Seven Sample Attorney Business Plans: Why Attorneys Must Have Business Plans
Share this article
Print/Download PDF

By Harrison Barnes
Rate this article
2434 Reviews Average: 5 out of 5
- Business plans are a dying art, especially in the legal profession.
- Needless to say, business plans are also essential for a lawyer’s career.
- As the adage goes, if you don't plan your career, someone else will plan it for you.

Many of you work in firms that don't have a business plan for the firm as a whole , let alone your practice group or individual attorneys. And some of you are not privy to the firm's plan, even if there is one.
- If you are interested in seeing the elements of a lateral partner business plan click here: Partner Business Plans: Key Elements
Even so, that's no reason to forgo developing a plan for yourself. Remember, if you don't plan your career, someone else will plan it for you.
Have no fear. Personal business planning is not about writing a 50-page manifesto outlining every detail of every day of your professional life for the next 10 years . In fact, personal business planning can be as simple as you want to make it, as you can see here with this sample business plan for law practice PDF . You don't even have to call it a business plan -- call it a career plan if you prefer.
No matter how simple you make it or what you call it, personal business planning is about taking inventory of where you are , determining where you want to go and building a roadmap for getting there. Once you have the plan in writing, all you have to do is revisit it periodically to check your course and make any necessary adjustments.


1. Take an inventory of where you are.
The first step in the personal business planning process is to survey your situation. Often, it helps to ask yourself a series of tough questions. What are your strengths and weaknesses? What practice areas and professional activities most interest you? What is the status of your network and your reputation? How does your personal situation compare with external factors such as your firm's goals and objectives? Are your goals in line with the objectives of your firm? What about the status of your competition, internally and externally? Are you looking to succeed in a field packed with attorneys having similar skills and goals? What are the trends taking shape in your geographic region , in your practice area, and in your clients' industries? Do your goals and objectives capitalize on these trends? Given this analysis, what threats do you need to avoid and what new opportunities can you capitalize on?
2. Determine where you want to go.
You know where you are, but where do you want to go? Think about creating a mission statement for yourself. I know it sounds corny, but the mere exercise of trying to come up with one is enlightening. Answer this question: Why am I practicing law and what do I want to achieve? The answer doesn't have to be unique or earth-shattering -- it just has to answer the question.
Your mission statement doesn't have to be long or eloquent. In fact, you should try to keep it to one sentence. The most important thing to remember is that whether you want to become a partner in your firm, help the less privileged, become a judge, move in-house or start your own firm, your mission is yours and yours alone. Your parents were right: You can do, and be, anything you want.
3. Build a map for getting there.
All that's left is to figure out the steps between your situation and your destination as described in your mission statement. The best way to map out these steps is to start at the end and work your way back to your situation. Here is how your analysis might work:
Establish long-term goals. To accomplish your mission, first think about what long-term goals you will need to achieve. For example, if your mission is to become a partner , you might want to set long-term goals of winning a certain amount of new business or developing a new practice area. You also might speak with those responsible for making partnership decisions, to hear what they want to see you accomplish to support the decision to make you a partner. Once you know their expectations, you can align your long-term goals with their expectations. And you can make exceeding their expectations one of your long-term goals.
If you are already a partner, your mission might be to become one of the firm's top rainmakers. To accomplish this, one of your long-term goals might be to develop a certain percentage of new business from your existing clients over the next two years.
- Set objectives for this year. To accomplish your long-term goals, think about what objectives you can achieve by the end of the year. To continue the above example, if your long-term goal includes developing new business, you might make it your objective to win two new clients this year that represent a certain percentage of your long-term business development goal. To develop a new practice area, you might try to work on three projects related to the new practice area. If your goal is to focus on developing new business with existing clients, your objective might be to have a certain number of face-to-face meetings with your clients to discuss their business and legal issues.
- Start implementing your strategies today . Finally, to accomplish this year's objectives, think about what short-term strategies or steps you can start taking. For example, to win two new clients, you might determine that you need to build your referral network and become more visible in your practice area. That might mean taking a leadership role in an association, writing articles and giving speeches. You might run for office in a bar association section that interests you. Or you might join Toastmasters, to hone your speaking skills. To identify writing opportunities , you could develop better relationships with key people in your firm's marketing department so that they think of you when there is a suitable writing opportunity.
To accomplish your objective of working on three projects in a new practice area, you might determine that you need guidance and additional skills. Then you could identify a mentor with experience building new practice areas . To acquire new skills, you could take continuing legal education courses or seek opportunities to work on the types of matters that will develop those skills.
To develop additional business from existing clients, you might start by scheduling regular entertainment outings with key clients and in the meantime educate yourself about their businesses. What's going on in their industries? What do their most recent annual reports reveal about their strategies? Who are their primary competitors? What legal needs might these clients have that your firm is not serving?
In the meantime, as you establish yourself with new and existing clients, it might be a good idea for you to establish an individual attorney marketing plan, either through an associate attorney marketing plan, or a partner business plan if you are a partner.
The key to building your roadmap is to make sure that each activity you plan to undertake has a clear deadline and is as specific, objective and measurable as possible: "I will take two CLE courses in complex litigation techniques by June 1" or "I will entertain Mr. Jones from ABC Inc. once each quarter."
Also, when it comes to planning, the biggest land mines are complexity and procrastination. Try to avoid creating a plan that overwhelms you or anyone you tell about it. And remember that any plan is better than no plan at all.
Strive to keep your plan simple and start taking action. As an attorney, you're well-versed in the areas of analysis and logic. In every work matter, you look at the situation and connect the dots to accomplish the desired objective. Apply the same approach to personal business planning and the dots you connect will lead you to the career you've always wanted.
- See 30 Ways to Generate Business as an Attorney for more information.
Business Plan For A Law Firm
How do i write a business plan for a law firm, what goes into a business plan, overview of the firm.
- A mission statement about the firm’s purpose.
- A vision statement or recitation of medium- and long-term goals for the firm.
- Important aspects of the firm’s history.
- Any important philosophies that the firm brings to legal practice.
Market Analysis
Do lawyers write business plans, 1. what are your goals.
- What do I want to achieve by starting my own law firm ?
- What is the impact I want to have?
- What am I good at?
- How do I want to service my clients?
- What problems do I want to help solve?
- What does success look like after starting this law firm?
2. Consider how much revenue you will need.
3. setting your fee structure, 4. determine how many cases you need to meet that revenue goal, how to create a law firm business plan, 1. executive summary.
- Mission statement: One or two sentences describing your firm’s purpose.
- Core values: What values are most important to the firm?
- Major goals: What are your firm’s overarching goals and objectives?
- Unique selling proposition: What sets your firm apart from other firms?
2. Firm Description
- Service(s): What type of law do you practice? What types of clients do you serve?
- Firm values: Restate your mission statement and core values.
- Legal structure: What sort of business entity are you? Are you in a sole proprietorship or a limited liability partnership?
- Location: Where is the office geographically located? What areas does the firm serve?
- Unique selling proposition: What makes your firm stand out? What technology or services give your firm an edge?
3. Market Analysis
- Ideal client: What demographics (like location, age, occupation), needs, and motivations would signify the best client match for your firm, and why?
- Industry description: What is the current and projected size of the market your firm is in? What are the trends in your legal niche?
- Competitive analysis: Who are your direct and indirect competitors, and how are they serving your target market? Where do your competitors succeed? What opportunities are there for your firm?
- Projections: How much can your ideal clients spend on legal services? How much can you charge?
4. Organization and Management Overview
- Describe what makes you unique and what sets you apart from other applicants.
- If applicable, include what makes each member of your team suitable for their particular roles.
- The organizational chart is a great visual aid if you have a larger practice.
5. Services
- What problems do your potential clients need your help with?
- How can your services uniquely help your clients solve their problems?
- What is the benefit of your services to clients?
- Why would potential clients choose your firm over another firm?
6. Marketing Strategy
- Ideal client: Where would you find your ideal client?
- Marketing goals: Detail what specific outcomes you hope to accomplish through marketing. Goals should include tactical objectives (more clients? Higher billing rates?) and overall objectives (like increased name recognition).
- Unique selling proposition: Restate what sets you apart and makes you uniquely able to best serve your clients.
- Competition: Detail who your competition is—and what they are doing to gain clients. Analyze their marketing strategies and assess where the cost of your services fits in with your competitors.
- Action plan: List the specific actions your firm will take to reach your target market and achieve your marketing goals (this could include a media/advertising strategy).
7. Financial Plan
- Revenue goal: How much money you want to make broken down by month.
- Financial projections: What you will really expect to earn, how many cases you think you will have the capacity to take on, and what you will be charging each client each month.
- Budget: A breakdown of your expenses and what your money will be going towards each month.
- Cash flow statement: What you actually earned and spent each month. This is different from your projections and budget and should be updated as the year progresses. You will find that you may have budgeted for something that cost you much less than you originally thought or made more in a month than you projected, these discrepancies should be recorded in your cash flow statement.
8. Start-Up Budget
- Hardware (laptops, printers, scanners, office furniture, etc.)
- Office space (Will you rent, or work from home?)
- Malpractice insurance
- Staff salaries (Are you planning to hire an administrative assistant or paralegal?)
- Utilities (Phone, internet, etc.)
- Practice management software or other technology services
- Partner Business Plans: Key Elements
- You Need to be Self-Managing and Responsible
- The Importance of Finding and Creating Demand
- The Importance of Asking the Right Questions, Self Improvement and Perception
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 1
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 2
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 3
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 4
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 5
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 6
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 7
Want to continue reading?
Become a free bcg attorney search subscriber..
Once you become a subscriber you will have unlimited access to all of BCG’s articles.
There is absolutely no cost!
Harrison Barnes does a weekly free webinar with live Q&A for attorneys and law students each Wednesday at 10:00 am PST. You can attend anonymously and ask questions about your career, this article, or any other legal career-related topics. You can sign up for the weekly webinar here: Register on Zoom
Harrison also does a weekly free webinar with live Q&A for law firms, companies, and others who hire attorneys each Wednesday at 10:00 am PST. You can sign up for the weekly webinar here: Register on Zoom
You can browse a list of past webinars here: Webinar Replays
You can also listen to Harrison Barnes Podcasts here: Attorney Career Advice Podcasts
You can also read Harrison Barnes' articles and books here: Harrison's Perspectives
Harrison Barnes is the legal profession's mentor and may be the only person in your legal career who will tell you why you are not reaching your full potential and what you really need to do to grow as an attorney--regardless of how much it hurts. If you prefer truth to stagnation, growth to comfort, and actionable ideas instead of fluffy concepts, you and Harrison will get along just fine. If, however, you want to stay where you are, talk about your past successes, and feel comfortable, Harrison is not for you.
Truly great mentors are like parents, doctors, therapists, spiritual figures, and others because in order to help you they need to expose you to pain and expose your weaknesses. But suppose you act on the advice and pain created by a mentor. In that case, you will become better: a better attorney, better employees, a better boss, know where you are going, and appreciate where you have been--you will hopefully also become a happier and better person. As you learn from Harrison, he hopes he will become your mentor.
To read more career and life advice articles visit Harrison's personal blog.
Article Categories
- Legal Recruiter ➝
- Harrison's Perspectives ➝
- Career Advice for Attorneys
Do you want a better legal career?
Hi, I'm Harrison Barnes. I'm serious about improving Lawyers' legal careers. My only question is, will it be yours?

