Critical Thinking Questions
Why are biological macromolecules considered organic?
What role do electrons play in dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis?
Amino acids have the generic structure seen below, where R represents different carbon-based side chains.
Describe how the structure of amino acids allows them to be linked into long peptide chains to form proteins.
Describe the similarities and differences between glycogen and starch.
Why is it impossible for humans to digest food that contains cellulose?
Draw the ketose and aldose forms of a monosaccharide with the chemical formula C 3 H 6 O 3 . How is the structure of the monosaccharide changed from one form to the other in the human body?
Explain at least three functions that lipids serve in plants and/or animals.
Why have trans fats been banned from some restaurants? How are they created?
Why are fatty acids better than glycogen for storing large amounts of chemical energy?
Part of cortisol’s role in the body involves passing through the plasma membrane to initiate signaling inside a cell. Describe how the structures of cortisol and the plasma membrane allow this to occur.
Explain what happens if even one amino acid is substituted for another in a polypeptide chain. Provide a specific example.
Describe the differences in the four protein structures.
Aquaporins are proteins embedded in the plasma membrane that allow water molecules to move between the extracellular matrix and the intracellular space. Based on its function and location, describe the key features of the protein’s shape and the chemical characteristics of its amino acids.
What are the structural differences between RNA and DNA?
What are the four types of RNA and how do they function?
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Mary Ann Clark, Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Biology 2e
- Publication date: Mar 28, 2018
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/3-critical-thinking-questions
© Jan 8, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


6.4: Protein Synthesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 27396

- Suzanne Wakim & Mandeep Grewal
- Butte College
The Central Dogma of Biology
Your DNA , or deoxyribonucleic acid, contains the genes that determine who you are. How can this organic molecule control your characteristics? DNA contains instructions for all the proteins your body makes. Proteins , in turn, determine the structure and function of all your cells. What determines a protein ’s structure? It begins with the sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Instructions for making proteins with the correct sequence of amino acids are encoded in DNA.

DNA is found in chromosomes. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes always remain in the nucleus, but proteins are made at ribosomes in the cytoplasm or on the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) . How do the instructions in DNA get to the site of protein synthesis outside the nucleus? Another type of nucleic acid is responsible. This nucleic acid is RNA or ribonucleic acid. RNA is a small molecule that can squeeze through pores in the nuclear membrane. It carries the information from DNA in the nucleus to a ribosome in the cytoplasm and then helps assemble the protein. In short:
DNA → RNA → Protein
Discovering this sequence of events was a major milestone in molecular biology. It is called the central dogma of biology . The two processes involved in the central dogma are transcription and translation.
Transcription
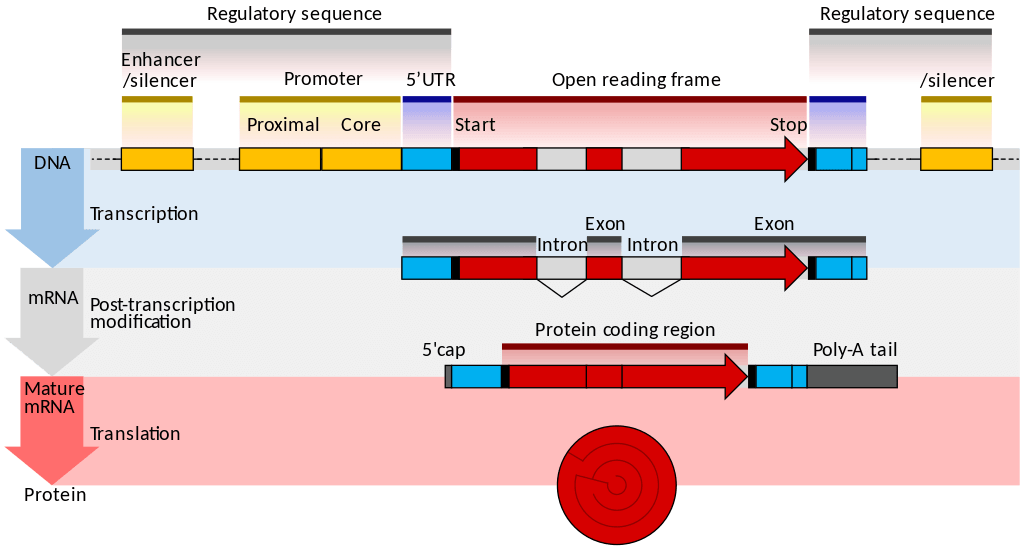
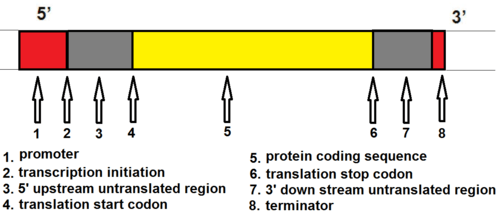
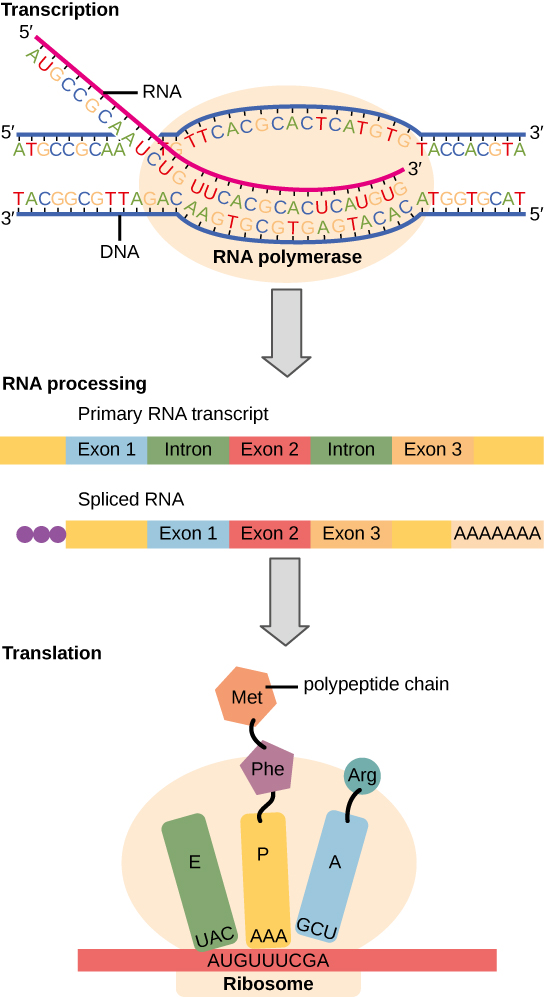
Transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA → RNA . It is the transfer of genetic instructions in DNA to mRNA. Transcription happens in the nucleus of the cell. During transcription, a strand of mRNA is made that is complementary to a strand of DNA called a gene. A gene can easily be identified from the DNA sequence. A gene contains the basic three regions, promoter, coding sequence (reading frame), and terminator. There are more parts of a gene which are illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\).
Steps of Transcription
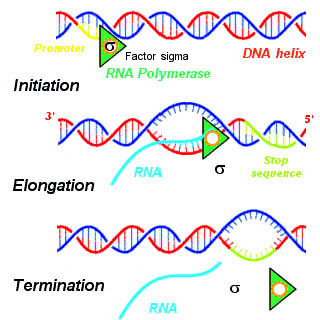
Transcription takes place in three steps, called initiation, elongation, and termination. The steps are illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\).
