

How to Write the Management Team Section of a Business Plan + Examples
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Over the last 20+ years, we’ve written business plans for over 4,000 companies and hundreds of thousands of others have used the best business plan template and our other business planning materials.
From this vast experience, we’ve gained valuable insights on how to write a business plan effectively , specifically in the management section.
What is a Management Team Business Plan?
A management team business plan is a section in a comprehensive business plan that introduces and highlights the key members of the company’s management team. This part provides essential details about the individuals responsible for leading and running the business, including their backgrounds, skills, and experience.
It’s crucial for potential investors and stakeholders to evaluate the management team’s competence and qualifications, as a strong team can instill confidence in the company’s ability to succeed.
Why is the Management Team Section of a Business Plan Important?
Your management team plan has 3 goals:
- To prove to you that you have the right team to execute on the opportunity you have defined, and if not, to identify who you must hire to round out your current team
- To convince lenders and investors (e.g., angel investors, venture capitalists) to fund your company (if needed)
- To document how your Board (if applicable) can best help your team succeed
What to Include in Your Management Team Section
There are two key elements to include in your management team business plan as follows:
Management Team Members
For each key member of your team, document their name, title, and background.
Their backgrounds are most important in telling you and investors they are qualified to execute. Describe what positions each member has held in the past and what they accomplished in those positions. For example, if your VP of Sales was formerly the VP of Sales for another company in which they grew sales from zero to $10 million, that would be an important and compelling accomplishment to document.
Importantly, try to relate your team members’ past job experience with what you need them to accomplish at your company. For example, if a former high school principal was on your team, you could state that their vast experience working with both teenagers and their parents will help them succeed in their current position (particularly if the current position required them to work with both customer segments).
This is true for a management team for a small business, a medium-sized or large business.
Management Team Gaps
In this section, detail if your management team currently has any gaps or missing individuals. Not having a complete team at the time you develop your business plan. But, you must show your plan to complete your team.
As such, describe what positions are missing and who will fill the positions. For example, if you know you need to hire a VP of Marketing, state this. Further, state the job description of this person. For example, you might say that this hire will have 10 years of experience managing a marketing team, establishing new accounts, working with social media marketing, have startup experience, etc.
To give you a “checklist” of the employees you might want to include in your Management Team Members and/or Gaps sections, below are the most common management titles at a growing startup (note that many are specific to tech startups):
- Founder, CEO, and/or President
- Chief Operating Officer
- Chief Financial Officer
- VP of Sales
- VP of Marketing
- VP of Web Development and/or Engineering
- UX Designer/Manager
- Product Manager
- Digital Marketing Manager
- Business Development Manager
- Account Management/Customer Service Manager
- Sales Managers/Sales Staff
- Board Members
If you have a Board of Directors or Board of Advisors, you would include the bios of the members of your board in this section.
A Board of Directors is a paid group of individuals who help guide your company. Typically startups do not have such a board until they raise VC funding.
If your company is not at this stage, consider forming a Board of Advisors. Such a board is ideal particularly if your team is missing expertise and/or experience in certain areas. An advisory board includes 2 to 8 individuals who act as mentors to your business. Usually, you meet with them monthly or quarterly and they help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. You typically do not pay advisory board members with cash, but offering them options in your company is a best practice as it allows you to attract better board members and better motivate them.
Management Team Business Plan Example
Below are examples of how to include your management section in your business plan.
Key Team Members
Jim Smith, Founder & CEO
Jim has 15 years of experience in online software development, having co-founded two previous successful online businesses. His first company specialized in developing workflow automation software for government agencies and was sold to a public company in 2003. Jim’s second company developed a mobile app for parents to manage their children’s activities, which was sold to a large public company in 2014. Jim has a B.S. in computer science from MIT and an M.B.A from the University of Chicago
Bill Jones, COO
Bill has 20 years of sales and business development experience from working with several startups that he helped grow into large businesses. He has a B.S. in mechanical engineering from M.I.T., where he also played Division I lacrosse for four years.
We currently have no gaps in our management team, but we plan to expand our team by hiring a Vice President of Marketing to be responsible for all digital marketing efforts.
Vance Williamson, Founder & CEO
Prior to founding GoDoIt, Vance was the CIO of a major corporation with more than 100 retail locations. He oversaw all IT initiatives including software development, sales technology, mobile apps for customers and employees, security systems, customer databases/CRM platforms, etc. He has a B.S in computer science and an MBA in operations management from UCLA.
We currently have two gaps in our Management Team:
A VP of Sales with 10 years of experience managing sales teams, overseeing sales processes, working with manufacturers, establishing new accounts, working with digital marketing/advertising agencies to build brand awareness, etc.
In addition, we need to hire a VP of Marketing with experience creating online marketing campaigns that attract new customers to our site.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Resources for Writing Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Executive Summary
- How to Expertly Write the Company Description in Your Business Plan
- How to Write the Market Analysis Section of a Business Plan
- The Customer Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
- Completing the Competitive Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
- Financial Assumptions and Your Business Plan
- How to Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan
- Everything You Need to Know about the Business Plan Appendix
- Business Plan Conclusion: Summary & Recap
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

How to make a business plan
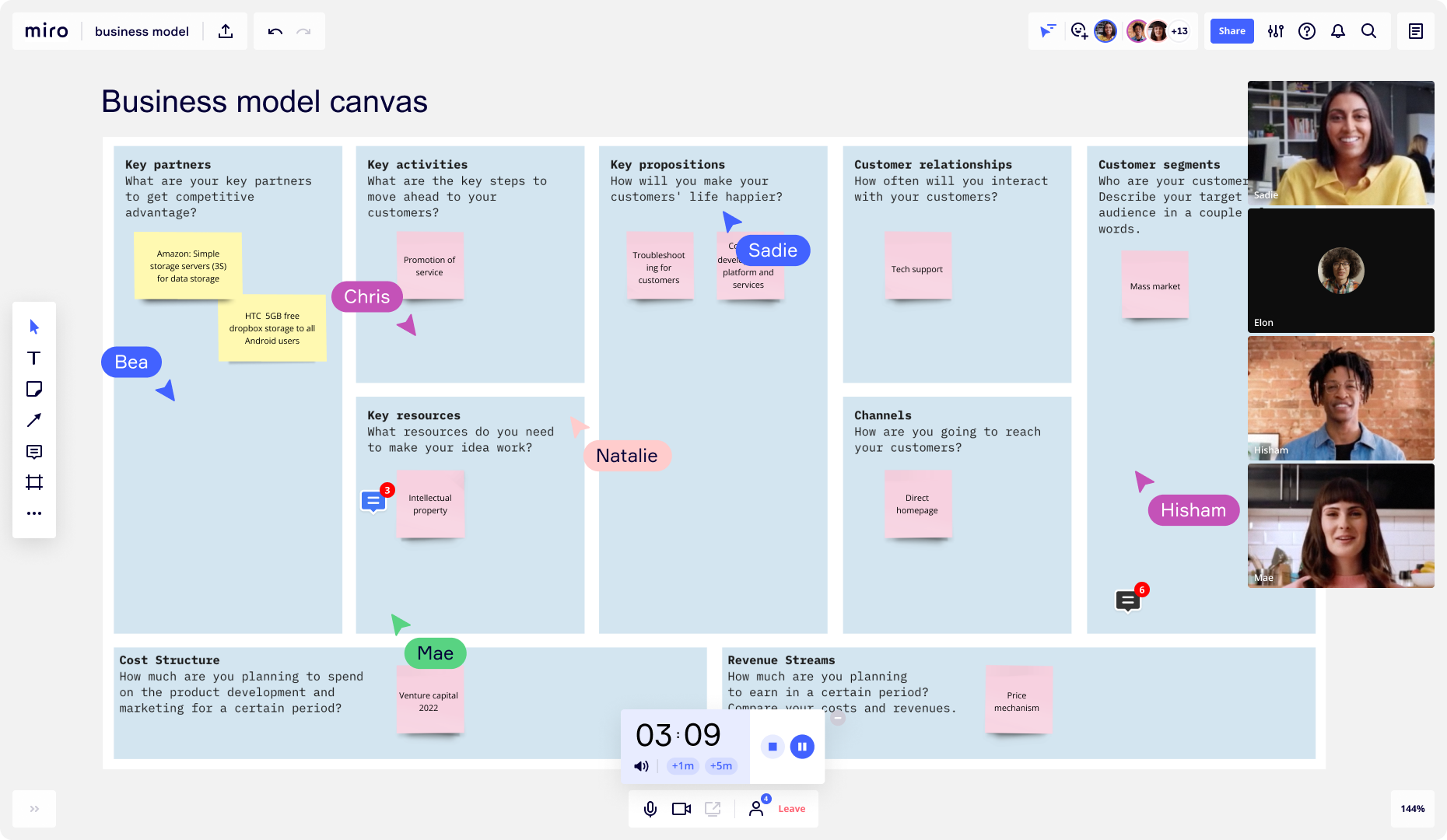
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
The Strategic Planning Process in 4 Steps
To guide you through the strategic planning process, we created this 4 step process you can use with your team. we’ll cover the basic definition of strategic planning, what core elements you should include, and actionable steps to build your strategic plan..
Free Strategic Planning Guide
What is Strategic Planning?
Strategic Planning is when a process where organizations define a bold vision and create a plan with objectives and goals to reach that future. A great strategic plan defines where your organization is going, how you’ll win, who must do what, and how you’ll review and adapt your strategy development.
A strategic plan or a business strategic plan should include the following:
- Your organization’s vision organization’s vision of the future.
- A clearly Articulated mission and values statement.
- A current state assessment that evaluates your competitive environment, new opportunities, and new threats.
- What strategic challenges you face.
- A growth strategy and outlined market share.
- Long-term strategic goals.
- An annual plan with SMART goals or OKRs to support your strategic goals.
- Clear measures, key performance indicators, and data analytics to measure progress.
- A clear strategic planning cycle, including how you’ll review, refresh, and recast your plan every quarter.

Overview of the Strategic Planning Process:
The strategic management process involves taking your organization on a journey from point A (where you are today) to point B (your vision of the future).
Part of that journey is the strategy built during strategic planning, and part of it is execution during the strategic management process. A good strategic plan dictates “how” you travel the selected road.
Effective execution ensures you are reviewing, refreshing, and recalibrating your strategy to reach your destination. The planning process should take no longer than 90 days. But, move at a pace that works best for you and your team and leverage this as a resource.
To kick this process off, we recommend 1-2 weeks (1-hour meeting with the Owner/CEO, Strategy Director, and Facilitator (if necessary) to discuss the information collected and direction for continued planning.)

Questions to Ask:
- Who is on your Planning Team? What senior leadership members and key stakeholders are included? Checkout these links you need help finding a strategic planning consultant , someone to facilitate strategic planning , or expert AI strategy consulting .
- Who will be the business process owner (Strategy Director) of planning in your organization?
- Fast forward 12 months from now, what do you want to see differently in your organization as a result of your strategic plan and implementation?
- Planning team members are informed of their roles and responsibilities.
- A strategic planning schedule is established.
- Existing planning information and secondary data collected.
Action Grid:

Step 1: Determine Organizational Readiness
Set up your plan for success – questions to ask:
- Are the conditions and criteria for successful planning in place at the current time? Can certain pitfalls be avoided?
- Is this the appropriate time for your organization to initiate a planning process? Yes or no? If no, where do you go from here?
Step 2: Develop Your Team & Schedule
Who is going to be on your planning team? You need to choose someone to oversee the strategy implementation (Chief Strategy Officer or Strategy Director) and strategic management of your plan? You need some of the key individuals and decision makers for this team. It should be a small group of approximately 12-15 people.
OnStrategy is the leader in strategic planning and performance management. Our cloud-based software and hands-on services closes the gap between strategy and execution. Learn more about OnStrategy here .
Step 3: Collect Current Data
All strategic plans are developed using the following information:
- The last strategic plan, even if it is not current
- Mission statement, vision statement, values statement
- Past or current Business plan
- Financial records for the last few years
- Marketing plan
- Other information, such as last year’s SWOT, sales figures and projections
Step 4: Review Collected Data
Review the data collected in the last action with your strategy director and facilitator.
- What trends do you see?
- Are there areas of obvious weakness or strengths?
- Have you been following a plan or have you just been going along with the market?
Conclusion: A successful strategic plan must be adaptable to changing conditions. Organizations benefit from having a flexible plan that can evolve, as assumptions and goals may need adjustments. Preparing to adapt or restart the planning process is crucial, so we recommend updating actions quarterly and refreshing your plan annually.