About Harrison Barnes
Harrison is the founder of BCG Attorney Search and several companies in the legal employment space that collectively gets thousands of attorneys jobs each year. Harrison is widely considered the most successful recruiter in the United States and personally places multiple attorneys most weeks. His articles on legal search and placement are read by attorneys, law students and others millions of times per year.
Find Similar Articles:
- Attorney Business Plans
- Business Development
- Business Plans
- Develop Additional Business
- Generate Business
- Lateral Partner Business Plan
- Legal Career
- Legal Job Market
- Partner Business Plans
- Partner Resources
- Personal Business Planning
Active Interview Jobs
Featured jobs.
Location: Kentucky - Louisville
Location: California - Emeryville
Location: California - Santa Ana
Most Viewed Jobs
Location: New York - New York City
Location: Ohio - Columbus
Location: California - Oakland
Upload Your Resume
Upload your resume to receive matching jobs at top law firms in your inbox.
Additional Resources
- Harrison's Perspectives
- Specific Practice Areas
- The Winning Mindset
BCG Reviews
[My favorite part about working with BCG Attorney Search was] the follow up, and not having to be the one contacting the.... Read more >
Billie Pierce
University of California Berkeley School of Law, Class Of 2010
Brian is an incredible, very effective team! They moved the process along quickly and were extremely responsive to all m.... Read more >
Lindsay Docto
Boalt, Class Of 2015
Basically, I didn't have to do anything until I got the job offer. I never had to check in, she would check in with me a.... Read more >
Abbey Jahnke
Case Western Reserve University School of Law, Class Of 2012
I have enjoyed working with my recruiter and I look forward to learning more from you in the future.
Jiayi Jiang
Harrison is very thorough, on top of it, proactive and hard working. It took a lot of pressure off me for you to do the .... Read more >
Stacey Bradford
Washington College of Law, American University, Class Of 1994
I would be remiss if I did not tell you how valuable I believe it has been to work with my New York recruiter in this pr.... Read more >
Linda Brower
Popular articles by harrison barnes.
- What is Bar Reciprocity and Which States Allow You to Waive Into the Bar?
- What Do Law Firm Titles Mean: Of Counsel, Non-Equity Partner, Equity Partner Explained
- Top 6 Things Attorneys and Law Students Need to Remove from Their Resumes ASAP
- Why Going In-house Is Often the Worst Decision a Good Attorney Can Ever Make
- Top 9 Ways For Any Attorney To Generate a Huge Book of Business
Helpful Links
- The BCG Attorney Search Guide to Basic Law Firm Economics and the Billable Hour: What Every Attorney Needs to Understand to Get Ahead
- Quick Reference Guide to Practice Areas
- Refer BCG Attorney Search to a Friend
- BCG Attorney Search Core Values
- Recent BCG Attorney Search Placements
- What Makes a World Class Legal Recruiter
- What Makes BCG Attorney Search The Greatest Recruiting Firm in the World
- Top 10 Characteristics of Superstar Associates Who Make Partner
- Off-the-Record Interview Tips From Law Firm Interviewers
- Relocating Overseas
- Writing Samples: Top-12 Frequently Asked Questions
- The 'Dark Side' of Going In-house
- "Waive" Goodbye To Taking Another Bar Exam: Typical Requirements and Tips to Effectively Manage the Waive-in Process
- Changing Your Practice Area
- Moving Your Career to Another City
- A Comprehensive Guide to Working with a Legal Recruiter
- A Comprehensive Guide to Bar Reciprocity: What States Have Reciprocity for Lawyers and Allow You to Waive into The Bar
Related Articles

Important Questions Attorneys Need to Ask Themselves Before ....
The Importance of a Great Business Plan

No Job Offer in Hand? Then You Need a Plan

Business Plans Revealed
When you use BCG Attorney Search you will get an unfair advantage because you will use the best legal placement company in the world for finding permanent law firm positions.
Don't miss out!
Submit Your Resume for Review
Register for Unlimited Access to BCG
Sign-up to receive the latest articles and alerts
Already a subscriber? Sign in here.

Law Firm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Law Firm Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 lawyers to create business plans to start and grow their law firms. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a law firm business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your law firm as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan
If you’re looking to start a law firm, or grow your existing law firm, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your law firm in order to improve your chances of success. Your law firm plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Law Firms
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a law firm are personal savings, credit cards and bank loans. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a law firm.
If you want to start a law firm or expand your current one, you need a business plan. Below are links to each section of your law firm plan template:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of law firm you are operating and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a law firm that you would like to grow, or are you operating law firms in multiple cities?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the law firm industry. Discuss the type of law firm you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of law firm you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types of law firms:
- Commercial Law : this type of law firm focuses on financial matters such as merger and acquisition, raising capital, IPOs, etc.
- Criminal, Civil Negligence, and Personal Injury Law: this type of business focuses on accidents, malpractice, and criminal defense.
- Real Estate Law: this type of practice deals with property transactions and property use.
- Labor Law: this type of firm handles everything related to employment, from pensions/benefits, to contract negotiation.
In addition to explaining the type of law firm you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of clients served, number of cases won, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the law firm industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the law firm industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your law firm plan:
- How big is the law firm industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your law firm? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your law firm plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: businesses, households, and government organizations.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of law firm you operate. Clearly, households would respond to different marketing promotions than nonprofit organizations, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most law firms primarily serve customers living in their same city or town, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Law Firm Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other law firms.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes accounting firms or human resources companies. You need to mention such competition as well.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other law firms with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be law firms located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What types of cases do they accept?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide better legal advice and services?
- Will you provide services that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you provide more responsive customer interactions?
- Will you offer better pricing or flexible pricing options?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a law firm plan, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of law firm company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to in-person consultation, will you provide virtual meetings, or any other services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the products and services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your law firm company. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your law firm located in a busy business district, office building, etc. Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your law firm marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local websites
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your law firm, including filling and filing paperwork, researching precedents, appearing in court, meeting with clients, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to file your 100th lawsuit, or be on retainer with 25 business clients, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your law firm to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your law firm’ ability to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing law firms. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with legal experience or with a track record of successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you file 25 lawsuits per month or sign 5 retainer contracts per month? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your law firm, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a law firm:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of licensing, software, and office supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your office location lease or your certificate of admission to the bar.
Putting together a business plan for your law firm is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert and know everything you need about starting a law firm business plan; once you create your plan, download it to PDF to show banks and investors. You will really understand the law firm industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful law firm.
Law Firm Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my law firm business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily complete your Law Firm Business Plan.
What is the Goal of a Business Plan's Executive Summary?
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of law firm you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have a law firm that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of law firms?
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Law Firm business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Log in to Lawyerist.com
Not a Subscriber yet? Register here. (It's free!)
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Forgot your password? Reset it here.
Subscribe to Lawyerist
Back to login.
- Hidden Date MM slash DD slash YYYY
- Name * First Last
- Password * Enter Password Confirm Password
- United States
- Which state is your firm's primary location? * Pick one. Alabama Alaska American Samoa Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware District of Columbia Florida Georgia Guam Hawaii Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Mississippi Missouri Montana Nebraska Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey New Mexico New York North Carolina North Dakota Northern Mariana Islands Ohio Oklahoma Oregon Pennsylvania Puerto Rico Rhode Island South Carolina South Dakota Tennessee Texas Utah U.S. Virgin Islands Vermont Virginia Washington West Virginia Wisconsin Wyoming Armed Forces Americas Armed Forces Europe Armed Forces Pacific State
- Which province is your firm's primary location? * Pick one. Alberta British Columbia Manitoba New Brunswick Newfoundland and Labrador Northwest Territories Nova Scotia Nunavut Ontario Prince Edward Island Quebec Saskatchewan Yukon Province
- What is the size of your firm? * Pick one. Solo practice Small firm (2–15 lawyers) Medium or large firm (16+ lawyers) I do not work at a law firm
- What is your role at your firm? * Pick one. Owner/partner Lawyer Staff Vendor (web designer, consultant, etc.) I do not work at a law firm
- What is your primary practice area? * Pick one. Bankruptcy Civil litigation (non-PI) Class Action Collections Corporate Criminal Education Employment Estate planning, probate, or elder Family General practice Immigration International Landlord/Tenant Mediation/ADR Personal injury Real estate Small business Sports/Entertainment Tax Trademark/IP Other I do not work in law
- Legal Technology Products and Services
- Building a Healthy Firm
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
You have read all five of your free articles this month. To read this article, log in or register.
Legal product reviews and business guidance from industry experts.
19 Mar 2020
How to Write Your Law Firm Business Plan

By Cari Twitchell
News Articles Healthy Strategy
Every new law practice needs a business plan . This is a guide to creating one.
Here is what should go in your business plan once you’ve decided about your law firm business model.
Section One: Executive Summary
This section provides a succinct overview of your full plan. It should also include the following:
- Mission statement. This statement should be one or two sentences at most, so you can quickly state it off the top of your head at any given moment. It should clearly state your value and offer inspiration and guidance, while being plausible and specific enough to ensure relevancy. For further direction on how to write a mission statement, read this Entrepreneur article .
- Core values. Your core values outline the strategy that underpins your business. When written well, they help potential employees and clients understand what drives you every day. When written incorrectly, they include meaningless platitudes that become yet another thing forgotten or ignored during practice. To pack the most punch into your core values, write them as actionable statements that you can follow. And keep them to a minimum: two to four should do just fine. You can read more about writing core values at Kinesis .
- What sets you apart. If you are like every other attorney out there, how will you stand out? This is known as your unique selling proposition (USP). What is it that will convince clients to turn to you instead of your competition? By clearly stating your USP, you identify what it is about your firm that will ensure your success.
Are you feeling slightly overwhelmed by all of this? Then write this section last, as you’ll find much of what you write here is a summary of everything you include in subsequent sections.
Section Two: Company Description
Write a succinct overview of your company. Here is what it should cover:
- Mission statement and values. Reiterate your mission statement and core values here.
- Geographic location and areas served. Identify where your offices are located and the geographic areas that you serve.
- Legal structure and ownership. State whether you are an LLC, S-Corp or other legal entity. If you are something other than a sole proprietor, identify the ownership structure of your firm. How does your law firm business model influence the ownership type?
- Firm history. If you are writing or updating a plan for a law firm already in existence, write a brief history that summarizes firm highlights and achievements.
This section is often the shortest. Do not spend much time or space here. Touch on the major points and move on.
Section Three: Market Analysis
Done correctly, a well thought out market analysis will help you identify exactly what your potential clients are looking for and how much you should charge for your services. It also enables you to identify your competitors’ weaknesses, which in turn helps you best frame your services in a way that attracts your preferred clientele. You probably already considered some of these subjects when deciding on the small law firm business model, but you need to document them.
Elements of a market analysis include:
- Industry description. Draft up a summary that encompasses where your particular legal niche is today, where it has been, and which trends will likely affect it in the future. Identify everything from actual market size to project market growth.
- Target audience. Define your target audience by building your ideal client persona. Use demographics such as location, age, family status, occupation and more. Map out the motivations behind their seeking your services and then how it is you are best able to satisfy their requirements.
- Competitive analysis. This is where you dive into details about your competitors. What do they do well? Where do they fall short? How are they currently underserving your target market? What challenges do you face by entering legal practice in your field of choice?
- Projections. Provide specific data on how much your target audience has to spend. Then narrow that down to identify how much you can charge per service.
A proper market analysis includes actual data to support your analysis. If you are unsure of where to find data, Bplans has a great list of resources for you to use. And if you would like to read further about conducting a market analysis, check out this article from the Small Business Administration.
Section Four: Organization & Management
This section goes into detail about you and any others who may have ownership interest in the firm. The small law firm business model section here should incorporated into the management documentation. Do not be afraid to brag a bit!
- What is your educational background?
- What experience do you currently have?
- Why are you the right person to run your firm?
If there are other individuals involved, it is a good idea to insert your organizational chart here. Visuals help quickly convey information and break up otherwise blocky text.
Section Five: Services
The Services section is the heart of your law firm business model plan. It is where you dive into all aspects of your services, including:
- The problem(s) you are addressing. What pain points do your preferred clients experience? What can they do right now to alleviate those pain points? Answer these questions, and then take the extra step to explain how those current solutions fail to adequately address their problems.
- The solution(s) you are providing. This describes how your solutions better resolve your prospective market’s needs. This not only includes the actual work you do, but the benefits that each client will receive based on your work.
- An overview of your competition. Describe your competition here. For instance, which other solo attorneys and firms provide the same solutions as you? What are your advantages over these competitors? What do you differently when providing your solutions? How will clients gain additional benefits by seeking out your services instead of working with your competitors?
Section 6: Marketing Strategy
Your marketing strategy section needs to address the three P’s:
- Positioning. How will you position your law firm and your services? What will you say to present your practice in the best light? What short statements can you use to entice a potential client to pursue your services?
- Pricing. How much will you charge? How does that fit within the legal industry? Within your niche industry? What do clients receive for that price?
- Promotion. Which sales channels and marketing activities will you pursue to promote your practice? Who is in charge of these activities? Even if you plan to build your law firm on the basis of word-of-mouth referrals, you must remember that most referrals will still look for information about you before contacting you. Know where they will look and ensure you are there.
Section Seven: Financials
Last comes the financials section. It is the key component to your plan if you are going to seek funding to get your practice off the ground. It is imperative that you complete this section even if you are not seeking funding, however, as you need to paint a clear financial picture before opening your doors.
Two main items make up this section: budgeting and forecasting (sales and cash flow). Answer these questions to help you address these items:
- How much starting capital do you need?
- How much money will it cost to keep your practice operating on a month-to-month basis?
- How many cases will you need to close each month to break even?
- How many cases would you need to close to make a profit?
- What is your projected profit and loss for the year?
This section often incorporates graphs and other images, including profit-and-loss and cash-flow tables. The more specific you get with your numbers, the more likely you are to succeed!
One final note: If your goal is to submit your business plan to potential funders, you want to do everything you can to make sure your plan stands out. One good way to do this is to work with a designer to artfully format your plan. Great presentation can take you a long way.
Originally published 2017-09-23. Republished 2020-07-31.
Cari Twitchell
About the Author
@CariTwitchell
/in/caritwitchell/
Website: https://www.customcontentllc.com
Share Article
Last updated October 7th, 2022
Learn the Latest from Our Partners and Community
11 Jan 2023
On The Lawyerist Podcast: Top Episodes of 2022
By Kyle Harrington
Lawyerist News News Articles Healthy Clients Healthy Owner Healthy Strategy Healthy Team
Everett Hosts Interactive Strategic Planning Session at Alaska...
Lawyerist News News Articles Healthy Strategy
Lawyerist Media Launches Redesigned Website to Better Help...
By the Lawyerist editorial team
Lawyerist News News Articles Healthy Strategy Law Firm Finances Law Firm Websites Lawyerist News Starting a Law Firm
27 May 2022
Lawyerist Values: Grow as People
Lawyerist News News Articles Healthy Strategy Lawyerist Values
Lawyerist’s Seek Candor Value Is More Than...
Develop a healthy strategy, how to competently reinvent your practice.
By Megan Zavieh
31 Dec 2019
Year-End Law Practice Checklist
19 Dec 2019
How to Use Aged A/R Reports
By Mary Juetten
News Articles Healthy Strategy Law Firm Finances
26 Nov 2019
Small Firm Roadmap Stories: Vision and Values
News Articles Healthy Strategy Lawyerist Lab Roadmap Starting a Law Firm
18 Oct 2019
Design Thinking for Lawyers
By Marshall Lichty
News Articles Healthy Strategy Healthy Systems
19 Aug 2019
Strategic Planning for Law-Firm Success and Growth
25 Oct 2018
How to Promote a Unique Value Proposition to...
By Karin Conroy
News Articles Healthy Strategy Law Firm Clients
23 Jan 2018
Rethinking Law-Firm Productivity Measurement for the Post Billable...
By Jordan Furlong
23 Mar 2017
How to Calculate Client Acquisition Cost
- Product Reviews
The original content within this website is © 2024. Lawyerist, Lawyerist Lab, TBD Law, Small Firm Dashboard, and
The Small Firm Scorecard are trademarks registered by Lawyerist Media, LLC.
Privacy policy // XML sitemap // Page ID: 83157
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Law Firm Business Plan
Start your own law firm business plan
Wy'East Law Firm
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Wy’East Law Firm (WLF) is a boutique technology law firm located in Portland, Oregon. The firm will be lead by Richard Bloom, a seasoned attorney previously with (name omitted)’s e-group. WLF will service all needs generated by technology firms, with specialization on mergers and acquisitions and qualified stock option plans; and handles both start-up and established companies.
In addition to WLF’s technology practice, we will offer public interest legal work at subsidized rates. The technology practice will allow the firm to be able to provide public interest organizations legal help at the cost of overhead.
WLF is a limited liability company founded and lead by Richard Bloom.
1.1 Objectives
The objectives for WLF for the first three years of operation include:
- To create a law firm whose primary goal is to exceed customer’s expectations.
- To develop a client list that includes at least 20 companies, each with revenues of over $3 million.
- To increase the ability to serve public interest organizations each year.
- To be able to offer each year some legal services at a subsidized rate.
1.2 Mission
The mission of Wy’East Law Firm is to provide the Portland community with technological and public interest legal guidance. We exist to attract and maintain customers and to support the public interest community. When we adhere to this maxim, everything else will fall into place.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
WLF is a law firm serving technology companies and public interest organizations, and will subsidize its public interest work with local companies. WLF specializes in mergers and acquisitions as well as stock option plans, but can handle most legal needs for a technology company.
The technology work will subsidize the company’s public interest work which will be billed out at the cost of overhead.

