- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans

How To Write the Management Section of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Ownership Structure
Internal management team, external management resources, human resources, frequently asked questions (faqs).
When developing a business plan , the 'management section' describes your management team, staff, resources, and how your business ownership is structured. This section should not only describe who's on your management team but how each person's skill set will contribute to your bottom line. In this article, we will detail exactly how to compose and best highlight your management team.
Key Takeaways
- The management section of a business plan helps show how your management team and company are structured.
- The first section shows the ownership structure, which might be a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation.
- The internal management section shows the department heads, including sales, marketing, administration, and production.
- The external management resources help back up your internal management and include an advisory board and consultants.
- The human resources section contains staffing requirements—part-time or full-time—skills needed for employees and the costs.
This section outlines the legal structure of your business. It may only be a single sentence if your business is a sole proprietorship. If your business is a partnership or a corporation, it can be longer. You want to be sure you explain who holds what percentage of ownership in the company.
The internal management section should describe the business management categories relevant to your business, identify who will have responsibility for each category, and then include a short profile highlighting each person's skills.
The primary business categories of sales, marketing , administration, and production usually work for many small businesses. If your business has employees, you will also need a human resources section. You may also find that your company needs additional management categories to fit your unique circumstances.
It's not necessary to have a different person in charge of each category; some key management people often fill more than one role. Identify the key managers in your business and explain what functions and experience each team member will serve. You may wish to present this as an organizational chart in your business plan, although the list format is also appropriate.
Along with this section, you should include the complete resumés of each management team member (including your own). Follow this with an explanation of how each member will be compensated and their benefits package, and describe any profit-sharing plans that may apply.
If there are any contracts that relate directly to your management team members, such as work contracts or non-competition agreements, you should include them in an Appendix to your business plan.
While external management resources are often overlooked when writing a business plan , using these resources effectively can make the difference between the success or failure of your managers. Think of these external resources as your internal management team's backup. They give your business credibility and an additional pool of expertise.
Advisory Board
An Advisory Board can increase consumer and investor confidence, attract talented employees by showing a commitment to company growth and bring a diversity of contributions. If you choose to have an Advisory Board , list all the board members in this section, and include a bio and all relevant specializations. If you choose your board members carefully, the group can compensate for the niche forms of expertise that your internal managers lack.
When selecting your board members, look for people who are genuinely interested in seeing your business do well and have the patience and time to provide sound advice.
Recently retired executives or managers, other successful entrepreneurs, and/or vendors would be good choices for an Advisory Board.
Professional Services
Professional Services should also be highlighted in the external management resources section. Describe all the external professional advisors that your business will use, such as accountants, bankers, lawyers, IT consultants, business consultants, and/or business coaches. These professionals provide a web of advice and support outside your internal management team that can be invaluable in making management decisions and your new business a success .
The last point you should address in the management section of your business plan is your human resources needs. The trick to writing about human resources is to be specific. To simply write, "We'll need more people once we get up and running," isn't sufficient. Follow this list:
- Detail how many employees your business will need at each stage and what they will cost.
- Describe exactly how your business's human resources needs can be met. Will it be best to have employees, or should you operate with contract workers or freelancers ? Do you need full-time or part-time staff or a mix of both?
- Outline your staffing requirements, including a description of the specific skills that the people working for you will need to possess.
- Calculate your labor costs. Decide the number of employees you will need and how many customers each employee can serve. For example, if it takes one employee to serve 150 customers, and you forecast 1,500 customers in your first year, your business will need 10 employees.
- Determine how much each employee will receive and total the salary cost for all your employees.
- Add to this the cost of Workers' Compensation Insurance (mandatory for most businesses) and the cost of any other employee benefits, such as company-sponsored medical and dental plans.
After you've listed the points above, describe how you will find the staff your business needs and how you will train them. Your description of staff recruitment should explain whether or not sufficient local labor is available and how you will recruit staff.
When you're writing about staff training, you'll want to include as many specifics as possible. What specific training will your staff undergo? What ongoing training opportunities will you provide your employees?
Even if the plan for your business is to start as a sole proprietorship, you should include a section on potential human resources demands as a way to demonstrate that you've thought about the staffing your business may require as it grows.
Business plans are about the future and the hypothetical challenges and successes that await. It's worth visualizing and documenting the details of your business so that the materials and network around your dream can begin to take shape.
What is the management section of a business plan?
The 'management section' describes your management team, staff, resources, and how your business ownership is structured.
What are the 5 sections of a business plan?
A business plan provides a road map showing your company's goals and how you'll achieve them. The five sections of a business plan are as follows:
- The market analysis outlines the demand for your product or service.
- The competitive analysis section shows your competition's strengths and weaknesses and your strategy for gaining market share.
- The management plan outlines your ownership structure, the management team, and staffing requirements.
- The operating plan details your business location and the facilities, equipment, and supplies needed to operate.
- The financial plan shows the map to financial success and the sources of funding, such as bank loans or investors.
SCORE. " Why Small Businesses Should Consider Workers’ Comp Insurance ."
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Transition to growth mode
with LivePlan Get 40% off now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated March 4, 2024
If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
If you’re stuck, start with a one-page business plan and check out our collection of over 550 business plan examples for inspiration. They’re broken out over dozens of industries—you can even copy and paste sections into your plan and rewrite them with information specific to your business.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

5 Min. Read
How To Create a Compelling Message With Your Business Plan to Help Sell Your Idea

8 Min. Read
How to Write a Franchise Business Plan + Template

7 Min. Read
How to Write an Online Boutique Clothing Store Business Plan + Example Templates

How to Write a Growth-Oriented Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Transform Tax Season into Growth Season
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
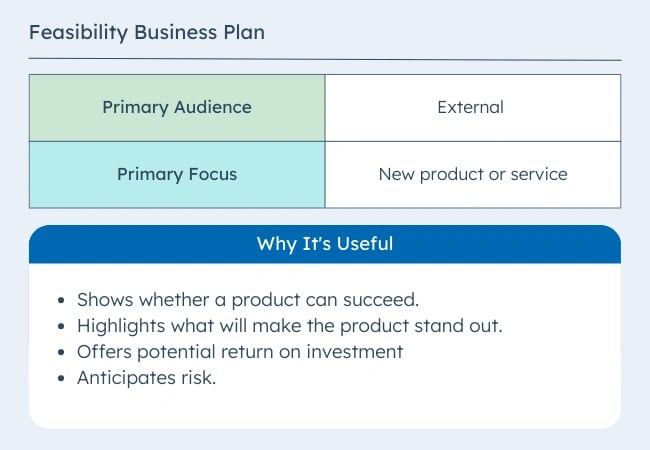
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![what is the business plan in management How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

19 Best Sample Business Plans & Examples to Help You Write Your Own

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![what is the business plan in management 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![what is the business plan in management The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
How to make a business plan
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.

Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.

Business Plan Organization and Management: How to Write Guide .
Sep 17, 2023 | Business Consulting , Business Plan , Organization and Management , Organizational Development , Strategy

Writing the Business Plan Organization and Management Section
It provides critical information for those looking for evidence that your staff has the necessary experience, skills, and pedigree to realize the objectives detailed in the rest of your business plan.
What Is the Organization and Management Section in a Business Plan?
The organization and management section of your business plan should provide details about your business structure and team. This section typically comes after the executive summary. However, some people have it further in the document after the market analysis section.
This section generally is separated into two parts. The first concerns the organization as a whole. It gives readers an overview of the company structure, which is an excellent opportunity for the reader to lift the roof off your office and peer into its inner workings. For your legal design, you may set up as a limited liability company (LLC) or nonprofit/ charity or form a partnership. It’s crucial to include this section. However, suppose you’re starting a home business or have an already operating business where you’re the only person involved. In that case, you can skip this section or show the company registration details from either the company’s house or the awarding .gov.
The second part focuses specifically on your management team and introduces readers to each member — your chance to impress them with the many accomplishments pinned to your organization’s management team.
This section may seem less important than some of the other parts of your business plan, but the truth is that your people are your business. If they’re highly competent and accomplished, the implication is that so is your business.
Of course, if you’re a sole proprietor with no management structure or any employees, this section is unnecessary other than to talk about yourself and your achievements.

