Center.
Rescheduling wouldn’t directly affect another marijuana business problem: difficulty accessing banks, particularly for loans, because the federally regulated institutions are wary of the drug’s legal status. The industry has been looking instead to a measure called the SAFE Banking Act . It has repeatedly passed the House but stalled in the Senate.
ARE THERE CRITICS? WHAT DO THEY SAY?
Indeed, there are, including the national anti-legalization group Smart Approaches to Marijuana. President Kevin Sabet, a former Obama administration drug policy official, said the HHS recommendation “flies in the face of science, reeks of politics” and gives a regrettable nod to an industry “desperately looking for legitimacy.”
Some legalization advocates say rescheduling weed is too incremental. They want to keep the focus on removing it completely from the controlled substances list, which doesn’t include such items as alcohol or tobacco (they’re regulated, but that’s not the same).
Paul Armentano, the deputy director of the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws, said that simply reclassifying marijuana would be “perpetuating the existing divide between state and federal marijuana policies.” Kaliko Castille, a past president of the Minority Cannabis Business Association, said rescheduling just “re-brands prohibition,” rather than giving an all-clear to state licensees and putting a definitive close to decades of arrests that disproportionately pulled in people of color.
“Schedule III is going to leave it in this kind of amorphous, mucky middle where people are not going to understand the danger of it still being federally illegal,” he said.
This story has been corrected to show that Kaliko Castille is a past president, not president, of the Minority Cannabis Business Association and that Columbia Care is now The Cannabist Company.
___ Peltz reported from New York. Associated Press writers Colleen Long in Washington and Carla K. Johnson in Seattle contributed to this report.

COMMENTS
Prism c. Rainbow d. inverted e. erect Answer 7 1. diverging 2.virtual 3.mirror 4.converging 5.orange 6. real Also Read. Notes. Light Class 7 Notes; NCERT Solutions. light Class 7 NCERT Solutions; Assignments. light Class 7 Worksheet; light Class 7 Questions and Answers
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 - Light. *According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 11. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light are provided here. In this chapter, students will learn about light, the reflection of light and much more. To score good marks in Class 7 Science ...
Class 7 Worksheets for Science on Vedantu. CBSE Class 7 Science Light Worksheets with Answers for Chapter 15 in PDF format to download prepared by expert Science teachers from the latest edition of CBSE (NCERT) books. Register Online for NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science tuition on Vedantu to score more marks in CBSE board examination.
Q.3. Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II. Ans. Q.4.State the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror. Ans. (i) Plane mirror forms an erect image. (ii) It forms a virtual image. (iii) Size of the image is same as that of the object. (iv)Image is formed at the same distance behind the mirror as the ...
Characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror are. (i) The image formed is virtual and erected. (ii) The image is laterally inverted. The left side appears on the right side of the image. (iii) It is of the same size as the object. (iv) The image is situated at the same distance from the mirror as the object. Question 5.
Conclusion. The NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 15 - Light, provided by Vedantu, is a valuable tool for Class 7 students. It helps introduce Science concepts in an accessible manner. The provided solutions and explanations simplify complex ideas, making it easier for Class 7 students to understand the material.
The extra and important questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 - Light engage in a concept-focused discussion, encompassing all chapter themes. This question-and-answer method proves time-saving during exam prep, offering an efficient way to revise the chapter and enhance understanding. Practicing these important questions streamlines ...
The seven colours that appear are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. These are also the colours of a rainbow we see after a rainfall. The splitting of white light into its component colours is called dispersion. To know more about Dispersion of white light through prism, visit here.
Fix a plane mirror strip vertically on the chart paper. Now direct the beam of light on the mirror from the torch with slits. Place the torch in such a way that its light is seen along the chart paper on the board. Now adjust its position so that the light from the torch strikes the plane mirror at an angle.
This comprehensive guide covers Chapter 15 (now chapter 11)- Light, designed for Class 7 Science. It explores the nature of light, its travel, reflection, refraction, and dispersion, along with practical applications of spherical mirrors and lenses. The notes are tailored to simplify complex concepts, making them accessible for young learners to grasp the fundamentals of light in science.
White light can be sunlight. So, now we can say that sunlight consists of seven colours. We can mix these colours to get white light. This can be done by using Newton's disc, let us try this. We hope the given CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 15 Light Pdf free download will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Class 7 Science ...
The questions in the chapter Light Assignment worksheet for Class 7 are provided with solutions. Through these solutions, students can easily solve all their doubts. By clearing the doubts of Light Assignment, students can build a strong foundation. Accordingly students can also score good marks in questions related to the chapter Light Assignment.
Frequently Asked Questions NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light. Q1. The image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size for an object kept at different positions in front of it. Identify the nature of the lens. The answer is concave lens.
The City School / Reinforcement Worksheet/ EoY 2015 / Science / Class 7/ Light Page 7 of 8 Q10a. The diagram below shows George using his laptop. Light from the lamp is reflected by the laptop screen. (i) On the diagram above draw a ray of light to show how George sees the light from the lamp reflected by the laptop screen. Use a ruler.
(c). The direction of light can be changed with the help of a mirror. (d). Right hand appears left in its image. (e). We can see a candle through a straight pipe but not through a bent pipe. Q.3. Answer the following questions. (a). State two properties of light (b). Suggest an activity which shows that light travels along a straight path ...
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light (Free PDF Download) Class 7 Science is a fascinating subject for young minds. The chapters included in the syllabus open new dimensions of knowledge and concepts for the students. One of the chapters in the Class 7 Science syllabus is based on light. It explains how light rays are emitted ...
Download now and prepare for CBSE Class 7 exam. Chapter 15 Light of Class 7 Science NCERT Book (PDF) is available here for download in PDF format. Chapter 15 of Class 7 Science NCERT Books is one ...
All these solutions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation. Class 7 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 11 includes all the textbook exercise questions and answers. These solutions will help students complete their assignments & homework. Class 7 Science Light Questions and Answers. Exercise Questions. Question 1: Fill in the blanks:
The area of the disc is divided into 7 equal parts and each part is coloured using each of the seven colours. If you rotate the disc fast it appears white in colour. Also Read. Notes. Light Class 7 Notes; NCERT Solutions. light Class 7 NCERT Solutions; Assignments. light Class 7 Worksheet; light Class 7 Questions and Answers
About Light - Class 7 Science Chapter 15. Light is simply energy travelling from one place to another, and it does not require any medium to travel and can travel in space, Unlike sound. Light is a fascinating topic for young minds, which lets them think about their limits. This chapter, named Light, provides a proper explanation of various ...
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science with Answers on a daily basis and score well in exams. Refer to the Light Class 7 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
Class 7, NCERT Exemplar Chapter 15: Light ... Class 7 Science Resources. Notes + Important Questions. NCERT Solutions. Helpbook Solutions. Sample Papers. Assignments. Class 7 Science Chapters. Nutrition in Plants . Nutrition in Animals . Fiber to Fabric . Heat . Acids, Bases and Salts . ... Light . Water A Precious Resource . Forests Our ...
WASHINGTON (AP) — The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration is moving toward reclassifying marijuana as a less dangerous drug. The Justice Department proposal would recognize the medical uses of cannabis, but wouldn't legalize it for recreational use. The proposal would move marijuana from the "Schedule I" group to the less tightly ...