- Project Management Metrics
- Project Portfolio Management
- Proof of Concept Templates
- Punch List Templates
- Requirements Traceability Matrix
- Resource Scheduling
- Roles and Responsibilities Template
- Stakeholder Mapping
- Team Charter
- What is Project Baseline
- Work Log Templates
- Workback Schedule
- Workload Management
- Work Breakdown Structures
- Agile Team Structure
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts
- Creating Project Charters
- Guide to Team Communication
- How to Prioritize Tasks
- Mastering RAID Logs
- Overcoming Analysis Paralysis
- Understanding RACI Model
- Eisenhower Matrix Guide
- Guide to Multi Project Management
- Procure-to-Pay Best Practices
- Procurement Management Plan Template to Boost Project Success
- Project Execution and Change Management
- Project Plan and Schedule Templates
- Resource Planning Templates for Smooth Project Execution
- Risk Management and Quality Management Plan Templates
- Risk Management in Software Engineering
- Stage Gate Process
- Stakeholder Management Planning
- Understanding the S-Curve
- Visualizing Your To-Do List
- 30-60-90 Day Plan
- Work Plan Template
- Weekly Planner Template
- Task Analysis Examples
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts for Planning
- Inventory Management Tecniques
- Inventory Templates
- Six Sigma DMAIC Method
- Visual Process Improvement
- Value Stream Mapping
- Creating a Workflow
- Fibonacci Scale Template
- Supply Chain Diagram
- Kaizen Method
- Procurement Process Flow Chart
- UML Activity Diagrams
- Class Diagrams & their Relationships
- Visualize flowcharts for software
- Wire-Frame Benefits
- Applications of UML
- Selecting UML Diagrams
- Create Sequence Diagrams Online
- Activity Diagram Tool
- Archimate Tool
- Class Diagram Tool
- Graphic Organizers
- Social Work Assessment Tools
- Using KWL Charts to Boost Learning
- Editable Timeline Templates
- Guides & Best Practices
- Kinship Diagram Guide
- Graphic Organizers for Teachers & Students
- Visual Documentation Techniques
- Visual Tool for Visual Documentation
- Visualizing a Dichotomous Key
- 5 W's Chart
- Circular Flow Diagram Maker
- Cladogram Maker
- Comic Strip Maker
- Course Design Template
- AI Buyer Persona
- AI Data Visualization
- AI Diagrams
- AI Project Management
- AI SWOT Analysis
- Best AI Templates
- Brainstorming AI
- Pros & Cons of AI
- AI for Business Strategy
- Using AI for Business Plan
- AI for HR Teams
- BPMN Symbols
- BPMN vs UML
- Business Process Analysis
- Business Process Modeling
- Capacity Planning Guide
- Case Management Process
- How to Avoid Bottlenecks in Processes
- Innovation Management Process
- Project vs Process
- Solve Customer Problems
- Startup Templates
- Streamline Purchase Order Process
- What is BPMN
- Approval Process
- Employee Exit Process
- Iterative Process
- Process Documentation
- Process Improvement Ideas
- Risk Assessment Process
- Tiger Teams
- Work Instruction Templates
- Workflow Vs. Process
- Process Mapping
- Business Process Reengineering
- Meddic Sales Process
- SIPOC Diagram
- What is Business Process Management
- Process Mapping Software
- Business Analysis Tool
- Business Capability Map
- Decision Making Tools and Techniques
- Operating Model Canvas
- Mobile App Planning
- Product Development Guide
- Product Roadmap
- Timeline Diagrams
- Visualize User Flow
- Sequence Diagrams
- Flowchart Maker
- Online Class Diagram Tool
- Organizational Chart Maker
- Mind Map Maker
- Retro Software
- Agile Project Charter
- Critical Path Software
- Brainstorming Guide
- Brainstorming Tools
- Visual Tools for Brainstorming
- Brainstorming Content Ideas
- Brainstorming in Business
- Brainstorming Questions
- Brainstorming Rules
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Brainstorming Workshop
- Design Thinking and Brainstorming
- Divergent vs Convergent Thinking
- Group Brainstorming Strategies
- Group Creativity
- How to Make Virtual Brainstorming Fun and Effective
- Ideation Techniques
- Improving Brainstorming
- Marketing Brainstorming
- Rapid Brainstorming
- Reverse Brainstorming Challenges
- Reverse vs. Traditional Brainstorming
- What Comes After Brainstorming
- Spider Diagram Guide
- 5 Whys Template
- Assumption Grid Template
- Brainstorming Templates
- Brainwriting Template
- Innovation Techniques
- 50 Business Diagrams
- Business Model Canvas
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- NOISE Analysis
- Profit & Loss Templates
- Scenario Planning
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Developing Action Plans
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New

Project Management Methodologies and Frameworks Every Project Manager Should Know

You might find yourself drowning in information, tools, and processes as a project manager. To stay afloat and thrive, you must choose the right project management methodologies and frameworks that suit your team and project needs.
Many different project management methodologies are available and deciding which one is right for you can be challenging. This article provides an overview of the most popular frameworks to get you started.
What is a Project Management Methodology?
A project management methodology is a set of principles, processes, guidelines, and tools that help to plan, manage, and control a project. The methodology helps to ensure that a project is on schedule, within budget, and that the project goals are met.
A project team or an organization uses a management framework to execute a project. The information generated is usually documented and shared with others. Recording the information is essential as it will help others understand the project requirements and responsibilities.
While most project management methodologies take a standardized approach, some are for specific purposes, i.e., manufacturing or software development.
Project Management Framework vs. Methodology
The terms framework and methodology are often used interchangeably in project management. However, there is a slight yet distinguishable difference between the two approaches.
A framework provides more flexibility and freedom. You can adopt new rules and change or remove existing ones as necessary. As such, a framework provides the structure and direction needed for a project without being too rigid or detailed.
On the other hand, a methodology is a set of principles and processes that guides the management of a project. It is a formal approach that is strictly defined and generally adheres to a strict code complete with steps and rules.
Another way to understand the two approaches is that most of the time, methodologies are for implementing ideas and values, while a framework provides a step-by-step guide to attain that idea or manage that project.
Project Life Cycle Processes
A project management framework includes the whole project management life cycle, which will guide you from the beginning to the end. In a project management life cycle , there are five steps:
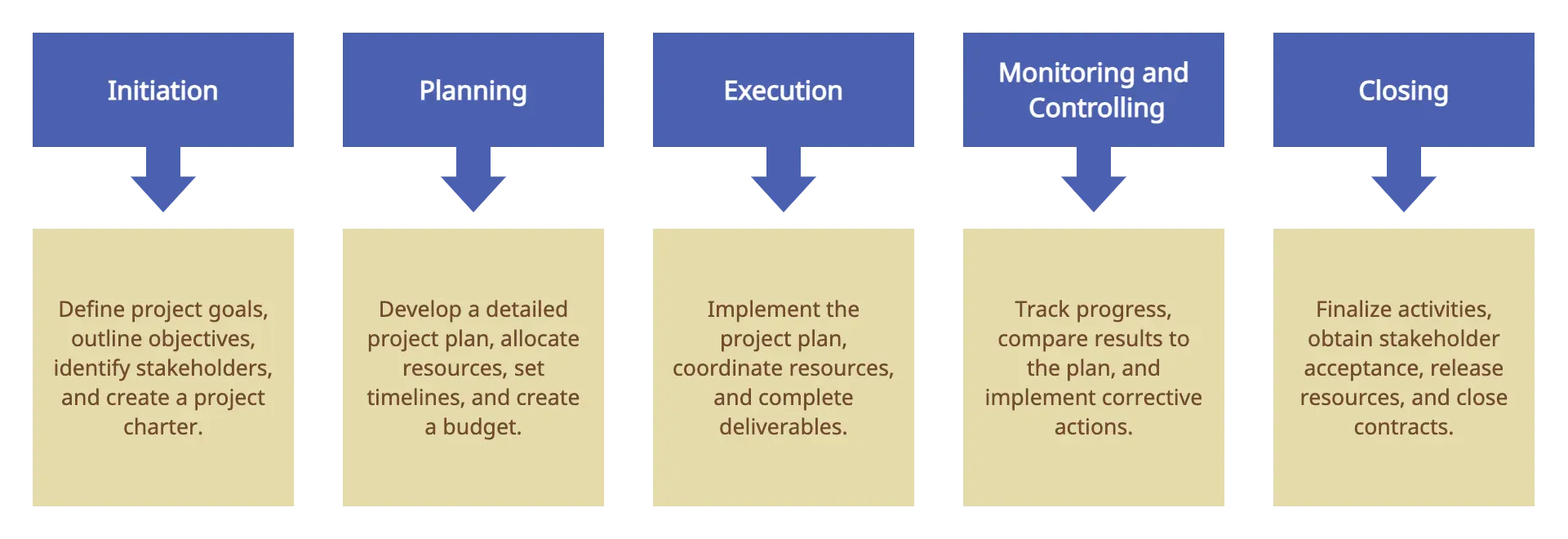
- Initiation : The beginning stage of the project, where the main focus is to narrow down the required key components to kickstart the project. Teams get together to research, brainstorm and conduct analysis and stakeholder mapping/interviews to gather information.
- Planning : Here, the teams and members working on the project are identified along with activities, milestones, risks, management structure, and success benchmarks.
- Execution : During this stage, the project kickstarts and is implemented.
- Management/Monitoring : At each milestone, the progress will be monitored, documented, and reported. Key progress and outputs will be shared with stakeholders as well.
- Review/Closing : This stage marks the end of the project. Project leaders and team members will review and analyze how the project progressed and setbacks to identify future improvements. Updates or replacements will be scheduled if necessary before wrapping up.
5 Key Project Management Methodologies and Frameworks
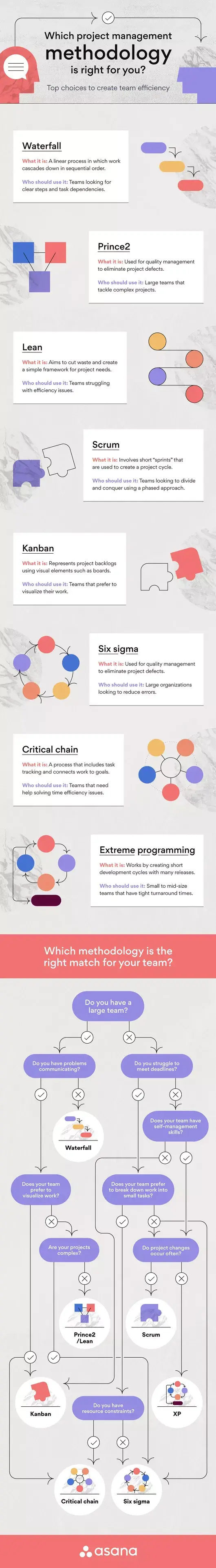
1. waterfall framework.
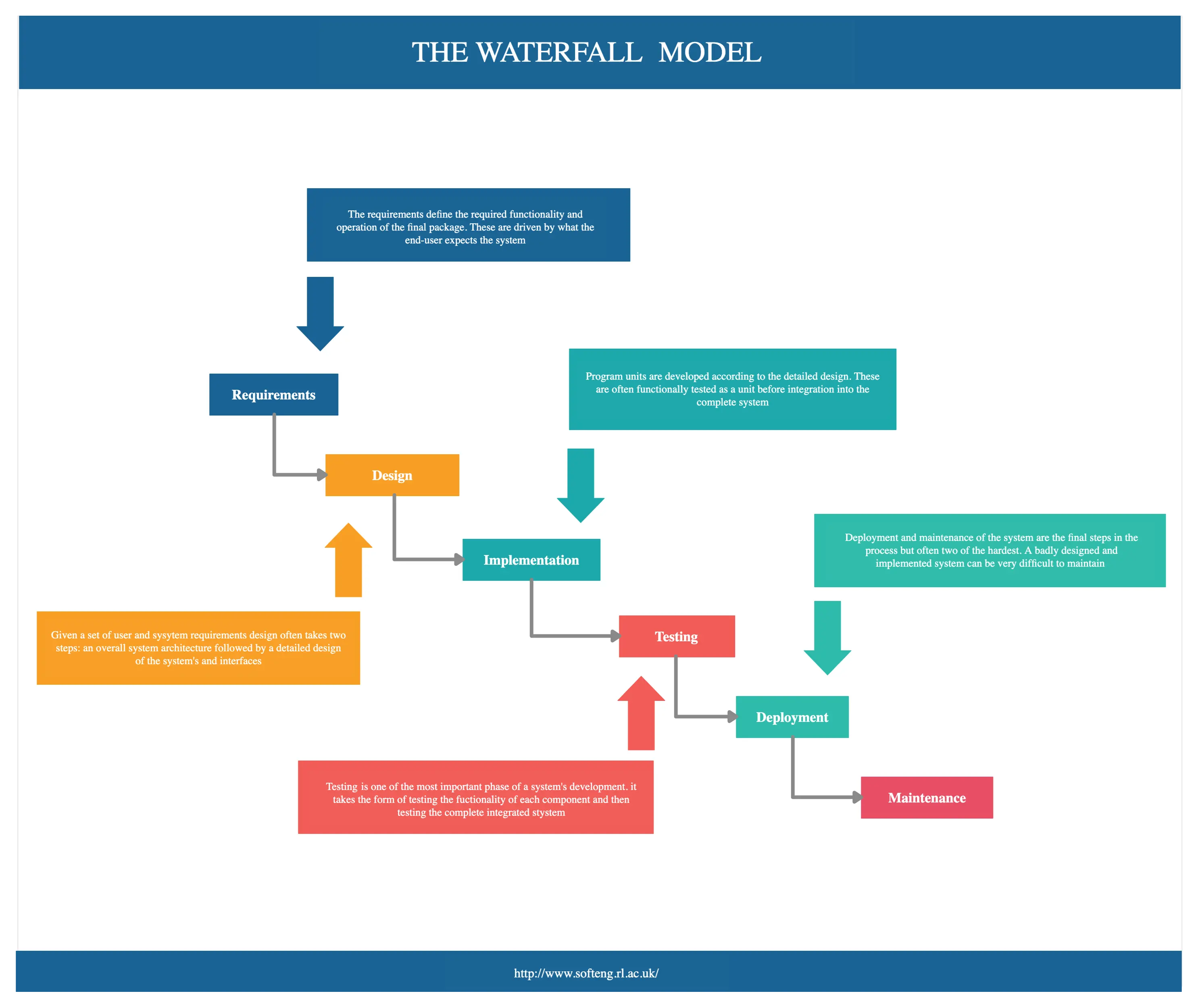
The Waterfall Framework is a linear approach that first gathers stakeholder and customer requirements before creating a sequential project plan to address the identified requirements. Consisting of five main stages, each stage is completed before progressing to the next–similar to a cascading waterfall.
The main stages of the waterfall framework are:
- Requirements : needs and requirements of the business/project are identified, analyzed, and documented.
- Design : possible solutions are explored before a detailed plan is made to achieve the goals.
- Implementation : the project plan and activities are set in motion along with progress measurements.
- Verification/Control : the product is reviewed, and the project plan is compared with the performance to address issues.
- Maintenance/Closure : the end result is shared with clients for feedback and final fixes. Approval is obtained before the project is closed.
- As project and client requirements are identified and agreed in the very first stage, it sets clear client expectations that are easier to plan.
- Extensive documentation ensures that each activity and task is well documented and that no knowledge is lost.
- The project schedule is laid out at the beginning stages. As such, project costs, deadlines, and other resources can be estimated accurately.
- Easier to measure and understand as you progress through each milestone one after the other.
Disadvantages
- Identifying all client/customer requirements at the very beginning is difficult.
- Changes to the product at the end stages are costly and difficult if the customer is unsatisfied.
- Lack of flexibility due to the linear nature of the framework, which provides minimal room for change and adaptation in case of unexpected events.
2. Lean Methodology
Lean methodology originated in the 1950s in Toyota and currently focuses on eliminating waste, maximizing value, and improving efficiencies. Many organizations have opted to adopt the Lean Framework as it can be applied to any business, regardless of size, to achieve objectives in a sustainable manner.
The two main guiding concepts in Lean are respect for people and continuous improvement. Accordingly, necessary training and tools are provided, constant improvement is encouraged, and management takes on a more active role in understanding and meeting the needs of employees to initiate better work performance.
Besides the above two concepts, lean has five core principles that support the methodology:
- Value : customer defines the value of the product offered.
- Value stream : a clear and in-depth understanding of the product’s life cycle from research to development. Each step of the value chain is analyzed to identify waste areas and improvements.
- Flow : every process should be in sync with one another, and the value stream should flow seamlessly.
- Pull : ensures that products are made only when required, leading to shorter delivery cycles and increased flexibility.
- Perfection : always strive for perfection by uncovering quality or waste issues and applying strict measures to address inefficiencies.
- The quality of products is high due to the constant attention to value.
- Reduced costs and increased profits as Lean focuses on providing value and minimizing waste.
- Improved customer relations as the focus is to deliver what the customer requires.
- Regular communications among employees, stakeholders and management pave the way for better decision-making.
- Emphasis on constant improvement leads to continuous learning opportunities.
- Organizations may focus too much on Lean principles that they lose sight of the bigger picture leading to a lack of strategy.
- If there are bottlenecks or resource issues, delivery can be delayed leading to unsatisfied customers.
3. Agile Methodology
Agile is often used in the software industry, though it has spilled into others recently due to its adaptability. It is an iterative approach that promotes collaboration among team members, emphasizing adaptive planning and early delivery of functional products. In an Agile project, development work is carried out in short-term periods called sprints, and the management focuses on continuous improvement throughout the project’s life cycle.
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Popular frameowkrs such as Scrum and Kanban stem from Agile, which acts as an umbrella term that encompasses several different frameworks. To learn more about Scrum and Kanban, check out The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Scrum and How to Better Manage Your Projects with Kanban Boards .
The Agile Manifesto highlights four core principles that are the building blocks of any agile approach. They are:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
- Agile promotes smaller teams, making it easier to keep up the pace and quickly adapt to necessary changes, leading to faster response times and ample flexibility.
- Faster turnaround times due to the ability to quickly detect and provide solutions to issues.
- Low wastage and costs as tasks are always up-to-date with constant feedback and follow-ups, allowing developers to experiment and test ideas.
- Agile is practiced by many and has a considerable following. Therefore, you can always reach out for help and share knowledge with others if you run into trouble.
- Difficult to measure the progress as it is estimated across several cycles, which may take time.
- Documentation is not given prominence, leading to misunderstandings and difficulty for newer members to be up-to-date.
- At times, there is no clear end date; therefore, the overall project may seem to go on forever. This can also lead to scope changes beyond what was initially agreed (scope creep).
- Due to the short cycle times, the design thinking process may be stinted, leading to a lack of cohesion and fragmentation.
- Teams may tend to avoid key features that may take too long to deliver.
- The need for constant communication can take a toll on team members who have to spend extra energy and time.
4. Critical Chain Project Management Framework
Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) is a project management framework that helps the planning and managing of projects by monitoring the resources required to execute the project tasks. The framework helps project managers to deliver projects in a cost-effective and timely manner.
Buffers are safety margins that ensure all tasks are completed within schedule. CCPM identifies strategic points in the project and inserts buffers to ensure that project milestones are met on time, regardless of constraints or uncertainties. There are several types of buffers used in CCPM.
- Project buffers : this is positioned between the completion date of the project and the last task allowing team members to catch up on any outstanding tasks or delays.
- Feeding buffers : this is positioned between the non-critical chain and the critical chain to prevent delays.
- Resource buffers : resources that are kept aside in case of extra support in terms of resources are required.
- Team members tend to be more efficient and pace themselves rather than working more as the deadline approaches.
- Work is scheduled around resource availability, thereby optimizing resource utilization.
- The insertion of various buffers to address issues on time.
- The minimum time required to finish the project is taken into consideration.
- Major planning packages do not often support the framework.
- If the team does not understand the endpoint, many losses and setbacks could occur.
5. PRINCE2 Framework
PRINCE stands for “PRojects IN Controlled Environments” and is a process-based framework focused on organization and control. The framework started as PRINCE with a particular focus on the IT industry before expanding into others.
PRINCE2 details what each step of the project should look like, deliverables, roles, and responsibilities, and also structure each stage of the project with no loose ends at the point of completion.
- PRINCE2 is a good beginner framework to start project management as it has a defined process with clear steps.
- Due to the detailed and step-by-step guide provided, PRINCE2 is relatively easy to understand and follow. Furthermore, the ability to divide the project into manageable stages is helpful in managing the project.
- PRINCE2 is flexible in nature and can be easily adapted to suit different projects.
- Roles and responsibilities are clearly defined, which improves accountability.
- Lessons learned can be tracked and updated for future reference and improvements.
- PRINCE2 is not ideal for projects in fast-changing environments (i.e., technology-driven) due to the extensive documentation required.
- Requires the buy-in of the senior management for success.
- Requires experience to be managed and delivered successfully.
Key Steps to Follow when Selecting a Methodology or Framework
1. assess the project in terms of size and scope.
Size and scope play a significant role when selecting a suitable project methodology or framework. Some projects may be small, requiring a team of no more than 3-4 people and a short period. In contrast, others would be large, with multiple teams working together for several years.
Larger projects with several cross-functional teams and extended time frames would benefit from adaptive project management frameworks such as agile. In comparison, smaller projects that are less complex would do well with methodologies such as waterfall.
2. Look into the available project management methodologies and frameworks
Once the project scope and size are determined, look into the available methodologies and frameworks. Compare notes, and weigh the pros and cons as to which one would suit your requirements the best while minimizing risks.
3. Obtaining the acceptance and buy-in of your team
Reach out to your team to see their reaction and input. Make sure you listen to their viewpoints and present your side accordingly to obtain their buy-in. Otherwise, conflicts and challenges may hinder the project’s smooth progress.
4. Confirm the selection
Before starting the project, re-confirm the feasibility of your selection by comparing and assessing the success rate of projects delivered using the same framework.
5. Obtain feedback and conduct self-assessments
As the project progresses, ask for feedback from your colleagues regarding the processes followed. Furthermore, make sure to conduct self-assessments to see if the methodology or framework is proceeding according to your expectations and whether it allows you to manage your team successfully.
Tools and Techniques for Project Management Methodologies and Frameworks
There are several tools and techniques relevant to project management methodologies and frameworks. While some specific tools and techniques are similar across multiple frameworks, there are some that may differ. Below are a few commonly used tools and techniques.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Work breakdown structures can be used to break down the larger deliverables of your project into manageable smaller tasks. This is a productivity technique that uses a step-by-step approach to project management.
Gantt Chart
Gantt charts are ideal for tracking tasks' start and end dates and milestones. It helps teams to plan their work and jobs to meet deadlines and allocate resources accordingly.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. For each project, the SWOT identifies the internal (Strengths and Weaknesses) and external (Opportunities and Threats) drivers affecting your ability to meet the goal. For example, suppose your organization is well known for its expertise in customer service. In that case, improving customer service will be a competitive advantage and a meaningful driver for meeting your goals.
RACI Matrix
RACI stands for responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed. RACI matrix is used to describe the roles and responsibilities of team members in a project.
Stakeholder Map
The stakeholder map is a tool to help you understand who your stakeholders are and their needs. Using this tool, you can map stakeholders according to their importance and potential impact on the project.
Decision Tree
A decision tree is used for effective decision-making and predicting potential outcomes when multiple courses of action exist. It allows the team to explore options and outcomes to understand the risks and rewards associated with each possible course of action.
Creately for Project Management
Creately has many tools to make your journey effortless and successful regardless of the type of project methodology or framework you decide to follow.
- Powerful documentation capabilities include doc blocks and attachments and image attachments to create reports and presentations.
- Built-in project management tools including Kanban boards, timelines, multi-role workflows, visual prioritization tools to enable any kind of workflow.
- Whiteboard and freehand drawing capabilities to brainstorm and discuss with colleagues and peers.
- Multiple templates and shapes to prepare project plans and schedules, Gantt charts, roadmaps, and other formats necessary for project management documentation and tracking.
- Multiple access and role levels to manage, share, edit and review, along with multiplayer editing capabilities to collaborate in real-time.
- Comment on anything, with context. Full comment threads and discussions for async collaboration.
- Data, note, and task panels to house information, assign roles and responsibilities, feed in information, and track the progress of activities.
- Integration with other platforms with 2-way syncing to manage data efficiently.
- Spotlight and presentation mode to conduct interactive and dynamic presentations right on the canvas.
Start your project management journey with Creately today!
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project management |
- Project management methodologies: 12 po ...
Project management methodologies: 12 popular frameworks

