Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State

Research Questions & Hypotheses
Generally, in quantitative studies, reviewers expect hypotheses rather than research questions. However, both research questions and hypotheses serve different purposes and can be beneficial when used together.
Research Questions
Clarify the research’s aim (farrugia et al., 2010).
- Research often begins with an interest in a topic, but a deep understanding of the subject is crucial to formulate an appropriate research question.
- Descriptive: “What factors most influence the academic achievement of senior high school students?”
- Comparative: “What is the performance difference between teaching methods A and B?”
- Relationship-based: “What is the relationship between self-efficacy and academic achievement?”
- Increasing knowledge about a subject can be achieved through systematic literature reviews, in-depth interviews with patients (and proxies), focus groups, and consultations with field experts.
- Some funding bodies, like the Canadian Institute for Health Research, recommend conducting a systematic review or a pilot study before seeking grants for full trials.
- The presence of multiple research questions in a study can complicate the design, statistical analysis, and feasibility.
- It’s advisable to focus on a single primary research question for the study.
- The primary question, clearly stated at the end of a grant proposal’s introduction, usually specifies the study population, intervention, and other relevant factors.
- The FINER criteria underscore aspects that can enhance the chances of a successful research project, including specifying the population of interest, aligning with scientific and public interest, clinical relevance, and contribution to the field, while complying with ethical and national research standards.
- The P ICOT approach is crucial in developing the study’s framework and protocol, influencing inclusion and exclusion criteria and identifying patient groups for inclusion.
- Defining the specific population, intervention, comparator, and outcome helps in selecting the right outcome measurement tool.
- The more precise the population definition and stricter the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the more significant the impact on the interpretation, applicability, and generalizability of the research findings.
- A restricted study population enhances internal validity but may limit the study’s external validity and generalizability to clinical practice.
- A broadly defined study population may better reflect clinical practice but could increase bias and reduce internal validity.
- An inadequately formulated research question can negatively impact study design, potentially leading to ineffective outcomes and affecting publication prospects.
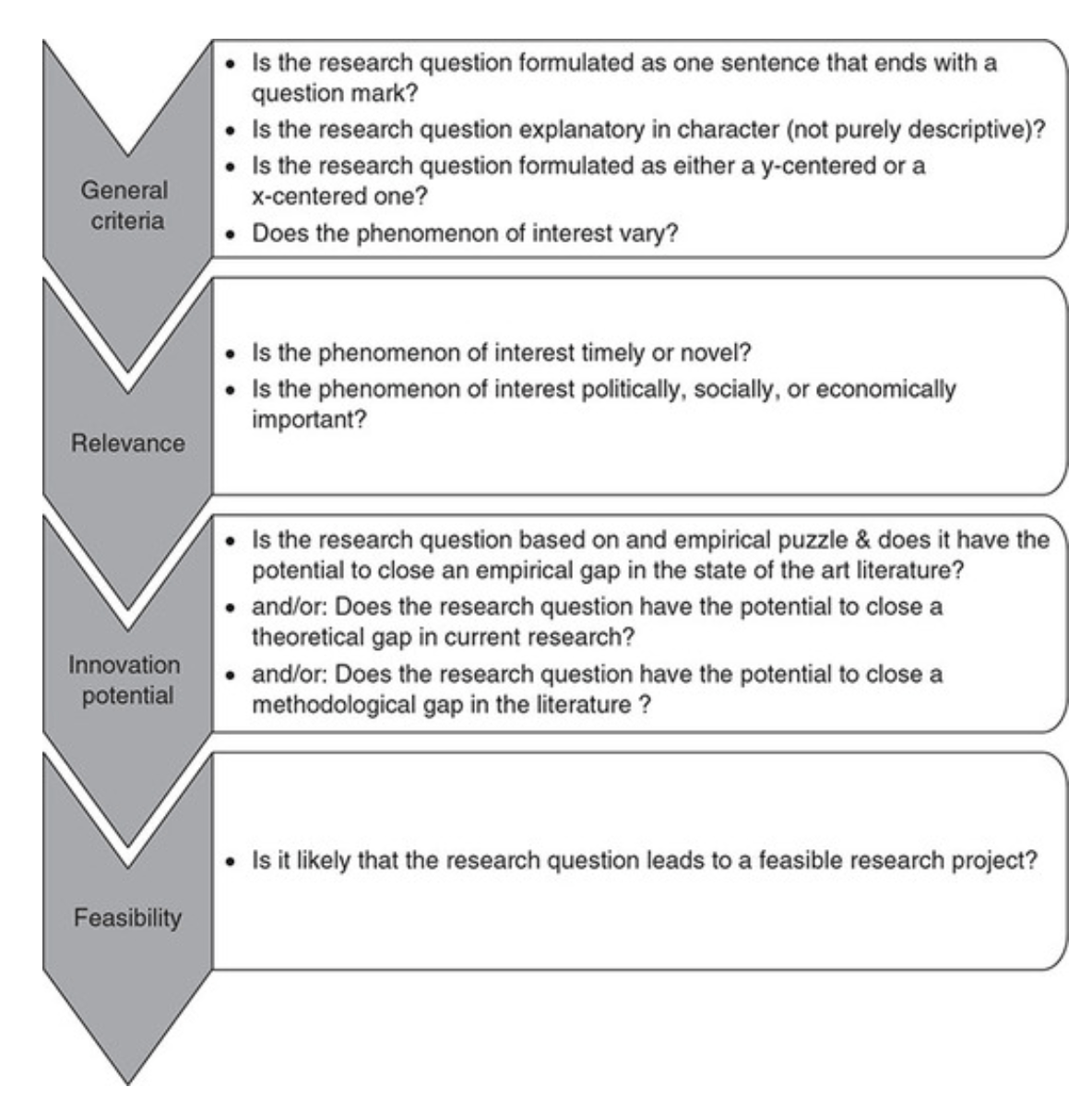
Checklist: Good research questions for social science projects (Panke, 2018)
Research Hypotheses
Present the researcher’s predictions based on specific statements.
- These statements define the research problem or issue and indicate the direction of the researcher’s predictions.
- Formulating the research question and hypothesis from existing data (e.g., a database) can lead to multiple statistical comparisons and potentially spurious findings due to chance.
- The research or clinical hypothesis, derived from the research question, shapes the study’s key elements: sampling strategy, intervention, comparison, and outcome variables.
- Hypotheses can express a single outcome or multiple outcomes.
- After statistical testing, the null hypothesis is either rejected or not rejected based on whether the study’s findings are statistically significant.
- Hypothesis testing helps determine if observed findings are due to true differences and not chance.
- Hypotheses can be 1-sided (specific direction of difference) or 2-sided (presence of a difference without specifying direction).
- 2-sided hypotheses are generally preferred unless there’s a strong justification for a 1-sided hypothesis.
- A solid research hypothesis, informed by a good research question, influences the research design and paves the way for defining clear research objectives.
Types of Research Hypothesis
- In a Y-centered research design, the focus is on the dependent variable (DV) which is specified in the research question. Theories are then used to identify independent variables (IV) and explain their causal relationship with the DV.
- Example: “An increase in teacher-led instructional time (IV) is likely to improve student reading comprehension scores (DV), because extensive guided practice under expert supervision enhances learning retention and skill mastery.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: The dependent variable (student reading comprehension scores) is the focus, and the hypothesis explores how changes in the independent variable (teacher-led instructional time) affect it.