Strategic Planning Phase 1: Determine Your Strategic Position
Want more? Dive into the “ Evaluate Your Strategic Position ” How-To Guide.
Action Grid
Step 1: identify strategic issues.
Strategic issues are critical unknowns driving you to embark on a robust strategic planning process. These issues can be problems, opportunities, market shifts, or anything else that keeps you awake at night and begging for a solution or decision. The best strategic plans address your strategic issues head-on.
- How will we grow, stabilize, or retrench in order to sustain our organization into the future?
- How will we diversify our revenue to reduce our dependence on a major customer?
- What must we do to improve our cost structure and stay competitive?
- How and where must we innovate our products and services?
Step 2: Conduct an Environmental Scan
Conducting an environmental scan will help you understand your operating environment. An environmental scan is called a PEST analysis, an acronym for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological trends. Sometimes, it is helpful to include Ecological and Legal trends as well. All of these trends play a part in determining the overall business environment.
Step 3: Conduct a Competitive Analysis
The reason to do a competitive analysis is to assess the opportunities and threats that may occur from those organizations competing for the same business you are. You need to understand what your competitors are or aren’t offering your potential customers. Here are a few other key ways a competitive analysis fits into strategic planning:
- To help you assess whether your competitive advantage is really an advantage.
- To understand what your competitors’ current and future strategies are so you can plan accordingly.
- To provide information that will help you evaluate your strategic decisions against what your competitors may or may not be doing.
Learn more on how to conduct a competitive analysis here .
Step 4: Identify Opportunities and Threats
Opportunities are situations that exist but must be acted on if the business is to benefit from them.
What do you want to capitalize on?
- What new needs of customers could you meet?
- What are the economic trends that benefit you?
- What are the emerging political and social opportunities?
- What niches have your competitors missed?
Threats refer to external conditions or barriers preventing a company from reaching its objectives.
What do you need to mitigate? What external driving force do you need to anticipate?
Questions to Answer:
- What are the negative economic trends?
- What are the negative political and social trends?
- Where are competitors about to bite you?
- Where are you vulnerable?
Step 5: Identify Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths refer to what your company does well.
What do you want to build on?
- What do you do well (in sales, marketing, operations, management)?
- What are your core competencies?
- What differentiates you from your competitors?
- Why do your customers buy from you?
Weaknesses refer to any limitations a company faces in developing or implementing a strategy.
What do you need to shore up?
- Where do you lack resources?
- What can you do better?
- Where are you losing money?
- In what areas do your competitors have an edge?
Step 6: Customer Segments

Customer segmentation defines the different groups of people or organizations a company aims to reach or serve.
- What needs or wants define your ideal customer?
- What characteristics describe your typical customer?
- Can you sort your customers into different profiles using their needs, wants and characteristics?
- Can you reach this segment through clear communication channels?
Step 7: Develop Your SWOT
A SWOT analysis is a quick way of examining your organization by looking at the internal strengths and weaknesses in relation to the external opportunities and threats. Creating a SWOT analysis lets you see all the important factors affecting your organization together in one place.
It’s easy to read, easy to communicate, and easy to create. Take the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats you developed earlier, review, prioritize, and combine like terms. The SWOT analysis helps you ask and answer the following questions: “How do you….”
- Build on your strengths
- Shore up your weaknesses
- Capitalize on your opportunities
- Manage your threats

Strategic Planning Process Phase 2: Developing Strategy
Want More? Deep Dive Into the “Developing Your Strategy” How-To Guide.
Step 1: Develop Your Mission Statement
The mission statement describes an organization’s purpose or reason for existing.
What is our purpose? Why do we exist? What do we do?
- What are your organization’s goals? What does your organization intend to accomplish?
- Why do you work here? Why is it special to work here?
- What would happen if we were not here?
Outcome: A short, concise, concrete statement that clearly defines the scope of the organization.
Step 2: discover your values.
Your values statement clarifies what your organization stands for, believes in and the behaviors you expect to see as a result. Check our the post on great what are core values and examples of core values .
How will we behave?
- What are the key non-negotiables that are critical to the company’s success?
- What guiding principles are core to how we operate in this organization?
- What behaviors do you expect to see?
- If the circumstances changed and penalized us for holding this core value, would we still keep it?
Outcome: Short list of 5-7 core values.
Step 3: casting your vision statement.

A Vision Statement defines your desired future state and directs where we are going as an organization.
Where are we going?
- What will our organization look like 5–10 years from now?
- What does success look like?
- What are we aspiring to achieve?
- What mountain are you climbing and why?
Outcome: A picture of the future.
Step 4: identify your competitive advantages.

A competitive advantage is a characteristic of an organization that allows it to meet its customer’s need(s) better than its competition can. It’s important to consider your competitive advantages when creating your competitive strategy.
What are we best at?
- What are your unique strengths?
- What are you best at in your market?
- Do your customers still value what is being delivered? Ask them.
- How do your value propositions stack up in the marketplace?
Outcome: A list of 2 or 3 items that honestly express the organization’s foundation for winning.
Step 5: crafting your organization-wide strategies.

Your competitive strategy is the general methods you intend to use to reach your vision. Regardless of the level, a strategy answers the question “how.”
How will we succeed?
- Broad: market scope; a relatively wide market emphasis.
- Narrow: limited to only one or few segments in the market
- Does your competitive position focus on lowest total cost or product/service differentiation or both?
Outcome: Establish the general, umbrella methods you intend to use to reach your vision.

Phase 3: Strategic Plan Development
Want More? Deep Dive Into the “Build Your Plan” How-To Guide.
Strategic Planning Process Step 1: Use Your SWOT to Set Priorities
If your team wants to take the next step in the SWOT analysis, apply the TOWS Strategic Alternatives Matrix to your strategy map to help you think about the options you could pursue. To do this, match external opportunities and threats with your internal strengths and weaknesses, as illustrated in the matrix below:
TOWS Strategic Alternatives Matrix
Evaluate the options you’ve generated, and identify the ones that give the greatest benefit, and that best achieve the mission and vision of your organization. Add these to the other strategic options that you’re considering.
Step 2: Define Long-Term Strategic Objectives
Long-Term Strategic Objectives are long-term, broad, continuous statements that holistically address all areas of your organization. What must we focus on to achieve our vision? Check out examples of strategic objectives here. What are the “big rocks”?
Questions to ask:
- What are our shareholders or stakeholders expectations for our financial performance or social outcomes?
- To reach our outcomes, what value must we provide to our customers? What is our value proposition?
- To provide value, what process must we excel at to deliver our products and services?
- To drive our processes, what skills, capabilities and organizational structure must we have?
Outcome: Framework for your plan – no more than 6. You can use the balanced scorecard framework, OKRs, or whatever methodology works best for you. Just don’t exceed 6 long-term objectives.

Step 3: Setting Organization-Wide Goals and Measures

Once you have formulated your strategic objectives, you should translate them into goals and measures that can be communicated to your strategic planning team (team of business leaders and/or team members).
You want to set goals that convert the strategic objectives into specific performance targets. Effective strategic goals clearly state what, when, how, and who, and they are specifically measurable. They should address what you must do in the short term (think 1-3 years) to achieve your strategic objectives.
Organization-wide goals are annual statements that are SMART – specific, measurable, attainable, responsible, and time-bound. These are outcome statements expressing a result to achieve the desired outcomes expected in the organization.
What is most important right now to reach our long-term objectives?
Outcome: clear outcomes for the current year..

Step 4: Select KPIs

Key Performance Indicators (KPI) are the key measures that will have the most impact in moving your organization forward. We recommend you guide your organization with measures that matter. See examples of KPIs here.
How will we measure our success?
Outcome: 5-7 measures that help you keep the pulse on your performance. When selecting your Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), ask, “What are the key performance measures we need to track to monitor if we are achieving our goals?” These KPIs include the key goals you want to measure that will have the most impact on moving your organization forward.
Step 5: Cascade Your Strategies to Operations

To move from big ideas to action, creating action items and to-dos for short-term goals is crucial. This involves translating strategy from the organizational level to individuals. Functional area managers and contributors play a role in developing short-term goals to support the organization.
Before taking action, decide whether to create plans directly derived from the strategic plan or sync existing operational, business, or account plans with organizational goals. Avoid the pitfall of managing multiple sets of goals and actions, as this shifts from strategic planning to annual planning.
Questions to Ask
- How are we going to get there at a functional level?
- Who must do what by when to accomplish and drive the organizational goals?
- What strategic questions still remain and need to be solved?
Department/functional goals, actions, measures and targets for the next 12-24 months
Step 6: Cascading Goals to Departments and Team Members
Now in your Departments / Teams, you need to create goals to support the organization-wide goals. These goals should still be SMART and are generally (short-term) something to be done in the next 12-18 months. Finally, you should develop an action plan for each goal.
Keep the acronym SMART in mind again when setting action items, and make sure they include start and end dates and have someone assigned their responsibility. Since these action items support your previously established goals, it may be helpful to consider action items your immediate plans on the way to achieving your (short-term) goals. In other words, identify all the actions that need to occur in the next 90 days and continue this same process every 90 days until the goal is achieved.
Examples of Cascading Goals:

Phase 4: Executing Strategy and Managing Performance
Want more? Dive Into the “Managing Performance” How-To Guide.
Step 1: Strategic Plan Implementation Schedule
Implementation is the process that turns strategies and plans into actions in order to accomplish strategic objectives and goals.
How will we use the plan as a management tool?
- Communication Schedule: How and when will you roll-out your plan to your staff? How frequently will you send out updates?
- Process Leader: Who is your strategy director?
- Structure: What are the dates for your strategy reviews (we recommend at least quarterly)?
- System & Reports: What are you expecting each staff member to come prepared with to those strategy review sessions?
Outcome: Syncing your plan into the “rhythm of your business.”
Once your resources are in place, you can set your implementation schedule. Use the following steps as your base implementation plan:
- Establish your performance management and reward system.
- Set up monthly and quarterly strategy meetings with established reporting procedures.
- Set up annual strategic review dates including new assessments and a large group meeting for an annual plan review.
Now you’re ready to start plan roll-out. Below are sample implementation schedules, which double for a full strategic management process timeline.

Step 2: Tracking Goals & Actions
Monthly strategy meetings don’t need to take a lot of time – 30 to 60 minutes should suffice. But it is important that key team members report on their progress toward the goals they are responsible for – including reporting on metrics in the scorecard they have been assigned.
By using the measurements already established, it’s easy to make course corrections if necessary. You should also commit to reviewing your Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) during these regular meetings. Need help comparing strategic planning software ? Check out our guide.
Effective Strategic Planning: Your Bi-Annual Checklist

