Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants.
Biology, Ecology, Health, Earth Science, Geography

Loading ...
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment . These harmful materials are called pollutants . Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic ash . They can also be created by human activity, such as trash or runoff produced by factories. Pollutants damage the quality of air, water, and land. Many things that are useful to people produce pollution. Cars spew pollutants from their exhaust pipes. Burning coal to create electricity pollutes the air. Industries and homes generate garbage and sewage that can pollute the land and water. Pesticides —chemical poisons used to kill weeds and insects— seep into waterways and harm wildlife . All living things—from one-celled microbes to blue whales—depend on Earth ’s supply of air and water. When these resources are polluted, all forms of life are threatened. Pollution is a global problem. Although urban areas are usually more polluted than the countryside, pollution can spread to remote places where no people live. For example, pesticides and other chemicals have been found in the Antarctic ice sheet . In the middle of the northern Pacific Ocean, a huge collection of microscopic plastic particles forms what is known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch . Air and water currents carry pollution. Ocean currents and migrating fish carry marine pollutants far and wide. Winds can pick up radioactive material accidentally released from a nuclear reactor and scatter it around the world. Smoke from a factory in one country drifts into another country. In the past, visitors to Big Bend National Park in the U.S. state of Texas could see 290 kilometers (180 miles) across the vast landscape . Now, coal-burning power plants in Texas and the neighboring state of Chihuahua, Mexico have spewed so much pollution into the air that visitors to Big Bend can sometimes see only 50 kilometers (30 miles). The three major types of pollution are air pollution , water pollution , and land pollution . Air Pollution Sometimes, air pollution is visible . A person can see dark smoke pour from the exhaust pipes of large trucks or factories, for example. More often, however, air pollution is invisible . Polluted air can be dangerous, even if the pollutants are invisible. It can make people’s eyes burn and make them have difficulty breathing. It can also increase the risk of lung cancer . Sometimes, air pollution kills quickly. In 1984, an accident at a pesticide plant in Bhopal, India, released a deadly gas into the air. At least 8,000 people died within days. Hundreds of thou sands more were permanently injured. Natural disasters can also cause air pollution to increase quickly. When volcanoes erupt , they eject volcanic ash and gases into the atmosphere . Volcanic ash can discolor the sky for months. After the eruption of the Indonesian volcano of Krakatoa in 1883, ash darkened the sky around the world. The dimmer sky caused fewer crops to be harvested as far away as Europe and North America. For years, meteorologists tracked what was known as the “equatorial smoke stream .” In fact, this smoke stream was a jet stream , a wind high in Earth’s atmosphere that Krakatoa’s air pollution made visible. Volcanic gases , such as sulfur dioxide , can kill nearby residents and make the soil infertile for years. Mount Vesuvius, a volcano in Italy, famously erupted in 79, killing hundreds of residents of the nearby towns of Pompeii and Herculaneum. Most victims of Vesuvius were not killed by lava or landslides caused by the eruption. They were choked, or asphyxiated , by deadly volcanic gases. In 1986, a toxic cloud developed over Lake Nyos, Cameroon. Lake Nyos sits in the crater of a volcano. Though the volcano did not erupt, it did eject volcanic gases into the lake. The heated gases passed through the water of the lake and collected as a cloud that descended the slopes of the volcano and into nearby valleys . As the toxic cloud moved across the landscape, it killed birds and other organisms in their natural habitat . This air pollution also killed thousands of cattle and as many as 1,700 people. Most air pollution is not natural, however. It comes from burning fossil fuels —coal, oil , and natural gas . When gasoline is burned to power cars and trucks, it produces carbon monoxide , a colorless, odorless gas. The gas is harmful in high concentrations , or amounts. City traffic produces highly concentrated carbon monoxide. Cars and factories produce other common pollutants, including nitrogen oxide , sulfur dioxide, and hydrocarbons . These chemicals react with sunlight to produce smog , a thick fog or haze of air pollution. The smog is so thick in Linfen, China, that people can seldom see the sun. Smog can be brown or grayish blue, depending on which pollutants are in it. Smog makes breathing difficult, especially for children and older adults. Some cities that suffer from extreme smog issue air pollution warnings. The government of Hong Kong, for example, will warn people not to go outside or engage in strenuous physical activity (such as running or swimming) when smog is very thick.
When air pollutants such as nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide mix with moisture, they change into acids . They then fall back to earth as acid rain . Wind often carries acid rain far from the pollution source. Pollutants produced by factories and power plants in Spain can fall as acid rain in Norway. Acid rain can kill all the trees in a forest . It can also devastate lakes, streams, and other waterways. When lakes become acidic, fish can’t survive . In Sweden, acid rain created thousands of “ dead lakes ,” where fish no longer live. Acid rain also wears away marble and other kinds of stone . It has erased the words on gravestones and damaged many historic buildings and monuments . The Taj Mahal , in Agra, India, was once gleaming white. Years of exposure to acid rain has left it pale. Governments have tried to prevent acid rain by limiting the amount of pollutants released into the air. In Europe and North America, they have had some success, but acid rain remains a major problem in the developing world , especially Asia. Greenhouse gases are another source of air pollution. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane occur naturally in the atmosphere. In fact, they are necessary for life on Earth. They absorb sunlight reflected from Earth, preventing it from escaping into space. By trapping heat in the atmosphere, they keep Earth warm enough for people to live. This is called the greenhouse effect . But human activities such as burning fossil fuels and destroying forests have increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This has increased the greenhouse effect, and average temperatures across the globe are rising. The decade that began in the year 2000 was the warmest on record. This increase in worldwide average temperatures, caused in part by human activity, is called global warming . Global warming is causing ice sheets and glaciers to melt. The melting ice is causing sea levels to rise at a rate of two millimeters (0.09 inches) per year. The rising seas will eventually flood low-lying coastal regions . Entire nations, such as the islands of Maldives, are threatened by this climate change . Global warming also contributes to the phenomenon of ocean acidification . Ocean acidification is the process of ocean waters absorbing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Fewer organisms can survive in warmer, less salty waters. The ocean food web is threatened as plants and animals such as coral fail to adapt to more acidic oceans. Scientists have predicted that global warming will cause an increase in severe storms . It will also cause more droughts in some regions and more flooding in others. The change in average temperatures is already shrinking some habitats, the regions where plants and animals naturally live. Polar bears hunt seals from sea ice in the Arctic. The melting ice is forcing polar bears to travel farther to find food , and their numbers are shrinking. People and governments can respond quickly and effectively to reduce air pollution. Chemicals called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are a dangerous form of air pollution that governments worked to reduce in the 1980s and 1990s. CFCs are found in gases that cool refrigerators, in foam products, and in aerosol cans . CFCs damage the ozone layer , a region in Earth’s upper atmosphere. The ozone layer protects Earth by absorbing much of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation . When people are exposed to more ultraviolet radiation, they are more likely to develop skin cancer, eye diseases, and other illnesses. In the 1980s, scientists noticed that the ozone layer over Antarctica was thinning. This is often called the “ ozone hole .” No one lives permanently in Antarctica. But Australia, the home of more than 22 million people, lies at the edge of the hole. In the 1990s, the Australian government began an effort to warn people of the dangers of too much sun. Many countries, including the United States, now severely limit the production of CFCs. Water Pollution Some polluted water looks muddy, smells bad, and has garbage floating in it. Some polluted water looks clean, but is filled with harmful chemicals you can’t see or smell. Polluted water is unsafe for drinking and swimming. Some people who drink polluted water are exposed to hazardous chemicals that may make them sick years later. Others consume bacteria and other tiny aquatic organisms that cause disease. The United Nations estimates that 4,000 children die every day from drinking dirty water. Sometimes, polluted water harms people indirectly. They get sick because the fish that live in polluted water are unsafe to eat. They have too many pollutants in their flesh. There are some natural sources of water pollution. Oil and natural gas, for example, can leak into oceans and lakes from natural underground sources. These sites are called petroleum seeps . The world’s largest petroleum seep is the Coal Oil Point Seep, off the coast of the U.S. state of California. The Coal Oil Point Seep releases so much oil that tar balls wash up on nearby beaches . Tar balls are small, sticky pieces of pollution that eventually decompose in the ocean.
Human activity also contributes to water pollution. Chemicals and oils from factories are sometimes dumped or seep into waterways. These chemicals are called runoff. Chemicals in runoff can create a toxic environment for aquatic life. Runoff can also help create a fertile environment for cyanobacteria , also called blue-green algae . Cyanobacteria reproduce rapidly, creating a harmful algal bloom (HAB) . Harmful algal blooms prevent organisms such as plants and fish from living in the ocean. They are associated with “ dead zones ” in the world’s lakes and rivers, places where little life exists below surface water. Mining and drilling can also contribute to water pollution. Acid mine drainage (AMD) is a major contributor to pollution of rivers and streams near coal mines . Acid helps miners remove coal from the surrounding rocks . The acid is washed into streams and rivers, where it reacts with rocks and sand. It releases chemical sulfur from the rocks and sand, creating a river rich in sulfuric acid . Sulfuric acid is toxic to plants, fish, and other aquatic organisms. Sulfuric acid is also toxic to people, making rivers polluted by AMD dangerous sources of water for drinking and hygiene . Oil spills are another source of water pollution. In April 2010, the Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico, causing oil to gush from the ocean floor. In the following months, hundreds of millions of gallons of oil spewed into the gulf waters. The spill produced large plumes of oil under the sea and an oil slick on the surface as large as 24,000 square kilometers (9,100 square miles). The oil slick coated wetlands in the U.S. states of Louisiana and Mississippi, killing marsh plants and aquatic organisms such as crabs and fish. Birds, such as pelicans , became coated in oil and were unable to fly or access food. More than two million animals died as a result of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Buried chemical waste can also pollute water supplies. For many years, people disposed of chemical wastes carelessly, not realizing its dangers. In the 1970s, people living in the Love Canal area in Niagara Falls, New York, suffered from extremely high rates of cancer and birth defects . It was discovered that a chemical waste dump had poisoned the area’s water. In 1978, 800 families living in Love Canal had to a bandon their homes. If not disposed of properly, radioactive waste from nuclear power plants can escape into the environment. Radioactive waste can harm living things and pollute the water. Sewage that has not been properly treated is a common source of water pollution. Many cities around the world have poor sewage systems and sewage treatment plants. Delhi, the capital of India, is home to more than 21 million people. More than half the sewage and other waste produced in the city are dumped into the Yamuna River. This pollution makes the river dangerous to use as a source of water for drinking or hygiene. It also reduces the river’s fishery , resulting in less food for the local community. A major source of water pollution is fertilizer used in agriculture . Fertilizer is material added to soil to make plants grow larger and faster. Fertilizers usually contain large amounts of the elements nitrogen and phosphorus , which help plants grow. Rainwater washes fertilizer into streams and lakes. There, the nitrogen and phosphorus cause cyanobacteria to form harmful algal blooms. Rain washes other pollutants into streams and lakes. It picks up animal waste from cattle ranches. Cars drip oil onto the street, and rain carries it into storm drains , which lead to waterways such as rivers and seas. Rain sometimes washes chemical pesticides off of plants and into streams. Pesticides can also seep into groundwater , the water beneath the surface of the Earth. Heat can pollute water. Power plants, for example, produce a huge amount of heat. Power plants are often located on rivers so they can use the water as a coolant . Cool water circulates through the plant, absorbing heat. The heated water is then returned to the river. Aquatic creatures are sensitive to changes in temperature. Some fish, for example, can only live in cold water. Warmer river temperatures prevent fish eggs from hatching. Warmer river water also contributes to harmful algal blooms. Another type of water pollution is simple garbage. The Citarum River in Indonesia, for example, has so much garbage floating in it that you cannot see the water. Floating trash makes the river difficult to fish in. Aquatic animals such as fish and turtles mistake trash, such as plastic bags, for food. Plastic bags and twine can kill many ocean creatures. Chemical pollutants in trash can also pollute the water, making it toxic for fish and people who use the river as a source of drinking water. The fish that are caught in a polluted river often have high levels of chemical toxins in their flesh. People absorb these toxins as they eat the fish. Garbage also fouls the ocean. Many plastic bottles and other pieces of trash are thrown overboard from boats. The wind blows trash out to sea. Ocean currents carry plastics and other floating trash to certain places on the globe, where it cannot escape. The largest of these areas, called the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, is in a remote part of the Pacific Ocean. According to some estimates, this garbage patch is the size of Texas. The trash is a threat to fish and seabirds, which mistake the plastic for food. Many of the plastics are covered with chemical pollutants. Land Pollution Many of the same pollutants that foul the water also harm the land. Mining sometimes leaves the soil contaminated with dangerous chemicals. Pesticides and fertilizers from agricultural fields are blown by the wind. They can harm plants, animals, and sometimes people. Some fruits and vegetables absorb the pesticides that help them grow. When people consume the fruits and vegetables, the pesticides enter their bodies. Some pesticides can cause cancer and other diseases. A pesticide called DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) was once commonly used to kill insects, especially mosquitoes. In many parts of the world, mosquitoes carry a disease called malaria , which kills a million people every year. Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Muller was awarded the Nobel Prize for his understanding of how DDT can control insects and other pests. DDT is responsible for reducing malaria in places such as Taiwan and Sri Lanka. In 1962, American biologist Rachel Carson wrote a book called Silent Spring , which discussed the dangers of DDT. She argued that it could contribute to cancer in humans. She also explained how it was destroying bird eggs, which caused the number of bald eagles, brown pelicans, and ospreys to drop. In 1972, the United States banned the use of DDT. Many other countries also banned it. But DDT didn’t disappear entirely. Today, many governments support the use of DDT because it remains the most effective way to combat malaria. Trash is another form of land pollution. Around the world, paper, cans, glass jars, plastic products, and junked cars and appliances mar the landscape. Litter makes it difficult for plants and other producers in the food web to create nutrients . Animals can die if they mistakenly eat plastic. Garbage often contains dangerous pollutants such as oils, chemicals, and ink. These pollutants can leech into the soil and harm plants, animals, and people. Inefficient garbage collection systems contribute to land pollution. Often, the garbage is picked up and brought to a dump, or landfill . Garbage is buried in landfills. Sometimes, communities produce so much garbage that their landfills are filling up. They are running out of places to dump their trash. A massive landfill near Quezon City, Philippines, was the site of a land pollution tragedy in 2000. Hundreds of people lived on the slopes of the Quezon City landfill. These people made their living from recycling and selling items found in the landfill. However, the landfill was not secure. Heavy rains caused a trash landslide, killing 218 people. Sometimes, landfills are not completely sealed off from the land around them. Pollutants from the landfill leak into the earth in which they are buried. Plants that grow in the earth may be contaminated, and the herbivores that eat the plants also become contaminated. So do the predators that consume the herbivores. This process, where a chemical builds up in each level of the food web, is called bioaccumulation . Pollutants leaked from landfills also leak into local groundwater supplies. There, the aquatic food web (from microscopic algae to fish to predators such as sharks or eagles) can suffer from bioaccumulation of toxic chemicals. Some communities do not have adequate garbage collection systems, and trash lines the side of roads. In other places, garbage washes up on beaches. Kamilo Beach, in the U.S. state of Hawai'i, is littered with plastic bags and bottles carried in by the tide . The trash is dangerous to ocean life and reduces economic activity in the area. Tourism is Hawai'i’s largest industry . Polluted beaches discourage tourists from investing in the area’s hotels, restaurants, and recreational activities. Some cities incinerate , or burn, their garbage. Incinerating trash gets rid of it, but it can release dangerous heavy metals and chemicals into the air. So while trash incinerators can help with the problem of land pollution, they sometimes add to the problem of air pollution. Reducing Pollution Around the world, people and governments are making efforts to combat pollution. Recycling, for instance, is becoming more common. In recycling, trash is processed so its useful materials can be used again. Glass, aluminum cans, and many types of plastic can be melted and reused . Paper can be broken down and turned into new paper. Recycling reduces the amount of garbage that ends up in landfills, incinerators, and waterways. Austria and Switzerland have the highest recycling rates. These nations recycle between 50 and 60 percent of their garbage. The United States recycles about 30 percent of its garbage. Governments can combat pollution by passing laws that limit the amount and types of chemicals factories and agribusinesses are allowed to use. The smoke from coal-burning power plants can be filtered. People and businesses that illegally dump pollutants into the land, water, and air can be fined for millions of dollars. Some government programs, such as the Superfund program in the United States, can force polluters to clean up the sites they polluted. International agreements can also reduce pollution. The Kyoto Protocol , a United Nations agreement to limit the emission of greenhouse gases, has been signed by 191 countries. The United States, the world’s second-largest producer of greenhouse gases, did not sign the agreement. Other countries, such as China, the world’s largest producer of greenhouse gases, have not met their goals. Still, many gains have been made. In 1969, the Cuyahoga River, in the U.S. state of Ohio, was so clogged with oil and trash that it caught on fire. The fire helped spur the Clean Water Act of 1972. This law limited what pollutants could be released into water and set standards for how clean water should be. Today, the Cuyahoga River is much cleaner. Fish have returned to regions of the river where they once could not survive. But even as some rivers are becoming cleaner, others are becoming more polluted. As countries around the world become wealthier, some forms of pollution increase. Countries with growing economies usually need more power plants, which produce more pollutants. Reducing pollution requires environmental, political, and economic leadership. Developed nations must work to reduce and recycle their materials, while developing nations must work to strengthen their economies without destroying the environment. Developed and developing countries must work together toward the common goal of protecting the environment for future use.
How Long Does It Last? Different materials decompose at different rates. How long does it take for these common types of trash to break down?
- Paper: 2-4 weeks
- Orange peel: 6 months
- Milk carton: 5 years
- Plastic bag: 15 years
- Tin can: 100 years
- Plastic bottle: 450 years
- Glass bottle: 500 years
- Styrofoam: Never
Indoor Air Pollution The air inside your house can be polluted. Air and carpet cleaners, insect sprays, and cigarettes are all sources of indoor air pollution.
Light Pollution Light pollution is the excess amount of light in the night sky. Light pollution, also called photopollution, is almost always found in urban areas. Light pollution can disrupt ecosystems by confusing the distinction between night and day. Nocturnal animals, those that are active at night, may venture out during the day, while diurnal animals, which are active during daylight hours, may remain active well into the night. Feeding and sleep patterns may be confused. Light pollution also indicates an excess use of energy. The dark-sky movement is a campaign by people to reduce light pollution. This would reduce energy use, allow ecosystems to function more normally, and allow scientists and stargazers to observe the atmosphere.
Noise Pollution Noise pollution is the constant presence of loud, disruptive noises in an area. Usually, noise pollution is caused by construction or nearby transportation facilities, such as airports. Noise pollution is unpleasant, and can be dangerous. Some songbirds, such as robins, are unable to communicate or find food in the presence of heavy noise pollution. The sound waves produced by some noise pollutants can disrupt the sonar used by marine animals to communicate or locate food.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrators
Educator reviewer, last updated.
March 6, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
Plastic Pollution
A global overview from our world in data.
These slides provide a global overview of plastics production, waste, and pollution of our oceans. They are designed to provide a summary of the plastics challenge and what this tells us about how to address it. A more detailed exploration of this topic can be found at our topic page on Plastic Pollution
- How much plastic does the world produce?
- What is the fate of our plastics?
- How much plastic waste do we produce & how much ends up in the ocean?
- Where does plastic waste come from?
- How much plastic waste is traded?
- How do we tackle plastic pollution?
Annual global production of plastics has increased more than 200-fold since 1950.
In 2019 the world produced more than 450 million tonnes of plastic.
By 2019 cumulative plastic production was around 9.5 billion tonnes.
This is equivalent to more than one tonne of plastic for every person alive today.
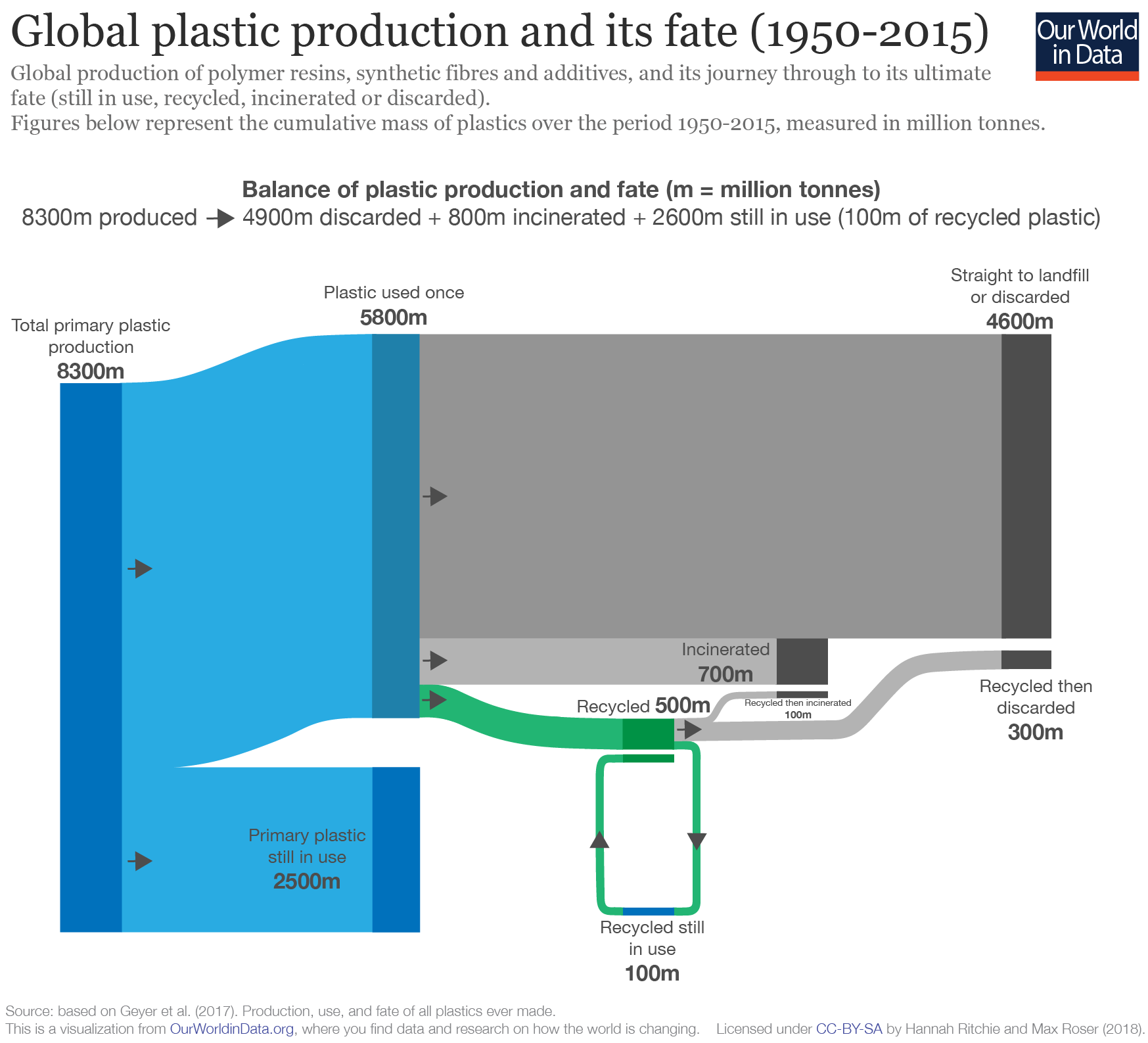
Of the global plastic produced over the period from 1950 to 2015:
- 55% straight to landfill
- 30% was still in use
- 8% was incinerated
- 6-7% was recycled
Of 5.8 billion tonnes of plastic no longer in use, ~9% was recycled.
You can explore how the trend in global recycling, incineration and landfill has changed over time here .
Whilst recycling is preferable to incineration or landfill by displacing new plastic production, most plastic can be recycled only once or twice .
This means that most recycled plastic eventually ends up in landfill or incineration.
"Recycling delays, rather than avoids, final disposal" (Geyer et al. 2017)

