You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Easy Pace Learning
- English Level 1
- English Level 2
- English Level 3
- Basic English
- Learning English level 1
- Learning English level 2
- Learning English level 3
- Learning English level 4
- Learning English grammar
- Basic English conversation
- English books for download PDFs free
- Learning English sport
- Learning about England
- Learning business English lessons
- Lesson categories
- Search site for English lesson
- English basics exercises
- English Exercises level 1
- English exercises level 2
- Parts of a plant
- Pictures from Facebook
- Contact us using Facebook
- Contact us form for your requests
- Contact us with Google plus
- English books for download pdf
- A list of phrasal verbs
- English books for SALE students learners and teachers
- List of idioms A - Z English phrases
- Verbs A to Z list learning English
- The big list of A to Z of words
- Big vocabulary list A to Z
- Slang words A to Z
- A to Z List of British words not used in the USA
- English Book
- Books for sale
- Animal idioms from A to Z
- Body parts idioms
- A to Z of clothes idioms
- Emails and electronic mail
- What are computers and their parts
- Advantages and disadvantages of computers
- Determiners
- Conjunctions
- Punctuation
- Prepositions
- Compound Words
- Mix Practice Sheets
- Practice Sentences Writing
- Silent Letters and Magic E
- Miscellaneous
- Synonyms and Antonyms
Lessons and exercises
- Basic lessons
- English basics level 1
- English basics level 2
- English level 3
- English level 4
- English Grammar
- Business lessons
- Exercises basics
- Exercise level 1
- Exercise level 2
Conversation about 2 friends who both need help
What is the conversation between 2 friends helping each other about.
The conversation is about 2 friends called Tim and Henry, who both have a separate problem. Henry is having problems with his homework and is friend Tim is having problems with building a doll house. They are hoping they can help each other.
Conversation between 2 friends hoping to help each other
Tim: Henry, what are you doing?
Henry: I have been trying to solve this physics problem for the last half hour, and I still have no idea how to do it.
Tim: When do you have to turn it in?
Henry: It is due at the end of this week.
Tim: Well, it is only Monday. Why don’t you get some after-school-tutoring tomorrow?
Henry: I have to sign up for it first. I guess I will go sign up for the Wednesday session tomorrow.
Tim: You should reread the chapter before you show up for the session. It will help you understand the subject matter better.
Henry: OK, I will do that.
Tim: Now that your problem is solved, I need you to lend me a hand with my problem.
Henry: What is up?
Tim: I need to build a new doll house for Nancy. I was putting her doll house away, and somehow I accidentally dropped it. It was broken into pieces.
Henry: How clumsy of you! Does she know?
Tim: I told her about it. I could not lie to her.
Henry: How did she take it?
Tim: My sister really liked that doll house, and obviously she was not very happy. But, I told her that I would build a better one for her. So, I need your help.
Henry: Me? Help you? I have never built anything in my life.
Tim: Me neither. But, don’t worry. Putting together pieces of wood is not going to be difficult.
Henry: It is more than just putting pieces of wood together. You need to put in windows and doors. Have you thought about how you would do that?
Tim: Who says houses need to have windows and doors?
Henry: So, you are going to build a doll house with no windows and no doors?
Tim: Yes, I do not see anything wrong with that. Do you?
Henry: No. It makes the project easier to handle now. But, are you sure that Nancy will not mind having a doll house with no doors and no windows?
Tim: Yes, I am sure.
Henry: Are you sure that Nancy will find this doll house with no doors and no windows prettier than the one you broke?
Tim: No, I am not sure. Why do you have to make things so complicated?
Henry: I am not trying to complicate things. You did tell Nancy that the new doll house would be better than the one you broke. I just want to remind you of your promise.
Tim: Ah, I wish I have not touched her doll house! What should I do then?
Henry: Get help from somebody who knows how to build a doll house. I would not be of any help to you in this project.
Tim: Who do you suggest I ask?
Henry: Mr. Brown used to be a carpenter. He will be glad to help you out. Why don’t you give him a call, and see whether he has some free time.
Tim: You are right. It will take us forever to build this doll house. With Mr. Brown’s help, I can finish it in no time.
Henry: OK, now that your problem is solved, can you help me trim the trees in the back yard?
Tim: Who? Me? Trim the trees in your back yard? It will take us ages to trim those trees. Let’s see who is good at trimming trees. Ah, you can ask Mr. Brown. He is also good at trimming trees. And, when you ask for his help, please ask him to help me build a doll house also.
EXPRESSIONS
Have a problem with
Have no idea how to do something
It is due at the end of the week
It would be wise to
Subject matter
Lend a hand to
What is up ?
Accidentally
Broken into pieces
How clumsy of you !
How did she take it ?
Don’t worry !
Have you thought about
Who says that
I don’t see anything wrong with it
Do you mind to ?
Complicate
Used to be
Have free time
Finish in no time
Print the lesson

Lessons that are related to the exercise
Conversation about 2 friends helping each other
Conversation about giving directions
Conversation between 4 people at the doctors office
Dictionary and how to use dictionaries
Click on the following link for the Online English dictionary - English lesson
Easy Pace Learning Forum
English books to download free.
- Idioms from A to Z in PDF
- Learning basic grammar book 1
- Learning basic grammar with exercises book 2
Download FREE dictionaries in pdf
- English dictionary
- English to Hindi dictionary

- Privacy Policy
- Refund Policy
- Terms&Conditions
Easy Pace Learning, 2024
- My Storyboards
How to Write Dialogue Between Two Characters
Conversational English can be very difficult. While knowing proper sentence structure and correct grammar is extremely important, conversational English is how you will interact with other English speakers on a daily basis. If you don’t feel ready to hold a conversation in English, or if you want more practice, write your own dialogue!
Imagining an example of a conversation between two characters can be challenging without providing context or prompts. Conversational English is very different from English you would use for a written assignment, or from English you would read in a book or on a news website. However, you normally go through the same motions when completing a written assignment that involves answering an essay question, and a written assignment that asks you to come up with a natural sounding conversation between two characters. Therefore, learning to write dialogues is a fundamental skill in language education. With guidance, advice, and lessons, students can be empowered to master the art of writing dialogues and become confident communicators in real-life situations.
The following guide provides a step-by-step approach to writing engaging dialogues between two characters, incorporating common phrases, examples, and techniques to create authentic and meaningful conversations.
- Establish the Characters: When writing your dialogue, it's good to start with a simple conversation between two friends and then add other conversational participants as it progresses. Introduce the two friends and provide a brief description of their relationship and background.
- Set the Scene: Describe the location and the context of the conversation between the two friends.
- Initiate the Dialogue: Begin the conversation with a friendly greeting or an opening question.
- Use Common Phrases and Expressions: Incorporate everyday language and expressions that friends might use when conversing.
- Include Examples of Dialogue Between Two Characters: Provide specific examples of their conversation, showcasing their interaction and the topics they discuss.
- Include a Misunderstanding: Introduce a moment of confusion or miscommunication between the friends.
- Write a Short and Engaging Dialogue: Keep the talking concise and engaging, capturing the essence of a conversation between two people. Make sure it flows naturally and maintains a conversational tone.
- Wrap Up the Conversation: Conclude the discussion with a closing remark or a future plan.
Remember to tailor your activity to the desired language proficiency level and ensure it aligns with the intended purpose of the conversation between the two friends.
Exploring the Use of Conversation Starters and Enders
Conversation starters and enders are vital tools that help set the tone and direction of a discussion between two characters. They serve as entry points into a rich exchange of thoughts and ideas. For example, a simple conversation between teacher and student in English, the teacher may be initiated with an open-ended question like, 'Tell me about something interesting you learned today.' This prompts the student to share their thoughts and encourages active participation. Likewise, in a conversation between two new friends, the use of warm greetings and introductory phrases like 'It's great to meet you!' or 'How has your day been so far?' fosters a welcoming atmosphere, fostering connection and sparking further conversation. However, misunderstandings can occur, leading to confusion or misinterpretation. In such instances, employing question tags becomes essential to seek clarification and resolve any potential ambiguity. For instance, you can write a conversation between two friends using question tags, for example, 'You're still up for the movie tonight, aren't you?' helps ensure mutual understanding and prevent any miscommunication. Overall, by incorporating common phrases, and question tags, dialogues between characters can evolve into engaging and meaningful exchanges, exploring diverse perspectives and enhancing the overall conversational experience.
Dialogue Writing Activities
These writing activities serve as invaluable tools, promoting effective communication and cultivating collaboration within the educational setting for those who are not native speakers. Whether undertaken individually or as part of a group, these activities provide unique advantages for both teachers and students, facilitating language development, fostering understanding of character dynamics, and nurturing the ability to construct meaningful dialogues. Worksheets can be designed for individual, paired, or group settings, accommodating different learning preferences and promoting collaboration among students. Individual worksheets offer students the opportunity to practice and develop their writing skills independently, allowing them to focus on their own ideas, creative expression, and personal growth in constructing meaningful dialogues. Paired activities for more than one person provide learners with the chance to engage in collaborative learning, where they can exchange ideas, perspectives, and feedback with a partner. Through the process of dialogue writing between two friends, students can hone their ability to create authentic and relatable conversations that reflect the nuances of real-life friendships.
Creating a Dialogue
Storyboard That gives you the opportunity to create visual scenarios in order to teach more natural conversations. Instead of writing out the conversation as lines of text, try to understand the context of the dialogue. There are a lot of nuances that come up in conversation that do not always appear in written communication, such as slang, colloquial expressions, interjections, immediate responses, interruptions, and more.