- Initiation is the beginning of transcription. It occurs when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a region of a gene called the promoter . This signals the DNA to unwind so the enzyme can “read” the bases in one of the DNA strands. The enzyme is ready to make a strand of mRNA with a complementary sequence of bases. The promoter is not part of the resulting mRNA
- Elongation is the addition of nucleotides to the mRNA strand.
Processing mRNA
In eukaryotes, the new mRNA is not yet ready for translation. At this stage, it is called pre-mRNA, and it must go through more processing before it leaves the nucleus as mature mRNA. The processing may include the addition of a 5' cap, splicing, editing, and 3' polyadenylation (poly-A) tail. These processes modify the mRNA in various ways. Such modifications allow a single gene to be used to make more than one protein. See Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) as you read below:
- 5' cap protects mRNA in the cytoplasm and helps in the attachment of mRNA with the ribosome for translation.
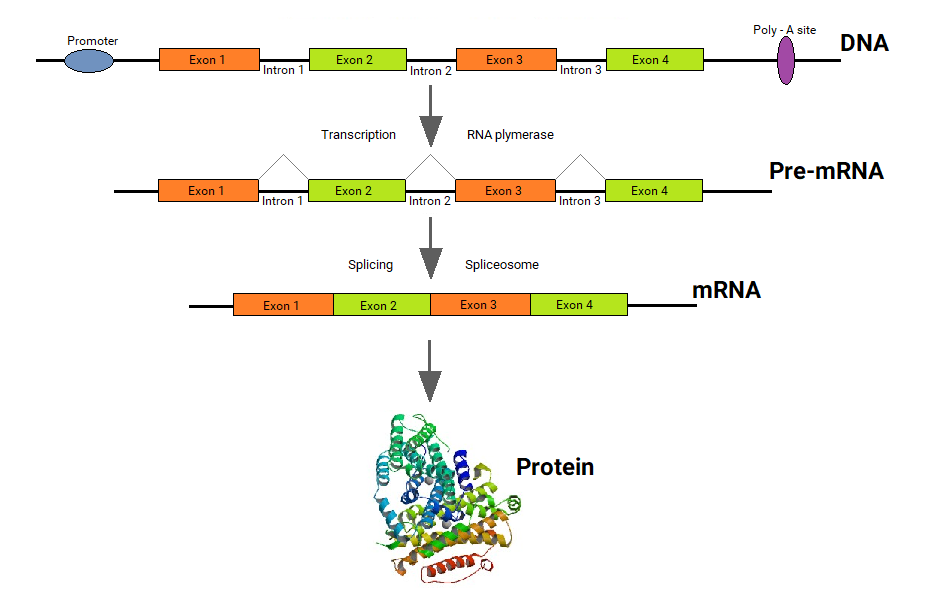
- Splicing removes introns from the protein-coding sequence of mRNA. Introns are regions that do not code for the protein. The remaining mRNA consists only of regions called exons that do code for the protein.
- Editing changes some of the nucleotides in mRNA. For example, a human protein called APOB, which helps transport lipids in the blood, has two different forms because of editing. One form is smaller than the other because editing adds an earlier stop signal in mRNA.
- Polyadenylation adds a “tail” to the mRNA. The tail consists of a string of As (adenine bases). It signals the end of mRNA. It is also involved in exporting mRNA from the nucleus, and it protects mRNA from enzymes that might break it down.
Translation
The translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: RNA --> Protein . It is the process in which the genetic code in mRNA is read to make a protein. The translation is illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\). After mRNA leaves the nucleus, it moves to a ribosome, which consists of rRNA and proteins. Translation happens on the ribosomes floating in the cytosol, or on the ribosomes attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The ribosome reads the sequence of codons in mRNA, and molecules of tRNA bring amino acids to the ribosome in the correct sequence.
To understand the role of tRNA, you need to know more about its structure. Each tRNA molecule has an anticodon for the amino acid it carries. An anticodon is complementary to the codon for an amino acid. For example, the amino acid lysine has the codon AAG, so the anticodon is UUC. Therefore, lysine would be carried by a tRNA molecule with the anticodon UUC. Wherever the codon AAG appears in mRNA, a UUC anticodon of tRNA temporarily binds. While bound to mRNA, tRNA gives up its amino acid. With the help of rRNA, bonds form between the amino acids as they are brought one by one to the ribosome, creating a polypeptide chain. The chain of amino acids keeps growing until a stop codon is reached.
Ribosomes, which are just made out of rRNA (ribosomal RNA) and protein, have been classified as ribozymes because the rRNA has enzymatic activity. The rRNA is important for the peptidyl transferase activity that bonds amino acids. Ribosomes have two subunits of rRNA and protein. The large subunit has three active sites called E, P, and A sites. These sites are important in the catalytic activity of ribosomes.
Just as with mRNA synthesis, protein synthesis can be divided into three phases: initiation, elongation, and termination. In addition to the mRNA template, many other molecules contribute to the process of translation, such as ribosomes, tRNAs, and various enzymatic factors
Translation Initiation: The small subunit binds to a site upstream (on the 5' side) of the start of the mRNA. It proceeds to scan the mRNA in the 5'-->3' direction until it encounters the START codon (AUG). The large subunit attaches and the initiator tRNA, which carries methionine (Met), binds to the P site on the ribosome.
Translation Elongation: The ribosome shifts one codon at a time, catalyzing each process that occurs in the three sites. With each step, a charged tRNA enters the complex, the polypeptide becomes one amino acid longer, and an uncharged tRNA departs. The energy for each bond between amino acids is derived from GTP, a molecule similar to ATP. Briefly, the ribosomes interact with other RNA molecules to make chains of amino acids called polypeptide chains, due to the peptide bond that forms between individual amino acids. Inside the ribosome, three sites participate in the translation process, the A, P, and E sites. Amazingly, the E. coli translation apparatus takes only 0.05 seconds to add each amino acid, meaning that a 200-amino acid polypeptide could be translated in just 10 seconds.
Translation Termination : Termination of translation occurs when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is encountered (see Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\). When the ribosome encounters the stop codon, the growing polypeptide is released with the help of various releasing factors and the ribosome subunits dissociate and leave the mRNA. After many ribosomes have completed translation, the mRNA is degraded so the nucleotides can be reused in another transcription reaction.