Never lose sight of the fact that strategic plans are guidelines, not rules. Every six months or so, you should evaluate your strategy execution and strategic plan implementation by asking these key questions:
- Will your goals be achieved within the time frame of the plan? If not, why?
- Should the deadlines be modified? (Before you modify deadlines, figure out why you’re behind schedule.)
- Are your goals and action items still realistic?
- Should the organization’s focus be changed to put more emphasis on achieving your goals?
- Should your goals be changed? (Be careful about making these changes – know why efforts aren’t achieving the goals before changing the goals.)
- What can be gathered from an adaptation to improve future planning activities?
Why Track Your Goals?
- Ownership: Having a stake and responsibility in the plan makes you feel part of it and leads you to drive your goals forward.
- Culture: Successful plans tie tracking and updating goals into organizational culture.
- Implementation: If you don’t review and update your strategic goals, they are just good intentions
- Accountability: Accountability and high visibility help drive change. This means that each measure, objective, data source and initiative must have an owner.
- Empowerment: Changing goals from In Progress to Complete just feels good!
Step 3: Review & Adapt
Guidelines for your strategy review.
The most important part of this meeting is a 70/30 review. 30% is about reviewing performance, and 70% should be spent on making decisions to move the company’s strategy forward in the next quarter.
The best strategic planners spend about 60-90 minutes in the sessions. Holding meetings helps focus your goals on accomplishing top priorities and accelerating the organization’s growth. Although the meeting structure is relatively simple, it does require a high degree of discipline.
Strategy Review Session Questions:
Strategic planning frequently asked questions, read our frequently asked questions about strategic planning to learn how to build a great strategic plan..
Strategic planning is when organizations define a bold vision and create a plan with objectives and goals to reach that future. A great strategic plan defines where your organization is going, how you’ll win, who must do what, and how you’ll review and adapt your strategy..
Your strategic plan needs to include an assessment of your current state, a SWOT analysis, mission, vision, values, competitive advantages, growth strategy, growth enablers, a 3-year roadmap, and annual plan with strategic goals, OKRs, and KPIs.
A strategic planning process should take no longer than 90 days to complete from start to finish! Any longer could fatigue your organization and team.
There are four overarching phases to the strategic planning process that include: determining position, developing your strategy, building your plan, and managing performance. Each phase plays a unique but distinctly crucial role in the strategic planning process.
Prior to starting your strategic plan, you must go through this pre-planning process to determine your organization’s readiness by following these steps:
Ask yourself these questions: Are the conditions and criteria for successful planning in place now? Can we foresee any pitfalls that we can avoid? Is there an appropriate time for our organization to initiate this process?
Develop your team and schedule. Who will oversee the implementation as Chief Strategy Officer or Director? Do we have at least 12-15 other key individuals on our team?
Research and Collect Current Data. Find the following resources that your organization may have used in the past to assist you with your new plan: last strategic plan, mission, vision, and values statement, business plan, financial records, marketing plan, SWOT, sales figures, or projections.
Finally, review the data with your strategy director and facilitator and ask these questions: What trends do we see? Any obvious strengths or weaknesses? Have we been following a plan or just going along with the market?
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations.
Subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.
How to succeed at team planning: 6 best practices
%20(2).jpg)
Your organization’s mission is clear, its yearly goals are pristine, and even its quarterly objectives have all been ironed out. As for individual projects, you’ve got plans for those too. You’re all set, right?
Not quite.
Between your ten-thousand-feet long-term plans and your ground-level short-term ones, there’s a whole world of priorities, processes, and potential.
That’s where team planning comes in.
But is all this planning really necessary? Although it may feel overwhelming putting together yet another set of goals and objectives down on paper, it’s a step that can nevertheless save you a lot of time and trouble in the long run. When done properly, an effective team plan will even serve as an essential connective tissue between what your team wants to get done today and what it needs to accomplish all year.
So let’s break down the basics of successful team planning, from all the benefits it can offer you to how to best get it done.
What is team planning?
Team planning is when you create a strategic document that outlines the team’s objectives for the next year or quarter against the organization’s long-term goals. This makes it possible to prioritize day-to-day projects, more effectively assign tasks and responsibilities, create realistic timeframes, and allocate resources more efficiently, among other benefits. Even more importantly, it helps teams understand their work within its larger context.
Let’s consider a marketing team at a new real estate tech startup. Their company was recently established with a mission to make it easier for property sellers to find interested buyers. This is their overall objective. Using team planning, the marketing team might first make sure everyone is aligned by establishing their own goals. For example, over the next year, they'll double the company’s conversion rates. Over the next quarter, they'll build out an integrated ad campaign. And over the next month, they'll make strategic hires to support their other goals.
From there, the team will be in a great place to start putting together plans for their other projects. They’ll have an understanding of the full context, alignment around everyone’s responsibilities, and a high-level strategy for getting it all done.
Why teams should have a defined planning process
If you can get everyone on the same page and come up with a strategy that everyone sticks with, your team plan can be one of the most valuable documents you spend time on all quarter. Here are a few benefits you can expect to get out of it:
- Clarify ways of working: Do you want to establish some quality control mechanisms? Or maybe you just want to make sure your team’s workflows are as efficient as possible? A team plan can help you clear up exactly how everything, no matter how simple or complex, should get done. And that can save an enormous amount of time and stress.
- Align and set measurable goals: With a well-structured planning process, you’ll be better able to agree on the goals that are most crucial, as well as define how they're measured. This will help the team evaluate their progress, track their performance, and make necessary adjustments as needed.
- Define roles and responsibilities: A team plan is a great chance to make explicit what you expect everyone to do. This can include both the big and the small, such as the projects they’ll take on, the tasks they’ll carry out, and the outcomes they’ll need to achieve. Putting down all this will also make everyone more accountable, which will help foster a sense of ownership among the team.
- Better time management and resource allocation: A good team plan will also help you go through, identify, and prepare all the resources you’ll need to reach your goals. This can include workforce, budget, specific technology, and more. Allocating all this ahead of time will prevent misuse, saving both time and money.
- Additional flexibility: Just because a team plan puts everything down on paper doesn’t mean you’ll be stuck to one path. In fact, the best team plan will help make the team more flexible and agile by giving them a structured foundation that clarifies priorities and reduces ambiguities. This will make it easier to exercise creativity when something unexpected happens.
Who should be involved with team planning?
As its name suggests, a team plan shouldn’t be a set of orders delivered from executives up high. Rather, it should ideally be an inclusive document that contains input from everyone on the team.
Of course, depending on the team’s size, its roles, and its functions, it may not be feasible to include absolutely everyone. But, at the very least, its creation should involve a representative group. For instance, team leaders and other senior managers should be there to make sure that the team plan aligns with the organization’s larger goals and objectives. Likewise, more junior-level team members need to be included so that there is buy-in from the bottom up. It can also be a good idea to include an external facilitator so that your team has a more impartial voice who can weigh in on sensitive matters and offer an outside perspective.
Regardless, try to include as much of your team as possible so that your plan is as collaborative as possible.
6 tips for improving your team planning sessions
The process of coming up with a team plan is a great opportunity to improve your team’s sense of communication and collaboration — but only if you have a strategy for walking them through it. Here are a few elements you should include to come up with a team plan that gets the job done.
1. Establish clear objectives and roles
A good place to begin building your plan is by first outlining what it is you want to do. During this initial meeting, you should discuss what you’d like your team plan to do. Should it merely be a rough guide for aligning individual projects with loftier company goals? Or should it get into the weeds regarding what each team member does?
Once you’re on the same page regarding your objectives, try to look ahead and establish how everyone will contribute. Will it be more efficient for a small group to come up with a plan that everyone votes on? Or would it be better to organize and run a larger committee? This can be a good time to build out a team charter that establishes the ground rules for how your team will work together and communicate — both on this team plan and on other projects. Whether you do this from scratch or are using a template , this team charter should help set expectations for your team as you move forward.
2. Organize a planning session
Now it’s time to start actually making your plan . That means getting everyone together to talk and hash out what this plan will involve. But what’s the best way to do that? Creating something as overarching as a team plan can feel daunting. That’s why, in order to keep your planning session focused, it can be smart to consider how it gets put together.
For instance, building out a plan that involves all of your team’s projects over the next year or quarter can include a lot of information. Rather than hoping everyone not only has access to that information, but also thoroughly reviews it ahead of time, why not help them prepare by consolidating everything in one place? You could get this done by preparing a shared drive or by filling out a pre-work template . That way, it'll be easy for everyone to get on the same page.
You might also want to consider how to promote inclusive, transparent, and productive discussions (that is, no groupthink ). After all, if there are team members who don’t feel included in the session, or who feel like their contributions aren’t getting heard, then the team plan may come out incomplete. Fortunately, there are a variety of ways to work around this. You could get the session started with an icebreaker , or give participants the option to share input before and after a session as well.
And, maybe most importantly, don’t forget to set up some ground rules at the outset of the meeting so that everyone feels comfortable and ready to engage.
3. Establish clear roles and responsibilities
As you start putting together your team plan, one of the most important tasks will be assigning what everyone will be responsible for. While job titles and past roles can be a guide, the evolving nature of many projects and the way many team members’ responsibilities often overlap can sometimes create confusion when it comes to who should do what.
One way to solve this is by agreeing on a framework for defining roles and responsibilities for different projects. This will help ensure accountability while giving your team enough flexibility to adapt to changing needs. For example, two popular frameworks are the RACI and DACI matrixes. Although similar, they each have four distinct roles that different tasks can be mapped onto.
For example, RACI uses the following four roles:
- Responsible: The person responsible for getting the work done.
- Accountable: The person accountable for the project’s outcome.
- Consulted: The person who shares their expertise by providing input or feedback.
- Informed: This person is kept informed about the project’s status, but is not directly involved.
In contrast, DACI uses these four roles:
- Driver: The person driving the project forward, either through coordination or production.
- Approver: The person who approves or rejects the project. They're responsible for its outcome.
- Contributor: The person who informs the project by sharing their expertise.
- Informed: This person is kept informed about the project’s status, but isn't directly involved.
Simple but highly adaptable, frameworks like these can help your team quickly and efficiently determine the work each person is responsible for any a project-by-project basis.
Note: Look out for a Mural template coming soon that'll help you leverage these two frameworks.
4. Define what success looks like
Just as your planning session should make explicit what everyone on your team is doing, so should it clarify what your team is working toward. By defining these goals, as well as what success will look like, you can both make sure that your team plan aligns with your larger organizational objectives, as well as give employees a powerful incentive as they work through their projects.
The trick is coming up with goals that are lofty enough to motivate and move the needle, but aren’t so ambitious they can’t be met. To achieve this, consider using the SMART goal criteria. Short for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound, these types of goals give you useful parameters that can help you remove guesswork and establish more effective metrics for success.
Let’s consider an example. Take this goal:
The team will help the company improve profit by next quarter.
While it may have a specific goal (improve profit) and a timeline (next quarter), there still isn’t much here to gauge the team’s performance or progress. How should they help turn a profit? How will profit be measured? Given the state of the company, how realistic is this goal?
Let’s rewrite it to address these concerns:
The team will increase the company’s net profit margin by 10% over the current margin, as measured by financial reports. They'll achieve this through cost-saving and efficiency measures, as well as by increasing sales by at least 20%. The timeframe for accomplishing this goal is the next quarter.
Now we have a highly specific goal that clearly instructs exactly what the team needs to accomplish (increase net profit margin by 10% over current margin) and how (cost-saving and efficiency measures, as well as a 20% or more increase in sales). This will make it much easier for the team to work toward this goal — and much more likely they’ll succeed.
5. Define potential costs, resources, requirements, and roadblocks
With your goals and metrics for success set, you should also take the opportunity to include any additional information that could be helpful for your team. This could include the projected costs of different projects, which team leaders and managers can use to properly prioritize what needs to be done. Alongside this, consider the resources your team will need for each project. Are these resources available? Or will they need to be allocated ahead of time? If so, you may want to create a plan for that as well.
You could also list out potential roadblocks and other challenges that might stand in the way. For instance, are there any dependencies that might slow down the start of a project? Or any prerequisites that'll need to be addressed? By identifying and calling these out, you’ll help prepare your team and save them time.
6. Create a project plan
Once you’ve made it through the team planning process, it can be worth seeing how it all comes together by creating an individual project plan. Hopefully, with your team’s goals laid out and mapped to organizational objectives, roles and responsibilities all properly defined, and success metrics established, all that'll be left to do is to size everything down for the scope of the project.
One easy way to do this is by plugging information into a project planning template . With predefined sections for different parts of the project (such as its goals, key participants, cost and budget, and more), you can quickly align team members while streamlining the work of matching the project plan to the larger strategy for the team. As you do this, take note of any places where you think the team and project plans might diverge. Do the project’s goals advance what the wider team is trying to accomplish? Does it make good use of resources or team members’ time?
Keep comparing your plans side by side and updating as needed. With your team plan serving as a check, you can make sure your projects all build toward your team’s larger success.
Help your teams plan to succeed
Every organization needs an overarching mission. And each project needs to be planned out. But one of the primary reasons that projects jump off the rails and don’t go as planned, or why carefully crafted mission statements get ignored, is a disconnect between an organization’s ideal and its day-to-day work. Building out an effective team plan helps solve for this.
While there’s no such thing as a 100 percent guarantee for success, a team plan can help get you much closer by providing you with a detailed roadmap for you to follow as you cycle through projects. And because it keeps you aligned with loftier objectives, even as you dig into the weeds, it’s a great way to get a quick gut check on your organization’s overall progress.
So what’s going to go into your team plan? If you can come up with it, Mural can cover it. Check out our library of templates or sign up today for free .
About the authors