How to Make a Dialogue?
Choose a scene or situation.
Open up the Storyboard Creator and you will see three empty cells. Look through the different scene options and try out different locations. Choose one that you like. Click on the scene and drag it to the empty cell. The scene may dictate the situation or conversation, so be creative!
Choose Characters
You need at least two people to talk to each other in a conversation. Storyboard That has many fun characters to choose from. Characters can be modern people, historical figures, animals, monsters, silhouettes, and more!
Give your characters names. If you are going to have a detailed discussion, you can think about personality traits or opinions, too!
Choose a Dialogue Topic
People talk about everything, so you can make a storyboard about anything! Here are some common things people talk about.
- Social Plans
- Current Events
- Environment
- Relationships
- Books, Movies, and Other Media
- School, Jobs, and Future Plans
- Opinions/Concerns on an Issue
When choosing a topic, think about relevant vocabulary that you want to include. If you find yourself struggling with the vocabulary, don't worry! Select a different topic or ask for help from a teacher or native speaker. This exercise can be completed more than one time, so there's plenty of opportunity to practice new dialogues and vocabulary.
Start a Conversation!
Once you have your topic, characters, and setting, you can start writing! Use the speech bubbles located in the "speech bubbles" section. For conversations, speech bubbles are really important. Like the characters and many of the scenes, you can change the appearance of the speech bubbles.
Write the conversation in order. Use a separate speech bubble each time a character speaks. Don’t try to make each sentence perfect yet, instead, focus on what the characters would say and how they might respond to each other.
Try to include some of the following in your dialogue.
- Greetings and pleasantries
- Expressions, idioms, slang terms
- Incomplete sentences or short responses
- Interjections, sounds of thinking, filler words
Remember that conversations are more than just words! There are reactions, emotional changes, actions, and more to think about in actual speech. You can pose and edit the characters too, so make sure to use facial expressions and arm motions, if needed.
After you have the basic conversation, go back and check your grammar, expressions, and vocabulary. Did you get most of it right the first time? It’s OK if you didn’t, that just means you need more practice. As you practice, the right conjugations and vocabulary will come to you more easily!
Here is a completed example.
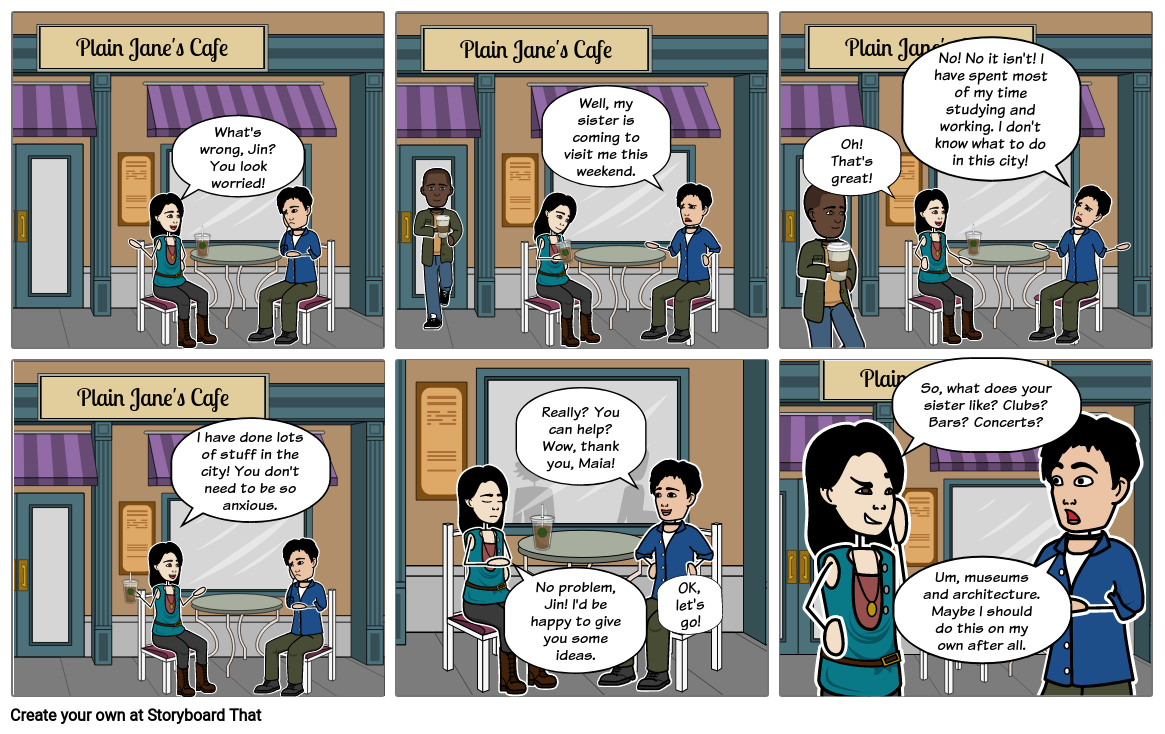
Examples of Dialogue Between Two Characters
Maia: What's wrong, Jin? You look worried!
Jin: Well, my sister is coming to visit me this weekend.
Maia: Oh! That's great!
Jin: No! No it isn't! I have spent most of my time studying and working. I don't know what to do in this city!
Maia: I have done lots of stuff in the city! You don't need to be so anxious.
Jin: Really? You can help? Wow, thank you, Maia!
Maia: No problem, Jin! I'd be happy to give you some ideas.
Jin: OK, let's go!
Maia: So, what does your sister like? Clubs? Bars? Concerts?
Jin: Um, museums and architecture. Maybe I should do this on my own after all.
Dialogues for Local Customs
Another great way for students to practice writing dialogues is to combine it with an activity that allows them to master local customs. When doing things like dining out, shopping, visiting a friend, or more, there may be expectations that they are unused to. These activities will let students practice various scenarios, and can be customized and adjusted for difficulty as desired!
Related Activities
How to Write Dialogue Between Two Characters that Uses Slang and Idioms
Determine the setting and characters of your story.
Think about the location and background of your story, as well as the characteristics of your characters. Are they from a certain region or cultural background? Are they teenagers or adults? This information will help you determine the appropriate slang and idioms to use.
Research Commonly Used Slang and Idioms
Do some research to find out what slang and idioms are commonly used by people in your characters' age group, region, or cultural background. You can consult online dictionaries or language references, or ask people who fit the demographic you are writing for.
Incorporate Slang and Idioms Naturally Into the Dialogue
When writing dialogue, it is important to use slang and idioms in a way that feels natural and not forced. To do this, try to imagine how your characters would really speak in conversation, and use the slang and idioms that would naturally come up. Avoid overusing slang or idioms, as this can make the conversation sound contrived or exaggerated.
Use Context to Clarify the Meaning of Slang and Idioms
Sometimes slang and idioms can be confusing or difficult to understand, especially for readers who are not familiar with them. To avoid confusion, try to use context clues to clarify the meaning of slang and idioms. For example, you can use the dialogue itself or the surrounding narrative to provide hints about the meaning of a phrase.
Edit and Refine Your Dialogue
After writing your dialogue, read it aloud to see how it sounds. Pay attention to the use of slang and idioms, and make sure they flow naturally and are easy to understand. If necessary, make adjustments to the dialogue to improve the use of slang and idioms.
Get Feedback from Others
Finally, share your dialogue with others and get feedback on the use of slang and idioms. Ask your beta readers if they were able to understand the slang and idioms, and if they felt the conversation was realistic. Use this feedback to further refine your dialogue and make it as natural and engaging as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dialogue Between Two Friends
What is dialogue.
Dialogue is a conversation between two or more people. In literature, it refers to the written or spoken exchange between characters in a story, play, or other literary work. It is a tool used to convey information, reveal character, and advance the plot. In everyday life, it is an essential part of communication, allowing people to share ideas, express opinions, and build relationships.
How do I create a dialogue on Storyboard That?
To create a dialogue on Storyboard That, you should start by choosing a scene or situation from the available options and dragging it to an empty cell. Next, select at least two characters to participate and give them names and possibly personality traits. Choose a topic, such as decisions, social plans, or opinions on an issue, and think about relevant vocabulary to include. Finally, use the speech bubbles located in the "speech bubbles" section to write the dialogue.
How do I write realistic and engaging dialogue for my storyboard?
To write realistic and engaging dialogue, think about the characters' personalities and motivations, and consider how they might speak to each other in the given situation. Use natural-sounding language and include pauses, interruptions, and nonverbal communication, such as body language and facial expressions. You can also use tags to add context and emotion to the conversation.
What are some prompt ideas for generating short dialogue examples for students learning ESL?
Here are some prompt ideas specifically designed to help generate short examples for students learning English as a second language:
- Imagine a dialogue conversation between two friends in English, discussing their favorite books or movies.
- Develop a conversation between an ESL teacher and a student, conversing in English about a challenging homework assignment.
- Write a dialogue between two characters in English, planning a surprise party for another friend, incorporating commonly used phrases.
- Write a conversation between an ESL student and a librarian in English, where the student seeks book recommendations, utilizing appropriate English conversation dialogues.
- Develop a scenario in an ESL learning context that revolves around a third party misunderstanding a discussion between two friends.
Try 1 Month For
30 Day Money Back Guarantee New Customers Only Full Price After Introductory Offer
Learn more about our Department, School, and District packages
- 30 Day Money Back Guarantee
- New Customers Only
- Full Price After Introductory Offer
How to Write Interesting and Effective Dialogue
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
Writing verbal conversations or dialogue is often one of the trickiest parts of creative writing. Crafting effective dialogue within the context of a narrative requires much more than following one quote with another. With practice, though, you can learn how to write natural-sounding dialogue that is creative and compelling.
The Purpose of Dialogue
Put simply, dialogue is narrative conveyed through speech by two or more characters. Effective dialogue should do many things at once, not just convey information. It should set the scene, advance action, give insight into each character, and foreshadow future dramatic action.
Dialogue doesn't have to be grammatically correct; it should read like actual speech. However, there must be a balance between realistic speech and readability. Dialogue is also a tool for character development. Word choice tells a reader a lot about a person: their appearance, ethnicity, sexuality, background, even morality. It can also tell the reader how the writer feels about a certain character.
How to Write Direct Dialogue
Speech, also known as direct dialogue, can be an effective means of conveying information quickly. But most real-life conversations are not that interesting to read. An exchange between two friends may go something like this:
"Hi, Tony," said Katy.
"Hey," Tony answered.
"What's wrong?" Katy asked.
"Nothing," Tony said.
"Really? You're not acting like nothing's wrong."
Pretty tiresome dialogue, right? By including nonverbal details in your dialogue, you can articulate emotion through action. This adds dramatic tension and is more engaging to read. Consider this revision:
"Hi, Tony."
Tony looked down at his shoe, dug in his toe and pushed around a pile of dust.
"Hey," he replied.
Katy could tell something was wrong.
Sometimes saying nothing or saying the opposite of what we know a character feels is the best way to create dramatic tension. If a character wants to say "I love you," but his actions or words say "I don't care," the reader will cringe at the missed opportunity.
How to Write Indirect Dialogue
Indirect dialogue doesn't rely on speech. Instead, it uses thoughts, memories, or recollections of past conversations to reveal important narrative details. Often, a writer will combine direct and indirect dialogue to increase dramatic tension, as in this example:
Katy braced herself. Something was wrong.
Formatting and Style
To write dialogue that is effective, you must also pay attention to formatting and style. Correct use of tags, punctuation , and paragraphs can be as important as the words themselves.
Remember that punctuation goes inside quotations. This keeps the dialogue clear and separate from the rest of the narrative. For example: "I can't believe you just did that!"
Start a new paragraph each time the speaker changes. If there is action involved with a speaking character, keep the description of the action within the same paragraph as the character's dialogue.
Dialogue tags other than "said" are best used sparingly, if at all. Often a writer uses them to try to convey a certain emotion. For example:
"But I don't want to go to sleep yet," he whined.
Instead of telling the reader that the boy whined, a good writer will describe the scene in a way that conjures the image of a whining little boy:
He stood in the doorway with his hands balled into little fists at his sides. His red, tear-rimmed eyes glared up at his mother. "But I don't want to go to sleep yet."
Practice Makes Perfect
Writing dialogue is like any other skill. It requires constant practice if you want to improve as a writer. Here are a few tips to help you prepare to write effective dialogue.
- Start a dialogue diary. Practice speech patterns and vocabulary that may be foreign to you. This will give you the opportunity to really get to know your characters.
- Listen and take notes. Carry a small notebook with you and write down phrases, words, or whole conversations verbatim to help develop your ear.
- Read. Reading will hone your creative abilities. It will help familiarize you with the form and flow of narration and dialogue until it becomes more natural in your own writing.
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech
- Writing a Lead or Lede to an Article
- Writing the Parts of a Stage Play Script
- Compose a Narrative Essay or Personal Statement
- How to Write Feature Stories
- How to Write a Personal Narrative
- detail (composition)
- How to Read Shakespeare Dialogue Aloud
- Interior Monologues
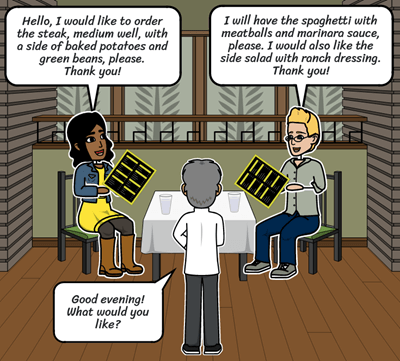
- Practice Restaurant Dialogue for Ordering Food
- Best Practices for Business Writing
- 5 Examples of How to Write a Good Descriptive Paragraph
- Tom Swifty (Word Play)
- Writers on Writing: The Art of Paragraphing
- 6 Traits of Writing
- Monologues in Speech and Composition
Florida State University
FSU | Writing Resources
Writing Resources
The English Department
- College Composition
- “Are we still talking about the dishes?”
“I think I’ve heard this one before”
Don’t mind me, let me rephrase that, from screen to page, why don’t you tell me how you really feel, "are we still talking about the dishes”.
Purpose of Exercise: Students will practice writing dialogue that builds tension through subtext and disagreement while avoiding dialogue as exposition.
Description: Beginning writers often have difficulty writing dialogue that is tense but not overt about that tension or the factors contributing to it.
Suggested Time: 30 minutes
Procedure: Have students write a scene in which two characters almost have an argument but don’t quite. The ostensible argument should be about something unimportant—cleaning, television, dishes—while the larger, unstated tension is much more significant.
Additional Information: This activity may be used in class or as a homework assignment but should be introduced with a discussion of strategies for indicating subtext. It is easy to find examples of dialogue in television shows in which people speak what should be revealed indirectly—either because they are announcing their feelings and intentions or because they are explaining context. Practicing for this exercise might start with watching one of these scenes and rewriting it so that the tension/emotions are unstated. Any episode of Grey’s Anatomy provides countless examples of characters elaborately explaining their feelings and motivations.
Back to Top
Purpose of Exercise: Students will practice managing large sections of dialogue in a single setting.
Description: Raymond Carver wrote several stories in which the action of the story is contained within a single setting and conversation. Though this model tends to prove difficult for beginning writers, practicing ways to create a story arc simply through what is said is often useful.
Procedure: Have students write a story in which one person tells another person a story. The listener should be reluctant to hear the story.
Additional Information: This activity may be used in class or as a homework assignment but should be introduced with a discussion of how conversation stories work. A good—and relatively short—example is Peter Orner’s “The Raft,” which was originally published in The Atlantic Monthly. Longer examples include Carver’s “Where I’m Calling From” and Charles Baxter’s “Poor Devil,” which is available online.
Purpose of Exercise: The purpose of this exercise is for students to develop their skills in writing dialogue that both reveals character and moves plot forward. Emphasis will be placed on diction and syntax.
Description: Have students eavesdrop on a conversation they are not part of. By listening in, encourage them to pay particularly attention not just to the conversation overall, but how the participants interact.
Procedure: For homework, have students listen in on a conversation on a bus, in a restaurant, before class. They don’t need to listen for long, just enough time to gain an idea of the speech patterns. Have them transcribe what they heard to the best of their abilities. What was the reason for the conversation, from what you can tell? Was their a conflict? How would you characterize each of the speakers? Consider word choice, word order, tone, and rate of speaking. How does dialogue contribute to our impressions of people? Students may wish to read aloud, and then open the floor to discussion.
Purpose of Exercise: The purpose of this exercise is for students to develop their skills in writing dialogue that both reveals character and moves plot forward. Emphasis will be placed on audience and diction.
Description: Students will write a conversation with a friend, and then revise it, retelling the same story to their grandmother. Attention will be placed on how we change our language based on our audience.
Suggested Time: class period
Procedure: Tell students to create a dialogue between themselves and their best friend at another university detailing a crazy night out. Encourage the students to appeal to all five senses in the dialogue with the friend. When students have completed the exercise, ask them to rewrite the “crazy night” as if they were talking to their grandmother. How was the evening revised? How did the tone, diction and syntax change? What does this suggest about dialogue? How does character change in the two dialogues?
Purpose of Exercise: The purpose of this exercise is for students to develop their skills of mixing dialogue with action.
Description: Communication is verbal and non-verbal. In this exercise, students will learn not only the value of dialogue, but of actions to characterize.
Procedure: In this exercise, have students watch a 30 second to 1 minute viral video, perhaps something funny and amusing. You may want to provide them with the dialogue. Have them watch the clip several times to get a sense of the nuances, particularly actions, props, and facial expressions. Have them add to the dialogue in way that indicates to the reader the tone and the subtler meaning the said words.
Back to Top
Description: Communication is verbal and non-verbal. In this exercise, students will learn not only the value of dialogue, but of actions to characterize. They will take the passage below, and revise it, adding dialogue and sensory details.
Procedure: Give students the following passage.
I was happy. My girlfriend was sad. I was curious. She became annoyed. I was confused. She became angry. I became angry. She became terrifying. I was scared. I am content now.
Tell them to replace each of the emotions with actions and dialogue to show what is told. None of the adjectives—happy, sad, curious, annoyed, confused, angry, terrifying, scared, content—can be used in the final version. However, each of those emotions should be detectable through actions, body language, facial expressions, and dialogue. Have the students share, explaining how they adapted the paragraph to a more visually appeally, resonant narrative.
- Essay Topics
- Homework Help
- Essay Types
- Essay Examples
- Become a Tutor
How to Write a Dialogue in an Essay with Example

This article will reveal all you need to know about how to write a dialogue, types of dialogues in an essay, and formatting . In addition, in this article, you will find several examples of English essay dialogue and dialogue between two characters.
What Is a Dialogue?
The definition of a dialogue is as simple as it gets. Dialogue is a conversation or discussion between two or more people in a book, play, or film. If you are wondering where the surprise part is coming in, here it is: it is not just any conversation. If you include a dialogue in an essay, it has to convey some kind of conflict, emotional tension, a surprising fact, or an interesting turn of events.
Dialogues in essays are not focused on mundane things because mundane things are just not interesting to read about.
There is a range of things NOT to include in your dialogue, such as:
- Throat-clearing sentences – parts of dialogue that do not add to the plot, but simply take space
- Rambling – this is the least relevant and interesting type of dialogue, which your readers are most likely to skip
- Words like “um”, “hm”, “like”, “sorta”, “kinda” – while it is important to speak the language of your readers to engage with them, avoid making them feel like they listen to a discussion between two people on the street.
- Profanities and slang – keep it classy instead of crassy.
It is surely rare to hear people in real life speaking like characters in Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s books, but this doesn’t mean dialogues shouldn’t be refined to sound realistic.
Types of Dialogues
While choosing how to convey the words of characters in an essay for the readers, you have two options: active and passive dialogue . Active dialogue includes quotes and quotation marks, while passive dialogue implies paraphrasing of the quotes and telling them from the narrator.
Examples of these types of dialogue are below:
1 Active dialogue example
Peter asked, “Joanna, can you take kids to your mother tonight?”
“Sure, I will drive them there as soon as they get back home from school,” she replied.
2 Passive dialogue example
Peter asked Joanna whether she would be able to take kids to her mother tonight. Joanna was exhausted by a long ride, however, agreed anyway, taking the chance to avoid the serious talk she needed to have with her husband.
From these short dialogues, we can see that active dialogue allows readers to imagine the situation much better, while passive dialogue can provide more details just by adding extra facts to the narration.
How to Put a Dialogue in an Essay?

The purpose of a dialogue in an essay is to create a more vivid picture for the audience. The functions of a dialogue in an essay include:
- Providing extra information about characters
- Unravel interesting or surprising plot twists and details about the story
- Attract readers’ attention
If your dialogue meets at least one of these criteria, it is a good dialogue to put in an essay. In fact, dialogues can help you tell a lot of information about the story and characters in a relatively short abstract. Adding descriptions of how people say something or why they say it is the key to describing their own behavior.
How to Format a Dialogue
Now let’s move on to the most intriguing part of writing a dialogue – punctuation and formatting . When you stumble upon a dialogue in any narrative essay or text, punctuation might seem to have a lot of different styles, which is confusing.
Of course, common errors in English are still relevant here, but dialogues have evolved their own punctuation rules.
There are three simple steps you need to follow in order to format your dialogue correctly in an essay:
1 In a dialogue, commas, exclamation marks, and question marks are inside the quotation marks:
“How could you do this? Moving a couch across the room isn’t a job for a fourteen-year-old girl!” Diane’s mom yelled in despair. “These macaroons are just exquisite! I would love it if you would give me a recipe,” my aunt asked me. “This movie was so scary that I could barely look at the screen!” her son complained after watching Jaws.
2 Use commas to set off dialogue tags, such as “he said” or “she exclaimed”:
“Enough of this,” he said, “I am absolutely tired of repairing this car! I will rather save up and buy a new one.” “Pepsi has too much sugar in it, this is diabetes in a can,” the grandmother said in a sad voice. “I have been reading The New York Times for years now,”the teacher said. “This newspaper has never disappointed me.”
3 If your quotation is at the end of the sentence, put a period inside the quotation marks as well:
Uncle Joe frowned, scratched his forehead, and finally replied, “I have no idea why my car keys are in the fridge.” He then told her the biggest lie he could ever tell, “I never left the wet towel on the bathroom floor.” Sarah pointed at zebra and asked her father, “Daddy, I have never seen a black and white horse.”
Pay attention to the following: if one person’s speech takes more than one paragraph, use opening quotation marks at the beginning of each paragraph, however, do not use closing marks till the end of the speech .
My new neighbor always seems to be the most enthusiastic to tell me about her perfumes. One day, I asked her, “How did you come to like and wear perfumes?” She replied, “I have always wondered about where perfumes came from. This huge industry has grown from our scent preferences, experience with different smells, and scent associations. Probably, this is connected to our evolution as species, where detecting specific smell would mean choosing safe food. “Until recently, I have never been wearing perfumes myself, but admired them from a distance. Now I have a small collection of fragrances. I have learned a lot about fragrance industry and notes used in perfumery.”
How to Write a Dialogue Between Two Characters
Now that you know all about the purpose of a dialogue in an essay as well as how to write it and use punctuation, learning how to write a dialogue between two characters will be a piece of cake.
The rules you should follow are:
- Give your characters a setting . Just like in movies, mise-en-scene is often as important as the dialogue itself. Set the scene for the dialogue by briefly describing where and when the dialogue takes place. This will help your readers imagine the picture more vividly.
- Keep it realistic . Unless it suits your essay style, there is no need to be smarty pants and write dialogues with words and scientific facts that are hard to understand for an average reader. While writing a dialogue, reread it several times and make sure it doesn’t make you think “nobody talks like that!”
- Let the dialogue flow naturally . Put yourself into your characters’ shoes and imagine how you would react to something being said to you. This is how you will find the way for the dialogue to seem natural and flow seamlessly.
- Don’t overuse it . While dialogue is a great tool for an essay, turning an essay into a play script with only quotes is another mistake you want to avoid.
- Make your characters human . Add details about feelings and emotions into the dialogue, both from the narrator and from the dialogue itself. Let your audience understand the tone and mood of the dialogue.
- Give the dialogue a purpose . By all means, discussion about whether a cake is tasty or not can be passionate, emotional, and tense altogether. However, this is not something to include in a dialogue. Your dialogue should have a purpose in the plot and affect the characters involved in it.
- Make sure to indicate who is who . This might seem like a rookie mistake in writing a dialogue in an essay, however, it happens. Have you ever read a long dialogue where you couldn’t understand anymore who talks? If your dialogue in an essay is longer than 5-6 quotes, make sure to add narrator’s text that will clarify who says those lines.
In a dialogue between two characters, it is easy to do because the readers do not need to remember many names or attributes. To avoid repetitions, use “he” or “she”, or specific features and roles, such as family member name (aunt, uncle, grandmother, nephew, etc.), significant appearance characteristic (blonde girl, tall man, lady in red, etc.), and specific roles people have (student, cashier, sale associate, doctor, nurse, etc.). In case you use any of those, make sure that you mention these attributes earlier in the text to avoid confusion.
Following these tips will help you write a truly meaningful dialogue between two characters and help readers understand additional information about them, their mood, features, preferences, role in the story, and relationships between them.
English Essay Dialogue Example
John finally returned home after a long day at work. It was raining cats and dogs and his raincoat was soaked. He opened the door, entered his apartment, and put his bag on the floor. suddenly , his phone started ringing. John took it out of his pocket and picked up. “Dad, itl burned down… I am so sorry,” he heard his daughter’s sad voice. She was crying. “What are you talking about?! Jen, are you alright?” “Dad, your summer cottage, it burned down to the ground” she was clearly devastated. John asked, “How did this happen?” “Just an accident, dad. You must have left the fire in the fireplace,” Jen replied. At this moment, John sighed with relief, even though his daughter might have thought he was very upset by the loss. She had no clue that her father insured their summer cottage and now the word “accident” meant lining his pocket from insurance money for sure.
So, now you know everything you need to write a dialogue in your essay successfully! Still, I strongly recommend to consider whether you need it at all — even when tutors assign such a creative writing, they are very meticulous in its evaluation. Moreover, pay attention to editing — due to sophisticated punctuation, dialogues are a never-ending source of students’ errors.
Did you know that Homework Lab is a student task sharing platform? You can work on tasks on your own or ask professional Geeks for help. Join anytime, anywhere for free.
If you have any questions about dialogues unanswered, please share your comment — I will get back and resolve any issues you have 😎.
Related articles