The section on organization and management should outline the hierarchy, individual roles, and corresponding responsibilities. It should also highlight each person’s strengths and qualifications for their positions.
Business Plan Organization Section
The organizational section of your business plan outlines the hierarchy of individuals involved in your business, typically in a chart format. This section identifies the President or CEO, CFO, Director of Marketing, and other roles for partnerships or multi-member LLCs. If you’re a single-person home business, this section is straightforward as you are the only person on the chart.
Although this section primarily focuses on owner members, you can include outsourced workers or virtual assistants if you plan to hire them. For example, you may have a freelance web admin, marketing assistant, or copywriter. You may even have a virtual assistant who coordinates with your other freelancers. While these individuals are not owners, they hold significant responsibilities in your business.
There are various business structures, such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, LLCs, and corporations.
Detail the Legal Structure within the Business Plan Organization and Management Section
Here is an indicative list of business structures. It would help if you talked to your accountant and legal advisors to determine which legal form is the best for your business proposition.
Sole Proprietorship
When embarking on a business venture, it’s essential to consider the various structures available. A sole proprietorship is a structure whereby the business is not regarded as separate from its owner’s finances. The owner retains complete control and responsibility for the company. However, they are unable to sell stocks or bring in new owners. The business becomes a sole proprietorship if not registered under any other structure.
Partnership
When forming a partnership, it can either be a limited partnership (LP) or a limited liability partnership (LLP). One partner assumes most liability in a limited partnership (LP). In contrast, the other partners have limited liability and control over the business. Alternatively, in a limited liability partnership (LLP), all partners have limited liability from debts and actions of other partners, and there is no general partner.
Limited Liability Company
A limited company (LTD) or limited liability company (LLC) is a mixture of business structures that mixes aspects of partnerships and corporations. It offers limited personal liability to the owner and passes profits through to their tax returns.
Corporation
There are various types of corporate structures. A C-corporation enables the issuance of stock shares, pays corporate taxes instead of personal returns, and provides the highest level of personal protection from business activities. On the other hand, nonprofit corporations are similar to C corporations. However, they do not aim to make profits and are exempt from state or federal income taxes.
More information on company legal structures is available on UK.Gov and USA.SBA websites.
Describe Your Company’s Organizational Structure
This first step illustrates the positions in your organization’s employee hierarchy and how they all relate to each other.
This is usually done graphically as a guide, using an organizational chart, or “org chart” for short. People use a Microsoft tool, i.e., PowerPoint or Excel, to help.
Organization Charts typically follow a top-down hierarchy, starting with your CEO/ Managing Director in the top box at the top of the page. Lines extend down from that person’s name to boxes containing the terms of the CEO’s direct reports.
We have included an example organizational chart below for guidelines only.
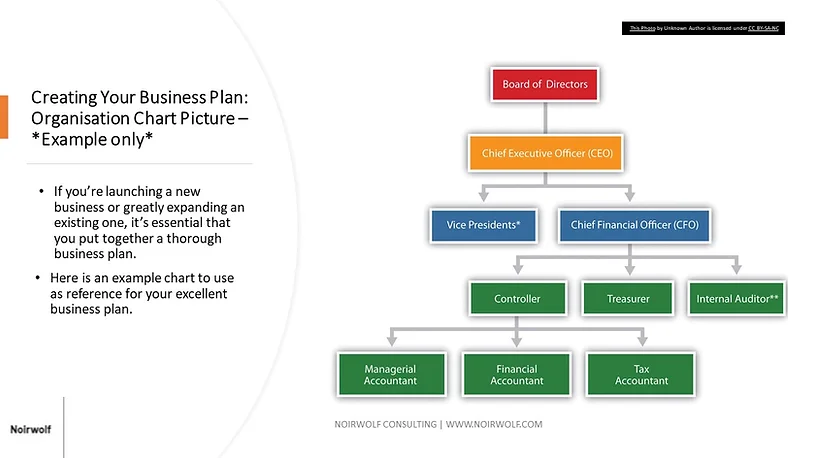
Identify your business organization structure and list your team members’ strengths and skills.
Those managers then have lines extending to those who report to them, and so on, down to your lowest staff positions.
This section will give your readers a quick understanding of your management and governance structure, the size of your organization, and your lines of control and communication.
Describe your Team in your Business Plan Organization and Management Section
In your business plan’s Organization and Management section, please provide a detailed description of your team. Y ou will discuss the company’s management team, starting with the owners.
This section highlights who is involved in the running of your business and who are the support professionals. It also includes the roles and responsibilities of managers.
Suppose the company structure is a multi-owner arrangement or some other multi-owner arrangement. In that case, you’ll want to include information for every member and their percentage of ownership and ongoing involvement in the company.
It’s important to discuss how ownership interests are split, their responsibilities, what they did before securing their current position, and how they came to be involved with the company.
Here, it would help if you talked about some of your critical team members. These people are directly responsible for large portions of your business operations.
Owner/Manager/Members
Within your business o rganization and management section, y ou should introduce the team and talk about their experience, qualifications, previous companies and achievements, role in the company, and any special skills they bring with them. Please provide the following details for each owner, manager, or member of the business within your business plan:
- Percentage of ownership (if applicable)
- Level of involvement (active or silent partner)
- Type of ownership (e.g., stock options, general partner)
- Position in the company (CEO, CFO, etc.)
- Responsibilities and Duties
- Educational background
- Relevant experience and skills
- Previous employment history
- Skills that will benefit the business
- Awards or recognition received
- Compensation structure
- How each individual’s skills and experience will complement and contribute to the business’s success
Perhaps they’re an entrepreneur, business coach, exclusive advisor, or industry specialist to help you grow.
This is an ideal opportunity for companies with an Executive Board of Directors, Governance Structure, or Advisory Board to introduce them to your readers.
Executive Board
Having a board of directors is essential for your management team. Without one, you may be missing out on crucial information. This section includes details similar to those found in the ownership and management team sub-section, such as the names, areas of expertise, positions (if applicable), and involvement with the company of each board member.
Strategic Advisors
Suppose you’re looking for funding for your business or to fill a gap in your knowledge, or you may not have the funds to hire an executive board. In that case, you must inform potential partners and investors that you have a team of professionals assisting you. This includes lawyers, accountants, and any freelancers or contractors you may be working with. When listing these individuals, include their name, title, educational background, certifications, services they provide to your business, and their relationship with you (i.e., hourly rates, projects, retainer, as-needed, regular). Additionally, highlight their skills and experience that make them an asset to your team you need
Does anything else make them stand out as quality professionals (awards, past working with credible brands)?
Spotlight on the Wider Team Structure
Now, you’ve showcased the management team in its entirety. You can provide brief bios for hiring team needs or secondary members and talk at length about how the team’s combined skills complement each other and how they amplify the team’s effectiveness.
It’s also important to point out any gaps in the knowledge your team is currently suffering. Your readers will likely be savvy enough to pick up on existing holes.
Therefore, you’ll want to get ahead of these criticisms and demonstrate that you’re already aware of the positions and complementary skill sets your management team still requires and how you plan to address the knowledge gaps with future hires.
Do you need help writing your business plan o rganization and management section ?
Every successful business plan should include the organization and management section, helping you communicate your legal structure and team.
Writing a business plan can seem overwhelming, especially when starting a small, one-person business. However, it can be a reasonably simple task. This section of the plan should be updated if there are any changes to the organization structure or team members, such as additional training, awards, or other resume changes that benefit the business.
Creating your comprehensive business plan takes planning, research, time, and a herculean effort. If, at any point, the work becomes too much to handle, we can step in to assist.
Do you want an expert “second opinion” before creating your business plan or financial forecasts? Let’s talk !
Get in Touch
Are you looking to grow your business but unsure where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We’ll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free 30-minute consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let’s get started!
Contact Noirwolf Consulting today using the website contact form or by emailing [email protected] or call us at +44 113 328 0868.
Recent posts .

What is Program Management?
Apr 2, 2024
Program management is a vital component of organizational success, as it enables the coordinated execution of interdependent projects that yield benefits beyond the scope of individual project management. It involves the judicious application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet specific program requirements. Our experience has demonstrated that organizations with well-developed program management and program management offices (PMOs) consistently outperform those that lack such structures. Therefore, it is imperative that organizations prioritize the establishment of robust program management frameworks to achieve their strategic objectives.

Business Transformation Strategy: A 10-Step Strategy Guide
Mar 4, 2024
Business transformation strategy is a complex and dynamic process that fundamentally restructures an organization’s strategy, processes, and systems. Though each business transformation is unique, several critical steps remain foundational to a successful change management plan. A comprehensive business transformation framework ensures a smooth and practical transformation. This framework should encompass various elements, such as defining the vision and aims of the transformation, assessing the current state of the business, identifying gaps and areas of improvement, developing a roadmap and action plan, implementing the changes, monitoring and measuring progress, and continuously refining the transformation approach as needed.

What is the Change Management Process?
Feb 2, 2024
Change is the only constant in today’s fast-paced world, and organizations must adapt to stay ahead. Fortunately, change management provides a structured and coordinated approach that enables businesses to move from their current state to a future desirable state. To deliver business value, organizations introduce change through projects, programs, and portfolios. However, introducing change is just the beginning! The real challenge is to embed the change and make it a new normal state for the organization. This calls for implementing the main principles of change management, which we will discuss in this article. Get ready to transform your organization and achieve your desired outcomes by mastering the art of change management!
Happy clients .
Trevor mcomber, us.
I recently worked with Zoe@Noirwolf, who provided me with an outstanding 5-year business plan. The expertise in financial planning, market research, SWOT analysis, and consulting was exceptional. Zoe provided me with a comprehensive and well-researched plan tailored to my business. The entire process was professional, timely, and communicative.
Bill Walton, Leeds
Zoe provided first-rate work and is an excellent business consultant. I was trying to figure out my cash flow forecast for my startup. Zoe gave me an interactive consultation session over MS teams, which was valuable and saved me a lot of time. She is super quick in excel and knowledgeable about what to include in your estimates. She was able to offer me ideas & choices that I hadn't considered. Highly recommended.
Jeendanie Lorthe, US
Warren kim, us, oscar sinclair, london, get in touch ..
Looking to grow your business but feeling unsure about where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We'll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free one-hour consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let's get started!
Business Plan Section 3: Organization and Management
This section explains how your business runs and who’s on your team. Learn how to present the information in this section of your business plan.

