Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Case Based Questions - Light, Shadow and Reflections
Sarah is conducting an experiment with different objects to understand the properties of light. She has a wooden box, a glass pane, and a candle. She is using a source of light to observe the behavior of these objects.
Q1: What type of object is the wooden box in this scenario, and why? Ans: The wooden box is an opaque object because it does not allow light to pass through it. Q2: If Sarah observes that she can see through the glass pane clearly, what type of object is it, and why? Ans: The glass pane is a transparent object because it allows light to pass through it clearly. Q3: How does the behavior of the candle differ from the wooden box and the glass pane in terms of emitting light? Ans: The candle is a luminous object because it emits its own light. Q4: Which of the following objects is an example of a translucent object? (a) Wooden box (b) Glass pane (c) Candle Ans: (b) Q5: What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes a luminous object from a non-luminous object? (a) Color (b) Shape (c) Ability to emit light Ans: (c)
Mark is using a pinhole camera to capture images. He is experimenting with the camera's focus and understanding the principles behind it.
Q6: Explain how the image formed by Mark's pinhole camera is different from the actual object in terms of size and orientation. Ans: The image formed by Mark's pinhole camera is inverted and smaller in size compared to the actual object. Q7: Describe the steps Mark should follow to make a pinhole camera. Ans: Steps to make a pinhole camera:
- Take two rectangular boxes that fit into one another without any gap.
- Cut open one side of each box.
- Make a small hole in the larger box at the center of the closed end opposite the side that has been cut open.
- Cut a square of side five centimeters in the smaller box in the closed end opposite the side that has been cut open.
- Cover this square with tracing paper.
- Slide the smaller box into the larger box, ensuring that the pinhole and the tracing paper are in line with one another but at opposite ends.
- Slide the smaller box to adjust the focus.
Q8: Why is it mentioned that "the image is not clear" in the context of a pinhole camera? Ans: The image is not clear because the pinhole camera uses a small hole to form the image, resulting in limited light and reduced clarity. Q9: What is the principle on which a pinhole camera works? (a) The principle of reflection of light. (b) The principle of refraction of light. (c) The principle of straight-line propagation of light. Ans: (c) Q10: Which type of surface reflects the entire light incident on it? (a) Transparent surface (b) Opaque surface (c) Plane mirror surface Ans: (c)
A group of students is discussing the difference between shadows and images. They are using a mirror and a flashlight to observe and learn about these phenomena.
Q11: Explain the similarities and differences between shadows and images. Ans: Similarities:
- Both shadows and images require a source of light.
- They are formed when light interacts with objects.
Differences:
- Shadows are black and have no color, while images can be colorful.
- Shadows change in length with the position of the sun, while images in a mirror remain the same size.
Q12: Describe the setup and conditions required to observe a shadow and an image. Ans: To observe a shadow, you need a source of light, an opaque object, and a screen. To observe an image in a mirror, you need a reflective surface and an object in front of it. Q13: Why do shadows change in length throughout the day, while images in a mirror do not? Ans: Shadows change in length throughout the day because of the changing angle and position of the sun. Images in a mirror do not change size. Q14: Which of the following statements is true regarding shadows and images? (a) Shadows are always colorful. (b) Images change in size with the position of the sun. (c) Shadows can be seen without the need for a screen. Ans: (c) Q15: What is the main reason behind the formation of shadows? (a) Reflection of light (b) Bending of light (c) Blocking of light Ans: (b)
A group of students is visiting an observatory, where they encounter a two-way mirror. They are curious about its functionality.
Q16: Explain how a two-way mirror works and its practical applications. Ans: A two-way mirror, also known as a one-way mirror, allows one side to act as a mirror (reflective) and the other side as plain glass (transparent). It is used for observing people without them knowing, such as in police stations or psychological institutions. Q17: Compare and contrast the behavior of a two-way mirror with a regular plane mirror. Ans: Comparison with a regular plane mirror:
- A plane mirror is always reflective, whereas a two-way mirror can switch between reflective and transparent properties.
Q18: In what situations might a two-way mirror be used for observation without detection? Ans: A two-way mirror might be used for covert observation without detection. Q19: A two-way mirror acts as: (a) A transparent medium (b) A translucent medium (c) A combination of a mirror and plain glass Ans: (c) Q20: What type of surface is a smooth plane mirror? (a) Transparent surface (b) Opaque surface (c) Reflective surface Ans: (c)
Tom is studying the concept of reflection and its importance in our daily lives. He is experimenting with various reflective surfaces.
Q21: Explain the concept of reflection of light and how it plays a role in forming images. Ans: The concept of reflection of light involves the bouncing back of light when it encounters a smooth shiny surface. Reflection plays a role in forming images by redirecting light rays. Q22: Describe the behavior of light when it is incident on a smooth shiny surface. Ans: When light is incident on a smooth shiny surface, it reflects back into the same medium following the laws of reflection. Q23: Provide examples of everyday situations where reflection of light is essential. Ans: Examples of everyday situations with reflection of light: Mirrors, shiny metal surfaces, glass windows, and still water surfaces. Q24: Which term best describes the likeness of an object carried and formed by light in a mirror? (a) Image (b) Shadow (c) Reflection Ans: (a) Q25: What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes a plane mirror from other reflective surfaces? (a) Color (b) Smoothness (c) Size of reflection Ans: (b)

Top Courses for Class 6
Important questions, shadow and reflections, study material, practice quizzes, mock tests for examination, sample paper, viva questions, past year papers, shortcuts and tricks, previous year questions with solutions, class 6 science chapter 8 case based questions - light, extra questions, objective type questions, semester notes, video lectures.

