An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Mol Cell Biol
- v.13(7); 2021 Jul


Obesity: causes, consequences, treatments, and challenges
Obesity has become a global epidemic and is one of today’s most public health problems worldwide. Obesity poses a major risk for a variety of serious diseases including diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic liver disease (NAFLD), cardiovascular disease, hypertension and stroke, and certain forms of cancer ( Bluher, 2019 ).
Obesity is mainly caused by imbalanced energy intake and expenditure due to a sedentary lifestyle coupled with overnutrition. Excess nutrients are stored in adipose tissue (AT) in the form of triglycerides, which will be utilized as nutrients by other tissues through lipolysis under nutrient deficit conditions. There are two major types of AT, white AT (WAT) and brown AT, the latter is a specialized form of fat depot that participates in non-shivering thermogenesis through lipid oxidation-mediated heat generation. While WAT has been historically considered merely an energy reservoir, this fat depot is now well known to function as an endocrine organ that produces and secretes various hormones, cytokines, and metabolites (termed as adipokines) to control systemic energy balance. Studies over the past decade also show that WAT, especially subcutaneous WAT, could undergo ‘beiging’ remodeling in response to environmental or hormonal perturbation. In the first paper of this special issue, Cheong and Xu (2021) systematically review the recent progress on the factors, pathways, and mechanisms that regulate the intercellular and inter-organ crosstalks in the beiging of WAT. A critical but still not fully addressed issue in the adipose research field is the origin of the beige cells. Although beige adipocytes are known to have distinct cellular origins from brown and while adipocytes, it remains unclear on whether the cells are from pre-existing mature white adipocytes through a transdifferentiation process or from de novo differentiation of precursor cells. AT is a heterogeneous tissue composed of not only adipocytes but also nonadipocyte cell populations, including fibroblasts, as well as endothelial, blood, stromal, and adipocyte precursor cells ( Ruan, 2020 ). The authors examined evidence to show that heterogeneity contributes to different browning capacities among fat depots and even within the same depot. The local microenvironment in WAT, which is dynamically and coordinately controlled by inputs from the heterogeneous cell types, plays a critical role in the beige adipogenesis process. The authors also examined key regulators of the AT microenvironment, including vascularization, the sympathetic nerve system, immune cells, peptide hormones, exosomes, and gut microbiota-derived metabolites. Given that increasing beige fat function enhances energy expenditure and consequently reduces body weight gain, identification and characterization of novel regulators and understanding their mechanisms of action in the beiging process has a therapeutic potential to combat obesity and its associated diseases. However, as noticed by the authors, most of the current pre-clinical research on ‘beiging’ are done in rodent models, which may not represent the exact phenomenon in humans ( Cheong and Xu, 2021 ). Thus, further investigations will be needed to translate the findings from bench to clinic.
While both social–environmental factors and genetic preposition have been recognized to play important roles in obesity epidemic, Gao et al. (2021) present evidence showing that epigenetic changes may be a key factor to explain interindividual differences in obesity. The authors examined data on the function of DNA methylation in regulating the expression of key genes involved in metabolism. They also summarize the roles of histone modifications as well as various RNAs such as microRNAs, long noncoding RNAs, and circular RNAs in regulating metabolic gene expression in metabolic organs in response to environmental cues. Lastly, the authors discuss the effect of lifestyle modification and therapeutic agents on epigenetic regulation of energy homeostasis. Understanding the mechanisms by which lifestyles such as diet and exercise modulate the expression and function of epigenetic factors in metabolism should be essential for developing novel strategies for the prevention and treatment of obesity and its associated metabolic diseases.
A major consequence of obesity is type 2 diabetes, a chronic disease that occurs when body cannot use and produce insulin effectively. Diabetes profoundly and adversely affects the vasculature, leading to various cardiovascular-related diseases such as atherosclerosis, arteriosclerotic, and microvascular diseases, which have been recognized as the most common causes of death in people with diabetes ( Cho et al., 2018 ). Love et al. (2021) systematically review the roles and regulation of endothelial insulin resistance in diabetes complications, focusing mainly on vascular dysfunction. The authors review the vasoprotective functions and the mechanisms of action of endothelial insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling pathways. They also examined the contribution and impart of endothelial insulin resistance to diabetes complications from both biochemical and physiological perspectives and evaluated the beneficial roles of many of the medications currently used for T2D treatment in vascular management, including metformin, thiazolidinediones, glucagon-like receptor agonists, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors, as well as exercise. The authors present evidence to suggest that sex differences and racial/ethnic disparities contribute significantly to vascular dysfunction in the setting of diabetes. Lastly, the authors raise a number of very important questions with regard to the role and connection of endothelial insulin resistance to metabolic dysfunction in other major metabolic organs/tissues and suggest several insightful directions in this area for future investigation.
Following on from the theme of obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction, Xia et al. (2021) review the latest progresses on the role of membrane-type I matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP), a zinc-dependent endopeptidase that proteolytically cleaves extracellular matrix components and non-matrix proteins, in lipid metabolism. The authors examined data on the transcriptional and post-translational modification regulation of MT1-MMP gene expression and function. They also present evidence showing that the functions of MT1-MMP in lipid metabolism are cell specific as it may either promote or suppress inflammation and atherosclerosis depending on its presence in distinct cells. MT1-MMP appears to exert a complex role in obesity for that the molecule delays the progression of early obesity but exacerbates obesity at the advanced stage. Because inhibition of MT1-MMP can potentially lower the circulating low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cancer metastasis and atherosclerosis, the protein has been viewed as a very promising therapeutic target. However, challenges remain in developing MT1-MMP-based therapies due to the tissue-specific roles of MT1-MMP and the lack of specific inhibitors for this molecule. Further investigations are needed to address these questions and to develop MT1-MMP-based therapeutic interventions.
Lastly, Huang et al. (2021) present new findings on a critical role of puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase (PSA), an integral non-transmembrane enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of amino acids near the N-terminus of polypeptides, in NAFLD. NAFLD, ranging from simple nonalcoholic fatty liver to the more aggressive subtype nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, has now become the leading chronic liver disease worldwide ( Loomba et al., 2021 ). At present, no effective drugs are available for NAFLD management in the clinic mainly due to the lack of a complete understanding of the mechanisms underlying the disease progress, reinforcing the urgent need to identify and validate novel targets and to elucidate their mechanisms of action in NAFLD development and pathogenesis. Huang et al. (2021) found that PSA expression levels were greatly reduced in the livers of obese mouse models and that the decreased PSA expression correlated with the progression of NAFLD in humans. They also found that PSA levels were negatively correlated with triglyceride accumulation in cultured hepatocytes and in the liver of ob/ob mice. Moreover, PSA suppresses steatosis by promoting lipogenesis and attenuating fatty acid β-oxidation in hepatocytes and protects oxidative stress and lipid overload in the liver by activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, the master regulator of antioxidant response. These studies identify PSA as a pivotal regulator of hepatic lipid metabolism and suggest that PSA may be a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for treating NAFLD.
In summary, papers in this issue review our current knowledge on the causes, consequences, and interventions of obesity and its associated diseases such as type 2 diabetes, NAFLD, and cardiovascular disease ( Cheong and Xu, 2021 ; Gao et al., 2021 ; Love et al., 2021 ). Potential targets for the treatment of dyslipidemia and NAFLD are also discussed, as exemplified by MT1-MMP and PSA ( Huang et al., 2021 ; Xia et al., 2021 ). It is noted that despite enormous effect, few pharmacological interventions are currently available in the clinic to effectively treat obesity. In addition, while enhancing energy expenditure by browning/beiging of WAT has been demonstrated as a promising alternative approach to alleviate obesity in rodent models, it remains to be determined on whether such WAT reprogramming is effective in combating obesity in humans ( Cheong and Xu, 2021 ). Better understanding the mechanisms by which obesity induces various medical consequences and identification and characterization of novel anti-obesity secreted factors/soluble molecules would be helpful for developing effective therapeutic treatments for obesity and its associated medical complications.
- Bluher M. (2019). Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis . Nat. Rev. Endocrinol . 15 , 288–298. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheong L.Y., Xu A. (2021). Intercellular and inter-organ crosstalk in browning of white adipose tissue: molecular mechanism and therapeutic complications . J. Mol. Cell Biol . 13 , 466–479. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cho N.H., Shaw J.E., Karuranga S., et al. (2018). IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045 . Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract . 138 , 271–281. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gao W., Liu J.-L., Lu X., et al. (2021). Epigenetic regulation of energy metabolism in obesity . J. Mol. Cell Biol . 13 , 480–499. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang B., Xiong X., Zhang L., et al. (2021). PSA controls hepatic lipid metabolism by regulating the NRF2 signaling pathway . J. Mol. Cell Biol . 13 , 527–539. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Loomba R., Friedman S.L., Shulman G.I. (2021). Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease . Cell 184 , 2537–2564. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Love K.M., Barrett E.J., Malin S.K., et al. (2021). Diabetes pathogenesis and management: the endothelium comes of age . J. Mol. Cell Biol . 13 , 500–512. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ruan H.-B. (2020). Developmental and functional heterogeneity of thermogenic adipose tissue . J. Mol. Cell Biol . 12 , 775–784. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xia X.-D., Alabi A., Wang M., et al. (2021). Membrane-type I matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP), lipid metabolism, and therapeutic implications . J. Mol. Cell Biol . 13 , 513–526. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Review article, childhood and adolescent obesity: a review.

- 1 Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Department of Pediatrics, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States
- 2 Division of Adolescent Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, Medical College of Wisconsin Affiliated Hospitals, Milwaukee, WI, United States
- 3 Division of Adolescent Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States
Obesity is a complex condition that interweaves biological, developmental, environmental, behavioral, and genetic factors; it is a significant public health problem. The most common cause of obesity throughout childhood and adolescence is an inequity in energy balance; that is, excess caloric intake without appropriate caloric expenditure. Adiposity rebound (AR) in early childhood is a risk factor for obesity in adolescence and adulthood. The increasing prevalence of childhood and adolescent obesity is associated with a rise in comorbidities previously identified in the adult population, such as Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension, Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver disease (NAFLD), Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), and Dyslipidemia. Due to the lack of a single treatment option to address obesity, clinicians have generally relied on counseling dietary changes and exercise. Due to psychosocial issues that may accompany adolescence regarding body habitus, this approach can have negative results. Teens can develop unhealthy eating habits that result in Bulimia Nervosa (BN), Binge- Eating Disorder (BED), or Night eating syndrome (NES). Others can develop Anorexia Nervosa (AN) as they attempt to restrict their diet and overshoot their goal of “being healthy.” To date, lifestyle interventions have shown only modest effects on weight loss. Emerging findings from basic science as well as interventional drug trials utilizing GLP-1 agonists have demonstrated success in effective weight loss in obese adults, adolescents, and pediatric patients. However, there is limited data on the efficacy and safety of other weight-loss medications in children and adolescents. Nearly 6% of adolescents in the United States are severely obese and bariatric surgery as a treatment consideration will be discussed. In summary, this paper will overview the pathophysiology, clinical, and psychological implications, and treatment options available for obese pediatric and adolescent patients.
Introduction
Obesity is a complex issue that affects children across all age groups ( 1 – 3 ). One-third of children and adolescents in the United States are classified as either overweight or obese. There is no single element causing this epidemic, but obesity is due to complex interactions between biological, developmental, behavioral, genetic, and environmental factors ( 4 ). The role of epigenetics and the gut microbiome, as well as intrauterine and intergenerational effects, have recently emerged as contributing factors to the obesity epidemic ( 5 , 6 ). Other factors including small for gestational age (SGA) status at birth, formula rather than breast feeding in infancy, and early introduction of protein in infant's dietary intake have been reportedly associated with weight gain that can persist later in life ( 6 – 8 ). The rising prevalence of childhood obesity poses a significant public health challenge by increasing the burden of chronic non-communicable diseases ( 1 , 9 ).
Obesity increases the risk of developing early puberty in children ( 10 ), menstrual irregularities in adolescent girls ( 1 , 11 ), sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) ( 1 , 12 ), cardiovascular risk factors that include Prediabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, High Cholesterol levels, Hypertension, NAFLD, and Metabolic syndrome ( 1 , 2 ). Additionally, obese children and adolescents can suffer from psychological issues such as depression, anxiety, poor self-esteem, body image and peer relationships, and eating disorders ( 13 , 14 ).
So far, interventions for overweight/obesity prevention have mainly focused on behavioral changes in an individual such as increasing daily physical exercise or improving quality of diet with restricting excess calorie intake ( 1 , 15 , 16 ). However, these efforts have had limited results. In addition to behavioral and dietary recommendations, changes in the community-based environment such as promotion of healthy food choices by taxing unhealthy foods ( 17 ), improving lunch food quality and increasing daily physical activity at school and childcare centers, are extra measures that are needed ( 16 ). These interventions may include a ban on unhealthy food advertisements aimed at children as well as access to playgrounds and green spaces where families can feel their children can safely recreate. Also, this will limit screen time for adolescents as well as younger children.
However, even with the above changes, pharmacotherapy and/or bariatric surgery will likely remain a necessary option for those youth with morbid obesity ( 1 ). This review summarizes our current understanding of the factors associated with obesity, the physiological and psychological effects of obesity on children and adolescents, and intervention strategies that may prevent future concomitant issues.
Definition of Childhood Obesity
Body mass index (BMI) is an inexpensive method to assess body fat and is derived from a formula derived from height and weight in children over 2 years of age ( 1 , 18 , 19 ). Although more sophisticated methods exist that can determine body fat directly, they are costly and not readily available. These methods include measuring skinfold thickness with a caliper, Bioelectrical impedance, Hydro densitometry, Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA), and Air Displacement Plethysmography ( 2 ).
BMI provides a reasonable estimate of body fat indirectly in the healthy pediatric population and studies have shown that BMI correlates with body fat and future health risks ( 18 ). Unlike in adults, Z-scores or percentiles are used to represent BMI in children and vary with the age and sex of the child. BMI Z-score cut off points of >1.0, >2.0, and >3.0 are recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) to define at risk of overweight, overweight and obesity, respectively ( 19 ). However, in terms of percentiles, overweight is applied when BMI is >85th percentile <95th percentile, whereas obesity is BMI > 95th percentile ( 20 – 22 ). Although BMI Z-scores can be converted to BMI percentiles, the percentiles need to be rounded and can misclassify some normal-weight children in the under or overweight category ( 19 ). Therefore, to prevent these inaccuracies and for easier understanding, it is recommended that the BMI Z-scores in children should be used in research whereas BMI percentiles are best used in the clinical settings ( 20 ).
As BMI does not directly measure body fat, it is an excellent screening method, but should not be used solely for diagnostic purposes ( 23 ). Using 85th percentile as a cut off point for healthy weight may miss an opportunity to obtain crucial information on diet, physical activity, and family history. Once this information is obtained, it may allow the provider an opportunity to offer appropriate anticipatory guidance to the families.
Pathophysiology of Obesity
The pathophysiology of obesity is complex that results from a combination of individual and societal factors. At the individual level, biological, and physiological factors in the presence of ones' own genetic risk influence eating behaviors and tendency to gain weight ( 1 ). Societal factors include influence of the family, community and socio-economic resources that further shape these behaviors ( Figure 1 ) ( 3 , 24 ).
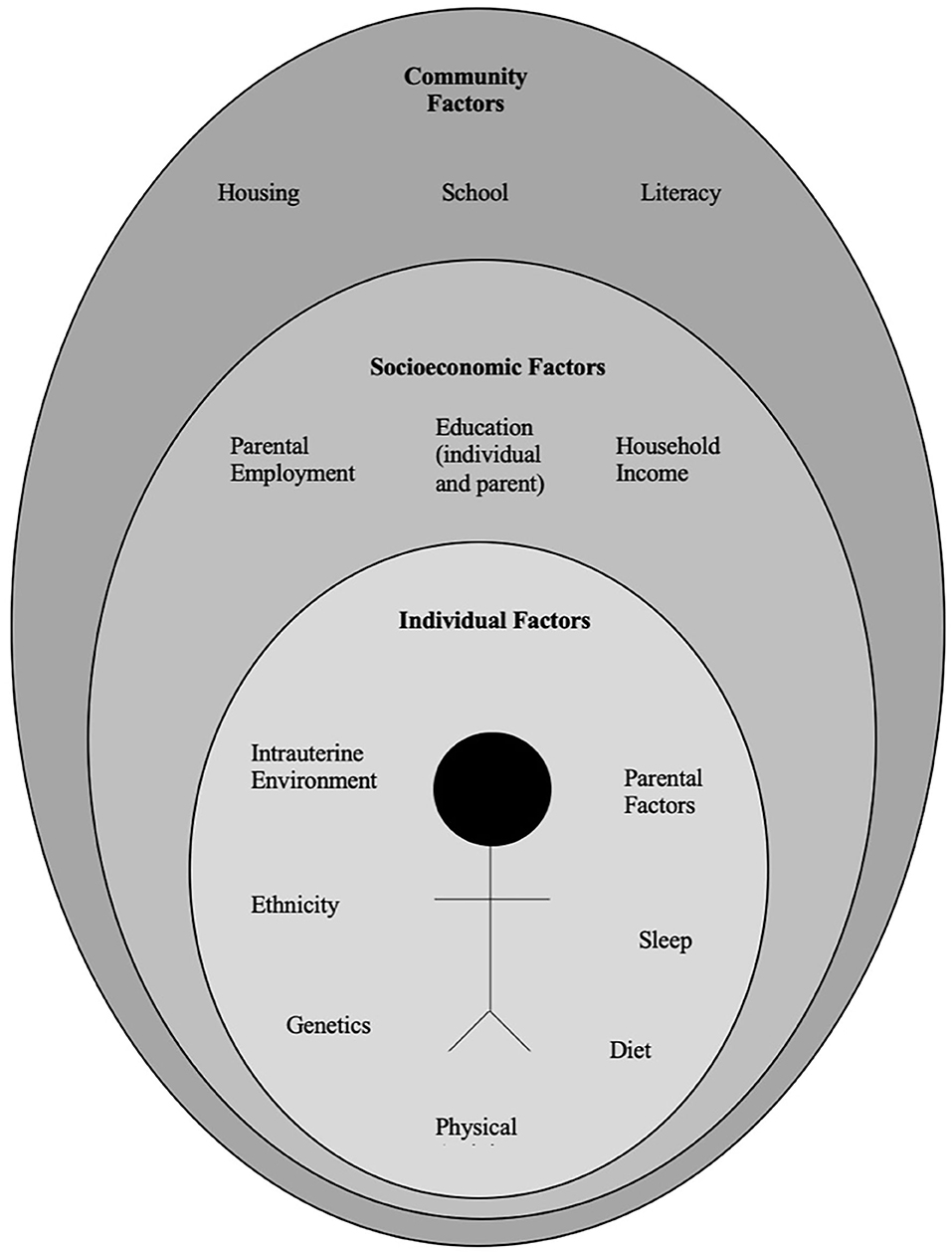
Figure 1 . Multidimensional factors contributing to child and adolescent obesity.
Biological Factors
There is a complex architecture of neural and hormonal regulatory control, the Gut-Brain axis, which plays a significant role in hunger and satiety ( Figure 2 ). Sensory stimulation (smell, sight, and taste), gastrointestinal signals (peptides, neural signals), and circulating hormones further contribute to food intake ( 25 – 27 ).
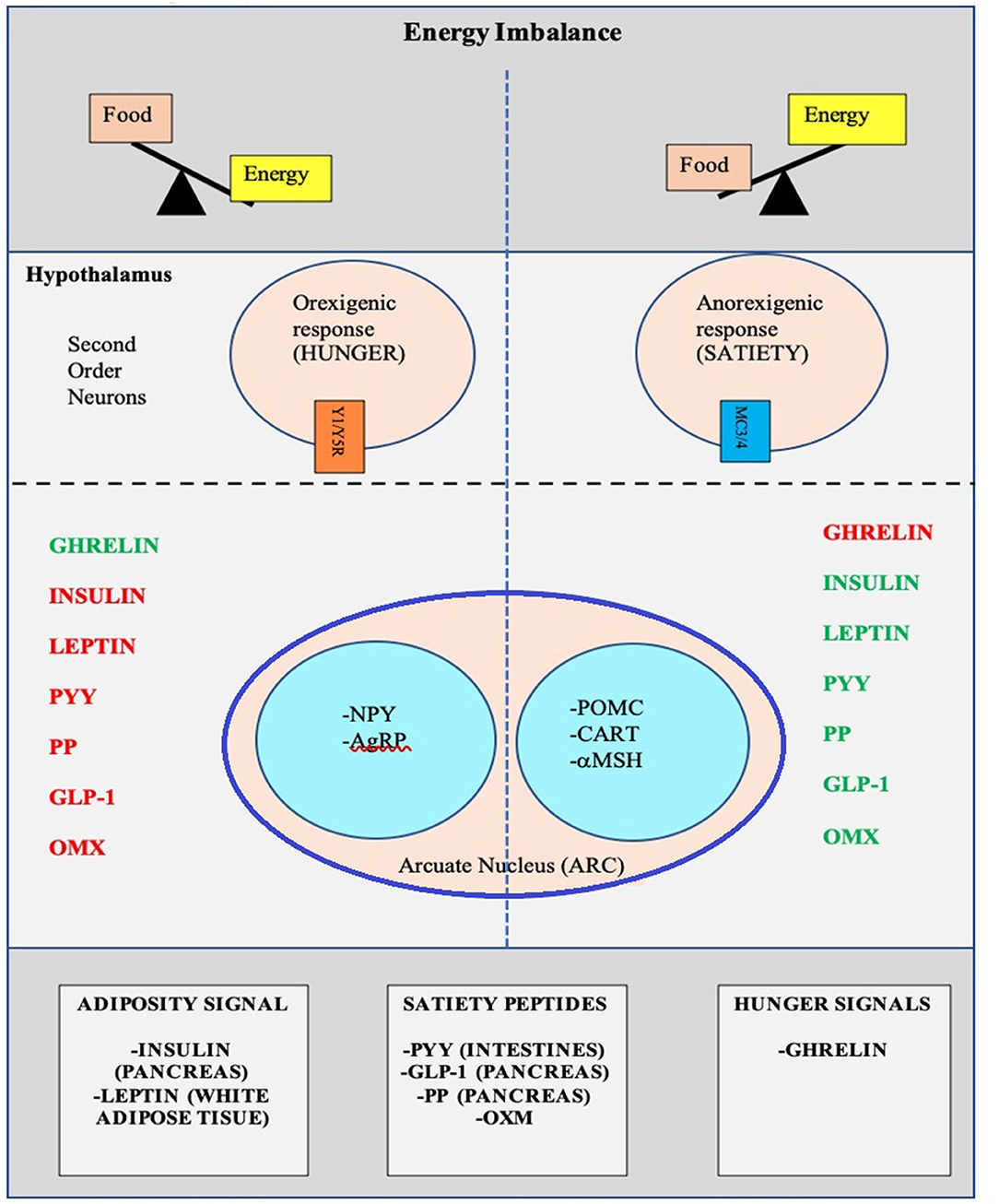
Figure 2 . Pictorial representation of the Hunger-Satiety pathway a and the various hormones b involved in the pathway. a, Y1/Y5R and MC3/4 are second order neuro receptors which are responsible in either the hunger or satiety pathway. Neurons in the ARC include: NPY, Neuropeptide Y; AgRP, Agouti-Related Peptide; POMC, Pro-Opiomelanocortin; CART, Cocaine-and Amphetamine-regulated Transcript; α-MSH, α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone. b, PYY, Peptide YY; PP, Pancreatic Polypeptide; GLP-1, Glucagon-Like Peptide- I; OMX, Oxyntomodulin.
The hypothalamus is the crucial region in the brain that regulates appetite and is controlled by key hormones. Ghrelin, a hunger-stimulating (orexigenic) hormone, is mainly released from the stomach. On the other hand, leptin is primarily secreted from adipose tissue and serves as a signal for the brain regarding the body's energy stores and functions as an appetite -suppressing (anorexigenic) hormone. Several other appetite-suppressing (anorexigenic) hormones are released from the pancreas and gut in response to food intake and reach the hypothalamus through the brain-blood barrier (BBB) ( 28 – 32 ). These anorexigenic and orexigenic hormones regulate energy balance by stimulating hunger and satiety by expression of various signaling pathways in the arcuate nucleus (ARC) of the hypothalamus ( Figure 2 ) ( 28 , 33 ). Dysregulation of appetite due to blunted suppression or loss of caloric sensing signals can result in obesity and its morbidities ( 34 ).
Emotional dysfunction due to psychiatric disorders can cause stress and an abnormal sleep-wake cycles. These modifications in biological rhythms can result in increased appetite, mainly due to ghrelin, and can contribute to emotional eating ( 35 ).
Recently, the role of changes in the gut microbiome with increased weight gain through several pathways has been described in literature ( 36 , 37 ). The human gut serves as a host to trillions of microorganisms, referred to as gut microbiota. The dominant gut microbial phyla are Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, Fusobacteria, and Verrucomicrobia, with Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes representing 90% of human gut microbiota ( 5 , 38 ). The microbes in the gut have a symbiotic relationship within their human host and provide a nutrient-rich environment. Gut microbiota can be affected by various factors that include gestational age at birth, mode of infant delivery, type of neonatal and infant feeding, introduction of solid food, feeding practices and external factors like antibiotic use ( 5 , 38 ). Also, the maturation of the bacterial phyla that occurs from birth to adulthood ( 39 ), is influenced by genetics, environment, diet, lifestyle, and gut physiology and stabilizes in adulthood ( 5 , 39 , 40 ). Gut microbiota is unique to each individual and plays a specific role in maintaining structural integrity, and the mucosal barrier of the gut, nutrient metabolism, immune response, and protection against pathogens ( 5 , 37 , 38 ). In addition, the microbiota ferments the indigestible food and synthesizes other essential micronutrients as well as short chain fatty acids (SCFAs') ( 40 , 41 ). Dysbiosis or imbalance of the gut microbiota, in particularly the role of SCFA has been linked with the patho-physiology of obesity ( 36 , 38 , 41 , 42 ). SCFAs' are produced by anaerobic fermentation of dietary fiber and indigestible starch and play a role in mammalian energy metabolism by influencing gut-brain communication axis. Emerging evidence has shown that increased ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes causes increased energy extraction of calories from diets and is evidenced by increased production of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs') ( 43 – 45 ). However, this relationship is not affirmed yet, as a negative relationship between SCFA levels and obesity has also been reported ( 46 ). Due to the conflicting data, additional randomized control trials are needed to clarify the role of SCFA's in obese and non-obese individuals.