David Young
Tagged Topics
Related blog posts

How to lead OKR planning that drives impact
%20(2).jpg)
How to hold effective strategic planning meetings
.jpg)
The 5 steps of the strategic planning process
Related blog posts.
%20(1).jpg)
Agile documentation: Examples and best practices
%20(1).jpg)
The ROI of teamwork: How to quantify the value of better collaboration
%20(1).jpg)
How to conduct a strategic analysis
Get the free 2023 collaboration trends report.
Extraordinary teamwork isn't an accident
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
- How to Use Your Business Plan Most Effectively
- The Basics of Writing a Business Plan
- 12 Reasons You Need a Business Plan
- The Main Objectives of a Business Plan
- What to Include and Not Include in a Successful Business Plan
- The Top 4 Types of Business Plans
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Presenting Your Business Plan in 10 Slides
- 6 Tips for Making a Winning Business Presentation
- 12 Ways to Set Realistic Business Goals and Objectives
- 3 Key Things You Need to Know About Financing Your Business
- How to Perfectly Pitch Your Business Plan in 10 Minutes
- How to Fund Your Business Through Friends and Family Loans and Crowdsourcing
- How to Fund Your Business Using Banks and Credit Unions
- How to Fund Your Business With an SBA Loan
- How to Fund Your Business With Bonds and Indirect Funding Sources
- How to Fund Your Business With Venture Capital
- How to Fund Your Business With Angel Investors
- How to Use Your Business Plan to Track Performance
- How to Make Your Business Plan Attractive to Prospective Partners
- Is This Idea Going to Work? How to Assess the Potential of Your Business.
- When to Update Your Business Plan
- How to Write the Management Team Section to Your Business Plan
- How to Create a Strategic Hiring Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary That Sells Your Idea
- How to Build a Team of Outside Experts for Your Business
- Use This Worksheet to Write a Product Description That Sells
- What Is Your Unique Selling Proposition? Use This Worksheet to Find Your Greatest Strength.
- How to Raise Money With Your Business Plan
- Customers and Investors Don't Want Products. They Want Solutions.
- 5 Essential Elements of Your Industry Trends Plan
- How to Identify and Research Your Competition
- Who Is Your Ideal Customer? 4 Questions to Ask Yourself.
- How to Identify Market Trends in Your Business Plan
- How to Define Your Product and Set Your Prices
- How to Determine the Barriers to Entry for Your Business
- How to Get Customers in Your Store and Drive Traffic to Your Website
- How to Effectively Promote Your Business to Customers and Investors
- What Equipment and Facilities to Include in Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Income Statement for Your Business Plan
- How to Make a Balance Sheet
- How to Make a Cash Flow Statement
- How to Use Financial Ratios to Understand the Health of Your Business
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Retail and Sales Businesses
- How to Make Realistic Financial Forecasts
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Manufacturers
- What Technology Needs to Include In Your Business Plan
- How to List Personnel and Materials in Your Business Plan
- The Role of Franchising
- The Best Ways to Follow Up on a Buisiness Plan
- The Best Books, Sites, Trade Associations and Resources to Get Your Business Funded and Running
- How to Hire the Right Business Plan Consultant
- Business Plan Lingo and Resources All Entrepreneurs Should Know
- How to Write a Letter of Introduction
- What To Put on the Cover Page of a Business Plan
- How to Format Your Business Plan
- 6 Steps to Getting Your Business Plan In Front of Investors
How to Write the Management Team Section to Your Business Plan Think you've got an all-star lineup? These are the key characteristics to showcase.
By Eric Butow • Oct 27, 2023
Key Takeaways
- Who to include in your org chart
- The key traits to highlight
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
This is part 1 / 8 of Write Your Business Plan: Section 3: Selling Your Product and Team series.
One crucial aspect of any business plan is the management team slide, which outlines the key employees in the organization. Here are some things to keep in mind when putting together your all-star lineup.
Put Yourself First
Don't be modest. If you're the head of the business, you should feature yourself first. After all, you are the entrepreneur behind the business venture, and you will have to put your neck on the line, answer the hard questions, and take the criticism— as well as the praise and acclaim, should there be some.
If you want to impress people with your management team, it's essential to let your readers know who is at the helm and who is selecting the management team. Explain your background, including your vision, your credentials, and why you chose the management team you did.
A business follows the lead of the founder, and as such, you need to briefly explain what is expected of this management team and the role you see it, as a group, playing in the future of this business.
Related: Does Your Team Have the Right Stuff to Attract Venture Capital?
Highlight These Characteristics
Identifying your managers is about presenting what they bring to the table. You can provide this by describing them in terms of the following characteristics:
Education Impressive educational credentials among company managers provide strong reasons for an investor or other plan reader to feel good about your company. Use your judgment in deciding what educational background to include and how to emphasize it. If you're starting a fine restaurant, for example, and your chef graduated at the top of her class from the Culinary Institute of America, play that front and center. If you're starting a courier service and your partner has an anthropology degree from a little-known school, mention it, but don't make a big deal out of it.
Employment Prior work experience in a related field is something many investors look for. If you've spent ten years in management in the retail men's apparel business before opening a tuxedo outlet, an investor can feel confident that you know what you're doing. Likewise, you'll want to explain your team members' key, appropriate positions. Describe any relevant jobs in terms of job title, years of experience, names of employers, and so on. But remember, this isn't a resume. You can feel free to skim over or omit any irrelevant experience. You do not have to provide exact dates of employment.
Related: How to Craft a Business Plan That Will Turn Investors' Heads
Skills A title is one thing, but what you learn while holding it is another. In addition to pointing out that you were a district sales manager for a stereo equipment wholesaler, you should describe your responsibilities and the skills you honed while fulfilling them. Again, list your management team's skills that pertain to this business. A great cook may have incredible accounting skills, but that doesn't matter in the new restaurant's kitchen.
Each time you mention skills that you or a management team member has spent years acquiring at another company, it will be another reason for an investor to believe you can do it at your own company.
Accomplishments Dust off your plaques and trot out your calculator for this one. If you or one of your team members has been awarded patents, achieved record sales gains, or once opened an unbelievable number of new stores in the space of a year, now's the time to talk about it. Don't brag. Just be factual and remember to quantify. If, for example, you have twelve patents, your sales manager had five years of thirty percent annual sales gains, and you oversaw the grand openings of forty-two stores in eleven months, this is the stuff investors and others reading your business plan will want to see. Investors are looking to back impressive winners, and quantifiable results speak strongly to businesspeople of all stripes.
Personal information Investors want to know with whom they're dealing in terms of the personal side. Personal information on each member of your management team may include age, city of residence, notable charitable or community activities, and, last but not least, personal motivation for joining the company. Investors like to see vigorous, committed, and involved people in the companies they back. Mentioning one or two of the relevant personal details of your key managers may help investors feel they know what they're getting into, especially in today's increasingly transparent business climate.
Related: How to Evaluate Your Startup Like a VC
Who to Include in Your Plan
Should you mention everyone in your organization down to shop foremen or stop with the people on your executive committee? The answer is probably neither. Instead, think about your managers in terms of the crucial functions of your business.
In deciding the scope of the management section of your plan, consider the following business functions, and make sure you've explained who will handle those that are important to your enterprise:
- Advertising
- Distribution
- Human Resources
- Technical Operations
Related: How To Build a Team of Outside Experts for Your Business
What Does Each Person Do?
There's more to a job than a title. A director in one organization is a high and mighty individual, whereas a director is practically nobody in another company. Many industries have unique job titles, such as managing editor, creative director, and junior accountant level II, with no counterparts in other industries.
In a longer plan, when you give your management team's background and describe their titles, don't stop there. Go on and tell the reader exactly what each management team member will be expected to do in the company. This may be especially important in a startup, where not every position is filled. If the CFO will handle your marketing work until you get further down the road, let readers know this upfront. You certainly can't expect them to figure that out on their own.
In a shorter business plan, or mini-plan , choose those people most vital to your business. If you are opening a martial arts studio, the instructors, or lead instructors, are significant, as is the software developer in a new software company. While you have room to describe these people in more detail in a longer plan, in the shorter miniplans, use one defining sentence for your top five people.
Related: 6 Tips for Making a Winning Business Presentation
Future Hires
If you do have significant holes in your management team, you'll want to describe your plans for filling them. You may say, for example, "Marketing duties are being handled temporarily by the vice president for finance. Once sales have reached the $500,000 per month level, approximately six months after startup, a dedicated vice president of marketing will be retained to fulfill that function."
In some cases, particularly if you're in a really shaky startup and need solid talent, you may have to describe in some detail your plans for luring a hotshot industry expert to your fledgling enterprise. Then, briefly describe your ideal candidate. For a mini-plan, you may write, "We plan to hire a marketing VP who excels in reaching our 20–29 target market."
Related: Vusi Thembekwayo's 7 Rules of Pitching
More in Write Your Business Plan
Section 1: the foundation of a business plan, section 2: putting your business plan to work, section 3: selling your product and team, section 4: marketing your business plan, section 5: organizing operations and finances, section 6: getting your business plan to investors.
Successfully copied link
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Discover how today’s most successful IT leaders stand out from the rest. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Read the report .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Business strategy |
- 7 strategic planning models, plus 8 fra ...
7 strategic planning models, plus 8 frameworks to help you get started
Strategic planning is vital in defining where your business is going in the next three to five years. With the right strategic planning models and frameworks, you can uncover opportunities, identify risks, and create a strategic plan to fuel your organization’s success. We list the most popular models and frameworks and explain how you can combine them to create a strategic plan that fits your business.
A strategic plan is a great tool to help you hit your business goals . But sometimes, this tool needs to be updated to reflect new business priorities or changing market conditions. If you decide to use a model that already exists, you can benefit from a roadmap that’s already created. The model you choose can improve your knowledge of what works best in your organization, uncover unknown strengths and weaknesses, or help you find out how you can outpace your competitors.
In this article, we cover the most common strategic planning models and frameworks and explain when to use which one. Plus, get tips on how to apply them and which models and frameworks work well together.
Strategic planning models vs. frameworks
First off: This is not a one-or-nothing scenario. You can use as many or as few strategic planning models and frameworks as you like.
When your organization undergoes a strategic planning phase, you should first pick a model or two that you want to apply. This will provide you with a basic outline of the steps to take during the strategic planning process.
![business planning team [Inline illustration] Strategic planning models vs. frameworks (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/89236d14-1abf-4f49-8b91-4187147f1c63/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
During that process, think of strategic planning frameworks as the tools in your toolbox. Many models suggest starting with a SWOT analysis or defining your vision and mission statements first. Depending on your goals, though, you may want to apply several different frameworks throughout the strategic planning process.
For example, if you’re applying a scenario-based strategic plan, you could start with a SWOT and PEST(LE) analysis to get a better overview of your current standing. If one of the weaknesses you identify has to do with your manufacturing process, you could apply the theory of constraints to improve bottlenecks and mitigate risks.
Now that you know the difference between the two, learn more about the seven strategic planning models, as well as the eight most commonly used frameworks that go along with them.
![business planning team [Inline illustration] The seven strategic planning models (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/23048ae4-8a18-4b9b-ad9e-33b0fc5d04ee/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
1. Basic model
The basic strategic planning model is ideal for establishing your company’s vision, mission, business objectives, and values. This model helps you outline the specific steps you need to take to reach your goals, monitor progress to keep everyone on target, and address issues as they arise.
If it’s your first strategic planning session, the basic model is the way to go. Later on, you can embellish it with other models to adjust or rewrite your business strategy as needed. Let’s take a look at what kinds of businesses can benefit from this strategic planning model and how to apply it.
Small businesses or organizations
Companies with little to no strategic planning experience
Organizations with few resources
Write your mission statement. Gather your planning team and have a brainstorming session. The more ideas you can collect early in this step, the more fun and rewarding the analysis phase will feel.
Identify your organization’s goals . Setting clear business goals will increase your team’s performance and positively impact their motivation.
Outline strategies that will help you reach your goals. Ask yourself what steps you have to take in order to reach these goals and break them down into long-term, mid-term, and short-term goals .
Create action plans to implement each of the strategies above. Action plans will keep teams motivated and your organization on target.
Monitor and revise the plan as you go . As with any strategic plan, it’s important to closely monitor if your company is implementing it successfully and how you can adjust it for a better outcome.
2. Issue-based model
Also called goal-based planning model, this is essentially an extension of the basic strategic planning model. It’s a bit more dynamic and very popular for companies that want to create a more comprehensive plan.
Organizations with basic strategic planning experience
Businesses that are looking for a more comprehensive plan
Conduct a SWOT analysis . Assess your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with a SWOT analysis to get a better overview of what your strategic plan should focus on. We’ll give into how to conduct a SWOT analysis when we get into the strategic planning frameworks below.
Identify and prioritize major issues and/or goals. Based on your SWOT analysis, identify and prioritize what your strategic plan should focus on this time around.
Develop your main strategies that address these issues and/or goals. Aim to develop one overarching strategy that addresses your highest-priority goal and/or issue to keep this process as simple as possible.
Update or create a mission and vision statement . Make sure that your business’s statements align with your new or updated strategy. If you haven’t already, this is also a chance for you to define your organization’s values.
Create action plans. These will help you address your organization’s goals, resource needs, roles, and responsibilities.
Develop a yearly operational plan document. This model works best if your business repeats the strategic plan implementation process on an annual basis, so use a yearly operational plan to capture your goals, progress, and opportunities for next time.
Allocate resources for your year-one operational plan. Whether you need funding or dedicated team members to implement your first strategic plan, now is the time to allocate all the resources you’ll need.
Monitor and revise the strategic plan. Record your lessons learned in the operational plan so you can revisit and improve it for the next strategic planning phase.
The issue-based plan can repeat on an annual basis (or less often once you resolve the issues). It’s important to update the plan every time it’s in action to ensure it’s still doing the best it can for your organization.
You don’t have to repeat the full process every year—rather, focus on what’s a priority during this run.
3. Alignment model
This model is also called strategic alignment model (SAM) and is one of the most popular strategic planning models. It helps you align your business and IT strategies with your organization’s strategic goals.
You’ll have to consider four equally important, yet different perspectives when applying the alignment strategic planning model:
Strategy execution: The business strategy driving the model
Technology potential: The IT strategy supporting the business strategy
Competitive potential: Emerging IT capabilities that can create new products and services
Service level: Team members dedicated to creating the best IT system in the organization
Ideally, your strategy will check off all the criteria above—however, it’s more likely you’ll have to find a compromise.
Here’s how to create a strategic plan using the alignment model and what kinds of companies can benefit from it.
Organizations that need to fine-tune their strategies
Businesses that want to uncover issues that prevent them from aligning with their mission
Companies that want to reassess objectives or correct problem areas that prevent them from growing
Outline your organization’s mission, programs, resources, and where support is needed. Before you can improve your statements and approaches, you need to define what exactly they are.
Identify what internal processes are working and which ones aren’t. Pinpoint which processes are causing problems, creating bottlenecks , or could otherwise use improving. Then prioritize which internal processes will have the biggest positive impact on your business.
Identify solutions. Work with the respective teams when you’re creating a new strategy to benefit from their experience and perspective on the current situation.
Update your strategic plan with the solutions. Update your strategic plan and monitor if implementing it is setting your business up for improvement or growth. If not, you may have to return to the drawing board and update your strategic plan with new solutions.
4. Scenario model
The scenario model works great if you combine it with other models like the basic or issue-based model. This model is particularly helpful if you need to consider external factors as well. These can be government regulations, technical, or demographic changes that may impact your business.
Organizations trying to identify strategic issues and goals caused by external factors
Identify external factors that influence your organization. For example, you should consider demographic, regulation, or environmental factors.
Review the worst case scenario the above factors could have on your organization. If you know what the worst case scenario for your business looks like, it’ll be much easier to prepare for it. Besides, it’ll take some of the pressure and surprise out of the mix, should a scenario similar to the one you create actually occur.
Identify and discuss two additional hypothetical organizational scenarios. On top of your worst case scenario, you’ll also want to define the best case and average case scenarios. Keep in mind that the worst case scenario from the previous step can often provoke strong motivation to change your organization for the better. However, discussing the other two will allow you to focus on the positive—the opportunities your business may have ahead.
Identify and suggest potential strategies or solutions. Everyone on the team should now brainstorm different ways your business could potentially respond to each of the three scenarios. Discuss the proposed strategies as a team afterward.
Uncover common considerations or strategies for your organization. There’s a good chance that your teammates come up with similar solutions. Decide which ones you like best as a team or create a new one together.
Identify the most likely scenario and the most reasonable strategy. Finally, examine which of the three scenarios is most likely to occur in the next three to five years and how your business should respond to potential changes.
5. Self-organizing model
Also called the organic planning model, the self-organizing model is a bit different from the linear approaches of the other models. You’ll have to be very patient with this method.
This strategic planning model is all about focusing on the learning and growing process rather than achieving a specific goal. Since the organic model concentrates on continuous improvement , the process is never really over.
Large organizations that can afford to take their time
Businesses that prefer a more naturalistic, organic planning approach that revolves around common values, communication, and shared reflection
Companies that have a clear understanding of their vision
Define and communicate your organization’s cultural values . Your team can only think clearly and with solutions in mind when they have a clear understanding of your organization's values.
Communicate the planning group’s vision for the organization. Define and communicate the vision with everyone involved in the strategic planning process. This will align everyone’s ideas with your company’s vision.
Discuss what processes will help realize the organization’s vision on a regular basis. Meet every quarter to discuss strategies or tactics that will move your organization closer to realizing your vision.
6. Real-time model
This fluid model can help organizations that deal with rapid changes to their work environment. There are three levels of success in the real-time model:
Organizational: At the organizational level, you’re forming strategies in response to opportunities or trends.
Programmatic: At the programmatic level, you have to decide how to respond to specific outcomes or environmental changes.
Operational: On the operational level, you will study internal systems, policies, and people to develop a strategy for your company.
Figuring out your competitive advantage can be difficult, but this is absolutely crucial to ensure success. Whether it’s a unique asset or strength your organization has or an outstanding execution of services or programs—it’s important that you can set yourself apart from others in the industry to succeed.
Companies that need to react quickly to changing environments
Businesses that are seeking new tools to help them align with their organizational strategy
Define your mission and vision statement. If you ever feel stuck formulating your company’s mission or vision statement, take a look at those of others. Maybe Asana’s vision statement sparks some inspiration.
Research, understand, and learn from competitor strategy and market trends. Pick a handful of competitors in your industry and find out how they’ve created success for themselves. How did they handle setbacks or challenges? What kinds of challenges did they even encounter? Are these common scenarios in the market? Learn from your competitors by finding out as much as you can about them.
Study external environments. At this point, you can combine the real-time model with the scenario model to find solutions to threats and opportunities outside of your control.
Conduct a SWOT analysis of your internal processes, systems, and resources. Besides the external factors your team has to consider, it’s also important to look at your company’s internal environment and how well you’re prepared for different scenarios.
Develop a strategy. Discuss the results of your SWOT analysis to develop a business strategy that builds toward organizational, programmatic, and operational success.
Rinse and repeat. Monitor how well the new strategy is working for your organization and repeat the planning process as needed to ensure you’re on top or, perhaps, ahead of the game.
7. Inspirational model
This last strategic planning model is perfect to inspire and energize your team as they work toward your organization’s goals. It’s also a great way to introduce or reconnect your employees to your business strategy after a merger or acquisition.
Businesses with a dynamic and inspired start-up culture
Organizations looking for inspiration to reinvigorate the creative process
Companies looking for quick solutions and strategy shifts
Gather your team to discuss an inspirational vision for your organization. The more people you can gather for this process, the more input you will receive.
Brainstorm big, hairy audacious goals and ideas. Encouraging your team not to hold back with ideas that may seem ridiculous will do two things: for one, it will mitigate the fear of contributing bad ideas. But more importantly, it may lead to a genius idea or suggestion that your team wouldn’t have thought of if they felt like they had to think inside of the box.
Assess your organization’s resources. Find out if your company has the resources to implement your new ideas. If they don’t, you’ll have to either adjust your strategy or allocate more resources.
Develop a strategy balancing your resources and brainstorming ideas. Far-fetched ideas can grow into amazing opportunities but they can also bear great risk. Make sure to balance ideas with your strategic direction.
Now, let’s dive into the most commonly used strategic frameworks.
8. SWOT analysis framework
One of the most popular strategic planning frameworks is the SWOT analysis . A SWOT analysis is a great first step in identifying areas of opportunity and risk—which can help you create a strategic plan that accounts for growth and prepares for threats.
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Here’s an example:
![business planning team [Inline illustration] SWOT analysis (Example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cfab4ed2-46d1-4636-b801-14b3d86c8367/inline-project-management-SWOT-analysis-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
9. OKRs framework
A big part of strategic planning is setting goals for your company. That’s where OKRs come into play.
OKRs stand for objective and key results—this goal-setting framework helps your organization set and achieve goals. It provides a somewhat holistic approach that you can use to connect your team’s work to your organization’s big-picture goals. When team members understand how their individual work contributes to the organization’s success, they tend to be more motivated and produce better results
10. Balanced scorecard (BSC) framework
The balanced scorecard is a popular strategic framework for businesses that want to take a more holistic approach rather than just focus on their financial performance. It was designed by David Norton and Robert Kaplan in the 1990s, it’s used by companies around the globe to:
Communicate goals
Align their team’s daily work with their company’s strategy
Prioritize products, services, and projects
Monitor their progress toward their strategic goals
Your balanced scorecard will outline four main business perspectives:
Customers or clients , meaning their value, satisfaction, and/or retention
Financial , meaning your effectiveness in using resources and your financial performance
Internal process , meaning your business’s quality and efficiency
Organizational capacity , meaning your organizational culture, infrastructure and technology, and human resources
With the help of a strategy map, you can visualize and communicate how your company is creating value. A strategy map is a simple graphic that shows cause-and-effect connections between strategic objectives.
The balanced scorecard framework is an amazing tool to use from outlining your mission, vision, and values all the way to implementing your strategic plan .
You can use an integration like Lucidchart to create strategy maps for your business in Asana.
11. Porter’s Five Forces framework
If you’re using the real-time strategic planning model, Porter’s Five Forces are a great framework to apply. You can use it to find out what your product’s or service’s competitive advantage is before entering the market.
Developed by Michael E. Porter , the framework outlines five forces you have to be aware of and monitor:
![business planning team [Inline illustration] Porter’s Five Forces framework (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d63265bc-23e2-4ce6-9b91-b3da5a756619/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Threat of new industry entrants: Any new entry into the market results in increased pressure on prices and costs.
Competition in the industry: The more competitors that exist, the more difficult it will be for you to create value in the market with your product or service.
Bargaining power of suppliers: Suppliers can wield more power if there are less alternatives for buyers or it’s expensive, time consuming, or difficult to switch to a different supplier.
Bargaining power of buyers: Buyers can wield more power if the same product or service is available elsewhere with little to no difference in quality.
Threat of substitutes: If another company already covers the market’s needs, you’ll have to create a better product or service or make it available for a lower price at the same quality in order to compete.
Remember, industry structures aren’t static. The more dynamic your strategic plan is, the better you’ll be able to compete in a market.
12. VRIO framework
The VRIO framework is another strategic planning tool designed to help you evaluate your competitive advantage. VRIO stands for value, rarity, imitability, and organization.
It’s a resource-based theory developed by Jay Barney. With this framework, you can study your firmed resources and find out whether or not your company can transform them into sustained competitive advantages.
Firmed resources can be tangible (e.g., cash, tools, inventory, etc.) or intangible (e.g., copyrights, trademarks, organizational culture, etc.). Whether these resources will actually help your business once you enter the market depends on four qualities:
Valuable : Will this resource either increase your revenue or decrease your costs and thereby create value for your business?
Rare : Are the resources you’re using rare or can others use your resources as well and therefore easily provide the same product or service?
Inimitable : Are your resources either inimitable or non-substitutable? In other words, how unique and complex are your resources?
Organizational: Are you organized enough to use your resources in a way that captures their value, rarity, and inimitability?
It’s important that your resources check all the boxes above so you can ensure that you have sustained competitive advantage over others in the industry.
13. Theory of Constraints (TOC) framework
If the reason you’re currently in a strategic planning process is because you’re trying to mitigate risks or uncover issues that could hurt your business—this framework should be in your toolkit.
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a problem-solving framework that can help you identify limiting factors or bottlenecks preventing your organization from hitting OKRs or KPIs .
Whether it’s a policy, market, or recourse constraint—you can apply the theory of constraints to solve potential problems, respond to issues, and empower your team to improve their work with the resources they have.
14. PEST/PESTLE analysis framework
The idea of the PEST analysis is similar to that of the SWOT analysis except that you’re focusing on external factors and solutions. It’s a great framework to combine with the scenario-based strategic planning model as it helps you define external factors connected to your business’s success.
PEST stands for political, economic, sociological, and technological factors. Depending on your business model, you may want to expand this framework to include legal and environmental factors as well (PESTLE). These are the most common factors you can include in a PESTLE analysis:
Political: Taxes, trade tariffs, conflicts
Economic: Interest and inflation rate, economic growth patterns, unemployment rate
Social: Demographics, education, media, health
Technological: Communication, information technology, research and development, patents
Legal: Regulatory bodies, environmental regulations, consumer protection
Environmental: Climate, geographical location, environmental offsets
15. Hoshin Kanri framework
Hoshin Kanri is a great tool to communicate and implement strategic goals. It’s a planning system that involves the entire organization in the strategic planning process. The term is Japanese and stands for “compass management” and is also known as policy management.
This strategic planning framework is a top-down approach that starts with your leadership team defining long-term goals which are then aligned and communicated with every team member in the company.
You should hold regular meetings to monitor progress and update the timeline to ensure that every teammate’s contributions are aligned with the overarching company goals.
Stick to your strategic goals
Whether you’re a small business just starting out or a nonprofit organization with decades of experience, strategic planning is a crucial step in your journey to success.
If you’re looking for a tool that can help you and your team define, organize, and implement your strategic goals, Asana is here to help. Our goal-setting software allows you to connect all of your team members in one place, visualize progress, and stay on target.
Related resources