Case Based Questions: Light, Shadows & Reflections Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: light, shadows & reflections, case based questions: light, shadows & reflections notes, case based questions: light, shadows & reflections class 6, study case based questions: light, shadows & reflections on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us Extra Questions and Answers
CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us Extra Questions and Answers is available here. Students can learn and download the PDF of these questions for free. These extra questions and answers are prepared by our expert teachers as per the latest NCERT textbook and guidelines. Learning these extra questions will help you to score excellent marks in the final exams.
Air Around Us Class 6 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very short answer questions.
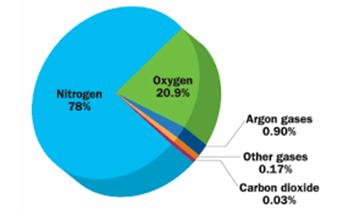
1. Name the main component of air. Answer: Nitrogen gas
2. What is the source of oxygen gas in air? Answer: Photosynthesis by green plants is source of oxygen gas in air.
3. What is the percentage of nitrogen in air? Answer: 78.1%
4. What is the percentage of oxygen in air? Answer: 20.9%
5. What is the source of carbon dioxide in air? Answer: Respiration by animals and plants and burning of fuel.
6. Mention one necessary condition for the combustion to take place. Answer: Presence of air.
7. Define atmosphere. Answer: The blanket of air that surrounds the earth is called atmosphere.
8. What is humidity? Answer: The amount of water vapour present in the air is called humidity.
9. Which gas is most abundant and is important for growth of plants and animals? Answer: Nitrogen
10. Name the component of air used by green plants to make their food. Answer: Carbon dioxide
11. Name any two musical instruments in which air plays an important role. Answer: Flute and saxophone
Short Answer Type Questions
1: What happens when air comes in contact with a cool surface?
Answer: When air comes in contact with a cool surface, it condenses and drops of water appear on cool surface.
2: Why do you think mountaineer carry oxygen cylinders with them, while climbing high mountains?
Answer: There is less oxygen at high places like mountains, so they carry oxygen cylinder with them to breathe there.
3: Why you feel suffocation in a closed room, where some material is burning?
Answer: Burning of some material releases smoke that contains few gases and fine dust particles that is harmful, thus we feel suffocation in a closed room, where some material is burning.
4: Why there are long chimneys in factories?
Answer: Chimneys take the harmful gases and smoke of factories away from our noses.
5: Air is necessary for combustion. Explain the statement.
Answer: Fix two candles in middle of a container containing water. Light both candles. Now cover the candles with an inverted transparent glass, you will observe that candles goes off. This happens because of absence of air. Thus, we can say that air is necessary for combustion.
6: Air occupies space. Explain the statement.
Answer: Blow a balloon, air from your body enters balloon at it gets bigger because air occupies space.
7: When the open mouth of an empty bottle is tilted in a bucket filled with water, we see bubbles coming out of it. Explain the phenomenon.
Answer: The bottle contains air so when it was titled air came out in the form of bubbles.
8: What is air made up of?
Answer: Air is made up of mixture of gases like – Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, dust particles and other gases.
9: Air contains dust particles, while inhaling air we also inhale dust particles. Give reason in support of the statement, whether it is true or false?
Answer: False, because our nose contains fine hair and mucus that trap all dust particles and prevent its entrance inside our body.
10: Why we should not breathe through our mouth?
Answer: If we will breathe through our mouth then dust particles present in air will enter our body and will cause harmful diseases.
11: Draw a diagram showing composition of air in atmosphere. Answer:
12: How does an organism living in soil breathe?
Answer: Through air present in soil.
13: How can you show that air is dissolved in water?
Answer: Take water in a pan and heat it. After sometimes just before it boils we can observe some bubbles at the inner surface of the pan. This is because of the air dissolved in water.
14: Why an animal living in soil does, comes out of soil for respiration in rainy season?
Answer: When it rains heavily, water fills up all the spaces occupied by the air in the soil. Therefore, organism living in soil has to come out for respiration.
15: Why does a lump of cotton wool shrink in water?
Answer: A lump of cotton wool shrinks in water because water filled up the empty space that the air has occupied.
16: List at least five activities that are possible due to the presence of air.
Answer: Respiration, burning, photosynthesis, movement of aeroplane and parachutes, generation of electricity by windmills.
17. Why is air considered as a mixture?
Answer: Air contains oxygen and nitrogen as its major constituents of air. These gases retain their properties in air. So, the air is called a mixture.
18. Name the major gas present in the (a) inhaled air (b) exhaled air.
Answer: (a) Oxygen (b) Carbon dioxide.
19. Write the necessary conditions for rusting of iron to take place.
Answer: Rusting of iron takes place in the presence of moisture and air. So, the presence of air and water vapour in air are two necessary conditions for rusting of iron.
20. Name a device which uses wind energy to generate electricity.
Answer: Windmills use the wind energy to convert wind energy into electrical energy
21: What is wind energy? Mention its two advantages.
Answer: Blowing air is called wind. Wind possesses kinetic energy. The kinetic energy possessed by wind is called wind energy.
Uses of Wind Energy are: (i) Wind energy is used to pump the ground water. (ii) Wind energy is used to generate electricity with the help of windmills.
22. Mention two uses of air.
Answer: The two uses of air are as below: (a) For respiration all organisms need air. (b) For burning of any substance air is needed.
23. What happens if the percentage of oxygen in the air reaches to 70%?
Answer: If any substance catches fire it will become difficult to extinguish the fire, as oxygen supports combustion.
