
- Research guides

Writing a Literature Review
Phase 1: scope of review, it's a literature review of what, precisely.
Need to Have a Precise Topic It is essential that one defines a research topic very carefully. For example, it should not be too far-reaching. The following is much too broad:
"Life and Times of Sigmund Freud"
However, this is more focused and specific and, accordingly, a more appropriate topic:
"An Analysis of the Relationship of Freud and Jung in the International Psychoanalytic Association, 1910-1914"
Limitations of Study In specifying precisely one's research topic, one is also specifying appropriate limitations on the research. Limiting, for example, by time, personnel, gender, age, location, nationality, etc. results in a more focused and meaningful topic.
Scope of the Literature Review It is also important to determine the precise scope of the literature review. For example,
- What exactly will you cover in your review?
- How comprehensive will it be?
- How long? About how many citations will you use?
- How detailed? Will it be a review of ALL relevant material or will the scope be limited to more recent material, e.g., the last five years.
- Are you focusing on methodological approaches; on theoretical issues; on qualitative or quantitative research?
- Will you broaden your search to seek literature in related disciplines?
- Will you confine your reviewed material to English language only or will you include research in other languages too?
In evaluating studies, timeliness is more significant for some subjects than others. Scientists generally need more recent material. However, currency is often less of a factor for scholars in arts/humanities. Research published in 1920 about Plato's philosophy might be more relevant than recent studies.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Phase 2: Finding Information >>
- Last Updated: Dec 5, 2023 2:26 PM
- Subjects: Education , General
- Tags: literature_review , literature_review_in_education

What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
| Annotated Bibliography | Literature Review | |
| Purpose | List of citations of books, articles, and other sources with a brief description (annotation) of each source. | Comprehensive and critical analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. |
| Focus | Summary and evaluation of each source, including its relevance, methodology, and key findings. | Provides an overview of the current state of knowledge on a particular subject and identifies gaps, trends, and patterns in existing literature. |
| Structure | Each citation is followed by a concise paragraph (annotation) that describes the source’s content, methodology, and its contribution to the topic. | The literature review is organized thematically or chronologically and involves a synthesis of the findings from different sources to build a narrative or argument. |
| Length | Typically 100-200 words | Length of literature review ranges from a few pages to several chapters |
| Independence | Each source is treated separately, with less emphasis on synthesizing the information across sources. | The writer synthesizes information from multiple sources to present a cohesive overview of the topic. |
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, academic integrity vs academic dishonesty: types & examples, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , the ai revolution: authors’ role in upholding academic..., the future of academia: how ai tools are..., how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide).

Main Navigation Menu
Writing a literature review.
- Definitions
Determine the scope of your review
A review of what, planning your literature review.
- Finding sources
- Annotating sources
- Organizing the review
- Writing the review
- Practical Tips
The length of the review depends on your objective.
- Are you writing a research paper as the final project in a specific course?
- Are you writing a senior or honor's capstone project or thesis?
- Are you writing for an undergraduate or graduate course?
- Are you writing a master's thesis?
- Are you writing a dissertation?
The majority of these projects will require a selective examination of the literature. Discuss the length of your review with your instructor or paper advisor.
- You must have a precise question to study. For example, your question cannot be too broad, nor too narrow.
- You must understand the limitations of your research. Limiting by time, geographic area, gender, age, and/or nationality are all good ways to develop a more focused topic.
- what will you cover?
- will your coverage be selective or exhaustive?
- are you focusing on a specific theory or methodology; a specific type of research?
- will you include information published in other languages?
- will you include information from related disciplines?
It will take time to locate and review the literature relevant to your research question. Starting early will allow you sufficient time to gather and review your sources. The process of writing a literature review normally includes the following elements:
1. Defining your research question
2. Planning the approach to your review and research
3. Searching the literature
4. Analyzing the material you find
5. Organizing the review
6. Writing the review
- << Previous: Definitions
- Next: Finding sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 13, 2024 8:36 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucmo.edu/literaturereview
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Aug 8, 2024 11:00 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview
Scoping Reviews
- Introduction
- Guidelines & procedures
- Management tools
- Define the question
- Check the topic
- Determine inclusion/exclusion criteria
- Develop a protocol
- Identify keywords
- Databases and search strategies
- Grey literature
- Manage and organise
- Screen & Select
- Locate full text
- Extract data
Example reviews
- Examples of scoping reviews
- Accessing help This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Style Reviews Guide This link opens in a new window
Please choose the tab below for your discipline to see relevant examples.
For more information about how to conduct and write reviews, please see the Guidelines section of this guide.
- Health & medicine
- Social sciences
- Technologically-enhanced psychological interventions for older adults: A scoping review. (2020).
- The effects of Toxic Early Childhood Experiences on depression according to Young Schema Model: A scoping review. (2019).
Rehab sciences
- Occupational therapists' contributions to fostering older adults' social participation: A scoping review. (2018).
- Physiotherapy interventions for people with dementia and a hip fracture—a scoping review of the literature. (2017).
- Speech, language and swallowing impairments in functional neurological disorder: A scoping review. (2019).
Veterinary sciences
- A scoping review of the evidence for efficacy of acupuncture in companion animals. (2017).
- Scoping review of indicators and methods of measurement used to evaluate the impact of dog population management interventions. (2017).
- Promoting social creativity in science education with digital technology to overcome inequalities: A scoping review. (2019).
- Simulation in social work education: A scoping review. (2020).
- Performance management: A scoping review of the literature and an agenda for future research. (2019).
- A scoping review of feed interventions and livelihoods of small-scale livestock keepers. (2020).
- Ice-jam flood research: A scoping review. (2018).
- << Previous: Publish
- Next: Accessing help >>
- Last Updated: Aug 28, 2024 3:06 PM
- URL: https://libguides.jcu.edu.au/scoping

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved August 29, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Online resources available. Physical building closed due to inclement weather

Take the Library Survey and enter to win a prize!
Literature review.
- Introduction to Literature Reviews
- Purpose and Scope
- Types of Lit Reviews
- Finding Published Literature Reviews
- Writing the Lit Review
- Books and Websites
The literature review analyzes relationships and connections among different works. This differs from an annotated bibliography which provides a list and brief description of articles, books, theses, and other documents. The literature review should not merely list and summarize one piece of research after another.
Through analysis of major works and subsequent scholarship the lit review lays out the evolution of scholarship on a topic and establishes a context for further research. This will help you to establish why the topic is important and place your research in a theoretical context.
A literature review will help you to avoid redundancy in your own research and to identify new problems, possibilities for further research, and to expand upon or ask new questions. The literature review allows you as a researcher to enter into an ongoing conversation with other scholars and researchers.
A literature review may be comprehensive or selective but should examine seminal or principal works and works that have been consequential in the field. The scope of a literature review will vary by assignment and discipline. The literature review may be part of a larger work or a stand-alone article, meaning that it is the entirety of a paper. The literature review may be part of the introduction, or a separate section to a thesis, dissertation, or research report setting up the context for the author's original research. The literature review:
- Compares and contrasts
- Identifies areas of consensus and dissent
- Reveals gaps or oversights
- Indicates areas needing further research
- Points out trends, themes, approaches, methodologies, theories, and frames of analysis
- Discusses major debates in the field
- Examines methodological or theoretical strengths and weaknesses
The importance of currency (timeliness of information) will vary by discipline and the purpose of the assignment. The sciences are typically more concerned with current research, practice, and findings. For example, in fields like health or medicine the lit review may only draw on recent literature which has been published within 5-10 years. However, inclusion of much older works is often relevant in fields such as the arts, humanities, philosophy, or history.
- << Previous: Introduction to Literature Reviews
- Next: Types of Lit Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Aug 29, 2024 1:40 PM
- URL: https://utopia.ut.edu/literaturereviews
Macdonald-Kelce Library - The University of Tampa - 401 W. Kennedy Blvd. - Tampa, FL 33606 - 813 257-3056 - [email protected] - Accessibility

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Trinity College Dublin, The University of Dublin

Trinity Search
Trinity menu.
- Faculties and Schools
- Trinity Courses
- Trinity Research
Writing a Literature Review
- Getting Started
Defining the topic
Limiting the scope.
- Finding the Literature
- Developing a Search Strategy
- Managing Your Research
- Writing the Review
- Systematic Reviews and Other Review Types
- Useful Books
- Useful Videos
- Useful Links
- Commonly Used Terms
Identifying a well-defined research question is the first step for writing a literature review. It should focus on something from the research field that needs to be explored, where there are gaps in the information. This will ensure that your contribution is valuable and that you are providing readers with a different angle or perspective on an issue or problem.
Your topic needs to be given careful consideration. A research question like “why are social networking sites harmful?” is too broad; there will be too much information to write a concise literature review. Change it to “how are online users experiencing or addressing privacy issues on Twitter and Facebook?" and it is more specific. It gives you a niche within the research field to focus on and explore.
Sometimes a broad topic can be narrowed by using one or more extra criteria, which can include:
- population group
- culture/ethnicity
- theoretical framework
- methodology (e.g., qualitative or quantitative, fieldwork/ethnography)
| Smoking cessation | Mindfulness therapeutic intervention in aiding smoking cessation |
| Social media in college and university | Use of Instagram and Twitter in university classrooms for educational purposes |
| Effect on the environment from global warming | Effect of glacial melting on penguins in Antarctica |
How you narrow the scope can be done in two broad ways, detailed in Developing a Search Strategy :
- add more search strands using AND to give fewer results (see Combining your terms: search operators )
- use "filters" in a database to eliminate results from outside those limits (see Using methodological search filters )
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Finding the Literature >>
- Last Updated: Oct 10, 2023 1:52 PM
- URL: https://libguides.tcd.ie/literature-reviews
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.

How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
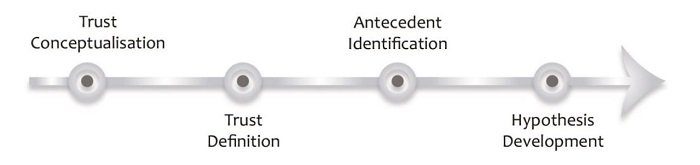
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
28 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Asking questions are actually fastidious thing if you are not understanding anything fully, but this article presents good understanding yet.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
- Privacy Policy

Home » Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Literature Review
Definition:
A literature review is a comprehensive and critical analysis of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It involves identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant literature, including scholarly articles, books, and other sources, to provide a summary and critical assessment of what is known about the topic.
Types of Literature Review
Types of Literature Review are as follows:
- Narrative literature review : This type of review involves a comprehensive summary and critical analysis of the available literature on a particular topic or research question. It is often used as an introductory section of a research paper.
- Systematic literature review: This is a rigorous and structured review that follows a pre-defined protocol to identify, evaluate, and synthesize all relevant studies on a specific research question. It is often used in evidence-based practice and systematic reviews.
- Meta-analysis: This is a quantitative review that uses statistical methods to combine data from multiple studies to derive a summary effect size. It provides a more precise estimate of the overall effect than any individual study.
- Scoping review: This is a preliminary review that aims to map the existing literature on a broad topic area to identify research gaps and areas for further investigation.
- Critical literature review : This type of review evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a critical analysis of the literature and identify areas where further research is needed.
- Conceptual literature review: This review synthesizes and integrates theories and concepts from multiple sources to provide a new perspective on a particular topic. It aims to provide a theoretical framework for understanding a particular research question.
- Rapid literature review: This is a quick review that provides a snapshot of the current state of knowledge on a specific research question or topic. It is often used when time and resources are limited.
- Thematic literature review : This review identifies and analyzes common themes and patterns across a body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the literature and identify key themes and concepts.
- Realist literature review: This review is often used in social science research and aims to identify how and why certain interventions work in certain contexts. It takes into account the context and complexities of real-world situations.
- State-of-the-art literature review : This type of review provides an overview of the current state of knowledge in a particular field, highlighting the most recent and relevant research. It is often used in fields where knowledge is rapidly evolving, such as technology or medicine.
- Integrative literature review: This type of review synthesizes and integrates findings from multiple studies on a particular topic to identify patterns, themes, and gaps in the literature. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Umbrella literature review : This review is used to provide a broad overview of a large and diverse body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to identify common themes and patterns across different areas of research.
- Historical literature review: This type of review examines the historical development of research on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a historical context for understanding the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Problem-oriented literature review : This review focuses on a specific problem or issue and examines the literature to identify potential solutions or interventions. It aims to provide practical recommendations for addressing a particular problem or issue.
- Mixed-methods literature review : This type of review combines quantitative and qualitative methods to synthesize and analyze the available literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research question by combining different types of evidence.
Parts of Literature Review
Parts of a literature review are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction of a literature review typically provides background information on the research topic and why it is important. It outlines the objectives of the review, the research question or hypothesis, and the scope of the review.
Literature Search
This section outlines the search strategy and databases used to identify relevant literature. The search terms used, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and any limitations of the search are described.
Literature Analysis
The literature analysis is the main body of the literature review. This section summarizes and synthesizes the literature that is relevant to the research question or hypothesis. The review should be organized thematically, chronologically, or by methodology, depending on the research objectives.
Critical Evaluation
Critical evaluation involves assessing the quality and validity of the literature. This includes evaluating the reliability and validity of the studies reviewed, the methodology used, and the strength of the evidence.
The conclusion of the literature review should summarize the main findings, identify any gaps in the literature, and suggest areas for future research. It should also reiterate the importance of the research question or hypothesis and the contribution of the literature review to the overall research project.
The references list includes all the sources cited in the literature review, and follows a specific referencing style (e.g., APA, MLA, Harvard).
How to write Literature Review
Here are some steps to follow when writing a literature review:
- Define your research question or topic : Before starting your literature review, it is essential to define your research question or topic. This will help you identify relevant literature and determine the scope of your review.
- Conduct a comprehensive search: Use databases and search engines to find relevant literature. Look for peer-reviewed articles, books, and other academic sources that are relevant to your research question or topic.
- Evaluate the sources: Once you have found potential sources, evaluate them critically to determine their relevance, credibility, and quality. Look for recent publications, reputable authors, and reliable sources of data and evidence.
- Organize your sources: Group the sources by theme, method, or research question. This will help you identify similarities and differences among the literature, and provide a structure for your literature review.
- Analyze and synthesize the literature : Analyze each source in depth, identifying the key findings, methodologies, and conclusions. Then, synthesize the information from the sources, identifying patterns and themes in the literature.
- Write the literature review : Start with an introduction that provides an overview of the topic and the purpose of the literature review. Then, organize the literature according to your chosen structure, and analyze and synthesize the sources. Finally, provide a conclusion that summarizes the key findings of the literature review, identifies gaps in knowledge, and suggests areas for future research.
- Edit and proofread: Once you have written your literature review, edit and proofread it carefully to ensure that it is well-organized, clear, and concise.
Examples of Literature Review
Here’s an example of how a literature review can be conducted for a thesis on the topic of “ The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers’ Mental Health”:
- Start by identifying the key terms related to your research topic. In this case, the key terms are “social media,” “teenagers,” and “mental health.”
- Use academic databases like Google Scholar, JSTOR, or PubMed to search for relevant articles, books, and other publications. Use these keywords in your search to narrow down your results.
- Evaluate the sources you find to determine if they are relevant to your research question. You may want to consider the publication date, author’s credentials, and the journal or book publisher.
- Begin reading and taking notes on each source, paying attention to key findings, methodologies used, and any gaps in the research.
- Organize your findings into themes or categories. For example, you might categorize your sources into those that examine the impact of social media on self-esteem, those that explore the effects of cyberbullying, and those that investigate the relationship between social media use and depression.
- Synthesize your findings by summarizing the key themes and highlighting any gaps or inconsistencies in the research. Identify areas where further research is needed.
- Use your literature review to inform your research questions and hypotheses for your thesis.
For example, after conducting a literature review on the impact of social media on teenagers’ mental health, a thesis might look like this:
“Using a mixed-methods approach, this study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes in teenagers. Specifically, the study will examine the effects of cyberbullying, social comparison, and excessive social media use on self-esteem, anxiety, and depression. Through an analysis of survey data and qualitative interviews with teenagers, the study will provide insight into the complex relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes, and identify strategies for promoting positive mental health outcomes in young people.”
Reference: Smith, J., Jones, M., & Lee, S. (2019). The effects of social media use on adolescent mental health: A systematic review. Journal of Adolescent Health, 65(2), 154-165. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2019.03.024
Reference Example: Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range. doi:0000000/000000000000 or URL

Applications of Literature Review
some applications of literature review in different fields:
- Social Sciences: In social sciences, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing research, to develop research questions, and to provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as sociology, psychology, anthropology, and political science.
- Natural Sciences: In natural sciences, literature reviews are used to summarize and evaluate the current state of knowledge in a particular field or subfield. Literature reviews can help researchers identify areas where more research is needed and provide insights into the latest developments in a particular field. Fields such as biology, chemistry, and physics commonly use literature reviews.
- Health Sciences: In health sciences, literature reviews are used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments, identify best practices, and determine areas where more research is needed. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as medicine, nursing, and public health.
- Humanities: In humanities, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing knowledge, develop new interpretations of texts or cultural artifacts, and provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as history, literary studies, and philosophy.
Role of Literature Review in Research
Here are some applications of literature review in research:
- Identifying Research Gaps : Literature review helps researchers identify gaps in existing research and literature related to their research question. This allows them to develop new research questions and hypotheses to fill those gaps.
- Developing Theoretical Framework: Literature review helps researchers develop a theoretical framework for their research. By analyzing and synthesizing existing literature, researchers can identify the key concepts, theories, and models that are relevant to their research.
- Selecting Research Methods : Literature review helps researchers select appropriate research methods and techniques based on previous research. It also helps researchers to identify potential biases or limitations of certain methods and techniques.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Literature review helps researchers in data collection and analysis by providing a foundation for the development of data collection instruments and methods. It also helps researchers to identify relevant data sources and identify potential data analysis techniques.
- Communicating Results: Literature review helps researchers to communicate their results effectively by providing a context for their research. It also helps to justify the significance of their findings in relation to existing research and literature.
Purpose of Literature Review
Some of the specific purposes of a literature review are as follows:
- To provide context: A literature review helps to provide context for your research by situating it within the broader body of literature on the topic.
- To identify gaps and inconsistencies: A literature review helps to identify areas where further research is needed or where there are inconsistencies in the existing literature.
- To synthesize information: A literature review helps to synthesize the information from multiple sources and present a coherent and comprehensive picture of the current state of knowledge on the topic.
- To identify key concepts and theories : A literature review helps to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to your research question and provide a theoretical framework for your study.
- To inform research design: A literature review can inform the design of your research study by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
Characteristics of Literature Review
Some Characteristics of Literature Review are as follows:
- Identifying gaps in knowledge: A literature review helps to identify gaps in the existing knowledge and research on a specific topic or research question. By analyzing and synthesizing the literature, you can identify areas where further research is needed and where new insights can be gained.
- Establishing the significance of your research: A literature review helps to establish the significance of your own research by placing it in the context of existing research. By demonstrating the relevance of your research to the existing literature, you can establish its importance and value.
- Informing research design and methodology : A literature review helps to inform research design and methodology by identifying the most appropriate research methods, techniques, and instruments. By reviewing the literature, you can identify the strengths and limitations of different research methods and techniques, and select the most appropriate ones for your own research.
- Supporting arguments and claims: A literature review provides evidence to support arguments and claims made in academic writing. By citing and analyzing the literature, you can provide a solid foundation for your own arguments and claims.
- I dentifying potential collaborators and mentors: A literature review can help identify potential collaborators and mentors by identifying researchers and practitioners who are working on related topics or using similar methods. By building relationships with these individuals, you can gain valuable insights and support for your own research and practice.
- Keeping up-to-date with the latest research : A literature review helps to keep you up-to-date with the latest research on a specific topic or research question. By regularly reviewing the literature, you can stay informed about the latest findings and developments in your field.
Advantages of Literature Review
There are several advantages to conducting a literature review as part of a research project, including:
- Establishing the significance of the research : A literature review helps to establish the significance of the research by demonstrating the gap or problem in the existing literature that the study aims to address.
- Identifying key concepts and theories: A literature review can help to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to the research question, and provide a theoretical framework for the study.
- Supporting the research methodology : A literature review can inform the research methodology by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
- Providing a comprehensive overview of the literature : A literature review provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge on a topic, allowing the researcher to identify key themes, debates, and areas of agreement or disagreement.
- Identifying potential research questions: A literature review can help to identify potential research questions and areas for further investigation.
- Avoiding duplication of research: A literature review can help to avoid duplication of research by identifying what has already been done on a topic, and what remains to be done.
- Enhancing the credibility of the research : A literature review helps to enhance the credibility of the research by demonstrating the researcher’s knowledge of the existing literature and their ability to situate their research within a broader context.
Limitations of Literature Review
Limitations of Literature Review are as follows:
- Limited scope : Literature reviews can only cover the existing literature on a particular topic, which may be limited in scope or depth.
- Publication bias : Literature reviews may be influenced by publication bias, which occurs when researchers are more likely to publish positive results than negative ones. This can lead to an incomplete or biased picture of the literature.
- Quality of sources : The quality of the literature reviewed can vary widely, and not all sources may be reliable or valid.
- Time-limited: Literature reviews can become quickly outdated as new research is published, making it difficult to keep up with the latest developments in a field.
- Subjective interpretation : Literature reviews can be subjective, and the interpretation of the findings can vary depending on the researcher’s perspective or bias.
- Lack of original data : Literature reviews do not generate new data, but rather rely on the analysis of existing studies.
- Risk of plagiarism: It is important to ensure that literature reviews do not inadvertently contain plagiarism, which can occur when researchers use the work of others without proper attribution.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to...