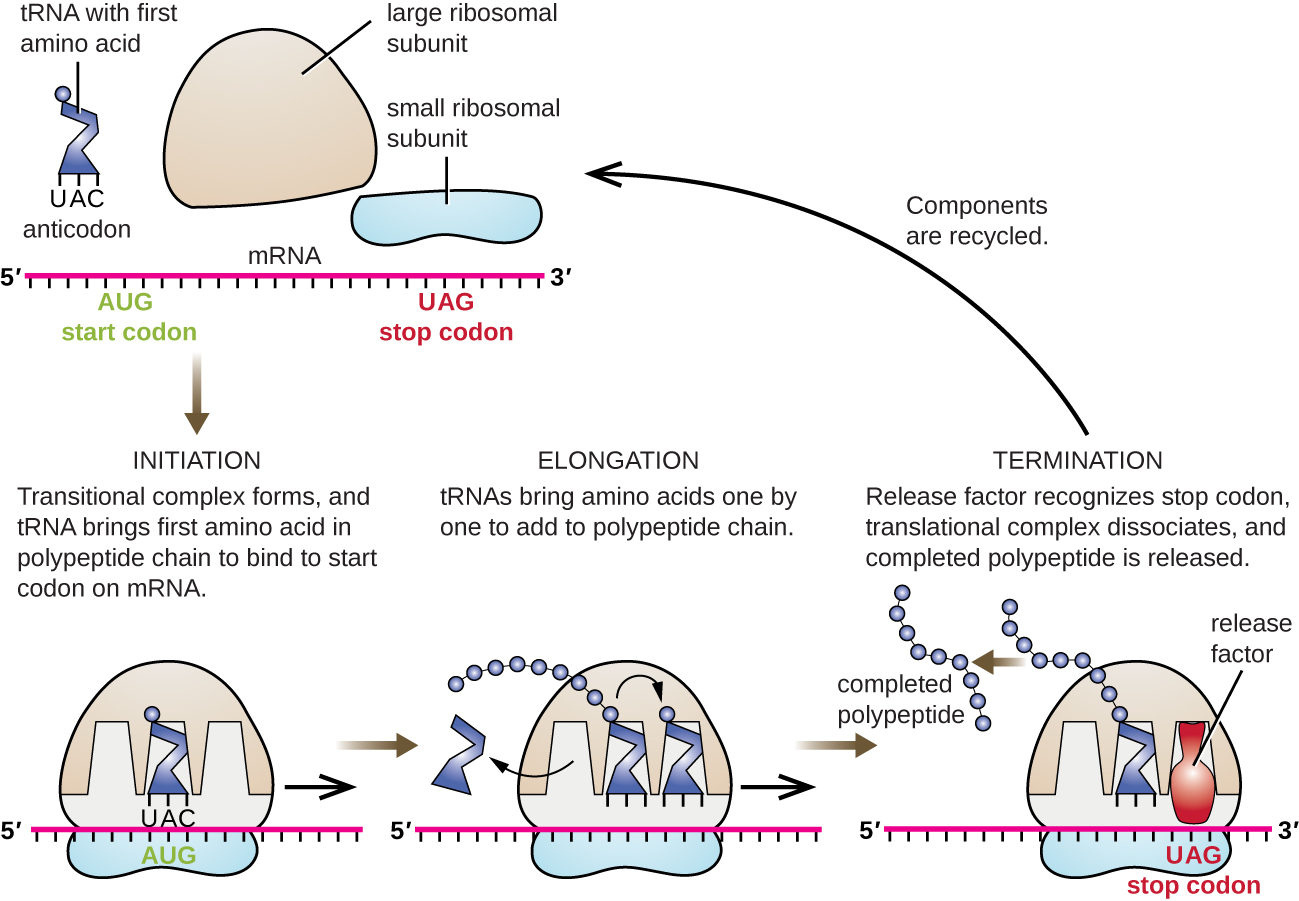
What Happens Next?
After a polypeptide chain is synthesized, it may undergo additional processes. For example, it may assume a folded tertiary shape due to interactions among its amino acids. It may also bind with other polypeptides or with different types of molecules, such as lipids or carbohydrates. Many proteins travel to the Golgi apparatus within the cytoplasm to be modified for the specific job they will do.
Summary of Central Dogma
- Relate protein synthesis and its two major phases to the central dogma of molecular biology.
- Identify the steps of transcription, and summarize what happens during each step.
- Explain how mRNA is processed before it leaves the nucleus.
- Describe what happens during the translation phase of protein synthesis.
- What additional processes may a polypeptide chain undergo after it is synthesized?
- Where does transcription take place in eukaryotes?
- Where does translation take place?
- Contains the codons
- Contains the anticodons
- Makes up the ribosome, along with proteins
- What is the complementary sequence on the other DNA strand?
- What is the complementary sequence in the mRNA? What is this sequence called?
- @hat is the resulting sequence in the tRNA? What is this sequence called? What do you notice about this sequence compared to the original DNA triplet on the template strand?
- Both A and B
- True or False. Introns in mRNA bind to tRNA at the ribosome.
- True or False. tRNAs can be thought of as the link between amino acids and codons in the mRNA.
Explore More
Messenger RNA molecules are "spliced" in order to create the mRNA involved in protein synthesis. Learn the process here:
Attributions
- How proteins are made by Nicolle Rager, National Science Foundation, public domain via Wikimedia Commons
- Gene structure eukaryote by Thomas Shafee , licensed CC BY 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
- Components of a gene by Mandeep Grewal, CC BY 4.0
- Transcription by Calibuon , released into the public domain via Wikimedia Commons
- Transcript and splicing by Ganeshmanohar , CC BY-SA 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
- Initiation and elongation by Jordan Nguyen, CC BY-SA 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
- Protein synthesis by OpenStax, CC BY 4.0
- Gene regulation by OpenStax, CC BY 4.0
- Text adapted from Human Biology by CK-12 licensed CC BY-NC 3.0
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
High school biology
Course: high school biology > unit 6.
- Molecular structure of RNA
- DNA replication and RNA transcription and translation
- Intro to gene expression (central dogma)
The genetic code
- Impact of mutations on translation into amino acids
RNA and protein synthesis review
Transcription and translation.
- Codons and mutations
Structure of RNA
- RNA uses the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose .
- RNA is generally single-stranded instead of double-stranded.
- RNA contains uracil in place of thymine.
Types of RNA
Central dogma of biology.
- First, we look at the left side of the table. The axis on the left side refers to the first letter of the codon, so we find C along the left axis. This tells us the (broad) row of the table in which our codon will be found.
- Next, we look at the top of the table. The upper axis refers to the second letter of the codon, so we find A along the upper axis. This tells us the column of the table in which our codon will be found.
Substitutions
- Silent mutations do not affect the sequence of amino acids during translation.
- Nonsense mutations result in a stop codon where an amino acid should be, causing translation to stop prematurely.
- Missense mutations change the amino acid specified by a codon.
Insertions and deletions
Common mistakes and misconceptions.
- Amino acids are not made during protein synthesis. Some students think that the purpose of protein synthesis is to create amino acids. However, amino acids are not being made during translation, they are being used as building blocks to make proteins.
- Mutations do not always have drastic or negative effects. Often people hear the term "mutation" in the media and understand it to mean that a person will have a disease or disfigurement. Mutations are the source of genetic variety, so although some mutations are harmful, most are unnoticeable, and many are even good!
- Insertions and deletions that are multiples of three nucleotides will not cause frameshift mutations. Rather, one or more amino acids will just be added to or deleted from the protein. Insertions and deletions that are not multiples of three nucleotides, however, can dramatically alter the amino acid sequence of the protein.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is how our bodies make proteins.

- Each amino acid is coded for by a specific sequence of three bases (called a codon).

Order of bases
- The order of the bases on the DNA tells us the order for combining amino acids to create particular proteins.

Different proteins
- We can change the protein made by a gene by altering the sequence of bases in that gene.