This section of your business plan, Organization and Management, is where you’ll explain exactly how you’re set up to make your ideas happen, plus you’ll introduce the players on your team.
As always, remember your audience. If this is a plan for your internal use, you can be a little more general than if you’ll be presenting it to a potential lender or investor. No matter what its purpose, you’ll want to break the organization and management section into two segments: one describing the way you’ve set up the company to run (its organizational structure), and the other introducing the people involved (its management).
Business Organization
Having a solid plan for how your business will run is a key component of its smooth and successful operation. Of course, you need to surround yourself with good people, but you have to set things up to enable them to work well with each other and on their own.
It’s important to define the positions in the company, which job is responsible for what, and to whom everyone will report. Over time, the structure may grow and change and you can certainly keep tweaking it as you go along, but you need to have an initial plan.
If you’re applying for funding to start a business or expand one, you may not even have employees to fit all the roles in the organization. However, you can still list them in your plan for how the company will ideally operate once you have the ability to do so.
Obviously, for small businesses, the organization will be far more streamlined and less complicated than it is for larger ones, but your business plan still needs to demonstrate an understanding of how you’ll handle the workflow. At the very least, you’ll need to touch on sales and marketing, administration, and the production and distribution of your product or the execution of your service.
For larger companies, an organizational plan with well-thought-out procedures is even more important. This is the best way to make sure you’re not wasting time duplicating efforts or dealing with internal confusion about responsibilities. A smooth-running operation runs far more efficiently and cost-effectively than one flying by the seat of its pants, and this section of your business plan will be another indication that you know what you’re doing. A large company is also likely to need additional operational categories such as human resources and possibly research and development.
One way to explain your organizational structure in the business plan is graphically. A simple diagram or flowchart can easily demonstrate levels of management and the positions within them, clearly illustrating who reports to whom, and how different divisions of the company (such as sales and marketing) relate to each other.
Here is where you can also talk about the other levels of employees in your company. Your lower-level staff will carry out the day-to-day work, so it’s important to recognize the types of people you’ll need, how many, what their qualifications should be, where you’ll find them, and what they’ll cost.
If the business will use outside consultants, freelancers, or independent contractors, mention it here as well. And talk about positions you’d want to add in the future if you’re successful enough to expand.
Business Management
Now that we understand the structure of your business, we need to meet the people who’ll be running it. Who does what, and why are they onboard? This section is important even for a single practitioner or sole proprietorship, as it will introduce you and your qualifications to the readers of your plan.
Start at the top with the legal structure and ownership of the business. If you are incorporated, say so, and detail whether you are a C or S corporation. If you haven’t yet incorporated, make sure to discuss this with your attorney and tax advisor to figure out which way to go. Whether you’re in a partnership or are a sole owner, this is where to mention it.
List the names of the owners of the business, what percent of the company each of them owns, the form of ownership (common or preferred stock, general or limited partner), and what kind of involvement they’ll have with day-to-day operations; for example, if they’re an active or silent partner.
Here’s where you’ll list the names and profiles of your management team, along with what their responsibilities are. Especially if you’re looking for funding, make sure to highlight the proven track record of these key employees. Lenders and investors will be keenly interested in their previous successes, particularly in how they relate to this current venture.
Include each person’s name and position, along with a short description of what the individual’s main duties will be. Detail his or her education, and any unique skills or experience, especially if they’re relevant to the job at hand. Mention previous employment and any industry awards or recognition related to it, along with involvement with charities or other non-profit organizations.
Think of this section as a resume-in-a-nutshell, recapping the highlights and achievements of the people you’ve chosen to surround yourself with. Actual detailed resumes for you and your management team should go in the plan’s appendix, and you can cross-reference them here. You want your readers to feel like your top staff complements you and supplements your own particular skill set. You also want readers to understand why these people are so qualified to help make your business a success.
This section will spell out the compensation for management team members, such as salary, benefits, and any profit-sharing you might be offering. If any of the team will be under contract or bound by non-compete agreements, you would mention that here, as well.
If your company will have a Board of Directors, its members also need to be listed in the business plan. Introduce each person by name and the position they’ll hold on the board. Talk about how each might be involved with the business (in addition to board meetings.
Similar to what you did for your management team, give each member’s background information, including education, experience, special skills, etc., along with any contributions they may already have had to the success of the business. Include the full resumes for your board members in the appendix.
Alternately, if you don’t have a Board of Directors, include information about an Advisory Board you’ve put together, or a panel of experts you’ve convened to help you along the way. Having either of these, by the way, is something your company might want to consider whether or not you’re putting together the organization and management section or your business plan.
NEXT ARTICLE > Business Plan Section 4: Products and Services
Apply for a loan, get started.
Loans from $5,000 - $100,000 with transparent terms and no prepayment penalty. Tell us a little about yourself, your business and receive your quote in minutes without impacting your credit score.
Thanks for applying!
Loans are originated and funded through our lending arm, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development. By clicking “Continue to Application,” you consent to, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development’s Terms of Use and Privacy Policy ; and to receive emails, calls and texts , potentially for marketing purposes, including autodialed or pre-recorded calls. You may opt out of receiving certain communications as provided in our Privacy Policy .
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Business Skills
- Business Writing
How to Write a Management Plan
Last Updated: September 18, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Madison Boehm . Madison Boehm is a Business Advisor and the Co-Founder of Jaxson Maximus, a men’s salon and custom clothiers based in southern Florida. She specializes in business development, operations, and finance. Additionally, she has experience in the salon, clothing, and retail sectors. Madison holds a BBA in Entrepreneurship and Marketing from The University of Houston. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 235,504 times.
A management plan describes how an organization or business is run. Writing a management plan allows you to formalize your management structure and operations. It also ensures that everyone is on the same page and that your goals will be accomplished. You can easily write your own management plan with a few simple steps.
Management Plan Outline and Example

Starting Your Management Plan

- Defining roles also creates accountability by making it clear who's fault it was that something did or did not happen. [3] X Trustworthy Source Kansas University Center for Community Health and Development Community-based research center focused on supporting public health development and education Go to source

- A section detailing management members and their responsibilities and authorities.
- A chart of section detailing interactions between and responsibilities of each level of the organization.
- A section explaining different aspects of your organization being managed and the policies and procedures of that management.
- A schedule for updating, enhancing, and growing management and the management plan. [6] X Research source

Describing Ownership and Management

- Include a copy of board policies, including election policies, term length, responsibility, authority, and conflict resolution. This information should already be stated in your operating agreement or other founding documents.

- List past positions and duties of each member that apply to their current management obligations. Explain how these obligations highlight applicable skills and strengthen the management positions.
- Highlight all relevant educational backgrounds for each of the managers. Explain how their training will benefit the company. Only include the education that is relevant to the positions that they currently hold.
- If you are the only employee in your business, be sure to include your own experience and strengths.

- Accountants.
- Insurance brokers.
- Consultants.

- For example, “Our team, with its diverse array of skills, have a combined forty years of experience in this field. With our coordinated democratic structure, they can work together effectively to produce results. With this team, we are confident that our business will become profitable in two years.”

Writing Out Policies and Procedures

- For example, a policy might be using and selling only green materials and products. The procedures to support that policy might be shopping from approved green vendors or checking the environmental impact of each material or product used.

Revising Your Plan

- When they approve, have all owners sign the plan before you submit it to your investors, bank, or fundraising bodies.

- Make sure there is a way for all management and employees to submit their feedback regarding the plan.
- Then, create a method by which changes to the plan can be approved and instituted. [20] X Trustworthy Source Kansas University Center for Community Health and Development Community-based research center focused on supporting public health development and education Go to source
Expert Q&A

- Many investors will read the management section of your business plan before any other section, including marketing and finances, so you want to make sure that you have the best proposal possible. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Do not neglect your management plan in favor of your financial plans. Both are equally important to a business plan. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ Madison Boehm. Business Advisor, Jaxson Maximus. Expert Interview. 24 August 2021.
- ↑ http://ctb.ku.edu/en/table-of-contents/leadership/effective-manager/management-plan/main
- ↑ https://www.brown.edu/research/conducting-research-brown/preparing-proposal/proposal-development-services/writing-management-plan
- ↑ https://www.thebalance.com/how-to-write-the-management-summary-2951561
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/humanresourcemanagement/chapter/4-1-the-recruitment-process/
- ↑ https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/241072
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/4533-business-plan-outline.html
About This Article

The best way to write a management report is to describe the company’s management structure in 10 to 20 pages. Name the board members and explain the company’s ownership policies. Introduce all management members and present the strengths of each team member. Then, write out workplace policies and procedures. Send the management report to the company’s bank, investors, or fundraising bodies. For more tips from our Financial Reviewer, like how to outline, format, and revise your plan, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Moshakge Molokwane
Apr 12, 2017
Did this article help you?
Mar 14, 2019
Jamie Willacy
Feb 1, 2023

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Sandeep Kashyap
What is business management? A comprehensive guide

Introduction
Managing a business is no cakewalk for any entrepreneur. Not everyone has a natural talent to understand the various responsibilities that come under the ambit of business management.
Don’t worry! This guide to What is Business Management will help you understand what it takes to help an organization grow and prosper.
First, let’s get clear with the basics.
What is business management?
Business management is the practice of overseeing and coordinating various activities within an organization to achieve goals efficiently, including planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources and processes.
Supercharge your productivity with ProofHub – Your all-in-one project management solution
What types of business management are there?