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Future Research – Thesis Guide
Jump to navigation

Cochrane Training
Chapter 2: determining the scope of the review and the questions it will address.
James Thomas, Dylan Kneale, Joanne E McKenzie, Sue E Brennan, Soumyadeep Bhaumik
Key Points:
- Systematic reviews should address answerable questions and fill important gaps in knowledge.
- Developing good review questions takes time, expertise and engagement with intended users of the review.
- Cochrane Reviews can focus on broad questions, or be more narrowly defined. There are advantages and disadvantages of each.
- Logic models are a way of documenting how interventions, particularly complex interventions, are intended to ‘work’, and can be used to refine review questions and the broader scope of the review.
- Using priority-setting exercises, involving relevant stakeholders, and ensuring that the review takes account of issues relating to equity can be strategies for ensuring that the scope and focus of reviews address the right questions.
Cite this chapter as: Thomas J, Kneale D, McKenzie JE, Brennan SE, Bhaumik S. Chapter 2: Determining the scope of the review and the questions it will address. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.4 (updated August 2023). Cochrane, 2023. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
2.1 Rationale for well-formulated questions
As with any research, the first and most important decision in preparing a systematic review is to determine its focus. This is best done by clearly framing the questions the review seeks to answer. The focus of any Cochrane Review should be on questions that are important to people making decisions about health or health care. These decisions will usually need to take into account both the benefits and harms of interventions (see MECIR Box 2.1.a ). Good review questions often take time to develop, requiring engagement with not only the subject area, but with a wide group of stakeholders (Section 2.4.2 ).
Well-formulated questions will guide many aspects of the review process, including determining eligibility criteria, searching for studies, collecting data from included studies, structuring the syntheses and presenting findings (Cooper 1984, Hedges 1994, Oliver et al 2017) . In Cochrane Reviews, questions are stated broadly as review ‘Objectives’, and operationalized in terms of the studies that will be eligible to answer those questions as ‘Criteria for considering studies for this review’. As well as focusing review conduct, the contents of these sections are used by readers in their initial assessments of whether the review is likely to be directly relevant to the issues they face.
The FINER criteria have been proposed as encapsulating the issues that should be addressed when developing research questions. These state that questions should be F easible, I nteresting, N ovel, E thical, and R elevant (Cummings et al 2007). All of these criteria raise important issues for consideration at the outset of a review and should be borne in mind when questions are formulated.
A feasible review is one that asks a question that the author team is capable of addressing using the evidence available. Issues concerning the breadth of a review are discussed in Section 2.3.1 , but in terms of feasibility it is important not to ask a question that will result in retrieving unmanageable quantities of information; up-front scoping work will help authors to define sensible boundaries for their reviews. Likewise, while it can be useful to identify gaps in the evidence base, review authors and stakeholders should be aware of the possibility of asking a question that may not be answerable using the existing evidence (i.e. that will result in an ‘empty’ review, see also Section 2.5.3 ).
Embarking on a review that authors are interested in is important because reviews are a significant undertaking and review authors need sufficient commitment to see the work through to its conclusion.
A novel review will address a genuine gap in knowledge, so review authors should be aware of any related or overlapping reviews. This reduces duplication of effort, and also ensures that authors understand the wider research context to which their review will contribute. Authors should check for pre-existing syntheses in the published research literature and also for ongoing reviews in the PROSPERO register of systematic reviews before beginning their own review.
Given the opportunity cost involved in undertaking an activity as demanding as a systematic review, authors should ensure that their work is relevant by: (i) involving relevant stakeholders in defining its focus and the questions it will address; and (ii) writing up the review in such a way as to facilitate the translation of its findings to inform decisions. The GRADE framework aims to achieve this, and should be considered throughout the review process, not only when it is being written up (see Chapter 14 and Chapter 15 ).
Consideration of opportunity costs is also relevant in terms of the ethics of conducting a review, though ethical issues should also be considered primarily in terms of the questions that are prioritized for answering and the way that they are framed. Research questions are often not value-neutral, and the way that a given problem is approached can have political implications which can result in, for example, the widening of health inequalities (whether intentional or not). These issues are explored in Section 2.4.3 and Chapter 16 .
MECIR Box 2.1.a Relevant expectations for conduct of intervention reviews
| Formulating review questions ( ) | |
|
| Cochrane Reviews are intended to support clinical practice and policy, not just scientific curiosity. The needs of consumers play a central role in Cochrane Reviews and they can play an important role in defining the review question. Qualitative research, i.e. studies that explore the experience of those involved in providing and receiving interventions, and studies evaluating factors that shape the implementation of interventions, might be used in the same way. |
| Considering potential adverse effects ( ) | |
|
| It is important that adverse effects are addressed in order to avoid one-sided summaries of the evidence. At a minimum, the review will need to highlight the extent to which potential adverse effects have been evaluated in any included studies. Sometimes data on adverse effects are best obtained from non-randomized studies, or qualitative research studies. This does not mean however that all reviews must include non-randomized studies. |
2.2 Aims of reviews of interventions
Systematic reviews can address any question that can be answered by a primary research study. This Handbook focuses on a subset of all possible review questions: the impact of intervention(s) implemented within a specified human population. Even within these limits, systematic reviews examining the effects of intervention(s) can vary quite markedly in their aims. Some will focus specifically on evidence of an effect of an intervention compared with a specific alternative, whereas others may examine a range of different interventions. Reviews that examine multiple interventions and aim to identify which might be the most effective can be broader and more challenging than those looking at single interventions. These can also be the most useful for end users, where decision making involves selecting from a number of intervention options. The incorporation of network meta-analysis as a core method in this edition of the Handbook (see Chapter 11 ) reflects the growing importance of these types of reviews.
As well as looking at the balance of benefit and harm that can be attributed to a given intervention, reviews within the ambit of this Handbook might also aim to investigate the relationship between the size of an intervention effect and other characteristics, such as aspects of the population, the intervention itself, how the outcome is measured, or the methodology of the primary research studies included. Such approaches might be used to investigate which components of multi-component interventions are more or less important or essential (and when). While it is not always necessary to know how an intervention achieves its effect for it to be useful, many reviews will aim to articulate an intervention’s mechanisms of action (see Section 2.5.1 ), either by making this an explicit aim of the review itself (see Chapter 17 and Chapter 21 ), or when describing the scope of the review. Understanding how an intervention works (or is intended to work) can be an important aid to decision makers in assessing the applicability of the review to their situation. These investigations can be assisted by the incorporation of results from process evaluations conducted alongside trials (see Chapter 21 ). Further, many decisions in policy and practice are at least partially constrained by the resource available, so review authors often need to consider the economic context of interventions (see Chapter 20 ).
2.3 Defining the scope of a review question
Studies comparing healthcare interventions, notably randomized trials, use the outcomes of participants to compare the effects of different interventions. Statistical syntheses (e.g. meta-analysis) focus on comparisons of interventions, such as a new intervention versus a control intervention (which may represent conditions of usual practice or care), or the comparison of two competing interventions. Throughout the Handbook we use the terminology experimental intervention versus comparator intervention. This implies a need to identify one of the interventions as experimental, and is used only for convenience since all methods apply to both controlled and head-to-head comparisons. The contrast between the outcomes of two groups treated differently is known as the ‘effect’, the ‘treatment effect’ or the ‘intervention effect’; we generally use the last of these throughout the Handbook .
A statement of the review’s objectives should begin with a precise statement of the primary objective, ideally in a single sentence ( MECIR Box 2.3.a ). Where possible the style should be of the form ‘To assess the effects of [ intervention or comparison ] for [ health problem ] in [ types of people, disease or problem and setting if specified ]’. This might be followed by one or more secondary objectives, for example relating to different participant groups, different comparisons of interventions or different outcome measures. The detailed specification of the review question(s) requires consideration of several key components (Richardson et al 1995, Counsell 1997) which can often be encapsulated by the ‘PICO’ mnemonic, an acronym for P opulation, I ntervention, C omparison(s) and O utcome. Equal emphasis in addressing, and equal precision in defining, each PICO component is not necessary. For example, a review might concentrate on competing interventions for a particular stage of breast cancer, with stage and severity of the disease being defined very precisely; or alternately focus on a particular drug for any stage of breast cancer, with the treatment formulation being defined very precisely.
Throughout the Handbook we make a distinction between three different stages in the review at which the PICO construct might be used. This division is helpful for understanding the decisions that need to be made:
- The review PICO (planned at the protocol stage) is the PICO on which eligibility of studies is based (what will be included and what excluded from the review).
- The PICO for each synthesis (also planned at the protocol stage) defines the question that each specific synthesis aims to answer, determining how the synthesis will be structured, specifying planned comparisons (including intervention and comparator groups, any grouping of outcome and population subgroups).
- The PICO of the included studies (determined at the review stage) is what was actually investigated in the included studies.
Reaching the point where it is possible to articulate the review’s objectives in the above form – the review PICO – requires time and detailed discussion between potential authors and users of the review. It is important that those involved in developing the review’s scope and questions have a good knowledge of the practical issues that the review will address as well as the research field to be synthesized. Developing the questions is a critical part of the research process. As such, there are methodological issues to bear in mind, including: how to determine which questions are most important to answer; how to engage stakeholders in question formulation; how to account for changes in focus as the review progresses; and considerations about how broad (or narrow) a review should be.
MECIR Box 2.3 . a Relevant expectations for conduct of intervention reviews
| Predefining objectives ( ) | |
|
| Objectives give the review focus and must be clear before appropriate eligibility criteria can be developed. If the review will address multiple interventions, clarity is required on how these will be addressed (e.g. summarized separately, combined or explicitly compared). |
2.3.1 Broad versus narrow reviews
The questions addressed by a review may be broad or narrow in scope. For example, a review might address a broad question regarding whether antiplatelet agents in general are effective in preventing all thrombotic events in humans. Alternatively, a review might address whether a particular antiplatelet agent, such as aspirin, is effective in decreasing the risks of a particular thrombotic event, stroke, in elderly persons with a previous history of stroke. Increasingly, reviews are becoming broader, aiming, for example, to identify which intervention – out of a range of treatment options – is most effective, or to investigate how an intervention varies depending on implementation and participant characteristics.
Overviews of reviews (see Chapter V ), in which multiple reviews are summarized, can be one way of addressing the need for breadth when synthesizing the evidence base, since they can summarize multiple reviews of different interventions for the same condition, or multiple reviews of the same intervention for different types of participants. It may be considered desirable to plan a series of reviews with a relatively narrow scope, alongside an Overview to summarize their findings. Alternatively, it may be more useful – particularly given the growth in support for network meta-analysis – to combine comparisons of different treatment options within the same review (see Chapter 11 ). When deciding whether or not an overview might be the most appropriate approach, review authors should take account of the breadth of the question being asked and the resources available. Some questions are simply too broad for a review of all relevant primary research to be practicable, and if a field has sufficient high-quality reviews, then the production of another review of primary research that duplicates the others might not be a sensible use of resources.
Some of the advantages and disadvantages of broad and narrow reviews are summarized in Table 2.3.a . While having a broad scope in terms of the range of participants has the potential to increase generalizability, the extent to which findings are ultimately applicable to broader (or different) populations will depend on the participants who have actually been recruited into research studies. Likewise, heterogeneity can be a disadvantage when the expectation is for homogeneity of effects between studies, but an advantage when the review question seeks to understand differential effects (see Chapter 10 ).A distinction should be drawn between the scope of a review and the precise questions within, since it is possible to have a broad review that addresses quite narrow questions. In the antiplatelet agents for preventing thrombotic events example, a systematic review with a broad scope might include all available treatments. Rather than combining all the studies into one comparison though, specific treatments would be compared with one another in separate comparisons, thus breaking a heterogeneous set of treatments into narrower, more homogenous groups. This relates to the three levels of PICO, outlined in Section 2.3 . The review PICO defines the broad scope of the review, and the PICO for comparison defines the specific treatments that will be compared with one another; Chapter 3 elaborates on the use of PICOs.
In practice, a Cochrane Review may start (or have started) with a broad scope, and be divided up into narrower reviews as evidence accumulates and the original review becomes unwieldy. This may be done for practical and logistical reasons, for example to make updating easier as well as to make it easier for readers to see which parts of the evidence base are changing. Individual review authors must decide if there are instances where splitting a broader focused review into a series of more narrowly focused reviews is appropriate and implement appropriate methods to achieve this. If a major change is to be undertaken, such as splitting a broad review into a series of more narrowly focused reviews, a new protocol must be written for each of the component reviews that documents the eligibility criteria for each one.
Ultimately, the selected breadth of a review depends upon multiple factors including perspectives regarding a question’s relevance and potential impact; supporting theoretical, biologic and epidemiological information; the potential generalizability and validity of answers to the questions; and available resources. As outlined in Section 2.4.2 , authors should consider carefully the needs of users of the review and the context(s) in which they expect the review to be used when determining the most optimal scope for their review.
Table 2.3.a Some advantages and disadvantages of broad versus narrow reviews
|
|
|
|
|
e.g. corticosteroid injection for shoulder tendonitis (narrow) or corticosteroid injection for any tendonitis (broad) | : Comprehensive summary of the evidence. Opportunity to explore consistency of findings (and therefore generalizability) across different types of participants. |
Manageability for review team. Ease of reading. |
|
| : Searching, data collection, analysis and writing may require more resources. Interpretation may be difficult for readers if the review is large and lacks a clear rationale (such as examining consistency of findings) for including diverse types of participants. |
Evidence may be sparse. Unable to explore whether an intervention operates differently in other settings or populations (e.g. inability to explore differential effects that could lead to inequity). Increased burden for decision makers if multiple reviews must be accessed (e.g. if evidence is sparse for the population of interest). Scope could be chosen by review authors to produce a desired result. |
|
e.g. supervised running for depression (narrow) or any exercise for depression (broad) | : Comprehensive summary of the evidence. Opportunity to explore consistency of findings across different implementations of the intervention. | : Manageability for review team. Ease of reading. |
|
| : Searching, data collection, analysis and writing may require more resources. Interpretation may be difficult for readers if the review is large and lacks a clear rationale (such as examining consistency of findings) for including different modes of an intervention. | : Evidence may be sparse. Unable to explore whether different modes of an intervention modify the intervention effects. Increased burden for decision makers if multiple reviews must be accessed (e.g. if evidence is sparse for a specific mode). Scope could be chosen by review authors to produce a desired result. |
|
e.g. oxybutynin compared with desmopressin for preventing bed-wetting (narrow) or interventions for preventing bed-wetting (broad) | : Comprehensive summary of the evidence. Opportunity to compare the effectiveness of a range of different intervention options. | : Manageability for review team. Relative simplicity of objectives and ease of reading. |
|
| : Searching, data collection, analysis and writing may require more resources. May be unwieldy, and more appropriate to present as an Overview of reviews (see ). | : Increased burden for decision makers if not included in an Overview since multiple reviews may need to be accessed. |
2.3.2 ‘Lumping’ versus ‘splitting’
It is important not to confuse the issue of the breadth of the review (determined by the review PICO) with concerns about between-study heterogeneity and the legitimacy of combining results from diverse studies in the same analysis (determined by the PICOs for comparison).
Broad reviews have been criticized as ‘mixing apples and oranges’, and one of the inventors of meta-analysis, Gene Glass, has responded “Of course it mixes apples and oranges… comparing apples and oranges is the only endeavour worthy of true scientists; comparing apples to apples is trivial” (Glass 2015). In fact, the two concepts (‘broad reviews’ and ‘mixing apples and oranges’) are different issues. Glass argues that broad reviews, with diverse studies, provide the opportunity to ask interesting questions about the reasons for differential intervention effects.
The ‘apples and oranges’ critique refers to the inappropriate mixing of studies within a single comparison, where the purpose is to estimate an average effect. In situations where good biologic or sociological evidence suggests that various formulations of an intervention behave very differently or that various definitions of the condition of interest are associated with markedly different effects of the intervention, the uncritical aggregation of results from quite different interventions or populations/settings may well be questionable.
Unfortunately, determining the situations where studies are similar enough to combine with one another is not always straightforward, and it can depend, to some extent, on the question being asked. While the decision is sometimes characterized as ‘lumping’ (where studies are combined in the same analysis) or ‘splitting’ (where they are not) (Squires et al 2013), it is better to consider these issues on a continuum, with reviews that have greater variation in the types of included interventions, settings and populations, and study designs being towards the ‘lumped’ end, and those that include little variation in these elements being towards the ‘split’ end (Petticrew and Roberts 2006).
While specification of the review PICO sets the boundary for the inclusion and exclusion of studies, decisions also need to be made when planning the PICO for the comparisons to be made in the analysis as to whether they aim to address broader (‘lumped’) or narrower (‘split’) questions (Caldwell and Welton 2016). The degree of ‘lumping’ in the comparisons will be primarily driven by the review’s objectives, but will sometimes be dictated by the availability of studies (and data) for a particular comparison (see Chapter 9 for discussion of the latter). The former is illustrated by a Cochrane Review that examined the effects of newer-generation antidepressants for depressive disorders in children and adolescents (Hetrick et al 2012).
Newer-generation antidepressants include multiple different compounds (e.g. paroxetine, fluoxetine). The objectives of this review were to (i) estimate the overall effect of newer-generation antidepressants on depression, (ii) estimate the effect of each compound, and (iii) examine whether the compound type and age of the participants (children versus adolescents) is associated with the intervention effect. Objective (i) addresses a broad, ‘in principle’ (Caldwell and Welton 2016), question of whether newer-generation antidepressants improve depression, where the different compounds are ‘lumped’ into a single comparison. Objective (ii) seeks to address narrower, ‘split’, questions that investigate the effect of each compound on depression separately. Answers to both questions can be identified by setting up separate comparisons for each compound, or by subgrouping the ‘lumped’ comparison by compound ( Chapter 10, Section 10.11.2 ). Objective (iii) seeks to explore factors that explain heterogeneity among the intervention effects, or equivalently, whether the intervention effect varies by the factor. This can be examined using subgroup analysis or meta-regression ( Chapter 10, Section 10.11 ) but, in the case of intervention types, is best achieved using network meta-analysis (see Chapter 11 ).
There are various advantages and disadvantages to bear in mind when defining the PICO for the comparison and considering whether ‘lumping’ or ‘splitting’ is appropriate. Lumping allows for the investigation of factors that may explain heterogeneity. Results from these investigations may provide important leads as to whether an intervention operates differently in, for example, different populations (such as in children and adolescents in the example above). Ultimately, this type of knowledge is useful for clinical decision making. However, lumping is likely to introduce heterogeneity, which will not always be explained by a priori specified factors, and this may lead to a combined effect that is clinically difficult to interpret and implement. For example, when multiple intervention types are ‘lumped’ in one comparison (as in objective (i) above), and there is unexplained heterogeneity, the combined intervention effect would not enable a clinical decision as to which intervention should be selected. Splitting comparisons carries its own risk of there being too few studies to yield a useful synthesis. Inevitably, some degree of aggregation across the PICO elements is required for a meta-analysis to be undertaken (Caldwell and Welton 2016).
2.4 Ensuring the review addresses the right questions
Since systematic reviews are intended for use in healthcare decision making, review teams should ensure not only the application of robust methodology, but also that the review question is meaningful for healthcare decision making. Two approaches are discussed below:
- Using results from existing research priority-setting exercises to define the review question.
- In the absence of, or in addition to, existing research priority-setting exercises, engaging with stakeholders to define review questions and establish their relevance to policy and practice.
2.4.1 Using priority-setting exercises to define review questions
A research priority-setting exercise is a “collective activity for deciding which uncertainties are most worth trying to resolve through research; uncertainties considered may be problems to be understood or solutions to be developed or tested; across broad or narrow areas” (Sandy Oliver, referenced in Nasser 2018). Using research priority-setting exercises to define the scope of a review helps to prevent the waste of scarce resources for research by making the review more relevant to stakeholders (Chalmers et al 2014).
Research priority setting is always conducted in a specific context, setting and population with specific principles, values and preferences (which should be articulated). Different stakeholders’ interpretation of the scope and purpose of a ‘research question’ might vary, resulting in priorities that might be difficult to interpret. Researchers or review teams might find it necessary to translate the research priorities into an answerable PICO research question format, and may find it useful to recheck the question with the stakeholder groups to determine whether they have accurately reflected their intentions.
While Cochrane Review teams are in most cases reviewing the effects of an intervention with a global scope, they may find that the priorities identified by important stakeholders (such as the World Health Organization or other organizations or individuals in a representative health system) are informative in planning the review. Review authors may find that differences between different stakeholder groups’ views on priorities and the reasons for these differences can help them to define the scope of the review. This is particularly important for making decisions about excluding specific populations or settings, or being inclusive and potentially conducting subgroup analyses.
Whenever feasible, systematic reviews should be based on priorities identified by key stakeholders such as decision makers, patients/public, and practitioners. Cochrane has developed a list of priorities for reviews in consultation with key stakeholders, which is available on the Cochrane website. Issues relating to equity (see Chapter 16 and Section 2.4.3 ) need to be taken into account when conducting and interpreting the results from priority-setting exercises. Examples of materials to support these processes are available (Viergever et al 2010, Nasser et al 2013, Tong et al 2017).
The results of research priority-setting exercises can be searched for in electronic databases and via websites of relevant organizations. Examples are: James Lind Alliance , World Health Organization, organizations of health professionals including research disciplines, and ministries of health in different countries (Viergever 2010). Examples of search strategies for identifying research priority-setting exercises are available (Bryant et al 2014, Tong et al 2015).
Other sources of questions are often found in ‘implications for future research’ sections of articles in journals and clinical practice guidelines. Some guideline developers have prioritized questions identified through the guideline development process (Sharma et al 2018), although these priorities will be influenced by the needs of health systems in which different guideline development teams are working.
2.4.2 Engaging stakeholders to help define the review questions
In the absence of a relevant research priority-setting exercise, or when a systematic review is being conducted for a very specific purpose (for example, commissioned to inform the development of a guideline), researchers should work with relevant stakeholders to define the review question. This practice is especially important when developing review questions for studying the effectiveness of health systems and policies, because of the variability between countries and regions; the significance of these differences may only become apparent through discussion with the stakeholders.
