
25+ JavaScript Coding Interview Questions (SOLVED with CODE)
Having a JavaScript Coding Interview Session on this week? Fear not, we got your covered! Check that ultimate list of 25 advanced and tricky JavaScript Coding Interview Questions and Challenges to crack on your next senior web developer interview and got your next six-figure job offer in no time!
Q1 : Explain what a callback function is and provide a simple example
A callback function is a function that is passed to another function as an argument and is executed after some operation has been completed. Below is an example of a simple callback function that logs to the console after some operations have been completed.
Q2 : Given a string, reverse each word in the sentence
For example Welcome to this Javascript Guide! should be become emocleW ot siht tpircsavaJ !ediuG
Q3 : How to check if an object is an array or not? Provide some code.
The best way to find whether an object is instance of a particular class or not using toString method from Object.prototype
One of the best use cases of type checking of an object is when we do method overloading in JavaScript. For understanding this let say we have a method called greet which take one single string and also a list of string, so making our greet method workable in both situation we need to know what kind of parameter is being passed, is it single value or list of value?
However, in above implementation it might not necessary to check type for array, we can check for single value string and put array logic code in else block, let see below code for the same.
Now it's fine we can go with above two implementations, but when we have a situation like a parameter can be single value , array , and object type then we will be in trouble.
Coming back to checking type of object, As we mentioned that we can use Object.prototype.toString
If you are using jQuery then you can also used jQuery isArray method:
FYI jQuery uses Object.prototype.toString.call internally to check whether an object is an array or not.
In modern browser, you can also use:
Array.isArray is supported by Chrome 5, Firefox 4.0, IE 9, Opera 10.5 and Safari 5
Q4 : How to empty an array in JavaScript?
How could we empty the array above?
Above code will set the variable arrayList to a new empty array. This is recommended if you don't have references to the original array arrayList anywhere else because It will actually create a new empty array. You should be careful with this way of empty the array, because if you have referenced this array from another variable, then the original reference array will remain unchanged, Only use this way if you have only referenced the array by its original variable arrayList .
For Instance:
Above code will clear the existing array by setting its length to 0. This way of empty the array also update all the reference variable which pointing to the original array. This way of empty the array is useful when you want to update all the another reference variable which pointing to arrayList .
Above implementation will also work perfectly. This way of empty the array will also update all the references of the original array.
Above implementation can also empty the array. But not recommended to use often.
Q5 : How would you check if a number is an integer?
A very simply way to check if a number is a decimal or integer is to see if there is a remainder left when you divide by 1.
Q6 : Implement enqueue and dequeue using only two stacks
Enqueue means to add an element, dequeue to remove an element.
Q7 : Make this work
Q8 : write a "mul" function which will properly when invoked as below syntax.
Here mul function accept the first argument and return anonymous function which take the second parameter and return anonymous function which take the third parameter and return multiplication of arguments which is being passed in successive
In JavaScript function defined inside has access to outer function variable and function is the first class object so it can be returned by function as well and passed as argument in another function.
- A function is an instance of the Object type
- A function can have properties and has a link back to its constructor method
- Function can be stored as variable
- Function can be pass as a parameter to another function
- Function can be returned from function
Q9 : Write a function that would allow you to do this?
You can create a closure to keep the value passed to the function createBase even after the inner function is returned. The inner function that is being returned is created within an outer function, making it a closure, and it has access to the variables within the outer function, in this case the variable baseNumber .
Q10 : FizzBuzz Challenge
Create a for loop that iterates up to 100 while outputting "fizz" at multiples of 3 , "buzz" at multiples of 5 and "fizzbuzz" at multiples of 3 and 5 .
Check out this version of FizzBuzz:
Q11 : Given two strings, return true if they are anagrams of one another
For example: Mary is an anagram of Army
Q12 : How would you use a closure to create a private counter?
You can create a function within an outer function (a closure) that allows you to update a private variable but the variable wouldn't be accessible from outside the function without the use of a helper function.
Q13 : Provide some examples of non-bulean value coercion to a boolean one
The question is when a non-boolean value is coerced to a boolean, does it become true or false , respectively?
The specific list of "falsy" values in JavaScript is as follows:
- "" (empty string)
- 0 , -0 , NaN (invalid number)
- null , undefined
Any value that's not on this "falsy" list is "truthy." Here are some examples of those:
- [ ] , [ 1, "2", 3 ] (arrays)
- { } , { a: 42 } (objects)
- function foo() { .. } (functions)
Q14 : What will be the output of the following code?
Above code would give output 1undefined . If condition statement evaluate using eval so eval(function f() {}) which return function f() {} which is true so inside if statement code execute. typeof f return undefined because if statement code execute at run time, so statement inside if condition evaluated at run time.
Above code will also output 1undefined .
Q15 : What will the following code output?
The code above will output 5 even though it seems as if the variable was declared within a function and can't be accessed outside of it. This is because
is interpreted the following way:
But b is not declared anywhere in the function with var so it is set equal to 5 in the global scope .
Q16 : Write a function that would allow you to do this
You can create a closure to keep the value of a even after the inner function is returned. The inner function that is being returned is created within an outer function, making it a closure, and it has access to the variables within the outer function, in this case the variable a .
Q17 : How does the this keyword work? Provide some code examples
In JavaScript this always refers to the “owner” of the function we're executing, or rather, to the object that a function is a method of.
Q18 : How would you create a private variable in JavaScript?
To create a private variable in JavaScript that cannot be changed you need to create it as a local variable within a function. Even if the function is executed the variable cannot be accessed outside of the function. For example:
To access the variable, a helper function would need to be created that returns the private variable.
Q19 : What is Closure in JavaScript? Provide an example
A closure is a function defined inside another function (called parent function) and has access to the variable which is declared and defined in parent function scope.
The closure has access to variable in three scopes:
- Variable declared in his own scope
- Variable declared in parent function scope
- Variable declared in global namespace
innerFunction is closure which is defined inside outerFunction and has access to all variable which is declared and defined in outerFunction scope. In addition to this function defined inside function as closure has access to variable which is declared in global namespace .
Output of above code would be:
Q20 : What will be the output of the following code?
Above code will output 0 as output. delete operator is used to delete a property from an object. Here x is not an object it's local variable . delete operator doesn't affect local variable.
Q21 : What will be the output of the following code?
Above code will output xyz as output. Here emp1 object got company as prototype property. delete operator doesn't delete prototype property.
emp1 object doesn't have company as its own property. You can test it like:
However, we can delete company property directly from Employee object using delete Employee.company or we can also delete from emp1 object using __proto__ property delete emp1.__proto__.company .
Q22 : What will the following code output?
This will surprisingly output false because of floating point errors in internally representing certain numbers. 0.1 + 0.2 does not nicely come out to 0.3 but instead the result is actually 0.30000000000000004 because the computer cannot internally represent the correct number. One solution to get around this problem is to round the results when doing arithmetic with decimal numbers.
Q23 : When would you use the bind function?
The bind() method creates a new function that, when called, has its this keyword set to the provided value, with a given sequence of arguments preceding any provided when the new function is called.
A good use of the bind function is when you have a particular function that you want to call with a specific this value. You can then use bind to pass a specific object to a function that uses a this reference.
Q24 : Write a recursive function that performs a binary search
Q25 : describe the revealing module pattern design pattern.
A variation of the module pattern is called the Revealing Module Pattern . The purpose is to maintain encapsulation and reveal certain variables and methods returned in an object literal. The direct implementation looks like this:
An obvious disadvantage of it is unable to reference the private methods
Rust has been Stack Overflow’s most loved language for four years in a row and emerged as a compelling language choice for both backend and system developers, offering a unique combination of memory safety, performance, concurrency without Data races...
Clean Architecture provides a clear and modular structure for building software systems, separating business rules from implementation details. It promotes maintainability by allowing for easier updates and changes to specific components without affe...
Azure Service Bus is a crucial component for Azure cloud developers as it provides reliable and scalable messaging capabilities. It enables decoupled communication between different components of a distributed system, promoting flexibility and resili...
FullStack.Cafe is a biggest hand-picked collection of top Full-Stack, Coding, Data Structures & System Design Interview Questions to land 6-figure job offer in no time.
Coded with 🧡 using React in Australia 🇦🇺
by @aershov24 , Full Stack Cafe Pty Ltd 🤙, 2018-2023
Privacy • Terms of Service • Guest Posts • Contacts • MLStack.Cafe
Top 50 JavaScript Interview Questions With Example Answers