The gut microbiota also has a bidirectional interaction with the liver, and various additional factors such as diet, genetics, and the environment play a key role in this relationship. The Gut- Liver Axis is interconnected at various levels that include the mucus barrier, epithelial barrier, and gut microbiome and are essential to maintain normal homeostasis ( 47 ). Increased intestinal mucosal permeability can disrupt the gut-liver axis, which releases various inflammatory markers, activates an innate immune response in the liver, and results in a spectrum of liver diseases that include hepatic steatosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ( 48 , 49 ).
Other medical conditions, including type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Metabolic Syndrome, eating disorders as well as psychological conditions such as anxiety and depression are associated with the gut microbiome ( 50 – 53 ).
Genetic Factors
Genetic causes of obesity can either be monogenic or polygenic types. Monogenic obesity is rare, mainly due to mutations in genes within the leptin/melanocortin pathway in the hypothalamus that is essential for the regulation of food intake/satiety, body weight, and energy metabolism ( 54 ). Leptin regulates eating behaviors, the onset of puberty, and T-cell immunity ( 55 ). About 3% of obese children have mutations in the leptin ( LEP ) gene and the leptin receptor (LEPR) and can also present with delayed puberty and immune dysfunction ( 55 , 56 ). Obesity caused by other genetic mutations in the leptin-melanocortin pathway include proopiomelanocortin (POMC) and melanocortin receptor 4 (MC4R), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and the tyrosine kinase receptor B (NTRK2) genes ( 57 , 58 ). Patients with monogenic forms generally present during early childhood (by 2 years old) with severe obesity and abnormal feeding behaviors ( 59 ). Other genetic causes of severe obesity are Prader Willi Syndrome (PWS), Alström syndrome, Bardet Biedl syndrome. Patients with these syndromes present with additional characteristics, including cognitive impairment, dysmorphic features, and organ-specific developmental abnormalities ( 60 ). Individuals who present with obesity, developmental delay, dysmorphic features, and organ dysfunction should receive a genetics referral for further evaluation.
Polygenic obesity is the more common form of obesity, caused by the combined effect of multiple genetic variants. It is the result of the interplay between genetic susceptibility and the environment, also known as the Gene-Environment Interaction (GEI) ( 61 – 64 ). Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified gene variants [single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs)] for body mass index (BMI) that likely act synergistically to affect body weight ( 65 ). Studies have identified genetic variants in several genes that may contribute to excessive weight gain by increasing hunger and food intake ( 66 – 68 ). When the genotype of an individual confers risk for obesity, exposure to an obesogenic environment may promote a state of energy imbalance due to behaviors that contribute to conserving rather than expending energy ( 69 , 70 ). Research studies have shown that obese individuals have a genetic variation that can influence their actions, such as increased food intake, lack of physical activity, a decreased metabolism, as well as an increased tendency to store body fat ( 63 , 66 , 67 , 69 , 70 ).
Recently the role of epigenetic factors in the development of obesity has emerged ( 71 ). The epigenetic phenomenon may alter gene expression without changing the underlying DNA sequence. In effect, epigenetic changes may result in the addition of chemical tags known as methyl groups, to the individual's chromosomes. This alteration can result in a phenomenon where critical genes are primed to on and off regulate. Complex physiological and psychological adjustment occur during infancy and can thereafter set the stage for health vs. disease. Developmental origins of health and disease (DOHaD) shows that early life environment can impact the risk of chronic diseases later in life due to fetal programming secondary to epigenetic changes ( 72 ). Maternal nutrition during the prenatal or early postnatal period may trigger these epigenetic changes and increase the risk for chronic conditions such as obesity, metabolic and cardiovascular disease due to epigenetic modifications that may persist and cause intergenerational effect on the health children and adults ( 58 , 73 , 74 ). Similarly, adverse childhood experiences (ACE) have been linked to a broad range of negative outcomes through epigenetic mechanisms ( 75 ) and promote unhealthy eating behaviors ( 76 , 77 ). Other factors such as diet, physical activity, environmental and psychosocial stressors can cause epigenetic changes and place an individual at risk for weight gain ( 78 ).
Developmental Factors
Eating behaviors evolve over the first few years of life. Young children learn to eat through their direct experience with food and observing others eating around them ( 79 ). During infancy, feeding defines the relationship of security and trust between a child and the parent. Early childhood eating behaviors shift to more self-directed control due to rapid physical, cognitive, communicative, and social development ( 80 ). Parents or caregivers determine the type of food that is made available to the infant and young child. However, due to economic limitations and parents having decreased time to prepare nutritious meals, consumption of processed and cheaper energy-dense foods have occurred in Western countries. Additionally, feeding practices often include providing large or super-sized portions of palatable foods and encouraging children to finish the complete meal (clean their plate even if they do not choose to), as seen across many cultures ( 81 , 82 ). Also, a segment of parents are overly concerned with dietary intake and may pressurize their child to eat what they perceive as a healthy diet, which can lead to unintended consequences ( 83 ). Parents' excessive restriction of food choices may result in poor self-regulation of energy intake by their child or adolescent. This action may inadvertently promote overconsumption of highly palatable restricted foods when available to the child or adolescent outside of parental control with resultant excessive weight gain ( 84 , 85 ).
During middle childhood, children start achieving greater independence, experience broader social networks, and expand their ability to develop more control over their food choices. Changes that occur in the setting of a new environment such as daycare or school allow exposure to different food options, limited physical activity, and often increased sedentary behaviors associated with school schedules ( 24 ). As the transition to adolescence occurs, physical and psychosocial development significantly affect food choices and eating patterns ( 25 ). During the teenage years, more independence and interaction with peers can impact the selection of fast foods that are calorically dense. Moreover, during the adolescent years, more sedentary behaviors such as video and computer use can limit physical exercise. Adolescence is also a period in development with an enhanced focus on appearance, body weight, and other psychological concerns ( 86 , 87 ).
Environmental Factors
Environmental changes within the past few decades, particularly easy access to high-calorie fast foods, increased consumption of sugary beverages, and sedentary lifestyles, are linked with rising obesity ( 88 ). The easy availability of high caloric fast foods, and super-sized portions, are increasingly common choices as individuals prefer these highly palatable and often less expensive foods over fruits and vegetables ( 89 ). The quality of lunches and snacks served in schools and childcare centers has been an area of debate and concern. Children and adolescents consume one-third to one-half of meals in the above settings. Despite policies in place at schools, encouraging foods, beverages, and snacks that are deemed healthier options, the effectiveness of these policies in improving children's dietary habits or change in obesity rate has not yet been seen ( 90 ). This is likely due to the fact that such policies primarily focus on improving dietary quality but not quantity which can impact the overweight or obese youth ( 91 ). Policies to implement taxes on sugary beverages are in effect in a few states in the US ( 92 ) as sugar and sugary beverages are associated with increased weight gain ( 2 , 3 ). This has resulted in reduction in sales of sugary drinks in these states, but the sales of these types of drinks has risen in neighboring states that did not implement the tax ( 93 ). Due to advancements in technology, children are spending increased time on electronic devices, limiting exercise options. Technology advancement is also disrupting the sleep-wake cycle, causing poor sleeping habits, and altered eating patterns ( 94 ). A study published on Canadian children showed that the access to and night-time use of electronic devices causes decreased sleep duration, resulting in excess body weight, inferior diet quality, and lower physical activity levels ( 95 ).
Infant nutrition has gained significant popularity in relation to causing overweight/obesity and other diseases later in life. Breast feeding is frequently discussed as providing protection against developing overweight/obesity in children ( 8 ). Considerable heterogeneity has been observed in studies and conducting randomized clinical trials between breast feeding vs. formula feeding is not feasible ( 8 ). Children fed with a low protein formula like breast milk are shown to have normal weight gain in early childhood as compared to those that are fed formulas with a high protein load ( 96 ). A recent Canadian childbirth cohort study showed that breast feeding within first year of life was inversely associated with weight gain and increased BMI ( 97 ). The effect was stronger if the child was exclusively breast fed directly vs. expressed breast milk or addition of formula or solid food ( 97 ). Also, due to the concern of poor growth in preterm or SGA infants, additional calories are often given for nutritional support in the form of macronutrient supplements. Most of these infants demonstrate “catch up growth.” In fact, there have been reports that in some children the extra nutritional support can increase the risk for overweight/obesity later in life. The association, however, is inconsistent. Recently a systemic review done on randomized controlled trials comparing the studies done in preterm and SGA infants with feeds with and without macronutrient supplements showed that macronutrient supplements may increase weight and length in toddlers but did not show a significant increase in the BMI during childhood ( 98 ). Increased growth velocity due to early introduction of formula milk and protein in infants' diet, may influence the obesity pathways, and can impact fetal programming for metabolic disease later in life ( 99 ).
General pediatricians caring for children with overweight/obesity, generally recommend endocrine testing as parents often believe that there may be an underlying cause for this condition and urge their primary providers to check for conditions such as thyroid abnormalities. Endocrine etiologies for obesity are rarely identified and patients with underlying endocrine disorders causing excessive weight gain usually are accompanied by attenuated growth patterns, such that a patient continues to gain weight with a decline in linear height ( 100 ). Various endocrine etiologies that one could consider in a patient with excessive weight gain in the setting of slow linear growth: severe hypothyroidism, growth hormone deficiency, and Cushing's disease/syndrome ( 58 , 100 ).
Clinical-Physiology of Pediatric Obesity
It is a well-known fact that early AR(increased BMI) before the age of 5 years is a risk factor for adult obesity, obesity-related comorbidities, and metabolic syndrome ( 101 – 103 ). Typically, body mass index (BMI) declines to a minimum in children before it starts increasing again into adulthood, also known as AR. Usually, AR happens between 5 and 7 years of age, but if it occurs before the age of 5 years is considered early AR. Early AR is a marker for higher risk for obesity-related comorbidities. These obesity-related health comorbidities include cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension, dyslipidemia, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes), hormonal issues, orthopedic problems, sleep apnea, asthma, and fatty liver disease ( Figure 3 ) ( 9 ).
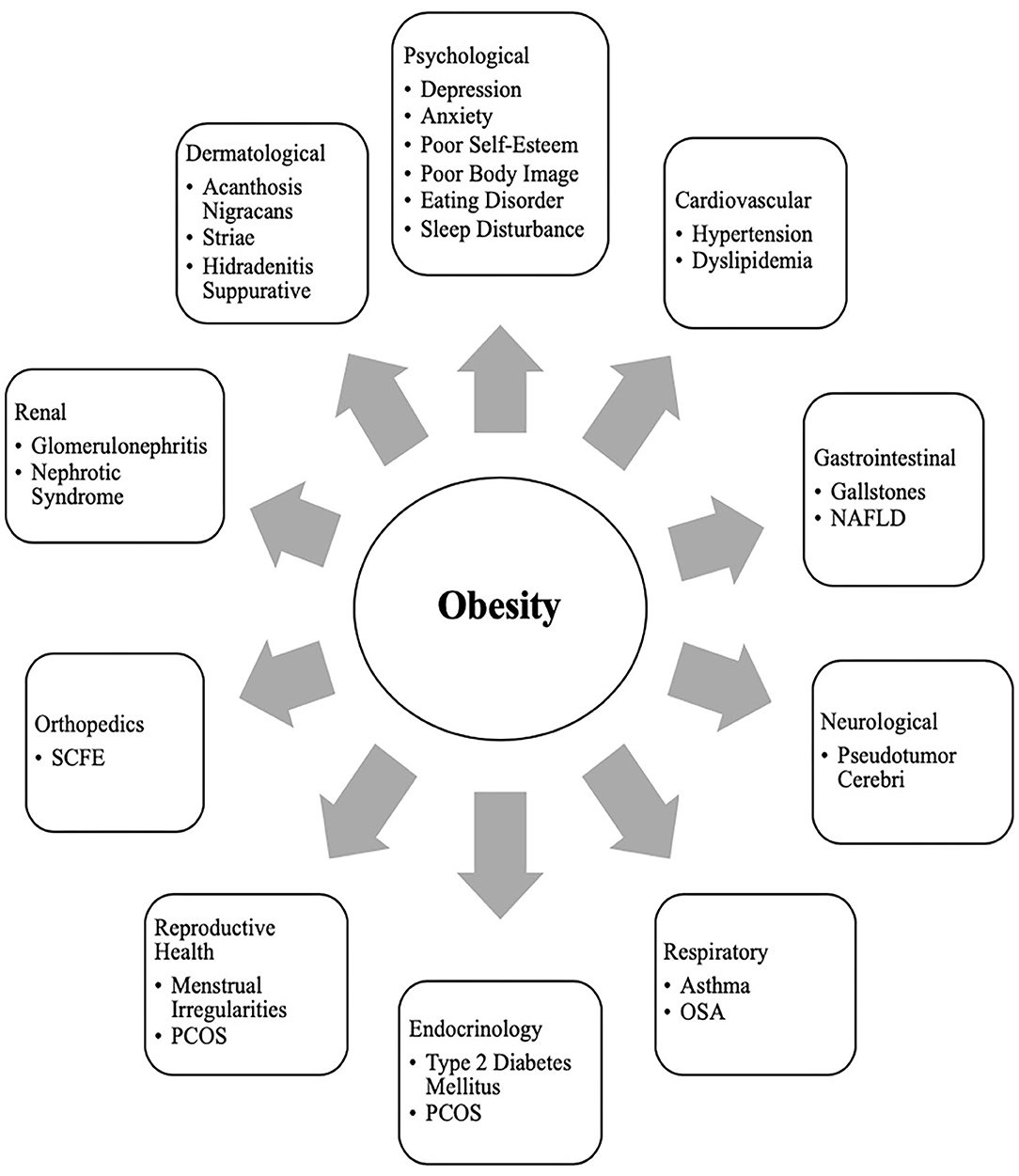
Figure 3 . Obesity related co-morbidities a in children and adolescents. a, NAFLD, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease; SCFE, Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis; PCOS, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome; OSA, Obstructive Sleep Apnea.
Clinical Comorbidities of Obesity in Children
Growth and puberty.
Excess weight gain in children can influence growth and pubertal development ( 10 ). Childhood obesity can cause prepubertal acceleration of linear growth velocity and advanced bone age in boys and girls ( 104 ). Hyperinsulinemia is a normal physiological state during puberty, but children with obesity can have abnormally high insulin levels ( 105 ). Leptin resistance also occurs in obese individuals who have higher leptin levels produced by their adipose tissue ( 55 , 106 ). The insulin and leptin levels can act on receptors that impact the growth plates with a resultant bone age advancement ( 55 ).
Adequate nutrition is essential for the typical timing and tempo of pubertal onset. Excessive weight gain can initiate early puberty, due to altered hormonal parameters ( 10 ). Obese children may present with premature adrenarche, thelarche, or precocious puberty (PP) ( 107 ). The association of early pubertal changes with obesity is consistent in girls, and is well-reported; however, data is sparse in boys ( 108 ). One US study conducted in racially diverse boys showed obese boys had delayed puberty, whereas overweight boys had early puberty as compared to normal-weight boys ( 109 ). Obese girls with PP have high leptin levels ( 110 , 111 ). Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence (HELENA) is a cross-sectional study and suggested an indirect relationship between elevated leptin levels, early puberty, and cardiometabolic and inflammatory markers in obese girls ( 112 ). Additionally, obese girls with premature adrenarche carry a higher risk for developing polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in the future ( 113 , 114 ).
Sleep Disorders
Obesity is an independent risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in children and adolescents ( 12 , 115 ). Children with OSA have less deleterious consequences in terms of cardiovascular stress of metabolic syndrome when compared to adolescents and adults ( 116 , 117 ). In children, abnormal behaviors and neurocognitive dysfunction are the most critical and frequent end-organ morbidities associated with OSA ( 12 ). However, in adolescents, obesity and OSA can independently cause oxidative systemic stress and inflammation ( 118 , 119 ), and when this occurs concurrently, it can result in more severe metabolic dysfunction and cardiovascular outcomes later in life ( 120 ).
Other Comorbidities
Obesity is related to a clinical spectrum of liver abnormalities such as NAFLD ( 121 ); the most important cause of liver disease in children ( 122 – 124 ). NAFLD includes steatosis (increased liver fat without inflammation) and NASH (increased liver fat with inflammation and hepatic injury). While in some adults NAFLD can progress to an end-stage liver disease requiring liver transplant ( 125 , 126 ), the risk of progression during childhood is less well-defined ( 127 ). NAFLD is closely associated with metabolic syndrome including central obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension ( 128 ).
Obese children are also at risk for slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) ( 129 ), and sedentary lifestyle behaviors may have a negative influence on the brain structure and executive functioning, although the direction of causality is not clear ( 130 , 131 ).
Clinical Comorbidities of Obesity in Adolescents
Menstrual irregularities and pcos.
At the onset of puberty, physiologically, sex steroids can cause appropriate weight gain and body composition changes that should not affect normal menstruation ( 132 , 133 ). However, excessive weight gain in adolescent girls can result in irregular menstrual cycles and puts them at risk for PCOS due to increased androgen levels. Additionally, they can have excessive body hair (hirsutism), polycystic ovaries, and can suffer from distorted body images ( 134 , 135 ). Adolescent girls with PCOS also have an inherent risk for insulin resistance irrespective of their weight. However, weight gain further exacerbates their existing state of insulin resistance and increases the risk for obesity-related comorbidities such as metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. Although the diagnosis of PCOS can be challenging at this age due to an overlap with predictable pubertal changes, early intervention (appropriate weight loss and use of hormonal methods) can help restore menstrual cyclicity and future concerns related to childbearing ( 11 ).
Metabolic Syndrome and Sleep Disorders
Metabolic syndrome (MS) is a group of cardiovascular risk factors characterized by acanthosis nigricans, prediabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), that occurs from insulin resistance caused by obesity ( 136 ). Diagnosis of MS in adults requires at least three out of the five risk factors: increased central adiposity, hypertension, hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, or low HDL level. Definitions to diagnose MS are controversial in younger age groups, and many definitions have been proposed ( 136 ). This is due to the complex physiology of growth and development during puberty, which causes significant overlap between MS and features of normal growth. However, childhood obesity is associated with an inflammatory state even before puberty ( 137 ). In obese children and adolescents, hyperinsulinemia during puberty ( 138 , 139 ) and unhealthy sleep behaviors increase MS's risk and severity ( 140 ). Even though there is no consensus on diagnosis regarding MS in this age group, when dealing with obese children and adolescents, clinicians should screen them for MS risk factors and sleep behaviors and provide recommendations for weight management.
Social Psychology of Pediatric Obesity in Children and Adolescents
Obese children and adolescents may experience psychosocial sequelae, including depression, bullying, social isolation, diminished self-esteem, behavioral problems, dissatisfaction with body image, and reduced quality of life ( 13 , 141 ). Compared with normal-weight counterparts, overweight/obesity is one of the most common reasons children and adolescents are bullied at school ( 142 ). The consequence of stigma, bullying, and teasing related to childhood obesity are pervasive and can have severe implications for emotional and physical health and performance that can persist later in life ( 13 ).
In adolescents, psychological outcomes associated with obesity are multifactorial and have a bidirectional relationship ( Figure 4 ). Obese adolescents due to their physique may have a higher likelihood of psychosocial health issues, including depression, body image/dissatisfaction, lower self-esteem, peer victimization/bullying, and interpersonal relationship difficulties. They may also demonstrate reduced resilience to challenging situations compared to their non-obese/overweight counterparts ( 9 , 143 – 146 ). Body image dissatisfaction has been associated with further weight gain but can also be related to the development of a mental health disorder or an eating disorder (ED) or disorder eating habits (DEH). Mental health disorders such as depression are associated with poor eating habits, a sedentary lifestyle, and altered sleep patterns. ED or DEH that include anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), binge-eating disorder (BED) or night eating syndrome (NES) may be related to an individual's overvaluation of their body shape and weight or can result during the treatment for obesity ( 147 – 150 ). The management of obesity can place a patient at risk of AN if there is a rigid focus on caloric intake or if a patient overcorrects and initiates obsessive self-directed dieting. Healthcare providers who primarily care for obese patients, usually give the advice to diet to lose weight and then maintain it. However, strict dieting (hypocaloric diet), which some patients may later engage in can lead to an eating disorder such as anorexia nervosa ( 151 ). This behavior leads to a poor relationship with food, and therefore, adolescents perseverate on their weight and numbers ( 152 ).
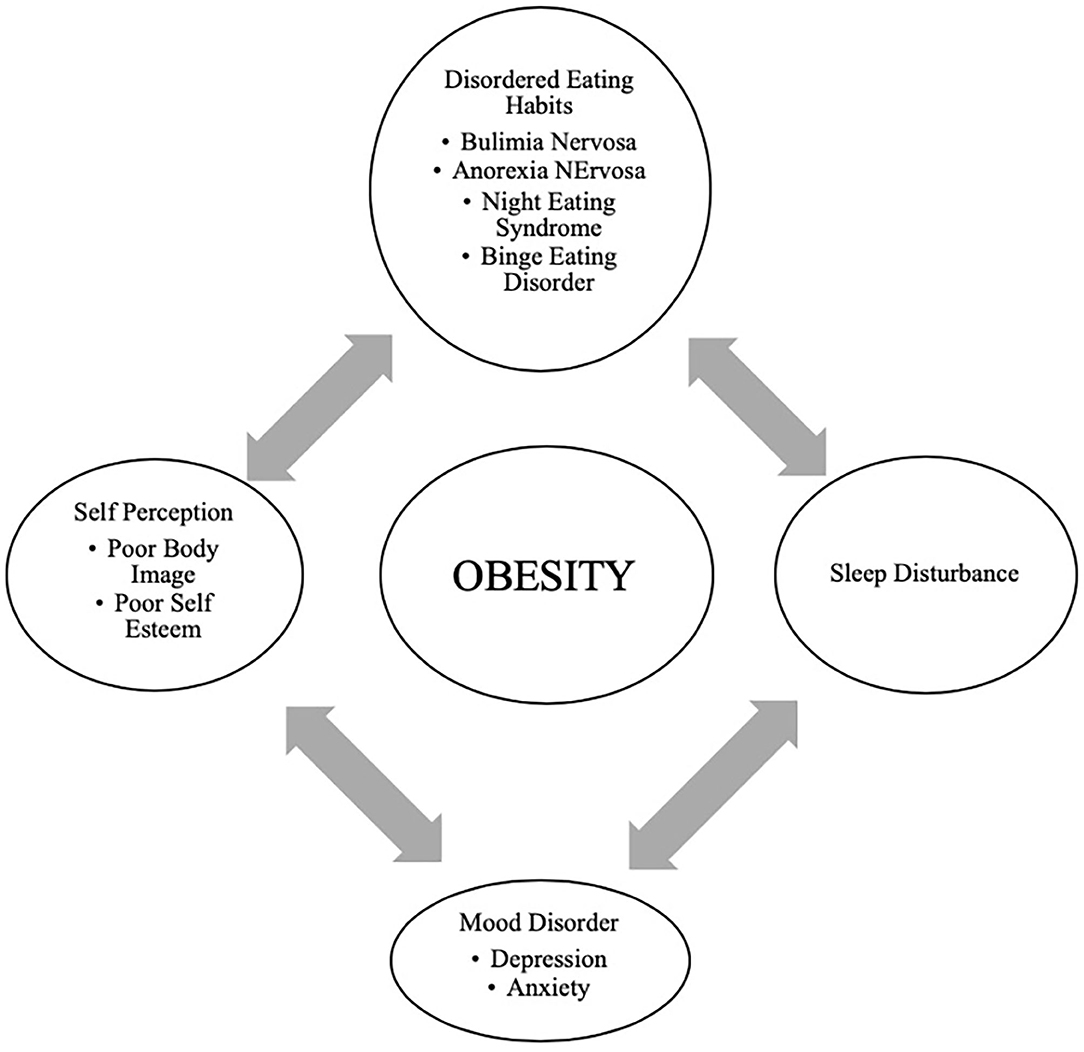
Figure 4 . Bidirectional relationship of different psychological outcomes of obesity.
Providers may not recognize DEHs when a morbidly obese patient loses the same weight as a healthy weight individual ( 149 ). It may appear as a positive result with families and others praising the individual without realizing that this youth may be engaging in destructive behaviors related to weight control. Therefore, it is essential to screen regarding the process of how weight loss was achieved ( 144 , 150 ).
Support and attention to underlying psychological concerns can positively affect treatment, overall well-being, and reduce the risk of adult obesity ( 150 ). The diagram above represents the complexity of the different psychological issues which can impact the clinical care of the obese adolescent.
Eating family meals together can improve overall dietary intake due to enhanced food choices mirrored by parents. It has also may serve as a support to individuals with DEHs if there is less attention to weight and a greater focus on appropriate, sustainable eating habits ( 148 ).
Prevention and Anticipatory Guidance
It is essential to recognize and provide preventive measures for obesity during early childhood and adolescence ( 100 , 153 , 154 ). It is well-established that early AR is a risk factor for adult obesity ( 66 – 68 ). Therefore, health care providers caring for the pediatric population need to focus on measures such as BMI but provide anticipatory guidance regarding nutritional counseling without stigmatizing or judging parents for their children's overweight/obesity ( 155 ). Although health care providers continue to pursue effective strategies to address the obesity epidemic; ironically, they frequently exhibit weight bias and stigmatizing behaviors. Research has demonstrated that the language that health care providers use when discussing a patient's body weight can reinforce stigma, reduce motivation for weight loss, and potentially cause avoidance of routine preventive care ( 155 ). In adolescents, rather than motivating positive changes, stigmatizing language regarding weight may negatively impact a teen and result in binge eating, decreased physical activity, social isolation, avoidance of health care services, and increased weight gain ( 156 , 157 ). Effective provider-patient communication using motivational interviewing techniques are useful to encourage positive behavior changes ( 155 , 158 ).