Popular articles

Writing dialogue: Complete guide to storied speech
Writing dialogue is an important skill to develop so that characters’ speech is imbued with voice and advances the story. Learn more in this complete guide to dialogue writing and formatting, with examples.
- Post author By Jordan
- 37 Comments on Writing dialogue: Complete guide to storied speech

This guide to writing dialogue is all about using speech and conversation in storytelling to make your characters’ voices drive plot, tension and drama. Use the links to jump to the dialogue-writing topic you want to learn more about right now.
What is dialogue? Key terms
Dialogue in writing is conversation between two or more people/animated voices (animated voices because it could be speech between a person and an inanimate object they personify, for example, an imaginary or supernatural voice, and so forth).
Dialogue can be compared to:
- A tennis or fencing match: Speakers may spar, score points, volley arguments or statements (and rebuttals to them) back and forth
- A dance: One speaker says one line, the other replies, and sometimes one person may lead, at other times, the other leads
- Pieces in a puzzle coming together: What different characters say may build up a gradual picture, for example an idea of the persona of a character who has not yet appeared in a story scene but has been spoken about by others
- Music: sometimes there is harmony (working together), other times discord (strife, heated conversation or disagreement)
Key terms in writing dialogue
There are several terms in dialogue worth knowing as they crop up often in discussing this element of writing craft:
Active listening: Dialogue is (usually) responsive
When somebody is engaged in ‘active listening’, they aren’t just waiting for their turn to speak. In a true conversation, people hear one another, respond.
There may be instances where your dialogue’s subtext or context (more on these below) calls for characters not to actively listen to one another, of course. There may be cause for them to interrupt, speak over, speak at cross purposes.
In these cases, it should be contextually or otherwise clear why characters aren’t properly responding to each other’s speech (the dialogue should not read or sound like random non sequiturs, each person’s utterances totally disconnected for no clear reason).
Context for dialogue
Effective dialogue involves its context. For example, in a frenzied car chase, the squeal of tires may drown out the exchange here or there. Speech and action in this context may reflect rapid decision-making, keeping pace.
In the middle of a bank heist, people may be curt, decisive (of course, inept thieves could wax lyrical and by talking too much make rookie mistakes).
Either way, context will inform how readers make sense of your dialogue, and helps to fill dialogue with tone and mood . Nobody whispers to each other standing next to Niagara falls (if they want to be heard).
Subtext and dialogue
Subtext in dialogue is the underlying meaning, motivation or feeling behind the words characters speak.
For example, a boss starts a casual conversation with a new employee but the subtext is that they’re having regrets at hiring the person and trying to come to a decision on whether to terminate in the trial period. The subtext will inform what language they will use (and this language would be different to someone ecstatic with their employee’s performance).
Subtext adds depth and complexity to dialogue, strata of the said and unsaid.
Purpose in dialogue
Why is the information you are writing in a scene given as dialogue? Knowing the purpose of dialogue (and writing dialogue that feels purpose-driven) is useful to ensure that every spoken line counts. In a stage play, dialogue and action are the two drivers of story.
In narrative fiction, you also get to use narration to convey meaning. A story where all character information is conveyed through narration may read oddly voiceless, impersonal. Dialogue makes your characters pause, take a breath, like real flesh and blood.
Recommended reading
Learn more about writing conversations that feel real and draw on cause and effect, call and response:
- Context and subtext in dialogue: Creating layered speech
- How to make dialogue in writing carry your story
- 7 dialogue rules for writing fantastic conversations
To the top ↑
I write plays because writing dialogue is the only respectable way of contradicting yourself. I put a position, rebut it, refute the rebuttal, and rebut the refutation. Tom Stoppard

GET YOUR FREE GUIDE TO SCENE STRUCTURE
Read a guide to writing scenes with purpose that move your story forward.
Why dialogue matters
Why do most stories benefit from liberal use of dialogue?
1. Dialogue brings characters and their differences to life
In dialogue, you could show a character’s personality in a handful of words. Here, for example, Dostoyevsky creates the sense of a decisive doctor, used to dealing with uncertain, anxious patients in The Double :
‘Krestyan Ivanovich … I …’ ‘Hm,’ interrupted the doctor, ‘what I’m telling you is that you need to radically change your whole lifestyle and in a sense you must completely transform your character.’ (Krestyan Ivanovich particularly emphasized the word ‘transform’ and paused for a moment with an extremely significant look.) Fyodor Dostoyevsky, The Double , trans. Ronald Wilks (1846, 2009), p. 11
There is an immediate sense of power dynamic (and differential) – the hesitating patient and his decisive doctor.
2. Dialogue splits up exposition into varied parts
If all the revelation of your characters and world is in long, wall-of-text narration, it becomes slightly draining to read.
Dialogue lifts us out of a ‘this happened, then that’ sense of explanation and throws us into the immediate – sound striking the eardrum. Tweet This
3. Dialogue advances a story
Characters may tell each other things that reveal – or shift – goals, motivations, conflicts. ‘But first, I must tell you Mr Bond…’ A villain may say too much, a lover, too little (or vice versa).
4. Conversation builds relationships
Some of the most beautiful relationships (or the most ugly) emerge through what people say to one another.
Ed’s note: As an undergraduate in English Literature, I attended a lecture on Pride and Prejudice where the lecturer illustrated how Lizzie and Darcy’s love is established through the grammar of their language and how it shifts. At one point, Darcy says, ‘You are loved by me’ – a different structure to the standard ‘I love you’ that places the subject first, in a way that reads as full of care.
We detect attraction and resentment in the language people use with one another. A conversation about the weather may imply feelings – it comes down to tone, address, mood, agreement and disagreement.
5. Dialogue brings humor, levity and persona to stories
Dialogue is often a vehicle for comedy. It’s a crucial part of how to write a funny story .
You can narrate that a character has grown wealthy and fallen out of touch with their humble origins. But in Dickens’ Great Expectations, when a character named ‘Trabb’s boy’, the tailor’s son, follows the main character Pip down the street mimicking him and saying, ‘Don’t know ya!’ after Pip is left wealth, it’s a brilliant and funny illustration of how people change (and perceive and react to changes in others).
Pip seems ‘too good for’ others now that he has wealth, and three words convey Trabb’s boy’s contempt with sly humor. Three words (paired with action, the following and mimicking) convey complex social dynamics and feelings.
Why else do you think dialogue matters? Tell us in the comments.
Learn more about writing dialogue that drives stories:

10 dialogue tips to hook readers
Hook readers into your story with dialogue that catches their attention.

- Writing movement and action in dialogue: 6 tips
How can movement and action make your dialogue more immersive? Find out.
Dialogue is the place that books are most alive and forge the most direct connection with readers. It is also where we as writers discover our characters and allow them to become real. Laini Taylor
How to format dialogue
Speech marks or quotation marks, and where do the line breaks go? Read on for how to format dialogue, common differences between UK and US formatting styles, and more:
Why do we format dialogue? Clarity, ease and flow
Try to write an exchange in dialogue all as block paragraph text and it becomes a nightmare trying to keep track of who says what:
“You’re late,” she said. “But I didn’t say what time I was coming.” “I don’t care, I’ve been waiting half an hour.” There was an awkward silence for a few seconds. “Well don’t say anything, whatever.”
It’s not clear from the above dialogue without line breaks and with no attribution for the last spoken sentence who says what at all times.
This is much easier to read because line breaks signal when the speaker changes:
It’s much easier to follow the back and forth (and because only two characters are present, the dialogue does not need excess attribution of who says what thanks to the line breaks clarifying this).
How to format dialogue in stories: 8 tips
To make sure it’s clear who’s speaking, when it changes, and when speech begins and ends (and narration or description interrupts):
1. Use quotation or speech marks to show when speech starts and stops
If a character is still speaking, don’t close speech marks prematurely.
2. Start a new line each time the speaker changes
Although it is common practice to use an indent for each change of speaker, make sure to use paragraph formatting in your word processor rather than the tab button as this can make indentation too large or wonky (using paragraph-wide settings is most precise).

3. Decide how you’ll format dialogue (and stick with it)
Speech marks with double quotations like the example from Colleen Hoover above (“) are more commonly used in the US, single quotation marks (‘) in books published in the UK.
Some contemporary novels don’t use speech marks at all, using an em dash at the start of a line or presenting dialogue another way. Whichever approach you use, consistency is key.
Example: Using single quotation marks to indicate speech

4. Always use a comma if there is an attributing tag
If dialogue is attributed using a tag such as ‘she said’ (read more on dialogue tags below), use a comma and not a period/full stop. For example:
“Writing dialogue is harder than I thought.” She said. ❌ “Writing dialogue is harder than I thought,” she said. ✔️
Remember: the tag continues the sentence.
5. Split long monologue over multiple paragraphs
What if the same character is speaking for a long time in dialogue?
To format this, the convention is to open speech marks for each new paragraph without closing speech marks for the previous one, until the speaker is finished talking.
Example: Dialogue where one speaker continues over paragraphs
“First I want to thank you all for being here on our special day. It does take a village (but you can put down the pitchforks, take off the creepy masks, and relax a little, guys, it’s not that kind of village) … Er eheh… OK I’m firing my joke writers.
“But in all seriousness, I couldn’t have chosen a better bride…zilla.”
6. Use the appropriate dialogue punctuation
If a speaker pauses, put it in with a comma or something longer such as a semicolon. This is where it helps to read dialogue out loud as you will hear where there is a natural pause that needs punctuating. Colons have an announcing effect. Example: “OK, here’s the kicker: The guard changes every forty-five minutes.”
If there is a question or exclamation, use the appropriate speech mark (that includes the occasional special effect, such as an interrobang (!?).
7. Write interruption or other changes in dialogue’s flow clearly
Ellipses are effective in showing a character trailing off or pausing to think for longer, mid-dialogue.
“Oh yes, I remember, it was … whatshername.”
There are several ways to show interruption. You could:
- Use an em-dash just after cut-off speech. Example: “If you’d just let me fini—”
- Use parentheses to show self-interruption. Example: “If you’d just let me finish what I was (actually, it’s fine, carry on).”
8. Format narration interrupting dialogue clearly
If you want to describe a character’s manner, movement, expression mid-dialogue, remember to use a comma before and resume dialogue without capitalization (unless the word is a proper noun):
“I can’t believe you said that,” John said, shaking his head, “and with absolutely zero remorse, too.”
Read more on how to ensure your dialogue reads clearly, including how to write ensemble dialogue with multiple characters present:
- Writing dialogue between multiple characters
Nothing teaches you as much about dialogue as listening to it. Judy Blume
Effective vs weak dialogue
Why does some dialogue scintillate, stir interest, while other dialogue reads like talking heads saying nothing of great impact in an inky void? There are several hallmarks of effective and less effective dialogue:
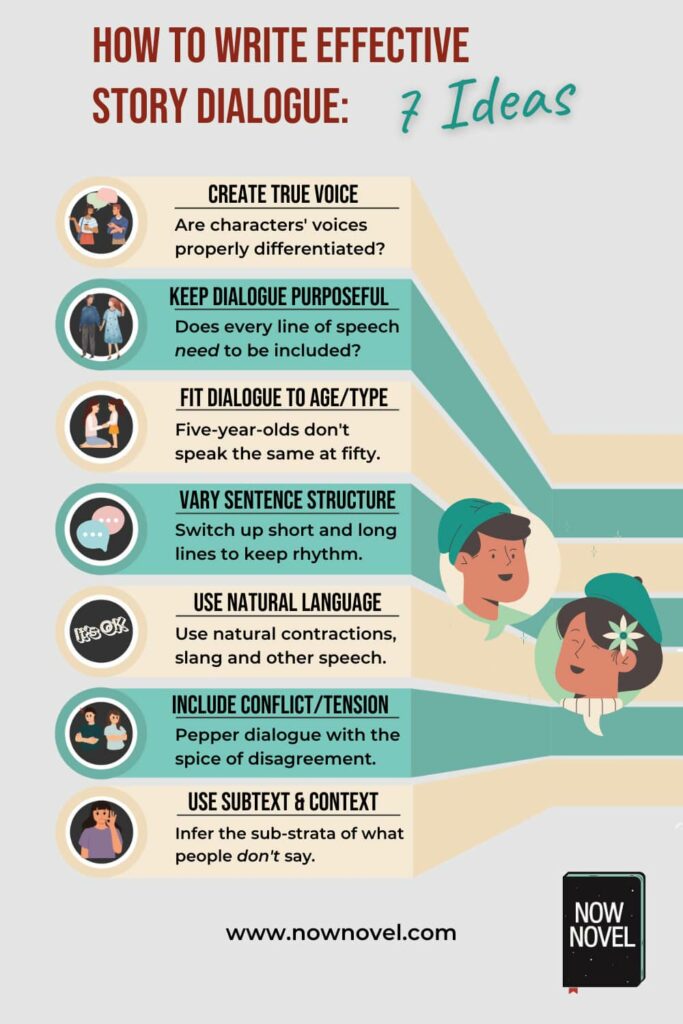
What makes dialogue effective:
- An authentic sense of voice. Do characters sound like cipher’s for an author’s pretension (this may be true to a specific stylistic choice, though) or like real people talking?
- Purpose-driven dialogue. Each line of dialogue should have identifiable purpose, whether it’s establishing character, advancing the story, building tone and mood, or dialogue serves another purpose.
- Aptness for type (or explicable ‘against type’ voice). Avoid confusing your reader by having a five-year old speak like a fifty-year-old (unless there’s a plot-given or other explicable reason for this anomaly).
- Varied structure. If every sentence is clipped or brusque, or every sentence is long and meandering, the eye (and ear) may tire. Switch it up if possible.
- Natural language. Contractions (e.g. ‘it’s’ for ‘it is’) and other ways people naturally speak (colloquial language or slang) lend further authenticity to voice.
- Conflict and tension . ‘As you know, Bob’ info dumps and happy people in happy land don’t make dialogue exciting (but tension, disagreement, doubt – sparks of contradiction – do).
- Movement and gesture. A gesture may change the entire meaning of a spoken phrase (a shrug, turn, sitting down, standing up, waving arms, and so on).
- Subtext and inference. What a character is truly thinking or feeling might not match up perfectly with what they’re saying. People lie, omit, embellish, and so forth.
What can weaken dialogue in fiction?
Dialogue in stories may feel bland or confusing (or too over the top and melodramatic) when:
- It’s all one note. If every utterance is an exclamation (with an exclamation mark), that gets old fast. Use special effects like salt – just enough to enhance the conversation.
- Connection is absent. Your reader may be confused if what characters reply to each other seems as though they’re having two different conversations (unless there is contextual explanation, e.g. both are hard of hearing).
- The scenery stays outside. If your characters are having an argument in the kitchen, does someone bang a pot, slam a drawer? Bring in surrounds.
- There is no differentiation. If everyone has the exact same vocabulary, mannerisms, and pattern of speech, characters start to become clone-like, like so many Agent Smiths.
- Excessive or bizarre tags. Characters shouldn’t honk or trumpet speech too often. Favor tags that you can say or express (no, “What!” she flabbergasted’). Leave out tags entirely if context tells your reader who speaks (and content of speech gives tone/mood).
- Excessive dialect or accent. At best excessive dialect or accent may read distracting, at worst, like hurtful stereotype or caricature.
- Adverbs clutter speech. Instead of overusing ‘she says softly’, leave space for the silence to come through.
- Dialogue dumps information. ‘As you know, Bob’ is a phrase used for dialogue where characters tell each other things both already know solely for the reader’s benefit. Find ways to make the retelling new/fresh, find what Bob doesn’t yet know and needs to be told.
Keep reading about ways to make dialogue characterful and engaging:
- Dialogue words: Other words for ‘said’ (and what to avoid)
- How to write accents and dialects: 6 tips
- Realistic dialogue: Creating characters’ speech patterns