Preparing for a JavaScript interview requires a lot of work. It’s important to be well-versed in the fundamentals but you also should have some grasp on how to debug JavaScript code, what some of the advanced functions are and how to build projects in it.
Common JavaScript Interview Questions
- What are the different data types in JavaScript?
- What is hoisting in JavaScript?
- What is the difference between null and undefined?
- What are closures in JavaScript?
- What is a callback function in JavaScript?
- What are promises in JavaScript?
- What is the purpose of the setTimeout() function in Javascript?
- How can you check if an array includes a certain value?
- How can you remove duplicates in an array?
- What is the purpose of async and await in JavaScript?
Below are some tips for preparing for the interview along with some common questions and answers to help you ace your next interview.
JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers With Examples
JavaScript interview questions range from the basics like explaining the different data types in JavaScript to more complicated concepts like generator functions and async and await. Each question will have answers and examples you can use to prepare for your own interview.
More on JavaScript How to Use the Ternary Operator in JavaScript
JavaScript Fundamentals
1. what is javascript.
A high-level, interpreted programming language called JavaScript makes it possible to create interactive web pages and online apps with dynamic functionality. Commonly referred to as the universal language, Javascript is primarily used by developers for front-end and back-end work.
2. What are the different data types in JavaScript?
JavaScript has six primitive data types:
It also has two compound data types:
3. What is hoisting in JavaScript?
Hoisting is a JavaScript concept that refers to the process of moving declarations to the top of their scope. This means that variables and functions can be used before they are declared, as long as they are declared before they are used in a function.
For example, the following code will print "Hello, world!" even though the greeting variable is not declared until after the console.log() statement.
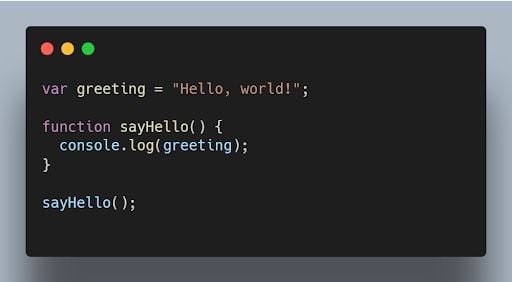
4. What is the difference between null and undefined?
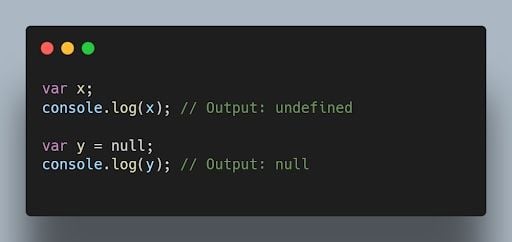
null is an assignment value that represents no value or an empty value , while undefined is a variable that has been declared but not assigned a value.
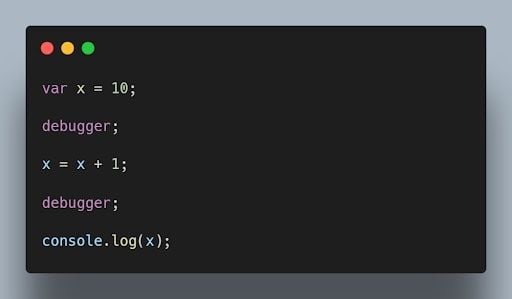
5. Why do we use the word “ debugger ” in JavaScript?
The word “debugger” is used in JavaScript to refer to a tool that can be used to step through JavaScript code line by line. This can be helpful for debugging JavaScript code, which is the process of finding and fixing errors in JavaScript code. To use the debugger , you need to open the JavaScript console in your browser. Then, you can use debugger commands to comb through your code line by line.
It's essential to know debugging techniques as well as the more general ideas behind code optimization and speed improvement. In addition to operating smoothly, efficient code significantly enhances the user experience.
For example, the following code will print the value of the x variable at each step of the debugger .
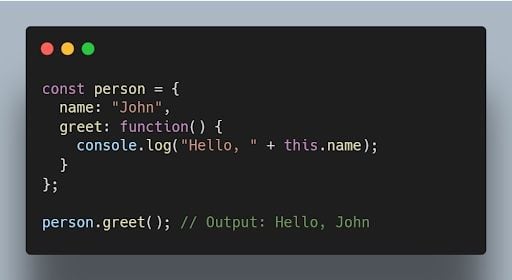
6. What is the purpose of the “ this” keyword in JavaScript?
The this keyword refers to the object that is executing the current function or method. It allows access to object properties and methods within the context of that object.
7. What is the difference between == and === operators in JavaScript?
The equality == operator is a comparison operator that compares two values and returns true if they are equal. The strict equality === operator is also a comparison operator, but it compares two values and returns true only if they are equal and of the same type.
For example , the following code will return true, because the values of the x and y variables are equal.
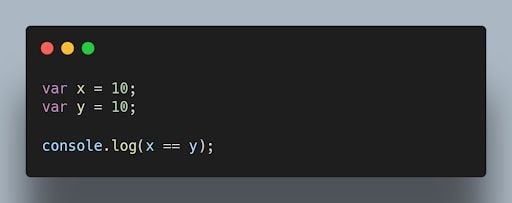
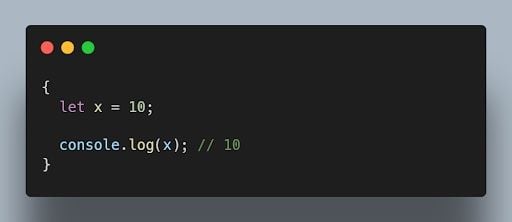
8. What is the difference between “ var” and “ let” keywords in JavaScript?
The var and let keywords are both used to declare variables in JavaScript. However, there are some key differences between the two keywords.
The var keyword declares a global variable, which means that the variable can be accessed from anywhere in the code. The let keyword declares a local variable, which means that the variable can only be accessed within the block of code where it is declared.
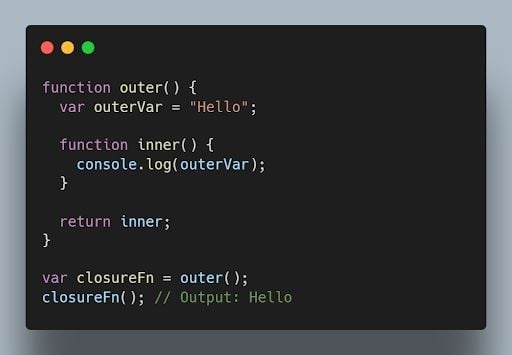
9. What are closures in JavaScript?
Closures ( closureFn ) are functions that have access to variables from an outer function even after the outer function has finished executing. They “remember” the environment in which they were created.
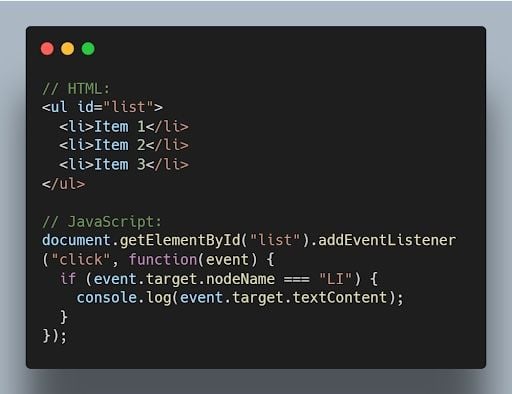
10. What is event delegation in JavaScript?
Event delegation is a technique where you attach a single event listener to a parent element, and that event listener handles events occurring on its child elements. It helps optimize performance and reduce memory consumption.
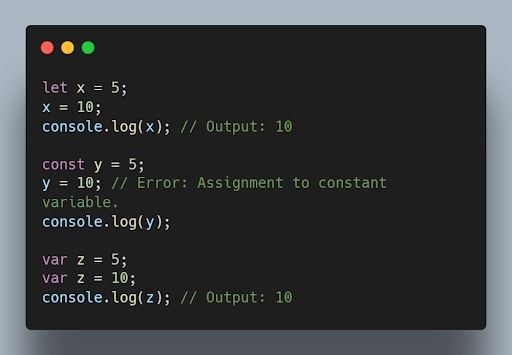
11. What is the difference between “ let” , “ const” , and “ var” ?
let and const were introduced in ES6 and have block scope. let is reassignable, and const is non-reassignable. var is function-scoped and can be redeclared and reassigned throughout the function.
12. What is implicit type coercion in JavaScript?
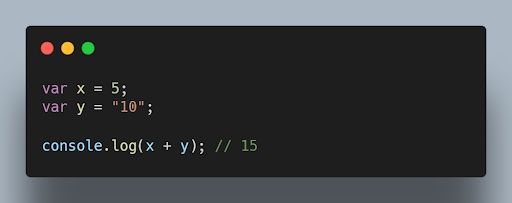
Implicit type coercion is a JavaScript concept that refers to the process of converting a value from one type to another. I f you try to add a string to a number, JavaScript will implicitly coerce the string to a number before performing the addition operation.
For example, the following code will add the string "10" to the number 5 . This is because JavaScript will implicitly coerce the string "10" to a number before performing the addition operation.
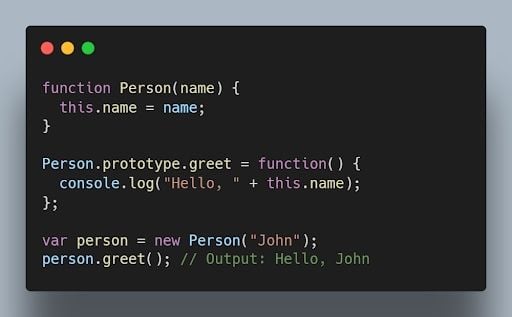
13. Explain the concept of prototypes in JavaScript.
Prototypes are a mechanism used by JavaScript objects for inheritance. Every JavaScript object has a prototype, which provides properties and methods that can be accessed by that object.
14. What is the output of the following code?
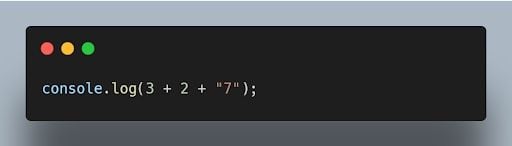
The output will be "57" . The addition operation is performed from left to right, and when a string is encountered, it performs concatenation.
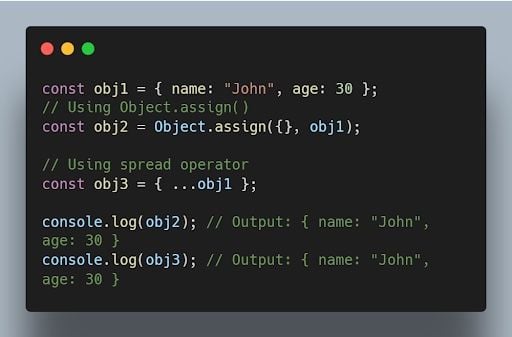
15. How can you clone an object in JavaScript?
There are multiple ways to clone an object in JavaScript. One common method is using the Object.assign() method or the spread operator (...) .
More on JavaScript JavaScript Question Mark (?) Operator Explained
Intermediate Concepts
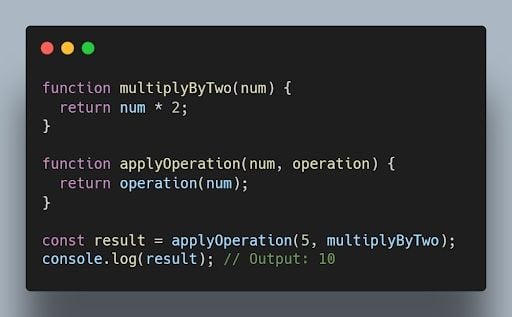
16. what are higher-order functions in javascript.
Higher order functions are functions that can accept other functions as arguments or return functions as their results. They enable powerful functional programming patterns in JavaScript.
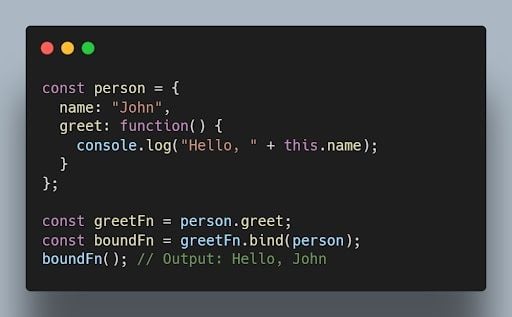
17. What is the purpose of the bind() method in JavaScript?
The bind() method is used to create a new function with a specified this value and an initial set of arguments. It allows you to set the context of a function permanently.
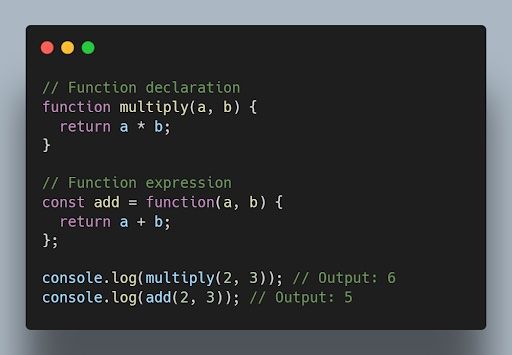
18. What is the difference between function declarations and function expressions?
Function declarations are defined using the function keyword, while function expressions are defined by assigning a function to a variable. Function declarations are hoisted, while function expressions are not.
19. What are the different types of errors in JavaScript?
JavaScript can throw a variety of errors, including:
- Syntax errors: These errors occur when the JavaScript code is not syntactically correct.
- Runtime errors: These errors occur when the JavaScript code is executed and there is a problem.
- Logical errors: These errors occur when the JavaScript code does not do what it is supposed to do.
20. What is memoization in JavaScript?
Memoization is a technique that can be used to improve the performance of JavaScript code. Memoization works by storing the results of expensive calculations in a cache. This allows the JavaScript code to avoid re-performing the expensive calculations if the same input is provided again.
For example , the following code calculates the factorial of a number. The factorial of a number is the product of all the positive integers from one to the number.
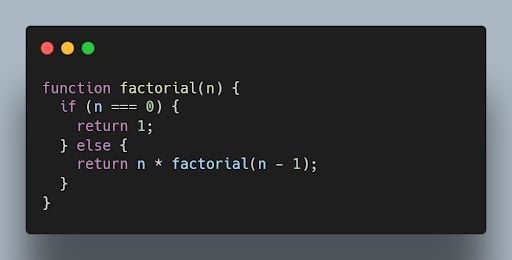
This code can be memoized as follows:
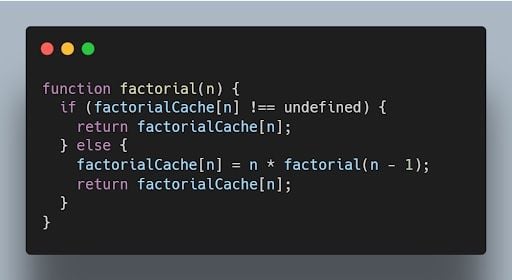
21. What is recursion in JavaScript?
Recursion is a programming technique that allows a function to call itself. Recursion can be used to solve a variety of problems, such as finding the factorial of a number or calculating the Fibonacci sequence .
The following code shows how to use recursion to calculate the factorial of a number:
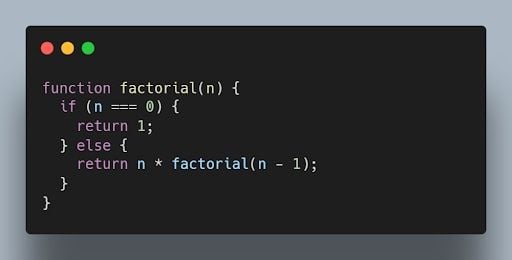
22. What is the use of a constructor function in JavaScript?
A constructor function is a special type of function that is used to create objects. Constructor functions are used to define the properties and methods of an object.
The following code shows how to create a constructor function:
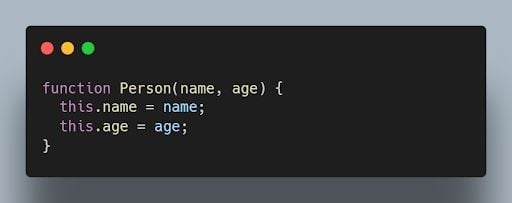
23. What is the difference between a function declaration and a function expression in JavaScript?
A function declaration is a statement that defines a function. A function expression is an expression that evaluates to a function.
The following code shows an example of a function declaration. This code defines a function named factorial. The factorial function calculates the factorial of a number.
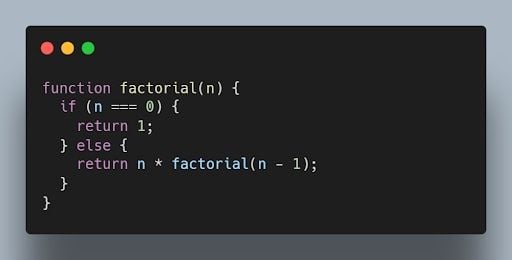
The following code shows an example of a function expression:
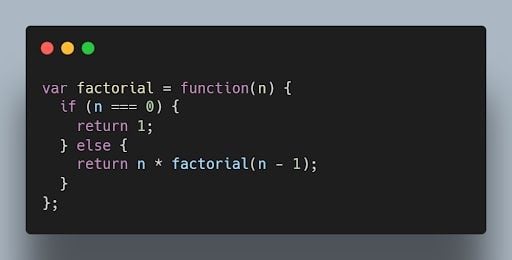
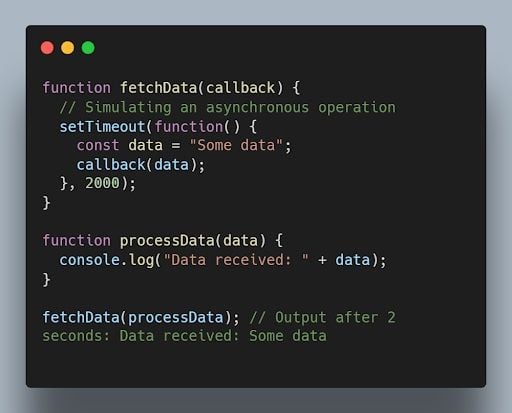
24. What is a callback function in JavaScript?
A callback function is a function passed as an argument to another function, which is then invoked inside the outer function. It allows asynchronous or event-driven programming.
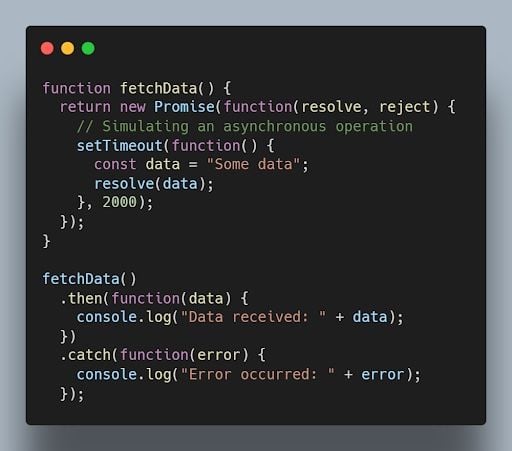
25. What are promises in JavaScript?
Promises are objects used for asynchronous operations. They represent the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation and allow chaining and handling of success or error cases.
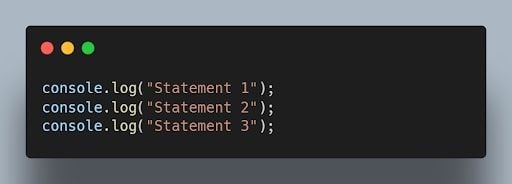
26. What is the difference between synchronous and asynchronous programming?
In synchronous programming, the program execution occurs sequentially, and each statement blocks the execution until it is completed. In asynchronous programming, multiple tasks can be executed concurrently, and the program doesn’t wait for a task to finish before moving to the next one.
Synchronous coding example:
Asynchronous code example:
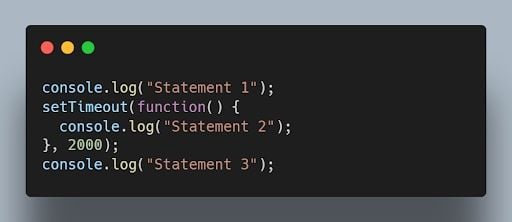
27. How do you handle errors in JavaScript?
Errors in JavaScript can be handled using try - catch blocks. The try block contains the code that may throw an error, and the catch block handles the error and provides an alternative execution path.
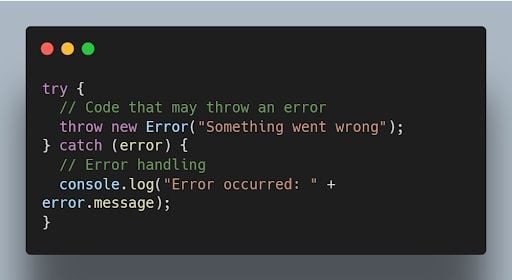
28. Explain the concept of event bubbling in JavaScript.
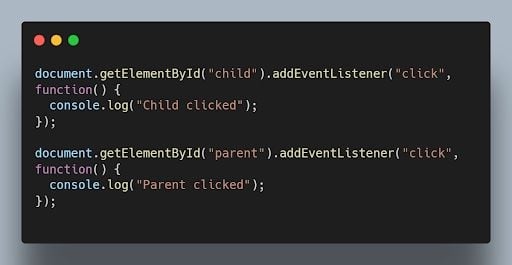
Event bubbling is the process where an event triggers on a nested element, and then the same event is propagated to its parent elements in the document object model (DOM) tree. It starts from the innermost element and goes up to the document root.
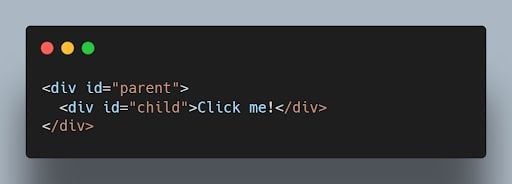
When you click on the child element, both the child and parent event handlers will be triggered, and the output will be:
29. What are arrow functions in JavaScript?
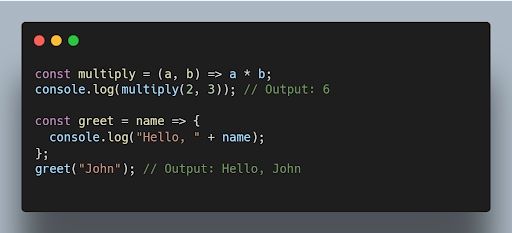
Arrow functions are a concise syntax for writing JavaScript functions. They have a more compact syntax compared to traditional function expressions and inherit the this value from their surrounding scope.
For example:
30. What is the difference between querySelector and getElementById ?
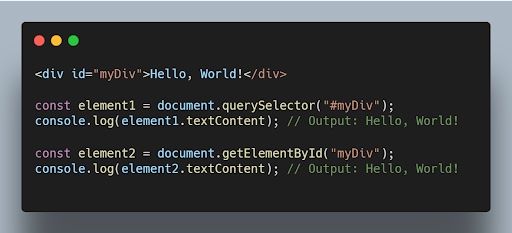
querySelector is a more versatile method that allows you to select elements using CSS -like selectors, while getElementById specifically selects an element with the specified ID.
31. What is the purpose of the setTimeout() function in JavaScript?
The setTimeout() function is used to delay the execution of a function or the evaluation of an expression after a specified amount of time in milliseconds.
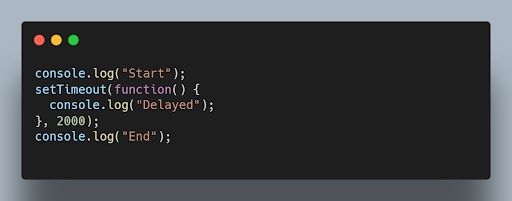
Output after two seconds:
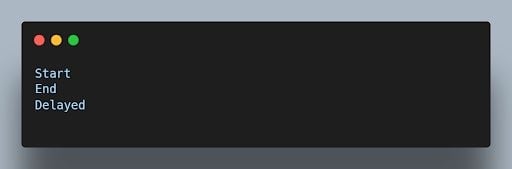
32. What is event delegation and why is it useful?
Event delegation is a technique where you attach a single event listener to a parent element to handle events occurring on its child elements. It’s useful for dynamically created elements or when you have a large number of elements.
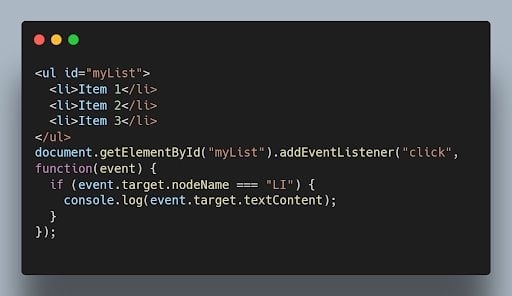
33. How can you prevent the default behavior of an event in JavaScript?
You can use the preventDefault() method on the event object within an event handler to prevent the default behavior associated with that event.
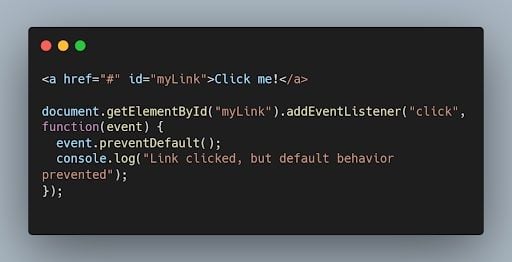
34. What is the difference between localStorage and sessionStorage in JavaScript?
Both localStorage and sessionStorage are web storage objects in JavaScript, but they have different scopes and lifetimes.
- localStorage persists data even after the browser window is closed and is accessible across different browser tabs/windows of the same origin.
- sessionStorage stores data for a single browser session and is accessible only within the same tab or window.
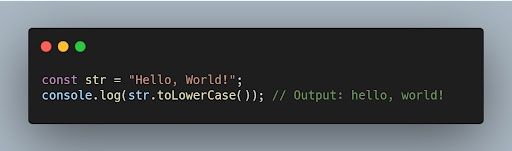
35. How can you convert a string to lowercase in JavaScript?
You can use the toLowerCase() method to convert a string to lowercase in JavaScript.
Advanced Concepts
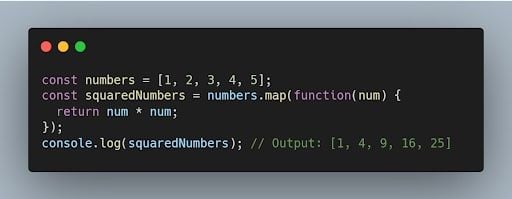
36. what is the purpose of the map() function in javascript.
The map() function is used to iterate over an array and apply a transformation or computation on each element. It returns a new array with the results of the transformation.
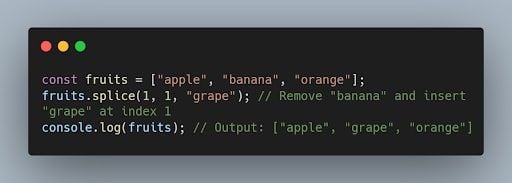
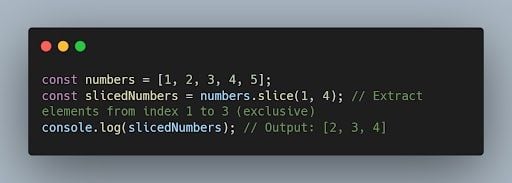
37. What is the difference between splice() and slice() ?
- splice() is used to modify an array by adding, removing, or replacing elements at a specific position.
- slice() is used to create a new array that contains a portion of an existing array, specified by the starting and ending indices.
Example of splice() :
Example of slice() :
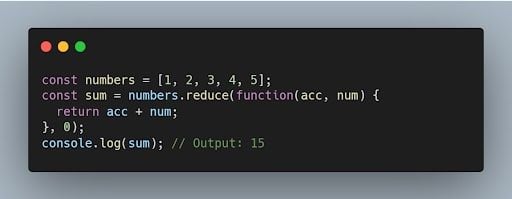
38. What is the purpose of the reduce() function in JavaScript?
The reduce() function is used to reduce an array to a single value by applying a function to each element and accumulating the result.
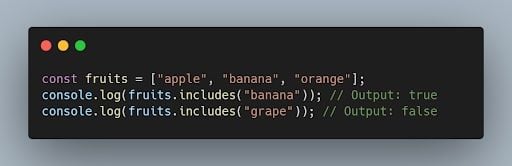
39. How can you check if an array includes a certain value in JavaScript?
You can use the includes() method to check if an array includes a specific value. It returns true if the value is found, and false otherwise.
40. What is the difference between prototype and instance properties in JavaScript?
A prototype property is a property that is defined on the prototype object of a constructor function. Instance properties are properties that are defined on individual objects that are created by a constructor function.
Prototype properties are shared by all objects that are created by a constructor function. Instance properties are not shared by other objects.
41. What is the difference between an array and an object in JavaScript?
An array is a data structure that can store a collection of values. An object is a data structure that can store a collection of properties.
Arrays are indexed by numbers. Objects are indexed by strings. Arrays can only store primitive data types and objects. Objects can store primitive data types, objects and arrays.
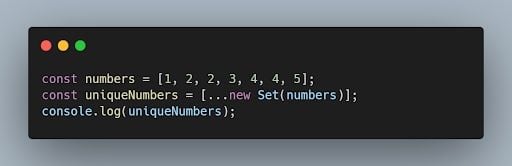
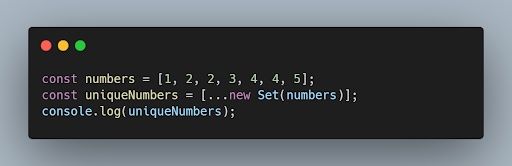
42. How can you remove duplicates from an array in JavaScript?
One way to remove duplicates from an array is by using the Set object or by using the filter() method with the indexOf() method.
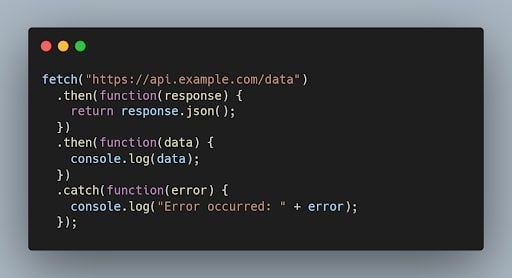
43. What is the purpose of the fetch() function in JavaScript?
The fetch() function is used to make asynchronous HTTP requests in JavaScript. It returns a Promise that resolves to the response from the server.
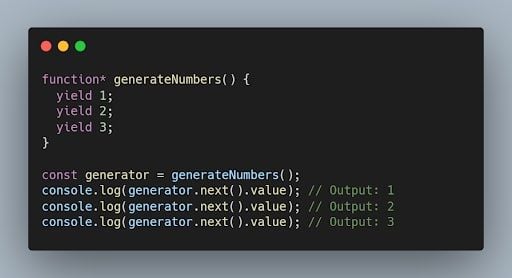
44. What is a generator function in JavaScript?
A generator function is a special type of function that can be paused and resumed during its execution. It allows generating a sequence of values over time, using the yield keyword.
45. What are the different events in JavaScript?
There are many different events in JavaScript, but some of the most common events include:
- Click : The click event occurs when a user clicks on an HTML element.
- Mouseover : The mouseover event occurs when a user's mouse pointer moves over an HTML element.
- Keydown : The keydown event occurs when a user presses a key on the keyboard.
- Keyup : The keyup event occurs when a user releases a key on the keyboard.
- Change : The change event occurs when a user changes the value of an HTML input element.
46. What are the different ways to access an HTML element in JavaScript?
There are three main ways to access an HTML element in JavaScript:
- Using the getElementById() method: The getElementById() method takes a string as an argument and returns the HTML element with the specified ID.
- Using the getElementsByTagName() method: The getElementsByTagName() method takes a string as an argument and returns an array of all the HTML elements with the specified tag name.
- Using the querySelector() method : The querySelector() method takes a CSS selector as an argument and returns the first HTML element that matches the selector.
47. What is the scope of a variable in JavaScript?
The scope of a variable in JavaScript is the part of the code where the variable can be accessed. Variables declared with the var keyword have a local scope, which means that they can only be accessed within the block of code where they are declared. Variables declared with the let keyword have a block scope, which means that they can only be accessed within the block of code where they are declared and any nested blocks. Variables declared with the const keyword have a global scope, which means that they can be accessed from anywhere in the code.
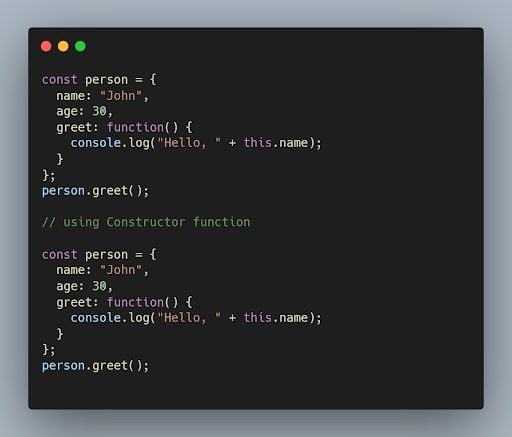
48. What are the different ways to create objects in JavaScript?
There are multiple ways to create objects in JavaScript, including object literals, constructor functions, the Object.create() method and the class syntax introduced in ECMAScript 2015 (ES6).
Example using object literals:
49. What is the purpose of the window object in JavaScript?
The window object represents the browser window. The window object can be used to access the browser’s features, such as the location bar, the status bar and the bookmarks bar.
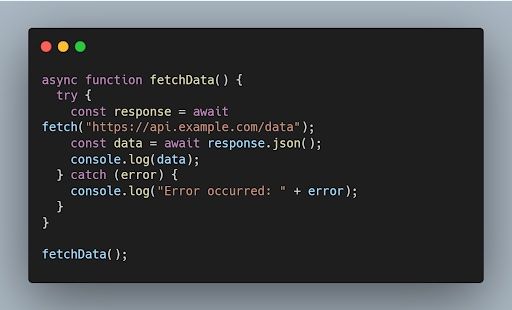
50. What is the purpose of the async and await keywords in JavaScript?
The async and await keywords are used for handling asynchronous operations in a more synchronous-like manner. The async keyword is used to define an asynchronous function, and the await keyword is used to pause the execution of an async function until a promise is fulfilled or rejected.
More on JavaScript JavaScript PreventExtensions Method Explained
How to Prepare for a JavaScript Interview
In order to ace a JavaScript interview, you need to be ready for anything. It’s important to practice your code, but you should also be able to clearly explain how different functions work, have real world experience working in JavaScript and understand how to debug.
7 Ways to Prepare for a JavaScript Interview
- Review JavaScript fundamentals.
- Master key concepts.
- Study common interview questions.
- Master debugging skills.
- Practice coding.
- Build projects.
- Mock interviews.
Fortunately, there are some basic steps you can take to be prepared and stand out from other applicants.
1. Review JavaScript Fundamentals
Make sure you are well-versed in the foundational concepts of JavaScript, such as data types , variables , operators, control structures, functions and objects .
2. Master Key Concepts
It’s also important to study up on key JavaScript topics like promises, asynchronous programming , hoisting, scope, closures, prototypes and ES6 features. You should understand how each of these works.
3. Study Common Interview Topics
Take the time to review JavaScript interview questions that are regularly asked, including those about closures, prototypes, callbacks, promises, AJAX (asynchronous JavaScript and XML), error handling and module systems. Most interviews follow a similar pattern. Preparing answers for those questions will help you stand out from other candidates.
4. Master Debugging Skills
Interviewers for JavaScript will often look to assess your code debugging skills. Practice using IDEs or browser developer tools to find and correct common JavaScript code issues. Learn how to read error messages and review basic debugging techniques.
5. Practice Coding
To develop your coding abilities, complete coding tasks and challenges. Concentrate on standard JavaScript data structures and algorithms such arrays, strings, objects, recursion and sorting techniques.
Online resources like LeetCode , CodeChef and HackerRank can be used to practice coding and get ready for interviews. These websites provide a wide variety of coding puzzles and challenges covering a range of subjects and levels of complexity. They are great resources for developing your coding expertise, problem-solving skills, and algorithmic thinking, all of which are necessary for acing technical interviews.
6. Build Projects
Take on modest JavaScript projects to get experience and show that you can create useful applications. Showing off your portfolio at the interview is also beneficial. In addition, developers can also work on JavaScript projects to obtain practical experience and show that they are capable of building effective applications. A diversified portfolio can be quite helpful when applying for jobs. Platforms like LeetCode, CodeChef, HackerRank and others enable users to develop projects gradually, starting with minor ones and eventually progressing to more ambitious ones.
7. Mock Interviews
With a friend or mentor, practice mock interviews paying particular attention to both behavioral and technical components. This enables you to hear useful criticism and become accustomed to the interview process.
It’s not just mastering the technical aspect of JavaScript, it’s about your body language and how you explain your answers. Many companies are also assessing your ability to work within a team and pair program . The better you can explain your actions and thought process, the more likely you’ll be to win over the interviewer.
Built In’s expert contributor network publishes thoughtful, solutions-oriented stories written by innovative tech professionals. It is the tech industry’s definitive destination for sharing compelling, first-person accounts of problem-solving on the road to innovation.
Great Companies Need Great People. That's Where We Come In.
37 Essential JavaScript Interview Questions *
Toptal sourced essential questions that the best javascript developers and engineers can answer. driven from our community, we encourage experts to submit questions and offer feedback..
Interview Questions
What is a potential pitfall with using typeof bar === "object" to determine if bar is an object? How can this pitfall be avoided?
Although typeof bar === "object" is a reliable way of checking if bar is an object, the surprising gotcha in JavaScript is that null is also considered an object!
Therefore, the following code will, to the surprise of most developers, log true (not false ) to the console:
As long as one is aware of this, the problem can easily be avoided by also checking if bar is null :
To be entirely thorough in our answer, there are two other things worth noting:
First, the above solution will return false if bar is a function. In most cases, this is the desired behavior, but in situations where you want to also return true for functions, you could amend the above solution to be:
Second, the above solution will return true if bar is an array (e.g., if var bar = []; ). In most cases, this is the desired behavior, since arrays are indeed objects, but in situations where you want to also false for arrays, you could amend the above solution to be:
However, there’s one other alternative that returns false for nulls, arrays, and functions, but true for objects:
Or, if you’re using jQuery:
ES5 makes the array case quite simple, including its own null check:
What will the code below output to the console and why?
Since both a and b are defined within the enclosing scope of the function, and since the line they are on begins with the var keyword, most JavaScript developers would expect typeof a and typeof b to both be undefined in the above example.
However, that is not the case. The issue here is that most developers incorrectly understand the statement var a = b = 3; to be shorthand for:
But in fact, var a = b = 3; is actually shorthand for:
As a result (if you are not using strict mode), the output of the code snippet would be:
But how can b be defined outside of the scope of the enclosing function? Well, since the statement var a = b = 3; is shorthand for the statements b = 3; and var a = b; , b ends up being a global variable (since it is not preceded by the var keyword) and is therefore still in scope even outside of the enclosing function.
Note that, in strict mode (i.e., with use strict ), the statement var a = b = 3; will generate a runtime error of ReferenceError: b is not defined , thereby avoiding any headfakes/bugs that might othewise result. (Yet another prime example of why you should use use strict as a matter of course in your code!)
The above code will output the following to the console:
In the outer function, both this and self refer to myObject and therefore both can properly reference and access foo .
In the inner function, though, this no longer refers to myObject . As a result, this.foo is undefined in the inner function, whereas the reference to the local variable self remains in scope and is accessible there.
Apply to Join Toptal's Development Network
and enjoy reliable, steady, remote Freelance JavaScript Developer Jobs
What is the significance of, and reason for, wrapping the entire content of a JavaScript source file in a function block?
This is an increasingly common practice, employed by many popular JavaScript libraries (jQuery, Node.js, etc.). This technique creates a closure around the entire contents of the file which, perhaps most importantly, creates a private namespace and thereby helps avoid potential name clashes between different JavaScript modules and libraries.
Another feature of this technique is to allow for an easily referenceable (presumably shorter) alias for a global variable. This is often used, for example, in jQuery plugins. jQuery allows you to disable the $ reference to the jQuery namespace, using jQuery.noConflict() . If this has been done, your code can still use $ employing this closure technique, as follows:
What is the significance, and what are the benefits, of including 'use strict' at the beginning of a JavaScript source file?
The short and most important answer here is that use strict is a way to voluntarily enforce stricter parsing and error handling on your JavaScript code at runtime. Code errors that would otherwise have been ignored or would have failed silently will now generate errors or throw exceptions. In general, it is a good practice.
Some of the key benefits of strict mode include:
- Makes debugging easier. Code errors that would otherwise have been ignored or would have failed silently will now generate errors or throw exceptions, alerting you sooner to problems in your code and directing you more quickly to their source.
- Prevents accidental globals. Without strict mode, assigning a value to an undeclared variable automatically creates a global variable with that name. This is one of the most common errors in JavaScript. In strict mode, attempting to do so throws an error.
- Eliminates this coercion . Without strict mode, a reference to a this value of null or undefined is automatically coerced to the global. This can cause many headfakes and pull-out-your-hair kind of bugs. In strict mode, referencing a a this value of null or undefined throws an error.
- Note: It used to be (in ECMAScript 5) that strict mode would disallow duplicate property names (e.g. var object = {foo: "bar", foo: "baz"}; ) but as of ECMAScript 2015 this is no longer the case.
- Makes eval() safer. There are some differences in the way eval() behaves in strict mode and in non-strict mode. Most significantly, in strict mode, variables and functions declared inside of an eval() statement are not created in the containing scope (they are created in the containing scope in non-strict mode, which can also be a common source of problems).
- Throws error on invalid usage of delete . The delete operator (used to remove properties from objects) cannot be used on non-configurable properties of the object. Non-strict code will fail silently when an attempt is made to delete a non-configurable property, whereas strict mode will throw an error in such a case.
Consider the two functions below. Will they both return the same thing? Why or why not?
Surprisingly, these two functions will not return the same thing. Rather:
will yield:
Not only is this surprising, but what makes this particularly gnarly is that foo2() returns undefined without any error being thrown.
The reason for this has to do with the fact that semicolons are technically optional in JavaScript (although omitting them is generally really bad form). As a result, when the line containing the return statement (with nothing else on the line) is encountered in foo2() , a semicolon is automatically inserted immediately after the return statement.
No error is thrown since the remainder of the code is perfectly valid, even though it doesn’t ever get invoked or do anything (it is simply an unused code block that defines a property bar which is equal to the string "hello" ).
This behavior also argues for following the convention of placing an opening curly brace at the end of a line in JavaScript, rather than on the beginning of a new line. As shown here, this becomes more than just a stylistic preference in JavaScript.
What will the code below output? Explain your answer.
An educated answer to this question would simply be: “You can’t be sure. it might print out 0.3 and true , or it might not. Numbers in JavaScript are all treated with floating point precision, and as such, may not always yield the expected results.”
The example provided above is classic case that demonstrates this issue. Surprisingly, it will print out:
A typical solution is to compare the absolute difference between two numbers with the special constant Number.EPSILON :
In what order will the numbers 1-4 be logged to the console when the code below is executed? Why?
The values will be logged in the following order:
Let’s first explain the parts of this that are presumably more obvious:
1 and 4 are displayed first since they are logged by simple calls to console.log() without any delay
2 is displayed after 3 because 2 is being logged after a delay of 1000 msecs (i.e., 1 second) whereas 3 is being logged after a delay of 0 msecs.
OK, fine. But if 3 is being logged after a delay of 0 msecs, doesn’t that mean that it is being logged right away? And, if so, shouldn’t it be logged before 4 , since 4 is being logged by a later line of code?
The answer has to do with properly understanding JavaScript events and timing .
The browser has an event loop which checks the event queue and processes pending events. For example, if an event happens in the background (e.g., a script onload event) while the browser is busy (e.g., processing an onclick ), the event gets appended to the queue. When the onclick handler is complete, the queue is checked and the event is then handled (e.g., the onload script is executed).
Similarly, setTimeout() also puts execution of its referenced function into the event queue if the browser is busy.
When a value of zero is passed as the second argument to setTimeout() , it attempts to execute the specified function “as soon as possible”. Specifically, execution of the function is placed on the event queue to occur on the next timer tick. Note, though, that this is not immediate; the function is not executed until the next tick. That’s why in the above example, the call to console.log(4) occurs before the call to console.log(3) (since the call to console.log(3) is invoked via setTimeout, so it is slightly delayed).
Write a simple function (less than 160 characters) that returns a boolean indicating whether or not a string is a palindrome .
The following one line function will return true if str is a palindrome; otherwise, it returns false.
For example:
Write a sum method which will work properly when invoked using either syntax below.
There are (at least) two ways to do this:
In JavaScript, functions provide access to an arguments object which provides access to the actual arguments passed to a function. This enables us to use the length property to determine at runtime the number of arguments passed to the function.
If two arguments are passed, we simply add them together and return.
Otherwise, we assume it was called in the form sum(2)(3) , so we return an anonymous function that adds together the argument passed to sum() (in this case 2) and the argument passed to the anonymous function (in this case 3).
When a function is invoked, JavaScript does not require the number of arguments to match the number of arguments in the function definition. If the number of arguments passed exceeds the number of arguments in the function definition, the excess arguments will simply be ignored. On the other hand, if the number of arguments passed is less than the number of arguments in the function definition, the missing arguments will have a value of undefined when referenced within the function. So, in the above example, by simply checking if the 2nd argument is undefined, we can determine which way the function was invoked and proceed accordingly.
Consider the following code snippet:
(a) What gets logged to the console when the user clicks on “Button 4” and why?
(b) Provide one or more alternate implementations that will work as expected.
(a) No matter what button the user clicks the number 5 will always be logged to the console. This is because, at the point that the onclick method is invoked (for any of the buttons), the for loop has already completed and the variable i already has a value of 5. (Bonus points for the interviewee if they know enough to talk about how execution contexts, variable objects, activation objects, and the internal “scope” property contribute to the closure behavior.)
(b) The key to making this work is to capture the value of i at each pass through the for loop by passing it into a newly created function object. Here are four possible ways to accomplish this:
Alternatively, you could wrap the entire call to btn.addEventListener in the new anonymous function:
Or, we could replace the for loop with a call to the array object’s native forEach method:
Lastly, the simplest solution, if you’re in an ES6/ES2015 context, is to use let i instead of var i :
Assuming d is an “empty” object in scope, say:
…what is accomplished using the following code?
The snippet of code shown above sets two properties on the object d . Ideally, any lookup performed on a JavaScript object with an unset key evaluates to undefined . But running this code marks those properties as “own properties” of the object.
This is a useful strategy for ensuring that an object has a given set of properties. Passing this object to Object.keys will return an array with those set keys as well (even if their values are undefined ).
The logged output will be:
arr1 and arr2 are the same (i.e. ['n','h','o','j', ['j','o','n','e','s'] ] ) after the above code is executed for the following reasons:
Calling an array object’s reverse() method doesn’t only return the array in reverse order, it also reverses the order of the array itself (i.e., in this case, arr1 ).
The reverse() method returns a reference to the array itself (i.e., in this case, arr1 ). As a result, arr2 is simply a reference to (rather than a copy of) arr1 . Therefore, when anything is done to arr2 (i.e., when we invoke arr2.push(arr3); ), arr1 will be affected as well since arr1 and arr2 are simply references to the same object.
And a couple of side points here that can sometimes trip someone up in answering this question:
Passing an array to the push() method of another array pushes that entire array as a single element onto the end of the array. As a result, the statement arr2.push(arr3); adds arr3 in its entirety as a single element to the end of arr2 (i.e., it does not concatenate the two arrays, that’s what the concat() method is for).
Like Python, JavaScript honors negative subscripts in calls to array methods like slice() as a way of referencing elements at the end of the array; e.g., a subscript of -1 indicates the last element in the array, and so on.
What will the code below output to the console and why ?
Here’s why…
The fundamental issue here is that JavaScript (ECMAScript) is a loosely typed language and it performs automatic type conversion on values to accommodate the operation being performed. Let’s see how this plays out with each of the above examples.
Example 1: 1 + "2" + "2" Outputs: "122" Explanation: The first operation to be performed in 1 + "2" . Since one of the operands ( "2" ) is a string, JavaScript assumes it needs to perform string concatenation and therefore converts the type of 1 to "1" , 1 + "2" yields "12" . Then, "12" + "2" yields "122" .
Example 2: 1 + +"2" + "2" Outputs: "32" Explanation: Based on order of operations, the first operation to be performed is +"2" (the extra + before the first "2" is treated as a unary operator). Thus, JavaScript converts the type of "2" to numeric and then applies the unary + sign to it (i.e., treats it as a positive number). As a result, the next operation is now 1 + 2 which of course yields 3 . But then, we have an operation between a number and a string (i.e., 3 and "2" ), so once again JavaScript converts the type of the numeric value to a string and performs string concatenation, yielding "32" .
Example 3: 1 + -"1" + "2" Outputs: "02" Explanation: The explanation here is identical to the prior example, except the unary operator is - rather than + . So "1" becomes 1 , which then becomes -1 when the - is applied, which is then added to 1 yielding 0 , which is then converted to a string and concatenated with the final "2" operand, yielding "02" .
Example 4: +"1" + "1" + "2" Outputs: "112" Explanation: Although the first "1" operand is typecast to a numeric value based on the unary + operator that precedes it, it is then immediately converted back to a string when it is concatenated with the second "1" operand, which is then concatenated with the final "2" operand, yielding the string "112" .
Example 5: "A" - "B" + "2" Outputs: "NaN2" Explanation: Since the - operator can not be applied to strings, and since neither "A" nor "B" can be converted to numeric values, "A" - "B" yields NaN which is then concatenated with the string "2" to yield “NaN2”.
Example 6: "A" - "B" + 2 Outputs: NaN Explanation: As exlained in the previous example, "A" - "B" yields NaN . But any operator applied to NaN with any other numeric operand will still yield NaN .
The following recursive code will cause a stack overflow if the array list is too large. How can you fix this and still retain the recursive pattern?
The potential stack overflow can be avoided by modifying the nextListItem function as follows:
The stack overflow is eliminated because the event loop handles the recursion, not the call stack. When nextListItem runs, if item is not null, the timeout function ( nextListItem ) is pushed to the event queue and the function exits, thereby leaving the call stack clear. When the event queue runs its timed-out event, the next item is processed and a timer is set to again invoke nextListItem . Accordingly, the method is processed from start to finish without a direct recursive call, so the call stack remains clear, regardless of the number of iterations.
What is a “closure” in JavaScript? Provide an example.
A closure is an inner function that has access to the variables in the outer (enclosing) function’s scope chain. The closure has access to variables in three scopes; specifically: (1) variable in its own scope, (2) variables in the enclosing function’s scope, and (3) global variables.
Here is an example:
In the above example, variables from innerFunc , outerFunc , and the global namespace are all in scope in the innerFunc . The above code will therefore produce the following output:
What would the following lines of code output to the console?
Explain your answer.
The code will output the following four lines:
In JavaScript, both || and && are logical operators that return the first fully-determined “logical value” when evaluated from left to right.
The or ( || ) operator. In an expression of the form X||Y , X is first evaluated and interpreted as a boolean value. If this boolean value is true , then true (1) is returned and Y is not evaluated, since the “or” condition has already been satisfied. If this boolean value is “false”, though, we still don’t know if X||Y is true or false until we evaluate Y , and interpret it as a boolean value as well.
Accordingly, 0 || 1 evaluates to true (1), as does 1 || 2 .
The and ( && ) operator. In an expression of the form X&&Y , X is first evaluated and interpreted as a boolean value. If this boolean value is false , then false (0) is returned and Y is not evaluated, since the “and” condition has already failed. If this boolean value is “true”, though, we still don’t know if X&&Y is true or false until we evaluate Y , and interpret it as a boolean value as well.
However, the interesting thing with the && operator is that when an expression is evaluated as “true”, then the expression itself is returned. This is fine, since it counts as “true” in logical expressions, but also can be used to return that value when you care to do so. This explains why, somewhat surprisingly, 1 && 2 returns 2 (whereas you might it expect it to return true or 1 ).
What will be the output when the following code is executed? Explain.
The code will output:
In JavaScript, there are two sets of equality operators. The triple-equal operator === behaves like any traditional equality operator would: evaluates to true if the two expressions on either of its sides have the same type and the same value. The double-equal operator, however, tries to coerce the values before comparing them. It is therefore generally good practice to use the === rather than == . The same holds true for !== vs != .
What is the output out of the following code? Explain your answer.
The output of this code will be 456 ( not 123 ).
The reason for this is as follows: When setting an object property, JavaScript will implicitly stringify the parameter value. In this case, since b and c are both objects, they will both be converted to "[object Object]" . As a result, a[b] and a[c] are both equivalent to a["[object Object]"] and can be used interchangeably. Therefore, setting or referencing a[c] is precisely the same as setting or referencing a[b] .
What will the following code output to the console:
The code will output the value of 10 factorial (i.e., 10!, or 3,628,800).
Here’s why:
The named function f() calls itself recursively, until it gets down to calling f(1) which simply returns 1 . Here, therefore, is what this does:
Consider the code snippet below. What will the console output be and why?
The output will be 1 , even though the value of x is never set in the inner function. Here’s why:
As explained in our JavaScript Hiring Guide , a closure is a function, along with all variables or functions that were in-scope at the time that the closure was created. In JavaScript, a closure is implemented as an “inner function”; i.e., a function defined within the body of another function. An important feature of closures is that an inner function still has access to the outer function’s variables.
Therefore, in this example, since x is not defined in the inner function, the scope of the outer function is searched for a defined variable x , which is found to have a value of 1 .
What will the following code output to the console and why:
What is the issue with this code and how can it be fixed.
The first console.log prints undefined because we are extracting the method from the hero object, so stoleSecretIdentity() is being invoked in the global context (i.e., the window object) where the _name property does not exist.
One way to fix the stoleSecretIdentity() function is as follows:
Create a function that, given a DOM Element on the page, will visit the element itself and all of its descendents ( not just its immediate children ). For each element visited, the function should pass that element to a provided callback function.
The arguments to the function should be:
- a DOM element
- a callback function (that takes a DOM element as its argument)
Visiting all elements in a tree (DOM) is a classic Depth-First-Search algorithm application. Here’s an example solution:
Testing your this knowledge in JavaScript: What is the output of the following code?
Why isn’t it 10 and 5 ?
In the first place, as fn is passed as a parameter to the function method , the scope ( this ) of the function fn is window . var length = 10; is declared at the window level. It also can be accessed as window.length or length or this.length (when this === window .)
method is bound to Object obj , and obj.method is called with parameters fn and 1 . Though method is accepting only one parameter, while invoking it has passed two parameters; the first is a function callback and other is just a number.
When fn() is called inside method , which was passed the function as a parameter at the global level, this.length will have access to var length = 10 (declared globally) not length = 5 as defined in Object obj .
Now, we know that we can access any number of arguments in a JavaScript function using the arguments[] array.
Hence arguments[0]() is nothing but calling fn() . Inside fn now, the scope of this function becomes the arguments array, and logging the length of arguments[] will return 2 .
Hence the output will be as above.
Consider the following code. What will the output be, and why?
var statements are hoisted (without their value initialization) to the top of the global or function scope it belongs to, even when it’s inside a with or catch block. However, the error’s identifier is only visible inside the catch block. It is equivalent to:
What will be the output of this code?
Neither 21, nor 20, the result is undefined
It’s because JavaScript initialization is not hoisted.
(Why doesn’t it show the global value of 21? The reason is that when the function is executed, it checks that there’s a local x variable present but doesn’t yet declare it, so it won’t look for global one.)
What will this code print?
It will print 0 1 2 3 4 , because we use let instead of var here. The variable i is only seen in the for loop’s block scope.
What do the following lines output, and why?
The first statement returns true which is as expected.
The second returns false because of how the engine works regarding operator associativity for < and > . It compares left to right, so 3 > 2 > 1 JavaScript translates to true > 1 . true has value 1 , so it then compares 1 > 1 , which is false .
How do you add an element at the begining of an array? How do you add one at the end?
With ES6, one can use the spread operator:
Or, in short:
Imagine you have this code:
a) Will this result in a crash?
b) What will this output?
a) It will not crash. The JavaScript engine will make array slots 3 through 9 be “empty slots.”
b) Here, a[6] will output undefined , but the slot still remains empty rather than filled with undefined . This may be an important nuance in some cases. For example, when using map() , empty slots will remain empty in map() ’s output, but undefined slots will be remapped using the function passed to it:
What is the value of typeof undefined == typeof NULL ?
The expression will be evaluated to true, since NULL will be treated as any other undefined variable.
Note: JavaScript is case-sensitive and here we are using NULL instead of null .
What would following code return?
typeof 1 will return "number" and typeof "number" will return string .
What will be the output of the following code:
Explain your answer. How could the use of closures help here?
The code sample shown will not display the values 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 as might be expected; rather, it will display 5, 5, 5, 5, and 5.
The reason for this is that each function executed within the loop will be executed after the entire loop has completed and all will therefore reference the last value stored in i , which was 5.
Closures can be used to prevent this problem by creating a unique scope for each iteration, storing each unique value of the variable within its scope, as follows:
This will produce the presumably desired result of logging 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 to the console.
In an ES2015 context , you can simply use let instead of var in the original code:
What is NaN ? What is its type? How can you reliably test if a value is equal to NaN ?
The NaN property represents a value that is “not a number”. This special value results from an operation that could not be performed either because one of the operands was non-numeric (e.g., "abc" / 4 ), or because the result of the operation is non-numeric.
While this seems straightforward enough, there are a couple of somewhat surprising characteristics of NaN that can result in hair-pulling bugs if one is not aware of them.
For one thing, although NaN means “not a number”, its type is, believe it or not, Number :
Additionally, NaN compared to anything – even itself! – is false:
A semi-reliable way to test whether a number is equal to NaN is with the built-in function isNaN() , but even using isNaN() is an imperfect solution .
A better solution would either be to use value !== value , which would only produce true if the value is equal to NaN. Also, ES6 offers a new Number.isNaN() function, which is a different and more reliable than the old global isNaN() function.
What will the following code output and why?
Output to the console will be “3”.
There are three closures in the example, each with it’s own var b declaration. When a variable is invoked closures will be checked in order from local to global until an instance is found. Since the inner closure has a b variable of its own, that is what will be output.
Furthermore, due to hoisting the code in inner will be interpreted as follows:
Discuss possible ways to write a function isInteger(x) that determines if x is an integer.
This may sound trivial and, in fact, it is trivial with ECMAscript 6 which introduces a new Number.isInteger() function for precisely this purpose. However, prior to ECMAScript 6, this is a bit more complicated, since no equivalent of the Number.isInteger() method is provided.
The issue is that, in the ECMAScript specification, integers only exist conceptually; i.e., numeric values are always stored as floating point values.
With that in mind, the simplest and cleanest pre-ECMAScript-6 solution (which is also sufficiently robust to return false even if a non-numeric value such as a string or null is passed to the function) would be the following use of the bitwise XOR operator:
The following solution would also work, although not as elegant as the one above:
The following function (or with Math.ceil() or Math.floor() in place of Math.round() ) might also seem useful, but the results are not exactly the same as with the above two functions:
The difference is, these Math -based solutions return true for Infinity and -Infinity , whereas the others (and notably ES6’s Number.isInteger() ) return false .
Another fairly common incorrect solution is the following:
While this parseInt -based approach will work well for many values of x , once x becomes quite large, it will fail to work properly. The problem is that parseInt() coerces its first parameter to a string before parsing digits. Therefore, once the number becomes sufficiently large, its string representation will be presented in exponential form (e.g., 1e+21 ). Accordingly, parseInt() will then try to parse 1e+21 , but will stop parsing when it reaches the e character and will therefore return a value of 1 . Observe:
How do you clone an object?
Now the value of objclone is {a: 1 ,b: 2} but points to a different object than obj .
Note the potential pitfall, though: Object.assign() will just do a shallow copy, not a deep copy. This means that nested objects aren’t copied. They still refer to the same nested objects as the original:
There is more to interviewing than tricky technical questions, so these are intended merely as a guide. Not every “A” candidate worth hiring will be able to answer them all, nor does answering them all guarantee an “A” candidate. At the end of the day, hiring remains an art, a science — and a lot of work .
Tired of interviewing candidates? Not sure what to ask to get you a top hire?
Let Toptal find the best people for you.
Our Exclusive Network of JavaScript Developers
Looking to land a job as a JavaScript Developer?
Let Toptal find the right job for you.
Job Opportunities From Our Network
Submit an interview question
Submitted questions and answers are subject to review and editing, and may or may not be selected for posting, at the sole discretion of Toptal, LLC.
Looking for JavaScript Developers?
Looking for JavaScript Developers ? Check out Toptal’s JavaScript developers.

