We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design

15 Effective Visual Presentation Tips To Wow Your Audience
By Krystle Wong , Sep 28, 2023

So, you’re gearing up for that big presentation and you want it to be more than just another snooze-fest with slides. You want it to be engaging, memorable and downright impressive.
Well, you’ve come to the right place — I’ve got some slick tips on how to create a visual presentation that’ll take your presentation game up a notch.
Packed with presentation templates that are easily customizable, keep reading this blog post to learn the secret sauce behind crafting presentations that captivate, inform and remain etched in the memory of your audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a visual presentation & why is it important?
15 effective tips to make your visual presentations more engaging, 6 major types of visual presentation you should know , what are some common mistakes to avoid in visual presentations, visual presentation faqs, 5 steps to create a visual presentation with venngage.
A visual presentation is a communication method that utilizes visual elements such as images, graphics, charts, slides and other visual aids to convey information, ideas or messages to an audience.
Visual presentations aim to enhance comprehension engagement and the overall impact of the message through the strategic use of visuals. People remember what they see, making your point last longer in their heads.
Without further ado, let’s jump right into some great visual presentation examples that would do a great job in keeping your audience interested and getting your point across.
In today’s fast-paced world, where information is constantly bombarding our senses, creating engaging visual presentations has never been more crucial. To help you design a presentation that’ll leave a lasting impression, I’ve compiled these examples of visual presentations that will elevate your game.
1. Use the rule of thirds for layout
Ever heard of the rule of thirds? It’s a presentation layout trick that can instantly up your slide game. Imagine dividing your slide into a 3×3 grid and then placing your text and visuals at the intersection points or along the lines. This simple tweak creates a balanced and seriously pleasing layout that’ll draw everyone’s eyes.
2. Get creative with visual metaphors
Got a complex idea to explain? Skip the jargon and use visual metaphors. Throw in images that symbolize your point – for example, using a road map to show your journey towards a goal or using metaphors to represent answer choices or progress indicators in an interactive quiz or poll.
3. Visualize your data with charts and graphs
The right data visualization tools not only make content more appealing but also aid comprehension and retention. Choosing the right visual presentation for your data is all about finding a good match.
For ordinal data, where things have a clear order, consider using ordered bar charts or dot plots. When it comes to nominal data, where categories are on an equal footing, stick with the classics like bar charts, pie charts or simple frequency tables. And for interval-ratio data, where there’s a meaningful order, go for histograms, line graphs, scatterplots or box plots to help your data shine.
In an increasingly visual world, effective visual communication is a valuable skill for conveying messages. Here’s a guide on how to use visual communication to engage your audience while avoiding information overload.

4. Employ the power of contrast
Want your important stuff to pop? That’s where contrast comes in. Mix things up with contrasting colors, fonts or shapes. It’s like highlighting your key points with a neon marker – an instant attention grabber.
5. Tell a visual story
Structure your slides like a storybook and create a visual narrative by arranging your slides in a way that tells a story. Each slide should flow into the next, creating a visual narrative that keeps your audience hooked till the very end.
Icons and images are essential for adding visual appeal and clarity to your presentation. Venngage provides a vast library of icons and images, allowing you to choose visuals that resonate with your audience and complement your message.
6. Show the “before and after” magic
Want to drive home the impact of your message or solution? Whip out the “before and after” technique. Show the current state (before) and the desired state (after) in a visual way. It’s like showing a makeover transformation, but for your ideas.
7. Add fun with visual quizzes and polls
To break the monotony and see if your audience is still with you, throw in some quick quizzes or polls. It’s like a mini-game break in your presentation — your audience gets involved and it makes your presentation way more dynamic and memorable.
8. End with a powerful visual punch
Your presentation closing should be a showstopper. Think a stunning clip art that wraps up your message with a visual bow, a killer quote that lingers in minds or a call to action that gets hearts racing.

9. Engage with storytelling through data
Use storytelling magic to bring your data to life. Don’t just throw numbers at your audience—explain what they mean, why they matter and add a bit of human touch. Turn those stats into relatable tales and watch your audience’s eyes light up with understanding.

10. Use visuals wisely
Your visuals are the secret sauce of a great presentation. Cherry-pick high-quality images, graphics, charts and videos that not only look good but also align with your message’s vibe. Each visual should have a purpose – they’re not just there for decoration.
11. Utilize visual hierarchy
Employ design principles like contrast, alignment and proximity to make your key info stand out. Play around with fonts, colors and placement to make sure your audience can’t miss the important stuff.
12. Engage with multimedia
Static slides are so last year. Give your presentation some sizzle by tossing in multimedia elements. Think short video clips, animations, or a touch of sound when it makes sense, including an animated logo . But remember, these are sidekicks, not the main act, so use them smartly.
13. Interact with your audience
Turn your presentation into a two-way street. Start your presentation by encouraging your audience to join in with thought-provoking questions, quick polls or using interactive tools. Get them chatting and watch your presentation come alive.

When it comes to delivering a group presentation, it’s important to have everyone on the team on the same page. Venngage’s real-time collaboration tools enable you and your team to work together seamlessly, regardless of geographical locations. Collaborators can provide input, make edits and offer suggestions in real time.
14. Incorporate stories and examples
Weave in relatable stories, personal anecdotes or real-life examples to illustrate your points. It’s like adding a dash of spice to your content – it becomes more memorable and relatable.
15. Nail that delivery
Don’t just stand there and recite facts like a robot — be a confident and engaging presenter. Lock eyes with your audience, mix up your tone and pace and use some gestures to drive your points home. Practice and brush up your presentation skills until you’ve got it down pat for a persuasive presentation that flows like a pro.
Venngage offers a wide selection of professionally designed presentation templates, each tailored for different purposes and styles. By choosing a template that aligns with your content and goals, you can create a visually cohesive and polished presentation that captivates your audience.
Looking for more presentation ideas ? Why not try using a presentation software that will take your presentations to the next level with a combination of user-friendly interfaces, stunning visuals, collaboration features and innovative functionalities that will take your presentations to the next level.
Visual presentations come in various formats, each uniquely suited to convey information and engage audiences effectively. Here are six major types of visual presentations that you should be familiar with:
1. Slideshows or PowerPoint presentations
Slideshows are one of the most common forms of visual presentations. They typically consist of a series of slides containing text, images, charts, graphs and other visual elements. Slideshows are used for various purposes, including business presentations, educational lectures and conference talks.

2. Infographics
Infographics are visual representations of information, data or knowledge. They combine text, images and graphics to convey complex concepts or data in a concise and visually appealing manner. Infographics are often used in marketing, reporting and educational materials.
Don’t worry, they are also super easy to create thanks to Venngage’s fully customizable infographics templates that are professionally designed to bring your information to life. Be sure to try it out for your next visual presentation!
3. Video presentation
Videos are your dynamic storytellers. Whether it’s pre-recorded or happening in real-time, videos are the showstoppers. You can have interviews, demos, animations or even your own mini-documentary. Video presentations are highly engaging and can be shared in both in-person and virtual presentations .
4. Charts and graphs
Charts and graphs are visual representations of data that make it easier to understand and analyze numerical information. Common types include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts and scatterplots. They are commonly used in scientific research, business reports and academic presentations.
Effective data visualizations are crucial for simplifying complex information and Venngage has got you covered. Venngage’s tools enable you to create engaging charts, graphs,and infographics that enhance audience understanding and retention, leaving a lasting impression in your presentation.

5. Interactive presentations
Interactive presentations involve audience participation and engagement. These can include interactive polls, quizzes, games and multimedia elements that allow the audience to actively participate in the presentation. Interactive presentations are often used in workshops, training sessions and webinars.
Venngage’s interactive presentation tools enable you to create immersive experiences that leave a lasting impact and enhance audience retention. By incorporating features like clickable elements, quizzes and embedded multimedia, you can captivate your audience’s attention and encourage active participation.
6. Poster presentations
Poster presentations are the stars of the academic and research scene. They consist of a large poster that includes text, images and graphics to communicate research findings or project details and are usually used at conferences and exhibitions. For more poster ideas, browse through Venngage’s gallery of poster templates to inspire your next presentation.

Different visual presentations aside, different presentation methods also serve a unique purpose, tailored to specific objectives and audiences. Find out which type of presentation works best for the message you are sending across to better capture attention, maintain interest and leave a lasting impression.
To make a good presentation , it’s crucial to be aware of common mistakes and how to avoid them. Without further ado, let’s explore some of these pitfalls along with valuable insights on how to sidestep them.
Overloading slides with text
Text heavy slides can be like trying to swallow a whole sandwich in one bite – overwhelming and unappetizing. Instead, opt for concise sentences and bullet points to keep your slides simple. Visuals can help convey your message in a more engaging way.
Using low-quality visuals
Grainy images and pixelated charts are the equivalent of a scratchy vinyl record at a DJ party. High-resolution visuals are your ticket to professionalism. Ensure that the images, charts and graphics you use are clear, relevant and sharp.
Choosing the right visuals for presentations is important. To find great visuals for your visual presentation, Browse Venngage’s extensive library of high-quality stock photos. These images can help you convey your message effectively, evoke emotions and create a visually pleasing narrative.
Ignoring design consistency
Imagine a book with every chapter in a different font and color – it’s a visual mess. Consistency in fonts, colors and formatting throughout your presentation is key to a polished and professional look.
Reading directly from slides
Reading your slides word-for-word is like inviting your audience to a one-person audiobook session. Slides should complement your speech, not replace it. Use them as visual aids, offering key points and visuals to support your narrative.
Lack of visual hierarchy
Neglecting visual hierarchy is like trying to find Waldo in a crowd of clones. Use size, color and positioning to emphasize what’s most important. Guide your audience’s attention to key points so they don’t miss the forest for the trees.
Ignoring accessibility
Accessibility isn’t an option these days; it’s a must. Forgetting alt text for images, color contrast and closed captions for videos can exclude individuals with disabilities from understanding your presentation.
Relying too heavily on animation
While animations can add pizzazz and draw attention, overdoing it can overshadow your message. Use animations sparingly and with purpose to enhance, not detract from your content.
Using jargon and complex language
Keep it simple. Use plain language and explain terms when needed. You want your message to resonate, not leave people scratching their heads.
Not testing interactive elements
Interactive elements can be the life of your whole presentation, but not testing them beforehand is like jumping into a pool without checking if there’s water. Ensure that all interactive features, from live polls to multimedia content, work seamlessly. A smooth experience keeps your audience engaged and avoids those awkward technical hiccups.
Presenting complex data and information in a clear and visually appealing way has never been easier with Venngage. Build professional-looking designs with our free visual chart slide templates for your next presentation.
What software or tools can I use to create visual presentations?
You can use various software and tools to create visual presentations, including Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, Adobe Illustrator, Canva, Prezi and Venngage, among others.
What is the difference between a visual presentation and a written report?
The main difference between a visual presentation and a written report is the medium of communication. Visual presentations rely on visuals, such as slides, charts and images to convey information quickly, while written reports use text to provide detailed information in a linear format.
How do I effectively communicate data through visual presentations?
To effectively communicate data through visual presentations, simplify complex data into easily digestible charts and graphs, use clear labels and titles and ensure that your visuals support the key messages you want to convey.
Are there any accessibility considerations for visual presentations?
Accessibility considerations for visual presentations include providing alt text for images, ensuring good color contrast, using readable fonts and providing transcripts or captions for multimedia content to make the presentation inclusive.
Most design tools today make accessibility hard but Venngage’s Accessibility Design Tool comes with accessibility features baked in, including accessible-friendly and inclusive icons.
How do I choose the right visuals for my presentation?
Choose visuals that align with your content and message. Use charts for data, images for illustrating concepts, icons for emphasis and color to evoke emotions or convey themes.
What is the role of storytelling in visual presentations?
Storytelling plays a crucial role in visual presentations by providing a narrative structure that engages the audience, helps them relate to the content and makes the information more memorable.
How can I adapt my visual presentations for online or virtual audiences?
To adapt visual presentations for online or virtual audiences, focus on concise content, use engaging visuals, ensure clear audio, encourage audience interaction through chat or polls and rehearse for a smooth online delivery.
What is the role of data visualization in visual presentations?
Data visualization in visual presentations simplifies complex data by using charts, graphs and diagrams, making it easier for the audience to understand and interpret information.
How do I choose the right color scheme and fonts for my visual presentation?
Choose a color scheme that aligns with your content and brand and select fonts that are readable and appropriate for the message you want to convey.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my visual presentation?
Measure the effectiveness of your visual presentation by collecting feedback from the audience, tracking engagement metrics (e.g., click-through rates for online presentations) and evaluating whether the presentation achieved its intended objectives.
Ultimately, creating a memorable visual presentation isn’t just about throwing together pretty slides. It’s about mastering the art of making your message stick, captivating your audience and leaving a mark.
Lucky for you, Venngage simplifies the process of creating great presentations, empowering you to concentrate on delivering a compelling message. Follow the 5 simple steps below to make your entire presentation visually appealing and impactful:
1. Sign up and log In: Log in to your Venngage account or sign up for free and gain access to Venngage’s templates and design tools.
2. Choose a template: Browse through Venngage’s presentation template library and select one that best suits your presentation’s purpose and style. Venngage offers a variety of pre-designed templates for different types of visual presentations, including infographics, reports, posters and more.
3. Edit and customize your template: Replace the placeholder text, image and graphics with your own content and customize the colors, fonts and visual elements to align with your presentation’s theme or your organization’s branding.
4. Add visual elements: Venngage offers a wide range of visual elements, such as icons, illustrations, charts, graphs and images, that you can easily add to your presentation with the user-friendly drag-and-drop editor.
5. Save and export your presentation: Export your presentation in a format that suits your needs and then share it with your audience via email, social media or by embedding it on your website or blog .
So, as you gear up for your next presentation, whether it’s for business, education or pure creative expression, don’t forget to keep these visual presentation ideas in your back pocket.
Feel free to experiment and fine-tune your approach and let your passion and expertise shine through in your presentation. With practice, you’ll not only build presentations but also leave a lasting impact on your audience – one slide at a time.
How To Write A Presentation 101: A Step-by-Step Guide with Best Examples
Jane Ng • 02 Nov 2023 • 8 min read
Is it difficult to start of presentation? You’re standing before a room full of eager listeners, ready to share your knowledge and captivate their attention. But where do you begin? How do you structure your ideas and convey them effectively?
Take a deep breath, and fear not! In this article, we’ll provide a road map on how to write a presentation covering everything from crafting a script to creating an engaging introduction.
So, let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a presentation , what should be in a powerful presentation.
- How To Write A Presentation Script
- How to Write A Presentation Introduction
Key Takeaways
Tips for better presentation.
- How to start a presentation
- How to introduce yourself

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Presentations are all about connecting with your audience.
Presenting is a fantastic way to share information, ideas, or arguments with your audience. Think of it as a structured approach to effectively convey your message. And you’ve got options such as slideshows, speeches, demos, videos, and even multimedia presentations!
The purpose of a presentation can vary depending on the situation and what the presenter wants to achieve.
- In the business world, presentations are commonly used to pitch proposals, share reports, or make sales pitches.
- In educational settings, presentations are a go-to for teaching or delivering engaging lectures.
- For conferences, seminars, and public events—presentations are perfect for dishing out information, inspiring folks, or even persuading the audience.
That sounds brilliant. But, how to write a presentation?

How To Write A Presentation? What should be in a powerful presentation? A great presentation encompasses several key elements to captivate your audience and effectively convey your message. Here’s what you should consider including in a winning presentation:
- Clear and Engaging Introduction: Start your presentation with a bang! Hook your audience’s attention right from the beginning by using a captivating story, a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a powerful quote. Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and establish a connection with your listeners.
- Well-Structured Content: Organize your content logically and coherently. Divide your presentation into sections or main points and provide smooth transitions between them. Each section should flow seamlessly into the next, creating a cohesive narrative. Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your audience through the presentation.
- Compelling Visuals: Incorporate visual aids, such as images, graphs, or videos, to enhance your presentation. Make sure your visuals are visually appealing, relevant, and easy to understand. Use a clean and uncluttered design with legible fonts and appropriate color schemes.
- Engaging Delivery: Pay attention to your delivery style and body language. You should maintain eye contact with your audience, use gestures to emphasize key points, and vary your tone of voice to keep the presentation dynamic.
- Clear and Memorable Conclusion: Leave your audience with a lasting impression by providing a strong closing statement, a call to action, or a thought-provoking question. Make sure your conclusion ties back to your introduction and reinforces the core message of your presentation.

How To Write A Presentation Script (With Examples)
To successfully convey your message to your audience, you must carefully craft and organize your presentation script. Here are steps on how to write a presentation script:
1/ Understand Your Purpose and Audience:
- Clarify the purpose of your presentation. Are you informing, persuading, or entertaining?
- Identify your target audience and their knowledge level, interests, and expectations.
- Define what presentation format you want to use
2/ Outline the Structure of Your Presentation:
Strong opening: .
Start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Some types of openings you can use are:
- Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: “Have you ever…?”
- Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: “Did you know that….?”
- Use a Powerful Quote: “As Maya Angelou once said,….”
- Tell a Compelling Story : “Picture this: You’re standing at….”
- Start with a Bold Statement: “In the fast-paced digital age….”
Main Points:
Clearly state your main points or key ideas that you will discuss throughout the presentation.
- Clearly State the Purpose and Main Points: Example: “In this presentation, we will delve into three key areas. First,… Next,… Finally,…. we’ll discuss….”
- Provide Background and Context: Example: “Before we dive into the details, let’s understand the basics of…..”
- Present Supporting Information and Examples: Example: “To illustrate…., let’s look at an example. In,…..”
- Address Counterarguments or Potential Concerns: Example: “While…, we must also consider… .”
- Recap Key Points and Transition to the Next Section: Example: “To summarize, we’ve… Now, let’s shift our focus to…”
Remember to organize your content logically and coherently, ensuring smooth transitions between sections.
Ending:
You can conclude with a strong closing statement summarizing your main points and leaving a lasting impression. Example: “As we conclude our presentation, it’s clear that… By…., we can….”
3/ Craft Clear and Concise Sentences:
Once you’ve outlined your presentation, you need to edit your sentences. Use clear and straightforward language to ensure your message is easily understood.
Alternatively, you can break down complex ideas into simpler concepts and provide clear explanations or examples to aid comprehension.
4/ Use Visual Aids and Supporting Materials:
Use supporting materials such as statistics, research findings, or real-life examples to back up your points and make them more compelling.
- Example: “As you can see from this graph,… This demonstrates….”
5/ Include Engagement Techniques:
Incorporate interactive elements to engage your audience, such as Q&A sessions , conducting live polls , or encouraging participation.
6/ Rehearse and Revise:
- Practice delivering your presentation script to familiarize yourself with the content and improve your delivery.
- Revise and edit your script as needed, removing any unnecessary information or repetitions.
7/ Seek Feedback:
You can share your script or deliver a practice presentation to a trusted friend, colleague, or mentor to gather feedback on your script and make adjustments accordingly.
More on Script Presentation

How to Write A Presentation Introduction with Examples
How to write presentations that are engaging and visually appealing? Looking for introduction ideas for the presentation? As mentioned earlier, once you have completed your script, it’s crucial to focus on editing and refining the most critical element—the opening of your presentation – the section that determines whether you can captivate and retain your audience’s attention right from the start.
Here is a guide on how to craft an opening that grabs your audience’s attention from the very first minute:
1/ Start with a Hook
To begin, you can choose from five different openings mentioned in the script based on your desired purpose and content. Alternatively, you can opt for the approach that resonates with you the most, and instills your confidence. Remember, the key is to choose a starting point that aligns with your objectives and allows you to deliver your message effectively.
2/ Establish Relevance and Context:
Then you should establish the topic of your presentation and explain why it is important or relevant to your audience. Connect the topic to their interests, challenges, or aspirations to create a sense of relevance.
3/ State the Purpose
Clearly articulate the purpose or goal of your presentation. Let the audience know what they can expect to gain or achieve by listening to your presentation.
4/ Preview Your Main Points
Give a brief overview of the main points or sections you will cover in your presentation. It helps the audience understand the structure and flow of your presentation and creates anticipation.
5/ Establish Credibility
Share your expertise or credentials related to the topic to build trust with the audience, such as a brief personal story, relevant experience, or mentioning your professional background.
6/ Engage Emotionally
Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning.
Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations. Aim for clarity and brevity to maintain the audience’s attention.
For example, Topic: Work-life balance
“Good morning, everyone! Can you imagine waking up each day feeling energized and ready to conquer both your personal and professional pursuits? Well, that’s exactly what we’ll explore today – the wonderful world of work-life balance. In a fast-paced society where work seems to consume every waking hour, it’s vital to find that spot where our careers and personal lives harmoniously coexist. Throughout this presentation, we’ll dive into practical strategies that help us achieve that coveted balance, boost productivity, and nurture our overall well-being.
But before we dive in, let me share a bit about my journey. As a working professional and a passionate advocate for work-life balance, I have spent years researching and implementing strategies that have transformed my own life. I am excited to share my knowledge and experiences with all of you today, with the hope of inspiring positive change and creating a more fulfilling work-life balance for everyone in this room. So, let’s get started!”
Check out: How to Start a Presentation?

Whether you’re a seasoned speaker or new to the stage, understanding how to write a presentation that conveys your message effectively is a valuable skill. By following the steps in this guide, you can become a captivating presenter and make your mark in every presentation you deliver.
Additionally, AhaSlides can significantly enhance your presentation’s impact. With AhaSlides, you can use live polls, quizzes, and word cloud to turn your presentation into an engaging and interactive experience. Let’s take a moment to explore our vast template library !
Frequently Asked Questions
1/ how to write a presentation step by step .
You can refer to our step-by-step guide on How To Write A Presentation Script:
- Understand Your Purpose and Audience
- Outline the Structure of Your Presentation
- Craft Clear and Concise Sentences
- Use Visual Aids and Supporting Material
- Include Engagement Techniques
- Rehearse and Revise
- Seek Feedback
2/ How do you start a presentation?
You can start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Consider using one of the following approaches:
3/ What are the five parts of a presentation?
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts:
- Introduction: Capturing the audience’s attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview.
- Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments.
- Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding and engage the audience.
- Conclusion: Summarizing main points, restating key message, and leaving a memorable takeaway or call to action.
- Q&A or Discussion: Optional part for addressing questions and encouraging audience participation.