Pay $0 for writing insights and how to’s
Be first to know whenever we publish and get bonus videos and the latest Now Novel news.
Dialogue devices for characterful speech
There are several dialogue devices that help to advance stories and create a sense of movement, tension and change:
Dialogue tags and action tags
What are dialogue tags and action tags?
Dialogue tag: The words added after dialogue that attribute who has spoken (and often the mood, emotion, or volume of speech).
“You might want that tattoo, but I know all your secrets and your twenty-first is coming up and don’t think for a second I’m above making an awkward speech,” mom warned.
“Shh!” he hissed in a half-whisper. “This freaking place is haunted.”
Action tag: Indicates the speaker’s movements or gestures in dialogue. This can be used to attribute speech and make dialogue livelier.
“You might want that tattoo, but …” Mom leaned over theatrically as though to confide something important. “I know all your secrets and […]’
Movement and gesture
Movement and gesture may punctuate dialogue, immersing the reader in a scene further.
‘Then go,’ said Mrs Williams, handing him the buckets and the coil of rope. ‘Swim,’ she said maliciously. She knew he was afraid of the sea. He carried his fear coiled and tangled in him like other boys carry twine and string in their crumb-filled pockets. Peter Carey, Oscar and Lucinda (1988), p. 16
Interruption
Interruption is a useful device in dialogue for argument, dramatic scenes with high stakes where characters are speaking over one another, and so forth.
“I could have killed you.” “Or I could have killed you,” Percy said. Jason shrugged. “If there’d been an ocean in Kansas, maybe.” “I don’t need an ocean—” “Boys,” Annabeth interrupted, “I’m sure you both would’ve been wonderful at killing each other. But right now, you need some rest.” Rick Riordan, The Mark of Athena (2012).
Conflict and suspense
Conflict and suspense in dialogue keep the reader intrigued. Characters may argue, refuse to speak, tell a fib the reader may know to be untrue, or otherwise stir tension.
“What’s this for?” Tessie asked suspiciously. “What do you mean, what is it for?” “It’s not my birthday. It’s not our anniversary. So why are you giving me a present?” “Do I have to have a reason to give you a present? Go on, open it.” Tessie crumpled up one corner of her mouth, unconvinced. Jeffrey Eugenides, Middlesex (2002), p. 10.
Read more on devices in dialogue, including dialogue tags vs action tags and how to create tension:
- 421 ways to say said? Simplify dialogue instead
- Dialogue 101: Using dialogue tags vs action tags
- Writing tense dialogue: 5 ways to add arresting tension
I never say ‘She says softly.’ If it’s not already soft, you know, I have to leave a lot of space around it so a reader can hear that it’s soft. Toni Morrison
Dialogue examples that work
Read examples of dialogue that works from a cross-selection of genres including fantasy, romance, science fiction, thriller, historical, contemporary and more:
1. Fantasy dialogue example ( A Game of Thrones )
Note how George R. R. Martin weaves in setting to create mood between utterances in this exchange from the prologue to A Game of Thrones :
“We should start back,” Gared urged as the woods began to grow dark around them. “The wildlings are dead.” “Do the dead frighten you?” Ser Waymar Royce asked with just the hint of a smile. Gared did not rise to the bait. He was an old man, past fifty, and he had seen the lordlings come and go. “Dead is dead,” he said. “We have no business with the dead.” George R. R. Martin, A Game of Thrones (1996).
2. Historical romance dialogue example ( The Duke and I )
Julia Quinn begins the first chapter in the first of her popular Regency-set romance novels with a typical Regency setting – a drawing room (and drama in letters):
“Oooooooooohhhhhhhhhh!” Violet Bridgerton crumped the single-page newspaper into a ball and hurled it across the elegant drawing room. Her daughter Daphne wisely made no comment and pretended to be engrossed in her embroidery. “Did you read what she said?” Violet demanded. “Did you?” Julia Quinn, The Duke and I (2000).
3. Mystery dialogue example ( The Murder of Roger Ackroyd )
Dame Agatha Christie’s The Murder of Roger Ackroyd is often voted one of her best detective novels. In the first chapter already, conversation turns to death and the topic of who knows what about whom (and how):
My sister’s nose, which is long and thin, quivered a little at the tip, as it always does when she is interested or excited over anything. “Well?” she demanded. “A bad business. Nothing to be done. Must have died in her sleep.” “I know, said my sister again. This time I was annoyed. “You can’t know,” I snapped. “I didn’t know myself until I got there and I haven’t mentioned it to a soul yet. If that girl Annie knows, she must be a clairvoyant.” Agatha Christie, The Murder of Roger Ackroyd (1926)
4. Science fiction dialogue example ( Hyperion )
Dan Simmons’ Hyperion which won a Hugo Award was hailed as ‘The book that reinvented Space Opera’. Note the weaving in of dialogue between human and machine in the prologue:
‘We need your help,’ said Meina Gladstone. ‘It is essential that the secrets of the Time Tombs and Shrike be uncovered. This pilgrimage may be our last chance. If the Ousters conquer Hyperion, their agent must be eliminated and the Time Tombs sealed at all cost. The fate of the Hegemony may depend upon it.’ The transmission ended except for the pulse of rendezvous coordinates. ‘Response?’ asked the ship’s computer. Dan Simmons, Hyperion (1989).
5. Psychological thriller dialogue example ( Sharp Objects )
Notice how in Gillian Flynn’s debut Sharp Objects how even a simple conversation between reporter Camille Preaker and her editor at the St. Louis Chronicle who sends her back to her hometown on assignment is laced with a sense of tension and avoidance:
“Tell me about Wind Gap.” Curry held the tip of a ballpoint pen at his grizzled chin. I could picture the tiny prick of blue it would leave among the stubble. “It’s at the very bottom of Missouri, in the boot heel. Spitting distance from Tennessee and Arkansas,” I said, hustling for my facts. Curry loved to drill reporters on any topics he deemed pertinent – the number of murders in Chicago last year, the demographics for Cook County, or, for some reason, the story of my hometown, a topic I preferred to avoid. Gillian Flynn, Sharp Objects (2006).
6. Humor dialogue example ( Lessons in Chemistry )
See here how Bonnie Garmus weaves together humorous dialogue and character description to create the portrait of a man who does not have much luck in love:
“I can’t believe you’re having trouble,” his Cambridge teammates would tell him. “Girls love rowers.” Which wasn’t true. “And even though you’re an American, you’re not bad looking.” Which was also not true. Part of the problem was Calvin’s posture. He was six feet four inches tall, lanky and long, but he slouched to the right – probably a by-product of always rowing stroke side. Bonnie Garmus, Lessons in Chemistry (2022).
7. Historical/fantasy dialogue example ( The Invisible Life of Addie LaRue )
V.E. Schwab creates a sense of early, 17th Century times in this conversation about prayer and witches’ fates in her historical fantasy novel that involves immortality and contemporary romance:
“How do you talk to them?” she asks. “The old gods. Do you call them by name?” Estele straightens, joints cracking like dry sticks. If she’s surprised by the question, it doesn’t show. “They have no names.” “Is there a spell?” Estele gives her a pointed look. “Spells are for witches, and witches are too often burned.” V.E. Schwab, The Invisible Life of Addie LaRue (2020).
8. Literary fiction dialogue example ( Home )
Toni Morrison is a master of capturing the authentic ring of a real human voice. See the difference between the Reverend and his wife who dismisses his jaundiced view of the world as ‘foolishness’ in this dialogue example:
“You from down the street? At that hospital?” Frank nodded while stamping his feet and trying to rub life back into his fingers. Reverend Locke grunted. “Have a seat,” he said, then, shaking his head, added, “You lucky, Mr. Money. They sell a lot of bodies out of there.” “Bodies?” Frank sank down on the sofa, only vaguely caring or wondering what the man was talking about. “Uh-huh. To the medical school.” “They sell dead bodies? What for?” “Well, you know, doctors need to work on the dead poor so they can help the live rich.” “John, stop.” Jean Locke came down the stairs, tightening the belt of her robe. “That’s just foolishness.” Toni Morrison, Home (2012).
What is a favorite section of dialogue from a book in your favorite genre? Share in the comments below.
Join The Process for weekly feedback on dialogue and other writing, webinars on dialogue writing and other writing craft topic, and structured writing tools to brainstorm and develop your story.
Now Novel has been invaluable in helping me learn about the craft of novel writing. The feedback has been encouraging, insightful and useful. I’m sure I wouldn’t have got as far as I have without the support of Jordan and the writers in the groups. Highly recommend to anyone seeking help, support or encouragement with their first or next novel. – Oliver
Recommended Reading
Read further examples of effective dialogue:
- Dialogue writing examples from top books vs AI (2023)
- Writing conversations using setting (examples)
- 5 types of dialogue your novel needs
Related Posts:
- Realistic dialogue: Creating characters' speech patterns
- Writing process: From discovery to done (complete guide)
- Tags dialogue examples , dialogue tags , how to write dialogue
Jordan is a writer, editor, community manager and product developer. He received his BA Honours in English Literature and his undergraduate in English Literature and Music from the University of Cape Town.
37 replies on “Writing dialogue: Complete guide to storied speech”
Thank you for this! I notice these are all first person narratives; could you do something also with stories told in third person?
It’s a pleasure! Happily. While not on dialogue specifically, you might find this post on starting a story in third person helpful: https://www.nownovel.com/blog/how-to-start-a-novel-in-third-person/
“Very illuminating,” I said.
Thanks, Rob!
thanks this really helped
I’m thrilled to hear that, Randolyn. Thank you for the feedback.
As Rob said, very illuminating!
Do you have any recommendations on books with similar dialogue? Or should I give Tartt’s whole bibliography a go?
Thanks for the insight! Dialogue is one of my worker points in writing and I aim to correct that.
Hi Marco! It’s a pleasure. Tartt’s writing is very punchy, but there are many authors who write fantastic dialogue. Another great one is Toni Morrison – she’s a great master of every element of story, from exposition to dialogue to description and more.
Good luck, with focus I’m sure it’ll improve to the level you want it to be quickly.
This was immensely helpful. I’ve always handed dialogue fairly well, I think, but these tips will help me clean it up and use it to move the story forward, rather than just using it as page filler.
That’s great to hear, Brianna. I hope your current WIP is coming along well 🙂
yes helpfull
Hi Umer, thank you for the feedback. Good luck with your story!
Hello this is a nice example…….
Thanks, Joel!
This is truly helpful. Thanks!
I’m glad to hear that, April. It’s a pleasure! I hope you’re writing great dialogue.
I am doing a class project on figurative language and i need examples but short ones do you have any i could use
This was surprisingly helpful. I’m so glad I came across this website. Writing dialogue has always been something I’ve had difficulty doing, but these tips have significantly improved my dialogue writing. Thank you so much.
We’re glad to hear that, Prakhar! Keep writing 🙂
it is really usefull to me madam thank u so much
I’m glad to hear that, Manjunatha. Have a great weekend!
Thanks, Nathan, I’m glad to hear that.
kinda helpful to me 😀
I got my 18,5 mark from this Amazing ?
Fantastic, Chihab – do give yourself some of the credit! Well done.
Very useful to me… Thanks !!☺☺
It’s a pleasure, thank you for reading our articles and taking the time to share your feedback ?
[…] some dialogue writing tips at the following blog and evaluate them with some fellow […]
I want to know about the rule of using open quotation mark at the end of the dialogue 1 ‘We are not allowed to-‘
Hi Jagadishkk, thank you for sharing your question. From the example you’ve written, do you mean using interruption at the end of a line of dialogue? The way you’ve written that example is correct, you would usually use a dash with the interrupting person’s dialogue appearing immediately below on a new line (with indentation if indenting changes of speaker as is a common formatting style choice).
Hi I want you to help me with dialogue first draft
Hi Peggy, you can get constructive feedback from our community in our writing groups, they’re free to join. You can sign up here .
What is a favorite section of dialogue from a book in your favorite genre? Here is one of mine from “Bring up the bodies” by H. Mantel.
“Majesty, the Muscovites has taken three hundred miles of Polish territory. They say fifty thousand men are dead.” “Oh,” Henry says. “I hope they spare the libraries. The scholars. There are very fine scholars in Poland.” “Mm? Hope so too.”
Tells us something about Henry VIII — he “doesn’t give a hoot” about libraries and scholars in Poland or dead men.
Hi Nara, thanks so much for sharing that dialogue example. I like that Henry VIII seems preoccupied or disinterested in his responses, the simplicity of monosyllabic words and even how Mantel has him drop the subject ‘I’ to make it read more cursory, saying the bare minimum. He was probably too busy marrying and remarrying (and beheading) 🙂
Hey Jordan,
fantastic article, thank you very much – it helped me a lot, especially because i am translating my German Novel into English right now! However there is still an open question to me:
Here is an example/ little excerpt of my novel, which I already translated but kept the original German Formatting. I am asking myself if the colon can stay like this ( Then she said: ) or do I have to replace it with a comma ( Then she said, ) and begin with the dialogue in the next line. Here is the example ->>
After my mother echoed Michael’s exact words, she looked at me with a fixed gaze for several seconds. Then she said: “Do you understand now, Jordan, why I opened my eyes so wide just now?” “Yes… I feel as if he is here right now, Mother. I know him, but I don‘t know where…” “But now I really want to ask you, were you aware of his words, Jordan?”
I really hope you can help me with this little question. Thank you in advance 🙂
Greetings from Germany Yannic
Hi Yannic, thank you for your kind feedback, I’m glad you found this guide to dialogue helpful. One can use a colon or a comma to precede quoted speech. Technically, it is usual to only use a colon if the introductory words form an independent clause or the quotation is a complete sentence. Because the mother’s words fit this rule, a colon is totally acceptable in this case.
Good luck with your translation, that is quite the undertaking.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Pin It on Pinterest
Samantha in Secondary
6 Dialogue Writing Activities for the Secondary ELA Classroom
April 18, 2022 by Samantha H.
Dialogue writing activities are always a mainstay in any of my narrative writing units. I love seeing the creative writing my students turn in, but I often see it lacks dialogue or uses it incorrectly. It’s a skill that needs to be refined, but is sometimes overlooked in the grand scheme of things. I like to set aside time for activities that help review the mechanics of proper dialogue writing, as well as unique dialogue writing activities that let students practice the skill themselves. Read on for creative dialogue writing activities for your secondary students.

1. Create a Scene
There are a lot of fun ways you can have students create scenes to practice writing dialogue. You can start with some premade options that you assign or students randomly select. You can also create Roll-a-Scene scenarios for your students (here’s my bundle of Roll a Story activities for inspo). In these activities, students use a dice and roll to receive story elements. In their story creation, have them create dialogue. This will allow your students to review the basic rules of dialogue and also let students practice creatively.
2. Write the Photo
Print a variety of photos for students to create the dialogue. You can go about this in a variety of ways. Print several options and use them as station activities or have everyone can write from the same photo as a bellringer. Find photos that have great facial expressions to help lead students who may struggle with writing, and use more ambiguous photos for more creative options where students must make inferences.
3. Use Mentor Texts
Pick from a lineup of strong mentor texts to use as examples. You can use from your current class readings, or select from top YA novels that your students already love. You can also have students select from their personal readings. Keep a variety of genres on hand so there’s always an example ready for students to use as a reference. You can use these for writing activities like having students continue a section, rewrite with different characters, update the language to something more contemporary or to fit in a new genre. If you need some ideas to add to your own classroom library, sign up for my email list to get a free list of 100 YA Novels to get you started.

[SPACE FOR OPT-IN]
4. Correct the Sample
Take either some mentor text examples or write your own for students to correct. This makes a great bellringer activity for quick reviews to keep it fresh in your students’ minds. Seeing how common mistakes can be corrected can help students visualize what needs done when they attempt their own writing. Consider working on some correction samples before students begin their own creative assignments. NoRedInk is another great option to allow students to practice correcting dialogue. Create a class, assign their pre-made dialogue writing activities, and you’re ready to go.
5. Turn Narrative into Dialogue
You can pull from mentor tasks again for this activity. Pull from your class reading, personal reading, popular novels, or just well-known scenes and have students write dialogue for sections of narrative. It can be an interesting take to see students write the same scene and compare their dialogue interpretations.


6. Learn from the Masters
If you’re looking for some more ideas there are a few more activity ideas here from Edutopia. The suggestions in the article are spot on and have great suggestions for dialogue activities to use with students.
If you’re looking for a great resource that combines many of the above activities already done for you, click here to grab the mini-lesson I use with my own students. The resource includes both print-and-go and digital versions, so you can use it however you may be teaching. My students love the creative dialogue writing activities included.

If you’re looking at your students’ writing and thinking it could use some more dialogue, or you know working with dialogue is a bit rusty – consider working in some daily practice or mini-lessons and activities to help solidify the skill.
Do you include dialogue writing activities in your own classroom? I’d love to hear about your favorites! Sound off in the comments below or follow me on IG or Facebook to join the discussion.
Happy teaching!
Subscribe to the newsletter to keep up to date on all things Samantha in Secondary.

