- 888-309-8227
- 732-384-0146
New User Registration
Forgot Password

Math Connects: Concepts, Skills, and Problem Solving Course 3, Grade: 8 Publisher: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Math connects: concepts, skills, and problem solving course 3, title : math connects: concepts, skills, and problem solving course 3, publisher : glencoe/mcgraw-hill, isbn : 78740509, isbn-13 : 9780078740503, use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement math connects: concepts, skills, and problem solving course 3., textbook resources.
- Call us toll-free
- FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
- Contact Lumos Learning – Proven Study Programs by Expert Teachers
Follow us: Lumos Learning -->
- 2024 © Lumos Learning
- Privacy Policy - Terms of Service - Disclaimers
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc... Read More
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc., the Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any state of the Union. Neither PARCC, Inc., nor The Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any member state has endorsed this product. No portion of any fees or charges paid for any products or services Lumos Learning offers will be paid or inure to the benefit of PARCC, Inc., or any state of the Union
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not aff... Read More
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC, was not... Read More
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC,was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved... Read More
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the prod... Read More
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved... Read More
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved... Read More
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved... Read More
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved... Read More
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
- TPC and eLearning
- Read Watch Interact
- What's NEW at TPC?
- Practice Review Test
- Teacher-Tools
- Subscription Selection
- Seat Calculator
- Ad Free Account
- Edit Profile Settings
- Classes (Version 2)
- Student Progress Edit
- Task Properties
- Export Student Progress
- Task, Activities, and Scores
- Metric Conversions Questions
- Metric System Questions
- Metric Estimation Questions
- Significant Digits Questions
- Proportional Reasoning
- Acceleration
- Distance-Displacement
- Dots and Graphs
- Graph That Motion
- Match That Graph
- Name That Motion
- Motion Diagrams
- Pos'n Time Graphs Numerical
- Pos'n Time Graphs Conceptual
- Up And Down - Questions
- Balanced vs. Unbalanced Forces
- Change of State
- Force and Motion
- Mass and Weight
- Match That Free-Body Diagram
- Net Force (and Acceleration) Ranking Tasks
- Newton's Second Law
- Normal Force Card Sort
- Recognizing Forces
- Air Resistance and Skydiving
- Solve It! with Newton's Second Law
- Which One Doesn't Belong?
- Component Addition Questions
- Head-to-Tail Vector Addition
- Projectile Mathematics
- Trajectory - Angle Launched Projectiles
- Trajectory - Horizontally Launched Projectiles
- Vector Addition
- Vector Direction
- Which One Doesn't Belong? Projectile Motion
- Forces in 2-Dimensions
- Being Impulsive About Momentum
- Explosions - Law Breakers
- Hit and Stick Collisions - Law Breakers
- Case Studies: Impulse and Force
- Impulse-Momentum Change Table
- Keeping Track of Momentum - Hit and Stick
- Keeping Track of Momentum - Hit and Bounce
- What's Up (and Down) with KE and PE?
- Energy Conservation Questions
- Energy Dissipation Questions
- Energy Ranking Tasks
- LOL Charts (a.k.a., Energy Bar Charts)
- Match That Bar Chart
- Words and Charts Questions
- Name That Energy
- Stepping Up with PE and KE Questions
- Case Studies - Circular Motion
- Circular Logic
- Forces and Free-Body Diagrams in Circular Motion
- Gravitational Field Strength
- Universal Gravitation
- Angular Position and Displacement
- Linear and Angular Velocity
- Angular Acceleration
- Rotational Inertia
- Balanced vs. Unbalanced Torques
- Getting a Handle on Torque
- Torque-ing About Rotation
- Properties of Matter
- Fluid Pressure
- Buoyant Force
- Sinking, Floating, and Hanging
- Pascal's Principle
- Flow Velocity
- Bernoulli's Principle
- Balloon Interactions
- Charge and Charging
- Charge Interactions
- Charging by Induction
- Conductors and Insulators
- Coulombs Law
- Electric Field
- Electric Field Intensity
- Polarization
- Case Studies: Electric Power
- Know Your Potential
- Light Bulb Anatomy
- I = ∆V/R Equations as a Guide to Thinking
- Parallel Circuits - ∆V = I•R Calculations
- Resistance Ranking Tasks
- Series Circuits - ∆V = I•R Calculations
- Series vs. Parallel Circuits
- Equivalent Resistance
- Period and Frequency of a Pendulum
- Pendulum Motion: Velocity and Force
- Energy of a Pendulum
- Period and Frequency of a Mass on a Spring
- Horizontal Springs: Velocity and Force
- Vertical Springs: Velocity and Force
- Energy of a Mass on a Spring
- Decibel Scale
- Frequency and Period
- Closed-End Air Columns
- Name That Harmonic: Strings
- Rocking the Boat
- Wave Basics
- Matching Pairs: Wave Characteristics
- Wave Interference
- Waves - Case Studies
- Color Addition and Subtraction
- Color Filters
- If This, Then That: Color Subtraction
- Light Intensity
- Color Pigments
- Converging Lenses
- Curved Mirror Images
- Law of Reflection
- Refraction and Lenses
- Total Internal Reflection
- Who Can See Who?
- Formulas and Atom Counting
- Atomic Models
- Bond Polarity
- Entropy Questions
- Cell Voltage Questions
- Heat of Formation Questions
- Reduction Potential Questions
- Oxidation States Questions
- Measuring the Quantity of Heat
- Hess's Law
- Oxidation-Reduction Questions
- Galvanic Cells Questions
- Thermal Stoichiometry
- Molecular Polarity
- Quantum Mechanics
- Balancing Chemical Equations
- Bronsted-Lowry Model of Acids and Bases
- Classification of Matter
- Collision Model of Reaction Rates
- Density Ranking Tasks
- Dissociation Reactions
- Complete Electron Configurations
- Elemental Measures
- Enthalpy Change Questions
- Equilibrium Concept
- Equilibrium Constant Expression
- Equilibrium Calculations - Questions
- Equilibrium ICE Table
- Intermolecular Forces Questions
- Ionic Bonding
- Lewis Electron Dot Structures
- Limiting Reactants
- Line Spectra Questions
- Mass Stoichiometry
- Measurement and Numbers
- Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
- Metric Estimations
- Metric System
- Molarity Ranking Tasks
- Mole Conversions
- Name That Element
- Names to Formulas
- Names to Formulas 2
- Nuclear Decay
- Particles, Words, and Formulas
- Periodic Trends
- Precipitation Reactions and Net Ionic Equations
- Pressure Concepts
- Pressure-Temperature Gas Law
- Pressure-Volume Gas Law
- Chemical Reaction Types
- Significant Digits and Measurement
- States Of Matter Exercise
- Stoichiometry Law Breakers
- Stoichiometry - Math Relationships
- Subatomic Particles
- Spontaneity and Driving Forces
- Gibbs Free Energy
- Volume-Temperature Gas Law
- Acid-Base Properties
- Energy and Chemical Reactions
- Chemical and Physical Properties
- Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
- Writing Balanced Chemical Equations
- Mission CG1
- Mission CG10
- Mission CG2
- Mission CG3
- Mission CG4
- Mission CG5
- Mission CG6
- Mission CG7
- Mission CG8
- Mission CG9
- Mission EC1
- Mission EC10
- Mission EC11
- Mission EC12
- Mission EC2
- Mission EC3
- Mission EC4
- Mission EC5
- Mission EC6
- Mission EC7
- Mission EC8
- Mission EC9
- Mission RL1
- Mission RL2
- Mission RL3
- Mission RL4
- Mission RL5
- Mission RL6
- Mission KG7
- Mission RL8
- Mission KG9
- Mission RL10
- Mission RL11
- Mission RM1
- Mission RM2
- Mission RM3
- Mission RM4
- Mission RM5
- Mission RM6
- Mission RM8
- Mission RM10
- Mission LC1
- Mission RM11
- Mission LC2