2.1 Company Ownership
WLF is a limited liability company, owned solely by Richard Bloom.
2.2 Start-up Summary
WLF’s start-up costs will include all equipment needed for the home office, website creation, and advertising.
The home office equipment will be the largest chunk of the start-up expenses. This equipment includes 4 computers, a fax machine, copier, cellular phone, office supplies, additional land line, a DSL connection, and office furniture.
Start-up expenses will also include advertising. Two methods will be used: a content-only website and the Yellow Pages.

WLF will provide provide law services to two different groups of customers.
- Technology law services . WLF will provide legal services to high technology clients, to both start-up companies and established firms. While the firm excels in mergers, acquisitions, and qualified stock option plans, we also have experience in almost any legal field that a tech firm encounters. These clients, billed at market rate, will subsidize the public interest clients.
- Public interest law . WLF will serve regional public interest organizations, with a concentration on environmental and civil rights organizations. For most public interest organizations, good legal help is expensive. By using technology clients to subsidize the cost of legal fees for public interest firms, WLF is able to make significant contributions back to the community.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
WLF’s customers can be divided into two groups, technology firms and public interest organizations.
- Public interest organizations . These clients will be diversified, some are environmental organizations others are civil rights groups. While some public interest organizations receive their legal services for free (pro bono) from some attorneys, there is an extreme shortage of legal help for these organizations. Therefore, it is quite attractive to these organizations to have the possibility of receiving top legal help at a subsidized rate. Attracting these clients will not be the problem, the difficulty will be for Richard to select which organization will receive his help.

4.1 Target Market Segment Strategy
WLF will be targeting high technology companies for two reasons.
- Although the economy has taken a recent plummet, particularly technology firms, technology is still a growing sector of the economy. This is evidenced by the fact that 17 out of the top 25 fastest growing companies are technology firms, according to The Business Journal of Portland.
- Technology is Richard’s area of expertise. Richard practiced law at one of the top three law firms in Portland and was in their e-group, concentrating on technology firms. His experience, coupled with his network of colleagues within the industry, makes technology firms attractive customers.
WLF will be targeting public interest organizations for one simple reason, a desire to give back to the community. Public interest work is inherently altruistic to some degree. Generally, the person performing the work receives a good feeling for his/her contribution, but in today’s capitalistic society, someone who donates his/her time at far below market wages should be considered altruistic.
4.2 Service Business Analysis
The technology law practice is fairly competitive in Portland. Most larger, more prestigious firms have attorneys who specialize in technology. Some smaller firms also have attorneys who do work for technology companies. Lastly, there are boutique firms, like WLF. As a service-based industry, the practice of law is driven by personal relationships and reputation. Potential clients choose attorneys based on reputation and who they are familiar with or are recommended to. Therefore, if the attorney is providing better service to a client, the client is likely to form a long lasting business relationship with the client.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
WLF has the advantage that when Richard left (name omitted) he brought 15 of his clients, which, for now, are almost enough to survive on.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
WLF will be courting new technology clients through networking and advertisements in the Yellow Pages, Business Journal of Portland, and other technology specific regional journals. As stated earlier, WLF has a sufficient amount of business at day one, however, more technology clients means the ability to perform more public interest work.
Richard will be attending the Portland Venture Group meetings as well as other informal gatherings of technology companies to network with the different technology firms in the region. These networking activities along with advertisements in appropriate media forms will allow WLF to steadily grow their list of clients.
5.1 Competitive Edge
WLF’s competitive advantage will be based on two factors, experience and specialization:
- Experience. Richard brings to WLF three years of practicing technology law at a top firm in Portland. Reputation carries a lot of weight and Richard’s time at (name omitted) means a lot in the Portland legal community and is very attractive to prospective clients. Additionally, beyond the reputation of working for a coveted firm, is the fact that the three years spent at (name omitted) provided Richard with big name clients.
- Specialization. As a boutique firm that concentrates on technology companies, WLF is in a desirable situation because it’s knowledge base is considerable, relative to other firms that practice a wide range of law.
5.2 Sales Strategy
WLF’s sales strategy will begin with months two through five with the goal of serving the existing customer base of clients. The absence of bringing in new clients during this time is purposeful, it allows WLF and the existing clients to form a new relationship at WLF, different from their previous relationship at (name omitted).
Month six will signal WLF’s conscious effort to generate new clients. Using the previously mentioned networking techniques, Richard, through personal communications, will convince prospective clients of the value of a boutique technology law firm, specifically the depth of knowledge and the close attention that the client will get when dealing with a small firm.
Regarding the public interest organizations, there will be less of a sale strategy, more of a choosing of the organizations that Richard wants to represent. There are so many needy public interest organizations that Richard will have to pick and choose those that he wishes to help out.
5.2.1 Sales Forecast
The first month will be spent setting up the home office. This will include setting up the office, a conference room, and all of the computer equipment. During the first month, Richard will also be serving some existing technology clients and some public interest clients. We project that if we spend 1/3 of our time on the technology clients, this would sufficiently subsidize the public interest clients so we would only have to cover overhead expenses.
By month six, Richard will begin actively soliciting new clients. Between months one and five he will continue networking, though will not be actively seeking customers. From month seven on and there will be a slight increase in clients taken aboard. There will be only a slight increase so as to create solid relationships with the new and existing clients. Richard will be cognizant of the possibility of growing too fast and not being able to offer the same quality service to his clients.
5.3 Milestones
WLF will have several milestones early on:
- Business plan completion.
- Set up home office.
- First month of total technology subsidy.
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Wy’East Law Firm is an Oregon Corporation founded and run by Richard Bloom. Richard has a degree in Political Science from the University of Colorado, Boulder, and a J.D. from Lewis and Clark University. While at Lewis and Clark, Richard was the President of the school’s Public Interest Student Organization. It was through this organization that Richard became fond of public interest law. After graduation, Richard went to work for (name omitted) for three years in the e-group which concentrated on technology. While working in the e-group, Richard worked on technology issues with a number of well known start-up organizations and established companies.
One of the perks working at (name omitted) was his ability to do pro bono work which counted toward his required yearly billable hours requirement. Richard has spent a fair amount of time with 1000 Friends of Oregon and other public interest organizations. After three years however, Richard was feeling constrained and desired more autonomy. He decided to leave and start his own firm. Richard was able to bring a fair number of his clients from (name omitted) to his new firm, helping the transition from leaving an established practice to hanging out his own shingle and starting over.
6.1 Personnel Plan
The staff will consist of Richard working full time. In addition to Richard, a part-time secretary and part-time paralegal will join WLF by month two. Month four will bring WLF a law clerk, and a second law clerk by month eight.
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The following sections will outline important financial information.
7.1 Important Assumptions
The following table details important assumptions.
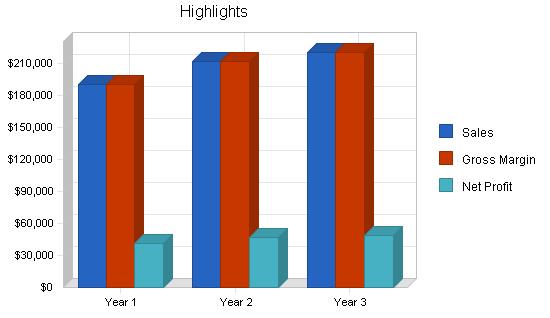
7.2 Projected Profit and Loss
The following table and charts present the projected profit and loss.

7.3 Break-even Analysis
The Break-even Analysis indicates what WLF will need in hours and revenue a month to reach the break-even point.

