

Getting Feedback
What this handout is about.
Sometimes you’d like feedback from someone else about your writing, but you may not be sure how to get it. This handout describes when, where, how and from whom you might receive effective responses as you develop as a writer.
Why get feedback on your writing?
You’ll become a better writer, and writing will become a less painful process. When might you need feedback? You might be just beginning a paper and want to talk to someone else about your ideas. You might be midway through a draft and find that you are unsure about the direction you’ve decided to take. You might wonder why you received a lower grade than you expected on a paper, or you might not understand the comments that a TA or professor has written in the margins. Essentially, asking for feedback at any stage helps you break out of the isolation of writing. When you ask for feedback, you are no longer working in a void, wondering whether or not you understand the assignment and/or are making yourself understood. By seeking feedback from others, you are taking positive, constructive steps to improve your own writing and develop as a writer.
Why people don’t ask for feedback
- You worry that the feedback will be negative. Many people avoid asking others what they think about a piece of writing because they have a sneaking suspicion that the news will not be good. If you want to improve your writing, however, constructive criticism from others will help. Remember that the criticism you receive is only criticism of the writing and not of the writer.
- You don’t know whom to ask. The person who can offer the most effective feedback on your writing may vary depending on when you need the feedback and what kind of feedback you need. Keep in mind, though, that if you are really concerned about a piece of writing, almost any thoughtful reader (e.g., your roommate, mother, R.A., brother, etc.) can provide useful feedback that will help you improve your writing. Don’t wait for the expert; share your writing often and with a variety of readers.
- You don’t know how to ask. It can be awkward to ask for feedback, even if you know whom you want to ask. Asking someone, “Could you take a look at my paper?” or “Could you tell me if this is OK?” can sometimes elicit wonderfully rich responses. Usually, though, you need to be specific about where you are in the writing process and the kind of feedback that would help. You might say, “I’m really struggling with the organization of this paper. Could you read these paragraphs and see if the ideas seem to be in the right order?”
- You don’t want to take up your teacher’s time. You may be hesitant to go to your professor or TA to talk about your writing because you don’t want to bother them. The office hours that these busy people set aside, though, are reserved for your benefit, because the teachers on this campus want to communicate with students about their ideas and their work. Faculty can be especially generous and helpful with their advice when you drop by their office with specific questions and know the kinds of help you need. If you can’t meet during the instructor’s office hours, try making a special appointment. If you find that you aren’t able to schedule a time to talk with your instructor, remember that there are plenty of other people around you who can offer feedback.
- You’ve gotten feedback in the past that was unhelpful. If earlier experiences haven’t proved satisfactory, try again. Ask a different person, or ask for feedback in a new way. Experiment with asking for feedback at different stages in the writing process: when you are just beginning an assignment, when you have a draft, or when you think you are finished. Figure out when you benefit from feedback the most, the kinds of people you get the best feedback from, the kinds of feedback you need, and the ways to ask for that feedback effectively.
- You’re working remotely and aren’t sure how to solicit help. Help can feel “out of sight, out of mind” when working remotely, so it may take extra effort and research to reach out. Explore what resources are available to you and how you can access them. What type of remote feedback will benefit you most? Video conferencing, email correspondence, phone conversation, written feedback, or something else? Would it help to email your professor or TA ? Are you looking for the back and forth of a real-time conversation, or would it be more helpful to have written feedback to refer to as you work? Can you schedule an appointment with the Writing Center or submit a draft for written feedback ? Could joining or forming an online writing group help provide a source of feedback?
Possible writing moments for feedback
There is no “best time” to get feedback on a piece of writing. In fact, it is often helpful to ask for feedback at several different stages of a writing project. Listed below are some parts of the writing process and some kinds of feedback you might need in each. Keep in mind, though, that every writer is different—you might think about these issues at other stages of the writing process, and that’s fine.
- The beginning/idea stage: Do I understand the assignment? Am I gathering the right kinds of information to answer this question? Are my strategies for approaching this assignment effective ones? How can I discover the best way to develop my early ideas into a feasible draft?