Although, there are many types of business management; given below are some of the major ones.
1. Financial management
Financial management strives to create a balance between profit and risk to ensure profit for the business.
It requires business managers to plan, direct, and coordinate with investing, banking, insurance, and other financial aspects of the business. There are three key elements of financial management – planning, control, and decision-making.
2. HR management
HR (Human Resource) management deals with a business’s hiring, training, and retention of an employee.
It is not the sole responsibility of the HR department to hire, retain and recruit new employees. The managers of every department are equally responsible for these as it impacts the future growth of an organization.
3. Operations management
Operations management requires business managers to ensure that all departments of an organization are functioning efficiently.
For this, they have to deal with numerous departments and formulate the best business strategies and processes.
The operations teams have to ensure proper acquisition, development, and utilization of resources the business needs.
4. Marketing management
Marketing management takes into consideration the practical application of a business’s marketing resources. There are four core areas of marketing management – Company, Collaborator, Customer, and Competitor analysis.
Brand management, Marketing strategy, and pricing are also three core components of effective marketing management.
5. Strategic management
The success of every business depends on its marketing, financial, and operational strategies. This is where strategic marketing comes into the picture. Strategic management refers to the application of strategic thinking to leading an organization.
This type of business management relies on questions like – Where does a business want to reach and how can it reach there?
To succeed in any type of business management described above, business managers have to be aware of a few practices.
Take control of your projects with ProofHub: Track, manage, and prioritize tasks effortlessly in one centralized platform!
What are some of the best business management tactics?

Given below are 5 of the best business management tactics every business manager should use to help an organization grow.
1. Engage the workforce
No business has ever reached its goal without active and hardworking team members. Business managers have to engage with team members from every department.
A motivated and enthusiastic team member is more likely to help the organization achieve its business goal as opposed to an alienated worker who is more interested in a paycheck.
2. Reward the winners
Some business managers feel that connecting or praising team members on a personal level undermines their authority, but this is not so.
Nothing can replace the motivation an employee feels after being praised for a job well done. Rewarding employees who help a business grow has a positive impact on others.
3. Be vulnerable
Many business managers believe that getting to know the employees makes them look weak, which is absolutely wrong.
Without the ability to be open and share their ideas regarding how a business should go , some business managers lose the trust of the team. This has a negative impact on the project’s and company’s future, not to forget it also impacts employee morale.
4. Embrace technology
Business managers need to be quick when it comes to adapting to the latest technology. It sends a positive message to the customers as well as company employees.
For example, in today’s world, it is vital for every business to not only have a website with smooth navigation and valuable content. Business managers need to ensure that customers can connect with them from anywhere and at any time.
In the long run, if a business wants to stay ahead of the competition then managers have to take up the mantle of adapting to the latest technology in their industry.
5. Have clarity
Many businesses are not able to meet their goals due to a lack of clarity amongst managers who either don’t understand the organization’s vision or are confused about how to achieve it.
To counter this issue, organizations should help them understand a few key concepts;
- Why do we exist?
- What do we do?
- What is most important at the moment?
- Who must do what?
Answering these questions gives business managers a clear idea about the company’s vision, mission, and its values.
There are different ways through which a business manager can help an organization grow and achieve its goal.
Streamline productivity, save time, and discover clarity with ProofHub!
Let us now take a look at the different management styles.
Different business management styles
Whether a business manager leads a department, team, or entire organization, it is vital to get familiar with the different management styles.
Knowing about these is an important part of understanding what is business management at its core.

That said, given below are 8 business management types a business manager can adapt to.
1. Democratic management style
The democratic management style helps create a bond of trust and mutual understanding between an organization’s employees and the upper management.
The leaders usually seek input from the employees before making a business decision. Business managers who follow this management style are open to experimenting with new ideas.
2. Laissez-faire management style
Business managers who adopt the Laissez Faire management style do not believe in micromanaging employees.
Employees have complete freedom when working on a given task. It is the best management style when it comes to managing a team of highly experienced professionals.
3. Autocratic management style
Autocratic business managers believe in focusing on results and efficiency. They micromanage the workforce to ensure that everyone follows the organization’s policy.
This management style comes in handy when there are inexperienced employees who need clear and strict instructions regarding a task.
4. Collaborative management style
The collaborative management style requires coordination between managers, supervisors, and employees to attain a common objective.
In this management style, all the employees from different departments work together to ensure the organization achieves its business objectives.
Work together effortlessly, streamline collaboration, and boost productivity with ProofHub!
5. Coach management style
Business managers who possess the qualities of a sports team coach can adapt to the coach management style. They have to focus on an employee’s development and know what motivates every team member.
Coach management style helps managers identify the strengths and weaknesses of every team member. It helps push an employee to perform beyond their limitations and improve their chances of growth.
6. Transformational management style
A transformational management style is an approach that business managers use to help an organization move in the right direction.
A transformational business manager not only supervises the various changes taking place in an organization. They also help in managing employee morale which might go low during such times.
7. Bureaucratic management style
The bureaucratic management style requires business managers to assign tasks to employees within a well-defined hierarchy.
This management style requires a focus on rules and procedures rather than collaboration. It is quite successful in heavily regulated industries but not so much in creative industries.
8. Transactional management style
Managers following a transactional management style believe in improving employee performance through bonuses and incentives.
They act as mentors and provide explicit instructions to increase performance and help employees meet the business’ expectations.
It has become easier for business managers to handle small as well as large teams within an organization with the help of various Business Management Systems available.
Who is a business manager?
The end goal of every business is to generate profit. The person who has to ensure this happens to be none other than a business manager.
The business manager is a professional who oversees an organization’s employees and day-to-day operations. Their primary responsibility is ensuring that all business activities remain streamlined at all times.
Business Managers ensure this by executing relevant operational strategies, conducting employee performance reviews, and keeping a tab on everyday activities. They also have to search for opportunities to grow the business and achieve its objective.
Apart from this, Business managers keep an eye on all ongoing projects to determine any area of improvement and identify potential roadblocks.
Effortlessly manage your teams and clients from one place.
Still, there is a certain set of skills that all business managers need to possess. Let us see what these are.
Skills every business manager should possess

A business manager has to supervise different teams to help them achieve the desired business goal.
Therefore, anyone looking to get into one of the many business management jobs should definitely possess the skills mentioned below;
1. Communication skills
A business manager has to communicate with project team managers, stakeholders, and higher management. Business managers have to form a positive and trustable relationship with the employees , management, and business owners.
They need to remain connected with the organization’s employees and stakeholders through phone, email & chat. But, for this to happen, they must possess excellent command over verbal and written communication.
No communication gaps, no more disorganized work, no more failed project in 2024!
2. Financial skills
A business manager has to set a budget for a project and ensure it gets completed within that budget. They have to ensure the project teams work according to the allocated budget. There are many business management tools that can help them perform this task with ease.
Being able to manage the project budget ensures the team completes it within the deadline and it is delivered to the client on time.
3. Leadership skills
A big responsibility on the shoulders of every business manager is boosting the morale of the workforce in the organization. A motivated employee will always give their best in comparison to undervalued employees.
Business managers can do this by interacting with every team socially, providing opportunities for career advancement, and recognizing high-performance team members.
4. Interpersonal skills
Business managers have to communicate regularly with different departments in an organization. Sometimes, they have to be the mediator between two departments that don’t see eye to eye on a project.
It is essential the departments have trust in the business manager. For this, business managers should organize team-building activities and social events. This helps them know the employees on a personal level.
5. Planning skills
Business managers play a vital role in handling day-to-day tasks for a business. However, at the same time, they also need to focus on the bigger picture.
They need to ensure that every task completed by a team helps bring the organization closer to its business goal.
A business manager must have a vision of how the decisions made today would impact the business’s future in the coming years.
6. Organizational skills
Business managers have to don many different hats at the same time. For this, they have to effectively organize and prioritize time to ensure every task is completed on time.
A capable business manager must be able to delegate tasks to different team members with ease. It requires them to know the individual skills of every team member before assigning tasks.
7. Problem-solving skills
Business managers have to make decisions that have a huge impact on an organization’s future.
This includes making quick decisions regarding a project or completing a task without spending too much time on it. They have to think quickly about the pros and cons of a decision.
For this, business managers need to develop a keen eye regarding what is happening in the company. This helps them detect any problems and take corrective measures before it is too late.
These are the essential skills that a business manager should have to excel at what they do. But, there is one more that can help them cover a long journey with the organization.
Business manager vs. business administrator
Still, there are business owners who think that business management is just a single industry. That is not so.
So, knowing about its various types will help you understand what is business management especially if you are just starting out as a business manager.
What is a business management system?
Whether you own a small online store or multiple ventures, there is a lot you need to do to handle both. It is here that having a well-defined business management system can help manage difficult tasks easily.
By definition, a Business Management System refers to a set of tools for planning and implementing the various policies, guidelines, and procedures of an organization to execute its business plan.
Having a Business Management system lays down a solid foundation for the successful implementation of strategic and tactical business decisions to meet its objectives.
“In 2020, 54% of enterprises agreed that cloud-based Business Intelligence was vital to their current and future initiatives”. – Forbes
One of the best and most exceptional business management systems that are utilized by leading businesses is ProofHub . It helps business managers handle project tasks, and ensure task deadlines are met by every team in the organization.
How ProofHub can help manage businesses
ProofHub is a cloud-based business management system that helps businesses keep everything organized in one place.
It is one of the best tools for business managers to streamline daily business operations and assign tasks effortlessly.
That is not all! Given below is how ProofHub can help manage businesses with ease.
1. Task management
ProofHub lets project and business managers create, manage, and track assigned tasks with ease. The Kanban boards and Gantt charts help plan and lay down every task in a visually appealing manner.
It lets you set task deadlines, get instant notifications regarding a task, and check out the overall project workflow.
Take control of your projects with ProofHub: Track, manage, and prioritize tasks effortlessly in one centralized platform.
2. Project collaboration
ProofHub keeps every project team member on the same page with its effortless collaboration capabilities.
It also offers Live Chat and Discussions to let project managers connect with team members round-the-clock.
Notes in ProofHub lets managers jot down vital information in one place and share it with the team members.
3. Time management
ProofHub timer tool lets managers keep track of the time spent by a team member on a particular task.
The time logging, monitoring, and reporting feature help increase employee accountability. The Timesheets in ProofHub help display time logged in by a project team member.
ProofHub comes with many advanced features like Time Tracking to help you keep track of every task in a project.
4. File management
ProofHub comes with smart file storage, versioning, and sorting capabilities. Its file management system offers 100 GB of file storage space for all projects.
This business management tool lets managers upload files, and divide them into separate folders. ProofHub also provides the option of attaching files in team chat and discussions.
5. Progress tracking
The Project Reports feature in ProofHub lets managers know if a project is completed on time or lagging behind.
It gives them enough time to take the appropriate action before things go out of hand.
ProofHub’s Activity Tracker makes it easier to keep track of any modifications or changes done to a project file.
To be a business manager requires an entrepreneur to develop many skills apart from being a business owner. With the right business management system by your side, handling day-to-day business operations is way easier than imagined.
FAQ’s
What are the most important components of effective business management.
There are six vital components that contribute to effective business management. These include strategy, marketing, finance, human resources, technology, and operations.
What skills do I need to learn to become a business manager?
To become a proficient business manager, there are 7 skills you need to learn:
* Sound decision-making
* Self-Awareness
* Building Trust
* Becoming a good communicator
* Regular Check-Ins
* Self-Reflection
* Business Management Training
Are there alternative careers in the field of business management?
Yes! Like every profession, business management is a skill required to succeed not only in the corporate world but also other industries like:
* Non-Profits
* Public Service
* Entrepreneurship
* Private Consultancy