Project management is an ever-evolving field that requires a number of approaches to be successful. Learning the most popular project management methodologies can help you become an industry expert.
In order to be the best possible project manager , learn about each of these 12 frameworks to find the one that best fits your team’s needs.
12 project management frameworks
What it is: The Agile project management methodology is one of the most common project management processes. But the reality is that Agile isn’t technically a methodology. Instead, it’s best defined as a project management principle.
The basis of an Agile approach is:
Collaborative
Fast and effective
Iterative and data-backed
Values individuals over processes
When it comes to putting the Agile manifesto in place, teams often choose specific methodologies to use alongside Agile. These could include Scrum, Kanban, extreme programming, crystal, or even Scrumban . That's because connecting Agile methodology with a more detailed approach produces a well-rounded project management philosophy and a tangible plan for delivering great work.
Who should use it: The Agile framework can be used for just about any team. This is because the principle behind it is rather universal. The real trick is deciding which methodology to use with it.
2. Waterfall
What it is: The waterfall model is also a very popular framework. But unlike Agile, waterfall is an actual methodology that is rather straightforward. The waterfall methodology , also known as software development life cycle (SDLC), is a linear process in which work cascades down (similar to a waterfall) and is organized in sequential order.
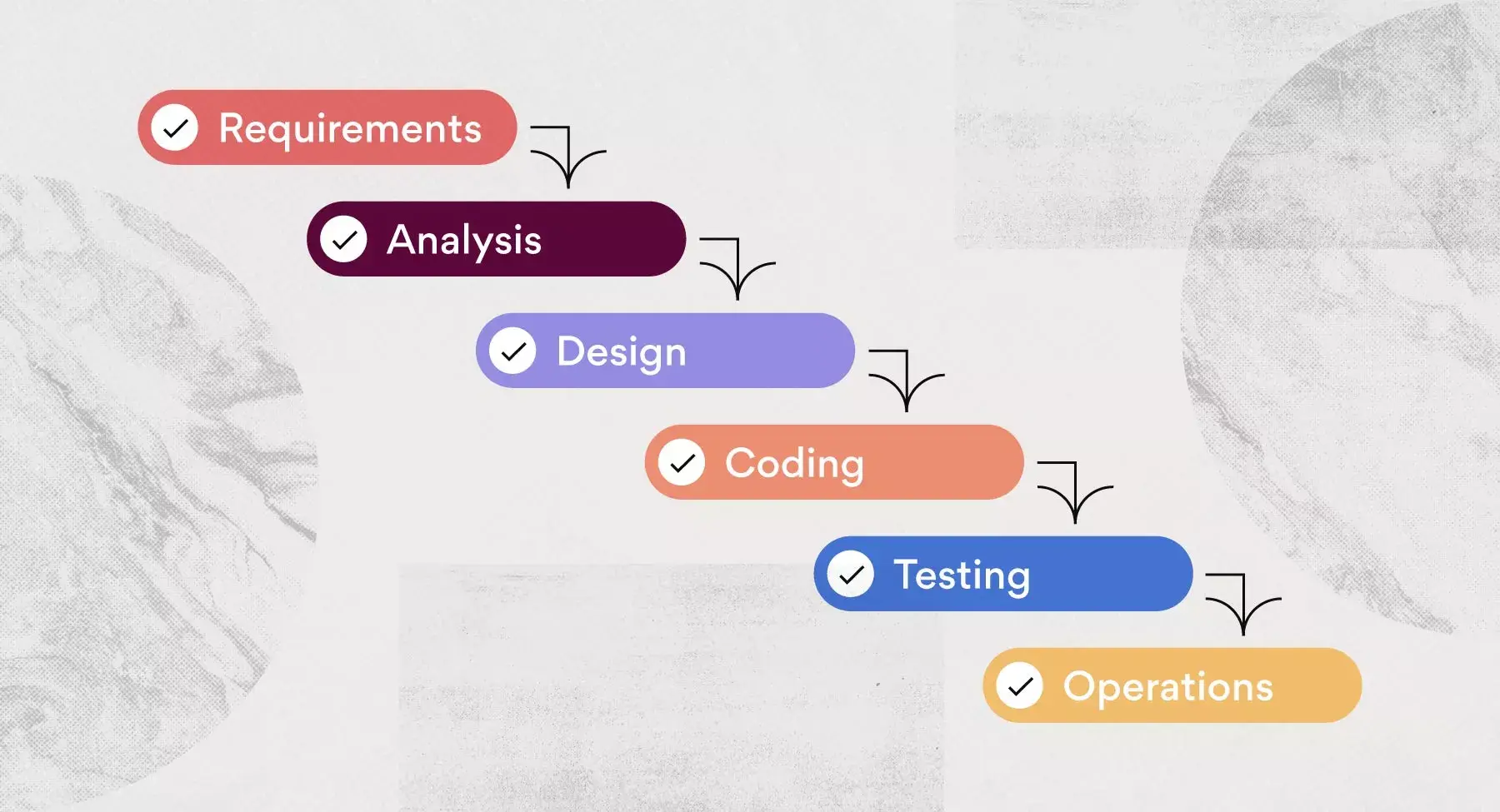
To achieve this approach, each work task is connected by a dependency. This means each task must be completed before the next task can be started. Not only does this ensure that work stays on track, but it also fosters clear communication throughout the process.
While viewed as a traditional approach by some modern organizations, this method is good for creating a predictable and thoroughly planned-out project plan .
Who should use it: Since the waterfall project management methodology is so detailed, it’s great for working on large projects with multiple different stakeholders. This is because there are clear steps throughout the project and dependencies that help track the work needed to reach goals.
What it is: The Scrum methodology involves short “sprints” that are used to create a project cycle. These cycles span one to two weeks at a time and are organized with teams of 10 or less. This is different from the waterfall approach where individual tasks are broken down into dependencies.
Scum is unique for a variety of reasons, one being the use of a Scrum master. Or, in other words, a project manager that leads daily Scrum meetings, demos, sprints, and sprint retrospectives after each sprint is completed. These meetings aim to connect project stakeholders and ensure tasks are completed on time.
While Scrum is technically a project management methodology in its own right, it’s most commonly associated with an Agile framework. This is because they share similar principles, such as collaboration and valuing individuals over processes.
Who should use it: Teams that use an Agile approach should use, or at least try, the Scrum methodology as well. Since sprints are divided into small teams, this approach can work for both small and large teams.
What it is: The Kanban methodology represents project backlogs using visual elements, specifically boards. This approach is used by Agile teams to better visualize workflows and project progress while decreasing the likelihood of bottlenecks. It’s also usually in the form of a software tool that allows you to change and drag boards seamlessly within projects, though it’s not a requirement.
Since this method doesn’t have a defined process like others, many teams use it differently. The main concept to keep in mind is that Kanban aims to focus on the most important project tasks, keeping the overall framework simple.
Who should use it: Kanban boards are great for teams of all sizes and specifically remote-first teams. This is because the visual capabilities of Kanban boards help team members stay on track no matter where they are.
5. Scrumban
What it is: As you may have guessed, Scrumban is a methodology that draws inspiration from both Scrum and Kanban frameworks. Some think of this as a hybrid approach that incorporates the best of each.
Scrumban uses a similar sprint cycle as Scrum but allows individual tasks to be pulled into the plan like Kanban. This allows the most important work to be completed and keeps project plans simple. Scrumban also uses Scrum meetings to enhance collaboration and keep goals top of mind.
Who should use it: If you like the idea of breaking down a project into smaller tasks, but likewise want to keep it visually simple, Scrumban might be for you. It’s the perfect intersection of simplicity and clarity.
What it is: PRINCE2 , otherwise known as PR ojects IN C ontrolled E nvironments, uses the overarching waterfall methodology to define stages within a project. It was initially created by the UK government for IT projects and still primarily suits large IT initiatives over the traditional product or market-focused projects.
There are seven main principles of PRINCE2, which include:
Starting a project
Directing a project
Initiating a project
Controlling a project
Managing product delivery
Managing a stage boundary
Closing a project
These seven principles create a thorough project process and make for an effective enterprise project methodology altogether. It aims to define roles and back management. Not only that, but PRINCE2 can be used to streamline a ton of individual project management tasks, like controlling a stage, managing product delivery, and initiating and closing a project.
Who should use it: Due to the particular nature of the PRINCE2 project management methodology, it’s best suited for large enterprise projects with a number of project stakeholders . Using it for small projects may create a longer and more complicated process than necessary.
7. Six Sigma
What it is: Unlike the other PM methodologies, Six Sigma is used for quality management and is frequently described as a philosophy rather than a traditional methodology. It is often paired with either a lean methodology or Agile framework, otherwise known as lean Six Sigma and Agile Six Sigma.
The main purpose of Six Sigma is to continuously improve processes and eliminate defects. This is achieved through continuous improvements by field experts to sustain, define, and control processes.
To take this method one step further, you can use a Six Sigma DMAIC process, which creates a phased approach. These phases include:
Define: Create a project scope , business case , and initial stand-up meeting.
Measure: Collect data that helps inform improvement needs.
Analyze: Identify the root causes of problems.
Improve: Solve the root causes found.
Control: Work to sustain the solutions for future projects.
Who should use it: Six Sigma is best for large organizations, usually those with a few hundred employees or more. This is when the need to eliminate project waste starts to have a larger impact on your organization.
8. Critical path method (CPM)
What it is: The critical path method works to identify and schedule critical tasks within a project. This includes creating task dependencies, tracking project goals and progress, prioritizing deliverables , and managing due dates—all of which are similar to a work breakdown structure .
The objective of this methodology is to properly manage successful projects at scale so that milestones and deliverables are mapped correctly.
Who should use it: The critical path method is best for small and mid-size projects and teams. This is because large projects require many deliverables with multiple stakeholders and the CPM isn’t built to manage complex projects.
9. Critical chain project management (CCPM)
What it is: The critical chain project management framework is closely related to the critical path methodology but is even more detailed, making it one of the most comprehensive options.
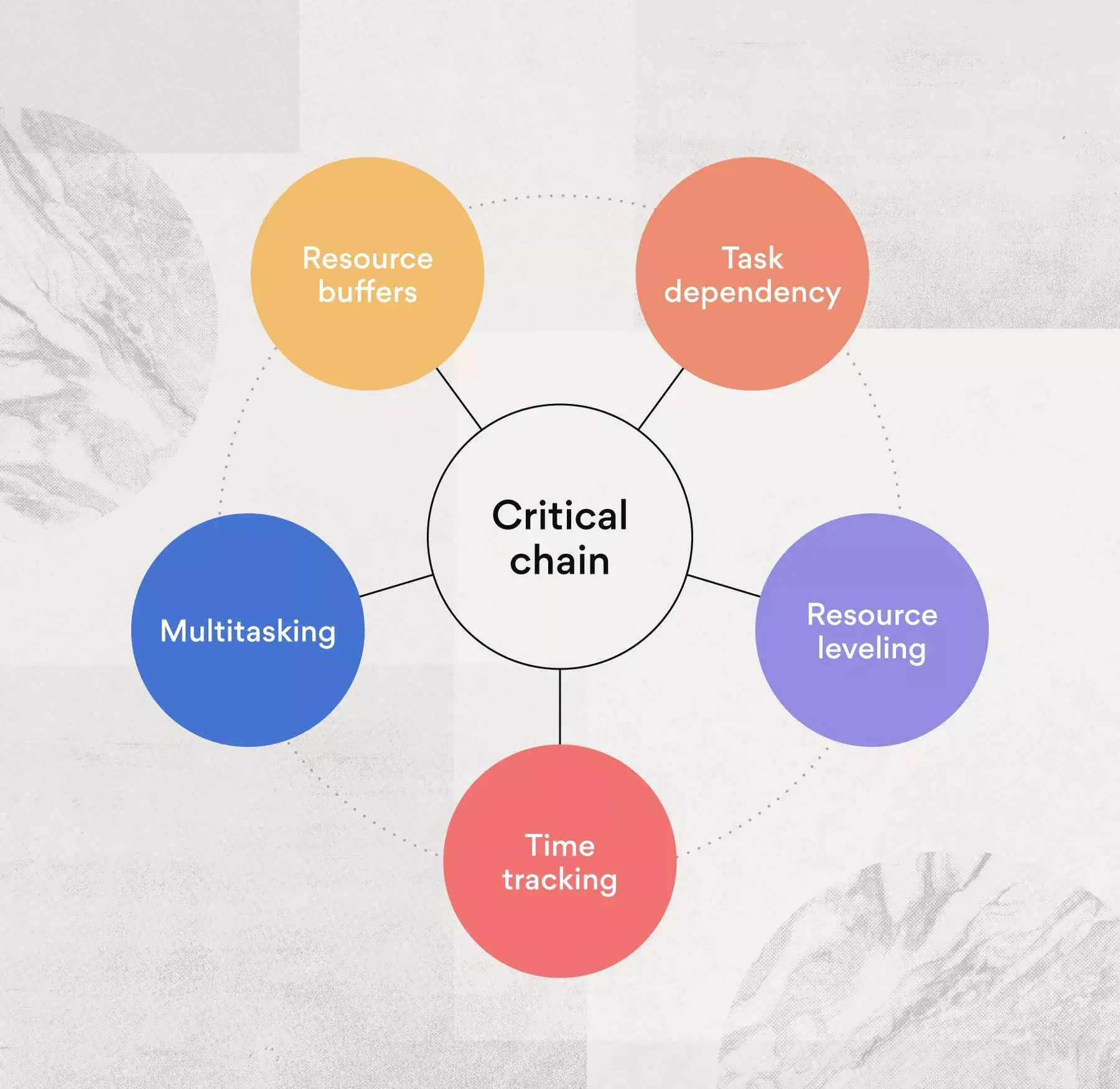
Along with implementing a work breakdown structure like CPM, CCPM includes specific time requirements for each task. This helps take task tracking one step further, making it clear when tasks are going over their allotted time. It also uses resource leveling which aims to resolve large workloads by distributing work across available resources.
Not only do these help both productivity and efficiency, but they also help connect the work needed to be completed with project goals. Many project management tools even have visual elements to better visualize these goals, creating an organized road map for team members.
Who should use it: CCPM is a great method for both small and large teams, but it mostly helps solve project efficiency problems . It can also be a great way to report work in progress to leadership.
What it is: The lean project management methodology aims to cut waste and create a simple framework for project needs. This ultimately means doing more with less in order to maximize efficiency and teamwork.
While reducing waste originally referred to a physical product (which dates back to the method used by Henry Ford and later by Toyota and Motorola), it now refers to wasteful practices. There are three Ms that represent this:
Muda (wastefulness): Practices that consume resources but don’t add value
Mura (unevenness): Occurs through overproduction and leaves behind waste
Muri (overburden): Occurs when there is too much strain on resources
As a project manager, your job is to prevent the three Ms in order to better execute projects and streamline processes. This is similar to the approach of rational unified process (RUP), which also aims to reduce waste. The difference is that RUP aims to reduce development costs instead of wasteful practices.
Who should use it: Since lean is all about reducing waste, it’s best suited for teams struggling with efficiency issues. While this will have a greater impact on large organizations, it can be helpful for project teams of all sizes.
11. Project management institute’s PMBOK® Guide
What it is: While the PMI’s Project Management Body of Knowledge is associated as a project management methodology, it’s more closely related to a set of best practices that take into account various development processes.
This framework focuses on implementing the five project management phases , all of which help easily manage a project from start to finish in a structured phase approach. The five phases include:
Project initiation
Project planning
Project executing
Project performance
Project closure
While this is a good foundation to keep in mind, the PMBOK® Guide isn’t necessarily as specific as other approaches. This means you’ll need to decide which tasks to complete in each phase.
Who should use it: The PMBOK® Guide can be used on its own for small teams on standard projects, though it’s a good idea to pair it with a more detailed methodology (like CPM) for large teams handling complex projects.
12. Extreme programming (XP)
What it is: As the name suggests, extreme programming is used for fast-paced projects with tight deadlines. The approach works by creating short development cycles with many releases. This makes for quick turnaround times and increased productivity .
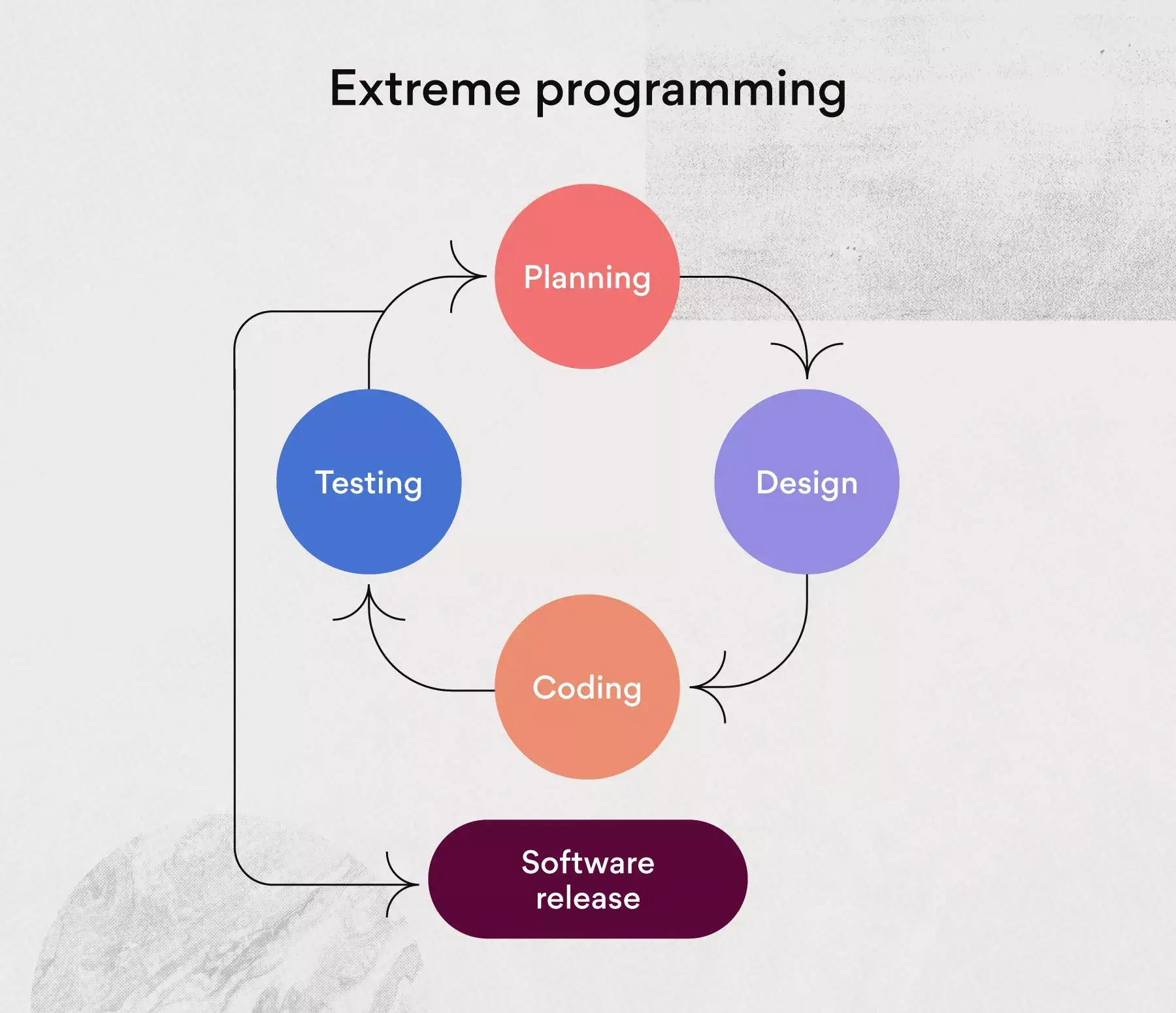
Extreme programming has a few core values, which include simplicity, communication, feedback, respect, and courage. It also includes a specific set of XP rules which includes all phases from planning to testing.
Who should use it: Extreme programming can be used for individual projects with tight deadlines, most commonly with small to midsize teams. Since XP is a fast-paced method, it should be used lightly in order to prevent burnout .
Choosing the right project management methodology for your team
There is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to project management methodologies. Each one offers unique principles to take a development project from an initial plan to final execution.
The main aspects to keep in mind are the size of your team and how your team prefers to work. Here are some additional tips to consider:
Your industry : Consider if you’re in an industry that changes frequently. For example, a technology company would be an industry that is ever-evolving. This will affect project consistency and should be paired with either a flexible or stagnant methodology.
Your project focus : Consider the objectives of your projects . Do you value people over efficiency? This will help pair you with a methodology that matches a similar objective.
The complexity of projects : Are your projects on the more complex side, or are they usually straightforward? Some methods aren’t as good as others at organizing complex tasks, such a CCPM.
The specialization of roles : Consider how niche the roles within your team are. Can multiple team members alternate the same type of work, or do you need a method that focuses on specialization?
Your organization’s size : The size of your organization and team should be weighed heavily when deciding on a methodology. Methods like Kanban are universal for team size, while options like CPM are better suited for small teams.
Whether your team members prefer a visual process like Kanban or a more traditional project management approach like the waterfall method, there’s an option for every type of team. To take a project management methodology one step further, consider a work management tool to better track and execute development projects.
Methods to manage your projects mindfully
With the right project management methodology in place, you’ll be able to take your projects to new levels of efficiency and implement processes that are right for your team, your organization, and yourself.
Related resources
Critical path method: How to use CPM for project management

15 project management interview questions, answers, and tips

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Top 10 Project Management Methodologies: An Overview