- Mission LC3
- Mission LC4
- Mission LC5
- Mission LC6
- Mission LC8
- Mission SM1
- Mission SM2
- Mission SM3
- Mission SM4
- Mission SM5
- Mission SM6
- Mission SM8
- Mission SM10
- Mission KG10
- Mission SM11
- Mission KG2
- Mission KG3
- Mission KG4
- Mission KG5
- Mission KG6
- Mission KG8
- Mission KG11
- Mission F2D1
- Mission F2D2
- Mission F2D3
- Mission F2D4
- Mission F2D5
- Mission F2D6
- Mission KC1
- Mission KC2
- Mission KC3
- Mission KC4
- Mission KC5
- Mission KC6
- Mission KC7
- Mission KC8
- Mission AAA
- Mission SM9
- Mission LC7
- Mission LC9
- Mission NL1
- Mission NL2
- Mission NL3
- Mission NL4
- Mission NL5
- Mission NL6
- Mission NL7
- Mission NL8
- Mission NL9
- Mission NL10
- Mission NL11
- Mission NL12
- Mission MC1
- Mission MC10
- Mission MC2
- Mission MC3
- Mission MC4
- Mission MC5
- Mission MC6
- Mission MC7
- Mission MC8
- Mission MC9
- Mission RM7
- Mission RM9
- Mission RL7
- Mission RL9
- Mission SM7
- Mission SE1
- Mission SE10
- Mission SE11
- Mission SE12
- Mission SE2
- Mission SE3
- Mission SE4
- Mission SE5
- Mission SE6
- Mission SE7
- Mission SE8
- Mission SE9
- Mission VP1
- Mission VP10
- Mission VP2
- Mission VP3
- Mission VP4
- Mission VP5
- Mission VP6
- Mission VP7
- Mission VP8
- Mission VP9
- Mission WM1
- Mission WM2
- Mission WM3
- Mission WM4
- Mission WM5
- Mission WM6
- Mission WM7
- Mission WM8
- Mission WE1
- Mission WE10
- Mission WE2
- Mission WE3
- Mission WE4
- Mission WE5
- Mission WE6
- Mission WE7
- Mission WE8
- Mission WE9
- Vector Walk Interactive
- Name That Motion Interactive
- Kinematic Graphing 1 Concept Checker
- Kinematic Graphing 2 Concept Checker
- Graph That Motion Interactive
- Two Stage Rocket Interactive
- Rocket Sled Concept Checker
- Force Concept Checker
- Free-Body Diagrams Concept Checker
- Free-Body Diagrams The Sequel Concept Checker
- Skydiving Concept Checker
- Elevator Ride Concept Checker
- Vector Addition Concept Checker
- Vector Walk in Two Dimensions Interactive
- Name That Vector Interactive
- River Boat Simulator Concept Checker
- Projectile Simulator 2 Concept Checker
- Projectile Simulator 3 Concept Checker
- Hit the Target Interactive
- Turd the Target 1 Interactive
- Turd the Target 2 Interactive
- Balance It Interactive
- Go For The Gold Interactive
- Egg Drop Concept Checker
- Fish Catch Concept Checker
- Exploding Carts Concept Checker
- Collision Carts - Inelastic Collisions Concept Checker
- Its All Uphill Concept Checker
- Stopping Distance Concept Checker
- Chart That Motion Interactive
- Roller Coaster Model Concept Checker
- Uniform Circular Motion Concept Checker
- Horizontal Circle Simulation Concept Checker
- Vertical Circle Simulation Concept Checker
- Race Track Concept Checker
- Gravitational Fields Concept Checker
- Orbital Motion Concept Checker
- Angular Acceleration Concept Checker
- Balance Beam Concept Checker
- Torque Balancer Concept Checker
- Aluminum Can Polarization Concept Checker
- Charging Concept Checker
- Name That Charge Simulation
- Coulomb's Law Concept Checker
- Electric Field Lines Concept Checker
- Put the Charge in the Goal Concept Checker
- Circuit Builder Concept Checker (Series Circuits)
- Circuit Builder Concept Checker (Parallel Circuits)
- Circuit Builder Concept Checker (∆V-I-R)
- Circuit Builder Concept Checker (Voltage Drop)
- Equivalent Resistance Interactive
- Pendulum Motion Simulation Concept Checker
- Mass on a Spring Simulation Concept Checker
- Particle Wave Simulation Concept Checker
- Boundary Behavior Simulation Concept Checker
- Slinky Wave Simulator Concept Checker
- Simple Wave Simulator Concept Checker
- Wave Addition Simulation Concept Checker
- Standing Wave Maker Simulation Concept Checker
- Color Addition Concept Checker
- Painting With CMY Concept Checker
- Stage Lighting Concept Checker
- Filtering Away Concept Checker
- InterferencePatterns Concept Checker
- Young's Experiment Interactive
- Plane Mirror Images Interactive
- Who Can See Who Concept Checker
- Optics Bench (Mirrors) Concept Checker
- Name That Image (Mirrors) Interactive
- Refraction Concept Checker
- Total Internal Reflection Concept Checker
- Optics Bench (Lenses) Concept Checker
- Kinematics Preview
- Velocity Time Graphs Preview
- Moving Cart on an Inclined Plane Preview
- Stopping Distance Preview
- Cart, Bricks, and Bands Preview
- Fan Cart Study Preview
- Friction Preview
- Coffee Filter Lab Preview
- Friction, Speed, and Stopping Distance Preview
- Up and Down Preview
- Projectile Range Preview
- Ballistics Preview
- Juggling Preview
- Marshmallow Launcher Preview
- Air Bag Safety Preview
- Colliding Carts Preview
- Collisions Preview
- Engineering Safer Helmets Preview
- Push the Plow Preview
- Its All Uphill Preview
- Energy on an Incline Preview
- Modeling Roller Coasters Preview
- Hot Wheels Stopping Distance Preview
- Ball Bat Collision Preview
- Energy in Fields Preview
- Weightlessness Training Preview
- Roller Coaster Loops Preview
- Universal Gravitation Preview
- Keplers Laws Preview
- Kepler's Third Law Preview
- Charge Interactions Preview
- Sticky Tape Experiments Preview
- Wire Gauge Preview
- Voltage, Current, and Resistance Preview
- Light Bulb Resistance Preview
- Series and Parallel Circuits Preview
- Thermal Equilibrium Preview
- Linear Expansion Preview
- Heating Curves Preview
- Electricity and Magnetism - Part 1 Preview
- Electricity and Magnetism - Part 2 Preview
- Vibrating Mass on a Spring Preview
- Period of a Pendulum Preview
- Wave Speed Preview
- Slinky-Experiments Preview
- Standing Waves in a Rope Preview
- Sound as a Pressure Wave Preview
- DeciBel Scale Preview
- DeciBels, Phons, and Sones Preview
- Sound of Music Preview
- Shedding Light on Light Bulbs Preview
- Models of Light Preview
- Electromagnetic Radiation Preview
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Preview
- EM Wave Communication Preview
- Digitized Data Preview
- Light Intensity Preview
- Concave Mirrors Preview
- Object Image Relations Preview
- Snells Law Preview
- Reflection vs. Transmission Preview
- Magnification Lab Preview
- Reactivity Preview
- Ions and the Periodic Table Preview
- Periodic Trends Preview
- Intermolecular Forces Preview
- Melting Points and Boiling Points Preview
- Reaction Rates Preview
- Ammonia Factory Preview
- Stoichiometry Preview
- Gaining Teacher Access
- Tasks and Classes
- Tasks - Classic
- Subscription
- Subscription Locator
- 1-D Kinematics
- Newton's Laws
- Vectors - Motion and Forces in Two Dimensions
- Momentum and Its Conservation
- Work and Energy
- Circular Motion and Satellite Motion
- Thermal Physics
- Static Electricity
- Electric Circuits
- Vibrations and Waves
- Sound Waves and Music
- Light and Color
- Reflection and Mirrors
- About the Physics Interactives
- Task Tracker
- Usage Policy
- Newtons Laws
- Vectors and Projectiles
- Forces in 2D
- Momentum and Collisions
- Circular and Satellite Motion
- Balance and Rotation
- Electromagnetism
- Waves and Sound
- Forces in Two Dimensions
- Work, Energy, and Power
- Circular Motion and Gravitation
- Sound Waves
- 1-Dimensional Kinematics
- Circular, Satellite, and Rotational Motion
- Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity
- Waves, Sound and Light
- QuickTime Movies
- About the Concept Builders
- Pricing For Schools
- Directions for Version 2
- Measurement and Units
- Relationships and Graphs
- Rotation and Balance
- Vibrational Motion
- Reflection and Refraction
- Teacher Accounts
- Task Tracker Directions
- Kinematic Concepts
- Kinematic Graphing
- Wave Motion
- Sound and Music
- About CalcPad
- 1D Kinematics
- Vectors and Forces in 2D
- Simple Harmonic Motion
- Rotational Kinematics
- Rotation and Torque
- Rotational Dynamics
- Electric Fields, Potential, and Capacitance
- Transient RC Circuits
- Light Waves
- Units and Measurement
- Stoichiometry
- Molarity and Solutions
- Thermal Chemistry
- Acids and Bases