- Outline/thesis: I have an idea about what I want to argue, but I’m not sure if it is an appropriate or complete response to this assignment. Is the way I’m planning to organize my ideas working? Does it look like I’m covering all the bases? Do I have a clear main point? Do I know what I want to say to the reader?
- Rough draft: Does my paper make sense, and is it interesting? Have I proven my thesis statement? Is the evidence I’m using convincing? Is it explained clearly? Have I given the reader enough information? Does the information seem to be in the right order? What can I say in my introduction and conclusion?
- Early polished draft: Are the transitions between my ideas smooth and effective? Do my sentences make sense individually? How’s my writing style?
- Late or final polished draft: Are there any noticeable spelling or grammar errors? Are my margins, footnotes, and formatting okay? Does the paper seem effective? Is there anything I should change at the last minute?
- After the fact: How should I interpret the comments on my paper? Why did I receive the grade I did? What else might I have done to strengthen this paper? What can I learn as a writer about this writing experience? What should I do the next time I have to write a paper?
A note on asking for feedback after a paper has been graded
Many people go to see their TA or professor after they receive a paper back with comments and a grade attached. If you seek feedback after your paper is returned to you, it makes sense to wait 24 hours before scheduling a meeting to talk about it. If you are angry or upset about a grade, the day off gives you time to calm down and put things in perspective. More important, taking a day off allows you to read through the instructor’s comments and think about why you received the grade that you did. You might underline or circle comments that were confusing to you so that you can ask about them later. You will also have an opportunity to reread your own writing and evaluate it more critically yourself. After all, you probably haven’t seen this piece of work since you handed it in a week or more ago, and refreshing your memory about its merits and weaknesses might help you make more sense of the grade and the instructor’s comments.
Also, be prepared to separate the discussion of your grade from the discussion of your development as a writer. It is difficult to have a productive meeting that achieves both of these goals. You may have very good reasons for meeting with an instructor to argue for a better grade, and having that kind of discussion is completely legitimate. Be very clear with your instructor about your goals. Are you meeting to contest the grade your paper received and explain why you think the paper deserved a higher one? Are you meeting because you don’t understand why your paper received the grade it did and would like clarification? Or are you meeting because you want to use this paper and the instructor’s comments to learn more about how to write in this particular discipline and do better on future written work? Being up front about these distinctions can help you and your instructor know what to expect from the conference and avoid any confusion between the issue of grading and the issue of feedback.
Kinds of feedback to ask for
Asking for a specific kind of feedback can be the best way to get advice that you can use. Think about what kinds of topics you want to discuss and what kinds of questions you want to ask:
- Understanding the assignment: Do I understand the task? How long should it be? What kinds of sources should I be using? Do I have to answer all of the questions on the assignment sheet or are they just prompts to get me thinking? Are some parts of the assignment more important than other parts?
- Factual content: Is my understanding of the course material accurate? Where else could I look for more information?
- Interpretation/analysis: Do I have a point? Does my argument make sense? Is it logical and consistent? Is it supported by sufficient evidence?
- Organization: Are my ideas in a useful order? Does the reader need to know anything else up front? Is there another way to consider ordering this information?
- Flow: Do I have good transitions? Does the introduction prepare the reader for what comes later? Do my topic sentences accurately reflect the content of my paragraphs? Can the reader follow me?
- Style: Comments on earlier papers can help you identify writing style issues that you might want to look out for. Is my writing style appealing? Do I use the passive voice too often? Are there too many “to be” verbs?
- Grammar: Just as with style, comments on earlier papers will help you identify grammatical “trouble spots.” Am I using commas correctly? Do I have problems with subject-verb agreement?
- Small errors: Is everything spelled right? Are there any typos?