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
More from AhaSlides


Engage your audience with powerful visual presentations.
Visual tools are critical to have in any presentation as they’re one of the key presentation aids that will help enhance your overall presentation .
We’ll give you tips on how to develop a sense of good presentation design whether you’re using PowerPoint, Prezi, Google Slides or any presentation software under the sun. The secret to creating a great presentation does not lie in a superior software, but understanding a few universal design concepts that can applied for all types of visual presentations.
Don’t be afraid to use a few presentation templates – there are ways to make the presentation ideas in those templates your own ideas and advance it in several different ways. Let’s make your next presentation on point and designed beautifully.
Presentations Are The Visual Communication Tool To Your Story

In the age of information, people remember facts faster through stories. Keep your bullet points and information short. You can use a rule of thumb to not put more than a paragraph and 3 points per slide to start.
Make your presentation the visual component of your story, but not something your audience has to read. Something that is short and succinct on screen will capture your audience’s attention and make sure they retain the main points of your message.
This does not mean incomplete slides. A common mistake presenters make is putting too little information on a slide in the name of simplicity when in fact they’re leaving out the main context.
A well designed visual presentation has a great story behind it and a well rehearsed voice telling it as well. Engaging the audience is also a great way to associate meaning or connection to the content of your slide decks. Ask questions and tell stories while showing off a great visual presentation! Think of writing the copy like writing for social media – you only have a certain amount of characters to use and a short audience attention span.
General Tips For Visual Presentations
Before you begin creating your presentation, you first need to know what makes effective presentations – storytelling. Such presentations target the audience’s emotions leading to a stronger connection to the audience member and the main point of the presentation.
Below are some storytelling tips for your slides, but remember to keep the presentation itself simple and practice makes perfect. And again, these are more for your spoken component that accompanies the visual component. These tips can be useful because they can be applied to all your presentations in general.
Step 1 is to ask yourself who your audience is and how to convey the key message you have in mind to them. Once you settle on your message, you can start designing your slides with that direction in mind.
You may wonder how to connect with an audience with your slides. Look to your own experiences, your own speaking style and tailor your message to what you know. Not many people want to hear others recite facts with no real meaning driving the story. Ask yourself, “Why does this matter to the audience and why should they care?”.
There is a lot of trust that can be built when the audience has a genuine connection to the presenter. Overall, if you have something that can solve a problem or teach someone complex things, that is enough to form a connection with your audience.
Think of the last app you used, the last email you read or perhaps the last business you purchased from. What was the content or visual elements that pulled you in?
Are you making a PowerPoint, Prezi or other form of visual presentation but it’s taking too much of your time? Enlist the help of Presentation Geeks and consider outsourcing your presentation design . Outsourcing your presentation slides allows you to free more of your time while still getting the results of an interesting presentation. You’ll have the support of expert slide designers who know what presentation visuals work and don’t work thanks to years of presentation feedback and background knowledge.
Color Design Tips For Presentation Slides
When designing your presentation, make sure you take into consideration the colors you’re using. We’ve listed a few background color combinations you might want to consider when developing the overall slide deck and the font to use.
Color Wheel Alignments:
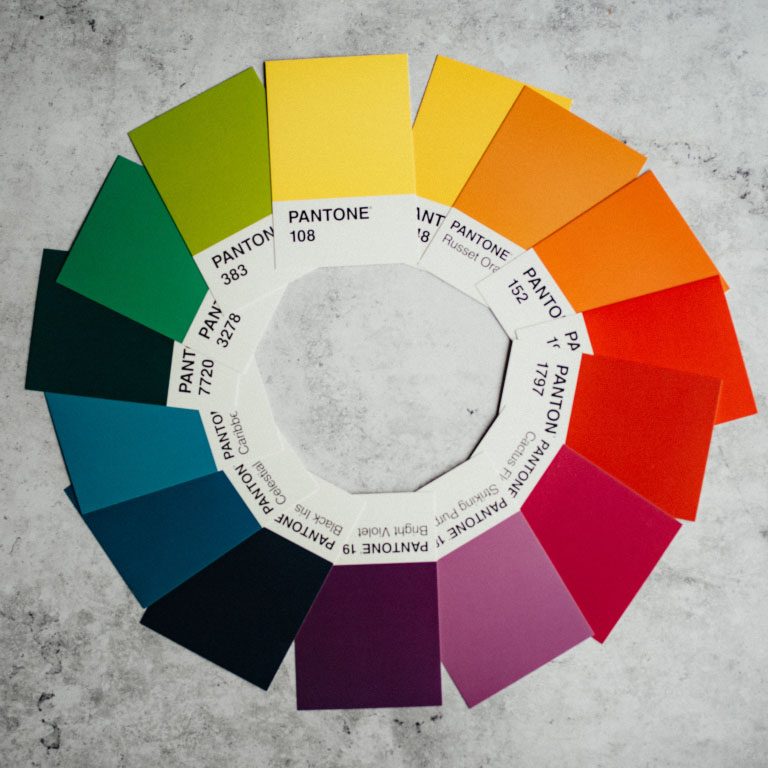

Primary Colors: Red, yellow, blue
Secondary Colors: Green, orange, purple
Tertiary Colors: Yellow-orange, red-orange, red-purple, blue-purple, blue-green & yellow-green
Analogous Colors: These are any three colors which are side by side on a color wheel. (Think green, lime green, yellow)
Complementary Colors: These are colors that are directly opposite of a color wheel. (Think green vs. purple, red vs. blue)
Monochromatic Colors: This is when you use one color and various shades or hues of it. It works well for minimal looks.
Color moods:
Red/Orange/Yellow: Generally these convey a sense of energy, are warm colors and catch your attention. Yellow is a happy warm color on one end and red is very striking and can warn of danger, and symbolizes importance, passion and sometimes violence.
Blue/Purple/Green: These colors are calming, reserved, elegant and often used for corporate slides. Think of how indigo blue is used for many large corporate entities. Green often is branded with earth or medical brands. Purple often conveys a sense of royalty, money and creativity.
Use The Power Of Photography Or Video

Pictures and videos are great visuals to incorporate into any presentation. Remember the saying, “A picture is worth a thousand words”? Well, it’s true! Photos help visualize complex information. You’ll often come across a lot of photos in research presentations as they help the audience understand examples better.
They can also save you from having to put a thousand thoughts into the PowerPoint presentation slide!
The first tip we can give to make a great visual presentation is to choose all your photos before you start. This way you can keep the consistency of the images across your slide deck and make sure they’re somewhat alike in terms of composition, mood and brand.
Use free stock photos
You don’t have to take the photos or videos yourself.
There are plenty of free resources and web pages for stock photos online – Unsplash , Pexels , Pixabay , Free Range , Creative Commons and some photos from Freepik are free to use with some accreditation.
Effective photo use
Make sure you pick an image that will focus on the main theme of the slide. One image is usually enough if the image choice is very relevant to the slide. If you have multiple photos, avoid poor or loose placement of photos all over the slide. Try to use a grid or gallery placement and it will immediately enhance the layout of the slide.
If you pick great images, making presentations can be faster. Instead of having to create an elaborate template with multiple elements, a photo with a couple of bullet points can go a long way in terms of capturing attention and making your presentation slides look professional. This is true on any presentation design platform – whether its PowerPoint, Google Slides, etc.

You can also embed videos whether they’re located on your computer, YouTube, Vimeo or other major video streaming sites. If you’re feeling nervous about your presentation or have a complex message that would be hard to condense in one slide, a video is a dynamic way of conveying your message in any type of presentation.
The Typography You Use Matters

Typography is how you will arrange and present the words in your presentation. An audience can engage when text is readable, functional and works well with the other elements in the presentation. Fonts and sizing are a good place to start establishing the tone of your presentation.
Overview of Font Choices
Elegant fonts often denote a sense of luxury or lifestyle tone. Use script fonts sparingly, but as titles they immediately give this polished and high-end look. This should not be used as body text or something lengthy to read. Think about if you sent an email in that text – it would be tedious to read. However, maybe if it were a title or a way to name email, the choice may be more correct.
Corporate fonts often are traditional, serif fonts or clean sans serif fonts that evoke a sense of trust and a clear message. Think of the fonts Lato, Helvetica or Arial – they’re go-to fonts that are easy to read, and work across many systems. This is especially helpful if you are working across teams when creating content or having to approve the content, idea or visuals.
Of course, you can incorporate more stylistic or playful fonts if you want to give your presentation a personal feel. Much like the scripted font, when used sparingly but in large titles, this choice of font can be very effective at conveying a certain personality.
Adding Symbols & Icons To Your Presentation

You can consolidate information by using symbols or icons to direct your eye to information such as an arrow symbol. What if you used a symbol instead of a bullet point? Think of symbols as anchors for the eye to quickly find information. You can collect symbols off free stock sites or use the built-in ones in PowerPoint that are free to use!
Depending on if your presentation is formal or informal , you may also want to consider adding emojis! Emojis are fun ways to express different emotions and can help connect with a younger demographic.
Overall Branding, Tone of Voice & Consistency

Another tool you may have at your disposal is if your brand, business or company has brand guidelines. It will be the guide and compass to your presentation’s information that goes within it. By keeping consistent you can achieve a polished look even if it looks very simple.
Use your business voice to communicate ideas and set the tone for your presentation. Are you in an investment banking business and want people to rely on the information given to you? That would inform perhaps using blues and purples, which are calmer colors and a cleaner look. Are you an influencer who’s buying power and spending choices matter to your audience? Maybe choosing bright colors with personal touches will make the connection. Are you designing an innovative app? Maybe more interactive slides would do the trick.
Use these questions to make sure your text and tone is consistent as this is a foundation of a well articulated brand or personal identity.
Consistent Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy is how you will arrange objects and text in relation to one another to guide your user and not confuse the objects and how they should read them in your slides. Setting rules helps differentiate and prioritize what’s important in order.
Look at the difference between these two.
Snoop Dogg just launched a wine and it’s coming to Canada
Daily hive branded content | aug 11 2020, 6:30 am.
Australian winery 19 Crimes recently announced that its new Cali Red wine, created in collaboration with Entertainment Icon, entrepreneur, and hip-hop artist Snoop Dogg, will be hitting shelves across Canada later this summer.
The collaboration offers a refreshing take on celebrity partnerships as the apparent shared values and history between the brand and famous rapper make for a perfectly organic pairing.
Comment Name:
By browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website. see our user agreement for the use of cookies..
You can see a clear distinction in the example below:
Think of hierarchy of a form of narration or story structure. Your eye goes to the title, then to the subtitle, then to the body copy in a logical manner. Where the eye travels is one of those things we don’t think about often. But you can also utilize eye lines in photos. Is your subject in the photo looking left or right? Consider placing text to where your subject is looking and see how effectively your eye travels to that text.
We’ll look at hierarchy strictly as sizing of words for now, but note you can establish hierarchy with type, white space, alignment, etc. As a general rule of thumb, you should have consistent sizing for your Header (or title slide / slide title), your subtitles and your body text. That’s it! If the sizing in your PowerPoint is consistent, your words will look uniform and clean. Everything will be much easier to read and the eye will be trained to move each slide.
Don’t Forget Your Own Style
Also don’t forget to incorporate your own style and what kind of visuals you like. Even if your early visuals may seem simple, build up that design muscle with the basics and design techniques that look clean and consistent.
You’ll find as you design these basics, you’ll probably start noticing other visuals and things you like in other mediums and presentations. Keep a note or screenshot the presentation that inspired you. Create a mood-board that you can refer to in the future for quick idea inspiration. Copying gets a bad rap, but learning how to design something you like even if it’s a clone copy will teach you many things about design. Build a collection of images that informs everything you do: for your color scheme, your designs, the cadence of images, etc.
That being said, you can also use free stock websites like Freepik for some design layouts inspiration. Creative Market is a paid website but the site offers a ton of design inspiration. This site has design templates for what’s currently in and trending. You can subscribe to an email newsletter on either site to get bite sized design influence each day that goes straight to your inbox.
However, don’t be afraid to try something new!
Once you get to a level of comfortable designing, these new ideas will be much easier to execute with the technical knowledge you amassed when you started. You could even try using a new app to design your ideas to keep your knowledge fresh! (Keep in mind that most online apps like SlideShare use cookies to improve functionality and performance.)
Ask your friends or people at your organization to give you feedback and critique, as that’s also crucial to honing your design skills. The people around you also represent different audiences!

The above image looks boring, right?
That’s because there are no visual elements!
Powerful visual presentations can engage audiences psychologically with both the presentation itself and the energy of the presenter. By understanding a few universal design concepts, you can begin your journey creating wonderful visual presentations and becoming a better presenter ! Thanks for reading this blog post, tell us your tips in the comments below.
Author: Content Team
Related posts.

FREE PROFESSIONAL RESOURCES DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX.
Subscribe for free tips, resources, templates, ideas and more from our professional team of presentation designers.
.css-1qrtm5m{display:block;margin-bottom:8px;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:14px;line-height:1.5714285714285714;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.35px;letter-spacing:-0.35px;font-weight:300;color:#606F7B;}@media (min-width:600px){.css-1qrtm5m{font-size:16px;line-height:1.625;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.5px;letter-spacing:-0.5px;}} Best Practices The #1 rule for improving your presentation slides
by Tom Rielly • May 12, 2020

When giving presentations, either on a video conference call or in person, your slides, videos and graphics (or lack of them) can be an important element in helping you tell your story or express your idea. This is the first of a series of blog posts that will give you tips and tricks on how to perfect your visual presentations.
Your job as a presenter is to build your idea -- step-by-step -- in the minds of your audience members. One tool to do that is presentation graphics, such as slides and videos.
Why graphics for your presentation?
A common mistake is using slides or videos as a crutch, even if they don’t actually add anything to your presentation. Not all presentations need graphics. Lots of presentations work wonderfully with just one person standing on a stage telling a story, as demonstrated by many TED Talks.
You should only use slides if they serve a purpose: conveying scientific information, art, and things that are hard to explain without pictures. Once you have decided on using slides, you will have a number of decisions to make. We’ll help you with the basics of making a presentation that is, above all, clear and easy to understand. The most important thing to remember here is: less is more.
Less is so much more
You want to aim for the fewest number of slides, the fewest number of photos, the fewest words per slide, the least cluttered slides and the most white space on your slides. This is the most violated slide rule, but it is the secret to success. Take a look at these examples.

As you can see in the above example, you don’t need fancy backgrounds or extra words to convey a simple concept. If you take “Everything you need to know about Turtles”, and delete “everything you need to know about” leaving just “turtles”, the slide has become much easier for your audience to read, and tells the story with economy.

The above example demonstrates that a single image that fills the entire screen is far more powerful than a slide cluttered with images. A slide with too many images may be detrimental to your presentation. The audience will spend more mental energy trying to sort through the clutter than listening to your presentation. If you need multiple images, then put each one on its own slide. Make each image high-resolution and have it fill the entire screen. If the photos are not the same dimensions as the screen, put them on a black background. Don’t use other colors, especially white.
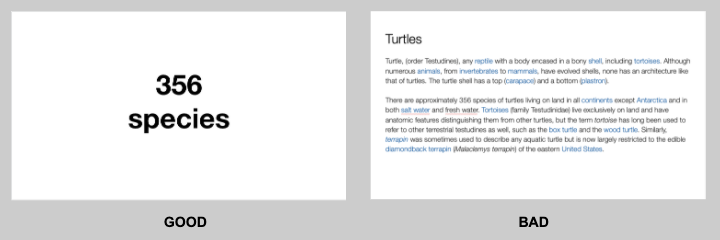
Your slides will be much more effective if you use the fewest words, characters, and pictures needed to tell your story. Long paragraphs make the audience strain to read them, which means they are not paying attention to you. Your audience may even get stressed if you move on to your next slide before they’ve finished reading your paragraph. The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says “any slide with more than 10 words is a document.” If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
Following a “less is more” approach is one of the simplest things you can do to improve your presentation visuals and the impact of your presentation overall. Make sure your visuals add to your presentation rather than distract from it and get your message across.
Ready to learn more about how to make your presentation even better? Get TED Masterclass and develop your ideas into TED-style talks.
© 2024 TED Conferences, LLC. All rights reserved. Please note that the TED Talks Usage policy does not apply to this content and is not subject to our creative commons license.
How to Create an Inspiring Presentation for your Workshop

Have you ever been at a presentation or workshop and found yourself forcing your eyes to stay open?
Bored out of your mind, and struggling to focus, the host is bleating on… and on. The concepts are too hard to follow, the words becoming a meaningless, tiresome cloud. Next time you struggle to sleep, it’ll be this guy’s waffling drivel that’ll send you to the land of nod.
Together, we’ll discover how to put the “Pow!” back into PowerPoint.
Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
In this article we’ll explore:
- Why visual presentations are important
- What to consider when planning presentations
How to design an engaging visual presentation
- How to choose an engaging format
- Which tools are best for designing presentations
- Tips on how to deliver your workshop presentation
Why Are Visual Presentations Important?
The purpose is to share brilliant ideas with an audience. This might be a piece of work or an educational concept in a workshop; the aim is to communicate with people, make them feel something , and take action. We all want our audience to leave an event feeling motivated and inspired, and that the workshop was of value.
The importance of visuals is often overlooked, either due to a lack of confidence in working with visual design, lack of time or both. For a workshop facilitator, using visual aids could actually save time, better represent our ideas and concepts to a group, and help you present more confidently. “How?”, you ask.
When it comes to saving time, a picture is really worth a thousand words. There is no need to type up your presentations or make wordy bullet points on every slide when a simple image can share the message for you.
Visual presentations put across an immediate message. Images are emotive and can deliver a story much faster than words, visuals are processed 60,000 times faster in the brain than text . An image that can share an idea, can be more memorable than trying to remember very specific terminology.
Creating visuals becomes part of a wider conversation in inclusive communication. Images are universally understood, and the eyes can “read” a picture with less effort than reading and comprehending several paragraphs. Imagine describing the color blue as a phrase. It is much easier to present it as it exists.
Graphics are easy to share, and 65% of us are Visual learners . For anyone who has missed out on the meeting, a visual booklet can do the job of sharing the subject with them, and the added benefit of being able to view it in their own time. The power of social media also plays a huge part in the spreading of information and well-designed infographic slides can take your presentations and workshops outside of the room, with the potential to make a global impact. Sharability goes further with visual elements.
For me, a visual presentation is a lifesaver! Using slides has saved me a lot of time and made me feel more confident whilst presenting too. I don’t fumble around with notes, as the visuals can act as a prompt to remind me of where I’m at in my talk.
When presenting online, I find the value of visuals and slides even more important. It takes the attention away from my actions, and onto the graphics themselves. The participants can hear what I’m saying, but their eyes focus on the visual information which helps in retaining information and ideas beyond the workshop.
What to consider when creating a visual presentation
I’m naturally quite a visual person, and I’ve often wondered if I could make a visual presentation without planning first what it is that I want to say. As an experiment, I gave it a go and it was a huge struggle. So, if you think that designing visuals is something that only designers can do and that they find it easy… it doesn’t and they don’t.
As a starting point: get out a pen and paper and write down everything you want to say. This ensures you have all of the ideas and information out in black and white . I find that by leaving space between the writing and structuring, coming back at it with fresh eyes is a perfect way to work without feeling rushed. I rarely add to what I’ve written, it’s mostly about removing.
Recently I had written a LOT of information for an event. A day later, I took a second view to edit. A lot of writing is quite self-indulgent, so it helps to consider the audience . I cut up sections of the paper, keeping only what was the most necessary information , and collated it together. The rest of the sentences didn’t make the cut. You can try the editing exercise here .
Less is More- an exercise in editing #presentation #presentation skills #writing #workshop #meeting design This exercise is ideal for editing written content in a hands-on way. A simple and effective exercise for editing workshop content or presentation text for talks. Use it when you have to write for a specific audience and want them to stay focused on the most important information.
As an expert in your field, it’s likely you’ll have a lot of content, and editing is so valuable to ensure your audience has relevant details. Don’t bore their socks off 😉