A Complete Guide To Writing Dialogue
One of the writer’s most effective tools is dialogue. A story with little or no conversation between characters can sometimes make the eyelids flicker. Too much may leave the reader breathless. Writing dialogue is tough and a skill that takes time to master.
However, there are plenty of useful tips, tools and methods to help you learn how to write dialogue in a story and how to format it too.
And for your benefit, you can find them all in this comprehensive guide.
Below, you can find the definition of dialogue, tags and formatting guidelines and a discussion on the different ways characters speak and converse.
And you can also find plenty of illuminating dialogue examples to help you gain a clear understanding of the mechanics and how you can apply it to our own writing.
You can jump through this guide by clicking below:
Choose A Chapter
What is dialogue, how to format dialogue.
- Should I Use ‘Said’ And Asked?
How To Write Dialogue Between Two Characters
How to write dialogue readers love, how to write internal dialogue, an exercise on how to write dialogue in a story, good dialogue examples from fiction, technical writing tip – how does dialogue impact the pacing of a story, how do you edit dialogue, more guides on creative writing.
Dialogue is defined as a conversation between two or more characters , particularly in the context of a book, film or play.
Specific to writing, dialogue is the conversation between characters.
A n author may use dialogue to provide the reader with new information about characters or the plot, delivered in a more natural way. They may also utilise it to speed up the pace of the story.
As we’ll see below, there seems to be one pervading guideline when it comes to writing great dialogue and that is clarity reigns supreme.
What Is Internal Dialogue?
Internal dialogue is that which happens within a character’s mind . This can sometimes be reflected in fiction with the use of italics. For example:
I hope they don’t come down here, Mycah thought.
Internal dialogue is a great way of delving deeper into a character’s mind and perspective and is a powerful weapon when it comes to characterization. We explore it in more detail below.
Writers have different stylistic preferences when it comes to dialogue. Below, we’ll take a look at some of the best practices and common literary conventions, such as the use of a dialogue tag and quotation marks.
Using Quotation Marks
If sticking to the principle of clarity reigns supreme, then for me, using double quotation marks is the most effective way of communicating dialogue.
They’re universally recognised as a means of conveying dialogue, and they stand out more on the page in contrast to single quotation marks. There are more reasons for using them, however, and that involves a criqute of the single quotation mark.
Writing Dialogue With Single Quotation Marks
This does come down to a matter of style.
The best format I’ve found, and by best I mean the approach readers find clearest, is to use speech marks (“) as opposed to a single apostrophe (‘).
If, for instance, a character is speaking and quotes someone else, single quotation marks can be used within the speech marks, therefore avoiding any confusion, for example:
“I can’t believe she called me ‘an ungrateful cow.’ She’s got some nerve.”
Format Dialogue On A Single Line
Another helpful approach to help maintain clarity is to begin a piece of dialogue on a new line whenever a new character speaks. For instance:
“Who was at the door?” Nick asked. “A couple of Mormons,” Sarah said.
Adding Dialogue Tags
Dialogue tags are simply a piece of prose that follows a piece of speech that identifies who spoke. You can see it in the example above featuring Nick and Sarah.
You can use a dialogue tag in lots of useful ways. For example body language.
If a character reacts to something another character says or does, to maintain clarity, pop the reaction on a new line, followed by dialogue. So for example:
“We’re all sold out,” Dan said. Jim sighed. “Have you not got any in the back?”
Do You Always Need To Use Dialogue Tags?
Something I’ve noticed some of my favourite writers doing—James Barclay and George R.R. Martin, in particular—is, when possible, avoid using an attribution altogether. Less is more, as they say. If just a couple of people are talking, it may already be clear from the voices and language of the characters who exactly is speaking.
Again, to aid clarity, if there are a number of people involved in a conversation, it helps to use an attribution whenever a different character speaks. Nobody wants to waste time re-reading passages to check who’s speaking. I don’t enjoy it and I’m sure others don’t either.
Repetitive use of attribution may grate on a reader. It can suggest a lack of trust in them to follow the story. It helps when editing to look for moments where it’s unclear who’s speaking and if necessary add an attribution.
A brief point on the styles of attribution. If you read a lot, you may notice some writers prefer the order “John said,” and some prefer “said John”. Sanderson is of the view that the character’s name should come first because that’s the most important bit of information to the reader. But the likes of Tolkien adopted the latter version. It’s all personal preference. Why not mix and match?
Should I Use “Said” And “Asked”?
When it comes to the questions I often see asked on how to write dialogue, this is perhaps the most common.
An attribution, also known as an identifier or tag, is the part of the sentence that follows a piece of dialogue. For example: “John said.” In his creative writing lectures, Brandon Sanderson shares a few useful tips.
- Try to place the attribution as early as possible to help make it clear in the reader’s mind who is speaking. This can be done mid-sentence, such as: “I don’t fancy that,” Milo said. “What else do you have?” Breaking away like this works well if a character is going to be speaking for a few lines or paragraphs. You can also use an attribution before the dialogue, though there’s something about this that I find jarring. Used sparingly it works well, but too often just seems annoying and archaic. It’s all personal preference though.
- Try using beats, but not too many. What’s a beat? A beat is a reaction to something said or done. So for example facial expressions like frowning, smiling, narrowing of the eyes, biting of the lip, and hand gestures such as pointing, clenching fists, and fidgeting. And then you’ve got physical movements, like pacing up and down, smashing a glass, punching a wall.
- Don’t worry about using ‘said’ and ‘asked’. To the reader, these words are almost invisible. What they care about is who exactly is speaking.
- When a character first speaks refer to them by name, but after that, it’s fine to refer to them as he or she, provided they’re still the one speaking. It’s even desirable to use the pronoun; repeating a name over and over can irritate a reader.
Remember the overarching principle for when it comes to writing dialogue: clarity reigns supreme. Using ‘said’ and ‘asked’ is often the clearest way of getting your point across.
What To Use Instead Of Said In Dialogue
Remember, there’s no problem with using the word ‘said’ after a piece of dialogue. But if you find when reading your piece aloud that the repeated use jars, especially in a dialogue-rich scene, you may want to mix things up.
Using words other than ‘said’ can help to characterize too—everybody reacts differently to things and those reactions reveal a lot about a person.
So, here’s a list of twenty words that you can use instead of ‘said’ when writing dialogue:
- Pointed out
- Interrupted
So, let’s take a look at how to write dialogue between two characters. If you’d rather have a visual explainer, check out this informative video below.
A useful distinction to make is between everyday dialogue and the dialogue we find in fiction.
The chatter we hear in real life is full of rambling, repetitive sentences, grumbles, grunts, ‘erms’ and ‘ahs’, with answers to questions filled with echoes (repeating a part of the question posed, e.g. “How are you?” asked A. “How am I?” B answered).
When we think of the dialogue we read in books, it contains little of the things we find in these everyday exchanges. According to Sol Stein, there’s a reason for this—it’s boring to read.
If it holds no relevance to the story, we don’t care if a character’s cat prefers to eat at your neighbour’s house instead of your own, or if they think their nail job isn’t worth the money they paid, or if they think the window cleaner isn’t cleaning their windows. There are some snippets we overhear on the street that are interesting—an unusual name, a section of a story we want to know more about. Rare diamonds in a mine miles deep. I’ve fallen into the trap of trying to achieve realistic dialogue and it makes for drawn-out scenes and boring exchanges.
According to Stein, dialogue ought not to be a recording of actual speech, but rather a semblance of it.
What is this semblance of dialogue why should we try and achieve it?
So, how do we write good dialogue?
When we scrutinise a person as they’re talking (all the boring stuff aside) we discover a lot about their character: who they are, what they believe in, and sometimes, if they reveal them, their motives. We glean all this from word choice, sentence structure, choice of topic, their behaviour as they say something.

It’s these little details we as writers must dig for, so when it comes to writing our own dialogue, we can use them to help characterise our own characters and, if possible, develop the plot. The key to mastering dialogue , according to Stein, is to factor in both characterisation and plot.
How do we do it? Let’s look at some dialogue writing examples:
Milford: How are you? Belle: How am I? I’m fine. How are you? Milford: Well thanks. And the family? Belle: Great
I had to stop myself from stabbing my eyes out with my pen. This example is mundane, riddled with echoes, and gives us no imagery about the characters involved. How about this version?
Milford: How are you? Belle: Oh, I’m sorry, didn’t see you there. Milford: Is this a bad time? Belle: No, no. Absolutely not.
See the difference? Milford asks Belle a question, which Belle doesn’t answer. This is an example of oblique dialogue . It’s indirect, evasive, and creates conflict.
It’s a great tool for when it comes to looking at how to write dialogue in a story using different approaches. Our character is not getting answers. Oblique language helps to reveal a bit about the characters and the plot, namely that Belle could be a bit shifty and up to something unsavoury.
Writing Realistic Dialogue
When it comes to knowing how to write natural dialogue, the question to ask yourself is whether or not this style is going to fit your story.
Natural dialogue suits some stories wonderfully. However, it can also work against your story, maybe confusing things for your readers or making it too difficult to read.
When it comes to writing natural dialogue, it’s important to bear in mind the principles discussed here. Give your conversations purpose, make them oblique or intriguing, and don’t give information up cheaply.
You can achieve this in a natural or more casual or informal style.
If you’re looking for more visual tips and advice on writing dialogue, check out this excellent video below:
Say It Aloud
When you’ve written a piece of dialogue, one of the best and simplest techniques to check how it works is to say it out loud.
In doing so you’ll get a sense of how natural it is or whether it jars, or even if it’s cringy or cliche—we’ve all been there.
If you don’t feel comfortable speaking it aloud, you can use a Text to Voice function, like on a website like Natural Readers which allows you to paste in text and then have it read it back to you (it’s free).
Add Slang From Your World
An effective way to write good dialogue that not only characterizes and drives the plot but adds to your world, is to use slang or world-specific references. This can be particularly useful in the fantasy and sci-fi genres .
For example, in my novel Pariah’s Lament , I refer to the world in place of phrases that refer to our own. So instead of “What in the world was that?” I’d say something like “What in Tervia was that?”
Small Talk And Hellos And Goodbyes
As a general rule, there’s no need to include small talk, hellos and goodbyes. The reader isn’t really too bothered about these niceties. They just want to get to the action, the conflict.
You can brush over things like small talk and hellos with short descriptions in your prose writing . For instance:
Stef and John stepped into the room. A sea of smiling faces welcomed them and before they knew it, they were shaking hands and embracing. “I wasn’t expecting such a warm welcome,” Stef said. “It’s like they have no idea what we’ve done,” John replied. “Maybe they don’t.” “Or maybe they do, and it’s all a ruse.” Stef looked at him a moment, thoughtful. “You’re getting paranoid.”
See here how the hellos were glided by and we’re straight into more interesting dialogue? You can also cut back on the odd superfluous dialogue tag too if it doesn’t add to your story.
Give Your Characters Their Own Voice
A character’s voice is an important factor in dialogue. Nobody speaks in the same way. Some people have lisps, some people say their ‘r’s’ like ‘w’s’, some people don’t enunciate properly, say words differently, speak in accents, and have a nasal twang. There are so many variables.
Introducing these features to some or all of your characters can help to make them more memorable and distinct.
How To Write Dialogue For A Drunk Character
When we’re writing our stories it’s likely that some of our characters may become intoxicated with alcohol or drugs. This creates the question in a writer’s mind, how do you write dialogue for a drunk character?
We can fall into the trap of spelling out the words that they try to say, factoring in the slurs, the missed words and the mispronunciations. The problem this can create is that it can go against our overarching principle of clarity reigns supreme.
Dialogue that’s too difficult to read can cause frustration in the reader. They may get fed up and stop reading altogether—the last thing we want.
The best technique is to provide a description of how the person is talking. Describe how they slur their words, how certain letters sound in their drunken state and so on. Including body language in this will help a great deal too. You can then write dialogue in a more natural and understandable way.
The same applies to the likes of writing stuttering in dialogue. It can be very frustrating for a person to listen to a person with a stutter. To include it in your writing can cause problems too. So again one of the best solutions is to describe the stutter first and then write dialogue naturally.
Hopefully, these tips will help you with how to write dialogue for our intoxicated characters.
An Author May Use Dialogue To Provide The Reader With Information, But Don’t Info Dump
An author may use dialogue to provide the reader with useful information. However, if done incorrectly it can have a negative effect.
In his book The First Five Pages , Noah Lukeman says that one of his biggest reasons for rejecting a manuscript is the use of informative dialogue. In other words, using dialogue as a means for conveying information, or info-dumping . He says it suggests the writer is lazy, too unimaginative to convey the information in a subtler way. If you’d like to learn more about avoiding info dumps, check out my guide on natural worldbuilding .
Sometimes dialogue will give us no information at all. Sometimes snippets. Often if you overhear a conversation between two people you’ll find you understand little of what they discuss. It’s the little details they reveal that are most interesting. Take the example of someone mentioning they went to the hospital. The person they’re with may know why they went, but you don’t. Give the reader pieces of the giant puzzle and leave them wanting more.
Lukeman suggests a few solutions to mend instances of informative dialogue. One is to highlight pieces of dialogue that merely convey information and do not reveal or suggest the character’s personality or wants. Break them apart and find a way to let them trickle into the story.
Understanding how to write internal dialogue can prove a key weapon in your writing arsenal.
This style of dialogue can be employed effectively in scenes or stories focused on lone characters. It can break up the monotony of long paragraphs of exposition, which provides welcome relief to readers. Unlike other forms, you don’t need to use a dialogue tag as such.
There are a couple of common ways that you can employ internal dialogue in writing:
- The first option is to italicise the comments made by your character internally. For example: “A door downstairs slammed shut. It’s not windy tonight. How the hell could that have happened?” The main idea here is that the italicised words make it clear to the reader that this is internal dialogue.
- Another option is to write internal dialogue as you would normal dialogue, with speech marks. The difference is what follows that passage of conversation. Usually, it’s something like, “I really do need to get that fixed,” Halle thought to herself. Here, you simply identify that the dialogue was spoken in the mind and not aloud.
As for which is best for how to write effective dialogue for internal thoughts, it’s all a matter of style. However, my personal preference is using italics. To me, it’s just clearer to readers, and that’s the main aim. So that is how to write internal dialogue.
As a little exercise, try and think of some oblique responses to the following line. I’ll give you an example to start. Remember to factor in Stein’s key ingredients— characterisation and plot:
Exercise: “You’re the most beautiful woman I’ve ever seen.”
Example: “Did you say the same thing to that blonde girl behind the bar?”
In this example of how to write dialogue, we get a response that avoids answering the statement. She could quite easily turn around and say “Thank you,” but that’s boring. Instead, we’re wondering about this man and what he’s about, and a bit more about the woman too, namely that she’s observant.
Let’s take a look at some good dialogue examples from some of the finest pieces of fiction to grave our bookshelves:
Dialogue Example #1 “The Silence of the Lambs” by Thomas Harris
“Good morning, Dr. Lecter. How are you feeling?”
“Better than your last visit, Clarice. Shall I have a chair brought in for you?”
“No thank you, I’d rather stand.”
“Please, sit. That’s better. You know, you remind me of someone. A young man I met long ago. He was a student like yourself, with a quick mind and a charming smile. I wonder what became of him.”
“I don’t know, Dr. Lecter. I’m here to ask you about Buffalo Bill.”
Dialogue Example #2 “The Catcher in the Rye” by J.D. Salinger
“You’re lucky. You’re really lucky. You know that, don’t you?” I said.
“Don’t worry about me,” Sally said. “I’ll be all right. I’m serious.”
“I know you will,” I said. “That’s why I’d like to talk to you for just a minute. This is no kidding. You’re going to have to have yourself a grand time this summer. Especially this summer. Have yourself a real need. Because you’re going to go to a lot of parties, and some of them are going to be quite grim, and you’re going to need that need.”
“I know I will,” Sally said. “Don’t worry about me.”
“I know you will,” I said. “But do it anyway. Do it for me. Okay?”
Dialogue Example #3 “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Atticus, are we going to win it?”
“No, honey.”
“Then why-”
“Simply because we were licked a hundred years before we started is no reason for us not to try to win,” Atticus said.
One of the most important things to know when it comes to looking at dialogue is the impact it has on pacing.
Dialogue has a knack for increasing the pace and moving the story forward. Readers can find themselves tearing through pages laden with dialogue. As if with all tools of the craft, it pays to know how best to use it. Literary agent Noah Lukeman said a writer must learn how to use restraint when it comes to dialogue, “to sustain suspense and let a scene unfold slowly.”
Again, it’s all a matter of preference.
It’s one thing to know how to write dialogue, it’s another to know how to edit it.
For sound editing advice a good person to turn to is a master editor. In his book on the craft of writing, Sol Stein provides a very helpful checklist when going over passages of conversation:
- What is the purpose of this exchange? Does it begin or heighten an existing conflict, for example?
- Does it stimulate curiosity in the reader?
- Does it create tension?
- What is the outcome of the exchange? Builds to a climax, or a turn of events in the story, or a change in relationship with the speakers?
- Has the correct dialogue tag been used for each character, one that enhances the tale.
One additional step Stein recommends is reading dialogue aloud in a monotone expression. Listen to the meaning of the words in your exchanges.
“What counts is not what is said but the effect of what it means… The reader takes from fiction the meaning of words. And above all, they take the emotion that meaning generates.”
So these are a few things that I’ve found helpful when it comes to writing dialogue. As we’ve seen, an author may use dialogue to provide the reader with interesting information, delivered in a compelling and intriguing way.
Perhaps the most important advice I’ve taken away from them all is to always maintain clarity while using obliqueness to give dialogue that snappy, enticing edge. It’s easier said than done, mind.
Before I leave you, I wanted to point you in the direction of some other guides I think you may find useful.
- Great Examples Of The 5 Senses In Writing
- Men Writing Women
- How To Avoid Duplicate Content Issues – if you need help with plagiarism or making your content unique, head here
- How To Plot A Story
- More Dialogue Writing Examples from Florida Gulf Coast University, with useful advice on making the best use of a dialogue tag
For more writing tips and guides , head here. Or you can find lots of links on all types of creative writing topics on my home page . Thanks for reading this guide on how to write dialogue that readers will love.
- Recent Posts
- 5 Tips to Help Your Child Learn and Succeed at Primary School - February 26, 2024
- The Advantages Of Using An AI Essay Typer Alternative - February 14, 2024
- Advice On Getting Help With Your Homework - January 26, 2024
8 thoughts on “A Complete Guide To Writing Dialogue”
I think crafting one’s own “book on writing” is a great exercise for any writer, regardless of whether or not they want to publish it. The act itself is a great way to organize one’s thoughts and ideas about writing, and compare one’s existing ideas to those one may encounter through others (books, blogs, interviews, etc.). I don’t know if mine will ever be fit for publication, but I find it very helpful to write such things down, instead of worrying about whether or not I’ll remember it.
Definitely! That’s one of the main reasons I’m doing it. We’ve got nothing to lose!
Mmm. And writing it out, organizing it, really helps us retain it afterwards. I feel like I rarely need to consult my notes, but the act of writing them out really helps.
Pingback: A Fantasy Writers’ Handbook by Richie Billing @Magpie_Richie #Spotlight #BookPromo – Chat About Books
Pingback: Great Examples Of The 5 Senses In Writing | Richie Billing
Pingback: How To Edit A Novel - Richie Billing
Pingback: What Is Foreshadowing In A Story? [Definition and Examples] - Richie Billing
Pingback: The Best Show Don't Tell Examples For Writers - Richie Billing
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