Possible sources of feedback and what they’re good for
Believe it or not, you can learn to be your own best reader, particularly if you practice reading your work critically. First, think about writing problems that you know you have had in the past. Look over old papers for clues. Then, give yourself some critical distance from your writing by setting it aside for a few hours, overnight, or even for a couple of days. Come back to it with a fresh eye, and you will be better able to offer yourself feedback. Finally, be conscious of what you are reading for. You may find that you have to read your draft several times—perhaps once for content, once for organization and transitions, and once for style and grammar. If you need feedback on a specific issue, such as passive voice, you may need to read through the draft one time alone focusing on that issue. Whatever you do, don’t count yourself out as a source of feedback. Remember that ultimately you care the most and will be held responsible for what appears on the page. It’s your paper.
A classmate (a familiar and knowledgeable reader)
When you need feedback from another person, a classmate can be an excellent source. A classmate knows the course material and can help you make sure you understand the course content. A classmate is probably also familiar with the sources that are available for the class and the specific assignment. Moreover, you and your classmates can get together and talk about the kinds of feedback you both received on earlier work for the class, building your knowledge base about what the instructor is looking for in writing assignments.
Your TA (an expert reader)
Your TA is an expert reader—they are working on an advanced degree, either a Master’s or a Ph.D., in the subject area of your paper. Your TA is also either the primary teacher of the course or a member of the teaching team, so they probably had a hand in selecting the source materials, writing the assignment, and setting up the grading scheme. No one knows what the TA is looking for on the paper better than the TA , and most of the TAs on campus would be happy to talk with you about your paper.
Your professor (a very expert reader)
Your professor is the most expert reader you can find. They have a Ph.D. in the subject area that you are studying, and probably also wrote the assignment, either alone or with help from TAs. Like your TA, your professor can be the best source for information about what the instructor is looking for on the paper and may be your best guide in developing into a strong academic writer.
Your roommate/friend/family member (an interested but not familiar reader)
It can be very helpful to get feedback from someone who doesn’t know anything about your paper topic. These readers, because they are unfamiliar with the subject matter, often ask questions that help you realize what you need to explain further or that push you to think about the topic in new ways. They can also offer helpful general writing advice, letting you know if your paper is clear or your argument seems well organized, for example. Ask them to read your paper and then summarize for you what they think its main points are.
The Writing Center (an interested but not familiar reader with special training)
While the Writing Center staff may not have specialized knowledge about your paper topic, our writing coaches are trained to assist you with your writing needs. We cannot edit or proofread for you, but we can help you identify problems and address them at any stage of the writing process. The Writing Center’s coaches see thousands of students each year and are familiar with all kinds of writing assignments and writing dilemmas.
Other kinds of resources
If you want feedback on a writing assignment and can’t find a real live person to read it for you, there are other places to turn. Check out the Writing Center’s handouts . These resources can give you tips for proofreading your own work, making an argument, using commas and transitions, and more. You can also try the spell/grammar checker on your computer. This shouldn’t be your primary source of feedback, but it may be helpful.
A word about feedback and plagiarism
Asking for help on your writing does not equal plagiarism, but talking with classmates about your work may feel like cheating. Check with your professor or TA about what kinds of help you can get legally. Most will encourage you to discuss your ideas about the reading and lectures with your classmates. In general, if someone offers a particularly helpful insight, it makes sense to cite them in a footnote. The best way to avoid plagiarism is to write by yourself with your books closed. (For more on this topic, see our handout on plagiarism .)
What to do with the feedback you get
- Don’t be intimidated if your professor or TA has written a lot on your paper. Sometimes instructors will provide more feedback on papers that they believe have a lot of potential. They may have written a lot because your ideas are interesting to them and they want to see you develop them to their fullest by improving your writing.
- By the same token, don’t feel that your paper is garbage if the instructor DIDN’T write much on it. Some graders just write more than others do, and sometimes your instructors are too busy to spend a great deal of time writing comments on each individual paper.
- If you receive feedback before the paper is due, think about what you can and can’t do before the deadline. You sometimes have to triage your revisions. By all means, if you think you have major changes to make and you have time to make them, go for it. But if you have two other papers to write and all three are due tomorrow, you may have to decide that your thesis or your organization is the biggest issue and just focus on that. The paper might not be perfect, but you can learn from the experience for the next assignment.