- Kinetics and Equilibrium
- Solution Equilibria
- Oxidation-Reduction
- Nuclear Chemistry
- NGSS Alignments
- 1D-Kinematics
- Projectiles
- Circular Motion
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism
- Graphing Practice
- About the ACT
- ACT Preparation
- For Teachers
- Other Resources
- Newton's Laws of Motion
- Work and Energy Packet
- Static Electricity Review
- Solutions Guide
- Solutions Guide Digital Download
- Motion in One Dimension
- Work, Energy and Power
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Purchasing the Download
- Purchasing the CD
- Purchasing the Digital Download
- About the NGSS Corner
- NGSS Search
- Force and Motion DCIs - High School
- Energy DCIs - High School
- Wave Applications DCIs - High School
- Force and Motion PEs - High School
- Energy PEs - High School
- Wave Applications PEs - High School
- Crosscutting Concepts
- The Practices
- Physics Topics
- NGSS Corner: Activity List
- NGSS Corner: Infographics
- About the Toolkits
- Position-Velocity-Acceleration
- Position-Time Graphs
- Velocity-Time Graphs
- Newton's First Law
- Newton's Second Law
- Newton's Third Law
- Terminal Velocity
- Projectile Motion
- Forces in 2 Dimensions
- Impulse and Momentum Change
- Momentum Conservation
- Work-Energy Fundamentals
- Work-Energy Relationship
- Roller Coaster Physics
- Satellite Motion
- Electric Fields
- Circuit Concepts
- Series Circuits
- Parallel Circuits
- Describing-Waves
- Wave Behavior Toolkit
- Standing Wave Patterns
- Resonating Air Columns
- Wave Model of Light
- Plane Mirrors
- Curved Mirrors
- Teacher Guide
- Using Lab Notebooks
- Current Electricity
- Light Waves and Color
- Reflection and Ray Model of Light
- Refraction and Ray Model of Light
- Classes (Legacy Version)
- Teacher Resources
- Subscriptions

- Newton's Laws
- Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity
- About Concept Checkers
- School Pricing
- Newton's Laws of Motion
- Newton's First Law
- Newton's Third Law
Ray Optics: Reflection and Mirrors
Calculator pad, version 2, reflection and mirrors: problem set.
A light ray approaches a mirror at an angle of incidence of 25°. What is the angle of reflection?
- Audio Guided Solution
- Show Answer
A light ray approaches a mirror at an angle of 22° with the mirror surface. What is the angle of reflection of this light ray?
Angle B = 38° Angle C = 52° Angle D = 38°
Anna Litical is doing the Plane Mirror Lab in physics class. She places a pin a distance of 4.9 cm from a plane mirror. How far behind the mirror can the image be expected to appear?
Baldwin Young stands 68 cm from his dresser mirror, inspecting his scalp. How far is the image of his scalp located from his scalp?
A meter stick (object) is placed in an upright position in front of a plane mirror as shown in the diagram at the right. The image of the meter stick is equidistant from the mirror. Suppose that the meter stick is equipped with a working eyeball capable of viewing the top and the bottom of its image. The eyeball is located at the 90-cm mark on the meter stick. Using either a ray diagram or geometry, determine … a. … the location of the intersection of the eye's line of sight with the mirror as the eyeball sights at the top of the image. b. … the location of the intersection of the eye's line of sight with the mirror as the eyeball sights at the bottom of the image. c. … the amount of mirror required by the meter stick to view the image.
a. 95 cm b. 45 cm c. 50 cm
A spherical concave mirror has a radius of curvature of +62 cm. What is the focal length of the mirror?
A decorative garden sphere has a diameter of 44 cm. The reflecting surface of the shiny sphere makes a great convex mirror. What is the focal point of the convex surface?
In a physics demonstration, a concave mirror having a 50.0 cm focal length is used to create images of a candle located at various locations along its principal axis. Beginning from a distance of several meters from the mirror, a candle is moved forward and its image is projected onto an opaque screen. Determine the image distances (distance from mirror to image) for object distances (distance from object to mirror) of … a. … 125.0 cm b. … 100.0 cm c. … 75.0 cm d. … 50.0 cm (Be careful with your math; the result is surprising.) e. … 25.0 cm
a. 83.3 cm b. 100.0 cm c. 150.0 cm d. No image. A solution to the mirror equation does not exist for this object distance. e. -50.0 cm
Problem 10:
Obtaining a large spherical mirror with a focal length of 0.654 m from the Physics Storeroom, Mr. H takes his last period class outside for a fascinating demo. A student volunteer holds the mirror at an angle such that the face of the mirror is directed towards the Sun - roughly 1.46x10 11 m away. Mr. H then uses a piece of paper with George Washington's picture on it to focus the image of the sun on the sheet of paper. Before the paper engulfs in flames, a bright image of the sun can be seen on the paper. Use the mirror equation to calculate the distance from the mirror to the image of the sun.
Problem 11:
Every morning Bob Gillette uses a shaving mirror with a focal length of 72 cm to view the image of his face. Supposing his face is 18 cm from the mirror, determine the image distance and the magnification of his face.
d i = -24 cm Magnification = 1.33
Problem 12:
The infamous Chinese magician Foo Ling Yu places a 56-mm tall light bulb a distance of 124 cm from a spherical concave mirror with a focal length of 62 cm. a. Determine the image distance and image height. b. Describe the orientation and type of the image.
a. d i = 124 cm and h i = -56 mm b. The image is inverted and real.
Problem 13:
In a physics lab, Anna Litical and Noah Formula position a small night light bulb at several locations along the principal axis of a concave mirror. Using a note card, they locate the image of the light bulb. The mirror has a focal length of 32.0 cm. What image distances would you expect Anna and Noah to observe when the object is located at distances of … a. … 85.3 cm from the mirror? b. … 64.0 cm from the mirror? c. … 48.1 cm from the mirror?
a. 51.2 cm b. 64.0 cm c. 95.6 cm
Problem 14:
Ima Primpin uses a cosmetic mirror to magnify her eyelashes during the traditional morning painting session. Her 1.2-cm long eyelashes are magnified to 1.6 cm when placed 5.8 cm from the mirror. a. Determine the image distance for such an upright image. b. Determine the focal length of the mirror.
a. -7.7 cm b. 23.2 cm
Problem 15:
In the Fall of 2006, the Sky Mirror sculpture was opened in Rockefeller Center in New York City. Standing three stories tall and weighing 23 tons, its concave side faced the Rockefeller Center and its convex side faced Fifth Avenue. a. A taxi on Fifth Avenue is located 38 m from the convex side of the sculpture and its image is one-fifth the size of the taxi. Determine the focal length of the mirror. b. Estimate the image size and image distance of the 260-m tall Rockefeller Center if it is located an estimated distance of 95 meters from the concave mirror surface. Assume the focal length of the concave side is the same magnitude as the focal length of the convex side.
a. -9.5 m b. d i = 11 m (rounded from 10.55 m) and h i = -29 m (- indicates inverted image)
Problem 16:
A convex spherical mirror has a focal point located a distance of 24.6 cm from the surface of the mirror. (You will have to decide for yourself whether f is + or -.) a. Find the image distance (in cm) for an object distance of 76.8 cm. b. Determine the magnification of this image.
a. d i = -18.6 cm b. M = 0.243
Problem 17:
A convenient store mounts a convex mirror in the corner of the store to serve as a security mirror and reduce the frequency of five-finger discounts . When Robin Storz is positioned a distance of 4.8 m from the mirror, her image is magnified by a factor of one-half. Determine the focal length of the mirror.