Anticipatory guidance includes educating the families on healthy eating habits and identifying unhealthy eating practices, encouraging increased activity, limiting sedentary activities such as screen time. Lifestyle behaviors in children and adolescents are influenced by many sectors of our society, including the family ( Figure 1 ) ( 3 , 24 ). Therefore, rather than treating obesity in isolation as an individual problem, it is crucial to approach this problem by focusing on the family unit. Family-based multi-component weight loss behavioral treatment is the gold standard for treating childhood obesity, and it is having been found useful in those between 2 and 6 years old ( 150 , 159 ). Additionally, empowering the parents to play an equal role in developing and implementing an intervention for weight management has shown promising results in improving the rate of obesity by decreasing screen time, promoting healthy eating, and increasing support for children's physical activity ( 160 , 161 ).
When dietary/lifestyle modifications have failed, the next option is a structured weight -management program with a multidisciplinary approach ( 15 ). The best outcomes are associated with an interdisciplinary team comprising a physician, dietician, and psychologist generally 1–2 times a week ( 15 , 162 ). However, this treatment approach is not effective in patients with severe obesity ( 122 ). Although healthier lifestyle recommendations for weight loss are the current cornerstone for obesity management, they often fail. As clinicians can attest, these behavioral and dietary changes are hard to achieve, and all too often is not effective in patients with severe obesity. Failure to maintain substantial weight loss over the long term is due to poor adherence to the prescribed lifestyle changes as well as physiological responses that resist weight loss ( 163 ). American TV hosts a reality show called “The Biggest Loser” that centers on overweight and obese contestants attempting to lose weight for a cash prize. Contestants from “The Biggest Loser” competition, had metabolic adaptation (MA) after drastic weight loss, regained more than they lost weight after 6 years due to a significant slow resting metabolic rate ( 164 ). MA is a physiological response which is a reduced basal metabolic rate seen in individuals who are losing or have lost weight. In MA, the body alters how efficient it is at turning the food eaten into energy; it is a natural defense mechanism against starvation and is a response to caloric restriction. Plasma leptin levels decrease substantially during caloric restriction, suggesting a role of this hormone in the drop of energy expenditure ( 165 ).
Pharmacological Management
The role of pharmacological therapy in the treatment of obesity in children and adolescents is limited.
Orlistat is the only FDA approved medication for weight loss in 12-18-year-olds but has unpleasant side effects ( 166 ). Another medicine, Metformin, has been used in children with signs of insulin resistance, may have some impact on weight, but is not FDA approved ( 167 ). The combination of phentermine/topiramate (Qsymia) has been FDA approved for weight loss in obese individuals 18 years and older. In studies, there has been about 9–10% weight loss over 2 years. However, caution must be taken in females as it can lead to congenital disabilities, especially with use in the first trimester of pregnancy ( 167 ).
GLP-1 agonists have demonstrated great success in effective weight loss and are approved by the FDA for adult obesity ( 168 – 170 ). A randomized control clinical trial recently published showed a significant weight loss in those using liraglutide (3.0 mg)/day plus lifestyle therapy group compared to placebo plus lifestyle therapy in children between the ages of 12–18 years ( 171 ).
Recently during the EASL conference, academic researchers and industry partners presented novel interventions targeting different gut- liver axis levels that include intestinal content, intestinal microbiome, intestinal mucosa, and peritoneal cavity ( 47 ). The focus for these therapeutic interventions within the gut-liver axis was broad and ranged anywhere from newer drugs protecting the intestinal mucus lining, restoring the intestinal barriers and improvement in the gut microbiome. One of the treatment options was Hydrogel technology which was shown to be effective toward weight loss in patients with metabolic syndrome. Hydrogel technology include fibers and high viscosity polysaccharides that absorb water in the stomach and increasing the volume, thereby improving satiety ( 47 ). Also, a clinical trial done in obese pregnant mothers using Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) showed that the mothers' who got DHA had children with lower adiposity at 2 and 4 years of age ( 172 ). Recently the role of probiotics in combating obesity has emerged. Probiotics are shown to alter the gut microbiome that improves intestinal digestive and absorptive functions of the nutrients. Intervention including probiotics may be a possible solution to manage pediatric obesity ( 173 , 174 ). Additionally, the role of Vitamin E for treating the comorbidities of obesity such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, NASH, and cardiovascular risk, has been recently described ( 175 , 176 ). Vitamin E is a lipid- soluble compound and contains both tocopherols and tocotrienols. Tocopherols have lipid-soluble antioxidants properties that interact with cellular lipids and protects them from oxidation damage ( 177 ). In metabolic disease, certain crucial pathways are influenced by Vitamin E and some studies have summarized the role of Vitamin E regarding the treatment of obesity, metabolic, and cardiovascular disease ( 178 ). Hence, adequate supplementation of Vitamin E as an appropriate strategy to help in the treatment of the prevention of obesity and its associated comorbidities has been suggested. Nonetheless, some clinical trials have shown contradictory results with Vitamin E supplementation ( 177 ). Although Vitamin E has been recognized as an antioxidant that protects from oxidative damage, however, a full understanding of its mechanism of action is still lacking.
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery has gained popularity since the early 2000s in the management of severe obesity. If performed earlier, there are better outcomes for reducing weight and resolving obesity-related comorbidities in adults ( 179 – 182 ). Currently, the indication for bariatric in adolescents; those who have a BMI >35 with at least one severe comorbidity (Type 2 Diabetes, severe OSA, pseudotumor cerebri or severe steatohepatitis); or BMI of 40 or more with other comorbidities (hypertension, hyperlipidemia, mild OSA, insulin resistance or glucose intolerance or impaired quality of life due to weight). Before considering bariatric surgery, these patients must have completed most of their linear growth and participated in a structured weight-loss program for 6 months ( 159 , 181 , 183 ). The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (AMBS) outlines the multidisciplinary approach that must be taken before a patient undergoing bariatric surgery. In addition to a qualified bariatric surgeon, the patient must have a pediatrician or provider specialized in adolescent medicine, endocrinology, gastroenterology and nutrition, registered dietician, mental health provider, and exercise specialist ( 181 ). A mental health provider is essential as those with depression due to obesity or vice versa may have persistent mental health needs even after weight loss surgery ( 184 ).
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB), laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG), and Gastric Banding are the options available. RYGB and LSG currently approved for children under 18 years of age ( 166 , 181 , 185 ). At present, gastric banding is not an FDA recommended procedure in the US for those under 18y/o. One study showed some improvements in BMI and severity of comorbidities but had multiple repeat surgeries and did not believe a suitable option for obese adolescents ( 186 ).
Compared to LSG, RYGB has better outcomes for excess weight loss and resolution of obesity-related comorbidities as shown in studies and clinical trials ( 183 , 184 , 187 ). Overall, LSG is a safer choice and may be advocated for more often ( 179 – 181 ). The effect on the Gut-Brain axis after Bariatric surgery is still inconclusive, especially in adolescents, as the number of procedures performed is lower than in adults. Those who underwent RYGB had increased fasting and post-prandial PYY and GLP-1, which could have contributed to the rapid weight loss ( 185 ); this effect was seen less often in patients with gastric banding ( 185 ). Another study in adult patients showed higher bile acid (BA) subtype levels and suggested a possible BA's role in the surgical weight loss response after LSG ( 188 ). Adolescents have lower surgical complication rates than their adult counterparts, hence considering bariatric surgery earlier rather than waiting until adulthood has been entertained ( 180 ). Complications after surgery include nutritional imbalance in iron, calcium, Vitamin D, and B12 and should be monitored closely ( 180 , 181 , 185 ). Although 5-year data for gastric bypass in very obese teens is promising, lifetime outcome is still unknown, and the psychosocial factors associated with adolescent adherence post-surgery are also challenging and uncertain.
Obesity in childhood and adolescence is not amenable to a single easily modified factor. Biological, cultural, and environmental factors such as readily available high-density food choices impact youth eating behaviors. Media devices and associated screen time make physical activity a less optimal choice for children and adolescents. This review serves as a reminder that the time for action is now. The need for interventions to change the obesogenic environment by instituting policies around the food industry and in the schools needs to be clarified. In clinical trials GLP-1 agonists are shown to be effective in weight loss in children but are not yet FDA approved. Discovery of therapies to modify the gut microbiota as treatment for overweigh/obesity through use of probiotics or fecal transplantation would be revolutionary. For the present, ongoing clinical research efforts in concert with pharmacotherapeutic and multidisciplinary lifestyle programs hold promise.
Author Contributions
AK, SL, and MJ contributed to the conception and design of the study. All authors contributed to the manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
1. Gurnani M, Birken C, Hamilton. J. Childhood obesity: causes, consequences, and management. Pediatr Clin North Am. (2015) 62:821–40. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2015.04.001
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Sahoo K, Sahoo B, Choudhury AK, Sofi NY, Kumar R, Bhadoria. AS. Childhood obesity: causes and consequences. J Family Med Prim Care. (2015) 4:187–92. doi: 10.4103/2249-4863.154628
3. Brown CL, Halvorson EE, Cohen GM, Lazorick S, Skelton JA. Addressing childhood obesity: opportunities for prevention. Pediatr Clin North Am. (2015) 62:1241–61. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2015.05.013
4. Qasim A, Turcotte M, de Souza RJ, Samaan MC, Champredon D, Dushoff J, et al. On the origin of obesity: identifying the biological, environmental, and cultural drivers of genetic risk among human populations. Obes Rev. (2018) 19:121–49. doi: 10.1111/obr.12625
5. Rinninella E, Raoul P, Cintoni M, Fransceschi F, Miggiano GAD, Gasbarrini A, et al. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? a changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms. (2019) 7:14. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7010014
6. Indrio F, Martini S, Francavilla R, Corvaglia L, Cristofori F, Mastrolia SA, et al. Epigenetic matters: the link between early nutrition, microbiome, and long-term health development. Front Pediatr. (2017) 5:178. doi: 10.3389/fped.2017.00178
7. Marcovecchio ML, Gorman S, Watson LPE, Dunger DB, Beardsall K. Catch-up growth in children born small for gestational age related to body composition and metabolic risk at six years of age in the UK. Horm Res Paediatr. (2020) 93:119–27. doi: 10.1159/000508974
8. Koletzko B, Fishbein M, Lee WS, Moreno L, Mouane N, Mouzaki M, et al. Prevention of childhood obesity: a position paper of the global federation of international societies of paediatric gastroenterology, hepatology nutrition (FISPGHAN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2020) 70:702–10. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002708
9. Pulgarón ER. Childhood obesity: a review of increased risk for physical and psychological comorbidities. Clin Ther. (2013) 35:A18–32. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.12.014
10. De Leonibus C, Marcovecchio ML, Chiarelli F. Update on statural growth and pubertal development in obese children. Pediatr Rep. (2012) 4:e35. doi: 10.4081/pr.2012.e35
11. Witchel SF, Burghard AC, Tao RH, Oberfield SE. The diagnosis and treatment of PCOS in adolescents. Curr Opin Pediatr . (2019) 31:562–9. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000778
12. Marcus CL, Brooks LJ, Draper KA, Gozal D, Halbower AC, Jones J, et al. Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics . (2012) 130:e714–55. doi: 10.1542/peds.2012-1672
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
13. Rankin J, Matthews L, Cobley S, Han A, Sanders R, Wiltshire HD, et al. Psychological consequences of childhood obesity: psychiatric comorbidity and prevention. Adolesc Health Med Ther . (2016) 7:125–46. doi: 10.2147/AHMT.S101631
14. Topçu S, Orhon FS, Tayfun M, Uçaktürk SA, Demirel F. Anxiety, depression, and self-esteem levels in obese children: a case-control study. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metabol. (2016) 29:357–61. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2015-0254
15. Katzmarzyk PT, Barlow S, Bouchard C, Catalano PM, Hsia DS, Inge TH, et al. An evolving scientific basis for the prevention and treatment of pediatric obesity. Int J Obes. (2014) 38:887–905. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2014.49
16. Brown T, Moore TH, Hooper L, Gao Y, Zayegh A, Ijaz S, et al. Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev . (2019) 7:CD001871. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001871.pub4
17. Smith E, Scarborough P, Rayner M, Briggs ADM. Should we tax unhealthy food and drink? Proc Nutr Soc. (2019) 77:314–20. doi: 10.1017/S0029665117004165
18. Adab P, Pallan M, Whincup PH. Is BMI the best measure of obesity? BMJ. (2018) 360:k 1274. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k1274
19. Anderson LN, Carsley S, Lebovic G, Borkhoff CM, Maguire JL, Parkin PC, et al. Misclassification of child body mass index from cut-points defined by rounded percentiles instead of Z-scores. BMC Res Notes. (2017) 10:639. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2983-0
20. Must A, Anderson SE. Body mass index in children and adolescents: consideration for population-based applications. Int J Obes. (2006) 30:590–4. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803300
21. Flegal KM, Wei R, Ogden C. Weight-for-stature compared with body mass index-for-age growth charts for the United States from the centers for disease control and prevention. Am J Clin Nutr. (2002) 75:761–6.22. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/75.4.761
22. Himes JH, Dietz WH. Guidelines for overweight in adolescent preventive services: recommendations from an expert committee. The expert committee on clinical guidelines for overweight in adolescent preventive services. Am J Clin Nutr. (1994) 59:307–16. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/59.2.307
23. Lazarus R, Baur L, Webb K, Blyth F. Body mass index in screening for adiposity in children and adolescents: systematic evaluation using receiver operating characteristic curves. Am J Clin Nutr. (1996) 63:500–6. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/63.4.500
24. McGinnis JM, Gootman JA. Food Marketing to Children and Youth: Threat or Opportunity? Institute of Medicine of the National Academies. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. (2006).
Google Scholar
25. Chaudhri OB, Salem V, Murphy KG, Bloom SR. Gastrointestinal satiety signals. Annu Rev Physiol. (2008) 70:239–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.70.113006.100506
26. Scaglioni S, De Cosmi V, Ciappolino V, Parazzini F, Brambilla P, Agostoni C. Factors influencing children's eating behaviours. Nutrients. (2018) 10:706. doi: 10.3390/nu10060706
27. Ahima RS, Antwi DA. Brain regulation of appetite and satiety. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. (2008) 37:811–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2008.08.005
28. Niswender KD, Baskin DG, Schwartz MW. Review insulin and its evolving partnership with leptin in the hypothalamic control of energy homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2004) 15:362–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2004.07.009
29. Niswender KD, Schwartz MW. Review insulin and leptin revisited: adiposity signals with overlapping physiological and intracellular signaling capabilities. Front Neuroendocrinol. (2003) 24:1–10. doi: 10.1016/S0091-3022(02)00105-X
30. Amitani M, Asakawa A, Amitani H, Inui. A. The role of leptin in the control of insulin-glucose axis. Front Neurosci. (2013) 7:51. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00051
31. Cowley MA, Smith RG, Diano S, Tschöp M, Pronchuk N, Grove KL, et al. The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron. (2003) 37:649–61. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00063-1
32. Buhmann H, le Roux CW, Bueter M. The gut–brain axis in obesity. Best Prac Res Clin Gastroenterol. (2014) 28:559–71. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2014.07.003
33. Cone RD. Review anatomy and regulation of the central melanocortin system. Nat Neurosci. (2005) 8:571–8. doi: 10.1038/nn1455
34. Timper K, Brüning JC. Hypothalamic circuits regulating appetite and energy homeostasis: pathways to obesity. Dis Model Mech. (2017) 10:679–89. doi: 10.1242/dmm.026609
35. Labarthe A, Fiquet O, Hassouna R, Zizzari P, Lanfumey L, Ramoz N, et al. Ghrelin-derived peptides: a link between appetite/reward, gh axis, and psychiatric disorders? Front Endocrinol. (2014) 5:163. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00163
36. Hills R. D Jr, Pontefract BA, Mishcon HR, Black CA, Sutton SC, Theberge CR. Gut microbiome: profound implications for diet and disease. Nutrients. (2019) 11:1613. doi: 10.3390/nu11071613
37. Torres-Fuentes C, Schellekens H, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. The microbiota-gut-brain axis in obesity. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 2:747–56. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30147-4
38. Gérard P. Gut microbiota and obesity. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2016) 73:147–62. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2061-5
39. Derrien M, Alvarez AS, de Vos WM. The gut microbiota in the first decade of life. Trends Microbiol. (2019) 27:997–1010.40. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2019.08.001
40. Dao MC, Clément K. Gut microbiota and obesity: concepts relevant to clinical care. Eur J Intern Med . (2018) 48:18–24.41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2017.10.005
41. Kim KN, Yao Y., Ju SY. Short chain fatty acids and fecal microbiota abundance in humans with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2512. doi: 10.3390/nu11102512
42. Castaner O, Goday A, Park YM, Lee SH, Magkos F, Shiow STE, et al. The gut microbiome profile in obesity: a systematic review. Int J Endocrinol. (2018) 2018:4095789. doi: 10.1155/2018/4095789
43. Riva A, Borgo F, Lassandro C, Verduci E, Morace G, Borghi E, et al. Pediatric obesity is associated with an altered gut microbiota and discordant shifts in firmicutes populations. Enviroin Microbiol. (2017) 19:95–105. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13463
44. Fernandes J, Su W, Rahat-Rozenbloom S, Wolever TMS, Comelli EM. Adiposity, gut microbiota and faecal short chain fatty acids are linked in adult humans. Nutr Diabetes . (2014) 4:e121. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2014.23
45. Rahat-Rozenbloom S, Fernandes J, Gloor GB, Wolever TMS. Evidence for greater production of colonic short-chain fatty acids in overweight than lean humans. Int J Obes . (2014) 38:1525–31. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2014.46
46. Barczyńska R, Litwin M, Slizewska K, Szalecki M, Berdowska A, Bandurska K, et al. Bacterial microbiota fatty acids in the faeces of overweight obese children. Pol. J. Microbiol. (2018) 67:339–45. doi: 10.21307/pjm-2018-041
47. Albillos A, de Gottardi A, Rescigno M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J Hepatol. (2020) 72:558–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.003
48. Yu EL, Golshan S, Harlow KE, Angeles JE, Durelle J, Goyal NP, et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children with obesity. J Pediatr. (2019) 207:64–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.11.021
49. Ranucci G, Spagnuolo MI, Iorio R. Obese children with fatty liver: Between reality and disease mongering. World J Gastroenterol. (2017) 23:8277–82. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8277
50. Cox AJ, West NP, Cripps A. W. Obesity, inflammation, and the gut microbiota. Lancet Diabet Endocrinol. (2015) 3:207–15. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70134-2
51. Seitz J, Trinh S, Herpertz-Dahlmann B. The microbiome and eating disorders. Psychiatr Clin North Am. . (2019) 42:93–103. doi: 10.1016/j.psc.2018.10.004
52. Deans E. Microbiome and mental health in the modern environment. J Physiol Anthropol. (2016) 36:1. doi: 10.1186/s40101-016-0101-y
53. Peirce JM, Alviña K. The role of inflammation and the gut microbiome in depression and anxiety. J Neurosci Res . (2019) 97:1223–41. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24476
54. Ranadive SA, Vaisse C. Lessons from extreme human obesity: monogenic disorders. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. (2008) 37:733–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2008.07.003
55. Soliman AT, Yasin M, Kassem A. Leptin in pediatrics: a hormone from adipocyte that wheels several functions in children. Indian J Endocrinol Metab . (2012) 16(Suppl. 3):S577–87. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.105575
56. Farooqi IS, Wangensteen T, Collins S, Kimber W, Matarese G, Keogh JM, et al. Clinical and molecular genetic spectrum of congenital deficiency of the leptin receptor. N Engl J Med. (2007) 356:237–47. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa063988
57. Mutch DM, Clément K. Unraveling the genetics of human obesity. PLoS Genet. (2006) 2:e188. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020188
58. Crocker MK, Yanovski JA. Pediatric obesity: etiology and treatment. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. (2009) 38:525–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2009.06.007
59. Huvenne H, Dubern B, Clément K, Poitou C. Rare genetic forms of obesity: clinical approach and current treatments in 2016. Obes Facts. (2016) 9:158–73. doi: 10.1159/000445061
60. Stefan M, Nicholls RD. What have rare genetic syndromes taught us about the pathophysiology of the common forms of obesity? Curr Diab Rep. (2004) 4:143–50. doi: 10.1007/s11892-004-0070-0
61. Hetherington MM, Cecil JE. Gene-Environment interactions in obesity. Forum Nutr. (2009) 63:195–203. doi: 10.1159/000264407
62. Reddon H, Guéant JL, Meyre D. The importance of gene-environment interactions in human obesity. Clin Sci. (2016) 130:1571–97. doi: 10.1042/CS20160221
63. Castillo JJ, Orlando RA, Garver WS. Gene-nutrient interactions and susceptibility to human obesity. Genes Nutr. (2017) 12:29. doi: 10.1186/s12263-017-0581-3
64. Heianza Y, Qi L. Gene-Diet interaction and precision nutrition in obesity. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:787. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040787
65. Goodarzi MO. Genetics of obesity: what genetic association studies have taught us about the biology of obesity and its complications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2018) 6:223–36. . doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30200-0
66. Bouchard L, Drapeau V, Provencher V, Lemieux S, Chagnon Y, Rice T, et al. Neuromedin beta: a strong candidate gene linking eating behaviors and susceptibility to obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. (2004) 80:1478–86. . doi: 10.1093/ajcn/80.6.1478
67. Grimm ER, Steinle NI. Genetics of eating behavior: established and emerging concepts. Nutr Rev. (2011) 69:52–60. . doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00361.x
68. van der Klaauw AA, Farooqi IS. The hunger genes: pathways to obesity. Cell. (2015) 161:119–32. . doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.008
69. Martinez JA. Bodyweight regulation causes of obesity. Proc Nutr Soc. (2000) 59:337–45. Review. doi: 10.1017/S0029665100000380
70. Rask-Andersen M, Karlsson T, Ek WE, Johansson Å. Gene-environment interaction study for BMI reveals interactions between genetic factors and physical activity, alcohol consumption and socioeconomic status. PLoS Genet. (2017) 5:1. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006977
71. Xulong S, Pengzhou L, Xiangwu Y, Weizheng L, Xianjie Q, Shaihong Z, et al. From genetics and epigenetics to the future of precision treatment for obesity. Gastroenterol Rep. (2017) 5:266–70. doi: 10.1093/gastro/gox033
72. Bianco-Miotto T, Craig JM, Gasser YP, van dijk SJ, Ozanne SE. Epigenetics and DOHaD: from basics to birth and beyond. J Dev Orig Health Dis. (2017) 8:513–9. doi: 10.1017/S2040174417000733
73. van Dijk SJ, Molloy PL, Varinli H, Morrison JL, Muhlhausler BS, Members of EpiSCOPE. Epigenetics and human obesity. Int J Obes . (2015) 39:85–97. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2014.34
74. Li Y. Epigenetic mechanisms link maternal diets and gut microbiome to obesity in the offspring. Front Genet . (2018) 9:342. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00342
75. Kaufman J, Montalvo-Ortiz JL, Holbrook H, O'Loughlin K, Orr C, Kearney C, et al. Adverse childhood experiences, epigenetic measures, and obesity in youth. J Pediatr. (2018) 202:150–6.76. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.06.051
76. May Gardner R, Feely A, Layte R, Williams J, McGavock J. Adverse childhood experiences are associated with an increased risk of obesity in early adolescence: a population-based prospective cohort study. Pediatr Res. (2019) 86:522–28. doi: 10.1038/s41390-019-0414-8
77. Cheon BK„ Hong YY. Mere experience of low subjective socioeconomic status stimulates appetite food intake. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA . (2017) 114:72–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1607330114
78. Alegría-Torres JA, Baccarelli A, Bollati V. Epigenetics lifestyle. Epigenomics . (2011) 3:267-77. doi: 10.2217/epi.11.22
79. Birch LL, Fisher JO. Development of eating behaviors among children and adolescents. Pediatrics . (2011) 101:539–49.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
80. Birch L, Savage JS, Ventura A. Influences on the development of children's eating behaviours: from infancy to adolescence. Can J Diet Pract Res. (2007) 68:s1–s56.