The stakeholders for a review could include consumers or patients, carers, health professionals of different kinds, policy decision makers and others ( Chapter 1, Section 1.3.1 ). Identifying the stakeholders who are critical to a particular question will depend on the question, who the answer is likely to affect, and who will be expected to implement the intervention if it is found to be effective (or to discontinue it if not).
Stakeholder engagement should, optimally, be an ongoing process throughout the life of the systematic review, from defining the question to dissemination of results (Keown et al 2008). Engaging stakeholders increases relevance, promotes mutual learning, improves uptake and decreases research waste (see Chapter 1, Section 1.3.1 and Section 1.3.2 ). However, because such engagement can be challenging and resource intensive, a one-off engagement process to define the review question might only be possible. Review questions that are conceptualized and refined by multiple stakeholders can capture much of the complexity that should be addressed in a systematic review.
2.4.3 Considering issues relating to equity when defining review questions
Deciding what should be investigated, who the participants should be, and how the analysis will be carried out can be considered political activities, with the potential for increasing or decreasing inequalities in health. For example, we now know that well-intended interventions can actually widen inequalities in health outcomes since researchers have chosen to investigate this issue (Lorenc et al 2013). Decision makers can now take account of this knowledge when planning service provision. Authors should therefore consider the potential impact on disadvantaged groups of the intervention(s) that they are investigating on disadvantaged groups, and whether socio-economic inequalities in health might be affected depending on whether or how they are implemented.
Health equity is the absence of avoidable and unfair differences in health (Whitehead 1992). Health inequity may be experienced across characteristics defined by PROGRESS-Plus (Place of residence, Race/ethnicity/culture/language, Occupation, Gender/sex, Religion, Education, Socio-economic status, Social capital, and other characteristics (‘Plus’) such as sexual orientation, age, and disability) (O’Neill et al 2014). Issues relating to health equity should be considered when review questions are developed ( MECIR Box 2.4.a ). Chapter 16 presents detailed guidance on this issue for review authors.
MECIR Box 2.4 . a Relevant expectations for conduct of intervention reviews
| Considering equity and specific populations ( ) | |
|
| Where possible reviews should include explicit descriptions of the effect of the interventions not only upon the whole population, but also on the disadvantaged, and/or the ability of the interventions to reduce socio-economic inequalities in health, and to promote use of the interventions to the community. |
2.5 Methods and tools for structuring the review
It is important for authors to develop the scope of their review with care: without a clear understanding of where the review will contribute to existing knowledge – and how it will be used – it may be at risk of conceptual incoherence. It may mis-specify critical elements of how the intervention(s) interact with the context(s) within which they operate to produce specific outcomes, and become either irrelevant or possibly misleading. For example, in a systematic review about smoking cessation interventions in pregnancy, it was essential for authors to take account of the way that health service provision has changed over time. The type and intensity of ‘usual care’ in more recent evaluations was equivalent to the interventions being evaluated in older studies, and the analysis needed to take this into account. This review also found that the same intervention can have different effects in different settings depending on whether its materials are culturally appropriate in each context (Chamberlain et al 2017).
In order to protect the review against conceptual incoherence and irrelevance, review authors need to spend time at the outset developing definitions for key concepts and ensuring that they are clear about the prior assumptions on which the review depends. These prior assumptions include, for example, why particular populations should be considered inside or outside the review’s scope; how the intervention is thought to achieve its effect; and why specific outcomes are selected for evaluation. Being clear about these prior assumptions also requires review authors to consider the evidential basis for these assumptions and decide for themselves which they can place more or less reliance on. When considered as a whole, this initial conceptual and definitional work states the review’s conceptual framework . Each element of the review’s PICO raises its own definitional challenges, which are discussed in detail in the Chapter 3 .
In this section we consider tools that may help to define the scope of the review and the relationships between its key concepts; in particular, articulating how the intervention gives rise to the outcomes selected. In some situations, long sequences of events are expected to occur between an intervention being implemented and an outcome being observed. For example, a systematic review examining the effects of asthma education interventions in schools on children’s health and well-being needed to consider: the interplay between core intervention components and their introduction into differing school environments; different child-level effect modifiers; how the intervention then had an impact on the knowledge of the child (and their family); the child’s self-efficacy and adherence to their treatment regime; the severity of their asthma; the number of days of restricted activity; how this affected their attendance at school; and finally, the distal outcomes of education attainment and indicators of child health and well-being (Kneale et al 2015).
Several specific tools can help authors to consider issues raised when defining review questions and planning their review; these are also helpful when developing eligibility criteria and classifying included studies. These include the following.
- Taxonomies: hierarchical structures that can be used to categorize (or group) related interventions, outcomes or populations.
- Generic frameworks for examining and structuring the description of intervention characteristics (e.g. TIDieR for the description of interventions (Hoffmann et al 2014), iCAT_SR for describing multiple aspects of complexity in systematic reviews (Lewin et al 2017)).
- Core outcome sets for identifying and defining agreed outcomes that should be measured for specific health conditions (described in more detail in Chapter 3 ).
Unlike these tools, which focus on particular aspects of a review, logic models provide a framework for planning and guiding synthesis at the review level (see Section 2.5.1 ).
2.5.1 Logic models
Logic models (sometimes referred to as conceptual frameworks or theories of change) are graphical representations of theories about how interventions work. They depict intervention components, mechanisms (pathways of action), outputs, and outcomes as sequential (although not necessarily linear) chains of events. Among systematic review authors, they were originally proposed as a useful tool when working with evaluations of complex social and population health programmes and interventions, to conceptualize the pathways through which interventions are intended to change outcomes (Anderson et al 2011).
In reviews where intervention complexity is a key consideration (see Chapter 17 ), logic models can be particularly helpful. For example, in a review of psychosocial group interventions for those with HIV, a logic model was used to show how the intervention might work (van der Heijden et al 2017). The review authors depicted proximal outcomes, such as self-esteem, but chose only to include psychological health outcomes in their review. In contrast, Bailey and colleagues included proximal outcomes in their review of computer-based interventions for sexual health promotion using a logic model to show how outcomes were grouped (Bailey et al 2010). Finally, in a review of slum upgrading, a logic model showed the broad range of interventions and their interlinkages with health and socio-economic outcomes (Turley et al 2013), and enabled the review authors to select a specific intervention category (physical upgrading) on which to focus the review. Further resources provide further examples of logic models, and can help review authors develop and use logic models (Anderson et al 2011, Baxter et al 2014, Kneale et al 2015, Pfadenhauer et al 2017, Rohwer et al 2017).
Logic models can vary in their emphasis, with a distinction sometimes made between system-based and process-oriented logic models (Rehfuess et al 2018). System-based logic models have particular value in examining the complexity of the system (e.g. the geographical, epidemiological, political, socio-cultural and socio-economic features of a system), and the interactions between contextual features, participants and the intervention (see Chapter 17 ). Process-oriented logic models aim to capture the complexity of causal pathways by which the intervention leads to outcomes, and any factors that may modify intervention effects. However, this is not a crisp distinction; the two types are interrelated; with some logic models depicting elements of both systems and process models simultaneously.
The way that logic models can be represented diagrammatically (see Chapter 17 for an example) provides a valuable visual summary for readers and can be a communication tool for decision makers and practitioners. They can aid initially in the development of a shared understanding between different stakeholders of the scope of the review and its PICO, helping to support decisions taken throughout the review process, from developing the research question and setting the review parameters, to structuring and interpreting the results. They can be used in planning the PICO elements of a review as well as for determining how the synthesis will be structured (i.e. planned comparisons, including intervention and comparator groups, and any grouping of outcome and population subgroups). These models may help review authors specify the link between the intervention, proximal and distal outcomes, and mediating factors. In other words, they depict the intervention theory underpinning the synthesis plan.
Anderson and colleagues note the main value of logic models in systematic review as (Anderson et al 2011):
- refining review questions;
- deciding on ‘lumping’ or ‘splitting’ a review topic;
- identifying intervention components;
- defining and conducting the review;
- identifying relevant study eligibility criteria;
- guiding the literature search strategy;
- explaining the rationale behind surrogate outcomes used in the review;
- justifying the need for subgroup analyses (e.g. age, sex/gender, socio-economic status);
- making the review relevant to policy and practice;
- structuring the reporting of results;
- illustrating how harms and feasibility are connected with interventions; and
- interpreting results based on intervention theory and systems thinking (see Chapter 17 ).
Logic models can be useful in systematic reviews when considering whether failure to find a beneficial effect of an intervention is due to a theory failure, an implementation failure, or both (see Chapter 17 and Cargo et al 2018). Making a distinction between implementation and intervention theory can help to determine whether and how the intervention interacts with (and potentially changes) its context (see Chapter 3 and Chapter 17 for further discussion of context). This helps to elucidate situations in which variations in how the intervention is implemented have the potential to affect the integrity of the intervention and intended outcomes.
Given their potential value in conceptualizing and structuring a review, logic models are increasingly published in review protocols. Logic models may be specified a priori and remain unchanged throughout the review; it might be expected, however, that the findings of reviews produce evidence and new understandings that could be used to update the logic model in some way (Kneale et al 2015). Some reviews take a more staged approach, pre-specifying points in the review process where the model may be revised on the basis of (new) evidence (Rehfuess et al 2018) and a staged logic model can provide an efficient way to report revisions to the synthesis plan. For example, in a review of portion, package and tableware size for changing selection or consumption of food and other products, the authors presented a logic model that clearly showed changes to their original synthesis plan (Hollands et al 2015).
It is preferable to seek out existing logic models for the intervention and revise or adapt these models in line with the review focus, although this may not always be possible. More commonly, new models are developed starting with the identification of outcomes and theorizing the necessary pre-conditions to reach those outcomes. This process of theorizing and identifying the steps and necessary pre-conditions continues, working backwards from the intended outcomes, until the intervention itself is represented. As many mechanisms of action are invisible and can only be ‘known’ through theory, this process is invaluable in exposing assumptions as to how interventions are thought to work; assumptions that might then be tested in the review. Logic models can be developed with stakeholders (see Section 2.5.2 ) and it is considered good practice to obtain stakeholder input in their development.
Logic models are representations of how interventions are intended to ‘work’, but they can also provide a useful basis for thinking through the unintended consequences of interventions and identifying potential adverse effects that may need to be captured in the review (Bonell et al 2015). While logic models provide a guiding theory of how interventions are intended to work, critiques exist around their use, including their potential to oversimplify complex intervention processes (Rohwer et al 2017). Here, contributions from different stakeholders to the development of a logic model may be able to articulate where complex processes may occur; theorizing unintended intervention impacts; and the explicit representation of ambiguity within certain parts of the causal chain where new theory/explanation is most valuable.
2.5.2 Changing review questions
While questions should be posed in the protocol before initiating the full review, these questions should not prevent exploration of unexpected issues. Reviews are analyses of existing data that are constrained by previously chosen study populations, settings, intervention formulations, outcome measures and study designs. It is generally not possible to formulate an answerable question for a review without knowing some of the studies relevant to the question, and it may become clear that the questions a review addresses need to be modified in light of evidence accumulated in the process of conducting the review.
Although a certain fluidity and refinement of questions is to be expected in reviews as a fuller understanding of the evidence is gained, it is important to guard against bias in modifying questions. Data-driven questions can generate false conclusions based on spurious results. Any changes to the protocol that result from revising the question for the review should be documented at the beginning of the Methods section. Sensitivity analyses may be used to assess the impact of changes on the review findings (see Chapter 10, Section 10.14 ). When refining questions it is useful to ask the following questions.
- What is the motivation for the refinement?
- Could the refinement have been influenced by results from any of the included studies?
- Does the refined question require a modification to the search strategy and/or reassessment of any decisions regarding study eligibility?
- Are data collection methods appropriate to the refined question?
- Does the refined question still meet the FINER criteria discussed in Section 2.1 ?
2.5.3 Building in contingencies to deal with sparse data
The ability to address the review questions will depend on the maturity and validity of the evidence base. When few studies are identified, there will be limited opportunity to address the question through an informative synthesis. In anticipation of this scenario, review authors may build contingencies into their protocol analysis plan that specify grouping (any or multiple) PICO elements at a broader level; thus potentially enabling synthesis of a larger number of studies. Broader groupings will generally address a less specific question, for example:
- ‘the effect of any antioxidant supplement on …’ instead of ‘the effect of vitamin C on …’;
- ‘the effect of sexual health promotion on biological outcomes ’ instead of ‘the effect of sexual health promotion on sexually transmitted infections ’; or
- ‘the effect of cognitive behavioural therapy in children and adolescents on …’ instead of ‘the effect of cognitive behavioural therapy in children on …’.
However, such broader questions may be useful for identifying important leads in areas that lack effective interventions and for guiding future research. Changes in the grouping may affect the assessment of the certainty of the evidence (see Chapter 14 ).
2.5.4 Economic data
Decision makers need to consider the economic aspects of an intervention, such as whether its adoption will lead to a more efficient use of resources. Economic data such as resource use, costs or cost-effectiveness (or a combination of these) may therefore be included as outcomes in a review. It is useful to break down measures of resource use and costs to the level of specific items or categories. It is helpful to consider an international perspective in the discussion of costs. Economics issues are discussed in detail in Chapter 20 .
2.6 Chapter information
Authors: James Thomas, Dylan Kneale, Joanne E McKenzie, Sue E Brennan, Soumyadeep Bhaumik
Acknowledgements: This chapter builds on earlier versions of the Handbook . Mona Nasser, Dan Fox and Sally Crowe contributed to Section 2.4 ; Hilary J Thomson contributed to Section 2.5.1 .
Funding: JT and DK are supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Collaboration for Leadership in Applied Health Research and Care North Thames at Barts Health NHS Trust. JEM is supported by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Career Development Fellowship (1143429). SEB’s position is supported by the NHMRC Cochrane Collaboration Funding Program. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR, the Department of Health or the NHMRC.
2.7 References
Anderson L, Petticrew M, Rehfuess E, Armstrong R, Ueffing E, Baker P, Francis D, Tugwell P. Using logic models to capture complexity in systematic reviews. Research Synthesis Methods 2011; 2 : 33–42.
Bailey JV, Murray E, Rait G, Mercer CH, Morris RW, Peacock R, Cassell J, Nazareth I. Interactive computer-based interventions for sexual health promotion. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010; 9 : CD006483.
Baxter SK, Blank L, Woods HB, Payne N, Rimmer M, Goyder E. Using logic model methods in systematic review synthesis: describing complex pathways in referral management interventions. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2014; 14 : 62.
Bonell C, Jamal F, Melendez-Torres GJ, Cummins S. ‘Dark logic’: theorising the harmful consequences of public health interventions. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 2015; 69 : 95–98.
Bryant J, Sanson-Fisher R, Walsh J, Stewart J. Health research priority setting in selected high income countries: a narrative review of methods used and recommendations for future practice. Cost Effectiveness and Resource Allocation 2014; 12 : 23.
Caldwell DM, Welton NJ. Approaches for synthesising complex mental health interventions in meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Mental Health 2016; 19 : 16–21.
Cargo M, Harris J, Pantoja T, Booth A, Harden A, Hannes K, Thomas J, Flemming K, Garside R, Noyes J. Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group guidance series-paper 4: methods for assessing evidence on intervention implementation. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2018; 97 : 59–69.
Chalmers I, Bracken MB, Djulbegovic B, Garattini S, Grant J, Gülmezoglu AM, Howells DW, Ioannidis JPA, Oliver S. How to increase value and reduce waste when research priorities are set. Lancet 2014; 383 : 156–165.
Chamberlain C, O’Mara-Eves A, Porter J, Coleman T, Perlen S, Thomas J, McKenzie J. Psychosocial interventions for supporting women to stop smoking in pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017; 2 : CD001055.
Cooper H. The problem formulation stage. In: Cooper H, editor. Integrating Research: A Guide for Literature Reviews . Newbury Park (CA) USA: Sage Publications; 1984.
Counsell C. Formulating questions and locating primary studies for inclusion in systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine 1997; 127 : 380–387.
Cummings SR, Browner WS, Hulley SB. Conceiving the research question and developing the study plan. In: Hulley SB, Cummings SR, Browner WS, editors. Designing Clinical Research: An Epidemiological Approach . 4th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 14–22.
Glass GV. Meta-analysis at middle age: a personal history. Research Synthesis Methods 2015; 6 : 221–231.
Hedges LV. Statistical considerations. In: Cooper H, Hedges LV, editors. The Handbook of Research Synthesis . New York (NY): USA: Russell Sage Foundation; 1994.
Hetrick SE, McKenzie JE, Cox GR, Simmons MB, Merry SN. Newer generation antidepressants for depressive disorders in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012; 11 : CD004851.
Hoffmann T, Glasziou P, Boutron I. Better reporting of interventions: template for intervention description and replication (TIDieR) checklist and guide. BMJ 2014; 348: g1687.
Hollands GJ, Shemilt I, Marteau TM, Jebb SA, Lewis HB, Wei Y, Higgins JPT, Ogilvie D. Portion, package or tableware size for changing selection and consumption of food, alcohol and tobacco. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015; 9 : CD011045.
Keown K, Van Eerd D, Irvin E. Stakeholder engagement opportunities in systematic reviews: Knowledge transfer for policy and practice. Journal of Continuing Education in the Health Professions 2008; 28 : 67–72.
Kneale D, Thomas J, Harris K. Developing and optimising the use of logic models in systematic reviews: exploring practice and good practice in the use of programme theory in reviews. PloS One 2015; 10 : e0142187.
Lewin S, Hendry M, Chandler J, Oxman AD, Michie S, Shepperd S, Reeves BC, Tugwell P, Hannes K, Rehfuess EA, Welch V, McKenzie JE, Burford B, Petkovic J, Anderson LM, Harris J, Noyes J. Assessing the complexity of interventions within systematic reviews: development, content and use of a new tool (iCAT_SR). BMC Medical Research Methodology 2017; 17 : 76.
Lorenc T, Petticrew M, Welch V, Tugwell P. What types of interventions generate inequalities? Evidence from systematic reviews. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 2013; 67 : 190–193.
Nasser M, Ueffing E, Welch V, Tugwell P. An equity lens can ensure an equity-oriented approach to agenda setting and priority setting of Cochrane Reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013; 66 : 511–521.
Nasser M. Setting priorities for conducting and updating systematic reviews [PhD Thesis]: University of Plymouth; 2018.
O’Neill J, Tabish H, Welch V, Petticrew M, Pottie K, Clarke M, Evans T, Pardo Pardo J, Waters E, White H, Tugwell P. Applying an equity lens to interventions: using PROGRESS ensures consideration of socially stratifying factors to illuminate inequities in health. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2014; 67 : 56–64.
Oliver S, Dickson K, Bangpan M, Newman M. Getting started with a review. In: Gough D, Oliver S, Thomas J, editors. An Introduction to Systematic Reviews . London (UK): Sage Publications Ltd.; 2017.
Petticrew M, Roberts H. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Oxford (UK): Blackwell; 2006.
Pfadenhauer L, Gerhardus A, Mozygemba K, Lysdahl KB, Booth A, Hofmann B, Wahlster P, Polus S, Burns J, Brereton L, Rehfuess E. Making sense of complexity in context and implementation: the Context and Implementation of Complex Interventions (CICI) framework. Implementation Science 2017; 12 : 21.
Rehfuess EA, Booth A, Brereton L, Burns J, Gerhardus A, Mozygemba K, Oortwijn W, Pfadenhauer LM, Tummers M, van der Wilt GJ, Rohwer A. Towards a taxonomy of logic models in systematic reviews and health technology assessments: a priori, staged, and iterative approaches. Research Synthesis Methods 2018; 9 : 13–24.
Richardson WS, Wilson MC, Nishikawa J, Hayward RS. The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP Journal Club 1995; 123 : A12–13.
Rohwer A, Pfadenhauer L, Burns J, Brereton L, Gerhardus A, Booth A, Oortwijn W, Rehfuess E. Series: Clinical epidemiology in South Africa. Paper 3: Logic models help make sense of complexity in systematic reviews and health technology assessments. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2017; 83 : 37–47.
Sharma T, Choudhury M, Rejón-Parrilla JC, Jonsson P, Garner S. Using HTA and guideline development as a tool for research priority setting the NICE way: reducing research waste by identifying the right research to fund. BMJ Open 2018; 8 : e019777.
Squires J, Valentine J, Grimshaw J. Systematic reviews of complex interventions: framing the review question. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013; 66 : 1215–1222.
Tong A, Chando S, Crowe S, Manns B, Winkelmayer WC, Hemmelgarn B, Craig JC. Research priority setting in kidney disease: a systematic review. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2015; 65 : 674–683.
Tong A, Sautenet B, Chapman JR, Harper C, MacDonald P, Shackel N, Crowe S, Hanson C, Hill S, Synnot A, Craig JC. Research priority setting in organ transplantation: a systematic review. Transplant International 2017; 30 : 327–343.
Turley R, Saith R, Bhan N, Rehfuess E, Carter B. Slum upgrading strategies involving physical environment and infrastructure interventions and their effects on health and socio-economic outcomes. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013; 1 : CD010067.
van der Heijden I, Abrahams N, Sinclair D. Psychosocial group interventions to improve psychological well-being in adults living with HIV. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017; 3 : CD010806.
Viergever RF. Health Research Prioritization at WHO: An Overview of Methodology and High Level Analysis of WHO Led Health Research Priority Setting Exercises . Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2010.
Viergever RF, Olifson S, Ghaffar A, Terry RF. A checklist for health research priority setting: nine common themes of good practice. Health Research Policy and Systems 2010; 8 : 36.
Whitehead M. The concepts and principles of equity and health. International Journal of Health Services 1992; 22 : 429–25.
For permission to re-use material from the Handbook (either academic or commercial), please see here for full details.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
Steps in the literature review process.
- What is a literature review?
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
- You may need to some exploratory searching of the literature to get a sense of scope, to determine whether you need to narrow or broaden your focus
- Identify databases that provide the most relevant sources, and identify relevant terms (controlled vocabularies) to add to your search strategy
- Finalize your research question
- Think about relevant dates, geographies (and languages), methods, and conflicting points of view
- Conduct searches in the published literature via the identified databases
- Check to see if this topic has been covered in other discipline's databases
- Examine the citations of on-point articles for keywords, authors, and previous research (via references) and cited reference searching.
- Save your search results in a citation management tool (such as Zotero, Mendeley or EndNote)
- De-duplicate your search results
- Make sure that you've found the seminal pieces -- they have been cited many times, and their work is considered foundational
- Check with your professor or a librarian to make sure your search has been comprehensive
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of individual sources and evaluate for bias, methodologies, and thoroughness
- Group your results in to an organizational structure that will support why your research needs to be done, or that provides the answer to your research question
- Develop your conclusions
- Are there gaps in the literature?
- Where has significant research taken place, and who has done it?
- Is there consensus or debate on this topic?
- Which methodological approaches work best?
- For example: Background, Current Practices, Critics and Proponents, Where/How this study will fit in
- Organize your citations and focus on your research question and pertinent studies
- Compile your bibliography
Note: The first four steps are the best points at which to contact a librarian. Your librarian can help you determine the best databases to use for your topic, assess scope, and formulate a search strategy.
Videos Tutorials about Literature Reviews
This 4.5 minute video from Academic Education Materials has a Creative Commons License and a British narrator.
Recommended Reading
- Last Updated: Aug 26, 2024 5:59 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Reference management. Clean and simple.
What is a literature review? [with examples]