The process of protein synthesis (creation) happens like this:

Template taken
- A template is taken from the DNA and leaves the nucleus.


Template used
- The template is used to guide protein synthesis on ribosomes located in the cytoplasm.

Delivery of amino acids
- Specific amino acids are delivered by carrier molecules to the protein chain, where they are added in the order shown on the template.
Unique structure created
- Once complete, the long protein chain folds up, giving it a unique structure.
- This unique structure is essential to the protein’s function, in the form of enzymes, hormones, or structural proteins (e.g. collagen).
1 Cell Biology
1.1 What's in Cells?
1.1.1 Types of Cells
1.1.2 Properties of Prokaryotes
1.1.3 Standard Form
1.1.4 Standard Form - Calculations
1.1.5 Addition in Standard Form - Calculations
1.1.6 Subtraction in Standard Form - Calculations
1.1.7 Multiplication in Standard Form - Calculations
1.1.8 Division in Standard Form - Calculations
1.1.9 Animal Cells
1.1.10 Plant Cells
1.1.11 Differences Between Animal & Plant Cells
1.1.12 Bacterial Cells
1.1.13 Types of Cells HyperLearning
1.1.14 Cell Specialisation in Animals
1.1.15 Sperm Cells
1.1.16 Nerve Cells
1.1.17 Muscle Cells
1.1.18 Cell Specialisation in Plants
1.1.19 Microscopy
1.1.20 Developments in Microscopy
1.1.21 Microscope Practical
1.1.22 Microscopy - Calculations
1.1.23 Culturing Microorganisms
1.1.24 Contamination
1.1.25 Avoiding Contamination
1.1.26 Calculating Bacteria
1.1.27 Calculating Bacteria - Calculations
1.1.28 End of Topic Test - What's in Cells?
1.1.29 Exam-Style Questions - Cell Structure & Microscopy
1.2 Cell Division
1.2.1 Chromosomes
1.2.2 The Cell Cycle
1.2.3 Mitosis
1.2.4 Exam-Style Questions - Mitosis & Cell Cycle
1.2.5 Stem Cells
1.2.6 Use of Stem Cells
1.2.7 Disadvantages of Stem Cells
1.3 Transport in Cells
1.3.1 Diffusion
1.3.2 Factors Affecting Diffusion
1.3.3 Surface Area : Volume
1.3.4 Surface Area : Volume - Calculations
1.3.5 Exchange Surfaces
1.3.6 Examples of Exchange Surfaces
1.3.7 Osmosis
1.3.8 Osmosis Practical
1.3.9 Active Transport
1.3.10 Transport in Cells
1.3.11 End of Topic Test - Cell Division & Transport
1.3.12 Grade 9 - Cell Transport
2 Organisation
2.1 Principles of Organisation
2.1.1 Cells & Tissues
2.1.2 Organs
2.1.3 Organ Systems
2.1.4 Organisms
2.2 Enzymes
2.2.1 Enzymes
2.2.2 Enzymes HyperFlashcards
2.2.3 Rate of Reaction
2.2.4 Calculating Rate of Reaction
2.2.5 Rate of Reaction - Calculations
2.2.6 Digestion
2.2.8 Examples of Digestive Enzymes - Amylase
2.2.9 Examples of Digestive Enzymes - Protease
2.2.10 Examples of Digestive Enzymes - Lipase
2.2.11 Testing for Biological Molecules
2.2.12 End of Topic Test - Organisation & Enzymes
2.2.13 Grade 9 - Enzymes
2.2.14 Exam-Style Questions - Enzymes
2.3 Circulatory System
2.3.1 Types of Blood Vessel
2.3.2 Blood Vessels - Arteries
2.3.3 Blood Vessels - Capillaries
2.3.4 Blood Vessels - Veins
2.3.5 The Heart - Structure
2.3.6 The Heart - Function
2.3.7 Important Blood Vessels
2.3.8 Double Circulatory System
2.3.9 Gas Exchange
2.3.10 Gas exchange - Calculations
2.3.11 Alveoli
2.3.12 Blood Components
2.3.13 Platelets
2.3.14 Red Blood Cells
2.3.15 White Blood Cells
2.3.16 End of Topic Test - Circulatory System
2.4 Non-Communicable Diseases
2.4.1 Health Issues
2.4.2 Disease Interactions
2.4.3 Sampling
2.4.4 Sampling - Calculations
2.4.5 Risk Factors
2.4.6 Examples of Risk Factors
2.4.7 Risk Factor Graphs
2.4.8 Coronary Heart Disease
2.4.9 Heart Valve Disease
2.4.10 Heart Failure
2.4.11 Treating Heart Disease
2.4.12 Cancer
2.4.13 Cancer Risk Factors
2.4.14 End of Topic Test - Non-Communicable Diseases
2.4.15 Exam-Style Questions - Coronary Heart Disease
2.5 Plant Tissues, Organs & Systems
2.5.1 Plant Tissues
2.5.2 Leaves
2.5.3 Transpiration
2.5.4 Rate of Transpiration
2.5.5 Measuring Transpiration
2.5.6 Translocation
2.5.7 Transpiration Tissues
2.5.8 Stomata
2.5.9 Premium Knowledge - Transpiration
2.5.10 End of Topic Test - Plants
2.5.11 Exam-Style Questions - Plant Tissues
3 Infection & Response
3.1 Communicable Disease
3.1.1 Spreading Disease
3.1.2 Viruses
3.1.3 Other Pathogens
3.1.4 Human Defence Systems
3.1.5 Human Defence Systems 2
3.1.6 Grade 9 - Immune System
3.1.7 Antibiotics
3.1.8 Drug Development
3.1.9 Drug Testing
3.1.10 Drug Testing / Efficacy - Calculations
3.1.11 End of Topic Test - Communicable Diseases
3.1.12 Exam-Style Questions - Microorganisms & Disease
3.2 Monoclonal Antibodies
3.2.1 Producing & Using Monoclonal Antibodies
3.2.2 Grade 9 - Monoclonal Antibodies
3.3 Plant Diseases
3.3.1 Diseases & Defence
3.3.2 Identifying Disease
3.3.3 End of Topic Test - Antibodies & Plant Disease
4 Bioenergetics
4.1 Photosynthesis
4.1.1 Photosynthesis
4.1.2 Photosynthesis 2
4.1.3 Photosynthesis - Calculations
4.1.4 Photosynthesis Experiments
4.1.5 Grade 9 - Photosynthesis Experiment
4.1.6 Exam-Style Questions - Rate of Photosynthesis
4.2 Respiration
4.2.1 Respiration
4.2.2 Respiration - Calculations
4.2.3 Exercise
4.2.4 Respiration HyperLearning
4.2.5 End of Topic Test - Photosynthesis and Respiration
4.2.6 Exam-Style Questions - Anaerobic Respiration
5 Homeostasis & Response
5.1 Homeostasis
5.1.1 Homeostasis
5.1.2 Homeostasis & Negative Feedback
5.1.3 Exam-Style Questions - Exercise & Homeostasis
5.2 The Human Nervous System
5.2.1 The Nervous System
5.2.2 The Nervous System HyperFlashcards
5.2.3 Synapses
5.2.4 Reflexes
5.2.5 Exam-Style Questions - Nervous System
5.2.6 The Brain
5.2.7 Eye Anatomy
5.2.8 Eye Function
5.2.9 Control of Body Temperature
5.2.10 Warming Up & Cooling Down
5.2.11 Body Temperature HyperLearning
5.2.12 End of Topic Test - Human Nervous System
5.3 Hormonal Coordination in Humans
5.3.1 Endocrine System
5.3.2 Thyroxine & Adrenaline
5.3.3 Blood Glucose
5.3.4 Diabetes
5.3.5 Control of Water Balance
5.3.6 Urine
5.3.7 Dialysis
5.3.8 Transplants
5.3.9 Puberty
5.3.10 Menstruation
5.3.11 Contraception
5.3.12 Contraception 2
5.3.13 Hormones for Infertility
5.3.14 End of Topic Test - Homeostasis & Hormones
5.3.15 Grade 9 - Hormonal Coordination
5.3.16 Exam-Style Questions - Hormones & Contraception
5.4 Plant Hormones
5.4.1 Plant Hormones
5.4.2 Plant Hormones 2
5.4.3 End of Topic Test - Hormones
6 Inheritance, Variation & Evolution