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning

How Asana uses work management for organizational planning

Solve your tech overload with an intelligent transformation

9 steps to craft a successful go-to-market (GTM) strategy

Business Planning

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on June 08, 2023
Get Any Financial Question Answered
Table of contents, what is business planning.
Business planning is a crucial process that involves creating a roadmap for an organization to achieve its long-term objectives. It is the foundation of every successful business and provides a framework for decision-making, resource allocation, and measuring progress towards goals.
Business planning involves identifying the current state of the organization, determining where it wants to go, and developing a strategy to get there.
It includes analyzing the market, identifying target customers, determining a competitive advantage, setting financial goals, and establishing operational plans.
The business plan serves as a reference point for all stakeholders , including investors, employees, and partners, and helps to ensure that everyone is aligned and working towards the same objectives.
Importance of Business Planning
Business planning plays a critical role in the success of any organization, as it helps to establish a clear direction and purpose for the business. It allows the organization to identify its goals and objectives, develop strategies and tactics to achieve them, and establish a framework of necessary resources and operational procedures to ensure success.
Additionally, a well-crafted business plan can serve as a reference point for decision-making, ensuring that all actions taken by the organization are aligned with its long-term objectives.
It can also facilitate communication and collaboration among team members, ensuring that everyone is working towards a common goal.
Furthermore, a business plan is often required when seeking funding or investment from external sources, as it demonstrates the organization's potential for growth and profitability. Overall, business planning is essential for any organization looking to succeed and thrive in a competitive market.
Business Planning Process
Step 1: defining your business purpose and goals.
Begin by clarifying your business's purpose, mission, and long-term goals. These elements should align with the organization's core values and guide every aspect of the planning process.
Step 2: Conducting Market Research and Analysis
Thorough market research and analysis are crucial to understanding the industry landscape, identifying target customers, and gauging the competition. This information will inform your business strategy and help you find your niche in the market.
Step 3: Creating a Business Model and Strategy
Based on the insights from your market research, develop a business model that outlines how your organization will create, deliver, and capture value. This will inform the overall business strategy, including identifying target markets, value propositions, and competitive advantages.
Step 4: Developing a Marketing Plan
A marketing plan details how your organization will promote its products or services to target customers. This includes defining marketing objectives, tactics, channels, budgets, and performance metrics to measure success.

Step 5: Establishing Operational and Financial Plans
The operational plan outlines the day-to-day activities, resources, and processes required to run your business. The financial plan projects revenue, expenses, and cash flow, providing a basis for assessing the organization's financial health and long-term viability.
Step 6: Reviewing and Revising the Business Plan
Regularly review and update your business plan to ensure it remains relevant and reflects the organization's current situation and goals. This iterative process enables proactive adjustments to strategies and tactics in response to changing market conditions and business realities.

Components of a Business Plan
Executive summary.
The executive summary provides a high-level overview of your business plan, touching on the company's mission, objectives, strategies, and key financial projections.
It is critical to make this section concise and engaging, as it is often the first section that potential investors or partners will read.
Company Description
The company description offers a detailed overview of your organization, including its history, mission, values, and legal structure. It also outlines the company's goals and objectives and explains how the business addresses a market need or problem.
Products or Services
Describe the products or services your company offers, emphasizing their unique features, benefits, and competitive advantages. Detail the development process, lifecycle, and intellectual property rights, if applicable.
Market Analysis
The market analysis section delves into the industry, target market, and competition. It should demonstrate a thorough understanding of market trends, growth potential, customer demographics, and competitive landscape.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Outline your organization's approach to promoting and selling its products or services. This includes marketing channels, sales tactics, pricing strategies, and customer relationship management .
Management and Organization
This section provides an overview of your company's management team, including their backgrounds, roles, and responsibilities. It also outlines the organizational structure and any advisory or support services employed by the company.
Operational Plan
The operational plan describes the day-to-day operations of your business, including facilities, equipment, technology, and personnel requirements. It also covers supply chain management, production processes, and quality control measures.
Financial Plan
The financial plan is a crucial component of your business plan, providing a comprehensive view of your organization's financial health and projections.
This section should include income statements , balance sheets , cash flow statements , and break-even analysis for at least three to five years. Be sure to provide clear assumptions and justifications for your projections.
Appendices and Supporting Documents
The appendices and supporting documents section contains any additional materials that support or complement the information provided in the main body of the business plan. This may include resumes of key team members, patents , licenses, contracts, or market research data.

Benefits of Business Planning
Helps secure funding and investment.
A well-crafted business plan demonstrates to potential investors and lenders that your organization is well-organized, has a clear vision, and is financially viable. It increases your chances of securing the funding needed for growth and expansion.
Provides a Roadmap for Growth and Success
A business plan serves as a roadmap that guides your organization's growth and development. It helps you set realistic goals, identify opportunities, and anticipate challenges, enabling you to make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively.
Enables Effective Decision-Making
Having a comprehensive business plan enables you and your management team to make well-informed decisions, based on a clear understanding of the organization's goals, strategies, and financial situation.
Facilitates Communication and Collaboration
A business plan serves as a communication tool that fosters collaboration and alignment among team members, ensuring that everyone is working towards the same objectives and understands the organization's strategic direction.

Business planning should not be a one-time activity; instead, it should be an ongoing process that is continually reviewed and updated to reflect changing market conditions, business realities, and organizational goals.
This dynamic approach to planning ensures that your organization remains agile, responsive, and primed for success.
As the business landscape continues to evolve, organizations must embrace new technologies, methodologies, and tools to stay competitive.
The future of business planning will involve leveraging data-driven insights, artificial intelligence, and predictive analytics to create more accurate and adaptive plans that can quickly respond to a rapidly changing environment.
By staying ahead of the curve, businesses can not only survive but thrive in the coming years.
Business Planning FAQs
What is business planning, and why is it important.
Business planning is the process of setting goals, outlining strategies, and creating a roadmap for your company's future. It's important because it helps you identify opportunities and risks, allocate resources effectively, and stay on track to achieve your goals.
What are the key components of a business plan?
A business plan typically includes an executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization and management structure, product or service line, marketing and sales strategies, and financial projections.
How often should I update my business plan?
It is a good idea to review and update your business plan annually, or whenever there's a significant change in your industry or market conditions.
What are the benefits of business planning?
Effective business planning can help you anticipate challenges, identify opportunities for growth, improve decision-making, secure financing, and stay ahead of competitors.
Do I need a business plan if I am not seeking funding?
Yes, even if you're not seeking funding, a business plan can be a valuable tool for setting goals, developing strategies, and keeping your team aligned and focused on achieving your objectives.