81. Nielsen SJ, Popkin BM. Patterns and trends in food portion sizes, 1977- 1998. JAMA. (2003) 289:450–53. . doi: 10.1001/jama.289.4.450
82. Munoz KA, Krebs-Smith SM, Ballard-Barbash R, Cleveland LE. Food intakes of US children and adolescents compared with recommendations. Pediatrics. (1997) 100:323–29. doi: 10.1542/peds.100.3.323
83. Fisher JO, Birch LL. Restricting access to palatable foods affects children's behavioral response, food selection, and intake. Am J Clin Nutr. (1999) 69:1264–72. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/69.6.1264
84. Faith MS, Scanlon KS, Birch LL, Francis LA, Sherry B. Parent-child feeding strategies and their relationships to child eating and weight status. Obes Res. (2004) 12:1711–22. . doi: 10.1038/oby.2004.212
85. Smith AD, Sanchez N, Reynolds C, Casamassima M, Verros M, Annameier SK, et al. Associations of parental feeding practices and food reward responsiveness with adolescent stress-eating. Appetite. (2020) 152:104715. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2020.104715
86. Lowe CJ, Morton JB, Reichelt AC. Adolescent obesity and dietary decision making-a brain-health perspective. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. (2020) 4:388–96. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(19)30404-3
87. Goran MI, Treuth MS. Energy expenditure, physical activity, and obesity in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. (2001) 48:931–53. doi: 10.1016/S0031-3955(05)70349-7
88. Romieu I, Dossus L, Barquera S, Blottière HM, Franks PW, Gunter M, et al. Energy balance and obesity: what are the main drivers? Cancer Causes Control. (2017) 28:247–58. doi: 10.1007/s10552-017-0869-z
89. Mattes R, Foster GD. Food environment and obesity. Obesity. (2014) 22:2459–61. doi: 10.1002/oby.20922
90. Ickovics JR, O'Connor Duffany K, Shebl FM, Peters SM, Read MS, Gilstad-Hayden KR, et al. Implementing school-based policies to prevent obesity: cluster randomized trial. Am J Prev Med. (2019) 56:e1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2018.08.026
91. Micha R, Karageorgou D, Bakogianni I, Trichia E, Whitsel LP, Story M, et al. Effectiveness of school food environment policies on children's dietary behaviors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. ( 2018 ) 13:e0194555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194555
92. Cawley J, Frisvold D, Hill A, Jones DJ. The impact of the philadelphia beverage tax on purchases and consumption by adults and children. Health Econ. (2019) 67:102225. doi: 10.1016/j.jhealeco.2019.102225
93. John Cawley J, Thow AM, Wen K, Frisvold D. The economics of taxes on sugar-sweetened beverages: a review of the effects on prices, sales, cross-border shopping, and consumption. Annu Rev Nutr. (2019) 39:317–38. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-082018-124603
94. Fuller C, Lehman E, Hicks S, Novick MB. Bedtime use of technology and associated sleep problems in children. Glob Pediatr Health. (2017) 4:2333794X17736972. doi: 10.1177/2333794X17736972
95. Chahal H, Fung C, Kuhle S, Veugelers PJ. Availability and night-time use of electronic entertainment and communication devices are associated with short sleep duration and obesity among Canadian children. Pediatr Obes. (2012) 8:42–51. doi: 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2012.00085.x
96. Minghua T. Protein intake during the first two years of life and its association with growth and risk of overweight. Int J Environ Res Public Health. ( 2018 ) 15:1742. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15081742
97. Azad MB, Vehling L, Chan D, Klopp A, Nickel NC, McGavock JM, et al. Infant feeding and weight gain: separating breast milk from breastfeeding and formula from food. Pediatrics. (2018) 142:e20181092. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-1092
98. Lin L, Amissah E, Gamble GD, Crowther CA, Harding JE. Impact of macronutrient supplements on later growth of children born preterm or small for gestational age: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised and quasirandomised controlled trials. PLoS Med. (2020) 17:e1003122. . doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003122
99. Rzehak P, Oddy WH, Mearin ML, Grote V, Mori TA, Szajewska H, et al. Infant feeding and growth trajectory patterns in childhood and body composition in young adulthood. Am J Clin Nutr. (2017) 106:568–80. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.116.140962
100. Styne DM, Arslanian SA, Connor EL, Farooqi IS, Murad MH, Silverstein JH. Pediatric obesity-assessment, treatment, and prevention: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2017) 102:709–57. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-2573
101. Whitaker RC, Pepe MS, Wright JA, Seidel KD, Dietz WH. Early adiposity rebound and the risk of adult obesity. Pediatrics . (1998) 101:E5. doi: 10.1542/peds.101.3.e5
102. Geserick M, Vogel M, Gausche R, Lipek T, Spielau U, Keller E, et al. Acceleration of BMI in early childhood and risk of sustained obesity. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:1303–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1803527
103. Jabakhanji SB, Boland F, Ward M, Biesma RJ. Body mass index changes in early childhood. Pediatrics. (2018) 202:106–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.06.049
104. Chung S. Growth and puberty in obese children and implications of body composition. J Obes Metab Syndr. (2017) 26:243–50. doi: 10.7570/jomes.2017.26.4.243
105. Tagi VM, Giannini C, Chiarelli F. Insulin resistance in children. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:342. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00342
106. Kelesidis I, Mantzoros CS. Leptin and its emerging role in children and adolescents. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol . (2006) 15:1–14. doi: 10.1297/cpe.15.1
107. Burt Solorzano CM, McCartney CR, Obesity and the pubertal transition in girls and boys. Reproduction . (2010) 140:399–410. doi: 10.1530/REP-10-0119
108. Li W, Liu Q, Deng X, Chen Y, Liu S, Story M. Association between obesity and puberty timing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2017) 14:1266. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14101266
109. Lee JM, Wasserman R, Kaciroti N, Gebremariam A, Steffes J, Dowshen S, et al. Timing of puberty in overweight vs. obese boys. Pediatrics. (2016) 137:e20150164. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-0164
110. He J, Kang Y, Zheng L. Serum levels of LH, IGF-1 and leptin in girls with idiopathic central precocious puberty (ICPP) and the correlations with the development of ICPP. Minerva Pediatr . (2018). doi: 10.23736/S0026-4946.18.05069-7
111. Kang MJ, Oh YJ, Shim YS, Baek JW, Yang S, Hwang IT. The usefulness of circulating levels of leptin, kisspeptin, and neurokinin B in obese girls with precocious puberty. Gynecol Endocrinol. (2018) 34:627–30. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2017.1423467
112. Rendo-Urteaga T, Ferreira de Moraes AC, Torres-Leal FL, Manios Y, Gottand F, Sjöström M, et al. Leptin and adiposity as mediators on the association between early puberty and several biomarkers in European adolescents: the helena study. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 31:1221–29. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2018-0120
113. Franks S. Adult polycystic ovary syndrome begins in childhood. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2002) 16:263–72. doi: 10.1053/beem.2002.0203
114. Franks S. Polycystic ovary syndrome in adolescents. Int J Obes. (2008) 32:1035–41. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.61
115. Jehan S, Zizi F, Pandi-Perumal SR, Wall S, Auguste E, Myers K, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and obesity: implications for public health. Sleep Med Disord. (2017) 1:00019.
116. Patinkin ZW, Feinn R, Santos M. Metabolic consequences of obstructive sleep apnea in adolescents with obesity: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Childhood Obes. (2017) 13:102–10. doi: 10.1089/chi.2016.0248
117. Kaditis A. From obstructive sleep apnea in childhood to cardiovascular disease in adulthood: what is the evidence? Sleep. (2010) 33:1279–80. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.10.1279
118. Marseglia L, Manti S, D'Angelo G, Nicotera A, Parisi E, Di Rose G, et al. Oxidative stress in obesity: a critical component in human diseases. Int J Mol Sci . (2014) 16:378–400. doi: 10.3390/ijms16010378
119. Eisele HJ, Markart P, Schulz R. Obstructive sleep apnea, oxidative stress, and cardiovascular disease: evidence from human studies. Oxid Med Cell Longev . (2015) 2015:608438. doi: 10.1155/2015/608438
120. Hui W, Slorach C, Guerra V, Parekh RS, Hamilton J, Messiha S, et al. Effect of obstructive sleep apnea on cardiovascular function in obese youth. Am J Cardiol. (2019) 123:341–7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.09.038
121. Matteoni CA, Younossi Z .m., Gramlich T, Boparai N, Liu YC, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology. (1999) 1999:116:1413. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(99)70506-8
122. Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the pediatric population. Clin Liver Dis. ( 2004 ) 8:549. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.04.010
123. Huang JS, Barlow SE, Quiros-Tejeira RE, Scheimann A, Skelton J, Suskind D, et al. Childhood obesity for pediatric gastroenterologists. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2013) 2013:56:99. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31826d3c62
124. Anderson EL, Howe LD, Jones HE, Higgins JPT, Lawlor DA, Fraser A. The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. ( 2015 ) 10:e0140908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140908
125. Nobili V, Alisi A, Newton KP, Schwimmer JB. Comparison of the phenotype and approach to pediatric vs adult patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. (2016) 150:1798–810. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.03.009
126. Rafiq N, Bai C, Fang Y, Srishord M, McCullough A, Gramlich T, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2009) 7:234–38. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2008.11.005
127. Feldstein AE, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Treeprasertsuk S, Benson JT, Enders FB, Angula P. The natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children: a follow-up study for up to 20 years. Gut. (2009) 58:1538. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.171280
128. Schwimmer JB, Pardee PE, Lavine JE, Blumkin AK, Cook S. Cardiovascular risk factors and the metabolic syndrome in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Circulation . (2008) 118:277. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.739920
129. Perry DC, Metcalfe D, Lane S, Turner S. Childhood obesity and slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Pediatrics. (2018) 142:e20181067. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-1067
130. Zavala-Crichton JP, Esteban-Cornejo I, Solis-Urra P, Mora-Gonzalez J, Cadenas-Sanchez C, Rodriguez-Ayllon M, et al. Association of sedentary behavior with brain structure and intelligence in children with overweight or obesity: Active Brains Project . (2020) 9:1101. doi: 10.3390/jcm9041101
131. Ronan L, Alexander-Bloch A, Fletcher PC. Childhood obesity, cortical structure, and executive function in healthy children. Cereb Cortex. (2019) 30:2519–28. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhz257
132. Baker ER. Body weight and the initiation of puberty. Clin Obstetr Gynecol. (1985) 28:573–9. doi: 10.1097/00003081-198528030-00013
133. Siervogel RM, Demerath EW, Schubert C, Remsberg KE, Chumlea WM, Sun S, et al. Puberty and body composition. Horm Res. (2003) 60:36–45. doi: 10.1159/000071224
134. Sadeeqa S, Mustafa T, Latif S. Polycystic ovarian syndrome- related depression in adolescent girls. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. (2018) 10:55–9. doi: 10.4103/JPBS.JPBS_1_18
135. Himelein MJ, Thatcher SS. Depression and body image among women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Health Psychol . (2006) 11:613–25. doi: 10.1177/1359105306065021
136. Magge SN, Goodman E, Armstrong SC. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: shifting the focus to cardiometabolic risk factor clustering. Pediatrics. (2017) 140:e20171603. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-1603
137. Mauras N, Delgiorno C, Kollman C, Bird K, Morgan M, Sweeten S, et al. Obesity without established comorbidities of the metabolic syndrome is associated with a proinflammatory and prothrombotic state, even before the onset of puberty in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 95:1060–8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-1887
138. Weiss R, Dziura J, Burgert TS, Tamborlane WV, Taksali SE, Yeckel CW, et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. (2004) 350:2362–74. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa031049
139. Erdmann J, Kallabis B, Oppel U, Sypchenko O, Wagenpfeil S, Schusdziarra V. Development of hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance during the early stage of weight gain. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metabol. (2008) 294:e568–75. . doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00560.2007
140. Pulido-Arjona L, Correa-Bautista JE, Agostinis-Sobrinho C, Mota J, Santos R, Correa-Rodrigues M, et al. Role of sleep duration and sleep- related problems in the metabolic syndrome among children and adolescents. Ital J Pediatr. (2018) 44:9. doi: 10.1186/s13052-018-0451-7
141. Harriger JA, Thompson JK. Psychological consequences of obesity: weight bias and body image in overweight and obese youth. Int Rev Psychiatry. (2012) 24:247–53. . doi: 10.3109/09540261.2012.678817
142. Bacchini D, Licenziati MR, Garrasi A, Corciulo N, Driul D, Tanas R, et al. Bullying and victimization in overweight and obese outpatient children and adolescents: an italian multicentric study. PLoS ONE. (2015) 10:e0142715. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142715
143. Loth KA, Watts AW, Berg PVD, Neumark-Sztainer D. Does body satisfaction help or harm overweight teens? A 10-year longitudinal study of the relationship between body satisfaction and body mass index. J Adolesc Health. (2015) 57:559–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2015.07.008
144. Gowey MA, Lim CS, Clifford LM, Janicke DM. Disordered eating and health-related quality of life in overweight and obese children. J Pediatr Psychol. (2014) 39:552–61. doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsu012
145. Mannan M, Mamun A, Doi S, Clavarino A. Prospective associations between depression and obesity for adolescent males and females- a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. PLoS ONE. (2016) 11:e0157240. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157240
146. Ruiz LD, Zuelch ML, Dimitratos SM, Scherr RE. Adolescent obesity: diet quality, psychosocial health, and cardiometabolic risk factors. Nutrients. (2019) 12:43. doi: 10.3390/nu12010043
147. Goldschmidt AB, Aspen VP, Sinton MM, Tanofsky-Kraff M, Wilfley DE. Disordered eating attitudes and behaviors in overweight youth. Obesity. (2008) 16:257–64. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.48
148. Golden NH, Schneider M, Wood C. Preventing obesity and eating disorders in adolescents. Pediatrics. (2016) 138:e1–e12. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-1649
149. Rastogi R, Rome ES. Restrictive eating disorders in previously overweight adolescents and young adults. Cleve Clin J Med. (2020) 87:165–71. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.19034
150. Hayes JF, Fitzsimmons-Craft EE, Karam AM, Jakubiak JL, Brown ME, Wilfley D. Disordered eating attitudes and behaviors in youth with overweight and obesity: implications for treatment. Curr Obes Rep. (2018) 7:235. doi: 10.1007/s13679-018-0316-9
151. Goldschmidt AB, Wall MM, Loth KA, Neumark-Sztainer D. Risk factors for disordered eating in overweight adolescents and young adults: Table I. J Pediatr Psychol. (2015) 40:1048–55. doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsv053
152. Follansbee-Junger K, Janicke DM, Sallinen BJ. The influence of a behavioral weight management program on disordered eating attitudes and behaviors in children with overweight. J Am Diet Assoc. (2010) 110:653–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2010.08.005
153. Blake-Lamb TL, Locks LM, Perkins ME, Woo Baidal JA, Cheng ER, Taveras EM. Interventions for childhood obesity in the first 1,000 days a systematic review. Am J Prev Med. (2016) 50:780–9. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2015.11.010
154. McGuire S. Institute of Medicine (IOM). Early childhood obesity prevention policies. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. Adv Nutr . (2011) 3:56–7. doi: 10.3945/an.111.001347
155. Pont SJ, Puhl R, Cook SR, Slusser W. Stigma experienced by children and adolescents with obesity. Pediatrics. (2017) 140:e20173034. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-3034
156. Puhl R, Suh Y. Health consequences of weight stigma: implications for obesity prevention and treatment. Curr Obes Rep. (2015) 4:182–90. doi: 10.1007/s13679-015-0153-z
157. Schwimmer JB, Burwinkle TM, Varni JW. Health-related quality of life of severely obese children and adolescents. JAMA. (2003) 289:1813–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.14.1813
158. Carcone AI, Jacques-Tiura AJ, Brogan Hartlieb KE, Albrecht T, Martin T. Effective patient-provider communication in pediatric obesity. Pediatr Clin North Am. (2016) 63:525–38. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2016.02.002
159. Coppock JH, Ridolfi DR, Hayes JF, Paul MS, Wilfley DE. Current approaches to the management of pediatric overweight and obesity. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. (2014) 16:343. doi: 10.1007/s11936-014-0343-0
160. Davison KK, Jurkowski JM, Li K, Kranz S, Lawson HA. A childhood obesity intervention developed by families for families: results from a pilot study. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. (2013) 10:3. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-10-3
161. Krystia O, Ambrose T, Darlington G, Ma DWL, Buchholz AC, Haines J. A randomized home- based childhood obesity prevention pilot intervention has favourable effects on parental body composition: preliminary evidence from the guelph family health study. BMC Obes. (2019) 6:10. doi: 10.1186/s40608-019-0231-y
162. Skjåkødegård HF, Danielsen YS, Morken M, Linde SRF, Kolko RP, Balantekin KN, et al. Study protocol: a randomized controlled trial evaluating the effect of family-based behavioral treatment of childhood and adolescent obesity–The FABO-study. BMC Public Health. (2016) 16:1106. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3755-9
163. Hall KD, Kahan S. Maintenance of lost weight and long-term management of obesity. Med Clin North Am. (2018) 102:183–97. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2017.08.012
164. Hall KD. Diet vs. exercise in “the biggest loser” weight loss competition. Obesity. (2013) 21:957–9. doi: 10.1002/oby.20065
165. Lecoultre V, Ravussin E, Redman LM. The fall in leptin concentration is a major determinant of the metabolic adaptation induced by caloric restriction independently of the changes in leptin circadian rhythms. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. (2011) 96:E1512–E516. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-1286
166. Kaur KK, Allahbadia G, Singh M. Childhood obesity: a comprehensive review of epidemiology, aetiopathogenesis and management of this global threat of the 21st century. Acta Sci Paediatr. (2019) 2:56–66. doi: 10.31080/ASPE.2019.02.0132
167. Crimmins NA, Xanthakos SA. Obesity. in Neinstein's Adolescent and Young Adult Health , Guide. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer (2016). p. 295–300.
168. Astrup A, Rossner S, Van Gaal L, Rissanen A, Niskanen L, Al Hakim M, et al. Effects of liraglutide in the treatment of obesity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet. (2009) 374:1606–16. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61375-1
169. Monami M, Dicembrini I, Marchionni N, Rotella CM, Mannucci E. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on body weight: a meta-analysis. Exp Diabetes Res. (2012) 2012:672658. doi: 10.1155/2012/672658
170. Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, Greenway F, Halpern A, Krempf, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:11–22 . doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411892
171. Kelly AS, Auerbach P, Barrientos-Perez M, Gies I, Hale PM, Marcus C, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of liraglutide for adolescents with obesity. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:2117–28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916038
172. Foster BA, Escaname E, Powell T, Larsen B, Siddiqui SK, Menchaca J, et al. Randomized controlled trial of DHA supplementation during pregnancy: child adiposity outcomes. Nutrients . (2017) 9:566. doi: 10.3390/nu9060566
173. Abenavoli L, Scarpellini E, Colica C, Boccuto L, Salehi B, Sharifi-Rad J, et al. Gut microbiota and obesity: a role for probiotics. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2690. doi: 10.3390/nu11112690
174. Vajro P, Mandato C, Veropalumbo C, De Micco I. Probiotics: a possible role in treatment of adult and pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann Hepatol. (2013) 12:161–63. doi: 10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31401-2
175. Zhao L, Fang X, Marshall M, Chung S. Regulation of obesity and metabolic complications by gamma and delta tocotrienols. Molecules. (2016) 21:344. doi: 10.3390/molecules21030344
176. Wong SK, Chin K-Y, Suhaimi FH, Ahmad F, Ima-Nirwana S. Vitamin E as a potential interventional treatment for metabolic syndrome: evidence from animal and human studies. Front Pharmacol. (2017) 8:444. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00444
177. Galli F, Azzi A, Birringer A, Cook-Mills JM, Eggersdorfer M, Frank J, et al. Vitamin E: Emerging aspects and new directions. Free Radic Biol Med. (2017) 102:16–36. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.09.017
178. Galmés S, Serra F, Palou A. Vitamin E metabolic effects and genetic variants: a challenge for precision nutrition in obesity and associated disturbances. Nutrients . (2018) 10:1919. doi: 10.3390/nu10121919
179. Ahn SM. Current issues in bariatric surgery for adolescents with severe obesity: durability, complications, and timing of intervention. J. Obes Metabol Syndrome. (2020) 29:4–11. doi: 10.7570/jomes19073
180. Lamoshi A, Chernoguz A, Harmon CM, Helmrath M. Complications of bariatric surgery in adolescents. Semin Pediatr Surg. (2020) 29:150888. doi: 10.1016/j.sempedsurg.2020.150888
181. Weiss AL, Mooney A, Gonzalvo JP. Bariatric surgery. Adv Pediatr. (2017) 6:269–83. doi: 10.1016/j.yapd.2017.03.005
182. Stanford FC, Mushannen T, Cortez P, Reyes KJC, Lee H, Gee DW, et al. Comparison of short and long-term outcomes of metabolic and bariatric surgery in adolescents and adults. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:157. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00157
183. Inge TH, Zeller MH, Jenkins TM, Helmrath M, Brandt ML, Michalsky MP, et al. Perioperative outcomes of adolescents undergoing bariatric surgery: the teen-longitudinal assessment of bariatric surgery (Teen-LABS) study . JAMA Pediatr . (2014) 168:47–53. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2013.4296
184. Järvholm K, Bruze G, Peltonen M, Marcus C, Flodmark CE, Henfridsson P, et al. 5-year mental health and eating pattern outcomes following bariatric surgery in adolescents: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Child AdolescHealth . (2020) 4:210–9. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30024-9
185. Xanthakos SA. Bariatric surgery for extreme adolescent obesity: indications, outcomes, and physiologic effects on the gut–brain axis. Pathophysiology. (2008) 15:135–46. doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2008.04.005
186. Zitsman JL, Digiorgi MF, Kopchinski JS, Sysko R, Lynch L, Devlin M, et al. Adolescent Gastric Banding: a five-year longitudinal study in 137 individuals. Surg Obes Relat Dis. (2018) 14. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2018.09.030
187. Inge TH, Jenkins TM, Xanthakos SA, Dixon JB, Daniels SR, Zeller MH, et al. Long-term outcomes of bariatric surgery in adolescents with severe obesity (FABS-5+). A prospective follow-up analysis. Lancet Diabet Endocrinol . (2017) 5:165–73. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)30315-1
188. Kindel TL, Krause C, Helm MC, Mcbride CL, Oleynikov D, Thakare R, et al. Increased glycine-amidated hyocholic acid correlates to improved early weight loss after sleeve gastrectomy. Surg Endosc. (2017) 32:805–12. doi: 10.1007/s00464-017-5747-y
Keywords: obesity, childhood, review (article), behavior, adolescent
Citation: Kansra AR, Lakkunarajah S and Jay MS (2021) Childhood and Adolescent Obesity: A Review. Front. Pediatr. 8:581461. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.581461
Received: 08 July 2020; Accepted: 23 November 2020; Published: 12 January 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Kansra, Lakkunarajah and Jay. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Alvina R. Kansra, akansra@mcw.edu
This article is part of the Research Topic
Pediatric Obesity: From the Spectrum of Clinical-Physiology, Social-Psychology, and Translational Research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 07 May 2024
Epidemiology and Population Health
Obesity: a 100 year perspective
- George A. Bray ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9945-8772 1
International Journal of Obesity ( 2024 ) Cite this article
425 Accesses
23 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Biological techniques
- Health care
- Weight management
This review has examined the scientific basis for our current understanding of obesity that has developed over the past 100 plus years. Obesity was defined as an excess of body fat. Methods of establishing population and individual changes in levels of excess fat are discussed. Fat cells are important storage site for excess nutrients and their size and number affect the response to insulin and other hormones. Obesity as a reflection of a positive fat balance is influenced by a number of genetic and environmental factors and phenotypes of obesity can be developed from several perspectives, some of which have been elaborated here. Food intake is essential for maintenance of human health and for the storage of fat, both in normal amounts and in obesity in excess amounts. Treatment approaches have taken several forms. There have been numerous diets, behavioral approaches, along with the development of medications.. Bariatric/metabolic surgery provides the standard for successful weight loss and has been shown to have important effects on future health. Because so many people are classified with obesity, the problem has taken on important public health dimensions. In addition to the scientific background, obesity through publications and organizations has developed its own identity. While studying the problem of obesity this reviewer developed several aphorisms about the problem that are elaborated in the final section of this paper.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
251,40 € per year
only 20,95 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Obesity and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases
Obesity-induced and weight-loss-induced physiological factors affecting weight regain
Normal weight obesity and unaddressed cardiometabolic health risk—a narrative review
Quetelet, Adolphe Sur l’homme et le developpement de ses facultes, ou essai de physique sociale ; Paris: Bachelier, 1835 (Transl of L-A-J. A Treatise on Man and the Development of His Faculties. IN: Bray GA. The Battle of the Bulge: A History of Obesity Research . Pittsburgh: Dorrance Publishing, 2007 pp 423-36.
Bray GA. Quetelet: quantitative medicine. Obes Res. 1994;2:68–71.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bray GA. Beyond BMI. Nutrients. 2023;15:2254.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Flegal KM. Use and misuse of BMI categories. AMA J Ethics. 2023;25:E550–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Keys A, Fidanza F, Karvonen MJ, Kimura N, Taylor HL. Indices of relative weight and obesity. J Chr Diseases. 1972;25:329–43.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bray GA. Definition, measurement, and classification of the syndromes of obesity. Int J Obes. 1978;2:99–112.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Garrow JS. Treat Obesity Seriouslv-A Clinical Manual . Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1981.
Rodgers A, Woodward A, Swinburn B, Dietz WH. Prevalence trends tell us what did not precipitate the US obesity epidemic. Lancet Public Health. 2018;3:e162–3.
Bray GA. Body fat distribution and the distribution of scientific knowledge. Obes Res. 1996;4:189–92.
Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Ross R. Waist circumference and not body mass index explains obesity-related health risk. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:379–84.
Weeks RW. An experiment with the specialized investigation. Actuar Soc Am Trans. 1904;8:17–23.
Google Scholar
Vague J. La differenciation sexuelle facteur determinant des formes de l’obesite, Presse Medicale. 1947;55:339 340. [Translated. IN: Bray GA. The Battle of the Bulge: A History of Obesity Research . Pittsburgh: Dorrance Publishing, 2007 pp 693–5].
Vague J. The degree of masculine differentiation of obesities: a factor determining predisposition to diabetes, atherosclerosis, gout, and uric calculous disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 1956;4:20–34.
Larsson B, Svardsudd K, Welin L, Wihelmsen L, Bjorntorp P, Tibbllne G. Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 13 year follow up of participants in the study of 792 men born in 1913. BMJ 1984;288:1401–4.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bjorntorp P. Visceral obesity: a “civilization syndrome. Obes Res. 1993;1:206–22.
Behnke AR, Feen BG, Welham WC. The specific gravity of healthy men. JAMA 1942;118:495–8.
Article Google Scholar
Roentgen WC. Ueber eine neue Art von Strahlen. S.B. Phys-med Ges Wurzburg. 1895;132–41.
Wong MC, Bennett JP, Leong LT, Tian IY, Liu YE, Kelly NN, et al. Monitoring body composition change for intervention studies with advancing 3D optical imaging technology in comparison to dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023:S0002-9165(23)04152-7
Church TS, Thomas DM, Tudor-Locke C, Katzmarzyk PT, Earnest CP, Rodarte RQ, et al. Trends over 5 decades in U.S. occupation-related physical activity and their associations with obesity. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e19657 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019657 .
Schwann TH; Smith H, Trans. Microsccopical researches into the accordance in the structure and growth of animals and plants . London: Sydenham Society 1847
Hassall A. Observations on the development of the fat vesicle. Lancet. 1849;1:163–4.
Hirsch J, Knittle JL. Cellularity of human obese and nonobese adipose tissue. Fed Proc. 1970;29:1516–21.
Garvey WT. New Horizons. A new paradigm for treating to target with second-generation obesity medications. JCEM. 2022;107:e1339–47.
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994;372:425–32.