So now that you have an idea of your core content, you can move along the process, considering these factors before jumping into the design stages:
Let’s start by asking, “ who is your audience? “
- if you are being commissioned to present a topic to a pre-determined group, then you’ll need to cater to their understanding of the topic. You’ll want to ensure that the information will be relevant and meets or goes beyond their expectations.
- if the topic is of your own choice, and the angle you’ve chosen to take, who do you want to take part? Finding them, and attracting them to the workshop will be part of your marketing efforts, as well as how you plan your structure and content.
We wouldn’t plan a workshop for ten-year-olds in the same way we might for adults. Consider what tone of voice you might use, the style in which we present how we use slides, and the content itself. You won’t be able to do this for each and every individual, but how you determine and empathize with your listeners can be done by creating a persona, or several personas .
Create an overarching idea of who might be present, then consider how to engage them and meet their needs by asking yourself the following in more depth:
Why are they there?
Let’s look at their reason for attending your event. Have they come to learn from you in particular? If you are a specialist in your field and the workshop is an area of great interest to people, you’ll most likely have a deep understanding, and along with that, expectations to be filled.
Have they come to gain a better understanding of the topic? Are they there to challenge themselves and their existing views, or perhaps yours?
How much do they know already?
Are your participants already proficient in the topic you’re delivering? You’d hopefully know this in advance of your workshop so you can adapt your material, and create a pitch in line with the group’s knowledge. If their experience level is unknown, an opener to your discussion might be to ask about their subject knowledge, ideas and expectations. That way you can tailor your language and approach.
It helps to be well versed in your workshop, to select sections you can skip out in favor of diving deeper into more advanced information. Improvisation isn’t usually a skill you’d immediately connect with presenting, but with practice, learning how to improvise can become an empowering tool to have.
For beginners, you’ll most likely take an introductory approach. This doesn’t mean it has to be dry or boring. Make it more interesting and engaging by weaving in an interactive exercise, or team debate within your presentation design. That way, the participants can gather more hands-on experience to support their understanding. This can of course use visual handouts, such as a workbook, or include a well-designed visual exercise on an interactive whiteboard.
What is their background and communication style?
Your presentation style, language, and cultural references should be considered in the writing and designing process. I recently attended a workshop on how we can create better inclusion for diverse audiences by considering the language we use. It really made me think about how we often lean towards using English as a “default” language, and how words often hold different weights and contexts in other languages.
Remote workshops and presentations mean we may have a very diverse audience than if we were presenting in-person, in one location. Online could mean 140 people in different time zones across different countries with different backgrounds. Being aware of differences makes it easier to use inclusive, easy-to-understand language in your presentation so that no one feels alienated. Speaking with clear articulation will make a big difference in how you are understood.
You might have the best workshop on the planet, but if you don’t communicate in the style of your group, the impact will be lost. Do they want a short and snappy talk with a clear outcome at the end? Some audiences appreciate a motivational and inspirational talk that is led through emotional storytelling. Knowing their communication preferences can win over or lose your audience.
Before you begin designing your presentation, it’s important to consider what your purpose is. This is your mission statement, your project brief and your raison d’être. Here is where you want to ask yourself, what is it that you want your audience to think, feel or do? Are we creating an emotional impact or an educational goal?
Be as clear as possible with your core message, making it as specific as possible, so that you can keep this in mind throughout the process of writing, editing, designing and delivering presentations. This will keep your focus sharp, and avoid any unnecessary derailments taking your viewers away from what it is you hope to achieve.
Common purposes are to: inspire, inform, persuade or entertain .
- I want to inspire the audience to help reduce food poverty by leading a cookery workshop using supermarket waste.
- I want to inform the group about the future of rural tourism, so they might consider how they could adapt their own farming businesses to host visitors.
- I want to persuade my team to reduce our use of plastic in the fashion industry, by presenting a viable alternative made from mushrooms.
- I want to entertain by pretending to be a Martian visiting Earth for the first time . My purpose is to help the participants understand their product from a new perspective!
A Martian Sends a Postcard Home #creative thinking #idea generation #remote-friendly #brainstorming #energizer #team Use Craig Raine’s poem A Martian Sends a Postcard Home to spur creative thinking and encourage perspective shifting in a group. After a warm-up, you can then use this martian perspective to describe your product or service and gain new insights and ideas.
I recently designed a workshop called Design Thinking for Beginners and ran a SessionLab show and tell session aimed at facilitators who would like to run the workshop for teams new to design thinking. If you missed it, you can watch it back here. My purpose was to inform the attendees of the challenges newbies have with design thinking, and how they can make it a fun and digestible process.
I chose to relate each stage of design thinking to an everyday project of choosing or baking a birthday cake. My presentation was broken down into manageable chunks. Describing design thinking could be a laborious task, but keeping the text definition simple, with plenty of white space highlighted the point in one sentence.
For the workshop itself, I incorporated interactive exercises throughout the process to lock in the understanding of design thinking and how we generate ideas. For the ideate stage of design thinking- I created a game show style exercise called the Ideas Vault where I chose to create a fun layout like a 90s computer game. The design process worked by gathering inspiration using a mix of pre-made Canva templates and adding my own twist. I talk more about Canva and design tools here .
The way you choose to structure a visual presentation will depend wholly on the purpose. The way you communicate your key message should be crafted in a way for the audience to follow along easily and act on those all-important takeaways at the end.
A solid structure will also make sure your points are clear so that you stay calm and on track when presenting. The structure of your topic, when written down and broken into manageable chunks will help hugely when it comes to creating the visual elements later. (we’ll get to that in the next section!)
Some common ways to structure your presentation could be
- Problem > Solution > Impact. Which you might use if your purpose is to inspire the audience to take action on a topic, by showing them a viable solution.
- You may start with an informative session and create a workshop as we mentioned before, to lead people through a learning process.
- A creative structure might be through storytelling , which might inspire and entertain. Once upon a time, this event happened, followed by the outcome and moral of the story.
- In any case, your presentation could follow the classic layout of: introduction, main body & conclusion, and you’d have a good foundation for your content.
Introduction
You have the first few seconds to grab people’s attention. First impressions are just as important as they’re made out to be! The introduction is the most important part, where the group will connect with you and decide if they want to listen to you or not. What would be a great hook for the audience to immediately buy into your presentation from the start?
Some people introduce themselves at the beginning- but you don’t have to. If you’re beginning with a story, this can be a very effective way to warm up your participants and make sure they’re really listening to you. Then you can introduce yourself when you know they have your attention, and they value what you have to say.
A quote or a provocative question or fact can get people thinking. You may use a thought-provoking image, which could be a prop, a video or a photo that introduces your presentation from the get-go. If you are offering a solution, go straight to the problem in your introduction.
Main body of presentation
Now that you’ve got your audience’s attention, and they have gathered an understanding and are intrigued to learn more, we can delve into the juice of your subject.
The main body involves presenting the data, and the important pieces of information. If you are offering a solution to the problem you introduced, expressing this with a visual, we place the subject right in front of them, and they don’t have to work so hard and use their imagination.
The main body doesn’t have to be a one-sided conversation. Listen! You might ask the group to interact, asking for their perspective. A talk or workshop can be a dialogue between the presenter and the group.
Your conclusion should be as snappy and engaging as your introduction. It may even loop back to the provocative question, or challenging problem. You’ll want to consider the impact on the attendees and most importantly, what you want them to do next! What action do you want them to take beyond the workshop?
What are the key takeaways? Highlight them as Problem > Solution > Impact.
An effective class should tie up the opening question and objective, but still leave space for further exploration and discussion. Like a great film! They should not be saying, “I’m glad that’s over”. If it’s been designed with the audience in mind, they should feel something- energized or excited.
Now that you’ve written the content and designed the structure, here are our top tips to get you creating impactful visuals to complement what you present verbally. We’ll cover:
- How to design your slides and what information to include
- How typography impacts accessibility and design
- Making smart color choices for both emotional connection and accessibility
Designing your slides
When approaching a blank canvas, it can be hard to know where to start. Some people start with deciding how many slides they’ll use- the question, “How many slides are too many slides?” crops up regularly in these types of articles. Expert presenters say not to go over 20 visual slides, but this will of course depend on the length and complexity of your subject. Another tip is not to spend more than a minute on each slide to keep it snappy and people engaged.
If I am creating a presentation from scratch, I’ll start with the first slide, and keep it very simple before moving on to the next one. Always asking “what is this slide saying? ” The first slide will be the title of my discussion, which will be visible to everyone joining the room. It sets the tone for what the topic will be about. If we were creating one around the topic of designing workshop slides, it might look like this:

I think the most important thing to remember is that each slide should have its own purpose, and not be overloaded with text. Where possible, use an image rather than words and think about how we might convey this message visually. Always start by defining the message and asking what the key takeaway for participants is. You can always further explain verbally.
When choosing an image, consider the audience and their context- a local photograph they can relate to, or a familiar face will often have more to say than a generic stock image.
Text will likely be used on your slides, and how much text is too much? If you begin planning your content by writing it all out and keeping only the most important parts, designing your slides will be a lot easier. I’d always recommend editing continuously throughout the process to create a meaningful message. If you can say something in 3 bullet points rather than 10, please do! Your audience will have a much easier time retaining the information.
“Good design is invisible”
Unless the subject of your presentation is about typography, it’s probably not the best time to be cracking out your most recently found, favorite font that’s “a bit different” or unusual. Stick to standard, trusted and most legible fonts that audiences can read and are familiar with. Otherwise, they’ll distract from the content. And content is King.
“Good design is invisible”, a true and very useful phrase from Dieter Rams, who considers functionality in design as honest, long-lasting and with as little design as possible. This is a good theory to take throughout the design process. When looking for the right font, consider the tone you are using throughout your delivery too, and the overall message you are giving.
Good typography is your best friend for a presentation. When creating visuals for screens, as mentioned before, we are not typing out our speech word-for-word. Any text that is visually presented will have a very definite purpose as to why it is being displayed. This might be a quote, some data or the title of a book along with some further information in short form. Presentation slides are not a book.
Legibility is the most important thing when it comes to designing your visuals. Sans serif fonts are typically the best option for reading on a screen. Help your audience understand what you are communicating as quickly and easily as possible by ensuring the font sizes are easy to read.
Create contrast and visual interest by choosing two fonts, one for headers and one for any body text. The contrast should still be harmonious, and not jarring to the eyes. Font hierarchy can help the audience differentiate between key points and more specific information. By choosing different weights and sizes, you can ensure your message is clearly heard and understood.
- Minimum font size for main copy and bullets: 18 points
- Preferred font size for main copy and bullets: 24 points
- Preferred font size for headers or titles: 36 to 44 points
Personally, I like to choose font sizes slightly larger than recommended for body text. When we have a text-heavy page, I prefer to give the text plenty of surrounding white space and edit the copy as much as possible. From a design perspective, it helps legibility; and from a content perspective, it doubly ensures only the relevant text is presented on screen. I would definitely edit again at this stage. In this example for screens, the body text is 28pt and written in Open Sans, and the “Ideate” heading is 44pt in Agrandir wide.
Before creating any printed material for presentations, consider if it will truly be used and the environmental impact. I’d usually opt for sharing a digital version for people to refer back to after the workshop. It’s good practice to create a black and white version so that if it is printed out, the printing costs will be lower. There are of course digital accessibility issues, and some people might prefer a printed version. If so, select a serif font for any long text in a workbook or feedback form, with a minimum font size of 10-12pt.
Key points:
- Use Contrast
Deciding on the color scheme for a presentation is one of my favorite parts! Of course, you may have been given a branded color scheme to use, but if you have free reign in color choice and you enjoy the creative process, it can be a lot of fun.
For my show and tell on Design Thinking, I used the analogy of baking a cake and I felt that they conjure up an image of pastels. I used a gradient on the background so that I could use an array of colors without it being overbearing. I selected five key pastel colors for each stage of design thinking and to evoke a playful feel throughout. I was careful not to allow the colors to take over, so you’ll primarily see black and white use of color at the forefront for legibility.
Here are the key elements of how to choose a color scheme to complement your content :
The first, and most important point when choosing colors, is to use contrast. Make sure your text and graphics stand out from the background and are easily seen. Contrast is the difference in opposing colors so that they don’t blend in together A light background should use dark text and perhaps one or two bold accent colors to highlight key points. A dark background should use light fonts.
If you’re unsure of how easy a slide is to read, there are an array of online tools that can check the contrast for you by following the web accessibility guidelines. On Contrast Checker , you can enter the HEX code of the background and foreground colors, and you’ll get an idea of legibility. The sliders in the tool can be used if you need to improve the contrast and amend the color choices. There are also resources to guide you in how to select the color with an online eyedropper tool in case you’re not familiar with the HEX color codes.
Another contrast checker tool also shows the background and foreground with text examples and gives a rating to the accessibility of the text. This website has a whole host of tools, and can even pick a suitable palette for you.
If you’re working with a client, they may already have their own brand packaging and presentation template, including their colors. You may feel that this removes your choice of colors as it has been decided already, for example, they may use an in-house color language to refer to particular data on a graph. But the opposite may be true and might mean further considerations for visuals. It is important to know how to choose because when you create graphics or diagrams because you may have to select colors so that explanatory text can be seen on top of a shape or part of a graph.
When working with a client, it is important to share any documentation with their design team, and the best way to do this is by providing editable files. Working with a designer can massively lift the load on creating your presentation visuals. If there is no design team, but you are given design assets to work with, sharing both your visuals and your presentation agenda for collaboration and sign-off is a must. Create your agenda in SessionLab , and attach your visual presentation for ease of sharability.
Studies have shown that color has an effect on expressing or feeling emotions. It will help to consider the tone that you are using throughout your presentation, the message you are delivering, and how you might want your audience to feel.
Warm colors, in the middle of the color spectrum, that aren’t too bold or too light create a warm and comfortable feeling. Bright reds and oranges can feel energetic and powerful. Or even create a sense of danger. In contrast, cooler colors such as greens, blues and purples can feel calm or evoke a sense of sadness.
We have an exercise that can help identify emotions and grow a better emotional vocabulary, the feelings wheel . It includes a visual attachment displaying the emotions in a range of colors- this may help select a tone for your color scheme.
The Feeling Wheel #emotional intelligence #self-awareness #icebreaker #team building #remote-friendly By growing our emotional vocabulary, we can better identify our emotions, and check in with ourselves. Doing so can help bring a level of self-awareness, and a better understanding of others.
How to choose an engaging presentation format
We are almost there! The content is edited and your visual slides are ready, the next stage is to consider the format in which you’ll deliver your workshop or meeting. This is when you can consider any additional tools that you can use to your advantage when presenting. This might be video, photography or visual data. Or even props. Consider which other visual aids may help people to better understand the process or story you are conveying.
What presentation method will keep them engaged? How will you inspire and capture their imagination?
I’d recommend simplicity, and not try to include every form of media. Consider the purpose and message and select which format delivers it most effectively. Used with intention, video can be great. But animated graphics or flashy text is unnecessary and will add to the cognitive load of your audience, especially if they have any visual impairments.
Video can be very effective, so long as it’s kept brief. If it’s longer than a minute, you may lose the attention of the audience, and the momentum of your presentation. A film clip should be creative and add another dimension, not an infomercial or promo piece, it’s a tool to say something that you cannot put across otherwise.
Films can have great benefits of showing a story. In a TED Talk about the intelligence of crows, the scientist showed a clip of the crow bending a hook to create a tool and fish a piece of food out of a tube. It put across his point better than anything he could’ve said.
I use recordings in situations like this, to demonstrate a case study. It’s often more powerful to have the original storyteller sharing their experience than me giving a second-hand account of the tale. Bringing in other voices in this way can add further diversity to your workshop.
Still images
JPEGs are compressed files and are used for photo formats. When a photo is taken, it is a RAW file that is editable. Once it’s compressed to a JPEG, it retains around a tenth of the information, meaning it is a smaller and less detailed file. JPEGS are used in photography, but not in vector graphics (drawings, typography, graphs, etc), as the detail lost can create pixelation if you aim to blow the image up to a larger size.
PNGs retain detail and are editable. They are still compressed files, but the pixels aren’t lost. Any graphics you create should be saved as a PNG, as you’ll be able to keep the image sharp, regardless of the size.
The photography you choose must be relatable. I’m definitely not against stock imagery per se, it’s amazing to have access to a library of searchable images to strengthen what you are saying. But, often you’ll see the same images repeated in different workshops and presentations and they’ll start to lose their meaning, or become too familiar. There are great free resources like Unsplash and if you spend time looking for a more unique way to put your point across, there are lots to choose from.
I’ve also had an Adobe Express subscription which gives access to photography and graphics and templates which you to customize in editing with little design skills. Ideally, being able to take your own photographs, or work with a professional photographer to capture exactly what you want is going to give your audience a far more unique experience. This is often a luxury.
As facilitators, a way around this could be to create our own library of photos that we capture at each presentation. When I’ve run crafting workshops, it feels quite natural to take photographs of the work we are creating. And those who are camera-shy, they’re more open to photographs of their hands in action. Over time, we’ll have a whole collection of resources.
If you enjoy photography, having a good camera as part of your kit might intrigue people, invite people to take photos of each other and the workshop process. This could be an exercise that you do to open or close your talk. Or in some cases, especially if it’s a visual presentation, and not too distracting, invite people to take their own photos and share after with a #hashtag (promo and photos in one!) And of course, get everyone’s signature attesting they are OK with photos.
Visual data & symbols
Visualizing data makes it more interesting, engaging and memorable than cold hard figures. For the majority of audiences, it’s easier to understand in a visual format than in a list of forgettable numbers. By creating charts, graphs or maps, we are able to see patterns and understand the context of the statistics. A pie chart displaying percentages in corresponding colors tells our brain quickly which section has the largest number.
Even when we analyze word-driven data, a visual representation is easier to see straight away. When I’ve worked with community groups in the design thinking process, we’ve often used Google surveys to capture written evidence. This type of qualitative data can be a challenge to sift through, so for an initial overview, a tool like word cloud can show how many times a particular word or phrase appears and turns it into an image. The more times a word appears, the larger it is on the image.

The use of icons and emojis (sparingly! And in context 😉) can add another element of visual understanding to presentations. Illustrations and hand-dawn symbols might better express your point than a photograph too. An opportunity to work with a live scribe or graphic facilitator whilst presenting could add an interesting dimension to a talk. If it involves audience participation, having someone on hand to capture the conversation visually can keep engagement and attention going!
The best tools for designing your presentation
Canva has become a much more powerful tool than it was. You can even edit your workshop recordings with it now! It’s perfect for anyone with little design knowledge as it has great templates for presentations, lots of which are free. It has social media templates too, which are perfect for advertising your upcoming workshop.
Adobe Creative Suite
I do love Creative Suite , and it still is a great package of tools for designers. Photoshop, Illustrator and InDesign are the industry standard for design tools and have all the capabilities you’d need as a graphic designer. If that package is beyond your scope, Adobe Express is a great option for pre-made templates and stock imagery. Like Canva, it also works well as an app on a smartphone.
Keynote
Keynote comes as standard with MacBook and has had a whole new upgrade including being able to use the camera on your Mac or an external camera to show yourself directly on the slides. Super handy for an online event! You can also show the screen of a connected iPad or iPhone and it now has co-hosting capabilities.
Of course! SessionLab is where you can keep all of your presentation notes, and break down the agenda into blocks, so if you decide to switch up parts of your presentation- you can drag and drop to a different section of your talk. It is a much easier process, as it will also keep any other attachments or exercises in that block neatly collated in one place. It’s easy to share with any co-hosts or clients before the presentation day arrives!
How to deliver a workshop presentation with visuals
Some people memorize their speech word for word, which can work well if you’re a dab hand at amateur dramatics.
On the other hand, that might feel too stressful or rigid. Bill Murray is famously known to read a script once and throw it away! For you, it may be better to consider the key points you’d like to make, and really know your subject matter so whatever arises, you’ve got it covered. Your visuals might act as a prompt for you too, the main message will be communicated visually, and you can feel free to go into more depth.
The best way to ensure that you nailed the slide design for your session is to practice. It’s important to practice noting your timing, that you’ve covered all the important points, and that each slide transitions smoothly from one to the next. You want the presentation to be as seamless as possible. The best way to practice is in front of someone and gather feedback.
Before our design thinking for beginners show and tell, I rehearsed in front of my fellow team members, instructing them to wear their “facilitator’s hats” whilst listening, so they could hear from a facilitator’s perspective and give constructive feedback.
Afterward, you can continue to add and edit, removing some sections, and making room for more key discussions to be had in-depth. If it is an informal presentation that you will run more than once, it could develop over time. If it is a one-off very important meeting, it’s vital to get as much preparation practice as possible.