No thanks, close this box
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
A research-based approach to relationships
Homework Assignment: Intimate Conversation
At the end of yesterday’s post on the 3 Skills (and 1 Rule!) of Intimate Conversation, we promised to follow-up with your Weekend Homework Assignment.
At the end of this post on the 3 Skills (and 1 Rule!) of Intimate Conversation, we promised to follow-up with your Weekend Homework Assignment. Here it is:
Set aside time this weekend to work on what you learned in Friday’s blog. Try initiating an intimate conversation with an open-ended question.
Examples of such questions are: “ What kinds of changes can we make together in the coming year to make it our best year ever?,” “What do you feel is going well for you these days?,” and “What do you feel is not going so well?”
You can also begin a conversation by simply asking, “How are you doing, baby?” or “How is life treating you? Talk to me. I’m listening.”
Putting Your Feelings into Words
If you find yourself struggling to put your feelings into words in the course of your conversation, you can use the list below as an aid. You might need to use more than one word or phrase, and you may experience emotions not covered in this list. If this happens, don’t panic! It’s totally normal! The list is just a starting point. Improvisation is encouraged.
I feel…
- uncomfortable
- like a failure
- unappreciated
- distant from you
- like I am not accepted
- comfortable
- misunderstood
- affectionate
Asking Open-Ended Questions
Explore your partner’s feelings and thoughts by asking questions that open the heart. Here are some examples you can try:
- Do you think this has affected our relationship? If so, how?
- What do your values tell you about this?
- What would you really like to ask me?
- What specifically is upsetting you in this situation?
- Think of someone you really admire. What would he/she do and how would he/she view this situation?
Expressing Empathy
To deepen intimacy in a conversation, it really helps to show your partner understanding and empathy. First, try to put yourself in your partner’s shoes, and comprehend what they are saying or feeling. Then, communicate to your partner that their thoughts or feelings really make sense to you. Below are some great statements for conveying understanding and empathy. Look them over and use any that ring true as a follow-up to your partner’s words:
- I wish I would have known that earlier. I’m sorry.
- You’re making total sense.
- That would have annoyed me too.
- I’m on your side here.
- That must make you feel so helpless.
Remember, i n an intimate conversation, your job is to understand and validate, not to argue for your perception. Both partners take turns being understood. In the early years of a relationship, questions of trust are paramount: “Will you be there for me when I’m upset?” “Do I come first in your life?” “Can I count on you to earn money for our family?” and so on.
Once you start practicing these skills, you may be surprised by how naturally they work their way into your daily interactions with loved ones… and by the positive changes they quickly effect in the relationships that matter most. Good luck!
The Gottman Institute’s Editorial Team is composed of staff members who contribute to the Institute’s overall message. It is our mission to reach out to individuals, couples, and families in order to help create and maintain greater love and health in relationships.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 5 best homework help websites (free and paid).
Other High School , General Education

Listen: we know homework isn’t fun, but it is a good way to reinforce the ideas and concepts you’ve learned in class. But what if you’re really struggling with your homework assignments?
If you’ve looked online for a little extra help with your take-home assignments, you’ve probably stumbled across websites claiming to provide the homework help and answers students need to succeed . But can homework help sites really make a difference? And if so, which are the best homework help websites you can use?
Below, we answer these questions and more about homework help websites–free and paid. We’ll go over:
- The basics of homework help websites
- The cost of homework help websites
- The five best homework websites out there
- The pros and cons of using these websites for homework help
- The line between “learning” and “cheating” when using online homework help
- Tips for getting the most out of a homework help website
So let’s get started!

The Basics About Homework Help Websites–Free and Paid
Homework help websites are designed to help you complete your homework assignments, plain and simple.
What Makes a Homework Help Site Worth Using
Most of the best sites allow users to ask questions and then provide an answer (or multiple possible answers) and explanation in seconds. In some instances, you can even send a photo of a particular assignment or problem instead of typing the whole thing out!
Homework help sites also offer more than just help answering homework questions. Common services provided are Q&A with experts, educational videos, lectures, practice tests and quizzes, learning modules, math solving tools, and proofreading help. Homework help sites can also provide textbook solutions (i.e. answers to problems in tons of different textbooks your school might be using), one-on-one tutoring, and peer-to-peer platforms that allow you to discuss subjects you’re learning about with your fellow students.
And best of all, nearly all of them offer their services 24/7, including tutoring!
What You Should Should Look Out For
When it comes to homework help, there are lots–and we mean lots –of scam sites out there willing to prey on desperate students. Before you sign up for any service, make sure you read reviews to ensure you’re working with a legitimate company.
A word to the wise: the more a company advertises help that veers into the territory of cheating, the more likely it is to be a scam. The best homework help websites are going to help you learn the concepts you’ll need to successfully complete your homework on your own. (We’ll go over the difference between “homework help” and “cheating” a little later!)

You don't need a golden piggy bank to use homework help websites. Some provide low or no cost help for students like you!
How Expensive Are the Best Homework Help Websites?
First of all, just because a homework help site costs money doesn’t mean it’s a good service. Likewise, just because a homework help website is free doesn’t mean the help isn’t high quality. To find the best websites, you have to take a close look at the quality and types of information they provide!
When it comes to paid homework help services, the prices vary pretty widely depending on the amount of services you want to subscribe to. Subscriptions can cost anywhere from $2 to $150 dollars per month, with the most expensive services offering several hours of one-on-one tutoring with a subject expert per month.
The 5 Best Homework Help Websites
So, what is the best homework help website you can use? The answer is that it depends on what you need help with.
The best homework help websites are the ones that are reliable and help you learn the material. They don’t just provide answers to homework questions–they actually help you learn the material.
That’s why we’ve broken down our favorite websites into categories based on who they’re best for . For instance, the best website for people struggling with math might not work for someone who needs a little extra help with science, and vice versa.
Keep reading to find the best homework help website for you!
Best Free Homework Help Site: Khan Academy
- Price: Free!
- Best for: Practicing tough material
Not only is Khan Academy free, but it’s full of information and can be personalized to suit your needs. When you set up your account , you choose which courses you need to study, and Khan Academy sets up a personal dashboard of instructional videos, practice exercises, and quizzes –with both correct and incorrect answer explanations–so you can learn at your own pace.
As an added bonus, it covers more course topics than many other homework help sites, including several AP classes.
Runner Up: Brainly.com offers a free service that allows you to type in questions and get answers and explanations from experts. The downside is that you’re limited to two answers per question and have to watch ads.
Best Paid Homework Help Site: Chegg
- Price: $14.95 to $19.95 per month
- Best for: 24/7 homework assistance
This service has three main parts . The first is Chegg Study, which includes textbook solutions, Q&A with subject experts, flashcards, video explanations, a math solver, and writing help. The resources are thorough, and reviewers state that Chegg answers homework questions quickly and accurately no matter when you submit them.
Chegg also offers textbook rentals for students who need access to textbooks outside of their classroom. Finally, Chegg offers Internship and Career Advice for students who are preparing to graduate and may need a little extra help with the transition out of high school.
Another great feature Chegg provides is a selection of free articles geared towards helping with general life skills, like coping with stress and saving money. Chegg’s learning modules are comprehensive, and they feature solutions to the problems in tons of different textbooks in a wide variety of subjects.
Runner Up: Bartleby offers basically the same services as Chegg for $14.99 per month. The reason it didn’t rank as the best is based on customer reviews that say user questions aren’t answered quite as quickly on this site as on Chegg. Otherwise, this is also a solid choice!

Best Site for Math Homework Help: Photomath
- Price: Free (or $59.99 per year for premium services)
- Best for: Explaining solutions to math problems
This site allows you to t ake a picture of a math problem, and instantly pulls up a step-by-step solution, as well as a detailed explanation of the concept. Photomath also includes animated videos that break down mathematical concepts to help you better understand and remember them.
The basic service is free, but for an additional fee you can get extra study tools and learn additional strategies for solving common math problems.
Runner Up: KhanAcademy offers in-depth tutorials that cover complex math topics for free, but you won’t get the same tailored help (and answers!) that Photomath offers.
Best Site for English Homework Help: Princeton Review Academic Tutoring
- Price: $40 to $153 per month, depending on how many hours of tutoring you want
- Best for: Comprehensive and personalized reading and writing help
While sites like Grammarly and Sparknotes help you by either proofreading what you write via an algorithm or providing book summaries, Princeton Review’s tutors provide in-depth help with vocabulary, literature, essay writing and development, proofreading, and reading comprehension. And unlike other services, you’ll have the chance to work with a real person to get help.
The best part is that you can get on-demand English (and ESL) tutoring from experts 24/7. That means you can get help whenever you need it, even if you’re pulling an all-nighter!
This is by far the most expensive homework site on this list, so you’ll need to really think about what you need out of a homework help website before you commit. One added benefit is that the subscription covers over 80 other subjects, including AP classes, which can make it a good value if you need lots of help!

Best Site for STEM Homework Help: Studypool
- Best for: Science homework help
- Price: Varies; you’ll pay for each question you submit
When it comes to science homework help, there aren’t a ton of great resources out there. The best of the bunch is Studypool, and while it has great reviews, there are some downsides as well.
Let’s start with the good stuff. Studypool offers an interesting twist on the homework help formula. After you create a free account, you can submit your homework help questions, and tutors will submit bids to answer your questions. You’ll be able to select the tutor–and price point–that works for you, then you’ll pay to have your homework question answered. You can also pay a small fee to access notes, lectures, and other documents that top tutors have uploaded.
The downside to Studypool is that the pricing is not transparent . There’s no way to plan for how much your homework help will cost, especially if you have lots of questions! Additionally, it’s not clear how tutors are selected, so you’ll need to be cautious when you choose who you’d like to answer your homework questions.

What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Homework Help Sites?
Homework help websites can be a great resource if you’re struggling in a subject, or even if you just want to make sure that you’re really learning and understanding topics and ideas that you’re interested in. But, there are some possible drawbacks if you don’t use these sites responsibly.
We’ll go over the good–and the not-so-good–aspects of getting online homework help below.
3 Pros of Using Homework Help Websites
First, let’s take a look at the benefits.
#1: Better Grades Beyond Homework
This is a big one! Getting outside help with your studies can improve your understanding of concepts that you’re learning, which translates into better grades when you take tests or write essays.
Remember: homework is designed to help reinforce the concepts you learned in class. If you just get easy answers without learning the material behind the problems, you may not have the tools you need to be successful on your class exams…or even standardized tests you’ll need to take for college.
#2: Convenience
One of the main reasons that online homework help is appealing is because it’s flexible and convenient. You don’t have to go to a specific tutoring center while they’re open or stay after school to speak with your teacher. Instead, you can access helpful resources wherever you can access the internet, whenever you need them.
This is especially true if you tend to study at off hours because of your extracurriculars, work schedule, or family obligations. Sites that offer 24/7 tutoring can give you the extra help you need if you can’t access the free resources that are available at your school.
#3: Variety
Not everyone learns the same way. Maybe you’re more of a visual learner, but your teacher mostly does lectures. Or maybe you learn best by listening and taking notes, but you’re expected to learn something just from reading the textbook .
One of the best things about online homework help is that it comes in a variety of forms. The best homework help sites offer resources for all types of learners, including videos, practice activities, and even one-on-one discussions with real-life experts.
This variety can also be a good thing if you just don’t really resonate with the way a concept is being explained (looking at you, math textbooks!).

Not so fast. There are cons to homework help websites, too. Get to know them below!
3 Cons of Using Homework Help Websites
Now, let’s take a look at the drawbacks of online homework help.
#1: Unreliable Info
This can be a real problem. In addition to all the really good homework help sites, there are a whole lot of disreputable or unreliable sites out there. The fact of the matter is that some homework help sites don’t necessarily hire people who are experts in the subjects they’re talking about. In those cases, you may not be getting the accurate, up-to-date, and thorough information you need.
Additionally, even the great sites may not be able to answer all of your homework questions. This is especially true if the site uses an algorithm or chatbot to help students…or if you’re enrolled in an advanced or college-level course. In these cases, working with your teacher or school-provided tutors are probably your best option.
#2: No Clarification
This depends on the service you use, of course. But the majority of them provide free or low-cost help through pre-recorded videos. Watching videos or reading info online can definitely help you with your homework… but you can’t ask questions or get immediate feedback if you need it .
#3: Potential For Scamming
Like we mentioned earlier, there are a lot of homework help websites out there, and lots of them are scams. The review comments we read covered everything from outdated or wrong information, to misleading claims about the help provided, to not allowing people to cancel their service after signing up.
No matter which site you choose to use, make sure you research and read reviews before you sign up–especially if it’s a paid service!

When Does “Help” Become “Cheating”?
Admittedly, whether using homework help websites constitutes cheating is a bit of a grey area. For instance, is it “help” when a friend reads your essay for history class and corrects your grammar, or is it “cheating”? The truth is, not everyone agrees on when “help” crosses the line into “cheating .” When in doubt, it can be a good idea to check with your teacher to see what they think about a particular type of help you want to get.
That said, a general rule of thumb to keep in mind is to make sure that the assignment you turn in for credit is authentically yours . It needs to demonstrate your own thoughts and your own current abilities. Remember: the point of every homework assignment is to 1) help you learn something, and 2) show what you’ve learned.
So if a service answers questions or writes essays for you, there’s a good chance using it constitutes cheating.
Here’s an example that might help clarify the difference for you. Brainstorming essay ideas with others or looking online for inspiration is “help” as long as you write the essay yourself. Having someone read it and give you feedback about what you need to change is also help, provided you’re the one that makes the changes later.
But copying all or part of an essay you find online or having someone write (or rewrite) the whole thing for you would be “cheating.” The same is true for other subjects. Ultimately, if you’re not generating your own work or your own answers, it’s probably cheating.

5 Tips for Finding the Best Homework Help Websites for You
Now that you know some of our favorite homework help websites, free and paid, you can start doing some additional research on your own to decide which services might work best for you! Here are some top tips for choosing a homework help website.
Tip 1: Decide How You Learn Best
Before you decide which site or sites you’re going to use for homework help, y ou should figure out what kind of learning style works for you the most. Are you a visual learner? Then choose a site that uses lots of videos to help explain concepts. If you know you learn best by actually doing tasks, choose a site that provides lots of practice exercises.
Tip 2: Determine Which Subjects You Need Help With
Just because a homework help site is good overall doesn’t mean that it’s equally good for every subject. If you only need help in math, choose a site that specializes in that area. But if history is where you’re struggling, a site that specializes in math won’t be much help. So make sure to choose a site that you know provides high-quality help in the areas you need it most.
Tip 3: Decide How Much One-On-One Help You Need
This is really about cost-effectiveness. If you learn well on your own by reading and watching videos, a free site like Khan Academy is a good choice. But if you need actual tutoring, or to be able to ask questions and get personalized answers from experts, a paid site that provides that kind of service may be a better option.
Tip 4: Set a Budget
If you decide you want to go with a paid homework help website, set a budget first . The prices for sites vary wildly, and the cost to use them can add up quick.
Tip 5: Read the Reviews
Finally, it’s always a good idea to read actual reviews written by the people using these homework sites. You’ll learn the good, the bad, and the ugly of what the users’ experiences have been. This is especially true if you intend to subscribe to a paid service. You’ll want to make sure that users think it’s worth the price overall!