- In X-centered research designs, the independent variable is specified in the research question. Theories are used to determine potential dependent variables and the causal mechanisms at play.
- Example: “Implementing technology-based learning tools (IV) is likely to enhance student engagement in the classroom (DV), because interactive and multimedia content increases student interest and participation.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: The independent variable (technology-based learning tools) is the focus, with the hypothesis exploring its impact on a potential dependent variable (student engagement).
- Probabilistic hypotheses suggest that changes in the independent variable are likely to lead to changes in the dependent variable in a predictable manner, but not with absolute certainty.
- Example: “The more teachers engage in professional development programs (IV), the more their teaching effectiveness (DV) is likely to improve, because continuous training updates pedagogical skills and knowledge.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: This hypothesis implies a probable relationship between the extent of professional development (IV) and teaching effectiveness (DV).
- Deterministic hypotheses state that a specific change in the independent variable will lead to a specific change in the dependent variable, implying a more direct and certain relationship.
- Example: “If the school curriculum changes from traditional lecture-based methods to project-based learning (IV), then student collaboration skills (DV) are expected to improve because project-based learning inherently requires teamwork and peer interaction.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: This hypothesis presumes a direct and definite outcome (improvement in collaboration skills) resulting from a specific change in the teaching method.
- Example : “Students who identify as visual learners will score higher on tests that are presented in a visually rich format compared to tests presented in a text-only format.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis aims to describe the potential difference in test scores between visual learners taking visually rich tests and text-only tests, without implying a direct cause-and-effect relationship.
- Example : “Teaching method A will improve student performance more than method B.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis compares the effectiveness of two different teaching methods, suggesting that one will lead to better student performance than the other. It implies a direct comparison but does not necessarily establish a causal mechanism.
- Example : “Students with higher self-efficacy will show higher levels of academic achievement.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis predicts a relationship between the variable of self-efficacy and academic achievement. Unlike a causal hypothesis, it does not necessarily suggest that one variable causes changes in the other, but rather that they are related in some way.
Tips for developing research questions and hypotheses for research studies
- Perform a systematic literature review (if one has not been done) to increase knowledge and familiarity with the topic and to assist with research development.
- Learn about current trends and technological advances on the topic.
- Seek careful input from experts, mentors, colleagues, and collaborators to refine your research question as this will aid in developing the research question and guide the research study.
- Use the FINER criteria in the development of the research question.
- Ensure that the research question follows PICOT format.
- Develop a research hypothesis from the research question.
- Ensure that the research question and objectives are answerable, feasible, and clinically relevant.
If your research hypotheses are derived from your research questions, particularly when multiple hypotheses address a single question, it’s recommended to use both research questions and hypotheses. However, if this isn’t the case, using hypotheses over research questions is advised. It’s important to note these are general guidelines, not strict rules. If you opt not to use hypotheses, consult with your supervisor for the best approach.
Farrugia, P., Petrisor, B. A., Farrokhyar, F., & Bhandari, M. (2010). Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Canadian journal of surgery. Journal canadien de chirurgie , 53 (4), 278–281.
Hulley, S. B., Cummings, S. R., Browner, W. S., Grady, D., & Newman, T. B. (2007). Designing clinical research. Philadelphia.
Panke, D. (2018). Research design & method selection: Making good choices in the social sciences. Research Design & Method Selection , 1-368.