About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
- Business Exit Strategies
- Buy-Sell Agreements
- Capital Planning
- Change-In-Control Agreements
- Cross-Purchase Agreements
- Decision Analysis (DA)
- Employee Retention and Compensation Planning
- Endorsement & Sponsorship Management
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Entity-Purchase Agreements
- Family Business Continuity
- Family Business Governance
- Family Limited Partnerships (FLPs) and Buy-Sell Agreements
- Human Resource Planning (HRP)
- Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II)
- Plan Restatement
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Find advisor near you, our recommended advisors.

Taylor Kovar, CFP®
WHY WE RECOMMEND:
Fee-Only Financial Advisor Show explanation
Certified financial planner™, 3x investopedia top 100 advisor, author of the 5 money personalities & keynote speaker.
IDEAL CLIENTS:
Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals
Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation

Claudia Valladares
Bilingual in english / spanish, founder of wisedollarmom.com, quoted in gobanking rates, yahoo finance & forbes.
Retirees, Immigrants & Sudden Wealth / Inheritance
Retirement Planning, Personal finance, Goals-based Planning & Community Impact
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
Hey, did we answer your financial question.
We want to make sure that all of our readers get their questions answered.
Great, Want to Test Your Knowledge of This Lesson?
Create an Account to Test Your Knowledge of This Topic and Thousands of Others.
Get Your Question Answered by a Financial Professional
Create a free account and submit your question. We'll make sure a financial professional gets back to you shortly.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Great thank you for voting..
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools
Tips on Writing the Management Team Section of a Business Plan

Free Ultimate Guide On Writing A Business Plan
- December 21, 2023
10 Min Read

A business is as efficient as its team and its management. It, therefore, becomes important for business owners to build a structured management team that achieves the objectives and goals set by the organization. Thus, making the management section of a business plan the most essential component.
Andrew Carnegie , an American steel magnate, beautifully summarized it –
Teamwork is the ability to work together toward a common vision. The ability to direct individual accomplishments toward organizational objectives. It is the fuel that allows common people to attain uncommon results.
A business management plan helps build an efficient team and formalize business operations . This helps businesses streamline strategies to achieve their goals.
It, therefore, becomes imperative that business owners pay utmost importance while writing the management section of a business plan.
So, if you are a business owner who is looking to formalize their business structure and write the management team section in their business plan , this guide is for you.
Here’s a sneak peek into what you’ll learn:
Table of Contents
- What Is the Management Section?
- Importance of the Management Section
- What to Include in the Management Section?
- Example of a Management Section Plan
- Ensure That the Management Section Is Fool-proof?
Sounds good? Let’s dive in.
What Is The Management Section Of A Business Plan?
The management section of a business plan is an in-depth description of a business’s team, its structure, and the ownership of a business.
The section discusses in detail who is on the management team – internal and external- their skill sets, experiences, and how meaningfully they would contribute to an organization’s goals and outcomes.
Now that we have defined what is the management section of a business plan, let’s understand why it is so important.
The Importance Of The Management Section Of A Business Plan
The management section helps you to:
1. Convince your investors (banks and government agencies) to disburse loans and grants for your business idea
2. Prove that your management team can execute your idea and if not, help hire the right fit for a position
3. Share how your advisory board can help your team succeed
What To Include In the Management Section Of A Business Plan?
The management section of a business plan helps in formalizing and structuring the management team plan and is comprised of
- The Management Team
- The Management Team Gaps
- The Management Structure
Let’s understand them in detail.
1. The Management Team
An organization’s entire management team can be divided into parts – the internal team and the external team.
The Internal Management Team
A business team consists of several departments. The most common departments are – Marketing, Sales, IT, Customer Service, Operations, Finance, and HR.
These departments may or may not be required. It purely depends on the nature and functioning of your business. For example, a dental clinic may not require a sales department per se.
The entire management team is compartmentalized according to their responsibility. This helps the business owners and investors be aware of the roles, benefits, ESOPs (if applicable), profit sharing (for sales), work contracts, NDAs (Non-Disclosure Agreements), and Non-Competition Agreements of the entire team.
It is recommended that business owners collect and document the following information about their team:
- Educational Background
- Work Experience
- Accomplishments
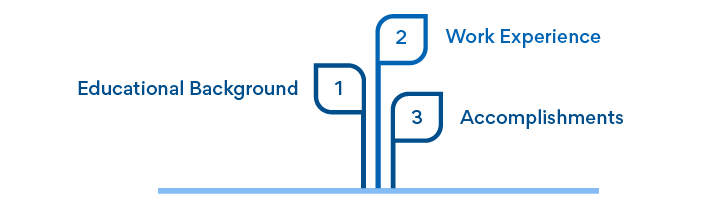
For example, your present VP of Marketing helped their previous company grow its bottom line from $3 million to $10 million over 18 months.
The External Management Team
The external management team is usually composed of – Advisory Board Members and Professional Services.
Advisory board members help by :
- Establishing trust, showing results, and experiencing the table.
- Increasing the confidence of investors and consumers.
This helps attract talented employees to the team. Credible advisory board members show great commitment to a company’s growth. Therefore, it becomes important to document their experience and specialization in the business management plan. The advisory board members can help give valuable advice that internal team members need or lack.
If your business has not or will not have VC funding, you may not require board members on your team.
Usually, board members meet quarterly or monthly to provide strategic guidance in place of stock options in your company. This helps attract the best advisors and motivates them to invest in your business.
For example, founders and business owners coming to raise funds in Shark Tank , a business television series, are looking for advisory members who would invest money and provide guidance on necessary steps.
On the other hand, Professional Service helps by
- Offering highly specialized advice and sharing knowledge.
- Business owners make key strategic management decisions.
Such services help businesses leverage skills that would be difficult to build and acquire over a short period.
Examples of such professional services are
- IT Consultants
- Business coaches and consultants
After a brief overview of the Management Team of an organization, let’s dive into what to include in Management Team Gaps.
2. The Management Team Gaps
The management team gap is an important part of the management section. Primarily because it helps document if your management team currently has gaps or missing skills. Your team may lack a few required skills while starting. The management team gaps help you to be aware and make efforts to close this gap.
As a business owner, you must document what positions are missing and who ought to fill that positions or take responsibility.
For example, if you need a VP of Sales, clearly document this in the section.
Also, write down the job description and key responsibilities to be undertaken,
Example – You might mention that role required 10 years of experience in the sales domain. The applicant must have experience handling a sales team, closing new accounts, working in tandem with the marketing team, and having relevant startup experience.
Be as detailed as possible. This will help you build a checklist while interviewing the right candidate and also win investor confidence in your managerial skills.
Following are a few key positions you would want to include in your management team:
- Founder and/or, CEO
- Chief Technical Officer (CTO)
- Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
- Chief Operating Officer (COO)
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
- Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO)
- Head of Product Management (PM)
- VP of Sales
- VP of Marketing
- UX Designer
- Digital Marketing Manager
- Business Development Manager
- Customer Service Manager
- Customer Success Manager
- Sales Managers/Sales Staff
- Advisory Board Members
Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of the management structure.
3. The Management Structure
The management structure defines how a business organizes its management hierarchy. A hierarchy helps determine the roles, positions, power, and responsibilities of all team members.
The management structure also depends upon the type of business ownership. Business ownership can be – a sole proprietorship, partnership, or simply an LLC.
Following is a sample management structure of an organization.
Now that we understand what details we need to document in the business management plan, let’s look at a few examples of the management plan.

Example Of A Management Section Plan
[management section of a hotel], [management team], internal team members.
Name: Charles Fargo Role: Owner Responsibility: Formulating key strategies, defining budgets, and building a business plan Experience: 35 years of owning multiple hotels in Las Vegas Educational Background: B.Sc in Hospitality Management from South Dakota State University.
Name: Michael Clark Role: General Manager Responsibility: Overall hotel operations – guest interactions, revenue management, brand ambassador of the hotel, customer satisfaction, and experience, leadership to all departments Experience: 25 years working with several technology hotels as the general manager. Educational Background: MBA from Wharton School
Name: George Trump Role: Department Manager Responsibility: Manage employees, smooth coordination amongst employees, plan daily affairs of the department, strategize, prepare reports, and deal with complaints and suggestions. Lead team members to function as a team Experience: 15 years working as a department manager Educational Background: BSc in Hotel Management from Texas University
Note: There can be multiple Department Managers depending on the nature of your business. In the case of hotels, departments can include – housekeeping, logistics, security, food, and banquets.
Name: Donald Clooney Role: Marketing and Sales Manager Responsibility: Increase occupancy and generate revenue. Position the hotel as an option for leisure activities, relaxation, and holidays. Experience: 11 years working as the marketing and sales manager for hotels Educational Background: MBA in Tourism and Hospitality from Midway University
External Team Members
Advisory Board Member
#1 Richard Branson Responsibility: Strategic advisory for sustainable growth and expansion Experience: Founder of Virgin Group
Professional Services
[management structure].
There is a gap in one key position in our startup.
#1 Chief Finance Officer (CFO) Responsibilities: Finance, Accounting, Tracking Profit and Loss, and overseeing FP&A (Financial Planning and Analysis)
How To Ensure That The Management Section Of Your Business Plan Is Fool-Proof?
“In preparing for battle I have always found that plans are useless, but planning is indispensable.” ― Dwight D. Eisenhower
By building a fool-proof management plan and ensuring that all the intricate details are accounted for, we can ensure that your business has a greater chance of succeeding.
Business planning software like Upmetrics ensures that business owners, like you, get the management section planning correct on the first attempt itself.
You can also get started with a free demo today to discover how Upmetrics can help you plan your business in a breeze.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Related Articles

How to Write an Operations Plan Section of your Business Plan

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix Section

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Assembling the Right People for Strategic Business Planning

Having the right people on your strategic business planning team is essential for achieving desired results. Leaders should include people who are aligned with the organization’s goals. It is also advisable to have people on your strategic business planning team who understand and agree with the logic used in making holistic business decisions, as well as the processes required to effect meaningful change.
Cross-functional teams of top- and mid-level leaders can be very impactful. By involving people from throughout the organization and giving them the opportunity to participate, it is more likely that everyone will be in alignment with the strategic business planning process and outcomes.
When assembling the right team:
- Include natural change agents and early adopters who are known to influence others in your company. Strong influencers can be powerful change agents since people trust and follow them.
- Consider high-potential individuals who have the ability to think outside-of-the-box. They can bring valuable insight to the strategic planning team because they are not stuck on keeping the status quo.
- Invite leaders who are traditionally resistant to change. Get them to buy-into and support the strategic plan.
- Bring local and front-line talent to the table when practical — they have first-hand knowledge of the processes and procedures that impact customer experiences.
- Involve external stakeholders in the process. They can provide insight in areas that your internal team might miss because they are looking at the strategic planning process from different perspectives.
Characteristics of good strategic business planning team members include:
- People who can focus on a new direction and strategy as the top priority.
- Team players who do not view their job or department’s success as good enough.
- People who are effective at communicating and debating ideas, but who can give themselves over to consensus after healthy deliberation.
- People who are mature enough to fully participate knowing that their role and others around them may be impacted.
- Individuals with high learning agility.
- People who can take a broad enterprise perspective.
Leaders need to communicate expected behaviors and champion enterprise thinking for the strategic business planning team. This includes defining the role of each team member. For example, top-line managers might have the right to vote on a change where front-line managers would only provide feedback.
While it is good to include all of the people necessary to make an impactful change, having too many participants on the strategic business planning team can slow down the process. It also requires more coordination and planning. Because it is a balancing act, think about the pros and cons of team composition and team size.
In a perfect situation, everyone on the strategic business planning team puts the best interest of the company before their own. It might be decided that certain business units no longer contribute value to an organization and should be eliminated. Team members who would be personally impacted by this decision should consider how it would benefit the entire organization instead of the impact to themselves or the people with whom they work. For example, during two days of intense conversations at a global supplier in the food industry, the executive team made the decision to shift the balance of organizational power. This decision eliminated the jobs of at least two people on the leadership team. Even so, everyone understood that the organization change they were going to implement was necessary to achieve the goals of the strategic business plan. Another group at a big box retailer began with a goal to cut costs and realized that a small but long-standing and respected group of expert technician-managers had to be eliminated. One of those managers was on the strategic planning team.
Strategic business planning is not an easy exercise. This is why it is so important to assemble the right team. Communicating the team’s mission, along with everyone’s role will ensure that the team operates efficiently and thinks holistically about what is in the best interests of the organization.

Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Plan Projections
ideas to numbers .. simple financial projections
Home > Business Plan > Management Team in a Business Plan

Management Team in a Business Plan
…we have put a team together…
What do the Investors look for in the Management Team?
Investors will be particularly interested to obtain answers to the following questions about the management team:
- Does the team know its weaknesses?
- Does each team member have a defined role to play?
- Are there any previous working relationships within the team?
- Is there a common objective for all team members?
- Is there relevant experience relating to the business idea in the team?
- What are the business ownership arrangements?
- Is the team fully committed?
Business Plan Management Team Presentation
There is no set style for the presentation of the management team information in a business plan, but we suggest a simple format similar to that shown below. Full details and complete CV’s can be included in an appendix or submitted later if requested.
For each individual, the format shows details of their name, title and role in the business, and a brief biography of the person. The biography should have particular emphasis on the following characteristics and skills and show how they link back to the business idea discussed in elevator pitch section of the business plan contents article.
- Past successes and failures.
- Education and professional training.
- Management and work experience.
- Special skills related to the business idea.
- Business reputation.
This is part of the financial projections and Contents of a Business Plan Guide a series of posts on what each section of a simple business plan should include. The next post in this series is defining the customer problem .
About the Author
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
You May Also Like

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 12 min read
Team Building Exercises – Strategy and Planning
Engaging ways to build core skills.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

No matter how brilliant your mind or strategy, if you’re playing a solo game, you’ll always lose out to a team.– Reid Hoffman.
How does your company approach strategic planning?
Traditionally, strategy is developed by an executive team and rolled out to the rest of the company for implementation. But today's rapidly changing commercial environment, coupled with the growing popularity of agile business practices, means that many organizations are now moving away from a formal, top-down approach.
Our current climate calls for a more flexible method that allows teams to shape their own path (while following organizational goals and guidelines). So, it's important that your team has the strategic thinking and planning skills it needs to contribute effectively.
Individuals with strong skills in these areas are also better at aligning their efforts with the broader objectives of the organization, so that their work contributes to a meaningful end goal.
This article explores three team building exercises that can help your people develop their strategic thinking and planning skills.
Strategic Thinking and Planning Exercises
Use the exercises below to strengthen your team's strategic thinking and planning skills. The activities should also help to improve communication and collaboration skills.
You can use them in various ways, for example with a group of new managers, or to refresh the skills of senior leaders.
Exercise 1: Early Bird vs. Second Mouse
This exercise was inspired by the saying (often attributed to American comedian Stephen Wright): "The early bird gets the worm, but the second mouse gets the cheese."
In it, two teams explore the implications of the phrase through presentation, debate and discussion.
This exercise helps teams analyze different strategic positions. It also emphasizes teamwork , presentation , argument and debate, and group decision making .
People and Materials
- Between eight and 30 people.
- A presenter from each team.
- Two flip charts, with pens.
- Flexible, typically 30-60 minutes.
Instructions
- Divide the group into two equal teams. Make one the "early bird" and the other the "second mouse."
- Give both teams five to 10 minutes to develop a short presentation outlining why their strategy is the best for business.
- A member of each team gives their presentation.
- When the presentations are over, ask each team to elect someone to debate the question, "Is it better in business to be the early bird or the second mouse?"
- Combine the teams into one big group and ask for a show of hands to determine which strategy is, indeed, the best.
Advice for the Facilitator
This simple exercise can be adapted in various different ways, depending on your objectives. For example, you may wish to make the exercise about generic business practice or specific to a particular industry or situation. You could also try debating which strategy is best for a particular scenario and then, after the vote, ask if people's opinions would be different if you changed the scenario.
You could ask the group to vote on which strategy is best at the beginning of the exercise and again at the end of the debate, to see if opinions change.
Possible topics for discussion after the exercise include different strategies for different situations, the relative virtues of adaptability versus consistency, how much people's values influence their choice of strategy, and so on.
Exercise 2: United Hearts
In this exercise, teams develop a strategy and compete for points in a card game. The United Hearts Game was published in " Quick Team Building Activities for Busy Managers ," by Brian Cole Miller. This is an adaptation of his original game.
This game strengthens strategic thinking skills. It also reminds players to stay flexible with their strategy and adjust it according to events.
- Between six and 15 people.
- One deck of cards.
- Thirty minutes.
Rules of the Game
The aim is to get as close to 30 points as possible by winning hearts. Aces are low, Jacks are worth 11, Queens 12, and Kings 13 points. All other cards have face value.
Each round begins when the dealer places a heart card face up on the table. Team leaders then pick a card from their own deck and place it face down. When all three have laid down a card, they flip them over and the highest card (irrespective of suit) wins the heart. The rest of the cards from that round are discarded.
When all of the cards have been played (13 rounds in all), teams count up the number of hearts they have won. The closest to 30 wins.
In the event of a tie, the team with the highest value heart is the winner.
- Put people into three teams of two to five members – group sizes don't need to be equal – and ask each to designate a "leader" who will play for them.
- Remove the hearts from the deck, and give each team a suit of cards.
- Explain the rules of the game, and give each team three minutes to plan how they will play.
- Before the game begins, each team is given time to discuss their strategies but, once it gets underway, discussion is no longer allowed, although team members can indicate which card to play through non-verbal gestures.
- Interrupt the game after the fifth and ninth rounds to allow the groups to analyze their progress and, if necessary, adjust their strategies.
When the game is over, ask the members of each team to describe what their initial strategy was, whether they thought it was successful, and how it evolved over time.
Discuss how their strategies would have differed if the aim of the game had been to get as high a score or as low a score as possible.
Ask them if other roles, besides leader, emerged within the team. For example, one person may have decided to keep track of which hearts had already been played, while another could have kept track of their competitors' running totals.
Adapted from "Quick Team-Building Activities for Busy Managers: 50 Exercises That Get Results in Just 15 Minutes." by Brian Cole Miller. ©️ 2003 by Brian Cole Miller. Used by permission of HarperCollins Leadership. www.harpercollinsleadership.com
Exercise 3: Capture the Flag
Capture the Flag is a classic outdoor game for larger groups. The goal is to successfully capture the other team's flag, without being caught on "enemy territory."
This game is excellent for building strategic thinking and communication skills. Teams assign roles (such as guards and raiders) and use battlefield tactics to successfully capture the opposing flag. It can be a great exercise to help new teams get to know each other, or to break down barriers between hierarchies or departments.
This game only works if all participants are prepared to play a vigorous outdoor game. You won't build a happy, engaged team if you try to force unwilling people to play.
- Enough people for at least two groups of five.
- Two "flags" – anything from a towel to a company flag.
- Boundary markers (if necessary).
- A large outdoor space, ideally one with trees, hills or buildings.
- Flexible, typically 30-45 minutes.
The rules of the game are simple. The group is divided into two opposing teams. Within each team, there are guards and raiders. Guards stay on their own territory and capture any enemies who try to take their flag. Raiders infiltrate enemy territory to locate and capture their opponents' flag. Both roles report to the team leader, who makes sure everyone follows the overall strategy.
Guards capture trespassing raiders by tagging them. The prisoner must then stay where he is put until a member from his own team sets him free by tagging him again. Once a prisoner is set free, he must return to his home territory before resuming play.
If a flag is successfully captured, it must be taken back to the team's home territory. If the flag bearer is caught before she reaches her territory, the flag is returned to its original hiding place, the bearer goes to prison, and the game continues.
- Begin by dividing the available space up into three parts, with team territories at opposite ends and a neutral "no man's land" in the middle. Mark where each territory begins.
- Explain the rules, then split the group into two teams.
- Give each team 10 minutes to choose a leader, assign roles, and discuss their strategy. Teams can decide for themselves how many guards and raiders to have but, once roles have been allocated, they remain for the duration of the game.
- Instruct each team to place its flag in plain sight. It should present a challenge, but not be impossible to find.
- Each team then waits in its home territory until you blow the whistle to signal that the game has begun.
- The game ends when one team successfully brings the other's flag into its home territory. Blow the whistle again to show that the game is over.
Bear in mind that this game may not suit everyone. It can be quite physical, with lots of running and, depending on the terrain, climbing and scrambling over trails, rocks and trees.
It's important that team members approach their roles with sensitivity towards others – both their team members and their "enemies." Make sure that guards understand that they must "tag," not "tackle," enemy raiders, so that no one gets hurt.
Encourage the team to be creative with their roles, so that everyone, regardless of physical ability, can make a positive contribution. For example, some guards could act as "lookouts," while raiders could be divided into "scouts," who use stealth to discover the whereabouts of the flag or prisoners being held captive, and "runners," who create a diversion while others go after the prize.
At the end of the game, gather the group together to discuss how it went. Ask how each person's role contributed to the overall strategy. Examine each team's strategy (or lack of one) and how well it worked out for them, and identify what gave the winning team their competitive advantage.
Team building exercises work best when, as well as improving team work, they help people to develop skills that benefit them in their day-to-day jobs, too. Check out our other team building resources for skills such as creativity , problem solving and decision making , and communication .
Strategic thinking is important for aligning your own and your team's daily activities are aligned with the long-term goals and objectives of your organization.
The games in this article can help your team members learn how to think more strategically, and work together.
Apply This to Your Life
- Think about how you could incorporate one of these games into your next team meeting, Away Day , or company retreat .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
The responsibility assignment matrix (ram).
Knowing Where the Buck Ultimately Stops
Developing Your Team
Improving Team Performance
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Try Mind Tools for FREE
Get unlimited access to all our career-boosting content and member benefits with our 7-day free trial.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

What Is Gibbs' Reflective Cycle?

Team Briefings
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Onboarding with steps.
Helping New Employees to Thrive
NEW! Pain Points Podcast - Perfectionism
Why Am I Such a Perfectionist?
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Accelerate: building strategic agility for a faster-moving world.
John P. Kotter
Book Insights
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for April 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

- Vincent Lehmann
- January 10, 2024
Everything you need to know about project team planning