Table of Contents
- Waterfall Methodology
- Agile Methodology
- Scrum Methodology
- PMI / PMBOK
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Kanban Methodology
- Extreme Programming (XP)
- Lean Methodology
What Is a Project Management Methodology?
A project management methodology is a set of principles, tools and techniques that are used to plan, execute and manage projects. Project management methodologies help project managers lead team members and manage work while facilitating team collaboration.
There are many different project management methodologies, and they all have pros and cons. Some of them work better in particular industries or projects , so you’ll need to learn about project management methodologies to decide which one works best for you.
We’ll go through some of the most popular project management methodologies, which are applied in many sectors such as software development, R&D and product development.
Top 10 Project Management Methodologies
If you manage projects, you need to learn about project management methodologies. Here’s a quick overview of the most commonly used project management methods that you can use.
1. Waterfall Methodology
This may be the most straightforward and linear of all the project management methods in this list, as well as the most traditional approach. The name is apt, as the waterfall methodology is a process in which the phases of the project flow downward. The waterfall model requires that you move from one project phase to another only once that phase has been successfully completed.
When to use it: The waterfall approach is great for manufacturing and construction projects , which are highly structured, and when it’s too expensive to pivot or change anything after the fact. The waterfall method makes use of Gantt charts for planning and scheduling.
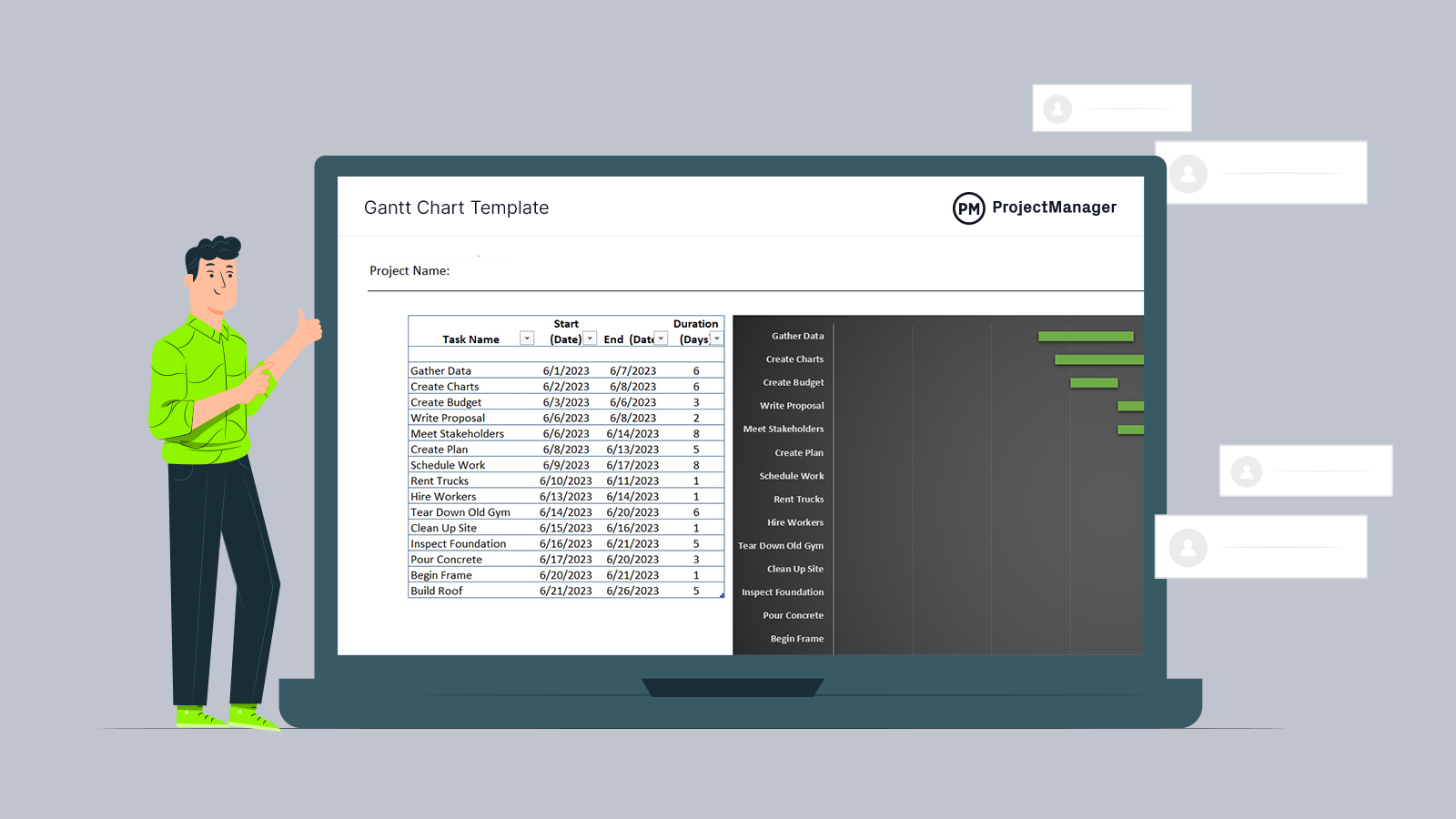
Get your free
Gantt Chart Template
Use this free Gantt Chart Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
2. Agile Methodology
What it is: In a nutshell, Agile project management is an evolving and collaborative way to self-organize across teams. When implementing the agile methodology , project planning and work management are adaptive, evolutionary in development, seeking early delivery and are always open to change if that leads to process improvement. It’s fast and flexible, unlike waterfall project management.
The agile methodology offers project teams a very dynamic way to work and collaborate and that’s why it is a very popular project management methodology for product and software development. That’s because what we think of as agile really appeared in 2001 with the publication of the “Manifesto for Agile Software Development,” authored by 17 software developers.
When to use it: The practice originated in software development and works well in that culture. How do you know if agile is for you? It has been applied to non-software products that seek to drive forward with innovation and have a level of uncertainty, such as computers, motor vehicles, medical devices, food, clothing, music and more. It’s also being used in other types of projects that need a more responsive and fast-paced production schedule , such as marketing.
3. Scrum Methodology
What it is: Scrum is a short “sprint” approach to managing projects. The scrum methodology is It’s ideal for teams of no more than 10 people and often is wedded to two-week cycles with short daily meetings, known as daily scrum meetings . It’s led by what is called a scrum master . Scrum works within an agile project management framework, though there have been attempts to scale Scrum to fit larger organizations.
The term scrum was introduced in a “Harvard Business Review” article from 1986 by Hirotaka Takeuchi and Ikujiro Nonaka. It became a part of agile when Ken Schwaber and Mike Beedle wrote the book “Agile Software Development with Scrum” in 2001. Schwaber formed the Scrum Alliance in 2002, a certified scrum accreditation series. Schwaber left the Scrum Alliance in 2009 to start a parallel accreditation organization called Scrum.org.
When to use it: Like agile, the scrum methodology has been used predominantly in software development, but proponents note it is applicable across any industry or business, including retail logistics, event planning or any project that requires some flexibility. It does require strict scrum roles , however.
4. Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK)
What it is: This is the granddaddy of methodologies if it’s a methodology at all. The Project Management Institute (PMI) is a not-for-profit membership association, project management certification and standards organization.
This organization produces a book called the “Project Management Body of Knowledge” or PMBOK. The PMBOK provides definitions and guidelines for project planning, scheduling, executing and controlling. For example, the project management process groups describe the project life cycle, while the 10 project management knowledge areas explain how to manage a project.

When to use it: Almost any project can benefit from PMBOK, as all projects big and small are going to go through the various stages of the project life cycle outlined in the book. It’s a great way to keep everyone on the same page, so to speak, and offers a clear definition of how a project is managed.
The Project Management Institute it’s also the organization that grants various project management certifications such as the project management professional (PMP) certification, which is the gold standard among project managers and is recognized all over the world. PMBOK is a great traditional framework to run a project.
5. Critical Path Method (CPM)
What it is: In the critical path method (CPM), you build a model of the project, including all the activities listed in a work breakdown structure , the duration of those tasks, what if any task dependencies there are and marking off milestones to indicated larger phases of the project or points in which your project deliverables are due.
With this information, you can identify the longest sequence of tasks to finish the project, which is called the critical path. You’ll need to keep an eye on those tasks because if one of them is delayed, the whole project will be delayed.
The critical path method was developed in the late 1950s by Morgan R. Walker of DuPont and James E. Kelley, Jr., of Remington Rand. DuPont was already using a precursor of CPM as early as the 1940s, and it was applied to the Manhattan Project.
When to use it: CPM works better with smaller or mid-sized projects. The larger the project, the more difficult it can be to take all the data you need to diagram and make sense of it without project management software .
6. Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)
What it is: In , you’re focusing on resources that you’ll be using to complete the project, such as teams, equipment, office space, etc. It’s a less technical method of project management that doesn’t put as much emphasis on task order or schedule , but rather on balancing resources and keeping them flexible.
First introduced in 1997, in the book “Critical Path” by Eliyahu M. Goldratt, it has been credited with making projects anywhere from 10-50% faster and/or cheaper.
When to use it: CCPM can be applied to both large and small companies, and for projects that include industries such as construction, software development and tech research and development.
7. Kanban Methodology
What it is: The kanban methodology is a visual approach to project management. The name is literally billboard in Japanese. It helps manage workflow by placing tasks on a kanban board where workflow and progress are clear to all team members. The kanban methodology helps reduce inefficiencies and is a great project management tool for many purposes such as lean manufacturing or agile projects.
Kanban project management has been around since the late 1940s when it was studied by Toyota used the rate of demand to control the rate of production of its vehicles. The car company applied it to its lean manufacturing model, known as the Toyota production system.

With the dawn of visual planning boards in software in our era, like Trello, there are now new uses for kanban tools and kanban methods. Agile teams use kanban boards for story-boarding user stories and for backlog planning in software development.
When to use it: Another process developed initially for manufacturing and for software teams, the kanban method has since expanded and has been used in human resources, marketing, organizational strategy, executive process and accounts receivable and payable. Almost anyone can plan with Kanban boards, adding cards to represent project phases, task deadlines, people, ideas and more. Kanban software makes this methodology especially accessible.
8. Extreme Programming (XP)
What it is: It sounds like some dangerous sport the kids are into, but in fact, XP is a type of agile software development with short development cycles and multiple releases to improve productivity. Customer requirements are sought and can adapt to the course of the project.
Created by Kent Beck while working on the Chrysler Comprehensive Compensation System payroll project, he literally wrote the book (“Extreme Programming Explained”) in 1999. But many of its practices have been around for a while.
When to use it: When requirements change frequently, then you’ll want to use a methodology such as XP. It’s good when your customer doesn’t have a clear idea of what they want.
9. Lean Methodology
What it is: Lean project management is what you’d think it is from its name: a way to cut waste and in so doing increase value in projects and manufacturing processes. So, lean focuses on eliminating waste from key processes to continuously be impacting positively on the value stream. It does this by optimizing separate technologies, assets and verticals.
Lean project management goes back to Henry Ford and his flow production for automating the process of building cars. Toyota picked up on the idea, as well, extending their idea beyond manufacturing to the continuous improvement of the product development process.
Today, software development teams run lean processes to focus on end-user feedback and increased value, which means Lean methodology has taken on a new meaning, particularly with the publishing of Lean Startup, by Eric Ries, who advocates for rapid prototyping, end-user feedback and early and rapid product delivery.
When to use it: Lean project management was first developed by Toyota and is obviously a great methodology for manufacturing. In fact, it’s also referred to as lean manufacturing , but it has been adopted by construction and education industries, among others in the manufacturing space and countless startups and software development firms looking to drive products focused on the end-user.
10. Six Sigma
What it is: Introduced by engineers working at Motorola in the mid-1980s, Six Sigma works to improve quality by identifying what is not working in the project. It applies quality management, including empirical statistics, and employs personnel who are experts in these disciplines. There is also a Lean Six Sigma that adds lean methodology to eliminate waste.
As a doctrine, it says that continued efforts to achieve results that are stable and expected are most important to success. Processes can be refined and improved. It takes the whole organization, from the top down, to sustain quality in a project.
When to use it: This methodology works best in larger organizations. Even companies with a few hundred employees are likely too small to take advantage of its benefits. It requires a certification to practice. Learn about six sigma certification here.
11. PRINCE2
What it is: PRINCE2 stands for Projects IN Controlled Environments and is a structured certified methodology. It was initially created by the UK government for IT projects. PRINCE2 is not like other traditional methods like waterfall, in that it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, but follows seven principles, themes and procedures.
When the UK government adopted standards for IT systems in 1989, they called in PRINCE. PRINCE2 came about in 1996 as a more general project management method. It is now a popular project management methodology throughout all UK governmental agencies and the United Nations.
When to use it: Adopted by many other countries’ governments, PRINCE2, so, as you can imagine, it’s not always suitable for smaller projects.
ProjectManager Works with Any Project Management Methodology
There are almost as many methods to manage as there are projects. But they all share one thing in common: getting deliverables done on time and within budget. No matter which project management methodology you choose ProjectManager is the one software you’ll need to do it.
Tools for Waterfall Project Management
Waterfall is structured. One thing follows the next and it’s all planned out. No problem. ProjectManager has an online Gantt chart . Import your task list to start a new project. Add due dates and the tasks populate a timeline. Link-dependent tasks to avoid bottlenecks. Set milestones to separate the project into phases. You control the project step by step.
Tools for Agile Project Management
Gantt charts aren’t going to help as much as other project tools if you’re working in an agile framework. That’s true, but ProjectManager is flexible enough to serve scrum teams with multiple project views.
Use the kanban view to map out your sprint. Product backlogs are collected on cards, which can be prioritized for scrum teams to know which user story to work on first. Then the sprint can be archived, so when doing a sprint retrospective, teams can learn from their mistakes and improve the process.
Multiple Views for Diverse Teams
What if your organization is larger, with different divisions, some that work with an agile project management framework and others with a more traditional waterfall methodology? What’s great about ProjectManager is that it can switch from one view to the other, giving IT teams a kanban board view for their scrum sprints and managers a Gantt chart for a bigger project planning overview.
The real-time dashboard and reporting features gather the same data and crunch the same numbers, so whatever project management method you use is tracking the same results.
Yes, ProjectManager is an award-winning project management software for a reason. It’s flexible enough to work in an agile environment, traditional waterfall methodology or a hybrid of the two. You decide, not the software, which means ProjectManager is the one tool to bring in your project, however, you manage it, successfully.
Related Content
- Project Integration Management
- Waterfall Project Management Software
- Agile Project Management Software
- Critical Path Software
There are more project management methodologies, but these are some of the most popular. Regardless of which you use, you need a project management tool to best manage all your processes and projects. ProjectManager is an online PM tool, so whatever methodology is right for you our software will help you apply it to a successful end. Try it free for 30 days and see for yourself.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.

Project Management
Learning outcomes:.
After you complete this section you will be able to:
- Learn how to create an action plan to successfully complete your project
- Develop strategies to manage your time effectively
- Learn useful tips for successful team work
- Learn how to manage risks associated with completing a project
What is project management?
The Project Management Institute (PMI) defines a project as a “temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result.” The ‘endeavour’ or ‘unique product’ in this case is your research project. It is about how you manage all aspects of writing your project so that you deliver a good piece of work by the deadline date for submission.
Project management (PM) involves setting clear goals, breaking down your project into bite-size tasks with clear deadlines, developing time management strategies to accomplish these tasks, and working with your supervisor and with other students. It also involves monitoring your project to ensure you are on schedule.
This short video gives tips on how to plan and monitor your project to ensure that you complete your research project on time.
To summarise :
In order to successfully complete your research project, you will need to:
- Set goals . An example of a goal is to list all of the tasks that you would like to accomplish in the first or second semester.
- Break down tasks . An example would be to arrange your tasks monthly and weekly and daily. If you have four writing goals for September, then you can place one in each week of the month. If you have two, then give yourself two weeks for each.
- Implement strategies for accomplishing your tasks.
- Monitor and adjust the project as you go along.
The library holds a number of books about project management for students which cover additional information about managing your research project. The following are recommended. Search the library’s online catalogue to find the books and their location in the library.
The next section is all about time management, looking at tips and tools to keep you on track.

Filter by Keywords
Project Management
Top 18 project management methodologies.
Erica Golightly
Senior Writer
February 7, 2022
Have you considered how a project management methodology can help you and your team achieve long-term success?
If you’re thinking, “I don’t work in industries like technology or construction, so this doesn’t apply to us,” think back to the last project you worked on. Did the team feel motivated? Productive from start to finish? Or did every day feel like this? ⬇️
We understand. As a project manager , it’s hard to deliver projects with often unclear direction from clients and stakeholders, let alone manage the process in between.
Project management methods establish a system of principles, standard processes, and control to manage multifaceted projects that come in all shapes and requirements— across all industries.
By the end of this article, you’ll learn:
- How to optimize the five phases of a project lifecycle
- The top 18 project management methodologies used across wide geographies
- Recommended features in ClickUp for specific project management methodologies
We invite you to ditch the messy, complicated, and inflexible processes for proven methodologies to leverage project management tools and various techniques for success. ⚙️⚖️🚀
The 5 Phases of a Project Lifecycle
Adaptive project framework (apf).
- Agifall/Hybrid
- Critical Path Method
- eXtreme Programming (XP)
Get Things Done (GTD)
- Integrated Project Management (IPM)
- New Product Introduction (NPI)
- Outcome Mapping
- Package Enabled Reengineering (PER)
Project Management Institute’s Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMI’s PMBOK)
Projects in controlled environments (prince2), rational unified process (rup), 100+ powerful tools in clickup for any project type.

Whether you’re a new or seasoned project manager, let’s refresh our minds on the five fundamental project lifecycle phases you need to know to run successful projects. This will help you in your decision to choose the right project management methodology.
👾 Phase 1: Initiation
A project always begins with a conversation. When you come out of the first meeting with a client or stakeholder , you should fully understand the project purpose, SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound) goals, communication expectations, and budget.
👾 Phase 2: Planning
The planning phase goes more in-depth than determining the project scope and schedule (which is only the beginning). If you’re using a timeline or Gantt chart tool, it’s critical also to disclose these key project details in a project charter :
- Estimates and cost for people and software resources
- Potential risks, assumptions, and blockers
- Dependencies
- Project teams (roles and workflows)
- Change process requirements
- Success criteria
- Did we mention dependencies?
👾 Phase 3: Execution
Dependencies are an absolute necessity for controlled project execution . If you’re a coffee person and you skip your morning cup and head straight to work, chances are, you make your day a little more difficult than it should be.
As you’re on the path to assigning individual tasks, have an open discussion with the project team about what can or can’t be started until a specific task is completed. You’ll save time and money with transparency and set everyone up for success from start to finish.
👾 Phase 4: Monitoring
Data is your north star metric to manage people, resources, budgets , and risks during the execution phase. Make sure you’re using a powerful productivity tool like ClickUp to know what project contributors are working on and what they need to do next.
Even more, track project goals and communicate with stakeholders and clients within ClickUp.
👾 Phase 5: Closing
After you turn in the final deliverables and wrap up loose ends, it’s advantageous to assess the performance of team members and resources. This reflection period will help improve the next project.
Have all deliverables been completed, validated, and archived?
Were issues and risks effectively managed?
Which processes were easy/challenging, and what would they change?
Relate: Project Management Examples !
Welcome to your pocket encyclopedia of the top 18 project management methodologies! 📘
A nod to agile project management methodology, the adaptive project framework is an iterative approach to satisfy a project’s goals and outcomes. Meaning, a project’s plan is broken into short iterations (or cycles) of tasks. This helps structure task dependencies and establishes clear deadlines.
The five steps in the adaptive project framework are:
- Project Scope : document the project plan with a project charter (download ClickUp’s Project Charter Template )
- Cycle Plan: define each task with all dependencies
- Cycle Completion : after one cycle completes, another begins
- Control Point : the client or stakeholder meets with the team to assess the quality and potential room for improvements in the next cycle
- Final Report : determines if results were achieved and successful
🟢 Adaptive Project Framework Pros
- Less time is spent on the first phase (defining project scope)
- Client and stakeholder satisfaction increases because of their involvement
- Teams create the most value with learnings in short cycles
🟡 Adaptive Project Framework Cons
- The project scope will potentially change throughout the lifecycle, reverting from a client or stakeholder’s original vision
- Too much flexibility for teams accustomed to fixed schedules
- Limited control over business processes
The hybrid model is the best of both Agile and Waterfall methods . Commonly used in product development companies, the planning phase uses waterfall method techniques but applies agile practices during execution .

🟢 Agifall/Hybrid Pros
- Continous collaboration and communication amongst different teams within a project
- A gateway to a complete transition into Agile methodology
- Using the best techniques of both methods to create a custom approach
🟡 Agifall/Hybrid Cons
- A good amount of time is required to plan a clear, clean, and understandable project approach
Today, one of the most popular project management methodologies, the agile methodology , is an incremental and iterative approach to managing projects in phases . Each iteration has a fixed scope (between 1-3 weeks) to maintain product release consistency, stability, and on-time delivery.
At its core, release management minimizes risks, tracks and audits requirements , and secures consistent implementation—in the least disruptive approach .
The five steps in the Agile methodology are:
- Defining the release plan and product roadmap
- Designing and building product feature(s)
- Testing and iterating
- Closing and maintenance

🟢 Agile Pros
- Increases customer satisfaction and retention
- Software code and testing standards are used repeatedly
- Specific roles with multiple project drivers to meet the same goal
🟡 Agile Cons
- Some organizations might find agile workflows to be a poor culture fit
- Potential lack of understanding in workflow flexibility
- An experienced agile professional might be necessary for teams new to agile
Project managers use the Critical Path Method to define the critical and non-critical tasks for timely delivery. After listing every activity and task required for completion, they will note dependencies and write a sequence of times for each.
Planning with the Critical Path Method allows teams to pinpoint opportunities to shorten task times and flag potential shifts when changes can affect critical tasks.

