
Best Nursing Research Topics for Students
What is a nursing research paper.
- What They Include
- Choosing a Topic
- Best Nursing Research Topics
- Research Paper Writing Tips

Writing a research paper is a massive task that involves careful organization, critical analysis, and a lot of time. Some nursing students are natural writers, while others struggle to select a nursing research topic, let alone write about it.
If you're a nursing student who dreads writing research papers, this article may help ease your anxiety. We'll cover everything you need to know about writing nursing school research papers and the top topics for nursing research.
Continue reading to make your paper-writing jitters a thing of the past.
A nursing research paper is a work of academic writing composed by a nurse or nursing student. The paper may present information on a specific topic or answer a question.
During LPN/LVN and RN programs, most papers you write focus on learning to use research databases, evaluate appropriate resources, and format your writing with APA style. You'll then synthesize your research information to answer a question or analyze a topic.
BSN , MSN , Ph.D., and DNP programs also write nursing research papers. Students in these programs may also participate in conducting original research studies.
Writing papers during your academic program improves and develops many skills, including the ability to:
- Select nursing topics for research
- Conduct effective research
- Analyze published academic literature
- Format and cite sources
- Synthesize data
- Organize and articulate findings
About Nursing Research Papers
When do nursing students write research papers.
You may need to write a research paper for any of the nursing courses you take. Research papers help develop critical thinking and communication skills. They allow you to learn how to conduct research and critically review publications.
That said, not every class will require in-depth, 10-20-page papers. The more advanced your degree path, the more you can expect to write and conduct research. If you're in an associate or bachelor's program, you'll probably write a few papers each semester or term.
Do Nursing Students Conduct Original Research?
Most of the time, you won't be designing, conducting, and evaluating new research. Instead, your projects will focus on learning the research process and the scientific method. You'll achieve these objectives by evaluating existing nursing literature and sources and defending a thesis.
However, many nursing faculty members do conduct original research. So, you may get opportunities to participate in, and publish, research articles.
Example Research Project Scenario:
In your maternal child nursing class, the professor assigns the class a research paper regarding developmentally appropriate nursing interventions for the pediatric population. While that may sound specific, you have almost endless opportunities to narrow down the focus of your writing.
You could choose pain intervention measures in toddlers. Conversely, you can research the effects of prolonged hospitalization on adolescents' social-emotional development.
What Does a Nursing Research Paper Include?
Your professor should provide a thorough guideline of the scope of the paper. In general, an undergraduate nursing research paper will consist of:
Introduction : A brief overview of the research question/thesis statement your paper will discuss. You can include why the topic is relevant.
Body : This section presents your research findings and allows you to synthesize the information and data you collected. You'll have a chance to articulate your evaluation and answer your research question. The length of this section depends on your assignment.
Conclusion : A brief review of the information and analysis you presented throughout the body of the paper. This section is a recap of your paper and another chance to reassert your thesis.
The best advice is to follow your instructor's rubric and guidelines. Remember to ask for help whenever needed, and avoid overcomplicating the assignment!
How to Choose a Nursing Research Topic
The sheer volume of prospective nursing research topics can become overwhelming for students. Additionally, you may get the misconception that all the 'good' research ideas are exhausted. However, a personal approach may help you narrow down a research topic and find a unique angle.
Writing your research paper about a topic you value or connect with makes the task easier. Additionally, you should consider the material's breadth. Topics with plenty of existing literature will make developing a research question and thesis smoother.
Finally, feel free to shift gears if necessary, especially if you're still early in the research process. If you start down one path and have trouble finding published information, ask your professor if you can choose another topic.
The Best Research Topics for Nursing Students
You have endless subject choices for nursing research papers. This non-exhaustive list just scratches the surface of some of the best nursing research topics.
1. Clinical Nursing Research Topics
- Analyze the use of telehealth/virtual nursing to reduce inpatient nurse duties.
- Discuss the impact of evidence-based respiratory interventions on patient outcomes in critical care settings.
- Explore the effectiveness of pain management protocols in pediatric patients.
2. Community Health Nursing Research Topics
- Assess the impact of nurse-led diabetes education in Type II Diabetics.
- Analyze the relationship between socioeconomic status and access to healthcare services.
3. Nurse Education Research Topics
- Review the effectiveness of simulation-based learning to improve nursing students' clinical skills.
- Identify methods that best prepare pre-licensure students for clinical practice.
- Investigate factors that influence nurses to pursue advanced degrees.
- Evaluate education methods that enhance cultural competence among nurses.
- Describe the role of mindfulness interventions in reducing stress and burnout among nurses.
4. Mental Health Nursing Research Topics
- Explore patient outcomes related to nurse staffing levels in acute behavioral health settings.
- Assess the effectiveness of mental health education among emergency room nurses .
- Explore de-escalation techniques that result in improved patient outcomes.
- Review the effectiveness of therapeutic communication in improving patient outcomes.
5. Pediatric Nursing Research Topics
- Assess the impact of parental involvement in pediatric asthma treatment adherence.
- Explore challenges related to chronic illness management in pediatric patients.
- Review the role of play therapy and other therapeutic interventions that alleviate anxiety among hospitalized children.
6. The Nursing Profession Research Topics
- Analyze the effects of short staffing on nurse burnout .
- Evaluate factors that facilitate resiliency among nursing professionals.
- Examine predictors of nurse dissatisfaction and burnout.
- Posit how nursing theories influence modern nursing practice.
Tips for Writing a Nursing Research Paper
The best nursing research advice we can provide is to follow your professor's rubric and instructions. However, here are a few study tips for nursing students to make paper writing less painful:
Avoid procrastination: Everyone says it, but few follow this advice. You can significantly lower your stress levels if you avoid procrastinating and start working on your project immediately.
Plan Ahead: Break down the writing process into smaller sections, especially if it seems overwhelming. Give yourself time for each step in the process.
Research: Use your resources and ask for help from the librarian or instructor. The rest should come together quickly once you find high-quality studies to analyze.
Outline: Create an outline to help you organize your thoughts. Then, you can plug in information throughout the research process.
Clear Language: Use plain language as much as possible to get your point across. Jargon is inevitable when writing academic nursing papers, but keep it to a minimum.
Cite Properly: Accurately cite all sources using the appropriate citation style. Nursing research papers will almost always implement APA style. Check out the resources below for some excellent reference management options.
Revise and Edit: Once you finish your first draft, put it away for one to two hours or, preferably, a whole day. Once you've placed some space between you and your paper, read through and edit for clarity, coherence, and grammatical errors. Reading your essay out loud is an excellent way to check for the 'flow' of the paper.
Helpful Nursing Research Writing Resources:
Purdue OWL (Online writing lab) has a robust APA guide covering everything you need about APA style and rules.
Grammarly helps you edit grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Upgrading to a paid plan will get you plagiarism detection, formatting, and engagement suggestions. This tool is excellent to help you simplify complicated sentences.
Mendeley is a free reference management software. It stores, organizes, and cites references. It has a Microsoft plug-in that inserts and correctly formats APA citations.
Don't let nursing research papers scare you away from starting nursing school or furthering your education. Their purpose is to develop skills you'll need to be an effective nurse: critical thinking, communication, and the ability to review published information critically.
Choose a great topic and follow your teacher's instructions; you'll finish that paper in no time.

Joleen Sams is a certified Family Nurse Practitioner based in the Kansas City metro area. During her 10-year RN career, Joleen worked in NICU, inpatient pediatrics, and regulatory compliance. Since graduating with her MSN-FNP in 2019, she has worked in urgent care and nursing administration. Connect with Joleen on LinkedIn or see more of her writing on her website.

Plus, get exclusive access to discounts for nurses, stay informed on the latest nurse news, and learn how to take the next steps in your career.
By clicking “Join Now”, you agree to receive email newsletters and special offers from Nurse.org. We will not sell or distribute your email address to any third party, and you may unsubscribe at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Writing in Nursing
Although there may be some differences in writing expectations between disciplines, all writers of scholarly work are required to follow basic writing standards such as writing clear, concise, and grammatically correct sentences; using proper punctuation; demonstrating critical thought; and, in all Walden programs, using APA style. When writing in nursing, however, students must also be familiar with the goals of the discipline and discipline-specific writing expectations.
Nurses are primarily concerned about providing quality care to patients and their families, and this demands both technical knowledge and the appropriate expression of ideas (“Writing in nursing,” n.d). As a result, nursing students are expected to learn how to present information succinctly, and even though they may often use technical medical terminology (“Writing in nursing,” n.d.), their work should be accessible to anyone who may read it. Among many goals, writers within this discipline are required to:
- Document knowledge/research
- Demonstrate critical thinking
- Express creative ideas
- Explore nursing literature
- Demonstrate understanding of learning activities. (Wagner, n.d., para. 2)
Given this broad set of objectives, nursing students would benefit from learning how to write diverse literature, including scholarly reports, reviews, articles, and so on. They should aim to write work that can be used in both the research and clinical aspects of the discipline. Walden instructors often ask nursing students to write position and reflective papers, critique articles, gather and analyze data, respond to case studies, and work collaboratively on a project. Although there may be differences between the writing expectations within the classroom and those in the workplace, the standards noted below, though more common in scholarly writing, require skills that are transferrable to the work setting.
Because one cannot say everything there is to say about a particular subject, writers present their work from a particular perspective. For instance, one might choose to examine the shortage of nurses from a public policy perspective. One’s particular contribution, position, argument, or viewpoint is commonly referred to as the thesis and, according to Gerring et al. (2004), a good thesis is one that is “new, true, and significant” (p. 2). To strengthen a thesis, one might consider presenting an argument that goes against what is currently accepted within the field while carefully addressing counterarguments and adequately explaining why the issue under consideration matters (Gerring et al., 2004). The thesis is particularly important because readers want to know whether the writer has something new or worthwhile to say about the topic. Thus, as you review the literature, before writing, it is important to find gaps and creative linkages between viewpoints with the goal of contributing innovative ideas to an ongoing discussion. For a contribution to be worthwhile you must read the literature carefully and without bias; doing this will enable you to identify some of the subtle differences in the viewpoints presented by different authors and help you to better identify the gaps in the literature. Because the thesis is essentially the heart of your discussion, it is important that it is argued objectively and persuasively.
With the goal of providing high quality care, the healthcare industry places a premium on rigorous research as the foundation for evidence-based practices. Thus, students are expected to keep up with the most current research in their field and support the assertions they make in their work with evidence from the literature. Nursing students also must learn how to evaluate evidence in nursing literature and identify the studies that answer specific clinical questions (Oermann & Hays, 2011). Writers are also expected to critically analyze and evaluate studies and assess whether findings can be used in clinical practice (Beyea & Slattery, 2006). (Some useful and credible sources include journal articles, other peer-reviewed sources, and authoritative sources that might be found on the web. If you need help finding credible sources contact a librarian.)
Like other APA style papers, research papers in nursing should follow the following format: title, abstract, introduction, literature review, method, results, discussion, references, and appendices (see APA 7, Sections 2.16-2.25). Note that the presentation follows a certain logic: In the introduction one presents the issue under consideration; in the literature review, one presents what is already known about the topic (thus providing a context for the discussion), identifies gaps, and presents one’s approach; in the methods section, one would then identify the method used to gather data; and in the results and discussion sections, one then presents and explains the results in an objective manner, noting the limitations of the study (Dartmouth Writing Program, 2005). Note that not all papers need to be written in this manner; for guidance on the formatting of a basic course paper, see the appropriate template on our website.
In their research, nursing researchers use quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods. In quantitative studies, researchers rely primarily on quantifiable data; in qualitative studies, they use data from interviews or other types of narrative analyses; and in mixed methods studies, they use both qualitative and quantitative approaches. A researcher should be able to pose a researchable question and identify an appropriate research method. Whatever method the researcher chooses, the research must be carried out in an objective and scientific manner, free from bias. Keep in mind that your method will have an impact on the credibility of your work, so it is important that your methods are rigorous. Walden offers a series of research methods courses to help students become familiar with the various research methods.
Instructors expect students to master the content of the discipline and use discipline- appropriate language in their writing. In practice, nurses may be required to become familiar with standardized nursing language as it has been found to lead to the following:
- better communication among nurses and other health care providers,
- increased visibility of nursing interventions,
- improved patient care,
- enhanced data collection to evaluate nursing care outcomes,
- greater adherence to standards of care, and
- facilitated assessment of nursing competency. (Rutherford, 2008)
Like successful writers in other disciplines and in preparation for diverse roles within their fields, in their writing nursing students should demonstrate that they (a) have cultivated the thinking skills that are useful in their discipline, (b) are able to communicate professionally, and (c) can incorporate the language of the field in their work appropriately (Colorado State University, 2011).
If you have content-specific questions, be sure to ask your instructor. The Writing Center is available to help you present your ideas as effectively as possible.
Beyea, S. C., & Slattery, M. J. (2006). Evidence-based practice in nursing: A guide to successful implementation . http://www.hcmarketplace.com/supplemental/3737_browse.pdf
Colorado State University. (2011). Why assign WID tasks? http://wac.colostate.edu/intro/com6a1.cfm
Dartmouth Writing Program. (2005). Writing in the social sciences . http://www.dartmouth.edu/~writing/materials/student/soc_sciences/write.shtml
Rutherford, M. (2008). Standardized nursing language: What does it mean for nursing practice? [Abstract]. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing , 13 (1). http://ojin.nursingworld.org/MainMenuCategories/ThePracticeofProfessionalNursing/Health-IT/StandardizedNursingLanguage.html
Wagner, D. (n.d.). Why writing matters in nursing . https://www.svsu.edu/nursing/programs/bsn/programrequirements/whywritingmatters/
Writing in nursing: Examples. (n.d.). http://www.technorhetoric.net/7.2/sectionone/inman/examples.html
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Collaborative Writing in Business & Management
- Next Page: Learning Agreements (LAs)
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Online Research Guide for Nursing Students

- Conducting Online Research
- Research Tools
Evaluating Sources
- Organizing Research
Are you ready to earn your online nursing degree?

Effective online nursing research skills can make a tremendous difference for your academic success in nursing school and throughout your career. Medicine and nursing change rapidly, and knowing how to conduct nursing research online keeps your skills and knowledge current.
Successful research includes both how to use nursing literature search engines and how to analyze the information you find. This helps you distinguish between reliable information that supports evidence-based nursing and misleading information that can influence your ability to care for patients.
This guide can help you find and effectively use the best nursing research websites and other research tools, whether you need a writing guide for nurses , continuing education coursework, or just hope to increase your knowledge in the field.
Conducting Online Research for Nursing Students
You can conduct most of your nursing research online, but some sources may not be available online. For example, your school library may subscribe to print journals not published on the internet. Many important books only exist in print.
Your school or hospital librarian is an invaluable resource to help you find materials online or in print. If your school or hospital doesn’t have a specific book or article, the librarian might be able to get it through an interlibrary loan service.
You can use only online nursing research tools if the most significant publications on a topic are available online. Otherwise, consider using print resources too.
Refining Your Search Results
When conducting online research, you must filter out unreliable sources and locate search results relevant to your topic. Fortunately, Google searches and other nursing literature search engines have tools to help you narrow your research to get the most reliable results.
In addition to open web searches, you can use the specialty nursing literature search engines listed below.
Google Scholar
Google Scholar has special features to make it easier to find the most relevant professional literature on a topic. Besides letting you refine your search by date, it displays related articles or other articles by the author. If the piece is available in full-text online, Google Scholar links to the page. If not, you can search to see if your library has the article or can get you a copy.
Google Scholar also tells you how many other papers cite a particular source. While this doesn’t necessarily mean that an article has reliable and current information, it does demonstrate the article’s influence.
The search engine also offers tools to help you manage your research projects and write papers. You can create a citation in several standard formats and save an article to a list. You can make as many lists as you like, such as one for different topics or assignments.
If you want to follow a specific topic, refine your search to give you preferred results, and then select “create alert.” You will then receive emails with new articles as Google Scholar indexes them.
Online Research Tools
Google reigns as the most popular search engine, but many other online resources exist. Students may use several search engines and databases geared specifically toward academic searches. Many of these sites offer free or discounted services to students. Your school’s library may also provide access.
The list below describes some of the most common resources for academic research, including some sites that focus on online research for nurses.
General Academic Research Tools
- BASE : Bielefeld Academic Search Engine offers results in a variety of academic disciplines. About 60% of the indexed documents are available for free. Results must meet BASE’s high academic standards for relevance and quality.
- CGP : The Catalog of U.S. Government Publications allows users to search official documents published by the U.S. government, including current and historical sources.
- CIA World Factbook : The Central Intelligence Agency’s World Factbook provides information on 267 countries and other entities around the world. This information includes maps and data on each entity’s history, people, geography, government, and economy.
- ERIC : The U.S. Department of Education’s Institute of Education Sciences hosts ERIC. This database uses a formal review process to decide which scholarly articles, papers, reports, and other documents to include in its index.
- iSeek Education : This resource compiles scholarly materials from noncommercial providers, including university and government sources. The searchable service allows users to bookmark items they wish to refer to later.
- National Archives : This searchable catalog includes descriptions for 85% of the National Archives’ holdings, including documents, web pages, pictures, audio files, and videos. Users can also view more than two million digitized copies of government records.
- OCLC : The OAIster catalog pools open-access resources from libraries, museums, archives, and cultural heritage organizations.
- CORE : CORE collects open-access research materials from sources around the world and indexes them in a searchable database. The public can use CORE free of charge.
Nursing Research Tools
- CINAHL Complete : The Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature offers a large database of research material for nurses and students. The site provides full-text access to resources, including journals, care sheets, and continuing education modules.
- MedScape : Medscape provides the latest medical news, research updates, case studies, continuing education opportunities, and disease and drug information for healthcare professionals around the world.
- National Institute of Nursing Research : Part of the National Institutes of Health, the NINR provides support for nursing research. The website hosts information on research conducted through their programs.
- Nursing Reference Center : The Nursing Reference Center features various resources for nurses, including care sheets about diseases and treatment options, drug information, information on treating patients from diverse cultural backgrounds, patient handouts, and lessons about diseases and conditions.
- PubMed : PubMed is a searchable database operated by the U.S. National Library of Medicine at the National Institutes of Health. The site provides abstracts and full-text articles from journals, books, and other publications about life science and medicine.
- Sigma Repository : The Sigma Repository boasts an open-access database of nursing research and practice materials created by nurses. Sigma Theta Tau International, the nursing honor society, sponsors this free resource.
When you conduct research on the web, you must evaluate the reliability of your sources. If your information comes from an untrustworthy source, the quality of your research will suffer and the data you gather may lead to incorrect conclusions.
When you need to determine an online information source’s reputation, you can ask yourself some questions to help evaluate its quality. The questions below include tips from Georgetown University and the University of Chicago Press.
Who Is the Author?
Find the name of the article’s author or creator. Then locate the author’s credentials to determine whether their education and experience qualifies them to speak as an authority on the topic. You also can search for the author’s other works or more information about them.
If the source does not list an author, look at the domain to see whether it belongs to a reputable entity.
What Is Its Purpose?
Look at the article and the hosting site. Who is the intended audience? Is the information for academics and experts or the general public? Why was it written and posted? Is it intended to inform or educate the reader, or does it attempt to persuade the reader to view a topic in a certain way? Is it meant to sell a product or service?
A noncommercial source that intends to educate the reader without persuasion is most likely to be reliable.
Does It Look Professional?
When you view the website and read the article, take note of any errors in grammar or spelling. The site’s content should appear clean and organized. Poorly organized content and errors in the text indicate unprofessionalism, as does the use of profanity.
If the site emphasizes images over text or appears to focus on selling products or services, it may not be a reliable source for scholarly information.
Is It Objective?
Academic sources should show objectivity and must not present opinions as hard data. Consider whether the information is fact or opinion. Does the author show any bias? Is the information officially endorsed or approved by an organization? If so, determine whether the organization takes an official position on the issue at hand.
Is It Current?
When researching science and medical topics, students must find the most current information. Scientific knowledge progresses rapidly, and new research appears frequently.
Check the publishing date listed on your source. If it is more than a few years old, look for more current sources on the same topic. If a website has not been updated recently, this also may indicate information is outdated.
What Sites Does It Link To?
The links featured in your source may provide clues about the information’s reliability. The links should relate to the site’s purpose or the topic at hand. In most cases, a source should link back to research which supports the text. Students may find this information within the text or in a references list.
Test the links to make sure they work. If the links are broken, the information may be old or outdated.
Organizing Your Research
You will most likely browse a large amount of information as you conduct research online. To avoid becoming overwhelmed, you must remain organized before, during, and after your search. Remember that you must cite all your sources accurately.
If you develop a consistent system for locating and organizing your information, your research efforts will be more efficient and accurate. Below are a few basic tips to help you manage and organize your online research.
Online Tools to Manage Your Research
- EasyBib : This tool helps you improve your writing, take notes, avoid unintentional plagiarism, and add citations in your choice of style. Options include MLA, APA, and Chicago. EasyBib offers basic services and MLA citations for free. Users pay a monthly fee for additional access.
- Endnote : This software package manages references and bibliographies. EndNote provides research tools and allows teams to share documents, files, and other materials. The software offers student pricing.
- Mendeley : Designed for science and technology research, Mendeley helps store and organize research documents and files. Mendeley manages citations and lets users connect with others in a research network.
- RefWorks : This web-based reference management tool stores the user’s reference database in an online portal. Some universities grant their students free access to RefWorks.
- Zotero : This free, open-source software helps users find research materials and organize their information. Zotero manages citations, documents, and other research materials.
Citing Online Resources for Nursing Students
When you write a research paper or create a research presentation, you must follow a consistent format and include a bibliography of all the sources you used. Several popular editorial styles exist. Science and social science disciplines, including nursing, most frequently use the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, commonly known as APA style .
Alternatively, some institutions require AMA style , created by the American Medical Association. The style you use depends on the institution you attend. These editorial styles establish a consistent format for researchers to follow when publishing their work. They cover aspects of writing, such as punctuation, accepted abbreviations, headings, and formatting for statistics and tables.
Style also dictates a specific format for listing citations, including the order in which the information must appear and the punctuation required. This formatting makes it easy for readers to retrieve sources that may interest them.
Several examples of APA style from the Purdue Online Writing Lab appear below. You can find an expanded list of such examples on the Purdue website.
Articles From Online Periodicals
What is a doi.
When an article is published electronically, the publisher assigns a unique digital object identifier (DOI) to it. The DOI provides a permanent identification code and internet link for the article. APA style recommends that you include the DOI in any citation for which it is available. See the examples below.
Author, A. A., & Author, B. B. (Date of publication). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number , page range. doi:0000000/000000000000 or http://doi.org/10.0000/0000
Brownlie, D. (2007). Toward effective poster presentations: An annotated bibliography. European Journal of Marketing, 41 , 1245-1283. doi:10.1108/03090560710821161
Without DOI
Author, A. A., & Author, B. B. (Date of publication). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number . Retrieved from https://www.journalhomepage.com/full/url/
Kenneth, I. A. (2000). A Buddhist response to the nature of human rights. Journal of Buddhist Ethics, 8 . Retrieved from https://www.cac.psu.edu/jbe/twocont.html
Newspaper Articles
Author, A. A. (Year, Month Day). Title of article. Title of Newspaper . Retrieved from https://www.homeaddress.com/
Parker-Pope, T. (2008, May 6). Psychiatry handbook linked to drug industry. The New York Times . Retrieved from https://well.blogs.nytimes.com/
Electronic Books
Last name, A. A. (n.d.). Title . Available from https://www.urlofebook.com/full/url/
Davis, J. (n.d.). Familiar birdsongs of the Northwest . Available from https://www.powells.com/cgi-bin/biblio? inkey=1-9780931686108-0
The AMA Manual of Style details official guidelines for writing and citing medical research. The style is maintained by the American Medical Association. The examples below originate from the Arizona Health Sciences Library website and the USciences website .
No Author Name Provided
Name of organization. Title of specific item cited. URL. Accessed date.
International Society for Infectious Diseases. ProMED-mail Website. https://www.promedmail.org. Accessed April 29, 2004.
Author Name Provided
Author A. Title. Name of website. URL. Updated date. Accessed date.
Sullivan D. Major search engines and directories. SearchEngineWatch Website. https://www.searchenginewatch.com/links/article.php/2156221. Updated April 28, 2004. Accessed December 6, 2005.
Online Journal Article With Six or Fewer Authors — DOI Included
Author A. Title. Name of online journal. URL. Publication year;volume(issue):page numbers. doi.
Florez H, Martinez R, Chakra W, Strickman-Stein M, Levis S. Outdoor exercise reduces the risk of hypovitaminosis D in the obese. J Steroid Biochem Mol Bio . 2007;103(3-5):679-681. doi:10.1016 /j.jsbmb.2006.12.032.
Online Journal Article With Six or More Authors — DOI Not Included
Author A. Title. Name of online journal. URL. Publication year;volume(issue):page numbers. Access date.
Siris ES, Miller PD, Barrett-Connor E, et al. Identification and fracture outcomes of undiagnosed low bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: results from the National Osteoporosis Risk Assessment. JAMA. 2001;286(22):2815-2822. https://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/reprint/286/22 /2815. Accessed April 4, 2007.
Related Articles