Home » Education » Difference Between Hypothesis and Research Question
Difference Between Hypothesis and Research Question
Main difference – hypothesis vs research question.
Research question and hypothesis are the foundations of a research study. Formulating the research question or developing the hypothesis can help you to decide on the approach of the research. A research question is the question the research study sets out to answer. Hypothesis is the statement the research study sets out to prove or disprove. The main difference between hypothesis and research question is that hypothesis is predictive in nature whereas research question is inquisitive in nature.
In this article, we’ll discuss,
1. What is a Hypothesis? – Meaning, Features, Characteristics, and Usage
2. What is a Research Question? – Meaning, Features, Characteristics, and Usage

What is a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It can be described as an educated guess about what happens in an experiment. Researchers usually tend to use hypotheses when significant knowledge is already available on the subject. The hypothesis is based on this existing knowledge. After the hypothesis is developed, the researcher can develop data, analyze and use them to support or negate the hypothesis.
Not all studies have hypotheses. They are usually used in experimental quantitative research studies. They are useful in testing a specific theory or model. A complete hypothesis always includes the variables, population and the predicted relationship between the variables. The main disadvantage of hypotheses is that their tendency to blind a researcher to unexpected results.

What is a Research Question
A research question is the question a research study sets to answer. However, a research study can have more than one research question. The research methodologies , tools used to collect data, etc. all depend on the research question.
Research questions are often used in qualitative research, which seek to answer open-ended questions . But they can also be used in quantitative studies. Research questions can be used instead of hypotheses when there is little previous research on the subject. Research questions allow the researcher to conduct more open-ended queries, and a wide range of results can be reported.
A properly constructed research question should always be clear and concise. It should include the variables, population and the topic being studied.
Hypothesis is a tentative prediction about the relationship between two or more variables.
Research Question is the question a research study sets to answer.
Hypothesis is predictive in nature.
Research Question is inquisitive in nature.
Existing Research
Hypothesis can be used if there is significant knowledge or previous research on this subject.
Research Question can be used if there is little previous research on the subject.
Quantitative vs Qualitative
Hypothesis is mainly used in experimental quantitative studies.
Research Question can be used in both quantitative and qualitative studies.
Hypothesis doesn’t allow a wide range of outcomes.
Research Question allows a wide range of outcomes.
Image Courtesy:
“Research: Mediterranean Center of Medical Sciences” by McmScience Mediterranean Center of Medical Sciences (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Question Vs Hypothesis
Research Question Vs Hypothesis
Table of Contents

Research questions and hypotheses are both important elements of a research study, but they serve different purposes.
Research Question
A Research Question is a clear, concise, and specific question that a researcher asks to guide their study. Research questions are used to define the scope of the research project and to guide the collection and analysis of data. Research questions are often used in exploratory or descriptive studies, and they are open-ended in nature. Research questions should be answerable through data collection and analysis and should be linked to the research objectives or goals of the study.
A Hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between two or more variables in a research study. Hypotheses are used in studies that aim to test cause-and-effect relationships between variables. A hypothesis is a tentative explanation for an observed phenomenon, and it is often derived from existing theory or previous research. Hypotheses are typically expressed as an “if-then” statement, where the “if” part refers to the independent variable, and the “then” part refers to the dependent variable. Hypotheses can be either directional (predicting the direction of the relationship between variables) or non-directional (predicting the presence of a relationship without specifying its direction).
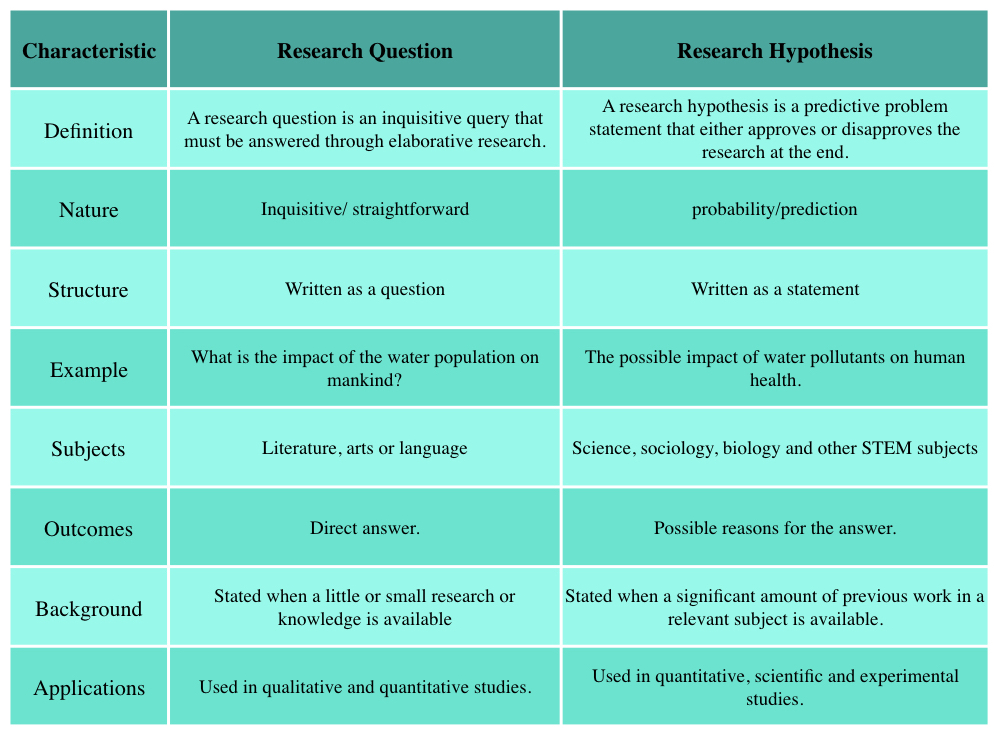
Difference Between Research Question and Hypothesis
Here are some key differences between research questions and hypotheses:
Both Research Questions and Hypotheses are essential elements of a research study, but they serve different purposes. Research questions guide the study and help researchers define its scope, while hypotheses are used to test specific cause-and-effect relationships between variables. The choice of which to use depends on the nature of the research question, the study design, and the research objectives.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Inductive Vs Deductive Research