🟢 Critical Path Method Pros
- Identifies the most important activities and tasks in a project
- Displays the complexities of whether a project is small or substantial
- Easily explained with a chart or graph
🟡 Critical Path Method Cons
- Mid-changes could disrupt the overall stability of the project
- Requires time and effort to build the CPM chart successfully
- Client and stakeholders must be comfortable with estimates on progress and delivery
Note : Critical Chain Project Management, a related project management methodology, focuses on managing resources and buffer duration between task chains and improving upon the Critical Path Method.
Test out these critical path templates !
The eXtreme Programming methodology takes elements of traditional software engineering practices to, well, extreme levels. However, it’s familiar to the agile framework like specific planning approach, on-site customer participation, and continuous testing.
Standard software development practices found in the eXtreme Programming method are:
- Pair Programming : two developers work together simultaneously on code
- Refactoring : implementing a feature without changing the behavior of the system
- Continuous Integration : integrating as soon as you identify issues decreases the number of bugs that could arise in production
- Short Release Cycles: every day is optimized, so by the end of the cycle, tested features are deployed for customer feedback
- The Planning Game : Customer and developers meet to discuss the upcoming release
- 40-Hour Week: developers must work fast and efficiently to maintain product quality, so keeping to a manageable work supports a healthy work-life balance
- Non-Complex Design : when design complications are found, it’s removed so developers can articulate product intention

🟢 eXtreme Programming Pros
- Fixed timeline length, typically 1-2 weeks
- Flexible to changes during the sprint cycle
- Higher customer satisfaction
🟡 eXtreme Programming Cons
- Requires engaged customer(s) to make informed project decisions
- Stressful if teams don’t fully understand the demanding workflow
- Geared towards product delivery businesses
The GTD (Get Things Done) method is a project management methodology less concerned with technical activities such as coding and testing. Instead, it emphasizes personal productivity to create the best systems for approaching life and work.
The five simple steps in the GTD method are:
- Capture : record your notes to make room for more headspace
- Clarify : review your notes and determine whether they should be converted into tasks, filed for referenced, or tossed
- Organize : dedicate a single place for your collection of ideas and tasks
- Reflect : visit your collection frequently to update for relevancy and opportunities
- Engage : use the system you’ve built to take action on your items
If you’re looking for a productivity tool to help gather your thoughts, tasks, schedule, and workflow in one place, learn how to use ClickUp with the GTD project management methodology. ⬇️
🟢 Get Things Done Pros
- Large or intimidating projects are broken down into manageable tasks
- Easily view which tasks take priority over others
- Entirely customizable for whatever season of life and work you’re in
🟡 Get Things Done Cons
- Requires time to set up a system for long term success
- Recording changes with the most up to date information are necessary to prevent backtracking
Check out these GTD apps !
The Integrated Project Management (IPM) project management methodology oversees the cross-functional communication and hand-off during all project phases . Since cross-functional teams have different processes and workflows, IPM helps resolve schedule conflicts, bottlenecks, and team bandwidths.
👉 Check out these project management communication resources to assist with Integrated Project Management planning:
- 7 Project Management Challenges And How To Solve Them
- How Toyin Olasehinde Uses ClickUp Comments to Streamline Communication
- 20+ Project Management Tips for Marketers
- Here’s How To Improve Your Team Communication
- 16 Unmissable Benefits of Project Management Software

🟢 Integrated Project Management Pros
- Projects are appropriately monitored and controlled
- Productivity accelerates to complete projects on time
- Complex resource planning becomes simple
🟡 Integrated Project Management Cons
- No cons to cohesive team communication and collaboration! 🤝
The Lean project management methodology focuses on tools and practices heavily centered on product value for customers . The commitment to constantly improve the reliability and quality of products helps businesses deliver faster . In addition, understanding the specific tasks and activities that need to be completed at a given time minimizes the chances of wasting time and resources.
The five principles of lean methodology are:
- Define Value : align processes to deliver on customer needs
- Map the Value Stream : remove barriers that disrupt the flow
- Create Flow : manage team member workloads and production steps to maintain a smooth process
- Establish Pull: remove overproduction of inventory by implementing a system for on-demand delivery
- Seek Perfection : continuously improve to make steps towards eliminating all mistakes

🟢 Lean Pros
- Understands all aspects of customer demands
- Promotes involving team members closest to the work
- Removes inventory waste, process barriers, and defective products
🟡 Lean Cons
- Not suitable for teams that don’t use a dashboard tool
- Not a culture fit for organizations resistant towards full transparency
- Experienced resource management professionals might be necessary for some teams
Bonus: Lean vs. Agile Project Management 💜
The New Product Introduction methodology is used by companies that continuously release new products . NPI streamlines time and efforts to achieve desired results by carefully vetting new ideas and surveying customers .
The six phases of New Product Introduction are:
- Ideation : brainstorming a product concept influenced by business risk and market research
- Product Definition : gathering product requirements
- Prototyping : building a model for the hardware or software product for performance analysis
- Detailed Design : refining the product model and fully designing to its final form
- Pre-Production (Validation/Testing) : validating the product to ensure high-performance results
- Manufacturing : all design, marketing, and sales efforts are carried out to deliver the final product

🟢 New Product Introduction Pros
- Creates a culture of development
- Drives higher value proposition
- Increases opportunities for businesses to innovate and grow within their industry
🟡 New Product Introduction Cons
- Not suitable for projects that are small in scale
- Product ideas can fail unexpectedly
The Outcome Mapping methodology is an approach for planning, monitoring, and evaluation developed by the International Development Research Centre (IDRC) , a Canadian grant-making organization. It’s distinct from all other methodologies mentioned in this list because it focuses on behavior changes of people and groups the project or program works with directly . (Organizations within policy development and research communication typically use this method.)
Outcome Mapping blends social learning, self-assessment, and adaptive management within an organization. The process allows organizations to gather data and encourage reflection about development impacts.
The three stages of Outcome Mapping are:
- Intentional Design : determining the vision, partners, tangible changes (outcomes), and contribution efforts
- Outcome and Performance Monitoring : using an Outcome Journal (tracking progress markers), Strategy Journal (testing strategy in wavering circumstances), and Performance Journal (recording practices and opportunities for improvement) to provide data
- Evaluation Planning : a detailed progress review to influence an evaluation plan and bring strategic benefits to the project

🟢 Outcome Mapping Pros
- Successful results contribute to sustainable improvements
- Incorporates being reflective about organizational and social learnings
- Flexible model to tailor to project needs
🟡 Outcome Mapping Cons
- Requires organizations to take a hard look at their views about development
- Regular communication and participation is necessary for success
- Not suitable for short software development lifecycles
The Package Enabled Reengineering methodology focuses on the original functionality of software packages as a framework for rethinking the design. It requires an analysis of challenges within the current process, management, people, and design to shape new systems.
Check out how to jumpstart your management and design workflows in ClickUp so you can organize your planning with the PER project management methodology. ⬇️
🟢 Package Enabled Reengineering Pros
- Optimizes productivity, resources, and communication strategically
🟡 Package Enabled Reengineering Cons
- Not suitable for organizations with already successful systems
Written by the Project Management Institute, a global “for-purpose” organization , the Project Management Body of Knowledge is a collection of tools, techniques , and best practices for a project manager to align with the evolving changes of project management.

🟢 PMI’s PMBOK Pros
- Resource for project managers studying for project management certification : CAPM (Certified Associate in Project Management) or PMP (Project Management Professional)
- Includes practices guides and comprehensive project management terms glossary
🟡 PMI’s PMBOK Cons
- Extensive 700+ page book not meant for reading cover to cover
The PRINCE2 project management methodology is globally adopted because of its practical and adaptive framework to divide projects into controllable stages . It focuses on an orderly approach in a project’s lifespan from beginning to end. The PRINCE2 methodology directly impacts day-to-day routines to deliver successful projects, from construction development projects to launching social campaigns.

🟢 PRINCE2 Pros
- PRINCE2 certification is available
- Improves project management skills with proven best practices
- Adapts to any project type and scale
🟡 PRINCE2 Cons
- Documentation heavy
- Without certification or experience, it might take longer to see results
The Rational Unified Process methodology is built on well-documented software processes focusing on an iterative approach throughout development. This allows for quick changes on high-risks throughout every stage . As a result, RUP’s structure lends itself to assembling high-quality software production .
The four project phases are:
- Inception : outlining the scope of work or statement of work , impact analysis, identify key use cases, and cost estimates
- Elaboration : designing an architected foundation for the product
- Construction : completing the bulk of the work to develop all software components
- Transition : introducing the product to the end-users, handling bug issues, and reviewing outcome goals

🟢 Rational Unified Process Pros
- Reduces time for initial integration as it’s built in the project stages
- Repeatable steps to apply to future projects
- Emphasizes documentation
🟡 Rational Unified Process Cons
- Not suitable for teams that are unable to keep up with documentation
- The project’s success rate is higher with experienced team members
Scrum project management adds to the agile approach by including a prominent role called the Scrum Master. The Scrum Master conducts a sprint planning meeting with the Product Owner and Development team. Then, they select the high-priority items from the Product Backlog —a list of collected feedback from customers and stakeholders—to release in one sprint. These high-priority items become a Sprint Backlog for the development team to build, test, and release.
Throughout the sprint cycle, a daily scrum meeting is held (typically at the start of the workday) for each project contributor to share: what they did yesterday, what they will do today, and any blockers in the way.
At the end of the sprint, a Sprint Review meeting is held with the Scrum Master, Product Owner, stakeholders, and development team to walk through accomplishments and changes. This review helps improve the performance of future sprints .

🟢 Scrum Pros
- Flexible timeline length, typically 2-4 weeks
- Teams are aligned around tasks and progress through daily scrum meetings
- Short sprints support faster changes from customer and stakeholder feedback
🟡 Scrum Cons
- Daily meetings might not be a culture fit for some teams
- The success rate is higher with experienced agile team members
- Adopting the Scrum framework in larger teams is difficult
Scrumban is the combination of Scrum and Kanban. Kanban adds metric visuals and process improvements to the Scrum methodology. For example, a distinct feature of the Scrumban method is the WIP (work in progress) board to help visualize all tasks from start to finish .
This board, divided into three sections—product backlog, work in progress, and completed—shows the collective work in a given section . With this data, the Scrum team can make adjustments to monitor workloads.
🟢 Scrumban Pros
- Adds a process improvement attribute to the Scrum methodology
- Issues can be pinpointed and resolved quickly on a progress board
- Promotes full transparency for all project team members
🟡 Scrumban Cons
- Boards that are not updated in real-time cause delay and confusion
- A fairly new methodology
- Daily standups are optional, which can be an advantage or disadvantage to a preferred workflow
Motorola introduced the Six Sigma methodology in the 1980s to bring down the defects in its manufacturing process. However, it’s suitable for all industries . It emphasizes a data-driven approach for continuous business transformation . Six means six standard deviations (a statistical benchmark), and the sigma symbol represents a standard deviation.
There are two models of the six sigma methodology:
Six Sigma DMAIC
- D efine the current problem, goals, and deliverables
- M easure the current process and performance
- A nalyze the causes of the problem
- Improve the process by proposing and testing solutions
- C ontrol the outcome by implementing changes in place if problems arise
Six Sigma DMADV
- D esign a process that meets customer expectations and needs
- V erify the design meets customer needs and it’s appropriately
The DMAIC and DMADV models in the six sigma methodology ensure each step is followed to achieve the best results.

🟢 Six Sigma Pros
- Reduces wastes and costs
- Enhances value and improves the quality of a company’s output
- Six Sigma certification is available
🟡 Six Sigma Cons
- An implementation period is necessary for success
- Complicated and requires statistical analysis
- It can get costly in the long run
Bonus: Check out the Top 10 Six Sigma Templates
The Waterfall methodology is one of the traditional project management methods. It has two main attributes: thorough initial planning and fixed-end requirements . Waterfall project management is predictive , meaning each stage starts when its predecessor ends. After a project has begun, it’s nearly impossible to make changes. (This characteristic of Waterfall is off-putting for organizations that experience altering project requirements while in progress.)
On the flip side, for businesses that need predicted outcomes , such as construction and manufacturing, this rigid framework is the best approach for their needs.
The stages of the Waterfall methodology are:
- Requirements Gathering
- Development

🟢 Waterfall Pros
- Easy and familiar to understand for new and seasoned teams
- No overlap between project phases
- Clear deadlines are determined and adhered to at the start of the project
Check out our Waterfall Management Template !
🟡 Waterfall Cons
- Top-down communication model
- Not suitable for software development or complex projects
- Not best for ongoing projects
Now that you know your best project methodologies options, where can you keep your people, processes, and projects organized? 🤔
One of the best ways to add value to your work and optimize your time is to use a software tool. Our recommendation? ClickUp! ✨

ClickUp is the ultimate productivity platform allowing teams to manage projects, collaborate smarter, and bring all work under one tool. Here are a few ClickUp features among the hundreds available that can be customized to any team size for consistent collaboration:
📊 Dashboards
ClickUp Dashboards are a time-saving resource to share high-level views with project stakeholders or project progress with anyone in their Workspace! Track sprints, task progress, portfolio management, and more with customizable widgets.
A must-have tool for these project management methodologies:
- Rational Unified Process
- Adaptive project framework (APF)


🤖 Automations

With ClickUp Automations , you’re able to set up combinations of Triggers and Actions to help automate repetitive actions—saving time and allowing you to focus on things that matter. Does your team use workflow software with external applications like GitHub? Automate your workflow within ClickUp using the GitHub integration !
🗒 List view
ClickUp’s powerful and flexible List view can sort, filter, or group columns in any way. Columns can be customized to show important information—task assignees, start and due dates, project briefs , website links, task comments—it’s up to you!

Subtasks in ClickUp add a layer to your work structure, allowing you to define more detailed goals inside of your tasks. This is a perfect solution for: action items that don’t warrant a new task, objectives that need to be completed to finish an overall task, and task dependencies.
🏃♀️ Sprint
Sprints in ClickUp are packed with additional ClickUp features to help teams better understand and manage their product roadmaps. Available on every ClickUp plan, Sprints use tasks as items of work so teams don’t have to rely on other software to get their work done.

🟫 Board view

Choose whether you want to zoom in on a single List, an entire Folder, or even all Spaces across your Workspace in Board view . For teams that prefer Kanban project management, Board’s view powerful drag-and-drop interface is perfect for visualizing tasks in progress.
ClickUp: A Powerful and Friendly Tool
Your ClickUp Workspace can be fully customized to optimize any project management methodology so you can do your best work and take it anywhere you go . Change the way you build and manage projects with ClickUp today!
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
Research management
Sponsored by
How to use a project management approach to help run research projects
Jon Gunnell explains how to adopt the PRINCE2 project management method to help overcome the many challenges of running a multi-year research project
Jon Gunnell
Additional links.

Elsevier helps researchers and healthcare professionals advance science and improve health outcomes for the benefit of society.
Discover elsevier.