Tips for Giving Presentations in Your Online Nursing Class
Online student presentations can seem scary. With this guide, expert nurses offer advice on the best presentation websites for students and other tips for online students.

Study Tips and Resources for Surviving Nursing Finals
Nursing finals can be an extremely stressful time for students. These expert tips from Dr. Audrey Auer can help you minimize your stress and study more efficiently.

Passing the NCLEX: Tips from Nurses
The NCLEX contains a significant amount of information, which can certainly feel overwhelming to anyone preparing. These expert tips and resources can guide you through the study process.
Whether you’re looking to get your pre-licensure degree or taking the next step in your career, the education you need could be more affordable than you think. Find the right nursing program for you.
You might be interested in

HESI vs. TEAS Exam: The Differences Explained
Nursing schools use entrance exams to make admissions decisions. Learn about the differences between the HESI vs. TEAS exams.

10 Nursing Schools That Don’t Require TEAS or HESI Exam

For Chiefs’ RB Clyde Edwards-Helaire, Nursing Runs in the Family

Curse of a Nurse
Exposed to the golden wind in awakening there is limitless life, liberation, and love in holy harmony, health, and happiness, writing a nursing research question – undergraduate nursing.
Most undergraduate BSN students take a Research and Evidence-Based Practice course. Students are often assigned a small research project or review paper. The assignment begins with writing either a research question, or a clinical question. Usually, the student is given a range of topics, but let’s assume the student is starting from scratch. A good research question is essential to good research and not only answering a question but filling the gaps. I suggest you start my thinking of a research paper as a “who done it” story. Who killed X. What is your method going to be for figuring out who the killer is. Then you apply methods to the facts. Next you identify the killer using for example fingerprints, interrogations, and ballistic testing of the bullet. After you have the evidence, your results, you discuss the results. Finally, discuss the effectiveness of the methods. You conclude by saying in the future you can use these methods to do X, Y, and Z.
STEP 1: Review Variables
Before you start thinking about writing a research question it is good to review the difference between independent and dependent variables.
- Independent variable – a variable that is presumed to influence another variable. It is the variable the researcher can manipulate.
- Dependent variable –the effect. Its value depends on changes in the independent variable. It is what is being measured.
You will also need an operational definition, so it is possible to measure and manipulate the variable. The operational definition is essentially your measure.
STEP 2: Find a Topic and then Narrow
What is your research problem? It should be an area of concern where there is a gap in knowledge necessary for good nursing practice.
STEP 3: Narrow the Topic
Even if a broad area is given, you still need to narrow the topic. Some ways to do that include:
- Choose an interesting topic from within the scope of your assignment.
- Start with general references sources. Most universities have a search engine such as WorldCat for books, journals, articles, and more. Another place to start may be GoogleScholar. You only need a few articles to see what scholars in the area are doing and to help narrow your topic.
- Are there subtopics?
- Do the subtopics raise any specific questions?
- What is of specific interest to you?
- Are there how and why questions about this topic I should ask?
- Consider who your intended audience is for your research. There may be a tendency to think it is your class or your professor, but I suggest you think broader and decide who you want to be your audience, not who the class requires.
- Identify a theory or research finding within the assignment that needs further testing.
- Consider a patient care experience that impacted on the nurse’s or the patient’s experience.
- Talk to your colleagues and classmates. Be willing to question authority. Too much of what we do results from the way it has always been.
- Identify a knowledge gap.
- Apply personal experience and take the time to consider what is important to you. The research question should be more than a class assignment. It is an opportunity to express your concern about what matters and your commitment to taking responsibility for what happens to patients and nurses.
- Make a final research question selection by considering whether the idea is innovative, significant, reasonable, ethical, and will promote health equity.
STEP 3: Write Your Research Question
The FINER criteria are one way to write a good question (Hulley et al., 2007).
- The question should be feasible . Focus on one problem that can be accomplished within the semester and the time allotted for the assignment and is within your ability. Try not to have more than one or two variables.
- The question should be interesting to you. Even within limited topic made available to you choose what is most interesting and tweak it. If you are interested in the topic you will be more motivated.
- The question should be novel . You should bring new insights to the chosen topic. This may include confirming or expanding on prior research. There must be primary and secondary sources available to help answer your question.
- The question must be ethical and avoid any deceptive practices, such as only including articles that support your conclusion. Your research question and study must be able to be approved by appropriate review boards or authorities.
- The questions should be relevant to the assignment and of interest to nursing. It should also be relevant to public interest.
Ratan et al. (2019) add to FINER in their research question guide. They suggested the purpose of your paper and should be feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, relevant, manageable, appropriate, have potential value and publishability, and be systematic (Read more: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6322175/ ).
- A manageable question can be managed by the researcher.
- The research question should be appropriate logically and scientifically.
- The research should have significant health impact and be of value and publishable .
Draft your research question based on what you hope to achieve. You can have primary and secondary research questions but remember that more questions generally mean more time and resources. McCombes (2019) suggest the table below as a way to consider drafting your research question.
Many nurses use the PICOT framework to construct research questions. If you prefer the PICOT format then follow this format.
- P – patient or population (age, gender, location, characteristics)
- I – intervention (diagnostic test, exposure, management strategy)
- C – comparison group (a comparison to the intervention or indicator)
- O – outcome (what are the consequences of the intervention)
- T – timeframe or type of the study (time periods that should be considered or study types most likely to have relevant information)
STEP 4: Evaluate Your Question
- Can you identify the relationship between the variables?
- Did you indicate the population to be studied?
- Did you identify a problem that can be addressed (in the time available)?
STEP 5: Making your research question strong
Focused, clear, feasible, specific, and researchable, complex and arguable, relevant, original, and clear.
Burns, N. and Grove, S.K. (2001) The Practice of Nursing Research: Conduct, Critique, and Utilization, 5 th ed. Elsevier Saunders.
Hulley, S.B., Summings, S.R., Browner, W.S., Grady, D.G., Newman, T.B. (2007) Desiging Clinical Research. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Kerlinger, F.N. (1979) Behavioral Research: A Conceptual Approach. Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
McCombes, S. (2021) Developing strong research questions. Scribbr. https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-questions/
Polit, D. and Beck. C.T. (2022) Essential of Nursing Research: Appraising Evidence for Nursing Practice, 10 th Ed. Wolters Kluwer.
Ratan, S. K., Anand, T., & Ratan, J. (2019). Formulation of Research Question – Stepwise Approach. Journal of Indian Association of Pediatric Surgeons , 24 (1), 15–20. https://doi.org/10.4103/jiaps.JIAPS_76_18 .
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Leave a Reply Cancel reply

- Welcome to the Lewis Library This link opens in a new window
- What is Peer-Reviewed Information?
- Literature Reviews
- Evidence-Based Practice
- Primo - The Library Discovery Tool
- Elements of Keyword Searching
- Using CINAHL Complete
Beginning a Nursing Research Assignment
- Types of Research Articles
- What Kind of Article Is This?
- Concept Analysis
- Nursing Theory / Conceptual Framework
- Find Articles with a Nurse as an Author
- Nonparametric Tests
- Global Group Presentation - Professional Development I
- Simulations and Streaming Video
- Health Statistics
- Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Citation Style Resources - APA
Beginning a Literature Search, first decide: What kind of Information do you need to find?
What is the assignment?
There may be many different types of research assignments that you may encounter throughout your nursing career. Here, we will explain some of the most common nursing research assignments that are encountered:
- Nursing Theory or Conceptual Framework
- Finding Articles Written by Nurses
Below are some general criteria that are almost always used in nursing research assignments :
- Peer-reviewed articles
- Must be within the last 5 years of publication
- The articles must be nursing-related, preferably from a nursing journal and/or having a nurse as one of its authors.
- Sometimes you must also find articles from an English-speaking country.
- << Previous: Using CINAHL Complete
- Next: Types of Research Articles >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2024 8:51 AM
- URL: https://lewisu.libguides.com/nursing

- EMU Library
- Research Guides
NURS 300 - Reading & Writing in Nursing Studies
- Introduction to Nursing Research
- Journal Article Databases
- Getting full-text articles
- Recognizing a Primary Research Article
- General Health Information
- Citing Sources
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Frequently Requested Definitions
- Contact a Librarian
- Class Handouts
Introduction – Read This Box!
Finding research materials to complete assignments for nursing can sometimes be difficult, but nursing students are smart, intelligent people, and are up to the challenge!
Follow each step below and use the instructions and resources on this page to help you find materials to complete your research assignments. View all five steps then review the sample search at the bottom of the page.
Read the rubric for your assignment(s) so you know what type of research you are expected to find for your particular assignment(s).
This is very important! When you are searching any database from the Halle Library, e.g., CINAHL , DO NOT CHECK the Linked to Full Text boxes ever . Doing this inhibits the green Find Text+ icon from accessing all of the full text materials that are available.
Read the materials and watch the videos linked below in the exact order in which they are listed. Each one explains a skill or a piece of information that will guide you to the next step and help you complete the assignment.
Videos to Watch and Materials to Read
https://guides.emich.edu/ld. php?content_id=42662440 https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=9dwQdDUV_dQ&feature=youtu.be
5) CINAHL - Limiting by Language - https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=r725aqglgiM&feature= youtu.be
Look at the topics from the table below. Evaluate which keyword or phrase from the table below most closely matches your research topic, then carefully select your keywords. Some of these keywords & phrases are more specific than others. Remember, the terms below are just a few ideas. You can always type in your own keywords.
In CINAHL , it is sometimes possible to locate more specific terms by searching the CINAHL Subject Headings . This is done by logging into CINAHL , clicking on the link located on the top of the page, on the blue bar called, CINAHL Subject Headings . Here is a short video that explains how to do optional activity: https://guides.emich.edu/c.php?g=653525&p=5516023&preview=5ef4d05ab8949abfaaf109e4c93573e9
CINAHL Keywords or Search Terms Commonly Used for Nursing Research Topics
A Sample Search
In this imaginary assignment, the topic I’m interested in researching centers around patient safety and how many patients are assigned to each nurse on a given shift.
Step #1 – I look over the keywords and phrases from the table above and decide that “nurse patient ratio” and “patient safety” most closely capture my topic. So, I copy and paste the search into the CINAHL search boxes. (By the way, it doesn’t matter which keyword or phrase is placed in which search box. Each box is treated equally.)
First search box: “nurse patient ratio”
Second search box : “patient safety”
I have read my assignment’s rubric, so I know I have to select a research-based article from a peer reviewed journal from the last 10 years, and I only read and speak the English language. So, I scroll down the Advanced Search page under the Search Options section and I:
- DO NOT check the box in front of Linked Full Text
Do check the box in front of:
- Research Article
- English Language (unless I’m fluent in another language)
- Scholarly (Peer Reviewed) Journals
- In the Published Date area, in the Year box, I type in 2010 in one box and 2020 in the other box
- Next: Journal Article Databases >>
'Basic Research & Writing Skills in Nursing' Workshop Video
- 'Basic Research & Writing Skills in Nursing' Workshop Video
- Last Updated: Feb 23, 2024 1:18 PM
- URL: https://guides.emich.edu/nurs300
Research Topics & Ideas: Nursing
50+ Nursing Research Topic Ideas To Fast-Track Your Project

Finding and choosing a strong research topic is the critical first step when it comes to crafting a high-quality dissertation, thesis or research project. If you’ve landed on this post, chances are you’re looking for a nursing-related research topic , but aren’t sure where to start. Here, we’ll explore a variety of nursing-related research ideas and topic thought-starters, including general nursing, medical-surgical nursing, pediatric nursing, obstetrics and gynaecological nursing, ICU and mental health nursing.
NB – This is just the start…
The topic ideation and evaluation process has multiple steps . In this post, we’ll kickstart the process by sharing some research topic ideas within the nursing domain. This is the starting point, but to develop a well-defined research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , along with a well-justified plan of action to fill that gap.
If you’re new to the oftentimes perplexing world of research, or if this is your first time undertaking a formal academic research project, be sure to check out our free dissertation mini-course. In it, we cover the process of writing a dissertation or thesis from start to end. Be sure to also sign up for our free webinar that explores how to find a high-quality research topic.
Overview: Nursing Research Topics
- General nursing-related topics
- Medical-surgical nursing
- Pediatric nursing
- Obstetrics and gynaecological nursing
- ICU nursing
- Mental health nursing
General Nursing Research Topics & Ideas
- The impact of cultural competence on patient care in the UK
- The importance of evidence-based practice in nursing for patients with HIV/AIDS
- The effects of workplace stress on nurse well-being and performance
- The role of nurse-patient communication for patients transitioning from adolescent to adult care
- The impact of technology on nursing practice and patient outcomes
- The importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in healthcare for the rehabilitation of patients post-surgery
- The effects of fatigue on nurse performance in the emergency room
- The impact of nurse staffing levels on patient outcomes in rural areas
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in managing chronic conditions: a case study of diabetes
- The impact of patient-centred care on health outcomes for the elderly
- The importance of patient safety in nursing: bedside nurse vigilance
- The effects of empathy and compassion in critical care nursing
- The role of nursing in disaster preparedness and response: a case study of the Haiti earthquake of 2021
- The impact of the level of nursing education on patient outcomes
- The importance of ethical considerations in frail care nursing practice
Topics & Ideas: Medical-Surgical Nursing
- The impact of bedside care on patient outcomes in medical-surgical units
- The role of the nurse in managing post-operative patient pain
- The effects of nurse-patient ratios on patient outcomes in medical-surgical units
- A systematic review of different approaches to patient education in medical-surgical units
- The relationship between nurse-patient communication and patient satisfaction in medical-surgical units: perspectives and recommendations to improving patient satisfaction
Topics & Ideas: Pediatrics Nursing
- The impact of family-centered care on pediatric patient outcomes with sickle cell anemia
- The role of nursing interventions in promoting developmental and behavioral health in pediatric patients
- The effects of play therapy on anxiety and pain in pediatric patients during hospitilisation
- A systematic review of different approaches to pain management in pediatric cancer patients
- The relationship between parent involvement and post-operative patient outcomes in pediatric units

Ideas: Obstetrics and Gynecological Nursing
- The impact of nurse-led prenatal care on maternal and fetal outcomes in African American communities
- The role of the nurse in promoting sexual and reproductive health for women in the UK
- The effects of midwifery care on maternal satisfaction of primiparous women and birth outcomes
- A comparative study of different approaches to childbirth education for expectant mothers and partners: perceptions of control
- The relationship between lactation support and breastfeeding success of primiparous women
Topics & Ideas: ICU Nursing
- The impact of nursing interventions on patient outcomes in intensive care units in a developing country
- The role of the nurse in managing palliative and end-of-life care in the ICU
- The effects of family presence on patient outcomes and satisfaction in the ICU: A systematic review of the literature
- A comparative study of different approaches to pain management for trauma patients in the ICU
- The relationship between nurse-patient communication and geriatric patient outcomes in ICU

Topics & Ideas: Mental Health Nursing
- The impact of nurse-led therapy on adolescent patient outcomes in mental health settings
- The role of the nurse in promoting recovery and resiliency in mental health patients through group interventions
- The effects of mindfulness-based interventions on stress and anxiety in mental health patients: A systematic literature review
- A comparative study of the role of nurses in applying different approaches to patient education in mental health settings
- The association between nurse-patient therapeutic alliance and patient outcomes in mental health settings
Nursing Dissertation & Theses
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a nursing-related research topic, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses to see how this all comes together.
Below, we’ve included a selection of research projects from various nursing-related degree programs to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- Nursing Workload and Interventions of Licensed Nurses in Nursing Homes: An Observational Time and Motion Study (Kang, 2021)
- Missed Nursing Care: Accounting for Education, Experience, and Job Satisfaction in Registered Nurses (Bechard, 2021)
- Examining Predictors of Attitudes and Knowledge of Registered Nurses and Nursing Students in Tennessee toward Pregnant and Perinatal Women with a Substance Use Disorder (Patrylo, 2021)
- A Program Evaluation of the Organizational Readiness for Pathway to Excellence at Two Community Hospitals (Behling, 2021)
- The Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic Policy Decisions on the Wellbeing of Nursing Home Residents in Missouri (White, 2022)
- Battling A Parallel Pandemic: An Evaluation of Sustainable System-Level Nursing Support in Response To COVID-19 (Gifford, 2022)
- Holistic Nursing Process Maps: a Tool for Student Nurses to Operationalize the Nursing Process to Increase Clinical Reasoning (Reyes, 2022)
- Satisfaction and Work-Life Balance in Undergraduate Nursing Faculty: A Mixed-Methods Study (Crawford, 2021)
- The Effect of Mindfulness Meditation on the Stress, Anxiety, Mindfulness, and Self-Compassion Levels of Nursing Students (Heinrich, 2022)
- Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Case Studies in Undergraduate Nursing Students (Becnel, 2022)
- A Telehealth Simulation Experiment: Exploring Prebriefing (Owen, 2022)
- Perceptions of Lateral Violence Among Vocational Nursing Students, Associate Degree Nursing Students, and Bachelor’s Degree Nursing Students (Martha, 2022)
- Nurse Educators’ Description of Ethics from a Disciplinary Perspective: A Qualitative Descriptive Research Study (Cuchetti, 2022)
- A Literature Review of the Relationship Between Oral Health and Pneumonia Risk in the Geriatric Nursing Home Population (Swift, 2021)
Looking at these titles, you can probably pick up that the research topics here are quite specific and narrowly-focused , compared to the generic ones presented earlier. This is an important thing to keep in mind as you develop your own research topic. That is to say, to create a top-notch research topic, you must be precise and target a specific context with specific variables of interest . In other words, you need to identify a clear, well-justified research gap.
Get 1-On-1 Help
If you’re still feeling a bit unsure about how to find a research topic for your nursing dissertation, thesis or research project, check out our private coaching services below.

You Might Also Like:

To learn from the GRAD Coach is a lofty goal for me. I am unable to express my gratitude for your teaching style. I need assistance with my thesis as a master’s in nursing candidate. Please assist me.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

The Ultimate Guide to Nursing Assignments: 7 Tips and Strategies
Nursing assignments are a critical component of every nursing student’s academic journey. They serve as opportunities to test your knowledge, apply theoretical concepts to real-world scenarios, and develop essential skills necessary for your future nursing career. However, tackling nursing assignments can often be overwhelming, particularly when you’re juggling multiple responsibilities. In this comprehensive guide, we provide valuable tips, strategies, and expert assignment help services to help you excel in your nursing assignments. Whether you’re struggling with research, structuring your assignment, or proofreading, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding the Nursing Assignments
To excel in nursing assignments , it’s crucial to start by thoroughly understanding the requirements. Take the time to carefully read the assignment prompt, paying close attention to the topic, word count, formatting guidelines, and any specific instructions provided by your instructor. Understanding these key components will ensure that you meet all the necessary criteria.