What is a literature review?
The purpose of a literature review, how to write a literature review, the format of a literature review, general formatting rules, the length of a literature review, literature review examples, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, related articles.
A literature review is an assessment of the sources in a chosen topic of research.
In a literature review, you’re expected to report on the existing scholarly conversation, without adding new contributions.
If you are currently writing one, you've come to the right place. In the following paragraphs, we will explain:
- the objective of a literature review
- how to write a literature review
- the basic format of a literature review
Tip: It’s not always mandatory to add a literature review in a paper. Theses and dissertations often include them, whereas research papers may not. Make sure to consult with your instructor for exact requirements.
The four main objectives of a literature review are:
- Studying the references of your research area
- Summarizing the main arguments
- Identifying current gaps, stances, and issues
- Presenting all of the above in a text
Ultimately, the main goal of a literature review is to provide the researcher with sufficient knowledge about the topic in question so that they can eventually make an intervention.
The format of a literature review is fairly standard. It includes an:
- introduction that briefly introduces the main topic
- body that includes the main discussion of the key arguments
- conclusion that highlights the gaps and issues of the literature
➡️ Take a look at our guide on how to write a literature review to learn more about how to structure a literature review.
First of all, a literature review should have its own labeled section. You should indicate clearly in the table of contents where the literature can be found, and you should label this section as “Literature Review.”
➡️ For more information on writing a thesis, visit our guide on how to structure a thesis .
There is no set amount of words for a literature review, so the length depends on the research. If you are working with a large amount of sources, it will be long. If your paper does not depend entirely on references, it will be short.
Take a look at these three theses featuring great literature reviews:
- School-Based Speech-Language Pathologist's Perceptions of Sensory Food Aversions in Children [ PDF , see page 20]
- Who's Writing What We Read: Authorship in Criminological Research [ PDF , see page 4]
- A Phenomenological Study of the Lived Experience of Online Instructors of Theological Reflection at Christian Institutions Accredited by the Association of Theological Schools [ PDF , see page 56]
Literature reviews are most commonly found in theses and dissertations. However, you find them in research papers as well.
There is no set amount of words for a literature review, so the length depends on the research. If you are working with a large amount of sources, then it will be long. If your paper does not depend entirely on references, then it will be short.
No. A literature review should have its own independent section. You should indicate clearly in the table of contents where the literature review can be found, and label this section as “Literature Review.”
The main goal of a literature review is to provide the researcher with sufficient knowledge about the topic in question so that they can eventually make an intervention.
How to write a literature review introduction (+ examples)

The introduction to a literature review serves as your reader’s guide through your academic work and thought process. Explore the significance of literature review introductions in review papers, academic papers, essays, theses, and dissertations. We delve into the purpose and necessity of these introductions, explore the essential components of literature review introductions, and provide step-by-step guidance on how to craft your own, along with examples.
Why you need an introduction for a literature review
In academic writing , the introduction for a literature review is an indispensable component. Effective academic writing requires proper paragraph structuring to guide your reader through your argumentation. This includes providing an introduction to your literature review.
It is imperative to remember that you should never start sharing your findings abruptly. Even if there isn’t a dedicated introduction section .
When you need an introduction for a literature review
There are three main scenarios in which you need an introduction for a literature review:
What to include in a literature review introduction
It is crucial to customize the content and depth of your literature review introduction according to the specific format of your academic work.
In practical terms, this implies, for instance, that the introduction in an academic literature review paper, especially one derived from a systematic literature review , is quite comprehensive. Particularly compared to the rather brief one or two introductory sentences that are often found at the beginning of a literature review section in a standard academic paper. The introduction to the literature review chapter in a thesis or dissertation again adheres to different standards.
Academic literature review paper
The introduction of an academic literature review paper, which does not rely on empirical data, often necessitates a more extensive introduction than the brief literature review introductions typically found in empirical papers. It should encompass:
Regular literature review section in an academic article or essay
In a standard 8000-word journal article, the literature review section typically spans between 750 and 1250 words. The first few sentences or the first paragraph within this section often serve as an introduction. It should encompass:
In some cases, you might include:
Introduction to a literature review chapter in thesis or dissertation
Some students choose to incorporate a brief introductory section at the beginning of each chapter, including the literature review chapter. Alternatively, others opt to seamlessly integrate the introduction into the initial sentences of the literature review itself. Both approaches are acceptable, provided that you incorporate the following elements:
Examples of literature review introductions
Example 1: an effective introduction for an academic literature review paper.
To begin, let’s delve into the introduction of an academic literature review paper. We will examine the paper “How does culture influence innovation? A systematic literature review”, which was published in 2018 in the journal Management Decision.
Example 2: An effective introduction to a literature review section in an academic paper
The second example represents a typical academic paper, encompassing not only a literature review section but also empirical data, a case study, and other elements. We will closely examine the introduction to the literature review section in the paper “The environmentalism of the subalterns: a case study of environmental activism in Eastern Kurdistan/Rojhelat”, which was published in 2021 in the journal Local Environment.
The paper begins with a general introduction and then proceeds to the literature review, designated by the authors as their conceptual framework. Of particular interest is the first paragraph of this conceptual framework, comprising 142 words across five sentences:
Thus, the author successfully introduces the literature review, from which point onward it dives into the main concept (‘subalternity’) of the research, and reviews the literature on socio-economic justice and environmental degradation.
Examples 3-5: Effective introductions to literature review chapters
Numerous universities offer online repositories where you can access theses and dissertations from previous years, serving as valuable sources of reference. Many of these repositories, however, may require you to log in through your university account. Nevertheless, a few open-access repositories are accessible to anyone, such as the one by the University of Manchester . It’s important to note though that copyright restrictions apply to these resources, just as they would with published papers.
Master’s thesis literature review introduction
Phd thesis literature review chapter introduction, phd thesis literature review introduction.
The last example is the doctoral thesis Metacognitive strategies and beliefs: Child correlates and early experiences Chan, K. Y. M. (Author). 31 Dec 2020 . The author clearly conducted a systematic literature review, commencing the review section with a discussion of the methodology and approach employed in locating and analyzing the selected records.
Steps to write your own literature review introduction
Master academia, get new content delivered directly to your inbox, the best answers to "what are your plans for the future", 10 tips for engaging your audience in academic writing, related articles, 37 creative ways to get motivation to study, minimalist writing for a better thesis, separating your self-worth from your phd work, how to develop an awesome phd timeline step-by-step.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1: Introduction
Learning objectives.
At the conclusion of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Identify the purpose of the literature review in the research process
- Distinguish between different types of literature reviews
1.1 What is a Literature Review?
Pick up nearly any book on research methods and you will find a description of a literature review. At a basic level, the term implies a survey of factual or nonfiction books, articles, and other documents published on a particular subject. Definitions may be similar across the disciplines, with new types and definitions continuing to emerge. Generally speaking, a literature review is a:
- “comprehensive background of the literature within the interested topic area…” ( O’Gorman & MacIntosh, 2015, p. 31 ).
- “critical component of the research process that provides an in-depth analysis of recently published research findings in specifically identified areas of interest.” ( House, 2018, p. 109 ).
- “written document that presents a logically argued case founded on a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge about a topic of study” ( Machi & McEvoy, 2012, p. 4 ).
As a foundation for knowledge advancement in every discipline, it is an important element of any research project. At the graduate or doctoral level, the literature review is an essential feature of thesis and dissertation, as well as grant proposal writing. That is to say, “A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research…A researcher cannot perform significant research without first understanding the literature in the field.” ( Boote & Beile, 2005, p. 3 ). It is by this means, that a researcher demonstrates familiarity with a body of knowledge and thereby establishes credibility with a reader. An advanced-level literature review shows how prior research is linked to a new project, summarizing and synthesizing what is known while identifying gaps in the knowledge base, facilitating theory development, closing areas where enough research already exists, and uncovering areas where more research is needed. ( Webster & Watson, 2002, p. xiii )
A graduate-level literature review is a compilation of the most significant previously published research on your topic. Unlike an annotated bibliography or a research paper you may have written as an undergraduate, your literature review will outline, evaluate and synthesize relevant research and relate those sources to your own thesis or research question. It is much more than a summary of all the related literature.
It is a type of writing that demonstrate the importance of your research by defining the main ideas and the relationship between them. A good literature review lays the foundation for the importance of your stated problem and research question.
Literature reviews:
- define a concept
- map the research terrain or scope
- systemize relationships between concepts
- identify gaps in the literature ( Rocco & Plathotnik, 2009, p. 128 )
The purpose of a literature review is to demonstrate that your research question is meaningful. Additionally, you may review the literature of different disciplines to find deeper meaning and understanding of your topic. It is especially important to consider other disciplines when you do not find much on your topic in one discipline. You will need to search the cognate literature before claiming there is “little previous research” on your topic.
Well developed literature reviews involve numerous steps and activities. The literature review is an iterative process because you will do at least two of them: a preliminary search to learn what has been published in your area and whether there is sufficient support in the literature for moving ahead with your subject. After this first exploration, you will conduct a deeper dive into the literature to learn everything you can about the topic and its related issues.
Literature Review Tutorial

1.2 Literature Review Basics
An effective literature review must:
- Methodologically analyze and synthesize quality literature on a topic
- Provide a firm foundation to a topic or research area
- Provide a firm foundation for the selection of a research methodology
- Demonstrate that the proposed research contributes something new to the overall body of knowledge of advances the research field’s knowledge base. ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
All literature reviews, whether they are qualitative, quantitative or both, will at some point:
- Introduce the topic and define its key terms
- Establish the importance of the topic
- Provide an overview of the amount of available literature and its types (for example: theoretical, statistical, speculative)
- Identify gaps in the literature
- Point out consistent finding across studies
- Arrive at a synthesis that organizes what is known about a topic
- Discusses possible implications and directions for future research
1.3 Types of Literature Reviews
There are many different types of literature reviews, however there are some shared characteristics or features. Remember a comprehensive literature review is, at its most fundamental level, an original work based on an extensive critical examination and synthesis of the relevant literature on a topic. As a study of the research on a particular topic, it is arranged by key themes or findings, which may lead up to or link to the research question. In some cases, the research question will drive the type of literature review that is undertaken.
The following section includes brief descriptions of the terms used to describe different literature review types with examples of each. The included citations are open access, Creative Commons licensed or copyright-restricted.
1.3.1 Types of Review
1.3.1.1 conceptual.
Guided by an understanding of basic issues rather than a research methodology. You are looking for key factors, concepts or variables and the presumed relationship between them. The goal of the conceptual literature review is to categorize and describe concepts relevant to your study or topic and outline a relationship between them. You will include relevant theory and empirical research.
Examples of a Conceptual Review:
- Education : The formality of learning science in everyday life: A conceptual literature review. ( Dohn, 2010 ).
- Education : Are we asking the right questions? A conceptual review of the educational development literature in higher education. ( Amundsen & Wilson, 2012 ).
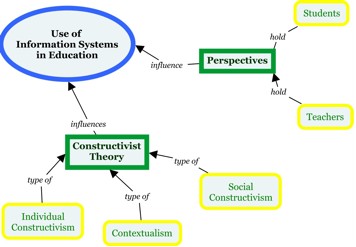
1.3.1.2 Empirical
An empirical literature review collects, creates, arranges, and analyzes numeric data reflecting the frequency of themes, topics, authors and/or methods found in existing literature. Empirical literature reviews present their summaries in quantifiable terms using descriptive and inferential statistics.
Examples of an Empirical Review:
- Nursing : False-positive findings in Cochrane meta-analyses with and without application of trial sequential analysis: An empirical review. ( Imberger, Thorlund, Gluud, & Wettersley, 2016 ).
- Education : Impediments of e-learning adoption in higher learning institutions of Tanzania: An empirical review ( Mwakyusa & Mwalyagile, 2016 ).
1.3.1.3 Exploratory
Unlike a synoptic literature review, the purpose here is to provide a broad approach to the topic area. The aim is breadth rather than depth and to get a general feel for the size of the topic area. A graduate student might do an exploratory review of the literature before beginning a synoptic, or more comprehensive one.
Examples of an Exploratory Review:
- Education : University research management: An exploratory literature review. ( Schuetzenmeister, 2010 ).
- Education : An exploratory review of design principles in constructivist gaming learning environments. ( Rosario & Widmeyer, 2009 ).

1.3.1.4 Focused
A type of literature review limited to a single aspect of previous research, such as methodology. A focused literature review generally will describe the implications of choosing a particular element of past research, such as methodology in terms of data collection, analysis and interpretation.
Examples of a Focused Review:
- Nursing : Clinical inertia in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A focused literature review. ( Khunti, Davies, & Khunti, 2015 ).
- Education : Language awareness: Genre awareness-a focused review of the literature. ( Stainton, 1992 ).
1.3.1.5 Integrative
Critiques past research and draws overall conclusions from the body of literature at a specified point in time. Reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way. Most integrative reviews are intended to address mature topics or emerging topics. May require the author to adopt a guiding theory, a set of competing models, or a point of view about a topic. For more description of integrative reviews, see Whittemore & Knafl (2005).
Examples of an Integrative Review:
- Nursing : Interprofessional teamwork and collaboration between community health workers and healthcare teams: An integrative review. ( Franklin, Bernhardt, Lopez, Long-Middleton, & Davis, 2015 ).
- Education : Exploring the gap between teacher certification and permanent employment in Ontario: An integrative literature review. ( Brock & Ryan, 2016 ).
1.3.1.6 Meta-analysis
A subset of a systematic review, that takes findings from several studies on the same subject and analyzes them using standardized statistical procedures to pool together data. Integrates findings from a large body of quantitative findings to enhance understanding, draw conclusions, and detect patterns and relationships. Gather data from many different, independent studies that look at the same research question and assess similar outcome measures. Data is combined and re-analyzed, providing a greater statistical power than any single study alone. It’s important to note that not every systematic review includes a meta-analysis but a meta-analysis can’t exist without a systematic review of the literature.
Examples of a Meta-Analysis:
- Education : Efficacy of the cooperative learning method on mathematics achievement and attitude: A meta-analysis research. ( Capar & Tarim, 2015 ).
- Nursing : A meta-analysis of the effects of non-traditional teaching methods on the critical thinking abilities of nursing students. ( Lee, Lee, Gong, Bae, & Choi, 2016 ).
- Education : Gender differences in student attitudes toward science: A meta-analysis of the literature from 1970 to 1991. ( Weinburgh, 1995 ).
1.3.1.7 Narrative/Traditional
An overview of research on a particular topic that critiques and summarizes a body of literature. Typically broad in focus. Relevant past research is selected and synthesized into a coherent discussion. Methodologies, findings and limits of the existing body of knowledge are discussed in narrative form. Sometimes also referred to as a traditional literature review. Requires a sufficiently focused research question. The process may be subject to bias that supports the researcher’s own work.
Examples of a Narrative/Traditional Review:
- Nursing : Family carers providing support to a person dying in the home setting: A narrative literature review. ( Morris, King, Turner, & Payne, 2015 ).
- Education : Adventure education and Outward Bound: Out-of-class experiences that make a lasting difference. ( Hattie, Marsh, Neill, & Richards, 1997 ).
- Education : Good quality discussion is necessary but not sufficient in asynchronous tuition: A brief narrative review of the literature. ( Fear & Erikson-Brown, 2014 ).
- Nursing : Outcomes of physician job satisfaction: A narrative review, implications, and directions for future research. ( Williams & Skinner, 2003 ).
1.3.1.8 Realist
Aspecific type of literature review that is theory-driven and interpretative and is intended to explain the outcomes of a complex intervention program(s).
Examples of a Realist Review:
- Nursing : Lean thinking in healthcare: A realist review of the literature. ( Mazzacato, Savage, Brommels, 2010 ).
- Education : Unravelling quality culture in higher education: A realist review. ( Bendermacher, Egbrink, Wolfhagen, & Dolmans, 2017 ).
1.3.1.9 Scoping
Tend to be non-systematic and focus on breadth of coverage conducted on a topic rather than depth. Utilize a wide range of materials; may not evaluate the quality of the studies as much as count the number. One means of understanding existing literature. Aims to identify nature and extent of research; preliminary assessment of size and scope of available research on topic. May include research in progress.
Examples of a Scoping Review:
- Nursing : Organizational interventions improving access to community-based primary health care for vulnerable populations: A scoping review. ( Khanassov, Pluye, Descoteaux, Haggerty, Russell, Gunn, & Levesque, 2016 ).
- Education : Interdisciplinary doctoral research supervision: A scoping review. ( Vanstone, Hibbert, Kinsella, McKenzie, Pitman, & Lingard, 2013 ).
- Nursing : A scoping review of the literature on the abolition of user fees in health care services in Africa. ( Ridde, & Morestin, 2011 ).
1.3.1.10 Synoptic
Unlike an exploratory review, the purpose is to provide a concise but accurate overview of all material that appears to be relevant to a chosen topic. Both content and methodological material is included. The review should aim to be both descriptive and evaluative. Summarizes previous studies while also showing how the body of literature could be extended and improved in terms of content and method by identifying gaps.
Examples of a Synoptic Review:
- Education : Theoretical framework for educational assessment: A synoptic review. ( Ghaicha, 2016 ).
- Education : School effects research: A synoptic review of past efforts and some suggestions for the future. ( Cuttance, 1981 ).
1.3.1.11 Systematic Review
A rigorous review that follows a strict methodology designed with a presupposed selection of literature reviewed. Undertaken to clarify the state of existing research, the evidence, and possible implications that can be drawn from that. Using comprehensive and exhaustive searching of the published and unpublished literature, searching various databases, reports, and grey literature. Transparent and reproducible in reporting details of time frame, search and methods to minimize bias. Must include a team of at least 2-3 and includes the critical appraisal of the literature. For more description of systematic reviews, including links to protocols, checklists, workflow processes, and structure see “ A Young Researcher’s Guide to a Systematic Review “.
Examples of a Systematic Review:
- Education : The potentials of using cloud computing in schools: A systematic literature review ( Hartmann, Braae, Pedersen, & Khalid, 2017 )
- Nursing : Is butter back? A systematic review and meta-analysis of butter consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and total mortality. ( Pimpin, Wu, Haskelberg, Del Gobbo, & Mozaffarian, 2016 ).
- Education : The use of research to improve professional practice: a systematic review of the literature. ( Hemsley-Brown & Sharp, 2003 ).
- Nursing : Using computers to self-manage type 2 diabetes. ( Pal, Eastwood, Michie, Farmer, Barnard, Peacock, Wood, Inniss, & Murray, 2013 ).
1.3.1.12 Umbrella/Overview of Reviews
Compiles evidence from multiple systematic reviews into one document. Focuses on broad condition or problem for which there are competing interventions and highlights reviews that address those interventions and their effects. Often used in recommendations for practice.
Examples of an Umbrella/Overview Review:
- Education : Reflective practice in healthcare education: An umbrella review. ( Fragknos, 2016 ).
- Nursing : Systematic reviews of psychosocial interventions for autism: an umbrella review. ( Seida, Ospina, Karkhaneh, Hartling, Smith, & Clark, 2009 ).
For a brief discussion see “ Not all literature reviews are the same ” (Thomson, 2013).
1.4 Why do a Literature Review?
The purpose of the literature review is the same regardless of the topic or research method. It tests your own research question against what is already known about the subject.
1.4.1 First – It’s part of the whole. Omission of a literature review chapter or section in a graduate-level project represents a serious void or absence of critical element in the research process.
The outcome of your review is expected to demonstrate that you:
- can systematically explore the research in your topic area
- can read and critically analyze the literature in your discipline and then use it appropriately to advance your own work
- have sufficient knowledge in the topic to undertake further investigation
1.4.2 Second – It’s good for you!
- You improve your skills as a researcher
- You become familiar with the discourse of your discipline and learn how to be a scholar in your field
- You learn through writing your ideas and finding your voice in your subject area
- You define, redefine and clarify your research question for yourself in the process
1.4.3 Third – It’s good for your reader. Your reader expects you to have done the hard work of gathering, evaluating and synthesizes the literature. When you do a literature review you:
- Set the context for the topic and present its significance
- Identify what’s important to know about your topic – including individual material, prior research, publications, organizations and authors.
- Demonstrate relationships among prior research
- Establish limitations of existing knowledge
- Analyze trends in the topic’s treatment and gaps in the literature
1.4.4 Why do a literature review?
- To locate gaps in the literature of your discipline
- To avoid reinventing the wheel
- To carry on where others have already been
- To identify other people working in the same field
- To increase your breadth of knowledge in your subject area
- To find the seminal works in your field
- To provide intellectual context for your own work
- To acknowledge opposing viewpoints
- To put your work in perspective
- To demonstrate you can discover and retrieve previous work in the area
1.5 Common Literature Review Errors
Graduate-level literature reviews are more than a summary of the publications you find on a topic. As you have seen in this brief introduction, literature reviews are a very specific type of research, analysis, and writing. We will explore these topics more in the next chapters. Some things to keep in mind as you begin your own research and writing are ways to avoid the most common errors seen in the first attempt at a literature review. For a quick review of some of the pitfalls and challenges a new researcher faces when he/she begins work, see “ Get Ready: Academic Writing, General Pitfalls and (oh yes) Getting Started! ”.
As you begin your own graduate-level literature review, try to avoid these common mistakes:
- Accepts another researcher’s finding as valid without evaluating methodology and data
- Contrary findings and alternative interpretations are not considered or mentioned
- Findings are not clearly related to one’s own study, or findings are too general
- Insufficient time allowed to define best search strategies and writing
- Isolated statistical results are simply reported rather than synthesizing the results
- Problems with selecting and using most relevant keywords, subject headings and descriptors
- Relies too heavily on secondary sources
- Search methods are not recorded or reported for transparency
- Summarizes rather than synthesizes articles
In conclusion, the purpose of a literature review is three-fold:
- to survey the current state of knowledge or evidence in the area of inquiry,
- to identify key authors, articles, theories, and findings in that area, and
- to identify gaps in knowledge in that research area.
A literature review is commonly done today using computerized keyword searches in online databases, often working with a trained librarian or information expert. Keywords can be combined using the Boolean operators, “and”, “or” and sometimes “not” to narrow down or expand the search results. Once a list of articles is generated from the keyword and subject heading search, the researcher must then manually browse through each title and abstract, to determine the suitability of that article before a full-text article is obtained for the research question.
Literature reviews should be reasonably complete, and not restricted to a few journals, a few years, or a specific methodology or research design. Reviewed articles may be summarized in the form of tables, and can be further structured using organizing frameworks such as a concept matrix.
A well-conducted literature review should indicate whether the initial research questions have already been addressed in the literature, whether there are newer or more interesting research questions available, and whether the original research questions should be modified or changed in light of findings of the literature review.
The review can also provide some intuitions or potential answers to the questions of interest and/or help identify theories that have previously been used to address similar questions and may provide evidence to inform policy or decision-making. ( Bhattacherjee, 2012 ).