Problem 18:
Kerry Uss is studying the convex side of her soup spoon. She notices that her 3.8-cm tall nose appears to be 1.2 cm tall when positioned a distance of 2.4 cm from the spoon. a. Determine the image distance for this particular object distance. b. Determine the focal length of the convex side of the spoon.
a. d i = -0.76 cm b. f = -1.1 cm
Problem 19:
A large spherical mirror sculpture is constructed in the town square at Physicston, Illinois. The sculpture consists of a large sphere with a diameter of 24 meters which is coated with a reflecting material. A 1.8 meter tall photographer stands a distance of 38 m from the concave side of the sculpture and takes a picture. Determine the image distance and the magnification of the photographer.
d i = 7.1 m Mag = -0.19
Problem 20:
Baxter Nachure lives in the country along Sinewave road. It is difficult to pull out of the driveway onto the road since the road is curved and trees prevent him from seeing around the corner. He recently installed a large convex mirror at one of the curves to give him a wider angle of view. It has a focal length of -1.54 meters. Determine the magnification of an oncoming car located 35.8 m from the mirror.
Problem 21:
A virtual image is formed 26.9 cm from a concave mirror having a radius of curvature of 48.1 cm. Determine the object distance.
Problem 22:
An 4.9-cm tall object is positioned 14.8 cm from a mirror. Determine the radius of curvature which the mirror must have in order to produce an upright image that is 7.2 cm tall?
Problem 23:
A dentist uses a spherical mirror to produce an upright image of a patient's tooth which is magnified by a factor of 4.5 when placed 1.8 cm from the tooth. (a) What type of mirror - concave or convex - is being used? (b) What is the focal length of the mirror?
a. Concave mirror. Convex mirrors do not magnify the image; they only reduce the image. b. 2.3 cm
Problem 24:
The real image produced by a concave mirror is observed to be six times larger than the object when the object is 34.2 cm in front of a mirror. Determine the radius of curvature of this mirror.
Problem 25:
A shiny bauble (ornament) hangs on Mr. H's Christmas tree. The bauble has a radius of 4.8 cm. Matthew looks into the bauble and observes an image of his face which is one-eighth the size of his face. How far from the bauble is Matthew's face?
Problem 26:
A child at an amusement park stands in front of a concave mirror with a focal length of 73.9 cm. With great amusement, the child holds her cotton candy close to the mirror and observes that its image is magnified by a factor of five. Determine the object distance which creates this magnification of five.
Return to Overview

View Audio Guided Solution for Problem:
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 9 Transformations and Congruence
There are multiple ways to learn maths. But choosing the best material is also important for the students to score good marks and also to improve their knowledge. This will be possible only with the help of our Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 9 Transformations and Congruence. You can get the explanation for all the questions in detail in Go Math Grade 8 Chapter 9 Transformations and Congruence Answer Key here. Refer to Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key for learning the problems in an easy manner.
Practice makes you perfect become a master in maths. Without proper knowledge on the subject, you cannot solve the problems in real-time. This will affect your exam. So, keeping this in our mind we have prepared the solutions briefly which will help you to understand the concept in depth. Get free access to Download Go Math Grade 8 Chapter 9 Transformations and Congruence Solution Key pdf. In this article, you will get the solutions according to the topics. Therefore, students who want to score good marks in the exam must practice with Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 9 Transformations and Congruence.
Lesson 1: Properties of Translations
- Properties of Translations – Page No. 282
- Properties of Translations – Page No. 283
- Properties of Translations Lesson Check – Page No. 284
Lesson 2: Properties of Reflections
- Properties of Reflections – Page No. 288
- Properties of Reflections – Page No. 289
- Properties of Reflections Lesson Check – Page No. 290
- Properties of Reflections Lesson Check 1 – Page No. 294
- Properties of Reflections Lesson Check 2 – Page No. 295
- Properties of Reflections Lesson Check 3 – Page No. 296
Lesson 3: Algebraic Representations of Transformations
- Algebraic Representations of Transformations – Page No. 300
- Algebraic Representations of Transformations – Page No. 301
- Algebraic Representations of Transformations Lesson Check – Page No. 302
Lesson 4: Congruent Figures
- Congruent Figures – Page No. 306
- Congruent Figures – Page No. 307
- Congruent Figures Lesson Check – Page No. 308
- Model Quiz – Page No. 309
Mixed Review
- Mixed Review – Page No. 310
Guided Practice – Properties of Translations – Page No. 282
Question 1. Vocabulary A __________________is a change in the position, size, or shape of a figure. ____________
Answer: transformation
Explanation: A transformation is a change in the position, size, or shape of a figure.
Question 2. Vocabulary When you perform a transformation of a figure on the coordinate plane, the input of the transformation is called the ________________, and the output of the transformation is called the_________________ . Type below: ____________
Answer: pre-image image
Explanation: When you perform a transformation of a figure on the coordinate plane, the input of the transformation is called the pre-image, and the output of the transformation is called the image.
Question 3. Joni translates a right triangle 2 units down and 4 units to the right. How does the orientation of the image of the triangle compare with the orientation of the preimage? Orientation is: _______
Answer: Orientation is: Same
Explanation: Since translation does not change the shape and size of a geometric figure, the two triangles are identical in shape and size, so they are congruent and the orientation is the same
Question 4. Rashid drew rectangle PQRS on a coordinate plane. He then translated the rectangle 3 units up and 3 units to the left and labeled the image P ‘Q ‘R ‘S ‘. How do rectangle PQRS and rectangle P ‘Q ‘R ‘S ‘ compare? They are: _______
Answer: congruent
Explanation: Since translation does not change the shape and size of a geometric figure, the two rectangles are identical in shape and size, so they are congruent.
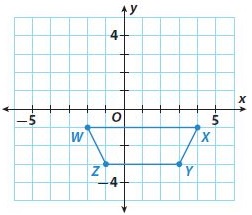
Answer: After translation: W'(-4, 3) X'(2, 3) Y'(1, 1) Z'(-3, 1)
ESSENTIAL QUESTION CHECK-IN
Question 6. What are the properties of translations? Type below: ____________
Answer: -> a translation is a geometric transformation that moves every point of a figure or space by the same amount in a given direction. -> So the figures are identical and are congruent.
9.1 Independent Practice – Properties of Translations – Page No. 283
Answer: 2 left, and 4 down
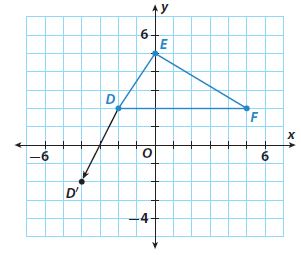
Question 7. b. How would you describe the translation? Type below: ____________
Answer: It has the same size, shape. and orientation, but a different location
Question 7. c. How does the image of triangle DEF compare with the preimage? ____________
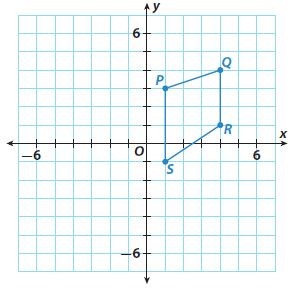
Question 8. b. On the same coordinate grid, graph the image of quadrilateral KLMN after a translation of 3 units to the right and 4 units up. Type below: ____________
Question 8. c. Which side of the image is congruent to side \(\overline { LM } \)? ___________ Name three other pairs of congruent sides. ___________ Type below: ____________
Answer: Line LM is congruent to Line L!M! Line KL is equal to K’L’ Line MN is equal to M’N’ Line KN is equal to K’N’
Draw the image of the figure after each translation.
Answer: After translation P'(-3, 1) Q'(0, 2) R'(0, -1) S'(-3, -3)
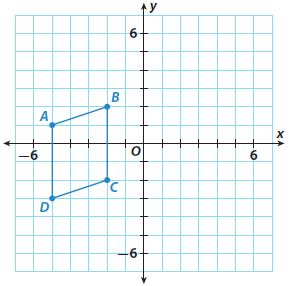
Answer: After translation A'(0, 4) B'(3, 5) C'(3, 1) D'(0, 0)
Properties of Translations – Page No. 284
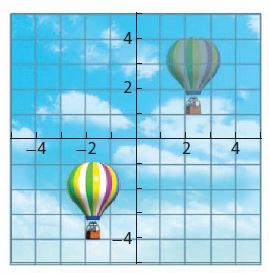
Answer: 4 units along positive X and 5 units along positive Y
Explanation: Initial coordinate of balloon = ( -2 , -4) Final coordinates of the balloon = (2,1) Translation along x axis = 2 – (-2) = 4 units along positive x direction Translation along y axis = 1-(-4) = 5 units along the positive y direction
Question 12. Critical Thinking Is it possible that the orientation of a figure could change after it is translated? Explain. _________
Answer: No, it is not possible to change the orientation just by translation. As translation means, a transformation in which a figure is moved to another location without any change in size or orientation.