Lavoisier AL, DeLaPlace PS. Memoir on Heat. Read to the Royal Academy of Sciences 28 June 1783 [IN: Bray GA. The Battle of the Bulge: A History of Obesity Research . Pittsburgh: Dorrance Publishing, 2007 pp 498–512].
Bray GA. Lavoisier and Scientific Revolution: The oxygen theory displaces air, fire, earth and water. Obes Res. 1994;2:183–8.
Helmholtz, Hermann von. Uber die Erhaltung der Kraft, ein physikalische Abhandlung, vorgetragen in der Sitzung der physicalischen Gesellschaft zu Berlin am 23sten Juli 1847. Berlin: G. Reimer, 1847.
Bray GA. Commentary on Atwater classic. Obes Res. 1993;1:223–7.
Bray GA. Energy expenditure using doubly labeled water: the unveiling of objective truth. Obes Res. 1997;5:71–7.
Lifson N, Gordon GB, McClintock R. Measurement of total carbon dioxide production by means of D 2 0 18 . J Appl Physiol. 1955;7:704–10.
Lichtman SW, Pisarska K, Berman ER, Pestone M, Dowling H, Offenbacher E, et al. Discrepancy between self-reported and actual caloric intake and exercise in obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 1992;327(Dec):1893–8.
Bray GA. Commentary on classics of obesity 4. Hypothalamic obesity. Obes Res. 1993;1:325–8.
Bruch H. The froehlich syndrome: report of the original case. Am J Dis Child. 1939;58:1281–90.
Babinski JP. Tumeur du corps pituitaire sans acromegalie et arret de development des organs genitaux. Rev Neurol. 1900;8:531–3. [Translation IN: Bray GA. The Battle of the Bulge: A History of Obesity Research . Pittsburgh: Dorrance Publishing, 2007 pp 740–1]
Cushing H. The Pituitary Body and Its Disorders . Philadelphia. PA: JB Lippincott; 1912.
Bray GA. Laurence, moon, Bardet Biedl: reflect a syndrome. Obes Res. 1995;3:383–6.
Laurence JZ, Moon RC. Four cases of “Retinitis Pigmentosa,” Occurring in the same family, and accompanied by general imperfections of development. Opthalmol Rev. 1866;2:32–41.
Bardet G. Sur un Syndrome d’Obesity Conginitale avec Polydactylie et Retinite Pigmentaire (Contribution a l’etude des formes clinique de 1 ’Obesite hypophysaire) . Paris: 1920. Thesis [Translation IN: Bray GA. The Battle of the Bulge: A History of Obesity Research . Pittsburgh: Dorrance Publishing, 2007 pp 740–1].
Biedl A. Geschwisterpaar mit adiposo-genitaler Dystrophie. Dtsch Med Woche. 1922;48:1630.
Cuenot L. Pure strains and their combinations in the mouse. Arch Zoot Exptl Gen. 1905;122:123.
Ingalls AM, Dickie MM, Snell GD. Obese, new mutation in the mouse. J Hered. 1950;41:317–8.
Coleman DL. Obesity and diabetes: two mutant genescausing obesity-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetalogia. 1978;14:141–8.
Zucker TF, Zucker LM. Fat accretion and growth in the rat. J Nutr. 1963;80:6–20.
Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ, Zeltser LM, Drewnowski A, Ravussin E, Redman LM, et al. Obesity pathogenesis: an endocrine society scientific statement. Endocr Rev. 2017;38:267–96.
Oral EA, Simha V, Ruiz E, Andewelt A, Premkumar A, Snell P, et al. Leptin-replacement therapy for lipodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:570–8.
Loos RJF, Yeo GSH. The genetics of obesity: from discovery to biology. Nat Rev Genet. 2022;23:120–33.
Blüher M. Metabolically healthy obesity. Endocr Rev. 2020;41:405–20.
Acosta A, Camilleri M, Abu Dayyeh B, Calderon G, Gonzalez D, McRae A, et al. Selection of antiobesity medications based on phenotypes enhances weight loss: a pragmatic trial in an obesity clinic. Obes. 2021;29:662–71.
Bray GA. Commentary on classics in obesity. 6. Science and politics of hunger. Obes Res. 1993;19:489–93.
Cannon WB, Washburn AL. An explanation of hunger. Am J Physiol. 1912;29:441–54.
Carlson AJ. Contributions to the physiology of the stomach -II. the relation between the concentrations of the empty stomach and the sensation of hunger. Am J Physiol. 1912;31:175–92.
Carlson AJ. Control of Hunger in Health and Disease . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press; 1916.
Flint A, Raben A, Astrup A, Holst JJ. Glucagon-like peptide 1 promotes satiety and suppresses energy intake in humans. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:515–20.
Bray GA. Eat slowly - From laboratory to clinic; behavioral control of eating. Obes Res. 1996;4:397–400.
Pavlov IP; Thompson WH, trans. The Work of the Digestive Glands . London: Charles Griffin and Co.; 1910.
Skinner BF. Contingencies of Reinforcement: A Theoretical Analysis . New York: Meredith Corporation; 1969.
Ferster CB, Nurenberger JI, Levitt EG. The Control of Eating. J. Math 1964;1:87-109.
Stuart RB. Behavioral control of overeating. Behav Res Ther. 1967;5:357–65. [Also IN: Bray GA. The Battle of the Bulge: A History of Obesity Research . Pittsburgh: Dorrance Publishing, 2007 pp 793–9]
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM. et a; Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(Feb):393–403.
The Look AHEAD Research Group, Wadden TA, Bantle JP, Blackburn GL, Bolin P, Brancati FL, Bray GA, et al. Eight-year weight losses with an intensive lifestyle intervention: the look AHEAD study. Obesity. 2014;22:5–13.
Bray GA, Suminska M. From Hippocrates to the Obesity Society: A Brief History. IN Handbook of Obesity (Bray GA, Bouchard C, Katzmarzyk P, Kirwan JP, Redman LM, Schauer PL eds). Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis 2024. Vol 2, pp 3–16.
Bray GA. Commentary on Banting Letter. Obes Res. 1993;1:148–52.
Banting W. Letter on Corpulence, Addressed to the Public . London: Harrison and Sons 1863. pp 1–21.
Harvey W. On corpulence in relation to disease” With some remarks of diet . London” Henry Renshaw, 1872.
Schwartz, H. Never Satisfied. A Cultural History of Diets, Fantasies and Fat . 1977.
Foxcroft, Louise. Calories and Corsets. A history of dieting over 2000 years . London: Profile Books, 2011.
Gilman, Sander L. Obesity. The Biography . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Linn R Stuart SL. The Last Chance Diet . A Revolutionary New Approach to Weight Loss 1977.
Magendie F. Rapport fait a l’Academie des Sciences au le nom de la Commission diet la gelatine. C.R. Academie Sci (Paris) 1841:237-83.
Bray GA. “The Science of Hunger: Revisiting Two Theories of Feeding. IN Bray GA. The Battle of the Bulge. A History of Obesity Research . Pittsburgh, Dorrance Publishing 1977 p. 238.
Sours HE, Frattalli VP, Brand CD, et al. Sudden death associated with very low calorie weight regimes. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981;34:453–61.
Bray GA. From very-low-energy diets to fasting and back. Obes Res. 1995;3:207–9.
Benedict, F.G. A Study of prolonged fasting . Washington: Carnegie Institution of Washington (Publ No 203), 1915.
Keys A, Brozek J, Henschel A, Mickelsen O,Taylor HL. The biology of human starvation . Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1950.
Cahill GF Jr, Herrera MG, Morgan AP, Soeldner JS, Steinke J, Levy PL, et al. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966;45:1751–69.
Benedict FG, Miles WR, Roth P, Smith HM. Human vitality and efficiency under prolonged restricted diet. Carnegie Instit Wash, Pub. No. 280. Washington: Carnegie Institution of Washington; 1919.
Evans FA, Strang JM. The treatment of obesity with low-calorie diets. JAMA 1931;97:1063–8.
Bloom WL. Fasting as an introduction to the treatment of obesity. Metabolism 1959;8:2 14–220.
CAS Google Scholar
Bray GA, Purnell JQ. An historical review of steps and missteps in the discovery of anti-obesity drugs. IN: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, et al. editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2022.
Lesses MF, Myerson A. Human autonomic pharmacology. NEJM 1938;218:119-24.
Cohen PA, Goday A, Swann JP. The return of rainbow diet pills. Am J Public Health. 2012;102:1676–86.
Bray GA. Nutrient intake is modulated by peripheral peptide administration. Obes Res. 1995;3:569S–572S.
Kissileff HR, Pi-Sunyer FX, Thornton J, Smith GP. C-terminal octapeptide of cholecystokinin decreases food intake in man. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981;34:154–60.
Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, Davies M, Van Gaal LF, Lingvay I, et al. STEP 1 study group. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:989–1002.
Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jódar E, Leiter LA, et al. SUSTAIN-6 investigators. semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1834–44.
Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, Wharton S, Connery L, Alves B, et al. SURMOUNT-1 investigators. tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N. Engl J Med. 2022;387:205–16.
Jastreboff AM, Kaplan LM, Frías JP, Wu Q, Du Y, Gurbuz S, et al. Retatrutide phase 2 obesity trial investigators. Triple-hormone-receptor agonist retatrutide for obesity - a phase 2 trial. N Engl J Med. 2023;389:514–26.
Bray GA. Obesity and surgery for a chronic disease. Obes Res. 1996;4:301–3.
Kremen AJ, Linner JH, Nelson CH. An experimental evaluation of the nutritional importance of proximal and distal small intestine. Ann Surg. 1954;140:439–48.
Payne JH, DeWind LT, Commons RR. Metabolic observations in patients with jejuno-colic shunts. Am J Surg. 1963;106:273–89.
Payne JH, DeWind LT. Surgical treatment of obesity. Am J Surg. 1969;118:141–6.
Buchwald H, Varco RL. Partial ileal bypass for hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1967;124:1231.
Mason EE, Ito C. Gastric bypass in obesity. Surg Clin North Am. 1967;47:1345–135.
O’Brien PE, MacDonald L, Anderson M, Brennan L, Brown WA. Long-term outcomes after bariatric surgery: fifteen-year follow-up of adjustable gastric banding and a systematic review of the bariatric surgical literature. Ann Surg. 2013;257:87–94.
Arterburn D, Wellman R, Emiliano A, Smith SR, Odegaard AO, Murali S, et al. PCORnet bariatric study collaborative. Comparative effectiveness and safety of bariatric procedures for weight loss: a PCORnet cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:741–50.
Picot J, Jones J, Colquitt JL, Gospodarevskaya E, Loveman E, Baxter L, et al. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2009;13:1–190.
Christou NV, Sampalis JS, Liberman M, et al. Surgery decreases long-term mortality, morbidity, and health care use in morbidly obese patients. Ann Surg. 2004;240:416–23.
Sjöström L. Review of the key results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) trial - a prospective controlled intervention study of bariatric surgery. J Intern Med. 2013;273:219–34.
Sjöström L. Swedish Obese Subjects, SOS: A review of results from a prospective controlled intervention trial. In: Bray GA, Bochard C, eds. Handbook of Obesity, Volume 2: Clinical Applications. New York: Informa; 2014.
Sjöström L, Narbro K, Sjöström CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H, et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish Obese Subjects. N. Engl J Med. 2007;357:741–52.
Sjöström L, Peltonen M, Jacobson P, Sjöström CD, Karason K, Wedel H, et al. Bariatric surgery and long-term cardiovascular events. JAMA 2012;307:56–65.
Carlsson LM, Peltonen M, Ahlin S, Anveden Å, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, et al. Bariatric surgery and prevention of type 2 diabetes in Swedish Obese Subjects. The New England. J Med. 2012;367:695–704.
Pories WJ, Swanson MS, MacDonald KG, Long SB, Morris PG, Brown BM, et al. Who would have thought it? an operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult-onset. Diabetes Mellit Ann Surg. 1995;222:339–52.
Bray GA. Life insurance and overweight. Obes Res. 1995;3:97–99.
The Association of Life Insurance Medical Directors and The Actuarial Society of America. Medico- Actuarial Mortality Investigation . New York: The Association of Life Insurance Medical Directors and ‘The Actuarial Society of America; 1913.
Keys A. Seven Countries: A Multivariate Analysis of Death and Coronary Heart Disease . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1980.
Dawber TR. The Framingham Study: The Epidemiology of Atherosclerotic Disease . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1980.
Bray, G.A. (Ed), Obesity in Perspective . Fogarty International Center Series on Preventive Med. Vol 2, parts 1 and 2, Washington, D.C.: U.S. Govt Prtg Office, 1976, DHEW Publication #75-708.
Fryar CD, Carroll MD, Afful J. Prevalence of overweight, obesity, and severe obesity among adults aged 20 and over: United States, 1960–1962 through 2017–2018. NCHS Health E-Stats. 2020.
Bray GA. Obesity: Historical development of scientific and cultural ideas. Int J Obes. 1990;14:909–26.
Bray GA. The Battle of the Bulge: A History of Obesity Research . Pittsburgh: Dorrance Publishing, 2007 p 30.
Short, T. A Discourse Concerning the Causes and Effects of Corpulency Together with the Method for Its Prevention and Cure , J. Robert, London, 1727.
Flemyng, M. A Discourse on the Nature, Causes and Cure of Corpulency , L Davis and C Reymers, London, 1760.
Wadd, W. Comments on corpulency lineaments of leanness mems on diet and dietetics. London: John Ebers and Co, 1829.
Chambers, TK. Corpulence, or excess fat in the human body. London: Longman, 1850.
Rony HR. Obesity and Leanness . Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1940.
Rynearson EH, Gastineau CF. Obesity . Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas, 1949.
Bray, G.A. The Obese Patient. Major Problems in Internal Medicine , Vol 9, Philadelphia, Pa.: W.B. Saunders Company, 1976, pp. 1-450.
Bray G.A. A Guide to Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome: Origins and Treatment . New York: CRC Press: Taylor and Francis Group. 2011.
Howard AN. The history of the association for the study of obesity. Intern J Obes. 1992;16:S1–8.
Bray GA, Greenwood MRC, Hansen BC. The obesity society is turning 40: a history of the early years. Obesity. 2021;29(Dec):1978–81.
McLean Baird I, Howard AN. Obesity: Medical and Scientific Aspects : Proceedings of the First Symposium of the Obesity Association of Great Britain held in London , October 1968. Edinburgh & London: E. S. Livingston, 1968.
Bray GA, Howard AN. Founding of the international journal of obesity: a journey in medical journalism. Int J Obes. 2015;39:75–9.
Bray G. The founding of obesity research/obesity: a brief history. Obes. 2022;30:2100–2.
Ziman J. The Force of Knowledge. The Scientific Dimension of Society . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1976.
Bray GA, Kim KK, Wilding JPH. Obesity: a chronic relapsing progressive disease process: a position paper of world obesity. Obes Rev. 2017;18:715–23.
Bray GA. Obesity is a chronic, relapsing neurochemical disease. Intern J Obes. 2004;28:34–8.
Allison DB, Downey M, Atkinson RL, Billington CJ, Bray GA, Eckel RH, et al. Obesity as a disease: a white paper on evidence and arguments commissioned by the Council of the Obesity Society. Obes. 2008;16:1161–77.
Garvey WT, Garber AJ, Mechanick JI, Bray GA, Dagogo-Jack S, Einhorn D, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology position statement on the 2014 advanced framework for a new diagnosis of obesity as a chronic disease. Endocr Pr. 2014;20:977–89.
Bray GA, Ryan DH. Evidence-based weight loss interventions: individualized treatment options to maximize patient outcomes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23:50–62.
Ge L, Sadeghirad B, Ball GDC, da Costa BR, Hitchcock CL, Svendrovski A, et al. Comparison of dietary macronutrient patterns of 14 popular named dietary programmes for weight and cardiovascular risk factor reduction in adults: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 2020;369:m696.
Sjöström L, Rissanen A, Andersen T, Boldrin M, Golay A, Koppeschaar HP, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss and prevention of weight regain in obese patients. European Multicentre Orlistat Study Group. Lancet 1998;352:167–72.
Pi-Sunyer FX, Aronne LJ, Heshmati HM, Devin J, Rosenstock J. Effect of rimonabant, a cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker, on weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight or obese patients: RIO-North America: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006;295:761–75.
Foster GD, Wadden TA, Vogt RA, Brewer G. What is a reasonable weight loss? Patients’ expectations and evaluations of obesity treatment outcomes. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1997;65:79–85.
DiFeliceantonio AG, Coppin G, Rigoux L, Thanarajah ES, Dagher A, Tittgemeyer M, et al. Supra-additive effects of combining fat and carbohydrate on food reward. Cell Metab. 2018;28:33–44.e3.
Thanarajah SE, Backes H, DiFeliceantonio AG, Albus K, Cremer AL, Hanssen R, et al. Food intake recruits orosensory and post-ingestive dopaminergic circuits to affect eating desire in humans. Cell Metab. 2019;29:695–706.e4.
Bray GA. Is sugar addictive? Diabetes 2016;65:1797–9.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Dr. Jennifer Lyn Baker for her helpful comments during the early stage of preparing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Pennington Biomedical Research Center/LSU, Baton Rouge, LA, 70808, USA
George A. Bray
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All contributions were made by the single author.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to George A. Bray .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
MSS # 2023IJO01171.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Bray, G.A. Obesity: a 100 year perspective. Int J Obes (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-024-01530-6
Download citation
Received : 13 November 2023
Revised : 23 April 2024
Accepted : 26 April 2024
Published : 07 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-024-01530-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- About Project
- Testimonials
Business Management Ideas

Essay on Obesity
List of essays on obesity, essay on obesity – short essay (essay 1 – 150 words), essay on obesity (essay 2 – 250 words), essay on obesity – written in english (essay 3 – 300 words), essay on obesity – for school students (class 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12 standard) (essay 4 – 400 words), essay on obesity – for college students (essay 5 – 500 words), essay on obesity – with causes and treatment (essay 6 – 600 words), essay on obesity – for science students (essay 7 – 750 words), essay on obesity – long essay for medical students (essay 8 – 1000 words).
Obesity is a chronic health condition in which the body fat reaches abnormal level. Obesity occurs when we consume much more amount of food than our body really needs on a daily basis. In other words, when the intake of calories is greater than the calories we burn out, it gives rise to obesity.
Audience: The below given essays are exclusively written for school students (Class 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12 Standard), college, science and medical students.
Introduction:
Obesity means being excessively fat. A person would be said to be obese if his or her body mass index is beyond 30. Such a person has a body fat rate that is disproportionate to his body mass.
Obesity and the Body Mass Index:
The body mass index is calculated considering the weight and height of a person. Thus, it is a scientific way of determining the appropriate weight of any person. When the body mass index of a person indicates that he or she is obese, it exposes the person to make health risk.
Stopping Obesity:
There are two major ways to get the body mass index of a person to a moderate rate. The first is to maintain a strict diet. The second is to engage in regular physical exercise. These two approaches are aimed at reducing the amount of fat in the body.
Conclusion:
Obesity can lead to sudden death, heart attack, diabetes and may unwanted illnesses. Stop it by making healthy choices.
Obesity has become a big concern for the youth of today’s generation. Obesity is defined as a medical condition in which an individual gains excessive body fat. When the Body Mass Index (BMI) of a person is over 30, he/ she is termed as obese.
Obesity can be a genetic problem or a disorder that is caused due to unhealthy lifestyle habits of a person. Physical inactivity and the environment in which an individual lives, are also the factors that leads to obesity. It is also seen that when some individuals are in stress or depression, they start cultivating unhealthy eating habits which eventually leads to obesity. Medications like steroids is yet another reason for obesity.
Obesity has several serious health issues associated with it. Some of the impacts of obesity are diabetes, increase of cholesterol level, high blood pressure, etc. Social impacts of obesity includes loss of confidence in an individual, lowering of self-esteem, etc.
The risks of obesity needs to be prevented. This can be done by adopting healthy eating habits, doing some physical exercise regularly, avoiding stress, etc. Individuals should work on weight reduction in order to avoid obesity.
Obesity is indeed a health concern and needs to be prioritized. The management of obesity revolves around healthy eating habits and physical activity. Obesity, if not controlled in its initial stage can cause many severe health issues. So it is wiser to exercise daily and maintain a healthy lifestyle rather than being the victim of obesity.
Obesity can be defined as the clinical condition where accumulation of excessive fat takes place in the adipose tissue leading to worsening of health condition. Usually, the fat is deposited around the trunk and also the waist of the body or even around the periphery.
Obesity is actually a disease that has been spreading far and wide. It is preventable and certain measures are to be taken to curb it to a greater extend. Both in the developing and developed countries, obesity has been growing far and wide affecting the young and the old equally.
The alarming increase in obesity has resulted in stimulated death rate and health issues among the people. There are several methods adopted to lose weight and they include different diet types, physical activity and certain changes in the current lifestyle. Many of the companies are into minting money with the concept of inviting people to fight obesity.
In patients associated with increased risk factor related to obesity, there are certain drug therapies and other procedures adopted to lose weight. There are certain cost effective ways introduced by several companies to enable clinic-based weight loss programs.
Obesity can lead to premature death and even cause Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cardiovascular diseases have also become the part and parcel of obese people. It includes stroke, hypertension, gall bladder disease, coronary heart disease and even cancers like breast cancer, prostate cancer, endometrial cancer and colon cancer. Other less severe arising due to obesity includes osteoarthritis, gastro-esophageal reflux disease and even infertility.
Hence, serious measures are to be taken to fight against this dreadful phenomenon that is spreading its wings far and wide. Giving proper education on benefits of staying fit and mindful eating is as important as curbing this issue. Utmost importance must be given to healthy eating habits right from the small age so that they follow the same until the end of their life.
Obesity is majorly a lifestyle disease attributed to the extra accumulation of fat in the body leading to negative health effects on a person. Ironically, although prevalent at a large scale in many countries, including India, it is one of the most neglect health problems. It is more often ignored even if told by the doctor that the person is obese. Only when people start acquiring other health issues such as heart disease, blood pressure or diabetes, they start taking the problem of obesity seriously.
Obesity Statistics in India:
As per a report, India happens to figure as the third country in the world with the most obese people. This should be a troubling fact for India. However, we are yet to see concrete measures being adopted by the people to remain fit.
Causes of Obesity:
Sedentary lifestyle, alcohol, junk food, medications and some diseases such as hypothyroidism are considered as the factors which lead to obesity. Even children seem to be glued to televisions, laptops and video games which have taken away the urge for physical activities from them. Adding to this, the consumption of junk food has further aggravated the growing problem of obesity in children.
In the case of adults, most of the professions of today make use of computers which again makes people sit for long hours in one place. Also, the hectic lifestyle of today makes it difficult for people to spare time for physical activities and people usually remain stressed most of the times. All this has contributed significantly to the rise of obesity in India.
Obesity and BMI:
Body Mass Index (BMI) is the measure which allows a person to calculate how to fit he or she is. In other words, the BMI tells you if you are obese or not. BMI is calculated by dividing the weight of a person in kg with the square of his / her height in metres. The number thus obtained is called the BMI. A BMI of less than 25 is considered optimal. However, if a person has a BMI over 30 he/she is termed as obese.
What is a matter of concern is that with growing urbanisation there has been a rapid increase of obese people in India? It is of utmost importance to consider this health issue a serious threat to the future of our country as a healthy body is important for a healthy soul. We should all be mindful of what we eat and what effect it has on our body. It is our utmost duty to educate not just ourselves but others as well about this serious health hazard.
Obesity can be defined as a condition (medical) that is the accumulation of body fat to an extent that the excess fat begins to have a lot of negative effects on the health of the individual. Obesity is determined by examining the body mass index (BMI) of the person. The BMI is gotten by dividing the weight of the person in kilogram by the height of the person squared.
When the BMI of a person is more than 30, the person is classified as being obese, when the BMI falls between 25 and 30, the person is said to be overweight. In a few countries in East Asia, lower values for the BMI are used. Obesity has been proven to influence the likelihood and risk of many conditions and disease, most especially diabetes of type 2, cardiovascular diseases, sleeplessness that is obstructive, depression, osteoarthritis and some cancer types.
In most cases, obesity is caused through a combination of genetic susceptibility, a lack of or inadequate physical activity, excessive intake of food. Some cases of obesity are primarily caused by mental disorder, medications, endocrine disorders or genes. There is no medical data to support the fact that people suffering from obesity eat very little but gain a lot of weight because of slower metabolism. It has been discovered that an obese person usually expends much more energy than other people as a result of the required energy that is needed to maintain a body mass that is increased.
It is very possible to prevent obesity with a combination of personal choices and social changes. The major treatments are exercising and a change in diet. We can improve the quality of our diet by reducing our consumption of foods that are energy-dense like those that are high in sugars or fat and by trying to increase our dietary fibre intake.
We can also accompany the appropriate diet with the use of medications to help in reducing appetite and decreasing the absorption of fat. If medication, exercise and diet are not yielding any positive results, surgery or gastric balloon can also be carried out to decrease the volume of the stomach and also reduce the intestines’ length which leads to the feel of the person get full early or a reduction in the ability to get and absorb different nutrients from a food.
Obesity is the leading cause of ill-health and death all over the world that is preventable. The rate of obesity in children and adults has drastically increased. In 2015, a whopping 12 percent of adults which is about 600 million and about 100 million children all around the world were found to be obese.
It has also been discovered that women are more obese than men. A lot of government and private institutions and bodies have stated that obesity is top of the list of the most difficult and serious problems of public health that we have in the world today. In the world we live today, there is a lot of stigmatisation of obese people.
We all know how troubling the problem of obesity truly is. It is mainly a form of a medical condition wherein the body tends to accumulate excessive fat which in turn has negative repercussions on the health of an individual.
Given the current lifestyle and dietary style, it has become more common than ever. More and more people are being diagnosed with obesity. Such is its prevalence that it has been termed as an epidemic in the USA. Those who suffer from obesity are at a much higher risk of diabetes, heart diseases and even cancer.
In order to gain a deeper understanding of obesity, it is important to learn what the key causes of obesity are. In a layman term, if your calorie consumption exceeds what you burn because of daily activities and exercises, it is likely to lead to obesity. It is caused over a prolonged period of time when your calorie intake keeps exceeding the calories burned.