Jay Johnston
Coding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript since his armed forces days in 1997, Jay enjoys bringing value to clients via eCommerce solutions, legacy integrations, and optimized PHP and JavaScript-driven applications. His preferred DevOps environment is AWS, where he has strong skills in (and not limited to): Relational Database Services (RDS), Redshift, Dynamo DB, Data Migration Services (DMS), Lambda (serverless and microservices), Cloudwatch, Cloudtrail, and Event Bridge.

Tyler Standley
Along with strong communication skills and an exemplary work ethic, Tyler brings his hands-on experience with a wide range of programming languages. Recently, though, his focus has been directed towards JavaScript libraries. Throughout his career, he’s worked on multiple agile teams as a core developer and is now interested in working on anything JavaScript-related.

Justin Michela
Justin is a technical professional with a passion for learning and 18+ years of experience leading teams to build enterprise-grade distributed applications that solve real-world problems. Justin firmly believes that collaboration across all facets of a business, from development to marketing to sales, is required to succeed in this endeavor.
Toptal Connects the Top 3% of Freelance Talent All Over The World.
Join the Toptal community.
Top 30 JavaScript Interview Questions + Answers (with Code Snippets)

Jacinto Wong

In This Guide:
Beginner javascript interview questions, intermediate javascript interview questions, advanced javascript interview questions, so how did you do.
Are you preparing for a job interview as a front-end developer, and want to brush up on your knowledge?
Well, good news! In this guide, I’m going to share 30 of the most common and relevant interview questions related to JavaScript.
And better still? For each question, I've provided a concise and easy-to-understand answer, along with a code snippet that illustrates the concept in action. This means, no more awkward situations of actually knowing an answer, but not being able to clearly explain it!
Ideally, you should know the answers to all these questions before sitting your interview, and just use this guide as a reminder / last minute prep.
However, if you find that you’re really struggling to understand some of the concepts, then be sure to check out Andrei’s complete Web Developer bootcamp to get a better understanding of the core elements of JavaScript, as well as his advanced JavaScript concepts course .
Also, if you want to put these principles into practice and build a stand out portfolio, then check out my top 20 JavaScript projects course .
Those 3 resources will not only cover any issues that you may encounter while learning this language, but they’ll also get you to the level where interviewers are seriously blown away with your skills.
(No joke, you can go from trying to get hired, to recruiters actively trying to bring you in instead!)

Anyways, with all that out of the way, let’s get into these interview questions!
Some of these questions will seem super basic or obvious, and you might think “ Why on earth would an interviewer ever ask these of me? ”.
The simple fact is that some initial interviews are done by non-technical people first as a quality filter, and they might ask simple questions around the language.
This means that it's worth being able to answer the basics very confidently and concisely to make sure you get past the gatekeeper and advance through to a 2nd interview with team leads where you'll get more advanced questions and/or live coding tests.
#1. What is JavaScript? What are some of its core ‘stand-out’ features?
JavaScript (also commonly known as JS), is a high-level programming language that is used to create interactive elements on the web.
One of the cool things about JavaScript is that it can change the content of a web page without needing to reload the whole thing.
For example: when you click on a button on a website and something happens, such as a new message appearing, that's often because of JavaScript, and it leads to a much better user experience.
JavaScript also has some other special features that make it powerful:
- It can ‘handle events’, which means it can respond to things like mouse clicks and keystrokes
- It can create objects, which are like containers that can hold data and perform actions
- JavaScript is also flexible in how it handles data. Unlike some other programming languages, you don't need to specify what kind of data a variable will hold. For example, you could create a variable called "x" and set it equal to a number, a string of text, or even an entire object
#2. What is the difference between let and var ?
In JavaScript, both let and var are used to declare variables, but they have some key differences in how they are scoped.
For example
Variables declared with var are function-scoped , meaning that they are visible throughout the entire function in which they are declared.
While variables declared with let are block-scoped , meaning that they are visible only within the block in which they are declared. (A block is typically defined by curly braces, such as in a loop or an if statement).
Another practical difference between let and var is that using let can help avoid bugs caused by variable hoisting .
(Variable hoisting is a behavior of JavaScript where variables declared with var are "hoisted" to the top of the function scope, even if they are declared later in the code.)
As you can imagine, this can lead to unexpected results if you are not careful, so here's a walkthrough of what might happen.
In this code snippet, we’ve defined a function called example that declares two variables, x and y .
x is declared with var , while y is declared with let . We then use console.log to output the values of x and y within the if block, and again after the if block.
As you can see in the image above, because x is declared with var , it is visible throughout the entire function, so we can output its value both inside and outside the if block.
However, because y is declared with let , it is only visible within the if block. This means that if you try to output the y value outside the block it will result in an error, because y is not defined in that scope.
#3. What is the difference between null and undefined ?
In JS, null and undefined are both used to represent the absence of a value, but they have different meanings.
null represents a deliberate non-value, often used to indicate that a variable intentionally has no value.
On the other hand, undefined represents a value that has not been initialized, often caused by a variable that has been declared but not assigned a value as in the previous answer.
In this code snippet, we define two variables, x and y . We set x equal to null , which explicitly indicates that x has no value.
We do not set a value for y , which means that it is automatically initialized to undefined.
We then use console.log to compare x and y to null and undefined , respectively.
In both cases, the comparison evaluates to true, indicating that x and y have the expected values.
#4. What is an example of an asynchronous function?
setTimeout is a great example of an asynchronous function in JavaScript.
It’s used to delay the execution of a piece of code by a specified amount of time, and is often used to simulate a long-running operation, such as a network request.
The setTimeout function is called with a delay time of 1000 milliseconds (1 second), and a callback function that outputs the message "Inside setTimeout" to the console.
This means that the message will be delayed by 1 second before it is output to the console.
#5. How would you expect == to behave differently from === ?
Although you might not think it, the amount of equal signs is very important.
Using just one = will assign a value, (which admittedly, is something I’ve done unintentionally once or twice), while == and === are both used to compare values, but they have different rules.
== is known as the "loose equality" operator, because it will try to convert the values being compared to a common type before making the comparison.
On the other hand, === is known as the "strict equality" operator, because it does not allow for type coercion, and requires that the types of the values being compared match exactly.
In this example, we use console.log to compare the values 1 and '1' using both == and === .
As you can see, when we use == , the comparison returns true, because JavaScript converts the string '1' to a number before making the comparison.
However, when we use === , the comparison returns false, because the types of the values do not match exactly.
This demonstrates the importance of understanding the difference between == and === when comparing values in JavaScript.
If you are not careful, using the wrong operator can lead to unpredictable results, especially when dealing with different data types. As a best practice, it is generally recommended to use === for strict equality comparisons whenever possible.
#6. What are the benefits of using a ternary operator?
The ternary operator is a shorthand way of writing an if statement that has a single expression for both the true and false cases.
Also, the ternary operator can make your code more concise and easier to read, especially in cases where you need to make a simple comparison and return a value based on the result.
However, it's important to note that the ternary operator is not always the best choice for every situation, and in some cases, an if statement may be more appropriate.
In the image above, you can see how both the ternary operator and if statements can be used to achieve the same result, and how you can choose the appropriate approach based on the specific requirements of your code.
In general though, the ternary operator is a good choice for simple comparisons that return a single value, while if statements are better suited for more complex logic or multiple expressions.
#7. What is a template literal and how is it used?
A template literal allows for string interpolation, which means that you can embed expressions inside the string literal.
This can be useful for creating more dynamic and flexible strings, such as HTML or SQL queries , where you need to include dynamic values or expressions.
In this code snippet, we declare a variable num and set its value to 42.
We then use a template literal to create a string that includes the value of the num variable.
(The syntax for a template literal is to enclose the string in backticks instead of single or double quotes, and to use ${} to embed expressions inside the string).
You can use template literals to create more readable and maintainable code, by avoiding the need for concatenation or complex string manipulation.
This is especially useful when you are giving some kind of alert to the user about updating a record, you can always pass the name of whatever they just updated dynamically.
#8. Why is it better to use textContent instead of innerHTML ?
Both textContent and innerHTML are used to manipulate the contents of an HTML element. However, there are some important differences between the two that make textContent a better choice.
The main difference between textContent and innerHTML is that textContent sets or retrieves only the text content of an element, while innerHTML sets or retrieves both the HTML content and the text content of an element.
This means that because textContent only deals with the text content of an element, it is generally faster and safer to use than innerHTML .
Not only that, but it's also more secure, thanks to the fact that textContent does not parse HTML tags or execute scripts, which can lead to security vulnerabilities and performance issues when using innerHTML .
In general, it is a good practice to use textContent whenever you need to manipulate the text content of an element, and to use innerHTML only when you need to manipulate the HTML content of an element.
#9. What are some common libraries and frameworks used in JavaScript?
Everyone will have a different answer if asked what their library or framework of choice is. I’m personally most familiar with Angular, after starting out learning React.
Both of these (and many others) are somewhat similar and at their core in that they are all JavaScript. They simply allow you to automate more of the process, using and re-using pre-built components, services, etc.
jQuery is a widely used library that makes it easier to manipulate HTML documents, handle events, and create animations.
Developers can write less code and achieve more functionality in some cases. It is actually easier in the sense that you can target any HTML element by almost any property and interact with it.
React is a library that enables developers to build fast, scalable, and dynamic user interfaces.
It is often used for creating single-page applications, mobile apps, and other interactive web experiences. Originally invented by Facebook as they were scaling their platform.
Angular is a popular framework that is well-documented and has a lot of tooling that automates things like making a progressive web app using the Angular CLI.
Google maintains it, and has a large and active community of developers contributing to its development.
There are many other libraries and frameworks available in JavaScript, each with their own strengths and weaknesses.
At the end of the day, your choice of library or framework depends mainly on your specific project requirements, your familiarity with the tool, and the overall community support and development behind it.
Andrei does a great job breaking down the pros and cons of React vs. Angular vs. Vue in this article here , if you want to dive deeper into three of the most popular JavaScript frameworks.
#10. How do you keep up with the latest developments in JavaScript?
Interviewers are trying to guage your curiosity and interest level. Generally speaking, people who truly "geek out" will end up being more successful than people who just want a job.
And since the industry evolves and changes so fast, you constantly need to be learning new things.
So it's important to show interviews how you're staying up-to-date.
There are a few different options:
- Reading popular blogs (ex: JavaScript Weekly, Hackernoon, etc.) and newsletters is the easiest way (ex: Andrei's Web Developer Monthly newsletter )
- Attending conferences and meetups is a great way to meet other developers and learn new things
- There are many online communities for JavaScript developers , including forums, chat rooms, and social media groups
- Applying what you learn in new projects! It’s not a new source, but showing that you're actually trying out new things on your own projects (and being able to explain why they are good or not good) is infinitely more valuable than only knowing what they are
#11. What are higher-order functions? Can you give an example?
A higher-order function takes one or more functions as arguments, or returns a function as the result, which allows for more concise and reusable code.
There are many ways to use higher order functions, but they are commonly used in functional programming, as well as in popular libraries and frameworks like React and Redux.
multiplyBy is a higher-order function that returns a new function that multiplies a given number, while the returned function is a closure that has access to the factor argument even after the multiplyBy function has returned.
We then use the multiplyBy function to create two new functions, double and triple, that multiply a given number by 2 and 3.
We can then call these functions with a number argument to get the result.
#12. What's the difference between a callback function and a Promise?
In JavaScript, a callback function is a function that is passed as an argument to another function and is called when that function has completed its task.
A Promise, on the other hand, is an object that represents the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation, and allows for more flexibility when handling an error by using the built-in .catch() method.
In both examples, we are using the hard-coded data array as the value, but you would usually have a GET call instead that is returning data.
In the first example, it would receive this data and then execute the callback function once complete to console.log the output in this case.
But in the second example, you would have some logic to decide whether or not to resolve or reject the promise. The benefit of the promise is that it has built-in methods to catch the error or execute the console.log when data is returned.
#13. How does the ‘this’ keyword work?
In JavaScript, the this keyword refers to the object that the current function or method is a property of, or the object that the function is invoked on, and can have different values depending on how a function is called.
In this example, we are able to pass the name John correctly and the this keyword refers to the person object.
However, when we try to assign the sayHello method to the variable greet, it becomes a stand-alone function and the name becomes undefined. The reason is that this refers to the global variable and not the person object the sayHello function is a method of.
This is something I’d commonly use in Angular to define global variables, created above the constructor, which are very helpful in allowing for different functions to share the same value.
#14. Explain the concept of prototypal inheritance and why you might use it
Prototypal inheritance is a mechanism where an object can inherit properties and methods from another prototype object. This means that every object has a prototype, which is an object that serves as a template for the new object…
Let me clear this up with an example.
Here you can see that animal is a prototype object and the dog object is inheriting the type property, as well as the eat method.
And because the dog object is created using Object.create , the type is then passed and when the dog.eat() method is called, it is able to console.log the type correctly, as so:
“The dog is eating”.
The benefits of using prototype objects like this is that it allows you to create hierarchies and reuse code in a more flexible and modular way.
#15. Can you give an example of when you would use map() , filter() , reduce() ?
map() , filter() , and reduce() are three commonly used array methods that allow developers to work with arrays in a more concise and functional way.
map() example
map() is used to create a new array by mapping each element of an existing array to a new value using a callback function, which takes three arguments:
- the current element
- the index of the current element, and
- the original array
Here's an example of using map() to create a new array of squared values:
filter() example
filter() is used to create a new array containing only the elements of an existing array that pass a certain condition, as determined by a callback function.
Note: The callback function takes the same three arguments as the map() method.
Here's an example of using filter() to create a new array of even numbers:
reduce() example
reduce() is used to reduce an array to a single value by applying a callback function to each element of the array, accumulating the results as it goes.
The callback function takes four arguments:
- the accumulator (which holds the current accumulated value)
Here's an example of using reduce() to find the sum of an array of numbers:
#16. What are the different ways to create an object? Which one do you prefer?
There are several ways to create objects and the simplest and most used method is object literals. They are created with curly braces ‘{}’ and include key-value pairs separated by ‘:’ as below:
Another option, introduced in ES6 is the ability to use class syntax. This is an option with more flexibility as it allows you to dynamically pass values.
In the example below, we’re passing the name and age separately, meaning this could be re-used in this case for many users.
The choice of which option to use is more personal preference, but I believe that if your goal is reusability then using the class syntax is the way to go .
#17. What is an example of how errors can be handled?
There is more than one way for errors to be handled, so here are a few methods.
Option #1. Catch blocks
Catch blocks are used for errors that occur during the execution of a method.
If there is an error in the try block, it will automatically pass the error to the next part of the function, in this case, console.logging it, but in the real world, you’d probably have a pop-up message for the users.
Option #2. Error objects
Another example are error objects, which are used to represent and handle errors.
They have properties, including ‘name’ and ‘message’ and can be customized to give more specific information.
The below example is using the ‘message’ property.
#18. When would you use a for loop or a forEach loop?
For loops and forEach loops are both used to iterate through arrays and perform some operation on each item within the array.
For loops use a counter variable, in this case represented by the ‘i’ variable.
This does make it easier to always pass this value as an index within the function itself. It also allows you to more easily go backwards through the loop, or it’s helpful if you have to loop through multiple arrays at once. (The console log would happen 5 separate times with a new number each time).
In this example, the console output is the same using a forEach loop, but you can see that the code is a little more concise, we don’t have to worry about adding the length of the array and iterating the index.
Ultimately, for loops are useful when you need to loop over an array and perform complex operations on each element, such as sorting or filtering, while ForEach loops are useful when you need to perform a simple operation on each element, such as logging or modifying the values.
#19. What is the difference between the setTimeout() and setInterval() methods?
The setTimeout() and setInterval() methods are like JavaScript's in-house timekeepers, helping you execute code after a certain amount of time has passed.
Although they share some similarities, there are key differences between these two methods.
setTimeout() swoops in to run a function just once after a specified number of milliseconds. It needs two arguments: the function to run and the milliseconds to wait before doing so.
In our example, setTimeout() is called to run the greet() function after a 1000-millisecond pause (aka one second). The function only gets executed once.
On the other hand, setInterval() is the go-to method for running a function repeatedly at a specified interval. It also takes two arguments: the function to run and the milliseconds to wait between each execution.
In this case, setInterval() is used to run the incrementCount() function every 1000 milliseconds (yes, one second again). The function keeps going, upping the count variable each time.
The key distinction between setTimeout() and setInterval() is that the first runs the specified function just once, while the latter keeps the party going at the specified interval.
In general, reach for setTimeout() when you need a function to run after a delay, and setInterval() when you want a function to run repeatedly at a specific interval.
Just remember to use these methods wisely, as overuse can lead to performance hiccups and other headaches.
#20. What is the event loop? How does it work?
The event loop is an important part of the runtime that handles asynchronous code execution in a single-threaded environment.
It works by always looping over two main components:
- the call stack, and
- the task queue
The call stack is a data structure that tracks the execution of function calls. When a function is called, it is added to the top of the call stack, and when it finishes executing, it is removed from the stack.
(The task queue is a data structure that tracks events that have completed, but have not yet been added to the call stack).
These events are typically asynchronous in nature, such as user input or network requests, and so when an asynchronous event occurs, it is added to the task queue.
In this example, we have a setTimeout() function that is set to execute after 0 milliseconds, and a Promise that is resolved immediately. We also have some console.log() statements to track the order of execution.
It starts with executing the ‘Start’ and ‘End’ logs, then the call stack is empty, so the task queue is then checked to find the Promise which gets resolved to output ‘Promise’.
With the call stack empty again, it loops through to find the setTimeout which gets executed last.
#21. Explain the difference between shallowCopy and deepCopy in JavaScript?
When we copy an object or an array, we can create either a shallowCopy or a deepCopy .
The main difference between them is that the shallowCopy of the object will continue to affect the original object, whereas the deepCopy will remain entirely separate.
We can see this occur when we try to modify the nested city property in the image above.
In the shallowCopy , the original city is changed from New York to San Francisco, whereas the deepCopy city of Los Angeles does not affect the original city.
#22. What design pattern do you prefer to use in JavaScript?
Design patterns are like secret recipes for crafting high-quality, manageable, and scalable code.
Among my favorites is the Module Pattern. It’s a powerful design pattern for creating organized, maintainable, and scalable code. It neatly bundles code into reusable modules for various applications or parts of the same app, while also preventing naming collisions, simplifies code, and enhances reusability.
The magic of the Module Pattern lies in the immediately invoked function expression (IIFE), which protects a module's variables and functions from global scope pollution and collisions.
In our example, we have a calculator module with add and subtract functions, which update a private result variable. The getResult method makes this variable public.
Our IIFE bubble wraps the module's code, keeping add and subtract functions hidden from outsiders.
#23. What are generators in JavaScript? Can you give an example of when you would use one?
Generators let developers wield control over JavaScript's flow of iteration, so that we can pause and play on demand, conjuring up a sequence of values over time.
We can implement this by using an asterisk (*) after the function keyword. We can then hit the pause button with the yield keyword, which returns a value and bookmarks the generator's state.
To hit play again, we just use the next() method, picking up where we left off.
Generators shine in various scenarios where we need to unveil a sequence of values over time, such as handling asynchronous data or processing giant datasets.
By letting us pause and play the value generation, generators are our secret weapon for controlling JavaScript's flow of iteration.
For example, we could create a generator function called fibonacci to whip up a sequence of Fibonacci numbers.
With variables a and b set to 0 and 1, our generator dives into an infinite loop, yielding a's current value and updating a and b to the next pair of Fibonacci numbers.
Next, we summon a generator instance using the fibonacci function and store it in a variable named fib. This means that with the next() method, we can stroll through the Fibonacci sequence, starting at 0 and 1.
#24. How would you effectively use every() or some() methods?
The every() and some() methods are like the dynamic duo of JavaScript array methods, helping developers quickly figure out if all or just a few elements in an array meet specific criteria.
They're perfect for writing sleek and efficient code for common array tasks, like searching for a particular value or seeing if all elements pass a certain test.
every() explained
The every() method checks if all elements in an array meet a particular condition.
It uses a callback function that runs for each element, and returns true if the callback is true for all elements, and false otherwise.
In our example, we employ the every() method to see if all elements in the numbers array are greater than zero or greater than three.
The callback function says "yay" (true) if the current element is greater than the given value, and "nay" (false) otherwise.
The every() method gives a thumbs up (true) when all elements pass, and a thumbs down (false) otherwise.
some() explained
The some() method is quite similar to every() , but it's satisfied with just one element in the array meeting the condition.
Here's an example:
In this case, we use the some() method to check if any elements in the numbers array are greater than three or greater than five. The callback function gives a "yup" (true) if the current element is greater than the given value, and "nope" (false) otherwise.
The some() method is content (true) with at least one element meeting the condition, and unhappy (false) otherwise.
To sum it up, the every() and some() methods are great for verifying if all or some elements in an array meet specific conditions. They provide a snappy and effective way to handle common array operations, boosting code readability and minimizing the risk of bugs.
#25. What is the event-driven programming paradigm? How does it work?
JavaScript uses event-driven programming to craft dynamic, interactive user interfaces, where the program's flow is driven by events happening in the system, rather than a fixed set of instructions.
In this paradigm, the program patiently awaits events like a user clicking a button or typing into a form field. When an event pops up, the program jumps into action, executing a predefined function or a callback function to handle the event.
JavaScript leans on the browser's Document Object Model (DOM) to manage events. The DOM is a family tree-like structure that represents the web page and lets you mingle with the different elements on it.
- When an event takes place, say, a user clicking a button, the DOM whips up an event object filled with info about the event, like the target element and event type
- This event object is handed over to a registered callback function
- The callback function then jazzes up the web page in response to the event, such as changing an element's text or updating a form field's value
In our example, we grab a button element using the document.getElementById() method.
Next, we sign up an event listener for the "click" event with the addEventListener() method.
When the button is clicked, the callback function we passed to addEventListener() springs into action, and "Button clicked!" is logged to the console. Huzzah!
All in all, event-driven programming is a powerful way to create lively, interactive web apps in JavaScript. By reacting to events in the system, we can design user interfaces that are responsive, intuitive, and delightful.
#26. What is the difference between a module and a namespace in JavaScript?
Modules and namespaces both offer ways of organizing code and dodging naming collisions, but there are subtle differences.
Modules explained
A module is a self-contained code unit packed with variables, functions, classes, or other code catering to a specific task or feature. Modules are great for breaking a large app into smaller, easier-to-handle pieces and keeping naming collisions at bay.
With ES6, JavaScript rolled out a built-in module system, letting developers effortlessly create, import, and export modules. Just use the export keyword to export a module and the import keyword to bring it in.
Namespaces explained
Namespaces help avoid naming collisions in sprawling applications. They are all about grouping related variables, functions, or objects under one roof.
You can create namespaces using an object literal and even nest them for a hierarchy.
In our example, we whip up a namespace called "MyApp" using an object literal. Next, we add some properties, like a message property and a sayHello() function.
By bundling these properties within a namespace, we dodge naming collisions with other parts of the app.
So, in a nutshell, modules and namespaces both keep JavaScript code organized and naming collisions at arm's length, but they serve distinct purposes. Modules craft self-contained code units that can be imported and exported in one piece, while namespaces corral related variables, functions, or objects under one name.
#27. What are decorators? How do you use them?
Decorators in JavaScript let you tweak the behavior of a class or function using a simple, elegant syntax. And as an added bonus, decorators play nice with classes, methods, and properties.
To use a decorator, just pop the @ symbol in front of the decorator function's name.
In our example, we whip up a decorator function called "log" that logs a message to the console. We then apply the decorator to a class named "MyClass" using the @log syntax.
As MyClass comes to life, the decorator function springs into action, logging "MyClass was called" to the console.
Decorators can also mingle with methods and properties, modifying their behavior. You could conjure a decorator that caches a function's result or one that adds validation to a property.
In another example, we craft a decorator function named "validate" that bestows validation on a property.
The decorator function tweaks the property's descriptor to intercept setter method calls and validate the input. If the input doesn't pass muster, an error is thrown. Next, we apply the decorator to the "name" property of a Person class, ensuring only strings are assigned to the property.
In a nutshell, decorators are a fantastic JavaScript feature that modifies the behavior of classes, methods, and properties in a flexible and reusable manner. With decorators, you can add nifty features like logging, caching, or validation to your code without drowning it in boilerplate.
#28. What is the difference between the async and defer attributes on a <script> tag in HTML?
The async and defer attributes work with HTML's <script> tag to manage script loading and execution.
The async attribute instructs the browser to download the script asynchronously while parsing the rest of the HTML document.
Why do this?
Simply because the script runs as soon as it's downloaded, even if the document hasn't fully loaded. This approach can speed up page load times, especially for non-critical scripts.
Conversely, the defer attribute tells the browser to download the script asynchronously but hold off on execution until the entire HTML document is parsed.
This means the script runs in the order it appears in the HTML document, after the DOM is fully constructed. This method also boosts page load times, particularly for DOM-manipulating scripts.
In essence, the distinction between async and defer lies in script execution timing. Async scripts run as soon as they're downloaded, while defer scripts wait until the DOM is completely constructed.
The choice between the two depends on your script's specific needs and its interaction with the page.
#29. What is the difference between localStorage and sessionStorage ?
localStorage and sessionStorage are JavaScript APIs that let web apps store data client-side, right in the browser, but they do have some key differences.
localStorage explained
localStorage is a persistent storage buddy, hanging onto your data even after you close the browser or restart your computer.
It's great for long-term data like user preferences or settings. Plus, it's a social butterfly, sharing data across tabs and windows in the same browser.
sessionStorage explained
sessionStorage , though, is more of a short-term pal. It sticks around only during the current browsing session, and its data disappears once you close the window or tab.
It's perfect for temporary data, like user input or state data for specific workflows.
They do have some similarities of course.
localStorage and sessionStorage both use key-value pairs and offer similar APIs like setItem() , getItem() , and removeItem() for data manipulation.
The main difference is simply how long the data sticks around.
In short, localStorage is your go-to for long-term storage, while sessionStorage has your back for short-term needs.
#30. What are some common performance optimization techniques for JavaScript, and why would you want to use them?
JavaScript is an amazing language that adds dynamic interactivity to web applications, creating truly engaging experiences. However, it's important to optimize JavaScript code to avoid performance issues, such as slow page load times and unresponsive user interfaces.
The good news is, there are plenty of performance optimization techniques for JavaScript to ensure a silky-smooth experience:
Minification: Make your code lean and mean by stripping away unnecessary characters and whitespace. This results in faster downloads and snappy load times
Bundling: Merge multiple JavaScript files into one, cutting down HTTP requests and reducing your code's overall size for a performance boost
Caching: Store JavaScript files in the browser's cache, enabling reuse on subsequent page loads. This significantly speeds up load times, especially for those returning visitors
Lazy loading: Wait to load JavaScript files until they're truly needed, rather than loading everything upfront. This helps cut down initial load time and delights users with a seamless experience
Code optimization: Fine-tune your JavaScript code to get even more performance gains. Techniques include reducing variable count, minimizing loop usage, and avoiding costly operations like DOM manipulation
Event delegation: Attach event listeners to parent elements instead of individual child elements. This helps keep the number of event listeners in check, giving your application a performance edge
Throttling and debouncing: Keep function execution rates in check with throttling and debouncing. Throttling limits the frequency of function calls, while debouncing delays execution until a specified time has passed since the last call. These techniques help improve performance by cutting down on unnecessary function calls
So there you have it - 30 of the most common JavaScript interview questions that you might face during a frontend developer interview.
Did you answer all 30 correctly? Congratulations! You’re ready to ace that interview.
Or did you struggle with some of them? If you knew the answers but forgot, just give yourself some time to recap before the interview.
Or did none of this make sense?
Not a problem either. As I mentioned earlier, Zero To Mastery has 3 JavaScript courses that can help you up your skills and advanced JS knowledge , so that you blow away any interview questions.
Heck… we even have detailed resources on how to ace the technical interview , how to get hired at FAANG , and even how to get through the door and wow them with your projects!
You’ll not only get access to step-by-step tutorials, but you can ask questions from me and other instructors, as well as other students inside our private Discord .
Either way, if you decide to join or not, good luck with your interview and go get that job!