7.4 Projected Cash Flow
The following chart and table show anticipated cash flow.

7.5 Projected Balance Sheet
The following table displays the projected balance sheet.
7.6 Business Ratios
Industry profile ratios based on the NAICS code 541110, Offices of Lawyers, are shown in the table below.
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Transform Tax Season into Growth Season
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

How to Create a Law Firm Business Plan Aimed at Success
Want a successful law firm? Start with a solid business plan. Our guide covers everything that will help you create a roadmap for success.
A firm exists to serve people- so its business plan must take into account those it aims to help. A law firm's business plan lays out the key pillars that will support a practice, from operational details to marketing strategies to financial projections. Furthermore, it should provide a clear roadmap for where the firm hopes to be in the coming years.
In this blog, we will guide you through the process of creating a comprehensive law firm business plan that will help you achieve your goals . Additionally, in our latest Grow Law Firm podcast, our host Sasha Berson conversed with Omar Ochoa, the founding attorney of Omar Ochoa Law Firm, to discuss the topic of creating a law firm business plan aimed at success.
Why Is a Business Plan Important for Law Firms?
A business plan is a vital tool for any law firm to achieve success. It outlines goals, strategies, and the feasibility of business ideas, providing a clear direction and focus for the firm. The plan can be used to secure funding from investors or financial institutions by demonstrating the potential for growth and profitability.

Moreover, a business plan supports decision-making by evaluating the feasibility of new ventures and assessing potential risks and rewards. It helps to manage resources effectively by setting financial goals and tracking progress, ensuring the firm is making the most of its resources and achieving objectives.
Lastly, a law firm's business plan enables growth by identifying new opportunities and developing strategies to capitalize on them. By planning for the future and setting realistic growth targets, law firms can take their businesses to the next level. Overall, a well-developed business plan is critical for success in the legal industry, providing direction and focus, supporting decision-making, managing resources effectively, and enabling growth.
General Tips for Creating an Attorney Business Plan

Building a business plan for law firms is not an easy or intuitive process. By considering the following issues before opening your doors to clients, you have a much better chance of having a stable firm that matches your values and has a clear set of goals.
— Stay Focused
Forming a law firm can feel overwhelming. You have a lot of freedom and can easily get sidetracked into issues that either can wait or do not deserve your attention.
If having a strong law firm website design is important enough for you to include in your plan, you will spend time on that instead of less important matters.
A plan also includes a budget. The process of planning your firm's finances can ensure that you do not overspend (or underspend) as you start your own firm.
The attention to detail that comes from having a plan will help you avoid spreading yourself too thin by focusing on every issue or the wrong issues. Instead, you will maintain your focus on the important issues.
Whether you have law partners or develop a solo law firm business plan, the plan will help you stay focused on your end goals.
— Keep Track of Goals and Results
It is easy to set goals when you start a law firm and then promptly forget about them.
Your plan will set out your goals and the metrics you will use to determine your progress toward meeting them. The plan should also explain how you will know when you have met them.
For example, you might have a growth goal of reaching five lawyers within two years. Or you might have a revenue goal of collecting $200,000 your first year.
Too many businesses, including law firms, meander on their developmental path. By setting goals and the path for meeting them, you will have guardrails to keep your firm on track.
"If you want to be the number one law firm in the country by revenue right in a 20 year time period, have that be your goal and everything that you do right is in service of that goal. You might not get there, but you're gonna find that you're gonna be very successful either way."
"If you want to be the number one law firm in the country by revenue right in a 20 year time period, have that be your goal and everything that you do right is in service of that goal. You might not get there, but you're gonna find that you're gonna be very successful either way." — Omar Ochoa
— Sort Out Your Own Law Firm Strategy
Developing a clear vision is important for establishing a strategic law firm plan aimed at long-term goals . As Omar Ochoa discusses in the podcast, having very specific milestone visions like where you want to be in five, ten, or fifteen years helps drive the strategy and actions needed to get there.
It's easy to say that you'll run your law firm better. But a plan actually helps you identify how to improve by articulating a concrete strategy. The process of creating the plan will help you pinpoint problems and solutions.
A plan forces consideration of operational details often overlooked. It equates to defining your firm's purpose and then pursuing that vision with purpose-driven strategies and actions. As Omar notes, marrying vision to action through knowledge of other successful law firm models is key to achieving goals.
One area that is frequently overlooked in plans is the inclusion of law firm marketing strategies . Developing this aspect is critical for attracting clients and sustaining growth.
Level Up Your Brand
Book a Free Consultation
— Move Forward
You should view your plan as a law firm business development plan that will guide the formation and growth of your firm .
You can review the document periodically to remind you and your law partners of your growth and expansion projections. After this review, you can ensure your growth and expansion remain on track to carry you to your goals.
The review will also tell you whether you need to update your firm's goals. When you started your law firm, you might have been unduly pessimistic or optimistic in your projections. Once you have some time to operate according to your plan, you can update your goals to keep them realistic. You can also update your processes to focus on what works and discard what does not.
The review can provide your projections for what you hope to accomplish and the roadmap for accomplishing it.
Law Firm Business Plan Template

Each of the websites below includes at least one attorney business development plan template:
- Business Plan Workbook
- PracticePro
- Smith & Jones, P.A.
- Wy'East Law Firm
You can use a law firm strategic plan example from these sites to start your firm's plan, then turn the plan into a document unique to your circumstances, goals, and needs.
What to Consider before Starting Law Firm Business Plans
Before starting a law firm business plan, think through a few key issues, including:
— Setting the Goals
Reflect deeply on your firm's purpose. Think about who you represent and how you can best meet their needs. A law firm exists for its clients. As you think about your law firm goals , think about goals for providing legal services to your clients.
"We continue to try to have the biggest impact that we can because ultimately, in my opinion at least, that's what lawyers are for, is to be able to help people and be able to move us forward." — Omar Ochoa
You need to set realistic and achievable goals. These goals should reflect your reasons for starting your law firm. Thus, if you started your law firm because you expected to make more money on your own than working for someone else, set some goals for collections.
While you are setting your goals, think about how you will reach them and the ways you will measure your success. For example, if you want to expand to include ten lawyers within three years, think about intermediate goals at the end of years one and two. This helps measure your progress.
— Choosing Partnership Structure
For lawyers considering a partnership structure, it's important to select partners that complement each other's strengths and weaknesses to help the firm function effectively.
There are 2 main partnership structure options:
- A single-tier model provides equal decision-making power and liability between partners.
- Meanwhile, a two-tier structure offers tiers like equity and non-equity partners, providing flexibility and career progression opportunities.
While similarly skilled individuals may clash, partners with differing abilities can succeed together. Some attorneys also choose to run their own firm for flexibility. This allows them to leverage different specialists through occasional joint ventures tailored for specific cases, without the constraints of a single long-term partnership. Furthermore, it highlights how the law firm partnership structures impacts freedom and sustainability.
— Thinking of the Revenue You Need
Calculate how much revenue you need to cover your overhead and pay your salary. Suppose your expenses include:
- $2,000 per month for office rent
- $36,000 per year for a legal assistant salary
- $600 per month for courier expenses
- $400 per month for a copier lease

Assume you want the median annual salary for lawyers of $127,990. You need $199,990 per year in revenue to cover your salary and expenses.
But revenue is not the end of the story. Your landlord, vendors, and employees expect to get paid monthly. So, you should also calculate how much cash flow you need each month to cover your hard expenses.
You also need a reserve. Clients expect you to front expenses like filing fees. Make sure you have a reserve to pay these costs and float them until clients reimburse you.
— Defining the Rate of Payment
You need to make some difficult decisions when it comes to setting your own fee structure. If you choose a higher billing rate, you will need to work less to meet your revenue goals. But you might not find many clients who are able to pay your fees.
Whether you charge a flat fee, contingent fee, or hourly fee, you should expect potential clients to compare your fees to those of your direct and indirect competitors. Remember, your firm competes against other lawyers, online services like LegalZoom , and do-it-yourself legal forms books.
Finally, you need to comply with your state's rules of professional conduct when setting your fees. The ABA's model rules give eight factors to determine the reasonableness of a fee. These factors include the customary fee for your location and the skill required to provide the requested legal services.
— Making the Cases in Your Law Practice Meet the Revenue Needs
Figure out how much you need to work to meet your revenue target . If you charge a flat fee, you can simply divide your revenue target by your flat fee.
Hourly fee lawyers can calculate the number of hours they need to bill and collect. However, law firm owners rarely bill 100% of the hours they work due to the administrative tasks they perform to run a firm. Also, you will probably not collect 100% of your billings, and clients could take 90 days or longer to pay.
Contingency fee lawyers will find it nearly impossible to project the cases they need. You have no way of knowing the value of your cases in advance. You also have no idea when your cases will settle. You could work on a case for years before you finally get paid.
Parts of a Business Plan for Law Firm Formation: Structure
A law firm business plan is a written document that lays out your law firm goals and strategies.
For many businesses, a business plan helps secure investors. But the ethical rules prohibit law firms from seeking funding from outside investors or non-lawyer shareholders .

Your business plan is for you and your law partners. It will help you manage everyone's expectations and roles in the firm. Here is a law firm business plan example to help you see the parts and pieces in action.
— Executive Summary
An executive summary combines the important information in the business plan into a single-page overview. Your plan will include details like projections, budgets, and staffing needs. This section highlights the conclusions from those detailed analyses.
Your executive summary should include :
- A mission statement explaining the purpose of your firm in one or two sentences
- A list of the core values that your firm will use whenever it makes decisions about its future
- The firm's overarching goals for itself, its lawyers, and the clients it serves
- The unique selling proposition that sets your firm apart from other firms in the legal industry
You should think of this section as a quick way for people like lenders, potential law partners, and merger targets, to quickly understand the principles that drive your firm.
— Law Firm Description and Legal Structure
First, you will describe what your law firm does. You will describe your law practice and the clients you expect to serve.
Second, you will describe how your firm operates. The organization and management overview will explain your legal structure and the management responsibilities of you and your law partners.
This section should fill in the details about your firm's operation and structure by:
- Describing the scope of the legal services you offer and your ideal clients
- Restating your mission statement and core values and expanding upon how they will guide your firm
- Explaining your location and where your clients will come from
- Describing your business entity type and management structure
- Detailing your unique selling proposition , including the features that distinguish your firm from your competitors
When someone reads this section, they should have a clear picture of what you will create.
— Financial Calculations
Your attorney business plan explains where your firm's revenue comes from and where it goes. This is where your skills as a lawyer begin to diverge from your skills as a business owner. You may need to learn a few new accounting concepts so you can perform the analyses expected in a financial plan.
You will need a financial plan for at least the first year.
If you plan to seek a bank loan or line of credit, your bank may need a financial plan that covers three years or longer.
You will need more than a few rough numbers for a useful business plan. Instead, you will need to estimate your expenses and revenues as accurately as possible.
"Take some financial statements courses, take some managerial accounting courses that teach you how to track costs, how to frame costs in a way that you're looking at the important costs." — Omar Ochoa
You might need to contact vendors and service providers to get precise costs. You will probably need to track your billings with your prior firm to predict your revenues. If you are opening a law firm after law school or an in-house job, you may need a competitive analysis to show what similar law firms earn in your location and practice area.
Some reports you may need in your business plan include:
- Revenue analysis listing the fees you will collect each month
- Budget describing your monthly and annual expenses
- Financial projections combining the revenue analysis and budgeted expenses to predict your profit margins
- Cash flow statement showing how your revenues and expenses affect your cash on hand.
Your cash flow statement might be the most important financial report because it explains how your bank balance will fluctuate over time. If your clients take too long to pay their bills or you have too many accounts payable due at the same time, your cash flow statement will show you when money might get tight.
— Market Analysis
A market analysis will tell you where you fit into the legal market in your location and field. You need a competitive analysis to understand the other lawyers and law firms that will compete with you for potential clients. You can also analyze their marketing messages to figure out how to stand out from the competition.
A competitive analysis will tell you what services other firms offer, how much they charge, and what features help your competitors succeed.
Your analysis should include a discussion about your :
- Ideal clients and what you can do to help them
- Market size and whether you offer something clients need
- Competitors and what they offer to clients
- Competitive advantages and how you can market them to potential clients
You can also develop and hone your marketing strategy based on the benefits you offer to clients over your competitors. Finally, a market analysis can tell you the locations and practice areas in which your firm may expand in the future.
Your market analysis helps you focus your efforts on your legal niche.
— Marketing Plan
A marketing plan sets out the steps you will take to reach your target market. Your marketing strategy will take your market analysis and turn it into a plan of action.
You will start with the results of your market analysis identifying your clients, your competitors, and your competitive advantages. You will then discuss the message you can deliver to potential clients that captures the advantages you have over your competition.