Exploratory Vs Explanatory Research

Basic Vs Applied Research

Generative Vs Evaluative Research

Reliability Vs Validity

Longitudinal Vs Cross-Sectional Research
Sciencing_Icons_Science SCIENCE
Sciencing_icons_biology biology, sciencing_icons_cells cells, sciencing_icons_molecular molecular, sciencing_icons_microorganisms microorganisms, sciencing_icons_genetics genetics, sciencing_icons_human body human body, sciencing_icons_ecology ecology, sciencing_icons_chemistry chemistry, sciencing_icons_atomic & molecular structure atomic & molecular structure, sciencing_icons_bonds bonds, sciencing_icons_reactions reactions, sciencing_icons_stoichiometry stoichiometry, sciencing_icons_solutions solutions, sciencing_icons_acids & bases acids & bases, sciencing_icons_thermodynamics thermodynamics, sciencing_icons_organic chemistry organic chemistry, sciencing_icons_physics physics, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-physics fundamentals, sciencing_icons_electronics electronics, sciencing_icons_waves waves, sciencing_icons_energy energy, sciencing_icons_fluid fluid, sciencing_icons_astronomy astronomy, sciencing_icons_geology geology, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geology fundamentals, sciencing_icons_minerals & rocks minerals & rocks, sciencing_icons_earth scructure earth structure, sciencing_icons_fossils fossils, sciencing_icons_natural disasters natural disasters, sciencing_icons_nature nature, sciencing_icons_ecosystems ecosystems, sciencing_icons_environment environment, sciencing_icons_insects insects, sciencing_icons_plants & mushrooms plants & mushrooms, sciencing_icons_animals animals, sciencing_icons_math math, sciencing_icons_arithmetic arithmetic, sciencing_icons_addition & subtraction addition & subtraction, sciencing_icons_multiplication & division multiplication & division, sciencing_icons_decimals decimals, sciencing_icons_fractions fractions, sciencing_icons_conversions conversions, sciencing_icons_algebra algebra, sciencing_icons_working with units working with units, sciencing_icons_equations & expressions equations & expressions, sciencing_icons_ratios & proportions ratios & proportions, sciencing_icons_inequalities inequalities, sciencing_icons_exponents & logarithms exponents & logarithms, sciencing_icons_factorization factorization, sciencing_icons_functions functions, sciencing_icons_linear equations linear equations, sciencing_icons_graphs graphs, sciencing_icons_quadratics quadratics, sciencing_icons_polynomials polynomials, sciencing_icons_geometry geometry, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geometry fundamentals, sciencing_icons_cartesian cartesian, sciencing_icons_circles circles, sciencing_icons_solids solids, sciencing_icons_trigonometry trigonometry, sciencing_icons_probability-statistics probability & statistics, sciencing_icons_mean-median-mode mean/median/mode, sciencing_icons_independent-dependent variables independent/dependent variables, sciencing_icons_deviation deviation, sciencing_icons_correlation correlation, sciencing_icons_sampling sampling, sciencing_icons_distributions distributions, sciencing_icons_probability probability, sciencing_icons_calculus calculus, sciencing_icons_differentiation-integration differentiation/integration, sciencing_icons_application application, sciencing_icons_projects projects, sciencing_icons_news news.
- Share Tweet Email Print
- Home ⋅
- Science Fair Project Ideas for Kids, Middle & High School Students ⋅
- Probability & Statistics
The Difference Between Research Questions & Hypothesis

To Calculate Arcsine, What Buttons Do You Press on a Scientific ...
Research questions and hypothesis are tools used in similar ways for different research methods. Both hypothesis and research questions are written before research begins and are used to help guide the research. Hypothesis are used in deductive research, where researchers use logic and scientific findings to either prove or disprove assumptions. Heuristic research is based on experience, where researchers use observations to learn about the research subject.
Definitions
A hypothesis is defined as an educated guess, while a research question is simply the researcher wondering about the world. Hypothesis are part of the scientific research method. They are employed in research in science, sociology, mathematics and more. Research questions are part of heuristic research methods, and are also used in many fields including literature, and sociology.
As its name suggests, research questions are always written as questions. Hypothesis are written as statements preceded with the words "I predict." For example, a research question would ask, "What is the effect of heat on the effectiveness of bleach?" A hypothesis would state, "I predict heat will diminish the effectiveness of bleach."
Before Writing
Before writing a hypothesis, the researcher must determine what others have discovered about this subject. On the other hand, a research question requires less preparation, but focus and structure is critical.
For example, a researcher using a hypothesis would look up studies about bleach, information on the chemical properties of the chemical when heated and data about its effectiveness before writing the hypothesis. When using a research question, the researcher would think about how to phrase the question to ensure its scope is not too broad, too narrow or impossible to answer.
Writing Conclusions
When writing the conclusion for research conducted using a hypothesis, the researcher will write whether the hypothesis was correct or incorrect, followed by an explanation of the results of the research. The researcher using only a research question will write the answer to the question, followed by the findings of the research.
Related Articles
To calculate arcsine, what buttons do you press on..., what does data mean in a science fair project, how to test for acidity with litmus paper, how to write a hypothesis of magic milk for 5th grade, difference between proposition & hypothesis, what are the 8 steps in scientific research, how to write a summary on a science project, how to calculate a p-value, what is a quotient & dividend, how to calculate calibration curves, research methods in science, test your knowledge on middle school science, how to use log on a ti-83, how to calculate solubilities, how to calculate a standard score, science project ideas & the scientific method, how to convert pounds per square foot to psi, density vs. concentration, what is an engineering goal in a science project, what is the purpose of factor analysis.
- The Research Assistant: The Relationship Between the Research Question, Hypotheses, Specific Aims, and Long-Term Goals of the Project
About the Author
Alane Michaelson began writing professionally in 2002. Her work has appeared in Michigan publications such as the "Detroit Free Press" and the "Flint Journal." Michaelson graduated from Oakland University in 2006, earning a Bachelor of Arts in journalism.
Photo Credits
Photos.com/liquidlibrary/Getty Images
Find Your Next Great Science Fair Project! GO
We Have More Great Sciencing Articles!
To Calculate Arcsine, What Buttons Do You Press on a Scientific Calculator?
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
- Editing Services
- Academic Editing Services
- Admissions Editing Services
- Admissions Essay Editing Services
- AI Content Editing Services
- APA Style Editing Services
- Application Essay Editing Services
- Book Editing Services
- Business Editing Services
- Capstone Paper Editing Services
- Children's Book Editing Services
- College Application Editing Services
- College Essay Editing Services
- Copy Editing Services
- Developmental Editing Services
- Dissertation Editing Services
- eBook Editing Services
- English Editing Services
- Horror Story Editing Services
- Legal Editing Services
- Line Editing Services
- Manuscript Editing Services
- MLA Style Editing Services
- Novel Editing Services
- Paper Editing Services
- Personal Statement Editing Services
- Research Paper Editing Services
- Résumé Editing Services
- Scientific Editing Services
- Short Story Editing Services
- Statement of Purpose Editing Services
- Substantive Editing Services
- Thesis Editing Services
Proofreading
- Proofreading Services
- Admissions Essay Proofreading Services
- Children's Book Proofreading Services
- Legal Proofreading Services
- Novel Proofreading Services
- Personal Statement Proofreading Services
- Research Proposal Proofreading Services
- Statement of Purpose Proofreading Services