The Complete Web Developer in 2024: Zero to Mastery
Learn to code from scratch and get hired as a Web Developer in 2024. This full-stack coding bootcamp will teach you HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, Node.js, Machine Learning & more.

JavaScript: The Advanced Concepts
Learn modern, advanced JavaScript practices to become a top 10% JavaScript Developer. Fun fact: this course is even used as a reference for some FAANG company interview processes.

JavaScript Web Projects: 20 Projects to Build Your Portfolio
Get hired or your first client by building your dream portfolio of modern, real-world JavaScript projects. Never spend time on confusing, out of date, incomplete tutorials anymore!
More from Zero To Mastery
![problem solving javascript interview questions [Guide] Computer Science For Beginners preview](https://images.ctfassets.net/aq13lwl6616q/3SYSMGBVgnRvlAY0JiEBOi/7065751f30d315eb4e7fb7f6b2e164c4/Computer_science_for_beginners.png?w=400&h=225&q=50&fm=png&bg=transparent)
You DO NOT need a CS Degree to get hired as a Developer. Learn Computer Sciences Basics today with this free guide by a Senior Dev with 10+ years of experience.

Hey Web Dev - do you want to sharpen your JavaScript skills? Then come join me and let's start building some awesome beginner friendly JavaScript projects to boost your portfolio & skills.

Learning how closures work will with simple examples and real-world cases will make your life a lot easier and save you stress when solving daily problems.

JavaScript Interview Prep Cheatsheet – Ace Your Coding Interviews with These Concepts

I've carefully gone through over 50 resources, I've been through 10 JavaScript interviews, and I've landed a job at a unicorn startup.
And throughout this entire process, I started to see a pattern in the most frequently asked JS interview questions.
In this article, I have tried to list the concepts which will cover 80% of any good JS interview.
So, if you are prepping for your next JS interview this is the perfect cheatsheet for you to review and solidify your skills. Go through this and you'll be ready to rock. 💃
📝Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of the web and programming
- Familiarity with HTML/CSS and JavaScript (especially ES6+ syntax)
Table Of Contents 📜
- JavaScript Basics – JS Variables and Array Methods
- Functional Programming in JavaScript – Scope, Closures, and Hoisting
- Objects in JavaScript – Prototypes and "this"
- Asynchronous JavaScript – Event Loops, Timers, and Promises
- Advanced JavaScript Concepts to Know - Async/defer, Polyfills, Debouncing, and Throttling
- Storage in JavaScript
Caveat: The focus here will largely be to cover concepts relevant to the interview and not to create a comprehensive booklet for learning the language. Treat this more like a cheatsheet.
If you want to dive in deeply and learn more JS concepts, check out freeCodeCamp's curriculum .
With that out of the way - let's go!
JavaScript Basics 👶
Let's start off with some basic concepts every JS developer needs to know.
Variables in JavaScript 📥
Variables are the building blocks of every programming language. You use them to store values. A variable can be a number, string, and many other types.
Now, JS is a loosely-typed language. You don't have to state the type of variable. You can just declare it, and JS will figure it out on its own.
Now, in JavaScript we have 3 ways to declare variables: var , let , and const .
Here are the key differences:
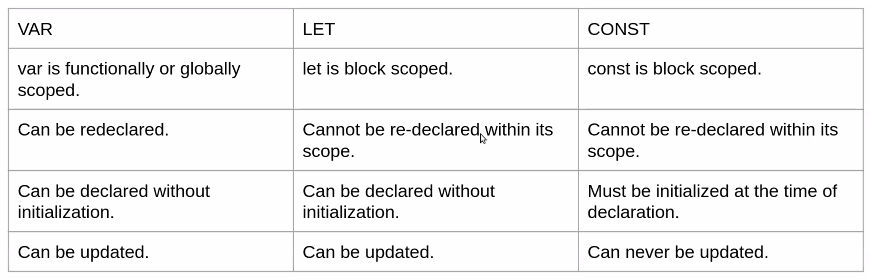
Let's try to understand them through examples.
We will cover scope later on. For now, let's focus on the other differences.
Note: In JavaScript, putting a semi-colon after the end of statement is optional. I will be skipping it here for the sake of readability.
== vs === in JavaScript
Let's compare some variables. There are two ways you can do that.
== only checks for the value
=== checks for value + type
Arrays in JavaScript
Now that we know a bit about variables, let's move on to arrays and array-methods.
If we have declared a lot of variables, it makes sense to store them somewhere. Otherwise it will be difficult to keep track of all of them. Arrays are one way of storing a variable.
But only storing variables in an array is kind of boring. We can do more stuff with this array (like accessing these variables or changing the order in which they are stored or how they are stored).
For that, JS has a lot of methods. Let's look at some of them now.
JavaScript Array Methods 🧰
The most frequently used array methods in JS are: map , filter , find , reduce , and forEach .
Let's cover map , filter , and forEach . You can explore more in this helpful article .
The map array method
map creates a new copy of the original array. We use it when we want to do something with the elements of the original array but don't want to change it.
map iterates over the original array and takes a callback function (which we'll cover later) as an argument. In the callback function, we tell it what to do with the elements.
The filter array method
filter creates a new array with elements that meet the given condition(s).
Let's look at an example. I have used arrow functions here. If you are a little uncomfortable with functions, you can cover the next section first and come back.
Try to do the exercises yourself first to test your knowledge. If you come up with different or better solutions, let me know!
Generally, a follow up to this: can you do it without the array method?
The forEach array method
forEach is very similar to map but has two key differences:
First of all, map returns a new Array, but forEach doesn't.
And second, you can do method chaining in map but not in forEach .
Note: map and forEach don't mutate (change) the original array.
Functional Programming in JavaScript 🛠
We have already used functions above. Let's cover them in more detail now.
Just like how we used variables to store values, we can use functions to store a piece of code which we can reuse.
You can make function in two ways:
Now, let's cover some important concepts related to functions.
Function Scope in JavaScript 🕵️
Scope determines from where the variables are accessible.
There are three types of scope:
- Global (declaration outside of any function)
- Function (declaration inside a function)
- Block (declaration inside a block)
Remember from before that var is globally scoped whereas let and const are block scoped. Let's understand that now.
Closures in JavaScript (❗important) 🔒
We have already used a closure without even realizing it. In the example below, prefix is a closed-over-variable.
This section will have a lot of fancy words, so bear with me. We will cover them one by one.
A function bundled together with its lexical environment forms a closure.
Okay, what is a lexical environment?
It is essentially the surrounding state – the local memory along with the lexical environment of its parent.
Whaaat? 🤯 I know it's a bit of a doozy. Let's understand it with a simple example.
When x is invoked, y is returned. Now, y is waiting to be executed. Kind of like a loaded gun waiting to be shot! 🔫
So, when we finally invoke z, y is invoked. Now, y has to log a so it first tries to find 🔍 it in the local memory but it's not there. It goes to its parent function. It finds a there.
Voila! There you have it - this is closure .
Even when functions are returned (in the above case y) they still remember their lexical scope (where it came from)
Totally unrelated quote for kicks 👻:
They may forget what you said - but they will never forget how you made them feel - Carl W. Buehner
I swear the rest of the article is legit 🤞 Keep reading.
Advantages of Closures in JavaScript 😎
- Data Hiding/Encapsulation
Suppose you want to create a counter application. Every time you call it, the count increases by 1. But you don't want to expose the variable outside the function. How to do it?
You guessed it – closures!
Don't worry about this and new . We have a whole section devoted to them down below.
Disadvantages of Closures in JavaScript 😅
- Overconsumption of memory or memory leaks can happen.
For example, the closed-over-variable will not be garbage collected. This is because, even if the outer function has run, the returned inner function still has a reference to the closed-over-variable.
Note: Garbage collection basically removes unused variables from the memory automatically.
Hoisting in JavaScript 🚩
This is JavaScript's default behavior of moving declarations to the top of the program.
- var declaration is hoisted up and initialized with undefined .
- let and const declarations are hoisted up but not initialized.
- function definitions are also hoisted up and stored as they are.
Let's look at an example:
Phew! I am done with functions here, but if you want more check out this amazing talk by Anjana Vakil on functional programming.
Objects in JavaScript 🔮
Just like arrays, objects are a way of storing data. We do so with the help of key-value pairs.
name is the key and Raj is the value . Keys are generally the name of the properties of the object.
We can store all sorts of data like functions inside an object. You can explore more here on the MDN .
What is this in JavaScript?
Now, working with objects is different in JS than in other popular programming languages like C++. And to understand that properly, we need a good grasp of the this keyword.
Let's try to understand it step-by-step.
In a program, at times, we need a way to point at stuff. Like saying this function right here belongs to this object. this helps us get this context.
You will understand what I am saying better when we look at some examples.
For now, think of this as something which provides context. And remember this important thing: its value depends on how and where it is called.
I know, I know. A lot of this 😬. Let's go over all this slowly.
Start a new program and just log this .
It will point to the window object.
Now, let's take an example with an object:
Now, this will point to the object. So what's happening here?
In the first example, we had nothing left of the . so it defaulted to the window object. But in this example, we have the object obj .
We again get the window object. So, we can see that the value of this depends on how and where are we doing the calling.
What we just did above is called Implicit Binding . The value of this got bound to the object.
There is another way to use this . Explicit binding is when you force a function to use a certain object as its this .
Let's understand why we need explicit binding through an example.
We are using this properly, but can you see the problem with the above code?
We are repeating code. And one of the principles of good programming is keep your code DRY! (Don't Repeat Yourself)
So, let's get rid of displayName_2 and simply do:
call forced displayName_1 to use the second object as its this .
There are a lot of other ways we can do this.
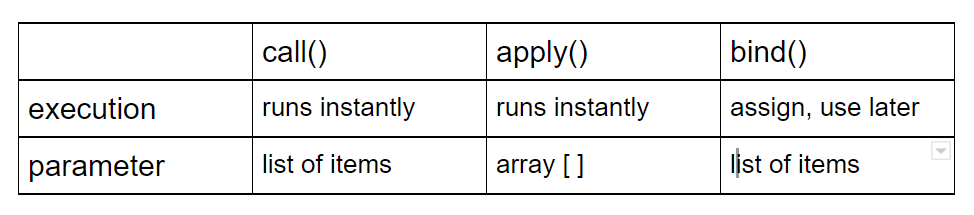
Try to solve the given problem yourself.
Finally, remember that I said that there are differences between arrow and regular functions.
The case of this is one of them.
For an arrow function, the value depends on the lexical scope – that is to say, the outer function where the arrow function is declared.
So, if we make the displayName() from above an arrow function, nothing will work.
Arrow functions basically inherit the parent's context which in the above case is the window .
Prototypes and Prototypal Inheritance in JavaScript 👪
Whenever we create anything (like an object or function) in JavaScript, the JS Engine automatically attaches that thing with some properties and methods.
All this comes via prototypes .
__proto__ is the object where JS is putting it all.
Let's see some examples. Fire up your consoles!
All this is called a prototype chain .
We can do the same with objects and functions as well.
We will always find Object.prototype behind the scenes. That's why you may have heard that everything in JS is an object. 🤯
What is Prototypal Inheritance in JavaScript?
Note: Don't modify prototypes this way. It's just for understanding. Here's the right way to do it .
By doing this, object2 gets access to the object's properties. So, now we can do:
This is prototypal inheritance .
Asynchronous JavaScript ⚡
So, JS is a single-threaded language. Things happen one at a time. Only after one thing is done can we move to the next thing.
But this creates problems in the real world, especially, when we are working with browsers.
For example, when we need to fetch data from the web - often times we don't know how long will it take to get it. And whether we will be able to get the data successfully.
To help with this, asynchronous JS comes into play.
And the most important concept to understand is the event loop.
Event Loops in JavaScript ➰
Instead of providing a half-baked explanation here, I highly recommend watching this video by Philip Roberts if you haven't already:
Learn all about event loops in JS here .
Timers in JavaScript – setTimeout, setInterval, clearInterval ⏱️
I hope you watched the video. It mentioned timers. Let's talk about them more now. These are very frequently asked about in interviews.
The setTimeout() method calls a function or evaluates an expression after a specified number of milliseconds.
setInterval() does the same for specified intervals.
You use clearInterval() to stop the timer.
Let's go over some questions that use these concepts.
Here's a slightly trickier one:
And here's a short explanation of what's going on there: when setTimeout comes again into the picture, the entire loop has run and the value of i has become 6,
Now, let's say we want the outcome to be 1 2 3 4 5 – what do we do?
Instead of var ➡️ use let .
Why this will work?
var is globally scoped but let is locally scoped. So for let a new i is created for every iteration.
Promises in JavaScript (❗important) 🤝
Promises are at the heart of Asynchronous JS.
The Promise object represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value.
A promise can be in one of these three states:
- Pending: initial state, neither fulfilled nor rejected
- Fulfilled: operation was completed successfully
- Rejected: operation failed
Note: resolve and reject are just conventional names. Call it pizza🍕 if you like.
Instead of then/catch , we can also use async/await :
One of the advantages of promises is that they are a much cleaner syntax. Before we had promises, we could easily get stuck in callback hell 🌋
Advanced JavaScript Concepts to Know
📚 polyfills in javascript.
A polyfill is a piece of code (usually JavaScript on the Web) used to provide modern functionality on older browsers that do not natively support it. MDN
- Let's implement it for map :
Notice how we use this . Here, we have basically created a new array and are adding values to it.
Async and defer in JavaScript ✔️
These concepts are frequently asked about in interviews by big corporations like Amazon, Walmart, and Flipkart. 🏢
To understand async and defer , we need to have an idea of how browsers render a webpage. First, they parse the HTML and CSS. Then DOM trees are created. From these, a render tree is created. Finally, from the render tree - a layout is created and the painting happens.
For a more detailed look, check out this video .
Async and defer are boolean attributes which can be loaded along with the script tags. They are useful for loading external scripts into your web page.
Let's understand with the help of pictures.
If there are multiple scripts which are dependant on each other, use defer . Defer script are executed in the order which they are defined.
If you want to load external script which is not dependant on the execution of any other scripts, use async .
Note: The async attribute does not guarantee the order of execution of scripts.
Debouncing in JavaScript ⛹️♂️
Debouncing is another favorite topic of interviewers.
Let's understand it by creating a search bar.
Demo: https://codesandbox.io/s/debounce-input-field-o5gml
Create a simple input field in index.html like this:
Now, in index.js . Don't forget to add it to index.html first:
First, we have selected the input and added an event listener to it. Then we created a debounce function which takes a callback function and delay.
Now, inside the debounce function we create a timer using setTimeout . Now, this timer's job is to make sure that the next call for getData only happens after 300 ms. This is what debouncing is.
Also, we use clearTimeout to remove it. Don't want too many of them hanging out there taking up memory space!
Phew! Lots of theory. Let's do a fun challenge. You must have seen the countdown before a game starts (it goes like 10, 9, 8, .... with some delay in between). Try to write a program for it.
Here's how you'd do it:
Were you able to solve it? Did you do it differently? Let me know your solution.
Throttling in JavaScript 🛑
Let's look at an example again. Suppose that on every window resize event we call an expensive function. Now, we want it such that the expensive function will only be executed once in the given time interval. This is what throttling is.
Create an index.html and an index.js with the following code:
Almost the same as debouncing. The key difference is the flag variable. Only, when it's true we are invoking the callback function. And it is set to true inside the setTimeout . So the value is true only after the desired time limit.
So, what's the difference between debounce and throttling❓
Let's take the search bar 🔍 example from above. When we are debouncing the input field, we are saying to only fetch the data when the difference between two keyup events is at least 300 ms.
In the case of throttling, we make a function call only after a certain period of time.
Suppose that you are searching for an encyclopedia in the search bar. The first call is made on e and it took us 300 ms to reach p . The next call will be made then only. All the events in between will be ignored.
So, to summarize, debouncing is when the difference between two keyup events is 300 ms. And throttling is when the difference between two function calls is 300 ms. Basically, the function is called after a certain interval of time.
Storage in JavaScript 💾
Finally, a small but important topic to wrap things up.
localStorage: Data persists even after closing your session
sessionStorage: You lose your data when your session is over, like when you close the browser on the tab.
And we are done! 🏁 I hope you feel more confident about your next JS interview now. I wish you all the best.
If you have any queries / suggestions / feedback, you can reach me on Twitter: https://twitter.com/rajatetc .
🗃️ Main References
- Akshay Saini
- Coding Addict
- Javascript_Interviews
software engineer, unacademy • rajatgupta.xyz • twitter.com/rajatetc • development, design, psychology, and startups
If you read this far, thank the author to show them you care. Say Thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
30 JavaScript Coding Interview Questions for Beginner, Mid-Level and Expert Developers
JavaScript is a leading programming language for creating interactive and dynamic web pages. You will see a lot of popular frameworks and libraries based on JavaScript, such as jQuery, VueJS, ReactJS, AngularJS and others. It is no surprise that JavaScript is the main programming language for the front-end development of software applications.
Today we will guide you on how to design coding challenges for evaluating JavaScript developers. We will suggest coding challenges for beginner, mid-level and expert JavaScript developers. Let’s start with coding challenges that are suitable for beginner-level developers.
Interview Questions for Beginner JavaScript Developers

When preparing interview questions for beginner-level JavaScript developers, focus on basic JavaScript syntax, array and string manipulation, objects and JSON, DOM manipulation, error handling and asynchronous programming. Here are 10 sample questions in this regard:
What will be the output of the below code:
Find the issue in the below code snippet.
Analyze the below code. Do you see any issue? If yes, what is that issue?
Create a JavaScript function that calculates the tip for a given bill amount and tip percentage. Bill amount and tip percentage will be input parameters while output will be calculated tip value.
What will be the output of below code snippet:
Will the below code return any error? If yes, identify the error.
Implement a simple shopping cart system with features to add items, remove items and calculate the total price. Use objects to represent items, including properties for the item name, price and quantity. Implement features to add items to the cart, remove items and calculate the total cost.
Analyze the below code snippet and advise what will be the output:
Find the issue with the below code snippet:
Question 10
What issue exists in the below code:
Interview Questions for Mid-level JavaScript Developers
When designing interview questions for mid-level JavaScript developers, you should prepare challenges to test the understanding of advanced JavaScript concepts and problem-solving skills. Some areas that should be considered for evaluation include functional programming, asynchronous programming, promises, working with APIs and advanced JavaScript features. Find below 10 coding challenges which are suited to mid-level JavaScript developers:
What is the issue in the below code:
Develop a simple URL shortener service using JavaScript. Implement a function that takes a long URL as an input parameter and the output will be a shortened URL. Create a reverse function as well. The reverse function takes the shortened URL and returns the original long URL. You can use simple in-memory objects to store the mapping between long and short URLs.
Implement an autocomplete feature for a search input field. Given an array of words, write a function that suggests words based on the current input. The output of the function will be an array of suggested words that start with the input characters, limiting the number of suggestions (e.g., a maximum of 7 suggestions).
Will the below code return any error? If yes, what will be the error?
Develop a function that throttles another function, allowing it to be called at most once every specified interval (e.g., 300ms). The throttling function will have two input parameters. One will be the function to be throttled and the second will be the interval in milliseconds. The throttled function should be called with the same arguments as the original function.
What is wrong with the below code:
Design a simple meeting scheduler that finds the first available time slot for a meeting between two people. Given two arrays of busy time intervals and a meeting duration, create a function that returns the earliest available time slot for the meeting when both people will be available. Each interval is represented as an array of two integers, where the first integer is the start time and the second integer is the end time.
Interview Questions for Expert JavaScript Developers
When preparing coding challenges for expert-level JavaScript engineers, you should test the advanced features of the language and performance optimization techniques. Some of the areas to evaluate include advanced JavaScript features, code architecture, design patterns, performance optimization and security. Below we have presented 10 coding challenges for expert JavaScript developers:
Is there any security vulnerability in the below code? If yes, identify it:
Identify the output of the below code.
What is the possible performance issue in the below code?
Suggest the output of the below code:
Design a social media platform that contains features like sign up, creating a profile and posting status updates. Users should be able to follow other users and view their posts on a newsfeed.
What is wrong with the below call to the API?
What will be the output of below code snippet?
Design an online code editor where users can write, save and run JavaScript code. The editor should include features like syntax highlighting, auto-completion and error checking.
The below code snippet uses closures to implement a counter. How will you optimize it to minimize memory usage:
Develop a fitness tracker application where users can enter their daily exercise routines and track their progress over time. The application should allow users to set goals, view their progress and receive reminders.
Evaluating JavaScript developers at varying skill levels requires well-designed code challenges. Syntax, data types and functions are some basic concepts to test first. More sophisticated topics like object-oriented programming, algorithms and data structures should be included when testing mid-level engineers. Complex issues like performance optimization, security and design patterns should be used to evaluate expert-level developers.
This article has presented numerous examples of coding challenges to help hiring managers spot promising JavaScript developers at different levels of experience.

Further reading:
- Java Coding Interview Questions
- Python Coding Interview Questions
- ReactJS Coding Interview Questions
- C# Coding Interview Questions
- C++ Coding Interview Questions
- PHP Coding Interview Questions
- 73 Advanced Coding Interview Questions
- Share on Facebook
- Email this Page
- Share on LinkedIn
- DSA with JS - Self Paced
- JS Tutorial
- JS Exercise
- JS Interview Questions
- JS Operator
- JS Projects
- JS Examples
- JS Free JS Course
- JS A to Z Guide
- JS Formatter
HTML Interview Questions
- HTML Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
- HTML Interview Questions and Answers (2024) - Intermediate Level
- HTML Interview Questions and Answers (2024) – Advanced Level
CSS Interview Questions
- CSS Interview Questions and Answers
JavaScript Interview Questions
Javascript interview questions and answers.
- JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers (2024) - Intermediate Level
- JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers (2024) - Advanced Level
TypeScript Interview Questions
- TypeScript Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
jQuery Interview Questions
- jQuery Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
- jQuery Interview Questions and Answers | Set-2
- jQuery Interview Questions and Answers | Set-3
Angular Interview Questions
- AngularJS Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
React Interview Questions
- React Interview Questions and Answers
- React Interview Questions and Answers (2024) - Intermediate Level
- React Interview Question and Answers (2024) - Advance Level
Node Interview Questions
- Node.js Interview Questions and Answers
- Node Interview Questions and Answers (2024) - Intermediate Level
- Node Interview Questions and Answers (2024) - Advanced Level
MERN Interview Questions
- Top MERN Stack Interview Questions
PHP Interview Questions
- PHP Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
- PHP Interview Questions and Answers (2024) | Set-2
Tailwind CSS Interview Questions
- Tailwind CSS Interview Questions and Answers
Frontend Developer Interview Questions
- Front End Developer Interview Questions and Answers
JavaScript (JS) is the most popular lightweight scripting and compiled programming language. It was developed by Brendan Eich in 1995 . It is well-known as a scripting language for web pages, mobile apps, web servers, and many more.
In this article, we will provide 60+ JavaScript interview questions and answers tailored for both freshers and experienced professionals with 3, 5, and 8 years of experience. Here, we cover everything, including Core JavaScript Concepts , ES6+ features, DOM manipulation, asynchronous JavaScript, error handling, JavaScript frameworks and libraries, and more, that will surely help you to crack your next JavaScript interview.
.webp)
JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Before proceeding to learn JavaScript interview questions and answers , first we learn the complete JavaScript Tutorial .
Table of Content
JavaScript Interview Questions for Freshers
Javascript intermediate interview questions, javascript interview questions for experienced.
Let’s discuss some common questions that you should prepare for the interviews. These questions will be helpful in clearing the interviews specially for the frontend development role.
1. What are the differences between Java and JavaScript?
JavaScript is a client-side scripting language and Java is object Oriented Programming language. Both of them are totally different from each other.
- JavaScript : It is a light-weighted programming language (“scripting language”) for developing interactive web pages. It can insert dynamic text into the HTML elements. JavaScript is also known as the browser’s language.
- Java : Java is one of the most popular programming languages. It is an object-oriented programming language and has a virtual machine platform that allows you to create compiled programs that run on nearly every platform. Java promised, “Write Once, Run Anywhere”.
2. What are JavaScript Data Types?
There are three major Data types in JavaScript.
3. Which symbol is used for comments in JavaScript?
Comments prevent the execution of statements. Comments are ignored while the compiler executes the code. There are two type of symbols to represent comments in JavaScript:
- Double slash: It is known as a single-line comment.
- Slash with Asterisk: It is known as a multi-line comment.
4. What would be the result of 3+2+”7″?
Here, 3 and 2 behave like an integer, and “7” behaves like a string. So 3 plus 2 will be 5. Then the output will be 5+”7″ = 57.
5. What is the use of the isNaN function?
The number isNan function determines whether the passed value is NaN (Not a number) and is of the type “Number”. In JavaScript, the value NaN is considered a type of number. It returns true if the argument is not a number, else it returns false.
6. Which is faster in JavaScript and ASP script?
JavaScript is faster compared to ASP Script. JavaScript is a client-side scripting language and does not depend on the server to execute. The ASP script is a server-side scripting language always dependable on the server.
7. What is negative infinity?
The negative infinity is a constant value represents the lowest available value. It means that no other number is lesser than this value. It can be generate using a self-made function or by an arithmetic operation. JavaScript shows the NEGATIVE_INFINITY value as -Infinity.
8. Is it possible to break JavaScript Code into several lines?
Yes, it is possible to break the JavaScript code into several lines in a string statement. It can be broken by using the backslash ‘\’ . For example:
The code-breaking line is avoid by JavaScript which is not preferable.
9. Which company developed JavaScript?
Netscape developed JavaScript and was created by Brenden Eich in the year of 1995.
10. What are undeclared and undefined variables?
- Undefined : It occurs when a variable is declare not not assign any value. Undefined is not a keyword.
- Undeclared : It occurs when we try to access any variable which is not initialize or declare earlier using the var or const keyword. If we use ‘typeof’ operator to get the value of an undeclare variable, we will face the runtime error with the return value as “undefined”. The scope of the undeclare variables is always global.
11. Write a JavaScript code for adding new elements dynamically.
12. what are global variables how are these variables declared, and what are the problems associated with them.
In contrast, global variables are the variables that define outside of functions. These variables have a global scope, so they can be used by any function without passing them to the function as parameters.
It is difficult to debug and test the code that relies on global variables.