24. Why is carbon-dioxide gas used to extinguish fire?
Answer: It is because carbon-dioxide does not support combustion. When sprayed on burning object it stops the supply of oxygen and extinguishes fire.
25. How will you prove that soil contains air in it?
Answer: Take a glass tumbler add some soil in it, then pour some water on the soil slowly, the air-bubbles comes out of the soil. This proves that soil holds air in it.
26. Why do we see the sky and air clear and clean after rainfall?
Answer: The dust particles which remain suspended in air get loaded and come down on the ground due to rainfall, this is the reason that the sky and the air look clean and clear after rainfall.
27. Explain why mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them?
Answer: As you go up, above the sea-level the atmospheric pressure goes on decreasing and the amount of oxygen also decreases at higher altitude.
28. Explain why during an incident of fire, one is advised to wrap a woollen blanket over a burning object.
Answer: Blanket cuts the supply of oxygen to the object that is burning, thereby prevents it from further burning.
29. Why does the transparent glass of windows, if not wiped off regularly, appears hazy?
Answer: Air contains dust and smoke along with the gases. These gets deposited on the glass windows and make them appear hazy.
30. Why during an incident of fire, one is advised to wrap a woollen blanket over a burning object?
Answer: For combustion to take place, oxygen is required. When a woollen blanket is wrapped over a burning object, fire loses contact with oxygen and, therefore, stops burning after sometime.
31. Why do you think, mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them, while climbing high mountains?
Answer: As we go higher on the mountains, the air becomes thinner. The amount of oxygen decreases and it becomes hard to breath. Therefore, mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them.
32. How do the organisms living in soil get the air they need, for respiration?
Answer: The spaces between the soil particles are filled with air. This air is taken up by plants and animals for respiration.
33. Why are factories fitted with tall chimneys?
Answer: Burning of fuel and materials produce smoke and other harmful gases which are released out of the factories by the chimneys.
Long Answer Type Questions
1: How do plants and animals help each other in the exchange of gases in the atmosphere?
Answer: Plants and animals help each other in the exchange of gases in the atmosphere Plants take carbon dioxide to prepare food and release oxygen during daytime. This oxygen is taken in by animals and carbon dioxide is released. Thus, plants and animals help in maintaining balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
2: Explain the role played by air in the life of human, animals and plants.
Answer: Living things cannot live without air. We can survive on planet earth because of atmosphere only. Plants cook their food by the process of photosynthesis because of air only. They use carbon dioxide gas of air and releases oxygen that is utilized by human and animals to breathe in. Air is necessary for combustion, flying of aeroplanes and birds. Thus, it is well said Air is life.
3. Describe balance of oxygen in the air.
Answer: The oxygen in air is used by the organisms present in air, water or soil or on earth for their respiration. During respiration carbon dioxide gas is released to air. But green plants during photosynthesis use carbon dioxide of air for preparing food and they release oxygen gas in the air. Thus, the balance of oxygen in air is maintained.
4. What happens if the percentage of carbon-dioxide increases in the air?
Answer: The increased percentage of carbon-dioxide will cause green house effect, i.e. it will not allow the hot rays of sun to escape from the atmosphere after reflection once they enter the earth’s atmosphere, thereby increasing the temperature of earth, ice on mountains will melt and water level will rise.
5. You must have seen during rainy season, when it rains the animals like earthworm, snakes, snails etc. are commonly seen. Explain why?
Answer: All these animals live in underground burrows or remain buried in the soil. They get oxygen from air that enters into the burrow through entrance of burrow or through pores in the soil. But when it rains, the water gets filled in their dwelling places and pores of the soil. So, they come out in search of air.
6. Why all the oxygen of atmosphere does not get used up though a large number of organisms are consuming it?
Answer: A large number of organisms take up oxygen for respiration and release carbon dioxide. Plants take up this carbon dioxide and release oxygen in the atmosphere. Therefore, this balance is maintained.
7. How will you prove that oxygen supports burning? Answer:
- Take three candles, two glass jars that can cover two candles but of different sizes and a watch.
- Light all the three candles at one time after fixing them on the table. Cover two candles with the jars. Leave one candle uncovered. Switch off the fan and close doors and windows. This will stop wind from blowing off the candles.
- After some time the candle covered with the small jar goes off first. Then the one with a bigger jar goes off. The candle in the open continues to burn. Thus, air supports burning.
8. How will you show that air is dissolved in water? Answer:
- Take some water in a glass vessel. Look carefully at the inner surface of the vessel.
- There are tiny bubbles on the inside of the vessel. These bubbles come from the air dissolved in water.
- Heat the water slowly on a tripod stand.
- We see the air dissolved in it escapes. On further heating, the water itself turns into vapour and finally begins to boil.
Thus, the animals living in water use the dissolved oxygen in water.
9. How is the level of oxygen maintained in the atmosphere?
Answer: The level of oxygen is maintained in the atmosphere by planting more and more trees and by avoiding excessive burning of fuels. The plants will take up the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to make their food and in turn will release oxygen. This oxygen is taken up by animals, including humans, for respiration and in turn release carbon dioxide.
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 6
- NCERT Class 6 Science
- Chapter 13: Fun With Magnets
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets is a beneficial study material required for the students studying CBSE board Class 6 Science. This solution has detailed answers and explanations to the exercise questions provided in the NCERT Class 6 Science textbook.
These NCERT Solutions will boost your confidence by helping you build your problem-solving abilities on a given topic. It is essential for students to get well-versed in this study material to score good marks in the examinations.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 provided here will help you to understand the discovery of magnets along with magnetic and non-magnetic materials, poles of the magnet, finding directions using magnets, construction of magnets, attraction and repulsion forces.