Some advantages you might have over other lawyers and law firms might include tangible benefits like lower billing rates or local office locations. Other advantages might provide some intangible benefits like more years of experience or state-bar-certified specialists in those states that allow specialization.
You will then discuss your marketing plan. A marketing plan explains :
- Characteristics of the target market you want to reach
- What your competition offers
- The distinct benefits you offer
- A message you can use to explain what separates you from your competition
- Your action plan for delivering your message
- Your goals for your action plan, such as the number of client leads, new clients, or new cases per month
Your action plan will include the marketing channels you want to use to spread your message. Marketing specialists can help you identify the best channels for your marketing message and client base.
For example, if you practice intellectual property law, you need to reach business owners and in-house lawyers who want to protect their companies' brands, inventions, artistic works, and trade secrets. A marketing agency may help you create a marketing strategy geared toward trade publications and business magazines.
However, IP lawyers require an entirely different marketing strategy than firms that practice family law. Family lawyers need to market to individuals and will tailor their marketing efforts toward different marketing channels and messages.
Even if you expect most of your client leads to come from referrals, you still need brand recognition for those leads to find you. You should consider a website, basic SEO, legal directory, and bar association listings.
— Your Law Firm Services
You will outline the services your law firm offers to clients. Lawyers with established clients and an existing legal practice can simply describe what they already do.
Any new law firm or lawyer transitioning from other practice areas should consider:
- Practice areas you know and enjoy
- Overlapping practice fields that will not require extra staff, such as personal injury and workers' comp
- Related legal services your clients may need, such as wills and guardianship
By offering needed services you can competently provide, you can gain clients and avoid referring existing clients out to other lawyers.
— Your Law Firm Budget
You should approach your budget as a living document. You will spend more money as you add more lawyers and staff members to your firm. But you can also look for ways to reduce your operating costs through investments in technology services and other cost-saving measures .
Your budget should set out the amount you expect to initially spend on start-up expenses. As you create your start-up budget, remember many of these expenses are not recurring. Furniture, computers, and office space build-outs can last several years. In short, your budget should answer the question, "What do you need to open a law firm?"
It should also lay out the amount you plan to spend each month to operate your firm. Here, you will include your recurring expenses, such as rent, staff salaries, insurance premiums, and equipment leases.

Home Committees, Members & Career Services Small Law Firm Center Overview Small Firm Resources Writing a Business Plan for Law Firm – Law Firm Business Plan Sample
Writing a Business Plan for Law Firm – Law Firm Business Plan Sample
Business plans for lawyers.
New York City Bar Association Small Law Firm Committee
Writing a Business Plans for Lawyers – The Non-Financial Side
1 Why write a law firm business plan?
First and foremost, it’s a Management Tool, It f orces you to think through important issues you may not otherwise consider The recipe to grow your law practice
- A roadmap, albeit a changing one, with milestones to help reach goals you already know and have yet to define
- A sales tool to obtain financing
- A sales tool when looking to form a partnership or join one
- Some parts of a business plan include stating the obvious, but should not be overlooked because they still form a part of the whole
- As you write it, ideas come, strategies unfold, beliefs you may have had change
- It also changes your mindset. You’re no longer thinking about starting a business, you’re now in the process of starting a business.
- If you write a business plan and put it away in a drawer you have not written one that is feasible or is going to do you any good. Continual updating – whether semi-annual, annual, biennial, whichever is best for you – is your own set of checks and balances.
If you are going to buy a book, look for one that offers general advice and suggestions applicable to all businesses. And, if you choose a software package, eliminate the “techy” things like their numbering system; that is a dead giveaway that you’re using a software program. Also, eliminate sections that are irrelevant!
Suggestion: Don’t just buy one from an online bookstore. Take the time go through a table of contents and thumb through.
Examples available from Barnes & Noble:
- Alpha Teach Yourself – Business Plans in 24 Hours by Michael Miller
- Successful Business Planning in 30 Days TM, 3/ed, Peter Patsula
- The Executive Summary
- Analysis of Your Market
- Description of Your Firm
- Competitors
- Your Marketing Strategy
No set formula for a successful practice
Before developing a plan for a lawyer, answer the following:
- Identify your practice niche(s)
- What skills and experience you bring to your practice
- What legal structure to use: sole proprietorship, PC, partnership, LLP, etc.
- What clients you currently have and might potentially acquire
- What clients you want
- What business and social contacts you have
- What other attorneys you can call upon to fill in practice gaps
- How your firm’s records will be kept
- What equipment and supplies will be needed
- What library and other information sources will be needed
- What insurance will be needed
- What other resources will be needed
- How you will compensate yourself
- Review your current finances re assets, current cash flow, expenses
- What financing may be needed
- What financial assets do you have
- What banking accounts will be needed
- Review your current non non-financial resources
- Identify your market
- Describe your startup plans
- Where will your office be located
- What will the name of your firm be
2 The Executive Summary
For some businesses this is the most important part of the business plan because it summarizes what the company does, where it is going and how to get there. Therefore, it must describe the company, the “product” and the market opportunities concisely.
It is written after the plan is complete but is the first and, sometimes, most important part read by investors.
How important this is for a legal business plan depends on your long and short term goals, e.g., whether they are to grow a partnership, join a firm, build up a practice that is enticing for acquisition by a larger firm, etc.
In order to provide that summary, go through a number of exercises:
- Mission statement – the firm’s purpose and what it will do
- Major goals
- Objectives/milestones needed to achieve those goals
- Vision statement – where you want to go and what you want your firm to become, not just 20 years down the road but where you want to be three or five years from now
- List what is out of your control e.g., nature of the law business, direction of the marketplace, competition, mergers and acquisitions among clients, and competitors, attorneys and firms already in place
- Analyze opportunities to face and threats
- List your firm’s specific capabilities and whatever you believe you can offer that is unique
- If you are not a solo practitioner, who is the management
- What is the legal organization
- What technology will you be capitalizing on
- What is the marketing potential
- Describe your basic strategies based on the information you have learned about the legal business, your competition and applicable markets within your field.
- Provide the basis for why you believe your strategy is the right one for your firm.
- What markers will you use to change direction
- Outline what your firm needs to make that strategy succeed
- Financial projections
- Back up of those projections with assumptions (so that they can be adjusted as necessary)
- Summary of revenues by month for at least three years
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow statement
- What actions you’re going to take to carry out the plan
- What changes will be needed or skills acquired to put the plan to work
3 Analysis of Your Market: The Legal “Business” that Affects You
Purpose: an accurate understanding of trends affecting law practice in general and your specializations, client demographics, client universe.
Keep track of impact factors, obstacles, opportunities and threats to better forecast and build the strategies.
- Identify who and what firms dominate and where they are
- What new technologies have already and may yet change the way your practice is done
- What laws and regulations have and may yet change your practice
- Describe the overall demand for your specialties
- What else besides price affects your client decisions to use your services
- What clients (people or companies) can influence your areas of practice
- Large firms, mid size, boutiques, solo practitioners
- In-house attorneys
- Government attorneys
- Divide into primary, secondary and, if necessary, tertiary levels
- Is there substitution, e.g., do it yourself or outsourcing to India
- List what is available and how it affects your practice
- Describe how technology is affecting your kind of practice
- Describe who controls the technologies that affect
- Describe how you keep up with new technology
- List all the things that will make it difficult for you to practice in your expertise and locale
- List the things that will make your exit from you area of expertise or your transition to a different one difficult
- What can relationships with suppliers do for you
- Could a supplier become a competitor, e.g.; for articles you write
- Colleagues and competitors
- Professional associations
- Community associations
- Social and business organizations
- Current and former clients
- Former employment colleagues
- Pro bono colleagues
- What ways improve your position with clients
- Does pricing affect
- What else affects your relationship
- What kind of follow up do you do after meeting someone who may be a potential client or who can introduce you
- Writing articles
- Giving speeches
- How can you use your other relationships
- What are the overall costs that affect your hourly, daily or matter rates?
- Profit margins
- What do suppliers of your technology, research, information, etc. offer by way of pricing, discounts
- Are there long term agreements that can be to your advantage/disadvantage
- Elasticity of demand for the rates you charge
- If on a regular retainer, are you realizing 100% of your hourly rate, or more/less
- Identify where the biggest costs of your practice come from
- Identify fixed and variable costs
- How to gain economies of scale
- Identify where you can lower costs
- Is the profit margin you’re working with the right one for your practice
- Describe the size of your primary market
- List the niche markets that can use your expertise
- Is your kind of practice a growing or shrinking market
- Identify new growth opportunities in your areas of expertise
- Economic slowdowns
- Changing statutes, regulations and decisions
- Social pressures
- By product, industry, size, geography
- Membership lists of trade organizations
- List of conference attendees
- By referral of current clients
- By referral of colleagues, bar association, etc.
- By referral from competitors with conflicts
- What untapped market is there
- What underserved market is there
- Trade associations made of small companies in the same field
- Part time general counsel for small companies
- Trade associations you can join and committees you can volunteer for
4 Describing and Analyzing Your Own Firm
- It’s not just a law firm.
- What’s the general history
- When was it formed and why
- What is your mission
- What are your goals
- What direct experience do you have? Your partners?
- How relevant is your experience to the current world?
- How often do you talk to prospective clients
- What do you current clients feel about you
- What is the maximum amount of business you can handle yourself without farming it out
- To whom can you farm
- Who is your backup when you are too busy, traveling on business, on vacation, sick
- What is unique about you or your practice
- Describe the areas you focus on and want to focus on
- What are the ancillary areas of law that often or usually involved or triggered by your focus area
- What need does your expertise serve
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of your areas of expertise
- Identify your own strengths and weaknesses
- Who are your clients
- Who among your clients makes the decisions to use your services
- What stage of business development are your clients in
- How sophisticated/knowledgeable are your clients
- Are your clients street smart and/or business savvy
- Do they use more than one lawyer at a time
- Long term objectives
- Short term objectives
- What problems do you face
- What problems do your clients face
- What do you consider milestones
- What are the legal (statutory, regulatory & case law) trends that will affect it
- What are the technological trends that will affect it
- What are the economic trends that will affect it
- What potential risks and opportunities to be faced?
- Do you use innovative technology
- Do you offer superior client care/service
- Is your hourly, daily, or matter pricing lower than the “norm”
- Is there a small group of firms or attorneys who offer the same expertise or specialization
- Are you well known for a book, a speech, an article, news coverage, etc.
- Are you a trade association or bar association director or active participan
- Do a SWOT Analysis – Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats
Strengths & Weaknesses are vis à vis your competitors, rather than your own history Focus on current competition and potential competition
- Are there advantages to your expertise areas
- What do you enjoy doing
- What resources to you have access to
- What do others see as your strengths
- What can you improve
- What don’t you do well
- What should you avoid
- Do others perceive a weakness you don’t agree with
- Are your competitors doing better than you
- How can you meet a potential client
- What are the good opportunities – are they new areas, new statutes & regulations, etc.
- How can changes in technology help you
- How can changes (or no changes) in government policy affect your area of expertise
- Are there changes in social patterns or lifestyle that can help
- What opportunities can open if a weakness is eliminated
- Family/emotional/physical challenges
- Technological challenges
- What is your competition doing you are not
- How can technological changes threaten you
5 Competitive Analysis and Target Market
- List law firm/solo practice trends
- List direct competition
- List indirect competition
- Describe the extent of the unserved market for your kind of legal services
- Who is your client/customer
- What is your price
- Profile your primary customer
- Traits: geographics, demographics, psychograhics
- List client needs
- Describe how your fill those needs
- List primary, secondary and tertiary competitors
- What services do they offer in addition to yours
- What do they charge
- How do competitor firms sell their services
- What are the competitor strengths
- What are the competitor weaknesses
- What size competes with you
- What other specialties do they offer
- Who are they representing
- What is their pricing
- What are their operational strengths and weaknesses
- Are they adequately financed
- How do your competitors advertise or promote themselves
- What are their conflicts
- How does your competition market itself
- Competitive Identification
- Direct competitor – offers the same benefit
- Indirect competitor – services the client can get instead of yours
- Visit and read competitor websites and their advertising, including separate websites by individual partners
- Subscribe to competitor law firm online or other newsletters
- Does it use innovative technology
- Does it offer superior client care/service
- Is its hourly, daily, or matter pricing lower than the “norm”
- Are they well known for a book, a speech, an article, news coverage, etc.
- Are they trade association or bar association directors or active participants
Generate similar info for potential clients to help identify the target that will be most interested in you
A marketing plan must have a detailed description of the target market for your services, an analysis of the trends and conditions of that marketplace and how the trends affect that marketplace
- Total size of targeted market
- Historical current and projected growth rates
- What social, economic &political changes could affect it and your services
- Describe recent developments in the law that affect your areas of expertise
- Are there identifiable niches
- What or will be your clients’ needs and wants
- How will potential customers find out about you
- What kind of marketing, if any, are your clients and potential clients receptive to
- What do existing clients like best about your services
- Are your target clients consumers, businesses or both
- Demographics, psychographics, legal service purchasing habits
- When and how does the client decide to use a lawyer & find a lawyer
- Does your potential client use the Internet, bar association, trade association, business referral, family referral, friend referral, etc. to find a lawyer
- What is your client’s level of education and occupation
- Are they Fortune 1000,500, 100, mid size or smaller
- Is your client industry specialized and do you know that industry
- Does the client use more than one lawyer or law firm
- How long does the client take to decide to use a lawyer
- Does more than one person at the client make the decisions to use a lawyer, and if so who are they
- Is the person who decides who is going to provide legal services the one who is going to receive those services
- What influences your client’s decision to retain a lawyer
- Is using a lawyer optional, a necessity or a luxury
- Is a lawyer needed all year round, seasonal or ad hoc
- How and how well do your clients market themselves
6 Marketing & Strategy
Once you analyze your client needs you can build a comprehensive marketing strategy,
- What is it you intend to accomplish
- What is the amount of increase in clients and/or billing that you want to achieve
- Make each goal measurable and explain each one specifically
- Set each goal to a planned schedule
- Be able and prepared to assess all components to revise when necessary
- Compare these goals to what you believe your competitors’ goals to be
- Tactical objectives = measurable tasks
- Create client value
- Name recognition among your clients and potential clients
- Client retention
- Attracting partners or merging into a bigger firm
- Create a timeline for the objectives or events
- Determine the time frame for the plan, e.g., every six months, every year, etc.
- Describe the need for your services from the client’s POV
- Define the impact on the client of your services
- Ask whether your clients currently obtain this service more cost-effectively than you can provide it
- Describe what would compel clients to change from the lawyers they are using to you or to add you to their lawyer rosters
- E.g., how you will use that list of relationships
- Marketing Mix – Networking, Advertising, Promotion, PR
- Inserts in papers
- Bus, taxi, etc. ads
- Space in professional and trade publications
- Street banners
- New resident welcome kits
- Trade and trade association show directories and handouts
- Trade and trade association show sponsorships
- Coupon mailers
- Press releases
- Sponsorship
- CRM (customer relationship marketing)
- Cost based = cost plus profit margin
- Cost plus profit = cost plus fixed percentage markup
- Market based = use the market norm and add or subtract
- Ask what the highest price your target market can bear
- Determine the price elasticity for your kind of legal services
- Should you offer an introductory rate
- Age of business
- Premises/location
- Competition
- Cost to acquire a client