Read Abstract 1. Refer to Types of Literature Reviews. What type of literature review do you think this study is and why? See the Answer Key for the correct response.
Nursing : To describe evidence of international literature on the safe care of the hospitalised child after the World Alliance for Patient Safety and list contributions of the general theoretical framework of patient safety for paediatric nursing.
An integrative literature review between 2004 and 2015 using the databases PubMed, Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Scopus, Web of Science and Wiley Online Library, and the descriptors Safety or Patient safety, Hospitalised child, Paediatric nursing, and Nursing care.
Thirty-two articles were analysed, most of which were from North American, with a descriptive approach. The quality of the recorded information in the medical records, the use of checklists, and the training of health workers contribute to safe care in paediatric nursing and improve the medication process and partnerships with parents.
General information available on patient safety should be incorporated in paediatric nursing care. ( Wegner, Silva, Peres, Bandeira, Frantz, Botene, & Predebon, 2017 ).
Read Abstract 2. Refer to Types of Literature Reviews. What type of lit review do you think this study is and why? See the Answer Key for the correct response.
Education : The focus of this paper centers around timing associated with early childhood education programs and interventions using meta-analytic methods. At any given assessment age, a child’s current age equals starting age, plus duration of program, plus years since program ended. Variability in assessment ages across the studies should enable everyone to identify the separate effects of all three time-related components. The project is a meta-analysis of evaluation studies of early childhood education programs conducted in the United States and its territories between 1960 and 2007. The population of interest is children enrolled in early childhood education programs between the ages of 0 and 5 and their control-group counterparts. Since the data come from a meta-analysis, the population for this study is drawn from many different studies with diverse samples. Given the preliminary nature of their analysis, the authors cannot offer conclusions at this point. ( Duncan, Leak, Li, Magnuson, Schindler, & Yoshikawa, 2011 ).
Test Yourself
See Answer Key for the correct responses.
The purpose of a graduate-level literature review is to summarize in as many words as possible everything that is known about my topic.
A literature review is significant because in the process of doing one, the researcher learns to read and critically assess the literature of a discipline and then uses it appropriately to advance his/her own research.
Read the following abstract and choose the correct type of literature review it represents.
Nursing: E-cigarette use has become increasingly popular, especially among the young. Its long-term influence upon health is unknown. Aim of this review has been to present the current state of knowledge about the impact of e-cigarette use on health, with an emphasis on Central and Eastern Europe. During the preparation of this narrative review, the literature on e-cigarettes available within the network PubMed was retrieved and examined. In the final review, 64 research papers were included. We specifically assessed the construction and operation of the e-cigarette as well as the chemical composition of the e-liquid; the impact that vapor arising from the use of e-cigarette explored in experimental models in vitro; and short-term effects of use of e-cigarettes on users’ health. Among the substances inhaled by the e-smoker, there are several harmful products, such as: formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, acroleine, propanal, nicotine, acetone, o-methyl-benzaldehyde, carcinogenic nitrosamines. Results from experimental animal studies indicate the negative impact of e-cigarette exposure on test models, such as ascytotoxicity, oxidative stress, inflammation, airway hyper reactivity, airway remodeling, mucin production, apoptosis, and emphysematous changes. The short-term impact of e-cigarettes on human health has been studied mostly in experimental setting. Available evidence shows that the use of e-cigarettes may result in acute lung function responses (e.g., increase in impedance, peripheral airway flow resistance) and induce oxidative stress. Based on the current available evidence, e-cigarette use is associated with harmful biologic responses, although it may be less harmful than traditional cigarettes. (J ankowski, Brożek, Lawson, Skoczyński, & Zejda, 2017 ).
- Meta-analysis
- Exploratory
Education: In this review, Mary Vorsino writes that she is interested in keeping the potential influences of women pragmatists of Dewey’s day in mind while presenting modern feminist re readings of Dewey. She wishes to construct a narrowly-focused and succinct literature review of thinkers who have donned a feminist lens to analyze Dewey’s approaches to education, learning, and democracy and to employ Dewey’s works in theorizing on gender and education and on gender in society. This article first explores Dewey as both an ally and a problematic figure in feminist literature and then investigates the broader sphere of feminist pragmatism and two central themes within it: (1) valuing diversity, and diverse experiences; and (2) problematizing fixed truths. ( Vorsino, 2015 ).
Image Attributions
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students Copyright © by Linda Frederiksen is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

PSYC 210: Foundations of Psychology
- Tips for Searching for Articles
What is a literature review?
Conducting a literature review, organizing a literature review, writing a literature review, helpful book.
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Google Scholar

A literature review is a compilation of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches
Source: "What is a Literature Review?", Old Dominion University, https://guides.lib.odu.edu/c.php?g=966167&p=6980532
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by a central research question. It represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted, and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow.
- Write down terms that are related to your question for they will be useful for searches later.
2. Decide on the scope of your review.
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment.
- Consider these things when planning your time for research.
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
- By Research Guide
4. Conduct your searches and find the literature.
- Review the abstracts carefully - this will save you time!
- Many databases will have a search history tab for you to return to for later.
- Use bibliographies and references of research studies to locate others.
- Use citation management software such as Zotero to keep track of your research citations.
5. Review the literature.
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question you are reviewing? What are the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze the literature review, samples and variables used, results, and conclusions. Does the research seem complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicted studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Are they experts or novices? Has the study been cited?
Source: "Literature Review", University of West Florida, https://libguides.uwf.edu/c.php?g=215113&p=5139469
A literature review is not a summary of the sources but a synthesis of the sources. It is made up of the topics the sources are discussing. Each section of the review is focused on a topic, and the relevant sources are discussed within the context of that topic.
1. Select the most relevant material from the sources
- Could be material that answers the question directly
- Extract as a direct quote or paraphrase
2. Arrange that material so you can focus on it apart from the source text itself
- You are now working with fewer words/passages
- Material is all in one place
3. Group similar points, themes, or topics together and label them
- The labels describe the points, themes, or topics that are the backbone of your paper’s structure
4. Order those points, themes, or topics as you will discuss them in the paper, and turn the labels into actual assertions
- A sentence that makes a point that is directly related to your research question or thesis
This is now the outline for your literature review.
Source: "Organizing a Review of the Literature – The Basics", George Mason University Writing Center, https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/writing-resources/research-based-writing/organizing-literature-reviews-the-basics
- Literature Review Matrix Here is a template on how people tend to organize their thoughts. The matrix template is a good way to write out the key parts of each article and take notes. Downloads as an XLSX file.
The most common way that literature reviews are organized is by theme or author. Find a general pattern of structure for the review. When organizing the review, consider the following:
- the methodology
- the quality of the findings or conclusions
- major strengths and weaknesses
- any other important information
Writing Tips:
- Be selective - Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. It should directly relate to the review's focus.
- Use quotes sparingly.
- Keep your own voice - Your voice (the writer's) should remain front and center. .
- Aim for one key figure/table per section to illustrate complex content, summarize a large body of relevant data, or describe the order of a process
- Legend below image/figure and above table and always refer to them in text
Source: "Composing your Literature Review", Florida A&M University, https://library.famu.edu/c.php?g=577356&p=3982811
- << Previous: Tips for Searching for Articles
- Next: Citing Your Sources >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://infoguides.pepperdine.edu/PSYC210
Explore. Discover. Create.
Copyright © 2022 Pepperdine University
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Request Info
- Search Search Site Faculty/Staff
- Open Navigation Menu Menu Close Navigation Menu
- Literature Review Guidelines
Making sense of what has been written on your topic.
Goals of a literature review:.
Before doing work in primary sources, historians must know what has been written on their topic. They must be familiar with theories and arguments–as well as facts–that appear in secondary sources.
Before you proceed with your research project, you too must be familiar with the literature: you do not want to waste time on theories that others have disproved and you want to take full advantage of what others have argued. You want to be able to discuss and analyze your topic.
Your literature review will demonstrate your familiarity with your topic’s secondary literature.
GUIDELINES FOR A LITERATURE REVIEW:
1) LENGTH: 8-10 pages of text for Senior Theses (485) (consult with your professor for other classes), with either footnotes or endnotes and with a works-consulted bibliography. [See also the citation guide on this site.]
2) NUMBER OF WORKS REVIEWED: Depends on the assignment, but for Senior Theses (485), at least ten is typical.
3) CHOOSING WORKS:
Your literature review must include enough works to provide evidence of both the breadth and the depth of the research on your topic or, at least, one important angle of it. The number of works necessary to do this will depend on your topic. For most topics, AT LEAST TEN works (mostly books but also significant scholarly articles) are necessary, although you will not necessarily give all of them equal treatment in your paper (e.g., some might appear in notes rather than the essay). 4) ORGANIZING/ARRANGING THE LITERATURE:
As you uncover the literature (i.e., secondary writing) on your topic, you should determine how the various pieces relate to each other. Your ability to do so will demonstrate your understanding of the evolution of literature.
You might determine that the literature makes sense when divided by time period, by methodology, by sources, by discipline, by thematic focus, by race, ethnicity, and/or gender of author, or by political ideology. This list is not exhaustive. You might also decide to subdivide categories based on other criteria. There is no “rule” on divisions—historians wrote the literature without consulting each other and without regard to the goal of fitting into a neat, obvious organization useful to students.
The key step is to FIGURE OUT the most logical, clarifying angle. Do not arbitrarily choose a categorization; use the one that the literature seems to fall into. How do you do that? For every source, you should note its thesis, date, author background, methodology, and sources. Does a pattern appear when you consider such information from each of your sources? If so, you have a possible thesis about the literature. If not, you might still have a thesis.
Consider: Are there missing elements in the literature? For example, no works published during a particular (usually fairly lengthy) time period? Or do studies appear after long neglect of a topic? Do interpretations change at some point? Does the major methodology being used change? Do interpretations vary based on sources used?
Follow these links for more help on analyzing historiography and historical perspective .
5) CONTENTS OF LITERATURE REVIEW:
The literature review is a research paper with three ingredients:
a) A brief discussion of the issue (the person, event, idea). [While this section should be brief, it needs to set up the thesis and literature that follow.] b) Your thesis about the literature c) A clear argument, using the works on topic as evidence, i.e., you discuss the sources in relation to your thesis, not as a separate topic.
These ingredients must be presented in an essay with an introduction, body, and conclusion.
6) ARGUING YOUR THESIS:
The thesis of a literature review should not only describe how the literature has evolved, but also provide a clear evaluation of that literature. You should assess the literature in terms of the quality of either individual works or categories of works. For instance, you might argue that a certain approach (e.g. social history, cultural history, or another) is better because it deals with a more complex view of the issue or because they use a wider array of source materials more effectively. You should also ensure that you integrate that evaluation throughout your argument. Doing so might include negative assessments of some works in order to reinforce your argument regarding the positive qualities of other works and approaches to the topic.
Within each group, you should provide essential information about each work: the author’s thesis, the work’s title and date, the author’s supporting arguments and major evidence.
In most cases, arranging the sources chronologically by publication date within each section makes the most sense because earlier works influenced later ones in one way or another. Reference to publication date also indicates that you are aware of this significant historiographical element.
As you discuss each work, DO NOT FORGET WHY YOU ARE DISCUSSING IT. YOU ARE PRESENTING AND SUPPORTING A THESIS ABOUT THE LITERATURE.
When discussing a particular work for the first time, you should refer to it by the author’s full name, the work’s title, and year of publication (either in parentheses after the title or worked into the sentence).
For example, “The field of slavery studies has recently been transformed by Ben Johnson’s The New Slave (2001)” and “Joe Doe argues in his 1997 study, Slavery in America, that . . . .”
Your paper should always note secondary sources’ relationship to each other, particularly in terms of your thesis about the literature (e.g., “Unlike Smith’s work, Mary Brown’s analysis reaches the conclusion that . . . .” and “Because of Anderson’s reliance on the president’s personal papers, his interpretation differs from Barry’s”). The various pieces of the literature are “related” to each other, so you need to indicate to the reader some of that relationship. (It helps the reader follow your thesis, and it convinces the reader that you know what you are talking about.)
7) DOCUMENTATION:
Each source you discuss in your paper must be documented using footnotes/endnotes and a bibliography. Providing author and title and date in the paper is not sufficient. Use correct Turabian/Chicago Manual of Style form. [See Bibliography and Footnotes/Endnotes pages.]
In addition, further supporting, but less significant, sources should be included in content foot or endnotes . (e.g., “For a similar argument to Ben Johnson’s, see John Terry, The Slave Who Was New (New York: W. W. Norton, 1985), 3-45.”)
8 ) CONCLUSION OF LITERATURE REVIEW:
Your conclusion should not only reiterate your argument (thesis), but also discuss questions that remain unanswered by the literature. What has the literature accomplished? What has not been studied? What debates need to be settled?
Additional writing guidelines
History and American Studies
- About the Department
- Major Requirements & Courses
- What courses will I take as an History major?
- What can I do with my History degree?
- History 485
- Methodology
- Choosing a Topic
- Book Reviews
- Historiographic Clues
- Understanding Historical Perspective
- Sample Literature Review
- Using Quotations
- Ellipses and Brackets
- Footnotes and Endnotes
- Content Notes
- Citation Guide
- Citing Non-Print Resources
- How to Annotate
- Annotated Examples
- Journals vs. Magazines
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Historians Define Plagiarism
- Plagiarism Tutorial
- UMW Honor System
- Presentation Guidelines
- Tips for Leading Seminars
- Hints for Class Discussion
- Speaking Center
- Guidelines for a Research Paper
- Library Research Plan
- How to Use ILL
- Database Guide
- Guide to Online Research
- Writing Guidelines
- Recognizing Passive Voice
- Introduction and Conclusion
- MS Word’s Grammar and Spellcheck
- Writing Center
- What You Need to Know
- Links to Online Primary Sources by Region
- What will I learn from my American Studies major?
- What courses will I take as an American Studies major?
- What can I do with my American Studies degree?
- American Studies 485
- For Prospective Students
- Honors and Award Recipients
- Internships
Alumni Intros

How have History & American Studies majors built careers after earning their degrees? Learn more by clicking the image above.
Recent Posts
- History and American Studies Symposium–April 26, 2024
- Fall 2024 Courses
- Fall 2023 Symposium – 12/8 – All Welcome!
- Spring ’24 Course Flyers
- Internship Opportunity – Chesapeake Gateways Ambassador
- Congratulations to our Graduates!
- History and American Studies Symposium–April 21, 2023
- View umwhistory’s profile on Facebook
- View umwhistory’s profile on Twitter
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to content