13. What do you mean by NULL in JavaScript?
The NULL value represents that no value or no object. It is known as empty value/object.
14. How to delete property-specific values?
The delete keyword deletes the whole property and all the values at once like
15. What is a prompt box?
The prompt box is a dialog box with an optional message prompting the user to input some text. It is often used if the user wants to input a value before entering a page. It returns a string containing the text entered by the user, or null.
16. What is the ‘this’ keyword in JavaScript?
Functions in JavaScript are essential objects. Like objects, it can be assign to variables, pass to other functions, and return from functions. And much like objects, they have their own properties. ‘this’ stores the current execution context of the JavaScript program. Thus, when it use inside a function, the value of ‘this’ will change depending on how the function is defined, how it is invoked, and the default execution context.
17. Explain the working of timers in JavaScript. Also elucidate the drawbacks of using the timer, if any.
The timer executes some specific code at a specific time or any small amount of code in repetition to do that you need to use the functions setTimout , setInterval, and clearInterval . If the JavaScript code sets the timer to 2 minutes and when the times are up then the page displays an alert message “times up”. The setTimeout() method calls a function or evaluates an expression after a specified number of milliseconds.
18. What is the difference between ViewState and SessionState?
- ViewState: It is specific to a single page in a session.
- SessionState: It is user specific that can access all the data on the web pages.
19. How to submit a form using JavaScript?
You can use document.form[0].submit() method to submit the form in JavaScript.
20. Does JavaScript support automatic type conversion?
Yes, JavaScript supports automatic type conversion.
21. What are all the looping structures in JavaScript ?
- while loop : A while loop is a control flow statement that allows code to be executed repeatedly based on a given Boolean condition. The while loop can be thought of as a repeating if statement.
- for loop : A for loop provides a concise way of writing the loop structure. Unlike a while loop, for statement consumes the initialization, condition and increment/decrement in one line thereby providing a shorter, easy to debug structure of looping.
- do while : A do-while loop is similar to while loop with the only difference that it checks the condition after executing the statements, and therefore is an example of Exit Control Loop.
22. How can the style/class of an element be changed?
To change the style/class of an element there are two possible ways. We use document.getElementByID method
23. Explain how to read and write a file using JavaScript?
- The readFile() functions is used for reading operation.
- The writeFile() functions is used for writing operation.
24. What is called Variable typing in JavaScript ?
The variable typing is the type of variable used to store a number and using that same variable to assign a “string”.
25. How to convert the string of any base to integer in JavaScript?
In JavaScript, parseInt() function is used to convert the string to an integer. This function returns an integer of base which is specified in second argument of parseInt() function. The parseInt() function returns Nan (not a number) when the string doesn’t contain number.
26. Explain how to detect the operating system on the client machine?
To detect the operating system on the client machine, one can simply use navigator.appVersion or navigator.userAgent property. The Navigator appVersion property is a read-only property and it returns the string that represents the version information of the browser.
27. What are the types of Pop up boxes available in JavaScript?
There are three types of pop boxes available in JavaScript.
28. What is the difference between an alert box and a confirmation box?
An alert box will display only one button which is the OK button. It is used to inform the user about the agreement has to agree. But a Confirmation box displays two buttons OK and cancel, where the user can decide to agree or not.
29. What is the disadvantage of using innerHTML in JavaScript?
There are lots of disadvantages of using the innerHTML in JavaScript as the content will replace everywhere. If you use += like “innerHTML = innerHTML + ‘html’” still the old content is replaced by HTML. It preserves event handlers attached to any DOM elements.
30. What is the use of void(0) ?
The void(0) is used to call another method without refreshing the page during the calling time parameter “zero” will be passed.
For further reading, check out our dedicated article on Intermediate Javascript Interview Questions . Inside, you’ll discover over 20 questions with detailed answers.
31. What is the ‘Strict’ mode in JavaScript and how can it be enabled?
Strict Mode is a new feature in ECMAScript 5 that allows you to place a program or a function in a “strict” operating context. This strict context prevents certain actions from being taken and throws more exceptions. The statement “use strict” instructs the browser to use the Strict mode, which is a reduced and safer feature set of JavaScript.
32. How to get the status of a CheckBox?
The DOM Input Checkbox Property is used to set or return the checked status of a checkbox field. This property is used to reflect the HTML Checked attribute.
If the CheckBox is checked then it returns True.
33. How to explain closures in JavaScript and when to use it?
The closure is created when a child functions to keep the environment of the parent’s scope even after the parent’s function has already executed. The Closure is a locally declared variable related to a function. The closure will provide better control over the code when using them.
34. What is the difference between call() and apply() methods ?
Both methods are used in a different situation
- call() Method: It calls the method, taking the owner object as argument. The keyword this refers to the ‘owner’ of the function or the object it belongs to. We can call a method that can be used on different objects.
- apply() Method: The apply() method is used to write methods, which can be used on different objects. It is different from the function call() because it takes arguments as an array.
35. How to target a particular frame from a hyperlink in JavaScript ?
This can be done by using the target attribute in the hyperlink. Like
36. Write the errors shown in JavaScript?
There are three different types of errors in JavaScript.
- Syntax error: A syntax error is an error in the syntax of a sequence of characters or tokens that are intended to be written in a particular programming language.
- Logical error: It is the most difficult error to be traced as it is the error on the logical part of the coding or logical error is a bug in a program that causes to operate incorrectly and terminate abnormally.
- Runtime Error: A runtime error is an error that occurs during the running of the program, also known as an exception.
37. What is the difference between JavaScript and Jscript?
- It is a scripting language developed by Netscape.
- It is used to design client and server-side applications.
- It is completely independent of Java language.
- It is a scripting language developed by Microsoft.
- It is used to design active online content for the word wide Web.
38. What does var myArray = [[]]; statement declares?
In JavaScript, this statement is used to declare a two-dimensional array.
39. How many ways an HTML element can be accessed in JavaScript code?
There are four possible ways to access HTML elements in JavaScript which are:
- getElementById() Method: It is used to get the element by its id name.
- getElementsByClass() Method: It is used to get all the elements that have the given classname.
- getElementsByTagName() Method: It is used to get all the elements that have the given tag name.
- querySelector() Method: This function takes CSS style selector and returns the first selected element.
40. What is the difference between innerHTML & innerText?
The innerText property sets or returns the text content as plain text of the specified node, and all its descendants whereas the innerHTML property sets or returns the plain text or HTML contents in the elements. Unlike innerText, inner HTML lets you work with HTML rich text and doesn’t automatically encode and decode text.
41. What is an event bubbling in JavaScript?
Consider a situation an element is present inside another element and both of them handle an event. When an event occurs in bubbling, the innermost element handles the event first, then the outer, and so on.
For further reading, check out our dedicated article on Advanced Javascript Interview Questions . Inside, you’ll discover 20+ questions with detailed answers.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- interview-preparation
- JavaScript-Interview-Questions
- JavaScript-Questions
- Web Technologies

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

65 JavaScript Interview Questions & Answers to Prepare For (Beg to Adv)

Practice common basic, intermediate, and advanced JavaScript interview questions and answers with this comprehensive guide. Good luck!
When hiring dedicated Node.js developers , it’s crucial to evaluate their expertise in JavaScript. Use these JavaScript interview questions and answers to help you practice and test your (or another job candidate’s) understanding of this popular programming language used in numerous modern frameworks.
In this guide, we break down the most important and most common JavaScript interview questions to know into three sections:
Basic JavaScript Interview Questions
Intermediate javascript interview questions, advanced javascript interview questions.
But, we don’t just give you the technical answer — you can head to any JavaScript tutorial or JS learning website for those.
Rather, on top of the standard technical answer, we give you the reasoning behind the question: why is the interviewer asking me this? What do they really want to know by asking me this question? How can my interview answer best respond to their question?
And, at the end of the article (as well as a few places throughout), we’ll link you to some other helpful interview advice and job hunting guides.
Let’s get started!
Looking to hire the best remote developers? Explore HireAI to see how you can:
⚡️ Get instant candidate matches without searching ⚡️ Identify top applicants from our network of 300,000+ devs with no manual screening ⚡️ Hire 4x faster with vetted candidates (qualified and interview-ready)
Try HireAI and hire top developers now →
The following set of questions should test your (or another candidate’s) basic knowledge of JavaScript and some of its core features.
1. What are logical operators in JavaScript?
Logical operators allow developers to compare variables and perform tasks based on the result of the comparison. As a hiring manager, you’d ask this question to gauge the candidate’s familiarity with the language and its fundamental features. Your candidate should be able to explain each logical operator and their behavior – stepping through each operand and computing its output.
There are four logical operators in JavaScript:
- || – OR
- && – AND
- ! – NOT
- ?? – Nullish Coalescing (see next question)
The “OR” operator is represented by two vertical lines ( || ). In JavaScript, the “OR” operator evaluates the values from left to right and returns the first truthy value. If none of the values are truthy, the “OR” operator will return the last operand.
The “AND” operator is represented by two ampersands ( && ). In JavaScript, the “AND” operator evaluates the values from left to right and returns the first falsy value. If all the operands are true, the “AND” operator will return the last operand.
The “NOT” operator is represented by an exclamation mark ( ! ). the “NOT” operator accepts a single argument and returns the inverse of its boolean value. The argument is first converted into a boolean ( true or false ). The argument’s boolean value is then inverted and returned ( true becomes false and vice versa).
2. What is the nullish coalescing operator in JavaScript?
Nullish coalescing is an addition to JavaScript that helps provide a nicer and more concise syntax for getting the first “defined” value. The candidate should be able to explain what nullish coalescing is at a high-level and how to use the operator when asked this JS interview question.
Nullish coalescing is a JavaScript logical operator represented by two question marks ( ?? ). Nullish coalescing is an operator that returns the first “defined” value. “defined” here refers to an expression whose value is neither null nor undefined .
Let’s look at how the operator works.
The output of the code above is as follows:
- if a is defined, the value of a is returned
- if a isn’t defined, the value of b is returned
Let’s look at a few examples of this operator when given a different set of arguments.
3. What is the difference between == and === operators?
JavaScript has two ways to test equality. Understanding the subtle difference between the two methods is important to prevent misusing each method. The candidate should be able to explain the differences and demonstrate a basic understanding of each method’s usage.
Both double-equals ( == ) and triple-equals ( === ) are comparison operators meant to compare the equality of two values.
Double-equals only compares the value of the element. Double-equals does type coercion, where the type of the variables is converted to a common type before checking their values. In short, the double-equals operator will return true for any two variables with the same value regardless of their type.
Triple-equals on the other hand, check for strict equality – both the value and type of the element being compared. Both the value and type of being compared has to match to satisfy the triple-equal operator
Read More : Common Interview Questions for Software Developer Jobs (Non-Technical)
4. What is a spread operator?
The spread operator is a feature from ES6 to help unpack an element. Candidates being asked this interview question on JavaScript should be able to demonstrate an understanding of how the spread operator expands an element – being able to come up with the output of a spread operator.
Spread operator allows iterables such as arrays, objects, and strings to be expanded into single arguments. The spread operator is denoted by three dots ( ... ) followed by the variable to be expanded.
Let’s look at an example where we combine two arrays using the spread operator. Below we have a male and female array containing a few strings each. The combined array combines the expanded male and female array, creating a single array with the contents from both male and female .
5. Explain loops in JavaScript.
We often require repeat actions. Loops are a way to execute the same code multiple times. The candidate should be able to explain how to use loops in JavaScript. An ideal answer should include the pros and cons of each looping method and its respective applications.
There are two main ways to create loops in JavaScript – while and for . Both methods consist of a condition to stop the loop and a “loop body”, the code that will be executed multiple times.
while loop
while loops are typically used when the “loop body” needs to be repeated an unknown number of times until the condition is met.
The code snippet below shows a simple while loop that prints the value of i on every iteration and stops when i is equal to 3.
for loop
A for loop, on the other hand, is better suited for executing the “loop body” a fixed number of times.
The same loop in the previous code snippet can be re-written using a for loop this way:
6. Explain the “this” keyword.
The this keyword is widely used in JavaScript applications. It behaves differently compared to other languages such as Java and Python. The candidate should have a thorough understanding of how the this keyword works and how it relates to its context.
The this keyword behaves differently depending on the caller’s context. Let’s look at a few contexts and what the this keyword refers to in each one
Global context
Global context refers to anything outside of any function – global object. this refers to the window object in web browsers and global object in Node.js applications.
If you assign a property to the this object in a web browser, JavaScript will add that property to the window object.
Function context
Functions can be invoked in four different ways.
Function invocation
Method invocation
Constructor invocation
Indirect invocation
Each of the invocations results in a different this behavior.
Depending on whether you are using “strict mode” or not, the this keyword refers to different values.
By default, the this keyword refers to the window or global object depending on where you are running the application.
In “strict mode”, JavaScript sets the this keyword to undefined .
When you call a method of an object ( getName in the example below), the this keyword is set to the object that owns the method ( user in the example below).
Constructor invocation is when the new keyword is used to create a new instance of a function object.
The new User('Bob') is a constructor invocation of the User function where a new instance of the User function is created. The this keyword in this case refers to the newly created object.
Indirect invocation is when the callee of the function uses the call or apply keyword to call a function. Both these methods allow passing in the this value ( bob and adam in the example below) as a parameter.
The apply keyword is identical to the call keyword above. Instead of accepting a single value as the second parameter, the apply keyword expects an array of values.
Read More : 31 Questions to Ask at an Interview for Software Development Jobs
7. What are the differences between call , apply , and bind ?
JavaScript has multiple ways to indirectly invoke a function. Your candidate needs to understand the differences between each and their use cases. You, as the candidate, should be able to explain not only their differences conceptually but also their use case and the reason behind it.
call , apply , and bind are different methods to tie a function to an object and call the function within the specified context.
The call method invokes the function with the specified context – the function is called as if it’s part of the object.
The function sayHello in the example below references this.name which is part of the user object (out of the scope of the sayHello function). We can use the call function and pass in the user object as the first argument to tie the sayHello function and the user object momentarily, giving it access to the this.name property.
The apply method is identical to the call method with the difference being in how each method accepts their arguments. The call method accepts an argument list, whereas the apply method accepts an array of arguments.
Using the same example as above, we can convert the call method to apply by wrapping the function’s arguments (excluding the context – user ) in an array before passing it to apply method.
Unlike call and apply , the bind method doesn’t execute the function immediately. Instead, it returns a function that is tied to the object that can be executed later.
Let’s update the example again to use the bind method. We’ll first bind the sayHello function to the user object and assign it to a new variable ( helloBill ). We can then invoke that function calling it as you would a regular function.
8. What are anonymous functions in JavaScript?
Anonymous functions serve numerous purposes in JavaScript. You might ask standard JavaScript interview questions like this one to gauge your candidates’ knowledge of functions in JavaScript and the various ways a function can be created and used. The candidate should be able to explain the difference between anonymous functions and other types of functions and what they are commonly used for
An anonymous function is a function that does not have any name associated with it. We usually use the function keyword followed by the function’s name to define a function in JavaScript. Anonymous functions omit the function name, making it not accessible after its creation.
An anonymous function can only be accessed by a variable. The anonymous nature of the function makes it great for passing in functions as arguments to other functions (higher-order functions) and functions that are invoked immediately upon initialization.
The following snippet is an example of an anonymous function that is assigned to a variable ( sayHello ). The function can then be called by calling the variable name ( sayHello ) with the required arguments.
9. What is hoisting in JavaScript?
Hoisting allows functions to be used safely before they are declared. This question will test the candidate’s familiarity with the JavaScript language and how classes, functions, and variables are interpreted by JavaScript. A basic understanding of hoisting can prevent unexpected errors caused by an incorrect order of declaration, initialization, and reference of a property. You may get other JavaScript hoisting interview questions, so study up!
Hoisting refers to the process where the interpreter moves the declaration of classes, functions, or variables to the top of their scope, before their execution.
Hoisting allows developers to reference variables, functions, and classes before they are declared. Without hoisting, the order of the example below would need to be reversed, with the function declaration first, followed by the caller.
However, JavaScript only hoists its declarations, not their initializations. Referencing a variable before its initialization would return the variable’s default value ( undefined for variables declared using the var keyword).
Read More : 8 Common Interview Mistakes Remote Software Developers Make
10. What is a callback function in JavaScript?
JavaScript runs code sequentially from the top-down. However, sometimes, we need code to run after something has happened (i.e. asynchronous operations). Callback functions are a way to make sure a function runs only after the set of operations is completed. A candidate should be able to explain both how callback functions work and how it relates to asynchronous programming.
A callback function is a function passed into another function as an argument. The callback function is then invoked inside the callee to complete an action.
The example below shows how the callback function is passed into and executed by another function. The last line ( greetPerson(sayHello) ) passes the sayHello function to the greetPerson function. greetPerson then executes the sayHello function by calling the callback variable, passing in the name value returned by the prompt function.
11. What are Promises in JavaScript?
Promises are an effective way to handle asynchronous operations in JavaScript. A candidate should be able to demonstrate a high-level understanding of Promises and how they handle asynchronous operations. An ideal answer would include the tradeoffs of using Promises and how they compare to callbacks and events.
A Promise is a proxy for a value not necessarily known when the promise is created. A promise is a way to handle asynchronous operations in JavaScript. You can think of Promises as an alternative to callbacks and events.
Promises are ideal for handling multiple asynchronous operations, providing a better flow of control definition and error handling.
Let’s look at an example of a Promise that waits for a setTimeout to complete:
12. What are the different states of a Promise?
Understanding the different states of a promise is important when dealing with promises to avoid unwanted side effects. You might ask this question to gain insight into the candidate’s familiarity with promises beyond the high-level concept.
Because of the asynchronous nature of Promises, a Promise has four states:
- Pending – Promise’s initial state, waiting for the operation to complete
- Fulfilled – Promise’s operation was completed successfully
- Rejected – Promise’s operation failed
- Settled – Promise is either fulfilled or rejected
Read More : 8 Behavioral Interview Questions Asked by Top Tech Companies
13. What is Promise chaining?
Promise chaining is a common requirement when working with multiple Promises that depend on each other. A candidate should ideally be able to explain both what promise chaining is and how it is done in JavaScript.
One of the benefits of Promises is its chaining ability. A Promise can be chained using the then and catch functions. The then function will be called when the Promise completes successfully (fulfilled) whereas the catch function will be called when the Promise failed (rejected).
Each then and catch block can contain more Promises and be further chained, providing you with granular control over how each asynchronous operation should be executed.
Let’s look at an example of chaining two Promises that waits for one second between each execution.
The first Promise in the code snippet above waits for one second before returning a result of 1 . The code then goes to the then block where it executes the second Promise, waiting for another second before returning a result of 2 .
14. What is Promise.all ?
JavaScript interview questions like this one might be asked as a follow-up to the Promise chaining question. JavaScript provides several utility functions that help with chaining Promises – Promise.all being one of them. A candidate should be able to describe the function of this type of Promise and also how it alters the flow of the asynchronous functions.
Promise.all is a type of Promise that accepts an array of Promises and waits for each Promise to resolve. Promise.all resolves once each of the Promise inputs resolves, emitting an array of results in the then block. A rejected Promise in the input will cause the Promise.all Promise to also get rejected.
The example below shows how the Promise.all function is used to execute two Promises – Promise1 and Promise2 , with a then block to capture the results of each Promise and a catch block to handle any errors.
15. Explain async/await in JavaScript.
Async and await are special syntax to work with Promises. In addition to the “what”, as an interviewer, you might also want to look for practical examples of async and await usages and how it differs from the Promise then syntax.
The async keyword is placed before a function to denote that the function is asynchronous and can be used as a Promise.
The await keyword, on the other hand, tells JavaScript to wait for the async operation to complete before proceeding to the next task in the function. The await keyword can only be used in an async function.
Line 6 in the code snippet below pauses the function execution as it waits for the promise to resolve. Once the promise resolves, it will continue the execution, assigning the result of the promise to the result variable.
Read More : 10+ Tips for Preparing for a Remote Software Developer Zoom Interview
Check out our entire set of software development interview questions to help you hire the best developers you possibly can.
- JavaScript Interview Questions
- Machine Learning Interview Questions
- MongoDB Interview Questions
- TypeScript Interview Questions
- Selenium Interview Questions
- Spring Interview Questions
- Data Engineer Interview Questions
- React Interview Questions
- Data Analyst Interview Questions
- Vue Interview Questions
- SQL Interview Questions
- DevOps Interview Questions
- Engineering Manager Interview Questions
- Java Interview Questions
- PHP Interview Questions
- Ruby on Rails Interview Questions
- Angular Interview Questions
- Android Interview Questions
- Data Warehouse Interview Questions
If you’re a developer, familiarize yourself with the non-technical interview questions commonly asked in the first round by HR recruiters and the questions to ask your interviewer !
Arc is the radically different remote job search platform for developers where companies apply to you. We’ll feature you to great global startups and tech companies hiring remotely so you can land a great remote job in 14 days. We make it easier than ever for software developers and engineers to find great remote jobs. Sign up today and get started .
More Basic JavaScript Interview Questions
Before we wrap this section up and get to the intermediate questions, here are a few other JavaScript basic interview questions you might want to ask your candidate during an interview:
- What are self-invoking functions?
- What is the purpose of the race method in a JavaScript Promise?
- What is a pure function?
- What are break and continue statements?
- What is variable shadowing in JavaScript?
- What is an event loop?
- What is an event flow?
- How do you sort elements in an array in JavaScript?
- What is a debugger statement?
- What is a short circuit condition?
The following questions should test the candidate’s intermediate knowledge of JavaScript and some of its widely used features.
1. What are rest parameters ?
The rest parameter is a JavaScript feature to provide a way to represent variadic functions in JavaScript. The candidate should be able to demonstrate an understanding of how the rest operator is used in a function and how its contents can be accessed.
The rest parameter syntax allows a function to accept an indefinite number of arguments as an array. The rest operator puts the contents of the variable after the rest operator into an array (rest parameter can only be used as the last parameter of a function).
Rest operator is represented by three dots ( ... ) followed by the variable name. The variable can then be used to access the array containing the contents of the function’s arguments.
The example below shows a function that accepts two parameters – greeting and name (with a rest operator). The rest operator on the name argument tells JavaScript to add any arguments from the second argument forward into an array called name .
2. What is memoization in JavaScript?
Optimization of processes becomes a necessity as applications grow and begin to perform heavier tasks. Memoization is an optimization technique that helps speed up expensive function calls using cached results. Understanding optimization techniques is important to keep your code fast and efficient. Your candidate should be able to explain memoization and how it relates to code optimization in general.
Memoization is an optimization technique that speeds up your code by storing the results of expensive function calls and reusing the stored result when the same input occurs again.
An expensive function refers to functions that consume a lot of resources (time and memory) during their execution due to heavy computation.
The result is immediately stored in a cache when an expensive function is called. When the same function is called again with the same parameters, it skips the computation required and returns the cached value instead. This process significantly reduces the time and memory your application consumes as the function doesn’t have to redo any calculations or computations that it has done previously.
3. What is currying in JavaScript?
Currying is an advanced technique of working with functions based on a concept from lambda calculus. You might ask intermediate JavaScript interview questions similar to this one to get an insight into the candidate’s level of understanding of functions in JavaScript. The candidate should be able to explain the concept of currying and how a function is decomposed and transformed following this concept.
Currying is a transformation of functions that translates a function from callable as f(a, b, c) into callable as f(a)(b)(c) . In other words, currying a function means the function takes one argument at a time and returns a new function expecting the next argument. Instead of taking all arguments at the same time, currying decomposes the function into a sequence of functions with a single argument.
Let’s look at an example of two functions that accepts three arguments and returns their sum. The first function ( ) is a regular function, whereas the second function ( ) is the curried version.
4. How do you empty a JavaScript array?
Arrays are widely used in JavaScript, making understanding their behavior and possible operations crucial when working with JavaScript. You might ask a JS question like this to gauge the candidate’s familiarity with JavaScript arrays and their operators. The candidate should be ready to explain a couple of different approaches and how they work at a high level.
There are various ways to empty an array in JavaScript. Below are a few common ways to do it.
- Set the target array to an empty array.
- Set the length of the target array to 0 .
- Use the splice method to update the target array’s contents.
5. What is a WeakMap in JavaScript?
A WeakMap is a map where the keys are weak – values are garbage collected when there are no more references to the key/value. The candidate should be able to explain what a WeakMap is along with their use case. You might also be looking to test the candidate’s understanding of the garbage collection mechanism, so make sure they explain how WeakMap relates to garbage collection in JavaScript.
By definition, a WeakMap is a collection of key/value pairs whose keys must be objects, with values of any arbitrary JavaScript type, and which do not create strong references to its keys.
A WeakMap provides a way to extend objects externally without interfering with JavaScript’s garbage collection mechanism. Once an object used as a key is collected, the object’s corresponding values in any WeakMap become candidates for garbage collection as well.
A WeakMap is especially useful when mapping keys to information about the key is valuable only if the key has not been garbage collected.
6. What is typecasting in JavaScript?
Converting between different data types is common in programming in general, and this is important for your candidate to get right. These could be when receiving a value from an external API, a user input, a third-party library, etc. A candidate should be able to demonstrate a basic understanding of what typecasting is and how to utilize the typecasts provided by JavaScript to convert between various data types.
Typecasting or coercion means to change the data type of a value to another data type. For example, a conversion from a string to an integer or vice versa.
Coercion can either be implicit or explicit. Implicit coercion is when the type conversion is automatic, whereas explicit coercion is when a developer explicitly writes code to convert the type of a value. The latter is also known as typecasting.
There are three typecasts provided by JavaScript:
- Boolean(value) – Casts the input value to a boolean value
- Number(value) – Casts the input value to a float or integer value
- String(value) – Casts the input value to a string
7. What are the various types of errors in JavaScript?
Every developer is bound to run into errors when programming in any language. JavaScript is no different. Debugging and resolving these errors are usually part of every developer’s day. Identifying the different error types can significantly help the developer narrow down the problem. The candidate should be able to identify and differentiate between the errors described below when asked this important JS interview question.
There are three types of errors in JavaScript:
- Syntax errors – Errors that occur at interpretation time such as during the loading of a web page due to incorrect syntax in the code.
- Runtime errors – Errors that occur during the runtime of the program after it is interpreted by the compiler. Calling functions that don’t exist is a common cause of this type of error.
- Logical Errors – Errors caused by the code’s logic itself. They are syntactically correct and don’t necessarily cause runtime errors. To think of this in terms of a sentence in the English language – the vocabulary and grammar of the sentence are correct, however, the meaning of the sentence is incorrect.
8. What is event bubbling in JavaScript?
Dealing with events is unavoidable, especially when working with the web. Event bubbling is an important concept that is commonly used either directly or via a framework or library. The candidate should be able to demonstrate a high-level understanding of what event bubbling is and how events work in JavaScript.
Event bubbling is a way of event propagation in the HTML DOM API, where events are handled from starting from the innermost element propagating outwards to its parent elements.
Let’s look at an example where an event occurs in a nested element where both elements have a registered event handler for the triggered event. Event bubbling causes the event to be captured and handled by the innermost element first. It is then propagated to the outer elements.
9. What is event capturing in JavaScript?
Similar to the previous question on event bubbling, event capturing is the opposite of event bubbling. You might ask this question as a follow-up to previous tough JavaScript interview questions to gauge the candidate’s understanding of events in JavaScript.
Event capturing is another way of event propagation in the HTML DOM API. Unlike event bubbling, event capturing propagates an event from the outermost element to the target element.
Bubbling is disabled by default on event listeners. To use event capturing, we will need to enable bubbling by passing true to the third argument of the addEventListener function.
10. What are the different ways an HTML element can be accessed in JavaScript?
If you are working with HTML with JavaScript, you will often find the need to access HTML elements from JavaScript. Although frameworks and libraries have abstractions that ease this process, a fundamental understanding of this is important. As a hiring manager or tech recruiter, you might ask this JS interview question to get an insight into the candidate’s level of understanding of accessing HTML elements beyond what the various frameworks and libraries offer.
There are four ways to access an HTML element in JavaScript:
- getElementById('idName') – Returns an element with the specified idName
- getElementByClass('className') – Returns all the elements containing the specified className
- getElementsByTagName('tagName') – Returns all the elements that contains the specified tagName
- querySelector('selectorName') – Returns the first element that contains the CSS style selector sepecified
More Intermediate JavaScript Interview Questions to Practice
Here are a few other intermediate JavaScript interview questions you might want to ask your candidates:
- How do you escape characters in JavaScript?
- What are JavaScript Cookies?
- What are the difference between escape() and unescape() functions?
- What is a microtask in JavaScript?
- What are higher-order functions in JavaScript?
- What are the different types of native errors in JavaScript?
- What is the difference between attributes and properties in JavaScript?
- What are the main differences between a forEach loop and a map loop?
- How do you compare two objects in JavaScript?
- How do you remove duplicates in a JavaScript array?