The world produces around 350 million tonnes of plastic waste each year.
Estimates vary, but studies suggest that 1 to 2 million tonnes enter the oceans annually.
That means 0.5% of plastic waste ends up in the ocean.
We can answer this in multiple ways:
- By land-based and marine sources
- By country or region
Packaging is the largest contributor to plastic waste.

Plastic waste can arise from land (via coastlines and rivers) and from marine sources (such as fishing nets, ropes, lines and abandoned vessels).
How significant is each source for ocean plastics?
However, in certain locations, marine sources can be more significant. The Great Pacific Garbage Patch has more than half (52%) from marine sources due to intensive fishing activity in the Pacific Ocean.
To identify the main geographical contributors to plastic pollution, we need to explore these figures in several steps:
- How much total plastic waste is generated by country
- How much plastic waste is generated by coastal populations - this is plastic which is most at risk of entering the ocean
- How much of coastal plastic waste is mismanaged (open, dumped or not enclosed) and can therefore enter waterways.
This interactive map shows the total plastic waste generation by country in 2010.
Here we see that the largest producers (China, USA, Brazil, Germany, Japan, Pakistan, Nigeria) span all continents.
But to understand the largest contributors to plastic pollution, we must correct for:
- coastal populations (taken as populations within 50km of a coastline)
- how much of this plastic is 'mismanaged'
Mismanaged plastic waste is waste which is inadequately managed (seen in the chart opposite), plus littered waste (seen here ).
High-income countries tend to have effective waste management systems and therefore low levels of inadequately managed waste.
Once we correct for these factors we can understand the geographical distribution of plastic waste at high risk of entering the ocean.
Here we see very strong regional dominance particularly across Asia.
When we aggregate by region we see the majority of plastic at risk of entering the ocean arises from Asia and Africa, with the Americas playing a notable role.
Global trade of plastics has changed a lot in the last few years.
Historically, China has been the largest plastic importer. But in 2017, it banned imports of non-industrial plastic waste.
A number of other middle-income countries have done the same.
We can see this income group's share of global plastic imports has fallen dramatically
You can also see that the amount of plastic waste that rich countries export has fallen.
This is because middle-income countries are less willing to trade.
“If we all do a little, we’ll only achieve a little”
David mackay (sustainable energy without the hot air), high-impact immediate priorities:, development of effective waste management infrastructure in all countries.
Most ocean plastic arises from countries with poor waste management infrastructure.
Cease plastic trade from rich to low or middle-income countries without sufficient investment in waste management infrastructure
The largest plastic exporters are some of the world's richest countries.
Rich countries should handle waste domestically & cease trade of plastic trade unless sufficient infrastructure is in place. A tax for exporting countries is one suggested method of raising funds for waste management services.
Strict legislation and management of fishing activity and waste
Marine plastics can be a major source of ocean pollution (most notably the Great Pacific Garbage Patch ).
Fishing activity should be better-regulated and managed to limit these sources.
Longer-term shifts in consumption models
- How essential plastic is in many aspects (e.g. preventing food losses & waste, sterile environments, construction, medical supplies)
- Plastic alternatives often have other environmental impacts . There are usually trade-offs
- To be globally effective, must be scalable and cheap
Explore this topic in detail at our:
Main topic on plastic pollution.
About the author: Hannah Ritchie is a scientist at the University of Oxford. She is a Researcher at the Oxford Martin Programme on Global Development . About Our World in Data: Our World in Data is an online publication that shows how living conditions are changing. The aim is to give a global overview and to show changes over the very long run, so that we can see where we are coming from, where we are today, and what is possible for the future. www.ourworldindata.org | @HannahRitchie02
Home Collections Nature Pollution Environmental Pollution PowerPoint Presentation
Environmental Pollution PPT Presentation & Google Slides

Creative Environmental Pollution PowerPoint Presentation
Download this Creative Environmental Pollution PowerPoint Presentation for all your impressive pollution presentations. This is a 100% user-friendly template. You can save time and ease your work with this pre-designed template. This is a well-built template with a professional touch.
About the template:
This Creative Environmental Pollution PowerPoint Presentation is one of the finest pollution templates from SlideEgg. This is a four nodded template. Environmental pollution is the contamination of the biological and physical elements of the earth/atmosphere system to the extent that standard environmental processes are adversely affected.
This template has a clipart diagram depicting environmental pollution in its background. It is placed in the center of this template. The nodes are arranged around this clipart diagram of this template.
Features of this template:
- 100% customizable slides and easy to download.
- Slides available in different nodes & colors.
- The slide contained 16:9 and 4:3 format.
- Easy to change the slide colors quickly.
- Well-crafted template with instant download facility.
- Fantastic four-node featured template.
- One of the best environment-themed templates from SlideEgg.
- Environmental Pollution
- Environmental Light Pollution
- Air Pollution
- Plastic Pollution
- Soil Pollution
- Pollution Infographics
- Industrial Emissions
- Waste Management
- Google Slides

25+ Templates

267+ Templates

127+ Templates

Agriculture
59+ Templates

53+ Templates

13+ Templates

Renewable Energy
61+ Templates

70+ Templates

55+ Templates

30+ Templates
You May Also Like These PowerPoint Templates

- Preferences

Environmental Pollution PowerPoint PPT Presentations


Pollution PPT | 30+ Best Pollution PPT Collection Download Free
Pollution ppt.
- Air Pollution PPT
- Water Pollution PPT
- Environmental Pollution PPT
- Marine Pollution PPT
- Thermal Pollution PPT
- Types of Pollution PPT
- Land Pollution PPT
- Plastic Pollution PPT
- Control of Air pollution PPT
- Air prevention and control of Pollution act 1981 PPT
- Industrial Pollution PPT
- Water Act 1974 PPT
- Groundwater pollution PPT
- Types of air pollution PPT
- Air pollution case study PPT
Noise Pollution PPT
- Photochemical Smog PPT
- Causes of Water Pollution PPT
- Indoor Air Pollution PPT
- Light Pollution PPT
- Prevention of Noise Pollution PPT
- Noise Pollution Act of 2000 PPT
- Visual Pollution PPT
- Air Quality PPT
- Effects of water pollution on human health PPT
- Soil Pollution PPT
- Oil Pollution PPT
- Ganga River Pollution PPT
- Ocean Pollution PPT
- Yamuna Pollution PPT
- Microplastic Pollution PPT