Translation
- Translation Services
Graphic Design
- Graphic Design Services
- Dungeons & Dragons Design Services
- Sticker Design Services
- Writing Services
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
How Does a Hypothesis Differ From a Research Question?

To understand the difference between a hypothesis and a research question , we must first define the exact nature of scientific inquiry . Essentially, scientific inquiry represents a structured and systematic approach to exploration and discovery, grounded in empirical evidence and guided by the principles of logical reasoning and critical analysis. At the heart of scientific inquiry lies a fundamental commitment to unbiased observation and the rigorous assessment of information, a process that seeks to generate verifiable knowledge based on well-founded theories and methodological robustness.
A pivotal facet of successful scientific investigation is the appropriate framing of research, which serves to delineate the scope and direction of the scholarly endeavor. The meticulous articulation of research parameters not only guides investigators in the methodical exploration of a particular phenomenon but also ensures the reliability and validity of the findings derived from it. Correctly framing a research endeavor equips scholars with a clear framework, thereby preventing research ambiguities and facilitating a coherent and purposeful investigative journey.
Central to the framing of research are two interrelated yet distinct elements: the research question and the hypothesis. While the research question generally articulates the primary inquiry or set of inquiries to be addressed in a study, offering a focal point for the exploration, a hypothesis presents a tentative, testable prediction regarding the expected outcomes of the research. It is grounded in the existing literature and theoretical frameworks, serving as a provisional answer to the research question that is subject to empirical verification.
In essence, a research question seeks to identify and explore potential relationships, patterns, or trends, fostering a deep understanding of the underlying phenomena. In contrast, a hypothesis endeavors to affirm or refute predetermined assumptions through methodical testing and validation, aiming to substantiate or discredit specific theoretical postulates.
To correctly formulate and differentiate between research questions and hypotheses, let us investigate each one in further detail.
Understanding hypotheses
Crafting a well-defined hypothesis is a pivotal step in scholarly research. This task necessitates a profound grasp of the subject matter alongside a comprehensive awareness of existing scholarly dialogues and theories relevant to the topic. The hypothesis acts as a foundational pillar that directs the analytical pathways of the investigation, anchoring the exploration with grounded expectations based on existing knowledge.
In the formulation of a hypothesis, researchers must adhere to vital principles to ensure the creation of a substantial and verifiable statement. A robust hypothesis is delineated by several attributes, including precision, testability, and a congruent alignment with established research and theories. Moreover, it is formulated to facilitate empirical substantiation, aiming to either confirm or refute the established propositions through systematic investigation.
To deepen our comprehension of a hypothesis, let us examine some examples in different research contexts, illustrating how a hypothesis can shape and steer a study:
- Individuals between the ages of 40 and 60 who engage in regular physical activity are less likely to develop heart diseases than those who do not.
- Adolescents who experience traumatic events during the COVID-19 pandemic have a higher prevalence of mental health issues than those who do not.
- Remote learning hampers the development of social skills in elementary school students more than traditional classroom learning does.
- Implementing multicultural education strategies diminishes the achievement gap in multicultural classrooms.
- Marine ecosystems that experience high levels of plastic pollution exhibit a substantial reduction in biodiversity.
- Urbanization leads to a significant decrease in biodiversity in metropolitan areas due to habitat loss.
- Voting behavior in urban communities is significantly influenced by the socioeconomic status of the individuals.
- The prevalent use of social media significantly influences the formation of societal norms and behaviors in contemporary society.
- The integration of artificial intelligence in manufacturing elevates efficiency and productivity.
- An increased dependence on digital platforms compromises personal privacy and heightens the risk of data security breaches.
Each of these hypothesis examples is constructed to offer focused and testable propositions, rooted in contemporary concerns, creating a pathway for empirical verification and the generation of data-driven insights.
Understanding research questions
A critical first step in any research endeavor is the formulation of a research question, a task that requires a deep understanding of both the topic at hand and the existing scholarly landscape surrounding it. The research question serves as the beacon that guides the trajectory of the investigation, providing a focal point that centers the research activities and objectives.
In constructing a research question, scholars must be guided by certain key principles to ensure that their inquiry is both meaningful and fruitful. A well-framed research question is characterized by clarity, specificity, and a sensible alignment with existing research, which aids in building upon established foundations to foster novel insights within its scholarly domain.
To further understand the concept of research questions, let us consider some concrete examples from various fields that illustrate how a well-articulated research question can guide a research project:
- How does lifestyle affect the risk of heart disease in adults aged 40-60?
- What impact has the COVID-19 pandemic had on mental health outcomes in adolescents?
- How does remote learning impact the academic performance and social skills of elementary school students?
- What strategies can be employed to reduce the achievement gap in multicultural classrooms?
- What are the effects of plastic waste on marine ecosystems?
- How does urbanization impact biodiversity in metropolitan regions?
- How do socioeconomic factors influence voting behavior in urban communities?
- What role does social media play in shaping contemporary societal norms and behaviors?
- How does the implementation of artificial intelligence in manufacturing enhance efficiency and productivity?
- What are the implications of increasing reliance on digital platforms for personal privacy and data security?
Each of these research question examples not only maintains a clear focus on a specific topic but also stands grounded in current concerns, thereby paving the way for empirical exploration and data-driven conclusions.
Key differences between a hypothesis and a research question
In scholarly research, it is imperative to differentiate clearly between a hypothesis and a research question. The following table delineates the comparative aspects of both concepts:
When to use which