Conducting Thorough Research
Once you have a clear understanding of the assignment, it’s time to conduct thorough research. Solid research forms the foundation of any successful nursing assignment. Begin by gathering relevant and credible sources, such as nursing textbooks, scholarly articles, reputable websites , and academic databases specific to nursing. These resources will provide you with evidence-based information to support your arguments and demonstrate your understanding of the topic.
Creating a Well-Structured Outline
A well-structured outline is essential for organizing your thoughts and ensuring a logical flow in your nursing assignment. An effective outline acts as a roadmap, guiding you through the writing process and ensuring that you cover all the necessary points.
At [Your Service Name], our expert writers can assist you in creating a comprehensive outline tailored to your specific assignment. By collaborating with us, you can receive personalized guidance in organizing your ideas effectively and structuring your assignment in a logical manner. Our writers understand the nuances of nursing assignments and can help you identify the most important concepts and supporting evidence to include.
Using a Professional Tone
Maintaining a professional tone throughout your nursing assignment is crucial. As aspiring healthcare professionals, it’s essential to communicate your ideas with clarity, conciseness, and professionalism. Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or slang that may hinder the reader’s understanding. Present your arguments and supporting evidence in a logical and coherent manner, demonstrating your ability to think critically and apply nursing principles.
Our expert writers have extensive experience in academic writing within the field of nursing. They possess a deep understanding of the professional tone required for nursing assignments and can ensure that your assignment is written to the highest standards. By collaborating with us, you can receive guidance in maintaining a professional tone and effectively conveying your ideas.

Incorporating Practical Examples
In addition to a professional tone, incorporating practical examples into your nursing assignment can greatly enhance its quality. Practical examples bring theoretical concepts to life, illustrating their application in real-life scenarios. They demonstrate your understanding of nursing principles and showcase your ability to bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Our team consists of experienced nursing professionals who can assist you in incorporating relevant practical examples into your assignment. Drawing from their extensive knowledge and expertise, they can provide you with real-life scenarios or case studies that strengthen the impact and credibility of your work. By collaborating with us, you can elevate the quality of your assignment by demonstrating your ability to apply nursing concepts in practical settings.
Proofreading and Editing
Proofreading and editing are essential steps in the assignment writing process. They ensure that your nursing assignment is polished, error-free, and effectively communicates your ideas. After completing the initial draft, it’s crucial to take a break and return to your work with fresh eyes. During the proofreading stage, carefully review your assignment for grammar, spelling, punctuation, and sentence structure. Correct any errors and inconsistencies that may affect the clarity and professionalism of your writing.
At nursingresearchhelp.com , we have a dedicated team of proofreaders and editors who specialize in nursing assignments. They meticulously review your work, ensuring that it adheres to formatting guidelines and meets the highest standards of academic writing. Our proofreaders and editors will help you refine your assignment, ensuring that it is polished and error-free. By collaborating with us, you can rest assured that your assignment will be thoroughly reviewed and refined before submission.
Seeking Help When Needed
In addition to proofreading and editing, it’s important to seek help when needed. Nursing assignments can be challenging, and it’s perfectly normal to require assistance. Whether you’re facing difficulties in understanding the assignment prompt, need guidance in specific areas, or simply want a fresh perspective on your work, don’t hesitate to reach out for support.
Our friendly and knowledgeable support team is always available to address any questions or concerns you may have. We understand the unique challenges faced by nursing students and can provide you with the guidance and clarification you need. By seeking help when needed, you can overcome obstacles and ensure the successful completion of your nursing assignments.
Mastering nursing assignments is within your reach with the right tips, strategies, and expert assignment help services. At nursingresearchhelp.com we are committed to supporting nursing students in excelling in their academic pursuits. Our experienced writers, proofreaders, and editors can provide personalized assistance throughout the assignment writing process, ensuring that your assignments meet the highest standards of quality and professionalism.
With our help, you can confidently tackle your nursing assignments and overcome any challenges you may face. Visit our website nursingresearchhelp.com to learn more about our services and how we can support you in achieving academic excellence. Whether you need guidance in understanding the assignment, conducting thorough research, creating a well-structured outline, using a professional tone, incorporating practical examples, or ensuring a polished final product, we are here to assist you. Trust us for reliable and professional assignment help tailored to your needs.
Don’t let the challenges of nursing assignments hold you back—reach out to us for reliable and professional assignment help tailored to your needs.
You might also like

Nursingresearchhelp.com is the fastest, easiest and most reliable way to have content written for your website. You’ll be able to post a project and 1000s of freelance writers from across the globe will have instant access to write your content quickly, professionally, and affordably.
QUICK LINKS
- HOW IT WORKS
- OUR SERVICES
- TERMS OF USE

Call/Text: +1 608 912 3884


Research Methods in Nursing
Qualitative, quantitative, observational, correlational, quasi-experimental, experimental, mixed-methods, triangulation, ask a librarian.
- Types of Studies
- Evidence Based Practice
- PICO & MeSH Searching
- Recommended Databases
- Evaluating Sources
- Library Instructional Videos
- Off Campus Access to Databases
- Citation Styles This link opens in a new window
- Monday-Thursday: 9 a.m. – 7 p.m.
- Friday: 9 a.m. – 5 p.m.
- Saturday: 2 – 6 p.m.
- Sunday: 1 – 5 p.m.
QUALitative research "is best suited for research aimed at rich description or in-depth understanding of a phenomenon, rather than determining causality; it is particularly useful in understanding the relevance of contextual features in the expression of the phenomenon. Qualitative approaches are most often chosen when little is known about a topic or when new perspectives are needed; other functions of qualitative approaches include generating hypotheses, refining theory, providing illustrative examples, creating taxonomies, and generating items for instrument development.
Relying primarily on inductive rather than deductive processes, qualitative studies generally share several “ground-up” features that differentiate them from “top-down” quantitative research. These features are driven by two central tenets: an orientation to cases rather than variables, as well as a preference for emergent rather than fixed designs."
More Information from Encyclopedia of Nursing Research
Four types of qualitative research design often applied to nursing research are:
- Phenomenology - the study of human life experiences and how they appear in human consciousness
- Grounded Theory - seeks to explain variations in social interactional and social structural problems and processes
- Ethnography - As a research process, ethnography is a comparative method for investigating patterns of human behavior and cognition through observations and interactions in natural settings
- Narrative Inquiry - the analysis of meaning in context through interpretation of persons' life experiences
For more details , look up these research designs in:
Encyclopedia of Nursing Research
Dictionary of Nursing Theory and Research
QUANtitative research "consists of the collection, tabulation, summarization, and analysis of numerical data for the purpose of answering research questions or hypotheses. The term quantitative research is of recent origin and is distinguished from qualitative research in design, process, and the use of quantification techniques to measure and analyze the data. The vast majority of all nursing studies can be classified as quantitative.
Quantitative research uses statistical methodology at every stage in the research process. At the inception of a research project, when the research questions are formulated, thought must be given to how the research variables are to be quantified, defined, measured, and analyzed. Study subjects are often selected for a research project through the statistical method of random sampling, which promotes an unbiased representation of the target population among the sample from whom generalizations will be made. Statistical methods are used to summarize study data, to determine sampling error, and in studies in which hypotheses are tested, to analyze whether results obtained exceed those that could be attributed to sampling error (chance) alone."
Quantitative Research Design can be Non-Experimental (Descriptive or Correlational) or Experimental (including Quasi-Experimental).
" Observational designs are nonexperimental, quantitative designs. In contrast to experimental designs in which the investigator manipulates the independent variable and observes its effect, the investigator conducting observational research observes both the independent and dependent variables. In observational studies, variation in the independent variable may be due to genetic endowment, self-selection, or occupational or environmental exposures."
" Correlational research examines the relationships between variables, but unlike experimental or quasi-experimental studies, correlational studies lack active manipulation of the independent variable(s). Therefore, postulation of relationships among study variables in causal terms is risky. Discussion of associations in correlational studies, however, sometimes gives an indication of how likely it is that a cause-and-effect relationship might exist."
More Information from Dictionary of Nursing Theory and Research
" Quasi-experimental research is similar to experimental research in that there is manipulation of an independent variable. It differs from experimental research because there is no control group, no random selection, no random assignment, and/or no active manipulation. Quasi-experimental research is a useful way to test causality in settings when it is impossible or unethical to randomly assign subjects to treatment and control groups or to withhold treatment from some subjects."
Experimental research "involves manipulation of the principal independent variable, i.e., the actual administration of treatments or interventions that comprise the categories of the independent variable. An investigation is made of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
A true experiment is characterized by random assignment of individual subjects to the treatment conditions and a high degree of control over unwanted influence of extraneous variables and other factors that could bias the results of the study."
"True experiments have the potential to provide strong evidence about the hypothesized causal relationship between independent and dependent variables. Experiments are characterized by manipulation, control, and randomization. The quality of experiments depends on the validity of their design."
" Mixed methods research is a term associated with research that uses a combination of methods that are usually identified with qualitative research and methods that are usually identified with quantitative research. It should not be confused with the terms mixed models or mixed effects that are used in other contexts such as the analysis of variance.
It is important to understand that the use of a mixed methods approach does not make research better or more valid than the use of either a qualitative or a quantitative approach."
"In nursing research, triangulation refers to the use of multiple sources to validate findings by the nursing researcher. It involves the combination of both quantitative and qualitative research methods within a single study."
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Types of Studies >>
- Last Updated: Dec 14, 2023 2:53 PM
- URL: https://angelo.libguides.com/nursingrm

Nursing Research
- Finding Nursing Books
- Overview - Finding Current Nursing Articles
Sample Assignment
- Searching CINAHL Complete
- Searching OVID Nursing Full Text Plus
- Accessing NCLEX Test Prep
- Films on Demand - Streaming Video
- Research Question
- Purpose Statement
- Literature Review
- Informed Consent
- Data Collection
- Data Analysis
- Discussion of Findings/Conclusion/Implications, and
- Recommendations for Future Research.
Article Critique # 1
What is the problem or research question?
What nursing theory was being tested?
15 pts
What were the findings of the literature review?
Was informed consent obtained? Was IRB Approval Required?
10 pts
How were the data collected and analyzed?
10 pts 0 Pts
Full Marks No Marks
What were the findings of the study?
What were the themes identified in the discussion of the findings?
What were the research implications?
Total Points
- << Previous: Overview - Finding Current Nursing Articles
- Next: Searching CINAHL Complete >>
- Last Updated: Jan 18, 2024 9:52 AM
- URL: https://sacguide.libguides.com/nursing-research
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Research Initiatives
- Meet Our Researchers
- Meet Our Program Officers
- RESEARCH LENSES
- Health Equity
- Social Determinants of Health
- Population and Community Health
- Prevention and Health Promotion
- Systems and Models of Care
- Funding Opportunities
- Small Business Funding
- Grant Applicant Resources
- Training Grants
- Featured Research
- Strategic Plan
- Budget and Legislation
- Connect With Us
- Jobs at NINR

Advancing health equity into the future.
NINR's mission is to lead nursing research to solve pressing health challenges and inform practice and policy – optimizing health and advancing health equity into the future.

Funding Opportunities Newsletter
Subscribe to receive the latest funding opportunities and updates from NINR.

Funding opportunities that improve health outcomes
NINR believes that nursing research is the key to unlocking the power and potential of nursing. NINR offers grants to individuals at all points in their career, from early investigators to established scientists. NINR grants also support small businesses and research centers.

Research Funding
Small Business

Training Funding
Homepage events stories, addressing public health challenges through research.
NINR-supported researchers explore and address some of the most important challenges affecting the health of the American people. Learn about accomplishments from the community of NINR-supported scientists across the United States.

Advancing social determinants of health research at NIH
Over 20 NIH Institutes, Centers, and Offices are working collaboratively to accelerate NIH-wide SDOH research across diseases and conditions, populations, stages of the life course, and SDOH domains.

Holman Library

- Library Instruction
- ASSIGNMENTS & VIDEO TUTORIALS
- PN (Practical Nursing) Students
- BSN (Bachelor of Science) Students
- Evaluate by Specific Criteria
- Distinguish Source Types: Popular, Trade and Scholarly Journals
- Identify & Analyze Scholarly Articles
- Identify Research Study Types
- Critically Appraise Research Study Methodology
- Explore Topic Ideas
- Start with Background Info
- PICOT: Develop Your Research Question
- Construct an Advanced Search
- Find Scholarly (Peer Reviewed) Articles
- Find Different Research Study Types
- Find Web Sites
- Find Images
- Find Nursing Videos
- Find Pharmacology Info
- Find NCLEX and other Nursing Exams Test Prep
- Citation Basics
- Avoid Plagiarism
- Create APA Citations
- Synthesize Sources
- APA Formatted Paper Example
- Publisher: Tips on Creating a Brochure
- Poster Printing
Research Assignments & Video Tutorials for Nursing Students
Click on the sub-pages to explore research assignments and video tutorials for nursing:.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: PN (Practical Nursing) Students >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2024 6:18 PM
- URL: https://libguides.greenriver.edu/nursing

- Reference Books - Print & Ebooks
- Videos - Finding Articles
- More Videos-Finding Articles
- CINAHL Video Tutorials
- Systematic Review Videos
- Interlibrary Loan: Step-by-Step Instructions
- Finding Qualitative/Quantitative Research Studies
- NUR 302 Library Assignment
- How to Read, Analyze & Comprehend Scholarly & Scientific Articles
- Professional / Clinical Resources
- APA Citation Style - 7th Ed.
- Clinical Practice Guidelines
- NCLEX-RN Review / Practice Tests
- Nursing Program Pre-Entrance Exam - Health Education Systems, Inc. (HESI) Pre-Admission Exam
- Course: Using PubMed in Evidence-Based Practice
- NUR 801 Evidence-Based Practice 1: Methods
- Nursing Theories & Theorists
Instructions for Library Assignment
Click on the Library Worksheet linked below; it is available as a Microsoft Word document and as a PDF file.
Click on "Enable Editing" at the top of the Word document in order to type in the form. I f you prefer, you can print out the blank worksheet and fill it in manually.
Answer questions 1 - 6 on this worksheet after watching all four videos (10 minutes total viewing time) on the Videos - Finding Articles page of this guide. P lease print and bring the worksheet to class with you.
- Nursing Library Assignment - Word Document
- Nursing Library Assignment - PDF
- << Previous: Finding Qualitative/Quantitative Research Studies
- Next: How to Read, Analyze & Comprehend Scholarly & Scientific Articles >>
- Last Updated: Mar 4, 2024 1:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.lehman.edu/nursing
100+ Medical Surgical Nursing Project Topics [Updated]

Medical surgical nursing is a crucial aspect of healthcare that focuses on providing care to patients before, during, and after surgical procedures. Medical surgical nursing includes many tasks, like checking patients before surgery and taking care of them afterward. Research is really important in making medical surgical nursing better by finding new information and helping patients get better. In this blog, we’ll delve into various medical surgical nursing project topics that can inspire both students and professionals alike.
What Is The Basic Concept Of Medical Surgical Nursing?
Table of Contents
The basic concept of medical surgical nursing revolves around providing comprehensive care to patients undergoing surgical procedures or experiencing medical conditions requiring surgical intervention.
This includes preoperative preparation, intraoperative support, and postoperative recovery, as well as the management of medical conditions that may necessitate surgery.
Medical surgical nurses focus on promoting patient well-being, preventing complications, and facilitating optimal outcomes throughout the surgical process.
100+ Medical Surgical Nursing Project Topics: Category Wise
Clinical practice topics.
- Nursing Care for Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Management of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus undergoing Surgery
- Postoperative Pain Management Strategies
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Care of Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in the Surgical Setting
- Assessment and Management of Perioperative Hypertension
- Preparing Patients for Orthopedic Surgery: Education and Rehabilitation
- Surgical Site Infection Prevention Measures
- Nursing Care for Patients with Sepsis following Surgery
- Role of the Nurse in Preoperative Assessment and Optimization
Surgical Intervention Topics
- Care of Patients undergoing Total Joint Replacement Surgery
- Nursing Management of Patients with Traumatic Injuries
- Postoperative Complications in Abdominal Surgery: Recognition and Management
- Nursing Care for Patients undergoing Bariatric Surgery
- Perioperative Care of Patients undergoing Organ Transplantation
- Management of Patients with Pressure Ulcers following Surgery
- Nursing Interventions for Patients undergoing Cosmetic Surgery
- Surgical Wound Dehiscence and Evisceration: Nursing Management
- Role of the Nurse in Intraoperative Patient Safety
- Care of Patients with Surgical Drains: Assessment and Management
Cardiovascular Nursing Topics
- Nursing Care for Patients undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery
- Management of Patients with Heart Failure undergoing Surgery
- Postoperative Arrhythmia Management
- Role of the Nurse in Cardiovascular Assessment during Surgery
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Peripheral Vascular Disease undergoing Surgery
- Hypothermia Prevention Strategies during Cardiac Surgery
- Care of Patients undergoing Cardiac Catheterization
- Nursing Management of Patients with Aortic Aneurysm
- Postoperative Care of Patients with Myocardial Infarction
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Cardiogenic Shock
Neurological Nursing Topics
- Care of Patients undergoing Craniotomy Surgery
- Management of Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries undergoing Surgery
- Postoperative Care of Patients with Brain Tumors
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Stroke undergoing Surgery
- Role of the Nurse in Intraoperative Neurological Monitoring
- Perioperative Care of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
- Nursing Management of Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury
- Postoperative Delirium: Assessment and Management
- Care of Patients undergoing Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Epilepsy undergoing Surgery
Gastrointestinal Nursing Topics
- Nursing Care for Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer undergoing Surgery
- Management of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease undergoing Surgery
- Postoperative Nutrition Support Strategies
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy following Surgery
- Role of the Nurse in Intraoperative Bowel Management
- Perioperative Care of Patients with Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Nursing Management of Patients with Pancreatitis undergoing Surgery
- Postoperative Care of Patients with Intestinal Obstruction
- Care of Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease undergoing Surgery
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Appendicitis undergoing Surgery
Respiratory Nursing Topics
- Nursing Care for Patients with Lung Cancer undergoing Surgery
- Management of Patients with Pneumonia undergoing Surgery
- Postoperative Respiratory Assessment and Monitoring
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Chronic Respiratory Failure undergoing Surgery
- Role of the Nurse in Intraoperative Airway Management
- Taking care of patients with COPD before, during, and after surgery
- Helping patients with ARDS after surgery breathe better and managing their care
- Postoperative Care of Patients with Pulmonary Embolism
- Care of Patients with Sleep Apnea undergoing Surgery
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Asthma undergoing Surgery
Renal Nursing Topics
- Nursing Care for Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma undergoing Surgery
- Management of Patients with Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) undergoing Surgery
- Postoperative Fluid and Electrolyte Management
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease undergoing Surgery
- Role of the Nurse in Intraoperative Renal Function Monitoring
- Perioperative Care of Patients with Renal Calculi
- Nursing Management of Patients with Hydronephrosis following Surgery
- Postoperative Care of Patients with Renal Transplantation
- Care of Patients with Polycystic Kidney Disease undergoing Surgery
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis undergoing Surgery
Endocrine Nursing Topics
- Nursing Care for Patients with Thyroid Disorders undergoing Surgery
- Management of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus undergoing Endocrine Surgery
- Postoperative Hormonal Assessment and Monitoring
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Adrenal Disorders undergoing Surgery
- Role of the Nurse in Intraoperative Endocrine Function Monitoring
- Perioperative Care of Patients with Pituitary Disorders
- Nursing Management of Patients with Parathyroid Disorders following Surgery
- Postoperative Care of Patients with Gonadal Disorders
- Care of Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors undergoing Surgery
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Pancreatic Disorders undergoing Surgery
Oncology Nursing Topics
- Nursing Care for Patients with Breast Cancer undergoing Surgery
- Management of Patients with Colorectal Cancer undergoing Surgery
- Postoperative Symptom Management in Cancer Patients
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Prostate Cancer undergoing Surgery
- Role of the Nurse in Intraoperative Oncological Safety Measures
- Perioperative Care of Patients with Ovarian Cancer
- Nursing Management of Patients with Lung Cancer following Surgery
- Postoperative Care of Patients with Melanoma
- Care of Patients with Head and Neck Cancer undergoing Surgery
- Nursing Interventions for Patients with Gynecological Cancers undergoing Surgery
Pediatric Nursing Topics
- Nursing Care for Pediatric Patients undergoing Surgery
- Management of Pediatric Patients with Congenital Anomalies undergoing Surgery
- Postoperative Pain Management in Children
- Nursing Interventions for Pediatric Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate undergoing Surgery
- Role of the Nurse in Intraoperative Pediatric Safety Measures
- Perioperative Care of Pediatric Patients with Hydrocephalus
- Nursing Management of Pediatric Patients with Spina Bifida following Surgery
- Postoperative Care of Pediatric Patients with Appendicitis
- Care of Pediatric Patients with Hirschsprung Disease undergoing Surgery
- Nursing Interventions for Pediatric Patients with Congenital Heart Disease undergoing Surgery
Gerontological Nursing Topics
- Nursing Care for Geriatric Patients undergoing Surgery
- Management of Geriatric Patients with Fractures undergoing Surgery
- Postoperative Delirium Prevention Strategies in Older Adults
- Nursing Interventions for Geriatric Patients with Dementia undergoing Surgery
- Role of the Nurse in Intraoperative Geriatric Safety Measures
How Do You Write A Nursing Project?
Writing a nursing project involves several key steps to ensure clarity, thoroughness, and relevance to the chosen topic. Here’s a general guide on how to write a nursing project:
- Select a Topic: Choose a topic that aligns with your interests, expertise, and the requirements of your assignment or research objectives. Consider the significance of the topic in the field of nursing and its potential impact on patient care or nursing practice.
- Research: Find books, articles, and other info about your topic. Look at what’s already been studied to see what’s missing or needs more info.
- Outline: Plan out your project with sections like intro, background, methods, results, and conclusion. Make it fit what you need.
- Introduction: Start your project with a bit about your topic, why it’s important, and what you’re trying to learn.
- Review: Look at all the info you found and figure out what’s important. See where there are questions or disagreements.
- Methods: Explain how you did your project, like who you studied, what you measured, and how you did it.
- Results: Show what you found in a clear way, like with tables or graphs. Talk about what it means.
- Implications: Think about what your findings mean for nursing. How can it help patients or other nurses? What else should be looked at?
- Conclusion: Sum up what you learned and why it’s important. Say what you think should happen next.
- Cite Sources: Give credit to the info you used in your project. Make sure to do it right.
- Proofread: Check your project for mistakes and fix them. Make sure it all makes sense and looks good.
- Seek Feedback: Before finalizing your project, seek feedback from peers, mentors, or instructors to gain valuable insights and suggestions for improvement. Consider incorporating constructive feedback to strengthen your project before submission or publication.
Future Directions and Recommendations
- Areas for Further Research in Medical Surgical Nursing: Identify emerging areas of interest and potential research gaps in medical surgical nursing, such as the impact of healthcare disparities on surgical outcomes , patient-reported outcomes following surgery, and the integration of complementary and alternative therapies into perioperative care.
- Strategies for Improving Surgical Nursing Practice: Propose recommendations for enhancing surgical nursing practice, including interdisciplinary collaboration, continuing education and professional development opportunities, and the implementation of evidence-based guidelines and protocols.
In conclusion, medical surgical nursing offers a vast array of fascinating project topics that can enrich our understanding of patient care, contribute to evidence-based practice, and drive innovation in healthcare delivery.
Whether you’re a student embarking on a research project or a seasoned nurse seeking to explore new avenues in your practice, these Medical surgical nursing project topics provide an excellent starting point for exploration and discovery in the dynamic field of medical surgical nursing.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Nursing School Assignments and Tips to Ace All of Them