Expect nerves
If I get nervous, I purposely talk slightly slower than I usually would naturally, and it calms the nerves down. There’s also no harm in mentioning that you’re nervous, it’s an honest approach and can create an authentic connection.
We’re all human. And no one would expect you to not be nervous. Nerves, to an extent, can be a good thing. They bring a bit of energy and focus to your talk, and a little adrenaline. If you know your subject matter inside out, all you really need to do is breathe, and talk.
Speaking with one of our community members, Yvonne Chin Irving on the subject of nerves, she suggested diaphragmatic breathing, or more a more fun term, “balloon breathing”:
Belly breathe. Slowly. Imagine your tummy has a balloon that fills up when you breathe. Exhale all the air. Notice your tummy as it flattens. Next, breathe in slowly and fill your “balloon” with breath 🎈. Do this a few times to help calm yourself down. You can start this on the way to your session, do it in the car or while you’re setting up for your session. (It really works) Yvonne Chin Irving
We’d love it if you joined the conversation in our SessionLab community!
Having a technical rehearsal beforehand can help avoid blips. Ensure the right people have screen-sharing abilities, and that screens in the in-person space work. Iron out any microphone issues or problems with echo prior to the big presentation! On the day itself a technical disaster could strike, so here are some practical tips to circumnavigate these and stay professional:
- Create different formats for your presentation. If it’s a Keynote or Powerpoint, have a PDF version available in case of any tech issues you’ll still have a high-quality version available.
- If including video, have backup screen-shots as images to demonstrate your points in case the video doesn’t run.
- Be analog ready. Know your presentation without the use of slides- or print them out so that if there is a complete technical breakdown, you can confidently present. This might include creating printed handouts for people to refer to when you direct them to do so. Or, if they have their own smartphones, send them the link to your visuals or any important videos to watch back after your talk, to avoid distractions as you speak.
Accessibility
Ensuring your audience has the best experience, requires being aware of accessibility needs. Is access to the building easy for anyone with physical disabilities? Are the seats comfortable, and allow for ease of viewing for people of different heights?
We’ve discussed the best way to use typography for ease of reading for anyone with visual impairments, and when setting up your screen, it is a good idea to see how it will look in the actual event environment. Additionally, you may share larger-print handouts on yellow paper for anyone with dyslexia. This is another reason why knowing your audience in the planning stage will make sure your presentation is enjoyable and accessible for everyone.
Agenda planning
SessionLab is an agenda planning tool that makes presenting a lot smoother! You are able to allocate time to each section of content to keep yourself on track throughout. In your preparation stage, you can attach all of your materials to your SessionLab agenda, knowing exactly when you’ll use each of them. It’s so neatly organized and easy to edit and shift blocks if you decide to change the order of content for a future session.
In conclusion
I hope you have found this guide valuable, and that it inspires lots of ideas when planning your next presentation! There are a wealth of resources dotted around this article, and I’ll include a few more here that I highly recommend:
Lean Presentation Design A whole website by Maurizo la Cava dedicated to presentation strategy
Ted Talk: How to Write Less, but say more is an excellent talk by Jim VandeHai about short and effective communication.
Five Things to Know About Your Audience Before You Present if You Want to Be Successful useful tips on how to empathize with your group for a more successful presentation.
Let us know below in the comments if you have any questions, or any tips of your own to add to the conversation!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
- Online Degree Explore Bachelor’s & Master’s degrees
- MasterTrack™ Earn credit towards a Master’s degree
- University Certificates Advance your career with graduate-level learning
- Top Courses
- Join for Free
What Are Effective Presentation Skills (and How to Improve Them)
Presentation skills are essential for your personal and professional life. Learn about effective presentations and how to boost your presenting techniques.
![how to write visual presentation [Featured Image]: The marketing manager, wearing a yellow top, is making a PowerPoint presentation.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/1JnKR1F6C7RrqtObyeUr79/acdb15f7a7e894a375012e8d158ada4f/GettyImages-1358219358.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
At least seven out of 10 Americans agree that presentation skills are essential for a successful career [ 1 ]. Although it might be tempting to think that these are skills reserved for people interested in public speaking roles, they're critical in a diverse range of jobs. For example, you might need to brief your supervisor on research results.
Presentation skills are also essential in other scenarios, including working with a team and explaining your thought process, walking clients through project ideas and timelines, and highlighting your strengths and achievements to your manager during performance reviews.
Whatever the scenario, you have very little time to capture your audience’s attention and get your point across when presenting information—about three seconds, according to research [ 2 ]. Effective presentation skills help you get your point across and connect with the people you’re communicating with, which is why nearly every employer requires them.
Understanding what presentation skills are is only half the battle. Honing your presenting techniques is essential for mastering presentations of all kinds and in all settings.
What are presentation skills?
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images.
You'll make presentations at various times in your life. Examples include:
Making speeches at a wedding, conference, or another event
Making a toast at a dinner or event
Explaining projects to a team
Delivering results and findings to management teams
Teaching people specific methods or information
Proposing a vote at community group meetings
Pitching a new idea or business to potential partners or investors
Why are presentation skills important?
Delivering effective presentations is critical in your professional and personal life. You’ll need to hone your presentation skills in various areas, such as when giving a speech, convincing your partner to make a substantial purchase, and talking to friends and family about an important situation.
No matter if you’re using them in a personal or professional setting, these are the skills that make it easier and more effective to convey your ideas, convince or persuade others, and experience success. A few of the benefits that often accompany improving your presentation skills include:
Enriched written and verbal communication skills
Enhanced confidence and self-image
Boosted critical thinking and problem-solving capabilities
Better motivational techniques
Increased leadership skills
Expanded time management, negotiation, and creativity
The better your presenting techniques, the more engaging your presentations will be. You could also have greater opportunities to make positive impacts in business and other areas of your life.
Effective presentation skills
Imagine yourself in the audience at a TED Talk or sitting with your coworkers at a big meeting held by your employer. What would you be looking for in how they deliver their message? What would make you feel engaged?
These are a few questions to ask yourself as you review this list of some of the most effective presentation skills.
Verbal communication
How you use language and deliver messages play essential roles in how your audience will receive your presentation. Speak clearly and confidently, projecting your voice enough to ensure everyone can hear. Think before you speak, pausing when necessary and tailoring the way you talk to resonate with your particular audience.
Body language
Body language combines various critical elements, including posture, gestures, eye contact, expressions, and position in front of the audience. Body language is one of the elements that can instantly transform a presentation that would otherwise be dull into one that's dynamic and interesting.
Voice projection
The ability to project your voice improves your presentation by allowing your audience to hear what you're saying. It also increases your confidence to help settle any lingering nerves while also making your message more engaging. To project your voice, stand comfortably with your shoulders back. Take deep breaths to power your speaking voice and ensure you enunciate every syllable you speak.
How you present yourself plays a role in your body language and ability to project your voice. It also sets the tone for the presentation. Avoid slouching or looking overly tense. Instead, remain open, upright, and adaptable while taking the formality of the occasion into account.
Storytelling
Incorporating storytelling into a presentation is an effective strategy used by many powerful public speakers. It has the power to bring your subject to life and pique the audience’s curiosity. Don’t be afraid to tell a personal story, slowly building up suspense or adding a dramatic moment. And, of course, be sure to end with a positive takeaway to drive your point home.
Active listening
Active listening is a valuable skill all on its own. When you understand and thoughtfully respond to what you hear—whether it's in a conversation or during a presentation—you’ll likely deepen your personal relationships and actively engage audiences during a presentation. As part of your presentation skill set, it helps catch and maintain the audience’s attention, helping them remain focused while minimizing passive response, ensuring the message is delivered correctly, and encouraging a call to action.
Stage presence
During a presentation, projecting confidence can help keep your audience engaged. Stage presence can help you connect with your audience and encourage them to want to watch you. To improve your presence, try amping up your normal demeanor by infusing it with a bit of enthusiasm. Project confidence and keep your information interesting.
Watch your audience as you’re presenting. If you’re holding their attention, it likely means you’re connecting well with them.
Self-awareness
Monitoring your own emotions and reactions will allow you to react well in various situations. It helps you remain personable throughout your presentation and handle feedback well. Self-awareness can help soothe nervousness during presentations, allowing you to perform more effectively.
Writing skills
Writing is a form of presentation. Sharp writing skills can help you master your presentation’s outline to ensure you stay on message and remain clear about your objectives from the beginning until the end. It’s also helpful to have strong writing abilities for creating compelling slides and other visual aids.
Understanding an audience
When you understand your audience's needs and interests, you can design your presentation around them. In turn, you'll deliver maximum value to them and enhance your ability to make your message easy to understand.
Learn more about presentation skills from industry experts at SAP:
How to improve presentation skills
There’s an art to public speaking. Just like any other type of art, this is one that requires practice. Improving your presentation skills will help reduce miscommunications, enhance your time management capabilities, and boost your leadership skills. Here are some ways you can improve these skills:
Work on self-confidence.
When you’re confident, you naturally speak more clearly and with more authority. Taking the time to prepare your presentation with a strong opening and compelling visual aids can help you feel more confident. Other ways to improve your self-confidence include practicing positive self-talk, surrounding yourself with positive people, and avoiding comparing yourself (or your presentation) to others.
Develop strategies for overcoming fear.
Many people are nervous or fearful before giving a presentation. A bad memory of a past performance or insufficient self-confidence can contribute to fear and anxiety. Having a few go-to strategies like deep breathing, practicing your presentation, and grounding can help you transform that fear into extra energy to put into your stage presence.
Learn grounding techniques.
Grounding is any type of technique that helps you steer your focus away from distressing thoughts and keeps you connected with your present self. To ground yourself, stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and imagine you’re a large, mature tree with roots extending deep into the earth—like the tree, you can become unshakable.
Learn how to use presentation tools.
Visual aids and other technical support can transform an otherwise good presentation into a wow-worthy one. A few popular presentation tools include:
Canva: Provides easy-to-design templates you can customize
Powtoon: Animation software that makes video creation fast and easy
PowerPoint: Microsoft's iconic program popular for dynamic marketing and sales presentations
Practice breathing techniques.
Breathing techniques can help quell anxiety, making it easier to shake off pre-presentation jitters and nerves. It also helps relax your muscles and get more oxygen to your brain. For some pre-presentation calmness, you can take deep breaths, slowly inhaling through your nose and exhaling through your mouth.
While presenting, breathe in through your mouth with the back of your tongue relaxed so your audience doesn't hear a gasping sound. Speak on your exhalation, maintaining a smooth voice.
Gain experience.
The more you practice, the better you’ll become. The more you doanything, the more comfortable you’ll feel engaging in that activity. Presentations are no different. Repeatedly practicing your own presentation also offers the opportunity to get feedback from other people and tweak your style and content as needed.
Tips to help you ace your presentation
Your presentation isn’t about you; it’s about the material you’re presenting. Sometimes, reminding yourself of this ahead of taking center stage can help take you out of your head, allowing you to connect effectively with your audience. The following are some of the many actions you can take on the day of your presentation.
Arrive early.
Since you may have a bit of presentation-related anxiety, it’s important to avoid adding travel stress. Give yourself an abundance of time to arrive at your destination, and take into account heavy traffic and other unforeseen events. By arriving early, you also give yourself time to meet with any on-site technicians, test your equipment, and connect with people ahead of the presentation.
Become familiar with the layout of the room.
Arriving early also gives you time to assess the room and figure out where you want to stand. Experiment with the acoustics to determine how loudly you need to project your voice, and test your equipment to make sure everything connects and appears properly with the available setup. This is an excellent opportunity to work out any last-minute concerns and move around to familiarize yourself with the setting for improved stage presence.
Listen to presenters ahead of you.
When you watch others present, you'll get a feel for the room's acoustics and lighting. You can also listen for any data that’s relevant to your presentation and revisit it during your presentation—this can make the presentation more interactive and engaging.
Use note cards.
Writing yourself a script could provide you with more comfort. To prevent sounding too robotic or disengaged, only include talking points in your note cards in case you get off track. Using note cards can help keep your presentation organized while sounding more authentic to your audience.
Learn to deliver clear and confident presentations with Dynamic Public Speaking from the University of Washington. Build confidence, develop new delivery techniques, and practice strategies for crafting compelling presentations for different purposes, occasions, and audiences.
Article sources
Forbes. “ New Survey: 70% Say Presentation Skills are Critical for Career Success , https://www.forbes.com/sites/carminegallo/2014/09/25/new-survey-70-percent-say-presentation-skills-critical-for-career-success/?sh=619f3ff78890.” Accessed December 7, 2022.
Beautiful.ai. “ 15 Presentation and Public Speaking Stats You Need to Know , https://www.beautiful.ai/blog/15-presentation-and-public-speaking-stats-you-need-to-know. Accessed December 7, 2022.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
The Visual Communication Guy
Learn Visually. Communicate Powerfully.

- About The VCG
- Contact Curtis
- Five Paragraph Essay
- IMRaD (Science)
- Indirect Method (Bad News)
- Inverted Pyramid (News)
- Martini Glass
- Narrative Format
- Rogerian Method
- Toulmin Method
- Apostrophes
- Exclamation Marks (Points)
- Parentheses
- Periods (Full Stops)
- Question Marks
- Quotation Marks
- Plain Language
- APPEALS: ETHOS, PATHOS, LOGOS
- CLUSTER ANALYSIS
- FANTASY-THEME
- GENERIC CRITICISM
- IDEOLOGICAL CRITICISM
- NEO-ARISTOTELIAN
- O.P.T.I.C. (VISUAL ANALSYIS)
- S.O.A.P.S.T.O.N.E. (WRITTEN ANALYSIS)
- S.P.A.C.E.C.A.T. (RHETORICAL ANALYSIS)
- BRANCHES OF ORATORY
- FIGURES OF SPEECH
- FIVE CANONS
- LOGICAL FALLACIES
- Information Design Rules
- Arrangement
- Organization
- Negative Space
- Iconography
- Photography
- Which Chart Should I Use?
- “P” is for PREPARE
- "O" is for OPEN
- "W" is for WEAVE
- “E” is for ENGAGE
- PRESENTATION EVALUTION RUBRIC
- POWERPOINT DESIGN
- ADVENTURE APPEAL
- BRAND APPEAL
- ENDORSEMENT APPEAL
- HUMOR APPEAL
- LESS-THAN-PERFECT APPEAL
- MASCULINE & FEMININE APPEAL
- MUSIC APPEAL
- PERSONAL/EMOTIONAL APPEAL
- PLAIN APPEAL
- PLAY-ON-WORDS APPEAL
- RATIONAL APPEAL
- ROMANCE APPEAL
- SCARCITY APPEAL
- SNOB APPEAL
- SOCIAL APPEAL
- STATISTICS APPEAL
- YOUTH APPEAL
- The Six Types of Résumés You Should Know About
- Why Designing Your Résumé Matters
- The Anatomy of a Really Good Résumé: A Good Résumé Example
- What a Bad Résumé Says When It Speaks
- How to Write an Amazing Cover Letter: Five Easy Steps to Get You an Interview
- Make Your Boring Documents Look Professional in 5 Easy Steps
- Business Letters
- CONSUMER PROFILES
- ETHNOGRAPHY RESEARCH
- FOCUS GROUPS
- OBSERVATIONS
- SURVEYS & QUESTIONNAIRES
- S.W.O.T. ANALYSES
- USABILITY TESTS
- CITING SOURCES: MLA FORMAT
- MLA FORMAT: WORKS CITED PAGE
- MLA FORMAT: IN-TEXT CITATIONS
- MLA FORMAT: BOOKS & PAMPHLETS
- MLA FORMAT: WEBSITES AND ONLINE SOURCES
- MLA FORMAT: PERIODICALS
- MLA FORMAT: OTHER MEDIA SOURCES
- Course Syllabi
- Checklists and Peer Reviews (Downloads)
- Communication
- Poster Prints
- Poster Downloads
- Handout & Worksheet Downloads
- QuickGuide Downloads
- Downloads License Agreements

How to Design a PowerPoint: A Visual Guide to Making Slides with Impact
Home > Speaking > How to Design a PowerPoint
A quick Google Images search for “worst PowerPoint slides” proves two very clear realities: 1) anybody can create a PowerPoint; and 2) many don’t know how to do them well.
That’s understandable, though. Unless you’ve recently taken courses or training in design, data visualization, and public speaking, you likely haven’t had any more education on how to create an effective slide deck than a ten-year-old.
And you’re not alone.
Bad PowerPoints are everywhere: professor lectures, science conferences, human resources trainings, team meetings, sales review gatherings, thesis and dissertation defenses, product pitches, job interviews, you name it. Some of the brightest people in the world have created some of the most awful PowerPoints. For most, it’s just not a natural skill.
That’s unfortunate, too, because a well-designed slide deck can make a tremendous difference in the reception of the message you’re trying to convey.
To start designing excellent slide decks right away, follow my quick guide to designing better PowerPoints right after this paragraph. To get a whole workshop’s worth of information about how to design better slides, scroll below. 🙂
Click image to enlarge.

The question is, does designing a nice PowerPoint actually matter?
Well, if you’ve made it this far, you already know my opinion. But the short answer is, YES! Effective slide decks can make a HUGE difference in the outcome of your presentation. Why? Because slides—which should be used to supplement and enhance your well-prepared script (not be the presentation, as we often see in slides that are nothing more than bulleted lists)—significantly improve engagement during the presentation and recall after the presentation.
Basically, if you want people to both pay attention AND remember what you said, good slides can make all the difference. Plus, research has shown that people trust information more when it’s well-designed. In sum, good slides will cause your audience to:
- Pay attention more and stay more engaged;
- Remember the key messages from your presentation better;
- Trust you and your information more; and
- Believe you are super smart and awesome. (I mean, you already are, but good slides will seal the deal.)
Bad slides, on the other hand, are not only distracting, but they can actually damage a person’s ability to understand and follow your message.
At best, poorly designed slides will make you look less professional. At worst, they’ll encourage people to not listen to anything you have to say. Bad slides (which are caused by a whole range of things, including being too text-heavy, too busy, too inconsistent, or too color crazy, etc. [see my article on 40 Ways to Screw Up a PowerPoint Slide ]), overwhelmingly distract from your presentation.
If a slide has too much text, people try to read it and listen to you at the same time—which damages their ability to do either well. If your slides are too busy, your audience won’t be able to understand the information quick enough. If it’s ugly, well…people just tune out and ignore (and judge you, to boot).
Okay, so enough of the why . Let’s get to making better slides!
The 9 Steps to Designing a Better PowerPoint Slide
Step 1: empathize with your audience.

The term “empathy” in this context comes from a relatively new theory called “design thinking,” in which you can apply the mindset of a designer to a variety of contexts. So, whether you’re creating a toothbrush, a video game, an automobile, or…a PowerPoint, you need to be thinking a like a designer—which starts with empathy.
Empathizing with an audience is like applying the Golden Rule: present unto them as you would like to be presented to. Of course, the content of presentation itself comes first and foremost, but the design of your slides should support and enhance your content, so you’ll be thinking of your script and your slides at the same time. To begin, it’s best to start with a few concrete questions about your audience:
- Why are they there? Are they at your presentation because they want to be, or because they have to be? Is your presentation the only one of the day, or is it one of many (like at a conference)? Are they expecting to learn, be entertained, be inspired, be trained? In essence, you want to know their state of mind before coming so you can plan to accommodate that as best you can.
- Why would they care? Dig deep here. Does your audience actually care about the topic as much as you do? And…if you don’t care, why don’t you? If the topic isn’t meaningful and you can’t make it feel that way, then why even present? But…if they do care, know why they do. What will they hope for and expect out of it? What can you do to meet and exceed their expectations?
- What do they need to know? And what DON’T they? How much about your subject do they already know? Are they novices, experts, or a blend of both? Does it make more sense to break your topic into separate presentations on separate days, rather than giving it all at once? Is it focused and narrow enough to make an impact? Can you leave anything that is irrelevant out?
- What will keep them engaged? Consider your content and your big takeaways. Consider the personalities and knowledge base of the audience? What can you do to keep them engaged? Now…remember that “engaged” doesn’t mean “entertained” (though it can). If you’re a scientist presenting on bacterial infections in the liver, entertainment is obviously not appropriate. But…if you don’t engage them, they may not appreciate your research, no matter how valuable it is. What will they want to see, hear, and know and how can you display that to them in a way that will keep them interested?
Once you have clear idea about your audience’s needs and desires, you can begin to develop slides (along with the content of your script) that will give them exactly what they’re looking for rather than wasting their time (and yours).

Step 2: Define the Story

Think of your presentation as a story and you, the presenter, as an author in real time. As you deliver a presentation, you are creating the tone, setting, and plot for what happens. Your execution of the presentation will, if done right, create a climax/conflict and an important resolution. Consider how your slide development functions like the five components of a story, then write down how you plan to control (define) that story:
- The Setting. You create a mood and presence by the way you enter the room, interact with the audience, and display your title. While you may not have full control over who comes and what the room looks like, you do have relative control over the tone and ambiance and how they will react to your message. Consider the title of your presentation. Does it capture your message while also creating a buzz about your topic? Can you add a photo on the title slide that will intrigue your audience? What colors will you use? How do you plan to interact with the slides and how will you keep the audience involved?
- The Characters. You may not know all the people in the room, but you should know as much about them as possible (start with Step 1). Still, you have a way to shape their interest and engagement in this topic. Characters in this story are stakeholders. Your ultimate goal for giving should be one of three things: help them think about something in a new, meaningful way; learn something valuable they didn’t know before; and/or act as a result of what they learned. If you can’t get them to one of those three points, you’ve never really developed the characters.
- The Plot . A plot in storytelling is a series of events that build towards a conclusion. A plot needs to have direction, with clear and meaningful series of events. As you develop your script, you should be thinking about your rhetorical progression of ideas—your building towards a final outcome or conclusion. The development of slides can help you with this and they can help your audience stay on track. The key is, you need to make sure your audience is following the plot. If the plot starts to feel loose, disconnected, fragmented, or…all over the place, you’ll lose them faster than a 0-star rated movie.
- The Conflict. There must be some reason why everyone is there to see you presentation. It’s possible they don’t fully understand it themselves, but you, as the presenter, must make their purpose evidently clear. You must make them care. The more and more you pull them into your subject matter, the more you have effectively built a climax, which is the key to any successful story.
- The Resolution . The resolution is the takeaway—it’s what resolves the conflict. If you’ve built a strong climax, you now need to make sure your audience leaves with something valuable. If they leave thinking in a new, meaningful way; if they have learned something valuable that they can apply today; or if they are ready and knowledgeable about how to act, then the resolution is there and you, the author, have done your job.
Step 3: Brand Your Message

Jeff Bezos is famous for having said, “Brand is what others say about you when you’re not in the room.” You might think similarly about your presentation. How will your audience feel about your presentation afterwards, when you’re not around?
That can be an intimidating question to ask. And, it may seem a little odd to think about your message as a “brand.” But…applying brand theory to messaging makes a lot of sense. You want people to get on board with what you have to say. To do that, you have to establish what they value, what motivates them, and what you’ll have to do meet or exceed their expectations.
Brand experts use a lot of terms to describe and define brands. Let’s address a few, and apply them to slide design:
- Differentiation. How yours is different from the rest. What can you do to make your message stand out from a world of clutter and information? What makes yours unique? Is it your approach, the stories you tell, your language, your humor, your ideas, something else?
- Authenticity . How much you genuinely care. Audiences can tell if you’re passionate or not. They know if you care about both your topic and them learning it. If you fake it, the message gets diluted. Use your slides to help showcase how much you care.
- History . What people already know about you, your topic, or your experience. Do you need to establish credibility, or do you already have it? Do you have experience you can lean into? Does your audience already like/agree with this topic? Is it totally new and unfamiliar to them? How can you bring the history of your topic and yourself into the presentation? Will you audience need a primer on the history or does it matter?
- Simplicity. Making the most important things stick. Good brands almost always have simple logos, simple taglines, and simple brand positioning statements. Many also focus on limited products—they focus on what they do well. Your message can work the same way. Can you simplify your entire message into 2 – 5 key points? Can you reduce the amount of information that has to be taken in all at once? Can you help organize and chunk information to be clearer and simpler to follow? People generally have a hard time remembering complex information all at once—determine what the real purpose of your presentation is and what your audience can reasonably get out of it, then simplify to make sure that happens.
- Visual Identity . Your message, like a brand, can be enhanced if people resonate with the overall look and feel. Just like with buying a brand of shoes, people will be drawn to the design of your information. If it looks static, cliche, poorly design, or just plain ugly, you’ve created an undesirable visual identity and people will have a harder time buying into it. But if you can take your message and harmonize with strong design and imagery, people will be more likely to be attracted by, latch onto, and “buy in” to what you have to say. What should your visual identity look like, considering your topic?
Step 4: Select Your Fonts

The choice of your font may seem a small thing, but it can make the difference between a sleek, professional presentation and one that is static, boring, or, worse, painfully obnoxious.
If you’re not a professional designer, being font savvy may not come natural. Fortunately, there just a few rules you can follow to help you make your choices:
- Avoid the Defaults . In PowerPoint (as in MS Word), the default font is Calibri. Before 2010, the default was Times New Roman. Other programs use Arial or Myriad Pro as the default. What’s wrong with defaults? The fonts themselves are actually fine fonts—that’s why Microsoft went with them. BUT…because they’re the defaults, they are so widely used that they’ve become dull. If you just leave the defaults, your audience will subconsciously feel that you didn’t design your PowerPoint (because you probably didn’t). Just changing the font can bolster your PowerPoint’s professionalism quickly.
- Stick to Simple, Modern Fonts. Okay, so you don’t want to use the defaults, but what DO you use? Something simple. Don’t go crazy. Find something that is similar to the default, with just a little variation. Find something that is super easy to read and looks clean, simple, and sleek. Nothing distracting. Remember: you want people to focus on your story and message, not the lettering. Look at the graphic above for a list of some good, simple, modern fonts. Avoid, at all costs, the notoriously ugly or cliched fonts: Comic Sans; Chiller; Papyrus; Algerian; Curlz MT; and so forth.
- Make Sure Your Fonts Are on the Computer(s) You’re Presenting On. Remember: fonts are installed on individual computers, not attached to a program. A misunderstanding that many people have is that a font comes with PowerPoint (or any other program you’re working on). That’s NOT accurate. Fonts are installed on your computer. So…if you use a cool font that was on your desktop PC, but you are presenting your slides on a MacBook laptop, you’ll want to check that both computers have the font you’re using. Some fonts are pretty standard and you’ll find them on pretty much all computers: Palatino Linotype, Century Gothic, Segoe UI, Garamond. Others, however, are proprietary and may not be on other computers: Acumin Pro, Raleway, Helvetica. If you know you’ll be presenting on multiple different computers, find a standard font. One I’ve always liked to use is Century Gothic.
- Consider Using Two Fonts . The “two-font rule” suggests that designs will be more attractive if they use two fonts—one for headings and titles, the other for body text. You can get away with just one font if you make your headings stand out in some way—by size, weight, or color—but it’s often a nice aesthetic to use two. Just be sure that the two fonts are obviously different from each other (don’t use both Arial AND Century Gothic—they’re too similar, which will look like an accident) and that they harmonize well together. It’s often good to use a serif font (the type with little “feet” like in Palatino Linotype) paired with a sans serif font (the kind without “feet,” like Century Gothic).
Step 5: Narrow Your Colors