Pollution PPT
- DEFINITION OF POLLUTION
- Types of Pollution
- Air Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Land Pollution
- Radio Active Pollution
- thermal pollution
- What is Atmosphere
- Pollution In Facts and Figures
- Pollution Control Measures
- The PPC Division
- Enforcement Mechanisms
- Causes of air pollution
- Effects of air pollution
- How to avoid air pollution
- Definition and causes and effects of water pollution
- Water pollution pictures
- How to avoid water pollution
- Noise pollution (causes, effects, and prevention)
- How to avoid noise pollution
- Definition, causes, and prevention of land pollution
- Land pollution pictures
Air pollution PPT
- What is air
- List of major air pollutants
- Sources and effects of air pollutants
- What is air pollutants?
- Six major air pollutants
- Major sources of pollutants
- Greenhouse gases
- What is air pollution
- Wildlife affected by air pollution
- Ozone layer
- Greenhouse effect
- Global warming
- Air problems caused by incineration of waste materials
- Controlling air pollution
Water pollution PPT
- Human and natural pollutants
- Sources of water pollution
- How do we measure water quality?
- Quantitative water quality tests
- Qualitative water tests
- What are some indicator species of water pollution
- Is the water safe to drink?
- What have developed countries done to reduce stream pollution
- What have developed countries done to reduce stream pollution
- Who reports on drinking water
- Clean water act 1972
- Safe water drinking act 1974
- Water purification
- What is water pollution?
- Types of water pollution
- Causes of water pollution
- Effects of water pollution
- What you can do
- Classification of water pollutant
- Common water-borne diseases
Water act 1974 PPT
- Introduction
- Salient provisions of water act (1974)
- Objectives & scope
- Powers and functions of boards
- Prevention and control of water pollution
- Penalties and procedure
- Miscellaneous
- Application and commencement
- Functions of the central board (sec. 16)
- Functions of the state board
- Ganga action plan ( gap)
- Water quality board actions
Environmental pollution PPT
- Degradable pollution
- Non-degradable pollution
- Types of pollution ( noise,air,water,land ,soil,thermal,nuclear)
- Air pollution
- Composition of air
- Types of pollutants
- Sources of air pollution
- Ozone depletion
- Water pollution ( meaning, types, definition, sources, causes and control and measures)
- Soil pollution
- Causes of soil degradation
- Marine pollution
- Causes, effects, control, and measure of marine pollution
- Control measures for oil pollution
- Noise pollution
- Levels of noise and vibration
- Decibel levels of common sounds DB
- Ambient noise levels DB
- Safe time exposure in DB
- Effects of noise pollution
- Control techniques
- Thermal pollution
- Nuclear hazards
- Effects of nuclear pollution
- Control measures
- Role of an individual in prevention of pollution
Environmental pollution PPT 2
- Types of pollution
- Water pollution
- Municipal wastewater
- Industrial waste
- Inorganic pollutants
- Organic pollutants
- Agricultural wastes
- Consequences of air pollution
- Land pollution
- Causes of land pollution
- Sources of noise pollution
- Solutions for noise pollution
- Ways to stop pollution
- Global warming and the greenhouse effect
- Difference between global warming and the greenhouse effect
- Some proof of global warming
Light pollution PPT
- What is light pollution?
- Types of light pollution
- Consequences
- Causes effect solution
Photochemical smog PPT
- Photochemical smog
- Air pollutant
- How photochemical smog is formed
- The process involving the formation of photochemical smog
- Effect on human health and plants
- Sources and effect of photochemical smog
- Factors affecting the formation of photochemical smog
- Mitigation measures for photochemical smog
- How to save the environment by preventing smog
Plastic pollution ppt
- What is pollution?
- What is plastic?
- What is plastic pollution?
- History of plastic
- Plastic pollution
- Chemicals in plastic
- Types of plastic products
- Sources of plastic pollution
- Causes of plastic pollution
- Effects of plastic pollution
- Solutions to plastic pollution
- Steps taken by govt
- Initiatives on plastic pollution
- Case studies
- Ways to mitigate plastic pollution
- Scary facts about plastic
Marine pollution PPT
- Types of marine pollution
- Causes & effects of marine pollution
- Prevention and control
- What is a pollution?
- What is marine pollution??
- Causes of marine pollution
- Major impacts of marine pollution
- The health of marine life
- Some examples of marine pollution
- Ways of pollutant inputs
- Human impacts on marine environments
- How to protect marine life?
- Oil pollution
- Garbage pollution
- Accidental loss or discharge of fishing gear
- Plan to reduce and store your garbage
- Garbage waste management onboard shore facilities
- Marine pollution threats and biodiversity conservation
- Ocean world
- Marine life and resources
- Marine ecosystem
- Marine biodiversity
- Marine pollution threats
- Pollutants types & sources
- Impact of marine pollution
- Coastal ecology
- Coastal regulation zone (crz)
- Aquaculture: the blue revolution?
- How to solve environmental pollution
- Role of marine biotechnology on environmental pollution
- Suggestions to protect marine environments
- World environmental day- June 5
- Policies and acts for the protection
Thermal pollution PPT
- Diagramatic representation
- Causes of thermal pollution
- Effects of thermal pollution
- Control of thermal pollution
- The Bentley manufacturing company
- Freeze fish breeding in Macquarie river
- Thermal pollution and the Hudson river
- Impacts of thermal pollution
- Thermal pollution causes and consequences
Land pollution PPT
- What is land pollution?
- Causes of land pollution
- Effects of land pollution
- Prevention of land pollution
- Solutions for land pollution
- WHAT IS NOISE POLLUTION
- Health Effects
- Sources of Noise Pollution
- Solutions for Noise Pollution

Agricultural pollution PPT
- What is agricultural pollution
- Types of agricultural pollution
- Main causes of agricultural pollution
- Effects of agricultural pollution
- Challenges of agricultural pollution
- Ways to reduce agricultural pollution
- Types of the mechanism of agricultural pollution
- Leaching and groundwater poisoning
- Water runoff
- Eutrophication
- Challenges or managements problems of agricultural pollution
- Prevention and techniques of agriculture pollution
- A figure showing irrigation drainage
Agriculture water pollution PPT
- Agriculture as a cause
- Sources of awp
- Impacts
Pollution and EVS PDF Books and Notes ( 4+ downloadable PDF) Pollution Handmade Assignment and Project PDF Pollution and EVS Project Videos Collection ( 20 + videos)
Similar Posts
💁Hello Friends, If You Want To Contribute To Help Other Students To Find All The Stuff At A Single Place, So Feel Free To Send Us Your Notes, Assignments, Study Material, Files, Lesson Plan, Paper, PDF Or PPT Etc. - 👉 Upload Here
अगर आप हमारे पाठकों और अन्य छात्रों की मदद करना चाहते हैं। तो बेझिझक अपने नोट्स, असाइनमेंट, अध्ययन सामग्री, फाइलें, पाठ योजना, पेपर, पीडीएफ या पीपीटी आदि हमें भेज सकते है| - 👉 Share Now
If You Like This Article, Then Please Share It With Your Friends Also.
Bcoz Sharing Is Caring 😃

- [1000+] B.Ed Lesson Plans
- B.Ed Practical Files and Assignments
- B.Ed Books and Notes PDF
- B.Ed Files Pics and Charts Collection
- BEd Model / Sample and Previous Year Papers
- All Subject Lesson Plans for Teachers
Post a Comment
Please Share your views and suggestions in the comment box
Contact Form

ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION
Jan 07, 2020
780 likes | 928 Views
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION. By Mrs. Vaibhavi Apte. Definition of Pollution. When Harmful Substances Contaminate the environment it is Called Pollution.
Share Presentation
- water pollution
- air pollution
- air pollutants
- ground water pollution
- central pollution control board