- Share on LinkedIn
- Email this Page
- Share on Facebook
- Share on WhatsApp
Try ProofHub, our powerful project management and team collaboration software, for free !
No per user fee. No credit card required. Cancel anytime.

Management Plan: Definition, Benefits & How To Create One?
“A goal without a plan is just a wish.”
In any business, you may have multiple operations running at any given time.
It’s necessary to stay on track with all these operations and the management of a firm plays a pivotal role in making sure they are carried out smoothly.
Managers need to be two steps ahead and prepare for any possible threats and anticipate upcoming changes.
For this a management plan needs to be in place, without it, you become vulnerable to changing trends that can threaten our business.
Management plans will help address a variety of issues, not just during the initial phases of an operation but throughout its execution.
Simply put, a management plan ensures that everything operates smoothly.
The good news is that setting up a management plan will help you optimize all your processes.
The bad news? Creating a management plan usually trips most managers. But that’s why we’re here to not let you fall into the same traps that most managers get themselves into.
Read on and soon you’ll become a management plan expert…
What is a Management Plan? (Definition)
A management plan is a comprehensive plan that provides the objectives of any given project, clearly defines roles and responsibilities, and more to make sure it’s a success!
Your management plan is a resource that everyone in the firm can use for better guidance.

It is a blueprint for the way your organization runs, both day-to-day and over the long term.

A management plan generally outlines:
- the aims and objectives of a firm — what are we trying to achieve?
- the strategies used to meet the objectives — how will we achieve it?
- the methods used to measure performance — how will we know if we are achieving it?
No matter the size of your organization, the core intent of your management plan will be to ensure that the organization is running as effectively as possible.
Let’s dive a little deeper and get to know management plans better…
Benefits Of A Management Plan
To make sure that an organization is working smoothly, a lot of processes need to be handled simultaneously.
If you leave everything for the last minute, hoping that it all works out when the problems arise, you’d be in deep waters.
So to keep up with daily tasks, manage emergencies as they arise, and to not let projects slip through, you need a management plan.
There are a lot of benefits of having a management plan in place, some of them are:
- Defines roles and responsibilities so everyone knows what’s expected of them : Employees need to know who their reporting managers are, who they should consult and go to in case of any need of information. They also need to be aware of the limits of their work, when they need a sign-off from some authority, and when they don’t. All of this can be easily done with the use of a management plan.
- Allocates Tasks : A management plan also divides the work within an organization in reasonable and feasible ways, so that everyone is not only achieving their goals but also doing them in a way that doesn’t burn them out.
- Increases accountability : When tasks and duties are determined, people can be easily accounted for. If daily tasks are not being attained within the allocated time, then the internal team is failing whereas if the CSR activities are not being conducted, then it’s the management who’s failing.
- Creates an effective timeline: A management plan creates a timeline that ensures that bills are being paid on time, staff members are where they’re supposed to be to provide the organization’s services, funding proposals get written and submitted, problems are quickly dealt with, and as a result, the organization functions effectively.
- It helps the organization define itself: The management plan establishes a solid plan that aligns with the organization’s mission and philosophy. This helps the organization to never forget about its core beliefs and communicate this with clarity to its staff, its customers, and the community as a whole.
Read more: What Is Change Management And How To Cope With It?
How To Create A Sound Management Plan? (With Steps)
Step 1. executive summary .
An executive summary is how you start your management plan.
It offers a brief overview of all the key components of the management plan. Be as concise as possible and keep your main points in mind as you write the summary.
Not every point needs to be included here but you need to ensure that the major ones are covered briefly. This summary should easily be understood and comprehended by people even if they don’t visit the entirety of the management plan.
Step 2. Vision Statement
The next step is to mention your vision statement . The vision statement is intended as a guide to help the organization make decisions that align with its philosophy and declared set of goals.
Vision statements are often confused with mission statements, but they generally serve long-term purposes whereas mission is more myopic.
Step 3. Mission Statement
The mission statement is a clear statement of what your organization does and how it will be managed. The mission statement describes:
- purpose of the facility — what is our business?
- why does it exist — what is our underlying philosophy?
- what it has to offer — what services or products do we provide?
- who will use it — what is our target group?
This helps to ensure that your team is committed to the mission. Both the vision and mission reflect the aspirations of the stakeholders.
Step 4. Goals
Once the mission and vision statement has been established, the next step is to work out how to achieve it. It is vital to identify the goals that will help you get to your mission. Goals reflect what you aim to achieve and give direction to your organization.

Goals are usually broad statements that have no time frames.
Step 5. Key Performance Areas
Key performance areas (KPA) focus on general areas of operation within an organization, where the desired outcome is required over the period of the management plan’s execution.
There are many key performance areas in your organization, you need to mention them all separately. Some of these KPAs are:
- Administration
- Human Resources
Create a separate section for each one of them and mention what tasks are expected of them to attain your goals.
Step 6. Mention Policies & Procedures
You need certain policies and procedures in place, to formalize the operations across your organization.
This helps to create consistency and a cohesive environment. You can include working hours, dress codes, leaves, and more, depending on the needs and size of your organization, take your time to define policies.
Step 7. Future Considerations
Every business is at a constant threat of surprises. Thus, you need to base all certain future projections on these unknown problems. For example:
- What resources will be required to remain competitive in a technological sense?
- What building extensions, modifications, or upgrades to your facility will be required in the future?
Step 8. Revisit Your Plan
Your management plan needs to be super-professional and free of any errors as it is a representation of what your organization stands for.
Check for any typos, ask someone else to take a look and proofread it. Make sure that each owner gets a copy. They may send you edits and revisions too. Consider all these carefully and create a powerful, full-proof management plan.
This way you’ll be prepared for unprecedented times and your employees can be ready for what’s expected of them.
Creating a management plan without an intuitive and robust tool can be overbearing on any person.
Gone are the days of boring management plans, today we want something enticing and informative. How can you do that?
Bit.ai is the answer! Let us tell you more…
Create Your Management Plan The Right Way With Bit.ai
Bit.ai is a new age online document collaboration tool that helps anyone create an awesome management plan or any other document, in minutes.
Take a look at some of the many wonderful Bit features:
Real-Time Collaboration: When working on a document as comprehensive as a management plan, it’s obvious that you’ll be working with a team. At such times, it’s more important than ever to have a seamless collaboration experience! Bit facilitates exactly that with its real-time collaboration feature that lets you work on the same document together, comment to exchange ideas and chat on the side.
Smart Workspaces: On Bit.ai, you can create as many workspaces as you want around different teams and communicate in a much better way. For example, once the management plan is created, you can send the document to other owners for approval. And after their approval, you can send it to all the departments within a few clicks!
Media Integrations: No more hopping from one app to the other in search of information, Bit.ai integrates with over 100+ popular applications (YouTube, Typeform, LucidChart, Spotify, Google Drive, etc.) to help teams weave information in their management plan beyond just text and images.
Sleek Editor: Creating a management plan requires constant revisions and edits, with Bit’s minimal document editor, you can write your management plan without the distraction of unnecessary buttons and tabs. And given its simple design, you won’t have to spend hours creating your report.
Sharing: Bit documents can be shared in a way that all changes that you make to the document will be updated in real-time. If you are sharing your management plan with anyone, they will always get your latest changes. Interesting right?
A plethora of features: With many intriguing templates , document tracking, cloud-upload, document locking, and a myriad of such features, BIt is an all-rounded tool for all your documentation needs!
Trust us, your data is secure here and your work will become more efficient than ever with Bit, and given its free plan, it’d be a shame not to give it a try!
Our team at bit.ai has created a few awesome business templates to make your business processes more efficient. Make sure to check them out before you go, y our team might need them!
- SWOT Analysis Template
- Business Proposal Template
- Business Plan Template
- Competitor Research Template
- Project Proposal Template
- Company Fact Sheet
- Executive Summary Template
- Operational Plan Template
- Pitch Deck Template
Conclusion
Effective management only comes after careful planning,
Your employees need to know how they can achieve the goals, the methods they need to use, and more for the smooth functioning of your projects.
Management plans offer that!
Having a management plan will shape your organization the way you want to and you’ll be able to improve your offerings too!
And trust us, there is no way around management plans, sooner or later you’ll realize their importance. With our tips and Bit by your side, you can create your management plans from scratch with precision and ease.
We suggest you get on with your management plan now and you’ll see the results they come bearing!
Have any queries? Tweet us @bit_docs and we’d love to hear from you and help you out with your management plan needs!
Further reads:
Resource Management Plan: What is it & How to Create it?
13 Types of Plans Your Business Must Have!
Management Report: What is it & How to Create it?
Mitigation Plan: What Is It & How To Create One?
Implementation Plan: What is it & How to Create it? (Steps & Process)
Business Development Plan: What is it & How to Create a Perfect One?
Process Improvement Plan: What is it & How to Create It? (Steps Included)

Annual Report: What is it & How to Create it?
Related posts
Maximizing digital agency success: 4 ways to leverage client portals, what is change management and how to cope with it, guerrilla marketing: what is it and how to use it for marketing, 6 crucial financial documents for every organization, 9 must-have internal communication software in 2024, influencer media kit: what is it & how to create it.