The following set of advanced JavaScript interview questions should test the candidate’s advanced knowledge of JavaScript and some of its more advanced concepts and features.
1. What is a closure in JavaScript?
Closures in JavaScript lets you associate data with a function that operates on that data. This has close ties to the object-oriented programming concept of objects allowing you to associate its properties with one or more methods. The candidate should not only explain what a closure is but also be able to provide examples and use cases where closures are useful.
A closure is an inner function that has access to the variables in the enclosing/outer function’s scope. The closure has access to variables from three scopes:
- within its own scope
- within the enclosing function’s scope
- global variables
Closures are particularly useful on the web because of the web’s event-based nature. A common pattern in front-end JavaScript is as follows: you define a behavior, then attach it to an event that is triggered by user input. An example of this is a click event handler.
Below is an example of how a closure is used to change the document body’s background color when the targetElement is clicked. The changeBackground function returns an inner function that sets the document body’s style.
2. What does the instanceof operator do?
Since we don’t explicitly define a type when we declare a variable, we sometimes need to know what the type of the variable is before performing any operation with it. The instanceof operator provides an easy way to perform a check on the variable’s type at run time. The candidate should be able to explain what is the instanceof operator and also its applications and usage.
The instanceof operator checks whether the prototype property of a constructor appears anywhere in the prototype chain of an object. In other words, the instanceof operator checks if the object is an instance of a class or not at run time.
The example below shows how the instanceof operator is used to test the type of the variable users .
3. How do you create a shallow copy of an object?
Cloning an object in JavaScript is a common task especially when you are working with objects. The candidate should be able to demonstrate a couple of ways to create a shallow copy and what characteristics the shallow copy has as it relates to the original object. A follow-up JS question an interviewer might ask is how to create a deep copy of an object.
Deep copying means that the value of the new variable is disconnected from the original variable while a shallow copy means that some values are still connected to the original variable.
First of all, a deep copy is a copy of an object completely disconnected from the original variable. A shallow copy on the other hand is a copy of the original variable where some values are still connected to the original variable.
There are two main ways to create a shallow copy of an object in JavaScript:
1. Using the spread operator
2. Using `Object.assign()
4. What is the difference between Object.freeze() and const ?
Developers work with a lot of objects in JavaScript. Understanding how objects work is very important and can help avoid bugs and unexpected behaviors that arise from using objects incorrectly. You might ask a question like this to gauge the candidate’s understanding on JavaScript objects and its mutability-related behavior. The candidate should be able to explain the key difference between Object.freeze() and const along with their respective applications.
Both Object.freeze() and const relates to the immutability of the object. However, they each address different aspects of the object’s immutability.
const creates immutable bindings. A variable declared with the const keyword can’t be assigned a new value.
Object.freeze() , on the other hand, makes the contents of the object immutable. You can’t modify the properties in the object.
5. What is Strict mode in JavaScript?
Strict mode is a feature of JavaScript ES5 to enforce stricter rules. The strict mode would cause code errors that would have been ignored or failed silently to generate errors. It is often good practice to use strict mode, though every use case is different. Your candidate should be able to explain the differences between using JavaScript’s strict mode and not.
Strict mode is a mode in JavaScript to enforce stricter parsing and error handling on your JavaScript code.
The main benefit of using strict mode is catching errors early and making debugging your code easier. Common errors such as assigning a value to an undeclared variable would throw an error in strict mode alerting you that there is something wrong in your code. You can master the art of secure coding with insights into anti-debugging techniques . This will safeguard your JavaScript applications and elevate your programming prowess to create robust, resilient software.
You need to add the string “use strict” above the file to enable strict mode for that file.
6. What is the difference between local storage and session storage ?
The web storage API contains two great tools to save key/value pairs – local storage and session storage. These are often used as an alternative to cookies. You might ask this difficult JavaScript interview question to get a better understanding of the candidate’s familiarity with client-side storage .
Local storage is a read-only property of the window interface to access a storage object. The stored data is saved indefinitely across browser sessions. Data stored in local storage is only cleared when removed explicitly through the browser’s settings or programmatically by the application.
Session storage is similar to local storage with the key difference being the data stored’s expiration time. Data stored in session storage gets cleared when the page session ends. A page session lasts as long as the tab or browser is open and persists between page reloads and restores.
7. What is the Temporal Dead Zone in JavaScript?
Temporal dead zone is a concept closely tied to hoisting. You might ask this question to gain an insight into your candidates’ familiarity with how hoisting works in JavaScript and JavaScript’s initialization process. Make sure your web developer know what temporal dead zone is and how to look for a temporal dead zone’s starts and ends.
In ES6, variables declared using let and const are hoisted similar to var , class and function . However, there is a period between the variable’s declaration and when it enters scope where the variable can’t be accessed. This period is called the Temporal dead zone (TDZ).
Below is an example where the variable name is declared using the let keyword but is assigned a value later in the code. The temporal dead zone is the period before the name variable is declared. Attempting to access the variable while in the temporal dead zone will throw a reference error.
8. What is a generator in JavaScript?
Generators when combined with Promises are a powerful tool for asynchronous programming as they help avoid problems associated with callbacks such as inversion of control and callback hell. The candidate should have a high-level understanding of what a generator is, how generator functions work in JavaScript, and their use cases .
Generators are functions that can be exited and re-entered at a later time. These type of functions saves and persists their context and variable-bindings across re-entrances.
A generator function is defined by a function* (keyword function followed by an asterisk ( * )) declaration.
When a generator function is initially called, it returns a type of iterator called a generator. The value is then consumed by calling the generator’s next method. The generator function continues its execution until it encounters the yield keyword.
There is no limit to the number of times a generator function can be called, however, each generator can only be iterated once.
Below is an example of a simple generator function that increments the current index and returns the incremented value.
9. What is the Prototype Design Pattern ?
This is a different type of question compared to the others you’ve seen in this section. This question is more conceptual, touching on design patterns, instead of discussing the features of JavaScript and how to perform a certain task. There are various design patterns used in software engineering, however since JavaScript is a prototypal language, a question about Prototype Design Pattern might be more relevant.
As the hiring manager, you might ask this question to test your candidates’ general knowledge of design patterns, their familiarity with the prototype design pattern, and how it could be used in the context of JavaScript._
The Prototype Design Pattern , also known as Properties Pattern is a creational design pattern based on prototypal inheritance. When an object is created, it acts as a prototype for other objects. You can think of the prototype object as a blueprint for other objects the constructor creates – the properties defined in the prototype object will also be present in the cloned object it creates.
The prototype model is mainly used for creating objects in performance-intensive situations. The prototype pattern helps eliminate the overhead of initializing an object.
Common applications of the prototype pattern are when you have a system independent of how its contents are created or when creating objects from a database whose values are copied to the newly created object.
10. What role do deferred scripts play in JavaScript?
This is an optimization question related to how JavaScript code is loaded. An understanding of how to optimize the loading of the script and its execution is important as an app grows and the delay becomes more and more noticeable. You may ask this type of question to test the candidate’s knowledge of the browser’s page load process and how familiar the candidate is with optimizing this process.
When a page loads, the browser starts to parse the HTML code. By default, when the browser runs into a script during the parsing process, it pauses processing the HTML code and starts executing the script. The browser then resumes parsing the HTML code once the script is done executing.
A slow server or a bulky script will cause a delay in the page load. Deferred scripts delay the script’s execution until the document has been parsed. This delay in the script’s execution results in a reduction in the load time of the webpage.
More JavaScript Advanced Interview Questions to Practice
Before we wrap this article up, here are a few other JavaScript advanced interview questions you might ask your candidates in your upcoming interview.
- How does JavaScript garbage collector work?
- What is a proper tail call?
- What is the difference between shallow and deep copy?
- How do you flatten a multi-dimensional array?
- What is the purpose of queueMicrotask ?
- What is the difference between shim and polyfill?
- What is the use of preventDefault method?
- What is a proxy object?
- What are JavaScript accessors? -What are the differences between mutable and immutable objects?
Whether you’re a hiring manager looking for the ideal candidate or a developer preparing for an interview, we hope these JavaScript interview questions help you through the process.
Keep in mind that technical skills and knowledge are only one part of the hiring process. Past experience and soft skills are equally important to make sure you land (or find the right candidate for) the job.
Keep in mind that many JavaScript interview questions are open-ended and don’t have one correct answer. When you’re interviewing a potential candidate, make sure to focus on evaluating not only their technical expertise but also on their thought process and problem-solving skills.
You can also explore HireAI to skip the line and:
⚡️ Get instant candidate matches without searching ⚡️ Identify top applicants from our network of 250,000+ devs with no manual screening ⚡️ Hire 4x faster with vetted candidates (qualified and interview-ready)
Read More : How to Write a Great Thank-You Email After an Interview
William Juan
Web & Mobile Front-End Developer
William is a front-end developer working primarily in the web and hybrid mobile spaces. The majority of his work has revolved around the Angular ecosystem, including working with other Angular-related frameworks such as NativeScript and Ionic. At Arc, he contributes the expertise he's gained over years as a writer on software development careers.
Further reading

20 Spring Interview Questions and Answers to Know (With MVC & Boot)

8 Questions to Ask Recruiters Before Committing to the Dev Hiring Process

29 Angular Interview Questions and Answers to Practice & Prepare For

21 MongoDB Interview Questions and Answers to Prep For (Beg. to Adv.)

15+ Top DevOps Interview Questions and Answers to Know

20 Machine Learning Interview Questions & Answers to Use
- Find Mentors
- Web Programming Web Programming AngularJS ASP.NET Django Express HTML/CSS jQuery Laravel Node.js Rails React Redux Vue.js
- Mobile App Programming Mobile App Programming Android iOS Ionic Kotlin React Native Swift Xcode Cordova Titanium
- Programming Language Programming Language C C++ C# Go Java JavaScript PHP Python R Ruby TypeScript
- Data Science/Engineering Data Science/Engineering AI Machine Learning Matlab Tableau Tensorflow
- Database/Operations Database/Operations AWS Database Docker GCP Heroku Linux MongoDB MySQL Postgres SQL
- Others Others Arduino Bash Electron Firebase Game Programming Git Rasberry Pi Selenium WebDriver Stripe Unity 3D Visual Studio Wordpress
- Programming Tutors Programming Tutors Java C# Python Computer Science
- Find Freelancers
- How it Works
- BECOME A MENTOR
How to Really Ace JavaScript Interview Questions: The Comprehensive Guide

Over the last few years, JavaScript has taken over the web development world becoming the primary language of choice for many new developers. That’s not just because JavaScript provides a great way to make web pages interactive – but also because that’s where the jobs are.
Why JavaScript?
The numbers speak for themselves. According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, web developer jobs are targeted to grow by 20% in 2012-2022 , which is much higher than any other stream. This is backed by many major publications and professional bodies listing JavaScript in their Top 10 Programming languages for 2015. IEEE ranks JavaScript at #8 , Inc puts it at #5 , and Mashable lists JavaScript at #2 . So, if you’re interviewing for any kind of web development position, or for Android / iPhone app developer positions, you’ve got to brush up your JavaScript skills.
Where/How to Learn JavaScript
For new programmers, here’s a few good resources to get you started.
- JavaScript Tutorial Codecademy (teaches the syntax, with live practical examples)
- JavaScript Fundamentals at Udemy (great place for beginners to start).
- JavaScript Programming for the Web at SitePoint (more indepth, with real world examples)
- The JavaScript Guide by Mozilla Developer Network
Here are a few other resources and developer tools to help you hone your JavaScript skills.
The catch is, most courses just teach the syntax, with a few examples thrown in. In a real interview, they are going to ask you more than just the syntax and theory.
What An Interviewer Really Looks For
In any programming interview, it’s not just about just knowing the syntax. It’s about knowing how to best use JavaScript concepts (and syntax), to solve an end problem.
- How well do you understand the language conceptually? How effectively can you use those concepts to solve real work problems.
- How do you write code (coding conventions, syntax, re-usability)? Will you spending half your time debugging syntax errors?
- What’s your thought process like? How do you think about problem, come up with a solution, and translate it to working code.
These things are better learnt by doing rather than reading. A major part of your interview preparation should include solving problems, creating real apps etc. This is best done with the help of a an expert who has field experience using JavaScript in the real world, solving real problems and can bring in that extra perspective.Try out CodeMentor’s monthly plan to get 1:1 guidance for the kind of JavaScript questions asked in interviews. Most mentors have been on both sides of the interview table themselves and can help guide you on the smartest way to prepare.
In the meanwhile, here are some of the most common interview questions to help get you started.
Want to ace your technical interview? Schedule a Technical Interview Practice Session with an expert now!
JavaScript Interview Questions: Conceptual
To make sure you know the basics, interviewers typically start off with a few theoretical or conceptual questions.
- How does type in JavaScript differ from that in other languages?
Unlike C++ and some other programming languages, JavaScript is loosely typed. This means that you can define variables without specifying a particular type. In such a situation, JavaScript automatically assigns the type depending on the value assigned to that variable. [Read more about JavaScript types and conversion here ]
- What are JavaScript timers? Are there any limitations?
In JavaScript you can use Timers to execute a function after a certain time, or repeat it at certain intervals. The functions used for this are setTimeout (function, delay) , setInterval (function, delay) , and clearInterval() .
The catch is that all timer events run in a single thread. So if you’ve set multiple timers, they may end up interfering with each other. For example, you may still be executing the handler for Timer1 at the moment when Timer2 was meant to fire.. and therefore Timer2 will get delayed. The same holds if Timer2 is just the next instance of a repeating timer.
- How does the virtual destructor work in JavaScript ?
[This is a trick question. The interviewer wants to make sure you’re not mixing up multiple languages]
JavaScript doesn’t have destructors. There’s no particular function called to ‘free’ objects. Instead JavaScript has a garbage collector that runs at regular intervals, cleaning up objects and freeing up memory that is no longer in use.
C++ has virtual destructors and I can explain that if you’d like. [Don’t launch into a detailed explanation. Check if the interviewer’s really interested.
- Are Scope and Context the same?
[Following the previous trick question, the interviewers want to see if you’ll fall for this and say they’re the same.]
Though these words are many times used similarly, they refer to different things. Scope refers to the lifetime or access of a variable when a function is invoked. Context on the other hand, is related to the object. Context is the value of the ‘ this ’ keyword – the object that owns the currently executing code. [ More about scope versus context here ]
- How does JavaScript interact with HTML or the DOM?
JavaScript is normally used to change HTML content or DOM elements. It can change HTML attributes, and HTML styles or it can be used to validate input data in forms. [You can read more about the JavaScript methods used for HTML manipulation over here.]
JavaScript Interview Questions: Syntax
Once they’ve verified you know the theory of how things work, interviewers will typically check your knowledge of syntax nuances.
- Have you ever used “ === ”? Is there any such thing?
In JavaScript, the “ == ” (double equal) operator checks for ‘equal to’ only in value – it ignores the type. The === (triple equal) is a special operator in JavaScript that checks for equal value AND type.
- What is the ‘this’ keyword used for?
It is used to reference the object that currently owns the code you are in.
- Can you write two ways in which the variable can be assigned to an empty object?
JavaScript Interview Questions: Programs
After they’ve verified basic concepts and syntax, the interviewer will ask you to write some code. This could be either real world problems or just hypothetical situations, to see how you code and the thought process behind it. This is the part you really want to practice for and perhaps work with a mentor to guide you.
- Given the below code, what line of JavaScript would allow icecream.getFlavor to return the value of foo.color , without using the word “icecream”?
[Yes, this is a simple answer. But the thing is we’re more used to writing code, than reading it. Interviewers ask these kinds of questions to see how quick you think on your feet and connect the dots.]
2. Implement the Fibonacci number calculator in JavaScript. Take a number as input from the user, and then print out the Fibonacci value for that number. [ The Fibonacci sequence is F0 = 0, F1 = 1, Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2 ] There are many ways to do this. You can use a loop to calculate the sequence, or use recursion.
One variant of this question is “It should execute in the fastest way possible”. In an interview you really don’t have the time to run the code and check which is the fastest method. But you do know that loops or recursion take up a lot of time. So, ask if you can put an upper limit to n. Say n has to be under 100 . You can then use a simple array to store the Fibonacci numbers and just access the array instead of computing it.
Hope this set of JavaScript interview questions helps you prepare for your big day. But again, this is just a limited set of questions. For a quick check on where you stand, try out this free JavaScript quiz over at W3Schools . If you want to go the extra mile to test your skills, you can also get certified through the W3School online certification program or better yet – just build a few real apps.
But to be truly prepared, try working with a mentor who has experience taking interviews – so you can get an understanding of what interviewers really look out for as well as practice writing code on the fly. Try Code Mentor’s Monthly pack (that comes with a 7 day free trial) or check out some of our JavaScript mentors here .
About the Author:

Sign Up and Get Help Now
Please accept our cookies! 🍪
Codementor and its third-party tools use cookies to gather statistics and offer you personalized content and experience. Read about how we use cookies and how to withdraw your consent in our Cookie Policy. If you continue to use this site, you consent to our use of cookies.
Please accept our cookies! Read Cookie Policy 🍪
Precision in Payroll - Acing Taxes and Compliance
Webinar HR Metrics Magic: Transforming Insights into Actions Register Now
- Interview Questions
Top 50 JavaScript coding Interview Questions and Answers
JavaScript is one of the widely used programming languages and used to create engaging and dynamic websites. Due to its vast scope, JavaScript interviews can be challenging . However, thorough preparation can help overcome these challenges. An interviewee should familiarize themselves with the most basic concepts to the most complex libraries and frameworks.
These top 50 JavaScript interview questions and answers will help an intervie wee to thoroughly practice and prepare for their interview.
Top 50 JavaScript Coding Interview Questions
Basic javascript coding questions.
Basic JavaScript questions cover concepts like data types, variables and scoping, array, string manipulation, OOP (Object Oriented Programming), control flow, error handling, DOM manipulation, and asynchronous programming. The basic JavaScript coding interview questions are:
1. Write a JavaScript function to calculate the sum of two numbers.
When managers ask this question, they are looking for the candidate’s basic understanding of JavaScript. They assess their understanding of basic syntax along with problem-solving skills. This also helps evaluate the candidate’s coding style and attention to detail.
Sample answer: I would take two parameters and the following function can be used to calculate the sum of any 2 numbers that are passed as arguments.
function sumOfTwoNumbers(a, b) {
return a + b;
2. Write a JavaScript program to find the maximum number in an array.
A hiring manager asks this question to analyze the candidate’s ability to write clear and efficient code. It’s crucial for candidates to explain the code step-by-step while demonstrating bug-free code.
Sample answer:
function findMaxNumber(arr) {
return Math.max(…arr);
3. Write a JavaScript function to check if a given string is a palindrome (reads the same forwards and backwards).
The interviewer is looking for the candidate’s familiarity with loop constructs, JavaScript string methods, and other basic JavaScript syntax. They will evaluate the candidate’s skills based on the approach used to solve the palindrome problem.
function isPalindrome(str) {
return str === str.split(”).reverse().join(”);
4. Write a JavaScript program to reverse a given string.
Hiring managers are expecting an accurate solution that demonstrates the interviewee’s proficiency in JavaScript programming.
const reverseString = (str) => str.split(”).reverse().join(”);
5. Write a JavaScript function that takes an array of numbers and returns a new array with only the even numbers.
Interviewers are looking for candidates who can not only clearly explain the solution along with the code, but also show the ability to think logically and articulate their thought processes.
Sample answer: By using the filter method on the array, I can check if each element is even or not by using the modulus operator (%) with 2. The element is even if the result is 0. This can be included in the new array.
function filterEvenNumbers(numbers) {
return numbers.filter(num => num % 2 === 0);
6. Write a JavaScript program to calculate the factorial of a given number.
By asking this question, managers aim to assess the candidate’s algorithmic thinking and understanding of JavaScript programming. The interviewer expects the candidate to demonstrate their knowledge of the factorial concept.
Sample answer: A factorial number is the product of all positive integers, which are equal to or less than the given number.
function factorial(number) {
if (number === 0 || number === 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return number * factorial(number – 1);
7. Write a JavaScript function to check if a given number is prime.
Interviewers can analyze the candidate’s knowledge of JavaScript algorithms and mathematical concepts. They expect the candidate to translate a mathematical concept into functional code.
Sample answer: To check if a given number is prime, loop from 2 to the square root of the number. If any integer evenly divides it, the number is not prime.
function isPrime(num) {
if (num <= 1) return false;
for (let i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i++) {
if (num % i === 0) return false;
return true;
8. Write a JavaScript program to find the largest element in a nested array.
When asking this question, interviewers are looking for the candidate’s ability to handle nested data structures and apply their knowledge of conditional statements, arrays, and loops. Candidates must apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios.
function findLargestElement(nestedArray) {
let largest = nestedArray[0][0];
for (let arr of nestedArray) {
for (let num of arr) {
if (num > largest) {
largest = num;
return largest;
9. Write a JavaScript function that returns the Fibonacci sequence up to a given number of terms.
This question helps hiring managers assess the interviewee’s understanding of fundamental algorithms in JavaScript. They expect the candidate to consider edge cases and handle errors.
function fibonacciSequence(numTerms) {
if (numTerms <= 0) return [];
if (numTerms === 1) return [0];
let sequence = [0, 1];
while (sequence.length < numTerms) {
let nextNumber = sequence[sequence.length – 1] + sequence[sequence.length – 2];
sequence.push(nextNumber);
return sequence;
10. Write a JavaScript program to convert a string to title case (capitalize the first letter of each word).
Interviewers analyze the candidate’s ability to break down a problem into manageable steps and demonstrate knowledge of string manipulation, looping, and basic JavaScript functions.
function toTitleCase(str) {
return str.replace(/\b\w/g, l => l.toUpperCase());
A dvanced JavaScript coding interview questions
Advanced JavaScript coding includes various complex concepts and techniques. Such key concepts are often tested in JavaScript interviews. Some of the concepts are – closure and scope, prototypal inheritance, functional programming , design patterns, memory management, ES6+ features, and many more.
1. Implement a debounce function in JavaScript that limits the frequency of a function’s execution when it’s called repeatedly within a specified time frame.
Interviewers expect the candidate to showcase their ability to clearly explain the purpose of the debounce function and its usage in scenarios where function calls need to be controlled. They are looking for the person’s ability to articulate technical concepts clearly.
Sample answer: By delaying the execution of the debounce function until the specified time frame has passed, the frequency can be limited.
function debounce(func, delay) {
let timer;
return function() {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(func, delay);
2. Write a function that takes an array of objects and a key, and returns a new array sorted based on the values of that key in ascending order.
By asking this question, hiring managers analyze how well the candidate can discuss the sorting algorithm and its time complexity. It’s also crucial for candidates to demonstrate their code’s robustness.
Sample answer: The following function takes an array of objects and a key to sort the array based on the values in ascending order.
function sortByKey(arr, key) {
return arr.sort((a, b) => a[key] – b[key]);
3. Implement a deep clone function in JavaScript that creates a copy of a nested object or array without any reference to the original.
Hiring managers want to assess the interviewee’s skill to handle complex coding tasks and understand the concept of avoiding reference issues while cloning.
Sample answer: By using two methods together and creating a deep clone, I can serialize the object to a JSON string. I would then parse it back into a new object, thereby removing any reference to the original object.
function deepClone(obj) {
return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj));
4. Write a recursive function to calculate the factorial of a given number.
Interviewers expect the candidate to write a concise recursive function that handles edge cases. Candidates must show their understanding of how recursion works to avoid infinite loops or stack overflow errors.
function factorial(num) {
if (num <= 1) return 1;
return num * factorial(num – 1);
5. Implement a function that takes two sorted arrays and merges them into a single sorted array without using any built-in sorting functions.
When interviewers ask this question, they seek to assess the knowledge of algorithms and efficiency in handling sorted data. They also look for the ability to think of and execute a correct solution.
Sample answer: I can implement a function that can efficiently merge two sorted arrays.
function mergeSortedArrays(arr1, arr2) {
return […arr1, …arr2].sort((a, b) => a – b);
6. Write a function that checks if a given string is a palindrome, considering only alphanumeric characters and ignoring case.
Interviewers analyze the interviewee’s approach to execute code and demonstrate familiarity with handling case-sensitive and alphanumeric checks, regular expressions, and JavaScript string methods.
const cleanStr = str.replace(/[^a-zA-Z0-9]/g, ”).toLowerCase();
const reversedStr = cleanStr.split(”).reverse().join(”);
return cleanStr === reversedStr;
7. Create a JavaScript class for a linked list with methods to insert a node at the beginning, end, or at a specific position, and to delete a node from a given position.
By asking this question, interviewers can evaluate how well a candidate can design and implement a class for a linked list while also presenting their problem-solving skills .
Sample answer: I would implement a linked list with methods to insert a node at the beginning, end, and at specific positions. Then, I would delete a node from a given position.
8. Implement a function that flattens a nested array in JavaScript, converting it into a single-level array.
Managers can gauge the candidate’s logical thinking skills and capability to handle complex data structures. Interviewees should demonstrate their knowledge of loops, recursion, and arrays.
const flattenArray = (nestedArray) => {
return nestedArray.flat(Infinity);
9. Write a function that determines if two strings are anagrams of each other
When interviewers present this question, they aim to measure how well the candidate can use appropriate string-related methods and identify anagrams accurately.
function areAnagrams(str1, str2) {
return str1.split(“”).sort().join(“”) === str2.split(“”).sort().join(“”);
10. Create a JavaScript function that returns the Fibonacci sequence up to a given number, utilizing memoization for optimized performance.
Interviewees are expected to show their proficiency in OOP and familiarity with recursion and memoization. They can also determine the candidate’s attention to detail in class design and organizing code.
Sample answer: By creating a function that uses an array to store the computed values, a Fibonacci sequence can be generated.
function fibonacciWithMemoization(n) {
let memo = [0, 1];
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
memo[i] = memo[i – 1] + memo[i – 2];
return memo;
Common JavaScript coding interview questions
Some of the common JavaScript coding interview questions typically cover these topics: checking for palindrome, finding missing/largest numbers, object manipulation, removing duplicates, merging, etc.
1. Write a function to check if a given string is a palindrome.
Hiring managers review how well a candidate can handle edge cases while handling case sensitivity, punctuation, and whitespace.
Sample answer: This function takes a string as input to convert it into lowercase and then compares it with its reverse. The string can be deemed a palindrome if the two match.
return str.toLowerCase() === str.toLowerCase().split(”).reverse().join(”);
2. Implement a function to reverse a string without using the built-in reverse() method.
Hiring managers aim to analyze the candidate’s knowledge of string manipulation in JavaScript while also measuring their ability to think of alternative solutions.
Sample answer: I would use a for lopp to iterate through the characters from the end to the beginning. By appending the character to a new string, it results in the reversed output.
function reverseString(str) {
let reversed = ”;
for (let i = str.length – 1; i >= 0; i–) {
reversed += str[i];
return reversed;
3. Given an array of numbers, write a function to find the largest and smallest numbers in the array.
By presenting the candidates with this question, managers can gauge how well a candidate is familiar with basic JavaScript functions and array manipulation.
Sample answer: I would use the following functions to find the smallest and largest numbers in the array.
function findMinMax(arr) {
let min = Math.min(…arr);
let max = Math.max(…arr);
return [min, max];
4. Write a function that takes an array of integers as input and returns a new array with only the unique elements.
Hiring managers can evaluate the candidate’s knowledge of JavaScript functions, array handling capabilities, and communicating technical concepts.
function getUniqueElements(arr) {
return Array.from(new Set(arr));
5. Implement a function to find the factorial of a given number.
Interviewers can determine the candidate’s capability to execute functional code and ability to handle input validation and edge cases. Interviewers also assess the ability to use concise and effective code and provide efficient code implementation.
if (number === 0 || number === 1) return 1;
return number * factorial(number – 1);
6. Write a function that determines if a given number is prime or not.
By asking this question, interviewers can understand how good the candidate is proficient in math operations and JavaScript logic. The interviewee should excute a clean and optimized solution that is efficient.
7. Implement a function to find the sum of all the numbers in an array.
Such a question helps understand if the interviewee can manipulate arrays and handle numeric values. This also helps managers assess problem-solving capabilities and ability to pay attention to code efficiency.
Sample answer: I would use the reduce method to implement the following function:
function findSum(arr) {
return arr.reduce((sum, num) => sum + num, 0);
8. Given a string, write a function to count the occurrences of each character in the string.
Hiring managers expect the candidate to be familiar with string manipulation and loop constructs. When they ask this question, they can evaluate whether the candidate knows data structures.
function countCharacterOccurrences(str) {
const charCount = {};
for (let char of str) {
charCount[char] = (charCount[char] || 0) + 1;
return charCount;
9. Implement a function to remove duplicates from an array.
When interviewers present the candidate with this question, they can gauge the level of understanding a candidate has regarding array methods and different approaches to solve the problem.
Sample answer: The following function duplicates from an array by converting it into a Set. This automatically removes duplicates. Next, the function converts the Set back into an array.
function removeDuplicates(arr) {
10. Write a function that sorts an array of numbers in ascending order.
Interviewees must show their knowledge of bubble sort, merge sort, sorting algorithms, and other approaches. The HR manager aims to measure the capability to execute strong algorithms and handle edge cases.
Sample answer: I can solve this by using JavaScript’s built-in sort method.
function ascendingSort(numbers) {
return numbers.sort((a, b) => a – b);
Tricky JavaScript coding questions
By asking tricky JavaScript coding questions, managers can assess problem—solving skills, JavaScript concepts, and critical thinking . These go beyond syntax knowledge and require the candidate to think creatively and logically to solve problems.
1. Write a function that reverses the order of words in a sentence without using the built-in reverse() method.
This question not only assesses the creativity of the candidates but also helps hiring managers understand how well a candidate can come up with a clean and understandable solution.
function reverseSentence(sentence) {
const words = sentence.split(‘ ‘);
const reversedWords = words.reverse();
return reversedWords.join(‘ ‘);
2. Implement a function that checks if a given string is a palindrome (reads the same forwards and backwards) while ignoring whitespace and punctuation.
Interviewers can gauge the interviewee’s capability to handle whitespace and punctuation gracefully while also maintaining the palindrome-checking logic. Candidates must express their knowledge of regular expressions or any other efficient approach.
const cleanedStr = str.replace(/[^\w]/g, ”).toLowerCase();
const reversedStr = cleanedStr.split(”).reverse().join(”);
return cleanedStr === reversedStr;
3. Write a function that takes an array of integers and returns the largest difference between any two numbers in the array.
Candidates should demonstrate their approach to finding the maximum difference between the array elements to handle edge cases and invalid inputs.
function largestDifference(arr) {
let min = arr[0];
let maxDiff = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < min) {
min = arr[i];
const diff = arr[i] – min;
if (diff > maxDiff) {
maxDiff = diff;
return maxDiff;
4. Implement a function that removes duplicates from an array, keeping only the unique elements.
Interviewers can analyze how well a candidate can effectively communicate code explanations and their familiarity with algorithmic efficiency.
return arr.filter((item, index) => arr.indexOf(item) === index);
5. Write a function that accepts a number and returns its factorial (e.g., factorial of 5 is 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1).
By presenting this question in the interview, hiring managers can assess the capability of the candidate to handle numeric calculations. They can also determine how well the interviewee can pay attention to handling edge cases, if applicable.
if (num === 0 || num === 1) {
return num * factorial(num – 1);
6. Implement a function that flattens a nested array into a single-dimensional array.
Interviewers expect the candidates to demonstrate their ability to work with complex data structures and use appropriate techniques to accomplish tasks.
function flattenArray(arr) {
return arr.flat();
7. Write a function that checks if a given string is an anagram of another string (contains the same characters in a different order).
Candidates should showcase how well they can handle complex algorithms and logic. Interviewers are specifically looking for knowledge in string methods, data structures, and loop constructs.
function isAnagram(str1, str2) {
const sortedStr1 = str1.split(”).sort().join(”);
const sortedStr2 = str2.split(”).sort().join(”);
return sortedStr1 === sortedStr2;
8. Implement a function that finds the second smallest element in an array of integers.
Interviewers can measure the candidate’s problem-solving skills and their understanding of conditional statements, loops, and arrays.
function secondSmallest(arr) {
const sortedArr = arr.sort((a, b) => a – b);
return sortedArr[1];
9. Write a function that generates a random alphanumeric string of a given length.
By asking this question, interviewers can understand how well a candidate can ensure the function produces a reliable and consistent random output.
function generateRandomString(length) {
const characters = ‘ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789’;
let result = ”;
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
const randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * characters.length);
result += characters.charAt(randomIndex);
return result;
10. Implement a function that converts a number to its Roman numeral representation.
Hiring managers can gauge a candidate’s capability to implement coding solutions and create an efficient algorithm.
Sample answers:
function toRomanNumeral(number) {
// Implement your code here
JavaScript array coding questions
JavaScript array coding interview questions are technical questions asked to gauge candidates’ ability to work with arrays along with their familiarity with fundamental data structures.
1. Write a function that returns the sum of all numbers in an array.
By asking such a question, hiring managers can evaluate whether the candidate would be able to perform common tasks and solve basic coding challenges.
Sample answer:
function sumArray(arr) {
return arr.reduce((total, num) => total + num, 0);
2. Implement a function that finds the maximum number in an array.
Depending on the candidate’s answer, the manager can determine how effectively the interviewee can work with arrays. The managers can also understand the capability to communicate technical solutions.
let max = arr[0];
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
return max;
3. Write a function that returns a new array containing only the unique elements from an input array.
The hiring manager is specifically looking for candidates who can demonstrate an understanding in data manipulation and JavaScript arrays. Additionally, interviewers evaluate how well the candidate strives for an optimized solution without duplicate elements.
function getUniqueElements(inputArray) {
return […new Set(inputArray)];
4. Implement a function that returns the average value of numbers in an array.
By asking this question, hiring managers can assess the candidate’s knowledge of arithmetic operations, array manipulation, and looping.
function calculateAverage(numbers) {
let sum = 0;
for (let number of numbers) {
sum += number;
return sum / numbers.length;
5. Write a function that sorts an array of strings in alphabetical order.
When interviewers present this question in the interview, they expect the candidate to be familiar with sorting algorithms and JavaScript array manipulation.
Sample answer:
function sortStrings(arr) {
return arr.slice().sort();
6. Implement a function that finds the index of a specific element in an array. If the element is not found, the function should return -1.
Interviewers aim to gauge the candidate’s proficiency in use of array methods, handling edge cases, and in JavaScript syntax. Candidates must implement the function proper error handling.
function findElementIndex(arr, element) {
const index = arr.indexOf(element);
return index !== -1 ? index : -1;
7. Write a function that removes all falsy values (false, null, 0, “”, undefined, and NaN) from an array.
Candidates must showcase communication skills and explain their solutions logically. Interviewers analyze the interviewee’s ability to write a function that filters false values from an array.
function removeFalsyValues(arr) {
return arr.filter(Boolean);
8. Implement a function that merges two arrays into a single array, alternating elements from each array.
Hiring managers determine a candidate’s ability to craft efficient algorithms and knowledge of array manipulation.
function mergeArrays(array1, array2) {
const mergedArray = [];
const maxLength = Math.max(array1.length, array2.length);
for (let i = 0; i < maxLength; i++) {
if (i < array1.length) mergedArray.push(array1[i]);
if (i < array2.length) mergedArray.push(array2[i]);
return mergedArray;
9. Write a function that finds the second largest number in an array.
Such a question reveals to the interviewers how well the candidate can use loops and array methods, work with them, and utilize logic to find solutions.
function findSecondLargest(arr) {
arr.sort((a, b) => b – a);
return arr[1];
10. Implement a function that groups elements in an array based on a given condition. For example, grouping even and odd numbers into separate arrays.
When interviews ask this question, they aim to evaluate a candidate’s understanding of concepts like array methods, conditional statements, and other technical concepts. Candidate should demonstrate good coding style.
function groupByCondition(arr, condition) {
return [
arr.filter(element => condition(element)),
arr.filter(element => !condition(element))
Tips to prepare for a JavaScript coding interview
There are 5 tips a candidate should keep in mind when attending a JavaScript coding interview:
- Master JavaScript basics: Candidates must have a solid understanding of core JavaScript fundamentals, including variables, loops, conditionals, objects, and data types. Additionally, practicing coding skills is important.
- Explore popular libraries and frameworks: Familiarizing oneself with the most common JavaScript libraries and frameworks like Vue.js, React, etc., helps understand key concepts.
- Practice whiteboard Java coding: Java coding skills can further be sharpened by practicing whiteboard coding. Candidates should solve coding challenges and explain their thought processes loudly. They should mainly focus on simplicity, clarity, and efficiency.
- Test code : After writing Java solutions, test it with various inputs and ensure it works correctly and can handle edge cases. Consider the time complexity of the solutions and aim for efficiency.
- Review JavaScript projects : Discussing JavaScript projects in the interview is essential. Interviewees should explain their approach clearly and how they overcame the challenges.
There are some red flags hiring managers should watch out for in a JavaScript coding interview:
- Lack of basic JavaScript knowledge
- Providing inefficient solutions
- No practical problem-solving abilities
- Limited knowledge of asynchronous programming
- Copy-pasting code
- Inability to articulate thought processes or provide a clear explanation of their approach to the problem
- Unfamiliarity with Modern JavaScript
- Failure to provide error handling and consider edge cases
Candidates are evaluated majorly on their understanding of core JavaScript concepts and skills. By mastering the fundamentals and practicing, candidates can crack their interview. Also, it’s important to focus on being clear, accurate , and honest in the interview.
Related Interview Questions
- Java programming interview questions and Answers
- Top 40 Java Interview Questions and Answers 2023
Related Job Descriptions
- Java Developer Job Description
- Full Stack Developer Job Description Template
By clicking “Accept", you consent to our website's use of cookies to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. You may visit "cookie policy” to know more about cookies we use.
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests...
Provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
js-interview-questions
Here are 19 public repositories matching this topic..., vvscode / js--interview-questions.
❔❓❔ Notes from technical (javascript) interviews. Tasks and quiz for different topics to discuss on interview / check self skills in javascript
- Updated Oct 27, 2022
Vasu7389 / JavaScript-Interview-Questions
Prepare for your next JavaScript interview with our comprehensive repository of questions and code snippets. 🚀 Be the knowledge superhero, by not only having all the answers but also contributing and updating questions for the community. 🚀 Worth to Star? ⭐
- Updated Mar 30, 2024
PavanAditya / JS-Playground
Basic ES6 Concepts covering prepartion topics for interviews. Includes all type of Javascript interview questions, Frontend Engineer Role Interview Questions and practice concepts
- Updated Jan 22, 2024
ramilabbaszade / Javascript-Interview-Questions-and-Simple-Answers
Javascript technical interview questions. Answers are simple and generated by ChatGPT 😉
- Updated Apr 3, 2023
BilgeGates / Js-Interview-Questions
List of 450 JavaScript Interview Questions
- Updated Jul 31, 2023
ayushkul / javascript-interview-series
- Updated Mar 15, 2022
Swastikyadav / JavaScript-Interview-and-DsAlgo-Questions
JavaScript interview and Ds-Algo Questions Practice.
- Updated Jan 25, 2024
shivamjain1 / Data-Structures-Javascript
This contains JS implementations of data structures and interview questions
- Updated Feb 17, 2021
manish-mehra / greatfrontendsolutions
Curated JavaScript challenges from the Great Frontend website with solutions.
- Updated Oct 22, 2023
haohcraft / exercises
Some basic javascript coding challenges and interview questions
- Updated Sep 13, 2017
devvanu / javascript-interview-questions
This repo will be containing list of JavaScript Interview Questions with their Solutions
- Updated Sep 21, 2022
bugged-codes / Pb_Js-Combined
Repo for all JS questions answers. Even includes questions from out of dashboard. 100+ questions.
- Updated Jan 19, 2023
AtahanKocc / Awesome-Javascript-Interview
Javascript Interview questions and answers
- Updated Oct 21, 2023
prajakta192 / JS-Interview-series
A public repository contains the best practices about JavaScript's beginners, intermediate, advance interview questions.
- Updated Jan 17, 2024
syket-git / Flattening-array-object-javascript
In this repo, flatting a multi dimensional/single array using JavaScript.
- Updated May 6, 2023
Davidalimazo / data_structure_and_algorithms_in_js
This repository contains implementation for data structures and algorithms using javaScript
- Updated Sep 17, 2022
MrAbdurakhimov / js-interview
🚀 In this repository, I am going to prepare for an interview with a junior and intermediate software engineer. You can also find out from the repo.
- Updated Oct 19, 2021
NadaMuhammad28 / DSA-PS
Problem solving notes and patterns
- Updated Jan 7, 2024
Improve this page
Add a description, image, and links to the js-interview-questions topic page so that developers can more easily learn about it.
Curate this topic
Add this topic to your repo
To associate your repository with the js-interview-questions topic, visit your repo's landing page and select "manage topics."
7 JavaScript Interview Questions Every Developer Should Know