Here are some of the key causes which are known to be the driving factors for obesity.
If your diet tends to be rich in fat and contains massive calorie intake, you are all set to suffer from obesity.
Sedentary Lifestyle:
With most people sticking to their desk jobs and living a sedentary lifestyle, the body tends to get obese easily.
Of course, the genetic framework has a lot to do with obesity. If your parents are obese, the chance of you being obese is quite high.
The weight which women gain during their pregnancy can be very hard to shed and this is often one of the top causes of obesity.
Sleep Cycle:
If you are not getting an adequate amount of sleep, it can have an impact on the hormones which might trigger hunger signals. Overall, these linked events tend to make you obese.
Hormonal Disorder:
There are several hormonal changes which are known to be direct causes of obesity. The imbalance of the thyroid stimulating hormone, for instance, is one of the key factors when it comes to obesity.
Now that we know the key causes, let us look at the possible ways by which you can handle it.
Treatment for Obesity:
As strange as it may sound, the treatment for obesity is really simple. All you need to do is follow the right diet and back it with an adequate amount of exercise. If you can succeed in doing so, it will give you the perfect head-start into your journey of getting in shape and bidding goodbye to obesity.
There are a lot of different kinds and styles of diet plans for obesity which are available. You can choose the one which you deem fit. We recommend not opting for crash dieting as it is known to have several repercussions and can make your body terribly weak.
The key here is to stick to a balanced diet which can help you retain the essential nutrients, minerals, and, vitamins and shed the unwanted fat and carbs.
Just like the diet, there are several workout plans for obesity which are available. It is upon you to find out which of the workout plan seems to be apt for you. Choose cardio exercises and dance routines like Zumba to shed the unwanted body weight. Yoga is yet another method to get rid of obesity.
So, follow a blend of these and you will be able to deal with the trouble of obesity in no time. We believe that following these tips will help you get rid of obesity and stay in shape.
Obesity and overweight is a top health concern in the world due to the impact it has on the lives of individuals. Obesity is defined as a condition in which an individual has excessive body fat and is measured using the body mass index (BMI) such that, when an individual’s BMI is above 30, he or she is termed obese. The BMI is calculated using body weight and height and it is different for all individuals.
Obesity has been determined as a risk factor for many diseases. It results from dietary habits, genetics, and lifestyle habits including physical inactivity. Obesity can be prevented so that individuals do not end up having serious complications and health problems. Chronic illnesses like diabetes, heart diseases and relate to obesity in terms of causes and complications.
Factors Influencing Obesity:
Obesity is not only as a result of lifestyle habits as most people put it. There are other important factors that influence obesity. Genetics is one of those factors. A person could be born with genes that predispose them to obesity and they will also have difficulty in losing weight because it is an inborn factor.
The environment also influences obesity because the diet is similar in certain environs. In certain environments, like school, the food available is fast foods and the chances of getting healthy foods is very low, leading to obesity. Also, physical inactivity is an environmental factor for obesity because some places have no fields or tracks where people can jog or maybe the place is very unsafe and people rarely go out to exercise.
Mental health affects the eating habits of individuals. There is a habit of stress eating when a person is depressed and it could result in overweight or obesity if the person remains unhealthy for long period of time.
The overall health of individuals also matter. If a person is unwell and is prescribed with steroids, they may end up being obese. Steroidal medications enable weight gain as a side effect.
Complications of Obesity:
Obesity is a health concern because its complications are severe. Significant social and health problems are experienced by obese people. Socially, they will be bullied and their self-esteem will be low as they will perceive themselves as unworthy.
Chronic illnesses like diabetes results from obesity. Diabetes type 2 has been directly linked to obesity. This condition involves the increased blood sugars in the body and body cells are not responding to insulin as they should. The insulin in the body could also be inadequate due to decreased production. High blood sugar concentrations result in symptoms like frequent hunger, thirst and urination. The symptoms of complicated stages of diabetes type 2 include loss of vision, renal failure and heart failure and eventually death. The importance of having a normal BMI is the ability of the body to control blood sugars.
Another complication is the heightened blood pressures. Obesity has been defined as excessive body fat. The body fat accumulates in blood vessels making them narrow. Narrow blood vessels cause the blood pressures to rise. Increased blood pressure causes the heart to start failing in its physiological functions. Heart failure is the end result in this condition of increased blood pressures.
There is a significant increase in cholesterol in blood of people who are obese. High blood cholesterol levels causes the deposition of fats in various parts of the body and organs. Deposition of fats in the heart and blood vessels result in heart diseases. There are other conditions that result from hypercholesterolemia.
Other chronic illnesses like cancer can also arise from obesity because inflammation of body cells and tissues occurs in order to store fats in obese people. This could result in abnormal growths and alteration of cell morphology. The abnormal growths could be cancerous.
Management of Obesity:
For the people at risk of developing obesity, prevention methods can be implemented. Prevention included a healthy diet and physical activity. The diet and physical activity patterns should be regular and realizable to avoid strains that could result in complications.
Some risk factors for obesity are non-modifiable for example genetics. When a person in genetically predisposed, the lifestyle modifications may be have help.
For the individuals who are already obese, they can work on weight reduction through healthy diets and physical exercises.
In conclusion, obesity is indeed a major health concern because the health complications are very serious. Factors influencing obesity are both modifiable and non-modifiable. The management of obesity revolves around diet and physical activity and so it is important to remain fit.
In olden days, obesity used to affect only adults. However, in the present time, obesity has become a worldwide problem that hits the kids as well. Let’s find out the most prevalent causes of obesity.
Factors Causing Obesity:
Obesity can be due to genetic factors. If a person’s family has a history of obesity, chances are high that he/ she would also be affected by obesity, sooner or later in life.
The second reason is having a poor lifestyle. Now, there are a variety of factors that fall under the category of poor lifestyle. An excessive diet, i.e., eating more than you need is a definite way to attain the stage of obesity. Needless to say, the extra calories are changed into fat and cause obesity.
Junk foods, fried foods, refined foods with high fats and sugar are also responsible for causing obesity in both adults and kids. Lack of physical activity prevents the burning of extra calories, again, leading us all to the path of obesity.
But sometimes, there may also be some indirect causes of obesity. The secondary reasons could be related to our mental and psychological health. Depression, anxiety, stress, and emotional troubles are well-known factors of obesity.
Physical ailments such as hypothyroidism, ovarian cysts, and diabetes often complicate the physical condition and play a massive role in abnormal weight gain.
Moreover, certain medications, such as steroids, antidepressants, and contraceptive pills, have been seen interfering with the metabolic activities of the body. As a result, the long-term use of such drugs can cause obesity. Adding to that, regular consumption of alcohol and smoking are also connected to the condition of obesity.
Harmful Effects of Obesity:
On the surface, obesity may look like a single problem. But, in reality, it is the mother of several major health issues. Obesity simply means excessive fat depositing into our body including the arteries. The drastic consequence of such high cholesterol levels shows up in the form of heart attacks and other life-threatening cardiac troubles.
The fat deposition also hampers the elasticity of the arteries. That means obesity can cause havoc in our body by altering the blood pressure to an abnormal range. And this is just the tip of the iceberg. Obesity is known to create an endless list of problems.
In extreme cases, this disorder gives birth to acute diseases like diabetes and cancer. The weight gain due to obesity puts a lot of pressure on the bones of the body, especially of the legs. This, in turn, makes our bones weak and disturbs their smooth movement. A person suffering from obesity also has higher chances of developing infertility issues and sleep troubles.
Many obese people are seen to be struggling with breathing problems too. In the chronic form, the condition can grow into asthma. The psychological effects of obesity are another serious topic. You can say that obesity and depression form a loop. The more a person is obese, the worse is his/ her depression stage.
How to Control and Treat Obesity:
The simplest and most effective way, to begin with, is changing our diet. There are two factors to consider in the diet plan. First is what and what not to eat. Second is how much to eat.
If you really want to get rid of obesity, include more and more green vegetables in your diet. Spinach, beans, kale, broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus, etc., have enough vitamins and minerals and quite low calories. Other healthier options are mushrooms, pumpkin, beetroots, and sweet potatoes, etc.
Opt for fresh fruits, especially citrus fruits, and berries. Oranges, grapes, pomegranate, pineapple, cherries, strawberries, lime, and cranberries are good for the body. They have low sugar content and are also helpful in strengthening our immune system. Eating the whole fruits is a more preferable way in comparison to gulping the fruit juices. Fruits, when eaten whole, have more fibers and less sugar.
Consuming a big bowl of salad is also great for dealing with the obesity problem. A salad that includes fibrous foods such as carrots, radish, lettuce, tomatoes, works better at satiating the hunger pangs without the risk of weight gain.
A high protein diet of eggs, fish, lean meats, etc., is an excellent choice to get rid of obesity. Take enough of omega fatty acids. Remember to drink plenty of water. Keeping yourself hydrated is a smart way to avoid overeating. Water also helps in removing the toxins and excess fat from the body.
As much as possible, avoid fats, sugars, refined flours, and oily foods to keep the weight in control. Control your portion size. Replace the three heavy meals with small and frequent meals during the day. Snacking on sugarless smoothies, dry fruits, etc., is much recommended.
Regular exercise plays an indispensable role in tackling the obesity problem. Whenever possible, walk to the market, take stairs instead of a lift. Physical activity can be in any other form. It could be a favorite hobby like swimming, cycling, lawn tennis, or light jogging.
Meditation and yoga are quite powerful practices to drive away the stress, depression and thus, obesity. But in more serious cases, meeting a physician is the most appropriate strategy. Sometimes, the right medicines and surgical procedures are necessary to control the health condition.
Obesity is spreading like an epidemic, haunting both the adults and the kids. Although genetic factors and other physical ailments play a role, the problem is mostly caused by a reckless lifestyle.
By changing our way of living, we can surely take control of our health. In other words, it would be possible to eliminate the condition of obesity from our lives completely by leading a healthy lifestyle.
Health , Obesity
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
Like this post? Don’t forget to share it!
Here are a few recommended articles for you to read next:
- Essay on Cleanliness
- Essay on Cancer
- Essay on AIDS
- Essay on Health and Fitness
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life

Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Preventing Childhood Obesity
- Health Care Strategies
- About Obesity
- What Can Be Done
- About Healthy Weight and Growth
- Body Mass Index (BMI)
- About Nutrition
- About Physical Activity
Risk Factors for Obesity
At a glance.
Obesity is a complex and costly chronic disease influenced by many factors. These factors include health behaviors, stress, health conditions and medications, genes, and people's environment. Knowing the risk factors can help individuals and communities take steps to prevent and reduce obesity.

Health behaviors
Certain health behaviors can contribute to excess weight gain and are risk factors for obesity:
- Lack of physical activity .
- Too many highly processed foods or added sugars , including too many sugar-sweetened beverages .
- Too little fiber and fruits and vegetables .
- Not enough sleep or poor quality sleep.
- Too much TV, computer, video games, and other screen time.
Long-term stress can affect your brain and trigger your body to make high levels of hormones, such as cortisol. These hormones help regulate energy balances and hunger urges. High levels of these hormones can increase your appetite and promote cravings for foods that are high in fats and added sugars. 1
Health conditions and medications
Some health conditions may lead to excess weight gain, obesity, or insulin resistance. These conditions include Cushing syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome, or underactive thyroid.
Some medications may also cause weight gain by disrupting the brain's signals for hunger or through other mechanisms. These medications can include:
- Psychiatric medications, such as antipsychotics and antidepressants.
- Certain types of hormonal birth control, such as progestins.
- Anti-seizure or mood-stabilizing drugs.
- Certain blood pressure and diabetes medications.
In specific, rare, single-gene disorders, genes can directly cause obesity. Examples of these disorders are Bardet-Biedl syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome.
It is more common for multiple genes to be responsible for a person's feelings of hunger, sense of fullness, and metabolism. 2
Systems and environment
Health is influenced by the conditions in which people live, learn, work, and play. Health can also be influenced by forces and policies that shape these conditions. These factors affect a person's ability to make healthy choices and influence their risk of gaining excess weight and developing obesity.
Examples include:
- Access to healthy, affordable foods and beverages.
- Access to safe places for physical activity .
- Community design to support activity-friendly routes to everyday destinations.
- Supportive childcare and school environments .
- Access to high-quality health care services .
- Safe housing and transportation .
- Economic stability .
Also, some chemicals in the environment can disrupt how our bodies work and cause excess weight gain. Understanding these factors and how we can use that knowledge to improve our health is ongoing.
- Scott KA, Melhorn SJ, Sakai RR. Effects of chronic social stress on obesity. Curr Obes Rep. 2012 Mar;1(1):16-25. doi: 10.1007/s13679-011-0006-3
- Mahmoud R, Kimonis V, Butler MG. Genetics of obesity in humans: a clinical review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 20;23(19):11005. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911005
CDC's obesity prevention efforts focus on policy and environmental strategies to make healthy eating and active living accessible for everyone.
For Everyone
Health care providers, public health.
Obesity: Predisposing Factors and Treatment Essay
Introduction, predisposing factors, tackling obesity.
In the recent years, obesity and its related conditions have plummeted to a high record. Obesity, a condition once considered as an adult problem, has spread among more young people in the 21 st century, than in the past. This disease can be explained as the presence of excess fat in the body. A simple way of diagnosing obesity is by the use of Body Mass Index (BMI), which is simply weight (kg)/height (m)2. Speaking about the youth, once the BMI is determined it is then compared to that of other children of the same age and sex. The World Health Organization (WHO) considers a BMI with more than 30kg/m² as obese (deOnis, Blossner, & Borghi, 2010). This paper will delve into the causes and the solutions of this problem.
Diet, in particular, plays a vital role in the health of a young person. Consumption of the processed foods with a high content of fat and sugar, affects the normal metabolism in the young body. This happens by causing a surge in the levels of blood glucose immediately after the consumption of the food. Moreover, this causes energy slumps in the body prompting a hunger impulse that in turn makes one eat a lot (Wieting, 2008).
Besides the constituents of the diet, other factors can predispose a young individual to develop obesity. To begin with, working parents increase the risk of their children developing obesity by being too busy to closely monitor or prepare what their children eat. Secondly, the fast food industry spends fortunes in advertisements to entice the youth to buy their products. Another factor is the proximity of these fast food outlets to schools and colleges. Finally, poor families often do not have enough funds to spend on healthy food and thus going for the cheaper options like junk foods (Danner, 2008).
Sedentary lifestyles
There is less physical activity among the youth today. Nowadays, most young people prefer remaining indoors and watch TV or play online virtual reality games. In turn, they rarely have time to get involved in physical activities. Schools, on the other hand, have also reduced the number of hours allocated to the physical education classes in an attempt to improve performance in state proficiency examinations (Wieting, 2008).
There is an increased possibility of a child born to obese parents to get the same condition. It has been noted that the condition is also more prevalent among the black Americans and Hispanics than in the Caucasians (Wieting, 2008).
Health issues
Some diseases may increase the risk of obesity. A good example is the Cushing’s disease that results from over secretion of a stress hormone called cortisol . It leads to the deposition of fat around the stomach and the upper side of the back. In addition, some drugs used in the treatment of mental problems/psychosis, such as diazepam, can lead to an increased appetite (Wieting, 2008).
A responsible guardian should analyse all areas of their children’s lives. They should also think over their own lifestyle choices, as they could be the source of the problem. The following are some of the suggested solutions in preventing and controlling obesity.
Changes in diet
A meal should always have three main food groups. High fiber foods are the best form of carbohydrates. These include foods such as whole grain flours, brown rice and yams. White meat sources of protein like chicken are preferred to red meat. Beans and peas are also good protein sources. Vegetables and fruits are the best sources of vitamins (Danner, 2008).
Parents should control the hours their children spend in front of the TV set. Instead of buying video games as gifts, they should substitute this with play kits such as a tennis racquets, bats, etc. Parents should also participate in these physical activities with their children in order to encourage them. Similarly, schools should allocate adequate time to physical education and encourage students to manage their time well to excel in their class work.
Screening for predisposing diseases
Children from families that have a disposition to develop Type 2 diabetes mellitus are supposed to be screened. Good dietary management is also very important for such an individual to prevent the condition, delay its onset or manage the symptoms if the condition is already present. Patients undergoing antipsychotic drug therapy should be put on a diet and exercise regimen by a nutritionist or physician.
There are no drugs recommended for children, however Orlistat (Xenical) can be used in teenagers. It causes a small but steady decline in weight. Its use is often recommended alongside that of good dietary management. Sibutramine is another example; however, it is obligatory to consult a doctor when opting to use this remedy (Wieting, 2008).
It is very clear that obesity is no longer an individual problem. The world needs to do something about this condition. In fact, it is important to note that preventing and controlling obesity reduces the costs that one would otherwise incur in treating obesity related ailments like stroke, heart conditions, and blood pressure. Everyone is at risk of becoming obese; it is important to take the above steps in order to protect children from developing this scourge.
Danner, F. W. (2008). A national longitudinal study of the association between hours of TV viewing and the trajectory of BMI growth among US children. Journal of Pediatric Psychology , 33 (10), 1100-1107.
deOnis, M., Blössner, M., & Borghi, E. (2010). Global prevalence and trends of overweight and obesity among preschool children. The American journal of clinical nutrition , 92 (5), 1257-1264.
Wieting, J. M. (2008). Cause and effect in childhood obesity: solutions for a national epidemic: JAOA. Journal of the American Osteopathic Association , 108 (10), 545-552.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, August 22). Obesity: Predisposing Factors and Treatment. https://ivypanda.com/essays/obesity-predisposing-factors-and-treatment/
"Obesity: Predisposing Factors and Treatment." IvyPanda , 22 Aug. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/obesity-predisposing-factors-and-treatment/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Obesity: Predisposing Factors and Treatment'. 22 August.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Obesity: Predisposing Factors and Treatment." August 22, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/obesity-predisposing-factors-and-treatment/.
1. IvyPanda . "Obesity: Predisposing Factors and Treatment." August 22, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/obesity-predisposing-factors-and-treatment/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Obesity: Predisposing Factors and Treatment." August 22, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/obesity-predisposing-factors-and-treatment/.
- Pathophysiology of Stress, Processed Foods, and Risky Alcohol Consumption
- Teenage Suicide Statistics
- Diabetes Risk Assessment and Prevention
- Cell Phones and Health Dangers
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- Public Health and Life Expectancy Improvement
- Environmental Health Factors: Positive & Negative
- Interprofessional Teams in Healthcare Delivery
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity among older adults in the nordic countries: a scoping review
- Fereshteh Baygi 1 na1 ,
- Sussi Friis Buhl 1 na1 ,
- Trine Thilsing 1 ,
- Jens Søndergaard 1 &
- Jesper Bo Nielsen 1
BMC Geriatrics volume 24 , Article number: 421 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
124 Accesses
Metrics details
Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity (SO) are age-related syndromes that may compromise physical and mental health among older adults. The Nordic countries differ from other regions on prevalence of disease, life-style behavior, and life expectancy, which may impact prevalence of sarcopenia and SO. Therefore, the aim of this study is to review the available evidence and gaps within this field in the Nordic countries.
PubMed, Embase, and Web of science (WOS) were searched up to February 2023. In addition, grey literature and reference lists of included studies were searched. Two independent researcher assessed papers and extracted data.
Thirty-three studies out of 6,363 searched studies were included in this scoping review. Overall prevalence of sarcopenia varied from 0.9 to 58.5%. A wide prevalence range was still present for community-dwelling older adults when definition criteria and setting were considered. The prevalence of SO ranged from 4 to 11%, according to the only study on this field. Based on the included studies, potential risk factors for sarcopenia include malnutrition, low physical activity, specific diseases (e.g., diabetes), inflammation, polypharmacy, and aging, whereas increased levels of physical activity and improved dietary intake may reduce the risk of sarcopenia. The few available interventions for sarcopenia were mainly focused on resistance training with/without nutritional supplements (e.g., protein, vitamin D).
The findings of our study revealed inadequate research on SO but an increasing trend in the number of studies on sarcopenia. However, most of the included studies had descriptive cross-sectional design, small sample size, and applied different diagnostic criteria. Therefore, larger well-designed cohort studies that adhere to uniform recent guidelines are required to capture a full picture of these two age-related medical conditions in Nordic countries, and plan for prevention/treatment accordingly.
Peer Review reports
The number of older adults with age-related disorders is expected to increase worldwide [ 1 , 2 ]. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity (SO) are both age-related syndromes that may compromise the physical and mental health of older adults and increase their need for health care services in old age [ 3 , 4 ], and this may challenge the sustainability of health care systems economically and by shortage of health care personnel [ 5 ].
Sarcopenia is characterized by low muscle mass in combination with low muscle strength [ 4 ]. SO is characterized by the co-existence of obesity (excessive adipose tissue) and sarcopenia [ 3 ]. Sarcopenia and SO are both associated with physical disability, risk of falls, morbidity, reduced quality of life and early mortality [ 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. In SO the consequences of sarcopenia and obesity are combined and maximized [ 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 ].
Etiology of sarcopenia and SO is multifactorial and closely linked to multimorbidity [ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Nevertheless, lifestyle and behavioral components particularly diet and physical activity, are important interrelated factors that potentially can be modified. Physical inactivity and sedentary behavior may accelerate age-related loss of muscle mass, reduce energy expenditure, and increase risk of obesity [ 3 , 11 ]. In addition, weight cycling (the fluctuations in weight following dieting and regain) and an unbalanced diet (particularly inadequate protein intake) may accelerate loss of muscle mass and increase severity of sarcopenia and SO in older adults [ 3 , 12 ]. International guideline for the treatment of sarcopenia emphasizes the importance of resistance training potentially in combination with nutritional supplementation to improve muscle mass and physical function [ 13 ]. Similar therapeutic approach is suggested for treatment of SO [ 14 ]. However, more research is needed to confirm optimal treatment of SO [ 14 ].
According to a recently published meta-analysis the global prevalence of sarcopenia ranged from 10 to 27% in populations of older adults ≥ 60 years [ 15 ]. Further the global prevalence of SO among older adults was 11% [ 8 ]. So, sarcopenia and SO are prevalent conditions, with multiple negative health outcomes and should be given special attention [ 16 ]. Despite the large burden on patients and health care systems, the awareness of the importance of skeletal muscle maintenance in obesity is low among clinicians and scientists [ 3 , 16 ].
A recent meta-analysis on publication trends revealed that despite an increase in global research on sarcopenia, the Nordic countries were only limitedly represented [ 6 ]. Nordic countries may differ from other regions on aspects associated with the prevalence and trajectory of sarcopenia and SO and challenge the representativeness of research findings from other parts of the world. These include a different prevalence pattern of noncommunicable diseases [ 17 ], different life-style behavior and life-style associated risk factors [ 15 , 18 ], and higher life expectancy [ 18 ].
The Nordic countries including Sweden, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Denmark, and three autonomous areas (Åland Islands, Greenland and Faroe Islands) share common elements of social and economic policies such as a comprehensive publicly financed health care system [ 18 , 19 ]. Additionally, these countries have a strong tradition of collaboration including a common vision of a socially sustainable region by promoting equal health and inclusive participation in society for older adults [ 20 ]. Therefore, more insight into the etiology, prevalence, and risk factors for sarcopenia and SO among older adults is a prerequisite for the development and implementation of effective strategies to prevent and treat these complex geriatric conditions in this geographic region. So, the aim of this study is to conduct a scoping review to systematically identify and map the available evidence while also addressing knowledge gaps and exploring the following research questions: (1) What are the prevalence of sarcopenia and SO in older adults living in the Nordic countries? (2) Which risk factors or contributing conditions are involved in the development of sarcopenia and SO in the Nordic Countries? (3) Which interventions to prevent or counteract negative health outcomes of sarcopenia and SO have been tested or implemented among older adults living in the Nordic countries?
Identification of relevant studies
The development and reporting of this review were done by following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [ 21 ].
The literature search was developed to target three main areas: Sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity, and aging (See Appendix 1 for full search strategy). All studies published before the end of February 2023 were included in this scoping review. The optimal sensitivity of search was obtained by simultaneous search of the following databases: PubMed, Embase, and Web of science (WOS). Additionally, a detailed search for grey literature was performed in relevant databases (e.g., Research Portal Denmark, Libris, Oria, Research.fi). Besides, reference lists of the included studies were reviewed to identify eligible studies. Duplicates and non-peer reviewed evidence (e.g., PhD thesis) were excluded but if the latter contained published articles of relevance, these were included. If more than one publication on similar outcomes (e.g., prevalence) were based on a single study, just one publication was included. Data were extracted from large studies with combined data from several countries only when findings were presented separately for the Nordic countries.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follow : Broad selection criteria were used to be comprehensive: (1) studies with any outcome (e.g., prevalence, risk factors, etc.) to address our research questions on sarcopenia and SO, (2) studies on subjects with age ≥ 60 years in any type of settings (e.g., community, nursing homes, general practice, hospital, outpatients, homecare, etc.), (3) studies using any definition of sarcopenia and SO without restriction for criteria and cutoff values, (4) all type of study designs (e.g., randomized control trials, cohort studies, cross-sectional, etc.), (5) studies should be conducted in the Nordic countries The exclusion criteria are as follow : (1) studies without relevant outcome to sarcopenia or SO, (2) studies without sufficient information to determine eligibility.
Study selection and data extraction
Two independent researchers screened literature and conducted data extraction. Any discrepancies between them were resolved through discussion.
First, duplicates were removed by using EndNote 20.6 software, then titles and abstracts were screened to narrow down the list of potentially eligible studies. Finally, the full text review was done to examine in detail the studies that were not excluded in first step. For more clarification, the reasons for the exclusion were recorded (Fig. 1 ).
PRISMA diagram for searching resources
The following information was extracted: (1) study characteristics (e.g., first author’s name, country, year of publication), (2) characteristics of the target population (e.g., age, sex), (3) study design, setting, intervention duration and follow-up time (if applicable), measurements, tools, criteria, and results.
Study selection
A combined total of 6,358 studies were identified through the initial electronic database and grey literature searches. An additional five articles were identified through other sources (citation searching). After removing duplication, 3,464 articles remained. A total of 3107 articles were excluded based on screening titles and abstracts. Out of the remaining 357 studies, 324 were excluded after the full-text review. Finally, 33 studies met our inclusion criteria and were included in this current scoping review [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ] (Fig. 1 ).