If you are about to start nursing school or considering enrolling in a nursing program, you would want to know what to expect. You will write many papers in nursing school and do many other assignments. This is true whether you pursue ADN, BSN, MSN, DNP, or PhD in Nursing.
Before we delve into the types of assignments and papers to expect in nursing school, let us begin by dispelling the myth that nursing school is hell; it is NOT. Instead, it is a beautiful and exciting journey into a noble profession. It entails a commitment to life-long continuous learning for you to grow.
Nursing school writing assignments are an excellent way for students to understand concepts taught in the classroom. You might wonder what kinds of assignments nursing students do. These assignments come in various forms and help students build critical thinking, creativity, research, clinical reasoning, and problem-solving skills that are critical in clinical settings.
This blog post looks at the diverse assignments you should expect or will cover in nursing school, including some tips to help you ace them and get better grades.
Common Nursing School Writing Assignments
Classwork forms the core of most nursing programs. You must have high-quality assignment submissions to attain better grades in nursing school. As soon as you decide to become a nursing student, you sign up for a marathon of writing different types of papers.
Whether you love or hate it, you will write papers before graduating from nursing school; that is the norm. Although not so many, you will encounter a few homework and assignments where you must submit a well-researched, formatted, and organized nursing paper.
The typical nursing school assignments include essays, research papers, term papers, and case studies. Others are article critiques/reviews, critical appraisal, evidence synthesis tables (synthesis matrix), PowerPoint Presentations, posters, discussion posts/ responses, and policy analysis papers. Other advanced papers include nursing care plans, SBAR template papers, evidence-based papers, capstone projects, theses, dissertations, proposals, etc.
These assignments are submitted either individually or as a group. Let us expound on this so you have a clear picture.
Essays for nursing classes come in various forms, including admission essays , scholarship essays, descriptive essays, persuasive essays, speech essays, expository essays, and narrative essays.
Notably, nursing essays focus on a single perspective, argument, or idea, which constantly forms the thesis of the paper.
Nursing essays focus on various topics relating to nursing practice and the broader healthcare field. You can write an essay examining a nursing theory or non-nursing theory or discuss a nursing issue .
Some essays, such as reflective nursing essays, use reflective models to reflect, analyze, and understand personal and professional encounters during clinical practice.
Each nursing essay should demonstrate your understanding of the topic, critical analysis, and organization skills. Besides, you should use evidence from peer-reviewed scholarly sources to support your arguments and ideas.
Discussion Board Posts
If you pursue a hybrid or exclusively online nursing program, you will be assigned to write weekly discussion forum posts and responses. Discussion board posts are short essay-like assignments posted in a threaded format so students can discuss nursing and healthcare topics.
You will write an original discussion post, between 200 and 300 words long, and post it on the forum. You are also expected to write a peer-response post in response to or to comment on an original post done by your peers.
Discussion boards help nursing students advance theoretical concepts, learn from one another, share ideas, and get feedback that can help them advance their knowledge in clinical reasoning and practice.
Research Papers
Nursing practice is evidence-driven, translating evidence into practice to ensure quality, accessible, and affordable healthcare. As such, nursing research takes precedence during studies and when practicing.
Nursing professors assign nursing students to write research papers on various evidence-based practice topics. The students must prove their worth by researching, analyzing, and organizing facts.
Related Writing Guides:
- How to write a nursing school research paper.
- Systematic Reviews vs Literature Review
Research papers help student nurses to review literature, conduct research, implement solutions, and draw evidence-based conclusions.
Research papers are critical in developing research and writing skills, maintaining good communication, and fostering creativity and clinical reasoning.
Potential nursing research paper topics can be quality improvement, healthcare/nursing informatics , healthcare policies, practice privileges, nursing ethics, ethical dilemmas , pathophysiology, and epidemiology .
Term Papers
In nursing school, a term paper is a type of assignment completed and submitted toward the end of the semester.
Usually, a professor can assign you a specific term paper topic, or they can let you choose a topic and consult with them for approval.
Term papers can be done individually or as a group project. A term paper has an impact on your final grade.
You should use credible scholarly sources published within the last five years for recent information.
Besides, also ensure that you plan your time well, do everything as per the instructions, and submit the nursing term paper before the deadline.
A term paper can also be a nursing process change report that is expected to address an area that needs change.
Case Studies
Nursing school case study assignments are an essential learning tool.
Most professors assign hypothetical clinical case studies or case scenarios (snippets) to test your clinical reasoning skills.
As a nursing educational tool, nursing case studies help you to develop practical, theoretical knowledge by simulating real-world experiences.
When analyzing a case study, you must use concepts and knowledge from class and class text to assess a patient, plan and implement care, and evaluate the outcomes.
Sometimes, you encounter simulated or digital clinical experience case studies such as iHuman and Shadow Health .
You should be very keen when analyzing a case study and when writing the analysis report.
Case studies help you get beyond books and use your creativity, clinical reasoning, problem-solving, and analytical skills to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world problems.
Your professor can give you a case study of a patient presenting with a given condition and expect you to take them through the care planning process, including admission and discharge, as you would in a real healthcare setting.
Other times, you can be asked to develop a hypothetical case study of a patient presenting with a chronic disease or a disorder and then use the case study guidelines, including head-to-toe assessment , diagnosis , nursing care planning , and discharge planning.
Related Guides:
- How to write a great nursing case study.
- How to complete a case conceptualization report (for psychiatric nursing students)
Nursing Care Plans and SOAP Notes
A nursing care plan can be part of a case study or a stand-alone assignment. Nursing care plans are essential in nursing education as they help students develop effective nursing care planning. Formulating a nursing care plan for a patient scenario or case helps treat them as you define the guidelines and roles of nurses in caring for the patient.
You also develop solid action plans for focused and patient-centred care by documenting the patient's needs. When they are part of an assignment, you can tabulate the nursing care plan using columns so that you explore every aspect independently.
Remember to use evidence from peer-reviewed scholarly sources when giving rationale.
The SOAP notes are a clinical tool healthcare professionals use to organize patient information to minimize confusion and assess, diagnose, and treat patients. Check our comprehensive guide on developing good SOAP Notes in nursing school .
Concept Maps
Another common nursing school assignment is concept maps. Concept mapping helps you visually organize, compartmentalize, and categorize information about nursing care planning, medical diagnosis, pathophysiology, SBAR, nursing responsibilities, etc.
A nursing concept map assignment equips you with strong critical thinking, analytical, and problem-solving skills. You also hone your clinical reasoning skills in the process.
Whether it is part of an assignment or a stand-alone, learn how to write great concept maps to score the best grades.
Concept Analysis Papers
If you are taking BSN, MSN, or DNP, you will likely be assigned to write a concept analysis paper. Make sure to distinguish this from a concept paper that is a proposal. A concept analysis paper examines the structure and function of a nursing concept.
The process entails a review of the literature and creativity in coming up with borderline, related, contrast, inverted, and illegitimate cases.
You also explore the antecedents and consequences of the concept before finalizing with empirical referents.
If you need to learn about the structure of a good concept analysis paper, check out our nursing concept analysis guide . We have listed concepts you can analyze depending on your speciality, instructions, and passion.
Capstone Projects
At an advanced stage in nursing school, students are expected to submit longer research papers; capstone project papers. A nursing capstone project is a final project that allows students to demonstrate the skills, knowledge, and concepts gained throughout the nursing program.
In nursing education, the capstone project typically covers an evidence-based practice issue or problem. You can write a nursing change paper, look into a clinical process, problem, or issue, and then develop recommendations based on a study.
Most of the MSN and DNP capstone projects focus on clinical change or quality improvement. You will be expected to develop a PICOT question and formulate a research study to examine the issue, implement a change process using evidence-based models, and make recommendations.
Nursing capstone projects are individual research projects based on nursing topics either of your professional or personal interest. You have to demonstrate competency and commitment to improve health outcomes.
Apart from capstone projects, you will also write a nursing thesis and dissertation papers, which depend on the program requirements and your professor's preferences.
Check out these specific writing guides for advanced papers:
- How to write a nursing dissertation or thesis
- Tips for choosing the best nursing dissertation topic
- How to write an excellent capstone project paper
- List of capstone project topics for nursing school
- How to formulate a PICOT question
- PICOT question examples to inspire nursing students
Group Assignments
In nursing school and practice, collaboration and teamwork are highly recommended. You will encounter collaborative group assignments such as presentations (PowerPoint slides, Prezi, or other platforms), simulation assignments, writing nursing reports, and group research projects.
Group projects allow you to research, learn, and organize ideas together so that you can understand concepts better. It is essential to avoid social loafing in a group to gain more. Besides, plan your time well and avoid excuses.
You can also be assigned to work on simulation exercises as a group of nursing students. The aim of such exercises is to build a collaborative, teamwork, and decision-making spirit among the team.
When in such groups, expect to work with your peers to assess the hypothetical patient, communicate with your peers, formulate a care plan, and manage any arising issues as you would in clinical settings. Do not take such activities for granted; they contribute significantly to your grade.
Presentations
Your professor can assign you to design a PowerPoint Slide accompanied by speaker notes and send it for grading or present it online or in class. Under presentations, you will also be requested to design flyers, posters, and other visual documents to disseminate information.
It could be about a disease, health promotion, or nursing research. You must also make PowerPoint slides when presenting a thesis, dissertation, or capstone for assessments. Remember, this is the chance to bring out your creativity.
Expect other assignments such as dosage calculations, HESI test exams, skills checkoffs, electronic medical record documentation, nursing student portfolio, online quizzes, drug write-ups, process recordings, group drug presentations, etc.
In most cases, you will be given a template to use wisely and make it as appealing as possible.
Tips to Help You Ace Nursing Assignments
A lot goes into getting the best grades in nursing school. One of the main determinants of your nursing school grades is the assignments, which you are required to do and complete within set deadlines.
Even though many nursing students perform better on clinical, that needs to reflect in written assignments. Most students fear research and writing or do not take writing assignments seriously. Regardless of the assignment, here are some practical and effective tips to help you ace your nursing school writing assignments and surprise everyone, including yourself.
1. Plan your Time
The number one challenge for nursing students that inhibits them from completing assignments is the need for more time management.
Most students are juggling studies and work to make ends meet. It worsens when you have a massive workload from more than one class and a family to look after.
The simple trick to beat this is to manage your time well. You can schedule your assignments for periods when you are free and when you can concentrate and cover more. Assignments have deadlines ranging from hours to days or a few weeks.
To succeed, keep track of your assignments and other academic activities, such as mid-term and final examinations, so that you can plan your study periods. You can use online time management tools and apps to allocate your nursing school homework time.
With proper planning, you should be reassured about the last-minute rush to complete your assignment, which is responsible for the colossal failure we are experiencing in nursing schools.
2. Follow the Course Guidelines to the T
Guidelines, prompts, and reading materials accompany each writing assignment and homework. Sometimes a professor can be generous enough also to give you access to the Rubric, which breaks down how they will assess assignments. Ensure you read everything and note what is required before working on any paper.
Pay attention to these, read, and familiarize yourself with the course guidelines. Understand the formatting requirements preferred by your school, such as Vancouver, APA, or Harvard. Most nursing schools will specify this in the course documents. Also, check the databases and journal articles you can use when writing your nursing assignments.
Preparing in advance by reading the course materials to identify the recommended study materials. You will have a deeper understanding, knowledge, and skills to handle every nursing assignment correctly.
3. Have an Active Study Buddy
A nursing study buddy can be one of your classmates whom you study with. Study buddies offer mutual support, which comes in handy when completing assignments.
Select a bright and committed person with something to offer so you are not only giving. Set the study hours and have accountability follow-ups to ensure you cover much of the syllabus and concepts in time.
A study buddy can help you understand nursing concepts, theories, models, and frameworks. They can also help you review your written papers and give valuable feedback when editing and proofreading your nursing papers.
A knowledgeable, accountable, committed study partner can help you revamp your grades by submitting high-quality assignments.
4. Join a Study Group
A study group is a tried and tested means of completing nursing assignments. Apart from building your teamwork and collaborative skills, you can brainstorm ideas, critique one another, and learn more about the class assignments. With diversity in thoughts, you can get valuable insights and inputs for personal-level work.
Besides, you are also guaranteed to ace the nursing group assignments with ease. When doing group work, try to rotate into new groups so that you can appreciate the diversity of thoughts and reasoning. You can also identify individuals from your groups, those that are active, as your study buddies.
When you have accountability partners within the group, you commit to given tasks and make necessary follow-ups. If you are a part-time student, consider having students whose free time is similar to yours to benefit everyone.
5. Get Writing Assignment Help
As with other subjects in college and university, nursing students face challenges such as time management, complexity of assignments, too many assignments, and writer's block. When you feel overwhelmed with completing your nursing class assignments, you can always pay someone to handle the class for you or at least do your coursework or assignments.
One sure way to get assistance without drawing too much attention is by trusting assignment help websites like NurseMyGrade.com with your papers. Many students do not have time to complete assignments or find them challenging. Consequently, many hire nursing assignment helpers from nursing paper writing platforms.
If you feel like hiring the right professionals, use NurseMyGrade. We offer customized writing solutions to nursing students at different academic levels. Our nursing experts can complete short and lengthy assignments. You will have a well-researched and formatted paper written in Vancouver, APA, MLA, ASA, AMA, Harvard, or any citation style you choose.
You can use the tips and insights above to master nursing school assignments. We wish you all the best as you strive towards excellence. Don't worry about the many assignments. Instead, be grateful that they will equip you with knowledge, skills, and experience to make you the best nurse.
How Many Papers to Write in Nursing School
We have so far covered the general aspects of the types of assignments to expect in nursing school. Under the assignments, you may ask yourself if you must write many papers in nursing school.
While the answer depends on your professor, institutional curriculum requirements, and nursing level, you will undoubtedly write a couple of academic papers before graduating from nursing school. You will write research papers, essays, proposals, white papers, policy analysis papers, capstone project papers, case studies, scholarship essays, personal statements, quality improvement reports, etc.
Suppose you are pursuing a Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) program. In that case, you will likely write between 13 and 15 papers during the LPN program, including short and long essays, reflective journals, essays, patient-based case studies, and others as your professor pleases.
If you are in a 2-year ADN program, expect to complete about 20 to 30 papers, including care plans, SBAR reports, essays, case studies analyses, research papers, reports, and other assignments.
For a 4-year Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program, you will write between 35 and 50 papers. If you are taking the online class program options, like the WGU BSN program, you might write more papers because they form the basis for your assessment.
BSN-level papers are demanding because you must strictly adhere to the formatting styles and be critical and organized in your presentation.
If you are taking a Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) program, an advanced-level study for registered nurses (RNs), you will do about 20-50 papers, given that it offers the foundation for nursing research. Again, at an advanced level, the MSN writing assignments are complex.
You need to plan well, research widely, and analyze facts thoroughly before drawing conclusions. During this level, expect to write papers such as MSN essays, discussion posts and responses, specialized case studies, research papers, clinical reports, advanced SOAP notes, nursing care plans, policy papers, position papers (white papers), dissertations, theses, capstone papers, project papers, and change project papers.
You are expected to show exquisite research skills for the Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) program, considered the highest level or terminal degree in nursing practice. At this level, you have specialized, advanced your knowledge, and have adequate experience.
Mostly, DNP papers are a little longer. You will write between 20-30 papers; depending on your nursing school curriculum and supervisor's preference, it could be less or more.
If you opt for the research route, you will write many research papers, technical papers, policy analysis papers, white papers, reflection papers, nursing dissertations, PICOT-based change project papers (DNP change project papers), and other assignments.
Finally, for the Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in nursing programs, you should expect to write between 10 and 15 papers covering research-oriented topics.
Attaining this degree makes you the epitome of success in the field. You can advance into a nursing researcher, educator, leader, or manager.
We have writers that can help you handle all these types of papers regardless of the academic level. Our Online Nursing Writing pros are available for hire anytime and any day.
Having worked successfully with many nursing clients/students, we are confident to help you achieve your dreams.
Before you go …
There are many assignments and papers to complete in nursing school, including written assignments, quizzes, exams (oral and written), reflective journals, journal entries, e-Portfolio, integrative reviews, teaching plans, presentations, etc. Whether taking an LPN program or advancing your career by pursuing a Ph.D. in Nursing, you will do many nursing school assignments.
Do not take assignments as a punishment. Instead, consider them as tools to equip and shape you into a desirable nurse practitioner.
If you feel overwhelmed, stressed, and anxious about completing the assignments, you can hire our nursing writers to help you. We can help you ace nursing assignments online and ensure that you get 100% well-researched, organized, and proofread papers.
Our papers are 100% original and non-plagiarized. The writers understand how to structure nursing papers, formulate great paragraphs using the MEAN, PEEL, or TEEL formats, and write desirable papers consistently, scoring the best grades. You can call us your nursing assignment slayers or acers because, in a few hours, we will help you get it all behind you. We can help you ace online nursing classes and tests/quizzes .
Click on the Order button and fill out the form to get our writers started in making you a nursing paper that gives the best grade. No topic is challenging for us, and we allow you direct communication with the writer in the process of getting help.
Struggling with
Related Articles

Ultimate Guide on how to Write A Student Nurse Resume

How to write a Great Annotated bibliography

Getting Over Embarrassment of Repeating as a Student Nurse
NurseMyGrades is being relied upon by thousands of students worldwide to ace their nursing studies. We offer high quality sample papers that help students in their revision as well as helping them remain abreast of what is expected of them.