You may also like
Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
A diy guide to starting your own journal, universities, ai and the common good, artificial intelligence and academic integrity: striking a balance, create an onboarding programme for neurodivergent students.
Academics face numerous pressures on their time even before managing the process of, for example, a five-year research project that needs to deliver real-world benefits.
Such a project at the University of Sheffield’s School of Law – titled Fortitude and funded by the European Research Council – aims to improve the “legal capability” of children in the UK. The project’s ultimate goal is to create gamified learning for children aged from three to 15 that will help them deal with legal issues they encounter in their everyday lives. For example, how does a child engage with a shop assistant who gives them incorrect change?
- A model for maximising the impact of small research units
- Five tips for building healthy academic collaborations
- How to change research cultures to support the well-being of PhD students
It is crucial – and difficult – for an academic team to ensure that a project like this is managed effectively and delivers its objectives. Managing research involves responsibility for other academics who, while accustomed to working independently, may be less familiar with delivering the outputs a project needs – and within a specific deadline. Plus, there may be a requirement to translate theoretical materials into something meaningful in the “real world” – in our case, devising gamified learning that children will use.
Adopting a project management approach in an academic setting – such as the PRINCE2 method , originally devised by the UK government to improve public sector project success and now used worldwide – can address the challenges of running a multi-year research project and avoid overwhelming academic teams.
Project management: the right discipline for managing research projects
A project – according to the PRINCE2 project management method – is defined as ‘‘a temporary organisation that is created for the purpose of delivering one or more business products according to an agreed business case’’.
Having a method to manage this entity means you have a safe and robust framework to operate in. It also helps ensure creativity and effective communication between team members. This is important because, without it, people tend to work in isolation. With a project management structure – including regular team meetings where people discuss problems and identify solutions – a team collaborates and tasks become actions and outputs.
The value of using a best practice method
Best practice project management methods such as PRINCE2 are the result of experts combining knowledge, experience and proven techniques gained from running various projects around the world.
Therefore, by either hiring a qualified project manager to run an academic research project, or training a relevant team member in the method, your project will be run according to clear principles:
− Defined project roles and responsibilities, which means people have clarity and there is less risk of just muddling through.
− A focus on deliverables (products or outputs), which ensures that everyone knows what the project aims to deliver.
− A business case to ensure that the project remains viable during its lifetime.
− Assurance, troubleshooting and audits to keep things on track.
− Learning and continuous improvement to avoid repeating mistakes and enhance quality.
− The ability to work with both an “agile” delivery approach (an evolving way of working involving regular testing and feedback) and a traditional “waterfall” project approach (linear and based on a plan agreed up front). For example, while our overall project approach is waterfall, briefing gaming companies to develop digital games for children is better handled with agile. But in either case, project management provides structure and control.
The key elements in PRINCE2 that help the research management process
There are numerous ways of working outlined in PRINCE2 that can support the management of a research project. These include:
1. The project plan
Having a project plan from the outset helps identify what a long-term project will look like, but with flexibility, as things might change. It also means that everyone involved can see the key milestones throughout the project.
2. Business case
Developing and revisiting a business case ensures that the project either remains viable or otherwise closes. In our project, this involved completing the European Research Council Grant Agreement: a document that brings together all the information necessary to obtain funding for the research project. On an annual basis, we also need to provide financial and scientific reports that outline what’s been spent, what’s been achieved and what’s planned.
3. Project benefits
Identifying benefits acknowledges that a successful project should change something for the better. In a research management context, that could mean discovering something groundbreaking.
4. Specifying business requirements
Identifies what the project requires for success and helps when tendering for suppliers. In our case, we’re now going out to tender with gaming companies to produce digital or physical games for children based on our research. Therefore, we have produced a specification document for the requirements.
5. Identifying risks
Pinpointing risks means anticipating what could impede the project and allows a project manager to find ways of minimising the risks and keeping stakeholders informed. For our project, we have a risk log that captures factors such as teachers’ strikes, which might mean school participants are unavailable at a crucial point. This helps us to replan an activity and keep the project on schedule.
6. Engaging stakeholders
Knowing who the project stakeholders are, mapping them according to their importance and agreeing how to interact with them ensures that they remain engaged throughout. For us, that can include internal stakeholders, such as the head of department in the university and external stakeholders, such as schools, who can support the project – and knowing how often we need to engage with them.
7. Developing a communication plan
Having different methods and channels to communicate with stakeholders is vital to demonstrate the work you’re doing and to share results and learnings. For example, we’ve communicated research findings and successes of the project periodically when attending external conferences and academic events at the university.
8. Regular, formal reporting
Delivering regular reports to a research project’s funding body might cover the latest research findings and how you are managing the budget. Without such reports, your funding could be at risk.
9. Documenting lessons learned
This helps the project team to reflect on different activities and how they could be improved next time. Questioning and capturing what’s gone well, what hasn’t and what you would do differently is also important for future projects.
How a project management method improves project outcomes
A project’s purpose is to deliver something new that will benefit an organisation or department. In other words, provide a positive outcome. In our case, having a project management method in place has helped us to deliver:
− An ethics approach for the project that meets both the University of Sheffield’s and the European Research Council’s requirements.
− A child-centred framework to measure legal capability, developed through research with children from a number of our partner schools.
− A GDPR approach that meets the requirements of the university and ensures the security of all personal data.
− A project website, which we have used as our key channel of communication for both project participants and stakeholders.
Replicating the value of project management in your institution
By including a project manager at the bid stage of a research project, the academic team can get dedicated support for the development of a project plan, which could then accompany their funding bid. And by sharing lessons learned and experiences gained across an institution, this can become the basis for developing and embedding best practice project management within any future projects.
Jon Gunnell is project manager at the University of Sheffield School of Law, UK.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
Click here for more information about the PRINCE2 project management method.
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
Global perspectives: navigating challenges in higher education across borders, how to help young women see themselves as coders, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, authentic assessment in higher education and the role of digital creative technologies, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
Project Management for Research
The tools you need to make your research project a success.
This toolkit includes a variety of tools for managing your research projects including recommendations for general project management software and tools to help you and your team manage activities from grant writing to implementation and project closeout.
Explore the toolkit below:
Grant Writing + Project Development
A Gantt Chart is a popular project management tool; it is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project’s schedule. The chart allows for organizing and viewing project activities and tasks against pre-established timeframes.
Gantt Chart Template Gantt Chart Instructions Gantt Chart Example
Graphic display of the flow or sequence of events that a product or service follows; it shows all activities, decision points, rework loops and handoffs.
Process maps allow the team to visualize the process and come to agreement on the steps of a process as well as examine which activities are duplicated. Process maps are used to:
- Capture current and new process information
- Identify the flow of a process
- Identify responsibility of different business functions
- Clearly show hand-off between functions
- Identify value added and non-value added activities
- Train team members in new process
Process Map Template Process Mapping Guide Process Map Example 1 Process Map Example 2
The Data Management Plan (DMP) defines the responsibilities related to the entry, ownership, sharing, validation, editing and storage of primary research data.
A data management plan must not only reflect the requirements of the protocol/project but also comply with applicable institutional, state and federal guidelines and regulations. The DMP Tool details your agencies expectations, has suggested language for REDCap and exports a properly formatted plan.
DMP Tool NIH Data Management & Sharing (DMS) Policy
The Project Charter's purpose is to define at a high level what the Project Team will deliver, what resources are needed and why it is justified.
The Project Charter also represents a commitment to dedicate the necessary time and resources to the project. It can be especially useful when organizing a multi-disciplinary, internally funded team. The document should be brief (up to three pages maximum).
Project Charter Template Project Charter Instructions Project Charter Example
Milestones are an effective way to track major progress in your research project.
A Gantt Chart is an effective tool for setting and tracking milestones and deliverables. It is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project’s schedule.
The proposal budget should be derived directly from the project description.
The proposal budget should follow the format specified by the sponsor. The Office of Sponsored Programs Budget Preparation webpages provide descriptions of the standard budget categories, lists of typical components of those categories, Ohio State rates where appropriate and other details to help ensure your budget is complete. Budget Preparation Resources from Office of Research The 398 grant form from the NIH is a template that includes standard categories required for an NIH grant (and many others) that you can use to develop a preliminary budget.
PHS 398 Forms PHS 398 Budget form for Initial Project Period Template PHS 398 Budget Form for Entire Proposal Project Template
The Risk Assessment and Mitigation Plan first assists the research team in anticipating risk that may occur during the research project before it happens.
The plan then specifies when to act to mitigate risk by defining thresholds and establishing action plans to follow. As a fundamental ethical requirement research risks are to be minimized to the greatest extent possible for all research endeavors. This includes not only prompt identification measures but also response, reporting and resolution. Risk Assessment and Mitigation Plan Template Risk Assessment and Mitigation Plan Example
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) organizes the research project work into manageable components.
It is represented in a hierarchical decomposition of the work to be executed by the research project team. It visually defines the scope into manageable chunks that the team can understand. WBS Instructions and Template WBS Structure Example
Implementation
A Gantt Chart is a popular project management tool; it is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project’s schedule.
The chart allows for organizing and viewing project activities and tasks against pre-established timeframes. A Gantt Chart can also be used for tracking milestones and major progresses within your research project.
The purpose is to define at a high level what the Project Team will deliver, what resources are needed and why it is justified.
It is represented in a hierarchical decomposition of the work to be executed by the research project team. It visually defines the scope into manageable chunks that the team can understand. WBS Instructions + Template WBS Structure Example
A communications plan facilitates effective and efficient dissemination of information to the research team members and major stakeholders in the research project.
It describes how the communications will occur; the content, security, and privacy of those communications; along with the method of dissemination and frequency.
Communications Plan Template Communications Plan Example
The Data Management Plan (DMP) defines the responsibilities related to the entry, ownership, sharing, validation, editing, and storage of primary research data.
A data management plan must not only reflect the requirements of the protocol/project but also comply with applicable institutional, state, and federal guidelines and regulations. The DMP Tool details your agencies expectations, has suggested language for REDCap, and exports a properly formatted plan.
DMP Tool DMP Tool Instructions Ohio State Research Guide: Data
The chart allows for organizing and viewing project activities and tasks against pre-established timeframes. Gantt Chart Template Gantt Chart Instructions Gantt Chart Example
This tool helps you capture details of issues that arise so that the project team can quickly see the status and who is responsible for resolving it.
Further, the Issue Management Tool guides you through a management process that gives you a robust way to evaluate issues, assess their impact, and decide on a plan for resolution.
Issue Management Tool Template Issue Management Tool Instructions Issue Management Example
A Pareto Chart is a graphical tool that helps break down a problem into its parts so that managers can identify the most frequent, and thus most important, problems.
It depicts in descending order (from left to right) the frequency of events being studied. It is based on the Pareto Principle or “80/20 Rule”, which says that roughly 80% of problems are caused by 20% of contributors. With the Pareto Principle Project Managers solve problems by identifying and focusing on the “vital few” problems. Managers should avoid focusing on “people” problems. Problems are usually the result of processes, not people.
Pareto Chart Template Pareto Chart Instructions Pareto Chart Example
Closeout, Transfer + Application
Completing a project means more than finishing the research.
There remain financial, personnel, reporting, and other responsibilities. These tasks typically need to be completed within a timeline that begins 60 to 90 days before the project end date and 90 days after. Specifics will vary depending on the project and the funding source. The Office of Sponsored Programs “Project Closeout” webpage provides a description closeout issues, a list of PI Responsibilities and other details to help ensure your project is in fact complete. Project Closeout Checklist Project Closeout Resources from Office of Research
A communications plan facilitates effective and efficient dissemination of information to the research team members and major stakeholders in the research project.
It describes how the communications will occur; the content, security and privacy of those communications; along with the method of dissemination and frequency.
Project Management Software
An open-source project management software similar to Microsoft Project.
OpenProject has tools to create dashboards, Gantt Charts, budgets, and status reports. Activities can be assigned to team members and progress monitored. OpenProject also has a tool for Agile Project Management. While the software is free, OpenProject must be installed and maintained on a local server and there will probably be costs associated with this. Talk to your departmental or college IT staff.
A secure, web-based project management system.
Basecamp offers an intuitive suite of tools at a minimal cost: ~$20/month or free for teachers. Basecamp facilitates collaboration between research team members with features such as to-do lists, messaging, file sharing, assignment of tasks, milestones, due dates and time tracking.
A project management tool that organizes tasks, activities, responsibilities and people on projects.
Trello can help manage research projects by keeping everyone on time and on task. It uses a distinctive interface based on cards and lists and may be especially useful for smaller projects.
If you have a disability and experience difficulty accessing this content, please submit an email to [email protected] for assistance.
Total with VAT: {{CartWithDetails.cartMaster.total_after_vat}} {{currency}}
Your cart is empty.
12 Project Management Methodologies: Types, Tools, Techniques, And How to Choose
Written By : Bakkah
27 Feb 2024
Table of Content
Definition of Project Management Methodologies:
Types of project management methodologies, project management methodologies tools , project management methodologies techniques, how to choose a project management methodology, explore bakkah's leading courses to boost your skills in project management and business analysis:, popular articles.
PRINCE2 Methodology - 2024 Full Guide About Advantages and Disadvantages
Prosci Methodology - Change Management Methodology
Application of PMO in government entities in Saudi Arabia
Project management methodologies are systematic frameworks and guidelines utilized by organizations to efficiently plan, execute, and complete projects. They offer structured approaches to project management, ensuring adherence to timelines, budgets, and objectives. These methodologies encompass diverse principles, practices, and tools designed to facilitate effective communication and coordination among project-implementing teams.
Project management methodologies vary in their approach, with some emphasizing flexibility and adaptability (e.g., Agile) while others focus on sequential and structured processes (e.g., Waterfall). The appropriate methodology must be selected according to the type of project and its unique circumstances. The goal is to enhance project efficiency, minimize risks, and deliver high-quality results, ultimately contributing to achieving the specified goals and objectives of the project.
Project management methodologies refer to the systematic frameworks, processes, and guidelines organizations follow to plan, execute, monitor, and complete projects. These methodologies provide a structured approach to managing projects, ensuring they are completed on time, within budget, and meet the specified goals and objectives.
Project management methodologies encompass diverse principles, practices, and tools designed to facilitate effective communication and coordination among project-implementing teams.
They can vary in their approach, with some methodologies emphasizing flexibility and adaptability (e.g., Agile), while others focus on sequential and structured processes (e.g., Waterfall). The appropriate methodology must be selected according to the type of project and its unique circumstances.
The goal of Project Management Methodologies is to enhance project efficiency, minimize risks, and deliver high-quality results, ultimately contributing to achieving the specified goals and objectives of the project.
Various tools support their implementation, enhancing collaboration and communication, while diverse techniques facilitate effective project planning, execution, and control.
There are diverse project management methodologies, each with different principles, processes, and approaches. Here are some common types:
1. Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall project management is a traditional approach to project management where tasks are completed sequentially and linearly.
The methodology is called "waterfall" because progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards through phases, like a waterfall. Each phase must be completed before moving on to the next one, and changes to the project are generally not allowed once a phase is closed.
Here are the main phases in the waterfall project management methodology:
- Requirements: Define project scope, objectives, and deliverables.
- Design: Create a detailed plan for how the solution meets requirements.
- Implementation (or Construction): Include coding or construction of the project.
- Testing: Ensure the project meets specified requirements through various testing phases.
- Deployment (or Implementation): Implement the project in the production environment after the success of testing.
- Maintenance and Support: Address issues and user concerns and make updates as needed.
The waterfall methodology is best suited for projects where the requirements are well-understood and unlikely to change significantly during the development process.
It is often used in industries like construction and manufacturing. However, one of its main drawbacks is its inflexibility to adapt to changes once the project has started, as it does not easily accommodate changes in requirements.
2. Agile Methodology
Agile methodology is an iterative and flexible approach to project management that focuses on collaboration, adaptability, and customer satisfaction.
Unlike the linear nature of the waterfall model, agile divides a project into small increments with minimal planning and delivers functional pieces of the project in short time frames, known as iterations or sprints.
Primary principles and practices of agile include:
- Projects are divided into small manageable iterations, delivering potentially shippable product increments.
- Collaboration and communication between team members, stakeholders, and customers are crucial for quick adaptation to changes and alignment with goals.
- Continuous customer feedback allows for adjustments based on changing requirements.
- Agile is flexible and adaptable to changes in requirements or priorities at any stage.
- Continuous delivery aims for a potentially shippable product at the end of each iteration, allowing for early and regular value delivery to the customer.
- Prioritization and timeboxing based on value and importance ensure focus and urgency in delivering value.
- Agile encourages self-organizing, cross-functional team formation that collectively possess the necessary skills to deliver a complete product.
Popular agile frameworks include Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP), each with specific practices and roles.
Agile is widely used in software development and various industries for its adaptability and customer-centric approach.
3. Scrum Framework
Scrum is one of the most widely used agile frameworks for managing complex software development projects. It provides a structured yet flexible approach to product development.
Key elements of the Scrum framework include:
- Roles: Include Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team.
- Artifacts: Comprise the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment.
- Events: Include Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-up, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
Scrum's iterative and incremental approach, along with its emphasis on collaboration and adaptability, makes it particularly effective for projects where requirements may change or evolve during development.
4. Kanban Methodology
Kanban is a project management methodology that visualizes workflow using boards, cards, and columns. It also limits tasks that are in progress simultaneously to prevent overloading the team and ensure a steady flow of work.
Emphasizing continuous improvement, Kanban employs feedback loops and a pull system, adapting work based on demand. Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are often used in Kanban to define the expected time frames.
Known for flexibility and adaptability, Kanban suits various industries like architecture, construction, marketing, education, software development, design, and law. Kanban fosters collaboration and shared responsibility and allows incremental process improvements based on specific needs and context.
5. Lean Project Management
Lean Project Management (LPM) is an approach to project management that draws inspiration from Lean principles. The Lean philosophy focuses on minimizing waste, optimizing efficiency, and continuously improving processes.
Lean principles are applied to enhance project delivery, reduce unnecessary activities, and deliver value more effectively.
Principal aspects of Lean Project Management methodology include eliminating waste, using value stream mapping, continuous improvement (Kaizen), customer focus, pull scheduling, visual management, batch size reduction, flexible planning, and cross-functional team use. LPM is suitable for industries like manufacturing, construction, and software development.
Its focus on efficiency and customer value makes it a valuable approach for organizations seeking to optimize their project delivery processes.
6. PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments)
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a widely adopted project management methodology developed by the UK government. It provides a structured and process-driven approach to project management, emphasizing flexibility and adaptability.
PRINCE2 divides projects into manageable stages, with defined roles and responsibilities, ensuring organized and controlled project execution.
The methodology consists of seven processes:
- Starting Up a Project (SU): Ensures project prerequisites are in place.
- Initiating a Project (IP): Defines project scope, objectives, and plans.
- Directing a Project (DP): Provides senior management with chief controls.
- Controlling a Stage (CS): Manages day-to-day project activities.
- Managing Product Delivery (MP): Ensures efficient product work.
- Managing a Stage Boundary (SB): Focuses on transitioning between stages.
- Closing a Project (CP): Formally closes the project and ties up loose ends.
PRINCE2 is known for its focus on continuous improvement and adaptability, making it a valuable tool for delivering successful projects within time, cost, and quality constraints.
Boost your career with Bakkah’s PRINCE2 courses:
- PRINCE2® Training Course Online
- PRINCE2® Agile Foundation & Practitioner Online Course and Certification
7. Critical Path Method (CPM)
Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that identifies the critical path of activities, potential risks, team roles, and the sequence of tasks determining the shortest project duration. Key steps:
- Task Breakdown: Identify and sequence project tasks.
- Duration Estimation: Assign time estimates to tasks.
- Network Diagram: Create a visual representation of task dependencies.
- Critical Path Identification: Find the path critical for project completion.
- Float/Slack Calculation: Determine non-critical task flexibility.
- Resource Allocation: Efficiently allocate resources.
- Monitoring and Control: Monitor progress continuously, update schedules, and take corrective actions., update schedules, and take corrective actions.
CPM is an essential tool for effective project planning and control. It aids in prioritizing critical tasks, managing time constraints, and optimizing project schedules. CMP can be used in several projects, such as engineering, manufacturing, construction, and science.
8. Six Sigma ( Continuous Improvement Methodology)
Six Sigma is a data-driven project management methodology focused on improving process efficiency continuously and reducing defects or errors. Developed by Motorola in the 1980s, Six Sigma seeks to minimize variations and achieve higher levels of quality in processes. It is often applied in manufacturing and process improvement projects. Here is a concise overview of the Six Sigma project management methodology:
- Define (D): Clearly articulate the problem, project goals, scope, and customer requirements.
- Measure (M): Establish metrics, collect data, and measure baseline performance.
- Analyze (A): Use statistical tools to identify root causes of defects or inefficiencies.
- Improve (I): Develop and implement solutions, testing and refining as needed.
- Control (C): Establish measures to sustain improvements and prevent recurrence of defects or issues.
The Six Sigma methodology is often represented by the acronym DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control). Additionally, for more complex or considerable process changes, there is another phase known as DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify).
Bakkah provides certification levels such as Six Sigma Green Belt and Six Sigma Black Belt are available for individuals to demonstrate proficiency in applying Six Sigma principles and methodologies. Organizations implementing Six Sigma often experience enhanced efficiency, reduced defects, and improved customer satisfaction.
9. RAD (Rapid Application Development)
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a project development methodology that prioritizes quick iterations and prototypes over extensive planning.
It involves user participation throughout the process, parallel development of system components, and a flexible, adaptive approach. Prototyping is a key feature, allowing for continuous refinement based on user feedback. RAD aims to deliver a functional product rapidly, focusing on time and cost efficiency.
Popular RAD tools include Microsoft Visual Basic, PowerBuilder, and OutSystems. The methodology suits projects with changing requirements but may not be ideal for highly structured endeavors.
10. Incremental and Iterative Methodologies
Incremental development involves dividing the project into small increments, each delivering a part of the final product's functionality linearly. User feedback is integrated after each increment, providing ongoing adaptability and the ability to identify and correct issues early. This approach enables early delivery and reduced project risk.
On the other hand, iterative development goes through cycles or iterations, refining the entire system with each iteration. It is highly flexible and accommodates changing requirements throughout the development process.
11. Hybrid Methodologies
Hybrid methodologies in project development involve blending elements from different traditional and agile approaches to create a flexible and tailored solution. That allows teams to adapt practices based on the project's unique requirements, leveraging both structured planning and iterative development.
In a hybrid methodology, the most appropriate elements from each methodology are identified and combined harmoniously. Examples include combining Waterfall and Scrum or integrating lean principles with agile practices.
The goal is to manage risks effectively, enhance flexibility, and address the project-specific needs. Effective communication is crucial to mitigate potential challenges introduced by diverse practices integration.
12. Extreme Programming (XP)
XP is an Agile methodology that emphasizes collaboration, adaptability, and delivering high-quality software through practices such as continuous testing and frequent releases.
Extreme Programming methodology is one of the famous methodologies for managing and developing software and other technical projects. It is based on diverse principles and practices, focusing on increasing software quality and improving team productivity.
A team needs to follow this method if the project is fast-paced or subject to regular change and thus has a dynamic rather than static nature.
The Extreme methodology also aims to achieve productive cooperation between team members and increase the quality of the final product and its flexibility in the face of changes.
Here are the main principles and practices of Extreme Programming:
- XP is built on a set of core values, including communication, simplicity, feedback, and courage.
- Developers work in pairs, one writing code and the other reviewing it in real time. That promotes collaboration, knowledge sharing, and code quality.
- Developers write tests before writing the actual code. That ensures that the code meets specifications and facilitates maintenance and updates.
- Code is integrated frequently to identify and address integration issues early in the development process.
- XP improves code design regularly without changing its functionality.
- XP keeps the design as simple as possible, making it easier to understand, modify, and maintain.
- Frequent and direct interaction with the customer allows for quick adjustments to changing requirements and priorities.
- XP emphasizes continuous improvement through regular reflection on the development process and changes in implementation to enhance efficiency and quality.
Bakkah provides a variety of accredited project management Courses for all professional certificates in project management, risk management, and others.
In brief, choosing the most suitable project management methodology depends on factors such as project size, complexity, industry, and organizational culture. Project managers often customize or combine methodologies to best fit the unique requirements of their projects.
Project management methodologies are often supported and implemented using various tools to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and communication throughout the project lifecycle. Here are some commonly used tools associated with project management methodologies:
1. Project Management Software
Tools like Microsoft Project, Asana, Jira, Trello, and Monday.com provide features for project planning, scheduling, task assignment, and progress tracking.
2. Version Control Systems
Git, SVN (Subversion), and Mercurial help manage changes to source code and documentation, ensuring version control and collaboration in software development projects.
3. Communication and Collaboration Tools
Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Discord facilitate real-time communication, file sharing, and collaboration among team members, supporting Agile and remote work environments.
4. Gantt Charts
Tools like GanttPRO and SmartDraw help create visual representations of project timelines, tasks, and dependencies, commonly used in Waterfall and traditional project management methodologies.
5. Kanban Boards
Trello, KanbanFlow, and LeanKit enable teams to visualize work and optimize workflow, particularly in Agile and Lean methodologies.
6. Scrum Tools
Jira, VersionOne, and Targetprocess support the Scrum framework with features for sprint planning, backlog management, and burndown charts.
7. Resource Management Tools
Workfront, Mavenlink, and TeamGantt assist in resource allocation, workload tracking, and managing team capacity in project management.
8. Risk Management Tools
RiskWatch, RiskyProject, and ProjectManager.com help identify, assess, and manage risks throughout the project lifecycle.
9. Collaborative Document Management
Tools like SharePoint, Google Workspace, and Dropbox Business enable teams to collaborate on documents, share project-related files, and ensure version control.
10. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) Tools
Jenkins, Travis CI, and GitLab CI/CD automate integration code changes process and deploying software, commonly used in Agile and DevOps methodologies.
11. Time Tracking and Timesheet Tools
Harvest, Toggl, and Clockify assist in tracking project-related activities, allowing for accurate time management and resource allocation.
12. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Tools
Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM support customer-centric projects. That helps teams manage client interactions, feedback, and requirements.
Project managers and teams should carefully select tools that align with their chosen methodologies and project requirements. Integrating these tools can significantly improve project management efficiency and contribute to successful project outcomes.
Project management methodologies involve various techniques to plan, execute, and control projects effectively. Here are some commonly used techniques associated with project management methodologies:
1. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Break a project into smaller, manageable tasks and create a hierarchical structure to define clearly the scope and deliverables.
2. PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) and CPM (Critical Path Method)
Techniques for scheduling and managing tasks by identifying critical paths and dependencies and estimating project duration.
2. SWOT Analysis
Evaluate the project's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
3. Risk Management
Identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks throughout the project lifecycle to minimize potential negative impacts.
4. Stakeholder Analysis
Identify and analyze stakeholders to understand their interests, influence, and expectations and ensure effective communication and engagement.
5. PERT Charts (Program Evaluation and Review Technique)
Graphical representations of project tasks and their dependencies, helping visualize the project schedule and critical path.
6. Scrum Meetings
Daily Standups, Sprint Planning, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective are regular Scrum meetings that facilitate communication and collaboration in Agile projects.
7. Earned Value Management (EVM)
Analyze project performance by measuring the planned value, earned value, and actual cost to assess progress and forecast future performance.
8. Quality Management
Implement techniques such as quality audits, inspections, and control charts to ensure project deliverables meet predefined quality standards.
9. Mind Mapping
Visualize project ideas, requirements, and tasks using mind maps to stimulate creative thinking and organize information in a structured way.
10. Critical Chain Method
Identify and manage resource dependencies to optimize project schedules and improve overall performance.
11. Prototyping
Creating a working model or prototype of a product or system to gather feedback early in the development process is common in Agile and iterative methodologies.
12. Benchmarking
Compare project performance metrics and processes against industry standards or best practices to identify areas for improvement.
13. Dependency Mapping
Identify and visualize dependencies between different tasks or project activities to understand their interrelationships and potential impacts.
14. Agile Estimation Techniques
Use techniques like Planning Poker, Relative Sizing, and Story Points to estimate the effort required for Agile project tasks.
15. Change Management
Implement strategies and techniques to manage and communicate changes effectively, ensuring minimal disruptions to project progress.
16. Communication Plans
Developing plans outlines how project information will be communicated to stakeholders, ensuring clear and consistent communication.
These techniques are often applied based on the specific requirements, characteristics, and principles of the chosen project management methodology. Project managers may tailor and combine these techniques to suit the needs of their projects.
Choosing a suitable project management methodology is crucial for the success of a project. The decision should be based on the project's characteristics, team dynamics, organizational culture, and the nature of the work to be performed. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to choose a project management methodology:
1. Understand Project Requirements
Clearly define the project scope, objectives, and deliverables. Consider the size, complexity, and nature of the project work.
2. Assess Team Skills and Experience
Evaluate the skills and experience of the project team. Consider their familiarity with different methodologies and their adaptability to new approaches.
3. Consider Project Flexibility
Assess the level of flexibility required throughout the project. Some projects may benefit from a more adaptive and iterative approach, while others may require a more structured and sequential process.
4. Examine Project Constraints
Identify any constraints such as budget limitations, time constraints, regulatory requirements, or client preferences that may influence the choice of methodology.
5. Evaluate Organizational Culture
Consider the existing organizational culture and whether it aligns with the principles of certain project management methodologies. Some organizations may prefer traditional, plan-driven approaches, while others may be more receptive to Agile or iterative methods.
6. Define Stakeholder Involvement
Determine the level of involvement and collaboration required from project stakeholders. Some methodologies, like Agile, emphasize continuous stakeholder engagement and feedback.
7. Analyze Project Risks
Evaluate the potential risks associated with the project. Some methodologies, such as Agile, are well-suited for projects with high uncertainty and evolving requirements.
8. Review Industry Standards
Consider industry standards and best practices. Certain industries or project types may have specific guidelines or regulations that align with particular methodologies.
9. Explore Hybrid Approaches
Assess the possibility of combining elements from different methodologies to create a hybrid approach tailored to the project's specific needs.
10. Pilot or Prototype
If feasible, consider running a pilot or prototype using a small-scale version of the project to test how well a methodology fits the team and project requirements.
11. Consult with Stakeholders
Seek input from key stakeholders, including team members, clients, and sponsors. Understand their preferences, expectations, and concerns regarding project management approaches.
12. Training and Transition Plan
Evaluate the readiness of the team to adopt a new methodology. Plan for necessary training and establish a transition plan to smoothly implement the chosen methodology.
13. Continuous Improvement
Be open to evaluating and adjusting the chosen methodology throughout the project. Continuous improvement is essential to address evolving project needs and improve overall project management processes.
Elevate your project management skills with Bakkah Learning's expert-led courses. From PMP to Prince2, Six Sigma to Agile, we offer tailored programs to suit your career goals. With interactive learning, flexible access, and certification preparation, we're your partner for professional growth. Start your journey to mastery today with Bakkah Learning!
Here are some Project Management Courses :
- Certified Associate in Project Management CAPM Course
- PMI-ACP® certification
- PgMP certification
- PMI Scheduling Professional - PMI-SP certification
Risk Management Courses And Certifications:
- Risk Management Professional - PMI-RMP Course
- MoR Certification and course
PRINCE2 Courses
- PRINCE2 Certification
- PRINCE2 Agile.
Project Management Tools:
- Primavera P6 Course
- MSP Course - Managing Successful Programmes
- Microsoft Project training course
Portfolio Management
- P3O Foundation certification
- Management of Portfolios MoP
- The Portfolio Management Professional – PfMP certificate
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Course
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Course
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Course
Ultimately, the choice of a project management methodology should be a thoughtful and informed decision that aligns with the unique characteristics of the project and the organization. Regularly reassess the chosen methodology to ensure its continued effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
Related Courses
Our learning programs are delivered through a tested and professionally designed methodology.

3,737.5 SAR
Live Online

5,621.2 SAR

6,152.5 SAR
Exam is included

Your experience on this site will be improved by allowing cookies.
Added to Cart
{{ convertjson(lastcartitem.course.title) }}, features with this course, total with vat, {{ parsefloat(totalfeatures(lastcartitem)) }} {{currency}}.