FOCUS ON HIGHER ORDER THINKING
Question 13. b. On the same coordinate grid, graph and label triangle X’Y’Z’, the image of triangle XYZ after a translation of 3 units to the left and 6 units up.
Question 13. c. Now graph and label triangle X”Y”Z”, the image of triangle X’Y’Z’ after a translation of 1 unit to the left and 2 units down. Type below: ____________
Question 13. d. Analyze Relationships How would you describe the translation that maps triangle XYZ onto triangle X”Y”Z”? Type below: ____________
Answer: Triangle XYZ has translated 4 units up and 4 units to the left
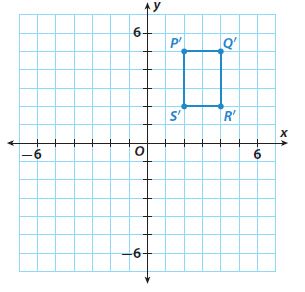
Question 15. Communicate Mathematical Ideas Explain why the image of a figure after a translation is congruent to its preimage. Type below: ____________
Answer: A translation is a geometric transformation that moves every point of a figure or space by the same amount in a given direction. So the 2 figures are identical and the translated figure is congruent to its pre-image.
Guided Practice – Properties of Reflections – Page No. 288
Question 1. Vocabulary A reflection is a transformation that flips a figure across a line called the __________ . ____________
Answer: Reflection Axis
Explanation: A reflection is a transformation that flips a figure across a line called the Reflection Axis.
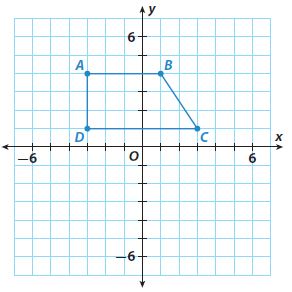
Answer: A'(-3, -4) B'(1, -4) C'(3, -1) D'(-3, -1)
Question 2. b. How do trapezoid ABCD and trapezoid A’B’C’D’ compare? ____________
Explanation: trapezoid ABCD and trapezoid A’B’C’D’ are congruent
Question 2. c. What If? Suppose you reflected trapezoid ABCD across the y-axis. How would the orientation of the image of the trapezoid compare with the orientation of the preimage? Type below: ____________
Answer: The orientation would be reversed horizontally.
Question 3. What are the properties of reflections? Type below: ____________
Answer: properties of reflections -> the size stays the same -> the shape stays the same -> the orientation does NOT stay the same
9.2 Independent Practice – Properties of Reflections – Page No. 289
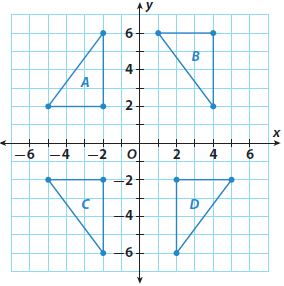
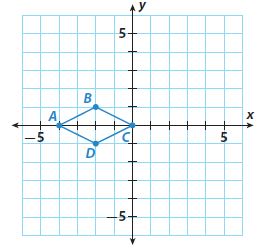
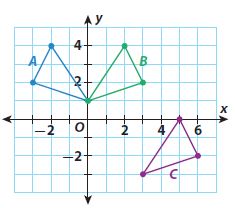
Question 4. Which two triangles are reflections of each other across the x-axis? Type below: ____________
Answer: Triangles A and C are the reflections of each other across the x-axis.
Question 5. For which two triangles is the line of reflection the y-axis? Type below: ____________
Answer: For triangle C & D the line of reflection is y-axis.
Question 6. Which triangle is a translation of triangle C? How would you describe the translation? Type below: ____________
Answer: Triangle B is the translation of triangle C. Lets take any one point of the triangle = (-2, -6) Lets take the corresponding side of triangle B = (4,2) Translation across x axis = 4 -(-2) = 6 units Translation across y axis = 2 -(-6) = 8 units
Question 7. Which triangles are congruent? How do you know? Type below: ____________
Answer: All the 4 triangles A, B, C, D are congruent. The length of base and height of all the four triangles are 3 units, 4 units respectively.
Explanation: All the 4 triangles A, B, C, D are congruent. If base and height are equal then the hypotenuse should also be equal. Thus all three sides of the triangles A,B,C,D are equal. Thus these triangles are congruent, The length of base and height of all the four triangles are 3 units, 4 units respectively.
Question 8. a. Graph quadrilateral WXYZ with vertices W(-2, -2), X(3, 1), Y(5, -1), and Z(4, -6) on the coordinate grid. Type below: ____________
Question 8. b. On the same coordinate grid, graph quadrilateral W’X’Y’Z’, the image of quadrilateral WXYZ after a reflection across the x-axis. Type below: ____________
Question 8. c. Which side of the image is congruent to side \(\overline { YZ } \)? _______________ Name three other pairs of congruent sides. _______________ Type below: ____________
Answer: Line YZ = Line Y’Z’ Line WX = Line W’X’ Line XY = Line X’Y’ Line WZ = Line W’Z’
Question 8. d. Which angle of the image is congruent to ∠X? _______________ Name three other pairs of congruent angles. _______________ Type below: ____________
Answer: Angle X’ Angle W and Angle W’ Angle Y and Angle Y’ Angle Z and Angle Z’
Properties of Reflections – Page No. 290
Question 9. Critical Thinking Is it possible that the image of a point after a reflection could be the same point as the preimage? Explain. ________
Answer: Yes
Explanation: It is possible that the image of a point after a reflection could be the same point as the preimage
Question 10. b. On the same coordinate grid, graph the image of the figure you drew in part a after a reflection across the x-axis. Type below: ____________
Question 10. c. Make a Conjecture What other sequence of transformations would produce the same final image from the original preimage? Check your answer by performing the transformations. Then make a conjecture that generalizes your findings. Type below: ____________
Answer: The same image can be obtained by reflecting first across the x-axis and then across the y-axis. Reflecting a figure first across the y-axis and then across the x-axis has the same outcome,. reflecting first across the x-axis and then across the y-axis.
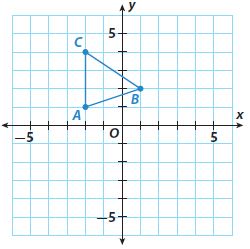
Question 11. a. Graph triangle DEF with vertices D(2, 6), E(5, 6), and F(5, 1) on the coordinate grid.
Question 11. b. Next graph triangle D ′E ′F ′, the image of triangle DEF after a reflection across the y-axis. Type below: ____________
Question 11. c. On the same coordinate grid, graph triangle D′′ E′′ F′′, the image of triangle D ′E ′F ′ after a translation of 7 units down and 2 units to the right. Type below: ____________
Question 11. d. Analyze Relationships Find a different sequence of transformations that will transform triangle DEF to triangle D ′′E ′′F ′′. Type below: ____________
Answer: Translate triangle DEF 7 units down and 2 units to the left. Then reflect the image across the y-axis.
Guided Practice – Properties of Reflections – Page No. 294
Question 1. Vocabulary A rotation is a transformation that turns a figure around a given _____ called the center of rotation. ____________
Answer: point
Explanation: A rotation is a transformation that turns a figure around a given point called the center of rotation.
Siobhan rotates a right triangle 90° counterclockwise about the origin.
Question 2. How does the orientation of the image of the triangle compare with the orientation of the preimage? Type below: ____________
Answer: Each leg in the preimage is perpendicular to its corresponding leg in the image.
Question 3. Is the image of the triangle congruent to the preimage? ______
Explanation: The image of the triangle is congruent to the preimage
Draw the image of the figure after the given rotation about the origin.
Answer: After 180° rotation A'(-2, -3) B'(-4, -1) C'(-2, 0) D'(0, -1)
Question 6. What are the properties of rotations? Type below: ____________
Answer: Rotations preserve size and shape but change orientation.