Nursing Research Assignment
?INTRODUCTION Nursing research is a systematic process by which nurses may used to confirm or refine existing knowledge and to explore new ideas about issues related to nursing practice (Borbasi, Jackson, & Langford, 2008). It falls largely into two areas, namely: Qualitative research and Quantitative research whereby qualitative research is based on the model of phenomenology, grounded theory, and ethnography and examines the experience of those receiving or delivering nursing care.
The research methods most commonly used in qualitative research are interviews, case studies, and ethnography. On the other hand, quantitative research is based in the paradigm of logical positivism and is focused upon outcomes for clients that are measurable, generally using statistics gathered from a survey questionnaire method of research (Parahoo, 1997). The objective of this nursing research assignment is to distinguish the identified three pieces of nursing research with a common issue that is relevant to my current clinical experience.
Don’t waste your time! Order your assignment!
The five phases of the research process will be outlined and discussed the findings of the researchers by providing examples from each study. For purposes of this assignment, the research topic which I want to examine is poor hygiene and failure to follow infection control practices, contributing to the spread of nosocomial infections especially those caused by antibiotic-resistant strain of bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a clinical setting.
The said topic was chosen because it has been observed during my clinical experience, that most of the time doctors, nurses, and other health professionals does not adhere to the implementation of existing guidelines pertinent to infection prevention and control practices maybe due to excessive workload and rapid turnover interval of patients but nonetheless, that is not an excuse. Further, the emergence of antibiotic resistance is primarily due to excessive and often unnecessary use of antibiotics to patients (Gould, 2008).
Risk factor for the spread of resistant bacteria in hospitals can be summarized as over-crowding and lapses in hygiene or poor infection control practices (Gopal Rao, 1998). The three identified nursing research articles relates to my current clinical experience wherein a common problem was determined specifically enumerating the factors for the spread of healthcare-associated infections (HCAIs) such as MRSA and providing some remedies to prevent and control the transmission of such infections.
Problems identified in relation to my clinical experience. Based on previous studies it was ascertained that the mode of transmission of micro -organisms in a healthcare setting include direct and indirect contact, inhalation or droplet, waterborne or body fluid route, foodborne, and sexual activity (Gould, 2008). The problems related to my clinical experience are poor hygiene and non-adherence to infection control guidelines by nursing staff and other health professionals.
Hence, it appears that infection control was not properly managed in a healthcare setting. In my clinical experience it was observed that most of the doctors and nurses do not wear disposable gloves and disposable apron during their visit to different patients especially for those patients who are in isolation room afflicted with different kinds of disease. This observation can be illustrated when a patient was admitted in the ward and lodged in an isolation room because the patient is MRSA positive.
The doctor enter into the patient’s room to do some medical assessment and most of the time doctor tend to forget to wear protective gear before conducted clinical assessments, despite the notice or sign posted in front of the patient’s room being an isolated area. Upon conducting the medical assessment on a patient who is MRSA positive, the doctor did not wash his hands instead continued his job by conducting medical check up on the other patients who are not in isolation area. In addition, nurses also tend to forget to follow infection control ractices. They failed to understand the chain of infection control, for example an E. coli, which is considered as an infection agent found in the large intestine of human form the greater part of the normal intestinal flora. Its port of exit is via faeces. The nurse removed the contaminated linen from the bed. The E. coli contaminated the hands of the nurse who then provided care to another patient without hand washing. The second patient has a foley catheter. The nurse manipulated the catheter tubing, the E. oli in the nurse’s hands contaminated the catheter tubing and ascending to the patient’s urinary tract and then into the bladder. The susceptible host, who is the second patient with the foley catheter is an elderly and had a chronic illness necessitating complete bed rest. The foley catheter contaminated by the E. coli organism provided a direct route into the urinary bladder causing the transmission of the infection from one patient to another. The most common mode of transmission of infection is by direct contact, often on the hands of health workers.
This is the way that most HCAIs are spread and explains why hand washing is emphasized as the most important way of breaking the chain of infection (Gould, 2008). Moreover, nurses were observed roaming around in the ward corridor wearing the disposable gloves and disposable gowns after providing nursing care to patients who are in isolation room. These actuations probe that nurses should have continuing education on the implementation of infection control practices to avoid cross-infection and transmission of contagious diseases among patients.
The essence of public health is taking sensible measures to prevent problems in the future. Good infection control in primary care has the potential to prevent grave consequences for patients. Nurses in primary care should play a crucial role in ensuring cleanliness, infection control practices and adhere to guidelines in this important area (Gould, 2008). Five phases of the research process The nursing research process contains an orderly series of phases or steps that outline the key points of research study.
Research article has both qualitative and quantitative research method to develop and answer the issues pertinent to the specific topic (Borbasi, et al. , 2008). The first phase of nursing research is to conceive the study by identifying the issue or problem to be studied relevant to the interest of the researcher that will include the goal of the study, review of literature, development of theoretical framework, and the formulation of research hypothesis (Borbasi, et al. , 2008).
Literature review serves to put the current study into the context of what is already known about the phenomenon (Parahoo, 1997). The three identified nursing research were conceived due to the following problems: In article one entitled Plastic apron wear during direct patient care, the researchers stated the problem as inconsistent practice in apron use by nurses in healthcare setting (Candlin & Stark, 2005). In this study an expansion of the general themes and concentration of the main report is given and the reader is able to make choice about the relevance of the article for the purpose.
The identified problem in article two entitled controlling the risk of MRSA infection: screening and isolating patients stated that there is a need to minimize the spread of antibiotic resistant infection through screening and isolating patients (Bissett, 2005). For article three, entitled bed occupancy, turnover interval and MRSA rates in Northern Ireland, the researchers identified the problem as the increasing rate of MRSA infection in the healthcare setting. Relative thereto, the aim of the study is to ascertain the relationship between bed percentage occupancy and MRSA patient episode rates (Cunningham, kernohan & Rush, 2006).
In the review of literature, the researchers of the three articles analyses the literatures from different sources such as Cinahl, Medline and Pubmed (Bissett, 2005), to help in the development of theoretical framework to explain or predict study outcomes (Borbasi, et al. , 2008). In article three the researchers develop theoretical framework to explain their findings by using the collected data from different sources. The second phase of nursing research is to design the study whereby the methodology for the conduct of research was identified (Borbasi, et al. , 2008).
It includes the process of data collection, whereby article three is an example of quantitative method of research wherein the researchers gathered the needed data from annual reports and hospital statistics. In article one, the researchers collected the information and data needed in their study from 15 journal articles which are relevant to their topic that contribute to the credibility of the outcome of the study and this is a representation of a qualitative method of research as the researchers analyses previous case studies relevant to their topic (Candlin & Stark, 2005).
Further, article two was identified as a quantitative study and clearly outlined the research question to be answered (Bissett, 2005). The conduct of the study is the third phase of nursing research and ethics is part of phase 3 of the nursing process. It is an important part of nursing research and it is an area in which the health professional is involved daily particularly in providing care to patients. Issues relating to the study, design, recruitment of participants, feedback and data collection methods are subject to scrutiny of a departmental ethics committee and approval should be obtained.
Consent was secured from the target participants by the researchers in support to their study (Borbasi, et al. , 2008). Phase 3 includes the actual data collection pertinent to the study. In article one, the researchers evaluated and analyses the information and data gathered from the documents. They separated the data into three categories in order to accurately determine and interpret their findings (Candlin & Stark, 2005).
Records show that the researchers of the three identified nursing research sought the approval of an institutional ethics committee prior to the conduct of their respective studies. However, such approval was not acknowledged in the content of their studies. The three nursing research studies encountered some limitations, which affect the validity of the outcome of their studies. For example, in article one and three, the researchers identified their method of data analysis as their limitation in the conduct of their studies.
Candlin & Stark (2005) stressed that the documentary analysis in their study have limited available data, which are incomplete, inaccurate and has inherent biases, while the researcher in article two explained that by using survey questionnaire in the data collection does not guarantee that the target participants will provide honest and accurate answers to the questions (Bissett, 205). The analysis of the study, which includes the interpretation of the gathered data is the fourth phase of the nursing research process.
The findings in article two, reveal that nursing staff doesn’t understand the proper implementation of infection control practices and the potential transmission of infections from one patient to another (Candlin & Stark, 2005). The findings in article one and three as presented were brief, concise and accurate which are easy to understand. In article three, the researchers presented the results of the study in tables and graphs, which were used as reference to explain the findings of the study.
The phase five of nursing research is use the study that completes the research process and ensures that results or findings of the study are shared with the target consumers (Borbasi, et al. 2008). This phase includes recommendations whether further study is needed to strengthen the findings of the study and conclusions, which are being used as reference to reinforce the outcome of the research study. It may include the evaluation of the study and a summary of the findings together with the relevance and importance of the study in nursing practice.
The researchers of the three articles presented their respective conclusions in a brief and concise manner. The researchers in article one outlined their conclusion as brief as possible and stated the implication of the study in relation to nursing practice. Nurses should adhere to the existing policies and guidelines pertinent to infection control practices such as use of disposable apron during direct patient care and nurses should have understanding on the said policies, to promote good practice and reduce risk of cross-infection, an area that cannot be ignored (Candlin & Stark, 2005).
The researcher in article two emphasized that health worker should follow and observe the existing guidelines on infection control and MRSA screening should be done to all patients who are subject for admission to minimize the risk of MRSA infections (Bissett, 2005). Finally, in article three, as part of the findings of the study, the researchers were able to establish the link between high bed occupancy, patient turnovers interval and MRSA rates considering that nurses do not have enough time to implement effective infection control practices (Cunningham, Kernohan & Rush, 2006).
Influence of the research study to the identified issue The study conducted in article one was able to identify the factors that influence the nurses to use plastic apron when providing direct patient care such as nurses’ uniforms are not considered as protective clothing. It promotes good practice for health workers as plastic apron protect themselves and other people in a healthcare setting from contagious diseases and other infections. The use of plastic apron will reduce the risk of cross-contamination and prevent the spread of micro-organisms.
This research study could influence the identified problem by calling the attention of the health service managers to ensure that a policy from apron use is implemented. The management shall make sure that nurses and other health professionals will have adequate access to disposable apron to protect themselves from contamination, and to guarantee the safety of the patients and staff member in a healthcare setting (Candlin & Stark, 2005). Article two is considered as an educational in nursing practice.
It provides information and data that described nosocomial infections caused by antibiotic-resistant strain of bacteria such as MRSA (Bissett, 2005). Likewise, the study enumerated some infection control strategy that can be applied in my clinical experience such as surveillance of infection, education and training production, review and dissemination of written policies and guidelines, etc. that will provide a safe environment in the clinical setting by protecting the clients and other staff members.
These infection control strategies will ensure safe and good nursing practice that will lead to proper management of infection control practices. It is interesting to note in this article, the findings of the researchers would serve as reference in combating healthcare-associated infections. It would educate the nursing staff as far as infection control practices that form part as an update of the existing policies and guidelines.
It reminds the nurses and other healthcare workers of the grave consequences for patients if there will be an outbreak of the infection in the clinical setting. Likewise, the author of the article suggested some infection control strategies that will be of help in reducing the risk of cross-contamination and preventing the spread or transmission of infections. Bissett (2005) stressed that isolation of patient who is MRSA positive is the most ideal precautionary measure to prevent the spread of infections coupled with hygiene and cleanliness within the hospital premises.
The data presented in article three are prevalent in my clinical experience and the findings of the study is evident in every healthcare setting that when there is a rapid turnover interval of patients meaning admission of patients is greater than the discharge it will caused high bed occupancy resulting to increase in the MRSA rate due to overcrowding and work overload of nurses and other healthcare workers in a hospital setting.
Such limitations will put the nurses and medical staff working under pressure and may tend to forget to follow hygiene procedures and infection control practices (Wenzel, 1993). This article may influence the identified problem in my clinical experience by introducing equitable distribution of workload among nurses and medical staff that will include the number of patients to be taken care of by each nurse or medical staff.
In this case, nurses could concentrate on the activities and care plan to be introduced to the patient including the promotion of proper hygiene and observance of infection control practices. Conclusion In conclusion, the main recommendations arising from this study suggest that nurses must be knowledgeable to the current policies and guidelines relative to proper hygiene and infection control practices. This recommendation relates to the competencies of nurses to promote an environment that enables client safety, independence, quality of life, and health.
Likewise, nurses must also be responsible for their own professional development (Weber & Kelly, 2003). All qualified nurses must develop competency critical evaluation of research. According to Borbasi, et. al. (2008), it must be evident that nursing care provided to clients if possible, is based on quality research – based evidence. Assessing critical evaluation skills takes time and practice. Working along with other nurses (senior staff) can make the process more effective.
This will ensure that the highest possible standard for evidence-based practice is provided for patients. Relative to the three pieces of nursing research, it appears that poor hygiene and failure to follow infection control practices by nurses and other healthcare workers are contributory to rapid transmission of nosocomial infections such as MRSA in a clinical setting (Bissett, 2005). To effectively address this issue existing policies and guidelines on infection control and prevention should be updated and strictly implemented in a clinical setting.
An audit tool to monitor compliance of nurses and other health professionals to the said guidelines and policies should be initiated as part of the strategies on how to minimize if cannot eradicate the spread of infections. This study can be considered as a wake up call for nurses, doctors, and other healthcare workers for them to religiously observe proper hygiene within the hospital setting and strictly follow the standards provided by the government to stop the spread of infections in a clinical setting as well as in community setting through effective information, and education campaign.
REFERENCES Bissett, L. (2005). Controlling the risk of MRSA infection: screening and isolating patients. British journal of Nursing, 14 (7), 396-390. Borbasi, S. , Jackson, D. , & Langford, R. (2008). Navigating the maze of nursing research 2e: An interactive learning adventure. Sydney, Australia: Elsevier Mosby. Candlin, J. , Stark, S. (2005). Plastic apron wear during direct patient care. Nursing Standard. 20, (2), 41-46. Cunningham, J. , Kernohan, W. , & Rush, T. (2006). Bed occupancy, turnover internal and MRSA rates in Northern Ireland. British Journal of Nursing, 15 (6), 324-328.
Gopal Rao, G. (1998). Risk factors for the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Department of Microbiology, University Hospital: Lewisham, London Gould, D. (2008). Isolation precaution to prevent the spread of contagious diseases. Nursing Standard. 23, (22), 47-55. Parahoo, K. (1997). Nursing Research: Principles, processes and issues. Macmillan. ISB No. 337-69918-1. Weber, J. & Kelly, J. , (2003). Health assessment in nursing. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Wenzel, RP. (1993). Prevention and control of nosocomial infections, (2nd ed. ). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
How to cite this assignment
Related assignments:.
- Clinical Decision Making in Nursing Assignment
- Nursing Leadership Assignment
- Ethical and Legal Issues in Nursing Assignment
- Evidence-Based Practice & Applied Nursing Research Assignment
Haven't Found The Paper You Want?
For Only $13.90/page
- Open access
- Published: 17 April 2024
Deciphering the influence: academic stress and its role in shaping learning approaches among nursing students: a cross-sectional study
- Rawhia Salah Dogham 1 ,
- Heba Fakieh Mansy Ali 1 ,
- Asmaa Saber Ghaly 3 ,
- Nermine M. Elcokany 2 ,
- Mohamed Mahmoud Seweid 4 &
- Ayman Mohamed El-Ashry ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7718-4942 5
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 249 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
123 Accesses
Metrics details
Nursing education presents unique challenges, including high levels of academic stress and varied learning approaches among students. Understanding the relationship between academic stress and learning approaches is crucial for enhancing nursing education effectiveness and student well-being.
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of academic stress and its correlation with learning approaches among nursing students.
Design and Method
A cross-sectional descriptive correlation research design was employed. A convenient sample of 1010 nursing students participated, completing socio-demographic data, the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), and the Revised Study Process Questionnaire (R-SPQ-2 F).
Most nursing students experienced moderate academic stress (56.3%) and exhibited moderate levels of deep learning approaches (55.0%). Stress from a lack of professional knowledge and skills negatively correlates with deep learning approaches (r = -0.392) and positively correlates with surface learning approaches (r = 0.365). Female students showed higher deep learning approach scores, while male students exhibited higher surface learning approach scores. Age, gender, educational level, and academic stress significantly influenced learning approaches.
Academic stress significantly impacts learning approaches among nursing students. Strategies addressing stressors and promoting healthy learning approaches are essential for enhancing nursing education and student well-being.
Nursing implication
Understanding academic stress’s impact on nursing students’ learning approaches enables tailored interventions. Recognizing stressors informs strategies for promoting adaptive coping, fostering deep learning, and creating supportive environments. Integrating stress management, mentorship, and counseling enhances student well-being and nursing education quality.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Nursing education is a demanding field that requires students to acquire extensive knowledge and skills to provide competent and compassionate care. Nursing education curriculum involves high-stress environments that can significantly impact students’ learning approaches and academic performance [ 1 , 2 ]. Numerous studies have investigated learning approaches in nursing education, highlighting the importance of identifying individual students’ preferred approaches. The most studied learning approaches include deep, surface, and strategic approaches. Deep learning approaches involve students actively seeking meaning, making connections, and critically analyzing information. Surface learning approaches focus on memorization and reproducing information without a more profound understanding. Strategic learning approaches aim to achieve high grades by adopting specific strategies, such as memorization techniques or time management skills [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
Nursing education stands out due to its focus on practical training, where the blend of academic and clinical coursework becomes a significant stressor for students, despite academic stress being shared among all university students [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Consequently, nursing students are recognized as prone to high-stress levels. Stress is the physiological and psychological response that occurs when a biological control system identifies a deviation between the desired (target) state and the actual state of a fitness-critical variable, whether that discrepancy arises internally or externally to the human [ 9 ]. Stress levels can vary from objective threats to subjective appraisals, making it a highly personalized response to circumstances. Failure to manage these demands leads to stress imbalance [ 10 ].
Nursing students face three primary stressors during their education: academic, clinical, and personal/social stress. Academic stress is caused by the fear of failure in exams, assessments, and training, as well as workload concerns [ 11 ]. Clinical stress, on the other hand, arises from work-related difficulties such as coping with death, fear of failure, and interpersonal dynamics within the organization. Personal and social stressors are caused by an imbalance between home and school, financial hardships, and other factors. Throughout their education, nursing students have to deal with heavy workloads, time constraints, clinical placements, and high academic expectations. Multiple studies have shown that nursing students experience higher stress levels compared to students in other fields [ 12 , 13 , 14 ].
Research has examined the relationship between academic stress and coping strategies among nursing students, but no studies focus specifically on the learning approach and academic stress. However, existing literature suggests that students interested in nursing tend to experience lower levels of academic stress [ 7 ]. Therefore, interest in nursing can lead to deep learning approaches, which promote a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter, allowing students to feel more confident and less overwhelmed by coursework and exams. Conversely, students employing surface learning approaches may experience higher stress levels due to the reliance on memorization [ 3 ].
Understanding the interplay between academic stress and learning approaches among nursing students is essential for designing effective educational interventions. Nursing educators can foster deep learning approaches by incorporating active learning strategies, critical thinking exercises, and reflection activities into the curriculum [ 15 ]. Creating supportive learning environments encouraging collaboration, self-care, and stress management techniques can help alleviate academic stress. Additionally, providing mentorship and counselling services tailored to nursing students’ unique challenges can contribute to their overall well-being and academic success [ 16 , 17 , 18 ].
Despite the scarcity of research focusing on the link between academic stress and learning methods in nursing students, it’s crucial to identify the unique stressors they encounter. The intensity of these stressors can be connected to the learning strategies employed by these students. Academic stress and learning approach are intertwined aspects of the student experience. While academic stress can influence learning approaches, the choice of learning approach can also impact the level of academic stress experienced. By understanding this relationship and implementing strategies to promote healthy learning approaches and manage academic stress, educators and institutions can foster an environment conducive to deep learning and student well-being.
Hence, this study aims to investigate the correlation between academic stress and learning approaches experienced by nursing students.
Study objectives
Assess the levels of academic stress among nursing students.
Assess the learning approaches among nursing students.
Identify the relationship between academic stress and learning approach among nursing students.
Identify the effect of academic stress and related factors on learning approach and among nursing students.
Materials and methods
Research design.
A cross-sectional descriptive correlation research design adhering to the STROBE guidelines was used for this study.
A research project was conducted at Alexandria Nursing College, situated in Egypt. The college adheres to the national standards for nursing education and functions under the jurisdiction of the Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education. Alexandria Nursing College comprises nine specialized nursing departments that offer various nursing specializations. These departments include Nursing Administration, Community Health Nursing, Gerontological Nursing, Medical-Surgical Nursing, Critical Care Nursing, Pediatric Nursing, Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing, Nursing Education, and Psychiatric Nursing and Mental Health. The credit hour system is the fundamental basis of both undergraduate and graduate programs. This framework guarantees a thorough evaluation of academic outcomes by providing an organized structure for tracking academic progress and conducting analyses.
Participants and sample size calculation
The researchers used the Epi Info 7 program to calculate the sample size. The calculations were based on specific parameters such as a population size of 9886 students for the academic year 2022–2023, an expected frequency of 50%, a maximum margin of error of 5%, and a confidence coefficient of 99.9%. Based on these parameters, the program indicated that a minimum sample size of 976 students was required. As a result, the researchers recruited a convenient sample of 1010 nursing students from different academic levels during the 2022–2023 academic year [ 19 ]. This sample size was larger than the minimum required, which could help to increase the accuracy and reliability of the study results. Participation in the study required enrollment in a nursing program and voluntary agreement to take part. The exclusion criteria included individuals with mental illnesses based on their response and those who failed to complete the questionnaires.
socio-demographic data that include students’ age, sex, educational level, hours of sleep at night, hours spent studying, and GPA from the previous semester.
Tool two: the perceived stress scale (PSS)
It was initially created by Sheu et al. (1997) to gauge the level and nature of stress perceived by nursing students attending Taiwanese universities [ 20 ]. It comprises 29 items rated on a 5-point Likert scale, where (0 = never, 1 = rarely, 2 = sometimes, 3 = reasonably often, and 4 = very often), with a total score ranging from 0 to 116. The cut-off points of levels of perceived stress scale according to score percentage were low < 33.33%, moderate 33.33–66.66%, and high more than 66.66%. Higher scores indicate higher stress levels. The items are categorized into six subscales reflecting different sources of stress. The first subscale assesses “stress stemming from lack of professional knowledge and skills” and includes 3 items. The second subscale evaluates “stress from caring for patients” with 8 items. The third subscale measures “stress from assignments and workload” with 5 items. The fourth subscale focuses on “stress from interactions with teachers and nursing staff” with 6 items. The fifth subscale gauges “stress from the clinical environment” with 3 items. The sixth subscale addresses “stress from peers and daily life” with 4 items. El-Ashry et al. (2022) reported an excellent internal consistency reliability of 0.83 [ 21 ]. Two bilingual translators translated the English version of the scale into Arabic and then back-translated it into English by two other independent translators to verify its accuracy. The suitability of the translated version was confirmed through a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), which yielded goodness-of-fit indices such as a comparative fit index (CFI) of 0.712, a Tucker-Lewis index (TLI) of 0.812, and a root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) of 0.100.
Tool three: revised study process questionnaire (R-SPQ-2 F)
It was developed by Biggs et al. (2001). It examines deep and surface learning approaches using only 20 questions; each subscale contains 10 questions [ 22 ]. On a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 0 (never or only rarely true of me) to 4 (always or almost always accurate of me). The total score ranged from 0 to 80, with a higher score reflecting more deep or surface learning approaches. The cut-off points of levels of revised study process questionnaire according to score percentage were low < 33%, moderate 33–66%, and high more than 66%. Biggs et al. (2001) found that Cronbach alpha value was 0.73 for deep learning approach and 0.64 for the surface learning approach, which was considered acceptable. Two translators fluent in English and Arabic initially translated a scale from English to Arabic. To ensure the accuracy of the translation, they translated it back into English. The translated version’s appropriateness was evaluated using a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). The CFA produced several goodness-of-fit indices, including a Comparative Fit Index (CFI) of 0.790, a Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) of 0.912, and a Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) of 0.100. Comparative Fit Index (CFI) of 0.790, a Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) of 0.912, and a Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) of 0.100.
Ethical considerations
The Alexandria University College of Nursing’s Research Ethics Committee provided ethical permission before the study’s implementation. Furthermore, pertinent authorities acquired ethical approval at participating nursing institutions. The vice deans of the participating institutions provided written informed consent attesting to institutional support and authority. By giving written informed consent, participants confirmed they were taking part voluntarily. Strict protocols were followed to protect participants’ privacy during the whole investigation. The obtained personal data was kept private and available only to the study team. Ensuring participants’ privacy and anonymity was of utmost importance.
Tools validity
The researchers created tool one after reviewing pertinent literature. Two bilingual translators independently translated the English version into Arabic to evaluate the applicability of the academic stress and learning approach tools for Arabic-speaking populations. To assure accuracy, two additional impartial translators back-translated the translation into English. They were also assessed by a five-person jury of professionals from the education and psychiatric nursing departments. The scales were found to have sufficiently evaluated the intended structures by the jury.
Pilot study
A preliminary investigation involved 100 nursing student applicants, distinct from the final sample, to gauge the efficacy, clarity, and potential obstacles in utilizing the research instruments. The pilot findings indicated that the instruments were accurate, comprehensible, and suitable for the target demographic. Additionally, Cronbach’s Alpha was utilized to further assess the instruments’ reliability, demonstrating internal solid consistency for both the learning approaches and academic stress tools, with values of 0.91 and 0.85, respectively.
Data collection
The researchers convened with each qualified student in a relaxed, unoccupied classroom in their respective college settings. Following a briefing on the study’s objectives, the students filled out the datasheet. The interviews typically lasted 15 to 20 min.
Data analysis
The data collected were analyzed using IBM SPSS software version 26.0. Following data entry, a thorough examination and verification were undertaken to ensure accuracy. The normality of quantitative data distributions was assessed using Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests. Cronbach’s Alpha was employed to evaluate the reliability and internal consistency of the study instruments. Descriptive statistics, including means (M), standard deviations (SD), and frequencies/percentages, were computed to summarize academic stress and learning approaches for categorical data. Student’s t-tests compared scores between two groups for normally distributed variables, while One-way ANOVA compared scores across more than two categories of a categorical variable. Pearson’s correlation coefficient determined the strength and direction of associations between customarily distributed quantitative variables. Hierarchical regression analysis identified the primary independent factors influencing learning approaches. Statistical significance was determined at the 5% (p < 0.05).
Table 1 presents socio-demographic data for a group of 1010 nursing students. The age distribution shows that 38.8% of the students were between 18 and 21 years old, 32.9% were between 21 and 24 years old, and 28.3% were between 24 and 28 years old, with an average age of approximately 22.79. Regarding gender, most of the students were female (77%), while 23% were male. The students were distributed across different educational years, a majority of 34.4% in the second year, followed by 29.4% in the fourth year. The students’ hours spent studying were found to be approximately two-thirds (67%) of the students who studied between 3 and 6 h. Similarly, sleep patterns differ among the students; more than three-quarters (77.3%) of students sleep between 5- to more than 7 h, and only 2.4% sleep less than 2 h per night. Finally, the student’s Grade Point Average (GPA) from the previous semester was also provided. 21% of the students had a GPA between 2 and 2.5, 40.9% had a GPA between 2.5 and 3, and 38.1% had a GPA between 3 and 3.5.
Figure 1 provides the learning approach level among nursing students. In terms of learning approach, most students (55.0%) exhibited a moderate level of deep learning approach, followed by 25.9% with a high level and 19.1% with a low level. The surface learning approach was more prevalent, with 47.8% of students showing a moderate level, 41.7% showing a low level, and only 10.5% exhibiting a high level.
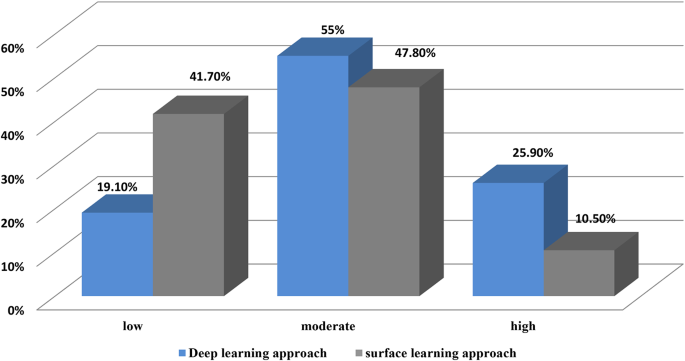
Nursing students? levels of learning approach (N=1010)