Organizational culture and project management methodology: research in the financial industry
International Journal of Managing Projects in Business
ISSN : 1753-8378
Article publication date: 30 March 2021
Issue publication date: 9 August 2021
Organizational culture has an impact on various activities in organizations, including project management (PM). The aim of the study is to answer the following research questions: RQ1: what significance is attributed to organizational culture compared to the objective project characteristics when choosing the dominant PM methodology in organizations? RQ2: which type of organizational culture is preferred for successful implementation of different PM methodologies? RQ3: what kind (if any) of relationship exists between the dominant type of organizational culture in organizations and the dominant PM methodology?
Design/methodology/approach
The author surveyed 100 project managers working in the financial industry in Poland with the use of personal structured interviews. The competing values framework (CVF) concept authored by Cameron and Quinn was used.
Project managers find organizational culture more important than objective project characteristics when choosing the dominant PM methodology in an organization. Although statistical analysis revealed a significant relationship between the preferred type of organizational culture and PM methodology, there is no significant relationship between the existing type of organizational culture and the PM methodology which prevails in the company.
Research limitations/implications
Future research should investigate other industries and other typologies of organizational culture.
Practical implications
The paper provides recommendations for management practice on how to shape organizational culture in the context of successful PM with the application of different PM methodologies.
Originality/value
This study fills a gap in the theory of PM by identifying and empirically verifying the theoretical linkage between the type of organizational culture and PM methodology.
- Human resource management
- Management approach
- Corporate culture
- Project success
- Organizational behavior
- Project competencies
- Eople in project-based organizations
Piwowar-Sulej, K. (2021), "Organizational culture and project management methodology: research in the financial industry", International Journal of Managing Projects in Business , Vol. 14 No. 6, pp. 1270-1289. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJMPB-08-2020-0252
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2021, Katarzyna Piwowar-Sulej
Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Introduction
The interest of researchers and practitioners in intangible management factors increased in the 1980s. Other types of noneconomic reasons which can affect the success or failure of an enterprise were investigated ( Webster and Jensen, 2006 ). Among these factors, organizational culture was of particular interest ( Alvesson, 1990 ).
Organizational culture represents the collection of beliefs, values, norms, attitudes and assumptions which dominate in a company and which do not have to be formulated. This set of elements influences people's behavior and the accomplishment of their tasks ( Schein, 1990 ). The culture which connects people in an organization remains very closely linked to the organization's performance ( Denison and Mishra, 1995 ; Martins and Terblanche, 2003 ; Mathew, 2007 ; Lucas, 2006 ; Hartog and Verburg, 2004 ). This is the key factor in fulfilling the company's mission and implementing its strategy while improving organizational efficiency and managing transformations.
Radical changes in the functioning of organizations have occurred within the last few decades. The increasingly uncertain and competitive environment and the growing expectations of customers and employees have forced companies to introduce changes. Repetitive, routine operations are gradually losing importance in favor of unique and complex activities – i.e. projects ( Piwowar-Sulej, 2020 ). In the 1990s, Drucker wrote that in 20 years, a typical large company would have half as many managerial levels and particular tasks would be performed by specialists focused on specific projects, functioning alongside traditional departments ( Drucker, 1992 ). Today, even in those industries where traditionally repetitive activities have been the basis of their operations, projects are beginning to play an increasingly important role.
One example of such an organization is a financial company. Every day, the main processes related to sales, e.g. loans and after-sales service, are carried out. Ancillary processes include administrative activities. The purpose of subsequent projects is, e.g. to open a new branch, to launch a new product or to develop an advertising campaign. Project initiation in organizations based on traditional structures involves the need to mobilize resources which belong to multiple organizational units, for the objectives to be carried out in a specific time frame and to be managed by project managers. An employee frequently performs a dual role: as a specialist in his/her line department and as a project team member.
A project can be defined as an “endeavor in which human, material, and financial resources are organized in an innovative way to carry out an extraordinary scope of work, in line with the defined specifications, within cost and time constraints, to achieve a positive change determined by quantitative and qualitative goals” ( Turner, 1993 , p. 8). Project management (PM), in turn, is the “application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques in relation to project activities in order to meet or exceed the needs and expectations of stakeholders associated with the project” ( Ward, 2000 , p. 468).
Projects can be managed in accordance with guidelines presented in PM methodologies. These methodologies are referred to as guides to the types of documentation and eligibilities necessary to complete particular project stages. The literature on the subject offers two general approaches toward running projects: traditional (managerial) and modern (agile, adaptive, dynamic or light). The traditional approach has its roots in the 1950s, while the modern one is from the 1990s. Traditional methodologies describe major processes and present, in a systematized way, a set of verified management techniques. Moreover, they imply that each stage of the project can only be initiated when the previous one has been fully completed. They also stress the completeness of documentation. Such an approach has become insufficient over the years, especially for software development projects ( Berger and Beynon-Davies, 2009 ). In the agile approach, the actions are adapted on an ongoing basis. The differences between these two approaches to PM should be also expressed in organizational culture because one of the main causes of project failure presented in the literature on the subject is that the organizational culture in which projects have to be delivered is not suitable for projects ( Larson and Gray, 2011 ).
The aim of the study is to present the significance of organizational culture as a factor which determines the choice of PM methodologies and the relationships between the two. In the first section of the paper, previous research in the literature on the linkages between organizational culture and PM issues is presented. This was the basis of the research questions. The second section, i.e. the empirical part of the paper, presents original research with its methodology, results and discussion. The paper ends with conclusions, limitations and directions for further research. It contributes to the scientific knowledge by (1) identifying and describing the linkages between the type of organizational culture and the type of PM methodology, (2) verifying the assumption through original research findings and (3) presenting directions for future research.
Literature background
Organizational culture and successful project management.
Organizational culture – like the subconscious – affects the aspirations, attitudes and behavior of employees. It focuses their actions along routine tracks in a nonverbal, imperceptible manner. Therefore, culture can be used to encapsulate all that is omitted from a written contract, offering it up as an all-encompassing psychological contract to address different situations ( Camerer and Vepsalainen, 1988 ). By influencing and consolidating certain attitudes and behaviors of employees, it may not be conducive of effective actions – it may even counteract them. Obviously, it can also support the functioning of an organization by facilitating human interactions.
Organizational culture is a concept which combines all of the various activities undertaken in an enterprise (including PM). This means that the implementation of PM can result in transformations in organizational culture. In turn, attributing the proper characteristics to an organizational culture beforehand can lead to favorable circumstances for the implementation of PM. The Organizational Competence Baseline ( International Project Management Association, 2016 ), as a guideline for setting up an appropriate organization for PM, emphasizes organizational alignment, which includes processes, structures and culture. Kerzner (2000) states that PM is more similar to a culture than policy or procedures. Finally, Cleland states that “project management meets the need for providing an organizational focus not found in the traditional form of organization. However justified, project management should not be used until the leaders of the organization are committed to its use and are willing to prepare a suitable culture for project management to germinate and grow” ( Cleland, 1994 , cited in Du Plessis and Hoole, 2002 ).
The literature on PM presents the issue of a specific culture, which covers strictly defined features that support the implementation of changes in an organization or in teamwork. At this point, however, it is worth emphasizing that in papers addressing the problem of PM, such terms as “project culture,” “project management culture,” “project climate” and “project environment” function interchangeably ( Du Plessis and Hoole, 2006 ). The climate, in turn, is only an external, easily observable layer of culture and stands for the subjective feelings of employees when referring to the atmosphere in the workplace ( Ostroff et al ., 2012 ).
The review conducted by Henrie and Sousa-Poza (2005) spanning the years 1993–2003 indicated that culture was not a widely reported or discussed topic in PM literature (journals specializing in PM). Today, we can say that various cultural aspects of PM are a popular research topic. A total of 557 documents were returned in a search of the Scopus database on February 28, 2020, with the following combination of queries: TITLE-ABS-KEY (“project management” AND “culture”) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “ar”) AND (LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA, “BUSI”) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, “English”). Another situation is when we search using more detailed terms like “project management culture” or “project culture”. The query “TITLE-ABS-KEY (‘project culture’) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, ‘ar’) AND (LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA, ‘BUSI’) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, ‘English’)” resulted in 33 documents and “TITLE-ABS-KEY (‘project management culture’) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, ‘ar’) AND (LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA, ‘BUSI’) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, ‘English’)” resulted in only in seven articles.
For example, Belassi et al . (2007) found a significant relationship between culture, a positive work environment with strong leadership and the success of projects for developing new products. A “positive work environment” refers to the perception of employees that it is their performance which matters most to their organization and that they feel free to open dialogues with their bosses. “Strong Leadership” means that long-term goals are the focus of all of top management's decisions and that employees are encouraged to keep trying if they fail in the process of creating something. Data for this research were collected from 95 manufacturing companies in the USA.
Ajmal and Koskinen (2008) discussed the impact of organizational culture on knowledge transfer in “non-project businesses” who adopt a “project-style” approach. The problem of such organizations is that knowledge created in one project is not transferred to future projects. The authors stated that for effective knowledge transfer in project-based businesses, it is the organizational culture must be ready to accept and adopt new ways to transfer knowledge. The role of project managers is to form one project culture out of differing organizational and professional cultures and to promote effective knowledge management.
The findings of Nguyen and Watanabe (2017) in the construction industry show that alignment of goals, the commitment of contractors and a focus on workers all lead to better performance and satisfaction among those involved. Labor productivity can be predicted using only two indicators of culture: contractor commitment and a cooperative attitude. In order to predict learning performance, goal alignment, trust and contractor commitment are key.
Morrison et al . (2008) provided evidence that organizational culture correlates with the effectiveness of PM. In particular, one should look to the relatively strong link between effective PM and such values as respect and interfunctional integration. Their study was conducted among matrix organizations representing a wide variety of industries. The majority were civil engineering consultancy firms (28%), while the other participating organizations were from the defense industry (17%), the government sector (14%), the industrial engineering and manufacturing sector (14%) and the finance and insurance industry (10%); the remaining participants (17%) came from the mining, national parastatal, telecommunications and information technology (IT) industries.
In turn, Graham and Englund (1997) outlined their eight factors which lead to successful projects: strategic emphasis, upper management support, project planning support, customer/end-user input, project team development, project execution support, communication and information system and organizational support. With these factors in place, teamwork and interfunctional tasks are emphasized, conflicts are identified and resolved and perfection is the driving force ( Larson and Gray, 2011 ).
In addition, project culture is based on values such as mutual trust, respect, open communication and risk and conflict tolerance of the disciplines, combined with a flexible, results-based approach and support and faith in making the right decisions, kindness and adherence to professional ethics ( Pinto and Slevin, 1987 ).
Some researchers have addressed the issue of national culture's influence on project outcomes. Building on Hofstede's work ( Hofstede, 1998 ), they feel that national culture shapes organizational culture, which, in turn, affects the execution of projects. Hofstede delineated such cultural dimensions as power distance, the degree of uncertainty avoidance, individualism and collectivism and long- or short-term orientation. Attention is primarily drawn to projects carried out by international teams and the fact that education in cultural differences can be necessary for them to be successful ( Shore and Cross, 2005 ). For example, the high power distance typical of people from Hong Kong can lead to the acceptance of inequality and the legitimacy of power groups within a project ( Rowlinson and Root, 1996 ). The impact of national differences on the specific tasks which make up PM, e.g. risk management, has also been analyzed. Risk is perceived and dealt with differently in different cultures. For example, one commonly held notion about Polish culture is the avoidance of uncertainty. This cultural trait can result in many rigorous terms and conditions being included in agreements with contractors ( Liu et al ., 2015 ).
National culture is also thought to play a role in the use of PM, in terms of the level of knowledge in this field and the extent of staff involvement in project work, as well as the adaptation of project discipline by individuals and groups. There is evidence that this deployment negatively correlates with both power distance and uncertainty avoidance but does not correlate with measures of individuality or masculinity ( Bredillet et al ., 2010 ).
There are many typologies of organizational cultures. Some of these locate organizational culture within the intensity scale of one feature (e.g. Hall's concept, ( Hall, 1976 )). Others are more complex, based on more than one dimension (e.g. the typology of Cameron and Quinn (2011) ). For example, Kivrak et al. (2014) used Hall's typology ( Hall, 1976 ) to illustrate how national culture determines knowledge sharing in an international project team. This typology distinguishes high- and low-context cultures. The messages in a low-context culture are unambiguous and fairly accurately reflect the speaker's intentions, requiring little additional context and leaving little room for interpretation. In the case of high-context communication, the message can be ambiguous and can constitute a strong barrier in the process of tacit knowledge sharing, according to some studies. Such cultural features as hierarchy and competition can also be an obstacle to knowledge sharing in international project teams. Kivrak et al. (2014) also showed that collectivism is conducive to knowledge sharing, though only within a project team (not with outsiders).
Silva and Gomes (2015) conducted research focusing on the typology of cultures proposed by Handy (1983) , who identified four characteristic types of organizational culture: power-, role-, goal- and people-oriented cultures. It is worth noting here that the goal culture is directly referred to as the task or project-oriented one. Organizations oriented toward goals treat tasks and their implementation as the most important issue. Individual competences and their contributions to specific actions are what matters most. Teams which follow these principles are able to easily adapt to the requirements of the situation. Groups and task teams are formed for specific purposes which determine the point behind their existence. Such a team works fast and makes decisions quickly. Individual team members enjoy flexibility and freedom but also face the responsibility for their work. The effects matter. Mutual relationships are usually quite loose, based more on the value of skills and input than age and formal status. The focus on action allows problems to be solved through discussions and negotiations, which provides a sense that solutions are created together. Such teams usually thrive in a dynamic and highly competitive environment. The qualitative research based on surveys with 12 respondents carried out by the abovementioned authors shows that diverse cultural types are present in different organizations which implement projects. The characteristics of the particular industry (e.g. energy, government or university) are important here. In addition, projects can be successful when other factors – apart from culture – also affect this success (e.g. selection of an appropriate PM methodology).
Although the studies presented above were focused on the cultural typologies by Hall and Handy, the hypothesis can be formulated that the typology of organizational cultures by Cameron and Quinn (2011) is most often discussed in studies addressing PM problems, although the output of management sciences includes numerous classifications of organizational cultures. The assessment tool proposed by these authors, the competing values framework (CVF), allows a company to identify a dominant cultural type across six key characteristics: dominant characteristics, leadership, human resources management (HRM), organizational glue, strategic emphasis and criteria of success. The CVF explains the complex nature of culture according to two dimensions: internal/external focus and stability/flexibility structure. These two dimensions create four quadrants, which represent four culture types: clan, adhocracy, hierarchy and market.
Clan culture is connected with a friendly, almost family-like atmosphere. A manager is treated as a mentor. The glue of an organization is loyalty and tradition. The key to success is usually taking care of the needs of clients and employees. The values are teamwork, participation and consensus.
Adhocracy comes from the Latin term “ad hoc,” which means “for this special purpose” and by extension and improvised. Adhocracy is a corporate culture which is based on the ability to adapt quickly to changing conditions – which can we define as agility. Organizations with such culture are characterized by flexibility, creativity, employee empowerment and an emphasis on individual initiative (with risk-taking). Although corporate levels exist in an adhocracy, they are less strictly defined than in more hierarchical environments. In a more general sense, adhocracy contrasts with bureaucracy, which is characterized by inflexibility and a rigid adherence to rules.
Hierarchy culture means a working environment which is structured and formalized. Employees use defined procedures in carrying out their everyday tasks. The values are effective coordination and order. The primary goal is to maintain effective functioning and stability, and the results are achieved by performing tasks efficiently. Success is defined by good planning and low costs.
Finally, market culture focuses on customer satisfaction and shareholder value. It emphasizes targets and deadlines. People are competitive and focused on goals. Leaders are hard drivers, producers and rivals. They can be tough with high expectations. The emphasis on winning keeps the organization together. Reputation and success are the most important. Long-term focus is on rival activities and reaching goals. Market dominance, achieving goals and great metrics are the definitions of success. Competitive prices and market leadership are important. The organizational style is based on competition.
For example, the research conducted by Yazici (2009) in the USA involving 86 project managers in 76 companies indicated a strong correlation between clan culture and high project effectiveness and overall organization performance. It appears that this type of culture – one focused on employee participation, social cohesion, shared values, commitment and high morale – guarantees that project goals will be achieved, client expectations will be met within the adopted time frame and satisfaction among team members will be high. Among the hypotheses presented by Yazici, attention should be paid to one in particular: “Project maturity and organizational culture have a joint impact on project implementation.” This joint impact, however, was not confirmed by the study. In total, 56% of the respondents were from the service sector (IT, banking, education, healthcare, consulting, retail and utility); 34% were from the manufacturing sector and only 10% were from government or construction.
Adhocracy and clan cultures have positive effects on tacit-oriented knowledge management strategy ( Keskin et al. , 2005 ). Wiewióra et al. (2012) in their research focused on knowledge management in projects. It was confirmed that clan culture – which promotes a collaborative environment in which people are encouraged to communicate – facilitates knowledge sharing between project team members. In turn, market culture, centered around such values as competitiveness, achievements and the focus on performance measurements, will probably hamper knowledge and skill sharing within the project. However, according to a study by Piwowar-Sulej (2014) , projects can be also successfully completed in organizational cultures with dominant “hierarchical-market” features.
Similar conclusions were drawn by Mashiane (2013) , who conducted research in a division of telecommunications company. The questionnaire was based on the management skills assessment instrument (MSAI) developed by Cameron et al. (2006) and on the project management culture assessment tool (PMCAT) developed by Du Plessis (2005) . A market-oriented culture was identified as the dominant one in the organization under study. This was not surprising for the researcher because the organization provides infrastructure hosting solutions and technical support to external clients. The strategy of the organization focuses on the market or on clients, and success is defined in terms of client satisfaction and retention. The second most dominant type of culture was adhocracy.
Finally, according to 50 human resources (HR) specialists from medium-sized and large companies, the most suitable culture for PM is adhocracy ( Piwowar-Sulej, 2016 ). These results are surprising in the context of new developing HRM concepts, such as sustainable HRM, which promotes long-term orientation and HR development ( Stankevičiūtė and Savanevičienė, 2019 ; Piwowar-Sulej, 2021 ). It should be mentioned that in the long run, adhocracies can turn out to be effective organizations, though they do not offer stable workplace environments.
Project management methodologies
As mentioned before, there are two main types of PM methodologies, i.e. the traditional one (Project Management Body of Knowledge – PMBoK – or Prince2) and the modern/agile one (which is more flexible, e.g. Scrum). Table 1 presents a comparison of these two approaches to PM.
The traditional methodology involves the mechanistic division of work, with an underlying assumption of manageability and predictability ( Saynisch, 2010 ). This approach is synonymous with the waterfall methodology. It was first outlined in 1970 by Royce, an American computer scientist and director at Lockheed Software Technology Center in Texas, as a response to managing the increasingly complex nature of software development. This approach takes the perspective that rigorous, hierarchical control best manages complexity.
The waterfall methodology is sequential. One phase continues downstream into the next stage. Each stage in this process is self-contained. The project work starts by collecting and analyzing requirements, designing a solution, implementing the solution and fixing any issues. The initial phases of the project are intended to set the stage for all project work, as well as establishing the project's scope and the requirements that are necessary to deliver it ( Thomas and Fernández, 2008 ). It is also heavily focused on requirements. One needs to have a crystal clear idea of what the project will demand before proceeding further. There is no room for correction once the project is underway.
Agile is a term which formally came into being in 2001 when several IT representatives released the “Agile Manifesto” during a meeting of 17 major players of new software development methodologies in Snowbird, Utah. Agile means “able to move quickly and easily” or “able to think quickly, mentally acute, or aware” ( Dictionary.com, 2020 ). Agile is used as a term which characterizes a given way of thinking (mindset) about complex task management (from projects to entire organizations), including openness toward change and high flexibility. The notion is also used in relation to all agile PM methodologies (e.g. Scrum, Extreme Programming or the dynamic systems development method), which are based on principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto ( Agilemanifesto.org, 2020 ).
The reason for declaring the Agile Manifesto was the increasing number of failed software development projects which were based on the waterfall approach. The inefficiency of the waterfall approach was and is connected with one of the basic assumptions of this model, i.e. focusing on delivering an IT project in the form which was specified in the first stage. Moreover, a project is carried out in organized, distinct and – in most cases – lengthy stages which makes it difficult to verify results in the course of the project. This way of working is not conducive to a culture of cooperation and ongoing communication, and it has a negative impact on the end result of a project.
The essence of agile PM lies in the fact that a project's goals are defined in less detail at the start of the project. The project schedule is also prepared approximately. The work is divided into equal iterations with assigned parts of the project scope. “In the beginning a team undertakes the most important functions, while leaving the least important ones for the end. Less important demands can later be omitted on the basis of the results of already finished iterations, the client's changed wishes/requests, the performers' proposals, or changes in the environment. A detailed specification of the iterations' products and precise scheduling of the iterations (the way of implementing, tasks, hours of work, performers, etc.) is created at the beginning of each iteration, taking into account the current results, new insights, the client's new wishes, or the ideas of developers, as well as changes to the original assumptions and requirements” ( Stare, 2014 , p. 297). The project team – not the formal project manager – is responsible for the execution plan and making the iterations.
Scrum is one of the agile PM methodologies. It implements working in “sprints” of 30 days and also focuses heavily on daily meetings (“daily scrum”) which are typically held in the same location and at the same time of day (preferably in the morning). The formal role of a project manager does not exist. There is a role of Scrum Master: a person who helps the team perform at the highest level. He/she also protects the team from both internal and external distractions and tries to fulfill Scrum values. The ideal size for a development team is between three and nine people, not including the Scrum Master and product owner. The team is self-organizing, cross-functional and as a team has all the skills necessary to create a product increment. There is no formal hierarchy within the teams. Scrum recognizes no titles for development team members, regardless of the work being performed by the person. Team members choose the project tasks themselves according to collective agreements, their skills and other factors (e.g. time). People who work on a team cannot be involved in other projects ( Schwaber and Sutherland, 2017 ).
Andersen (2006) states that an organization should apply methodologies assigned to specific types of projects. According to Cohen (2019) , traditional PM methodologies are best for short, simple projects, projects with clear and fixed requirements and projects with changing resources that depend on in-depth documentation, while the agile approach is appropriate for projects with no fixed end (with only a general idea of a product), when the project needs to accommodate quick changes and if collaboration and communication are more important than planning. Cohen emphasizes not only objective project characteristics, e.g. duration or complexity (with its many dimensions, see ( San Cristóbal et al. , 2018 )), but also organizational values (bureaucracy vs collaboration). The significance of organizational culture in comparison to objective project characteristics seems to be an interesting research topic.
Taking into account the objective project characteristics, it is worth noting that there is no common agreement on this issue. For example, Jovanović and Berić (2018) found that general characteristics of traditional methodologies (e.g. Project Management Institute [PMI] or International Project Management Association [IPMA]) make them more suitable for larger and more complex projects, such as investment or manufacturing, while agile methodologies are more appropriate for use in IT projects and some smaller and less complex projects, such as devising various studies, project reports, etc. Stare (2014) noted that almost all research studies published between 1999 and 2009 and focused on the agile approach referred to IT projects.
Špundak (2014) states that there are factors other than the characteristics of projects which determine the choice of PM methodology. Traditional PM methodologies are recommended if there is a lack of agreement between project team members or a huge fluctuation of project team members during the course of the project or if the contact between team members is more virtual. It is also possible that the nature of cooperation with external partners (contractors or suppliers) will be an important criterion in the selection of an appropriate PM methodology.
The relationship between specific features of organizational culture and PM methodology is an interesting research problem, as well. The features of “project management culture” presented above, such as trust or open communication, are so general that they will stimulate projects regardless of the PM methodology used. When trying to assess a relationship between a culture and a methodology, it is worth taking into account cultural differences – which are highlighted in organizational culture typologies.
Llanos et al . (2017) found that adhocracy culture has more positive impact on organizational agility than clan culture. On the basis of above-presented characteristics of agile PM, one can state that they are similar to clan culture or adhocracy culture, while the features of traditional PM are similar to hierarchy culture. However, at this point, it is worth highlighting the fact that the hybrid PM approach is currently being implemented as a combination of traditional and agile PM methodologies. In general, this new approach takes the best parts of both waterfall (e.g. a work breakdown structure) and agile (speed and leanness) and combines them in a flexible but structured approach. In hybrid, the planning is done using the waterfall approach, while the execution and delivery are handled by the agile method ( Cooper, 2016 ).
What significance is attributed to organizational culture compared to the objective project characteristics when choosing the dominant PM methodology in organizations?
Which type of organizational culture is preferred for successful implementation of different PM methodologies?
What kind (if any) of relationship exists between the dominant type of organizational culture in organizations and the dominant PM methodology?
Research methodology
This study investigates a subject that is rooted in two academic disciplines: HRM (and/or organizational behavior) and PM. Figure 1 presents the stages of the research process used for the purposes of this study. An exploratory and descriptive research design was chosen in order to identify the determinants of the choice of PM methodology and the abovementioned relationships between different factors and PM methodologies. The interpretative approach was used in this study, which means that the perceptions of the cultural factor from the viewpoint of practicing project managers were recognized as important ( Du Plessis and Hoole, 2006 ).