JavaScript has emerged as the cornerstone of modern web development, enabling dynamic and interactive experiences that shape the digital landscape. As a result of its widespread use, it also happens to be one of the world’s most in-demand programming languages .
As a JavaScript developer, excelling in technical interviews is paramount for showcasing your expertise and securing coveted positions in the industry, and a great way to prepare is to put your skills to the test.
In this blog post, we’ll explore seven intermediate-to-advanced JavaScript interview questions that will push the boundaries of your problem-solving skills, challenge your understanding of key concepts, and demonstrate your ability to navigate complex scenarios. Whether you are a seasoned JavaScript developer seeking to refresh your interview readiness or a hiring manager looking to identify top talent, this guide will equip you with invaluable insights and practical examples.
Inside a JavaScript Interview
JavaScript , often referred to as the “ language of the web ,” is a versatile programming language that plays a vital role in modern web development. It is primarily used to create interactive and dynamic elements on websites, enabling a rich user experience.
When it comes to JavaScript interviews, they serve as a critical evaluation of a candidate’s JavaScript proficiency, problem-solving skills, and understanding of key concepts. A JavaScript interview can take various forms, depending on the company and position. However, it typically involves one or more of the following assessment formats:
- Technical screenings
- Coding challenges
- Whiteboard exercises
- Take-home assignments
- Pair programming sessions
- Behavioral interviews
These components are designed to assess different aspects of a candidate’s capabilities and provide a comprehensive evaluation of their JavaScript knowledge and expertise.
Roles that require candidates to complete a JavaScript interview span a wide range of technical positions. Web developers, back-end developers , front-end developers , and software engineers often encounter JavaScript interview questions as part of the hiring process. Additionally, positions in mobile app development , UI/UX design, and even emerging technologies like serverless computing may involve JavaScript assessments to gauge a candidate’s ability to work with its frameworks and libraries.
#1. Reverse Words in a Sentence
This question focuses on reversing the order of words in a given sentence, demonstrating a developer’s proficiency with string manipulation, loops, conditionals, and other programming constructs.
Task: Write a JavaScript function called reverseWords that takes a sentence as input and returns the sentence with the order of words reversed.
Input Format: The input will be a string representing the sentence.
Constraints:
- The sentence will contain only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
- There will be no leading or trailing spaces.
- The sentence will have at least one word.
Output Format: The output will be a string representing the sentence with the words reversed.
Sample Input: JavaScript is awesome
Sample Output: awesome is JavaScript
Sample Code:
function reverseWords(sentence) {
const words = sentence.split(” “);
const reversedWords = words.reverse();
const reversedSentence = reversedWords.join(” “);
return reversedSentence;
Explanation:
- The reverseWords function starts by splitting the sentence into individual words using the split(” “) method. This creates an array of words.
- Next, the function uses the reverse() method to reverse the order of the words in the array.
- The reversed words are then joined back together using the join(” “) method, where the space character ” “ is used as the separator.
- Finally, the reversed sentence is returned.
#2. Find the Nth Largest Element in an Array
This question delves into array manipulation and algorithmic problem solving, showcasing a developer’s ability to work with arrays and efficiently find the nth largest element.
Task: Write a JavaScript function called findNthLargest that takes an array of numbers and an integer n as input, and returns the nth largest element from the array.
Input Format
- The input will be an array of numbers.
- An additional integer n will be provided.
Constraints
- The array will contain at least n elements.
- The array may have duplicates.
- The values in the array can be both positive and negative.
Output Format: The output will be the nth largest element as a number.
Sample Input:
const numbers = [10, 5, 3, 8, 2];
const n = 3;
Sample Output: 5
function findNthLargest(numbers, n) {
numbers.sort((a, b) => b – a);
return numbers[n – 1];
The findNthLargest function starts by sorting the numbers array in descending order using the sort() method with a custom comparison function (a, b) => b – a . This places the largest numbers at the beginning of the array.
Then, the function returns the element at index n – 1 since arrays are zero-indexed. In our example, we want to find the 3rd largest element, so we access numbers[2] , which is 5 .
#3. Implementing a Linked List
This question focuses on data structures and their implementation in JavaScript, specifically the Linked List. Demonstrating proficiency in data structures showcases a developer’s ability to design efficient and scalable solutions.
Task: Implement a Linked List in JavaScript with the following operations:
- insert(value) : Inserts a new node with the given value at the end of the list.
- delete(value) : Removes the first occurrence of the node with the given value from the list.
- search(value) : Returns true if a node with the given value exists in the list, false otherwise.
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
insert(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
delete(value) {
return;
if (this.head.value === value) {
this.head = this.head.next;
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
while (current && current.value !== value) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
if (!current) {
previous.next = current.next;
search(value) {
while (current) {
if (current.value === value) {
return true;
return false;
// Usage example:
const linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.insert(5);
linkedList.insert(10);
linkedList.insert(15);
linkedList.delete(10);
console.log(linkedList.search(5)); // Output: true
console.log(linkedList.search(10)); // Output: false
The code snippet above demonstrates the implementation of a Linked List in JavaScript.
The Node class represents a single node in the Linked List, containing a value property to store the node’s value and a next property to reference the next node in the list.
The LinkedList class represents the Linked List itself. It has a head property that initially points to null . The insert method inserts a new node with the given value at the end of the list by traversing to the last node and appending the new node. The delete method removes the first occurrence of a node with the given value from the list by updating the next references of the surrounding nodes. The search method traverses the list to check if a node with the given value exists.
In the usage example, we create a new Linked List, insert nodes with values 5, 10, and 15, delete the node with value 10, and then perform search operations to check for the existence of nodes with values 5 and 10.
#4. Implementing a Class Hierarchy with Inheritance
This question delves into object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts in JavaScript, specifically class hierarchies and inheritance. Demonstrating proficiency in OOP showcases a developer’s ability to design modular and reusable code.
Task: Implement a class hierarchy in JavaScript with inheritance, following the given specifications:
- name : a string representing the name of the shape.
- area() : a method that calculates and returns the area of the shape (to be implemented by subclasses).
- width : a number representing the width of the rectangle.
- height : a number representing the height of the rectangle.
- Implement the area() method to calculate and return the area of the rectangle.
- radius : a number representing the radius of the circle.
- Implement the area() method to calculate and return the area of the circle.
Sample Code
class Shape {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
area() {
// To be implemented by subclasses
class Rectangle extends Shape {
constructor(name, width, height) {
super(name);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
return this.width * this.height;
class Circle extends Shape {
constructor(name, radius) {
this.radius = radius;
return Math.PI * Math.pow(this.radius, 2);
const rectangle = new Rectangle(“Rectangle”, 5, 3);
console.log(rectangle.area()); // Output: 15
const circle = new Circle(“Circle”, 4);
console.log(circle.area()); // Output: 50.26548245743669
The code snippet above demonstrates the implementation of a class hierarchy in JavaScript using inheritance.
The Shape class serves as the base class, providing a common name property for all shapes and a placeholder area() method that is meant to be implemented by subclasses.
The Rectangle class extends the Shape class using the extends keyword. It introduces additional properties width and height and overrides the area() method to calculate and return the area of a rectangle based on its width and height.
The Circle class also extends the Shape class and adds the radius property. The area() method is implemented to calculate and return the area of a circle based on its radius, using the formula π * r^2 .
In the usage example, we create instances of the Rectangle and Circle classes, passing the necessary parameters. We then call the area() method on each instance to calculate and display the area of the respective shape.
#5. Finding the Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
This question focuses on problem-solving skills and string manipulation. It challenges developers to find an efficient algorithm for finding the longest substring in a given string without repeating characters.
Task: Write a JavaScript function called findLongestSubstring that takes a string as input and returns the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Input Format: The input will be a string.
- The string may contain uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, symbols, or spaces.
- The string can have both single and multiple words.
Output Format: The output will be an integer representing the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Sample Input: abcabcbb
Sample Output: 3
function findLongestSubstring(str) {
let maxLength = 0;
let start = 0;
const charMap = {};
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
const currentChar = str[i];
if (charMap[currentChar] >= start) {
start = charMap[currentChar] + 1;
charMap[currentChar] = i;
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, i – start + 1);
return maxLength;
The findLongestSubstring function utilizes the sliding window technique to efficiently find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
The function initializes maxLength to 0, start to 0, and an empty charMap object to keep track of the most recent occurrence of each character in the string.
The function then iterates through the string using a for loop. For each character, it checks if the character has been previously encountered within the current substring (i.e., its index is greater than or equal to start ). If so, it updates the start index to the next position after the previous occurrence of the character.
The function updates the charMap with the current character’s index. It also calculates the length of the current substring by subtracting start from the current index and adding 1. The maximum length is updated using Math.max() to keep track of the longest substring found so far.
Finally, the function returns the maxLength , representing the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
#6. Sum of Two Numbers in an Array
This question challenges your problem-solving skills and array manipulation techniques. It requires finding two numbers in an array that add up to a given target sum.
Task: Write a JavaScript function called findSumOfTwo that takes an array of numbers and a target sum as input and returns an array containing the two numbers that add up to the target sum. If no such pair is found, return an empty array.
Input Format: The input will be an array of numbers and a target sum.
- The array may contain positive and negative integers.
- The array can be empty.
Output Format: The output will be an array containing the two numbers that add up to the target sum, or an empty array if no such pair is found.
const arr = [2, 4, 7, 11, 15];
const target = 9;
Sample Output: [2, 7]
function findSumOfTwo(arr, target) {
const numMap = {};
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
const num = arr[i];
const complement = target – num;
if (numMap[complement] !== undefined) {
return [complement, num];
numMap[num] = i;
return [];
The findSumOfTwo function utilizes a hash map to efficiently find the pair of numbers that add up to the target sum.
The function initializes an empty numMap object to store the numbers and their corresponding indices encountered during the iteration.
It then iterates through the array using a for loop. For each number num , it calculates the complement by subtracting num from the target .
The function checks if the complement exists as a key in the numMap object. If it does, it means that a pair of numbers that adds up to the target sum has been found. The function returns an array containing the complement and num .
If no such pair is found during the iteration, the function returns an empty array [] .
#7. Working with Asynchronous JavaScript and Callbacks
This question dives into asynchronous programming in JavaScript and challenges developers to work with callbacks to handle asynchronous operations.
Task: Write a JavaScript function called fetchData that simulates an asynchronous API call and takes a callback function as an argument. The callback function should be invoked with the retrieved data as its parameter.
Input Format: The input will be a callback function.
Output Format: The output will be the retrieved data passed to the callback function.
function handleData(data) {
console.log(“Received data:”, data);
fetchData(handleData);
Sample Output:
Received data: { name: ‘John’, age: 28, city: ‘New York’ }
function fetchData(callback) {
// Simulating an asynchronous API call with a setTimeout
setTimeout(() => {
const data = { name: ‘John’, age: 28, city: ‘New York’ };
callback(data);
}, 2000);
The fetchData function simulates an asynchronous API call using setTimeout . In this example, it waits for 2,000 milliseconds (2 seconds) before invoking the callback function with the retrieved data.
In the sample input, the handleData function is defined as the callback function. When fetchData is called, it waits for 2 seconds and then invokes the handleData function, passing the retrieved data as the parameter.
The handleData function in this case simply logs the received data to the console.
Resources to Improve JavaScript Knowledge
- HackerRank JavaScript Skills Certification
- HackerRank Interview
This article was written with the help of AI. Can you tell which parts?
Get started with HackerRank
Over 2,500 companies and 40% of developers worldwide use HackerRank to hire tech talent and sharpen their skills.
Recommended topics
- Coding Questions
- Front-End Development
- Interview Preparation

What Is Node.js? Navigating the New Wave of Web Development
- Knowledge Base
- Free Resume Templates
- Resume Builder
- Resume Examples
- Free Resume Review
As a versatile programming language, JavaScript has become an essential skill for developers looking to make their mark in the industry.
JavaScript is a powerhouse in the world of web development, powering the interactive and dynamic aspects of countless websites and applications.
In fact, 2022 marks JavaScript's 10th year in a row as the most commonly used programming language in the industry.
However, with its growing popularity comes fierce competition in the job market, making it crucial for aspiring JavaScript developers to excel in interviews and showcase their expertise.
Preparing well for JavaScript interviews not only demonstrates your technical prowess but also boosts your confidence during the hiring process.
It enables you to showcase your understanding of key concepts, problem-solving abilities, and coding proficiency.
In this guide, we will delve into the world of JavaScript interview questions, ranging from the basics to more advanced topics along with sample answers and tips to help you navigate these interviews with ease.
So, let’s get started!
- What are some common JavaScript interview questions and answers?
- What are the top JavaScript interview coding questions?
- What are some advanced javascript interview questions for experienced candidates?
- What are some tips to help you overcome JavaScript interview challenges?
Common JavaScript Interview Questions
Common JavaScript interview questions are a set of basic JavaScript interview questions that are asked by recruiters to assess a candidate's understanding of JavaScript concepts, syntax, and best practices.
By asking these questions, interviewers can assess the candidates’ suitability for the role and determine their level of proficiency in JavaScript programming.
Given below are some basic JavaScript interview questions with sample answers for your reference:
What is the difference between null and undefined in JavaScript?
Sample Answer: In JavaScript, null is a value that represents the intentional absence of an object value, while undefined is a variable that has been declared but has not been assigned a value. In other words, null is assigned by developers, whereas undefined is automatically assigned by JavaScript.
Also Read: What is a good resume sample of a full-stack JavaScript developer?
What is the significance of closures in JavaScript?
Sample Answer: Closures are an important concept in JavaScript that allow functions to access variables from their outer lexical environment, even after the outer function has finished executing. They help in creating private variables, implementing data encapsulation, and maintaining state in functional programming.
Also Read: How to make a Node.js resume?
Explain the concept of prototypal inheritance in JavaScript.
Sample Answer: Prototypal inheritance is a fundamental feature of JavaScript that allows objects to inherit properties and methods from other objects. Every object in JavaScript has a prototype property, and when a property or method is accessed on an object, JavaScript looks for it in the object itself and then in its prototype chain.
Also Read: What are some commonly asked React.js interview questions?
How does event delegation work in JavaScript?
Sample Answer: Event delegation is a technique in JavaScript where you attach an event listener to a parent element instead of individual child elements. The event then "bubbles up" from the child elements to the parent, allowing you to handle events efficiently and dynamically, especially for elements that are added or removed dynamically.
Also Read: How to make a front-end developer resume in 2023?
What are the differences between let, const, and var in JavaScript?
Sample Answer: Let and const are block-scoped variables introduced in ES6, while var is function-scoped. let allows reassigning values, while const is used for variables that are intended to remain constant. Additionally, var variables are hoisted to the top of their scope, while let and const variables are not.
Also Read: What are the top software developer interview questions in 2023?
JavaScript Coding Interview Questions
JavaScript coding interview questions are almost always part of the technical interviews for developers.
Interviewers ask these questions as it allows them to evaluate a candidate's technical proficiency and problem-solving skills in practicality.
These JavaScript coding questions also allow interviewers to gauge a candidate's logical thinking, algorithmic understanding, and ability to handle complex scenarios in JavaScript development.
Listed below are some commonly asked JavaScript coding interview questions:
Write a function to reverse a string in JavaScript.
Sample Answer: To reverse a string, you can split it into an array of characters, reverse the array, and then join the characters back into a string.

How can you determine if a given string is a palindrome using JavaScript?
Sample Answer: To check if a string is a palindrome, you can compare the string with its reversed version. If they are the same, the string is a palindrome.
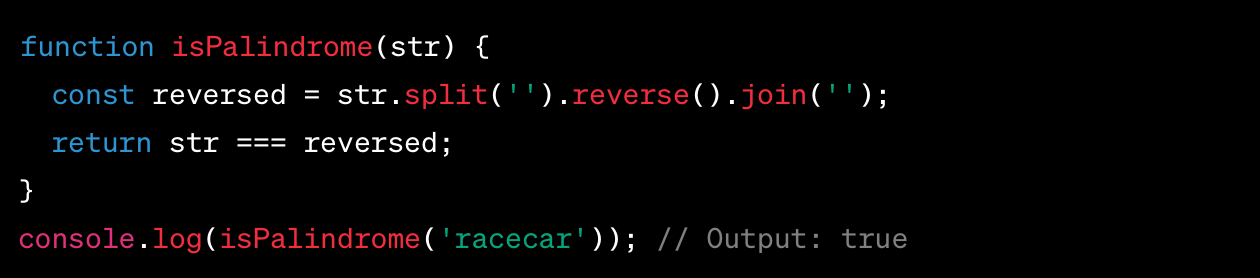
How can you find the largest number in an array using JavaScript?
Sample Answer: To find the largest number in an array, you can iterate through the array and keep track of the largest number encountered so far.

Write a function to remove duplicates from an array in JavaScript.
Sample Answer: To remove duplicates from an array, you can create a new array and only add elements to it if they haven't been added before.

How do you implement a function to check if a given number is prime in JavaScript?
Sample Answer: To check if a number is prime, you can iterate from 2 up to the square root of the number and check if it is divisible by any of the numbers in that range.
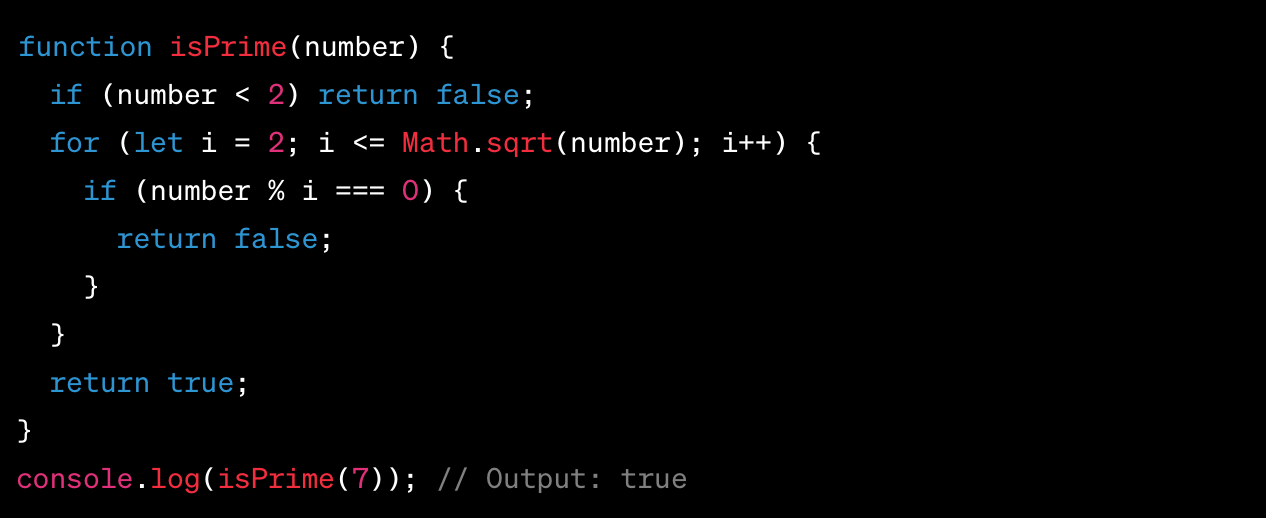
Also Read: What are some of the best coding classes that can boost your career in 2023?
Advanced JavaScript Interview Questions for Senior Developers
Advanced JavaScript interview questions are specific and in-depth questions that assess a candidate's deep understanding and proficiency in JavaScript concepts, best practices, and advanced programming techniques.
These questions go beyond the basics and test the candidate's ability to solve complex problems, work with advanced language features, and demonstrate expertise in JavaScript development.
Here are 5 advanced JavaScript interview questions for senior developers along with sample answers:
What is hoisting in JavaScript? Provide an example.
Sample Answer: Hoisting is a JavaScript behavior where variable and function declarations are moved to the top of their scope during the compilation phase.
For example: "console.log(x); // Output: undefined var x = 5;"
Explain the concept of closures in JavaScript with an example.
Sample Answer: Closures are functions that have access to variables from an outer (enclosing) function's scope, even after the outer function has returned.
For example: "function outer() { var x = 10; return function inner() { console.log(x); // Output: 10 }; } var innerFunc = outer(); innerFunc();"
Sample Answer: Null represents the intentional absence of any object value, while undefined represents an uninitialized variable or a missing property. In other words, null is assigned by developers, whereas undefined is assigned by JavaScript.
How does event delegation work in JavaScript? Explain with an example.
Sample Answer: Event delegation is a technique where you attach an event listener to a parent element instead of individual child elements. Events that occur on the child elements are handled by the parent element. For example: "document.querySelector('.parent').addEventListener('click', function(event) { if (event.target.classList.contains('child')) { console.log('Child element clicked!'); } });"
Sample Answer: Prototypal inheritance is a mechanism in JavaScript where objects can inherit properties and methods from other objects. Each object has an internal prototype property that links to another object, which serves as its prototype. Properties and methods can be accessed by traversing this prototype chain.
Also Read: What is the right way of listing programming projects on a resume?
Tips for Answering JavaScript Interview Questions in the Best Way
Answering JavaScript interview questions in a good way is crucial as it provides an opportunity to showcase your expertise and leave a positive impression on the interviewer to increase your chances of securing the job.
Besides, you only have one chance at interviews. Therefore, you must prepare well in advance.
Given below are some tips for answering JavaScript interview questions in the best way:
Understand the question: Take the time to fully comprehend the question before diving into the answer. Clarify any doubts or ambiguities with the interviewer to ensure you're addressing the specific requirement.
Structure your response: Organize your answer clearly and logically. Break down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps, and provide a concise introduction, a well-structured solution, and a brief conclusion.
Show your thought process: Simply answering JavaScript coding interview questions with codes or formulas is not enough. You must articulate your thinking and reasoning behind your approach. Explain the different options you considered and the factors influencing your decision-making to demonstrate your problem-solving skills and analytical thinking.
Provide examples and real-world scenarios: Make sure to support your answers with relevant examples or practical applications. Illustrate how you have applied JavaScript concepts in previous projects or work experiences to showcase your hands-on expertise.
Be aware of best practices: Demonstrate your knowledge of JavaScript best practices, such as writing clean and efficient code, using appropriate naming conventions, and following coding standards. Emphasize the importance of readability, maintainability, and scalability in your answers.
Also Read: What are some excellent interview tips that will help you land your dream job in 2023?
FAQs on JavaScript Interview Questions
How to prepare for javascript interview questions.
To prepare for JavaScript interview questions, start by reviewing core JavaScript concepts, such as data types, functions, objects, and control flow. Practice coding exercises and solve problems on platforms like LeetCode or HackerRank to sharpen your problem-solving skills. Additionally, familiarize yourself with common JavaScript frameworks, libraries, and industry best practices to demonstrate a well-rounded understanding of JavaScript development.
What is ‘function’ in JavaScript interview questions?
Function in JavaScript interview questions refers to inquiries that assess a candidate's knowledge and understanding of JavaScript functions, including their syntax, purpose, usage, and advanced concepts like higher-order functions and closures.
What do you need to know for a JavaScript interview?
For a JavaScript interview, it is important to have a strong understanding of core JavaScript concepts such as variables, data types, functions, objects, arrays, and control flow. Additionally, knowledge of JavaScript frameworks, libraries, DOM manipulation, asynchronous programming, and common coding patterns is beneficial.
What are HTML CSS JavaScript interview questions?
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript interview questions are inquiries that assess a candidate's knowledge and proficiency in web development, covering topics such as HTML tags and attributes, CSS styling and layout techniques, JavaScript syntax and programming concepts, and their application in building interactive and responsive web pages.
Wish to prepare for your upcoming JavaScript interview questions with professional help? Use Hiration’s ChatGPT-powered Interview Preparation Tool with 24x7 chat support.

Share this blog
Subscribe to Free Resume Writing Blog by Hiration
Get the latest posts delivered right to your inbox
Stay up to date! Get all the latest & greatest posts delivered straight to your inbox
Is Your Resume ATS Friendly To Get Shortlisted?
Upload your resume for a free expert review.

10 Common JavaScript Interview Questions (and Answers)
Ravi Sharma
Bits and Pieces
1. Find the frequency of elements in array
Method 1 : using reduce method of array, method 2 : using an object, 2. group items on the basis of age of given array of object, 3. program to c heck a string with balanced brackets., 4. find the pairs of array element for which sum is equal to given target value ( two sum problem), 5. find the missing number from unsorted array with o(n) complexity.
- Create a variable sum = 1 which will store the missing number and a counter variable c = 2 .
- Traverse the array from start to end.
- Update the value of sum as sum = sum — array[i] + c and update c as c++ .
- Print the missing number as a sum.
6. Find the missing number from sorted array with O(n) complexity
7. find the nth largest element in a sorted array, 8. remove duplicates from an array and return unique values in o(n) complexity., 9. print all duplicate elements of an array, 10. collect books from array of objects and return collection of books as an array.
I hope you have found this quick list of common JavaScript interview questions and answers useful. Thank you for reading!
Build Apps with reusable components, just like Lego
Bit ’s open-source tool helps 250,000+ devs to build apps with components.
Turn any UI, feature, or page into a reusable component — and share it across your applications. It’s easier to collaborate and build faster.
→ Learn more
Split apps into components to make app development easier, and enjoy the best experience for the workflows you want:
→ Micro-Frontends
→ design system, → code-sharing and reuse, learn more:, how we build micro frontends, building micro-frontends to speed up and scale our web development process..
blog.bitsrc.io
How we Build a Component Design System
Building a design system with components to standardize and scale our ui development process., how to reuse react components across your projects, finally, you completed the task of creating a fantastic input field for the form in your app. you are happy with the…, 5 ways to build a react monorepo, build a production-grade react monorepo: from fast builds to code-sharing and dependencies., how to create a composable react app with bit, in this guide, you’ll learn how to build and deploy a full-blown composable react application with bit. building a….