A hallmark of any good design is a simple, consistent color scheme. Keep your slide designs to fewer than four colors. Often, it’s good to use black, white, gray, and then one or two accent colors. Years ago, when I was new to design, I had someone tell me that a brochure I created looked like a clown exploded on the page. You DON’T want your slides to look like a clown exploded! To avoid that, find your color scheme in advance and stick to it.
Color can be tricky. If you work for a company that already has a pre-established style guide and color scheme, definitely use it! Not only is that important for your company’s brand, it makes your life a whole lot easier. If you do have to choose colors yourself, though, consider going to this website first: color.adobe.com . You can type things into the “explore” bar and you’ll be led to color schemes that look nice.
What you want to look for are colors that are a bit muted and won’t overwhelm the eyes of your viewers. Remember that you want to keep a high contrast so it doesn’t strain your audience members’ eyes. So…stick to black or really dark gray for text. Keep a white or very light background. Use the accent color for headings or important pieces of content. And…just make sure the colors match your topic or industry.
Step 6: Divide into Sections

Good presentations are well organized. Your slides should visually reflect your organization by using different slide “types” for different parts of your presentation or content.
All presentations should have at least three slide types: a title slide, a body slide, and a closing slide. Most presentations will have a fourth: a section slide. Section slides are used to transition your presentation from one major topic to the next. Many presentations can also benefit from callout slides, which are used to designate unique types of content that show up periodically—like for direct quotes or polling questions to audience members.
If you’ve ever taken a college course on public speaking, you probably remember your professor telling you to use “signposts.” A signpost is a metaphor for visual or oral cues that let your reader know where they’re at in the journey. Signposts keep your audience oriented. Sectioning your slides provides a visual signifier to your audience that you are shifting gears—plus, it just makes your slides feel cohesive, professional, and organized.
Take the time to design your slide types first. Then, fill in the content from your presentation script.
A quick note about body slides, though. These are going to be the most frequently used slides, the ones that you put the majority of your content on. Note that body slides don’t all have to look identical. They need to be consistent in design—repeating the same fonts, colors, photography style, highlights, etc.—but the layouts can change. Providing some visual variation is good for your audience.
Step 7: Visualize Every Slide

One of the biggest errors inexperienced presenters make is believing that audience members need to be able to read a lot of text to understand the message.
The reality is, when you put a lot of text on the screen—even if it’s in a bulleted list—you end up creating more difficulty for your audience. They’ll try to read while also trying to listen to you, creating a conflict of noise that will eventually cause them to only catch about half of what you wanted them to. Plus, a lot of text is boring and not efficient for the human brain.
Research has actually shown (and there is significant evidence to prove this) that making information visual is good for humans for four reasons: engagement, cognition, trust, and recall.
- Visual information is more engaging . Most all people will tell you that they are “visual learners.” The reality is that pretty much all humans are. We pay attention to visual information because our brains are designed to process visual information faster. When you provide visuals—photographs, charts, diagrams, icons, etc.—people will pay far more attention than if you just have text. In fact, if you just have text on a screen, people will likely zone out.
- Visual information is easier to understand. If designed well and related to the topic, people will understand visual information faster than they will from reading. Even as you read this article (assuming you’re still here!), the information that is really going to help you are the visual examples and explanations I’ve added for each section. That’s the stuff where you’ll say, “aha! now I know what Curtis is telling me to do.” All this text—it’s just ancillary stuff to provide more detail. But the photos/graphics are what you’ll really learn from.
- Visualized information builds trust. For better or for worse, humans are wired to trust information more when it has been visualized, especially when it looks professional. If you take a table of data and turn it into a data visualization that is professionally design, people will tend to trust it more. Something about taking the time to visualize information makes people assume you know what you’re talking about. Now, that said, you have to make sure your data visualizations are accurate. The real pitfall here is that people will tend to trust it more, even if it’s misleading. If they discover any flaws, your entire argument (and credibility) will go out the window.
- Visual information is easier to remember . Research studies have shown that visual information will be retained more than six times better if visuals are attached to it. If you actually want people to remember your presentation you must do two things: tell stories and use pictures. If you simply regurgitate information and make it very text-heavy, your audience will forget almost everything you said within three days. If you add pictures, though, they’ll have mental images to trigger memory, helping them retain your message much longer.
Find ways to visualize every chance you can, making sure that your visuals emphasize, clarify, or enhance the content you are talking about. Look at the examples above. Find ways to reduce text and enlarge graphics; turn bullets into images or icons; and use simple, easy to understand graphics that draw attention to the most important point.
Step 8: Play with Photos and Layouts

This is the one that takes the most practice, but it can be the most fun and rewarding. Recognize that your body slides can take multiple forms and that there are endless ways to organize, crop, and adjust visualizations, photos, headings, and designs. As long as you keep your color scheme, fonts, and highlighting techniques consistent, the slides will still feel uniform and professional, while giving variety to your slides.
Some things to think about as you play with the design of your slides:
- CONTRAST: Make sure you use high contrast in colors, especially for areas where you have text (black text on white backgrounds almost always work best). In addition, make sure that things that are different actually look significantly different. If two fonts are different sizes, make them obviously different sizes. If you’re using two colors, make them completely different colors. When two things look similar, there isn’t much contrast, which looks accidental and/or visually dull.
- REPETITION: Repetition is all about consistency in design. Repeat design elements throughout: fonts, colors, highlights, logos, shapes, styles, etc. Repeat the same visual feel for photos. Use the same types of icons and graphics. The more unified the design, the strong the appeal and the more professional you look.
- ALIGNMENT: Make sure everything on your slide is aligned with something else. Nothing should be “floating,” or placed arbitrarily. Align photos to titles, words to other words, rules/lines to other elements. Keep it all tightly aligned and crisp.
- PROXIMITY: Put things that are related close together and things that aren’t apart from each other. The brain will automatically assume that, if two things are next to each other (like a photo and a caption) that they are connected. Avoid confusing your audience by separating things that are different and connecting things that go together.
- Move Photos to the Bleeds . The term “bleed” is a graphic design principle that describes moving photos to the edge of page (where the ink “bleeds” off) in order to reduce visual noise. An old design principles developed by Josef Albers, 1+1=3, suggests that when you insert two objects, you automatically create a third—the space between. When you insert a photo, you end up creating a margin of white space around the edges. If that white space isn’t necessary, just make the image larger and push clear to the edge of the screen. This will remove the margin and the noise. Plus, it just makes slides look simpler and more professional and it really draws the eyes to the photo.
Step 9: Orient Your Audience

In addition to creating section slides (see Step 6 above), you can help your audience—and yourself—stay organized by giving visual cues and textual information in footers, slide counts, and headers or sidebars.
These orienting features of a slide deck can be especially valuable if you’re giving a long presentation, workshop, or training.
Start by creating a footer. These aren’t required and you don’t need them on every slide, but in most costs, presentations will benefit from some information in the footer. Some of the most common things to include in a footer:
- Company logo
- Company name
- Name of presenter
- Name of event or conference
- Title of presentation
- Copyright information
Beyond the footer, you can also include a slide count (in example above, look at the bottom right of the slide). While some argue that this can be distracting, most would say that a slide count will help audience members know how much more to expect, putting their “I’m being held hostage by this presenter!” fears away.
If your presentation is particularly long (like, say, 45 minutes or more) or you’re giving a workshop, you can really help your audience by giving them a sort of contents or guide, so that they know where they’re at in relation to everything else. You might, for example, create a small sidebar on the left that includes the section they’re in with the subsection. Or, as in the example at the top (see top left of example), you might just include which section you’re on and a summary title of that section.
There is no one or perfect way to orient your audience members. Just make sure it’s on the forefront of your mind as you work to build empathy into your slide design. The presentation is for them, after all, not you. Give them as much as you can to help them appreciate the message you’re delivering.
- ← Is a Doctor of Nursing Practice Degree Worth it?
- 6 Things You Should Do to Preserve Your Wealth →
Shop for your perfect poster print or digital download at our online store!
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, audiovisual presentations made easy(-ier): tips for creating an effective powerpoint, prezi, or keynote.
- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 by E . Jonathan Arnett

At some point in your academic or professional life, you’ll have to stand in front of people and give a talk about a subject, and quite often, you’ll be asked to prepare visual materials to accompany your talk. You might prepare handouts, but odds are, you’ll be asked to prepare materials that you can project on a video screen.
The classic version of these projected materials is the overhead transparency, a thin sheet of clear plastic that you can run through a laser printer or write on with special markers; this medium is slowly disappearing, but it’s still around. Sometimes, you might be able to prepare paper documents and project them to a screen via a document camera, but doc cams aren’t entirely common, and they can only present static images. Instead, you’ll usually be asked to create a dynamic presentation using software such as PowerPoint, Prezi, or Keynote. Many other programs exist, including what Google has to offer, but these are the three most common presentation programs.
Each program has its own special abilities and strengths, but they all share common basic principles that you can manipulate to create memorable, effective, and interesting presentations. Here, you’ll learn basic principles to
- select an effective presentation format
- choose readable typefaces
- place visual elements onscreen
- choose colors
- select appropriate backgrounds
- choose visual and audio effects
- deliver a memorable, effective presentation
Three Major Presentation Formats
You can choose from three basic type of format for a presentation based on PowerPoint, Prezi, or Keynote:
- bullet points
- illustrated points
- speaker’s prop
The format you choose should fit your audience and your presentation’s subject.
Bullet Points. The bullet point format is the default layout that most PowerPoint users and viewers are familiar with. Slides created in this format commonly include a title across the top and a cascading series of bulleted lines of text inside a slide’s main text box. An example of this kind of slide appears below, in Figure 1.
Figure 1: PPT slide using bullet point format
Bullet point-format presentations have several benefits:
- They are easy to prepare. Just type, press Enter for a new line, and press Tab to create a smaller bullet or Shift+Tab to make a larger bullet.
- They are useful for highlighting important words or naming concepts that an audience needs to learn.
- They project a serious tone.
However, bullet-point format presentations also can be boring, and an overload of words will make your audience cringe. You have probably endured at least one bad PowerPoint in your life, and odds are, that bad presentation used the bullet point format.
Illustrated Points. The illustrated points format is similar, but slides created in this type of presentation focus on pictures, and text appears in a supporting role. An example of this kind of slide appears in Figure 2.

Figure 2: PPT slide using illustrated points format
Illustrated points-format slides have several benefits:
- They are excellent for showing conceptual relationships or demonstrating physical relationships between objects.
- People often respond positively to pictures, so illustrated points-format slides also tend to capture viewers’ interest more than all-text presentations do.
These slides require more detailed preparation, though, and they tend to be more visually “busy,” so if your audience has problems concentrating, or if it’s vital that you highlight important words, you may want a more text-based approach.
Illustrated points-format slides can also be combined with bullet point-format slides inside the same presentation. See Figure 3 for an example of a PowerPoint that includes both types of slide.

Figure 3: Combination of bullet points (top) and illustrated points (bottom) slides in one PowerPoint
Speaker’s Prop. The speaker’s prop format is similar to the illustrated points format, but a speaker’s prop almost entirely consists of simple pictures that flash onscreen in rapid sequence. Any text that appears is usually very short, uses a large font, and only appears for a moment.
A speaker’s prop is appropriate for abstract subjects (e.g, the nature of free will), and if it is done well, it can be fascinating and will engage an audience.
However, this type of presentation is often more complex and time-consuming to prepare than a presentation in the other formats, and you run the risk of making it so entertaining that the audience may remember the presentation but forget what you said.
A well-done example of a speaker’s prop presentation appears in this video:

Figure 4: Screen capture of speaker’s prop presentation
Whichever format you choose, remember that the presentation software is your servant; don’t let it tell you what to do. Always modify a template to suit your needs.
As an excellent example of what not to do, consider Peter Norvig’s classic Gettysburg PowerPoint: http://norvig.com/Gettysburg/ . It’s a satirical example of how an excellent speech—in this case, Abraham Lincoln’s famous Gettysburg Address, widely considered one of the classic speeches in the English language—can be ruined by using presentation software default settings and following a built-in template without modifying it.
How to Choose a Typeface
When you create a presentation, make sure that the fonts you choose are
- appropriate for the subject and audience
- readable from anywhere in the room
- compatible with the computer you’ll be using for the presentation
Appropriateness. Each typeface projects a visual “personality” of some sort, and you should match the font with the audience and subject you’re addressing. For example, Comic Sans is a cheerful, happy-looking font and projects a somewhat childlike ethos; it’s a good match for an upbeat subject for a younger audience. In contrast, Times New Roman is a much more serious-looking font and would be appropriate for an older audience discussing a serious subject.
Readability. Not all fonts are equally readable, and you need to pick typefaces that allow your audience to read what’s onscreen from the back of the room. You should choose fonts that
- have relatively tall lower-case letters
- don’t use extra-thick or extremely thin lines
- have large, open spaces inside the loops, and
- (for a serif font) have large, blunt serifs.
See Figure 5 for examples of typefaces available in PowerPoint, and consider which fonts are most and least readable onscreen.

Figure 5: Examples of readable and unreadable font choices
Of these twelve fonts, the fonts that are most readable onscreen are Tahoma, Georgia, Trebuchet, and Verdana. In fact, Georgia and Verdana were designed for use onscreen. Of the rest, only Book Antiqua is workable, but the letters’ thin parts can be hard to see onscreen, particularly if the background isn’t a single flat color.
Sans-serif fonts are usually easier to read onscreen than serif fonts are, so consider using a serif font for headings and a sans-serif font for slides’ main text. Also, limit yourself to two fonts. If you use more, the screen will look very busy, and the visual clutter may distract your audience.
Most programs have built-in lists of fonts that you can use. For example, PowerPoint 2013 includes the list of combinations that appears in Figure 6.

Figure 6: List of built-in font combinations in PowerPoint 2013
Here is a link to a brief YouTube video that demonstrates how to access PowerPoint’s built-in list of font combinations: https://www.dropbox.com/sh/812erramvb8lvjk/AADwNcH2rqBrl_FjJgcxL3gsa/PowerPoint%20built-in%20font%20combinations.mp4?dl=0 .
Feel free to use one of these combinations, but remember that just because they’re built-in doesn’t mean they’re well-chosen or appropriate for your needs. You should always consider changing the default settings.
Compatibility. Not every typeface is available on every operating system, so find out what kind of computer you’ll use while delivering the presentation and choose fonts that will work on that computer.
For example, Helvetica is available on Mac, but it is not available on Windows-based systems; the Windows equivalent to Helvetica is Arial. Thus, if you create a PowerPoint presentation on a PC and then open the file on a Mac, or vice versa, the fonts may not transfer over, and your PowerPoint’s appearance will change, often for the worse.
Here’s a link to a list of fonts shared by Mac and PC versions of Microsoft Office: .
How to Think about Layout
When you place text or pictures onscreen, make sure you
- apply the CRAP design principles
- avoid clutter
- avoid text overload
CRAP Principles. The CRAP design principles are Contrast, Repetition, Alignment, and Proximity. In brief, they work like this:
Contrast: If things aren’t in the same category, make them look very different (e.g., use different fonts for slide headings and main text).
Repetition: Make visual elements consistent throughout every slide (e.g., use consistent colors, callout shapes, font sizes, picture and text box locations, background images).
Alignment: Place things on the screen with a purpose. Don’t just plop images and text in random locations (e.g., equalize spaces between multiple pictures, consistently center or left-align text, line up bullets and numbers).
Proximity: Place related items close to each other (e.g., use a narrow space between a name and job title, a picture and its caption, a main bullet item and its related sub-bullet items).
(The CRAP acronym was invented by a graphic designer named Robin Williams [no, not that Robin Williams] and explained in her book The Non-Designer’s Design Book. If you’re interested in visual design, you might find it fascinating.)
When you design your PowerPoint, you should consider using the built-in Master Slide tool to make sure the visual design elements (e.g., fonts, colors, backgrounds, bulleted items’ alignment) follow the Repetition principle. Here is a link to a YouTube video demonstrating how this powerful function works:
Clutter. Keep your presentation’s design and contents relatively simple.
- Include spaces between lines of text.
- Include spaces between images or other visual elements.
- Make sure that the text is readable.
- Use simple graphics.
If you overload the screen, your audience will feel overwhelmed, and they won’t be able to follow your ideas.
For example, Figure 7 demonstrates a cluttered information graphic full of “chartjunk.” Its 3-D design is unnecessary, the forced perspective prevents the audience from seeing the towers’ actual heights, the callouts overlap, the towers’ transparency doesn’t provide any information for the viewer, and the beveled edges and shadows are distracting.

Figure 7: Cluttered infographic
Figure 8 shows the same data in a simple, clean infographic that an audience can follow.

Figure 8: Uncluttered infographic
Similarly, avoid stuffing slides full of text and creating a “wall o’ words” like in Figure 9. Too much text makes a slide difficult to read and will intimidate your audience.

Figure 9: Wall o’ Words
Try to limit a bullet point-format slide to no more than seven bullets, with relatively short entries under each bullet. Of course, you can actually use as many bullets as you want, but only if you follow the CRAP principles very well. (See Figure 10 for an example of a slide that contains ten bulleted points but is still readable.)

Figure 10: Almost but not quite a “wall o’ words”
How to Choose Good Colors
Black-on-white presentations are easy to read, but they’re often very stark-looking, and your audience may not wish to stare at a bright white screen. Thus, you probably will want to use color in your presentation, and you need to choose your presentation’s colors carefully.
Contrast. Pick colors with high luminance contrast—in other words, one color should be much brighter than the other—so that your viewers will be able to read text quickly and with minimal eyestrain. Avoid extremely high color contrast, though, because extremes in color contrast can make text very hard to read. See Figure 11 for examples.

Figure 11: Examples of color and luminance combinations
Similarly, you probably want to avoid pure white text on a black screen; it’s OK for special cases, but for an entire presentation, it’s overwhelming. See Figure 12.

Figure 12: White-on-black slide design
Emotional Impact. Also consider the emotional effect of colors that you choose. The “cool” colors (darker green, blue-green, light blue, dark blue, blue-violet, purple) are calm and soothing, while the “warm” colors (red-violet, red, red-orange, orange, yellow-orange, yellow, yellow-green) are stimulating. Choose colors that are appropriate for the subject and emotional impact of your presentation. See Figure 13 for an example.

Figure 13: Emotional effects of colors
How to Choose Appropriate Backgrounds
Always make your presentation’s background relate to its topic. PowerPoint, Prezi, and Keynote all allow you to choose from built-in or downloadable background “theme” templates; insert and customize solid colors, gradients, or patterns; or import your own image to use as a background for your presentation. You can use any of these options, but whatever option you choose, the background absolutely must mesh with the topic.
For example, if you are speaking about a computer-related subject, the “Organic” PowerPoint theme template would be a very poor choice. (See Figure 14.) It looks like a sheet of paper attached to a piece of wood by a ribbon, and its text uses a serif body font; there’s nothing about the template that suggests “computer technology.” The same theme template would look entirely appropriate for a food-related subject, though.

Figure 14: Inappropriate and appropriate backgrounds
Also, consider whether the audience has seen the background before. There are only so many built-in theme templates, and chances are that your audience has seen the same background used for a different presentation or has used that same template themselves. In fact, if an event features multiple speakers, sometimes more than one presenter will use the same template, and the audience may get confused and not remember who said what. It is always a good idea to import your own image as a background or to customize templates to fit your needs. See Figure 15 for an example.

Figure 15: Customized “Apex” template from MS PowerPoint 2010
This brief YouTube video demonstrates PowerPoint’s built-in slide designs and how to access and use its Format Background tool: https://www.dropbox.com/sh/812erramvb8lvjk/AADoikR7jSjHHObIwOKX1qCOa/PowerPoint%20built-in%20backgrounds.mp4?dl=0
(As noted in the “How to Think About Layout” section, it would be a good idea to use the Master Slide tool when you customize backgrounds in order to make all the slides look uniform.)
Visual and Audio Effects
You can and should use between-slides transitions, within-slide animations, and sound effects, but don’t go overboard. Instead, use subtle effects, use them sparingly, and only use them to support your points.
Visual Effects. Transitions and animations can help you emphasize points, show connections between ideas, or simply capture your audience’s attention and prevent their eyes from glazing over. (See Figure 16 for a screenshot of the animations menu in PowerPoint 2013.)

Figure 16: Expanded list of animations available in PowerPoint 2013
However, if you overload your slideshow with visual effects, or if you choose splashy effects, you will likely encounter several problems:
- Your audience will pay more attention to the moving images than to the subject you’re talking about.
- Your audience won’t be able to tell if an effect means they should pay special attention or if it’s just another effect.
- Effects will take longer than you expect to finish running, or you’ll forget to cue them. You’ll then go silent as you wait for the animations to finish, and your audience will realize you screwed up.
- Effects will introduce a lighthearted note into your presentation and detract from your professional ethos or undermine a serious subject.
Here is a link to a video that demonstrates how to use PowerPoint’s built-in Animation tool and Animation Pane:
These same cautions apply to Prezi, but Prezi has its own special problems. Instead of switching between slides, you set up a flat “canvas” on which you place text and images, and when you present your talk, Prezi’s camera traces a path between those elements and zooms in on them. (See Figure 17 for an example of paths in Prezi.) Thus, transitions and animations are part and parcel of Prezi, which means it’s doubly important that you control their intensity.
- Prezi will let you place elements at peculiar angles and then “rotate” the camera to emphasize them. If you rotate the camera too frequently, you’ll make your audience seasick.
- You can locate text or images anywhere on the canvas and set up arbitrary motion paths between them. If you make the camera move long distances between elements, you’ll disorient your audience members.