The decision to use a hypothesis or a research question largely hinges on the nature and objectives of the study. Essentially, researchers delineate between exploratory and confirmatory research . The former seeks to explore new phenomena and generate new insights, while the latter aims to verify existing theories and hypotheses. Understanding the correct circumstance for employing either a research question or a hypothesis can significantly streamline the research process, directing it towards more targeted conclusions. Let's delve into the specific situations where one may be more appropriate over the other.
Situations where a hypothesis is more appropriate
- Confirmatory Research: When the research is grounded in existing theories and seeks to validate or invalidate a specific claim or relationship.
- Quantitative Studies: In research designs that predominantly involve statistical analysis of numerical data to address the research problem.
- Experimental Research: Where controlled experiments are conducted to explore the causal relationships between different variables.
- Deductive Approaches: When the research follows a deductive approach , deriving a specific prediction from a general theory.
Situations where a research question is more appropriate
- Exploratory Research: In studies aiming to explore a new field or topic without much existing literature or established theories.
- Qualitative Research: When the study involves analyzing non-numerical data such as texts, interviews, or observational data to garner insights.
- Pilot Studies: Preliminary studies that aim to identify potential issues and refine research tools before a large-scale study.
- Inductive Approaches: Research approaches that work from specific observations to broader generalizations, aiming to develop new theories.
The interrelation between hypotheses and research questions
Understanding how a research question can give rise to hypotheses.
In scholarly inquiries, the formation of a hypothesis often finds its genesis in a well-articulated research question. This dynamic represents a pivotal juncture in research methodology, facilitating a transition from questioning to hypothesizing and setting the stage for focused analytical scrutiny. Leveraging the exploratory nature of research questions can foster the formulation of grounded hypotheses, guiding the investigative trajectory towards evidence-based conclusions.
Indeed, a well-structured research question can give rise to a series of hypotheses, each presenting a plausible answer to the research question and serving as a focal point for systematic investigation. This correlation facilitates a scaffolded approach to exploration, where researchers can build a layered understanding through a structured inquiry process.
Can a hypothesis transform into a research question?
This iterative process we have described can be envisioned as a cyclic pathway rather than a linear trajectory, wherein hypotheses, once tested and analyzed, can refine or even reformulate the initial research questions. This reflexive relationship fosters a deepened understanding and a more nuanced exploration of the research topic at hand.
To illustrate, consider a research question in the field of healthcare: "What are the primary factors influencing sleep quality in adults?" From this question, a researcher might derive several hypotheses, such as "Adults who engage in regular physical activity experience better sleep quality than those who do not." Once this hypothesis is tested, the findings could lead to further questions, fine-tuning the initial research query to delve into specific age groups, lifestyle factors, or physiological aspects, thereby perpetuating a cycle of inquiry that propels the research into deeper and more focused directions.
Research questions serve as the launchpad for scientific exploration, fostering a direction and scope that steer investigations towards relevant and focused pathways. Conversely, hypotheses act as tentative answers to these research questions, laying a grounded foundation for systematic investigations and guiding the trajectory towards evidence-based conclusions.
Selecting the right approach—whether formulating a hypothesis or crafting a research question—is not merely a procedural choice; it is a strategic decision that significantly influences the outcome of the investigation. Recognizing the interdependent and reflexive relationship between the two can foster a more robust and nuanced approach to scientific inquiry.
By embracing the cyclic pathway that intertwines questioning with hypothesizing, researchers can unlock deeper levels of understanding, paving the way for profound discoveries enriched with insight. Remember, the quality of the answers we obtain is invariably linked to the quality of the questions we ask and the hypotheses we formulate.
Header image by Luke Tanis .
Related Posts

7 Time Management Tips for Academic Writers

Need to Make Your Essay Longer? Here's How
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Advance your scientific manuscript with expert editing
Clarifying the Research Questions or Hypotheses
- First Online: 28 March 2017
Cite this chapter

- Kenan Dikilitaş 3 &
- Carol Griffiths 4
1039 Accesses
This chapter deals with the important, but often neglected, issue of establishing research questions or hypotheses, whether this is done before or (in the “real world”) often after the study has been conducted. The point is made that, in fact, research questions tend to be more common than hypotheses in action research, and guidelines are suggested for delineating such questions and deciding on appropriate question types according to the research purpose. Some example questions are provided to stimulate ideas, and an example action research study which will proceed in stages throughout the book is begun here.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Educational Sciences, Bahçeşehir University, Istanbul, Turkey
Kenan Dikilitaş
Freelance, Istanbul, Turkey
Carol Griffiths
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Dikilitaş, K., Griffiths, C. (2017). Clarifying the Research Questions or Hypotheses. In: Developing Language Teacher Autonomy through Action Research. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50739-2_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50739-2_2
Published : 28 March 2017
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-50738-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-50739-2
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Social Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Research Hypothesis vs. Research Question: What's the Difference?
Key Differences
Comparison chart, formulation, directionality, relationship to research process, research hypothesis and research question definitions, research hypothesis, research question, what is a research hypothesis, what is a research question, why is a research hypothesis important, how does a research hypothesis differ from a research question, can a study have both a research hypothesis and a research question, what types of research questions are there, what makes a good research question, how do you formulate a research hypothesis, what is a null research hypothesis, how specific should a research hypothesis be, why is a research question important, can a research hypothesis be proven, how broad can a research question be, how do research questions evolve during a study, how do you formulate a research question, how does a research hypothesis guide experimental design, how does a research question influence literature review, what role does a research question play in qualitative research, can a research hypothesis be modified, what happens if a research hypothesis is refuted.