- Home – AI for Research

How to write a scoping review
This article explains how to conduct a scoping review. If you’re interested in a free tool that helps you write literature reviews quicker, check out Avidnote .
A scoping review presents a relatively “new” approach to synthesizing research literature which is different from the traditional systematic review. The difference of scoping review concern primarily the purpose and aims of the review. With a scoping review, the primary goal is to give the reader an overview of the current evidence from the literature with respect to a specific research topic without giving a summary answer to a discrete research question. Scoping reviews are typically less exhaustive than systematic reviews. The general purpose for conducting a scoping review is to map and identify the available evidence (Anderson et al., 2008; Arksey and O’Malley, 2005)
Scoping reviews can be preferred to systematic reviews in cases where the review’s objectives include identification of gaps in knowledge, interrogating a body of literature, describing concepts, or scrutinizing research conduct. They can also act as useful precursors to systematic reviews (Munn et al., 2018) as well as help determine the suitability of inclusion criteria and likely research questions. Because of the exploratory nature of scoping reviews, it is not necessary that each review must be a holistic coverage of all the extant body of knowledge in the subject matter being reviewed.
What is a scoping review?
According to the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, scoping reviews are:
“exploratory projects that map the literature available on a topic, identifying key concepts, theories, sources of evidence and gaps in the research.”
A more extensive definition was given by Colquhoun, et al (2014).
“A scoping review or scoping study is a form of knowledge synthesis that addresses an exploratory research question aimed at mapping key concepts, types of evidence, and gaps in research related to a defined area or field by systematically searching, selecting, and synthesizing existing knowledge” Colquhoun, et al. J of Clin Epi. 2014, 67, p. 1292-94
How to perform a scoping study in 5 easy steps
In the sections below, I intend to summarize the guidelines provided by the Joana Briggs Institute for conducting a scoping review.
Step 1 – Define the topic that you will be reviewing; its objectives and any potential sub-questions.
Step 2 – Develop a review protocol. The protocols functions as the plan behind your review. Here you’ll state eligibility criteria (for inclusion/exclusion), how you screened the literature and the charting process that you utilized.
Step 3 – Apply PCC framework
Step 4 – Perform systematic literature searches
Step 5 – Screen the obtained results and only include studies that meet your eligibility criteria
Step 6 – Extract and chart the data you extracted from the collected studies
Step 7 – Write a summary of the evidence to answer your research question(s).
The list above summarizes the process behind performing a scoping review. Below, we elaborate further, based on recommendations from the Joana Briggs Institute.
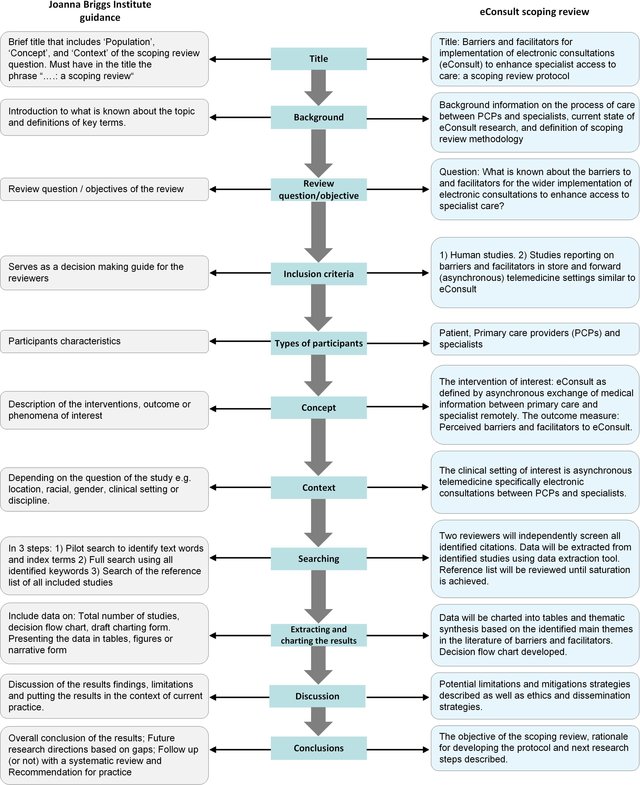
Title of the review protocol
The suggested length according to JBI of the length for the introduction section of the scoping review protocol is roughly 1,000 words. The protocol (and the review itself) should have an informative title that helps shed light on the topic of the scoping review. To this end, the phrase – “…: a scoping review” should be attached to the title. Such an attachment will enable readers to easily have an idea of what the document is about. Be sure to include the word “protocol” if that is what the document is about.
For example, “Assessing the impact of treating anxiety using nigella sativa: a scoping review protocol.”
You should also avoid constructing titles in question format. The Joana Briggs Institute (JBI) recommends a “PCC” mnemonic to help in generating a clear and meaningful title for a scoping review. The acronym PCC stands for population, concept, and context. According to the Institute:
- the population aspect focuses on “important characteristics of participants, including age and other qualifying criteria.”
- concept may include details related to elements that would appear in a standard systematic review. Among such details are “interventions” and/or “phenomena of interest” and/or “outcomes.”
- context can be made up of cultural factors like geographic location and/or particular gender or racial-based interests. In some reviews, context can also include information about the particular setting.
Adopting the PCC mnemonic also enables the reviewers to craft a title that conveys important details to readers, e.g., the focus and scope of the review as well as how the reviews can be applied to their needs. In a nutshell, the PCC concept is necessary to establish concord between the title, review question(s), and inclusion criteria.
Scoping review question(s)
Just like the title, the scoping review question(s), should also reflect the PCC elements. The question guides and directs the reviewers to develop inclusion criteria that are suitable for the scoping review. Moreover, a clearly expressed question helps in constructing the protocol, makes for an optimal literature search, and offers a clarified structure for developing the scoping review. A Scoping review will usually come with only one primary question. For example,
Are there any side effects in the various treatments for depression?
However, sub-questions may be necessary, especially if the primary question neither sufficiently reflects the PCC nor the review’s objective(s). In such a scenario, sub-questions can help shed more light on the specific characteristics of a population, concept, or context. Sub-questions can also help to highlight the most likely way to map evidence with respect to the PCC elements. Using context, for example, the above primary question which deals with just the side effects of depression treatments can be expanded to:
Are there any geographical contexts that depression treatments have been associated with side effects?
Introduction
The introduction should be broad enough to capture all the key elements of the topic being reviewed. It should include the reason for carrying out the scoping review (including the rationale behind each of the elements as well as the information the review intends to disseminate in addition to the objective(s) of the review.
Be sure to explain any definitions that are relevant to the topic under review. You should also ensure that the introductory information must be presented in a way that sufficiently sheds light on the inclusion criteria. For instance, information about the existence or otherwise of scoping reviews, systematic reviews, research syntheses, and/or primary research papers on the topic. This will help reinforce your reason or rationale for undertaking the scoping review.
The concluding phase of the introduction should indicate that the reviewer has already conducted a preparatory search for available scoping reviews (and maybe systematic reviews as well) on the topic. The dates of such searches, the databases, and journals searched and search platforms used must also be included. Some examples in this regard include the JBI Evidence Synthesis, Evidence for Policy and Practice Information (EPPI), and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
If scoping and/or systematic reviews about the topic are available, the reviewers then have to clearly justify how their proposed review will differ from those they have identified. This will enable readers to easily determine any new insight or knowledge which the forthcoming review espouses when compared to existing evidence syntheses.
Finally, the concluding phase of the introduction should explain how the review’s objective(s) align with the main elements of the inclusion criteria, for example, the PCC.
Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria capture the reviewers’ reasons for selecting which sources that will be part of their scoping review (or otherwise). These reasons should be clearly explained in a way that enables readers to easily comprehend the reviewers’ ideas. As stated earlier, there must be concord or synergy between the title, question(s), and inclusion criteria.
Search strategy
Even with time and resource constraints, the search strategy for a scoping review should try to be as broad-based as possible. This will help the reviewers to fish out both published and unpublished primary sources of evidence and reviews. The reviewers should endeavor to narrate and rationalize any limitations that negatively impacted the scope of their search strategy.
It is recommended that the search strategy follows the three steps enumerated below.
1) Conducting a preliminary search on not less than a couple of web-based databases determined to be relevant to the topic.
2) A second search that includes all identified keywords and index terms to be conducted on all the selected databases.
3) Identified reports and articles should be searched.
The reviewer has to specify both the languages he or she will consider for inclusion and the timeframe. They should also provide clear reasons for such specifications. To ensure an optimal search strategy, several search iterations may be necessary especially if the evidence base becomes clearer to reviewers thus leading to the knowledge of additional keywords, sources, and search terms. Because of this possibility for repetitions, it is very essential to ensure that the whole search strategy is characterized by transparency and audit capacity. To this end, a research librarian or information/data scientist can be a useful partner to help design and refine the search strategy.
The process of conducting a literature search can itself be divided into 5 steps:
- Decide on research question(s) in your specific subject area
- Find relevant databases you will search
- Create a list of relevant keywords and phrases for your literature search
- Begin the literature search while taking notes from each database to keep track of your queries
- Begin the scoping review and compile your results into an article
- If needed, revise your original research question(s)
Source of evidence selection
A scoping review protocol should include a description of all the stages of the source selection process based on title and abstract examination as well as on full-text examination. It should be premised on the inclusion criteria and also explain the mechanisms for resolving disagreements among reviewers. The source selection (both the title and abstract examination and the full-text screening) should be conducted by a couple of reviewers or more. Disagreements arising between the reviewers can be resolved either by consensus or by a third reviewer.
The process should be explained through a narrative description which has to include a flowchart of the review process (from the PRISMA-ScR statement). The chart shows the flow from the search through source selection, duplicates, full-text retrieval, and all inclusions from the third search, data extraction, and presentation of the evidence.
Information on the retrieved full-text articles should be provided. Separate appendices providing information on included sources should also be provided. The appendices should briefly disclose all excluded sources as well as the reasons for their exclusion.
The reviewers should mention the software used to manage the results of the search. Examples include Covidence, JBI SUMARI, etc. Before venturing into source selection across a team, it may be necessary to pilot test the source selectors to enable the team to refine their source selection tool (assuming they are using such a tool).
Data extraction
The data extraction process is often referred to as “data charting” in scoping reviews. Data charting is a logical and descriptive summary of the results which are in alignment with the objective(s) and question(s) of the scoping review. It is necessary to construct and pilot a data charting table or form during the protocol stage. This will help the reviewers to record important details about the source such as those below.
- Publication year
- Origin/country of origin (where the source was published or conducted)
- Aims or purposes
- Population and sample size within the source of evidence (if applicable)
- Methodology / methods
- Intervention type, comparator, and information on these (e.g. duration of the intervention) (if applicable). Duration of the intervention (if applicable)
- Outcomes and information on these (e.g. how it was measured, if applicable)
- Important findings relating to the scoping review question(s)
These details can be refined in the review stage albeit this will necessitate an updating of the charting table. Careful record-keeping is necessary on the part of the reviewers since it will ensure ease of reference and tracking as well as help them to identify and chart every source as well as any other additional unanticipated data. This implies that charting the results can be a repetitive process of continuous updating of data.
In summary, it is very important that the reviewers exhibit transparency and clarity in their data extraction methods. Like in source of evidence selection, pilot testing is also necessary.
Analysis of the evidence
Many scoping reviews are usually analyzed through simple counting of concepts, populations, characteristics and so forth. However, other reviews may need a more complex analyses, e.g., descriptive qualitative content analysis which includes basic coding of data .
For quantitative data, more sophisticated techniques can be utilized instead of simple frequency counts to determine the occurrence of concepts, characteristics, populations, etc. However, such in-depth analyses are not common in scoping reviews. Areas like meta-analysis and interpretive qualitative analysis have very small probabilities of being used in scoping reviews.
The nature of data analysis in scoping reviews is largely determined by the purpose of the review and the reviewers’ evaluations. The most vital concern is the level of transparency of the analytical method used and the ability of the reviewers to rationalize their approach in addition to a priori planning of the review.
Presentation of the results
It is important provide a plan for the presentation of results (one that includes the type of charts, tables and/or figures that will be used) during protocol development. The essence of early planning is to have some knowledge of the kinds of data that might emerge and the best way to present such data with respect to both the objective(s) and research question(s) of the scoping review. This knowledge can be modified during the review process when the reviewers must have become more aware of all data from the included sources.
It is possible to present the results of a scoping review in a descriptive format and/or as a map of the data from the included sources, e.g., tables and other diagrams. The PCC concept can be an essential guide on how to map data efficiently.
For more information regarding scoping reviews, please refer to Arksey, H. and O’Malley paper [1] or JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis [2], this article is based primarily on the latter source.
✅ Also check out
This post was produced as part of a research guide series by Avidnote which is a free web-based app that helps you to write and organize your academic writing online. Click here to find out more.
Anderson S, Allen P, Peckham S, Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2008;6(1):1.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Arksey, H. and O’Malley paper (2015). Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International journal of social research methodology , 8 (1), pp.19-32.
Colquhoun, H.L., Levac, D., O’Brien, K.K., Straus, S., Tricco, A.C., Perrier, L., Kastner, M. and Moher, D., 2014. Scoping reviews: time for clarity in definition, methods, and reporting. Journal of clinical epidemiology , 67 (12), pp.1291-1294.
JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. Source: https://wiki.jbi.global/display/MANUAL/11.2.6+Source+of+evidence+selection
Munn, Z., Peters, M.D., Stern, C., Tufanaru, C., McArthur, A. and Aromataris, E., 2018. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC medical research methodology , 18 (1), pp.1-7.
Osman, M.A., Schick-Makaroff, K., Thompson, S., Featherstone, R., Bialy, L., Kurzawa, J., Okpechi, I.G., Habib, S., Shojai, S., Jindal, K. and Klarenbach, S., 2018. Barriers and facilitators for implementation of electronic consultations (eConsult) to enhance specialist access to care: a scoping review protocol. BMJ open , 8 (9), p.e022733.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview
Adding {{itemName}} to cart
Added {{itemName}} to cart
Advertisement
The 100 Best Books of the 21st Century: A Printable List
By The New York Times Books Staff Aug. 26, 2024
- Share full article
Print this version to keep track of what you’ve read and what you’d like to read. See the full project, including commentary about the books, here.
A PDF version of this document with embedded text is available at the link below:
Download the original document (pdf)
The New York Times Book Review I've I want THE 100 BEST BOOKS OF THE 21ST CENTURY read to it read it 1 My Brilliant Friend, by Elena Ferrante 26 26 Atonement, by lan McEwan 2 The Warmth of Other Suns, by Isabel Wilkerson 27 Americanah, by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie 3 Wolf Hall, by Hilary Mantel 28 Cloud Atlas, by David Mitchell 4 The Known World, by Edward P. Jones 29 The Last Samurai, by Helen DeWitt 5 The Corrections, by Jonathan Franzen 30 Sing, Unburied, Sing, by Jesmyn Ward 6 2666, by Roberto Bolaño 31 White Teeth, by Zadie Smith 7 The Underground Railroad, by Colson Whitehead 32 The Line of Beauty, by Alan Hollinghurst 8 Austerlitz, by W.G. Sebald 33 Salvage the Bones, by Jesmyn Ward 9 Never Let Me Go, by Kazuo Ishiguro 34 Citizen, by Claudia Rankine 10 Gilead, by Marilynne Robinson 35 Fun Home, by Alison Bechdel 11 The Brief Wondrous Life of Oscar Wao, by Junot Díaz 36 Between the World and Me, by Ta-Nehisi Coates 12 The Year of Magical Thinking, by Joan Didion 37 The Years, by Annie Ernaux 13 The Road, by Cormac McCarthy 38 The Savage Detectives, by Roberto Bolaño 14 Outline, by Rachel Cusk 39 A Visit From the Goon Squad, by Jennifer Egan 15 Pachinko, by Min Jin Lee 40 H Is for Hawk, by Helen Macdonald 16 The Amazing Adventures of Kavalier & Clay, by Michael Chabon 41 Small Things Like These, by Claire Keegan 17 The Sellout, by Paul Beatty 42 A Brief History of Seven Killings, by Marlon James 18 Lincoln in the Bardo, by George Saunders 43 Postwar, by Tony Judt 19 Say Nothing, by Patrick Radden Keefe 44 The Fifth Season, by N.K. Jemisin 20 Erasure, by Percival Everrett 45 The Argonauts, by Maggie Nelson 21 Evicted, by Matthew Desmond 46 The Goldfinch, by Donna Tartt 22 22 Behind the Beautiful Forevers, by Katherine Boo 47 A Mercy, by Toni Morrison 23 Hateship, Friendship, Courtship, Loveship, Marriage, by Alice Munro 48 Persepolis, by Marjane Satrapi 24 The Overstory, by Richard Powers 49 The Vegetarian, by Han Kang 25 25 Random Family, by Adrian Nicole LeBlanc 50 Trust, by Hernan Diaz I've I want read to it read it
The New York Times Book Review I've I want THE 100 BEST BOOKS OF THE 21ST CENTURY read to it read it 51 Life After Life, by Kate Atkinson 52 52 Train Dreams, by Denis Johnson 53 Runaway, by Alice Munro 76 77 An American Marriage, by Tayari Jones 78 Septology, by Jon Fosse Tomorrow, and Tomorrow, and Tomorrow, by Gabrielle Zevin 54 Tenth of December, by George Saunders 55 The Looming Tower, by Lawrence Wright 56 The Flamethrowers, by Rachel Kushner 57 Nickel and Dimed, by Barbara Ehrenreich ཤྲཱ རྒྱ སྐྱ A Manual for Cleaning Women, by Lucia Berlin The Story of the Lost Child, by Elena Ferrante Pulphead, by John Jeremiah Sullivan. Hurricane Season, by Fernanda Melchor 58 Stay True, by Hua Hsu 83 When We Cease to Understand the World, by Benjamín Labatut 59 Middlesex, by Jeffrey Eugenides 84 The Emperor of All Maladies, by Siddhartha Mukherjee 60 Heavy, by Kiese Laymon 85 Pastoralia, by George Saunders 61 Demon Copperhead, by Barbara Kingsolver 86 Frederick Douglass, by David W. Blight 62 10:04, by Ben Lerner 87 Detransition, Baby, by Torrey Peters 63 Veronica, by Mary Gaitskill 88 The Collected Stories of Lydia Davis 64 The Great Believers, by Rebecca Makkai 89 The Return, by Hisham Matar 65 The Plot Against America, by Philip Roth 90 The Sympathizer, by Viet Thanh Nguyen 66 We the Animals, by Justin Torres 91 The Human Stain, by Philip Roth 67 Far From the Tree, by Andrew Solomon 92 The Days of Abandonment, by Elena Ferrante 68 The Friend, by Sigrid Nunez 93 Station Eleven, by Emily St. John Mandel 69 59 The New Jim Crow, by Michelle Alexander 94 On Beauty, by Zadie Smith 10 70 All Aunt Hagar's Children, by Edward P. Jones 95 Bring Up the Bodies, by Hilary Mantel 71 The Copenhagen Trilogy, by Tove Ditlevsen 96 Wayward Lives, Beautiful Experiments, by Saidiya Hartman 72 22 Secondhand Time, by Svetlana Alexievich 97 Men We Reaped, by Jesmyn Ward 73 The Passage of Power, by Robert A. Caro 98 Bel Canto, by Ann Patchett 74 Olive Kitteridge, by Elizabeth Strout 99 How to Be Both, by Ali Smith 75 15 Exit West, by Mohsin Hamid 100 Tree of Smoke, by Denis Johnson I've I want read to it read it
An official website of the United States government.
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- American Job Centers
- Apprenticeship
- Demonstration Grants
- Farmworkers
- Federal Bonding Program
- Foreign Labor Certification
- Indians and Native Americans
- Job Seekers
- Layoffs and Rapid Response
- National Dislocated Worker Grants
- Older Workers
- Skills Training Grants
- Trade Adjustment Assistance
- Unemployment Insurance
- Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA)
- WIOA Adult Program
- Advisories and Directives
- Regulations
- Labor Surplus Area
- Performance
- Recovery-Ready Workplace Resource Hub
- Research and Evaluation
- ETA News Releases
- Regional Offices
- Freedom of Information Act
- Office of Apprenticeship
- Office of Foreign Labor Certification
- Office of Grants Management
- Office of Job Corps
- Office of Unemployment Insurance (1-877-S-2JOBS)
Equity in Grant-Making: A Review of Barriers and Strategies for Funders Considering Improvement Opportunities
Publication info, research methodology, description.
In 2023 the Chief Evaluation Office partnered with the Employment and Training Administration (ETA) to fund a study focused on exploring approaches to measure and increase equity in ETA’s discretionary grant-making programs. This study sought to explore how grant-makers – such as Federal agencies, State and local government agencies, and philanthropic organizations – define, assess, and increase equity in their grant-making process.
This study explores research and strategies related to equity in the discretionary grant-making process based on a review of publicly available literature and Federal agency Equity Action Plans as well as interviews with Federal and philanthropic grant-makers. The report describes how funders define equity in the context of awarding grants, common barriers and promising action steps to increase equity in each stage of the grant-making process (pre-award, collection of applications, funding of awards, and post-award), and measurement strategies to help funders track their progress.
This report can support a variety of grant-makers examining equity, whether at government agencies (including at Federal, State, and local levels) or foundations. Recognizing that grant-making organizations vary in size, policy area, and scope, the study team provides findings and suggestions that funders can tailor to meet their context and goals. The findings focus on domestic (U.S.-based) grant-making, though international or transnational grant-makers may also find useful insights.
Key takeaways include:
- When selecting strategies to increase equity, grant-makers may invest time and resources to communicate the new approach to potential applicants and build trust, particularly with organizations and groups that provide services to underrepresented communities. For example, reviewed resources encourage funders to expand the networks they use to announce new funding opportunities and participate in community events. These trust-building activities may encourage new organizations to apply for grant programs and create space to provide feedback on challenging or inequitable aspects of the grant-making process.
- Study interviewees also emphasized the value of continued internal communications with funding staff to build organizational motivation to implement and refine equity initiatives. Communication efforts include describing goals and progress, holding training sessions to increase awareness of action steps, and sharing tools to streamline implementation and affect change.
- By implementing strategies to increase equity in grant-making, funders take a critical step toward addressing systemic inequities in the type of organizations, individuals, and communities that receive grant funding.
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 30 August 2024
A scoping review of stroke services within the Philippines
- Angela Logan 1 , 2 ,
- Lorraine Faeldon 3 ,
- Bridie Kent 1 , 4 ,
- Aira Ong 1 &
- Jonathan Marsden 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 1006 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Stroke is a leading cause of mortality and disability. In higher-income countries, mortality and disability have been reduced with advances in stroke care and early access to rehabilitation services. However, access to such services and the subsequent impact on stroke outcomes in the Philippines, which is a lower- and middle-income countries (LMIC), is unclear. Understanding gaps in service delivery and underpinning research from acute to chronic stages post-stroke will allow future targeting of resources.
This scoping review aimed to map available literature on stroke services in the Philippines, based on Arksey and O’Malley’s five-stage-process.
Summary of review
A targeted strategy was used to search relevant databases (Focused: MEDLINE (ovid), EMBASE (ovid), Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), PsycINFO (ebsco); broad-based: Scopus; review-based: Cochrane Library, International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO), JBI (formerly Joanna Briggs Institute) as well as grey literature (Open Grey, Google scholar). The searches were conducted between 12/2022-01/2023 and repeated 12/2023. Literature describing adults with stroke in the Philippines and stroke services that aimed to maximize well-being, participation and function were searched. Studies were selected if they included one or more of: (a) patient numbers and stroke characteristics (b) staff numbers, qualifications and role (c) service resources (e.g., access to a rehabilitation unit) (d) cost of services and methods of payment) (e) content of stroke care (f) duration of stroke care/rehabilitation and interventions undertaken (g) outcome measures used in clinical practice.
A total of 70 papers were included. Articles were assessed, data extracted and classified according to structure, process, or outcome related information. Advances in stroke services, including stroke ready hospitals providing early access to acute care such as thrombectomy and thrombolysis and early referral to rehabilitation coupled with rehabilitation guidelines have been developed. Gaps exist in stroke services structure (e.g., low number of neurologists and neuroimaging, lack of stroke protocols and pathways, inequity of stroke care across urban and rural locations), processes (e.g., delayed arrival to hospital, lack of stroke training among health workers, low awareness of stroke among public and non-stroke care workers, inequitable access to rehabilitation both hospital and community) and outcomes (e.g., low government insurance coverage resulting in high out-of-pocket expenses, limited data on caregiver burden, absence of unified national stroke registry to determine prevalence, incidence and burden of stroke). Potential solutions such as increasing stroke knowledge and awareness, use of mobile stroke units, TeleMedicine, TeleRehab, improving access to rehabilitation, upgrading PhilHealth and a unified national long-term stroke registry representing the real situation across urban and rural were identified.
This scoping review describes the existing evidence-base relating to structure, processes and outcomes of stroke services for adults within the Philippines. Developments in stroke services have been identified however, a wide gap exists between the availability of stroke services and the high burden of stroke in the Philippines. Strategies are critical to address the identified gaps as a precursor to improving stroke outcomes and reducing burden. Potential solutions identified within the review will require healthcare government and policymakers to focus on stroke awareness programs, primary and secondary stroke prevention, establishing and monitoring of stroke protocols and pathways, sustainable national stroke registry, and improve access to and availability of rehabilitation both hospital and community.
What is already known?
Stroke services in the Philippines are inequitable, for example, urban versus rural due to the geography of the Philippines, location of acute stroke ready hospitals and stroke rehabilitation units, limited transport options, and low government healthcare insurance coverage resulting in high out-of-pocket costs for stroke survivors and their families.
What are the new findings?
The Philippines have a higher incidence of stroke in younger adults than other LMICs, which impacts the available workforce and the country’s economy. There is a lack of data on community stroke rehabilitation provision, the content and intensity of stroke rehabilitation being delivered and the role and knowledge/skills of those delivering stroke rehabilitation, unmet needs of stroke survivors and caregiver burden and strain,
What do the new findings imply?
A wide gap exists between the availability of stroke services and the high burden of stroke. The impact of this is unclear due to the lack of a compulsory national stroke registry as well as published data on community or home-based stroke services that are not captured/published.
What does this review offer?
This review provides a broad overview of existing evidence-base of stroke services in the Philippines. It provides a catalyst for a) healthcare government to address stroke inequities and burden; b) development of future evidence-based interventions such as community-based rehabilitation; c) task-shifting e.g., training non-neurologists, barangay workers and caregivers; d) use of digital technologies and innovations e.g., stroke TeleRehab, TeleMedicine, mobile stroke units.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
In the Philippines, stroke is the second leading cause of death, with a prevalence of 0·9% equating to 87,402 deaths per annum [ 1 , 2 ]. Approximately 500,000 Filipinos will be affected by stroke, with an estimated US$350 million to $1·2 billion needed to meet the cost of medical care [ 1 ]. As healthcare is largely private, the cost is borne out-of-pocket by patients and their families. This provides a major obstacle for the lower socio-demographic groups in the country.
Research on implementation of locally and regionally adapted stroke-services and cost-effective secondary prevention programs in the Philippines have been cited as priorities [ 3 , 4 ]. Prior to developing, implementing, and evaluating future context-specific acute stroke management services and community-based models of rehabilitation, it was important to map out the available literature on stroke services and characteristics of stroke in the Philippines.
The scoping review followed a predefined protocol, established methodology [ 5 ] and is reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews Guidelines (PRISMA-ScR) [ 6 , 7 ]. Healthcare quality will be described according to the following three aspects: structures, processes, and outcomes following the Donabedian model [ 8 , 9 ].The review is based on Arksey and O'Malley’s five stages framework [ 5 ].
Stage 1: The research question:
What stroke services are available for adults within the Philippines? The objective was to systematically scope the literature to describe the availability, structure, processes, and outcome of stroke services for adults within the Philippines.
Stage 2: Identifying relevant studies:
The following databases were searched. Focused: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), PsycINFO; broad-based: Scopus; review-based: Cochrane Library, Prospero, JBI (formerly Joanna Briggs Institute); Grey literature: Herdin, North Grey, Grey matters, MedRxiv, NIHR health technology assessment, Department of Health Philippines, The Kings Fund, Ethos, Carrot2. Additionally, reference lists of full text included studies were searched.
The targeted search strategy, developed in consultation with an information scientist, was adapted for each database (see supplemental data). Search terms were peer reviewed using the PRESS (Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies) checklist [ 10 ].
The key search concepts from the Population, Concept and Context (PCC) framework were ≥ 18 years with a stroke living in the Philippines ( population ), stroke services aiming to maximize well-being, participation and function following a stroke ( concept ) and stroke services from acute to chronic including those involving healthcare professionals, non-healthcare related personnel or family or friends ( context ). Search tools such as medical subject headings (MESH) and truncation to narrow or expand searches were used. Single and combined search terms were included (see supplemental data). The search was initially conducted over two weeks in December 2022 and re-run in December 2023.
Studies were selected if they described stroke care in the Philippines in terms of one or more of the following: (a) patient numbers and stroke characteristics (b) staff numbers, qualifications and role (c) service resources (e.g., number of beds/access to a rehabilitation unit, equipment used) (d) cost of services and methods of payment (UHC, Insurance, private) (e) content of stroke care (f) duration of stroke care (hours of personnel contact e.g., Therapy hours per day); interventions undertaken (g) outcome measures used in clinical practice.
Additional criteria:
Context: all environments (home, hospital, outpatients, clinic, academic institute).
Date limits: published between 2002 onwards. This is based on the Philippines Community Rehabilitation Guidelines published in 2009 that would suggest that papers earlier than 2002 may not reflect current practice [ 11 ].
Qualitative and quantitative studies including grey literature.
Language: reported in English or Filipino only.
Publication status: no limit because the level of rigor was not assessed.
Type of study: no limit which included conference abstracts, as the level of rigor was not assessed.
Studies were excluded if they were in non-stroke populations or the full text article could not be obtained. Conference abstracts were excluded if there were insufficient data about methods and results.
Searches of databases were performed by one researcher (JM) and searches of grey literature were performed by one researcher (AO). All retrieved articles were uploaded into Endnote X9 software™, and duplicates identified and removed before transferring them to Rayyan [ 12 ] for screening.
Stage 3: study selection
The title and abstract were selected using eligibility criteria. Two pairs of researchers independently screened abstracts and titles;(Databases: JM and AL and grey literature by AO and LF). Where a discrepancy existed for title and abstract screening, the study was automatically included for full text review and discussed among reviewers.
Two reviewers (JM and AL) undertook full-text screening of the selected studies. Discrepancies were resolved through consensus discussions without the need for a third reviewer. There were no discrepancies that required a third reviewer. Reason for exclusion were documented according to pre-determined eligibility criteria. References of included full text articles were screened by each reviewer independently and identified articles were subjected to the same screening process as per the PRISMA-ScR checklist (Fig. 1 ).