Written by Ravi Sharma
JavaScript Developer | https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC9MmyicGIveu0AId8OFAOmQ
More from Ravi Sharma and Bits and Pieces

Top 30 JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers for 2024
Prepare for your next javascript interview with confidence.
Ruvani Jayaweera
Implementing the API Gateway Pattern in a Microservices Based Application with Node.js
Build your own api gateway using node.js in under 5 minutes.

Ashan Fernando
Top 10 Tools Every React Developer Needs in 2024
Enhancing efficiency and creativity in the react ecosystem using these highly effective tools.

Stackademic
Top 40 ReactJS Interview Questions and Answers for 2024
Reactjs has become a cornerstone of modern web development, with its component-based architecture and efficient rendering making it a go-to…, recommended from medium.

53 JavaScript Frontend Interview Questions
Introduction.
General Coding Knowledge
Stories to Help You Grow as a Software Developer
Coding & Development
Syed Khizaruddin
Frontend Weekly
Javascript Interview Questions with Answers
100 questions with answers..

Francesco Saviano
Mastering JavaScript Arrays: 10 Progressive Exercises

Top 20 JavaScript Interview Questions for Mastering Data Structures
Data structures are the foundation of efficient algorithms and play an important role in technical assessments. the following are the top….

Difference between subject and behaviour subject
Source: difference between subject and behaviour subject.
Text to speech
Download Interview guide PDF
Star interview questions, download pdf.
Are you having difficulty answering interview questions in a concise manner? When interviewing, how can you share your accomplishments without appearing boastful? How can you demonstrate to the interviewer that you are the best candidate? As we all know, job interview questions can be stressful at times, but some are more difficult to answer than others. When ranked by difficulty level, behavioral questions would probably rank first for most people.
If this is also the case for you, you will be delighted with the STAR method. Situation, Task, Action, and Result are the four pillars of the STAR acronym. Preparing for behavioral interview questions and situational interview questions can be accomplished using the STAR interview method. By answering interview questions this way, you will be able to provide concrete examples of your experience and skills for the job without sounding boastful. The following STAR method examples will assist you in preparing clear and concise responses.

Throughout this article, we will take a look at what is the STAR method , as well as 30+ of the most common STAR interview questions and answers that can be encountered during behavioral interviews.
STAR Method Interview Questions: Tips and Sample Answers
- Questions about the STAR Method
- Question about Problem-Solving
Question about Teamwork
Questions about self-management skills, questions about creativity thinking skills, questions about time-management skills, questions about communication skills, how to answer star interview questions, questions about star method, 1. what does star stand for explain it..
A STAR is an acronym for Situation, Task, Action, and Result.
- Situation: Give details about the situation and your example.
- Task: Outline your responsibilities in that situation.
- Action: Describe how you resolved the problem.
- Result: Explain the outcome of the actions you took.
A STAR interview method (Situation, Task, Action, and Result) offers a straightforward format for structuring your responses. Using this technique of interviewing, you will have the ability to tell your story in a simple, straightforward manner by outlining the Situation, Task, Action, and Result of the situation. It is particularly helpful to use this strategy when answering a competency-based question in a job interview. By keeping these four components in mind, you are much more likely to provide the interviewer with a concise, compelling narrative of what you have accomplished.
Sample Answer:
During my time at my last employer, I was eager to advance into the position of a senior software engineer as soon as possible, so that I would have a better grasp of the technology. ( Situation ) Having been there for over two years, I set a target of completing my goal in three years. So I only had a year to achieve it. ( Task) During this period, I worked diligently to enhance my skills and knowledge, as well as take on more challenging projects. Even though I had no prior experience with such projects, I tried to deliver superior quality. ( Action ) My supervisor finally put me at ease and I got promoted within period of six months of setting that goal. ( Result )
2. Can you tell me about one of your proudest professional accomplishments?
This question allows employers to determine whether you have the skills and work ethics they are looking for and if your attitude fits into their culture. Choosing your greatest achievement will demonstrate what is important to you, and how you achieved it will reveal your work style. You will be able to convey both your hard and soft skills in answering this question.
- Take pride in your work, but don't flaunt your accomplishments. When answering, be sure to provide examples and explain your thought process.
- Your reply to the interview should be pragmatic and reflect your approach to success and hard work, and make sure you sound down to earth.
- It is recommended that you use the STAR method to structure your answer for clarity.
During my last employment, our technology development team had to let go of one of our colleagues due to relocation. (Situation) His role was to lead the iOS development of the app. No one else on the team had experience developing apps for iOS. Since I had developed iOS apps in the past, I volunteered to take the lead on the app development process. (Task) Together with the other team members, I worked on creating and troubleshooting the new application. (Action) It took me 40 days to complete the development ahead of schedule. As of now, it has over 220 positive reviews in the iTunes Store, offering the company another revenue stream. (Result)
Question about Problem Solving
1. when have you been faced with a challenging situation what solution did you come up with.
Interviewers ask this question to find out how you handle challenges in the workplace. Take a moment to think about the last time you faced a challenge and overcame it. You may also discuss an experience that has helped you learn more about your craft and improve your performance.
Sample Answer
I was working on a project with my team, and one of our team members decided to quit the team in the middle of the project due to personal reasons. ( Situation ) I know that in any case, I had to finish the project to keep the organization's reputation intact. ( Task ) However, I went to the other member and we agreed to divide the remaining work equally. We went above and beyond to complete the tasks until we reached our goal. ( Action ) Despite the tight deadline, we were able to complete the project on time. ( Result )
2. When was the last time a client asked you for the impossible? What was your approach to explaining this to them?
As part of the interview process, the interviewer may ask how you deal with difficult clients so they can gain a deeper understanding of your client service skills. With this question, you will be evaluated specifically on your problem-solving skills, interpersonal skills, and ability to deal with stress and diffuse tense situations.
A client asked for a complex feature to be delivered within an unrealistic timeframe. ( Situation ) I had to explain the challenges and limitations of the project and suggest a more feasible approach. ( Task ) I made sure to listen carefully to the client's requirements and concerns, explained to them the technical challenges involved, and highlighted the risks of rushing the development process. ( Action ) The client appreciated my transparent communication, agreed on a more realistic timeline, and the project was completed successfully within the new timeline. ( Result )
3. Have you ever had to correct a mistake made by a superior? What was your approach to that situation?
The interviewer wants to know how you would handle a potentially uncomfortable situation with a superior. Explain your thought process and the action you would take in response to this question. Ensure that your answer demonstrates your professional approach to the potential employer.
Sample Answer
I identified a mistake made by my superior in a software project. ( Situation ) I took the task upon myself to correct the mistake and communicate the issue to my superior. ( Task ) Firstly, I reviewed the code and identified the issue in detail. Then, I discussed the mistake with my superior in a professional and respectful manner, providing evidence and suggesting possible solutions. ( Action ) My superior acknowledged the mistake and appreciated my input. Together, we corrected the issue and implemented necessary changes to prevent similar mistakes in the future. The project was completed successfully with improved quality. ( Result )
- Software Dev
- Data Science
4. How do you cope with sudden workplace changes?
The purpose of asking this question is to learn more about how you cope in a fast-paced, ever-changing work environment. Interviewers may want to know that you are confident and poised as you face these challenges. They may also be interested in hearing how you have used those skills in a previous role.
As a software developer, I have faced sudden workplace changes in the past multiple times. ( Situation ) I cope with sudden workplace changes by following a few key strategies. ( Task ) Firstly, I assess the impact of the change and the tasks that need to be completed. Next, I communicate with my team members and seek their opinions and suggestions to better adapt to the changes. I also stay organized by breaking down my tasks into smaller manageable units and prioritizing them accordingly. Finally, I remain flexible and adaptable to adjust to the new situation. ( Action ) By following these strategies, I have been able to cope effectively with sudden workplace changes and ensure that my work is completed efficiently and effectively. ( Result )
1. Has there ever been a conflict between you and a co-worker? What solutions did you come up with?
When handling such behavioral questions, it is essential to be careful. Collaboration and the ability to resolve conflict can increase productivity and foster a more pleasant working environment. It is therefore necessary for you to clearly describe the conflict and how you resolved it in your answer. It is important for you to be respectful and not bad-mouth the co-worker no matter how enraging the situation was. The outcome should be clearly stated.
Once, a team member thought my method of tackling a project was incorrect. The way he came across sounded harsh to me. ( Situation ) Having to cooperate on this project was going to be a challenge, and the person wasn't too thrilled about the idea, to be honest. While explaining something to them, they would often interrupt me. ( Task ) I chose not to get mad at them but instead politely asked them if they had any other suggestions that might work. They shared their thoughts, and we discussed them as a team. They gave us a better idea and we decided to go with it as a team. ( Action ) As a result, we recorded better results. We also sorted out our misunderstanding in the process and we became good friends. ( Result )
2. When was the last time you worked with another department to complete a project?
Often interviewers ask these questions when cross-functional teamwork is a critical component of their work environment. Among the teamwork skills you want to remember are active listening, communication, conflict management, developing consensus, encouraging others to pull their weight, and so on.
At my previous company, we had the C-suite of Marketing and Operations, Creative Services, the Content and Communications department, and Consumer Insights. ( Situation ) We had to work with them to understand the business requirements better for developing new software applications. Collaboration across departments was an integral part of our work all of the time. ( Task ) We came up with a plan to meet on a weekly basis to discuss bigger projects and then collaborate throughout the rest of the week based on our needs. ( Action ) In all, the set-up proved to be excellent and helped to ensure the smooth progress of the project at every stage. ( Result )
3. Do you have any strategies for dealing with coworkers who are too incompetent or unwilling to cooperate?
Many employers ask about your experience handling difficult coworkers in order to assess how well you handle them. It is important to be respectful while answering this. You may be asked if you are a team player who can work well with others or if you enjoy any type of interpersonal relationship. It is common for organizations to look for people who can cope with difficult situations and are able to remain calm in the midst of them.
Sample Answer:
As a client support specialist, I and my coworker were responsible for contacting clients to verify login information. ( Situation ) Unfortunately, we miscommunicated how the client list should be divided up between the two of us. Originally, I thought I would get in touch with clients with names A through K; and my colleague hoped to get in touch with clients with names L through Z. We were not on the same page regarding this and it caused confusion amongst us. It also caused confusion and frustration for our clients as we contacted them twice. ( Task ) As we both expressed our frustrations with one another, we both admitted that we misheard one another. For future projects like this, I suggested using a color-coded spreadsheet that represented who would work with what clients. ( Action ) The new system has been working well for us since this incident, and we have not had any similar issues. ( Result )
1. Do you ever have to make unpopular decisions? What did you do?
The downside of managing or leading involves making decisions that not everyone agrees with. It is important to tell the interviewer that although you made a decision to press forward, you were very careful to communicate with the other employees and even increase their support.
When I was working at my previous job, I was assigned to supervise a small team of coworkers for a huge project. (Situation)
Since the project was huge, it could significantly impact the company's reputation, and it needed to be completed quickly. (Task)
Due to time constraints, we were unable to complete the project during the week, so we decided to work on Saturdays to finish it by guaranteeing incentives to my team for their hard work. As soon as I broke the news of overtime work to my coworkers, they complained and developed resentment against me. But I assured them of proper incentives and made them understand why it was important to gain that deal. (Action)
As a result, my team was convinced and they onboarded to complete the project and we even successfully managed to acquire new clients. Additionally, my team was rewarded for their work with incentives and due recognition. At the end, everyone was happy. (Result)
2. Can you tell me about a time when you disagreed with your manager and how you resolved the matter?
Basically, this particular question is designed to test the level of communication skills you have. Interviewers are looking for several qualities in your response, including emotional maturity, validity, loyalty, and responsibility.
There was once a disagreement between me and my manager over the best way to assist an intern. (Situation)
To avoid confronting him in front of everyone, I spoke off the floor with him instead. I explained my concerns about his behavior openly and honestly. (Task)
During the course of the conversation, it became apparent that there had been a simple misunderstanding. (Action)
A disagreement with my colleagues taught me the importance of communication to prevent bigger problems. (Result)
3. Have you ever persuaded someone to do something?
Interviewers use this question to assess your ability to persuade. You will be asked to describe specific situations and actions in which you were able to influence others.
During my previous job as a software developer, I noticed that one of my colleagues was not following the best practices for code documentation. (Situation)
It was important to me that we maintain consistency in our team's code quality and documentation, so I needed to persuade my colleague to change his approach. (Task)
I approached my colleague and explained my concerns about the lack of documentation in his code. I also highlighted the benefits of maintaining high-quality code and how it could save time in the long run. To persuade him, I shared some best practices, provided examples, and offered to assist him with any questions or concerns he may have had. (Action)
My colleague was initially hesitant to change his approach, but after listening to my suggestions and seeing the benefits, he agreed to improve the documentation in his code. As a result, the code quality improved, and we were able to collaborate more efficiently on future projects. (Result)
4. Do you have experience motivating others? What steps did you take to achieve this?
The purpose of this question is to determine whether you are capable of working in a team environment and motivating your coworkers. Being able to influence others around you will help you fit in well with any team. Do not forget to mention the result of your motivation.
During my last position, a member of my team was never fully committed to the project thereby impacting their deliverables. (Situation)
It took conscious effort on my part to visit their desk every morning in order to understand what they were going through and motivate them. (Task)
They opened up to me about their problems and how they were unable to focus due to lack of confidence. I motivated them consistently by highlighting how their skills were crucial for the project we were working on and provided regular feedback on their progress. (Action)
As time went on, they began to express their opinions and suggest original, creative ideas during staff meetings. They felt valued and recognized which boosted their self-confidence and at the end, things worked well for our team too. (Result)
1. When was the last time you had to be highly strategic to achieve a goal?
In asking this question, the interviewer is interested in learning how you deal with priorities as well as the ability to work under pressure. A key work competency for individual contributors and managers alike is the ability to prioritize confidently in the face of the incapacity to complete all tasks.
Since my job involved a number of competing priorities, it was often very challenging to determine what was most critical and urgent in order to carry out my duties. ( Situation ) My manager and I worked out a scale for judging the importance and urgency of a task so that it's clear what should take the highest priority from the start. ( Task ) Priority was given to things that are both important and urgent (IU). Next was important and not urgent (INU), followed by urgent and not important (UNI), and lastly not important and not urgent (NINU). I received requests from my manager labelled as IU, INU, UNI, and NINU when the rating system was in use. ( Action ) Due to this prioritization rating system, my overall productivity increased considerably over the past year. ( Result )
2. Tell us about a time you failed. Have you learned anything from this experience?
If the interviewer specifically asks for a work-related example, try to recall a long-gone incident that is related to your job role. It is best to choose a story in which something significant didn't go according to plan as a result of your actions (or lack of actions)—not something more trivial.
Early in my career as a software developer, I was tasked with developing a new feature for a web application. ( Situation ) I was responsible for developing the feature within a specific timeline and ensuring that it worked seamlessly with the existing application. ( Task ) I approached the task with enthusiasm and started coding immediately. However, I realized after a few days that my code was not working correctly, and I was unable to identify the source of the issue. Realizing my mistake, I reached out to my supervisor and explained the problem. He was able to help me debug the code and identify the issue. ( Action ) Unfortunately, because of the time it took to debug the code, we missed the deadline for the feature's launch. I learned that I should have approached the task more systematically, taking more time to plan and test my code before starting to code. ( Result )
3. Can you recall your first job? How did you learn the ropes and adapt to your new environment?
By asking this question, the interviewers want to know how you work with individuals who have different personalities, and how you motivate individuals to become personally invested in the job or project beyond just a paycheck. Their interest is in seeing how you cope with job-related challenges and learning from them.
My first job as a software developer was at a small software development company. I was fresh out of college and eager to apply my skills in a professional setting. (Situation) My task was to develop a new feature for an existing web application, which required me to learn the company's coding standards and work processes. (Task) To learn the ropes, I spent the first few days observing and asking questions about the company's coding practices and processes. I also familiarized myself with the codebase by reading the existing code. Once I had a good understanding of the company's work processes and coding standards, I started working on the new feature. I made sure to communicate regularly with my supervisor and colleagues, asking for feedback on my code and how I could improve it. (Action) Through my hard work and dedication, I was able to complete the new feature on time and to the satisfaction of my supervisor and colleagues. (Result)
1. When was the last time you took charge and demonstrated initiative to manage a situation?
Interviewers ask this question to determine if you are a self-starter with a strong desire to innovate. Whether you put your best effort into something out of your own desire, not out of obligation.
Recently, I was working on a project that had a tight deadline. As we approached the deadline, we realized that there were some missing requirements that had not been addressed. ( Situation ) My task was to take charge of the situation and ensure that we could meet the deadline by addressing these missing requirements. ( Task ) I took the initiative to convene a meeting with the project team and stakeholders to discuss the missing requirements. During the meeting, I asked questions and took notes to ensure that everyone was on the same page. After the meeting, I identified the tasks that needed to be completed and assigned them to the team members. I made sure to provide regular updates to the stakeholders, keeping them informed of our progress. ( Action ) Through my proactive approach, we were able to address the missing requirements and meet the project deadline. The stakeholders were pleased with our work and appreciated our efforts to keep them informed. ( Result )
2. Tell us about a situation in which you used logic or data to make a recommendation.
Employers usually ask this question so they can assess your critical thinking skills, including your ability to handle unexpected obstacles. The hiring manager often values employees who are able to apply logic to determine the most appropriate course of action in various situations. You can demonstrate your problem-solving skills by providing concrete examples of how you could fit into an organization.
Sample Answer
During my tenure in my previous organization, I analyzed datasets daily to research competitor strategies. ( Situation ) The monthly sales of significant competitors increased by 5% during a high-traffic month, which deviated substantially from our forecasts at the time. ( Task ) With updated market research and key historical data, I determined our competitor analytics model would produce more accurate forecasts going forward. ( Action ) With multiple tests of each adjustment, I was able to increase our forecast accuracy by 20%. ( Result )
3. When was the last time you set a goal and achieved it?
Specifically, the interviewer is trying to get a sense of your ambitions and initiative by asking this question. It is likely that the hiring manager is attempting to determine if you have the ability to achieve the goals you have set for yourself. It might be a good idea to emphasize your planning skills in an effort to show what you are capable of and distinguish yourself from other candidates.
As a software developer, I wanted to improve my skills in a specific programming language that I had only a basic knowledge of. (Situation) My task was to set a goal to improve my skills in this programming language and then achieve that goal through dedicated practice. (Task) To achieve my goal, I started by setting a specific and measurable target for my improvement. I then identified online resources and practice exercises that would help me achieve my goal. I dedicated a specific amount of time each day to practising my skills in the programming language, and I tracked my progress regularly to stay motivated. (Action) Through my dedication and consistent effort, I was able to achieve my goal and improve my skills in the programming language significantly. I felt a great sense of accomplishment and was proud of myself for achieving this goal. (Result)
4. Describe a time when you failed to meet a client's expectations. What steps did you take to deal with the situation?
Candidates are often challenged with this question since it forces them to talk about failure. Interviewers aren't just interested in how you failed; they are also interested in why you failed. Most of the time, the answer lies in the circumstances and the blame game that follows. Are you accountable for not meeting a deadline? Or is it all the fault of others? It is important to answer respectfully and not to be a part of the blame game.
At my current job, I have both a dotted line manager and a direct line manager to work with. As a result of an urgent firefighting request made by my dotted line manager, I had to interrupt my primary project in order to meet that request. ( Situation ) Although my direct line manager approved it, it put me behind my primary delivery deadline. I eventually resolved the firefighting issue and completed my primary project despite having been delayed for over a week, leading to frustration with this client. ( Task ) Upon discussing this with my direct line manager, we agreed to include contingency buffers in future projects to enable me to divert to the dotted line department if necessary. ( Action ) Also, I talked with my dotted line manager about the possibility of training someone else so that I wouldn't have to handle these kinds of situations on my own. ( Result )
1. Describe a situation in which you exceeded your duties for a job or task.
In asking this question, interviewers want to know that you will go the extra mile when possible, specifically in ways that will benefit them and their team. Further, this question shows interviewers whether or not you're motivated and if you simply settle for "good enough" rather than striving for greatness.
Having been promoted to a senior software developer in my last role, I was in charge of leading a major client's project. The client requested a particularly unique feature that would normally take a month to complete but I had to finish it in three weeks. ( Situation ) Since it was my first project post-promotion, I agreed to complete this. Afterwards, I realized that it would take me a while to finish it and make it of high quality. ( Task) Right away, I contacted the client and requested an extension by providing a detailed presentation on why it would take longer., which they generously granted. With my extensive research and regular follow-ups, I was able to work with the team and make sure the wireframes were created for the website/app and finalized. ( Action ) The project was completed and delivered before the extended deadline. However, I learned to manage my time more efficiently and to never overpromise on something that I am unable to deliver. ( Result )
2. Is there any time you have been under a lot of pressure at work? What did you do in response?
Interviewers use this question to determine how you cope with various stressful workplace situations. This means you should emphasize your skills and use real-life examples to demonstrate your competence.
Sample Answer-
During my previous job as a software developer, we had a tight deadline for a project that had to be delivered within a month. ( Situation ) As a part of the team, I was responsible for developing a complex module that required a lot of coding and debugging. ( Task ) To deal with the pressure, I broke down the project into smaller achievable tasks and created a schedule with daily and weekly goals. I worked on the most important and time-sensitive tasks first and then delegated some of the less critical tasks to junior developers in the team, which helped to reduce my workload. I also communicated regularly with my team leader to keep him informed about my progress and any potential issues that may arise. ( Action ) By managing my time effectively, I was able to complete the module on time and deliver it to the team leader for review. The team leader was impressed with my ability to work well under pressure, and the module received positive feedback from both the team leader and the client. ( Result )
3. Employees are sometimes overburdened by their employers. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by work? What did you do in this situation?
An interviewer uses this question to determine if you are capable of handling heavy workloads and high volumes. Your well-prepared answer would demonstrate your maturity and ability to work beyond your contracted hours when necessary. A prospective employer wants to know how you handle tough situations.
The latest version of our product, which was released last year, was incredibly buggy. ( Situation ) As a member of the front-line customer support team, the first two weeks after the release probably were one of the most challenging times for me. The line was always crowded with people waiting. In the course of the two weeks, you ended one call just to begin another, and I did not stop at all during that time. ( Task ) However, I knew that it was a temporary situation, that the engineering team was working hard to fix the bugs, and that a critical update was on its way. So, I patiently took part in supporting the clients along with coordinating with the engineering team regarding the release updates. ( Action ) The release with bug fixes happened exactly after 2 weeks and the customer support team survived the tough period, and things returned to normal afterwards. ( Result )
1. Steps to prepare your STAR interview response
- Make sure your response is relevant to the job description. Consider what skills and qualities are most important for the role and how they relate to your position, then choose stories that demonstrate these qualities.
- Pick a few examples that are both strong and versatile. Prepare a few stories you can tweak and adapt for different questions based on your experiences.
- To ensure your answer feels natural and comfortable, practice it in a mirror or mock interview before the interview.
- Embrace the opportunity to show how your contribution made a difference. Include the EXACT results of your actions, use numbers and data to support your claim, and mention what you learned from the experience.
To put it simply, behavioral interview questions are based on how you would likely behave if you were faced with a certain situation in the future. A behavioral interview, along with a coding test and a technical interview, will be used by the hiring manager to determine if your past performance can assist you in putting your best foot forward in your new role, as well as determining if you have what it takes to succeed there.
A concise way of answering behavioral questions is through the STAR method. In short, the STAR method stands for Situation, Task, Action, Result, and it helps you create a story that's easy to follow and has a clear conflict and resolution. In sharing your stories, make sure you specify a situation, task, action, and result, and emphasize skills and abilities most relevant to the job. You may be asked to share non-work-related examples, so think about challenges you have overcome personally.
- Privacy Policy

- Practice Questions
- Programming
- System Design
- Fast Track Courses
- Online Interviewbit Compilers
- Online C Compiler
- Online C++ Compiler
- Online Java Compiler
- Online Javascript Compiler
- Online Python Compiler
- Interview Preparation
- Java Interview Questions
- Sql Interview Questions
- Python Interview Questions
- Javascript Interview Questions
- Angular Interview Questions
- Networking Interview Questions
- Selenium Interview Questions
- Data Structure Interview Questions
- Data Science Interview Questions
- System Design Interview Questions
- Hr Interview Questions
- Html Interview Questions
- C Interview Questions
- Amazon Interview Questions
- Facebook Interview Questions
- Google Interview Questions
- Tcs Interview Questions
- Accenture Interview Questions
- Infosys Interview Questions
- Capgemini Interview Questions
- Wipro Interview Questions
- Cognizant Interview Questions
- Deloitte Interview Questions
- Zoho Interview Questions
- Hcl Interview Questions
- Highest Paying Jobs In India
- Exciting C Projects Ideas With Source Code
- Top Java 8 Features
- Angular Vs React
- 10 Best Data Structures And Algorithms Books
- Best Full Stack Developer Courses
- Best Data Science Courses
- Python Commands List
- Data Scientist Salary
- Maximum Subarray Sum Kadane’s Algorithm
- Python Cheat Sheet
- C++ Cheat Sheet
- Javascript Cheat Sheet
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Java Cheat Sheet
- Data Structure Mcq
- C Programming Mcq
- Javascript Mcq
1 Million +

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
FullStack.Cafe is a biggest hand-picked collection of top Full-Stack, Coding, Data Structures & System Design Interview Questions to land 6-figure job offer in no time. Check 25+ JavaScript Coding Interview Questions (SOLVED with CODE) and Land Your Next Six-Figure Job Offer! 100% Tech Interview Success!
Review these common JavaScript interview questions and answers and practice your coding fundamentals with this guide to ace your next interview. ... They are great resources for developing your coding expertise, problem-solving skills, and algorithmic thinking, all of which are necessary for acing technical interviews. ...
Interview Question 1: How to Get Passengers' Names. Let's get the passengers' names as requested. The first solution is through a 'for loop' method. So we first need to use an empty array to push the passengers' names right inside it at the end of the loop.
Toptal Connects the Top 3% of Freelance Talent All Over The World. Comprehensive, community-driven list of essential JavaScript interview questions. Whether you're a candidate or interviewer, these interview questions will help prepare you for your next JavaScript interview ahead of time.
JavaScript is also flexible in how it handles data. Unlike some other programming languages, you don't need to specify what kind of data a variable will hold. For example, you could create a variable called "x" and set it equal to a number, a string of text, or even an entire object. #2.
The silly way to understand the " this" keyword is, whenever the function is invoked, check the object before the dot. The value of this . keyword will always be the object before the dot. If there is no object before the dot-like in example1, the value of this keyword will be the global object. Example 4:
Advanced JavaScript Concepts to Know - Async/defer, Polyfills, Debouncing, and Throttling. Storage in JavaScript. Caveat: The focus here will largely be to cover concepts relevant to the interview and not to create a comprehensive booklet for learning the language. Treat this more like a cheatsheet.
Interview Questions for Mid-level JavaScript Developers. When designing interview questions for mid-level JavaScript developers, you should prepare challenges to test the understanding of advanced JavaScript concepts and problem-solving skills. Some areas that should be considered for evaluation include functional programming, asynchronous ...
5. What is the use of the isNaN function? The number isNan function determines whether the passed value is NaN (Not a number) and is of the type "Number". In JavaScript, the value NaN is considered a type of number. It returns true if the argument is not a number, else it returns false. 6.
Advanced JavaScript Interview Questions. The following set of advanced JavaScript interview questions should test the candidate's advanced knowledge of JavaScript and some of its more advanced concepts and features. 1. What is a closure in JavaScript? Closures in JavaScript lets you associate data with a function that operates on that data.
2. Implement the Fibonacci number calculator in JavaScript. Take a number as input from the user, and then print out the Fibonacci value for that number. [ The Fibonacci sequence is F0 = 0, F1 = 1, Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2 ] There are many ways to do this. You can use a loop to calculate the sequence, or use recursion.
Boost your coding interview skills and confidence by practicing real interview questions with LeetCode. Our platform offers a range of essential problems for practice, as well as the latest questions being asked by top-tier companies.
The basic JavaScript coding interview questions are: 1. Write a JavaScript function to calculate the sum of two numbers. When managers ask this question, they are looking for the candidate's basic understanding of JavaScript. They assess their understanding of basic syntax along with problem-solving skills.
Actions. Projects. Security. Insights. sudheerj/javascript-interview-questions. This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository. List of 1000 JavaScript Interview Questions. Contribute to sudheerj/javascript-interview-questions development by creating an account on GitHub.
About this course. You'll need to pass a technical interview if you want to be hired for a technical role. Don't worry — these interviews are pretty predictable, and the same kinds of problems appear again and again. Even if you don't have a technical interview scheduled just yet, practicing these common problems will help you grow as a ...
Javascript FizzBuzz Interview Question [Modulo Operator] Q: Write code to print all the numbers between 1 and 100. But in place of multiples of 3, print "Fizz" and for multiples of 5 print "Buzz.". When a number is a multiple of both, print, "FizzBuzz." (Solution from CodeBurst .) for (var i=1; i < 101; i++) {.
Add this topic to your repo. To associate your repository with the js-interview-questions topic, visit your repo's landing page and select "manage topics." GitHub is where people build software. More than 100 million people use GitHub to discover, fork, and contribute to over 420 million projects.
When it comes to JavaScript interviews, they serve as a critical evaluation of a candidate's JavaScript proficiency, problem-solving skills, and understanding of key concepts. A JavaScript interview can take various forms, depending on the company and position. However, it typically involves one or more of the following assessment formats:
JavaScript Coding Interview Questions. JavaScript coding interview questions are almost always part of the technical interviews for developers. Interviewers ask these questions as it allows them to evaluate a candidate's technical proficiency and problem-solving skills in practicality.
7. Find the nth largest element in a sorted array. 8. Remove duplicates from an array and return unique values in O (n) complexity. 9. Print all duplicate elements of an array. 10. Collect books from array of objects and return collection of books as an array. I hope you have found this quick list of common JavaScript interview questions and ...
Q-1: Write a function that would allow you to do this. You can create a closure to keep the value of a even after the inner function is returned. The inner function that is being returned is ...
This question tests your understanding of JavaScript's equality operators. Explain that "==" checks for value equality, allowing type coercion, while "===" checks for both value and type ...
Problem-Solving using javascript in-built methods — Part 1. Problem 1: Reverse a string. Input: javascript is awesome. Output: "awesome is javascript"
Here's how you can handle complex problem-solving questions during an interview. Powered by AI and the LinkedIn community. 1. Understand Issue. Be the first to add your personal experience. 2 ...
Throughout this article, we will take a look at what is the STAR method, as well as 30+ of the most common STAR interview questions and answers that can be encountered during behavioral interviews. STAR Method Interview Questions: Tips and Sample Answers. Questions about the STAR Method; Question about Problem-Solving; Question about Teamwork