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

Law Firm Business Plan Template [Updated 2024]
Law Firm Business Plan Template
If you want to start a Law Firm or expand your current Law Firm, you need a business plan.
The following Law Firm business plan template gives you the key elements to include in a winning Law Firm business plan.
You can download our Business Plan Template (including a full, customizable financial model) to your computer here.
Law Firm Business Plan Example
I. executive summary, business overview.
[Company Name] is a law firm in [insert location here]. The Company primarily focuses on litigation law, but also provides a wide range of legal services as requested by clients. [Company Name]’s legal services range from mergers and acquisitions to product liability, to intellectual property to real estate. Our team of lawyers works with each client to ensure successful outcomes. The Company’s goal is to become one of the leading law firms in the area.
[Company Name] will provide the following legal services to its clients:
- Arbitration & Mediation
- Business Formation
- Business and Commercial Transactions
- Collections and Credit Matters
- Commercial Real Estate Law
- Construction Law
- Corporate Governance and Compliance
- Creditor’s Rights
- Employment Law
- General Counsel Services
- Immigration Law
- Insurance Law
- Real Estate Consultancy and Advisory Services
Customer Focus
[Company Name] will primarily serve service sector businesses and individual clients within a 20-mile radius of its location. Potential customers in this area include:
- 1,500 private businesses with annual payroll exceeding $1 million
- 120,000 individuals
Management Team
[Company Name] is led by [Founder’s name], who has been in the legal industry for [x] years. [Founder’s name] graduated from the University of ABC, where he majored in law. During his apprenticeship in the legal industry, he acquired in-depth skills in practicing law and is well aware of the practices related to the legal industry. Additionally, he worked in a law firm alongside a professional, learning how to manage and run a law firm before starting [Company name].
Success Factors
[Company Name] is qualified to succeed due to the following reasons:
- There is currently a high demand for legal services within the community. In addition, the company surveyed the local population and received highly positive feedback pointing towards an explicit demand for the services, supporting the business after launch.
- The Company’s location is in a high-volume traffic area and will thus be highly convenient for a significant number of people visiting nearby.
- The management team has a track record of success in the legal business.
- The upscale legal business is a proven business and has succeeded in communities throughout the United States.
- Market trends such as high disposable income and spending power are propelling the demand for legal services.
Financial Highlights
[Company Name] is currently seeking $170,000 to launch its law firm. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Office design/build: $60,000
- Working capital: $110,000 to pay for marketing, salaries, and lease costs until [Company Name] reaches break-even
II. Company Overview
Who is [company name].
[Company Name], located in [insert location here], is a new, upscale law firm that provides a wide range of legal services to both individual and business clients. The Company has built an impressive reputation for providing superior legal advocacy and delivering consistently exceptional results to the area’s companies, businesses, and professionals. As a solution-oriented law firm, the Company makes it their primary objective to support, guide, and protect their clients.
[Company Name]’s History
[Founder’s Name] is an entrepreneur who has worked extensively with law firms & lawyers to enhance his business development skills on a personal and commercial level. He has restructured the firm to keep pace with the legal developments in the regional and international community by creating ethical, legal practices with a highly qualified legal team focusing on providing comprehensive, professional, and creative legal solutions to fully meet the confidence and expectations of the clients locally and internationally.
Upon surveying the local customer base and finding the potential retail location, [Founder’s Name] incorporated [Company Name] as an S-Corporation on [date of incorporation].
[Founder’s Name] has selected an initial location and is currently undergoing due diligence on each property and the local market to assess the most desirable location for the Law Firm.
Since incorporation, the company has achieved the following milestones:
- Found office space and signed Letter of Intent to lease it
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Created the list of services to be offered
- Determined equipment and inventory requirements
- Began recruiting key employees with experience in the legal industry
[Company Name]’s Products/Services
[Company Name] will provide a variety of legal services ranging from mergers and acquisitions to product liability, from intellectual property to real estate. The Company’s services are listed below:
III. Industry Analysis
The market size of the law firm industry in the U.S. is expected to increase 5.3% to reach $330 billion. The law firm industry in the US is the 2nd ranked professional services industry by market size in the US.
Growth in the historic period resulted from strong economic growth in emerging markets, increased mergers and acquisitions (M&A), a rise in consumer spending/increase in disposable income, and deregulation of the legal industry. Moreover, increasing demand for transactional practice areas, the growing legal tech industry, and globalization will drive the growth.
The increasing number of transactional practices in the upcoming period is expected to drive the legal services market. Transactional practice includes research, preparations, and review of documents for individuals and companies for corporate, tax, and real estate work and mergers and acquisitions.
IV. Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
[Company Name] will provide its services to businesses within a 20-mile radius of its location.
Customer Segmentation
The Company will primarily target the following customer segments:
- Individuals: [Company name] will target individuals who require assistance in terms of legal processes.
- Businesses: The Company will provide its services to businesses within a variety of sectors that require legal consulting services in [Location].
V. Competitive Analysis
Direct & indirect competitors.
Gold Law Partners In business for 15 years, Gold Law Partners is a leading full service/multi-disciplinary law firm offering transactional, regulatory, advisory, dispute resolution services. With its principal offices in Washington and New York, the firm advises a diverse clientele, including domestic and international companies, banks and financial institutions, funds, promoter groups, and public sector undertakings.
The Company was set up with a desire to bring client service into sharper focus, to provide commercially viable legal advice and committed legal representation to the clients across all sectors. The firm has successfully been able to establish its identity outside its origins, dealing with significant depth in complex domestic and international matters.
Premiere Legal Premiere Legal is an international full-service legal practice that serves the needs of many of the largest multinational corporations. The company aims to combine the highest international standards with local expertise so it can provide seamless assistance to the top corporations in their most important and challenging assignments. Through the network, the company offers a full range of commercial legal services, combined with an in-depth knowledge of local practices, in a total of 18 countries in four continents, including some of the most challenging and fast-growing emerging markets.
R&R Legal R&R Legal is a growing consortium of local law firms, providing a consistent standard of outstanding legal expertise and a considerate, personal service to clients throughout the US. Whenever required, the company will suggest input obtained from specialist barristers and other suitably qualified third-party advisors. The company has good relationships with many accountants, barristers, estate agents, bankers, surveyors, and other professionals, both locally and further afield. This adds depth to the service the company would provide when support and collaboration are needed.
Competitive Advantage
[Company Name] enjoys several advantages over its competitors. These advantages include:
- Management: The Company’s management team has xx years of business, legal consulting, and marketing experience that allows them to market and serve customers in an improved and sophisticated manner than the competitors.
- Relationships: Having lived in the community for xx years, [Founder’s Name] knows all of the local leaders, newspapers, and other influencers. As such, it will be relatively easy for [Company Name] to build brand awareness and an initial customer base.
- Great service at an affordable price: The wide range of legal consulting services offered by [Company Name] nearly equals the most prestigious positioned competitor, [Competitor Name]. However, [Company Name] will offer its services at a much more affordable price.
- Personal Service: The Company will tailor its service to the client’s requirements. Individuals can choose the way they wish to communicate with us either by email, phone, or fax, and the company will work closely with you to achieve the best result for individuals or the business.
VI. Marketing Plan
The [company name] brand.
[Company name] seeks to position itself as a renowned, upper-middle-market competitor in the law firm industry. Customers can expect to receive effective and efficient legal consulting services.
The [Company Name] brand will focus on the company’s unique value proposition:
- Expert Management Team
- Industry Relationships
- Great Services at an affordable price
- Providing excellent customer service
Promotions Strategy
[Company Name] expects its target market to be residents and service sector businesses within a 50-mile radius of the [location]. The Company’s promotions strategy to reach the audience includes:
Website The Company will create a professional website for domestic and international business prospects, which will provide easy access to essential information about the company offerings, contact details, and other information. The website will be updated and optimized to enhance the company’s online presence.
Advertisement Advertisements in print publications like newspapers, magazines, etc., are an excellent way for businesses to connect with their audience. The Company will advertise its offerings in popular magazines and news dailies. Obtaining relevant placements in industry magazines and journals will also help in increasing brand visibility.
Public Relations [Company Name] will hire an experienced PR agency/professional(s) to formulate a compelling PR campaign to boost its brand visibility among the target audience. It will look to garner stories about the company and its offerings in various media outlets like newspapers, podcasts, television stations, radio shows, etc.
Social Media Marketing Social media is one of the most cost-effective and practical marketing methods for improving brand visibility. The Company will use social media to develop engaging content in terms of different jewelry designs and post customer reviews that will increase audience awareness and loyalty. Engaging with prospective clients and business partners on social media platforms like Twitter and LinkedIn will also help understand changing customer needs.
Word of Mouth Marketing [Company name] will encourage word-of-mouth marketing from loyal and satisfied clients. The Company will use recommendations and word-of-mouth marketing to grow the customer base through the network of its existing customers. The Company will be incentivizing its existing customer base to encourage their friends to come and try their service for the first time.
Pricing Strategy
[Company Name]’s pricing will be moderate, so customers feel they receive great value when availing of the services they are paying for. The customer can expect to receive effective and efficient legal services at a far more affordable price than what they pay at an already well-established law firm.
VII. Operations Plan
Functional roles.
To execute on [Company Name]’s business model, the company needs to perform several functions, including the following:
Administrative and Service Functions
- Legal Aides
- General & administrative functions including legal, marketing, bookkeeping, etc.
- Executive Assistant
- Human Resources
VIII. Management Team
Management team members.
[Company Name] is led by [Founder’s Name], who has been in the legal consulting industry for xx years. While [Founder] has never operated a legal firm himself, he has worked extensively with domestic and international clients for different projects. [Founder’s name] graduated from the University of ABC, where he majored in law. During his apprenticeship in the legal industry, he acquired in-depth skills in practicing law and is well aware of the practices related to the legal industry.
Additionally, he worked in a law firm alongside a professional, learning how to manage and run a law firm before starting [Company name].
Hiring Plan
[Founder] will serve as the CEO. To launch the law firm, the company will need to hire the following personnel:
- Lawyers [Number]
- Legal Consultants [Number]
- Marketing & Sales Executive [Number]
IX. Financial Plan
Revenue and cost drivers.
[Company Name]’s revenues will come from the legal services offered to its customers. The major costs for the company will be salaries of the staff, rewarding them for performance and making specialists will be an active part in business retention and development. In the initial years, the company’s marketing spend will be high, as it establishes itself in the market. Moreover, rent for the prime location is also one of the notable cost drivers for the [Company Name].
Capital Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
5 Year Annual Income Statement
Comments are closed.

- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
California fast-food workers will get $20 minimum wage, starting Monday

Vanessa Romo

Alina Selyukh

A McDonald's worker hands food to a customer at a drive-thru window in Los Angeles, on Sept. 28. Damian Dovarganes/AP hide caption
A McDonald's worker hands food to a customer at a drive-thru window in Los Angeles, on Sept. 28.
California fast-food workers cooking Big Macs or whipping Frappuccinos will start making a minimum wage of $20 an hour on Monday. For many, this means a 25% raise.
The new state minimum uniquely focuses on a particular segment, fast food, affecting some of the country's biggest chains, including McDonald's, Starbucks, Subway and Pizza Hut.
It's a big win for cooks, cashiers and other fast-food workers – some of the lowest-paid jobs in the U.S. – whose wages have been growing at a faster clip since the pandemic, after decades of stagnation.
California is one of the country's most expensive states; about half a million people are estimated to work in fast food here, mostly women, immigrants and people of color. Many live below the poverty line.

Uber and Lyft threaten to halt operations in Minneapolis over minimum wage law
Sandra Jauregui from Sacramento is counting down the days to her first bigger paycheck in two weeks. After 18 years working at several Jack in the Box franchises, her pay will jump from $17.50 to $20. That means she could be bringing home another $120 each paycheck.
"It's super great," says Jauregui, 52, speaking in Spanish. "At the very least it'll give me some breathing room ... and make it easier to pay the rent and other bills."
Chipotle, McDonald's warn of price hikes, less work
But the dramatic pay raise has also touched off a heated debate about the impact on local businesses. Smaller franchise restaurant owners warn they'll have to raise prices, reduce worker's hours, cut jobs or even close shop.
California's pay hike is a result of a contentious deal struck by labor leaders, including the large Service Employees International Union, and fast-food companies last year. The new wage law applies to fast-food chains with at least 60 locations nationwide, with exemptions for some bakeries and smaller fast-food outposts inside grocery stores, airports and other venues.
Several fast-food executives have suggested prices would go up 2.5% to 3.5% to offset higher wages; Jack in the Box, Starbucks, McDonald's and Chipotle have all warned of upcoming price hikes. That's on top of price increases many restaurants have been rolling out for months. The cost of eating out has stubbornly inched higher even as inflation has cooled elsewhere .
Other chains plan to speed up their use of automation, including kiosks and robots. A major Pizza Hut franchisee cited the wage hike as the reason for layoffs of more than 1,000 delivery drivers this year, in a switch to apps like Uber Eats and DoorDash that pushes more delivery fees onto shoppers.

One big Pizza Hut franchisee in California cited the upcoming wage hike as a reason for laying off more than 1,000 delivery drivers in a shift to delivery apps like Uber Eats and DoorDash. Justin Sullivan/Getty Images hide caption
One big Pizza Hut franchisee in California cited the upcoming wage hike as a reason for laying off more than 1,000 delivery drivers in a shift to delivery apps like Uber Eats and DoorDash.
Franchisees weigh cuts to workers' hours
Many restaurant owners expect workers to be working fewer hours. That was the main side-effect a decade ago, when Seattle hiked its minimum wage to $15, research suggests .
"I am used to being a champion of labor and I'm in this odd position," says Michaela Mendelsohn, a longtime advocate for LGBT workers and also owner of six El Pollo Loco restaurants with about 170 employees.
Her restaurants lost shoppers after a pre-emptive price increase in February, she says. Now, the focus is on cutting costs by simplifying operations, changing how long it takes workers to make sauces, for example, or to close up for the night.

Minimum-wage workers in 22 states will be getting raises on Jan. 1
"We're having to get more efficient," Mendelsohn says. "So really what's left is ... to reduce labor hours. And I hate saying that."
In recent years, the battle for higher minimum wages has increasingly played out at the city, county and state levels as the federal minimum wallows at $7.25 an hour .
Broadly, California often sets the bar for many business decisions that other states later follow. Advocates hope something similar will happen with fast-food pay – spreading to other industries in the state and across the country.
California's minimum previously rose to $16 an hour on Jan. 1.
Workers are thrilled, but also anxious
Employers' warnings have left many workers with mixed feelings about the raise, despite the potential for extra spending power.
The Jack in the Box worker Jauregui, 52, has been cobbling together two salaries, working about 54 hours a week between the restaurant and a laundromat.
She says she's always trying to save a bit to treat her grandchildren – she has custody of three of them – who are constantly growing out of clothes and shoes. And although she marched alongside fellow SEIU members to win the wage increase, she is fearful of the downside.

These millionaires want to tax the rich, and they're lobbying working-class voters
"My boss told me that he won't reduce my hours but that he will cut others' hours," Jauregui said.
All this makes California's wage hike a high-profile case study for how exactly a higher minimum wage reverberates through the local economy.
"This policy is going to be really different in different parts of California," says Jacob Vigdor, professor of public policy and governance at the University of Washington, who has studied the effects of Seattle's 2014 minimum wage hike.
The research found that after the minimum wage rose from $9.47 to $13 – in the early years of the Fight For $15 labor campaign – workers generally didn't lose jobs even though they did lose hours. And they ended up with higher pay.
"The restaurant business is a really tough business," Vigdor says. "Restaurants open and close all the time, even in places where the minimum wage hasn't changed for more than a decade. ... Generally speaking, we found that in the restaurant industry, businesses were able to find ways to adapt to higher wage costs."
KQED's Farida Jhabvala Romero contributed to this report.
- fast food workers
- minimum wage
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
DealBook Newsletter
Regulators Force Another Microsoft Split
The tech giant is unbundling Teams from its Office software suite, as it faces mounting scrutiny on both sides of the Atlantic.
By Andrew Ross Sorkin , Ravi Mattu , Bernhard Warner , Sarah Kessler , Michael J. de la Merced , Lauren Hirsch and Ephrat Livni