In order to eliminate biases, one should take into account the significant differences in organizational environment and types of projects. Thus, the research included 100 project managers working in different companies from the same industry. Companies from a given sector are influenced by the same external factors (the industry macroculture) – legal regulations – for example.
The respondents were employed in medium-sized and large enterprises (i.e. those which employ over 50 people) of the financial sector in Poland (banking, financial services, leasing and factoring). This industry implements many technological innovations in the form of projects. Important projects are aimed at developing security and risk management. The convenience for customers using financial services is also changing. Around 7–8 years ago, new-generation IT systems began to appear, replacing the previous ones which were based on a tabular approach. It was understood that the client not only needs accounting statements but also wants to learn how to spend and invest their money. Personalized solutions are also important. New products and services are constantly emerging. In addition, due to the changing and very restrictive legal regulations (e.g. regarding protection of personal data), companies are forced to implement changes in processes and IT systems. One can state that these regulatory projects take top priority and are often selected at the expense of other nonregulatory projects. The PM maturity level in the financial industry is high – in comparison with other industries in Poland ( Wyrozębski et al ., 2012 ).
According to data from the Central Statistical Office, in 2018, this sector consisted of main players such as 15 banks with private capital, 13 insurance companies, 47 companies specializing in credit intermediation or lending from their own funds, 11 factoring companies and 38 leasing companies ( Statistics Poland, 2019 ). It is worth noting that many companies run more than one business activity at the same tame (e.g. credit and leasing intermediation or leasing and factoring).
In order to collect the contact information of respondents, companies were selected from a list created from information accessible in secondary sources (listings of companies, websites, industry newsletters, etc.). The research, based on a quantitative approach, was conducted in December 2019 and January 2020. In the process of gathering information in the survey, the personal structured interviews (paper-and-pencil interview [PAPI]) method was used. The direct contact with respondents helped to avoid misunderstandings about the questions. Interviews with each of the respondents lasted about three hours. The interview questionnaire was designed for the purposes of a larger research project. This paper presents only the results which are pertinent to the chosen research questions and cultural typology, based on the CVF.
Statistical analyses were conducted with the use of IBM SPSS software. For the purpose of this paper, Pearson's chi-squared test and the Kruskal–Wallis test were used. These tests examine the relationship between two variables when at least one is qualitative. The chi-squared test allows the researcher to examine the significance of differences in percentage structures. It is based on comparing observed values (i.e. those obtained in the study) with expected values (i.e. those assumed by the test if there were no relationship between the variables). If the difference between the observed and expected values is large (statistically significant), it can be stated that there is a relationship between the two variables.
For the correct interpretation of the findings of the quantitative research, the in-depth interview method was used. Such interviews can provide much more information which builds a context to previous outcome data. They offer a more complete picture of the state and causes of a research problem. In total, three direct, unstructured interviews with project managers (from a bank, a leasing company and a credit provider) were used. Each of them lasted about one hour.
Results and discussion
At first, it is worth presenting the general characteristics of the industry in question. The CVF has already been discussed in relation to organizational culture in banking by Thakor (2015) , though the author did not conduct any empirical research on this topic. He only presented the assumptions of the CVF concept and implications for managers in banking. In turn, Barth (2015) showed that different types of organizational culture have different preferences for risk-taking. He found that banks with a market-oriented organizational culture have higher excess returns. Finally, Joseph and Kibera (2019) found that clan and hierarchy are the dominant cultural types in the microfinance industry in Kenya.
During the interviews conducted for this study, the dominant and secondary cultural types in the companies were identified. Table 2 shows the three cultural types which were indicated as being the dominant cultural type in the respondents' organizations as well as the dominant PM methodology used in the companies under study. Analysis revealed similar findings to above-presented resulted from research by Joseph and Kibera (2019) .
Clan culture – emphasizing development of shared understanding and commitment instead of a formalized communication process – is the most popular cultural type. At the same time, the cultural type most often indicated as a secondary one was market culture (54 responses). This type of culture is a results-oriented one. The “second” culture type in the survey was defined as one which simultaneously coexists with the first but is less expressed. The commonality between hierarchy culture and market culture is that both focus on stability and control. The difference lies in the fact that market culture promotes fast changes, while hierarchy lends itself more to incremental changes. In turn, adhocracy and market cultures have an external focus in common. The most interesting result is the combination of clan and market cultures because they are focused on completely different issues. The latter is focused on the outside of an organization, differentiation and fast changes, while the former focuses on flexibility, integration and long-term changes. These contrasting cultural types are combined in the form of employee participation (clan) linked with costumer focus (market). They can be also found together in hybrid PM methodology, which was the most popular one in the companies under study ( Table 2 ).
The in-depth interviews demonstrated that hybrid methodology was implemented because of problems with other, previously used PM approaches. At the beginning, the waterfall approach was used. A few years ago, agile PM methodology was implemented as a trendy new approach. However, numerous barriers have been noticed in the successful development of projects. Despite many years of working together, the employees had significant problems carrying out their new roles or even problems transferring their current roles to the new model. Other barriers were the unavailability or insufficient availability of internal clients and communication problems. The dominant position of traditional methodologies in the organization is associated with certain employee habits. The implementation of novelty in the form of agile moved them out of their comfort zone. The hybrid approach provided compliance with employee expectations, which is a characteristic of clan culture.
In addition, the priorities in some organizations change quite often (adhocracy culture) because of changes in legal regulations and – in the case of leasing companies – changes in the operations of the banks which finance the assets. The agile approach seems to be the most suitable in such situation. In turn, “hierarchical” banks had to meet the challenges in terms of ensuring the agile model's compliance with legal requirements. Official legal regulations emphasize a strong and active role of the bank's management board in the decision-making process and in the organization of day-to-day operations (hierarchy). The agile model assumes a limited role of the managing body. The management board is supposed to set the strategic goals but without interfering or supervising – choosing the way the goals are met. The hybrid approach allowed organizations to reconcile the business and legal requirements.
Respondents were asked about which factor has a greater impact on the project methodology used in the organization. They had the three following options to choose from: organizational culture (OC), project characteristics (e.g. duration, complexity, innovativeness and scope of cooperation with external partners) (P) and equal importance of organizational culture and project characteristics (OC + P). The results are shown in Table 3 .
The findings are partially in line with Špundak's (2014) statement that there are other factors than projects' characteristics which influence the choice of PM methodology. Organizational culture is seen to be a more important factor ( n = 41) than objective project characteristics ( n = 27) in the context of choosing the dominant PM methodology in organizations; however, a chi-squared test did not reveal any significant relationships between the factors taken into account ( χ 2 [4, N = 100] = 5.40; p = 0.249).
The research therefore shows that other factors or a bundle of factors should be taken into account when analyzing the basics of decision-making on the choice of a particular PM methodology. Špundak (2014) believes that the company size can play a role. He hypothesizes that large organizations are more likely to use the traditional approach because it helps them to control the work. However, the respondents who participated in this study worked in medium-sized and large companies, and the most frequently reported PM methodology was a hybrid one. As indicated in the in-depth interviews, such factors as the vogue for new PM approaches and the need to reconcile employees' needs (maintaining of tradition), business requirements (implementing innovations) and legal regulations are of great importance.
Results of previous research which utilized the CVF emphasized relationships between clan culture and project effectiveness ( Yazici, 2009 ) and clan culture and knowledge sharing in a project team ( Wiewiora et al. , 2012 ). The presented research shows clan culture in a slightly different context. Table 4 presents the types of organizational culture that are preferred for successful implementation of different PM methodologies.
Within the traditional PM methodology, hierarchy culture (70%) was considered to be the most appropriate environment; clan culture followed by adhocracy is considered being the most appropriate environment for agile approach. The results are reverse in relation to findings obtained by Llanos et al . (2017) in their research on the impact of organizational culture on the organizational agility. Contrary to expectations, this research also revealed a positive link between hierarchy culture and agile Approach. As Llanos et al . (2017) stated, such findings may suggest that certain features inherent to hierarchy culture lead to more agile management. Finally, according to the respondents, a successful implementation of hybrid PM methodology requires an adhocracy culture. The relationship between preferred cultural types in the context of different PM methodologies is statistically significant ( χ 2 [4, N = 100] = 81.47; p < 0.001).
These findings were compared with the cultural types indicated as dominant in the respondents' organizations. Due to the low number of indications of the “Market culture” variant ( Table 2 ) as the dominant cultural type, a reliable measurement with the chi-squared test of the relationships between all cultural types and PM methodologies in the organizations studied was not possible. However, focusing on only the three most popular types of organizational culture, it can be stated that there is no significant relationship between existing dominant cultural types and existing dominant PM methodology ( χ 2 [4, N = 91] = 1.02; p = 0.907).
Next, a series of Kruskal–Wallis tests was conducted in order to examine whether there is a relationship between the dominant culture and the indicators of project effectiveness (see Table 5 ). The respondents noted the percentage of successful projects, taking into account criteria such as time, budget and scope requirements and achieving client, team member and supplier satisfaction.
Project success strictly depends on team members commitment ( Araujo and Pedron, 2014 ), and Acar (2012) found that clan and adhocracy cultures have positive effects on employees' commitment. This study did not confirm previous findings that only clan culture ensures high project effectiveness ( Yazici, 2009 ). The analysis revealed a statistically significant difference between the types of dominant cultural type and “Project completed within the project scope requirements” ( X 2 [3] = 10.75; p = 0.013). The follow-up pairwise comparison showed that the project managers who chose hierarchy as the dominant cultural type (mean = 93.94; median = 100) regarded project completion to be more successful than those who chose clan as the dominant culture (mean = 87.77; median = 90; p = 0.030). No other statistically significant differences were found. The reason for these discrepancies can be a national culture and composition of team members related to their individual values. Yazici (2009) conducted research in the USA, while this paper presents research conducted in Poland. For respondents – project team members – the best cultural environment for traditional PM can be hierarchy; however, people working in projects can represent individual values congruent with adhocracy-specific values. This congruency contributes to organizational performance outcomes ( Titov and Umarova, 2017 ).
As was highlighted during the in-depth interviews, measuring the impact that culture may have on project outcomes is difficult. The level of project success is influenced by many factors, both endogenous and exogenous. Internal factors include the competencies of the project team and individual values of team members. The competences – according to the respondents – seem to be the most important factor since highly skilled project managers and project team members can deliver high-quality project outcomes, despite an unfavorable organizational culture.
Conclusions, implications and directions for further research
This research contributes to knowledge by showing a linkage between the type of organizational culture and the type of PM methodology. In answer to RQ1 , it can be said that organizational culture is seen as the most important factor which determines the PM methodology used as the standard in organizations. When it comes to RQ2 , the results of both theoretical studies and empirical research show that the most appropriate cultural type for traditional PM is hierarchy. Clan culture is most suitable for agile PM approach, while adhocracy is best for hybrid PM methodology. Nevertheless, in practice, there is no relationship between the dominant type of organizational culture and the dominant PM methodology ( RQ3 ). Moreover, projects – taking into account five out of the six project success indicators – are equally likely to be successfully completed, despite differences in organizational cultures.
There are several recommendations for management practice based on this research. Firstly, organizational culture can be developed intentionally ( Gagliardi, 1986 ; Bendak et al. , 2020 ). There is still room for improvement in the field of project effectiveness. The missing percentage of successfully completed projects could be made up with a more suitable organizational culture. Therefore, it is worth determining both current and expected cultural types by the use of survey and/or interviews among project team members and other employees. On this basis, managers should take up actions which will stimulate a cultural transformation of the company. They have to play a role of ambassadors of changes ( Kane-Urrabazo, 2006 ).
If, for example, organizational culture should have more clan features, managers should turn to their employees, find what people value, use open feedback in order to collect employees' ideas and allow them to act. Inspirational motivation (by, e.g. trust and pushing decisions to the lowest levels, allowance for mistakes) and individualized consideration effects clan culture ( Chan, 1997 ; Acar, 2012 ). Design of the workspace is also important. In clan culture, teams have to interact effectively with one another. Therefore, smaller footprints should be allocated to the individual than the team and workstation panel heights should be lower, if not nonexistent ( ISS, 2020 ). In turn, transformation into more hierarchical culture requires buttoning up processes, ensuring clear goals for teams and individuals and a workspace which provides a sense of stability. Management-by-exceptions also effects hierarchy culture ( Acar, 2012 ).
Secondly, human competencies are of the utmost value. A good understanding of the cultural aspects of PM is also emphasized. Conscious project managers and highly skilled team members will be able to deliver a high-quality product despite an unfavorable organizational culture. There is a need to develop not only technical but also cultural competences. The importance of these competencies has been so far discussed but mainly in the context of multinational projects ( Isern, 2015 ; Vlahov et al ., 2016 ). Training in this issue is a developmental field for educational institutions.
This paper has two main shortcomings, though it nevertheless provides directions for future research. Firstly, the sample population in this study was collected from project managers working for companies in the financial industry in Poland. In order to extend the applicability of the findings, more samples from different industries – and even from different countries – should be studied. Secondly, all respondents were project managers who volunteered to participate in this research. They subjectively assessed the dominant and coexisting cultural types of their companies. Since the companies were of medium and large size, their organizational culture may be fragmented. This means that different divisions of the organizations can represent slightly different cultural types. Future studies could overcome such a limitation. Further triangulation of the methods and the involvement of more respondents from a single company can be used in order to achieve more objective measures and to identify the mechanism of choosing the PM standards. Further research can also adopt different cultural typologies than those presented by Cameron and Quinn.
The research process
Traditional vs agile project management – own study based on Špundak (2014) , Cohen (2019) , Piwowar-Sulej (2020 )
Cultural types regarded as dominant and the popularity of different PM methodologies in respondents' companies
Factors taken into account in the decision-making process about appropriate PM methodology – frequency distribution
Cultural types matched with PM methodology – frequency distribution
Dominant cultural type and project success – results of Kruskal–Wallis test
Acar , A.Z. ( 2012 ), “ Organizational culture, leadership styles and organizational commitment in Turkish logistics industry ”, Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences , Vol. 58 , pp. 217 - 226 , doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.09.995 .
Agilemanifesto.org ( 2020 ), “ Agile Manifesto ”, available at: https://agilemanifesto.org/ .
Ajmal , M.M. and Koskinen , K.U. ( 2008 ), “ Knowledge transfer in project-based organizations: an organizational culture perspective ”, Project Management Journal , Vol. 39 No. 1 , pp. 7 - 15 , doi: 10.1002/pmj.20031 .
Alvesson , M. ( 1990 ), “ On the popularity of organizational culture ”, Acta Sociologica , Vol. 33 No. 1 , pp. 31 - 49 , doi: 10.1177/000169939003300103 .
Andersen , E.S. ( 2006 ), “ Toward a project management theory for renewal projects ”, Project Management Journal , Vol. 37 No. 4 , pp. 15 - 30 , doi: 10.1177/875697280603700403 .
Araujo , C.C.S.D. and Pedron , C.D. ( 2014 ), “ IT project management success: the influence of project manager competencies and team commitment ”, Proceedings of the 11th CONTECSI International Conference on Information Systems and Technology Management , TECSI . doi: 10.5748/9788599693100-11CONTECSI/PS-588 .
Barth , A. ( 2015 ), “ The role of corporate culture in the financial industry ”, Annual Conference 2015 (Muenster): Economic Development – Theory and Policy 112922 , Frankfurt , German Economic Association , available at: https://farapaper.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/The-Role-of-Corporate-Culture-in-the-Financial-Industry.pdf .
Belassi , W. , Kondra , A.Z. and Tukel , O.I. ( 2007 ), “ New product development projects: the effects of organizational culture ”, Project Management Journal , Vol. 38 No. 4 , pp. 12 - 24 , doi: 10.1002/pmj.20017 .
Bendak , S. , Shikhli , A.M. and Abdel-Razek , R.H. ( 2020 ), “ How changing organizational culture can enhance innovation: development of the innovative culture enhancement framework ”, Cogent Business and Management , Vol. 7 No. 1 , 1712125 , doi: 10.1080/23311975.2020.1712125 .
Berger , H. and Beynon-Davies , P. ( 2009 ), “ The utility of rapid application development in large-scale, complex projects ”, Information Systems Journal , Vol. 19 No. 6 , pp. 549 - 570 , doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2575.2009.00329.x .
Bredillet , C. , Yatim , F. and Ruiz , P. ( 2010 ), “ Project management deployment: the role of cultural factors ”, International Journal of Project Management , Vol. 28 No. 2 , pp. 183 - 193 , doi: 10.1016/j.ijproman.2009.10.007 .
Camerer , C. and Vepsalainen , A. ( 1988 ), “ The economic efficiency of corporate culture ”, Strategic Management Journal , Vol. 9 No. S1 , pp. 115 - 126 , doi: 10.1002/smj.4250090712 .
Cameron , K.S. and Quinn , R.E. ( 2011 ), Diagnosing and Changing Organizational Culture , Based on the Competing Values Framework , 3rd ed. , Jossey-Bass , San Francisco .
Cameron , K.S. , Quinn , R.E. , DeGraff , J. and Thakor , A.V. ( 2006 ), Competing Values Leadership: Creating Value in Organizations , Edward Elgar Publishing , Northampton .
Chan , A. ( 1997 ), “ Corporate culture of a clan organization ”, Management Decision , Vol. 35 No. 2 , pp. 94 - 99 , doi: 10.1108/00251749710160232 .
Cleland , D.I. ( 1994 ), Project Management – Strategic Design and Implementation , 2nd ed. , McGraw-Hill , New York .
Cohen , E. ( 2019 ), “ The definitive guide to project management methodologies ”, available at: https://www.workamajig.com/blog/project-management-methodologies .
Cooper , R.G. ( 2016 ), “ Agile–stage-gate hybrids ”, Research-Technology Management , Vol. 59 No. 1 , pp. 21 - 29 , doi: 10.1080/08956308.2016.1117317 .
Denison , D.R. and Mishra , A.K. ( 1995 ), “ Toward a theory of organizational culture and effectiveness ”, Organization Science , Vol. 6 No. 2 , pp. 204 - 223 , doi: 10.1287/orsc.6.2.204 .
Dictionary.com ( 2020 ), “ Agile ”, available at: https://www.dictionary.com/browse/agile?s=t .
Drucker , P. ( 1992 ), “ The new society of organizations ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 70 No. 5 , pp. 95 - 104 .
Du Plessis , Y. ( 2005 ), The Development of an Assessment Tool for Measuring Project Management Culture in Organisations , University of Pretoria , available at: http://hdl.handle.net/2263/25349 .
Du Plessis , Y. and Hoole , C. ( 2002 ), “ The development of a project management culture assessment framework ”, PMI® Research Conference 2002: Frontiers of Project Management Research and Applications , Washington , Poject Management Institute , available at: https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/development-pm-culture-assessment-framework-1938 .
Du Plessis , Y. and Hoole , C. ( 2006 ), “ An operational ‘project management culture’ framework (Part 1) ”, SA Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 4 No. 1 , doi: 10.4102/sajhrm.v4i1.79 .
Englund , R.L. and Graham , R.J. ( 1997 ), Creating an Environment for Successful Projects , Jossey-Bass Publishers , San Francisco .
Gagliardi , P. ( 1986 ), “ The creation and change of organizational cultures: a conceptual framework ”, Organization Studies , Vol. 7 No. 2 , pp. 117 - 134 , doi: 10.1177/017084068600700203 .
Hall , E.T. ( 1976 ), Beyond Culture , Doubleday , New York .
Handy , C. ( 1983 ), Understanding Organizations , Oxford University Press , New York .
Hartog , D.N. and Verburg , R.M. ( 2004 ), “ High performance work systems, organisational culture and firm effectiveness ”, Human Resource Management Journal , Vol. 14 No. 1 , pp. 55 - 78 , doi: 10.1111/j.1748-8583.2004.tb00112.x .
Henrie , M. and Sousa-Poza , A. ( 2005 ), “ Project management: a cultural literary review ”, Project Management Journal , Vol. 36 No. 2 , pp. 5 - 14 , doi: 10.1177/875697280503600202 .
Hofstede , G. ( 1998 ), “ Attitudes, values and organizational culture: disentangling the concepts ”, Organization Studies , Vol. 19 No. 3 , pp. 477 - 493 , doi: 10.1177/017084069801900305 .
International Project Management Association ( 2016 ), Organizational Competence Baseline for Developing Competence in Managing by Projects , IPMA , Amsterdam .
Isern , G. ( 2015 ), “ Intercultural project management for IT: issues and challenges ”, Journal of Intercultural Management , Vol. 7 No. 3 , pp. 53 - 67 , doi: 10.1515/joim-2015-0021 .
ISS ( 2020 ), “ How office design can shape your company culture ”, available at: https://www.servicefutures.com/office-design-can-shape-company-culture .
Joseph , O.O. and Kibera , F. ( 2019 ), “ Organizational culture and performance: evidence from microfinance institutions in Kenya ”, SAGE Open , Vol. 9 No. 1 , doi: 10.1177/2158244019835934 .
Jovanovic , P. and Beric , I. ( 2018 ), “ Analysis of the available project management methodologies ”, Management:Journal of Sustainable Business and Management Solutions in Emerging Economies , Vol. 23 No. 3 , p. 1 , doi: 10.7595/management.fon.2018.0027 .
Kane-Urrabazo , C. ( 2006 ), “ Management's role in shaping organizational culture ”, Journal of Nursing Management , Vol. 14 No. 3 , pp. 188 - 194 , doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2934.2006.00590.x .
Kerzner , H. ( 2000 ), Applied Project Management. Best Practices on Implementation , John Willey and Sons , New York .
Keskin , H. , Akgün , AE. , Günsel , A. and İmamoğlu , S.Z. ( 2005 ), “ The relationships between adhocracy and clan cultures and tacit oriented KM strategy ”, Journal of Transnational Management , Vol. 10 No. 3 , pp. 39 - 53 , doi: 10.1300/J482v10n03_04 .
Kivrak , S. , Arslan , G. , Tuncan , M. and Birgonul , M.T. ( 2014 ), “ Impact of national culture on knowledge sharing in international construction projects ”, Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering , Vol. 41 No. 7 , pp. 642 - 649 , doi: 10.1139/cjce-2013-0408 .
Larson , E.W. and Gray , C.F. ( 2011 ), Project Management – The Managerial Process , 11th ed. , McGraw-Hill Hills , New York .
Liu , J. , Meng , F. and Fellows , R. ( 2015 ), “ An exploratory study of understanding project risk management from the perspective of national culture ”, International Journal of Project Management , Vol. 33 No. 3 , pp. 564 - 575 , doi: 10.1016/j.ijproman.2014.08.004 .
Llanos , C.M.F. , Roldán , J.L. and Leal-Rodriguez , A.L. ( 2017 ), “ Impact of organizational culture values on organizational agility ”, Sustainability , Vol. 9 No. 12 , p. 2354 , doi: 10.3390/su9122354 .
Lucas , L.M. ( 2006 ), “ The role of culture on knowledge transfer: the case of the multinational corporation ”, The Learning Organization , Vol. 13 No. 3 , pp. 257 - 275 , doi: 10.1108/09696470610661117 .
Martins , E.C. and Terblanche , F. ( 2003 ), “ Building organisational culture that stimulates creativity and innovation ”, European Journal of Innovation Management , Vol. 6 No. 1 , pp. 64 - 74 , doi: 10.1108/14601060310456337 .
Mashiane , L. ( 2013 ), “ Investigating an organisational culture conducive to project management, Essays Innovate ”, available at: https://www.up.ac.za/media/shared/Legacy/sitefiles/file/44/1026/2163/8121/innovate8/9195investigating_an_organisational_culture_conducive_to_project_managementbyloriummashiane.pdf .
Mathew , J. ( 2007 ), “ The relationship of organisational culture with productivity and quality ”, in Budhwar, P.S. (Ed.) , Employee Relations , Vol. 29 , No. 6 , pp. 677 - 695 , doi: 10.1108/01425450710826140 .
Morrison , J.M. , Brown , C.J. and Smit , E.V.D.M. ( 2008 ), “ The impact of organizational culture on project management in matrix organizations ”, South African Journal of Business Management , Vol. 39 No. 4 , pp. 27 - 36 , doi: 10.4102/sajbm.v39i4.569 .
Nguyen , L. and Watanabe , T. ( 2017 ), “ The impact of project organizational culture on the performance of construction projects ”, Sustainability , Vol. 9 No. 5 , p. 781 , doi: 10.3390/su9050781 .
Ostroff , C. , Kinicki , A.J. and Muhammad , R.S. ( 2012 ), “ Organizational culture and climate ”, Handbook of Psychology , 2nd ed. , John Wiley and Sons , Hoboken, New Jersey . doi: 10.1002/9781118133880.hop212024 .
Pinto , J.K. and Slevin , D.P. ( 1987 ), “ Critical factors in successful project implementation ”, IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management , Vols EM-34 No. 1 , pp. 22 - 27 , doi: 10.1109/TEM.1987.6498856 .
Piwowar-Sulej , K. ( 2014 ), “ Kultura organizacyjna i jej wpływ na działalność projektową – studium przypadku ”, Marketing i Rynek , Vol. 5 , pp. 143 - 148 , doi: 10.13140/2.1.1346.1769 .
Piwowar-Sulej , K. ( 2016 ), “ Kultura organizacyjna jako determinanta sukcesu organizacji zorientowanych na projekty – optyka specjalistów HR ”, Zarządzanie i Finanse , Vol. 2 No. 2 , pp. 275 - 284 .
Piwowar-Sulej , K. ( 2020 ), “ Types of organizational culture in the context of project management methodologies ”, in Soliman Khalid , S. (Ed.), Education Excellence and Innovation Management: A 2025 Vision to Sustain Economic Development during Global Challenges , International Business Information Management Association (IBIMA) , Sevilla .
Piwowar‐Sulej , K. ( 2021 ), “ Core functions of sustainable human resource management. A hybrid literature review with the use of H‐classics methodology ”, Sustainable Development , sd.2166 , doi: 10.1002/sd.2166 .
Rowlinson , S. and Root , D. ( 1996 ), “ The impact of culture on project management ”, available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305397606 .
San Cristóbal , J.R. , Carral , R. , Diaz , E. , Fraguela , J.A. and Iglesias , G. ( 2018 ), “ Complexity and project management, a general overview ”, Complexity , Vol. 2018 , pp. 1 - 10 , doi: 10.1155/2018/4891286 .
Saynisch , M. ( 2010 ), “ Beyond frontiers of traditional project management: an approach to evolutionary, self-organizational principles and the complexity theory – results of the research program ”, Project Management Journal , Vol. 41 No. 2 , pp. 21 - 37 , doi: 10.1002/pmj.20159 .
Schein , E.H. ( 1990 ), “ Organizational culture ”, American Psychologist , Vol. 45 No. 2 , pp. 109 - 119 , doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.45.2.109 .
Schwaber , K. and Sutherland , J. ( 2017 ), “ The scrum guide, the definitive guide to scrum: the rules of the game ”, available at: https://www.scrumguides.org/docs/scrumguide/v2017/2017-Scrum-Guide-US.pdf .
Shore , B. and Cross , B.J. ( 2005 ), “ Exploring the role of national culture in the management of large-scale international science projects ”, International Journal of Project Management , Vol. 23 No. 1 , pp. 55 - 64 , doi: 10.1016/j.ijproman.2004.05.009 .
Silva , M.D.C. and Gomes , C.F.S. ( 2015 ), “ Practices in project management according to Charles Handy's organizational culture typologies ”, Procedia Computer Science , Vol. 55 , pp. 678 - 687 , doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2015.07.074 .
Špundak , M. ( 2014 ), “ Mixed agile/traditional project management methodology – reality or illusion? ”, Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences , Vol. 119 , pp. 939 - 948 , doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.03.105 .
Stankevičiūtė , Ž. and Savanevičienė , A. ( 2019 ), “ Can sustainable HRM reduce work-related stress, work-family conflict, and burnout? ”, International Studies of Management and Organization , Routledge , Vol. 49 , No. 1 , pp. 79 - 98 , doi: 10.1080/00208825.2019.1565095 .
Stare , A. ( 2014 ), “ Agile project management in product development projects ”, Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences , Vol. 119 , pp. 295 - 304 , doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.03.034 .
Statistics Poland ( 2019 ), Specialized Segments of Financial Market 2018 , Central Statistical Office , Warsaw .
Thakor , A.V. ( 2015 ), “ Corporate culture in banking ”, SSRN Electronic Journal . doi: 10.2139/ssrn.2565514 .
Thomas , G. and Fernández , W. ( 2008 ), “ Success in IT projects: a matter of definition? ”, International Journal of Project Management , Vol. 26 No. 7 , pp. 733 - 742 , doi: 10.1016/j.ijproman.2008.06.003 .
Titov , E. and Umarova , L. ( 2017 ), “ Impact of real and propagated values on organisational success ”, Congruence of Personal and Organizational Values , InTech . doi: 10.5772/intechopen.69460 .
Turner , R.J. ( 1993 ), The Handbook of Project-Based Management – Improving the Processes for Achieving Strategic Objectives , MCGraw-Hill , London .
Vlahov , R.D. , Mišić , S. and Radujković , M. ( 2016 ), “ The influence of cultural diversity on project management competence development – the Mediterranean experience ”, Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences , Vol. 226 , pp. 463 - 469 , doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.06.212 .
Ward , L.J. ( 2000 ), Dictionary of Project Management Terms , ESI International , Darlington Virginia .
Webster , E. and Jensen , P.H. ( 2006 ), “ Investment in intangible capital: an enterprise perspective* ”, The Economic Record , Vol. 82 No. 256 , pp. 82 - 96 , doi: 10.1111/j.1475-4932.2006.00296.x .
Wiewióra , A. , Murphy , G.D. , Trigunarsyah , B. and Coffey , V. ( 2012 ), “ Uncovering the impact of organisational culture types on the willingness to share knowledge between projects ”, in Williams , J. (Ed.), Proceedings of the PMI Research and Education Conference 2012 , Project Management Institute , pp. 1 - 16 .
Wyrozębski , P. , Juchniewicz , M. and Metelski , W. ( 2012 ), Wiedza, dojrzałość, ryzyko w zarządzaniu projektami , Warsaw School of Economics , Warsaw .
Yazici , H.J. ( 2009 ), “ The role of project management maturity and organizational culture in perceived performance ”, Project Management Journal , Vol. 40 No. 3 , pp. 14 - 33 , doi: 10.1002/pmj.20121 .
Acknowledgements
The project is financed by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education in Poland under the program “Regional Initiative of Excellence” 2019–2022 project number 015/RID/2018/19 total funding amount 10,721,040.00 PLN.
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Project Management Research Topics: Breaking New Ground