6.1 Reproduction
6.1.1 Reproduction
6.1.2 Reproduction 2
6.1.3 Genome
6.1.5 Protein Synthesis
6.1.6 Genetic Inheritance
6.1.7 Genetic Crosses
6.1.8 Inherited Disorders
6.1.9 Inherited Disorders 2
6.1.10 Genetic Crosses - Calculations
6.1.11 Genome Screening & Sex Determination
6.1.12 End of Topic Test - Reproduction
6.1.13 Exam-Style Questions - DNA & Genetics
6.2 Variation & Evolution
6.2.1 Variation & Evolution
6.2.2 Selective Breeding
6.2.3 Selective Breeding 2
6.2.4 Genetic Engineering
6.2.5 Uses of Genetic Modification
6.2.6 Cloning
6.2.7 Cloning 2
6.2.8 End of Topic Test - Variation & Evolution
6.2.9 Exam-Style Questions - Selective Breeding
6.3 Genetics & Evolution
6.3.1 Natural Selection
6.3.2 Speciation
6.3.3 Evidence for Evolution
6.3.4 Genetics & Extinction
6.3.5 Grade 9 - Evolution
6.4 Classification
6.4.1 Classification of Living Organisms
6.4.2 Classification of Living Organisms 2
6.4.3 End of Topic - Genetics & Classification
7.1 Adaptations & Interdependence
7.1.1 Communities
7.1.2 Communities 2
7.2 Organisation of Ecosystems
7.2.1 Population Dynamics
7.2.2 Environmental Change
7.2.3 Assessing Ecosystems
7.2.4 Assessing Ecosystems - Calculations
7.2.5 The Cycling of Materials
7.2.6 Decay
7.2.7 Decay Practical
7.2.8 End of Topic Test - Organisation of Ecosystems
7.2.9 Grade 9 - Ecosystems
7.2.10 Exam-Style Questions - Decomposition
7.3 Biodiversity
7.3.1 Human Interactions with Ecosystems
7.3.2 Human Interactions with Ecosystems 2
7.3.3 Greenhouse Gases
7.3.4 Greenhouse Gases 2
7.3.5 Hardest Questions - Humans & the Environment
7.3.6 End of Topic Test - Adaptations & Biodiversity
7.4 Trophic Levels
7.4.1 Trophic Levels
7.4.2 Trophic Levels 2
7.4.3 Transfer efficiency - Calculations
7.4.4 Premium Knowledge - Trophic Levels & Food Chains
7.4.5 Exam-Style Questions - Food Chains
7.5 Food Production
7.5.1 Food Production
7.5.2 Farming & Fishing
7.5.3 Food Production - Calculations
7.5.4 End of Topic Test - Food & Trophic Levels
Jump to other topics

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered
Genetic Inheritance
Biology Extended Essay Topics and RQs for IBDP

Table of contents
- Writing Metier
It’s time for our exploration of Biology extended essay topics, a resource designed to spark your curiosity and guide your research interests in the vast and vibrant field of biology.
Whether you’re fascinated by the intricate workings of ecosystems or intrigued by the complexities of cellular processes, this article offers a diverse range of topics collected by expert academic writers to suit your interests.
NB! If you need assistance with your Biology assignments, you can use our biology essay writing service , which will surely assist you. Now, let’s get back to the main question of the article – BIO EE topic ideas.
Bio EE topic categories
List of biology extended essay topic categories I’ll cover in this article.
- Impact of Urban Development on Local Ecosystems – Investigating the effects of urban expansion on biodiversity in a specific area.
- Marine Biology and Ocean Acidification – Studying the impact of changing pH levels on marine life.
- Invasive Species and Their Impact on Biodiversity – Analyzing how a particular invasive species has affected native wildlife.
- Conservation Efforts for Endangered Species – Evaluating the effectiveness of current conservation strategies for a specific endangered species.
- Climate Change and Its Effects on Ecosystems – Researching how a particular ecosystem has been impacted by climate change.
- Nutrition and Diet’s Impact on Human Health – Exploring the effects of a specific diet on human health.
- Exercise Physiology – Investigating how different types of exercise affect a particular aspect of human health.
- Neurobiology of Sleep – Studying the effects of sleep patterns on cognitive functions.
- Genetic Factors in Diseases – Exploring the role of genetics in the susceptibility to a specific disease.
- Impact of Environmental Factors on Allergies – Analyzing how environmental changes have influenced the prevalence of allergies.
- Gene Expression in Cancer Cells – Investigating how gene expression differs in cancerous versus normal cells.
- Protein Synthesis and Its Regulation – Studying the regulation of protein synthesis in a specific organism or cell type.
- Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine – Exploring the potential of stem cells in treating a specific condition.
- Viral Replication and Host Interaction – Examining how a particular virus replicates and interacts with its host.
- DNA Repair Mechanisms – Investigating the efficacy of different DNA repair mechanisms under various conditions.
- Photosynthesis Variations Among Plant Species – Comparing photosynthetic efficiency in different plant species.
- Impact of Climate Change on Plant Growth – Studying how changing climates affect the growth of a specific plant species.
- Medicinal Properties of Plants – Investigating the medicinal properties of a specific plant.
- Plant Defense Mechanisms Against Pathogens – Exploring how a particular plant species defends itself against pathogens.
- Genetic Modification and Crop Improvement – Analyzing the impacts of genetic modification on a specific crop’s traits.
- Social Behavior in Insects – Studying the social structures and behaviors of a specific insect species.
- Bird Migration Patterns – Investigating the factors influencing migration patterns of a specific bird species.
- Physiological Adaptations in Marine Mammals – Exploring adaptations that enable marine mammals to survive in their environments.
- Impact of Environmental Stressors on Animal Behavior – Analyzing how specific stressors affect the behavior of a particular animal species.
- Endocrine Regulation in Animals – Studying how the endocrine system regulates processes in a specific animal.
- Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria – Investigating the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in a specific bacterial strain.
- Use of Microorganisms in Bioremediation – Exploring the use of microorganisms in cleaning up environmental pollutants.
- Genetic Engineering and Its Applications – Analyzing the applications and implications of genetic engineering in a specific field.