What’s Next?
If you want to get good grades on your homework, it’s a good idea to learn how to tackle it strategically. Our expert tips will help you get the most out of each assignment…and boost your grades in the process.
Doing well on homework assignments is just one part of getting good grades. We’ll teach you everything you need to know about getting great grades in high school in this article.
Of course, test grades can make or break your GPA, too. Here are 17 expert tips that’ll help you get the most out of your study prep before you take an exam.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
How to Format Dialogue: Complete Guide
Dialogue formatting matters. Whether you’re working on an essay, novel, or any other form of creative writing. Perfectly formatted dialogue makes your work more readable and engaging for the audience.
In this article, you’ll learn the dialogue formatting rules. Also, we’ll share examples of dialogue in essays for you to see the details.
What is a Dialogue Format?
Dialogue format is a writing form authors use to present characters' communication. It's common for play scripts, literature works, and other forms of storytelling.
A good format helps the audience understand who is speaking and what they say. It makes the communication clear and enjoyable. In dialogue writing, we follow the basic grammar rules like punctuation and capitalization. They help us illustrate the speaker’s ideas.
General Rules to Follow When Formatting a Dialogue
Dialogue writing is an essential skill for both professionals and scholars . It shows your ability to express the issues and ideas of other people in different setups. The core rules of formatting are about punctuation. So, below is a quick reminder on punctuation marks’ names:

And now, to practice.
Please follow these rules for proper dialogue formatting:
- Use quotation marks. Enclose the speaker’s words in double quotations. It helps readers distinguish between a character’s speech and a narrator’s comments.
- Place punctuation inside quotation marks. All punctuation like commas, exclamations, or interrogation marks, go inside the double quotations.
- Keep dialogue tags behind quotation marks. A dialogue tag is (1) words framing direct speech to convey the context and emotions of a conversation. For example, in (“I can’t believe this is you,” she replied.), the dialogue tag is “she replied.”
- Use an ellipsis or em-dashes for pauses or interruptions. To show interruptions or pauses, end phrases with ellipses inside quotations. Em-dashes go outside quotations. No other extra marks are necessary here.
- Remember a character’s voice. Ensure that each character’s phrases reflect their background and personality.
5 More Rules to Know (+ Examples of Dialogue)
For proper formatting of dialogue in writing, stick to the following rules:
1. Each speaker’s saying comes in a new paragraph
Begin a new paragraph whenever a new character starts speaking. It allows you to differentiate speakers and make their conversation look more organized. (2)
“Has Mr. de Winter been in?” I said. “Yes, Madam,” said Robert; “he came in just after two, and had a quick lunch, and then went out again. He asked for you and Frith said he thought you must have gone down to see the ship.” “Did he say when he would be back again?” I asked. “No, Madam.” — from Rebecca by Daphne du Maurier
2. Separate dialogue tags with commas
When using dialogue tags ( e.g., “she said,” “he replied,”), separate them with commas.
For example:
“You’ve got to do something right now , ” Aaron said , “Mom is really hurting. She says you have to drive her to the hospital.” “Actually, Dad , ” said Caleb, sidling in with his catalog , “There’s someplace you can drive me, too.” “No, Caleb.” — from The Corrections by Jonathan Franzen
3. When quoting within dialogue, place single quotes
If a character cites somebody or something while speaking, we call it a reported dialogue. In this case, use single quotations within double ones you place for a direct speech. It will help readers see that it’s a quote.
John started to cry. “When you said, ‘I never wanted to meet you again in my life!’ It hurts my feelings.”
4. You can divide a character’s long speech into paragraphs
Dialogue writing is different when a person speaks for a longer time. It’s fine to divide it into shorter paragraphs. Ensure the proper quotation marks placing:
The first quotation mark goes at the beginning of the dialogue. Each later paragraph also starts with it until that direct speech ends.
The second quotation mark — the one “closing” the monologue — goes at the dialogue’s end.
Josphat took a deep breath and began. “ Here’s the things about lions. They’re dangerous creatures. They only know how to kill. Have you ever seen a lion in an open area? Probably not. Because if you had you’d be dead now. “ I saw a lion once. I was fetching firewood to cook lunch. All of a sudden I found myself face to face with a lion. My heart stopped. I knew it was my end on earth. If it wasn’t the poachers we wouldn’t be having this talk. ”
Yet, you can keep a long text as a whole by adding some context with dialogue tags. Like here:
As you can see, there’s no quotation mark at the end of the paragraph in red. It’s because the next “Ha! ha!” paragraph continues the character’s speech.
5. Use action beats
Describe actions to provide context and keep readers engaged. Help them “hear” your characters. Punctuation also helps here: exclamation (!) or interrogation with exclamations (?!) demonstrate the corresponding tone of your narrative.
He slammed the door and shouted , “I can’t believe you did that ! “
Mistakes to Avoid When Formatting Dialogue
A good dialogue is a powerful instrument for a writer to show the character’s nature to the audience. Below are the mistakes to avoid in formatting if you want to reach that goal.
So, please don’t :
- Allow characters to speak for too long. Writing long paragraphs will bore the reader, making them skip through your speech. Short but sweet talk is the best. When writing, aim to be brief, dynamic, and purposeful. If your character speaks too much, generating opinion essays , ensure this speech makes sense and serves a bigger purpose.
- Overburden dialogue with exposition. Avoid telling the story background or building sophisticated words in your characters’ speeches. Instead, reveal the narrative content in small bursts and blend it around the rest of the prose. Convey it through your character’s actions and thoughts rather than summaries and explanations.
- Create rhetorical flourishes. Make your characters sound natural. Let them speak the way they’d do if they were real people. Consider their age, profession, and cultural background — and choose lexical items that fit them most.
- Use repetitive dialogue tags. Constant “he asked” and “she said” sounds monotonous. Diversify your tags: use power verbs, synonyms, and dialogue beats.
Frequently Asked Questions by Students
How to format dialogue in an essay.
Formatting a dialogue in an essay is tricky for most students. Here’s how to do it: Enclose the speaker’s words with double quotations and start every other character’s line from a new paragraph. Stick to the citation styles like APA or MLA to ensure credibility.
How to format dialogue in a novel?
A dialogue in a novel follows all the standard rules for clarity and readability. Ensure to use attributions, quotation marks, and paragraph format. It makes your dialogue flow, grabbing the reader’s attention.
How to format dialogue in a book?
Dialogue formatting in a book is critical for storytelling. It helps the audience distinguish the hero’s words. Follow the general rules we’ve discussed above:
Use double quotations and isolate dialogue tags with commas. Remember to place the discussion in blocks for better readability.
How to format dialogue between two characters?
A two-character dialogue offers the best way to prove successful formatting skills. Ensure you use action beats, quotations, and attribution tags. It allows readers to follow the conversation and understand it better.
What is the purpose of dialogue in a narrative essay?
Dialogue writing is the exchange of views between two or more people to reach a consensus. It reveals the character’s attitude and argumentation. Last but not least, it helps convey the descriptive nature of your narrative essay.
References:
- https://valenciacollege.edu/students/learning-support/winter-park/communications/documents/WritingDialogueCSSCTipSheet_Revised_.pdf
- https://www.ursinus.edu/live/files/1158-formatting-dialogue
- Essay samples
- Essay writing
- Writing tips
Recent Posts
- Writing the “Why Should Abortion Be Made Legal” Essay: Sample and Tips
- 3 Examples of Enduring Issue Essays to Write Yours Like a Pro
- Writing Essay on Friendship: 3 Samples to Get Inspired
- How to Structure a Leadership Essay (Samples to Consider)
- What Is Nursing Essay, and How to Write It Like a Pro

Content Writing Dialogue Writing Tips – Style, Format, Examples

- 1) What is Dialogue Writing?
- 2) Some Important Benefits of Dialogue Writing
- 3) Suitable Situations for Dialogue Writing
- 4.1) Sound natural
- 4.2) Use dialogue tags sparingly
- 4.3) Show, don’t tell
- 4.4) Add Variation in Sentence Structure
- 4.5) Use subtext
- 4.6) Add interruptions and overlaps
- 4.7) Give each character a distinct voice
- 5.1) Pick Your Characters:
- 5.2) Set the Goal:
- 5.3) Strong Opening:
- 5.4) Add Expressions
- 5.5) Impressive Ending
- 5.6) What is a dialogue writing format? (Free Template)
- 5.7) What are the 10 rules of dialogue?
- 6) Conclusion
Dialogue is a crucial element in storytelling . It can bring characters to life and advance the plot. However, writing effective dialogue can be challenging. Here are some tips to help you improve your dialogue writing skills.
What is Dialogue Writing?
Dialogue writing is the art of creating conversation between characters in a story , play, or screenplay. It is a way to bring characters to life and move the plot forward.
Here is an example of dialogue writing:
“I can’t believe you did that,” John said.
“What are you talking about?” Mary asked.
“You know exactly what I’m talking about,” John replied, his voice rising. “You promised you wouldn’t tell anyone.”
“I didn’t tell anyone,” Mary protested.
“Liar!” John shouted. “Everyone knows about it now.”
In this example, the dialogue between John and Mary creates conflict and tension, revealing their personalities and motivations. It also advances the plot and engages the reader.
Some Important Benefits of Dialogue Writing
There are many benefits of dialogue writing, including:
- Brings characters to life: Dialogue can help bring characters to life by giving them unique voices, personalities, and perspectives.
- Advances the plot: Dialogue can be used to advance the plot, reveal character motivations, and add conflict or tension to the story.
- Makes the story more engaging: Well-written dialogue can make the story more engaging and immersive for the reader.
- Increases emotional impact: Dialogue can be used to convey emotions and create a deeper connection between the reader and the characters.
- Improves writing skills: Writing effective dialogue requires practice and skill, which can improve overall writing abilities.
Suitable Situations for Dialogue Writing
Dialogue writing can be used in a variety of writing genres and formats, including fiction, plays, screenplays, and even nonfiction.
Here are some common situations where dialogue writing can be used:
- In fiction, dialogue can be used to reveal character personalities and motivations, create conflict or tension, and advance the plot .
- In plays and screenplays, dialogue is essential for creating dialogue-driven scenes and conveying the story through the spoken word.
- In nonfiction, dialogue can be used to add context and convey interviews , speeches, or conversations that took place in real life.
Useful Dialogue Writing for Beginners
Here are some helpful dialogue writing tips:
Sound natural
People tend to speak in a casual and informal way, using contractions, slang, and sentence fragments. Therefore, you should try to make your dialogue sound like real conversation.
For Example:
Incorrect: “I will be going to the store tomorrow.”
Correct: “I’ll be heading to the store tomorrow.”
Use dialogue tags sparingly
Dialogue tags are the phrases that identify who is speaking, such as “he said” or “she asked.” While these are necessary, try to avoid overusing them, as it can become repetitive and tedious to read.
Incorrect: “I don’t think we should go,” John said. “Why not?” Mary asked. “Because it’s too dangerous,” John replied.
Correct: “I don’t think we should go,” John said. “Why not?” Mary asked. “It’s too dangerous,” he replied.
Show, don’t tell
Dialogue can be an excellent tool for conveying information about a character or situation. However, it’s important to avoid using dialogue to simply tell the reader what’s happening. Instead, use dialogue to show the reader what’s happening.
Incorrect: “I’m really angry right now,” Jane said.
Correct: “Jane slammed her fist on the table. ‘I can’t believe you did that!'”
Add Variation in Sentence Structure
To make dialogue more interesting, vary the sentence structure and length. This can help to create a more natural flow and prevent the dialogue from becoming monotonous.
Incorrect: “What do you want for dinner?” Tom asked. “I don’t know,” Jane replied. “How about pizza?” Tom suggested.
Correct: “What do you want for dinner?” Tom asked. “I don’t know,” Jane replied. “I was thinking maybe we could try that new Thai place down the street,” Tom suggested.
Use subtext
Subtext is the underlying meaning of a conversation, which is often left unsaid. Using subtext can add depth to your dialogue and create tension or intrigue.
Incorrect: “I’m not sure if I want to go to the party,” Sarah said.
Correct: “Sarah twirled her hair nervously. ‘I just don’t know if it’s my scene, you know?'”
Add interruptions and overlaps
Instructions: Real conversation is rarely smooth and uninterrupted. To make dialogue sound more natural, use interruptions and overlaps to create a sense of chaos.
Incorrect: “I can’t believe you did that,” John said. “What are you talking about?” Mary asked. “You know what I’m talking about,” John said.
Correct: “I can’t believe you did that,” John said. “What are you talking–” Mary began, before John cut her off. “You know what I’m talking about!”
Give each character a distinct voice
Each character should have their own unique voice and way of speaking. This can help to differentiate characters and make them feel more real.
Incorrect: “I’m really tired,” Jack said. “Me too,” Jill replied.
Correct: “I’m beat,” Jack said. “Same here,” Jill agreed with a yawn.
How do you write a dialogue?
Writing dialogue involves creating a conversation between two or more characters. Here are some steps to follow when writing a dialogue:
Pick Your Characters:
Identify the characters involved in the conversation and their personalities, backgrounds, and motivations. This will help you create authentic dialogue that reflects their unique voices.
Set the Goal:
Determine the purpose of the conversation. What do the characters want to achieve or convey to each other? This will help you structure the dialogue and keep it focused.
Strong Opening:
Start the dialogue with a strong opening line that captures the reader’s attention and sets the tone for the conversation.
Add Expressions
Use body language, actions, and facial expressions to add depth to the conversation and convey the characters’ emotions.
Impressive Ending
End the dialogue with a strong closing line that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
Pro Tip: Read your dialogue out loud to ensure that it sounds realistic and flows smoothly.
What is a dialogue writing format? (Free Template)
Dialogue writing follows a specific format to make it clear who is speaking and what they are saying. Here’s a template for dialogue writing:
Character 1 name: [Dialogue], she said, twirling her hair nervously.
Character 2 name: [Dialogue], he replied with a shrug.
You can also use dialogue tags, such as “said,” “asked,” or “replied,” to indicate who is speaking, like this:
Character 1 name: [Dialogue], she said:
Character 2 name: [Dialogue], he replied:
Each line represents a character speaking. Use the character’s name or a pronoun to identify who is speaking. Use quotation marks around the dialogue to make it clear that it’s spoken aloud. Punctuation marks like commas, periods, and exclamation points go inside the quotation marks.
Here’s an example:
Tom: “What are you doing this weekend?”
Sara: “I’m going camping with some friends. How about you?”
Tom: “I’m thinking about going to the beach, but I haven’t decided yet.”
In this example, Tom and Sara are having a conversation. Tom asks Sara a question, and she responds with her plans. Then Tom answers her question and shares his own plans. The dialogue is formatted so it’s clear who is speaking and what they’re saying.
What are the 10 rules of dialogue?
Here are 10 rules for writing effective dialogue:
- Keep it concise: Avoid long-winded speeches or overly complex sentences. Don’t forget to add quotation marks enclosing every character’s dialogue.
- Sound Natural: Dialogue should sound like real people speaking, so avoid stilted or overly formal language.
- Use contractions: Contractions like “I’m” and “don’t” sound more natural and conversational than their non-contracted counterparts.
- Avoid information dumps: Don’t use dialogue solely as a way to convey information to the reader. Instead, use it to reveal character and advance the plot .
- Show, don’t tell: Use dialogue to show character traits and emotions rather than simply telling the reader about them.
- Use interruptions: Interruptions can add realism to dialogue and make it feel more natural.
- Use subtext: Dialogue doesn’t always have to say exactly what it means. Use subtext to create tension and depth.
- Use dialect and accents sparingly: Overuse of dialect or accents can be distracting and difficult to read.
- Make each character’s voice unique: Each character should have their own way of speaking that sets them apart from the others.
- Use dialogue tags sparingly: Use “said” or “asked” instead of fancier dialogue tags like “exclaimed” or “interjected.” And avoid using dialogue tags too often; instead, use actions and body language to indicate who is speaking.
Writing good dialogue takes practice, but with these tips on style, format, and examples, you’ll be on your way to creating more compelling conversations between your characters. Keep experimenting and refining your technique, and you’ll soon be a master of dialogue writing.
Recommended Reads:
- What is a Literary Analysis and How to Write it Correctly?
- How to Write a Query Letter – Templates & Examples
- How to Write a Memoir to Gain Reader’s Attention?
- How to Write a Tagline? Top Writing Tips

Recent Posts
- Applications of Generative AI in Healthcare – Uses and Challenges
- AI Powered B2B Lead Generation [2024]
- What is Content Automation And Which Tools are Best for It?
- AI Personalized Content: Beginner’s Guide & Prompts
- What is AI as a Service? Definition, Types, Benefits & Trends
- Affiliate Marketing
- Artificial Intelligence
- Content Scaling
- Business Pitch Deck
- Copywriting
- Newsletters
- Product Description
- Social Media
- Songwriting
- Title and Headline
- Writing Ideas
- Call to Action (CTA)
- Email Marketing
- NLP (Natural Language Processing)
- Proposal Writing
- Writer's Block Problem
Email Address
- « What are Essential Copywriting Skills Every Writer Must Learn?
- What is GPT-4 and What New Changes it Brings? »
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Chat with AI
- AI Email Generator
- Social Media Ads Generator
- Blog Idea Generator
- Blog Outline Generator
- Complete Article Generator
- All use cases >
- Bloggers & Vloggers
- Digital Marketing Agency
- Local Stores
- Freelancers
- All industries >
- Affiliate Program
- Comparisons
- System Status
Get in Touch
Looking to publish? Meet your dream editor, designer and marketer on Reedsy.
Find the perfect editor for your next book
1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Sep 21, 2023
How to Write Fabulous Dialogue [9 Tips + Examples]
This post is written by author, editor, and bestselling ghostwriter Tom Bromley. He is the instructor of Reedsy's 101-day course, How to Write a Novel .
Good dialogue isn’t about quippy lines and dramatic pauses.
Good dialogue is about propelling the story forward, pulling the reader along, and fleshing out characters and their dynamics in front of readers. Well-written dialogue can take your story to a new level — you just have to unlock it.
In this article, I’ll break down the major steps of writing great dialogue, and provide exercises for you to practice your own dialogue on.
Here's how to write great dialogue in 9 steps:
1. Use quotation marks to signal speech
2. pace dialogue lines by three , 3. use action beats , 4. use ‘said’ as a dialogue tag , 5. write scene-based dialogue, 6. model any talk on real life , 7. differentiate character voices, 8. "show, don't tell" information in conversation , 9. delete superfluous words, which dialogue tag are you.
Find out in just a minute.