Figure 2 provides the types of academic stress levels among nursing students. Among nursing students, various stressors significantly impact their academic experiences. Foremost among these stressors are the pressure and demands associated with academic assignments and workload, with 30.8% of students attributing their high stress levels to these factors. Challenges within the clinical environment are closely behind, contributing significantly to high stress levels among 25.7% of nursing students. Interactions with peers and daily life stressors also weigh heavily on students, ranking third among sources of high stress, with 21.5% of students citing this as a significant factor. Similarly, interaction with teachers and nursing staff closely follow, contributing to high-stress levels for 20.3% of nursing students. While still significant, stress from taking care of patients ranks slightly lower, with 16.7% of students reporting it as a significant factor contributing to their academic stress. At the lowest end of the ranking, but still notable, is stress from a perceived lack of professional knowledge and skills, with 15.9% of students experiencing high stress in this area.
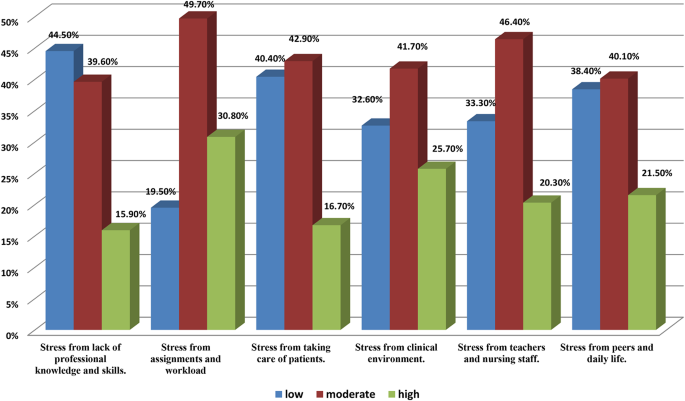
Nursing students? levels of academic stress subtypes (N=1010)
Figure 3 provides the total levels of academic stress among nursing students. The majority of students experienced moderate academic stress (56.3%), followed by those experiencing low academic stress (29.9%), and a minority experienced high academic stress (13.8%).
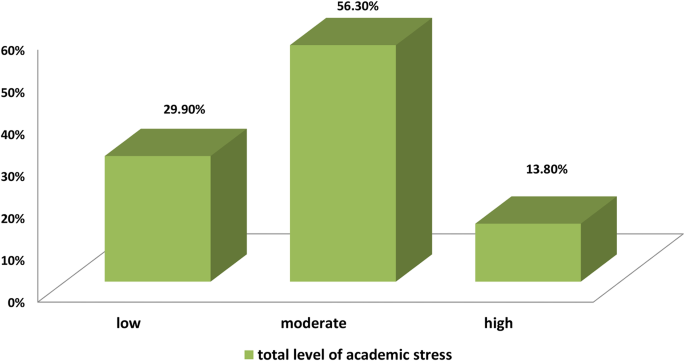
Nursing students? levels of total academic stress (N=1010)
Table 2 displays the correlation between academic stress subscales and deep and surface learning approaches among 1010 nursing students. All stress subscales exhibited a negative correlation regarding the deep learning approach, indicating that the inclination toward deep learning decreases with increasing stress levels. The most significant negative correlation was observed with stress stemming from the lack of professional knowledge and skills (r=-0.392, p < 0.001), followed by stress from the clinical environment (r=-0.109, p = 0.001), stress from assignments and workload (r=-0.103, p = 0.001), stress from peers and daily life (r=-0.095, p = 0.002), and stress from patient care responsibilities (r=-0.093, p = 0.003). The weakest negative correlation was found with stress from interactions with teachers and nursing staff (r=-0.083, p = 0.009). Conversely, concerning the surface learning approach, all stress subscales displayed a positive correlation, indicating that heightened stress levels corresponded with an increased tendency toward superficial learning. The most substantial positive correlation was observed with stress related to the lack of professional knowledge and skills (r = 0.365, p < 0.001), followed by stress from patient care responsibilities (r = 0.334, p < 0.001), overall stress (r = 0.355, p < 0.001), stress from interactions with teachers and nursing staff (r = 0.262, p < 0.001), stress from assignments and workload (r = 0.262, p < 0.001), and stress from the clinical environment (r = 0.254, p < 0.001). The weakest positive correlation was noted with stress stemming from peers and daily life (r = 0.186, p < 0.001).
Table 3 outlines the association between the socio-demographic characteristics of nursing students and their deep and surface learning approaches. Concerning age, statistically significant differences were observed in deep and surface learning approaches (F = 3.661, p = 0.003 and F = 7.983, p < 0.001, respectively). Gender also demonstrated significant differences in deep and surface learning approaches (t = 3.290, p = 0.001 and t = 8.638, p < 0.001, respectively). Female students exhibited higher scores in the deep learning approach (31.59 ± 8.28) compared to male students (29.59 ± 7.73), while male students had higher scores in the surface learning approach (29.97 ± 7.36) compared to female students (24.90 ± 7.97). Educational level exhibited statistically significant differences in deep and surface learning approaches (F = 5.599, p = 0.001 and F = 17.284, p < 0.001, respectively). Both deep and surface learning approach scores increased with higher educational levels. The duration of study hours demonstrated significant differences only in the surface learning approach (F = 3.550, p = 0.014), with scores increasing as study hours increased. However, no significant difference was observed in the deep learning approach (F = 0.861, p = 0.461). Hours of sleep per night and GPA from the previous semester did not exhibit statistically significant differences in deep or surface learning approaches.
Table 4 presents a multivariate linear regression analysis examining the factors influencing the learning approach among 1110 nursing students. The deep learning approach was positively influenced by age, gender (being female), educational year level, and stress from teachers and nursing staff, as indicated by their positive coefficients and significant p-values (p < 0.05). However, it was negatively influenced by stress from a lack of professional knowledge and skills. The other factors do not significantly influence the deep learning approach. On the other hand, the surface learning approach was positively influenced by gender (being female), educational year level, stress from lack of professional knowledge and skills, stress from assignments and workload, and stress from taking care of patients, as indicated by their positive coefficients and significant p-values (p < 0.05). However, it was negatively influenced by gender (being male). The other factors do not significantly influence the surface learning approach. The adjusted R-squared values indicated that the variables in the model explain 17.8% of the variance in the deep learning approach and 25.5% in the surface learning approach. Both models were statistically significant (p < 0.001).
Nursing students’ academic stress and learning approaches are essential to planning for effective and efficient learning. Nursing education also aims to develop knowledgeable and competent students with problem-solving and critical-thinking skills.
The study’s findings highlight the significant presence of stress among nursing students, with a majority experiencing moderate to severe levels of academic stress. This aligns with previous research indicating that academic stress is prevalent among nursing students. For instance, Zheng et al. (2022) observed moderated stress levels in nursing students during clinical placements [ 23 ], while El-Ashry et al. (2022) found that nearly all first-year nursing students in Egypt experienced severe academic stress [ 21 ]. Conversely, Ali and El-Sherbini (2018) reported that over three-quarters of nursing students faced high academic stress. The complexity of the nursing program likely contributes to these stress levels [ 24 ].
The current study revealed that nursing students identified the highest sources of academic stress as workload from assignments and the stress of caring for patients. This aligns with Banu et al.‘s (2015) findings, where academic demands, assignments, examinations, high workload, and combining clinical work with patient interaction were cited as everyday stressors [ 25 ]. Additionally, Anaman-Torgbor et al. (2021) identified lectures, assignments, and examinations as predictors of academic stress through logistic regression analysis. These stressors may stem from nursing programs emphasizing the development of highly qualified graduates who acquire knowledge, values, and skills through classroom and clinical experiences [ 26 ].
The results regarding learning approaches indicate that most nursing students predominantly employed the deep learning approach. Despite acknowledging a surface learning approach among the participants in the present study, the prevalence of deep learning was higher. This inclination toward the deep learning approach is anticipated in nursing students due to their engagement with advanced courses, requiring retention, integration, and transfer of information at elevated levels. The deep learning approach correlates with a gratifying learning experience and contributes to higher academic achievements [ 3 ]. Moreover, the nursing program’s emphasis on active learning strategies fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. These findings align with Mahmoud et al.‘s (2019) study, reporting a significant presence (83.31%) of the deep learning approach among undergraduate nursing students at King Khalid University’s Faculty of Nursing [ 27 ]. Additionally, Mohamed &Morsi (2019) found that most nursing students at Benha University’s Faculty of Nursing embraced the deep learning approach (65.4%) compared to the surface learning approach [ 28 ].
The study observed a negative correlation between the deep learning approach and the overall mean stress score, contrasting with a positive correlation between surface learning approaches and overall stress levels. Elevated academic stress levels may diminish motivation and engagement in the learning process, potentially leading students to feel overwhelmed, disinterested, or burned out, prompting a shift toward a surface learning approach. This finding resonates with previous research indicating that nursing students who actively seek positive academic support strategies during academic stress have better prospects for success than those who do not [ 29 ]. Nebhinani et al. (2020) identified interface concerns and academic workload as significant stress-related factors. Notably, only an interest in nursing demonstrated a significant association with stress levels, with participants interested in nursing primarily employing adaptive coping strategies compared to non-interested students.
The current research reveals a statistically significant inverse relationship between different dimensions of academic stress and adopting the deep learning approach. The most substantial negative correlation was observed with stress arising from a lack of professional knowledge and skills, succeeded by stress associated with the clinical environment, assignments, and workload. Nursing students encounter diverse stressors, including delivering patient care, handling assignments and workloads, navigating challenging interactions with staff and faculty, perceived inadequacies in clinical proficiency, and facing examinations [ 30 ].
In the current study, the multivariate linear regression analysis reveals that various factors positively influence the deep learning approach, including age, female gender, educational year level, and stress from teachers and nursing staff. In contrast, stress from a lack of professional knowledge and skills exert a negative influence. Conversely, the surface learning approach is positively influenced by female gender, educational year level, stress from lack of professional knowledge and skills, stress from assignments and workload, and stress from taking care of patients, but negatively affected by male gender. The models explain 17.8% and 25.5% of the variance in the deep and surface learning approaches, respectively, and both are statistically significant. These findings underscore the intricate interplay of demographic and stress-related factors in shaping nursing students’ learning approaches. High workloads and patient care responsibilities may compel students to prioritize completing tasks over deep comprehension. This pressure could lead to a surface learning approach as students focus on meeting immediate demands rather than engaging deeply with course material. This observation aligns with the findings of Alsayed et al. (2021), who identified age, gender, and study year as significant factors influencing students’ learning approaches.
Deep learners often demonstrate better self-regulation skills, such as effective time management, goal setting, and seeking support when needed. These skills can help manage academic stress and maintain a balanced learning approach. These are supported by studies that studied the effect of coping strategies on stress levels [ 6 , 31 , 32 ]. On the contrary, Pacheco-Castillo et al. study (2021) found a strong significant relationship between academic stressors and students’ level of performance. That study also proved that the more academic stress a student faces, the lower their academic achievement.
Strengths and limitations of the study
This study has lots of advantages. It provides insightful information about the educational experiences of Egyptian nursing students, a demographic that has yet to receive much research. The study’s limited generalizability to other people or nations stems from its concentration on this particular group. This might be addressed in future studies by using a more varied sample. Another drawback is the dependence on self-reported metrics, which may contain biases and mistakes. Although the cross-sectional design offers a moment-in-time view of the problem, it cannot determine causation or evaluate changes over time. To address this, longitudinal research may be carried out.
Notwithstanding these drawbacks, the study substantially contributes to the expanding knowledge of academic stress and nursing students’ learning styles. Additional research is needed to determine teaching strategies that improve deep-learning approaches among nursing students. A qualitative study is required to analyze learning approaches and factors that may influence nursing students’ selection of learning approaches.
According to the present study’s findings, nursing students encounter considerable academic stress, primarily stemming from heavy assignments and workload, as well as interactions with teachers and nursing staff. Additionally, it was observed that students who experience lower levels of academic stress typically adopt a deep learning approach, whereas those facing higher stress levels tend to resort to a surface learning approach. Demographic factors such as age, gender, and educational level influence nursing students’ choice of learning approach. Specifically, female students are more inclined towards deep learning, whereas male students prefer surface learning. Moreover, deep and surface learning approach scores show an upward trend with increasing educational levels and study hours. Academic stress emerges as a significant determinant shaping the adoption of learning approaches among nursing students.
Implications in nursing practice
Nursing programs should consider integrating stress management techniques into their curriculum. Providing students with resources and skills to cope with academic stress can improve their well-being and academic performance. Educators can incorporate teaching strategies that promote deep learning approaches, such as problem-based learning, critical thinking exercises, and active learning methods. These approaches help students engage more deeply with course material and reduce reliance on surface learning techniques. Recognizing the gender differences in learning approaches, nursing programs can offer gender-specific support services and resources. For example, providing targeted workshops or counseling services that address male and female nursing students’ unique stressors and learning needs. Implementing mentorship programs and peer support groups can create a supportive environment where students can share experiences, seek advice, and receive encouragement from their peers and faculty members. Encouraging students to reflect on their learning processes and identify effective study strategies can help them develop metacognitive skills and become more self-directed learners. Faculty members can facilitate this process by incorporating reflective exercises into the curriculum. Nursing faculty and staff should receive training on recognizing signs of academic stress among students and providing appropriate support and resources. Additionally, professional development opportunities can help educators stay updated on evidence-based teaching strategies and practical interventions for addressing student stress.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to restrictions imposed by the institutional review board to protect participant confidentiality, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Liu J, Yang Y, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Li J. Stress and coping styles among nursing students during the initial period of the clinical practicum: A cross-section study. Int J Nurs Sci. 2022a;9(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2022.02.004 .
Saifan A, Devadas B, Daradkeh F, Abdel-Fattah H, Aljabery M, Michael LM. Solutions to bridge the theory-practice gap in nursing education in the UAE: a qualitative study. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02919-x .
Alsayed S, Alshammari F, Pasay-an E, Dator WL. Investigating the learning approaches of students in nursing education. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2021;16(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2020.10.008 .
Salah Dogham R, Elcokany NM, Saber Ghaly A, Dawood TMA, Aldakheel FM, Llaguno MBB, Mohsen DM. Self-directed learning readiness and online learning self-efficacy among undergraduate nursing students. Int J Afr Nurs Sci. 2022;17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijans.2022.100490 .
Zhao Y, Kuan HK, Chung JOK, Chan CKY, Li WHC. Students’ approaches to learning in a clinical practicum: a psychometric evaluation based on item response theory. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2018.04.015 .
Huang HM, Fang YW. Stress and coping strategies of online nursing practicum courses for Taiwanese nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative study. Healthcare. 2023;11(14). https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11142053 .
Nebhinani M, Kumar A, Parihar A, Rani R. Stress and coping strategies among undergraduate nursing students: a descriptive assessment from Western Rajasthan. Indian J Community Med. 2020;45(2). https://doi.org/10.4103/ijcm.IJCM_231_19 .
Olvera Alvarez HA, Provencio-Vasquez E, Slavich GM, Laurent JGC, Browning M, McKee-Lopez G, Robbins L, Spengler JD. Stress and health in nursing students: the Nurse Engagement and Wellness Study. Nurs Res. 2019;68(6). https://doi.org/10.1097/NNR.0000000000000383 .
Del Giudice M, Buck CL, Chaby LE, Gormally BM, Taff CC, Thawley CJ, Vitousek MN, Wada H. What is stress? A systems perspective. Integr Comp Biol. 2018;58(6):1019–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/icy114 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bhui K, Dinos S, Galant-Miecznikowska M, de Jongh B, Stansfeld S. Perceptions of work stress causes and effective interventions in employees working in public, private and non-governmental organisations: a qualitative study. BJPsych Bull. 2016;40(6). https://doi.org/10.1192/pb.bp.115.050823 .
Lavoie-Tremblay M, Sanzone L, Aubé T, Paquet M. Sources of stress and coping strategies among undergraduate nursing students across all years. Can J Nurs Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/08445621211028076 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ahmed WAM, Abdulla YHA, Alkhadher MA, Alshameri FA. Perceived stress and coping strategies among nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. Saudi J Health Syst Res. 2022;2(3). https://doi.org/10.1159/000526061 .
Pacheco-Castillo J, Casuso-Holgado MJ, Labajos-Manzanares MT, Moreno-Morales N. Academic stress among nursing students in a Private University at Puerto Rico, and its Association with their academic performance. Open J Nurs. 2021;11(09). https://doi.org/10.4236/ojn.2021.119063 .
Tran TTT, Nguyen NB, Luong MA, Bui THA, Phan TD, Tran VO, Ngo TH, Minas H, Nguyen TQ. Stress, anxiety and depression in clinical nurses in Vietnam: a cross-sectional survey and cluster analysis. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2019;13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13033-018-0257-4 .
Magnavita N, Chiorri C. Academic stress and active learning of nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2018.06.003 .
Folkvord SE, Risa CF. Factors that enhance midwifery students’ learning and development of self-efficacy in clinical placement: a systematic qualitative review. Nurse Educ Pract. 2023;66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2022.103510 .
Myers SB, Sweeney AC, Popick V, Wesley K, Bordfeld A, Fingerhut R. Self-care practices and perceived stress levels among psychology graduate students. Train Educ Prof Psychol. 2012;6(1). https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026534 .
Zeb H, Arif I, Younas A. Nurse educators’ experiences of fostering undergraduate students’ ability to manage stress and demanding situations: a phenomenological inquiry. Nurse Educ Pract. 2022;65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2022.103501 .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. User Guide| Support| Epi Info™ [Internet]. Atlanta: CDC; [cited 2024 Jan 31]. Available from: CDC website.
Sheu S, Lin HS, Hwang SL, Yu PJ, Hu WY, Lou MF. The development and testing of a perceived stress scale for nursing students in clinical practice. J Nurs Res. 1997;5:41–52. Available from: http://ntur.lib.ntu.edu.tw/handle/246246/165917 .
El-Ashry AM, Harby SS, Ali AAG. Clinical stressors as perceived by first-year nursing students of their experience at Alexandria main university hospital during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2022;41:214–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apnu.2022.08.007 .
Biggs J, Kember D, Leung DYP. The revised two-factor study process questionnaire: R-SPQ-2F. Br J Educ Psychol. 2001;71(1):133–49. https://doi.org/10.1348/000709901158433 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Zheng YX, Jiao JR, Hao WN. Stress levels of nursing students: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Med (United States). 2022;101(36). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000030547 .
Ali AM, El-Sherbini HH. Academic stress and its contributing factors among faculty nursing students in Alexandria. Alexandria Scientific Nursing Journal. 2018; 20(1):163–181. Available from: https://asalexu.journals.ekb.eg/article_207756_b62caf4d7e1e7a3b292bbb3c6632a0ab.pdf .
Banu P, Deb S, Vardhan V, Rao T. Perceived academic stress of university students across gender, academic streams, semesters, and academic performance. Indian J Health Wellbeing. 2015;6(3):231–235. Available from: http://www.iahrw.com/index.php/home/journal_detail/19#list .
Anaman-Torgbor JA, Tarkang E, Adedia D, Attah OM, Evans A, Sabina N. Academic-related stress among Ghanaian nursing students. Florence Nightingale J Nurs. 2021;29(3):263. https://doi.org/10.5152/FNJN.2021.21030 .
Mahmoud HG, Ahmed KE, Ibrahim EA. Learning Styles and Learning Approaches of Bachelor Nursing Students and its Relation to Their Achievement. Int J Nurs Didact. 2019;9(03):11–20. Available from: http://www.nursingdidactics.com/index.php/ijnd/article/view/2465 .
Mohamed NAAA, Morsi MES, Learning Styles L, Approaches. Academic achievement factors, and self efficacy among nursing students. Int J Novel Res Healthc Nurs. 2019;6(1):818–30. Available from: www.noveltyjournals.com.
Google Scholar
Onieva-Zafra MD, Fernández-Muñoz JJ, Fernández-Martínez E, García-Sánchez FJ, Abreu-Sánchez A, Parra-Fernández ML. Anxiety, perceived stress and coping strategies in nursing students: a cross-sectional, correlational, descriptive study. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-020-02294-z .
Article Google Scholar
Aljohani W, Banakhar M, Sharif L, Alsaggaf F, Felemban O, Wright R. Sources of stress among Saudi Arabian nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(22). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182211958 .
Liu Y, Wang L, Shao H, Han P, Jiang J, Duan X. Nursing students’ experience during their practicum in an intensive care unit: a qualitative meta-synthesis. Front Public Health. 2022;10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.974244 .
Majrashi A, Khalil A, Nagshabandi E, Al MA. Stressors and coping strategies among nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic: scoping review. Nurs Rep. 2021;11(2):444–59. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep11020042 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Our sincere thanks go to all the nursing students in the study. We also want to thank Dr/ Rasha Badry for their statistical analysis help and contribution to this study.
The research was not funded by public, commercial, or non-profit organizations.
Open access funding provided by The Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in cooperation with The Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nursing Education, Faculty of Nursing, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
Rawhia Salah Dogham & Heba Fakieh Mansy Ali
Critical Care & Emergency Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
Nermine M. Elcokany
Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
Asmaa Saber Ghaly
Faculty of Nursing, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, Egypt
Mohamed Mahmoud Seweid
Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
Ayman Mohamed El-Ashry
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Ayman M. El-Ashry & Rawhia S. Dogham: conceptualization, preparation, and data collection; methodology; investigation; formal analysis; data analysis; writing-original draft; writing-manuscript; and editing. Heba F. Mansy Ali & Asmaa S. Ghaly: conceptualization, preparation, methodology, investigation, writing-original draft, writing-review, and editing. Nermine M. Elcokany & Mohamed M. Seweid: Methodology, investigation, formal analysis, data collection, writing-manuscript & editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript and accept for publication.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ayman Mohamed El-Ashry .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The research adhered to the guidelines and regulations outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki (DoH-Oct2008). The Faculty of Nursing’s Research Ethical Committee (REC) at Alexandria University approved data collection in this study (IRB00013620/95/9/2022). Participants were required to sign an informed written consent form, which included an explanation of the research and an assessment of their understanding.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Dogham, R.S., Ali, H.F.M., Ghaly, A.S. et al. Deciphering the influence: academic stress and its role in shaping learning approaches among nursing students: a cross-sectional study. BMC Nurs 23 , 249 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01885-1
Download citation
Received : 31 January 2024
Accepted : 21 March 2024
Published : 17 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01885-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Academic stress
- Learning approaches
- Nursing students
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Design-based Research Method in PBL/PjBL: A case in Nursing Education
Article sidebar, main article content.
Design-based Research (DBR) focuses on real-world problems, emphasizes studying an educational intervention in its supposed context, uses a cyclical process of design, implementation, evaluation, and improvement, utilizes mixed research methods, stresses reciprocal relationships between theories and practice, and involves a close collaborative relationship between researchers and practitioners. Three iterative DBR research cycles were conducted on a project-based learning (PjBL) implementation in three population health nursing clinical PjBL blocks at a Midwest university. Data were collected at the end of each cycle through surveys, focus group interviews with students, faculty, and clinical agency contacts, as well as student work and performance. The data were analyzed, and revisions and improvements were planned for subsequent blocks and future use in the course.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License .
1. Publication and Promotion : In consideration of the Publisher’s agreement to publish the Work, Author hereby grants and assigns to Publisher the non-exclusive right to print, publish, reproduce, or distribute the Work throughout the world in all means of expression by any method now known or hereafter developed, including electronic format, and to market or sell the Work orany part of it as Publisher sees fit. Author further grants Publisher the right to use Author’s name in association with the Work inpublished form and in advertising and promotional materials
2. C opyright : Copyright of the Work remains in Author’s name.
3. Prior Publication and Attribution : Author agrees not to publish the Work in print form prior to publication of the Work by the Publisher. Author agrees to cite, by author, title, and publisher, the original Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-based Learning publication when publishing the Work elsewhere
4. Author Representations : The Author represents and warrants that the Work:
(a) is the Author’s original Work and that Author has full power to enter into this Agreement;
(b) does not infringe the copyright or property of another;
(c) contains no material which is obscene, libelous, defamatory or previously published, in whole or in part.
Author shall indemnify and hold Publisher harmless against loss of expenses arising from breach of any such warranties.
5. Licensing and Reuse : Reuse of the published Work will be governed by a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0; http://creativecommons.org/licenses/ by-nc/4.0/). This license lets others remix, tweak, and build upon the Work non-commercially; although new works must acknowledge the original Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-based Learning publication and be non-commercial, they do not have to be licensed on the same terms.
Joni Tweeten, University of North Dakota
Joni Tweeten is a Clinical Associate Professor in the Nursing Department at the University of North Dakota and is working on her Education, Health, and Behavioral Studies PhD with a specialization in Instructional Design and Technology.
Woei Hung, University of North Dakota
Woei Hung is currently a professor and graduate director of the Instructional Design and Technology Program in the College of Education and Human Development at the University of North Dakota. His research areas include problem-based learning (PBL), complex problem solving, systems thinking and modeling, concept mapping and formation, and microlearning. He has published numerous journal articles and book chapters in the areas of PBL problem and curriculum design. He is currently an executive board member and the treasurer of the PAN PBL Association of Problem-Based Learning and Active Learning Methodologies.
American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN). (2021, April 6). The essentials: Core competencies for professional nursing education. https://www.aacnnursing.org/Portals/0/PDFs/Publications/Essentials-2021.pdf
American Nurses Association (ANA). (2022). Public health nursing scope and standards of practice (3rd ed.). American Nurses Publishing.
American Public Health Association (APHA), Public Health Nursing Section. (2013). The definition and practice of public health nursing: A statement of the public health nursing section. https://www.apha.org/~/media/files/pdf/membergroups/phn/nursingdefinition.ashx .
Anderson, T., & Shattuck, J. (2012). Design-based research: A decade of progress in education research? Educational Researcher, 41(1), 16–25. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X11428813
Arif, Y. & Putri, Z. M. (2022). Project based learning method: Improving critical thinking and problem-solving skills for nursing students. Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities Research, 650, 48-52. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Educational Development and Quality Assurance (ICED-QA 2021). http://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.220303.010
Bannan-Ritland, B., & Baek, J. Y. (2008). Investigating the act of design in design research: The road taken. In Handbook of design research methods in education (pp. 209–319). Routledge.
Barab, S., & Squire, K. (2004). Introduction: Design-based research: Putting a stake in the ground. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 13(1), 1–14.
Bassi, S. (2011, May/June). Undergraduate nursing students’ perceptions of service-learning through a school-based community project. Nursing Education Perspectives, 32(3), 162-167. http://doi.org/10.5480/1536-5026-32.3.162
Brown, A. L. (1992). Design experiments: Theoretical and methodological challenges in creating complex interventions in classroom settings. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 2(2), 141–178.
Buck Institute for Education (BIE). (n.d.). What is PBL? PBL Works. https://www.pblworks.org/what-is-pbl
Collins, A. (1992). Toward a design science of education. In E. Scanlon & T. O’Shea (Eds.), New directions in educational technology. Spinger-Verlag.
Collins, A., Joseph, D., & Bielaczyc, K. (2004). Design research: Theoretical and methodological issues. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 13(1), 15–42.
Daley, C. S. & Sciegaj, M. (2021). Incorporating a project-based learning approach in an advanced undergraduate course on long-term care administration: A spark that ignites the flame. Journal of Health Administration Education, 38(2), 517-532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2020.101586
Dick, W., Carey, L., & Carey, J. O. (2009). The systematic design of instruction (7th ed.). Pearson.
Gravemeijer, K., & Cobb, P. (2006). Outline of a method for design research in mathematics education. In Educational Design Research (pp. 17–51). Routledge.
Hanklang, S. & Sivasan, S. (2019). Effectiveness of the project-based learning program on Thai nursing student competency for elderly care in the community. Journal of Health Research, 35, 132-146. http://doi.org/10.1108/JHR-07-2019-0160
Herrington, J., & Oliver, R. (2000). An instructional design framework for authentic learning environments. Educational Technology Research and Development, 48(3), 23–48.
Hung, W. (2006). The 3C3R Model: A conceptual framework for designing problems in PBL. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.7771/1541-5015.1006
Jonassen, D. H. (2000). Toward a design theory of problem solving. Educational Technology Research and Development, 48(4), 63–85.
Jonassen, D. H., Cernusca, D., & Ionas, G. (2007). Constructivism and instructional design: The emergence of the learning sciences and design research. In trends and issues in instructional design and technology. (pp. 45–52). Peasron.
Jonassen, D., & Hung, W. (2008). All problems are not equal: Implications for problem-based learning. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 2(2). https://doi.org/10.7771/1541-5015.1080
Kokotsaki, D., Menzies, V., & Wiggins, A. (2016). Project-based learning: A review of the literature. Improving Schools, 19(3), 267–277. https://doi.org/10.1177/1365480216659733
Koo, H-Y., Gu, Y-E., & Lee, B-R. (2022, April 26). Development of a project-based learning program on high-risk newborn care for nursing students and its effects: A quasi-experimental study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(9), 5249. http://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095249
McKenney, S., & Reeves, T. C. (2019). Conducting educational design research (2nd ed.). Routledge.
Moallem, M., Hung, W., & Dabbagh, N. (2019). The Wily Handbook of problem-based learning. Wiley-Blackwell.
Neville, A. J. (2009). Problem-based learning and medical education forty years on. A review of its effects on knowledge and clinical performance. Medical Principles and Practice: International Journal of the Kuwait University, Health Science Centre, 18(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000163038
Pascon, D. M., Vaz, D. R., Peres, H. H. C., & Leonello, V. M. (2022, August). Project-based learning in remote teaching for undergraduate nursing students. Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP, (56), e20220058. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-220X-REEUSP-2022-0058en
Quad Council Coalition Competency Review Task Force (Quad Council). (2018). Community/public health nursing [C/PHN] competencies. http://www.quadcouncilphn.org/documents-3/2018-qcc-competencies/
Reeves, T. C., Herrington, J., & Oliver, R. (2005). Design research: A socially responsible approach to instructional technology research in higher education. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 16(2), 96–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02961476
Reinking, D., & Bradley, B. A. (2008). Formative and design experiments: Approaches to language and literarcy research. Teachers College Press.
Sandoval, W. (2014). Conjecture Mapping: An approach to systematic educational design research. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 23(1), 18–36.
Shavelson, R. J., Phillips, D. C., Towne, L., & Feuer, M. J. (2003). On the science of education design studies. Educational Researcher, 32(1), 25–28.
Sung, T-W., Wu, T-T. (2018, March). Learning with e-books and project-based strategy in a community health nursing course. Computers, Informatics, and Nursing, 36(3), 140-146. http://doi.org/10.1097/CIN.0000000000000398
Sweller, J., Clark, R. E., & Kirschner, P. A. (2011). Teaching general problem solving does not lead to mathematical skillsor knowledge. Newsletter of the European Mathematical Society, 41–42.
Tanner, C. A. (2006, June). Thinking like a nurse: A research-based model of clinical judgment in nursing. Journal of Nursing Education, 45(6), 204-211. http://doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20060601-04
The Design-Based Research Collective. (2003). Design-based research: An emerging paradigm for educational inquiry. Educational Researcher, 32(1), 5–8. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X032001005
Wahyuningsih, B. D., Sudarsih, S., & Zainudin, M. (2020). The differences of project based learning and cooperative learning models to influence of critical thinking ability in student medical and surgical subject 3rd semester of DIII nursing study program. International Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Science, 4(2), 105-111. http://doi.org/10.29082/IJNMS/2020/Vol4/
Wang, F., & Hannafin, M. J. (2005). Design-Based Research and Technology-Enhanced Learning Environments. Educational Technology Research and Development, 53(4), 5–23.
Wozniak, H. (2015). Conjecture mapping to optimize the educational design research process. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 31(5), Article 5. https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.2505
Zeydani, A., Atashzadeh-Shoorideh, F., Abdi, F., Hosseini, M., Zohari-Anboohi, S., & Skerrett, V. (2021, November 18). Effect of community-based education on undergraduate nursing students’ skills: A systematic review. BMC Nursing, 20(11), 1472-6955. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-021-00755-4
Finding Solutions For Burnout Among Nurses of Color
The Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research at the School of Nursing brought together nurses and researchers for the Solutions to Health Inequities & Nurses’ Emotional Exhaustion Invitational.
This story originally appeared in Penn Today. It was written by Erica Moser, Science News Officer in University Communications. Photo by Kelvin Amenyedor/CHOPR.