9.3 Independent Practice – Properties of Reflections – Page No. 295
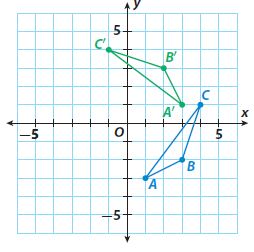
Answer: ABC was rotated 90º counterclockwise about the origin
Question 7. b. What are the coordinates of the image? Type below: ____________
Answer: A'(3, 1) B'(2, 3) C'(-1, 4)
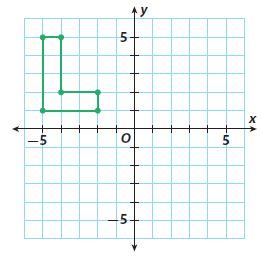
Answer: The figure was rotated 180º about the origin.
Question 8. b. Can you describe this as a transformation other than a rotation? Explain. ____________
Explanation: This can also be described as a reflection across the y-axis.
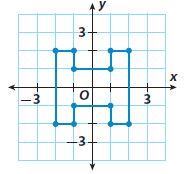
Answer: A 180º rotation about the origin will preserve the orientation of the H-shaped figure in the grid.
Question 10. A point with coordinates (-2, -3) is rotated 90° clockwise about the origin. What are the coordinates of its image? (_______ , _______)
Answer: (-3, 2)
Explanation: The new coordinates are (-3, 2)
Complete the table with rotations of 180° or 90°. Include the direction of rotation for rotations of 90°.
Properties of Reflections – Page No. 296
Answer: After 180° A'(4, 0) B'(2, -1) C'(0, 0) D'(2, 1)
Answer: After 270º counterclockwise rotation A'(1, 2) B'(2, -1) C'(4, 2)
Question 16. Is there a rotation for which the orientation of the image is always the same as that of the preimage? If so, what? ______
Explanation: A 360º rotation will always be the same as the original image
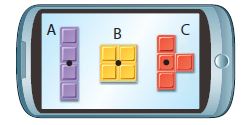
Answer: Figure A: 2 time(s) Figure B: 1 time(s) Figure C: 4 time(s)
Explanation: 2 times to return to original orientation 1 time to return to original orientation 4 times to return to original orientation
Question 18. Make a Conjecture Triangle ABC is reflected across the y-axis to form the image A′B′C′. Triangle A′B′C′ is then reflected across the x-axis to form the image A″B″C″. What type of rotation can be used to describe the relationship between triangle A″B″C″ and triangle ABC? Type below: ____________
Answer: Triangle A’B’C’ is a 90º rotation of triangle ABC Triangle A”B”C” is a 90º rotation of triangle A’B’C’ Therefore, Triangle A”B”C” is a 180º rotation of triangle ABC
Question 19. Communicate Mathematical Ideas Point A is on the y-axis. Describe all possible locations of image A′ for rotations of 90°, 180°, and 270°. Include the origin as a possible location for A. Type below: ____________
Answer: If Point A is on the y-axis, Point A’ will be on the x-axis for 190° and 270° rotations and on the y-axis for 180° rotation If point A is at the origin, A’ is at the origin for any rotation about the origin.
Guided Practice – Algebraic Representations of Transformations – Page No. 300
Answer: After a translation of 6 units to the right: X'(3, -2) Y'(5, 0) Z'(7, -6)
Question 2. Describe what happens to the x- and y-coordinates after a point is reflected across the x-axis. Type below: ____________
Answer: The x-coordinate remains the same, while the sign of the y-coordinate changes
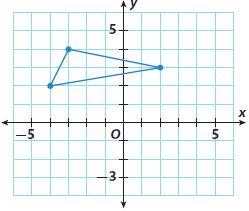
Answer: The triangle is rotated 90º clockwise about the origin
Question 4. How do the x- and y-coordinates change when a figure is translated right a units and down b units? Type below: ____________
Answer: The x-coordinates increase by a, and the y-coordinates decrease by b
9.4 Independent Practice – Algebraic Representations of Transformations – Page No. 301
Write an algebraic rule to describe each transformation.Then describe the transformation.
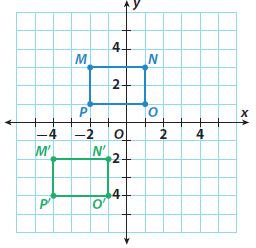
Answer: algebraic rule (x, y) -> (x-2, y-5) transformation translation of 2 units to the left and 5 units down new coordinates M'(-4, -2) N'(-2, -2) O'(-1, -4) P'(-4, -4)
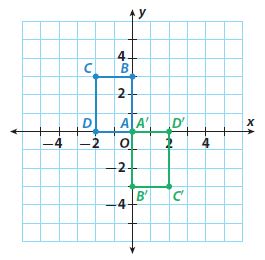
Answer: algebraic rule (x, y) -> (-x, -y) transformation rotation of 180º new coordinates A'(0, 0) B'(0, -3) C'(2, -3) D'(2, 0)
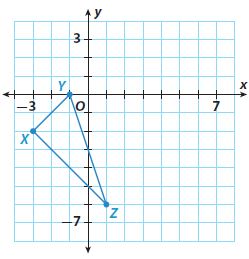
Question 7. Triangle XYZ has vertices X(6, -2.3), Y(7.5, 5), and Z(8, 4). When translated, X′ has coordinates (2.8, -1.3). Write a rule to describe this transformation. Then find the coordinates of Y′ and Z′. Type below: ____________
Answer: algebraic rule (x, y) -> (x-3.2, y+1) new coordinates Y'(4.3, 6) Z'(4.8, 5)
Question 8. Point L has coordinates (3, -5). The coordinates of point L′ after a reflection are (-3, -5). Without graphing, tell which axis point L was reflected across. Explain your answer. ____________
Answer: Point L was reflected on the y-axis. When you reflect a point across the y-axis, the sign of the x-coordinate changes, and the sign of the y-coordinate remains the same
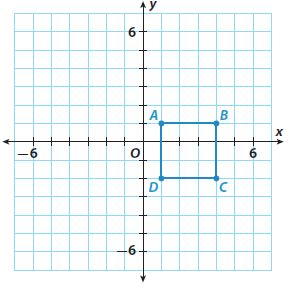
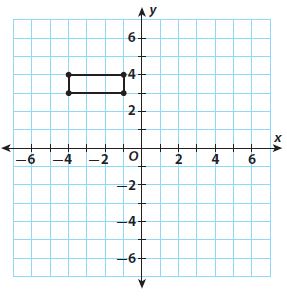
Answer: The rectangle is translated 2 units to the left and 4 units down
Question 10. Parallelogram ABCD has vertices A(−2, −5\(\frac{1}{2}\)), B(−4, −5\(\frac{1}{2}\)),C(-3, -2), and D(-1, -2). Find the vertices of parallelogram A′B′C′D′ after a translation of 2 \(\frac{1}{2}\) units down. Type below: __________
Answer: after a translation of 2 \(\frac{1}{2}\) units A'(-2, -8) B'(-4, -8) C'(-3, -4 \(\frac{1}{2}\)) D'(-1, -4 \(\frac{1}{2}\))
Algebraic Representations of Transformations – Page No. 302
Answer: (x,y) –> (x+1,y-0.5) (x+1,y-0.5) –> (x+0.5,y-0.25)
Explanation: translation in units (x,y) –> (x+1,y-0.5) This step converts translation rule in units to translation rule in inches. (Divide by 2 since graph paper is half inch paper. (x+1,y-0.5) –> (x+0.5,y-0.25)
Question 12. Kite KLMN has vertices at K(1, 3), L(2, 4), M(3, 3), and N(2, 0). After the kite is rotated, K′ has coordinates (-3, 1). Describe the rotation, and include a rule in your description. Then find the coordinates of L′, M′, and N′. Type below: __________
Answer: rotation 90 counterclockwise rule (x, y) -> (-y, x) new coordinates L'(-4, 2) M'(-3, 3) N'(0, 2)
Answer: (-5, 5) has the same coordinates
Question 13. b. What is the equation of a line through the origin and this point? Type below: __________
Answer: x and y are equal so switching x and y has no effect on the coordinates
Question 13. c. Describe the transformation of the triangle. Type below: __________
Question 14. Critical Thinking Mitchell says the point (0, 0) does not change when reflected across the x- or y-axis or when rotated about the origin. Do you agree with Mitchell? Explain why or why not. _______
Answer: Yes, I agree with Mitchell
Explanation: Reflecting across the x-axis or y-axis changes the sign of the y or x coordinate 0 cannot change signs. Rotating about the origin does not change the origin (0, 0)
Question 15. Analyze Relationships Triangle ABC with vertices A(-2, -2), B(-3, 1), and C(1, 1) is translated by (x, y) → (x – 1, y + 3). Then the image, triangle A′B′C′, is translated by (x, y) → (x + 4, y – 1), resulting in A″B″C″. a. Find the coordinates for the vertices of triangle A″B″C″. Type below: __________
Answer: A”(-2-1+4, -2+3-1) = A”(1, 0) B”(-3-1+4, 1+3-1) = B”(0, 3) C”(1-1+4, 1+3-1) = C”(4, 3)
Question 15. b. Write a rule for one translation that maps triangle ABC to triangle A″B″C″. Type below: __________
Answer: (x, y) -> (x-1+4, y+3-1) (x, y) -> (x+3, y+2)
Guided Practice – Congruent Figures – Page No. 306
Answer: A. After transformation (1, 3) (1, 4) (4, 4) (4, 3) B. After transformation (3, -1) (4, -1) (4, -4) (3, -4) C. After transformation (1, -1) (2, -1) (2, -4) (1, -4) D. After transformation (1, 1) (1, 2) (4, 2) (4, 1) E. After transformation (-6, -1) (-6, 0) (-3, 0) (-3, -1)
Question 2. What transformation is used to transform figure A into figure B? Type below: __________
Answer: Reflection across the y-axis
Explanation: Reflection across the y-axis is used to transform figure A into figure B
Question 3. What transformation is used to transform figure B into figure C? Type below: __________
Answer: Translation 3 units right and 4 units down
Explanation: Translation 3 units right and 4 units down is used to transform figure B into figure C
Question 4. What sequence of transformations is used to transform figure A into figure C? Express the transformations algebraically. Type below: __________
Answer: Reflection across the y-axis is used to transform figure A into figure B Translation 3 units right and 4 units down is used to transform figure B into figure C Algebraically: (x, y) -> (-x, y) (x, y) -> (x +3, y-4)
Question 5. Vocabulary What does it mean for two figures to be congruent? Type below: __________
Answer: Two figures are congruent when the figures have the same size and the same shape.