Important topics covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- How Magnets were Discovered
- Magnetic and non-magnetic materials
- Poles of magnet
- Finding directions
- Make your own magnet
- Attraction and repulsion between magnets
- Chapter 1 Food: Where Does It Come From?
- Chapter 2 Components of Food
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Sorting Materials into Groups
- Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
- Chapter 6 Changes Around Us
- Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
- Chapter 8 Body Movements
- Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflection
- Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 14 Water
- Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage Out
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next

Access Answers of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
Exercise Questions
1. Fill in the blanks in the following
(i) Artificial magnets are made in different shapes such as __________, __________ and ____________.
(ii) The materials which are attracted towards a magnet are called________.
(iii) Paper is not a ______ material.
(iv) In the olden days, sailors used to find direction by suspending a piece of ___________.
(v) A magnet always has __________ poles.
(i) Artificial magnets are made in different shapes such as bar magnet , horse shoe and cylindrical.
(ii) The materials which are attracted towards a magnet are called magnetic.
(iii) Paper is not a magnetic material.
(iv) In the olden days, sailors used to find direction by suspending a piece of magnet .
(v) A magnet always has two poles.
2. State whether the following statements are true or false:
(i) A cylindrical magnet has only one pole.
(ii) Artificial magnets were discovered in Greece.
(iii) Similar poles of a magnet repel each other.
(iv) Maximum iron filings stick in the middle of a bar magnet when it is brought near them.
(v) Bar magnets always point towards North-South direction.
(vi) A compass can be used to find East-West direction at any place.
(vii) Rubber is a magnetic material.
v) True (Freely suspended bad magnet)
3. It was observed that a pencil sharpener gets attracted by both the poles of a magnet although its body is made of plastic. Name a material that might have been used to make some part of it.
Iron might have been used to make some part of it.
4. Column I shows different positions in which one pole of a magnet is placed near that of the other. Column II indicates the resulting action between them for each situation. Fill in the blanks.
5. Write any two properties of a magnet.
Properties of a magnet are as follows
- It attracts objects made of Nickel, Cobalt and Iron.
- Like poles of two magnets repel each other and opposite poles attract each other.
6. Where are poles of a bar magnet located?
On two ends of a bar magnet.
7. A bar magnet has no markings to indicate its poles. How would you find out near which end is its north pole is located?
A bar magnet is hung in the air, and the end pointing to the north is the north pole of the magnet.
8. You are given an iron strip. How will you make it into a magnet?
Take a bar magnet and keep in contact with one of its poles with one edge of the bar of iron.
- Without lifting the bar magnet, move it along the length of the iron bar till you reach the other end.
- Lift the magnet and bring the pole (the same pole you started with) to the same point of the iron bar from which we began.
- Move the magnet again along the iron bar in the same direction as you did before.
- Repeat this process for about 30-40 times.
9. How is a compass used to find directions?
A compass always shows north and south directions; by keeping this as a reference, we can always find east and west directions also.
10. A magnet was brought from different directions towards a toy boat that has been floating in water in a tub. The effect observed in each case is stated in Column I. Possible reasons for the observed effects are mentioned in Column II. Match the statements given in Column I with those in Column II.
BYJU’S innovative learning approaches help students across the country to excel in their academics. The notes, videos, animations, infographics, tips, and tricks we provide will help the students learn and remember the concepts easily. To get an experience of personalised learning, download BYJU’S – The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13
List out any two properties of a magnet from chapter 13 of ncert solutions for class 6 science., what concepts can i learn from chapter 13 of ncert solutions for class 6 science, are the ncert solutions for class 6 science chapter 13 pdf absolutely free of cost, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
its is very nice learing app. it is very helpful for everyone. everything is as easy as we wont. excellent app
this is nice learning app👌👌
It is a very useful app for learning
Very nice app.
It is amazing app
It’s very good 👍 👍👍👍👍👍👍👍←_←
Amazing👍👍👍👍👍
It is amazing
It’s very good. I Like it!!
The first best app I have ever used. I just love it!
These site is very amazing 😍😍
Thank you byjus amazing
Very nice App .I ever very used . I just love it 😍😍
Nice app for finding answers and learning easily
Its very nice
Its very ! Very! very! Amazing
This app is very good to get information 😊👍
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 6 Science Components of Food
Case study questions class 6 science chapter 2 components of food.
CBSE Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Components of Food. Important Case Study Questions for Class 6 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Components of Food.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 6 Science Components of Food
Case study 1.
We know that each dish is usually made up of one or more ingredients, which we get from plants or animals. These ingredients contain some components that are needed by our body. These components are called nutrients. The major nutrients in our food are named carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. In addition, food contains dietary fibres and water which are also needed by our body.
With some simple methods we can test whether cooked food or a raw ingredient contains one or more of these nutrients. For carrying out these tests, you will need solutions of iodine, copper Sulphate and caustic soda. You will also need a few test tubes and a dropper. Try these tests on cooked food items as well as raw materials. If the required solutions are not available in readymade form, you can prepare them as given in the Table 1. There are many types of carbohydrates. The main carbohydrates found in our food are in the form of starch and sugars.

Que. 1) Starch and sugar are the forms of carbohydrates mainly present in our food?
Que. 2) To make the solution of caustic soda, we need to dissolve ………………………………………………………………………….…….. in 100ml of ……………………………………………………………….….. ?
(a) Iodine and water
(b) Salt and water
(c) Caustic soda and salt
(d) Caustic soda and water
Que. 3) Which of the following is NOT required to test the presence of nutrients in food?