She and study co-author Jacqueline Nikpour, postdoctoral fellow in the Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research (CHOPR) at Penn Nursing, spoke about their findings and in particular, issues impacting nurses of color by bringing nursing researchers and practitioners to the Solutions to Health Inequities & Nurses’ Emotional Exhaustion (SHINE) Invitational.
Brooks Carthon said the nurse practitioners (NPs) she spoke to for the study had expressed deep emotional exhaustion, often the result of the uncompensated labor of championing health equity and fighting for organizational change, along with experiences of racism and microaggressions. Yet in ongoing discussions about the burnout crisis in nursing, she said it’s uncommon to hear about the disproportionate burden on nurses of color.
“If we’re going to develop solutions, we need to center their experiences,” Brooks Carthon said. “The reason this is called SHINE is because we wanted to shine a light on the fact that, yes, burnout is at crisis levels, but the disproportionate weight of the burnout crisis is falling on the shoulders of nurses of color, and we need to do something about it. We are the solution we’ve been waiting for.”
The one-day conference brought about 40 attendees not only from Penn and other Philadelphia universities, but also people from New York, Maryland, California, Texas, and elsewhere in the country. The attendees included half of the 16 NPS interviewed for the study.
Charlotte Thomas-Hawkins, associate dean at the Rutgers University School of Nursing and a recipient of two nursing degrees from Penn, shared findings from a study she led, “Effects of Race, Workplace Racism, and COVID Worry on the Emotional Well-Being of Hospital-Based Nurses: A Dual Pandemic.” That study found that nonwhite nurses reported higher emotional distress, more racial microaggressions, and more negative views about the racial climate at their workplace.
“I am hopeful because we are here with a common cause, we’re leaders, we’re accomplished, we’re respected in our profession, and we have an equity passion.”
Penn Nursing Dean Antonia M. Villarruel addressed the topic in remarks following the presentation, noting that these inequities have an effect. “It’s exhausting; it takes a toll,” she said. But she said those gathered have an opportunity to identify what needs to happen in work environments to support nurses of color.
“I am hopeful because we are here with a common cause, we’re leaders, we’re accomplished, we’re respected in our profession, and we have an equity passion,” Villarruel said. In introductions, attendees shared some of their specific equity passions: maternal outcomes, disparities among LGBTQ+ populations, diabetes, immigrant nurses in long-term care, and Black women experiencing violence in their communities.
The invitational also included small group discussions about experiences with burnout and emotional exhaustion, addressing health disparities, barriers to advancing health equity, policies that could address health equity, and factors contributing to burnout; the presentation of findings from the American Nurses Association’s National Commission to Address Racism in Nursing; and the setting of priority areas for research.
For Brooks Carthon, part of the goal of the gathering was the opportunity to connect nurses who share equity passions. She said she also wanted attendees to be aware of funding opportunities, such as a Notice of Special Interest from the National Institute of Nursing Research seeking research studies to prevent and mitigate nurse burnout and the American Association of Critical- Care Nurses’ announcement of grants to support nursing work environments and health equity.
“We can start the conversation here,” Brooks Carthon said, “and we think the real magic is going to happen because we’re fostering these connections.”
What’s Next?
SHINE participants have agreed to host additional events going forward—a significant commitment to continued dialogue and action. The decision to form a partnership between scholars and practitioners underscores the importance of supporting evidence-based strategies for transformative change, signaling a move towards more research in clinical areas and convening key partners for meaningful engagement.
More From This Issue
Don’t go keeping nursing at the bedside, dnp project showcase: promising approaches, bright ideas, see yourself here.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Development of a Nursing Assignment Tool Using Workload Acuity Scores
To determine a just and consistent practice for creating nursing assignments.
BACKGROUND:
Traditional methods of assigning patients to nurses may lead to unbalanced nursing workload. This article describes the ongoing, hospital-wide effort to evaluate and implement a nursing assignment tool based on electronic health record (EHR) functionality and auto-calculated nursing workload scores.
EHR records of individual patient workload scores from all hospital units were collected from August 2017 to June 2018. A nurse-specific total workload score was summed for each staff. Then, each hospital unit’s mean nurse workload score and standard deviation, along with the unit’s nurse-to-patient ratio, were used to calculate levels of high, medium, and low nursing workload measurement (NWM).
Mean patient-specific workload scores varied greatly across hospital units. Unit-specific nurse-to-patient ratios were factored into NWM scores to create ranges for assignments that were relatively consistent across the institution.
CONCLUSION:
The use of objective, electronically generated nursing workload scores, combined with traditional nurse-to-patient ratios, provides accurate real-time nurse staffing needs that can inform best practice in staffing. The confirmation of individual patient workload scores and an appreciation for the complexity of EHR vendor rules are necessary for successful implementation. Automation ensures patient safety, staff satisfaction, and optimal resource allocation.
The focus in healthcare has been to increase quality while maintaining costs. Donabedian’s model for improving quality is based on the triad of structure, process, and outcomes and is often used in current patient outcomes and value-based payment models. 1 Newer methodologies include the Quality Health Outcome Model, which uses pathways for associating nursing care and quality. Others focus on the National Database of Nursing Quality Indicators (NDNQI) to review nurse staffing and outcomes. 2 Research has shown that when administrators decrease staff in an effort to lower costs, quality decreases and adverse events increase. 3 , 4 Given that nurse staffing comprises 40% of hospital budgets, it is imperative that optimal nurse assignments continue to meet standards of quality care and improve patient outcomes. 3 , 4 The process of how nursing assignments are distributed in healthcare settings has evolved from uninformed to scientific. 5 Multiple factors, from budgeting and operations to staff satisfaction and patient safety, have driven this evolution. Nursing assignments are often based on room proximity, mandated nurse-to-patient ratio, patient’s medical diagnosis, and continuity of care from shift to shift. In reality, nursing activity will vary throughout a patient’s length of stay based on a combination of prescribed tasks including education, nursing interventions, and psychosocial needs, in addition to medical diagnosis. The NDNQI method for staff assignments uses the hours per patient day (HPPD) as a standard when evaluating staffing. 4 – 6 Managers take into account the average number of staff they have on a given unit and compute the assignment from that information. However, using the traditional methods of creating assignments without objective data may lead to unbalanced nurse workload; in other words, intensity of nursing care varies based on patient-specific needs and abilities. Ideally, assignments should take into account changes in any patient-related tasks, inclusive of psychosocial status, medical status, care transitions, and nursing plans of care. NDNQI has proven to be more accurate than HPPD in determining patient needs as it includes admission, discharge, transfer, and other activities that take up a nurse’s time. 7 Through appropriate documentation of patient-specific activity and utilization of a standard and reliable workload measurement system, nursing assignments become more equitable. 2 To create a process that takes the complexity of nursing care into consideration when making shift assignments, it is 1st necessary to assess the amount of nursing activity required by a single patient and translate into a workload score. 8 – 10
The 2nd step, and focus of the current article, is to sum the patient workload score attributed to each nurse on duty to plan nursing assignments and distribute the total work of the unit safely and equitably. Workload-based staffing technology satisfies an essential function that meets diverse patient needs when determining nursing assignments.
Calculating a workload score takes into account dynamic patient care demands that often change from shift to shift or even hour to hour. Historically, resource allocation and staff assignment did not take the ever-changing patient care requirements into consideration. 5 According to the American Nurses Association (ANA), “Greater benefit can be derived from staffing models that consider the number of nurses and/or the nurse-to-patient ratios and can be adjusted to account for unit and shift level factors.” 11 Using a workload score in combination with an electronic health record (EHR)–based assignment tool offers an opportunity for real-time patient-centered resource allocation. By leveraging existing documentation, the nursing workload measurement (NWM) allows for agility and accuracy in nurse staffing assignments.
It has been well documented that HPPD-based or diagnostic related group–based assignments do not accurately equate to perceived nursing workload. 7 The term workload is interpreted differently among healthcare professionals. Given that, according to Merriam-Webster, 12 the medical definition of workload is keenness of sense perception , it is vital to clarify this in relation to patient care. For this project, the operational definition of workload included the amount of nursing care needed, patient reliance on nursing, staff allocation, and workload measurement. 5 , 13 The term workload-based reflects an aggregate of medical- and nursing-related tasks, as well as other aspects, such as risk factors, admission, transfer, and discharge activities. 14 The intention of a patient-specific workload score generated by EHR documentation is to estimate the intensity of nursing work the patient will require in the upcoming shift. Unless a standard is applied to account for the intensity of nursing activity required for a patient during a shift, the process of distributing nursing assignments becomes biased.
Significance
Aiken et al 15 have led the battle regarding patient safety and the level of staffing needed to maintain this goal. There are currently no federal regulations to establish appropriate guidelines for safe patient care related to nurse staffing. The Safe Staffing for Nurse and Patient Safety Act of 2018 (S. 2446, H.R. 5052) proposes clear directives related to nurse staffing levels for hospitals that receive reimbursement from Medicare. 15 One such requirement is that minimum ratios are identified and adaptable based on “the level and variability of intensity of care required by patient under existing conditions.” 16 In this Act, Congress acknowledged the abundance of evidence supporting the correlation between safe nurse staffing and improved patient outcomes. The fact that this federal legislation has not passed should not negate its importance when addressing safe staffing. States are also actively addressing safe staffing legislation. Regulations are beginning to affect payments based on staffing models, and union contracts are demanding that healthcare organizations adopt workload-driven systems. 11 The proposed federal legislation acknowledged that Connecticut, Illinois, Nevada, Ohio, Oregon, Texas, and Washington have enacted this as recommended. 11 As stated in the Lippincott Blog: “14 states currently addressed nurse staffing in hospitals in law/regulations: CA, CT, IL, MA, MN, NV, NJ, NY, OH, OR, RI, TX, VT, and WA.” 17 California is the only state with unit-specific mandated minimum nurse ratios, whereas other states have developed committees and public disclosure of ratios. Massachusetts has written into law specific nurse-to-patient ratios for the ICU of 1:1 or 1:2. Man-dating a minimum nurse-to-patient ratio by no means restricts the ability of organizations to increase ratios according to need. 16
In this study, we are motivated by the current national discussion to provide insight on how to harness emerging EHR technologies to provide hospital-wide nurse staffing assignments based on real-time patient need. Our aim is to incorporate the ANA position on staffing, namely, that staffing should focus not only on ratio, and there is variation between nurse experience, hospitals, units, and shifts. 11 The current study integrates regularly captured patient workload scores with traditional nurse-to-patient ratios into an automated data nursing assignment tool (NAT).
Materials and Methods
In the fall of 2017, our organization, an approximately 400-bed tertiary care, rural academic medical center, located in New England, implemented an EHR-based workload tool that measures patient-specific nursing workload. The institutional review board granted exempt status to conduct this quality improvement work.
Prior to implementation, decisions were made by the organization to adapt EHR rules to a point value associated with each nursing task. There are 9 components that make up an individual patient score: assessments, medications, lines/drains/airways, risks, wounds, orders, activities of daily living, admission and transfer/discharge. The tool automates an individual patient workload score based on 300 available rules that look retrospectively and prospectively for certain elements within existing documentation as well as orders. The proprietary nature of the tool does not allow the authors to disclose the details of the rules that drive the workload score. The score is updated at the following times: 3:00 AM, 9:00 AM, 3:00 PM, and 9:00 PM. The times are set to allow for “filed status” of scores. It is important to note that the times were not set to allow for late documentation, but for the batch job to run. The next phase, and the focus of this article, was to use this individual patient-level EHR data as the driver to implement a patient-centered objective and automated NAT.
To create an impartial assignment, the average workload scores on each unit were addressed. The authors felt this was important to compare unit scores so we would know if it was appropriate to use a universal assignment score, or whether this should be department specific. Having implemented the nursing workload tool, data were collected from August 2017 to June 2018. EHR-generated data were obtained using a web-based report of all patients and their workload numbers. We compiled the summary score of all patients assigned to one nurse, which is equivalent to the total workload score for that nurse. We examined the mean, SD, and median values to understand the distribution of the data. Nurse workload scores were aggregated at the department level and transformed into 3 categories indicating low, medium, and high workload, based on 1 SD from the mean department score. To set the ranges for these categories, the department level mean ± 1 SD was multiplied by each department-specific nurse-to-patient ratio. In some instances, fractional numbers were used to accommodate for units that have different nurse-to-patient ratios on the night shift. For example, a nurse-to-patient ratio of 3.5:1 was used for a unit with a 3:1 nurse-to-patient ratio on days and 4:1 nurse-to-patient ratio on nights. The result was department-specific NWM categories for nurse assignments that were represented with a color to indicate when the combined patient assignments for each nurse fell within a low, medium, or high range. The upper limit of the high range was determined by adding 200 to the lower limit of the high category. This value is only needed to program the ranges in the EHR, so it is somewhat arbitrary. However, after examining maximum values since August 2017, it is unlikely that this number will be exceeded.
The mean patient workload score varied greatly across departments, ranging from a mean score in pediatrics of 64 to a mean in ICU medical of 196 ( Table 1 ). Aggregated patient scores at the nurse level were summed across all units and compared. This aggregated number represents the NWM for a single nurse assignment having taken into account the unit’s nurse-to-patient ratio. The NWM score falls within the predefined ranges of low, medium, or high. For medium, the optimal NWM range in pediatrics with a nurse-to-patient ratio multiplier of 4 is 144 to 432, whereas in ICU medical, a nurse-to-patient ratio multiplier of 2 defines an optimal range of 272 to 512. As a visual indicator of the ranges, the NAT will be implemented with stoplight colors, with green representing the medium-level, or ideal, range. Yellow will indicate that the assignment is in the low range, indicating that a nurse still has capacity to care for additional patients, and red is in the high range relative to nursing workload. These categories will provide decision support to charge nurses and managers to determine nurse-to-patient ratios and assignments in real time, according to patient-centered needs.
Patient-Level and Nurse Assignment–Level Work Acuity Scores Across Departments in an Academic Hospital
All scores from Web Intelligence over 11.5 months (7/17 to 6/18 four times per day).
Nurse-to-patient ratio multiplier is an average in cases when a unit has different ratio standards for day and night shifts.
Strengths and Limitations
Because of the proprietary limitations of the EHR vendor, the direct application of ranges reported in our study cannot be generalized to other institutions. Nonetheless, the process of evaluating department-specific measures to derive appropriate ranges and staffing assignments can be universally adopted. Data were collected from a single academic center, which reduces the generalizability of our study. However, the sample size included 26,985 records and covered a 12-month period across all departments.
The major finding of this article demonstrates that patient workload scores, combined with minimum department-specific nurse-to-patient ratios, provide accurate patient needs to generate fair, hospital-wide staff assignments. As expected, patient workload scores varied by department. What was not expected were the higher scores observed in departments that were traditionally viewed as having lower patient care needs; that is, in the hospice unit, when we looked closer, scores were comparable to the ICU.
Our work demonstrates that a NAT allows the person responsible for making nursing assignments, usually the charge nurse, to quickly assess and adjust a nurse’s workload. The cumulative NWM score is translated into a visual indicator using color and a slide bar. The colors change based on a range of scores customized to each unit. When developing our approach, research into other organizations’ strategy to develop the ranges for the NAT yielded sparse results. It was determined that a descriptive statistical approach would be utilized to define and maintain each unit’s optimal range. Nurse managers were presented with the proposed ranges and educated on the logic behind the process and development of the tool. Work is ongoing to fully implement this assignment tool into everyday practice at the institution to ensure staff assignments are fair and unbiased. Most managers responded positively and are eager to use this tool when available. However, there was some reluctance to using patient workload scores as a basis for a staff assignment tool. The inpatient psychiatric unit staff initially did not feel this tool would be applicable to their care model. The range of scores for this unit was 30 to 90, with an outlier of 205. Data revealed that outliers in the psychiatric unit were dramatically visible and could be directly attributed to increased patient care needs, which we believe reinforced the reliability of the workload scores.
The next phase of developing an improved practice of assigning staff will require that staff schedules are batch uploaded to the EHR and into the NAT. The availability of the daily nurse schedule is a vital component for successful implementation; however, it was outside the scope of the current project. Once implemented, the staff responsible for assigning patients will drag and drop a patient’s name to the assigned nurse. A bar under the staff nurse’s name will fill with the color to indicate the current status of his/her assigned workload. The patient’s workload score will be automatically updated 4 times per day to adjust to real-time documentation and upcoming orders. As the score is dependent on nursing documentation, complete and real-time documentation of patient care will produce the most reliable score ( Figure 1 ).