About Bit.ai
Bit.ai is the essential next-gen workplace and document collaboration platform. that helps teams share knowledge by connecting any type of digital content. With this intuitive, cloud-based solution, anyone can work visually and collaborate in real-time while creating internal notes, team projects, knowledge bases, client-facing content, and more.
The smartest online Google Docs and Word alternative, Bit.ai is used in over 100 countries by professionals everywhere, from IT teams creating internal documentation and knowledge bases, to sales and marketing teams sharing client materials and client portals.
👉👉Click Here to Check out Bit.ai.
Recent Posts
Developer experience(dx): importance, metrics, and best practices, top 12 ai assistants of 2024 for maximized potential, how to create wikis for employee onboarding & training, what is support documentation: key insights and types, how to create a smart company wiki | a guide by bit.ai.

10 Simple Tips to Write a Successful Business Plan
"The absolute biggest business plan mistake you can make is to not plan at all." So writes Noah Parsons in his helpful blog post 17 Key Business Plan Mistakes to Avoid in 2023 . But how does one pull together all of the necessary components of a cohesive plan? It can feel overwhelming.
Eric Butow, CEO of online marketing ROI improvement firm Butow Communications Group, has teamed up with Entrepreneur Media to update the second edition of our best-selling book Write Your Business Plan to provide you with a simple, step-by-step process for creating a successful business plan. In the following excerpt, he gives ten tips to gather all of the critical information you will need to succeed.
1. Know your competition.
You need to name them and point out what makes you different from (and better than) each of them. But do not disparage your competition.
2. Know your audience.
You may need several versions of your business plan. For example, you may need one for bankers or venture capitalists, one for individual investors, and one for companies that may want to do a joint venture with you rather than fund you.
3. Have proof to back up every claim you make.
If you expect to be the leader in your field in six months, you have to say why you think that is. If you say your product will take the market by storm, you have to support this statement with facts. If you say your management team is fully qualified to make the business a success, be sure staff resumes demonstrate their experience.
Order Write Your Own Business Plan Now and Get 1 Month of Free Access to Business Planning Software Liveplan Premium
- Easy step-by-step business plan generator
- Built-in financial calculators
- 500+ sample plans and templates
4. Be conservative in all financial estimates and projections.
If you feel certain you'll capture 50 percent of the market in the first year, you can say why you think so and hint at what those numbers may be. But make your financial projections more conservative. For example, a 10 percent market share is much more credible.
5. Be realistic with time and resources available.
If you're working with a big company before you buy a business, you may think things will happen faster than they will once you have to buy the supplies, write the checks, and answer the phones yourself. Being overly optimistic with time and resources is a common error entrepreneurs make. Being realistic is important because it lends credibility to your presentation. Always assume things will take 20 percent longer than you anticipated. Therefore, twenty weeks is now twenty-four weeks.
6. Be logical.
Think like a banker and write what they would want to see.
7. Have a strong management team.
Make sure it has good credentials and expertise. Your team members don't have to have worked in the field. However, you need to draw parallels between what they've done and the skills needed to make your venture succeed. Don't have all the skills you need? Consider adding an advisory board of people skilled in your field and include their resumes.
Write Your Own Business Plan is available now at Entrepreneur Bookstore | Barnes & Noble | Amazon
8. Document why your idea will work.
Have others done something similar that was successful? Have you made a prototype? Include all the variables that can have an impact on the result or outcome of your idea. Show why some of the variables don't apply to your situation or explain how you intend to overcome them or make them better.
9. Describe your facilities and location for performing the work.
That includes equipment you use to create your products and/or services. If you'll need to expand, discuss when, where, and why.
10. Discuss payout options for the investors.
Some investors want a hands-on role. Some want to put associates on your board of directors. Some don't want to be involved in day-to-day activities at all. All investors want to know when they can get their money back and at what rate of return. Most want out within three to five years. Provide a brief description of options for investors, or at least mention that you're ready to discuss options with any serious prospect.
To dig deeper, buy Write Your Own Business Plan and get 1 month of free access to business planning software Liveplan Premium.

Why technology needs to be part of your risk management plan

Why a risk management plan is critical for your business
When your “to-do” list is full of things that feel immediate and concrete, planning for the unexpected may not be your top priority. But managing risks proactively can help avoid negative impacts to your business.
Put simply, a risk management plan helps your business become more resilient. It can help you protect your reputation, minimise losses and avoid wasting time reacting to issues without a clear plan.
What is a risk management plan?
A risk management plan details how you can manage any significant risks that could impact your business. To create one, you first need to identify potential risks. Then assess them to decide which are the most important to consider. And from there you can develop a clear plan to minimise or manage those risks.
There are multiple ways you can approach this. The government offers a range of tools to help businesses with risk management planning.
Identify business risks
It’s important to understand the different types of risks your business might face. It will vary business to business. Some of the areas you might consider include:
- Workplace health and safety risks
- Environmental risks
- Security risks
- Financial risks
- Competitive risks
When exploring financial, legal, or regulatory risks, it’s critical to consider where you need professional help by engaging experts.
Technology and risk management
Many businesses use digital tools to perform critical tasks. From mobile phones to collaboration apps, cloud services, your website, EFTPOS solutions and many more. These tools rely on multiple layers of technology to operate – power, devices, network connectivity and applications that may operate from servers around the world.
As part of risk management planning, you should audit the technology you’re using and how you’re using it. You can then work through any risks you need to manage. Below we explore some things you could consider.
Business applications
What applications do you use and what business functions do they support? If there was an issue with any of these applications, how would it impact your business?
Some business apps may work across multiple devices or offer functionality while offline. This means you and your team may have some flexibility to switch devices or perform some activities even if you’re not connected to a network.
Make sure you set up applications on all relevant devices and you’re clear on any important offline features. This could be helpful in reducing downtime, by refocusing attention to offline activities.
By thinking about these areas before an issue arises, you can develop an action plan. This will let you react more quickly should a disruption occur.
Connectivity
You may have business applications that rely on an internet connection to function. Consider how you connect to the internet and any risks associated with potential network disruptions.
Having more than one way to connect to the internet gives you an alternative if your primary connection is disrupted. So, you might want to consider how to enable your business apps on a range of devices so you can connect via fixed or mobile network options if needed. This can help boost the resilience of your business operations and offer you more flexibility in where and how you work.
- Cyber security
Risks to business and customer data are growing as cyber criminals are becoming more sophisticated. Take time to understand threats such as business email compromise .
There are a range of steps you can take to help protect your business from cyber criminals. They include:
- Staying aware of the latest cyber security trends
- Putting in place steps to get the basics of cyber security right
- Developing a cyber secure mindset
- Training your staff via programs like Cyber Wardens
- Making sure you understand what to do if you're targeted by cyber crime
Think about where and how you use technology
Creating a safe workplace for you, your employees and your customers is also part of risk management planning. This can help minimise injuries and illness.
The shift to remote or hybrid working models has changed the meaning of ‘workplace’ for some businesses. And things are still evolving for many businesses.
Consider how to make hybrid working work for you, your staff and your customers . As part of this, think about your occupational health and safety obligations with respect to remote workers. It’s important to seek specialist advice if you need to.
Digitisation as part of your business continuity plan
The use of new digital technologies can also help you manage certain risks to your business. The Small Business and Family Enterprise Ombudsman highlights how small and family businesses can get more prepared, by digitising critical information.
Implementing the right backup strategy for your data will help ensure you can access it when and where you need to. Choosing solutions with security features built in, can also help you minimise the risks of data breaches.
A risk management plan can help ensure your business future
Thinking about risks to your business proactively and systematically will help you develop a strong risk management plan. Consider how the technology you use might create risks, but also how it can help you minimise risks.
Building digital skills or engaging experts can help you enhance how you manage risks associated with technology and how you use technology to build a resilient business. Involve trusted partners who can help you think about risk management and disaster planning .
A clear action plan for dealing with the risks most likely to impact your business will help give you peace of mind. You’ll be able to react more quickly, should something go wrong and help protect your business into the future.

Connect with confidence, using internet built for business
Get fast business nbn® with help from start to finish using our dedicated nbn connection manager.
Explore more on this topic
- Digitisation
- Business internet

Empower yourself to get the most from technology
Learn how to choose the right technology solutions. Get help to boost efficiency, build skills, and integrate tech.
Other articles you might like

Why is cloud security important for your business?