Study characteristics
Table 1 summarized characteristics of the included studies.
The number of documents showed an increasing trend between 2020 and 2021. A peak in the number of publications was observed in 2021 (24.2% of all documents). All the studies were conducted across four (Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finland) out of the five Nordic countries and three autonomous areas. The highest contribution in this field was made by Sweden ( n = 12).
Most studies were conducted in community-dwelling settings [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 35 , 36 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 42 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 54 ]. Seven studies included patients with acute diseases (hospital-setting) [ 26 , 27 , 33 , 37 , 50 , 51 , 52 ], while four studies included patients with chronic conditions (out-patient setting) [ 25 , 32 , 41 , 44 ], and one study including nursing-home residents [ 34 ]. In terms of study design, most of the studies were observation studies with a cross-sectional or longitudinal design ( 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ), while three studies [ 32 , 35 , 46 ] applied interventions. It appears, however, that one study [ 32 ] out of the above three interventions is sub-project conducted within the framework of larger intervention program. Sample size ranged from 49 in a cross-sectional case control study [ 52 ] to 3334 in a cohort study [ 30 ].
Five studies were among males only [ 22 , 24 , 36 , 45 , 53 ] and three studies included females only [ 38 , 47 , 54 ]. The rest of the studies had a mixed sample. Top subject area was sarcopenia (31 out of the 33 included studies), and on this subject, publications were categorized into the following research areas (with some studies addressing more areas): prevalence [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 29 , 30 , 33 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 40 , 42 , 44 , 45 , 47 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ], risk factors [ 24 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 38 , 40 , 42 , 44 , 47 , 49 , 50 , 51 ], and effectiveness of interventions on sarcopenia or indicator of sarcopenia [ 32 , 35 , 46 ].
In most studies sarcopenia was defined according to the criteria set by the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People in the updated version from 2019 (EWGSOP2) ( n = 15) or the original version from 2010 (EWGSOP) ( n = 14). However, in some studies multiple criteria such as EWGSOP, EWGSOP2, and National Institutes of Health Sarcopenia Project definition (FNIH) were applied [ 27 , 39 , 43 ], and in other studies alternative criteria were used [ 26 , 33 , 35 , 45 , 57 ].
Different assessment methods of muscle mass including Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) [ 22 , 24 , 25 , 27 , 29 , 30 , 32 , 33 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 52 , 53 , 54 ], Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) [ 28 , 31 , 34 , 44 , 48 , 49 ], Bioimpedance Spectroscopy (BIS) [ 35 , 42 , 43 ], Computed Tomography (CT) [ 33 ], and Computed Tomography Angiogram (CTA) [ 26 ] were used in the included studies.
SO were defined by the co-existence of sarcopenia with obesity. Studies on SO used the EWGSOP2 criteria [ 39 ], or the EWGSOP2 criteria for hand grip strength only (probable sarcopenia) [ 23 ] in combination with obesity estimated from BMI cut points [ 23 , 39 ], waist circumference [ 23 , 39 ], and fat mass percentage [ 39 ]. Lastly, one study used measures of body composition measures that reflect adiposity as estimates of SO [ 48 ].
Four studies reported the prevalence of “probable sarcopenia” [ 23 , 30 , 36 , 45 ], while two studies reported the prevalence of sarcopenia and comorbidities (e.g., osteopenia, pre-frailty, malnutrition) [ 33 , 40 ].
Narrative synthesis
Due to the heterogeneity of the studies in definition of sarcopenia, settings, and sample size, the overall reported prevalence was variable and ranged from 0.9% [ 54 ] to 58.5% [ 26 ]. However, according to the most commonly used criteria (EWGSOP2) the highest (46%) and lowest (1%) prevalence of sarcopenia was reported in Sweden among inpatients in geriatric care [ 27 ], and community-dwelling older adults [ 30 ], respectively.
Prevalence of sarcopenia according to population and definition criteria is illustrated in Table 2 . Higher prevalence rates of sarcopenia were found in females compared to males among community-dwelling older adults [ 49 ] and in older adults acutely admitted to hospital [ 51 ]. Further, acutely admitted female patients also presented with more severe sarcopenia compared to male patients [ 51 ].
Frequency of sarcopenia was higher (9.1–40.0%) in patients with diabetes (with and without complications of charcot osteoarthropathy), compared to age-matched healthy adults [ 52 ].
The prevalence of “probable sarcopenia” ranged between 20.4% (reduced muscle strength only) and 38.1% (fulfilling one of the following criteria: reduced muscle strength, reduced muscle mass, or low physical function) in Finnish community-dwelling adults [ 23 , 36 ], while longitudinal studies on Swedish community-dwelling old (70 years) and very old adults (≥ 85 years) the prevalence of “probable sarcopenia” (reduced muscle strength only) ranged from 1.8 to 73%, respectively [ 30 , 45 ]. Lastly, in a Swedish study among nursing home residents the prevalence of probable sarcopenia was 44% (evaluated by an impaired chair stand test) [ 34 ].
Prevalence of Osteosarcopenia (sarcopenia and osteoporosis) was 1.5% [ 36 ], and the prevalence of co-occurrence of all three following conditions: pre-frail, malnutrition, and sarcopenia was 7% [ 34 ].
We only identified two studies with prevalence of SO [ 39 ] and probable SO [ 23 ]. The prevalence of SO in a Swedish population was 4% and 11% in females and males, respectively, while the prevalence of probable SO among Finnish community-dwelling ranged between 5.8% and 12.6%, depending on the criteria to define the obesity (e.g., BMI, waist circumference, etc.) [ 23 ].
Several studies investigated aspects of etiology and risk factors for sarcopenia [ 24 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 36 , 38 , 40 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 47 , 49 , 50 , 51 ] and one study focused on SO [ 49 ]. Higher physical activity was associated with a decreased likelihood of sarcopenia [ 30 ]. In addition, adhering to world health organization (WHO) guidlines for physical activity and the Nordic nutritional recommendations for protein intake was positively associated with greater physical function and lower fat mass in older female community-dwellers [ 38 ]. In older adults who are physically active, eating a healthy diet (based on the frequency of intake of favorable food like fish, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains versus unfavorable foods like red/processed meats, desserts/sweets/sugar-sweetened beverages, and fried potatoes) was associated with lower risk of sarcopenia [ 28 ]. Further, among older adults who already meet the physical activity guidelines, additional engagement in muscle-strengthening activities was associated with a lower sarcopenia risk score and improved muscle mass and chair rise time [ 31 ].
Associations between sarcopenia, risk of sarcopenia and malnutrition or nutritional status was identified in geriatric patients [ 27 , 51 ], older patients with hip fracture [ 50 ], nursing home residents [ 34 ] and in community-dwelling older adults [ 49 ]. Moreover, the importance of nutritional intake was investigated in the following studies [ 24 , 36 , 47 ]. A study among community-dwelling men revealed an inverse association between total energy intake, protein intake (total, plant, and fish protein), intake of dietary fibers, fat (total and unsaturated), and vitamin D with sarcopenia status [ 36 ]. In a cohort of 71-year-old men a dietary pattern characterized by high consumption of fruit, vegetables, poultry, rice and pasta was associated with lower prevalence of sarcopenia after 16 years [ 24 ]. A longitudinal Finnish study on sarcopenia indices among postmenopausal older women, showed that lower adherence to the Mediterranean (focuses on high consumption of olive oil) or Baltic Sea (focuses on the dietary fat quality and low-fat milk intake) diets resulted in higher loss of lean mass over a 3-year period [ 47 ]. Further, a higher adherence to the Baltic Sea diet was associated with greater lean mass and better physical function, and higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with greater muscle quality [ 47 ].
In a study of patients with hip fracture age, polypharmacy, and low albumin levels was associated with sarcopenia [ 50 ]. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency was an independent risk factor for sarcopenia [ 44 ]. This study also revealed that sarcopenia was associated with reduced quality of life, physical function, and increased risk of hospitalization [ 44 ]. In a longitudinal study of community-dwelling adults (+ 75 years) at risk of sarcopenia, high physical function, muscle strength, muscle mass and low BMI predicted better physical function and reduced need for care after four years [ 42 ]. Furthermore, in community-dwelling adults with sarcopenia, muscle mass, muscle strength and physical function are independent predictors of all-cause mortality. As a result, they have been proposed by researchers as targets for the prevention of sarcopenia-related over-mortality [ 43 ]. Lastly, community-dwelling older adults with sarcopenia had lower bone mineral density compared to those without sarcopenia and they were more likely to develop osteoporosis (Osteosarcopenia) [ 40 ].
Regarding SO risk factors, a longitudinal study among community-dwelling older adults in Finland found that SO (operationalized by measures of adiposity) were associated with poorer physical function after ten years [ 48 ].
Our literature search identified three randomized controlled trials investigating the effectiveness of interventions to prevent or counteract sarcopenia in older adults of Norway, Finland, and Sweden, respectively [ 32 , 35 , 46 ]. The Norwegian study [ 32 ] was a double-blinded randomized controlled trial (RCT). The study included those who were at risk of developing sarcopenia, including patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or individuals who showed diagnostic indications of sarcopenia. Participants received either vitamin D 3 or placebo supplementation for 28 weeks. Additionally, resistance training sessions were provided to all participants from weeks 14 to 27. Vitamin D supplementation did not significantly affect response to resistance training in older adults at risk of sarcopenia with or without COPD [ 32 ].
Furthermore, a RCT among pre-sarcopenic Swedish older adults investigated the effectiveness of three weekly sessions of instructor-led progressive resistance training in combination with a non-mandatory daily nutritional supplement (175 kcal, 19 g protein) compared to control group. The 10 weeks intervention resulted in significant between group improvements of physical function and a significant improvement in body composition in the intervention group [ 46 ].
Another intervention study revealed that a 12-month intervention with two daily nutritional supplements (each containing 20 g whey protein) did not attenuate the deterioration of physical function and muscle mass in sarcopenic older community-dwelling adults compared to isocaloric placebo supplements or no supplementation. All participants were given instructions on home-based exercises, importance of dietary protein and vitamin D supplementation [ 35 ].
Based on our broad literature search 33 studies were identified that concerned sarcopenia and SO and met the inclusion criteria. However, research on SO was very limited with only three studies identified. Narrative synthesis of the included studies revealed that the most reported classification tool for sarcopenia in Nordic countries was the EWGSOP2. Moreover, some studies estimated sarcopenia using EWGSOP. The overall prevalence of sarcopenia in Nordic countries according to EWGSOP2 ranged between 1% and 46% [ 25 , 28 ]. The prevalence of SO, however, was reported only in one study in Sweden (4–11%) [ 39 ]. Even though the previous systematic reviews and meta-analysis have reported the prevalence of sarcopenia and SO in different regions and settings (e.g., community-dwelling, nursing home, etc.) [ 8 , 15 , 55 , 56 ], this current scoping review is to the best of our knowledge the first study that provides an overview of research on sarcopenia and SO in the Nordic countries.
Based on our findings from 24 studies, there were large variability in prevalence of sarcopenia in studies conducted in the Nordic countries. We think that the wide variation in estimated prevalence of sarcopenia in our scoping review might be due to a different definition/diagnostic criterion (e.g., EWGSOP, EWGSOP2, FNIH), methodology to measure muscle mass (DXA, BIA, CT), and heterogeneity in characteristics of the study population (e.g., setting, age, medical conditions, co-occurrence of multiple risk factors). A previous study on prevalence of sarcopenia in Swedish older people showed significant differences between prevalence of sarcopenia based on EWGSOP2 and EWGSOP1 [ 29 ]. Therefore, researchers stressed that prevalence is more dependent on cut-offs than on the operational definition [ 29 , 57 ]. Further, we know that various international sarcopenia working groups have issued expert consensus and such diagnostic criteria are being updated [ 4 , 58 ]. Since the revision of criteria focuses primarily on the adjustment of cut-off values, the main reason for differences in prevalence even when using an updated version of one diagnosis criteria is modification in cut-off values. For instance, if the cut-off value for gait speed was increased by 0.2 m/s, the prevalence of sarcopenia may increase by 8.5% [ 57 ]. Meaning that even a small change in cut-off value can have a big impact on how sarcopenia is diagnosed. Besides when we take definition criteria into account (Table 2 ), the prevalence of sarcopenia is still variable in the population of community-dwelling adults for instance. We believe it is basically because studies have applied different assessment tools and tests to identify older adults with low muscle mass and muscle strength, although using the same definition criteria (Table 1 ). Previous studies have illustrated that choice of methodology to assess muscle strength (e.g., hand grip strength, chair rise) [ 59 ] and muscle mass (e.g., DXA, BIA, anthropometry) [ 60 , 61 , 62 ] in older adults may impact findings and this variability may explain some of the variability in our findings. So, adherence to the latest uniform diagnostic criteria for future studies is recommended to simplify the comparison of findings within the same country, across countries, and regions. Moreover, we suggest that medical community particularly GPs to come to an agreement on assessment methods for muscle mass and muscle strength and the use of one set of definition criteria for sarcopenia.
In previous meta-analyses [ 15 ], sub-group analyses based on region and classification tool, revealed that the prevalence of sarcopenia was higher in European studies using EWGSOP (12%) compared to rest of the studies using Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia (AWGS), FNIH, and EWGSOP (3%) [ 15 ]. In our scoping review, we also found a high prevalence of sarcopenia in Nordic countries. Longevity and life expectancy is higher in the Nordic countries compared to estimates for rest of the world [ 18 ], which means that in this region many people reach old age, and consequently they are more likely to be diagnosed with sarcopenia as an age-related disorder. Therefore, the authors of this current scoping review emphasis the importance of preventive strategies targeted major risk factors and effective interventions to limit the consequences of sarcopenia in the Nordic populations. Besides, we think that the health care system in the Nordic countries should be better equipped with the necessary healthcare resources for both a timely diagnosis and dealing with this major age-related issue in the years to come. However, due to the limitations regarding the timely diagnosis, we highly recommend a comprehensive approach including establishment of support services, implement educational programs, offer training for health care professionals, and engage the community.
Many countries have conducted research on SO [ 7 , 39 , 63 , 64 , 65 ]. Based on our findings, however, among the Nordic countries only Sweden and Finland have investigated the prevalence of probable SO and SO [ 23 , 29 ]. Besides, we only found one study investigating the association between body adiposity and physical function over time [ 54 ]. We did not find any literature on risk factors or interventions among older adults with SO in this region. Therefore, we call on medical and research community in Nordic countries to attach importance to screening of SO in elderly people to capture a full picture of this public health risk to aging society and allocate healthcare resources accordingly.
In terms of risk factors for sarcopenia, our study revealed that malnutrition, low levels of physical activity, specific diseases (e.g., diabetes, osteoporosis), inflammation, polypharmacy (multiple medicines), BMI, and ageing are potential risk factor for sarcopenia in populations of the Nordic region. However, evidence on risk factors derived mainly from cross-sectional associations [ 27 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 40 , 44 , 49 , 50 , 51 ], and only to a limited extend from longitudinal studies [ 24 , 38 , 43 , 47 ]. Therefore, the associations between risk factors and sarcopenia should be interpreted with caution due to the possibility of reverse causality and confounding affecting the results. Moreover, our findings on risk factors mainly came from community-dwelling older adults, and only to a limited extend hospital and nursing home settings. We think that risk factors may vary depending on population characteristics (e.g., age, sex, health condition) and setting (e.g., hospital, nursing home, community). Therefore, we encourage researchers of the Nordic countries to perform well-designed prospective cohort studies in different settings to enhance the possibility to establish causal inference as well as understanding degree and direction of changes over time.
A recently published meta-analyses revealed a higher risk of having polypharmacy in Europe among individuals with sarcopenia compared to people without this condition [ 66 ]. A nationwide register-based study in Swedish population also showed that the prevalence of polypharmacy has increased in Sweden over the last decade [ 67 ]. Sarcopenia itself is associated with morbidity (identified by specific disease or inflammatory markers) and different health-related outcomes (e.g., disability) [ 7 ]; therefore, future research should investigate whether polypharmacy is a major factor to sarcopenia development [ 66 ]. Although we lack information on polypharmacy in Nordic countries other than Sweden, we encourage researchers in this region to examine the above research gap in their future studies.
According to previous studies physiological changes in ageing include systemic low-grade inflammation which results in insulin resistance, affect protein metabolism and leads to increased muscle wasting [ 68 ]. Acute and chronic disease may increase the inflammatory response and accelerate age-related loss of muscle mass and increase risk of sarcopenia [ 68 , 69 ]. Hence, we think that special attention should be made by health care professionals particularly GPs to older adults with acute or chronic conditions to limit the risk of sarcopenia.
Literature from the Nordic countries also indicated that higher levels of physical activity and different dietary patterns (e.g., higher protein intake, fruit, vegetables, fibers) were associated with reduced risk of sarcopenia or improvement in indicators of sarcopenia. There was a large heterogeneity in the studied aspect which makes direct comparison of studies difficult. Nevertheless, according to findings from a recent systematic review of meta-analyses on sarcopenia the identified risk factors are in alignment with previously identified risk factors globally [ 70 ]. Other potential lifestyle-related risk factors suggested from the above meta-analysis included smoking and extreme sleep duration. However, we did not identify studies investigating these health behaviors in the Nordic populations. Therefore, high-quality cohort studies are needed to deeply understand such associations with the risk of sarcopenia.
In this current review, we only found three intervention studies in Nordic countries. However, two of them were sub-projects of big intervention programs, meaning that such studies were not designed explicitly for the prevention/treatment of sarcopenia. Therefore, explicit intervention studies on sarcopenia in this region is recommended.
We believe that on a global level, research on sarcopenia will carry on with nutrition, exercise, and understanding of molecular mechanisms. Furthermore, examining the link between sarcopenia and other medical conditions/diseases would be the next step [ 6 ]. In the Nordic countries, however, already performed studies have a basic and descriptive design, so that, well-designed research and advanced analyses are lacking. Hence, we recommend conducting large well-designed and adequately powered studies to (a) explore the scale of this age-related health issue on country and regional level, (b) investigate the patterns of physical activity and sedentary behavior to understand if this should be a target in older adults with SO and sarcopenia, (c) determine whether elderly populations are suffering from nutritional deficiency or are at risk of malnutrition. The latest can support further studies to assess the impact of combined physical activity and dietary intake, which are still lacking globally [ 6 ].
A previous systematic review on therapeutic strategies for SO revealed that exercise-based interventions (e.g., resistance training) reduced total adiposity and consequently improved body composition. However, evidence of other therapeutic strategies (e.g., nutritional supplementation) was limited due to scarcity of data and lack of unique definition for SO [ 69 ]. Therefore, authors suggested that more research should be done to clarify optimal treatment options for various age-groups and not only for older adults [ 14 ].
In our scoping review, the included studies, did not provide a status of either SO or the prevention/treatment methods in this region. We believe that SO is practically neglected in clinical practice and research as well, and this is mainly because it is difficult to separate it from general obesity. The consequence of lacking knowledge in this research area is that when older adults with SO are recommended weight loss- a frequently used strategy for management of general obesity- this may accelerate the loss of muscle mass and increase the severity of the sarcopenia [ 3 ]. Consequently, we think that this issue may have adverse effects both on patients (e.g., decreasing quality of their life) and on the health care system (e.g., increasing the health care demands) of this region. Therefore, we encourage researchers to perform cohort studies to understand the epidemiology and etiological basis of SO, which are poorly understood even on a global scale [ 8 ]. We think that the consensus definition on SO from the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) and European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) which was published in 2022 [ 3 ], can positively affect the ability to define studies on prevalence and prevention of SO. Besides, we recommend conducting further research to find the optimal treatment for SO and reduce its adverse consequences both at individual and society levels. Additionally, we think that the concepts of sarcopenia and SO might be somehow unfamiliar to health care personnel. Therefore, it is highly recommended that more information be provided to bring their attention to the significance of prevention, timely diagnosis, and treatment of these two aging disorders.
Strengths and limitations of the study
This is the first study providing an overview of available evidence on sarcopenia and SO among older adults in the Nordic countries. These countries have important similarities in welfare sectors and on a population level and we believe that our findings will be a significant benefit for researchers and health care providers to understand the knowledge gaps and plan for future studies in this geographical region. However, the current scoping review has limitations. This review was limited to studies among individuals more than 60 years old which may limit the overview of available research in this field, as well as understanding risk factors, confounders for prevention, and the potential for early detection of these two diseases in younger age population. The included cross-sectional studies in our review cannot provide information on causality of the associations.
Sarcopenia and SO are generally prevalent syndromes among older adults in Nordic countries, even though the prevalence of them varies according to the criteria for definition, population, and setting. Research among older adults with SO was very limited in this region. Besides, studies on risk factors were primarily cross-sectional and only few intervention studies were identified. Therefore, we encourage researchers performing well-designed studies (e.g., prospective cohorts) to understand the epidemiology and etiological basis of these two age-related disorders. For the next step, implementation of interventions targeting risk factors (e.g., combined physical activity and dietary intake) and evaluating of their impact on prevention or treatment of sarcopenia and SO is recommended. Furthermore, for the comprehensive advancement of muscle health in older adults, we recommend implementing interventions directed at health care personnel and encouraging more collaboration among clinicians, professional societies, researchers, and policy makers to ensure comprehensive and effective approach to health care initiatives.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
sarcopenic obesity
Web of science
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses
European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People in the updated version from 2019
National Institutes of Health Sarcopenia Project definition
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
Bioimpedance Spectroscopy
Computed Tomography
Computed Tomography Angiogram
World Health Organization
General Practitioner
Randomized Controlled Trial
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
European Association for the Study of Obesity
United, Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs., Population Division (2019). World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/423).
United, Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs., Population Division (2019). World Population Ageing 2019: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/430).
Donini LM, Busetto L, Bischoff SC, Cederholm T, Ballesteros-Pomar MD, Batsis JA, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Dicker D, Frara S, Frühbeck G, Genton L, Gepner Y, Giustina A, Gonzalez MC, Han HS, Heymsfield SB, Higashiguchi T, Laviano A, Lenzi A, Nyulasi I, Parrinello E, Poggiogalle E, Prado CM, Salvador J, Rolland Y, Santini F, Serlie MJ, Shi H, Sieber CC, Siervo M, Vettor R, Villareal DT, Volkert D, Yu J, Zamboni M, Barazzoni R. Definition and diagnostic criteria for sarcopenic obesity: ESPEN and EASO Consensus Statement. Obes Facts. 2022;15(3):321–35. doi: 10.1159/000521241. Epub 2022 Feb 23. PMID: 35196654; PMCID: PMC9210010.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, Cooper C, Landi F, Rolland Y, Sayer AA, Schneider SM, Sieber CC, Topinkova E, Vandewoude M, Visser M, Zamboni M, Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16–31. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afy169 . Erratum in: Age Ageing. 2019;48(4):601. PMID: 30312372; PMCID: PMC6322506.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Cylus J, Figueras J, Normand C. Will population ageing spell the end of the welfare state? A review of evidence and policy options [Internet]. Sagan A, Richardson E, North J, White C, editors. Copenhagen (Denmark): European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies; 2019. PMID: 31820887.
Yuan D, Jin H, Liu Q, Zhang J, Ma B, Xiao W, Li Y. Publication trends for Sarcopenia in the World: a 20-Year bibliometric analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:802651. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.802651 . PMID: 35223902; PMCID: PMC8873525.
Marengoni A, Angleman S, Melis R, Mangialasche F, Karp A, Garmen A, Meinow B, Fratiglioni L. Aging with multimorbidity: a systematic review of the literature. Ageing Res Rev. 2011;10(4):430–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2011.03.003 . Epub 2011 Mar 23. PMID: 21402176.
Gao Q, Mei F, Shang Y, Hu K, Chen F, Zhao L, Ma B. Global prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2021;40(7):4633–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2021.06.009 . Epub 2021 Jun 21. PMID: 34229269.
Molino S, Dossena M, Buonocore D, Verri M. Sarcopenic obesity: an appraisal of the current status of knowledge and management in elderly people. J Nutr Health Aging. 2016;20(7):780-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-015-0631-8 . PMID: 27499312.
Khadra D, Itani L, Tannir H, Kreidieh D, El Masri D, El Ghoch M. Association between sarcopenic obesity and higher risk of type 2 diabetes in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Diabetes. 2019;10(5):311–23. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v10.i5.311 . PMID: 31139318; PMCID: PMC6522758.
Aggio DA, Sartini C, Papacosta O, Lennon LT, Ash S, Whincup PH, Wannamethee SG, Jefferis BJ. Cross-sectional associations of objectively measured physical activity and sedentary time with Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in older men. Prev Med. 2016;91:264–72. Epub 2016 Aug 26. PMID: 27575317; PMCID: PMC5061552.
Rossi AP, Rubele S, Calugi S, Caliari C, Pedelini F, Soave F, Chignola E, Vittoria Bazzani P, Mazzali G, Dalle Grave R, Zamboni M. Weight cycling as a risk factor for low muscle mass and strength in a population of males and females with obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019;27(7):1068–1075. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22493 . PMID: 31231958.
Dent E, Morley JE, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Arai H, Kritchevsky SB, Guralnik J, Bauer JM, Pahor M, Clark BC, Cesari M, Ruiz J, Sieber CC, Aubertin-Leheudre M, Waters DL, Visvanathan R, Landi F, Villareal DT, Fielding R, Won CW, Theou O, Martin FC, Dong B, Woo J, Flicker L, Ferrucci L, Merchant RA, Cao L, Cederholm T, Ribeiro SML, Rodríguez-Mañas L, Anker SD, Lundy J, Gutiérrez Robledo LM, Bautmans I, Aprahamian I, Schols JMGA, Izquierdo M, Vellas B. International clinical practice guidelines for sarcopenia (ICFSR): screening, diagnosis and management. J Nutr Health Aging. 2018;22(10):1148–1161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-018-1139-9 . PMID: 30498820.
Poggiogalle E, Parrinello E, Barazzoni R, Busetto L, Donini LM. Therapeutic strategies for sarcopenic obesity: a systematic review. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2021;24(1):33–41. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000714 . PMID: 33323715.