Nursing assignment tool workflow.
There will be ongoing monitoring of this tool to ensure usability following implementation. Some nurse managers expressed concern with the stoplight color scheme and have suggested that a gradation of a single color may be more useful. The middle range is the optimal assignment. An assignment classified as red may be construed as precarious or undesirable. Color scheme changes will be considered pending feedback after implementation. Continued review of the ranges will also be necessary as documentation standards change or updates to the EHR are made that may lead to breakage of rules used to calculate scores.
Patient safety issues are rightly at the center of concern regarding ineffective staffing models. Studies have drawn a direct line between nursing workload and staffing ratios and avoidable deaths. 6 , 10 , 16 Patient safety is only one of the concerns that can be addressed by utilizing a NAT for staffing decisions. Other areas of concern that may be addressed include staff retention, burnout, and work satisfaction. 8 Identifying and remediating workload disparities will allow managers to allocate staffing resources appropriately, including using flexible staff when needed. 13 “Fixed staffing numbers or ratios only identify minimum staffing levels and do not adjust for the ever-changing nature of patient care needs.” 3
The national conversation continues to reflect positively on agile nursing assignment processes that flex with patient needs. 9 , 18 , 19 However, there are logistic and cultural barriers to implementation. Another challenge to the adoption of this technology may be the geography related to specific patient locations in the hospital unit. Adjusting nursing assignments based strictly on nursing workload may fail to take location of patients into consideration. Some departments currently base assignment on room location, as there are physical barriers in the unit design. Changing the status quo of the process to assign patients to nurses may be challenging in some units. One unit manager reported that they assign nurses up to 24 hours in advance, making the every 6-hour update to the nurse workload score less valuable and less sensitive to acuity and condition changes, as well as nurse competence. Clearly, each institution will require adjustments that can be easily managed from the back end of this flexible product. Engagement with operational leaders is a vital component of implementation. Such systems that leverage EHR technology have the potential to impact excellence in nursing practice.
Future versions of this tool will allow a charge nurse to quickly match patients to nurses based on continuity of care, expertise, and location. Coordinating care at this level of granularity will help ensure the patient is paired with the right nurse for the current phase of care to achieve patient safety, staff satisfaction, and optimal resource allocation. The use of objective, data-driven, electronically generated NWM scores based on actual patient workload, combined with nurse-to-patient ratios, provides accurate real-time nurse staffing needs that can lead to best practice in staffing. The validation of workload scores and an appreciation for the complexity of vendor rules are necessary for successful implementation.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Geoffrey Tarbox, MBA, RN, for his work on the Excel spreadsheets; and Petrice DiDominic, MSN, RNC-OB, for her help with the Workload Acuity Tool.
R.T.E. was supported by award number UL1TR001086 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Designing implementation strategies for the inclusion of LGBTQIA+ and key populations content in undergraduate nursing curricula in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: Protocol for a Multi-Methods Research Project
Affiliations.
- 1 Durban University of Technology, Academic Development Unit, Faculty of Health Sciences, 7 Ritson Road, Berea, Durban, ZA.
- 2 University of KwaZulu-Natal, Centre for Rural Health, School of Nursing and Public Health, Durban, ZA.
- 3 University of KwaZulu-Natal, Discipline of Nursing, School of Nursing and Public Health, Durban, ZA.
- 4 University of KwaZulu-Natal, Discipline of Occupational Therapy, School of Health Sciences, Durban, ZA.
- 5 University of San Francisco California, Centre for AIDS Prevention Studies, San Francisco, California, US.
- 6 University of San Francisco California, Department of Community Health Systems, San Francisco, US.
- PMID: 38598816
- DOI: 10.2196/52250
Background: Literature suggests that Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Intersex, Queer and Allied (LGBTQIA+) individuals encounter challenges with access and engagement with health services. Studies have reported that LGBTQIA+ individuals' experiences stigma, discrimination and health workers' micro aggression when accessing healthcare. There is compelling evidence to suggest that the LGBTQIA+ community are faced with disproportionate rates of HIV infection, mental health disorders, substance abuse and other non-communicable diseases. The South African National Strategic Plan (NSP) on HIV/AIDS, TB and STI's (2023-2028) recognises the need for providing affirming LGBTQIA+ health care as part of the country's HIV/AIDS response strategy that is rooted in comprehensive and holistic care underpinned by the principles of community oriented primary healthcare. However, current anecdotal evidence suggests paucity of LGBTQIA+ and key populations health content in the undergraduate health science curricula in South Africa. Moreover, literature reveals a general lack of health worker training regarding the health needs of LGBTQIA+ persons and other key populations such as sex workers, People Who Inject Drugs (PWID) and Men who have Sex with Men (MSM).
Objective: This protocol paper describes the design of a project that aims at facilitating the inclusion of health content related to the LGBTQIA+ community and other key populations in the undergraduate nursing curricula of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.
Methods: A multi-methods design encompassing collection of primary and secondary data using multiple qualitative designs and quantitative approaches will be used to generate evidence that will inform the co-design, testing and scale-up of strategies to facilitate the inclusion of LGBTQIA+ and key populations content in undergraduate nursing curricula in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Data will be collected using a combination of convenience, purposive and snow ball sampling techniques from LGBTQIA+ persons, academic staff, undergraduate nursing students and other key populations such as MSM, PWID and sex workers. Primary data will be collected through individual in-depth interviews, focus groups discussions and surveys guided by semi-structure and structured data collection tools. Data collection and analysis will be an iterative process guided by the respective research design to be adopted. The continuous quality improvement process to be adopted during data gathering and analysis will ensure contextual relevance and sustainability of the resultant co-designed strategies that are to be scaled-up as part of the overarching objective of this study.
Results: The proposed study is designed in response to recent contextual empirical evidence highlighting the multiplicity of health challenges experienced by LGBTQIA+ individuals and key populations in relation to health service delivery and access to healthcare. The potential findings of the study may be appropriate for contributing to the education of nurses as one of the means to ameliorate these problems.
Conclusions: This research has potential implications for nursing education in South Africa and worldwide as it addresses up-to-date problems in the nursing discipline as it pertains to undergraduate students' preparedness for addressing the unique needs and challenges of the LGBTQIA+ community and other key populations. The findings may also provide baseline data to inform knowledge transfer to other health sciences disciplines that have not included LGBTQIA+ content in their undergraduate curricula in South Africa.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Clinical Nursing Research Topics. Analyze the use of telehealth/virtual nursing to reduce inpatient nurse duties. Discuss the impact of evidence-based respiratory interventions on patient outcomes in critical care settings. Explore the effectiveness of pain management protocols in pediatric patients. 2.
They should aim to write work that can be used in both the research and clinical aspects of the discipline. Walden instructors often ask nursing students to write position and reflective papers, critique articles, gather and analyze data, respond to case studies, and work collaboratively on a project. Although there may be differences between ...
The 6 Main Steps for Writing a Nursing Research Paper. Writing assignments are an essential training aspect for nursing students. No wonder professors will stress that you write essays, discussion posts, responses, or proposals well. They are doing so to prepare you for research roles somewhere in your nursing career.
Nursing Research Tools. CINAHL Complete: The Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature offers a large database of research material for nurses and students. The site provides full-text access to resources, including journals, care sheets, and continuing education modules.
Impacts of nursing ethics on evidence-based practice. Strategies to address the implementation gap between practice, research, and knowledge in nursing. Using social media to promote the dissemination of evidence-based practice. Strategies for implementing and translating evidence-based practice. Benefits of frequently training nursing staff on ...
Most undergraduate BSN students take a Research and Evidence-Based Practice course. Students are often assigned a small research project or review paper. The assignment begins with writing either a research question, or a clinical question. Usually, the student is given a range of topics, but let's assume the student is starting from scratch.
Below are some general criteria that are almost always used in nursing research assignments: Peer-reviewed articles; Must be within the last 5 years of publication; The articles must be nursing-related, preferably from a nursing journal and/or having a nurse as one of its authors. Sometimes you must also find articles from an English-speaking ...
Evidence-based practice is now widely recognized as the key to improving healthcare quality and patient outcomes. Although the purposes of nursing research (conducting research to generate new knowledge) and evidence-based nursing practice (utilizing best evidence as basis of nursing practice) seem quite different, an increasing number of research studies have been conducted with the goal of ...
Finding research materials to complete assignments for nursing can sometimes be difficult, but nursing students are smart, intelligent people, and are up to the challenge! Follow each step below and use the instructions and resources on this page to help you find materials to complete your research assignments.
Abstract. Teaching a graduate-level nursing research course can be quite challenging, especially one that is offered online and asynchronously. One of the assignments required of master of science in nursing (MSN) students is to develop a paper that examines a clinical problem that might be improved by using research knowledge.
Finding and choosing a strong research topic is the critical first step when it comes to crafting a high-quality dissertation, thesis or research project. If you've landed on this post, chances are you're looking for a nursing-related research topic, but aren't sure where to start. Here, we'll explore a variety of nursing-related research ideas and topic thought-starters, including ...
Whether you're struggling with research, structuring your assignment, or proofreading, we're here to support you every step of the way. Understanding the Nursing Assignments. To excel in nursing assignments, it's crucial to start by thoroughly understanding the requirements. Take the time to carefully read the assignment prompt, paying ...
Four types of qualitative research design often applied to nursing research are: Phenomenology - the study of human life experiences and how they appear in human consciousness; Grounded Theory - seeks to explain variations in social interactional and social structural problems and processes ; Ethnography - As a research process, ethnography is a comparative method for investigating patterns of ...
Details of this programme are described elsewhere (Chlan et al., 2019; National Institute of Nursing Research, 2016). The project team developed a model of nursing research to guide the foci for nurse scientists' research at the institution and to generate new nursing knowledge based on needs that arise from the practice setting. The model was ...
Sample Assignment. Select a Qualitative nursing research article pertaining to an area of interest that you may have clinically. The research article must contain the parts of a research study which includes: Research Question. Hypothesis. Purpose Statement.
Nursing research is an art of scientific investigation that aims to solve healthcare problems or nursing issues. It uses disciplined methods to collect and analyze data to develop meaningful findings that help solve problems. ... One must select a topic that is within the parameters of the assignment. Nursing instructions give students ...
The mission of the National Institute of Nursing Research (NINR) is to promote and improve the health of individuals, families, and communities. To achieve this mission, NINR supports and conducts clinical and basic research and research training on health and illness, research that spans and integrates the behavioral and biological sciences, and that develops the scientific basis for clinical ...
Click on the sub-pages to explore research assignments and video tutorials for Nursing: PN (Practical Nursing) Students. BSN (Bachelor of Science) Students.
Instructions for Library Assignment. Click on the Library Worksheet linked below; it is available as a Microsoft Word document and as a PDF file. Click on "Enable Editing" at the top of the Word document in order to type in the form. If you prefer, you can print out the blank worksheet and fill it in manually. Answer questions 1 - 6 on this ...
It is defined as "The nursing professional development (NPD) practitioner integrates scholarship, evidence, and research findings into practice" (p. 104). There is often confusion between quality improvement, evidence-based practice, and research. A seminal article by Shirey and colleagues. [2] differentiated these three topics.
Here's a general guide on how to write a nursing project: Select a Topic: Choose a topic that aligns with your interests, expertise, and the requirements of your assignment or research objectives. Consider the significance of the topic in the field of nursing and its potential impact on patient care or nursing practice. Research: Find books ...
Most students fear research and writing or do not take writing assignments seriously. Regardless of the assignment, here are some practical and effective tips to help you ace your nursing school writing assignments and surprise everyone, including yourself. 1. Plan your Time.
Nursing Research Assignment. ?INTRODUCTION Nursing research is a systematic process by which nurses may used to confirm or refine existing knowledge and to explore new ideas about issues related to nursing practice (Borbasi, Jackson, & Langford, 2008). It falls largely into two areas, namely: Qualitative research and Quantitative research ...
A research project was conducted at Alexandria Nursing College, situated in Egypt. The college adheres to the national standards for nursing education and functions under the jurisdiction of the Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education. Alexandria Nursing College comprises nine specialized nursing departments that offer various nursing ...
Mapping of research evidence to nursing classification seems feasible; however, three specific challenges were identified: different content orientation; content granularity; and operationalization of knowledge. ... The frequency of assignment of LEP Nursing 3 interventions to FIT synopses are highly variable. For example, while 72.7% ...
Three iterative DBR research cycles were conducted on a project-based learning (PjBL) implementation in three population health nursing clinical PjBL blocks at a Midwest university. ... Undergraduate nursing students' perceptions of service-learning through a school-based community project. Nursing Education Perspectives, 32(3), 162-167. http ...
After the height of the COVID-19 pandemic and the murder of George Floyd, J. Margo Brooks Carthon, Tyson Family Endowed Term Chair for Gerontological Research in the School of Nursing, worked on a research study interviewing Black nurse practitioners in the greater Philadelphia area about their efforts to address inequities in care.
This article describes the ongoing, hospital-wide effort to evaluate and implement a nursing assignment tool based on electronic health record (EHR) functionality and auto-calculated nursing workload scores. EHR records of individual patient workload scores from all hospital units were collected from August 2017 to June 2018.
Conclusions: This research has potential implications for nursing education in South Africa and worldwide as it addresses up-to-date problems in the nursing discipline as it pertains to undergraduate students' preparedness for addressing the unique needs and challenges of the LGBTQIA+ community and other key populations. The findings may also ...
A research project supported by BioCurate's Proof of Concept fund led by Monash University will move into the next exciting phase as an exclusive licence in the BioCurate Portfolio. The research, led by Monash University's Dr Rimma Goldberg and Associate Professor Joshua Ooi, has identified a promising new cell therapy approach to treating ...