What is two-factor and multi-factor authentication?

5 cyber security trends for 2024
At Telstra we recognise and acknowledge the existing, original and ancient connection Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples have to the lands and waterways across the Australian continent. We pay our respects to the elders past and present. We commit to working together to build a prosperous and inclusive Australia .
Business Plan Management Structure: What You Need to Know
A business plan management structure can help your business identify its goals, growth plan, and structure for management. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
Business Organization
Every business, regardless of size, needs to have a solid plan in place for how it will be run. Without a business plan, it is nearly impossible to run the company smoothly or successfully. One aspect of the business plan should include the positions in the company and definitions for each position. Those definitions can identify roles and responsibilities, as well as the reporting structure for each role. As the needs of the business change and shift, the business structure likely will change as well. It's easier to make changes as you go when you have a plan in place.
When you're starting a business and need funding, you might not have any employees to fit the roles you have outlined in your plan. This list of roles could be more idealistic for how the company will operate when you have funding and more opportunities to hire employees. Smaller businesses tend to have less complicated needs than larger ones, so the process is usually more streamlined. However, all businesses need to show a clear understanding of workflow and demonstrate how it will be handled through every phase of growth and expansion.
The business plan should include:
- Administration
- Marketing and sales
- Production and distribution of product or service execution
Larger companies need a more detailed organizational plan with procedures that have been well thought out and documented. By creating this detailed plan, you can avoid internal confusion about who is responsible for what as well as avoid duplicated efforts that waste time. When your business runs and operates smoothly, it will be more cost-effective and efficient than a business that is disorganized. With a detailed and informative business plan, it becomes clear to potential investors and employees that you know what you're doing as a business owner. Larger companies may also need additional resources to operate, such as research and development or human resources.
Organizational Structure
You can use graphics to show your company's organizational structure. Simple flowcharts and diagrams offer visual representations of the management levels within your business, as well as the positions that fall beneath each level. With a graphic, it's easier to show the reporting structure and how various departments and divisions work together. This graphic will also help you show the other employee levels within the business.
The lower-level employees are responsible for the daily tasks of the business, so you'll need to identify and recognize the types of individuals you plan to hire, the number of people needed, and their qualifications. You might choose to include details about your hiring plan, such as where you will find employees and their estimated salaries. Don't forget to include your plan for hiring independent contractors, freelance workers, or consultants. Finally, the hiring plan should include any future positions that would be added if the business is able to expand.
Management Team Section of a Business Plan
Your company's management team is essential to business success. The management team is responsible for identifying and analyzing the objectives and goals of the company. After completing these tasks, experienced management professionals can implement and enforce strategies that will lead to success. In your business plan, this team should include the managers, owners, and board of directors (if applicable).
You can include information about the management team in several sections of your business plan, depending on the style. Regardless of where you place the details in the plan, make sure to include information about the company's legal structure and a list of owners. The owner's education, experience, and other related skills should be outlined. Discuss how much of the company each owner has, as well as the role of each owner in the business operations.
If your company has a board of directors, include the name of each member. Along with their names, you should also expand on their experience, background, and credentials, as well as include their contact information. Provide additional details on the contributions provided by each member to the company, along with information about how the members will contribute to the future growth and expansion of the business.
If you need help with a business plan management structure, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Details of a Business Plan
- Creating a Business Plan
- Service Business Plan
- Sample of a Good Business Plan
- LLC Business Plan Template
- Purpose of Business Plan Sample: Everything You Need To Know
- Business Plan for Existing Company
- Do I Need a Business Plan
- Management Plan in a Business Plan
- Parts of Business Plan and Definition

The site navigation utilizes arrow, enter, escape, and space bar key commands. Left and right arrows move across top level links and expand / close menus in sub levels. Up and Down arrows will open main level menus and toggle through sub tier links. Enter and space open menus and escape closes them as well. Tab will move on to the next part of the site rather than go through menu items.
Team Collaboration in Pension Risk Transfer is a Key Ingredient For Success
- Christina Wissman

Pension risk transfer (PRT) is a booming sector of the insurance industry. In this article, originally published in The Actuary , explore the elements of a successful PRT transaction, and how the key teams work together to package a competitive quote for a pension plan.
As recent reports have shown, pension risk transfer (PRT) is a booming sector of the insurance industry. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) says a PRT is “when a defined-benefit pension provider seeks to remove some or all of its obligation to pay guaranteed retirement income or post-retirement benefits to plan participants.” With $52 billion in premiums paid, 2022 was a record year for PRT transactions in the U.S. market, and sales are expected to continue climbing.
What are the elements of a truly successful PRT transaction, and how do the various teams work together to package a competitive quote for a pension plan? I believe multiple functions within a company could come together to become a strong player in the bustling PRT market. In the “recipe” for an efficient PRT deal, these teams are the ingredients. And as with a culinary recipe, the individual ingredients combine to create a dish that is more than the sum of its parts—a carefully crafted transaction that offloads the significant risk of plan liabilities.
The Teams (Ingredients)
Before getting into how the various functions can collaborate to increase effectiveness, it is important to understand the role each function plays in the PRT quote process. Here is information on some (but not all) of the players in a PRT quote.
The PRT pricing function involves setting assumptions and modeling both retirees who have commenced benefits and deferred participants who have not yet commenced benefits. The pricing team then presents a final premium, along with associated metrics, to management. Modeling retirees is usually a simple process similar to modeling an immediate annuity—there are no premiums and all that needs to be modeled is the future stream of payments to the pensioner. The benefit amount and form of payment (e.g., single life, joint and survivor, etc.) are already known. However, modeling deferred participants is more complicated and involves setting election assumptions (such as age at commencement and form of payment) and interpreting plan provisions to correctly calculate future payments.
Business Development and Project Management
The business development and project management functions are the main connection between the broker and the rest of the team on a given transaction. They are responsible for communicating all information regarding the transaction to the various internal teams and setting frequent check-ins. Additionally, if any of the functions have questions for the broker regarding any aspect of the transaction, the business development team is expected to pass along the questions and relay any responses.
Together, business development and pricing develop a competitive strategy that provides attractive premiums to clients at return levels acceptable to the company.
Because PRT transactions often have quick and inflexible timelines compared to the pricing of other insurance products, it is critical that a project plan runs on schedule. A delay for any deliverable risks not getting a premium out on the day of the bid. Together, business development and pricing develop a competitive strategy that provides attractive premiums to clients at return levels acceptable to the company.
Investments
The investments team is responsible for creating an investment and reinvestment strategy for a given transaction that results in either an earned rate or an asset portfolio for asset and liability modeling. The request for proposal (RFP) for a transaction will specify what market date to use for all rounds of bidding. Because the earned rate or asset portfolio will need to be provided at an earlier date for purposes of working on pricing, the investments team should monitor how markets are moving in the weeks and days leading up to the quote so the pricing team can adjust accordingly.
Investments has additional work when the plan requests quotes on both a cash and assets-in-kind (AIK) basis. For a cash quote, the plan will pay the premium amount in cash or cash-equivalent assets. For an AIK quote, the plan will replace some of the cash with existing assets. As part of an AIK transaction, the investments function must sift through the list of the plan’s available assets and determine which they would accept or reject as a part of the transaction. Depending on the insurer’s investment strategy, cash vs. AIK quotes may result in different premiums.

How collaboration can enhance the work product (The Recipe)
For the sake of brevity, these examples focus on collaboration among the pricing function and the other functions. However, all teams working on a PRT transaction can employ creative strategies to effectively collaborate with other functions.
The pricing team can enhance the business development team’s project plan by providing estimates for key pricing deliverables and explaining any tight deadlines. Throughout the process, the pricing team can keep the business development team up to date on any progress, so they can have a good idea of how the process is moving.
When developing a premium for a quote, the pricing team should communicate with the business development team on which combination of results and metrics is useful for review. PRT quote processes usually involve at least two rounds: a preliminary and a final quotation. Between the preliminary and final quotations, it is suggested that pricing and business development align on follow-up questions or outstanding assumptions. They also should collaborate on current assumptions, outstanding unknowns and any anticipated changes to the pricing request. Strong collaboration between the business development and pricing teams allows for more clarity in obtaining approvals during internal governance processes and, ultimately, developing the final quotation.
At minimum, pricing will provide the investments team with best-estimate cash flows or some duration target to start building a portfolio. However, the more information that pricing provides, the more effectively investments can build the portfolio.
By providing alternate cash-flow scenarios, pricing can assist investments in understanding and managing the underlying risks.
For example, a material deferred population will include additional participant optionality, which could require more dynamic future portfolio management. In addition, the underlying investment portfolio may differ for a buyout vs. a buy-in transaction. In a buyout transaction, the administration of and responsibility for payments will transfer to the chosen bidder in a relatively quick time frame—usually a few months. A buy-in transaction results in a longer transition period where the plan still administers the business before it ultimately transfers responsibility to the chosen bidder. During the transition period, the plan also may offer a lump-sum window to deferred participants, which creates more uncertainty around the size and shape of future cash flows. By providing alternate cash-flow scenarios in these situations, pricing can assist investments in understanding and managing the underlying risks.
Although the pricing team members may be the go-to experts in liability modeling most of the time, this collaboration with the investments team can enhance their asset knowledge as well.
Once a deal is won, in-force management would take models from the pricing team to register the transaction in the company’s systems and model and monitor the future course of the business. Pricing and in-force management can work together to prepare for the deliverables the in-force management team will require if a deal is won. This will ensure a smoother transition and reduce the need for the in-force management team to request files piecemeal.
Because the pricing team was working with the business development team during the presale process, they will be the experts on product features and plan provisions. Pricing professionals should be prepared to field questions about the transaction from in-force management as they set up their models. As stated previously, the pricing team also can serve as a resource during the data true-up process.
Knowing that the in-force management team will rely on the pricing team’s models and files, the pricing team can sharpen their documentation and model management skills to ensure that the in-force management team receives the most recent versions of all files and that files are organized and easy to use.
Create your own recipe
Within a complex PRT transaction, each team can fulfill its basic function fairly independently. However, when teams collaborate and share information, each team can find ways to do its individual job more effectively, which benefits the project as a whole.
While collaboration is key to the recipe for success, how the teams (ingredients) work together best will be different for every company. Think about how your team is currently operating and consider how the various functions can elevate one another through 1+1=3 collaborations. Similarly, don’t be afraid to try adding new ingredients. Are there any teams not currently included in the PRT quote process that could provide value?
Whatever the mix of ingredients, the goal of the recipe is the same: Efficiently and effectively craft a risk transfer approach that offloads risk, stabilizes liability profiles and simplifies investment strategies.
More Like This...
- Articles October 2022 Global Financial Solutions: North America | Ryan Stevens Read More about Global Financial Solutions: North America | Ryan Stevens
- Articles March 2024 Defusing the Pension Time Bomb: Lessons from pension risk transfer Read More about Defusing the Pension Time Bomb: Lessons from pension risk transfer
- Articles March 2024 Financial Insights and Strategy | Laura Cockrill Read More about Financial Insights and Strategy | Laura Cockrill
- View All RGA Articles
Related Solutions
- Reinsurance Solutions
- Financial Solutions
- View All RGA Solutions
Meet the Authors & Experts