According to a study by the Project Management Institute (PMI), a significant 11.4% of business investments go to waste due to subpar project performance.
That’s why students need to study project management in college - to move the progress further and empower businesses to perform better. It is crucial for students as it equips them with essential skills, including organization, teamwork, problem-solving, and leadership, which are highly transferable and sought after in the professional world. It enhances their career prospects, teaches adaptability, and fosters a global perspective, preparing them for success in a diverse and rapidly evolving job market.
In this article, you will learn the definition of a project management research paper, discover 120 excellent topics and ideas, as well as receive pro tips regarding how to cope with such an assignment up to par.
Definition of What is Project Management
Project management is the practice of planning, executing, controlling, and closing a specific project to achieve well-defined goals and meet specific success criteria. It involves efficiently allocating resources, including time, budget, and personnel, to ensure that a project is completed on time, within scope, and within budget while delivering the intended results or deliverables.
Project management encompasses various methodologies, tools, and techniques to ensure that projects are successfully initiated, planned, executed, monitored, and completed in an organized and systematic manner.
Students can learn project management in colleges and universities, online courses, professional associations, specialized schools, and continuing education programs. Despite the type of institution, most students rely on an essay writing service to ensure their academic progress is positive.
Achieve Excellence in Project Management Essays
Need a standout essay on the latest project management trends? Our experienced writers are here to provide you with a meticulously researched and expertly written paper, ensuring you stay ahead in your academic journey.
What Is a Project Management Research Paper?
Project management research papers are academic documents that explore various aspects of project management as a field of study. These papers typically delve into specific topics, issues, or questions related to project management and aim to contribute new knowledge or insights to the discipline. Project management research papers often involve rigorous analysis, empirical research, and critical evaluation of existing theories or practices within the field.
Key elements of a project management research paper include:
%20(1).webp)
- Research Question or Problem: Clearly defines the research question, problem, or topic the paper aims to address.
- Literature Review: A comprehensive review of existing literature, theories, and relevant studies related to the chosen topic.
- Methodology: Describing the research methods, such as surveys, case studies, interviews, or data analysis techniques.
- Data Collection and Analysis: If applicable, presenting and analyzing data to support the research findings.
- Discussion: An in-depth discussion of the research findings and their implications for the field of project management.
- Conclusion: Summarizing the key findings, their significance, and potential future research directions.
Project management research papers can cover various topics, from best practices in project management to emerging trends, challenges, and innovations in the field. They are a valuable resource for both academics and practitioners, offering insights that can inform project management practices and decision-making.
Project Management Research Topics Selection Tips
Selecting an appropriate topic for a project management research paper is crucial for the success of your research. Here are some tips to help you choose the right research topic:
- Start by considering your own interests and passion within the field of project management.
- Choose a topic that has practical applications and can contribute to the discipline.
- Avoid overly broad topics. Instead, narrow down your focus to a specific aspect or issue within project management.
- Seek guidance from your professors, academic advisors, or mentors.
- Conduct a preliminary literature review to see what research has already been done in your area of interest.
- Aim for originality by proposing a research topic or question that hasn't been extensively explored in the existing literature.
- Consider the feasibility of your research. Ensure your research is practical and achievable within your constraints.
- Clearly define your research questions or objectives.
- Think about the practical applications of your research.
- Ensure that your research topic and methodology adhere to ethical standards.
- Think about the research methods you will use to investigate your topic.
- Consider involving stakeholders from the industry, as their insights can provide practical relevance to your research.
- Keep in mind that your research may evolve as you delve deeper into the topic.
- Be open to adapting your research questions and methodology if necessary.
By following these tips, you can select a project management research topic that is not only relevant and original but also feasible and well-aligned with your academic and career goals. Sounds challenging and time-consuming? Simply type ‘ write an essay for me ,’ and our experts will help you settle the matter.
Best Project Management Research Topics and Ideas
Here is a list of the 50 best topics for a project management paper. These topics cover many project management areas, from traditional project management methodologies to emerging trends and challenges in the field. You can further refine and tailor these topics to match your specific research interests and objectives.
- Agile Project Management in Non-IT Industries.
- Risk Management Strategies for Large-Scale Projects.
- The Role of Leadership in Project Success.
- Sustainability Integration in Project Management.
- Challenges in Virtual Project Management.
- The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Project Management.
- Project Management Best Practices in Healthcare.
- Lean Project Management Principles.
- Project Portfolio Management in Multinational Corporations.
- The Use of Blockchain in Project Management.
- Cultural Diversity and Its Effects on Global Project Teams.
- Managing Scope Creep in Project Management.
- Project Management in Crisis Situations.
- Agile vs. Waterfall: A Comparative Analysis.
- Project Governance and Compliance.
- Critical Success Factors in Public Sector Projects.
- Benefits Realization Management in Project Management.
- Agile Transformation in Traditional Organizations.
- Project Management in the Digital Age.
- Sustainable Project Procurement Practices.
- The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Project Leadership.
- Project Management in the Healthcare Industry.
- Effective Communication in Virtual Project Teams.
- Agile Project Management in Software Development.
- The Impact of Project Management Offices (PMOs).
- Project Management in the Construction Industry.
- Project Risk Assessment and Mitigation.
- IT Project Management Challenges and Solutions.
- Project Management in Startups and Entrepreneurship.
- Lean Six Sigma in Project Management.
- Project Management Software Tools and Trends.
- The Role of Change Management in Project Success.
- Conflict Resolution in Project Teams.
- Project Management in the Pharmaceutical Industry.
- Scrum vs. Kanban: A Comparative Study.
- Managing Cross-Cultural Teams in International Projects.
- The Future of Project Management: Trends and Forecasts.
- Effective Resource Allocation in Project Management.
- Project Procurement and Vendor Management.
- Quality Assurance in Project Management.
- Risk Assessment in IT Project Management.
- Benefits and Challenges of Hybrid Project Management Models.
- Agile Transformation in Large Organizations.
- The Role of Data Analytics in Project Management.
- Project Management for Non-Profit Organizations.
- Continuous Improvement in Project Management.
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Project Management Practices.
- The Role of Project Management in Innovation.
- Project Management in the Aerospace Industry.
- The Influence of Project Management on Organizational Performance.
Simple Project Management Research Ideas
Here are 10 simple project management research ideas that can serve as a foundation for more in-depth research:
The Impact of Effective Communication on Project Success: Investigate how clear and efficient communication within project teams influences project outcomes.
Project Management Software Adoption and Its Effects: Examine the adoption of project management software tools and their impact on project efficiency and collaboration.
Factors Affecting Scope Creep in Project Management: Identify the key factors contributing to scope creep and explore strategies to prevent it.
The Role of Project Management Offices (PMOs) in Organizational Performance: Analyze the performance, improving project success rates and enhancing overall project management maturity.
Agile Project Management in Non-Software Industries: Study how Agile project management principles can be adapted and applied effectively in non-IT industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, or construction.
Project Risk Management Strategies: Investigate the best practices and strategies for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks in project management.
Stakeholder Engagement in Project Success: Explore the significance of stakeholder engagement and its impact on project outcomes, including scope, quality, and stakeholder satisfaction.
Project Management in Small Businesses: Analyze the unique challenges and opportunities of project management in small businesses and startups, considering resource constraints and growth objectives.
Sustainability Practices in Project Management: Investigate how project managers can integrate sustainability principles into project planning and execution, with a focus on environmental and social responsibility.
Change Management in Project Transitions: Examine the role of change management in ensuring smooth transitions between project phases or methodologies, such as moving from Waterfall to Agile.
Interesting Project Management Research Paper Topics
These research paper topics offer opportunities to explore diverse aspects of project management, from leadership and ethics to emerging technologies and global project dynamics.
- The Impact of Effective Communication on Project Success.
- Project Management Software Adoption and Its Effects.
- Factors Affecting Scope Creep in Project Management.
- The Role of Project Management Offices (PMOs) in Organizational Performance.
- Agile Project Management in Non-Software Industries.
- Project Risk Management Strategies.
- Stakeholder Engagement in Project Success.
- Project Management in Small Businesses and Startups.
- Sustainability Practices in Project Management.
- Change Management in Project Transitions.
Still can’t find an interesting topic? Maybe you’re in writer’s block. But we have a solution to this, too - a research paper writing service from real academic professionals!
Research Project Topics in Business Management
Here are ten research project topics in business management. They encompass various aspects of business management, from leadership and diversity to sustainability and emerging trends in the business world.
- The Impact of Leadership Styles on Employee Motivation and Productivity.
- Strategies for Enhancing Workplace Diversity and Inclusion.
- The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Effective Leadership.
- Sustainable Business Practices and Their Effects on Corporate Social Responsibility.
- Innovation and Technology Adoption in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs).
- Financial Management Strategies for Small Businesses and Startups.
- Effective Marketing Strategies in the Digital Age.
- The Challenges and Opportunities of Global Expansion for Multinational Corporations.
- Supply Chain Management in a Post-Pandemic World: Resilience and Adaptability.
- Consumer Behavior and Market Trends in E-Commerce.
Software Project Management Dissertation Topics
These dissertation topics cover a range of critical issues and strategies in software project management, from risk management to AI integration and agile methodologies.
- Effective Software Project Risk Management Strategies.
- Agile vs. Waterfall: Comparative Analysis in Software Project Management.
- Requirements Management in Software Development Projects.
- The Role of DevOps in Accelerating Software Project Delivery.
- Software Project Management Challenges in Distributed and Remote Teams.
- Quality Assurance and Testing Practices in Software Project Management.
- Managing Scope Changes and Requirements Volatility in Software Projects.
- Vendor Management in Outsourced Software Development Projects.
- Project Portfolio Management in Software Organizations.
- The Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing Software Project Management.
Remember that research paper topics might also be used to write a dissertation. Check them out as well!
Ten Construction Project Management Research Topics
Offering you ten research topics in construction project management, which delve into various aspects of construction project management, from sustainability and safety to technology adoption and stakeholder engagement.
- Optimizing Construction Project Scheduling and Time Management.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation in Large-Scale Construction Projects.
- Green Building Practices and Sustainable Construction Management.
- The Role of Technology in Improving Construction Project Efficiency.
- Safety Management and Accident Prevention in Construction.
- Contract Management in Public Infrastructure Projects.
- Resource Allocation and Cost Control in Construction Project Management.
- The Impact of Lean Construction Principles on Project Delivery.
- Innovations in Prefabrication and Modular Construction Methods.
- Stakeholder Collaboration and Communication in Complex Construction Projects.
Ten Outstanding Project Administration Ideas for Research Paper
Let’s gain insights into the key aspects and focus areas of each research paper topic in project administration. Researchers can further refine these 10 topics to address specific research questions and objectives.
Innovative Strategies for Effective Project Communication and Collaboration: This topic explores innovative communication and collaboration methods that enhance project team coordination and overall project success. It may include the use of technology, virtual tools, or novel approaches to foster effective communication.
Integrating Sustainability into Project Management Practices: This research examines how project managers can incorporate sustainability principles into project planning, execution, and decision-making, contributing to environmentally and socially responsible project outcomes.
The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Project Leadership and Team Dynamics: This topic delves into the significance of emotional intelligence in project leadership, focusing on how emotional intelligence influences team dynamics, motivation, and project performance.
Agile Project Management in Non-Traditional Industries: Opportunities and Challenges: It explores adopting Agile project management methodologies outside the software development domain, discussing the opportunities and challenges of applying Agile in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, or construction.
Crisis Management and Resilience in Project Administration: This topic investigates crisis management strategies and the development of project resilience to navigate unexpected disruptions, disasters, and unexpected events affecting project progress.
The Impact of Change Management in Successful Project Implementation: It examines the critical role of change management in ensuring smooth transitions between project phases, methodologies, or organizational changes, contributing to project success.
Ethical Decision-Making in Project Management: Balancing Objectives and Integrity: This research delves into the ethical dilemmas and decision-making processes project managers face and explores frameworks for ethical behavior in project management.
Technology Integration and Digital Transformation in Project Administration: It discusses how the integration of technology, such as AI, IoT, and automation, is transforming project administration practices and improving efficiency and project outcomes.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning in Large-Scale Projects: This topic focuses on risk management strategies and the development of effective contingency plans to mitigate risks in complex, large-scale projects.
Project Governance and the Influence of Regulatory Compliance: It explores project governance structures, including the impact of regulatory compliance on project management, risk management, and decision-making processes. In case you need aid with complex senior year papers, consult capstone project writing services .
Ten Healthcare Project Management Research Topics
These research topics address various aspects of healthcare project management, from facility construction and technology implementation to quality improvement and crisis management. Researchers can explore these topics to contribute to the improvement of healthcare project outcomes and patient care.
- Optimizing Healthcare Facility Construction and Renovation Projects.
- Effective Implementation of Electronic Health Records (EHR) in Hospitals.
- Managing Change in Healthcare Organizations: A Project Management Perspective.
- Telemedicine Project Management and its Impact on Healthcare Delivery.
- Healthcare Project Risk Management: A Case Study Analysis.
- Patient-Centered Care Initiatives and Project Management Best Practices.
- Quality Improvement Projects in Healthcare: Challenges and Success Factors.
- Healthcare Supply Chain Management and Project Efficiency.
- The Role of Project Management in Healthcare Crisis Response (e.g., Pandemics).
- Measuring the Impact of Lean Six Sigma in Healthcare Process Improvement Projects.
When you find a topic - what’s next? Check out this guide on how to research a topic !
Project management is a dynamic and ever-evolving discipline, offering a rich landscape for research and exploration. Whether you are a student seeking captivating project management research topics or a seasoned professional looking to address real-world challenges, our list of topics provides a valuable starting point.
The key to successful research in project management lies in identifying a topic that aligns with your interests and objectives, allowing you to make meaningful contributions to the field while addressing the pressing issues of today and tomorrow.
So, delve into these research topics, choose the one that resonates with your passion, and embark on a journey of discovery and advancement in the world of project management. If you feel stressed or overwhelmed with the workload at some point, pay for a research paper to gain a competitive edge and save valuable time.
Elevate Your Project Management Research
Let our team of expert writers help you create a comprehensive and well-researched essay, tailored to your specific academic requirements!
Related Articles
.webp)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This entry of the series focuses on papers about management science (aka, operations research) models and practice methodologies (e.g., processes, heuristics, tools, and techniques). Project management grew out of management science and was indistinguishable from the field of its origins for many years.
A project management methodology is a set of principles, processes, guidelines, and tools that help to plan, manage, and control a project. The methodology helps to ensure that a project is on schedule, within budget, and that the project goals are met. A project team or an organization uses a management framework to execute a project.
ABSTRACT. Design Methods and Practices for Research of Project Management is the most comprehensive guide on how to do research of and in project management. Project management as a discipline has experienced near-exponential growth in its application across the business and not-for-profit sectors. This second edition of the authoritative ...
12 project management frameworks. Manage projects with one tool. 1. Agile. What it is: The Agile project management methodology is one of the most common project management processes. But the reality is that Agile isn't technically a methodology. Instead, it's best defined as a project management principle. The basis of an Agile approach is ...
A project management methodology is a set of principles that project managers and team leaders use to plan, execute and manage a successful project. One of the most common is the Agile project ...
2. Design: The critical design phase is when you'll plan what the final product will look like and what steps your team needs to take to get there. 3. Implementation: This is where all your planning gets put into action. For software projects, this is when programmers will write the actual code. 4.
A project management methodology is a set of principles, tools and techniques that are used to plan, execute and manage projects. Project management methodologies help project managers lead team members and manage work while facilitating team collaboration. ... software development and tech research and development. 7. Kanban Methodology. What ...
As the leading community for project managers around the globe, PMI is committed to defining and developing the future of project management by supporting the work of scholars through research, teaching, and education programs. Join the Academic Network for updates and browse tools for educators, researchers, and academic programs below.
The Project Management Process. Watch on. To summarise: In order to successfully complete your research project, you will need to: Set goals. An example of a goal is to list all of the tasks that you would like to accomplish in the first or second semester. Break down tasks. An example would be to arrange your tasks monthly and weekly and daily.
The lean project management methodology was developed in the early 2000s as a way to streamline project management processes and eliminate waste. ... Research Your Options. Once you know what you're looking for, it's time to start researching your options. There are many online resources available that can help you compare different ...
The four project phases are: Inception: outlining the scope of work or statement of work, impact analysis, identify key use cases, and cost estimates. Elaboration: designing an architected foundation for the product. Construction: completing the bulk of the work to develop all software components.
Project management: the right discipline for managing research projects. A project - according to the PRINCE2 project management method - is defined as ''a temporary organisation that is created for the purpose of delivering one or more business products according to an agreed business case''. Having a method to manage this entity ...
The tools you need to make your research project a success. This toolkit includes a variety of tools for managing your research projects including recommendations for general project management software and tools to help you and your team manage activities from grant writing to implementation and project closeout. ... Process maps allow the ...
Stages of the waterfall model. 1. Requirements: In this first phase, you'll work with stakeholders to clearly define the project scope and requirements. 2. Design: The critical design phase is when you'll plan what the final product will look like and what steps your team needs to take to get there. 3.
Survival is one of the most crucial driving forces for many companies today. Once executives recognize that project management is needed to make it happen, changes occur quickly. However, failing to use a project management methodology (PMM) may jeopardize an organisation's efforts and overall effectiveness, in respect to knowledge management, repeatability, comparability, quality, and future ...
This article investigates the benefits and supports provided by project management methodologies (PMMs) to project managers for the management and delivery of information technology/information system (IT/IS) projects. Using a qualitative approach, through case study strategy, the role of PMMs is examined in different business and project contexts.
Project methodologies are an integral part of the core make-up of a project because all companies using project methodologies expect greatly improved project performance. Each company must decide the best approach to select the most suitable methodology and whether to have one or more variations of a methodology. Research is split whether implementing a standardized or customized methodology ...
Types of Project Management Methodologies. There are diverse project management methodologies, each with different principles, processes, and approaches. Here are some common types: 1. Waterfall Methodology. Waterfall project management is a traditional approach to project management where tasks are completed sequentially and linearly.
Purpose. Organizational culture has an impact on various activities in organizations, including project management (PM). The aim of the study is to answer the following research questions: RQ1: what significance is attributed to organizational culture compared to the objective project characteristics when choosing the dominant PM methodology in organizations?
Today, Six Sigma is one of the. most popular and re liable project management methodologies, ev en worldwide. The essential approach o f this methodology, in order to ensure the accuracy and ...
12 popular project management methodologies. Often one of the first decisions you will make as a project manager involves which methodology to follow. As the industry has evolved over the years, so have the PM methodology options. ... Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet ...
Here is a list of the 50 best topics for a project management paper. These topics cover many project management areas, from traditional project management methodologies to emerging trends and challenges in the field. You can further refine and tailor these topics to match your specific research interests and objectives.
This methodology provides the framework for project management when developing ISO or IEC documents. This methodology is a customised approach from ISO 21502, Project, programme and portfolio management - Guidance on project management which is the reference in terms of concepts and processes of project management that are important for, and
This course covers foundations of the research process for experimental Psychology: reviewing and evaluating published journal articles, refining new research questions, conducting pilot studies, creating stimuli, sequencing experiments for optimal control and data quality, analyzing data, and communicating scientific methods and results clearly...