(a) Vinegar solution
(b) Iodine solution
(c) Copper Sulphate
(d) Caustic soda solution
Que. 4) What are nutrients? Give one example?
Que. 5) Name all the components present in our food?
Que. 1) a)True
Que. 2) d) Caustic soda and water
Que. 3) a) Vinegar solution
Que. 4) Answer: Our food is made up of one or more ingredients. These ingredients contain components that are needed by our body. These components are called Nutrients. For example- Proteins
Que. 5) Answer: The major nutrients in our food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Apart from nutrients, food also contains dietary fibres and water.
Case study 2
The tests for presence of carbohydrates, proteins and fats are simpler to do as compared to the tests for other nutrients. Let us begin by testing different food items to see if they contain carbohydrates. Take a small quantity of a food item or a raw ingredient. Put 2-3 drops of dilute Iodine solution on it. Observe if there is any change in the colour of the food item. A blue-black colour indicates that it contains starch.To test the presence of proteins in food we need to take a small quantity of a food item for testing. If the food you want to test is a solid, you first need to make a paste of it or powder it. Grind or mash a small quantity of the food item. Put some of this in a clean test tube, add 10 drops of water to it and shake the test tube. Now, using a dropper, add two drops of solution of copper sulphate and ten drops of solution of caustic soda to the test tube. Shake well and let the test tube stand for a few minutes. You will see that the contents of the test tube will turn violet. A violet colourindicates presence of proteins in thefood item.
For fats, take a small quantity of a food item.Wrap it in a piece of paper and crush it.Take care that the paper does not tear.Now, straighten the paper and observeit carefully. If you see an oily patch on paper,then it shows that the food item contains fat. The food items may sometimes contain a little water. Therefore, after you have rubbed an item on paper, let the paper dry for a while. If there were any water that may have come from food, it would dry up after some time. If no oily patch shows up after this, the food item does not contain any fat.
Que.1)Which colour indicates the presence of proteins in the food items?
d) Blue – black
Que.2) We put drops of dilute Iodine solution to test the presence of …………………………………………………………………………………………. ?
Que.3)If the colour of the food item turns blue- black, then it contains fat.
Que.4) How can we test the presence of fats in food items?
Que.5) Solutions of Copper sulphate and caustic soda are used to test the presence of which nutrient? Elaborate how its presence is detected?
Que.1. a)Violet
Que.2. b) Starch
Que.3. b) False
Que.4) Answer: The presence of fats in food items can be test by taking a small quantity of a food item. Wrapping it in a piece of paper and crushing it. Next, straightening the paper and observing it carefully. If you see an oily patch on paper, then it shows that the food item contains fat.
Que.5) Answer: Solutions of both the copper sulphate and caustic soda are used to test the presence of proteins in food items.
When the colour of the food item turns violet, it indicates the presence of proteins in the food item.

Case study 3
Foods containing fats and carbohydrates are also called ‘energy giving foods’. Proteins are needed for the growthand repair of our body. Foods proteins are often called ‘body building foods’. Vitamins help in protecting our body against diseases. Vitamins are of different kinds known by different names. Our body needs all types of vitamins in small quantities. Vitamin A keeps ourskin and eyes healthy. Vitamin C helpsbody to fight against many diseases.Vitamin D helps our body to use calcium for bones and teeth.
However, in a given raw material, one particular nutrient may be present in much larger quantity than in others. For example, rice has more carbohydrates than other nutrients. Thus, we say that rice is a “carbohydrate Rich” source of food.
Besides these nutrients, our body needs dietary fibres and water. Dietary fibres are also known as Roughage. Roughage is mainly provided by plant products in our foods. Whole grains and pulses, potatoes, fresh fruits and vegetables are main sources of roughage.
Que.1) …………………………..…………………..…………………… keeps our skin and eyes healthy?
a) Vitamin D
b) Vitamin C
c) Vitamin E
d) Vitamin A
Que.2)Food containing Proteins are also known as “energy giving foods”?
Que.3) Name the nutrientneeded for the growth and repair of the body?
a)Carbohydrates
b) Roughage
c) Minerals
d) Proteins
Que.4) what are Roughages?
Que.5) Mention ways in which Vitaminsare helpful for the body?
Que.1. a) Vitamin A
Que.2. b) False
Que.3. d) Proteins
Que.4) Answer: Dietary fibres are also known as Roughages. It is mainly provided by plant products in our foods. The main sources of roughages are whole grains and pulses, potatoes, fresh fruits and vegetables.
Que.5) Answer: Vitamins help in protecting our body against diseases. Vitamins are of different kinds known by different names. Our body needs all types of vitamins in small quantities. Vitamin A keeps our skin and eyes healthy. Vitamin C helps body to fight against many diseases. Vitamin D helps our body to use calcium for bones and teeth.
Case study 4
The food we normally eat in a day is our diet. For growth and maintenance of good health, our diet should have all the nutrients that our body needs, in right quantities. Not too much of one and not too little of the other. The diet should also contain a good amount of roughage and water. Such a diet is called a balanced diet.Pulses, groundnut, soyabean,Sprouted seeds (moong and BengalGram), fermented foods (South IndianFoods such as idlis), a combination ofFlours (missi roti, thepla made fromCereals and pulses), banana, spinach,Sattu, jaggery, available vegetables and other such foods provide many Nutrients.
Eating the right kind of food is not enough. It should also be cooked properly so that its nutrients are notlost. But there are some nutrients that get lost in the process of cooking and preparations. If the vegetables and fruits are washed after cutting or peeling them, it may result in the loss of some vitamins.