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
US judge in Nevada hands wild horse advocates rare victory in ruling on mustang management plans
FILE - A wild horse stands on a hillside on the Fort McDermitt Paiute-Shoshone Indian Reservation, April 24, 2023, near McDermitt, Nev. Wild horse advocates in Nevada scored a rare legal victory when a federal judge in Reno, Nev., ruled Thursday, March 28, 2024, that U.S. land managers failed to adopt a legal herd management plan or conduct the necessary environmental review before 31 mustangs died during the roundup of more than 2,000 animals in Nevada the previous summer. (AP Photo/Rick Bowmer, File)
- Copy Link copied
RENO, Nev. (AP) — In a rare legal victory for wild horse advocates, a judge has ruled U.S. land managers failed to adopt a legal herd management plan or conduct the necessary environmental review before 31 mustangs died during the roundup of more than 2,000 horses in Nevada last summer.
U.S. District Court Judge Miranda Du in Reno ordered the Bureau of Land Management to complete a formal herd management plan for the Pancake complex in eastern Nevada by next March 24. She also ordered the agency to reopen an environmental assessment to include the potential impact of roundups on wildfire risks.
Du specifically rejected the argument the agency has made for years that its broader resource management plans combined with individual roundup plans for overpopulated herds satisfies the requirement that it adopt a formal herd management area plan (HMAP) for the long-term health of the herds and the rangeland in a particular area or herd complex.
“The court finds that BLM must be compelled to prepare a herd management area plan (HMAP),” Du wrote in the 29-page ruling issued Thursday.
Horse advocates who cheered the ruling said that while it comes too late for the horses that were captured or killed last summer, it sets a precedent that will help provide more protection for mustangs roaming federal lands in the West going forward.
“This is an amazing day for our beloved wild ones.” said Laura Leigh, founder and president of the lead plaintiff in the case, Nevada-based Wild Horse Education.
“The Wild Free-Roaming Horses and Burros Act is about more than just removal. Today, the court affirmed the intention of that law,” she said Friday.
A spokesman for the Bureau of Land Management said Friday the agency was reviewing the ruling but had no immediate comment.
Last summer, another U.S. judge in Reno refused to grant an injunction sought by horse advocates to halt the roundup that was underway after dozens of horses died during the roundup.
Judge Larry Hicks concluded in August the agency had not violated laws protecting the animals from inhumane treatment. But he allowed Wild Horse Education to continue with the lawsuit it first filed in 2022 that alleged the agency was acting illegally because it never implemented the herd management plan that was required since the management area was established in 1986.
Du did not address allegations of inhumane treatment of the animals. She agreed with the agency’s argument that it had the authority to round up horses as soon as it determined the herd was overpopulated. And she rejected horse advocates’ attempt to force the agency to specifically consider cutbacks in livestock grazing or incorporate different procedures to estimate the sizes of herds.
But Du said the bureau could not continue to respond to lawsuits by explaining it was still in the process of completing a formal herd management area plan (HMAP) with no definitive assurance it actually would complete one.
“The duty to prepare an HMPA arose as soon as the BLM created the HMAs,” Du wrote. “That duty arose when BLM promulgated the regulation 38 years ago in 1986. BLM’s decades-long delays in developing and approving HMAPs have therefore been ‘nothing short of egregious’ and clearly violate the rule of reason.”
Leigh said that, among other things, the agency’s failure to complete the plan denied the public a chance to address how forage is divided between horses and livestock, herd genetics can be preserved or mitigation measures can be adopted for mining and livestock expanding in the area.
“For over 12 years I have been trying to address critical issues of on-range management planning with BLM and have been repeatedly denied,” Leigh said. “This ruling has finally opened the door to advocacy and actually has the opportunity to engage in management practices.”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The management section of a business plan helps show how your management team and company are structured. The first section shows the ownership structure, which might be a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation. The internal management section shows the department heads, including sales, marketing, administration, and production.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
A business plan is a document that communicates a company's goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered. A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals.
The management section of your business plan is an excellent space to highlight the members of your management team. Tell your readers and potential investors who will be managing your company, where they come from, how they will help your venture, and anything else that will signal your venture's future success.
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Growth plan: An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up. Internal plan: A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders - ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts. Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture. 2. Feasibility Business Plan. This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing ...
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
In your business plan's Organization and Management section, please provide a detailed description of your team. Y ou will discuss the company's management team, starting with the owners. This section highlights who is involved in the running of your business and who are the support professionals. It also includes the roles and ...
This section of your business plan, Organization and Management, is where you'll explain exactly how you're set up to make your ideas happen, plus you'll introduce the players on your team. As always, remember your audience. If this is a plan for your internal use, you can be a little more general than if you'll be presenting it to a ...
Every business plan has key sections such as management and marketing. It should also have an executive summary, which is a synopsis of each of the plan sections in a one- to two-page overview.
A management team business plan is a section of a proposal that indicates the credentials and expertise of a team of managers in a company. Its purpose is to show prospective investors that the professionals your company has appointed are educated and experienced, making them capable of fulfilling leadership positions.
A management plan describes how an organization or business is run. Writing a management plan allows you to formalize your management structure and operations. It also ensures that everyone is on the same page and that your goals will be accomplished. You can easily write your own management plan with a few simple steps.
By definition, a Business Management System refers to a set of tools for planning and implementing the various policies, guidelines, and procedures of an organization to execute its business plan. Having a Business Management system lays down a solid foundation for the successful implementation of strategic and tactical business decisions to ...
A goal without a plan is just a wish." In any business, you may have multiple operations running at any given time. It's necessary to stay on track with all these operations and the management of a firm plays a pivotal role in making sure they are carried out smoothly.. Managers need to be two steps ahead and prepare for any possible threats and anticipate upcoming changes.
An unrealistic plan is as unattractive to investors as a lack of vision and ambition. 3. Seek professional input. Don't be afraid to ask for help. Experienced business advisors, accountants, and ...
1. Know your competition. You need to name them and point out what makes you different from (and better than) each of them. But do not disparage your competition. Continue reading. 2. Know your ...
Business continuity management (BCM) is a strategic framework for enabling organizations to rapidly restore their operations in the event of a disaster. It includes identifying potential risks, such as natural disasters or cyberattacks, and implementing measures and protocols to reduce the impact that such adverse events could have on business ...
A risk management plan can help ensure your business future. Thinking about risks to your business proactively and systematically will help you develop a strong risk management plan. Consider how the technology you use might create risks, but also how it can help you minimise risks. Building digital skills or engaging experts can help you ...
The management team is responsible for identifying and analyzing the objectives and goals of the company. After completing these tasks, experienced management professionals can implement and enforce strategies that will lead to success. In your business plan, this team should include the managers, owners, and board of directors (if applicable ...
NWCG's Publication Management System (PMS) includes standards, guides, job aids, position taskbooks, training curricula, and other documents. Publications are distributed through hardcopy print, web pages, mobile device applications, and other digital media. NWCG web portals include key information that is updated on a continuous schedule.
Business Development and Project Management. ... The pricing team can enhance the business development team's project plan by providing estimates for key pricing deliverables and explaining any tight deadlines. Throughout the process, the pricing team can keep the business development team up to date on any progress, so they can have a good ...
"The court finds that BLM must be compelled to prepare a herd management area plan (HMAP)," Du wrote in the 29-page ruling issued Thursday. Horse advocates who cheered the ruling said that while it comes too late for the horses that were captured or killed last summer, it sets a precedent that will help provide more protection for mustangs roaming federal lands in the West going forward.
The strategic plan also described risk management and the role it plays in the safety enterprise. While there are inherent risks in all the DAF does, DAF safety incorporates policy development, systems acquisitions and testing, operational procedures, and data analysis to manage that risk and to support Airmen and Guardians.