Alfred Hitchcock once said, “Drama is life with all the boring bits cut out.”
Similarly, I could say that good dialogue in a novel is a real conversation without all the fluff — and with quotation marks.
Imagine, for instance, if every scene with dialogue in your novel started out with:
'Hey, buddy! How are you doing?"
“Great! How are you?""
'Great! Long time no see! Parking was a nightmare, wasn’t it?"
Firstly, from a technical perspective, the quotation marks are inconsistent and incorrectly formatted. To learn about the mechanics of your dialogue and how to format it, we also wrote this full post on the topic that I recommend reading.
Secondly, from a novel perspective, such lines don’t add anything to the story. And finally, from a reading perspective, your readers will not want to sit through this over and over again. Readers are smart: they can infer that all these civilities occur. Which means that you can skip the small talk (unless it’s important to the story) to get to the heart of the dialogue from the get-go.
For a more tangible example of this technique, check out the dialogue-driven opening to Barbara Kingsolver's novel, Unsheltered .
Screenwriter Cynthia Whitcomb once proposed an idea called the “Three-Beat Rule.” What this recommends, essentially, is to introduce a maximum of three dialogue “beats” (the short phrases in speech you can say without pausing for breath) at a time. Only after these three dialogue beats should you insert a dialogue tag, action beat, or another character’s speech.
Here’s an example from Jane Gardam’s short story, “Dangers”, in which the boy Jake is shooting an imaginary gun at his grandmother:

In theory, this sounds simple enough. In practice, however, it’s a bit more complicated than that, simply because dialogue conventions continue to change over time. There’s no way to condense “good dialogue” into a formula of three this, or two that. But if you’re just starting out and need a strict rule to help you along, then the Three-Beat Rule is a good place to begin experimenting.

FREE COURSE
How to Write Believable Dialogue
Master the art of dialogue in 10 five-minute lessons.
Let’s take a look at another kind of “beats” now — action beats.
Action beats are the descriptions of the expressions, movements, or even internal thoughts that accompany the speaker’s words. They’re always included in the same paragraph as the dialogue, so as to indicate that the person acting is also the person speaking.
On a technical level, action beats keep your writing varied, manage the pace of a dialogue-heavy scene, and break up the long list of lines ending in ‘he said’ or ‘she said’.
But on a character level, action beats are even more important because they can go a level deeper than dialogue and illustrate a character’s body language.
When we communicate, dialogue only forms a half of how we get across what we want to say. Body language is that missing half — which is why action beats are so important in visualizing a conversation, and can help you “show” rather than “tell” in writing.
Here’s a quick exercise to practice thinking about body language in the context of dialogue: imagine a short scene, where you are witnessing a conversation between two people from the opposite side of a restaurant or café. Because it’s noisy and you can’t hear what they are saying, describe the conversation through the use of body language only.
Remember, at the end of the day, action beats and spoken dialogue are partners in crime. These beats are a commonly used technique so you can find plenty of examples — here’s one from Never Let Me Go by Kazuo Ishiguro .
If there’s one golden rule in writing dialogue, it’s this: ‘said’ is your friend.
Yes, ‘said’ is nothing new. Yes, ‘said’ is used by all other authors out there already. But you know what? There’s a reason why ‘said’ is the king of dialogue tags: it works.
Pro-tip: While we cannot stress enough the importance of "said," sometimes you do need another dialogue tag. Download this free cheatsheet of 270+ other words for said to get yourself covered!
FREE RESOURCE
Get our Dialogue Tag Cheatsheet
Upgrade your dialogue with our list of 270 alternatives to “said.”
The thinking goes that ‘said’ is so unpretentious, so unassuming that it focuses readers’ attention on what’s most important on the page: the dialogue itself. As writer Elmore Leonard puts it:
“Never use a verb other than ‘said’ to carry dialogue. The line of dialogue belongs to the character; the verb is the writer sticking his nose in. But ‘said’ is far less intrusive than ‘grumbled,’ ‘gasped,’ ‘cautioned,’ ‘lied.’”
It might be tempting at times to turn towards other words for ‘said’ such as ‘exclaimed,’ or ‘declared,’ but my general rule of thumb is that in 90% of scenarios, ‘said’ is going to be the most effective dialogue tag for you to use while writing dialogue.
So now that we have several guidelines in place, this is a good spot to pause, reflect, and say that there’s no wrong or right way to write dialogue. It depends on the demands of the scene, the characters, and the story. Great dialogue isn’t about following this or that rule — but rather learning what technique to use when .
If you stick to one rule the whole time — i.e. if you only use ‘said,’ or you finish every dialogue line with an action beat — you’ll wear out readers. Let’s see how unnaturally it plays out in the example below with Sophie and Ethan:

All of which is to say: don’t be afraid to make exceptions to the rule if the scene asks for it. The key is to know when to switch up your dialogue structure or use of dialogue tags or action beats throughout a scene — and by extension, throughout your book.
Tell us about your book, and we'll give you a writing playlist
It'll only take a minute!
Dialogue isn’t always about writing grammatically perfect prose. The way a person speaks reflects the way a person is — and not all people are straight-A honor students who speak in impeccable English. In real life, the way people talk is fragmented, and punctuated by pauses.
That’s something that you should also keep in mind when you’re aiming to write authentic dialogue.
It can be tempting to think to yourself, “ Oh, I’ll try and slip in some exposition into my dialogue here to reveal important background information.” But if that results in an info-dump such as this — “ I’m just going to the well, Mother — the well that my brother, your son, tragically fell down five years ago ” — then you’ll probably want to take a step back and find a more organic, timely, and digestible way to incorporate that into your story.

Kay Adams is Michael’s date at his sister’s wedding in this scene. Her interest in his family is natural enough that the expository conversation doesn’t feel shoehorned in.
A distinctive voice for each character is perhaps the most important element to get right in dialogue. Just as no one person in the world talks the same as each other, no one person in your book should also talk similarly.
To get this part of writing dialogue down pat, you need to start out by knowing your characters inside out. How does your character talk? Do they come with verbal quirks? Non-verbal quirks?
Jay Gatsby’s “old sport,” for example, gives him a distinctive, recognizable voice. It stands out because no one else has something as memorable about their speech. But more than that, it reveals something valuable about Gatsby’s character: he’s trying to impersonates a gentleman in his speech and lifestyle.
Likewise, think carefully about your character’s voice, and use catchphrases and character quirks when they can say something about your character.
Which famous author do you write like?
Find out which literary luminary is your stylistic soulmate. Takes one minute!
“Show, don’t tell” is one of the most oft-repeated rules in writing, and a conversation on the page can be a gold mine for “showing.”

Authors can use action beats and descriptions to provide clues for readers to read between the lines. Let’s revisit Sophie and Ethan in this example:
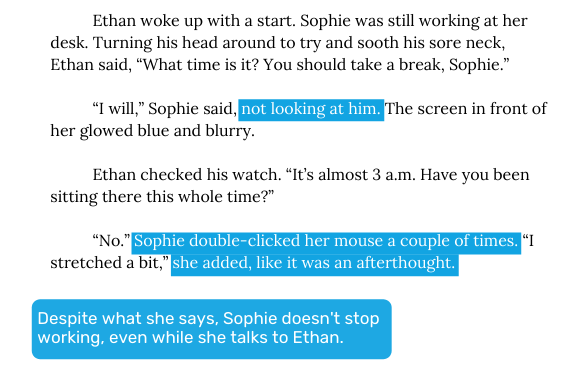
While Sophie claims she hasn’t been obsessing over this project all night, the actions in between her words indicate there’s nothing on her mind but work. The result is that you show , through the action beats vs. the dialogue, Sophie being hardworking—rather than telling it.

Show, Don't Tell
Master the golden rule of writing in 10 five-minute lessons.
As always when it comes to writing a novel: all roads lead back to The Edit, and the dialogue you’ve written is no exception.
So while you’re editing your novel at the end, you may find that a “less is more” mentality will be helpful. Remember to cut out the unnecessary bits of dialogue, so that you can focus on making sure the dialogue you do keep matters. Good writing is intentional and purposeful, always striving to keep the story going and readers engaged. The importance lies in quality rather than quantity.
One point I haven’t addressed yet is repetition. If used well (i.e. with clear intention), repetition is a literary device that can help you build motifs in your writing. But when you find yourself repeating information in your dialogue, it might be a good time to revise your work.
For instance, here’s a scene with Sophie and Ethan later on in the story:

As I’ve mentioned before, good dialogue shows character — and dialogue itself is a playground where character dynamics play out. If you write and edit your dialogue with this in mind, then your dialogue will be sharper, cleaner, and more organic.
I know that writing dialogue can be intimidating, especially if you don’t have much experience with it. But that should never keep you from including it in your work! Just remember that the more you practice — especially with the help of these tips — the better you’ll get.
And once you’re confident with the conversational content you can conjure up, follow along to the next part of our guide to see how you can punctuate and format your dialogue flawlessly .

As an editor and publisher, Tom has worked on several hundred titles, again including many prize-winners and international bestsellers.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

Try our novel writing master class — 100% free
Sign up for a free video lesson and learn how to make readers care about your main character.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
- Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled Stories
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs

Download & Print Only $6.89
Writing dialogue practice
Prompts and hints.
Students write dialogue for a scene following a prompt. The worksheets provide hints on punctuation and using a variety of verbs.

These worksheets are available to members only.
Join K5 to save time, skip ads and access more content. Learn More
More punctuation worksheets
Explore all of our punctuation worksheets , from ending punctuation to commas, apostrophes, contractions and punctuating letters and stories.
What is K5?
K5 Learning offers free worksheets , flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads.
Our members helped us give away millions of worksheets last year.
We provide free educational materials to parents and teachers in over 100 countries. If you can, please consider purchasing a membership ($24/year) to support our efforts.
Members skip ads and access exclusive features.
Learn about member benefits
This content is available to members only.
- Forgot Password?

Sign in to add this item to your wishlist, follow it, or mark it as ignored
Sign in to see reasons why you may or may not like this based on your games, friends, and curators you follow.
Coming soon
About this game, welcome to ravenwood academy, foster relationships, choose your path, investigate strange incidents, test yourself with trials, see a different side of the spiral, system requirements.
- OS: Windows 10 64-bit
- Processor: 2GHz
- Memory: 4 GB RAM
- Graphics: Intel Integrated, requiring additional 1-2GB RAM
- DirectX: Version 9.0
- Storage: 14 GB available space
More like this
You can write your own review for this product to share your experience with the community. Use the area above the purchase buttons on this page to write your review.

You can use this widget-maker to generate a bit of HTML that can be embedded in your website to easily allow customers to purchase this game on Steam.
Enter up to 375 characters to add a description to your widget:
Copy and paste the HTML below into your website to make the above widget appear

Popular user-defined tags for this product: (?)
Sign in to add your own tags to this product.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Maria: We have the same homework and I can't complete all these within time, I think your routine can help me. I will make a similar routine following your one. Sania: You can't follow the same. Maria: No, I will make some changes according to my own preferences. I hope that will be so much better for me.
100 Dialogue Exercises with 17 examples from great writers to illustrate 7 DOs of Dialogue, 3 DONT's of Dialogue, 4 Mechanics of Dialogue, and dialogue as the Interplay of PLOT and CHARACTERS Within the SCENE. ... do your homework. Read fiction and non-fiction, watch film and documentaries, or go out into that culture, listen and observe ...
The conversation is about 2 friends called Tim and Henry, who both have a separate problem. Henry is having problems with his homework and is friend Tim is having problems with building a doll house. They are hoping they can help each other. Conversation between 2 friends hoping to help each other. Tim: Henry, what are you doing?
Include a Misunderstanding: Introduce a moment of confusion or miscommunication between the friends. Write a Short and Engaging Dialogue: Keep the talking concise and engaging, capturing the essence of a conversation between two people. Make sure it flows naturally and maintains a conversational tone. Wrap Up the Conversation: Conclude the ...
Brainly is the knowledge-sharing community where hundreds of millions of students and experts put their heads together to crack their toughest homework questions. Brainly - Learning, Your Way. - Homework Help, AI Tutor & Test Prep
Listen and take notes. Carry a small notebook with you and write down phrases, words, or whole conversations verbatim to help develop your ear. Read. Reading will hone your creative abilities. It will help familiarize you with the form and flow of narration and dialogue until it becomes more natural in your own writing.
Purpose of Exercise: Students will practice writing dialogue that builds tension through subtext and disagreement while avoiding dialogue as exposition. Description: Beginning writers often have difficulty writing dialogue that is tense but not overt about that tension or the factors contributing to it. Suggested Time: 30 minutes.
The rules you should follow are: Give your characters a setting. Just like in movies, mise-en-scene is often as important as the dialogue itself. Set the scene for the dialogue by briefly describing where and when the dialogue takes place. This will help your readers imagine the picture more vividly. Keep it realistic.
How to format dialogue in stories: 8 tips. To make sure it's clear who's speaking, when it changes, and when speech begins and ends (and narration or description interrupts): 1. Use quotation or speech marks to show when speech starts and stops. If a character is still speaking, don't close speech marks prematurely. 2.
In these activities, students use a dice and roll to receive story elements. In their story creation, have them create dialogue. This will allow your students to review the basic rules of dialogue and also let students practice creatively. 2. Write the Photo. Print a variety of photos for students to create the dialogue.
Get homework done fast with 10+ million textbook and homework solutions, 24/7 expert help on demand, and math solver for instant solutions to even the toughest math problems. Get your first week for just 4.99!* ... butthe water level on the right does not change. Consider the following student dialogue: Student 1: "The pressure at point F ...
The best technique is to provide a description of how the person is talking. Describe how they slur their words, how certain letters sound in their drunken state and so on. Including body language in this will help a great deal too. You can then write dialogue in a more natural and understandable way.
To deepen intimacy in a conversation, it really helps to show your partner understanding and empathy. First, try to put yourself in your partner's shoes, and comprehend what they are saying or feeling. Then, communicate to your partner that their thoughts or feelings really make sense to you. Below are some great statements for conveying ...
Best Site for Math Homework Help: Photomath. Price: Free (or $59.99 per year for premium services) Best for: Explaining solutions to math problems. This site allows you to take a picture of a math problem, and instantly pulls up a step-by-step solution, as well as a detailed explanation of the concept.
It's okay; I can do it myself. Don't worry; I'll do it. No, thank you. (I just have a look) Finally, a few words you might need: Good luck with learning English! See you soon! Don't forget to share useful information with your friends. 😉. "We can't help everyone, but everyone can help someone.".
Keep dialogue tags behind quotation marks. A dialogue tag is (1) words framing direct speech to convey the context and emotions of a conversation. For example, in ("I can't believe this is you," she replied.), the dialogue tag is "she replied.". Use an ellipsis or em-dashes for pauses or interruptions.
This will help you structure the dialogue and keep it focused. Strong Opening: Start the dialogue with a strong opening line that captures the reader's attention and sets the tone for the conversation. Add Expressions. Use body language, actions, and facial expressions to add depth to the conversation and convey the characters' emotions. ...
Here's how to write great dialogue in 9 steps: 1. Use quotation marks to signal speech. 2. Pace dialogue lines by three. 3. Use action beats. 4. Use 'said' as a dialogue tag.
K5 Learning offers free worksheets, flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads. Students write dialogue for a scene following a prompt. The worksheets provide hints on punctuation and using a variety of verbs.
Upper grade students can use this Dialogue Writing Worksheet to practice turning sentences into dialogue by using proper punctuation and sentence structure. Supports students learning to use quotation marks. This is a great tool to help with punctuation and revising during the writing process. Once students accomplish this, they can add dialogue to their own writing pieces.
This helpful guide will show you how to use dialogue in a sentence.It will show you the definition of dialogue, as well as synonyms, antonyms, and the types of connotations that the word can carry.. Usage for dialogue. Definition: conversation or exchange of ideas between at least two people Part(s) of speech: noun Antonyms: silence; soliloquy Synonyms: communication; discourse; discussion
In this lesson you will learn how to set out dialogue correctly. Visit us at https://www.helpmedomyhomework.co.uk and see our comprehensive collection of Mat...
Plead your case during faculty disciplinary hearings and present evidence through dialogue options. Sometimes you'll be saving a friend accused of misdeeds, while other times you might be trying to save your own hide! See a Different Side of the Spiral Get a glimpse into Ravenwood Academy before the events of Wizard101.