Here is a link to a brief YouTube video demonstrating motion paths in Prezi: https://www.dropbox.com/sh/812erramvb8lvjk/AAC9SRhZy9v-CxNmAvQQtlf7a/Prezi%20sample.mp4?dl=0
Figure 17: Numbered sequence indicating a “path” in Prezi
Sound Effects. Audio cues have the same potential benefits and drawbacks as transitions and animations, but they also have several unique problems of their own:
- Audio clips will sound distorted or tinny unless the computer you are using to present is connected to a good-quality sound system.
- If the audio clip is more than a few seconds long, you’ll need to shout to be heard over it.
- It’s almost impossible to talk over rock or hip-hop. Your voice just can’t compete with the backbeat.
- Music samples longer than a few seconds consume massive amounts of memory, and your file size will be huge.
- Song snippets may be so short that they’re unrecognizable.
- Nobody else likes your taste in music.
In short, no matter what program you use, keep your presentation’s visual and audio effects relatively simple and use them to support your message. The effects should enhance the presentation; they shouldn’t be the presentation.
Delivery Techniques
Your slideshow shouldn’t be the main focus of your talk. Instead, YOU and your message are the main focus, and the presentation should support your talk. Don’t hide behind the presentation or use it as a crutch.
Prepare Notes. Write down key phrases on notecards or, if you will have access to a speaker’s computer while you’re talking, the program’s Notes view. It’s not a good idea to write out a line-for-line script because if you read from a script, the presentation will sound stilted. The best presentations are thoroughly prepared but sound ad-libbed.
Whatever you do, DO NOT read every single word on the screen. Your audience members can read, and you’ll only annoy them. See Figure 18 for an example.

Figure 18: Example of Presenter View in PowerPoint
Practice. Run through your talk and slideshow before you stand in front of an audience. Start up the presentation, say what you intend to say out loud, advance the presentation to match your speech, and time yourself. If you don’t practice, your audience will know.
Face Your Audience. Turn your face toward the audience and make eye contact with them when you speak. If you do, the audience will be able to hear you, and they will be more likely to believe what you say.
When you create a PowerPoint, Prezi, or Keynote presentation, be sure to consider the principles discussed in this webtext. You now know how to
- choose an effective presentation format
- identify readable typefaces
- position visual elements onscreen
- pick appropriate colors
- choose relevant, useful backgrounds
- choose effective visual and audio effects
- present memorable, effective audiovisual materials
and you can create a successful presentation that will both capture your audience’s attention and provide the audience with clearly presented, easily-extracted information.

Brevity – Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence – How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow – How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity – Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style – The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing

A Short Guide To Making An Outstanding Visual Presentation
Using PowerPoint or any form of visual presentation is key to attracting potential business. A good picture or visual can attract and keep attention almost like nothing else. Keep reading to see how you can own these visual presentation skills.
The easiest exact procedure to follow to get your message through to your audience and have your brand stand out from the rest is to have amazing visual presentations.
Visual presentations will almost certainly lead to positive feedback and great responses from your audience. We’ve all been through one of those presentations that you wish would end already. So let’s learn how to avoid situations like that.
The purpose of a PowerPoint presentation is to, well, make your point powerfully . And how do you do that? By being visually compelling and, accordingly, making the viewing process enjoyable.
Why Are Visuals The Stepping Stone For An Impactful Presentation? 💁🏻♀️
So how can you make the most of your presentation 🗒, take away 💁🏻♂️.
Important disclosure: we're proud affiliates of some tools mentioned in this guide. If you click an affiliate link and subsequently make a purchase, we will earn a small commission at no additional cost to you (you pay nothing extra).
Visuals Are Attention-Grabbers 👀

We all know the saying— Show, don't tell.
It's a common mistake to include a lot of text in your presentation but rather include meaningful visuals (make sure the picture conditions are great to better the viewing experience) for a higher rate of participation in your presentation.
Carefully selected imagery is the key to engaging with your public. Sometimes, it's significantly easier to explain complex concepts through a short video or an infographic .
Overall, shorter presentation times can often lead to your audience understanding complex ideas, even if they have no prior background knowledge of the subject.
The normal viewing times of videos or presentations of your audience are decreasing day by day, which is why the visual display of your presentation is so important to keep their attention.
The pair of images that you choose to use isn't there to undermine your point. Their purpose is to make your audience attentive and to emphasize what you have to say.
Images Are Action-Inspiring 🙌

Using a visual display in your presentation will make your audience react. You can use them to raise awareness about a certain topic or to inspire your public to take a specific action.
More often than not, messages delivered visually receive a more powerful reaction and a higher rate of participation from people.
Is All That Text Necessary? 🧐
You can try to follow the 6 x 6 guidelines for one slide as a general rule. This means you should have a maximum of 6 key points, each with six words. This way, you can keep everything succinct, organized, and easy to understand.
Even when you're preparing an audio-visual presentation (which can be a better choice for people with learning difficulties), your focus should still be to keep the text short and sweet on each of the individual images.
Having no more than 140 characters on your slide will leave you with a lot of white space. This will make your presentation look more clean and organized. But also, it will help your audience focus on the key points you're trying to make.
Make sure that your background color combinations emphasize the key points and don't take attention away from them.
Use Straightforward And Precise Fonts 𝘼𝙖

While you might be tempted to break the mold with your presentation, fonts are not the place to do this. Try to use standard sans serif fonts, like Open Sans, Tahoma, Verdana .
These are easily recognizable and look good on the viewing window. Try not to use more than 2 or 3 different fonts in your presentation. The key to having an outstanding slide deck is organization and consistency.
Using too many different elements will distract and confuse your audience.
Any feedback activity from your audience will also result in this conclusion, and if your audience is confused, your rate of participation from the audience declines.
Say No To Poor Quality Images 🙅🏽♂️
Needless to say, high-quality images will make your presentation look professional . Try as much as possible to color-coordinate your visuals with the color scheme you’ve chosen for your slide deck.
Their purpose is to enhance and underline, not to overwhelm the slide, so make sure the picture conditions in your presentation are top-notch! Using binary image classification might also be a good idea to simplify complex concepts.
To avoid bad quality on your pair of images used in your presentation, make sure that your laptop display resolution agree with your presentation.
Another thing you should keep in mind: not using too many individual images . Generally, it’s good to try and use a single picture—or 2, if they’re relevant. Your presentation isn’t a photo album.
Use Contrast For Emphasis And Grabbing Attention 💁🏻♀️
You can use contrast cleverly in your presentation. First of all, it can help your message "pop" with a high-level contrast between your background and your text.
You can also add a bar of color behind your text —to make it more legible and bring it to the center of attention. Binary image classification is also a great way to emphasize the contrast between concepts.
Contrast can also be used to highlight your key points . Choose a color from your palette to emphasize important text on your slide. Make sure that your key points are a few times larger than the supplementary information given.
By making your key points a few times larger than supplementary info, you're creating contrast and thus pointing your viewers into the right direction of where to look, helping those with possible learning difficulties.
Nevertheless, it will lose its power if you use this trick too often. So use it wisely. Using an arrow symbol during your presentation will also emphasize the important points.
Limit Your Color Palette 👈🏽
Yes, rainbows are really pretty, but not in your presentation . Be mindful of what colors you choose and if they come together harmoniously.
There's no need to go overboard—you can grab attention without using complex textures or gradients. You can, for example, use a background of blocks to emphasize the message in front of it.
Even though it's tempting to make an art-inspired presentation, keep this for a more fitting audience and not for business proposals.
To choose the right colors for your presentation, you can use tools like Kuler or coolors.co . Using these can help you learn a bit about which colors go together and which ones don't.
Additionally, suppose you want to do this right. In that case, you can even look at an analysis of color theory to see how your palette can influence your audience's emotions.
Doing this avoids the risk of presenting a pair of images and evoking the wrong response from your audience.
Data Visualization Is Your Salvation 📊
Project management presentations or anything with a lot of numbers and data to present can be dreadful.
Luckily, you can use a lot of elements to make your life easier in your individual images — charts, graphs, radials , binary image classification, and more.
By doing this, you can simplify complex information or even a lot of information in a short period of time, even if the audience doesn't have prior background knowledge of the subject.
Shorter presentation times often work better for explaining complex ideas. Additionally, you can always look online for some free timeline templates to showcase progress or presumptions, or learn how to make your own timelines in PowerPoint.
The key is taking all the data and putting it into individual images that are easy to remember and understand.
Skip The Bullet Points 📝
Ideally, you should focus on a single idea for each slide. This means that instead of having five bullet points, you should have five slides focusing on each key point to do an in-depth analysis.
This way, you can make sure that people remember what you say, and your audience will be able to draw comparisons between the five slides. Also, bullet points are kind of old , aren’t they?
Surely, you can find more attractive ways to structure information within a slide. Try content boxes, bubbles, all sorts of frames—just don’t go overboard with your elements.
Mind The Visual Hierarchy 🎨
Even if you have no background knowledge in graphic design , you can still organize elements on your slide or picture, depending on their importance.
The purpose of this procedure is to let your audience know where their eyes should go first on each picture, and then second, and so forth.
You can do this by making use of size, the correct laptop display resolutions, white space between elements, or proximity between elements. Another smart thing to do is to use repetition to your advantage in your visual display.
Having only one element in your viewing window will make it pop—so your audience will know that is the main point. When your audience is viewing your presentation, they shouldn't wonder where to look on your PowerPoint.
Audio And Video Elements 🎙📹
Choosing tasks using video and audio elements can help you explain complex concepts so much easier. An audio-visual presentation is also a great way to create interaction with your public.
Using these gives you a break from talking and your audience a new point of focus. Embedding a video into a PowerPoint presentation is not hard if you decide to go this route.
However, make sure not to pick a 10-minute video, but rather use shorter presentation times.
You should use these items as a short, fresh breath of air—not let them have the presentation for you.
Additionally, make sure this content is relevant not only to your content but also to the audience— or you will lose their attention, as this is a big feedback influence.
What Do You Think About Interactivity? 👨🏾💻
No matter how good your presentation is, there is always going to be a low-energy moment . A good way to recover from this is to directly interact with your audience and strive for a high rate of participation.
For example, you can make them vote on subject comparisons, stand up for some reason, or conduct a short quiz.
To make this more interesting, you can add links to your presentation —either between slides, on the middle image of the presentation, or elements.
This way, when they choose and answer, something happens. Creating a unique slideshow can help you keep your audience attentive and create longer viewing times for your audience.
Transitions And Animations

You either love transitions, or you hate them. There’s no in-between. The safest route is to go all static and grab attention through colors, textures, and so forth.
This way, nobody gets distracted, and we all remember something at the end of your presentation.
However, if you want some pizzaz on your slides, you can use animations and transitions to become memorable.
However, keep them consistent and don’t get too excited . Not every element on your slide has to move. Use motion as an emphasis, not as a distraction.
Have An Interesting Cover Style 😍
The cover slide should be the one to grab your public’s attention and curiosity. It should say something about the subject but still be mysterious.
You can think of it as a movie trailer—you give people a taste of what’s to come, but without spoiling the whole thing. These slides are your chance to be creative and inventive. You can’t afford to be boring on this one.
Here, you should draw inspiration from an art-inspired presentation. However, as with any part of your art-inspired presentation — don’t go overboard.
Using too many elements or too many colors can put your whole slide deck in a bad light.
Reserve A Couple Of Slides At The End To Summarize Your Main Points
By doing this, you emphasize them and make sure that they will be remembered.
You don’t have to go through everything once more — just some keywords to jolt the memory of your public.
However, be careful. If your presentation is already quite lengthy— you might want to skip this one or make it short. If your speech is too long, the only thing your public will want is to escape and go home as fast as possible.
Accordingly, the attention span and the desired viewing times of the audience will be low.
It might sound easy, but building a visually compelling presentation is not that simple. There are a lot of factors and small details that can either make or break your whole work.
For example—using colors, but too many of them, a pair of images, but making sure the picture conditions are great, using the right type of font, but at the wrong sizes, and so forth.
However, if you check all the points made in the article—and maybe do a little research and analysis on your own , you’ll be just fine, and your feedback will surely be positive. Most rules are basic common sense for anyone who has seen a presentation before.
The most important thing here is to feel comfortable with your presentation in a way that it seems as though you have background knowledge on the subject.
If you’re happy about it—and passionate about the subject you’re talking about, then you can’t go wrong. Feelings are contagious, so your audience will sense your happiness.
If you find yourself pressed for time or lacking the necessary expertise to create a visually stunning presentation, you can explore options such as SketchBubble to access professionally designed PowerPoint templates that you can download.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Subscribe to be notified of new content on marketsplash..
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 12 min read
Creating Effective Presentation Visuals
Connecting people with your message.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Apple® founder Steve Jobs was known widely for his great presentations. His unveiling of the iPhone® in 2007 is considered to have been one of his best presentations ever, and, if you were one of the millions who watched it online, you'll know why. The presentation was engaging, and passionate.
Jobs was particularly well known for building his presentations around powerful visual aids. He knew that slides are most effective when they tell a story rather than convey information, so his visuals were simple, elegant, and image-based. They complemented and reinforced his message, and they never competed with him for his audience's attention.
You don't have to be Steve Jobs to give a great presentation, but you do need great visuals. They convey a powerful message about your ideas and your brand, so it's essential to get them right. In this article, we'll look at how you can create effective presentation visuals – slides that connect your audience with your message.
Why Simplicity Speaks Volumes
The saying "A picture is worth a thousand words" is popular for a good reason: the human brain processes information more effectively when it is accompanied by images, or by short, memorable statements. This means that when you use simple, image-based slides to support your message, your audience can better grasp the information you're communicating.
However, many people use too many slides, or they build presentations around visual aids that are word-heavy or excessively complex.
These kinds of visual aids can negatively affect your presentation. Let's look at some examples:
- You're trying to convince the board to support a new product idea. Your slides are made up of graphs, numbers, and blocks of text from top to bottom, and board members spend most of their time reading the slides instead of listening to you. The result? You don't make a real connection, and your passion for the project is lost on them. They vote unanimously not to take the idea forward.
- You're pitching to a promising potential client. You spent a lot of time creating your slides, using many colors, animations, and fonts. However, the slides are so complex that your client has trouble understanding them. She leaves the presentation feeling overwhelmed and tired, and avoids using your firm because she fears, subconsciously, that dealing with your firm in the future could be similarly draining.
- You're giving a presentation to your department to highlight its good work. You want to feature everyone, so you make a slide detailing each person's accomplishments. Your department has dozens of people, so by the end, your team cares more about leaving than their results.
Now think about what happens when you use simple and engaging visuals. Instead of generating confusion or exhaustion, your slides create a positive connection with your audience. People might not remember exactly what you said, but they will remember a powerful image. They'll recall the positive emotions that they experienced during your presentation, and they'll start to associate your brand with clear, intelligent communication.
The results will be profound. You'll win new clients, convince colleagues to act on your ideas, and earn recognition for your team members' hard work. In short, you'll make positive impressions that will remain in people's minds long after the details of your presentation have faded.
Creating Great Visuals
Your visual aids have one job: to support your presentation . However, it takes considerable time, creativity, and effort to develop slides that do this well. Use the tips below to make the most of your preparation time.
1. Be Consistent
A common mistake is choosing different colors and fonts for each slide. This can confuse your audience and divert attention away from your message. Stay consistent with your slides, so that they form part of a seamless whole.
First, choose colors carefully, as color will affect your presentation's mood and tone. Also, think about the space that you'll be presenting in. If the room will be dark (with lights off), choose a darker background color, such as dark blue, black, or gray, with white or light-colored text. If the room will be light (with lights on or plenty of ambient light), choose a white or light-colored background, with black or dark-colored text.
You also need to match color with the tone and message of your presentation. Bright colors convey energy and excitement, while darker colors may seem more conservative and serious. Align the color palette you choose with your subject matter.
Microsoft® PowerPoint and Apple's Keynote are the most widely used presentation packages. They feature useful templates and tools, and most people are familiar with the layout of their presentations.
However, cloud-based presentation tools have features and templates that might be new to your audience, increasing the potential impact of your presentations.
2. Consider Culture
Before you create your visuals, make sure that you understand your audience. This is especially true if you're presenting to a culturally diverse group.
For example, not everyone reads from left to right, and people from some cultures may consider a particular color offensive or bad luck in business settings (look out for examples of this in our Managing Around the World articles). Additionally, jargon or slang may cause confusion with your audience.
When designing your visuals, use images and photographs that reflect the culture to which you're speaking. If you're presenting to a culturally diverse group, use pictures and images that reflect this diversity.
And keep graphics and phrases simple; remember, not everyone in the room will be a native English speaker. Whenever possible, use images to replace bullet points and sentences.
Our article on Cross-Cultural Communication has more tips for communicating with an ethnically diverse group.
3. Use Images Intelligently
When Steve Jobs unveiled the MacBook Air® , he needed to show just how small this new laptop was. The audience wasn't going to remember that it was 0.68 x 11.8 x 7.56 inches; those numbers don't create an emotional response. Instead, he showed them that the MacBook Air would fit easily into a standard manila envelope. This was a powerful way to show its size.
This kind of creativity is essential when choosing images. Your audience has probably seen plenty of bad clip-art and too many pictures of cross-cultural handshakes. Brainstorm creative, clever approaches with your imagery, and look for photographs or illustrations that tell a story in a less obvious way.
Thoughtful images will keep your audience engaged, reinforce your professionalism, and make a lasting impression.
4. Break Complex Data Down
When you have to communicate complex data or large chunks of information, avoid putting it all on one slide, as your audience may struggle to take in all of the details. Instead, either summarize the information, or split it up over several slides.
You can also use handouts to communicate complex information. Handouts allow your audience to look at data closely. This is especially important when you're presenting to analytical people, such as engineers, scientists, or finance professionals. They are trained to be skeptical about data, and a handout will give them a closer look. Once again, this kind of attention to the needs of your audience will highlight your professionalism and support your message.
5. Keep It Simple
Each slide should focus on one idea or concept. This allows your audience to grasp quickly what you want to communicate. Keep your text to a bare minimum (10 words or fewer if possible), and, where you can, use an image to convey a message rather than words: for example, consider using a graph instead of a list to show changing trends. Each slide should take three seconds or fewer to process. If it takes longer, the slide is probably too complex.
It can sometimes be helpful to follow a clear structure when creating your presentation; for example, if it is focused on a document or process with which audience members are familiar. This will help them make connections between your content and their existing knowledge.
Avoid bulleted lists whenever possible; they make it too easy to put several ideas on one slide, which can be overwhelming for your audience. If you do need to use bullets, don't use sentences; instead, simply list the fact, statistic, or idea you want to communicate. Then use your narrative to educate the audience about what these mean.
To simplify the wording on your slides further, highlight the key word in every sentence.
Next, look at the layout of your slides. Aim to use a plain background and plenty of blank space: this will help to focus audience members' eyes on your message. Avoid decorating slides with background pictures, logos or patterns that could distract attention.
Last, consider using blank slides when you need the audience's complete focus; a blank slide is equivalent to a pause, and it will add drama, tension, and focus to your words.
Many people underestimate how much time they need to set aside to prepare for a presentation. They'll spend days creating content and visuals but only a few hours practicing. Allow extra preparation time to hone your message and feel fully confident in your presentation.
First, take our interactive quiz, How Good Are Your Presentation Skills? to get an idea of how well you speak. Our articles on Delivering Great Presentations and Better Public Speaking contain tips and strategies that will help you communicate with clarity and intention.
When you practice your presentation, use your visuals. You should be able to glance at each slide and know exactly what you want to say.
If you're not confident in creating your own slides, think about outsourcing the task to a professional. This can be a smart option when a lot is at stake, or when you don't have the technical skills to create the type of presentation you want.
Consider using an outsourcing service such as Elance , Guru , or PeoplePerHour to find a suitable professional.
If you do, keep in mind that managing a freelancer requires a different approach from managing a regular staff member. Be clear about the project details, communicate your goals for the presentation, and set deadlines that give you plenty of time to revise and add as necessary.
Presentations that are too complex or lengthy can undermine your message. To create better visuals, do the following:
- Stay consistent.
- Consider culture.
- Use images intelligently.
- Break down complex data.
- Keep it simple.
If the stakes are high with your presentation and you don't feel confident with your technical skills, consider outsourcing slide preparation.
"iPhone," "Apple," "MacBook Air," and "Keynote" are trademarks of Apple Inc. (see www.apple.com ). "Microsoft" and "PowerPoint" are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation (see www.microsoft.com ). We have no association or connection with these organizations.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Expert Interviews
The Art of Public Speaking
With Professor Steve Lucas
Great Presentations
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 20% off your first year of Mind Tools
Our on-demand e-learning resources let you learn at your own pace, fitting seamlessly into your busy workday. Join today and save with our limited time offer!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Pain Points Podcast - Balancing Work And Kids

Pain Points Podcast - Improving Culture
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Pain points podcast - what is ai.
Exploring Artificial Intelligence
Pain Points Podcast - How Do I Get Organized?
It's Time to Get Yourself Sorted!
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Action programs.
Becoming Exceptionally Well Organized
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Presentations
How to Make a Presentation
Last Updated: October 4, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Vikas Agrawal . Vikas Agrawal is a Visual Content Marketing Expert & Entrepreneur, as well as the Founder of Full Service Creative Agency Infobrandz. With over 10 years of experience, he specializes in designing visually engaging content, such as infographics, videos, and e-books. He’s an expert in Making content marketing strategies and has contributed to and been featured in many publications including Forbes, Entrepreneur.com, and INC.com. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 50,712 times.
Presentations can be nerve-wracking to give. You’re far more likely to walk into a board meeting with confidence if your writing and visuals are compelling. Take time to carefully compose your story, practice and make a slideshow that will impress your audience. Thankfully, there are plenty of modern tools and programs that provide beautiful presentation templates.
Writing a Presentation

Creating Visual Aids

- The more you visualize the text and information available in the presentation, the better impact it is going to create on the audience's mind.

Using Presentation Tools

- There are many more web-based services that you can use to develop your presentation. Some of these allow you to make and edit the presentation from a tablet or phone.