The skins of many vegetables and fruits contain vitamins and minerals. Similarly, repeated washing of rice and pulses may remove some vitamins and minerals present in them. We all know that cooking improves the taste of food and makes it easier to digest. At the same time, cooking also results in the loss of certain nutrients. Many useful proteins and considerable amounts of minerals are lost if excess water is used during cooking and is then thrown away. Vitamin C gets easily destroyed by heat during cooking.Also It can be very harmful for us to eat too much of fat rich foods and we may end up suffering from a condition called obesity.
Que.1) An example of fermented fooditem is ……………………………………………………………………………………. .
d) Sprouted seeds
Que.2) A considerable amount of …………………………………………………………………………..………….…….. And ……………………………………………………………….….. are lost if we use water in excessive amount during cooking?
a) Vitamins and minerals
b) Proteins and fibre
c) Minerals and proteins
d) Vitamins and fibre
Que. 3) Eating too much of fat rich foods can lead to a condition called obesity?
Que.4) What do you understand by the term “balanced diet?”
Que.5) Mention the disadvantages of cooking food?
Que.1. b)Idli
Que.2. c) Minerals and proteins
Que.3. a)True
Que.4) Answer: Our food should have all the necessary nutrients in right quantities, along with a good amount of roughage and water. Such a diet is known as a balanced diet.
Que.5) Answer: Cooking results in the loss of certain nutrients. Many useful proteins and considerable amounts of minerals are lost if excess water is used during cooking and is then thrown away. Vitamin C gets easily destroyed by heat during cooking.
Case Study 5
Our meals usually have at least one item made of some kind of grain. Other items could be a dal or a dish of meat and vegetables. It may also include items like curd, butter milk and pickles. Some examples of meals from different regions are given in table 1. Select food items you depicted on the map in Chapter 1. Add some more meals to this list and enter these in Table 1. Sometimes, we may not really have all this variety in our meals. If we are travelling, we may eat whatever is available on the way. It may not be possible for some of us, to eat such a variety of items, most of the time. There must be some reason though, why meals usually consist of such a distribution. Do you think that our body needs different kinds of food for some special purpose?

Q 1.) Name the grain most commonly eaten by the people of Punjab?
a) Makki roti
Q 2.) The item among these we usually have in our meal is ………………………..……………………………………………. .
Q 3.) Which vegetable is commonly eaten by people of Punjab?
c) Sarson saag
Q 4. Write the common meal consumed by people of Andra Pradesh?
Q 5. Write one situation when it is not possible for us to have a healthy distribution of meal?
Q 1. Answer: a) Makki roti.
Q 2. Answer: b) Grain.
Q 3 Answer: c) Sarson saag.
Q 4 Answer: People of Andra Pradesh eat rice, tuar dal, rasam and kunduru along with other items such as buttermilk, ghee and pickle.
Q 5 Answer: Usually when we are travelling we have to eat whatever is available to us on the way. So in such a situation it is not possible to have a variety of meal.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Integers worksheet class 7 with answer (total marks 80), rs aggarwal class 8 chapter 1 assertion reason solutions, west bengal board class 6 science moulik jougik o misro podartho solution, sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 4a picture reading solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits

CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits - Free PDF Download
Class 6 Science explains fascinating concepts to young minds. They learn many new things and find exciting new facts about different topics. The 12 th chapter of the Class 6 NCERT Science book focuses on explaining current, electricity, and circuits. This chapter will introduce the children to the world of electricity and circuits. After finishing answering the exercise questions, you can proceed to solve the Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions .
All these questions have been developed following the concepts delivered in this chapter. The questions will hold a higher level in terms of concepts. You will find what other questions can be formed and asked in the exams. Download these NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions and complete your preparation of this chapter. Resolve all your doubts by referring to the solution provided in the same file. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions for other chapters:
Study Important Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 – Electricity and Circuit
Very Short Answer Questions: 1 Mark
Choose the correct answer from the options given.
1. An electric cell has _____________ terminals.
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Ans: Option - b.
2. An electric cell has a
a) Positive and negative terminal
b) Two positive terminals
c) Two negative terminals
d) None of the above
Ans: Option - a.
3. An electric cell
a) Uses electricity
b) Uses light
c) Produces electricity
Ans: Option - c.
4. An electric cell uses ___________ to produce electricity.
a) Electricity
b) Heat
c) Light
d) Chemicals
Ans: Option - c.
5. An electric cell does not produce electricity when
a) Chemicals inside get completely used up
b) The terminals are not connected properly
c) Both of the above
Short Answer Questions: 3 Marks
1. How does a light bulb produce light?
Ans: A thin wire like structure known as filament is present inside the bulb. When we switch on the bulb, electricity passes through filament causing it to heat up and glow to produce light. In this process the electric energy changes into light energy.
2. What is an electric circuit?
Ans: The closed path in which electric current flows is called an electric circuit. Generally, an electric circuit consists of wire, battery, switch and an appliance which needs electricity to work. The current in the electric circuit flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. The switch is used to break the flow of the current when the appliance is not in use.
3. How does a bulb fuse?
Ans: Inside the bulb there is a thin wire like structure called filament. Filament is made of substances having a low melting point. Filament gets heated and emits light when we switch on the bulb. But when there is excess flow of current through the filament it melts down due to excessive heat. This causes fusing of the bulb.
4. Explain the role of a switch in a circuit. What is it made up of?
Ans: An electric switch is a circuit component that can be used to control the flow of electricity through the circuit. It has the ability to both complete and break the circuit. A conducting substance is used to make the switch. The circuit is complete and power flows through it when the switch is in the "ON" position. The circuit is broken and power cannot flow through it while the switch is in the "OFF" position.