PRISMA-ScR flow diagram
Stage 4: Charting the data
Two reviewers independently extracted the data using a piloted customized and standardized data extraction form including (1) Structure: financial (e.g., costs, insurance, government funding), resources (structure and number of stroke facilities, staff (number, profession/specialism, qualifications etc.), stroke characteristics (2) Process: duration of care, content of stroke care within acute, secondary care, community, outcome measures used; (3) Outcome: survival, function, patient satisfaction, cost (admission and interventions), and (4) year of publication, geographical location (including if Philippines only or multiple international locations) and type of evidence (e.g., policy, review, observational, experimental, clinical guidelines). Critical appraisal of included studies was not undertaken because the purpose of the review was to map available evidence on stroke services available within the Philippines.
Stage 5: Collating, summarising and reporting the results
The search identified 351 records from databases and registers. A total of 70 records are included and reasons for non-inclusion are summarized in Fig. 1 .
Study descriptors
The characteristics of included studies are shown in Supplementary Material Table 1. Of the 70 included studies, 36 were observational with most being based on a retrospective review of case notes ( n = 31), two were audits, eight were surveys or questionnaires, four were consensus opinion and/or guideline development, three were randomized controlled trial (RCT) or feasibility RCT, 1 was a systematic review, two were policy and guidelines, 11 were narrative reviews or opinion pieces, two were case series or reports and one was an experimental study.
Of the 70 studies, 32 (45.7%) were based in a single tertiary hospital site. There were only three papers based in the community (4.3%). Papers that were opinion pieces or reviews were classified as having a national focus. Of the 22 papers classified as having a national focus, 10 (45.5%) were narrative reviews/ opinion pieces (Table 1 ).
The primary focus of the research studies (excluding the 11 narrative reviews and 2 policy documents) were classified as describing structure ( n = 8, 14%); process ( n = 21,36.8%) or outcomes ( n = 29, 49.2%). The structure of acute care was described in seven studies out of eight studies ( n = 7/8 87.5%) whilst neurosurgery structures were described in one out of eight studies (12.5%). Acute care processes were described in 11 out of 21 studies ( n = 11/21 52.3%) whilst rehabilitation processes were described in six out of 21 studies (28.6%), with three out of 21 studies primarily describing outcome measurement (14.3%). The primary focus of the outcomes were stroke characteristics (25 out of 28 papers, 89.2%) in terms of number of stroke (prevalence), mortality or severity of stroke. Measures of stroke quality of life were not reported. Healthcare professional knowledge was described in two studies ( n = 2/28 7.1%) whilst risk factors for stroke were described in one study ( n = 1/28, 3.6%). Carer burden was described in one study ( n = 1/28, 3.6%).
A summary of the findings is presented in Table 2 .
This scoping review describes the available literature on stroke services within the Philippines across the lifespan of an adult (> 18 years) with a stroke. The review has identified gaps in information about structures, processes and outcomes as well as deficits in provision of stroke services and processes as recommended by WHO. These included a low number of specialist clinicians including neurologists, neuro-radiographers and neurosurgeons. The high prevalence of stroke suggests attention and resources need to focus on primary and secondary prevention. Awareness of stroke is low, especially in terms of what a stroke is, the signs/symptoms and how to minimize risk of stroke [ 25 ]. Barriers exist, such as lack of healthcare resources, maldistribution of health facilities, inadequate training on stroke treatment among health care workers, poor stroke awareness, insufficient government support and limited health insurance coverage [ 22 ].
The scoping review also highlighted areas where further work is needed, for example, descriptions and research into the frequency, intensity, and content of rehabilitation services especially in the community setting and the outcome measures used to monitor recovery and impairment. PARM published stroke rehabilitation clinical practice guidelines in 2012, which incorporated an innovative approach to contextualize Western clinical practice guidelines for stroke care to the Philippines [ 42 ]. Unfortunately, availability and equitable access to evidence-based rehabilitation for people with stroke in the Philippines pose significant challenges because of multiple factors impacting the country (e.g., geographical, social, personal, environmental, educational, economic, workforce) [ 25 , 40 , 43 ].
The number of stroke survivors with disability has not been reported previously, thus, the extent and burden of stroke from acute to chronic is unknown. The recent introduction of a national stroke registry across public and private facilities may provide some of this data [ 82 ]. The project started in 2021 and captures data on people hospitalized for transient ischemic attack or stroke in the Philippines. National stroke registries have been identified as a pragmatic solution to reduce the global burden of stroke [ 83 ] through surveillance of incidence, prevalence, and outcomes (e.g., death, disability) of, and quality of care for, stroke, and prevalence of risk factors. For the Philippine government to know the full impact and burden of stroke nationally, identify areas for improvement and make meaningful changes for the benefit of Filipinos, the registry would need to be compulsory for all public and private facilities and include out of hospital data. This will require information technology, trained workforces for data capture, monitoring and sharing, as well as governance and funding [ 83 ].
This scoping review has generated a better understanding of the published evidence focusing on availability of stroke services in the Philippines, as well as the existing gaps through the lens of Donabedian’s Structure , Process and Outcome framework. The findings have helped to inform a wider investigation of current stroke service utilization conducted using survey and interview methods with stroke survivors, carers and key stakeholders in the Philippines, and drive forward local, regional and national policy and service changes.
Conclusions
This scoping review describes the existing evidence-based relating to structure, processes and outcomes of stroke services for adults within the Philippines. The review revealed limited information in certain areas, such as the impact of stroke on functional ability, participation in everyday life, and quality of life; the content and intensity of rehabilitation both in the hospital or community setting; and the outcome measures used to evaluate clinical practice. Developments in stroke services have been identified however, a wide gap exists between the availability of stroke services and the high burden of stroke in the Philippines. Strategies are critical to address the identified gaps as a precursor to improving stroke outcomes and reducing burden. Potential solutions identified within the review will require a comprehensive approach from healthcare policymakers to focus on stroke awareness programs, primary and secondary prevention, establishing and monitoring of stroke protocols and pathways, implementation of a compulsory national stroke registry, use of TeleRehab, TeleMedicine and mobile stroke units and improve access to and availability of both hospital- and community-based stroke rehabilitation. Furthermore, changes in PhilHealth coverage and universal credit to minimize catastrophic out-of-pocket costs.
Limitations
Although a comprehensive search was undertaken, data were taken from a limited number of located published studies on stroke in the Philippines. This, together with data from databases and grey literature, may not reflect the current state of stroke services in the country.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Navarro JC, Baroque AC, Lokin JK, Venketasubramanian N. The real stroke burden in the Philippines. Int J Stroke. 2014;9(5):640–1.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Philippines TSSot. Phillipines: stroke 2024. Available from: https://www.strokesocietyphilippines.org/philippines-stroke/#:~:text=Stroke%20is%20the%20Philippines'%20second,or%2014.12%25%20of%20total%20deaths .
Banaag MS, Dayrit MM, Mendoza RU. Health Inequity in the Philippines. In: Batabyal A, Higano Y, Nijkamp P (eds). Disease, Human Health, and Regional Growth and Development in Asia. New Frontiers in Regional Science: Asian Perspectives, vol 38. Singapore: Springer; 2019.
Hodge A, Firth S, Bermejo R, Zeck W, Jimenez-Soto E. Utilisation of health services and the poor: deconstructing wealth-based differences in facility-based delivering in teh Philippines. BMC Public Health. 2016;16:1–12.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8:19–32.
Article Google Scholar
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5:69.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Donabedian A. The quality of care. How can it be assessed? JAMA. 1988;260(12):1743–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
McDonald KM, Sundaram V, Bravata DM, Lewis R, Lin N, Kraft SA, et al. Closing the quality gap: a critical analysis of quality improvement strategies. Tech Rev. 2007;7(9).
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, Cogo E, Foerster V, Lefebvre C. PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 guideline statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;75:40–6.
McGlade B, Mendoza VE. Philippines CBR manual: an inclusive development strategy. Philippines: CBM-CBR Coordinating office; 2009.
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, et al. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5(210). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4 .
Baliguas B. Adherence to the clinical practice guidelines of the stroke society of the Philippines in the management of ischemic stroke in young adults admitted in 3 tertiary hospitals in Bacolod City, Philippines from May to October 2010. Neurology. 2018;90(15).
Barcelon EA, Moll MAKDN, Serondo DJ, Collantes MEV. Validation of the Filipino version of national institute of health stroke scale. Clinical Neurology. 2016;56:S379.
Google Scholar
Baticulon RE, Lucena LLN, Gimenez MLA, Sabalza MN, Soriano JA. The Neurosurgical Workforce of the Philippines. Neurosurgery. 2024;94(1):202–11. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000002630 .
Berroya RM. Incidence of symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage after thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke at St. Luke’s Medical Center-Global City from January 2010 to February 2017. J Neurol Sci. 2010;2017(381):398–9.
Carcel C, Espiritu-Picar R. Circadian variation of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes in adults at a tertiary hospital: a retrospective study. J Neurol Sci. 2009;285:S174.
Cayco CS, Gorgon EJR, Lazaro RT. Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation to improve motor outcomes in older adults with chronic stroke. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2019;24(1):53–60.
Co COC, Yu JRT, Macrohon-Valdez MC, Laxamana LC, De Guzman VPE, Berroya-Moreno RMM, et al. Acute stroke care algorithm in a private tertiary hospital in the Philippines during the COVID-19 pandemic: a third world country experience. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020;29(9):105059.
Co COC, Yu JRT, Laxamana LC, David-Ona DIA. Intravenous thrombolysis for stroke in a COVID-19 positive Filipino patient, a case report. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;77:234–6.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Collantes ME. Evaluation of change in stroke care in the Philippines using RES-Q data. Eur Stroke J. 2019;4:318.
Collantes ME. Improving stroke systems of care in lmic: Philippines. Int J Stroke. 2021;16(2):4.
Collantes ME, Navarro J, Belen A, Gan R. Stroke systems of care in the Philippines: addressing gaps and developing strategies. Front Neurol. 2022;13:1046351.
Collantes MEV, Yves Miel H, Zuñiga Uezono DR. Incidence and prevalence of stroke and its risk factors in the Philippines: a systematic review. Acta Medica Philippina. 2022;56:26–34.
Collantes MV, Zuniga YH, Granada CN, Uezono DR, De Castillo LC, Enriquez CG, et al. Current state of stroke care in the Philippines. Front Neurol. 2021;12:665086.
Constantino GA, Soliven JA. Points of in-hospital delays in thrombolytic therapy among patients with acute ischemic stroke: a single center 5-year retrospective study. Neurology. 2020;94(15). https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.94.15_supplement.2901 .
Constantino GAA, Señga MMA, Soliven JAR, Jocson VED. Emerging Utility of Endovascular Thrombectomy in the Philippines: A Single-center Clinical Experience. Acta Med Philipp [Internet]. 2023;57(5). Available from: https://actamedicaphilippina.upm.edu.ph/index.php/acta/article/view/5113 . [cited 2024 Aug 21].
Dans AL, Punzalan FE, Villaruz MV. National Nutrition and Health Survey (NNHeS): atherosclerosis-related diseases and risk factors. Philipp J Intern Med. 2005;43:103–15.
De Castillo LL, Collantes ME. Thrombolysis for stroke at the Philippine general hospital: a descriptive analysis. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019;48:54.
de Castillo LLC, Diestro JDB, Tuazon CAM, Sy MCC, Añonuevo JC, San Jose MCZ. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021;30(7):105831.
Delfino JPM, Carandang-Chacon CA. Comparison of acute ischemic stroke care quality before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in a private tertiary hospital in metro Manila, Philippines. Neurol Asia. 2023;28(1):13–7.
Department of Health. Department of Health Administrative Order 2011-0003. 2011. [Accessed online: 12/2022], from the Philippine Department of Health].
Department of Health. The national policy framework on the prevention, control and management of acute stroke in the Philippines. 2020.
Diestro JDB, Omar AT, Sarmiento RJC, Enriquez CAG, Castillo LLC, Ho BL, et al. Cost of hospitalization for stroke in a low-middle-income country: Findings from a public tertiary hospital in the Philippines. Int J Stroke. 2021;16(1):39–42.
Duenas M, Ranoa G, Benjamin VS. Assessment of post-stroke caregivers’ burden through the modified caregivers strain index (MCSI) in a tertiary center in the Philippines: a cross-sectional study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019;48:56–7.
Duya JE, Hernandez K, San Jose MC. The evolving clinical and echocardiographic profile of patients admitted for acute cardioembolic stroke at a Tertiary Hospital in the Philippines. J Hong Kong Coll Cardiol. 2019;27(1):58.
Espiritu AI, San Jose MCZ. A call for a stroke referral network between primary care and stroke-ready hospitals in the philippines: a narrative review. Neurologist. 2021;26(6):253–60.
Gambito ED, Gonzalez-Suarez CB, Grimmer KA, Valdecañas CM, Dizon JM, Beredo ME, et al. Updating contextualized clinical practice guidelines on stroke rehabilitation and low back pain management using a novel assessment framework that standardizes decisions. BMC Res Notes. 2015;8:643.
Gelisanga MA, Gorgon EJ. Upright motor control test: interrater reliability, retest reliability, and concurrent validity in adults with subacute stroke. Eur Stroke J. 2017;2(1):357–8.
Gonzalez-Suarez C, Grimmer K, Alipio I, Anota-Canencia EG, Santos-Carpio ML, Dizon JM, et al. Stroke rehabilitation in the Philippines: an audit study. Disabil CBR Inclusive Develop. 2015;26(3):44–67.
Gonzalez-Suarez CB, Grimmer K, Cabrera JTC, Alipio IP, Anota-Canencia EGG, Santos-Carpio MLP, et al. Predictors of medical complications in stroke patients confined in hospitals with rehabilitation facilities: a Filipino audit of practice. Neurology Asia. 2018;23(3):199–208.
Gonzalez-Suarez CB, Grimmer-Somers K, Margarita Dizon J, King E, Lorenzo S, Valdecanas C, et al. Contextualizing Western guidelines for stroke and low back pain to a developing country (Philippines): an innovative approach to putting evidence into practice efficiently. J Healthc Leadersh. 2012;4:141–56.
Gonzalez-Suarez CB, Margarita J, Dizon R, Grimmer K, Estrada MS, Uyehara ED, et al. Implementation of recommendations from the Philippine Academy of Rehabilitation Medicine's Stroke Rehabilitation Guideline: a plan of action. Clin Audit. 2013;5:77–89.
Ignacio KHD, Diestro JDB, Medrano JMM, Salabi SKU, Logronio AJ, Factor SJV, et al. Depression and anxiety after stroke in young adult Filipinos. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022;31(2):106232.
Inting K, Canete MT. Ischemic stroke subtypes: a comparison between causative and phenotypic classifications in a tertiary hospital in the Philippines. Int J Stroke. 2021;16(2):28.
Jaca PKM, Chacon CAC, Alvarez RM. Clinical characteristics of cerebrovascular disease with COVID-19: a single-center study in Manila. Philippines Neurology Asia. 2021;26(1):15–25.
Jamora RDG, Corral EV, Ang MA, Epifania M, Collantes V, Gan R. Stroke recurrence among Filipino patients taking aspirin for first-ever non-cardioembolic ischemic stroke. Neurol Clin Neurosci. 2017;5:1–5.
Jamora RDG, Prado MB Jr, Anlacan VMM, Sy MCC, Espiritu AI. Incidence and risk factors for stroke in patients with COVID-19 in the Philippines: an analysis of 10,881 cases. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022;31(11).
Juangco DN, Mariano GS. Endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke: a review of cases and outcomes from a primary stroke center (a 5-year retrospective study). Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;41:54.
Leochico CFD, Austria EMV, Gelisanga MAP, Ignacio SD, Mojica JAP. Home-based telerehabilitation for community-dwelling persons with stroke during the COVID-19 pandemic: a pilot study. J Rehabil Med. 2023;55:jrm4405.
Loo KW, Gan SH. Burden of stroke in the Philippines. Int J Stroke. 2013;8(2):131–4.
Mansouri A, Ku JC, Khu KJ, Mahmud MR, Sedney C, Ammar A, et al. Exploratory analysis into reasonable timeframes for the provision of neurosurgical care in low- and middle-income countries. World Neurosurg. 2018;117:e679–91.
Mendoza RA. The clinical profile and treatment outcome of acute ischemic stroke patients who underwent thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator therapy, Philippine experience: a retrospective study. J Neurol Sci. 2009;285:S85–6.
Navarro J. Prevalence of stroke: a community survey. Philipp J Neurol. 2005;9(2):11–5.
Navarro JC, Venketasubramanian N. Stroke burden and services in the Philippines. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2021;11(2):52–4.
Navarro JC, Baroque AC 2nd, Lokin JK. Stroke education in the Philippines. Int J Stroke. 2013;8 Suppl A100:114–5.
Navarro JC, Chen CL, Lee CF, Gan HH, Lao AY, Baroque AC, et al. Durability of the beneficial effect of MLC601 (NeuroAiD™) on functional recovery among stroke patients from the Philippines in the CHIMES and CHIMES-E studies. Int J Stroke. 2017;12(3):285–91.
Navarro JC, Escabillas C, Aquino A, Macrohon C, Belen A, Abbariao M, et al. Stroke units in the Philippines: an observational study. Int J Stroke. 2021;16(7):849–54.
Navarro JC, San Jose MC, Collantes E, Macrohon-Valdez MC, Roxas A, Hivadan J, et al. Stroke thrombolysis in the Philippines. Neurol Asia. 2018;23(2):115.
Ng JC, Churojana A, Pongpech S, Vu LD, Sadikin C, Mahadevan J, et al. Current state of acute stroke care in Southeast Asian countries. Interv Neuroradiol. 2019;25(3):291–6.
Ocampo FF, De Leon-Gacrama FRG, Cuanang JR, Navarro JC. Profile of stroke mimics in a tertiary medical center in the Philippines. Neurol Asia. 2021;26(1):35–9.
Pascua R, Hiyadan JH. Outcome of decompressive hemicraniectomy without evacuation of hematoma in supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage in a tertiary government hospital in the Philippines: a retrospective study. Eur Stroke J. 2023;8(2):586.
Prado M, Jamora RD, Charmaine Sy M, Anlacan M, Espiritu A. Determinants and Outcomes of Cerebrovascular Disease in Patients with COVID19 in the Philippines: An Analysis of 10881 Cases. Neurology. 2022;98(18). https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.98.18_supplement.2076 .
Qua CV, Tiqui V, Villatima NE, Perales DJ, Rubio SM, Santos ER, et al. A predictive assessment of early neurological deterioration among Filipino acute ischemic stroke patients utilizing hematological, lipid profile, and metabolic parameters in a tertiary hospital in Pampanga. Philippines Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022;51:101.
Que DL, Cuanang J, San Jose MC. Clinical profile, management and outcomes of patients with cerebralvenous thrombosis in atertiary hospital in the Philippines. Int J Stroke. 2020;15(1):511.
Quiles LEP, Diamante PAB, Pascual JLV. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in the acute stroke admissions and outcomes in a Philippine Tertiary Hospital. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2022;12(2):76–84.
Roxas AA. The RIFASAF project: a case-control study on risk factors for stroke among Filipinos. Philippine J Neurol. 2002;6(1):1–7.
Roxas AAC, Carabal-Handumon J. Knowledge and perceptions among the barangay health workers in Plaridel, Misamis Occidental. Philipp J Neurol. 2002;6(1):44.
Sasikumar S, Bengzon Diestro JD. Global & community health: acute ischemic stroke in Toronto and Manila: bridging the gap. Neurology. 2020;95(13):604–6.
Senga MM, Reyes JPB. Cerebral venous thrombosis in a single center tertiary hospital of a South East Asian country (CVSTS study)-a retrospective study on the clinical profiles of patients with cerebral venous thrombosis. Neurology. 2019;92(15). https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.92.15_supplement.P5.3-011 .
Sese LVC, Guillermo MCL. Strengthening stroke prevention and awareness in the Philippines: a conceptual framework. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1258821.
Suwanwela NC, Chen CLH, Lee CF, Young SH, Tay SS, Umapathi T, et al. Effect of combined treatment with MLC601 (NeuroAiDTM) and rehabilitation on post-stroke recovery: the CHIMES and CHIMES-E studies. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;46(1–2):82–8.
Talamera AF, Franco DS. Validation study of Siriraj stroke score in Southern Philippines. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;32:9.
Tan A, Navarro J. Outcomes and quality of care outcome of patients with primary intracerebral hemorrhage in a single center in the philippines. Int J Stroke. 2014;9:269.
Tangcuangco NC, Bitanga ES, Roxas AA, Pascual JL, Saniel E, Reyes JP, et al. Intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (IV-rtPA) use in acute ischemic stroke in a private tertiary hospital: a Philippine setting. Int J Stroke. 2010;5:107.
Tsang ACO, Yang IH, Orru E, Nguyen QA, Pamatmat RV, Medhi G, et al. Overview of endovascular thrombectomy accessibility gap for acute ischemic stroke in Asia: a multi-national survey. Int J Stroke. 2020;15(5):516–20.
Vatanagul J, Cantero-Auguis C. Awareness on acute stroke management among family medicine and internal medicine residents in Metro Cebu. Philippines J Neurol Sci. 2015;357:e418–9.
Vatanagul J, Rulona IA. The incidence of post-stroke depression in a tertiary hospital in Cebu City, Philippines. J Neurol Sci. 2015;357:e419.
Vatanagul JAS, Rulona IA, Belonguel NJ. Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVST): study of four Filipino patients and literature review. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;36:81.
Venketasubramanian N, Yoon BW, Pandian J, Navarro JC. Stroke epidemiology in south, east, and south-east Asia: a review. J Stroke. 2017;19(3):286–94.
Yu RF, San Jose MC, Manzanilla BM, Oris MY, Gan R. Sources and reasons for delays in the care of acute stroke patients. J Neurol Sci. 2002;199(1–2):49–54.
Philippine Neurological Association One Database - Stroke DsSMG. Multicentre collection of uniform data on patients hospitalised for transient ischaemic attack or stroke in the Philippines: the Philippine Neurological Association One Database-Stroke (PNA1DB-Stroke) protocol. BMJ Open. 2022;12(5):54.
Feigin VL, Owolabi MO, Group WSOLNCSC. Pragmatic solutions to reduce the global burden of stroke: a world stroke organization-lancet neurology commission. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(12):1160–206.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the TULAY collaborators: Dr Roy Francis Navea, Dr Myrna Estrada, Dr Elda Grace Anota, Dr Maria Mercedes Barba, Dr June Ann De Vera, Dr Maria Elena Tan, Dr Sarah Buckingham and Professor Fiona Jones. We are grateful to Lance de Jesus and Dr Annah Teves, Research Assistants on the TULAY project, for their contribution to some of the data extraction.
This research was funded by the NIHR Global Health Policy and Systems Research Programme (Award ID: NIHR150244) in association with UK aid from the UK Government to support global health research. The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NIHR or the UK’s Department of Health and Social Care.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Health, Intercity Place, University of Plymouth, Plymouth, Devon, PL4 6AB, UK
Angela Logan, Bridie Kent, Aira Ong & Jonathan Marsden
Royal Devon University Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust, William Wright House, Barrack Road, Exeter, Devon, EX2 5DW, UK
Angela Logan
De La Salle University-Evelyn D. Ang Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Health Technologies, 2401 Taft Avenue, Malate, Manila, 1004, Philippines
Lorraine Faeldon
The University of Plymouth Centre for Innovations in Health and Social Care: A JBI Centre of Excellence, Faculty of Health, Intercity Place, University of Plymouth, Plymouth, Devon, PL4 6AB, UK
Bridie Kent
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualisation, methodology and setting search terms, AL, LF, AO, JM, BK. Searches and screening, AL, JM, LF, AO. Data extraction, AL, LF, AO, JM, LdJ, AT. Original draft preparation, AL, JM. All authors provided substantive intellectual and editorial revisions and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Angela Logan .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Logan, A., Faeldon, L., Kent, B. et al. A scoping review of stroke services within the Philippines. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 1006 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11334-z
Download citation
Received : 20 March 2024
Accepted : 22 July 2024
Published : 30 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11334-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Stroke care
- Low- middle-income countries
- Developing countries
- Philippines
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Performance Review Examples: A Comprehensive Guide
- linkedin Icon