- Role of Microbiome in Human Health – Studying how the human microbiome influences health and disease.
- Yeast Fermentation and Its Industrial Applications – Investigating the fermentation process in yeast and its uses in industry.
- Evolutionary Adaptations to Environmental Changes – Exploring how a particular species has adapted to environmental changes over time.
- Genetic Diversity and Population Health – Studying the impact of genetic diversity on the health of a specific population.
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance – Investigating the molecular mechanisms of inheritance in a specific organism.
- Speciation and Genetic Drift – Analyzing the role of genetic drift in the speciation process.
- Human Evolutionary Biology – Studying aspects of human evolution, such as the development of specific traits.
Every category and its subcategories provide a comprehensive overview, from the microscopic wonders of microbiology to the grand scale of evolutionary biology.
With the help of our IB writers team, I have managed to collect all these ideas for you, so I hope you will be enjoying this. I aim to inspire your investigative spirit and help you select a topic that satisfies the IB criteria and aligns with your passion for biology.
IB Bio extended essay topics

So, let’s begin with a list of IB Biology EE topics list.
Ecology and Environmental Science
I’m stoked to talk about Ecology and Environmental Science . It’s all about how living things interact with each other and their surroundings. Think of it like a complex dance of life, where every move affects the whole scene.
From the hustle and bustle of city ecosystems to the quiet, yet dynamic, world of marine biology, we’ll explore how these interactions shape our planet. We’ll also explore the hot topics of invasive species and their impacts, the heroic efforts in conservation, and the big elephant in the room – climate change.
So, let’s get ready to explore the intricate tapestry of life that makes our world fascinating!
Impact of Urban Development on Local Ecosystems
- Research Question: How does the presence of urban green spaces affect bird species diversity in [City Name]?
- Research Question: What impact do urban heat islands have on the behavior and distribution of [Specific Animal Species] in [City Name]?
Marine Biology and Ocean Acidification
- Research Question: How does ocean acidification affect coral bleaching events in the [Specific Coral Reef Location]?
- Research Question: What is the impact of increasing ocean acidification on the shell growth and survival of [Specific Shellfish Species]?
Invasive Species and Their Impact on Biodiversity
- Research Question: What has been the impact of the invasive Zebra Mussel on native species in the Great Lakes?
- Research Question: How do invasive plant species [Specify Species] affect the growth and survival of native plants in [Specific Region]?
Conservation Efforts for Endangered Species
- Research Question: How effective have conservation strategies been in increasing the population of the Giant Panda in China?
- Research Question: What are the impacts of anti-poaching measures on the survival of Rhinoceros populations in Africa?
Climate Change and Its Effects on Ecosystems
- Research Question: How is the melting of Arctic sea ice affecting the habitat and migration patterns of polar bears?
- Research Question: What are the effects of rising global temperatures on plant and animal life in the Alpine ecosystems?
Transitioning from the external world of Ecology and Environmental Science, we now turn to the internal intricacies of Human Physiology and Health.
This shift brings us from exploring external ecosystems to understanding our body’s inner workings, a world where lifestyle choices meet biological responses.
Human Physiology and Health
Let’s chat about Human Physiology and Health, the amazing science of how our bodies work and how we keep them ticking. We’re diving headfirst into the world of nutrition and diet – what you eat isn’t just about taste, it’s about your health too!
Then, we’ll check out how exercise, that thing we all know we should do more of, affects our bodies in awesome ways. Ever wondered about the science of sleep and how it messes with your brain when you don’t catch enough Z’s? We’ll cover that, along with the mysteries of genetics in diseases, and how our environment plays a sneaky role in triggering allergies.
It’s going to be an eye-opening ride through the wonders of our bodies!
Nutrition and Diet’s Impact on Human Health
- Research Question: How does adherence to the Mediterranean diet affect cardiovascular health indicators in adults?
- Research Question: What is the impact of a long-term vegan diet on nutrient absorption and health in teenagers?
Exercise Physiology
- Research Question: How does HIIT affect cardiovascular fitness in young adults?
- Research Question: What are the effects of regular yoga practice on stress and anxiety levels in college students?
Neurobiology of Sleep
- Research Question: How does sleep deprivation impact cognitive performance and memory in high school students?
- Research Question: What is the relationship between sleep patterns and academic performance in IB students?
Genetic Factors in Diseases
- Research Question: How do specific genetic factors contribute to the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease?
- Research Question: What is the contribution of genetics to the onset of Type 2 Diabetes in populations with high prevalence rates?
Impact of Environmental Factors on Allergies
- Research Question: What is the correlation between air pollution levels and the prevalence of respiratory allergies in urban children?
- Research Question: How has climate change influenced the prevalence and severity of allergic diseases in [Specific Region]?
Moving from Human Physiology and Health, we zoom into the realm of Cellular and Molecular Biology.
Here, we swap the broader human health perspective for a closer look at life’s building blocks, delving into the microscopic universe that operates within every living being.
Cellular and Molecular Biology
Ready to geek out on Cellular and Molecular Biology? This is where we get down to the nitty-gritty of life – the cells and molecules that make up every living thing.
We’re talking about the big bad world of cancer cells and what makes them tick, the fascinating process of how our cells make proteins, and the cutting-edge stuff like stem cell research and how viruses play a game of cat and mouse with our bodies.
Meanwhile, make sure also to check our article with biology research paper topics for all students.
Plus, we’ll unravel the mysteries of how our cells fix their own DNA. It’s like being a detective, but for biology. Trust me, it’s cooler than it sounds!
Gene Expression in Cancer Cells
- Research Question: How does gene expression in breast cancer cells differ from that in normal breast tissue?
- Research Question: What role do specific oncogenes play in the development of colorectal cancer?
Protein Synthesis and Its Regulation
- Research Question: How is protein synthesis regulated in response to physical exercise in human muscle cells?
- Research Question: How do bacterial cells regulate protein synthesis under environmental stress conditions?
Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine
- Research Question: What is the potential of stem cell therapy in the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease?
- Research Question: How can stem cells be used to repair damaged heart tissue?
Viral Replication and Host Interaction
- Research Question: How does HIV replicate within human cells, and what is its impact on the immune system?
- Research Question: How does the Influenza virus adapt to host immune responses over time?
DNA Repair Mechanisms
- Research Question: How do DNA repair mechanisms change as human cells age?
- Research Question: How effective are DNA repair mechanisms in skin cells exposed to different levels of UV radiation?
After diving into the microcosm of cells and molecules, we transition to Plant Biology.
This shift steers us from the foundations of life at the cellular level to the diverse world of plants, exploring how these organisms harness and embody basic biological principles.
Plant Biology
Let’s dive into the world of Plant Biology! Plants are not just pretty to look at; they’re the backbone of all life on Earth.
We’ll be talking about how they turn sunlight into food – a process that’s as important as it is fascinating. Ever wonder how plants are coping with our changing climate or what superpowers medicinal plants have? We’ve got that covered.
We’ll also explore the secret life of plants, how they defend themselves against enemies, and the science behind making them stronger and better through genetic modification.
It’s time to get our hands dirty and uncover the secrets of the plant world!
Photosynthesis Variations Among Plant Species
- Research Question: How does photosynthetic efficiency compare between C3 and C4 plants under varying light conditions?