Sign Up for FREE and start using Teambook in seconds!
Table of Contents
Are you new to organizing project teams? Here’s all the information you need to get started.
Organizations can derive significant financial and business benefits from team planning, which supports their growth and strategic objectives. To achieve this, a comprehensive team planning process is required.
But what is team planning, how is it implemented and why is it the sign of a high-performance team? Let’s find out!
What is team planning?
The process of establishing your team’s annual operational and strategic plans is known as team planning. It involves carefully aligning the work of your staff with the overall direction of the company. By defining your team’s strategic objectives and breaking them down into specific projects, goals and activities, it provides a clear roadmap for success. Team planning helps us to see the bigger picture by allowing us to zoom out and not just focus on day-to-day tasks.
This type of preparation ensures that all your team members know exactly what they need to do to succeed. It also enables you to show how your team meets needs and how your efforts contribute to the company’s profitability.
Why develop a team plan?
By developing a plan, your team will gain focus and strategic alignment. It ensures that every task performed by your staff benefits your business.
By simplifying the process of determining priorities and allocating the necessary resources, it eliminates the uncertainties associated with project planning. What’s more, by planning ahead, it becomes easier to determine whether you have the necessary resources to meet business priorities, or whether you need to hire additional staff.
Some companies don’t use team planning because they find it tedious and time-consuming. Why take the time to be more precise when the business plan serves as a basis for analysis?
Unfortunately, this is a false economy. The “big picture” is too big without a team plan. Your team can be working on the wrong things at the wrong time without even realizing it if there’s no team-level supervision.
Is a team plan necessary?
Every team, regardless of size or industry, needs a strategy. The difference between HOPING to achieve your goals and actually achieving them lies in a team plan. If you want your team to perform at a high level, it’s an indispensable tool.
- Do you know what targets the company has set itself for this year?
- Do you know how our team contributes to these goals?
- Do you know what your personal contribution to these goals is?
- Do you know exactly what success means for you personally and for the team?
If you can’t answer these questions, you’d better come up with a team plan fast!
Why do you need a team plan? Because without a team plan, your team members won’t know exactly what needs to be done, when or why, or whether it’s been done successfully.
Team cohesion, motivation and production can suffer from a lack of planning, for example:
- Prioritize unimportant activities because they don’t understand the importance of specific deliverables or when they are required.
- Prioritize self over team goals and inadvertently postpone important projects
- Lack of motivation due to their ignorance of the crucial role they play in the success of companies
- Disappointment at not receiving feedback on performance against KPIs
What are the advantages of team planning?
Team planning has many benefits for the company, the team and the individual. By participating in team planning, you can create a more satisfied and cohesive team, while reaping significant financial and business rewards.
Making a difference for your company
Thanks to team planning, which synchronizes work with the company’s strategy, your team actively supports the company’s expansion and success. Teams with a plan are more likely to perform well and prove their value to the company.
Assigning the best team members and preparing projects in advance are two aspects of team planning. This is known as resource planning, and has been shown to increase productivity and reduce inefficiencies, resulting in faster, more efficient and smarter work.
Building your group
Team planning promotes team growth and reduces unfavorable employee turnover.
It gives people a stage on which they can showcase their special talents and be recognized for their contributions. It also pinpoints areas where your staff can improve their skills, so you’re ready for the future. What’s more, it ensures that your team is neither overloaded nor under-utilized – a technique known as value for money – maximizing team productivity without depleting it.
By examining the team’s objectives, its fundamental principles and the way in which members work together rather than acting alone, team planning also promotes cohesion.
When team members feel empowered and engaged, they produce excellent work and stay with the team, boosting both employee performance and retention. Payroll software provider Gusto reports that 37% of workers cite “working with a great team” as their main motivation for staying with their company.
Recognize problems proactively
Team planning enables you to anticipate problems before they arise and develop plans to solve them, such as resource constraints, conflicts or bottlenecks. It’s the epitome of the proverb “Prevention is better than cure”.
It also contributes to capacity planning, a crucial strategic procedure for determining whether your company has the necessary resources for the projects in its portfolio. If you expect to be understaffed, a thorough team strategy will also provide you with elements to present to your management to request additional resources.
What distinguishes team execution planning from team strategy planning?
A strategic team plan describes the goals a team must achieve in order to support the company’s overall objectives. An execution plan gives the team detailed instructions on how to get there.
Achieving a goal is not the same as setting one. Developing a comprehensive team plan, which encompasses both the strategic direction and the organization of implementation, ensures that your group fulfills its commitments.
Make sure your execution and strategy plans are well linked. Things will go wrong if there’s a discrepancy between your execution strategy and your team’s strategic plan.
An execution plan describes what needs to be done, when and by whom. To ensure that each team member understands how his or her contribution fits into the whole, it’s helpful to outline the interdependencies. The aim is to get everyone on the same page.
It also solves an often overlooked problem in the workplace: people are too embarrassed to ask for help when they don’t know what to do. Never assume that your team members will be able to convert abstract goals into achievable task-based strategies on their own. Provide them with a clear roadmap for individual and organizational achievements using team planning.
What is the team planning procedure?
The following steps are included in team planning:
- Strategic alignment : In order to understand how his team fits into the wider business plan for the year, the team leader meets with senior management at this stage. They’ll talk about the company’s overall direction and what it wants to achieve in the coming year. Next, they discuss the role their team is to play in achieving the company’s objectives.
- Team planning session : This gathering of team members provides an opportunity to discuss objectives for the coming year. It usually begins with a presentation by the team leader on how his or her work fits into the company’s plan, and a statement of the team’s annual goals. Team members then work together to decide how each of them will achieve these objectives.
- Creating the team plan : After the team planning meeting, the team plan is formalized and documented. You will refer to this living text regularly. Each team member will use it to review their missions, deadlines and key performance indicators. Team leaders will also use it to monitor the team’s overall progress towards objectives.
- Reviewing the team’s plan : It’s essential to regularly evaluate progress to ensure that objectives are on track. It may be a good idea to hold a formal evaluation meeting every quarter. You can also put “team plan review” on the agenda of your weekly or monthly meetings.
When planning a team, who is involved?
The following people must be included in team planning:
The full line-up
Team planning requires the participation of the entire group. We mean business. It’s not just a perk. The participation of every team member in the planning process is crucial.
Team leaders benefit from knowing what assets they have, and what capabilities and strengths they possess. By talking to the people who do the work every day, team leaders can honestly assess the feasibility of their ideas.
It also gives each team member a sense of authority and ownership for the year ahead, and clarifies his or her important role within the overall project.
Team captain(s)
The role of the team leader is crucial. They liaise between the team and operational execution, as well as between senior management and strategy. They take the lead in discussions and ensure that the day achieves its objectives on the day of the team planning session.
An executive supervisor
To conduct these crucial strategic planning conversations, the team leader will need to interact with a more senior member of the organization. Depending on the size and structure of your team, this may be a direct discussion with a member of senior management. Or it may be a mid-level member of management. In either case, you need a senior manager to communicate strategic objectives to your team at all levels of the organization’s hierarchy.
A third-party coordinator
It can be useful to call on an outside facilitator, especially if your team is large. His or her professional experience and understanding of team planning methods can help you develop a more effective team plan than you could on your own.
They can also be very useful at team planning meetings. They allow the team leader to concentrate on interacting with his or her team, overseeing the day’s program and organization.
When is the right time to plan as a team?
In principle, team planning should take place once a year, following the presentation of the organization’s overall strategy. A team strategy should only cover the next six to twelve months. If you wait longer than a year, the company’s priorities may change and your plan may become obsolete.
How often should my team strategy be reviewed?
It’s a good idea to carry out a quarterly evaluation of your team plan. This will enable you to monitor progress towards your objectives, and change course if necessary to achieve them.
By reviewing your team strategy, you can anticipate these problems and take swift action to prevent them from derailing your annual target.
Five components of a successful team strategy
There’s no one-size-fits-all formula for team planning. It’s up to you to devise a strategy that benefits both you and your group. But there are several essential elements you need to include.
To be productive, your team needs to rally around a common goal. At the very least, this section should explain how your team’s work fits into the company’s overall operational picture. But you can also address the team’s objectives and principles, depending on your organization’s culture. What is your team’s passion? What makes them tick? How do they communicate with the rest of the company?
Methodical organization
The strategic alignment between your team and the company as a whole is illustrated in the section on the strategic plan. In addition to providing high-level details of the action your team will take, you should make reference to the areas of the organization plan that your team will support. These should be ranked in order of importance to both strategic objectives and financial performance.
Execution plan
This section provides a detailed, task-oriented plan. It divides the year’s activities into distinct team projects. It contains details of the timetable, resources required, budget, key performance indicators, etc.
The execution plan can help determine the interdependence of projects and prevent conflicts, such as conflicting demands for the same resources. By anticipating these conflicts, you can allocate resources more wisely and avoid potentially costly bottlenecks.
An execution plan also contributes to capacity planning by enabling you to assess the availability of your resources and develop appropriate plans to carry out future projects.
Emergency preparedness
One of the essential elements of team planning is contingency planning. If X, then Y” is the key. If circumstances change, you have the freedom to modify or reorganize your plan. According to a study published in the Harvard Business Review, “if-then” planners are 300% more likely to succeed than “fixed” planners. So, if you can, include some flexibility in your team’s plan.
It’s better to assign team members to another project, rather than leaving them idle and underused, if one of your projects depends on another team’s project being completed on time, and that project’s schedule slips.
Monitoring and measurement
How you will monitor progress against the strategy should be described in your team plan. This plan may apply only at project or team level. It can also take into account the performance of individual team members. It is essential to make it clear that team members will not be pressured or humiliated if their performance falls short of their KPIs. Rather, the aim is to check that the plan is heading in the right direction and, if not, to make the necessary adjustments to change course.
Six guidelines for a productive team planning meeting
- Invite the right people. You already know that you need to include your whole team, the team leader(s) and a senior manager, as we’ve already talked about the importance of involving the right people in team planning. To take notes and record the results, you can also enlist the help of a facilitator on the day.
- Set a convincing agenda. It’s great to get your whole team together. But pandemonium can strike at any time. So make sure you set clear objectives and stick to them. Remember, the purpose of this meeting is to document your plans and objectives for the rest of the year.
- Start on a high note. Start the meeting with an activity that focuses on the team’s strengths to help everyone get into the right frame of mind. Ask everyone to list something about their team or workplace that they’re grateful for, for example. Then everyone puts the paper into a ball and throws it at each other. Once everything is well mixed, each person chooses a piece of paper to read aloud to the group.
- Establish a safe space: it’s essential that everyone feels comfortable saying what they think during the planning process, which can involve difficult subjects. Make it clear that you value and encourage openness and constructive criticism. However, to prevent the “grumpies” from taking center stage, be aware of their presence and have a plan to deal with them.
- Change: you may want to divide up into smaller groups for your planning session. However, “groupthink” can seriously compromise your planning process. It limits your staff to topics they already know, stifling creativity and new ideas. Wherever possible, try to rotate people so that they don’t just converse with their colleagues on a daily basis.
- Take a break. Make sure your group has enough free time. Tired teammates won’t be as motivated or inventive. Avoid overloading the meeting or letting it drag on too long. It’s better to organize two shorter sessions than one longer one.
Apps and tools for team planning
Put an end to your search for an “Excel team resource planning template”. Instead, invest in a team planning tool tailored to your needs.
Dedicated workforce capacity planning software such as Teambook, for example, comes with tools and automations for:
- Define the skills and analyze the availability of team members
- Allocate tasks to your project teams in an operational manner
- Plan capacity for future projects and make any necessary resource requests.
- Identify bottlenecks and reallocate resources to other projects at the click of a button
- Monitor workload and compare with planned times
Sounds better, doesn’t it, than constantly copying and pasting sheets and cells?
We hope we’ve made a convincing case for team planning in your company.
“Failure to plan is planning to fail”, as the saying goes.
That’s why the most successful teams structure, focus and evaluate their work using proven methods such as resource planning, capacity planning, project management, portfolio management and team planning, among others.
Optimize the planning and follow-up of your teams with Teambook’s visual and intuitive interface – Make sure time is used efficiently!
- Integrations
- Android app
- Knowledge base
- Product demo
Learn to Build a Better Business Plan

Sample Business Plan Gallery
Browse our library of over 550 free business plan examples to kickstart your own plan.
Browse our library of over 550 free business plan examples.

How to Write a Business Plan
Step-by-step guide to establish the foundation of your business quickly and efficiently.
Step-by-step guide to establish the foundation of your business.

Business Plan Template
Build your business using the proven planning template designed by the experts at Bplans.
Use the planning template designed by the experts at Bplans.

Subscribe to Bplans business insights
Stay up to date with the latest business planning, management, growth, and funding trends from bplans..
We care about your privacy. See our Privacy Policy .
Popular Downloads

SWOT Analysis
Easily evaluate your competitive position and develop effective growth strategies.
Refine your competitive strategy using a SWOT analysis.

Cash Flow Forecast
Improve the health of your business by easily estimating your business’s financial future.
Estimate and improve the financial health of your business.

Lean Business Plan Template
Fast, simple, and shareable. Start with a one-page plan to grow alongside your business.
Start with a simple one-page plan to grow alongside your business…
Start Your Business

Business Startup Guide
Get everything in order to start your business and write your business plan.
Get everything in order to start your business.

How to start a business with no money
Is it possible to start a business with no money? Check out this proven process to get your business…
Is it possible to start a business with no money? Check out this.…

Startup Checklist
Break down the startup process and check all the necessary boxes.

Estimating Startup Costs
What will it cost to start your business? These are the expenses you will need to consider.
Do you know what it will cost to start your business?

Write Your Business Plan

Business Planning in Under an Hour
Learn how to write your business plan in under an hour.

1-Page Business Plan Template
A faster, more efficient way to develop your business strategy.
Perfect Your Elevator Pitch

Pitch Guide
Learn how to create a winning elevator pitch deck and speech that will impress investors.
Impress investors with a winning pitch deck and elevator pitch.

Elements of the Elevator Pitch
If you're pitching to investors or building a pitch deck, here are the 7 things you need.
Here are the 7 things you need to include in your elevator pitch.

Components of a Pitch Deck
Here are the 11 slides you must have in your pitch deck.

Investor Pitch Template
Start your pitch off right with a proven pitch deck template.

Get Your Business Funded

Funding Guide
Learn how to prepare your business plan and pitch to secure funding for your business.
Prepare your plan and pitch to secure funding for your business.

Ways to Fund Your Business
When it comes to funding, there isn't a one-size-fits-all method. Here are your options.
Find out what funding options are available for your business.
Grow Your Business

How to Grow Your Business
Growing your business can be just as difficult as starting. Here are proven ways to grow.
Try these proven methods to continue growing your business.

Grow Using Your Business Plan
Turn your business plan into a growth-oriented business strategy.

Set Clear and Actionable Goals
Grow your business by setting clear goals and establishing key metrics for success.
Learn to set clear and actionable goals to grow your business.

How to Forecast Cash Flow
Create a cash flow forecast to help keep your business healthy and plan for the future.
Keep your business healthy using a cash flow forecast.

Tim Berry Blog
Learn from renowned business planning expert and founder of Bplans, Tim Berry.

Business Glossary
Definitions for common terminology and acronyms that every small business owner should know.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A management team business plan is a section in a comprehensive business plan that introduces and highlights the key members of the company's management team. This part provides essential details about the individuals responsible for leading and running the business, including their backgrounds, skills, and experience. ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
Consider following these instructions to create an impressive team business plan: 1. Collect resumes from each manager. Resumes typically discuss a professional's credentials, including education, work experience and soft and technical skills. You can use your management team's resumes to guide you into creating content for your business plan.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Estimated Duration. Determine organizational readiness. Owner/CEO, Strategy Director. Readiness assessment. Establish your planning team and schedule. Owner/CEO, Strategy Leader. Kick-Off Meeting: 1 hr. Collect and review information to help make the upcoming strategic decisions. Planning Team and Executive Team.
Here are a few elements you should include to come up with a team plan that gets the job done. 1. Establish clear objectives and roles. A good place to begin building your plan is by first outlining what it is you want to do. During this initial meeting, you should discuss what you'd like your team plan to do.
This is part 1 / 8 of Write Your Business Plan: Section 3: Selling Your Product and Team series. One crucial aspect of any business plan is the management team slide, which outlines the key ...
In fact that's expected; no one does anything worthwhile on their own. Just make plans to get help from the right people. Finally, when you create your Management section, focus on credentials but ...
1. Basic model. The basic strategic planning model is ideal for establishing your company's vision, mission, business objectives, and values. This model helps you outline the specific steps you need to take to reach your goals, monitor progress to keep everyone on target, and address issues as they arise.
Team planning is the process of setting strategic and operational plans for your team for the year. It involves strategically aligning your team's work to the overall direction of travel for the business. It provides a clear roadmap to success by identifying the strategic objectives for your team and breaking these down into specific projects ...
These are 12 topics the business planning process often includes: 1. Members of the planning team. Before the business planning process begins, it's important to determine who creates the business plan. If the business plan is for an existing business, it makes sense to include staff members from different departments and teams to understand ...
Business planning is a crucial process that involves creating a roadmap for an organization to achieve its long-term objectives. It is the foundation of every successful business and provides a framework for decision-making, resource allocation, and measuring progress towards goals. Business planning involves identifying the current state of ...
Upmetrics Team. Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
February 3, 2016. Having the right people on your strategic business planning team is essential for achieving desired results. Leaders should include people who are aligned with the organization's goals. It is also advisable to have people on your strategic business planning team who understand and agree with the logic used in making holistic ...
The management team is a crucial factor when drawing up a business plan proposal for investors. The investors will be much more concerned about the executive team than they are about the business idea itself. They know that the manner in which the business plan is put into practice and the difference between success and failure will depend on ...
Use the exercises below to strengthen your team's strategic thinking and planning skills. The activities should also help to improve communication and collaboration skills. You can use them in various ways, for example with a group of new managers, or to refresh the skills of senior leaders. Exercise 1: Early Bird vs.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
By developing a plan, your team will gain focus and strategic alignment. It ensures that every task performed by your staff benefits your business. By simplifying the process of determining priorities and allocating the necessary resources, it eliminates the uncertainties associated with project planning. What's more, by planning ahead, it ...
Business Glossary. Definitions for common terminology and acronyms that every small business owner should know. Bplans offers free business plan samples and templates, business planning resources, how-to articles, financial calculators, industry reports and entrepreneurship webinars.
There are plenty of things to accomplish during this day and lots of team building and business ideas to choose from. Here are three of our team's most effective exercises, so you can use them ...