Presentation Transcript
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION By Mrs. VaibhaviApte
Definition of Pollution • When Harmful Substances Contaminate the environment it is Called Pollution. • It can be defined as any undesirable change in the physical, chemical, biological characteristics of any component of the environment which can cause harm to life and property.
Types of Pollution
Air pollution
What is Atmosphere? • Atmosphere is the life blanket of Earth.
Air.... • Air supplies us with oxygen which is essential for our bodies to live. • Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, carbon dioxide and inert gases. • Human activities can release substances into the air, some of which can cause problems to humans, plants, and animals. • Natural Composition of Gases
Definition • Air pollution : An atmospheric condition in which certain substances (including normal constituents in excess) are present in concentrations which can cause undesirable effects on man and his environment. • They are in the form of gases (Nox, Sox, CO,VOC); Particulate matter(dust, smoke, fumes, etc) & Radioactive (rado-222, Iodine-131, etc)
Sources of Air Pollution
Classification of Air Pollutants • Air pollutants may be particulate or gaseous. On the basis of origin they are divided as • Primary pollutants ---- Are emitted directly from the point source. e.g. : CO, NO2, SO2 • Secondary pollutants ---- formed by interaction of primary pollutants e.g. : PAN, Smog, Ozone etc
Criteria of Pollutants
Indoor air pollution • Many people spend large portion of time indoors - as much as 80-90% of their lives. • We work, study, eat, drink and sleep in enclosed environments where air circulation may be restricted • Children, women more exposed to risk • Radon gas • Burning of dung cakes for fuel, wood, kerosene • Incomplete combustion produces CO • Cigarette smoke.
Effects of Air Pollution Air Pollution affects??? • Human health • Animals • Plants • Materials • Environment
Effect on Human health • Main problems are related to Respiratory Track - Asthma, hay fever, and other allergic diseases. • Irritation of the eye, nose and throat. In severe cases there may be headaches, nausea, and loss of coordination. • Prolonged exposure can cause damage to the nervous system, digestive problems, and in some cases cause Lung cancer. • It lowers our resistance to colds and pneumonia. • CO has affinity towards Hb which cause disturbance in transportation of Oxygen, impairing our concentration, slow our reflexes, and make us confused and sleepy. • SO2 in the air leads to diseases of the lung and other lung disorders such as wheezing and shortness of breath. • Chronic respiratory disease, lung cancer, heart disease, and even damage to the brain, nerves, liver, or kidneys. • Effects of Arsenic, Asbestos, Mercury , Benzene etc.
Effect on Plants • Pollutants enter through stomata • Destroy chlorophyll and Affect photosynthesis • Cuticle( Wax Layer on Leaves) is lost • Necrosis – Damage to Leaf Structure • Chlorosis - Loss/ reduction of Chlorophyll • Abscission - Dropping of leaf • Epinasty – Downward curling of Leaf • DEATH
Effect on Animals and materials • Corrosion of metal surfaces, fading • SO2 & water form H2S – corrosion as well as disfigurement of statues made up of limestone or Marble • Air pollutants mix with rain water and increase acidity (Acid Rain) of water body and kill fish. • Ozone causes crackling of rubber
Effect on Environment • Visibility • Pollutants in the presence of sunlight produce photochemical Smog • Emission of Green House Gases tend to Global Warming • CFC’s cause Ozone Depletion
National Ambient Air Quality Standards
Annual Average : Annual Arithmetic Mean of minimum 104 measurements in a year taken twice a week 24-hourly at uniform interval • 24 Hours Average : 24-hourly/8-hourly values should be met 98% of the time in a year. However 2% of the time, it may exceeded but not two consecutive days. • 1. The levels of air quality necessary with an adequate margin of safety, to protect the public health, vegetation and property. • 2. Whenever and wherever two consecutives values exceeds the limit specified above for the respective category, it shall be considered adequate, reason to institute regular / continuous monitoring and further investigations. • HIGH VOLUME SAMPLER, GASEOUS SAMPLERS
Control Of Air Pollution • Proper air pollution control devices in industries • Using low sulphur coal • Regular engine tune up, replacement of old more polluting vehicles • Using mass transport system, bicycles etc • Shifting to less polluting fuels • Planting more trees • No to FIRE CRACKERS in Diwali and other occasions
Pollution Control Devices Cyclone Separator Bag House Filter
NATIONAL AIR QUALITY MONITORING PROGRAMME (NAMP) • Central Pollution Control Board is executing a nation-wide programme of ambient air quality monitoring known as National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP). • The network consists of three hundred and forty two (342) operating stations covering one hundred and twenty seven (127) cities/towns in twenty six (26) states and four (4) Union Territories of the country. • Under N.A.M.P., four air pollutants viz ., Sulphur Dioxide (SO2), Oxides of Nitrogen as NO2, Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM) and Respirable Suspended Particulate Matter (RSPM / PM10) have been identified for regular monitoring at all the locations. • The monitoring of meteorological parameters such as wind speed and wind direction, relative humidity (RH) and temperature were also integrated with the monitoring of air quality.
Water Pollution The Contamination of water with undesirable substances which make it unfit for usage is termed water Pollution.
Pollution Sources • Point sources are direct discharges to a single point; • examples include discharges from sewage treatment plants, injection wells and some industrial sources. • Non-point sources are diffused across a broad area and their contamination cannot be traced to a single discharge point. • Examples include runoff of excess fertilizers, herbicides, and insecticides from agricultural lands and residential areas; oil, grease, and toxic chemicals from urban runoff and energy production; and sediment from improperly managed construction sites, crop and forest lands, and eroding stream banks.
Surface Water Pollution • Sewage • Industrial effluents • Synthetic detergents • Agrochemicals • Oil • Waste heat
Domestic Sewage • Refers to waste water that is discarded from households. Also referred to as sanitary sewage, such water contains a wide variety of dissolved and suspended impurities. • It is large by volume and contains impurities such as organic materials and plant nutrients that tend to rot. • The main organic materials are food and vegetable waste, plant nutrient come from chemical soaps, washing powders, etc. • Domestic sewage is also very likely to contain disease-causing microbes.
Industrial Effluents • Waste water from manufacturing or chemical processes in industries • Industrial waste water usually contains specific and readily identifiable chemical compounds. • Mainly in the form of toxic wastes and organic pollutants. • Chromium, mercury, lead, copper, cadmium etc
Synthetic Detergents And Oils • Added because of washing clothes, cleaning utensils. • In industries for washing • Add surfactants and soaps to water • Toxic to fish, aquatic life. • Oceans are polluted by oil on a daily basis from oil spills, routine shipping, run-offs and dumping. • Oil spills make up about 12% of the oil that enters the ocean. The rest come from shipping travel, drains and dumping.
Agricultural Run Off • Routine applications of fertilizers and pesticides for agriculture and uncontrolled run off in water bodies. • Adds Nitrogen and Phosphorus to water • Causes Eutrophication and algal blooms. • Nitrate concentration is above the permissible level of 45 ppm in 11 states, covering 95 districts and 2 blocks of Delhi.
Ground Water Pollution • Is less comparatively as soil acts as a filter Still... • Septic tanks • Mining • Deep well injection • Presence of heavy metals in groundwater is found in 40 districts from 13 states, viz., Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and five blocks of Delhi. • Arsenic , Nitrate, Fluoride
Fluoride Poisoning • The incidence of fluoride above permissible levels of 1.5ppm occur in 14 Indian states, namely: • Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, • Orissa, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal affecting a total of 69districts, according to some estimates. • Some other estimates find that 65 per cent of India’s villages are exposed to fluoride risk.
Fluoride Poisoning • A recent survey by the International Water Management Institute (IWMI) in north Gujarat showed 42 per cent of the people covered in the sample survey (28,425) were affected; while 25.7 per cent were affected by dental fluorosis, 6.2 per cent were affected by muscular skeletal fluorosis and 10 per cent by both. • Fluoride had been reported to cause depressions in DNA and RNA synthesis in cultured cells. • Another study on the effects of fluorides in mice showed significant reductions in DNA and RNA levels. • Conditions including ageing, cancer, and arteriosclerosis are associated with DNA damage and its disrepair.
Arsenic Poisoning • High levels of arsenic above the permissible levels of 50 parts per billion (ppb) are found in the alluvial plains of Ganges covering six districts of West Bengal. • Arsenic contamination of drinking water causes a disease called arsenicosis, for which there is no effective treatment. • Arsenic contamination is by far the biggest mass poisoning case in the world putting 20 million people from West Bengal and Bangladesh at risk though some other estimates put the figure at 36 million people.
Effects • Depletion of dissolved oxygen • Eutrophication • Pathogen….spreading diseases • Bio-magnification • Genetic deformities • Blue baby Syndrome • Minamata disease • Itai-Itai
DEPLETION OF OXYGEN • Low DO and High • Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) • Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) • Biodegradable and organic waste leads to Oxygen depletion • DO levels less than 4 mg / l disastrous. • Polluted waters have 0 DO
Pathogen Spread • Stagnant water and other untreated water provide a habitat for the mosquito and a host of other parasites and insects that cause a large number of diseases especially in the tropical regions. • Among these, malaria is undoubtedly the most widely distributed and causes most damage to human health.
Biomagnification
Pesticides. The organophosphates and the carbonates present in pesticides affect and damage the nervous system and can cause cancer. • Some of the pesticides contain carcinogens that exceed recommended levels. They contain chlorides that cause reproductive and endocrinal damage. • Lead. Lead is hazardous to health as it accumulates in the body and affects the central nervous system. Children and pregnant women are most at risk. • Petrochemicals. Benzene and other petrochemicals can cause cancer even at low exposure levels. • Chlorinated solvents. These are linked to reproduction disorders and to some cancers. • Other heavy metals. –Heavy metals cause damage to the nervous system and the kidney, and other metabolic disruptions.
Case Study of Vultures • Veterinary use of the drug diclofenac—used in the treatment of livestock—has been linked to the collapse of vulture populations throughout South Asia. • Vultures are keystone species that perform a vital ecosystem service by disposing of carrion and their decline has had dramatic ecological and socio-economic consequences. • Vultures feeding on the carcasses of animals recently treated with the drug suffer renal failure and die.
Blue Baby Syndrome • Blue Baby Syndrome or Methemoglobinemia is caused by decreased ability of blood to carry oxygen, resulting in oxygen deficiency in different body parts. • Infants are more susceptible than adults. • The disease can be caused by intake of water and vegetables high in nitrate, exposure to chemicals containing nitrate, or can even be hereditary. • As different parts of the body get deprived of oxygen, clinical symptoms of oxygen starvation start to appear, the main being cyanosis (derived from ‘cyano’, meaning dark blue; from Greek, kyanos). • The lips or even the skin start to take on a blue colouration, hence the common name, the blue baby syndrome/ disease.
Minamata Disease • First detected in 1956 • In Minamata, Japan, mercury was used in the industrial production of acetaldehyde. • Discharged into the nearby bay and was ingested by organisms. • Fish and other creatures in the sea were soon contaminated and eventually residents of this area who consumed the fish suffered from MeHg (methyl mercury) intoxication
ITAI-ITAI • Itai-itai disease ("ouch ouch sickness"), • Was the documented case of mass cadmium poisoning in Toyama Prefecture, Japan, starting around 1912. • The cadmium poisoning caused softening of the bones and kidney failure. The disease is named for the severe pains (Japanese:itai) caused in the joints and spine. • The cadmium was released into rivers by mining companies. This Cadmium contaminated water was used to irrigate rice fields.
Control of Water Pollution • Treatment of water before leaving in water bodies. • Restoration of polluted water bodies. • Ganga Action Plan • River Water Monitoring
Marine Pollution • Marine Pollution is caused due to Sewage Sludge, Indutrial Effluents, Detergents, solid waste, plastic, etc. • Sources : • River- Bring pollutants from drainage basins • Catchment Area- Human Settlements • Oil Drilling & Shipment • Effects : • Fishes show mortality • Oil disrupts the insulating capacity of feathers • Due to loss of Buoyancy and subsequent drowning of Birds cause Deaths
Control measures • Effluents should not be discharged • Treatment before discharge • Strict law enforcement- regarding drilling in Ecosensitive zones, dumping of toxic & Hazardous wastes • Minimum developmental activities on shore • CRZs: Coastal regulation Zones
GlobalEnvironmental Monitoring Stations/ Monitoring of Indian National Aquatic Resource • CPCB in collaboration with concerned SPCBs/PCCs established a nationwide network of water quality monitoring comprising 2500 stations in 28 States and 6 Union Territories. • The monitoring is done on monthly or quarterly basis in surface waters and on half yearly basis in case of ground water. • The monitoring network covers 445 Rivers, 154 Lakes, 12 Tanks, 78 Ponds, 41 Creeks/Seawater, 25 Canals, 45 Drains, 10 Water Treatment Plant (Raw Water) and 807 Wells. • Among the 2500 stations, 1275 are on rivers, 190 on lakes, 45 on drains, 41 on canals, 12 on tanks, 41 on creeks/seawater, 79 on ponds, 10 Water Treatment Plant (Raw Water) and 807 are groundwater stations • Water samples are being analysed for 28 parameters consisting of 9 core parameters, 19 other physico-chemical and bacteriological parameters apart from the field observations. Besides this, 9 trace metals and 15 pesticides are also analysed in selected samples. • Biomonitoring is also carried out on specific locations.
Thermal Pollution • Definition : Presence of waste heat in the water which can cause undesirable changes in natural environment. • Causes: • Heat producing Industries • Power plants utilize only 1/3rd energy produced by fossil fuel rest is wasted as heat • Cold water is taken from water body for cooling ….used and left in the water body….back with increase of 10-15 Deg.
- More by User

ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION AIR POLLUTION Lecture - 1
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION AIR POLLUTION Lecture - 1. Air Necessary for Existence Colorless, odorless mixture of gases Quality of air varies in different environments Urban vs. Rural Emission of Particulate Matter from: Anthropogenic (Man-made) Sources (Industry)
2.07k views • 79 slides

Environmental Pollution
Environmental Pollution .
320 views • 11 slides

ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION . LAND & WATER POLLUTION By Dr. Frank Elwell. The Environment. THROUGHOUT HUMAN HISTORY, PEOPLE'S ACTIVITIES HAVE HAD AN ENORMOUS IMPACT ON THE PHYSICAL WORLD, AND NEW ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS HAVE BEEN CREATED BY THE SOLUTIONS TO OLD ONES. The Environment.
962 views • 71 slides

Environmental pollution in Russia
Environmental pollution in Russia. Major problems. Forest resources. Forest resources in Russia are used irrationally. When deforestation is a lot of waste. In processing lost about 20% of wood. In the forests decreased species diversity of flora and fauna . Sea pollution.
634 views • 9 slides

Food safety Environmental Pollution
Food safety Environmental Pollution. The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components:
567 views • 12 slides

Environmental Pollution. Pollution Control to save the Earth. Contents. What is Environmental Pollution?. The word pollution comes from the Latin word “ pollutionem ” meaning to defile or to make dirty.
6.62k views • 22 slides

ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION. Dr VISHAL SHARMA Assoc. Prof. Botany Department Post Graduate College for Girls-11, Chandigarh. AIR POLLUTION:
592 views • 29 slides

ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION. Atmospheric Pollution By Dr. Frank Elwell. The Environment. THROUGHOUT HUMAN HISTORY, PEOPLE'S ACTIVITIES HAVE HAD AN ENORMOUS IMPACT ON THE PHYSICAL WORLD, AND NEW ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS HAVE BEEN CREATED BY THE SOLUTIONS TO OLD ONES. The Environment.
1.33k views • 69 slides

Safety Food Environmental Pollution
Safety Food Environmental Pollution. The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components:
173 views • 7 slides

ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION. Assoc. prof. Jānis Zaļoksnis. PEOPLE – ENVIRONMENT - POLLUTION. The past, present and potential global threat of environmental pollution and degradation is one of the main factors that has an effect on the formation of society’s environment.
1.3k views • 52 slides

ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION. ÇEVRE KİRLİLİĞİ. DESCRIPTION - TANIMI.
454 views • 29 slides

ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION. DONE BY, ARYA.M.L ANILA.G.R AISWARYA.M.J ANU.H.M X R GGHSS COTTON HILL. INTRODUCTION. Air,water,soil,human beings,animals and plants etc exists in a mutually interacting and interdependent manner. This is called the environment.
1.49k views • 8 slides

Environmental Pollution.
. Environmental Pollution. Participants. Merlin babu Hema.p R.anusuya devi. Praveena. 10E COTTON HILL GIRLS SCHOOL TVRM. INTRODUCTION. Now a day pollution is increasing . Pollution is divided into four.They are, air pollution water pollution soil pollution
682 views • 14 slides

498 views • 21 slides

Causes Of Environmental Pollution
Sewerleaks.com survey method allows clients to view large areas and discover problems that are often difficult to observe, and often continue to contaminate water bodies. Survey techniques include aerial, multi-band infrared platforms guided by autopilot over GIS data layers.
141 views • 6 slides

344 views • 8 slides

Environmental Pollution. Environmental pollution can be defined as any undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological characteristics of any component of the environment ( air, water, soil), which can cause harmful effects on various form of life or property.
1.32k views • 99 slides

Environmental Pollution. Air Pollution. The Atmosphere. Atmospheric pressure (millibars). 0. 200. 400. 600. 800. 1,000. 120. 75. Temperature. 110. Pressure. 65. 100. Thermosphere. 90. 55. Mesopause. 80. Heating via ozone. 45. 70. Mesosphere. Altitude (kilometers).
327 views • 26 slides

ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION. By Miss. M. Shanthi MCA. Definition of Pollution. When Harmful Substances Contaminate the environment it is Called Pollution.
904 views • 71 slides

Environmental Pollution. What’s Environmental Pollution?. Environmental pollution in any an undesirable change in physical,chemical, or biological characteristics of any component of the environment. Forms of Environmental Pollution. *Soil contamination *Air pollution *Water pollution
339 views • 16 slides

Environmental Pollution. Petr Kristen 9.B Zš Broumovská. Overwiew. Definition of pollution Types of pollution Air pollution Water pollution Noise pollution Land pollution Radio-active pollution. Definition of pollution.
226 views • 10 slides

- Professionals
- Environmental Pollution Template
We understand that environmental pollution refers to any component that is harmful to nature, whether physical, biological or chemical. Mostly the cause of this is caused by human activity, such as greenhouse gas emission or massive export of natural resources. Today you can find in Environmental Pollution template a unique opportunity to represent presentations oriented on care and protection of ecosystems.
The professionally designed Environmental Pollution template for PowerPoint and Google Slides offers you a lot of vectors and images inspired by the deterioration of the planet. The powerful amount of 40 slides available for Canva, opens up opportunities like recording yourself in real time or inserting multimedia content totally free of charge. So now you have no excuse to join the care of the environment, what are you waiting for, download this free ppt resource and show a really meaningful presentation for society.
Free Environmental Pollution Template for PowerPoint and Google Slides

Main features
- 40 slides 100% editable
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all screens
- High quality royalty-free images
- Easy to edit layouts for presenting or printing
- Included resources: charts, graphs, timelines and diagrams
- More than 100 icons customizable in color and size
- Main font: Bohemian Typewriter
- Predominant color: Black
Download this template
If you want to promote ideas and actions concerning the care of the planet, then there is no doubt that you must enter our collection of PowerPoint templates and themes Google Slides pollution. Here you will find digital tools totally ideal for developing presentations aimed at the protection of ecosystems.
We use cookies to improve the experience of everyone who browses our website. Cookies Policy
Accept Cookies