5. Label the parts in the following diagram. Indicate the positive and negative terminals.
Long Answer Questions: 5 Marks
1. Differentiate between conductors and insulators.
Ans: The differences between conductors and insulators are as follows:
2. In the following diagram explain whether the bulb will glow in each of the cases.
Ans: a) The bulb will glow as the circuit is complete.
b) The bulb will not glow as the circuit is incomplete.
c) The bulb will not glow as the circuit is incomplete.
d) The bulb will not glow as both wires are connected only to the negative terminal of the cell.
e) The bulb will not glow as both wires from the bulb are connected only to the positive terminal of the cell.
f) The bulb will glow as the circuit is complete.
Electricity and Circuits: NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Summary
You might have come across the term ‘current’ in other chapters of different subjects. A current represents a flow of anything. It can be water, a substance, or wind. Anything that flows can be explained as a current. People flocking in a busy station by forming a line can also be considered as an example of human current. This chapter will explain what a current is and it is defined in the context of electricity. The Important Questions on Electricity and Circuits for Class 6 will be based on these concepts. These questions will also be answered by the top teachers.
Let us check what the chapter will cover and what kind of questions you will find in this file.
Students will learn what current means. They will also learn how the flow of electrons is considered to be an electric current. An electric current has a set of features that you should learn from this chapter. This is when you will develop the foundation of concepts based on electricity. Using this foundation, you will then proceed to learn new advanced concepts in the higher classes related to this chapter.
You will learn how an electric current is formed and flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal when connected to a battery. For the first time, you will learn what a circuit means. Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions will be based on those new concepts of this chapter. Make sure you study them well to answer these questions easily. On proceeding further, you will come to know about an electric cell and how it works to generate electricity when connected to a circuit. Certain factors determine the flow of current from one terminal to the other. Find out how an electric cell gets exhausted from use.
In the next section of the chapter, you will study how an electric bulb is connected to a circuit and how it glows using the electric current flowing in it. The various components of the electric circuit along with the bulb will be described and the Important Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 will be based on this topic. Learn how an electric bulb functions when connected to a live circuit. You will also come to know different kinds of wires used in a circuit and what materials are used to make them. Delve deeper into the chapter and learn more about conductors, insulators, keys, switches, resistors, etc.
Why Should You Prefer Studying Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions?
Vedantu has prepared a set of NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions to provide the following benefits to the students.
Suggestions Related to Possible Questions from this Chapter
The important questions can be followed to find the possible questions a teacher can ask in an exam. Apart from the exercise questions, this list of questions will work as a suggestive set for students to solve and prepare the chapter well.
Best Ways to Approach and Answer Conceptual Questions
The Electricity and Circuits Class 6 Important Questions will also suggest how to approach and answer conceptual questions. Even if you have properly understood the prime concepts of this chapter, you will need assistance to form answers in the best way possible so that you can fetch good marks in the exams.
Doubt Clarification
The more you study and solve questions based on a chapter, the better your concepts will be cleared. Your understanding level will increase and you will become more efficient in clarifying doubts on your own. Hence, studying these Important Questions on Electricity and Circuits for Class 6 along with answers will help you understand the concepts perfectly.
Important Related Links for CBSE 6 Science
Reviewing all the crucial questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits provides students with a solid grasp of the chapter's topics. The extra and important questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits engage in a concept-focused discussion encompassing all chapter themes. This question-and-answer method proves time-saving during exam prep, offering an efficient way to revise the chapter and enhance understanding. Practising these important questions streamlines preparation and boosts confidence for the upcoming exams.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits
1. What is an Electric Current?
The electrical charges flowing through a conductor from the positive end to the negative end of a battery is called an electric current. As per the answers of Class 6 Science Ch 12 Important Questions, an electric current is produced when there is a difference in potential between the two terminals.
2. Why Should You Choose Vedantu for Downloading NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions?
Vedantu has always been the leading choice for Class 6 students to find important questions related to the Science chapters. These conceptual questions and answers help students to develop their knowledge regarding electricity and circuits.
3. What is class 6 Science chapter 12 about?
Class 6 Science chapter 12 is about Electricity and Electric circuits. When you read this chapter, you come to know about various things related to electric current or electricity. This is a major necessity for mankind for their day to day activities and if you are curious to know about how electric current is produced or how it flows throughout your house etc then you will find this chapter interesting. Focus on the concepts in order to do well in exams.
4. What do you mean by electric circuit?
Electric current needs a path to flow. This well-structured path designed for the flow of electric current is called the electric circuit. This path usually consists of a source of current that is a cell or battery. The circuit is made of conducting materials like copper wire and there is a switch to start or stop the flow of current and there are other parts too that are attached to the circuit which helps in conduction and measurement of the flowing current.
5. What is a fuse?
A fuse is an electric object that is attached to the electric circuit in order to stop the excess flow of current or to detach the circuit when needed. This works by stopping the current flow in case of urgency that would help to prevent any kind of short circuit. It is a useful electric appliance that must be connected to all households or places that have an electric connection. To know more, solve the important questions by visiting the page Important questions for Class 6 Science and download a free PDF of the same.
6. What is the difference between insulator and conductor?
Insulators and conductors are terms related to electricity. Insulators are those materials that restrict the electric current to flow through them. They are made of non-conducting materials that cause resistance to the flow of current. But conductors are just the opposite. These are materials that allow the electric current to flow through them. They are mostly used in making electric wires, circuits, filaments etc. To know more and practice questions students can download the vedantu app.