Question 6. After a sequence of translations, reflections, and rotations, what is true about the first figure and the final figure? Type below: __________
Answer: After a sequence of translations, reflections, and rotations, the first and final figures have the same size and shape. (They are congruent)
9.5 Independent Practice – Congruent Figures – Page No. 307
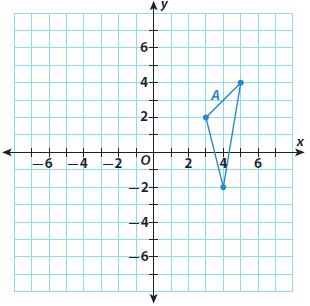
For each given figure A, graph figures B and C using the given sequence of transformations. State whether figures A and C have the same or different orientation.
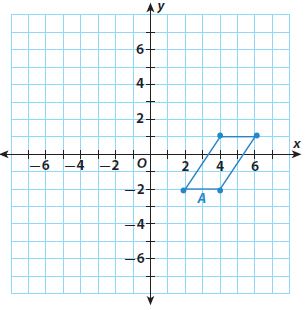
Answer: Different orientation
Congruent Figures – Page No. 308
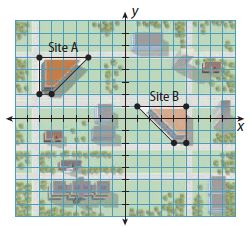
Answer: From Site A to Site B: Translation 2 units right and 4 units down The size did NOT change The orientation changed
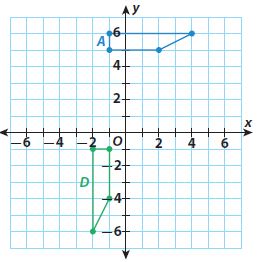
Answer: From figure A to D: Reflection across the x-axis (-1, -5) (-1, -6) (2, -5) (4, -6) 90º clockwise rotation (4, -1) (5, -1) (5, -4) (4, -6) translation 6 units left (4, -1) (5, -1) (5, -4) (4, -6)
Question 13. Counterexamples The Commutative Properties for Addition and Multiplication state that the order of two numbers being added or multiplied does not change the sum or product. Are translations and rotations commutative? If not, give a counterexample. ________
Answer: No, Translation and rotations are not commutative
Explanation: The point (2, 2) becomes (2, -4) when translated 2 units to the right then rotated 90 around the origin. The point (2, 2) becomes (4, -2) when rotated 90 around the origin then translated 2 units to the right. The above two points are not the same.
Question 14. Multiple Representations For each representation, describe a possible sequence of transformations. a. (x, y) → (-x – 2, y + 1) Type below: ____________
Answer: translation 2 units right and 1 unit up reflection across y-axis
Question 14. b. (x, y) → (y, -x – 3) Type below: ____________
Answer: rotation 90º clockwise around the origin translation 3 units down
Ready to Go On? – Model Quiz – Page No. 309
9.1–9.3 Properties of Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
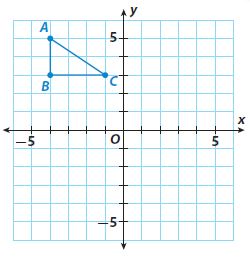
Answer: After translation: A'(2, 1) B'(2, -1) C'(5, -1)
Question 2. On the same coordinate grid, graph the image of triangle ABC after a reflection across the x-axis. Label the vertices of the image A”, B”, and C”. Type below: ____________
Answer: After reflection: A”(-4, -5) B”(-4, -3) C”(-1, -3)
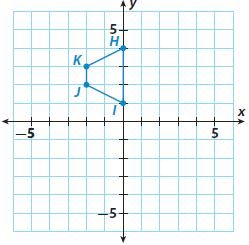
Answer: After rotation: H'(0, -4) I'(0, -1) J'(2, -2) K'(2, -3)
9.4 Algebraic Representations of Transformations
Question 4. A triangle has vertices at (2, 3), (−2, 2), and (−3, 5). What are the coordinates of the vertices of the image after the translation (x, y) → (x + 4, y − 3)? Type below: ____________
Answer: After translation: (6, 0) (2, -1) (1, 2)
9.5 Congruent Figures
Question 5. Vocabulary Translations, reflections, and rotations produce a figure that is _____ to the original figure. Type below: ____________
Explanation: Vocabulary Translations, reflections, and rotations produce a figure that is congruent to the original figure.
Question 6. Use the coordinate grid for Exercise 3. Reflect H’I’J’K’ over the y-axis, then rotate it 180° about the origin. Label the new figure H″I″J″K″. Type below: ____________
Answer: after reflection H'(0, -4) I'(0, -1) J'(-2, -2) K'(-2, -3) after rotation H”(0, 4) I”(0, 1) J”(2, 2) K”(2, 3)
ESSENTIAL QUESTION
Question 7. How can you use transformations to solve real-world problems? Type below: ____________
Answer: Transformational properties allow the systematic movement of congruent figures while maintaining or adjusting their orientation.
Selected Response – Mixed Review – Page No. 310
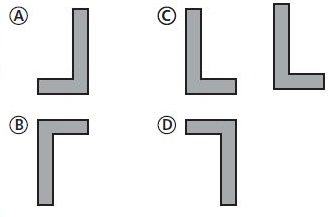
Answer: c. C
Explanation: After a translation of 8 units right and 3 units up, the orientation of figure L stays the same.
Question 2. Figure A is reflected over the y-axis and then lowered 6 units. Which sequence describes these transformations? Options: a. (x, y) -> (x, -y) and (x, y) -> (x, y – 6) b. (x, y) -> (-x, y) and (x, y) -> (x, y – 6) c. (x, y) -> (x, -y) and (x, y) -> (x – 6, y) d. (x, y) -> (-x, y) and (x, y) -> (x – 6, y)
Answer: b. (x, y) -> (-x, y) and (x, y) -> (x, y – 6)
Explanation: reflection over y-axis: (x, y) -> (-x, y) Translation 6 units down (x, y) -> (x, y-6)
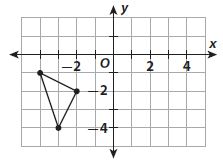
Answer: d. IV
Explanation: After a rotation of 90° counterclockwise about the origin, the triangle will be in QIV
Question 4. Which rational number is greater than −3 \(\frac{1}{3}\) but less than −\(\frac{4}{5}\)? Options: a. −0.4 b. −\(\frac{9}{7}\) c. −0.19 d. −\(\frac{22}{5}\)
Answer: b. −\(\frac{9}{7}\)
Question 5. Which of the following is not true of a trapezoid that has been reflected across the x-axis? Options: a. The new trapezoid is the same size as the original trapezoid. b. The new trapezoid is the same shape as the original trapezoid. c. The new trapezoid is in the same orientation as the original trapezoid. d. The x-coordinates of the new trapezoid are the same as the x-coordinates of the original trapezoid.