Petermann-Rocha F, Balntzi V, Gray SR, Lara J, Ho FK, Pell JP, Celis-Morales C. Global prevalence of Sarcopenia and severe Sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1):86–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12783 . Epub 2021 Nov 23. PMID: 34816624; PMCID: PMC8818604.
Prado CM, Wells JC, Smith SR, Stephan BC, Siervo M. Sarcopenic obesity: a critical appraisal of the current evidence. Clin Nutr. 2012;31(5):583–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2012.06.010 . Epub 2012 Jul 17. PMID: 22809635.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Balaj M, Huijts T, McNamara CL, Stornes P, Bambra C, Eikemo TA. Non-communicable diseases and the social determinants of health in the nordic countries: findings from the European Social Survey (2014) special module on the social determinants of health. Scand J Public Health. 2017;45(2):90–102. Epub 2017 Jan 27. PMID: 28128015.
Nordic Burden of Disease Collaborators. Life expectancy and disease burden in the Nordic countries: results from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2017. Lancet Public Health. 2019;4(12): e658-e669. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30224-5. Epub 2019 Nov 20. PMID: 31759894; PMCID: PMC7098475.
Stockmarr A, Hejgaard T, Matthiessen J. Obesity prevention in the Nordic Countries. Curr Obes Rep. 2016;5(2):156 – 65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-016-0206-y . PMID: 27033877.
Cuadrado A, Stjernberg M, Huynh D. Active and healthy ageing: heterogenous perspectives and nordic indicators. Nordens välfärdscenter/Nordic Welfare Centre; 2022.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336 – 41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007 . Epub 2010 Feb 18. Erratum in: Int J Surg. 2010;8(8):658. PMID: 20171303.
Sallfeldt ES, Mallmin H, Karlsson MK, Mellström D, Hailer NP, Ribom EL. Sarcopenia prevalence and incidence in older men - a MrOs Sweden study. Geriatr Nurs. 2023 Mar-Apr;50:102–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2023.01.003 . Epub 2023 Feb 10. PMID: 36774676.
Sääksjärvi K, Härkänen T, Stenholm S, Schaap L, Lundqvist A, Koskinen S, Borodulin K, Visser M. Probable Sarcopenia, obesity, and risk of all-cause mortality: a pooled analysis of 4,612 participants. Gerontology. 2023;69(6):706–15. Epub 2023 Jan 30. PMID: 36716714.
Karlsson M, Becker W, Cederholm TE, Byberg L. A posteriori dietary patterns in 71-year-old Swedish men and the prevalence of Sarcopenia 16 years later. Br J Nutr Camb Univ Press. 2022;128(5):909–20. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521003901 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Dolin TG, Mikkelsen MK, Jakobsen HL, Vinther A, Zerahn B, Nielsen DL, Johansen JS, Lund CM, Suetta C. The prevalence of Sarcopenia and cachexia in older patients with localized colorectal cancer. J Geriatr Oncol. 2023;14(1):101402. Epub 2022 Nov 21. PMID: 36424269.
Paajanen P, Lindström I, Oksala N, Väärämäki S, Saari P, Mäkinen K, Kärkkäinen JM. Radiographically quantified Sarcopenia and traditional cardiovascular risk assessment in predicting long-term mortality after endovascular aortic repair. J Vasc Surg. 2022;76(4):908–e9152. Epub 2022 Mar 31. PMID: 35367563.
Sobestiansky S, Åberg AC, Cederholm T. Sarcopenia and malnutrition in relation to mortality in hospitalised patients in geriatric care - predictive validity of updated diagnoses. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021;45:442–8. Epub 2021 Jul 16. PMID: 34620352.
Papaioannou KG, Nilsson A, Nilsson LM, Kadi F. Healthy eating is Associated with Sarcopenia Risk in physically active older adults. Nutrients. 2021;13(8):2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082813 . PMID: 34444973; PMCID: PMC8401667.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wallengren O, Bosaeus I, Frändin K, Lissner L, Falk Erhag H, Wetterberg H, Rydberg Sterner T, Rydén L, Rothenberg E, Skoog I. Comparison of the 2010 and 2019 diagnostic criteria for Sarcopenia by the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older people (EWGSOP) in two cohorts of Swedish older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):600. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-021-02533-y . PMID: 34702174; PMCID: PMC8547086.
Scott D, Johansson J, Gandham A, Ebeling PR, Nordstrom P, Nordstrom A. Associations of accelerometer-determined physical activity and sedentary behavior with Sarcopenia and incident falls over 12 months in community-dwelling Swedish older adults. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;10(5):577–84. Epub 2020 Feb 5. PMID: 34088651; PMCID: PMC8500807.
Veen J, Montiel-Rojas D, Nilsson A, Kadi F. Engagement in muscle-strengthening activities lowers Sarcopenia Risk in older adults already adhering to the Aerobic Physical Activity guidelines. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(3):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030989 . PMID: 33499423; PMCID: PMC7908493.
Mølmen KS, Hammarström D, Pedersen K, Lian Lie AC, Steile RB, Nygaard H, Khan Y, Hamarsland H, Koll L, Hanestadhaugen M, Eriksen AL, Grindaker E, Whist JE, Buck D, Ahmad R, Strand TA, Rønnestad BR, Ellefsen S. Vitamin D3 supplementation does not enhance the effects of resistance training in older adults. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(3):599–628. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12688 . Epub 2021 Mar 31. PMID: 33788419; PMCID: PMC8200443.
Simonsen C, Kristensen TS, Sundberg A, Wielsøe S, Christensen J, Hansen CP, Burgdorf SK, Suetta C, de Heer P, Svendsen LB, Achiam MP, Christensen JF. Assessment of Sarcopenia in patients with upper gastrointestinal tumors: prevalence and agreement between computed tomography and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Clin Nutr. 2021;40(5):2809–16. Epub 2021 Mar 26. PMID: 33933747.
Faxén-Irving G, Luiking Y, Grönstedt H, Franzén E, Seiger Å, Vikström S, Wimo A, Boström AM, Cederholm T. Do malnutrition, sarcopenia and frailty overlap in nursing-home residents? J Frailty Aging. 2021;10(1):17–21. https://doi.org/10.14283/jfa.2020.45 . PMID: 33331617.
Björkman MP, Suominen MH, Kautiainen H, Jyväkorpi SK, Finne-Soveri HU, Strandberg TE, Pitkälä KH, Tilvis RS. Effect of protein supplementation on physical performance in older people with sarcopenia-a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(2):226–e2321. Epub 2019 Nov 14. PMID: 31734121.
Jyväkorpi SK, Urtamo A, Kivimäki M, Strandberg TE. Macronutrient composition and sarcopenia in the oldest-old men: the Helsinki businessmen study (HBS). Clin Nutr. 2020;39(12):3839–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2020.04.024 . Epub 2020 Apr 24. PMID: 32376097.
Probert N, Lööw A, Akner G, Wretenberg P, Andersson ÅG. A comparison of patients with hip fracture, ten years apart: morbidity, malnutrition and sarcopenia. J Nutr Health Aging. 2020;24(8):870–877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-020-1408-2 . PMID: 33009538.
Sjöblom S, Sirola J, Rikkonen T, Erkkilä AT, Kröger H, Qazi SL, Isanejad M. Interaction of recommended levels of physical activity and protein intake is associated with greater physical function and lower fat mass in older women: Kuopio osteoporosis risk Factor- (OSTPRE) and fracture-Prevention Study. Br J Nutr. 2020;123(7):826–39. Epub 2020 Jan 8. PMID: 31910914; PMCID: PMC7054249.
von Berens Å, Obling SR, Nydahl M, Koochek A, Lissner L, Skoog I, Frändin K, Skoglund E, Rothenberg E, Cederholm T. Sarcopenic obesity and associations with mortality in older women and men - a prospective observational study. BMC Geriatr. 2020;20(1):199. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-020-01578-9 . PMID: 32517653; PMCID: PMC7285448.
Nielsen BR, Andersen HE, Haddock B, Hovind P, Schwarz P, Suetta C. Prevalence of muscle dysfunction concomitant with osteoporosis in a home-dwelling Danish population aged 65–93 years -the Copenhagen Sarcopenia Study. Exp Gerontol. 2020;138:110974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2020.110974 . Epub 2020 May 25. PMID: 32464171.
Van Ancum JM, Alcazar J, Meskers CGM, Nielsen BR, Suetta C, Maier AB. Impact of using the updated EWGSOP2 definition in diagnosing Sarcopenia: a clinical perspective. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2020 Sep-Oct;90:104125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2020.104125 . Epub 2020 May 23. PMID: 32534364.
Björkman M, Jyväkorpi SK, Strandberg TE, Pitkälä KH, Tilvis RS. Sarcopenia indicators as predictors of functional decline and need for care among older people. J Nutr Health Aging. 2019;23(10):916–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-019-1280-0 . PMID: 31781719.
Björkman MP, Pitkala KH, Jyväkorpi S, Strandberg TE, Tilvis RS. Bioimpedance analysis and physical functioning as mortality indicators among older sarcopenic people. Exp Gerontol. 2019;122:42–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2019.04.012 . Epub 2019 Apr 24. PMID: 31026498.
Olesen SS, Büyükuslu A, Køhler M, Rasmussen HH, Drewes AM. Sarcopenia associates with increased hospitalization rates and reduced survival in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2019;19(2):245–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2019.01.006 . Epub 2019 Jan 14. PMID: 30665702.
Sobestiansky S, Michaelsson K, Cederholm T. Sarcopenia prevalence and associations with mortality and hospitalisation by various sarcopenia definitions in 85–89 year old community-dwelling men: a report from the ULSAM study. BMC Geriatr. 2019;19(1):318. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-019-1338-1 . PMID: 31747923; PMCID: PMC6864927.
Vikberg S, Sörlén N, Brandén L, Johansson J, Nordström A, Hult A, Nordström P. Effects of resistance training on functional strength and muscle mass in 70-Year-old individuals with pre-sarcopenia: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019;20(1):28–34. Epub 2018 Nov 7. PMID: 30414822.
Isanejad M, Sirola J, Mursu J, Rikkonen T, Kröger H, Tuppurainen M, Erkkilä AT. Association of the baltic sea and mediterranean diets with indices of sarcopenia in elderly women, OSPTRE-FPS study. Eur J Nutr. 2018;57(4):1435–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1422-2 . Epub 2017 Mar 16. PMID: 28303397.
Mikkola TM, von Bonsdorff MB, Salonen MK, Simonen M, Pohjolainen P, Osmond C, Perälä MM, Rantanen T, Kajantie E, Eriksson JG. Body composition as a predictor of physical performance in older age: a ten-year follow-up of the Helsinki Birth Cohort Study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2018 Jul-Aug;77:163–8. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2018.05.009. Epub 2018 May 14. PMID: 29783137; PMCID: PMC5994345.
Ottestad I, Ulven SM, Øyri LKL, Sandvei KS, Gjevestad GO, Bye A, Sheikh NA, Biong AS, Andersen LF, Holven KB. Reduced plasma concentration of branched-chain amino acids in sarcopenic older subjects: a cross-sectional study. Br J Nutr. 2018;120(4):445–53. Epub 2018 Jun 18. PMID: 29909813.
Steihaug OM, Gjesdal CG, Bogen B, Kristoffersen MH, Lien G, Ranhoff AH. Sarcopenia in patients with hip fracture: a multicenter cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(9):e0184780. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184780 . PMID: 28902873; PMCID: PMC5597226.
Jacobsen EL, Brovold T, Bergland A, Bye A. Prevalence of factors associated with malnutrition among acute geriatric patients in Norway: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2016;6(9):e011512. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011512 . PMID: 27601491; PMCID: PMC5020767.
Jansen RB, Christensen TM, Bülow J, Rørdam L, Holstein PE, Svendsen OL. Sarcopenia and body composition in diabetic Charcot osteoarthropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 2015 Sep-Oct;29(7):937–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.05.020 . Epub 2015 Jun 5. PMID: 26139557.
Frost M, Nielsen TL, Brixen K, Andersen M. Peak muscle mass in young men and Sarcopenia in the ageing male. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(2):749–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-014-2960-6 . Epub 2014 Nov 22. PMID: 25416073.
Patil R, Uusi-Rasi K, Pasanen M, Kannus P, Karinkanta S, Sievänen H. Sarcopenia and osteopenia among 70-80-year-old home-dwelling finnish women: prevalence and association with functional performance. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(3):787–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-012-2046-2 . Epub 2012 Jun 12. PMID: 22688541.
Papadopoulou SK, Tsintavis P, Potsaki P, Papandreou D. Differences in the prevalence of sarcopenia in community-dwelling, nursing home and hospitalized individuals. a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nutr Health Aging. 2020;24(1):83–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-019-1267-x . PMID: 31886813.
Mayhew AJ, Amog K, Phillips S, Parise G, McNicholas PD, de Souza RJ, Thabane L, Raina P. The prevalence of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults, an exploration of differences between studies and within definitions: a systematic review and meta-analyses. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):48–56. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afy106 . PMID: 30052707.
Cao M, Lian J, Lin X, Liu J, Chen C, Xu S, Ma S, Wang F, Zhang N, Qi X, Xu G, Peng N. Prevalence of Sarcopenia under different diagnostic criteria and the changes in muscle mass, muscle strength, and physical function with age in Chinese old adults. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22(1):889. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-022-03601-7 . PMID: 36418979; PMCID: PMC9682713.
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y, Schneider SM, Topinková E, Vandewoude M, Zamboni M, European working group on sarcopenia in older people. sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: report of the European working group on sarcopenia in older people. Age Ageing. 2010;39(4):412–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afq034 . Epub 2010 Apr 13. PMID: 20392703; PMCID: PMC2886201.
Verstraeten LMG, de Haan NJ, Verbeet E, van Wijngaarden JP, Meskers CGM, Maier AB. Handgrip strength rather than chair stand test should be used to diagnose s in geriatric rehabilitation inpatients: restoring health of acutely unwell adulTs (RESORT). Age Ageing. 2022;51(11):afac242. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afac242 . PMID: 36413590; PMCID: PMC9681126.
Cheng KY, Chow SK, Hung VW, Wong CH, Wong RM, Tsang CS, Kwok T, Cheung WH. Diagnosis of sarcopenia by evaluating skeletal muscle mass by adjusted bioimpedance analysis validated with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(6):2163–73. Epub 2021 Oct 4. PMID: 34609065; PMCID: PMC8718029.
Sousa-Santos AR, Barros D, Montanha TL, Carvalho J, Amaral TF. Which is the best alternative to estimate muscle mass for sarcopenia diagnosis when DXA is unavailable? Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2021 Nov-Dec;97:104517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2021.104517 . Epub 2021 Sep 3. PMID: 34547538.
González Correa CH, Marulanda Mejía F, Castaño González PA, Vidarte Claros JA, Castiblanco Arroyabe HD. Bioelectrical impedance analysis and dual x-ray absorptiometry agreement for skeletal muscle mass index evaluation in sarcopenia diagnosis. Physiol Meas. 2020;41(6):064005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6579/ab8e5f . PMID: 32348971.
Hwang B, Lim JY, Lee J, Choi NK, Ahn YO, Park BJ. Prevalence rate and associated factors of sarcopenic obesity in Korean elderly population. J Korean Med Sci. 2012;27(7):748–55. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.7.748 . Epub 2012 Jun 29. PMID: 22787369; PMCID: PMC3390722.
Kera T, Kawai H, Hirano H, Kojima M, Fujiwara Y, Ihara K, Obuchi S. Differences in body composition and physical function related to pure Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity: a study of community-dwelling older adults in Japan. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2017;17(12):2602–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.13119 . Epub 2017 Jun 28. PMID: 28657168.
Aibar-Almazán A, Martínez-Amat A, Cruz-Díaz D, Jiménez-García JD, Achalandabaso A, Sánchez-Montesinos I, de la Torre-Cruz M, Hita-Contreras F. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in Spanish community-dwelling middle-aged and older women: Association with balance confidence, fear of falling and fall risk. Maturitas. 2018;107:26–32. Epub 2017 Oct 7. PMID: 29169576.
Prokopidis K, Giannos P, Reginster JY, Bruyere O, Petrovic M, Cherubini A, Triantafyllidis KK, Kechagias KS, Dionyssiotis Y, Cesari M, Ibrahim K, Scott D, Barbagallo M, Veronese N, the Task Force on Pharmaceutical Strategy of the European Geriatric Medicine Society (EuGMS). Special interest group in Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses and sarcopenia is associated with a greater risk of polypharmacy and number of medications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023;14(2):671–683. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.13190 . Epub 2023 Feb 13. PMID: 36781175; PMCID: PMC10067503.
Zhang N, Sundquist J, Sundquist K, Ji J. An increasing Trend in the prevalence of polypharmacy in Sweden: a nationwide register-based study. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:326. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00326 . PMID: 32265705; PMCID: PMC7103636.
Dalle S, Rossmeislova L, Koppo K. The role of inflammation in age-related sarcopenia. Front Physiol. 2017;8:1045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.01045 . PMID: 29311975; PMCID: PMC5733049.
Riuzzi F, Sorci G, Arcuri C, Giambanco I, Bellezza I, Minelli A, Donato R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of sarcopenia: the S100B perspective. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018;9(7):1255–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12363 . Epub 2018 Nov 30. PMID: 30499235; PMCID: PMC6351675.
Yuan S, Larsson SC. Epidemiology of sarcopenia: prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metabolism. 2023;144:155533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155533 . Epub 2023 Mar 11. PMID: 36907247.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Open access funding provided by University of Southern Denmark
This work was done without any fund.
Author information
Fereshteh Baygi, Sussi Friis Buhl contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Research Unit of General Practice, Department of Public Health, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark
Fereshteh Baygi, Sussi Friis Buhl, Trine Thilsing, Jens Søndergaard & Jesper Bo Nielsen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
FB conceived and designed the review, participated in literature review, data extraction, interpretation of the results and wrote the manuscript. SFB designed the review, participated in literature review, data extraction, and revised the manuscript. TT, JBN and JS contributed to the conception of the study and revised the manuscript critically. All the authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Fereshteh Baygi or Sussi Friis Buhl .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Baygi, F., Buhl, S.F., Thilsing, T. et al. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity among older adults in the nordic countries: a scoping review. BMC Geriatr 24 , 421 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-024-04970-x
Download citation
Received : 12 November 2023
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-024-04970-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Sarcopenic obesity
- Nordic countries
BMC Geriatrics
ISSN: 1471-2318
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Obesity — Obesity in America
Obesity in America
- Categories: Childhood Obesity Obesity
About this sample

Words: 704 |
Published: Jan 30, 2024
Words: 704 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, historical context and causes of obesity, health impacts of obesity, economic and social impacts of obesity, government policies and interventions, role of education and media in addressing obesity.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, June 29). Adult Obesity Facts. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html
- Alpert, J. (2018, July 18). The Policy and Politics of Obesity Prevention. Health Affairs. https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/hblog20180712.613083/full/
- Swinburn, B. A., Sacks, G., Hall, K. D., McPherson, K., Finegood, D. T., Moodie, M. L., & Gortmaker, S. L. (2011). The global obesity pandemic: shaped by global drivers and local environments. The Lancet, 378(9793), 804-814. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60813-1
- Cohen, D. A., & Babey, S. H. (2012). Contextual influences on eating behaviours: heuristic processing and dietary choices. Obesity Reviews, 13(9), 766-779. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2012.01001.x

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 476 words
5 pages / 2799 words
1 pages / 619 words
13 pages / 5869 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Obesity
People’s sense of security, health, social engagement and overall wellbeing are generally affected by where they live (Linda, 2015). A-2018 report, titled: “Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic”, by World Health [...]
According to the World Health Organization, in 2016, more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight, of which around 650 million were obese. In the United States alone, more than 42% of the population is considered obese. This [...]
Adams, C. (2007). Reframing the obesity debate: McDonald’s role may surprise you. Journal of Law, Medicine, and Ethics, 35, 154-157.
Obesity has become a major health issue in recent times, with over 39% of adults around the world being overweight and 13% being obese. In the United States, 42.4% of adults are obese, costing the country a staggering $147 [...]
“What if a war on obesity only makes the problem worse”? argues Author Daniel Engber in his article “Glutton Intolerance”. Discrimination against the obese in our society makes the obesity problem worse. The treatment against [...]
It is well known today that the obesity epidemic is claiming more and more victims each day. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention writes “that nearly 1 in 5 school age children and young people (6 to 19 years) in the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Obesity has become a global epidemic and is one of today's most public health problems worldwide. Obesity poses a major risk for a variety of serious diseases including diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic liver disease (NAFLD), cardiovascular disease, hypertension and stroke, and certain forms of cancer (Bluher, 2019).Obesity is mainly caused by imbalanced energy intake and expenditure due to a ...
Despite public health efforts, these disorders are on the rise, and their consequences are burgeoning. 1 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that during 2017 to 2018, the prevalence of obesity in the United States was 42.4%, which was increased from the prevalence of 30.5% during 1999 to 2002. 2 Among those afflicted with ...
Worldwide adult obesity has more than doubled since 1990, and adolescent obesity has quadrupled. In 2022, 2.5 billion adults (18 years and older) were overweight. Of these, 890 million were living with obesity. In 2022, 43% of adults aged 18 years and over were overweight and 16% were living with obesity. In 2022, 37 million children under the ...
Besides health complications, obesity causes an array of psychological effects, including inferiority complex among victims. Obese people suffer from depression, emanating from negative self-esteem and societal rejection. In some cases, people who become obese lose their friends and may get disapproval from teachers and other personalities ...
Obesity is a complex disease that occurs when an individual's weight is higher than what is considered healthy for his or her height. Obesity affects children as well as adults. Many factors can contribute to excess weight gain including eating patterns, physical activity levels, and sleep routines. Social determinants of health, genetics ...
Obesity prevalence among children is >30% in the Cook Islands, Nauru and Palau, with a notable increase over the past few decades. Worldwide prevalence of obesity increased at an alarming rate in ...
Background. There has been a significant global increase in obesity rate during the last 50 years. Obesity is defined as when a person has a body mass index [BMI (kg/m 2), dividing a person's weight by the square of their height] greater than or equal to 30, overweight is defined as a BMI of 25.0-29.9.Being overweight or obesity is linked with more deaths than being underweight and is a more ...
Conclusion. In conclusion, obesity is a complex issue with multiple causes and significant effects on individuals and society. Poor dietary habits, sedentary lifestyles, and genetic factors contribute to its prevalence. The health consequences, economic costs, and social and psychological effects of obesity are profound and demand attention.
Some genetic and lifestyle factors affect an individual's likelihood of adult obesity; thus, the significant clusters of obesity observed in specific geographical regions and contexts also signal the impact of socioeconomic and environmental factors in "obesogenic" environments [13].Understanding the causes and determinants of obesity is a critical step toward creating effective policy and ...
Obesity is a complex condition that interweaves biological, developmental, environmental, behavioral, and genetic factors; it is a significant public health problem. The most common cause of obesity throughout childhood and adolescence is an inequity in energy balance; that is, excess caloric intake without appropriate caloric expenditure. Adiposity rebound (AR) in early childhood is a risk ...
carbohydrate is a crucial factor in the obesity epidemic. 18 Soft drinks, alcoholic beverages and fast food tend to be calorie rich. In Britain, there has been a signi cant rise in the amount of ...
Obesity as a reflection of a positive fat balance is influenced by a number of genetic and environmental factors and phenotypes of obesity can be developed from several perspectives, some of which ...
Obesity is a global problem that affects millions of people. The causes of obesity are multifactorial and involve genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Obesity has serious health, psychological, and social consequences. Prevention of obesity requires a multifaceted approach that involves education, healthy eating, and physical activity.
Essay on obesity! Find high quality essays on 'Obesity' especially written for school, college, science and medical students. These essays will also guide you to learn about the causes, factors, treatment, management and complications related to obesity. Obesity is a chronic health condition in which the body fat reaches abnormal level.
Obesity is a complex and costly chronic disease influenced by many factors. These factors include health behaviors, stress, health conditions and medications, genes, and people's environment. Knowing the risk factors can help individuals and communities take steps to prevent and reduce obesity.
This essay will explore the various causes of obesity and their effects on individuals and society as a whole. One of the primary causes of obesity is dietary habits and nutritional intake. The consumption of high-calorie, low-nutrient foods, such as fast food, sugary beverages, and processed snacks, has become increasingly prevalent in modern ...
Obesity, a condition once considered as an adult problem, has spread among more young people in the 21 st century, than in the past. This disease can be explained as the presence of excess fat in the body. A simple way of diagnosing obesity is by the use of Body Mass Index (BMI), which is simply weight (kg)/height (m)2.
This Review describes current knowledge on the epidemiology and causes of child and adolescent obesity, considerations for assessment, and current management approaches. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, obesity prevalence in children and adolescents had plateaued in many high-income countries despite levels of severe obesity having increased. However, in low-income and middle-income countries ...
The obesity epidemic is not just a matter of personal responsibility or willpower, but is influenced by a complex interplay of social, economic, and environmental factors. In this essay, we will explore the causes and consequences of obesity in America, as well as potential solutions to address this pressing issue.
The primary care provider is ideally suited, through long-term trusting relationships with families, to screen for obesity and associated risk factors and co-morbid conditions and to offer sensitive, respectful advice that mitigates the negative impact stigma and bias. Primary care providers should focus their childhood obesity intervention ...
Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity (SO) are age-related syndromes that may compromise physical and mental health among older adults. The Nordic countries differ from other regions on prevalence of disease, life-style behavior, and life expectancy, which may impact prevalence of sarcopenia and SO. Therefore, the aim of this study is to review the available evidence and gaps within this field in ...
However, those factors will remain to increase with the increase of the consumer number. Although, Increased consumption of sweetened drinks has contributed significantly to the raised carbohydrate intake of most young American adults over the last three decades. ... Obesity: A Satirical Look at a Growing Epidemic Essay. Obesity has become a ...
Introduction. Obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. In America, the prevalence of obesity has been steadily increasing over the past few decades, with currently around 42% of the population being classified as obese. Addressing this issue is significant as it has far-reaching impacts on both individual and ...