What Is The Best Way To Start a Presentation?
Expert Q&A

Things You'll Need
- Desktop computer, laptop, tablet or phone
You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you'd like to learn more about making effective presentations, check out our in-depth interview with Vikas Agrawal .
- ↑ https://www.comm.pitt.edu/oral-comm-lab/audience-analysis
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/oralcommunication/guides/how-to-engage-your-audience-and-keep-them-with-you
- ↑ https://www.washington.edu/doit/presentation-tips-0
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://libguides.wilmu.edu/presentations
About This Article

To make a good presentation, use a lot of visuals, like graphs, charts, and infographics, to make your presentation more interesting. Also, if you're presenting a slideshow, avoid using a lot of text in your slides since it could overwhelm and bore your audience. Instead, leave plenty of white space and focus on one key point per slide. When you're giving your presentation, take time to explain why it's relevant to your audience or how it affects their lives, which will make them more interested in what you're saying. For tips on how to choose a presentation tool, like PowerPoint or Prezi, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Sep 23, 2020
Did this article help you?
Tyna Appiah
May 13, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
14.2 Incorporating Effective Visuals into a Presentation
Learning objectives.
- Recognize the characteristics of effective visual aids.
- Analyze different types of visual aids and appropriate ways to use them.
- Determine how to create original visual aids and how to locate visual aids created by others.
Good communication is a multisensory experience. Children first learning how to read often gravitate toward books with engaging pictures. As adults, we graduate to denser books without pictures, yet we still visualize ideas to help us understand the text. Advertisers favor visual media—television, magazines, and billboards—because they are the best way to hook an audience. Websites rely on color, graphics, icons, and a clear system of visual organization to engage Internet surfers.
Bringing visuals into a presentation adds color, literally and figuratively. There is an art to doing it well. This section covers how to use different kinds of visual aids effectively.
Using Visual Aids: The Basics
Good writers make conscious choices. They understand their purpose and audience. Every decision they make on the page, from organizing an essay to choosing a word with just the right connotations, is made with their purpose and audience in mind.
The same principle applies to visual communication. As a presenter, you choose the following:
- When to show images or video for maximum impact
- Which images will best produce the effect you want
- When to present information using a table, chart, or other graphic
- How much text to include in slides or informational graphics
- How to organize graphics so they present information clearly
Your goal is to use visual media to support and enhance your presentation. At the same time, you must make sure these media do not distract your audience or interfere with getting your point across. Your ideas, not your visuals, should be the focus.
As you develop the visual side of your presentation, you will follow a process much like the process you follow when you write. You will brainstorm ideas, form an organizational plan, develop drafts, and then refine and edit your work. The following sections provide guidelines to help you make good decisions throughout the process.
What Makes Visual Aids Effective?
To help you get a sense of what makes visual media work, think about what does not work. Try to recall occasions when you have witnessed the following visual media failures:
- Websites crammed with so many images, flashing phrases, and clashing colors that they are almost unreadable
- Assembly instructions with illustrations or diagrams that are impossible to follow
- Photographs that are obviously (and badly) altered with photo-editing software
- Distracting typos or other errors in signs, advertisements, or headlines
- Tables, charts, or graphs with tiny, dense text or missing labels
In each case, the problem is that the media creator did not think carefully enough about the purpose and audience. The purpose of images, color, or flashing text on a website is to attract attention. Overusing these elements defeats the purpose because the viewer may become overwhelmed or distracted. Tables, charts, and graphs are intended to simplify complex information, but without clear labels and legible text, they will confuse the audience.
In contrast, effective visual elements are chosen or created with the purpose and audience in mind. Although a photo shoot for a magazine article might result in dozens of images, editors choose those few that work best with the article. Web designers and video game creators have an audience test their products before they are released, to ensure that people will understand how to use them. Understanding the function of different visual aids will help you use them with purpose.
Types of Visual Aids
Visual aids fall into two main categories—images and informational graphics. Images include photographs, illustrations and clip art, and video footage. Informational graphics include tables, charts, bar graphs, and line graphs.
These visual aids serve two purposes: to add emotional impact to your presentation and to organize information more clearly. With that in mind, read to find out how specific types of visual aids achieve those purposes.
Photographs
A striking photograph can capture your audience’s attention far more successfully than words can. Consider including photographs at the beginning or end of your presentation to emphasize your main ideas or to accompany a particularly important point in the body of your presentation. Remember that, as with other types of graphics, less is often more. Two or three well-chosen photographs are more effective than a dozen mediocre ones.
When you choose photographs, ask yourself these questions:
- What purpose does this image serve? Will it surprise the audience? Will it provoke a strong emotional response? Does it support an important point?
- Will this photograph be more effective if shown with only a caption, or does it need additional text?
- Will the audience understand what is happening in the photograph? Is the meaning immediately evident, or does the photo need some context?
- Would editing the image make it more effective? Consider using image-editing software to crop the photo, change the brightness, or make other cosmetic changes. (Do not go overboard, though. A slightly imperfect but authentic image is preferable to one that has been obviously altered.)
To illustrate the sense of helplessness people felt in the midst of tragedy, a student could use a photograph that shows fear, weariness, or defeat on the face of the photograph’s subject.
Figure 14.3

Neil Moralee – On The Scrap Heap . – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Illustrations
Illustrations, such as editorial or political cartoons, serve much the same purpose as photographs. Because an illustration does not capture a moment in time the way a photo does, it may have less impact. However, depending on your topic and the effect you want to achieve, illustrations can still be very useful. Use the same criteria for choosing photographs to help you choose illustrations.
Figure 14.4

Humor Blog – Political Cartoon about Budget Cuts – CC BY 2.0.
The style of an illustration or photograph affects viewers just as the content does. Keep this in mind if you are working with the stock images available in office software programs. Many of these images have a comical tone. This may be fine for some topics—for instance, a presentation on television shows for children. However, if you need to project a more serious tone, make sure you choose images to suit that purpose. Many free (or reasonably priced) image banks are available online.
Video Footage
Even more than photographs, video footage can create a sense of immediacy, especially if your video includes sound. Showing a brief video clip can help your audience feel as if they are present at an important event, connect with a person being interviewed, or better understand a process. Again, ask yourself the following questions to ensure you are using the footage well:
- What purpose does this video serve? (Never rely on video clips just to fill time.)
- How much footage should be shown to achieve your purpose?
- What will need to be explained, before or after showing the video, to ensure that your audience understands its significance?
- Will it be necessary to edit the video to stay within time requirements or to focus on the most important parts?
Informational graphics, such as tables, charts, and graphs, do not provoke the same response that images do. Nevertheless, these graphics can have a powerful impact. Their primary purpose is to organize and simplify information.
Tables are effective when you must classify information and organize it in categories. Tables are an especially good choice when you are presenting qualitative data that are not strictly numerical. Table 14.1 “Example of Qualitative Data Table” was created for a presentation discussing the subprime mortgage crisis. It presents information about people who have held powerful positions both in the government and at one of the investment banking firms involved in the subprime mortgage market.
Table 14.1 Example of Qualitative Data Table
Sources: http://www.rollingstone.com/politics/news/%3Bkw=%5B3351,11459%5D ; http://www.nytimes.com/2008/10/19/business/19gold.html ; http://topics.nytimes.com/top/reference/timestopics/people/p/henry_m_jr_paulson/index.html?inline=nyt-per ; http://topics.nytimes.com/top/reference/timestopics/people/r/robert_e_rubin/index.html?inline=nyt-per , http://www.nytimes.com/2002/12/13/us/man-in-the-news-economic-adviser-from-other-side-of-the-deficit-stephen-friedman.html ; http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/342086.stm .
If you are working with numerical information, consider whether a pie chart, bar graph, or line graph might be an effective way to present the content. A table can help you organize numerical information, but it is not the most effective way to emphasize contrasting data or to show changes over time.
Pie charts are useful for showing numerical information in percentages. For example, you can use a pie chart to represent presidential election results by showing what percentage of voters voted for the Democratic presidential candidate, the Republican candidate, and candidates from other political parties.
Figure 14.5
Source: http://www.fec.gov/pubrec/fe2008/2008presgeresults.pdf
Bar graphs work well when you want to show similarities and differences in numerical data. Horizontal or vertical bars help viewers compare data from different groups, different time periods, and so forth. For instance, the bar graph in Figure 14.6 allows the viewer to compare data on the five countries that have won the most Olympic medals since the modern games began in 1924: Norway, the United States, the former Soviet Union, Germany, and Austria. Bar graphs can effectively show trends or patterns in data as well.
Figure 14.6
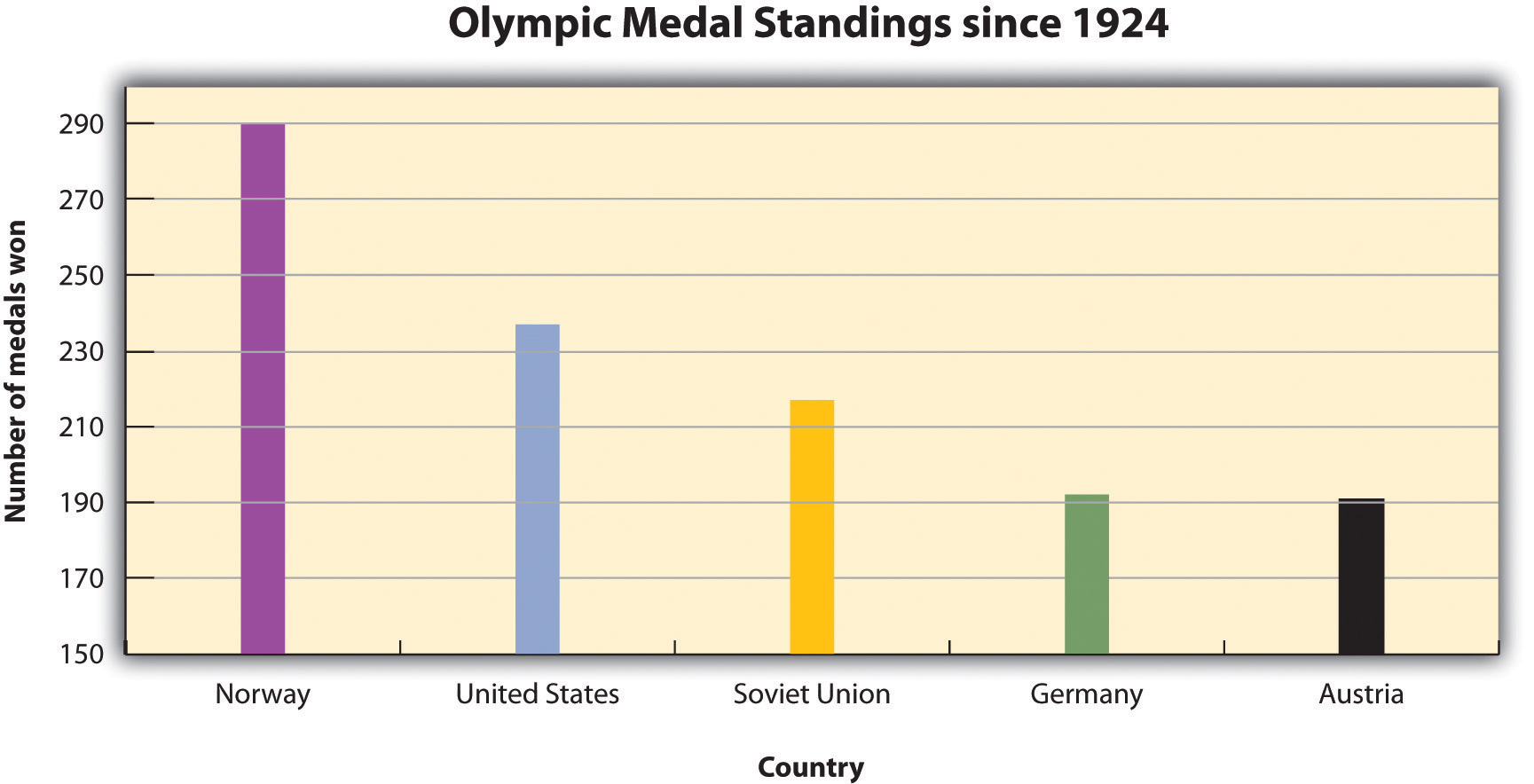
Source: http://www.nbcolympics.com/medals/all-time-standings/index.html
Line Graphs
Like bar graphs, line graphs show trends in data. Line graphs are usually used to show trends in data over time. For example, the line graph in Figure 14.7 shows changes in the Dow Jones Industrial Average—an economic index based on trading information about thirty large, US-based public companies. This graph shows where the Dow closed at the end of each business day over a period of five days.
Figure 14.7
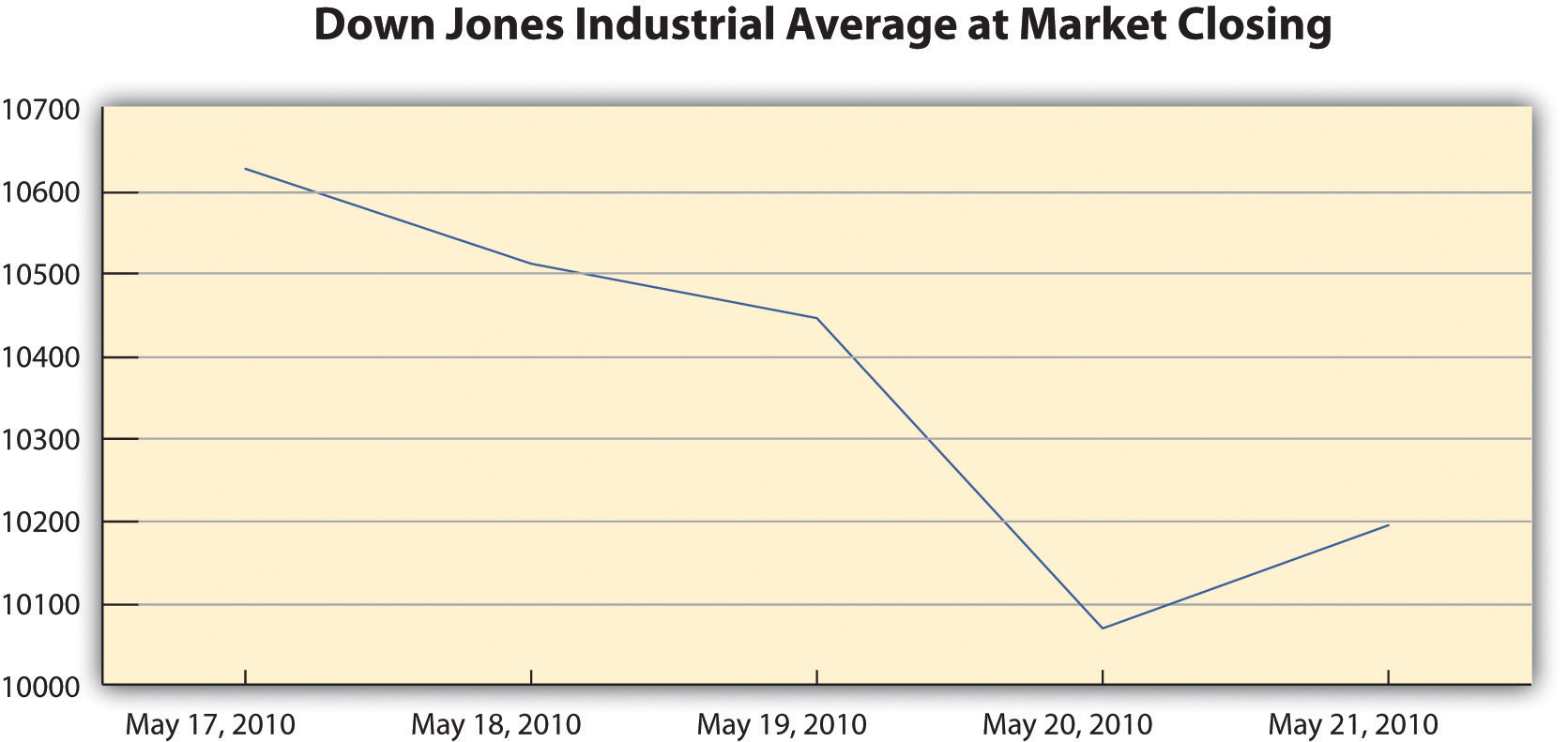
Source: http://www.google.com/finance/historical?cid=983582&startdate=May+17%2C+2010&enddate=May+21%2C+2010
In this exercise, you will begin to refine your ideas for incorporating media into your presentation. Complete the following steps on your own sheet of paper.
- Revisit the list you brainstormed for Note 14.12 “Exercise 3” in Chapter 14 “Creating Presentations: Sharing Your Ideas” , Section 14.1 “Organizing a Visual Presentation” and the annotated outline you developed for Note 14.17 “Exercise 4” .
- Analyze the two different types of visual aids: images and informational graphics. Identify at least two places in your presentation where you might incorporate visual aids.
- Evaluate the purpose of the visual aid. Does it create emotional impact, or does it organize information? Is the visual effective?
- Determine whether you will be able to create the visual aid yourself or will need to find it.
Creating Original Visual Aids
You will include original visual aids in your presentation to add interest, present complex information or data more clearly, or appeal to your audience’s emotions. You may wish to create some visual aids by hand—for instance, by mounting photographs on poster board for display. More likely, however, you will use computer-generated graphics.
Computer-generated visual aids are easy to create once you learn how to use certain office software. They also offer greater versatility. You can print hard copies and display them large or include them in a handout for your audience. Or, if you are working with presentation software, you can simply insert the graphics in your slides.
Regardless of how you proceed, keep the following guidelines in mind:
- Create visual aids with purpose. Think carefully about how they will enhance your message, and choose a form that is appropriate for your content.
- Strive for quality. You do not need the skills of a professional photographer or designer, but do take time to make sure your visual aids are neat, attractive, and legible. Proofread for errors, too.
Using Software to Create Visual Aids
You can use standard office software to create simple graphics easily. The following guidelines describe how to work with word-processing software and presentation software.
Working with Photographs
Most personal computers come equipped with some basic image-editing software, and many people choose to purchase more advanced programs as well. You can upload photographs from a digital camera (or in some cases, a cell phone) or scan and upload printed photographs. The images can then be edited and incorporated into your presentation. Be sure to save all of your images in one folder for easy access.
Creating Tables
To create a table within a word-processing document consult your software program’s help feature or an online tutorial. Once you have created the table, you can edit and make any additional changes. Be sure that the table has no more than six to seven rows or columns because you do not want to compromise the size of the text or the readability. Aligning with precision will help your table look less crowded. Also, the row and column titles should spell out their contents.
Creating Graphs
Figure 14.8
Pie charts and bar and line graphs can also be created using standard office software. Although you can create these graphics within a document, you will need to work with both your word-processing application and your spreadsheet application to do so. The graph should visually explain the data using colors, titles, and labels. The use of color will help the audience distinguish information; however, avoid colors that are hard on the eyes, such as lime green or hot pink. The title should clearly state what the graph explains. Lastly, avoid using acronyms in the titles and other labels.
Creating Graphics in an Electronic Presentation
If you plan to work only with hard copy graphics during your presentation, you may choose to create them as word-processing documents. However, if you are using presentation software, you will need to choose one of the following options:
- Create your graphics using the presentation software program.
- Create your graphics within another program and import them.
Standard office presentation software allows you to create informational graphics in much the same way you would create them within a word-processing application. Keep the formatting palette, a menu option that allows you to customize the graphic, open while you use the software. The formatting menu provides options for inserting other types of graphics, such as pictures and video. You may insert pictures from an image bank available within the program, or insert images or video from your own desktop files. Shape your use of multimedia in accordance with the message your presentation is trying to convey, the purpose, and your audience.
Creating Visual Aids by Hand
Most of the time, using computer-generated graphics is more efficient than creating them by hand. Using office software programs helps give your graphics a polished appearance while also teaching you skills that are useful in a variety of jobs. However, it may make sense to use hand-created visual aids in some cases—for instance, when showing a 3-D model would be effective. If you follow this route, be sure to devote extra time to making sure your visual aids are neat, legible, and professional.
Flip charts are inexpensive and quick visual aids used during face-to-face presentations. The flip chart can be prepared before, as well as during, the presentation. Each sheet of paper should contain one theme, idea, or sketch and must be penned in large letters to be seen by audience members farthest away from the speaker.
Writing Captions
Any media you incorporate should include a caption or other explanatory text. A caption is a brief, one- to two-sentence description or explanation of a visual image. Make sure your captions are clear, accurate, and to the point. Use full sentences when you write them.
Captions should always be used with photographs, and in some cases, they can be useful for clarifying informational graphics, which represent qualitative data visually. However, informational graphics may not require a caption if the title and labels are sufficiently clear. For other visual media, such as video footage, providing explanatory text before or after the footage will suffice. The important thing is to make sure you always include some explanation of the media.
In this exercise, you will begin to develop visual aids for your presentation. Complete the steps in this exercise—and enjoy the chance to be creative. Working with visuals can be a pleasant way to take a break from the demands of writing.
- Revisit the ideas you developed in Note 14.24 “Exercise 1” . Choose at least two ideas that you can create. ( Note: If you are using software to develop a slideshow presentation, count this as one of your self-created visual aids. Include at least one other self-created visual aid, such as an original photograph, within your slideshow.)
- Get creative! Take your photographs, construct a 3-D model, create informational graphics, or work on your presentation slides. Develop good working drafts.
- After you have completed drafts of your visual aids, set them aside for a while. Then revisit them with a critical eye. First, check any text included with the graphic. Make sure your facts are correct, your words are clear and concise, and your language is free of errors.
- Next, evaluate how well your aids work visually. Are they large enough to be seen and read from a distance? Are captions and labels easy to find? Are photographs of reasonably high quality? Ask someone else for feedback, too.
- Begin making any needed changes. As you proceed through the rest of this section, continue to revisit your work to improve it as needed.
Collaboration
Please share the first version of your visual aids with a classmate. Examine what they have produced. On a separate piece of paper, note both the elements that catch your attention and those that would benefit from clarification. Return and compare notes.
Testing and Evaluating Visual Aids
Regardless of how you create your visual aids, be sure to test-drive them before you deliver your presentation. Edit and proofread them, and if possible, show them to someone who can give you objective feedback. Use the following checklist.
Checklist 14.1
Visual Aid Evaluation Checklist
- Visual aids are clearly integrated with the content of the presentation
- Photographs and illustrations suit the overall tone of the presentation
- Images and text are large and clear enough for the viewer to see or read
- Images are shown with explanatory text or a caption
- Informational graphics include clear, easy-to-read labels and headings
- Text within informational graphics is easy to read (Watch out for wordiness and crowded text or a font that is too small and hard to read.)
- Formatting choices (color, different fonts, etc.) organize information effectively
- Any text within graphics is free of errors
- Hyperlinks within slides function properly
- Display text for hyperlinks is concise and informative (Never paste a link into a slide without modifying the display text.)
Writing at Work
Office software includes many options for personalizing a presentation. For instance, you can choose or create a theme and color scheme, modify how one slide transitions to the next, or even include sound effects. With so many options, students and employees sometimes get carried away. The result can seem amateurish and detract from, rather than enhance, your presentation.
Remember, you are delivering a presentation, not producing a movie. Use the customization options to help give your presentations a consistent, polished, appearance. However, do not let these special effects detract from the substance of your slides.
Using Existing Visual Media
Depending on your topic, you may be able to find images and other graphics you can use instead of creating your own. For instance, you might use photographs from a reputable news source or informational graphics created by a government agency. If you plan to use visual aids created by others, keep the following guidelines in mind:
- Set a purpose before you begin your search. You will search more efficiently if you start with a general idea of what you are looking for—a line graph of unemployment rates for the past twelve months, for example, or a video clip of the most recent State of the Union address.
- Filter out visual aids that are not relevant. You may come across eye-catching graphics and be tempted to use them even if they are only loosely related to your topic, simply because they are attention getting. Resist the temptation. If the graphic is not clearly connected to your point, it does not belong in your presentation.
- Read carefully. In addition to reading labels, headings, and captions, read any text that accompanies the visual. Make sure you understand the visual in its original context. For informational graphics, make sure you understand exactly what information is being represented. (This may seem obvious, but it is easy to misread graphic information. Take the time to examine it carefully.)
- Evaluate sources carefully and record source information. When you look for visual media to complement your presentation, you are conducting research. Apply the same standards you used for your research paper. Choose reliable sources, such as reputable news organizations, government and nonprofit organizations, and educational institutions. Verify data in additional sources. Finally, be sure to document all source information as you proceed.
Searching Efficiently for Visual Media
You will probably find it most efficient to use the Internet to search for visual aids. Many students begin by typing keywords into a search engine to locate related images. However, this search technique is not necessarily efficient, for several reasons:
- It often pulls up hundreds or even thousands of images, which may be only loosely related to your search terms.
- It can sometimes be difficult to understand the image in its original context.
- It can be hard to find copyright information about how you may use the image.
A more efficient strategy is to identify a few sources that are likely to have what you are looking for, and then search within those sites. For instance, if you need a table showing average life expectancy in different countries, you might begin with the website of the World Health Organization. If you hope to find images related to current events, news publications are an obvious choice. The Library of Congress website includes many media related to American history, culture, and politics.
Searching this way has the following advantages:
- You will often find what you are looking for faster because you are not wasting time scrolling through many irrelevant results.
- If you have chosen your sources well, you can be reasonably certain that you are getting accurate, up-to-date information.
- Images and informational graphics produced by reputable sources are likely to be high quality—easy to read and well designed.
If you do choose to use a search engine to help you locate visual media, make sure you use it wisely. Begin with a clear idea of what you are looking for. Use the advanced search settings to narrow your search. When you locate a relevant image, do not download it immediately. Read the page or site to make sure you understand the image in context. Finally, read the site’s copyright or terms of use policy—usually found at the bottom of the home page—to make sure you may use the material.
If you are unable to find what you are looking for on the Internet consider using print sources of visual media. You may choose to mount these for display or scan them and incorporate the files into an electronic presentation. (Scanning printed pages may lower the quality of the image. However, if you are skilled at using photo-editing software, you may be able to improve the quality of the scanned image.)
Inserting Hyperlinks in an Electronic Presentation
If you are working with images, audio, or video footage available online, you may wish to insert a link within your presentation. Then, during your presentation, you can simply click the link to open the website in a separate window and toggle between windows to return to your presentation slides.
To insert a hyperlink within your presentation, click on insert in the toolbar and then select hyperlink from the menu. Doing so will open a dialogue box where you can paste your link and modify the accompanying display text shown on your slide.
Copyright and Fair Use
Before you download (or scan) any visual media, make sure you have the right to use it. Most websites state their copyright and terms of use policy on their home page. In general, you may not use other people’s visual media for any commercial purpose without contacting the copyright holder to obtain permission and pay any specified fees.
Copyright restrictions are somewhat more ambiguous when you wish to download visual media for educational uses. Some educational uses of copyrighted materials are generally considered fair use —meaning that it is legally and ethically acceptable to use the material in your work. However, do not assume that because you are using the media for an educational purpose, you are automatically in the clear. Make sure your work meets the guidelines in the following checklist. If it does, you can be reasonably confident that it would be considered fair use in a court of law and always give credit to the source.
Checklist 14.2
Media Fair Use Checklist
- You are using the media for educational purposes only.
- You will make the work available only for a short period and to a limited audience. For instance, showing a copyrighted image in a classroom presentation is acceptable. Posting a presentation with copyrighted images online is problematic. In addition, avoid any uses that would allow other people to easily access and reproduce the work.
- You have used only as much of the work as needed for your purposes. For video and audio footage, limit your use to no more than 10 percent of the media—five minutes of an hour-long television show, for example. Image use is harder to quantify, but you should avoid using many images from the same source.
- You are using the media to support your own ideas, not replace them. Your use should include some commentary or place the media in context. It should be a supporting player in your presentation—not the star of the show.
- You have obtained the material legally. Purchase the media if necessary rather than using illegally pirated material.
- Your use of the media will not affect the copyright holder or benefit you financially.
By following these guidelines, you are respecting the copyright holder’s right to control the distribution of the work and to profit from it.
In some fields, such as teaching, job applicants often submit a professional portfolio to a prospective employer. Recent college graduates may include relevant course work in their portfolios or in applications to graduate school. What should you do if your course work uses copyrighted visual media?
This use of media is acceptable according to fair use guidelines. Even though you are using the work for your personal professional advancement, it is not considered an infringement on copyright as long as you follow the additional guidelines listed in the previous checklist.
Crediting Sources
As you conduct your research, make sure you document sources as you proceed. Follow the guidelines when you download images, video, or other media from the Internet or capture media from other sources. Keep track of where you accessed the media and where you can find additional information about it. You may also provide a references page at the end of the presentation to cite not only media and images but also the information in the text of your presentation. See Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” for more information on creating a reference page.
Write captions or other explanatory text for visual media created by others, just as you would for media you created. Doing so helps keep your audience informed. It also helps ensure that you are following fair use guidelines by presenting the media with your commentary, interpretation, or analysis. In your caption or elsewhere in your presentation, note the source of any media you did not create yourself. You do not need to provide a full bibliographical citation, but do give credit where it is due.
In this exercise, you will locate visual aids created by others and continue developing the work you began earlier. Complete these steps.
1. Revisit the ideas you developed in Note 14.24 “Exercise 1” . Choose at least two ideas for which it would make more sense to find the visual aid than to create it yourself. 2. Use the search tips provided in this section to locate at least two visual aids from reputable sources that you can use. Prepare them for your presentation by adding clarifying text as needed. Be sure to credit your source. 3. Incorporate the visual aids you created in Note 14.26 “Exercise 2” and Note 14.32 “Exercise 3” into your presentation. This may involve preparing physical copies for display or inserting graphic files into an electronic presentation.
4. Take some time now to review how you will integrate the visual and verbal components of your presentation.
- If you are working with presentation software, refine your slides. Make sure the visual approach is consistent and suits your topic. Give your text a final proofread.
- If you are not using presentation software, review the annotated outline you created in Note 14.24 “Exercise 1” . Update it as needed to reflect your current plan. Also, determine how you will physically set up your visual aids.
Key Takeaways
- Visual aids are most effective when they are chosen with the purpose and audience in mind. They serve to add emotional impact to a presentation and to organize information more clearly.
- Visual aids should always be clearly related to the presenter’s ideas. Captions, labels, and other explanatory text help make the connection clear for the audience.
- Like writing, developing the visual components of a presentation is a process. It involves generating ideas, working with them in a draft format, and then revising and editing one’s work.
- Visual aids can be divided into two broad categories—image-based media and informational graphics.
- Widely available software programs make it relatively easy to create visual aids electronically, such as photo images, charts, and graphs.
- When using visual aids created by others, it is important to apply good research skills, follow guidelines for fair use, and credit sources appropriately.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Presentations > How to create an educational presentation
How to create an educational presentation
Using presentations can be an effective way to teach lessons and ensure that your audience can retain new facts. With visual aids, video and animated clips, and even interactive quizzes, you can use presentation software like Microsoft PowerPoint to dazzle your students.