Performance reviews are a critical part of any organization's employee management strategy. They provide an opportunity for feedback, goal-setting, and development, helping both the employee and the company to grow.
However, conducting effective performance reviews can be challenging.
To get it right, you need to understand the different types of performance reviews, why they are important, common mistakes to avoid, and most importantly, how to provide constructive feedback.
This article delves into performance review examples, covering the essentials of effective performance management , how to structure your reviews, and real-world examples to guide you through the process.
What Are Performance Reviews and Why Are They Important?
Performance reviews, also known as employee evaluations or performance appraisals, are formal assessments where managers evaluate an employee’s work performance over a specific period. This process often includes feedback on what the employee did well, areas for improvement, and goals for future performance.
Why Conduct Performance Reviews?
Performance reviews serve multiple purposes, each contributing to the overall success of the organization. Here are some key reasons to conduct regular performance reviews:
Employee Development: Performance reviews provide a structured opportunity to offer employees constructive feedback. This feedback helps employees understand what they’re doing well and where they need to improve, supporting their growth and development.
Goal Alignment: Reviews help align employee goals with the company's objectives, ensuring that everyone is working toward the same outcomes. This alignment is crucial for long-term success and fosters a sense of purpose within the team.
Increased Engagement: When done correctly, performance reviews can increase employee engagement by making workers feel valued and understood. Regular check-ins show employees that their contributions are recognized, boosting morale and motivation.
Accountability: Performance reviews promote accountability by documenting progress, achievements, and areas needing attention. Employees and managers can track improvements over time, creating a transparent record of performance.
Talent Management: Effective performance reviews help identify high performers for promotions, leadership roles, and other growth opportunities. They also provide insight into underperforming areas, allowing managers to take corrective actions early on.
Types of Performance Reviews
Not all performance reviews are the same. Depending on the goals, the company's culture, and the employee's role, different types of performance reviews may be used. Understanding the various types allows you to choose the right approach for your organization.
1. Annual Performance Reviews
Annual performance reviews are the most traditional type of performance evaluation. As the name suggests, they occur once a year and involve a comprehensive review of the employee's performance over the past 12 months. These reviews typically include detailed feedback, ratings, and goal-setting for the upcoming year.
In an annual review, a manager might assess an employee's achievements, including key projects completed, contribution to team goals, and overall performance. The manager may also discuss areas for development, such as improving time management or enhancing communication skills.
2. Quarterly Performance Reviews
Quarterly performance reviews break down the annual review process into more frequent, manageable segments. These reviews are shorter and often focus on specific, short-term goals or performance indicators. Quarterly reviews allow for more regular feedback and course corrections throughout the year.
In a quarterly review, a manager might focus on the employee’s progress toward quarterly targets, providing feedback on performance so far and discussing any challenges the employee has faced. This could involve assessing progress on specific projects, reviewing KPI achievements, and setting new short-term goals for the next quarter.
3. 360-Degree Feedback Reviews
360-degree feedback reviews involve collecting feedback from a variety of sources, including peers, subordinates, and even customers, in addition to the employee's direct supervisor. This method provides a holistic view of the employee’s performance and how they are perceived across the organization.
A 360-degree review for a team leader might include feedback from their direct reports on leadership style, comments from peers on collaboration, and insights from upper management on strategic thinking. This feedback is then combined to give a comprehensive view of the employee’s performance.
4. Self-Assessment Reviews
Self-assessment reviews ask the employee to evaluate their own performance. These reviews encourage employees to reflect on their work, achievements, and areas for improvement. Self-assessment is often used in conjunction with other review types, providing a more balanced perspective on performance.
An employee might complete a self-assessment where they rate their performance in key areas such as productivity, teamwork , and problem-solving. The self-assessment can then be compared with the manager's evaluation to identify alignment or discrepancies.
5. Project-Based Reviews
Project-based reviews occur at the conclusion of a significant project or milestone. Rather than focusing on a specific time period, these reviews evaluate performance based on the completion of a particular project, providing targeted feedback on the employee's contributions to that project’s success.
After completing a major product launch, a project-based review might focus on how the employee managed deadlines, collaborated with the team, and contributed innovative ideas. The review could also assess how effectively the employee addressed any challenges that arose during the project.
Common Mistakes in Performance Reviews
While performance reviews have the potential to be powerful tools for growth and development, they can also go wrong if not handled correctly. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when conducting performance reviews:
1. Being Too Vague
One of the biggest mistakes managers make during performance reviews is providing feedback that is too vague. Generic comments like "You're doing great" or "You need to improve" don’t offer actionable insights for the employee.
How to Avoid It:
Be specific in your feedback. If the employee is performing well, highlight exactly what they are doing right. If there are areas for improvement, point out specific examples and suggest ways to address them. For example, instead of saying "Improve your communication," you might say, "In your last project update, you didn't include the necessary details about the deadline changes. Going forward, make sure to communicate any schedule shifts clearly to all team members."
2. Focusing Only on the Negative
It’s easy to get caught up in addressing problems and areas for improvement during a performance review, but focusing solely on the negatives can be demoralizing for employees.
Balance your feedback by acknowledging the employee’s strengths and achievements as well as areas that need improvement. Even if there are serious issues to address, make sure to highlight the positives too. This helps maintain motivation and shows the employee that their efforts are recognized.
3. Not Setting Clear Goals
Another common mistake is failing to set clear, actionable goals for the employee’s future performance. Without clear goals, employees may leave the review feeling unsure about what is expected of them.
Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals during the review. For instance, instead of saying "Improve your sales numbers," set a goal like "Increase sales by 10% over the next quarter by targeting new client segments."
4. Making It a One-Way Conversation
Performance reviews should not be a monologue from the manager. Employees should have the opportunity to provide feedback, ask questions, and discuss their own perspectives on their performance.
Encourage a two-way conversation during the review. Ask open-ended questions like "How do you feel about your performance this quarter?" or "What challenges have you faced recently, and how can I help?" For instance, you can use an AI form generator to create a feedback form that asks relevant, open-ended follow-up questions based on previous answers. This invites dialogue and fosters a collaborative atmosphere.
5. Ignoring Ongoing Feedback
Relying solely on the performance review to provide feedback is a common mistake. If employees only hear about their performance during formal reviews, they may miss opportunities to improve throughout the year.
Provide ongoing feedback between formal reviews. Regular check-ins and informal feedback sessions ensure that employees have the guidance they need to stay on track. Performance reviews should be a summary of ongoing conversations, not the first time employees hear about an issue.
Performance Review Examples for Different Scenarios
Here are some specific examples of how to approach performance reviews in different scenarios. These examples highlight both positive feedback and constructive criticism, providing a balanced approach that can help employees grow.
Example 1: High Performer in a Leadership Role
Strengths: "You have consistently demonstrated strong leadership skills by effectively managing your team and delivering projects on time . Your ability to motivate others and maintain a high level of productivity is a significant asset to the organization."
Opportunities for Growth: "Moving forward, I’d like to see you focus on developing your delegation skills. While your hands-on approach has been effective, delegating more tasks to your team will allow you to focus on strategic initiatives."
Goals: "Over the next six months, let’s work on identifying key tasks that can be delegated and ensuring that your team has the resources they need to take ownership of those tasks."
Example 2: Mid-Level Employee with Performance Issues
Strengths: "You have shown great initiative in taking on new projects, and your creativity is evident in the solutions you’ve proposed. Your willingness to tackle challenges head-on is commendable."
Areas for Improvement: "However, I’ve noticed that your time management has been an issue. Several deadlines have been missed, and this has impacted the team's overall progress. Let’s work on creating a more structured approach to managing your tasks and meeting deadlines."
Goals: "Over the next quarter, I want you to focus on improving your time management. Let’s set up weekly check-ins to review your progress on key tasks and ensure that you’re staying on track."
Example 3: New Employee in an Entry-Level Role
Strengths: "In your first few months, you’ve quickly adapted to the team and demonstrated a strong work ethic. Your attention to detail has been excellent, particularly in the way you’ve handled data entry and reporting tasks."
Opportunities for Growth: "As you continue to grow in your role, I’d like to see you take on more proactive responsibilities. Don’t be afraid to ask questions or propose new ideas—you have a lot of potential, and I’d love to see you contribute more actively in meetings."
Goals: "For the next six months, let’s set a goal of contributing at least one new idea in each team meeting and taking on one additional project that challenges your current skill set."
Performance reviews are an essential part of employee development and organizational growth. Whether you are conducting annual reviews, using 360-degree feedback, or focusing on project-based evaluations, the key to success lies in providing clear, constructive feedback that motivates and guides employees. Avoid common pitfalls like vague feedback, focusing only on negatives, or neglecting goal-setting, and ensure that performance reviews are a two-way conversation that promotes continuous development.
By understanding the different types of performance reviews and using real-world examples as a guide, managers can conduct effective reviews that drive improvement and engagement, ultimately leading to a stronger, more productive team. For those evaluating various tools, considering fera review app alternative s might be beneficial for comprehensive feedback management.
If you found this post useful #share it:
You may also like to read these..
Explore the extensive resources compiled by experts in the field.

No Excuses for Firing: A Guide to Employee Termination
Navigate the tricky waters of employee termination with our guide. Get insights and tips to handle dismissals professionally.

Split, Day Or 3rd Shift Hours? The Ultimate Shift Types Guide
Uncover the Ultimate Shift Types Guide - From flexible schedules to night shifts, this comprehensive resource covers many different shift types.

How Much is Overtime Pay? Here Is How To Find Out
Do you know how to determine your overtime pay? Get the answers you need on our blog post today!

Payroll App Hourly: 2024 Review
Looking for a reliable payroll solution? Check out this payroll app Hourly review for 2024. You will also learn about better payroll services here.
We've got more awesome content!
Focus on the fun parts of work.
Let Unrubble handle all your boring stuff .
Automate work schedule planning , work time tracking , pto management , and much more.

This website uses cookies, pixel tags, and local storage for performance, personalization, and marketing purposes. We use our own cookies and some from third parties. Only essential cookies are turned on by default.

COMMENTS
In specifying precisely one's research topic, one is also specifying appropriate limitations on the research. Limiting, for example, by time, personnel, gender, age, location, nationality, etc. results in a more focused and meaningful topic. Scope of the Literature Review. It is also important to determine the precise scope of the literature ...
A literature review is a comprehensive analysis of existing research on a topic, identifying trends, gaps, and insights to inform new scholarly contributions. Read this comprehensive article to learn how to write a literature review, with examples.
Includes definitions, approaches to literature reviews, finding sources, organizing the literature review, and practical tips.
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing This guide will provide research and writing tips to help students complete a literature review assignment.
Example reviews. Please choose the tab below for your discipline to see relevant examples. For more information about how to conduct and write reviews, please see the Guidelines section of this guide. Technologically-enhanced psychological interventions for older adults: A scoping review. (2020).
A literature review is a survey of scholarly knowledge on a topic. Our guide with examples, video, and templates can help you write yours.
Scope. A literature review may be comprehensive or selective but should examine seminal or principal works and works that have been consequential in the field. The scope of a literature review will vary by assignment and discipline. The literature review may be part of a larger work or a stand-alone article, meaning that it is the entirety of a ...
Write the Review STEP ONE: DEFINE THE SCOPE Look for relevant models in journals in your field (e.g., a target journal for publication) and papers, qualifying exams, proposals, and dissertations of colleagues. While none of these will necessarily provide you with literature relevant to your topic, they will be good guides for scope in terms of: 1.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
This guide will help you get started on your literature review by providing basic information on what a review is, how to write it and where to do the research.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7]. In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights ...
The reasons for undertaking a literature review are numerous and include eliciting information for developing policies and evidence-based care, a step in the research process and as part of an academic assessment. To many qualified nurses and nursing students faced with undertaking a literature review the task appears daunting.
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure. Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you'll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don't worry though - in this post, we'll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).
Learn everything you need to know about how to write literature reviews — how long it should be, the different types, how to write a literature review, among many other things.
A literature review is a comprehensive and critical analysis of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It involves identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant literature, including scholarly articles, books, and other sources, to provide a summary and critical assessment of what is known about the topic.
As outlined in Section 2.4.2 , authors should consider carefully the needs of users of the review and the context (s) in which they expect the review to be used when determining the most optimal scope for their review.
Steps in the Literature Review Process Define the research question (for more ) You may need to some exploratory searching of the literature to get a sense of scope, to determine whether you need to narrow or broaden your focus Identify databases that provide the most relevant sources, and identify relevant terms (controlled vocabularies) to add to your search strategy Finalize your research ...
Definition. A literature review is an assessment of the sources in a chosen topic of research. In a literature review, you're expected to report on the existing scholarly conversation, without adding new contributions. If you are currently writing one, you've come to the right place. In the following paragraphs, we will explain: the objective ...
The introduction to a literature review serves as your reader's guide through your academic work and thought process. Explore the significance of literature review introductions in review papers, academic papers, essays, theses, and dissertations. We delve into the purpose and necessity of these introductions, explore the essential components of literature review introductions, and provide ...
This paper discusses literature review as a methodology for conducting research and offers an overview of different types of reviews, as well as some guidelines to how to both conduct and evaluate a literature review paper. It also discusses common pitfalls and how to get literature reviews published. 1.
An empirical literature review collects, creates, arranges, and analyzes numeric data reflecting the frequency of themes, topics, authors and/or methods found in existing literature. Empirical literature reviews present their summaries in quantifiable terms using descriptive and inferential statistics.
A literature review is a compilation of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.. Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic ...
Making sense of what has been written on your topic. GOALS OF A LITERATURE REVIEW: Before doing work in primary sources, historians must know what has been written on their topic. They must be familiar with theories and arguments-as well as facts-that appear in secondary sources. Before you proceed with your research project, you […]
We discuss how to perform a scoping review study. Scoping reviews are a type of literature review that are becoming more popular.
From Lesson 51-56, we have discussed chapter one of the research proposal. From now until lesson 60, we shall discuss chapter two of the research proposal which is referred to as Literature Review ...
The systematic literature review retrieved a total of 38 articles. After undergoing several stages, 25 articles met the criteria and were subsequently subjected to a more in-depth analysis.
The New York Times Book Review I've I want THE 100 BEST BOOKS OF THE 21ST CENTURY read to it read it 51 Life After Life, by Kate Atkinson 52 52 Train Dreams, by Denis Johnson 53 Runaway, by Alice ...
For example, reviewed resources encourage funders to expand the networks they use to announce new funding opportunities and participate in community events. ... .This study explores research and strategies related to equity in the discretionary grant-making process based on a review of publicly available literature and Federal agency Equity ...
The scoping review followed a predefined protocol, established methodology [] and is reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews Guidelines (PRISMA-ScR) [6, 7].Healthcare quality will be described according to the following three aspects: structures, processes, and outcomes following the Donabedian model [8, 9].The ...
Performance Review Examples for Different Scenarios. Here are some specific examples of how to approach performance reviews in different scenarios. These examples highlight both positive feedback and constructive criticism, providing a balanced approach that can help employees grow. Example 1: High Performer in a Leadership Role