Answer: d. The x-coordinates of the new trapezoid are the same as the x-coordinates of the original trapezoid.
Explanation: The x-coordinates of the new trapezoid are the same as the x-coordinates of the original trapezoid.
Question 6. A triangle with coordinates (6, 4), (2, −1), and (−3, 5) is translated 4 units left and rotated 180° about the origin. What are the coordinates of its image? Options: a. (2, 4), (-2, -1), (-7, 5) b. (4, 6), (-1, 2), (5, -3) c. (4, -2), (-1, 2), (5, 7) d. (-2, -4), (2, 1), (7, -5)
Answer: d. (-2, -4), (2, 1), (7, -5)
Question 7. A rectangle with vertices (3, -2), (3, -4), (7, -2), (7, -4) is reflected across the x-axis and then rotated 90° counterclockwise. a. In what quadrant does the image lie? ____________
Answer: After reflection and rotation, the image lies in QII
Question 7. b. What are the vertices of the image? Type below: ____________
Answer: image vertices (-2, 3) (-4, 3) (-2, 7) (-4, 7)
Question 7. c. What other transformations produce the same image? Type below: ____________
Answer: A reflection across the y-axis and 90º clockwise rotation will produce the same result.
Conclusion:
The Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 9 Transformations and Congruence pdf are available both online and offline. We have provided in pdf format so that students can practice the problems offline. We know that maths is the scoring and also typical among all the subjects. But you can make it easy if you understand the concept of the chapter. Students can refer to the Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key in their convenient way. Practice well and make maths your favorite subject. Best of Luck!!!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Lesson 2 Problem-Solving Practice Relations 1. MONEY The Happy Place charges $30 per hour for parties. Make a table of ordered pairs in which the x-coordinate represents the hours and the y-coordinate represents the total cost for 2, 3, 4, and 5 hours. xy 2. Graph the ordered pairs from Exercise 1 and state the domain and range. 0 40 60 100 140 ...
Lesson 2 Skills Practice Reflections Graph each figure and its reflection over the indicated axis. Write an algebraic representation that explains the effect of the reflection. Then determine the coordinates of the reflected image. 1. triangle ABC with vertices A(-3, 4), B(1, 4), and C(3, 1) over the x-axis 2.
Lesson 2 Problem-Solving Practice Theoretical and Experimental Probability HOBBIES For Exercises 1-4, use the 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Singing Hanging with friends Building things Bike riding T.V. Computer Roller skating Sports What is your favorite hobby? 1 3 1 2 3 3 3 8 Number of Students graph of a survey of 24 seventh-grade students asked to ...
2. Yes. Possible answer: If the figure was moved along the vector 4, 3 , then moved along the vector − 2, 5 , they could be combined to create the vector. 4 − 2, 3 + 5 or 2, 8 . 3. The image can be translated down and left the same distance by subtracting the values instead of adding them.
Reflections Activity—Answer Key Part I. Exploring Reflections Reflect the figure across the line identified in each problem using your reflection tool. Record the coordinates of each new figure. Tip: It may be helpful to re-draw the line of reflection on the coordinate graph and label each new point in a different color. After you have ...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to enVision Geometry - 9780328931583, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Reflections. Section 3-2: Translations. Section 3-3: Rotations. Section 3-4: Classification of Rigid Motions. Section 3-5: Symmetry. Page 143: Topic Review. ... Practice and Problem Solving.
Properties of Reflections Practice and Problem Solving: A/B Use the graph for Exercises 1-3. 1. Quadrilateral J is reflected across the x-axis. What is the image of the reflection? _____ 2. Which two quadrilaterals are reflections of each other across the y-axis? _____ 3. How are quadrilaterals H and J related? _____ Draw the image of the ...
Our resource for enVisionmath 2.0: Grade 8, Volume 2 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers ...
Reflections . Practice and Problem Solving: A/B . In Exercises 1-3: a) Find the coordinates of the image of ABC. after a reflection over the given line b)Graph ... LESSON . 2-2 . 3 . For 8 - 11 Determine whether the coordinate plane shows a reflection in the . xaxis-, y-axis, or . neither.
Exercise 1. Exercise 2. Exercise 3. Exercise 4. Exercise 5. Exercise 6. Exercise 7. Exercise 8. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Algebra 2 Practice and Problem Solving Workbook - 9780133688894, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.
a reflection across the y-axis. Draw the image of the given figure after the two transformations. 4. Translate 8 units right and 1 unit up. 5. Reflect across the y-axis. Reflect across the x-axis. Translate 2 units left and 5 units up. 3.
Edit lesson 2 2 reflections practice and problem solving a b answer key form. Add and change text, add new objects, move pages, add watermarks and page numbers, and more. Then click Done when you're done editing and go to the Documents tab to merge or split the file. If you want to lock or unlock the file, click the lock or unlock button.
everyday world.The materials are organized by chapter and lesson, with one Skills Practice worksheet for every lesson in Glencoe Math Connects, Course 2. ... 2-7 Problem-Solving Investigation: Look for a Pattern .....17 2-8 Dividing Integers ... 10-10 Reflections.....85 CONTENTS 00i-0iv_FM-881053 1/14/08 5:09 PM Page iii epg ju104:MHGL149:Quark ...
Title : Math Connects: Concepts, Skills, and Problem Solving Course 3 Publisher : Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Grade : 8 ISBN : 78740509 ISBN-13 : 9780078740503
Problem 14: Ima Primpin uses a cosmetic mirror to magnify her eyelashes during the traditional morning painting session. Her 1.2-cm long eyelashes are magnified to 1.6 cm when placed 5.8 cm from the mirror. a. Determine the image distance for such an upright image. b. Determine the focal length of the mirror.
001_009_CRM01_881031. Use the four-step plan to solve each problem. 1. GEOGRAPHY. The president is going on a campaign trip to California, first. flying about 2,840 miles from Washington, D.C., to San Francisco and. then another 390 to Los Angeles before returning the 2,650 miles back to.
2.10 A Problem Solving Model . Section One: My Resources . Resource . Check One ... Go to page 10 of Lesson 2.10. Choose the problem you will solve, by selecting one of the scenarios on page 10 or by thinking of a real problem you have faced or are now facing. ... ask and answer important questions. Look for causes and related problems or ...
Title: 099_114_CC_A_RSPC3_C07_662332.indd Author: ntv Created Date: 7/28/2011 8:01:16 AM
Practice and Problem Solving: A/B ... Use principles of rotations to answer Problems 6-8. 6. What clockwise rotation produces the same image as a counterclockwise rotation of 220°? _____° clockwise 7. Tony Hawk was the first skateboarder to do a "900," a rotation of 900°. ... LESSON 2-3 Practice and Problem Solving: A/B
The lesson 2 2 reflections practice and problem solving a b isn't an exception. Handling it utilizing electronic tools differs from doing this in the physical world. ... Use airSlate SignNow to electronically sign and share Lesson 2 2 Reflections Answer Key for collecting e-signatures. be ready to get more. Create this form in 5 minutes or ...
Write this amount in exponential form. 3. VOLUME To find the volume of a rectangular box you multiply the length times the width times the height. In a cube all sides are the same length. If the cube has length, width, and height of 6 inches, write the volume as a product. Then write it in exponential form. 4.
P. 12 - L2 P.P. Key 2 3x 1 2 5x 1 10 6x 2 10x 2 1035S)olve for x: 2 3x-1 -2 -5x+1 =10. Express your answer as a fraction. 7 36) The total cost, t, in dollars, for c children to attend a camp is estimated by the equation t = 650c + 5,600. If $20,000 is available to pay for children to attend the
Therefore, students who want to score good marks in the exam must practice with Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 9 Transformations and Congruence. Lesson 1: Properties of Translations. Lesson 2: Properties of Reflections. Lesson 3: Algebraic Representations of Transformations.