Trending Comparisons

Popular Comparisons

New Comparisons

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection .
Example: Hypothesis
Daily apple consumption leads to fewer doctor’s visits.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more types of variables .
- An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls.
- A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
If there are any control variables , extraneous variables , or confounding variables , be sure to jot those down as you go to minimize the chances that research bias will affect your results.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Step 1. ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2. Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to ensure that you’re embarking on a relevant topic . This can also help you identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalize more complex constructs.
Step 3. Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
4. Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
- H 0 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has no effect on their final exam scores.
- H 1 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has a positive effect on their final exam scores.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/hypothesis/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, operationalization | a guide with examples, pros & cons, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

10 Significant Differences Between Research Question vs Research Hypothesis
Stating, developing and addressing a research question and developing & justifying the research hypothesis has vital significance in the research process. Both help researchers to approach PhD/research/ projects.
“Research” is a word important for PhD which includes complex processes of finding new knowledge. A PhD candidate has to prepare a project & research proposal, identify a research gap , state a question, prepare a hypothesis and then do research.
It includes tedious pre-preparation, lucrative research and frustrating post-preparations phases. So overall the research process though is inquisitive but can be managed by discipline and zero date planning.
So to prepare for PhD, do it with ease and complete it joyfully; one has to understand every element correctly before starting their research. And for that tons and tons of articles and previous research must be read first.
In addition, as we talked about, precisely identified research problem helps in stating an excellent research question or research hypothesis. Notwithstanding, students usually don’t understand what a research question or hypothesis is!
The present blog content will focus on differences between research question and hypothesis and may let you understand what each term is. I hope this article will help you learn the PhD research process more accurately.
Stay tuned,
Research question: Does this article explain some common differences between a research question and a research hypothesis?
Research hypothesis: This article explains the major differences between the research question and the research hypothesis.
Example of research question:
Some other examples of research questions are: , example of research hypothesis: , some of the examples of research hypotheses: , summary: research question vs hypothesis: , wrapping up: , what is a research question- simple explanation.
Put simply, a research question is a clear and concise question of the study that must be answered at the end. The answer usually is Yes/No type but clearly fills the gap.
Let’s take an example,
What are some common problems the LGBT community faces globally?
Suppose, this one is one research question around which the researcher has to prepare its study. What can he or she do with this topic?
- Conduct gatherings of the community.
- Conduct one on one interviews.
- Conduct News sessions
- Study previous literature.
- Organize some Games and invite LGBT community people to take part.
That’s it, Nothing else he or she can do.
No statistical analysis is required and performed for this study so the outcome of this study possibly is “problems”. And it can be solved, perhaps. Note that in-depth mathematical models, statistical analysis and other scientific studies aren’t required here.
- What are the side effects of social media addiction on youth?
- What are the factors that negatively impact the mental health of US people?
- How effective carbon emission control strategies are?
Now let’s understand the research hypothesis.
What is a research hypothesis?- Simpler explanation
A research hypothesis is postulated in order to predict the results either negative or positive. Notedly is used so often in scientific, experimental and quantitative research.
The research hypothesis is a predictive model for getting results.
Let’s take an example,
The effect of time and temperature on biological sample transportation.
This study includes exclusive statistical analysis and data-driven studies to investigate the effect of various temperatures and times on biological specimen transportation.
Outcomes of the study will prove that at which temperature a biological sample can be safely transported.
The outcomes are,
- Statistics
- The temperature which isn’t good
- The temperature which has is best
- The tolerable zone for transportation
To interpret these kinds of results in-depth mathematical models, statistical analysis, scientific experiments and other biological studies are needed.
- The effect of time and temperature on biological sample transportation.
- Effect of various doses of antiviral Oseltamivir drug against viral pathogenicity.
- Various global warming agents and their impact.
I think you get a brief idea about how each term is different. Some of the technical differences between the research question and hypothesis are explained here.
Differences between research question and research hypothesis:
A research question is developed depending upon the problem or gap identified while the hypothesis is prepared based on the existing knowledge.
More than one research question is present in a single study, while the entire research is developed around a single hypothesis that is either proven or disproven at last.
In-depth knowledge of the subject and huge data or research studies are required to state a research hypothesis; whereas the research question can be stated using a small group of research data or knowledge.
This indicates that the relatedness among different variables is pretty uncertain for the research question while is highly related in the case of hypothesis.
A research question is “brief” yet includes all the important information and is open to debate which typically gives an excellent varied degree of output.
On the other hand, the research hypothesis is a kind of formal statement- (will be proved or disproved) which assumes the relatedness between two or more variables selected for the study.
For example,
The number of patients, population size, sample type or method selected for the study.
Both- qualitative and quantitative studies rely on the research question, however, the hypothesis can be postulated mostly for the quantitative or experimental studies.
Depending upon the nature of the study, the research questions are of three various types which are casual, descriptive and comparative questions while the hypotheses are causal, null, directional or non-directional.
A thesis question must be answered; A hypothesis must be tested.
The research question is more an elaborative research term while the hypothesis is more scientific and predictive in nature.
Henceforth, research questions are usually used in elaborate studies in subjects such as language, arts and literature. And as we said, that’s pretty straightforward.
The impact of the “Macbeth play” on European people.
On the other hand, the research hypothesis is based on possibilities and probabilities whose final results either or neither prove the study and therefore include a purely scientific explanation, mathematics, equations and statistical analysis.
Studies in science, biology and sociology rely on hypotheses (that must be tested first).
For example, the impact of temperature and time duration on sample transportation and storage.
If you are designing scientific research for your PhD, perhaps stating a hypothesis may help you more, although you can raise a question as well to investigate the knowledge.
Research, as I said, is a complex process, needs the experience to design.
Early learning may pretty helpful for students to understand the thing well. And hence this article and series of articles on this blog are meant for PhD students.