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
JavaScript appears to be disabled on this computer. Please click here to see any active alerts .
Final Rule to Strengthen Standards for Synthetic Organic Chemical Plants and Polymers and Resins Plants
April 9, 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced a set of final rules that will significantly reduce emissions of toxic air pollution from chemical plants, including the potent air toxics ethylene oxide (EtO) and chloroprene. The reductions dramatically reduce the number of people with elevated air toxics-related cancer risks in communities surrounding the plants that use those two chemicals, especially communities historically overburdened by air toxics pollution.
Regulatory Documents
- Final Rule (prepublication version) (pdf) (5 MB)
- Regulatory Impact Analysis for the Final Rule (pdf) (1.3 MB)
Fact Sheets, Infographic and Presentation
- Fact Sheet: Overview of the Final Rule (pdf) (287.6 KB)
- Fact Sheet: Key Things to Know About the Final Rule (pdf) (192.9 KB)
- Infographic: EPA’s Air Toxics Rules for the Synthetic Organic Chemical Manufacturing and Polymers & Resins Industries (pdf) (54.7 MB)
- Overview Presentation: EPA's Final Rules for the Synthetic Organic Chemical Manufacturing Industry and Group I & II Polymers and Resins Industry (pdf) (711.3 KB)
Additional Documents
- List of facilities covered by National Emissions Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants for Synthetic Organic Chemical Plants and Group I and Group II Polymers and Resins Plants
Documents from Proposal
- Proposed Rule
- Regulatory Impact Analysis for the Proposal
- Fact Sheet on EPA's Community Risk Assessment and Risk Based Demographic Assessment
Web Pages for Individual Air Toxics Rules Included in the Final Action
Synthetic Organic Chemical Manufacturing Industry: Organic National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) - 40 CFR 63 Subparts F,G,H,I
Group I Polymers and Resins: National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP)
Group 2 Polymers and Resins: Epoxy Resins Production and Non-Nylon Polyamides: National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP)
- Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Home
- EPA Actions To Reduce Risk
- Our Current Understanding
- EtO Risk and Your Health
- Addressing and Learning About EtO
- EtO Community Engagement
- Federal Partnerships on EtO
- EtO Additional Questions
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

suicide prevention
8 templates

46 templates

tropical rainforest
29 templates

spring season
34 templates

american football
16 templates

32 templates
Environmental Protection
Environmental protection presentation, premium google slides theme and powerpoint template.
This visually stimulating template on environmental protection, compatible with Google Slides and PowerPoint, adopts a naturally gentle, cream color scheme, accented by vibrant, illustrative symbols that encapsulate the spirit of Mother Nature herself. Ready to be fully customized to best suit your needs, this presentation template delivers bits of ready content on topics like circular economy, recycling and individual contributions to environmental protection. Share facts and inspire discussion to pave the way towards a more sustainable future!
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 35 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
What are the benefits of having a Premium account?
What Premium plans do you have?
What can I do to have unlimited downloads?
Don’t want to attribute Slidesgo?
Gain access to over 22700 templates & presentations with premium from 1.67€/month.
Are you already Premium? Log in
Related posts on our blog

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Register for free and start editing online

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Environmental pollution. The document defines and describes five main types of pollution: air, water, noise, land, and radioactive. It provides details on the causes and effects of each type of pollution, as well as some methods to prevent or reduce pollution. The five types of pollution covered are air (from vehicles, industries), water (from ...
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants. Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic ash. They can also be created by human activity, such as trash or runoff produced by factories. Pollutants damage the quality of air, water, and land.
Although environmental pollution can be caused by natural events such as forest fires and active volcanoes, use of the word pollution generally implies that the contaminants have an anthropogenic source—that is, a source created by human activities. Pollution has accompanied humankind ever since groups of people first congregated and remained for a long time in any one place.
Pollution Presentation templates There's only one planet Earth, that's for sure. Help raise awareness about climate change and its effects on the environment by creating presentations for Google Slides or PowerPoint with our templates. Filter by ... Environment Pollution Diseases
2. ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION Environmental Pollution can be defined as any undesirable change in physical, chemical, or biological characteristics of any component of the environment i.e. air, water, soil which can cause harmful effects on various forms of life or property. Pollution: The term pollution can be defined as influence of any substance causing nuisance, harmful effects, and ...
Plastic alternatives often have other environmental impacts. There are usually trade-offs; To be globally effective, must be scalable and cheap; Explore this topic in detail at our: Main topic on Plastic Pollution. About the author: Hannah Ritchie is a scientist at the University of Oxford.
Effects of Air pollution 3) Effect on climate - • Increase of CO2 • Global warming • Melting of ice, glaciers • Thinning of ozone layer • Penetration of UV rays. Effects of Air pollution 4) Effects on aquatic life - Air pollutants mixing up with rain can cause high acidity (lower pH) in fresh water lakes. This affects aquatic life ...
Environment Presentation templates Create very inspiring presentations thanks to our free Google Slides themes and PowerPoint templates. You will be able to talk about the Environment with a captivating slide deck. ... Soil pollution is a very important issue that needs to be addressed, as it affects the vegetables and the fruit that we grow ...
Pollution in cities is commonplace. However, it causes numerous diseases and increases the likelihood of many others. That is why it is important to raise awareness of our role in protecting the environment. To talk about this medical issue and how it affects our health, today we bring you this simple and modern design proposal. The gray color ...
Presenting this set of slides with name environment sustainability trends with reduction in plastic pollution ppt powerpoint presentation outline clipart images pdf. This is a five stage process. The stages in this process are huge reductions in plastic pollution, opting for sustainable building materials, recycling and repurposing resources ...
This Creative Environmental Pollution PowerPoint Presentation is one of the finest pollution templates from SlideEgg. This is a four nodded template. Environmental pollution is the contamination of the biological and physical elements of the earth/atmosphere system to the extent that standard environmental processes are adversely affected.
They can be used by environmental organizations, government agencies, educational institutions, and businesses looking to promote their eco-friendly initiatives. Download your presentation as a PowerPoint template or use it online as a Google Slides theme. 100% free, no registration or download limits. Create captivating presentations about the ...
Environmental pollution is a major concern these days all over the world as it directly affects the health of human, animal, aquatic life etc. This Environmental pollution PPT is all about environment pollution, types of environment pollution, harmful effects of environmental pollution and ways to control environmental pollution.
31 likes • 36,699 views. Dr. Tanuja Nautiyal. One of the greatest problems that the world is facing today is that of environmental pollution, increasing with every passing year and causing grave and irreparable damage to the earth. Environmental pollution consists of five basic types of pollution, namely, air, water, soil, noise and light.
Water Pollution Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies e.g. lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers and groundwater) This form of environmental degradation occurs when pollutants are directly or indirectly discharged into water bodies without adequate treatment to remove harmful compounds. Water pollution affects the entire biosphere.
Simple Environmental Pollution Consulting Slides. Use our photo-centric Powerpoint templates to educate and bring awareness to the daunting businesses' environmental impacts. With a minimalist style and prominent hues of blue and brown, this template suits marketing presentations or educational sessions on climate change.
If you are searching for Pollution PPT.Then this is the right place. Here you will get more than 30 + PPT Powerpoint presentation on Pollution on all the topics related to pollution and the environment which you can easily download. Note: Because we have given more than 30 PPT in one place. So It may take time to open the preview of all the PPTs.
Get your hands on our high-quality Environmental Pollution PowerPoint template to describe the harmful impacts on the environment due to the release of various pollutants and substances. These pre-designed slides will reduce your presentation preparation time.
Download the "Biggest Environmental Issues" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic resources.
Environmental Pollution. Environmental Pollution. Environmental pollution can be defined as any undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological characteristics of any component of the environment ( air, water, soil), which can cause harmful effects on various form of life or property. 1.32k views • 99 slides
Free Environmental Pollution Template for PowerPoint and Google Slides. Main features. 40 slides 100% editable. 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all screens. High quality royalty-free images. Easy to edit layouts for presenting or printing. Included resources: charts, graphs, timelines and diagrams. More than 100 icons customizable in color ...
On April 6, 2023, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced a proposal to significantly reduce emissions of toxic and other harmful air pollution from chemical plants, including the highly toxic chemicals ethylene oxide (EtO) and chloroprene
This visually stimulating template on environmental protection, compatible with Google Slides and PowerPoint, adopts a naturally gentle, cream color scheme, accented by vibrant, illustrative symbols that encapsulate the spirit of Mother Nature herself. Ready to be fully customized to best suit your needs, this presentation template delivers ...