- Research Question: What is the effect of varying light intensities on the rate of photosynthesis in [Specific Aquatic Plant Species]?
Impact of Climate Change on Plant Growth
- Research Question: How are Arctic tundra plants adapting their growth patterns in response to global warming?
- Research Question: What is the impact of elevated atmospheric CO2 levels on the growth of [Specific Plant Species]?
Medicinal Properties of Plants
- Research Question: What are the anti-inflammatory properties of [Specific Medicinal Plant] and how can they be harnessed?
- Research Question: What is the antioxidant capacity of different herbal teas, and how does it affect human health?
Plant Defense Mechanisms Against Pathogens
- Research Question: How do [Specific Plant Species] defend themselves against fungal infections?
- Research Question: What role do secondary metabolites play in the defense mechanisms of [Specific Plant Species] against herbivores?
Genetic Modification and Crop Improvement
- Research Question: How effective are genetically modified crops in resisting drought conditions compared to traditional varieties?
- Research Question: What is the impact of genetic modification on the nutrient content of [Specific Crop]?
From the stationary life of plants, we now step into the dynamic world of Animal Behavior and Physiology. This change of scene introduces us to the complex behaviors and physiological adaptations of animals, offering a contrasting perspective to plant biology.
Animal Behavior and Physiology
Let’s jump into the wild and wonderful world of Animal Behavior and Physiology. This is where we get to spy on the animal kingdom and learn about their secret lives.
From the social gossip of insects to the globe-trotting adventures of migratory birds, animals have some amazing stories to tell.
We’ll also look at how marine animals have adapted to their deep and mysterious homes, how animals respond when their environment goes bonkers, and the hormonal soap operas that dictate their lives.
It’s like being a fly on the wall in the most interesting nature documentary ever!
Social Behavior in Insects
- Research Question: How does the social structure of honeybee colonies affect their survival and productivity?
- Research Question: What are the primary communication mechanisms used in ant colonies, and how do they impact colony efficiency?
Bird Migration Patterns
- Research Question: How has climate change affected the migration routes of [Specific Bird Species]?
- Research Question: How do magnetic fields influence the migration patterns of [Specific Bird Species]?
Physiological Adaptations in Marine Mammals
- Research Question: What physiological adaptations allow sperm whales to dive to extreme depths?
- Research Question: How do polar bears regulate their body temperature in the Arctic environment?
Impact of Environmental Stressors on Animal Behavior
- Research Question: How does underwater noise pollution affect the behavior and communication of dolphins?
- Research Question: What are the effects of urban light pollution on the nocturnal activities of [Specific Nocturnal Animal Species]?
Endocrine Regulation in Animals
- Research Question: How do hormones regulate the reproductive behaviors in [Specific Bird Species]?
- Research Question: How do stress-induced cortisol levels affect the behavior of [Specific Wild Animal Species] in their natural habitat?
Leaving the observable world of animals, we enter the less visible but equally important sphere of Microbiology and Biotechnology. This transition takes us from larger life forms to the microscopic, where tiny organisms significantly impact our health, environment, and technology.
Microbiology and Biotechnology
Alright, microbe hunters and tech wizards, it’s time to zoom in on Microbiology and Biotechnology. This is the world of the tiny, where bacteria and viruses hang out, and where science meets innovation .
We’re going to explore the battleground of antibiotic resistance, how we can use tiny organisms to clean up our messes, and the mind-blowing possibilities of genetic engineering.
Ever thought about how your gut buddies – the microbiome – affect your health? We’ll get into that too, along with the yeast party that’s behind some of your favorite bread and beverages.
Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria
- Research Question: What factors have contributed to the rise of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in hospitals?
- Research Question: What are the primary mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli strains found in [Specific Environment]?
Use of Microorganisms in Bioremediation
- Research Question: How effective are specific bacterial species in the bioremediation of oil spills?
- Research Question: What is the effectiveness of using fungi in the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals?
Genetic Engineering and Its Applications
- Research Question: What is the potential of CRISPR-Cas9 technology in preventing genetic diseases?
- Research Question: How has genetic engineering been used to enhance the nutritional quality of [Specific Crop]?
Role of Microbiome in Human Health
- Research Question: What is the relationship between the gut microbiome and obesity in adults?
- Research Question: How does the diversity of the human microbiome affect immune system functioning?
Yeast Fermentation and Its Industrial Applications
- Research Question: How efficient is yeast fermentation in the production of biofuels compared to traditional methods?
- Research Question: How do different yeast strains affect the flavor profiles in beer brewing?
Finally, we shift from the practical applications in Microbiology and Biotechnology to the historical narrative of Evolution and Genetics. This move links present-day biological understanding to the historical journey of life, unraveling how genetic heritage and evolutionary processes shape all living things.
Evolution and Genetics
Ready to unravel the tales of Evolution and Genetics? This is where we figure out how life on Earth got to be as diverse and fantastic as it is. We’ll be exploring the incredible adaptations organisms have made to survive and thrive, how genetic diversity is crucial for the health of species, and the molecular secrets behind inheritance.
Ever pondered how new species come into being or what genetics reveal about our own ancient history ? Well, you’re in for a treat. We’re about to walk through time and genes to discover the roots and branches of the tree of life. Buckle up!
Evolutionary Adaptations to Environmental Changes
- Research Question: What evolutionary adaptations have enabled cacti to thrive in harsh desert environments?
- Research Question: How have Galápagos finches undergone adaptive radiation in response to their environment?
Genetic Diversity and Population Health
- Research Question: How does genetic diversity affect the health and survival of animal populations on isolated islands?
- Research Question: How can conservation genetics be used to enhance the survival prospects of [Specific Endangered Species]?
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Research Question: What is the molecular basis of inheritance for Sickle Cell Anemia?
- Research Question: How can mitochondrial DNA be used to trace maternal lineage in human populations?
Speciation and Genetic Drift
- Research Question: What role has genetic drift played in the speciation of cichlids in Lake Victoria?
- Research Question: How does genetic drift affect the genetic diversity of small, isolated animal populations?
Human Evolutionary Biology
- Research Question: What evolutionary factors contributed to the development of bipedalism in early humans?
- Research Question: What are the key genetic adaptations that enable humans to live at high altitudes?
These topics and questions aim to inspire in-depth exploration and research, allowing students to delve into various aspects of biology, from molecular to ecosystem levels.
Use them as an inspiration for your future Ib extended essay.
Select your topic wisely!
The world of biology is rich with diverse topics suitable for an Extended Essay. From the tiny intricacies of cellular biology to the broad complexities of environmental science, each area offers a unique perspective and a chance for in-depth exploration .
The key to a successful essay is choosing a topic that not only interests you but also challenges your analytical and research skills.
Need Extra Support?
If you’re seeking guidance with your topic selection, or if you need assistance in writing or editing your Biology Extended Essay , our team at Writing Metier is here to help.

Our experienced IB writers are equipped to provide the support you need to refine your ideas and enhance your writing. Contact us for personalized assistance, or simply fill out our online order form with details of your IB EE and ensure your essay is a reflection of your best efforts.
Free topic suggestions
Vasy kafidoff.