Dr. Tushar Chauhan is a Scientist, Blogger and Scientific-writer. He has completed PhD in Genetics. Dr. Chauhan is a PhD coach and tutor.
Share this:

- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on Linkedin
- Share via Email
About The Author

Dr Tushar Chauhan
Related posts.
What is PhD?- History, Definition, Origin, Requirement, Fees, Duration and Process

How to write a PhD thesis?
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A hypothesis is a statement you can approve or disapprove. You develop a hypothesis from a research question by changing the question into a statement. Primarily applied in deductive research, it involves the use of scientific, mathematical, and sociological findings to agree to or write off an assumption. Researchers use the null approach for ...
The primary research question should originate from the hypothesis, not the data, and be established before starting the study. Formulating the research question and hypothesis from existing data (e.g., a database) can lead to multiple statistical comparisons and potentially spurious findings due to chance.
The difference between Research Question and Hypothesis is that the research question is the question whose answer needs to be found through the research paper, whereas a hypothesis is an assertion that either approves or negates the matter in question. The two also differ in their structure, aim, nature, and so on.
A research question is the question the research study sets out to answer. Hypothesis is the statement the research study sets out to prove or disprove. The main difference between hypothesis and research question is that hypothesis is predictive in nature whereas research question is inquisitive in nature. In this article, we'll discuss, 1.
A Hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between two or more variables in a research study. Hypotheses are used in studies that aim to test cause-and-effect relationships between variables. A hypothesis is a tentative explanation for an observed phenomenon, and it is often derived from existing theory or previous research.
A hypothesis is defined as an educated guess, while a research question is simply the researcher wondering about the world. Hypothesis are part of the scientific research method. They are employed in research in science, sociology, mathematics and more. Research questions are part of heuristic research methods, and are also used in many fields ...
Quick tips on writing a hypothesis. 1. Be clear about your research question. A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem.
A hypothesis is a predictive statement about the relationship between 2 or more variables. Research questions are similar to hypotheses, but they are in question format. We expand on that general definition by splitting research questions into 3 basic types: difference questions, associational questions, and descriptive questions. For difference and associational questions, basic means that ...
The development of the research question, including a supportive hypothesis and objectives, is a necessary key step in producing clinically relevant results to be used in evidence-based practice. A well-defined and specific research question is more likely to help guide us in making decisions about study design and population and subsequently ...
What is the difference between a research question and a hypothesis? • A research question is exactly what it says: it asks a question and is punctuated with a question mark. A research project requires at least one question, but there may be several (Nunan 1992). • A hypothesis contains the researcher's prediction/s (Dörnyei 2007).
To understand the difference between a hypothesis and a research question, we must first define the exact nature of scientific inquiry. Essentially, scientific inquiry represents a structured and systematic approach to exploration and discovery, grounded in empirical evidence and guided by the principles of logical reasoning and critical analysis. At the heart of scientific inquiry lies a ...
What is the difference between a research question and a hypothesis? A research question is exactly what it says: it asks a question and is punctuated with a question mark. A research project requires at least one question, but there may be several (Nunan 1992). A hypothesis contains the researcher's prediction/s (Dörnyei 2007).
A research hypothesis requires a certain level of theoretical background to propose a predicted relationship, a research question can be developed with a more exploratory approach. The research hypothesis is grounded in the literature, suggesting a cause-and-effect relationship that can be empirically tested.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on research hypothesis 1. What is the difference between research question and research hypothesis? A research question defines the problem and helps outline the study objective(s). It is an open-ended statement that is exploratory or probing in nature. Therefore, it does not make predictions or assumptions.
Research Questions and Hypotheses I nvestigators place signposts to carry the reader through a plan for a ... difference (or relationship)" between the groups. ... illustrates a null hypothesis. Designing Research Example 7.3 A Null Hypothesis An investigator might examine three types of reinforcement for children with autism: verbal cues, a ...
When you have finished these activities, continue to the next section of the module: "Identifying research questions and hypotheses".Answers for the last activity: A is good; it describes a big-picture question, mentions a theory that provides a link from the big-picture question to specific experiment results, and explains what is expected to happen in the experiment under a given big-picture ...
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
RESEARCH QUESTIONS Nature of Hypothesis The hypothesis is a clear statement of what is intended to be investigated. It should ... We would write H0: there is no difference between the two drugs on average. The alternative hypothesismight be that: the new drug has a different effect, on average, compared to that of the ...
A thesis question must be answered; A hypothesis must be tested. The research question is more an elaborative research term while the hypothesis is more scientific and predictive in nature. Henceforth, research questions are usually used in elaborate studies in subjects such as language, arts and literature.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
The research question will also give us the hypothesized parameter value. This is the number that goes in the hypothesis statements (i.e., \(\mu_0\) and \(p_0\)). For the difference between two groups, regression, and correlation, this value is typically 0.
The difference between Research Question and Hypothesis is that the research question is the question whose answer needs to be found through the research paper, whereas a hypothesis is an assertion that either approves or negates the matter in question. The two also differ in their structure, aim, nature, and so on.
A hypothesis is a statement that expresses a possible relationship between variables or phenomena, based on existing knowledge, theory, or observation. A research question, on the other hand, is a ...