7. Why does the bulb give light?
An electric bulb is an illuminating device that lights up when the switch is connected. Now this happens due to the thin filament that is present inside the bulb. This is a delicate conducting material and is connected to thick wires which further connects to the current source. When current flows through the wires and is passed on to the filament, it gets heated up and results in the bulb glowing and produces light.
Chapter wise Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science
Cbse study materials.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Case Study Question. Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Case Study Question. Chapter 8 Body Movements Case Study Question. Chapter 9 The Living Organisms - Characteristics and Habitats Case Study Question. Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Case Study Question. Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Case ...
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 6 Science Water Case study 1. Heating is essential to convert water into its vapour.
Que.3. a)Parallel venation. Que.4) Answer: The stem of a plant helps in upward movement of water. The water and minerals go to leaves and other plant parts attached to the stem. Que.5) Answer: The design made by veins in a leaf is called the leaf venation.
10 months ago July 18, 2023 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Sorting Materials into Groups. ... Toppers Answer Sheets. Marks Wise Questions. ICSE & ISC. Syllabus. Sample Papers. Study Notes. Revision Notes. Short Notes. Important Questions. Previous Year Papers. JEE. Physics. Chemistry. Maths.
Here is an example of case study or passage-based questions for class 6 Science: Passage: Rahul conducted an experiment to investigate how different liquids affect the rusting of iron nails. He placed four iron nails in four separate beakers containing water, vinegar, oil, and saltwater. After one week, he observed the nails and recorded his ...
CBSE 6th Standard CBSE all English medium question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 6th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place
What is Case Study Question for Class 6 Science? Case study or passage-based questions in class 6 Science typically require students to read a given scenario or passage and answer questions based on the information provided. These questions assess students' comprehension, analytical thinking, and application of scientific concepts.
Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances. Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection. Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits. Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets. Chapter 14 Water. Chapter 15 Air Around Us. Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage Out. Chapter-wise extra questions for CBSE class 6 science with answers are given below.
The Case Based Questions: Light, Shadows & Reflections is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 6 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 6 Science Body Movements Case study 1
Class 6 Important Questions for Science are designed according to the CBSE NCERT syllabus. All types of questions are covered in the PDF ranging from one-word answers to one-liners, from short answer types to long-answer types of five marks each. Thus students can prepare for the exams and even clarify their concepts through these.
The CBSE Class 6 Science NCERT Solutions contains a total of 16 chapters. The answers to all these chapters are provided in the links mentioned below: Chapter 1 Components of Food. Chapter 2 Sorting Materials into Groups. Chapter 3 Separation of Substances. Chapter 4 Getting to Know Plants. Chapter 5 Body Movements.
What is Case Study Question for Class 6 Science? Case study or passage-based questions in class 6 Science typically require students to read a given scenario or passage and answer questions based on the information provided. These questions assess students' comprehension, analytical thinking, and application of scientific concepts.
What is Case Study Question for Class 6 Science? Case study or passage-based questions in class 6 Science typically require students to read a given scenario or passage and answer questions based on the information provided. These questions assess students' comprehension, analytical thinking, and application of scientific concepts.
Important Questions For CBSE Class 6 Science. Chapter 1 - Food: Where Does It Come From. Chapter 2 - Components of Food. Chapter 3 - Fibre to Fabric. Chapter 4 - Sorting materials Into Groups. Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances. Chapter 6 - Changes Around Us. Chapter 7 - Getting To Know Plants. Chapter 8 - Body Movements.
Here is the list of Extra Questions for Class 6 Science with Answers based on latest NCERT syllabus prescribed by CBSE. Chapter 1 Food Where Does It Come From Class 6 Extra Questions. Chapter 2 Components of Food Class 6 Extra Questions. Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Class 6 Extra Questions. Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups Class 6 Extra ...
13. Give one difference between a cell and a battery. Answer: A cell produces electricity by chemical reactions taking place in it whereas battery is made up of two or more cells joined together. 14. Write any two uses of electric cells. Answer: It is used in alarm clocks and wrist watches.
Answer: Respiration by animals and plants and burning of fuel. 6. Mention one necessary condition for the combustion to take place. Answer: Presence of air. 7. Define atmosphere. Answer: The blanket of air that surrounds the earth is called atmosphere. 8.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with magnets will help students in the CBSE board class 6 Science examination. This study material comprises of various types of questions such as fill in the blanks, true or false and descriptive answer questions. Login. Study Materials ... The effect observed in each case is stated in Column ...
Light Shadows and Reflection Class 6 Extra Questions. Electricity and Circuits Class 6 Extra Questions. Fun with Magnets Class 6 Extra Questions. Water Class 6 Extra Questions. Air Around Us Class 6 Extra Questions. Garbage In Garbage Out Class 6 Extra Questions. We hope the given CBSE NCERT Chapter Wise Extra Questions for Class 6 Science with ...
These ingredients contain components that are needed by our body. These components are called Nutrients. For example- Proteins. Que. 5) Answer: The major nutrients in our food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Apart from nutrients, food also contains dietary fibres and water.
The types of questions that are commonly asked in the exam from Class 6 Science Chapter 1- Food: Where Does it Come From are as follows. Questions on 'Fill in the blanks' carrying 1 mark each. Very Short Answer Questions carrying 2 marks each. Long Answer Questions carrying 5 marks each. For the reference of students, all these types of ...
CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits - Free PDF Download. Class 6 Science explains fascinating concepts to young minds. They learn many new things and find exciting new facts about different topics. The 12th chapter of the Class 6 NCERT Science book focuses on explaining current, electricity, and circuits.