The advantages of PowerPoint presentations in education
Students have different learning styles : some are visual learners, who retain images and videos more effectively than speech. Some take to audio and sound more easily. Others prefer to interact with their lessons—which usually refers to holding physical objects but can also be directly related to guessing answers and responding to questions.
Fortunately, PowerPoint’s versatility means that it can appeal to all of these diverse learning styles. You can embed multimedia elements such as videos, audio clips, and interactive graphics, creating a multi-sensory experience. PowerPoint can also be helpful when considering any visual impairments that your audience members may have so that you can present with different forms of media to cater to all learning styles.

Tell your story with captivating presentations
Powerpoint empowers you to develop well-designed content across all your devices
Before diving into PowerPoint, consider the following factors to help your audience retain as much information as possible:
- Define lesson objectives: Set a goal for what kind of lesson you want to impart to your audience. What do you want students to learn? You can answer this question by outlining your lesson objectives and clearly defining your goals, which will also guide the structure and content of your presentation.
- Organize your content: Divide your lesson into key points and organize them into a logical sequence that builds in complexity. Start with basic points or even a review of previous concepts before diving into more intricate or complicated aspects of your lesson. Each point should be presented on a separate slide to maintain clarity and focus.
- Use visuals effectively: Enhance your presentation with relevant visuals such as images, videos, audio clips, or interactive simulations to cater to different learning preferences and keep the presentation engaging. These can convey complex information more efficiently than text alone. At the same time, it can be easy to be carried away by inundating your audience with too many visual elements, so ensuring smooth flow and transitions is key.
- Encourage interaction: Foster active participation by including interactive elements like quizzes, polls, or discussion prompts to prompt student engagement. After you introduce a new concept in your lesson, these interactive elements can reinforce them and make them stick.
- Practice delivery: Public speaking isn’t always easy. One of the most effective ways to sound confident is to practice delivering your presentation before the day of your lesson. Familiarize yourself with the content and also the way that it’s presented: pacing, transitions, and interactive elements. This preparation will boost your confidence, ensure a smooth flow, and help you address any potential challenges during the actual presentation.
Staid lessons can be livened up thanks to the power of presentation! No matter what you’re teaching—the ABCs to a kindergarten class, or nuclear physics to a graduate department—you can check out more tips for effective presenting such as how to create compelling presentation designs , using the 10-20-30 rule for presenting, or discovering the history of PowerPoint .
Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

Five tips for choosing the right PowerPoint template
Choose an appropriate PowerPoint template to elevate your presentation’s storytelling. Consider time length, audience and other presentation elements when selecting a template.

How you can use AI to help you make the perfect presentation handouts
Learn how AI can help you organize and create handouts for your next presentation.

How to use AI to help improve your presentations
Your PowerPoint presentations are about to get a boost when you use AI to improve a PowerPoint presentation.

How to password protect your PowerPoint presentations
Learn how to password protect your PowerPoint presentations and secure your valuable files.

Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories
- Online magazine

Felipe Dana and Renata Brito
Adrift is a digital investigation that combines writing, photography, video and graphics into an immersive presentation that retraces the voyage of 43 people lost in the Atlantic as they tried to reach Europe. The project is accompanied by a 13-minute short documentary that takes viewers behind the scenes of the two-year-long investigation.
In May 2021 a boat from Mauritania full of dead men was found off the coast of the Caribbean Island of Tobago. Who were these men and why were they on the other side of the Atlantic Ocean? Two visual journalists sought answers, uncovering a story about migrants from West Africa who seek opportunity in Europe via an increasingly popular but treacherous Atlantic route. Many never arrive, their vessels adrift on dangerous currents that bring these “ghost ships” to the Caribbean. Gathering forensic evidence, and with the help of their network of sources across three continents, the reporters identified one of the men as Alassane Sow, bringing closure to his family in Mali. Photography, cinematography and text: Renata Brito and Felipe Dana, Associated Press | Video Editor: Bram Janssen | Illustration: Peter Hamlin | Motion Graphics: Marshall Ritzel | Creative Direction: Raghu Vadarevu and Nat Castañeda | Design and Development: Linda Gorman, Kati Perry and Dan Kempton Experience the interactive website.
Felipe Dana is a Brazilian photojournalist and cinematographer documenting conflict, violence and social issues around the globe. He has covered some the most notable events of the last decade for the Associated Press, from focusing on the social issues and endemic violence in his native Rio de Janeiro to the...
Jury comment
The jury awarded this project for its intimate approach to a shocking transatlantic migration story. They were moved by the extensive data collection and effective web-presentation. The meaningful collaboration enables a multimedia narrative to drive the story forward. Furthermore, it sets a new standard for international journalism– moving beyond parachute journalism to engage comprehensively with the story– that the photojournalism community ought to aspire to.
2024 Photo Contest, Africa, Open Format
Africa,Honorable Mention
Associated Press
We use cookies to analyse the use of our website, identify individual preferences after obtaining your explicit consent, and enhance your user experience.
By agreeing, you are giving us consent to set cookies and accept our Cookie Policy .
The Definitive Voice of Entertainment News
Subscribe for full access to The Hollywood Reporter
site categories
New ‘matrix’ movie in the works with drew goddard writing, directing.
The filmmaker approached Warner Bros. with a new idea to extend the franchise, known for its pioneering visual effects.
By Borys Kit
Senior Film Writer
- Share this article on Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter
- Share this article on Flipboard
- Share this article on Email
- Show additional share options
- Share this article on Linkedin
- Share this article on Pinit
- Share this article on Reddit
- Share this article on Tumblr
- Share this article on Whatsapp
- Share this article on Print
- Share this article on Comment
Warner Bros. is heading back into The Matrix , and this time Drew Goddard is leading the charge.
Goddard, the fan-favorite writer-director whose credits include The Martian, The Cabin in the Woods and World War Z, has been tapped to write and direct a new Matrix feature for the studio, Warners announced Wednesday.
Related Stories
Jonathan glazer donates signed 'zone of interest' posters to gaza humanitarian relief auction, the high highs and low lows of alan ritchson.
“Drew came to Warner Bros. with a new idea that we all believe would be an incredible way to continue the Matrix world, by both honoring what Lana and Lilly began over 25 years ago and offering a unique perspective based on his own love of the series and characters,” said Warner Bros. Motion Pictures president of production Jesse Ehrman in a statement. “The entire team at Warner Bros. Discovery is thrilled for Drew to be making his new Matrix film, adding his vision to the cinematic canon the Wachowskis spent a quarter of a century building here at the studio.”
Released just over 25 years ago, The Matrix swept the imaginations of audiences with a mind-bending story, envelope-pushing special effects and a defining performance from Keanu Reeves. Co-written and co-directed by the Wachowskis, the film revealed how our world was a simulated reality with humans actually being used as batteries for intelligent machines and how one messiah-like figure named Neo was chosen to lead a rebellion. Introducing the idea of “bullet time” as a special effect concept, the movie earned Oscars for best visual effects, editing, sound and sound editing. The movie, grossing $467 million worldwide at the time, became a pop culture touchstone for years afterwards and made Reeves a $20 million player.
Still, Matrix loomed large over pop culture, and Lana Wachowski returned to the franchise in 2021 with The Matrix Resurrections . That one, however, seemed like the end of the line for Neo as the movie grossed only $159 million worldwide amid a day-and-date release on streaming and pandemic challenges in theaters.
The studio clearly has other plans.
Goddard has the genre cred to tackle something such as The Matrix . He began his career writing on the ’90s hit series Buffy the Vampire Slayer and later worked on shows like Angel, Alias and Lost. He created Netflix’s Marvel show Daredevil and was an exec producer on the acclaimed dramedy The Good Place , which dealt with fantasy-like worlds that may or may not be heaven and hell and featured an architect figure.
On the feature side, UTA-repped Goddard wrote the monster movie Cloverfield as well as horror-genre blending Cabin in the Woods , on which he also made his directorial debut. And he earned an Oscar nomination for penning The Martian , the hit space drama directed by Ridley Scott that starred Matt Damon.
“It is not hyperbole to say The Matrix films changed both cinema and my life,” said Goddard in a statement. “Lana and Lilly’s exquisite artistry inspires me on a daily basis, and I am beyond grateful for the chance to tell stories in their world.”
THR Newsletters
Sign up for THR news straight to your inbox every day
More from The Hollywood Reporter
‘scoop’ review: gillian anderson and rufus sewell find nothing new in the bbc’s infamous prince andrew interview, hunter schafer faces horrors at german resort in neon’s ‘cuckoo’ trailer, minnie driver claims ‘hard rain’ producers denied her a wetsuit because “they wanted to see my nipples”, carla gugino says it was “physically totally impossible” that she played a mother in 2001’s ‘spy kids’, bambi goes on a rampage in first teaser for poohniverse movie ‘bambi: the reckoning’, ‘boiling point’ director philip barantini to helm dennis lehane adaptation ‘a bostonian’ (exclusive).

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
7. Add fun with visual quizzes and polls. To break the monotony and see if your audience is still with you, throw in some quick quizzes or polls. It's like a mini-game break in your presentation — your audience gets involved and it makes your presentation way more dynamic and memorable. 8.
6/ Engage Emotionally. Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning. Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations.
These tips can be useful because they can be applied to all your presentations in general. Step 1 is to ask yourself who your audience is and how to convey the key message you have in mind to them. Once you settle on your message, you can start designing your slides with that direction in mind. You may wonder how to connect with an audience ...
Start with a presentation template. Use the 20/30 rule when designing presentations. Prioritize visual appeal in design. The importance of organization. Form a brand identity. The power of color in brand identity. Emphasize data with charts, graphics and infographics. Utilize icons to add dynamics to your presentation.
The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says "any slide with more than 10 words is a document.". If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
Create different formats for your presentation. If it's a Keynote or Powerpoint, have a PDF version available in case of any tech issues you'll still have a high-quality version available. If including video, have backup screen-shots as images to demonstrate your points in case the video doesn't run. Be analog ready.
Writing skills. Writing is a form of presentation. Sharp writing skills can help you master your presentation's outline to ensure you stay on message and remain clear about your objectives from the beginning until the end. It's also helpful to have strong writing abilities for creating compelling slides and other visual aids.
Effective visual presentations are a must. They cater to the expectations of modern audiences and help you tell a story with images, graphs, and more. The visual angle of a presentation explains ideas in a way that reaches your audience. The easiest way to tell a great visual story is to start with a template that already has a wealth of visual ...
Tip #17: Use Negative Space to Your Advantage. Negative space, or white space, is your best friend when it comes to making a visually appealing presentation slide. While many times overlooked or seen as a design inconvenience, you can use extra space to actually make your design look ten times better.
Follow these steps to create a presentation based on your ideas: Determine your purpose and identify the key ideas to present. Organize your ideas in an outline. Identify opportunities to incorporate visual or audio media, and create or locate these media aids. Rehearse your presentation in advance.
As you deliver a presentation, you are creating the tone, setting, and plot for what happens. Your execution of the presentation will, if done right, create a climax/conflict and an important resolution. Consider how your slide development functions like the five components of a story, then write down how you plan to control (define) that story:
Don't hide behind the presentation or use it as a crutch. Prepare Notes. Write down key phrases on notecards or, if you will have access to a speaker's computer while you're talking, the program's Notes view. It's not a good idea to write out a line-for-line script because if you read from a script, the presentation will sound stilted.
Use Straightforward And Precise Fonts 𝘼𝙖. While you might be tempted to break the mold with your presentation, fonts are not the place to do this. Try to use standard sans serif fonts, like Open Sans, Tahoma, Verdana. These are easily recognizable and look good on the viewing window.
How to Write a Presentation Outline. Now that we know why we need to make a presentation outline. Let's dive deeper into how you can write a presentation outline. 1. Decide the Purpose of the Presentation. Decide on the goal of your presentation before you start writing any notes. It serves as a base for the remainder of your outline.
2 Lay Out Your Project Plan. Once you've set your goals, the next big step is to outline how you'll achieve them. An excellent place to start is by organizing your project into an actionable plan and steps for execution. You might wonder why this step is important for creating a successful project presentation.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
6. Prepare. Many people underestimate how much time they need to set aside to prepare for a presentation. They'll spend days creating content and visuals but only a few hours practicing. Allow extra preparation time to hone your message and feel fully confident in your presentation.
Imagine you are writing a story and need to map out the plot. 2. Use the rule of threes. Structure your report to respond to three aspects of the thing you are presenting or answer three questions, such as "what," "why" and "how.". The human mind is set up to respond positively to three things in a list or in a presentation.
Exercise 2. In this exercise, you will begin to develop visual aids for your presentation. Complete the steps in this exercise—and enjoy the chance to be creative. Working with visuals can be a pleasant way to take a break from the demands of writing. Revisit the ideas you developed in Note 14.24 "Exercise 1".
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
The advantages of PowerPoint presentations in education. Students have different learning styles: some are visual learners, who retain images and videos more effectively than speech.Some take to audio and sound more easily. Others prefer to interact with their lessons—which usually refers to holding physical objects but can also be directly related to guessing answers and responding to ...
Adrift is a digital investigation that combines writing, photography, video and graphics into an immersive presentation that retraces the voyage of 43 people lost in the Atlantic as they tried to reach Europe. The project is accompanied by a 13-minute short documentary that takes viewers behind the scenes of the two-year-long investigation.
Think of your presentation as a video from the very beginning. Take the time to create an outline or storyboard of your slides. Make sure the information flows from one slide, or scene, to another. Preview your presentation as you put it together, making sure it flows well. Add animations and motion graphics only if they bring visual value.
New 'Matrix' Movie in the Works With Drew Goddard Writing, Directing. The filmmaker approached Warner Bros. with a new idea to extend the franchise, known for its pioneering visual effects.