Vasyl Kafidoff is a co-founder and CEO at WritingMetier. He is interested in education and how modern technology makes it more accessible. He wants to bring awareness about new learning possibilities as an educational specialist. When Vasy is not working, he’s found behind a drum kit.
Similar posts
100+ ib extended essay topic ideas for your ease.
One of the very important requirements of an IB diploma is the extended essay. This really helps bring up the total score. And one problem students face here is gathering ideas for their IB extended essay. Here is some guiding information that can help with extended essay topics.
Business Management Extended Essay Topic Ideas and RQs
Looking for the perfect topic for your IB Business Management Extended Essay? Dive into our comprehensive guide, covering everything from organizational leadership to the latest trends in 2023. And if you need a bit of extra help, Writing Metier is just a click away to assist with topic suggestions, writing, and editing.
Economics Extended Essay Topic Ideas for IB Students
This article serves as a launchpad for students crafting their Economics Extended Essays, offering a diverse array of topics that span from the intricacies of microeconomic market structures to the broad strokes of macroeconomic policy. It provides a rich tapestry of ideas, inviting exploration into the complex interplay between economic theory and real-world application across various branches such as labor, environmental, and health economics.
English B Extended Essay Topic Ideas
Discover the perfect English B Extended Essay topic with our curated list, designed to spark your creativity and intellectual curiosity. And if you're looking for a bit of expert assistance in crafting your masterpiece, Writing Metier is just a message away. Let's turn your Extended Essay into a standout success!
70+ IB Physics IA Topics and Research Questions
In the realm of IB Physics IA, students have the golden opportunity to explore a diverse range of topics, from the wonders of quantum mechanics to the principles governing our vast universe. This guide has been crafted to assist you in pinpointing a topic that not only piques your interest but also aligns with your academic pursuits. As you sift through these carefully selected topics and research questions, we hope you find that perfect match that leads to a successful and insightful project
37 IB SL Math IA Topic Ideas that Actually Work!
If you are here because you are stuck with an idea for your IB Mathematics Standard Level (SL) essay topic, you have come to the right place. We understand that the IB Math is the toughest subject (no kidding, we feel you) and therefore, we are here to aid you as much as we can.
We rely on cookies to give you the best experince on our website. By browsing, you agree to it. Read more

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit. Give today and help us reach more students. Help. OpenStax. This free textbook is an OpenStax resource written to increase student access to high-quality, peer-reviewed learning materials.
Chapter 7-10 Possible Essay Questions: From book, class, coarse objectives on website . Chapter 7 Essay Questions . 1. ... codons of a segment of m-RNA and indicating the sequence of amino acids that would be coded for in the process of protein synthesis. 6. Distinguish among the three processes of genetic recombination in procaryotes:
Proteins questions. Google Classroom. A new drug is developed which selectively cleaves covalent bonds between two sulfur atoms of non-adjacent amino acids in a polypeptide chain. Which level of protein structure in affected molecules would be most directly affected by the drug? Choose 1 answer:
Essay # 7. Energetics of Protein Synthesis: It has been roughly estimated that the standard free energy of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond is about - 5.0 kcal. The process of protein synthesis is an energy-consuming process and, in E. coli, it consumes as much as 90% of the cellular energy.
Instructions for making proteins with the correct sequence of amino acids are encoded in DNA. Figure 6.4.1 6.4. 1: Transcription and translation (Protein synthesis) in a cell. DNA is found in chromosomes. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes always remain in the nucleus, but proteins are made at ribosomes in the cytoplasm or on the rough ...
Essay Questions Possible essay topics for student assessment are given below. They are given under ... in prokaryotic protein synthesis with the mechanisms that place the second and subsequent amino acids in the A site. What common features or shared strategies can be discerned? {Chapter 8}
Like DNA, RNA is made up of nucleotide consisting of a 5-carbon sugar ribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. However, there are three main differences between DNA and RNA: RNA uses the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. RNA is generally single-stranded instead of double-stranded. RNA contains uracil in place of thymine.
(Note: In unaffected individuals, the number of repeats in the huntingtin protein is <27; in fragile X mental retardation protein, it is 5-44; and in myotonic dystrophy protein kinase, it is 5-34.) UTR = untranslated region; A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; U = uracil ; Q = single-letter abbreviation for glutamine. Splice site mutations
Biology is detailed and comprehensive A-level content, uses appropriate terminology, and is very well written and always clearly explained. No significant errors or irrelevant material. For top marks in the band, the answer shows evidence of reading beyond specification requirements. 16-20. Relational.
D1.2.1— Transcription as the synthesis of RNA using a DNA template. Define transcription. List the roles of RNA polymerases in the process of transcription. . D1.2. 2 — Role of hydrogen bonding and complementary base pairing in transcription. State the complementary base pairing utilized in transcription.
17 of 17. Quiz yourself with questions and answers for Protein Synthesis Practice test, so you can be ready for test day. Explore quizzes and practice tests created by teachers and students or create one from your course material.
Unique structure created. Once complete, the long protein chain folds up, giving it a unique structure. This unique structure is essential to the protein's function, in the form of enzymes, hormones, or structural proteins (e.g. collagen). Protein synthesis is how our bodies make proteins.
Protein Synthesis is the process whereby DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) codes for the production of essential proteins, such as enzymes and hormones. Proteins are long chains of molecules called amino acids. Different proteins are made by using different sequences and varying numbers of amino acids. The smallest protein consists of fifty amino ...
BIOL10008 Tutorial practice exam essay question Q2 Describe the processes of protein production in a cell from i. the transcription of a gene for a protein ii. the translation into protein iii. transport through the endomembrane system iv. the export of that protein from the cell 10 marks, 10 mins. Marking scheme i.
Protein Synthesis Essay. Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis is the process whereby DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) codes for the production of essential proteins, such as enzymes and hormones. Proteins are long chains of molecules called amino acids. Different proteins are made by using different sequences and varying numbers of amino acids.
Life Sciences Questions and Answers - Protein Synthesis. This set of Life Sciences Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on "Protein Synthesis". 1. Conversion of messages carried by mRNA into amino acid sequences is called___________. 2. tRNA has peptidal transferase activity.
Question. 5 answers. Dec 10, 2021. After the organism receives the antigen stimulation, through a series of immune reactions, the B cell finally produces the antibody. The essence of antibody is ...
This stage of protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. After leaving the nucleus, the mRNA molecule attaches to a ribosome. The ribosome ' reads ' the code on the mRNA in groups of three. Each triplet of bases on the mRNA molecule (known as a codon) codes for a specific amino acid. In this way, the ribosome translates the ...
Protein synthesis is one of the most fundamental biological processes. To start off, a protein is made in a ribosome. There are many cellular mechanisms involved with protein synthesis. Before the process of protein synthesis can be described, a person must know what proteins are made out of. There are four basic levels of protein organization.
View Answer. 1c 2 marks. Figure 1 shows the exposed bases (anticodons) of two tRNA molecules involved in the. synthesis of a protein. Figure. UGC. AAC. Complete the boxes to show the codon sequence of bases found along the corresponding section of the mRNA strand.
It's time for our exploration of Biology extended essay topics, a resource designed to spark your curiosity and guide your research interests in the vast and vibrant field of biology. ... Protein Synthesis and Its Regulation - Studying the regulation of protein synthesis in a specific organism or cell type. Stem Cell Research and ...