Microsoft unbundles, again
Microsoft is separating Teams , its popular video and chat app, from its Office software suite in markets around the world, broadening a split that began in the European Union last fall.
It appears to be the latest effort by the software giant to head off investigations by global antitrust enforcers as regulators examine the power of Big Tech.
Rivals have complained about the Teams-Office bundle for years. Microsoft first added the video and document collaboration program to its business software suite in 2017, and saw Teams’s popularity soar after the coronavirus pandemic unleashed a boom in hybrid and remote working.
At the height of the lockdown in 2020, Slack filed a complaint with the European Commission accusing Microsoft of anticompetitive behavior by bundling Teams with Office. (Three months later, Slack agreed to sell itself to Salesforce for $27.7 billion.) And last summer, Eric Yuan, the C.E.O. of Zoom, called on the F.T.C. to follow the E.U. in investigating the Teams-Office tie-up.
It’s unclear if Microsoft’s decision will help it avoid an E.U. fine, which could cost the company up to 10 percent of global revenue. The company told Reuters that the move “addresses feedback from the European Commission by providing multinational companies more flexibility when they want to standardize their purchasing across geographies.”
It comes as tech behemoths are facing investigations by regulators worldwide. Last month, the Justice Department sued Apple over its tight control of the iOS operating system, while Google is awaiting a judge’s verdict in a U.S. lawsuit over its search monopoly.
And Microsoft has drawn scrutiny over its investments in A.I. start-ups like OpenAI and the French company Mistral.
The move is reminiscent of Microsoft’s unbundling of Windows in the 2000s, after a bruising antitrust battle with the Justice Department over the tech company’s efforts to shut rivals out of its platform.
But it’s unclear how consequential this breakup will be. Shares in Microsoft rose on Monday despite the news, as analysts questioned whether the move would mean much for the tech giant’s bottom line. Data from the research firm Sensor Tower showed that use of Teams stayed relatively stable even after the program was cleaved out of Office in the E.U.
That suggests rivals may not experience a surge in new customers. (Shares in Zoom fell nearly 1 percent on Monday.) “Teams is so embedded into workflows that I don’t think this has that same impact,” Rishi Jaluria, an analyst at RBC Capital Markets, told Reuters.
HERE’S WHAT’S HAPPENING
Donald Trump posts a $175 million bond to avert seizure of his assets. In securing the bond for his civil fraud case, the former president avoided paying a $454 million penalty while he appeals the judgment. Separately, shares in Trump Media & Technology Group plunged 21 percent on Monday, after the parent company of the Truth Social online platform disclosed just $4 million in revenue for last year.
Disney is said to be winning its proxy fight against the financier Nelson Peltz. The entertainment giant’s slate of board nominees has secured the backing of big shareholders , including BlackRock and T. Rowe Price, ahead of the company’s annual meeting on Wednesday. More than half of Disney’s voting shares have been accounted for, but a big question is how the company’s unusually high percentage of individual shareholders will vote.
A regulator is reportedly scrutinizing investments by Vanguard, BlackRock and State Street in U.S. banks. The F.D.I.C. is examining whether the big money managers are maintaining a sufficiently passive role in managing their stakes, according to The Wall Street Journal. Such firms are exempt from current rules that require regulatory approval to own more than 10 percent of a bank — if they don’t exert influence on management or boards.
A $4.1 billion bet on sports
One of the biggest players in the booming business of sports just got bigger: The private equity firm Arctos Partners has raised another $4.1 billion to do more deals.
The fund-raising shows investor appetite for sports deals is growing as competition ramps up between private equity firms and Gulf countries like Saudi Arabia and Qatar.
Arctos is one of the busiest sports deal makers. Since its founding in 2019, the firm has invested in Formula One, basketball, baseball and soccer clubs. They include the Utah Jazz and Fenway Sports Group.
Sports deals are booming on the back of the skyrocketing value for media rights . John Malone’s Liberty Media, which owns F1, said on Monday that it had bought MotoGP , the motorcycle racing championship, for €4.2 billion ($4.5 billion).
The deal follows a record year for sports M.& A. , with transaction values up 27 percent to roughly $25 billion in 2023, according to Bloomberg calculations. That included big investments by Arctos in the Qatar-owned French soccer club Paris Saint-Germain and the Aston Martin F1 team.
Sovereign investors are the big new players. Saudi Arabia is pouring billions into soccer and golf, and may be looking at tennis next. And Qatar last year bought a stake in the owner of Washington’s professional basketball and hockey teams.
Arctos sees itself as part of a new wave of long-term deal makers that treat teams like an asset class. As sports leagues have loosened their rules to allow for institutional investors, firms like Blue Owl and Dynasty Equity say they are committed to long-term investments that aren’t tied to economic volatility.
“We’re not a control buyer. And we’re not a leveraged buyout fund,” Ian Charles, an Arctos co-founder, told DealBook.
Arctos played down the rising competition. Charles told DealBook that sports leagues put heavy restrictions on allowing state-backed investment, if they allow them at all. He declined to say whether Arctos had raised money from sovereign wealth funds, though the company said in a statement that its latest fund-raising round included pension funds and “global wealth platforms.”
The latest report card for Bridgewater’s post-Dalio era
Ray Dalio gave up day-to-day management of Bridgewater Associates 18 months ago. Since then, Nir Bar Dea, his successor atop the giant hedge fund, has been under pressure to show that one of the world’s most successful investment firms can maintain its dominance.
Results from the first three months of 2024 suggest that Bridgewater is performing well. But can changes to how the firm is run keep it in the top tier of industry performers?
Its flagship Pure Alpha fund is up 15.9 percent year to date, according to a notice sent to investors on Monday that DealBook has reviewed. That’s up more than sevenfold over the Bloomberg Macro Hedge Fund Index , which tracks funds with a similar strategy.
Pure Alpha is now up 38.4 percent, net of fees, since the creation of Bridgewater’s investment committee in August 2020.
The hard part is maintaining that performance. For much of 2022 and 2023, Pure Alpha has performed well — only to tumble precipitously at the end of each of those years. Bridgewater as a whole lost $2.6 billion last year, one of just two top-tier firms to lose money, according to the research firm LCH Investments.
That continued a string of poor performance in the 2010s that tarnished Bridgewater’s reputation as a profit machine. (It also raised questions about Dalio’s famously idiosyncratic and brutally blunt management style, including baseball cards that featured ratings of each worker based on colleagues’ assessments of them.)
Bar Dea has sought to make Bridgewater more flexible in how it arrives at investment decisions, Bloomberg reports . That includes increasing the number of people who review those moves and pledges to embrace artificial intelligence.
Will that be enough to keep clients happy? Some unidentified investors told Bloomberg that they were considering cutting ties if the firm didn’t pick up its performance.
That said, Bar Dea is reportedly planning to shrink Pure Alpha and return more money to clients — a move that could make the fund more nimble.
“The Western world urgently needs a significant increase in productivity growth as the burden of rising government debt and entitlement spending strains almost every major economy.”
— Ken Griffin . The Citadel founder used his annual letter to investors to warn about his growing worries on debt and share his view that the economy will grow only modestly this year as the Fed tries to bring down inflation to its 2 percent target.
Is A.I. actually boosting productivity?
Investor enthusiasm around artificial intelligence has added trillions in market value to a select few tech companies. But its broader economic impact has been harder to measure.
Economists are divided on the A.I. productivity conundrum. On earnings calls , business leaders have been more eager to share with Wall Street how they plan to use the technology in their operations. But whether these tools will achieve widespread productivity gains for the economy is less clear.
“The enthusiasm about large language models and ChatGPT has gone a bit overboard,” the Northwestern University economist Robert Gordon told The Times . Others are more hopeful, including Erik Brynjolfsson at Stanford University, who has bet Gordon $400 that productivity will take off this decade.
While that wager catches the attention of some in academia, a parade of companies is putting the technology to use:
Walmart has built a generative A.I. chat bot for internal use that answers common H.R. questions including “Do I have dental insurance?”
Abercrombie & Fitch has turned to generative A.I. to brainstorm ideas for clothing designs and to write blurbs for its website and app.
Ben & Jerry’s put cameras that use A.I. into the freezers at grocery stores to alert the company and its distributors when a location was running low on a particular ice cream flavor.
Will such use cases impact workers? David Autor, a labor economist at M.I.T. whose work has focused on how technology can erode earning potential, argues it might not be all bad news. The technology could help people with less expertise to do more valuable work, lifting the middle class . Critics are unconvinced.
In other A.I. news: OpenAI introduced a new tool that mimics human voices with high accuracy, showing how the technology is quickly expanding beyond text, but it could also pose a new misinformation threat.
THE SPEED READ
Sam Altman, the C.E.O. of OpenAI, is no longer listed as the leader of the venture arm of the artificial intelligence start-up . (The Information)
Tiger Global Management, the embattled start-up investor, has reportedly collected $2.2 billion for its latest fund , nearly two-thirds below its goal. (Bloomberg)
Two board members of Warner Bros. Discovery stepped down amid a Justice Department inquiry into whether their presence violated antitrust law. (NYT)
The company that owns the ship that hit the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore last week is invoking a 173-year-old “Titanic Law” to cap its legal liability to $43 million. (The Lever)
“Poor Nations Are Writing a New Handbook for Getting Rich ” (NYT)
Best of the rest
United Airlines is asking its pilots to take unpaid time off next month, citing late plane deliveries from Boeing. (CNBC)
The owner of Sports Illustrated sued an energy drinks mogul whose media company missed nearly $49 million in publishing-rights payments. (NYT)
“ How a Houthi-Bombed Ghost Ship Likely Cut Off Internet for Millions” (Wired)
We’d like your feedback! Please email thoughts and suggestions to [email protected] .
Andrew Ross Sorkin is a columnist and the founder and editor at large of DealBook. He is a co-anchor of CNBC’s "Squawk Box" and the author of “Too Big to Fail.” He is also a co-creator of the Showtime drama series "Billions." More about Andrew Ross Sorkin
Ravi Mattu is the managing editor of DealBook, based in London. He joined The New York Times in 2022 from the Financial Times, where he held a number of senior roles in Hong Kong and London. More about Ravi Mattu
Bernhard Warner is a senior editor for DealBook, a newsletter from The Times, covering business trends, the economy and the markets. More about Bernhard Warner
Sarah Kessler is an editor for the DealBook newsletter and writes features on business and how workplaces are changing. More about Sarah Kessler
Michael de la Merced joined The Times as a reporter in 2006, covering Wall Street and finance. Among his main coverage areas are mergers and acquisitions, bankruptcies and the private equity industry. More about Michael J. de la Merced
Lauren Hirsch joined The Times from CNBC in 2020, covering deals and the biggest stories on Wall Street. More about Lauren Hirsch
Ephrat Livni reports from Washington on the intersection of business and policy for DealBook. Previously, she was a senior reporter at Quartz, covering law and politics, and has practiced law in the public and private sectors. More about Ephrat Livni

COMMENTS
How to write a law firm business plan. Once you've got the starting points of your business plan worked out, it's time to put pen to paper. While your law firm business plan should be tailored to your unique situation, the following list will walk you step-by-step through all key sections you need to have a comprehensive business plan: 1.
Download your free law firm sample business plan. Download our law firm sample business plan for free right now and use it for reference as you write your own plan. You can even copy and paste sections from the sample plan and customize them for your business. Just make sure you're taking the time to do your own research.
The lawyer or lawyers who will make up the firm at the time of launch. The location of the firm and the areas it serves. The general approach the firm takes when representing clients. 3. Market Analysis. A competitive analysis is one of the most compelling components of well-written business plans.
Personal business planning is not about writing a 50-page manifesto outlining every detail of every day of your professional life for the next 10 years. In fact, personal business planning can be as simple as you want to make it, as you can see here with this sample business plan for law practice PDF. You don't even have to call it a business ...
Law Firm Plan. Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 lawyers to create business plans to start and grow their law firms. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a law firm business plan template step-by-step so you can create your ...
Section Two: Company Description. Write a succinct overview of your company. Here is what it should cover: Mission statement and values. Reiterate your mission statement and core values here. Geographic location and areas served. Identify where your offices are located and the geographic areas that you serve.
Call 1-888-858-2546 or email [email protected]. Our sales team is available Monday to Friday from 8 a.m. to 8 p.m. EST. Download our free law firm business plan template. Start your law firm on the right foot with a clear plan that explains where you're going, and how you're getting there.
Follow these tips to quickly develop a working business plan from this sample. 1. Don't worry about finding an exact match. We have over 550 sample business plan templates. So, make sure the plan is a close match, but don't get hung up on the details. Your business is unique and will differ from any example or template you come across.
It should also contain some deeper information about the firm's identity and aspirations. This would include: A mission statement about the firm's purpose. A vision statement or recitation of medium- and long-term goals for the firm. Important aspects of the firm's history. Any important philosophies that the firm brings to legal practice.
A law firm business plan is a document that outlines your business goals and strategies to achieve those goals. It includes your law firm overview, your reason to start your firm, the services you will offer, a budget or funding requirements, and strategies to get and manage your clients.
Section Two: Law Firm Description. This section of your business plan provides a deeper dive into your firm's background, history, legal specializations, and legal structure and ownership. This section should provide a concise yet informative overview of your firm's identity and history. Here's what this section should cover: Mission ...
A business plan template for lawyers can provide several benefits to help you effectively manage and grow your legal practice: Clearly define your objectives and goals to keep your practice focused and on track. Identify your target clients and develop strategies to attract and retain them. Create a comprehensive marketing plan to increase your ...
Executive Summary. Wy'East Law Firm (WLF) is a boutique technology law firm located in Portland, Oregon. The firm will be lead by Richard Bloom, a seasoned attorney previously with (name omitted)'s e-group. WLF will service all needs generated by technology firms, with specialization on mergers and acquisitions and qualified stock option ...
By planning for the future and setting realistic growth targets, law firms can take their businesses to the next level. Overall, a well-developed business plan is critical for success in the legal industry, providing direction and focus, supporting decision-making, managing resources effectively, and enabling growth.
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Law Firms is designed to help law firms outline their strategic goals, target market, revenue projections, operational details, and marketing strategies, ensuring they can effectively manage their legal practices and attract clients and investment. This template includes:
LAW FIRM BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE. A business plan is an important component of opening anrunning a law firm. Think of d your plan as a roadmap that details where you are going and how you plan to get there. Whether it will be for your eyes only or will be shared with others, a detailed business plan will help you envision and improve your practice.
It is written after the plan is complete but is the first and, sometimes, most important part read by investors. How important this is for a legal business plan depends on your long and short term goals, e.g., whether they are to grow a partnership, join a firm, build up a practice that is enticing for acquisition by a larger firm, etc.
Use this free law firm business plan template to quickly & easily create a great business plan to start, grow and/or raise funding for your business. Food & Retail Business Plan Templates Service Business Plan Templates
When to use a Business Plan: You want to start a new business and want to set out the blueprint for the new venture. You will present your plan to potential investors to clearly outline the business goals, financials, and strategies. You are a business owner who wants all your employees and leaders to know the mission and goals for your business.
A Sample Law Firm Business Plan Template 1. Industry Overview. The services of lawyers are needed in every part of the united states of America. Statistics has it that the United States of America has about 165,000 law offices and they generate about $180 billion in annual revenue.
If we actually want a business plan, it should be focused on our firm specifically.". Your business plan ideally connects these dots: (1) what the firm wants to accomplish, (2) what you want to accomplish, and (3) how coming together could help you both accomplish these mutual goals.
Articles of Incorporation: File this document with the government to form a corporation. Purchase of Business Agreement: Purchase all assets or shares of a company from an individual or corporate party. Risk Management Plan: Identify, evaluate and mitigate risks that impact your business. 15 Best States for Employers in 2023.
Which kind of plan you may need, and the components of each plan; You can use a business plan template or simply follow the guidance provided here on how to write the plan. ... Talk to a Lawyer When Writing a Business Plan. A lawyer can help in many business scenarios. While you can certainly write a business plan on your own, an experienced ...
Get your free guide, business plan template and cash flow forecast template to help you manage your business and achieve your goals. ... These articles and related content is not a substitute for the guidance of a lawyer (and especially for questions related to GDPR), tax, or compliance professional. When in doubt, please consult your lawyer ...
on their law practice business management by taking the step of drafting a business plan. THE POINT OF A BUSINESS PLAN We'll discuss the components of a business plan in a moment, but first, let's talk about why this exercise is valuable. For another type of business, a business plan may be useful in attracting investors or securing financing.
California fast-food workers cooking Big Macs or whipping Frappuccinos will start making a minimum wage of $20 an hour on Monday. For many, this means a 25% raise. The new state minimum uniquely ...
Advertisement. When an employee receives a PIP, there are three steps that I suggest that they follow. 1. Read the PIP very carefully. Many people are so shocked that they receive a PIP that they ...
A $4.1 billion bet on sports . One of the biggest players in the booming business of sports just got bigger: The private equity firm Arctos Partners has raised another $4.1 billion to do more deals.
Last month, the Education Department implemented a provision of the SAVE plan ahead of schedule: $1.2 billion in debt relief for 153,000 borrowers who originally borrowed $12,000 or less and made ...
Riverplace Tower at 1301 Riverplace Blvd. Alex B Baker Jr - RATIO Image, LLC. Apr 4, 2024. One of Florida's oldest law firms will get a $2.5 million office renovation. Dav-Lin Interiors ...