- Read ALL of the feedback that you get. Many people, when receiving a paper back from their TA or professor, will just look at the grade and not read the comments written in the margins or at the end of the paper. Even if you received a satisfactory grade, it makes sense to carefully read all of the feedback you get. Doing so may help you see patterns of error in your writing that you need to address and may help you improve your writing for future papers and for other classes.
- If you don’t understand the feedback you receive, by all means ask the person who offered it. Feedback that you don’t understand is feedback that you cannot benefit from, so ask for clarification when you need it. Remember that the person who gave you the feedback did so because they genuinely wanted to convey information to you that would help you become a better writer. They wouldn’t want you to be confused and will be happy to explain their comments further if you ask.
- Ultimately, the paper you will turn in will be your own. You have the final responsibility for its form and content. Take the responsibility for being the final judge of what should and should not be done with your essay.
- Just because someone says to change something about your paper doesn’t mean you should. Sometimes the person offering feedback can misunderstand your assignment or make a suggestion that doesn’t seem to make sense. Don’t follow those suggestions blindly. Talk about them, think about other options, and decide for yourself whether the advice you received was useful.
Final thoughts
Finally, we would encourage you to think about feedback on your writing as a way to help you develop better writing strategies. This is the philosophy of the Writing Center. Don’t look at individual bits of feedback such as “This paper was badly organized” as evidence that you always organize ideas poorly. Think instead about the long haul. What writing process led you to a disorganized paper? What kinds of papers do you have organization problems with? What kinds of organization problems are they? What kinds of feedback have you received about organization in the past? What can you do to resolve these issues, not just for one paper, but for all of your papers? The Writing Center can help you with this process. Strategy-oriented thinking will help you go from being a writer who writes disorganized papers and then struggles to fix each one to being a writer who no longer writes disorganized papers. In the end, that’s a much more positive and permanent solution.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 10 Types of Essay Feedback and How to Respond to Them

The moment of truth has arrived: you’ve got your marked essay back and you’re eagerly scanning through it, taking in the amount of red pen, and looking at the grade and hastily scrawled feedback at the end.
You should also read…
- The Complete Guide to Research Skills for Essay-Writing
- How to Write Dazzlingly Brilliant Essays
After deciphering the handwriting, you’re able to see a brief assessment of how you’ve performed in this essay, and your heart either leaps or sinks. Ideally, you’d receive detailed feedback telling you exactly where you fell short and providing helpful guidance on how to improve next time. However, the person marking your essay probably doesn’t have time for that, so instead leaves you very brief remarks that you then have to decode in order to understand how you can do better. In this article, we look at some of the common sorts of remarks you might receive in essay feedback, what they mean, and how to respond to them or take them on board so that you can write a better essay next time – no matter how good this one was!
1. “Too heavily reliant on critics”

We all fall into the trap of regurgitating whatever scholarship we happen to have read in the run-up to writing the essay, and it’s a problem that reveals that many students have no idea what their own opinion is. We’re so busy paraphrasing what scholars have said that we forget to think about whether we actually agree with what they’ve said. This is an issue we discussed in a recent article on developing your own opinion , in which we talked about how to approach scholarship with an open and critical mind, make up your own mind and give your own opinion in your essays. If you’ve received this kind of feedback, the person marking your essay has probably noticed that you’ve followed exactly the same line of thinking as one or more of the books on your reading list, without offering any kind of original comment. Take a look at the article linked to just now and you’ll soon be developing your own responses.
2. “Too short”
If your essay falls significantly short of the prescribed word count, this could suggest that you haven’t put in enough work. Most essays will require extensive reading before you can do a topic justice, and if you’ve struggled to fill the word count, it’s almost certainly because you haven’t done enough reading, and you’ve therefore missed out a significant line of enquiry. This is perhaps a sign that you’ve left it too late to write your essay, resulting in a rushed and incomplete essay (even if you consider it finished, it’s not complete if it hasn’t touched on topics of major relevance). This problem can be alleviated by effective time management, allowing plenty of time for the research phase of your essay and then enough time to write a detailed essay that touches on all the important arguments. If you’re struggling to think of things to say in your essay, try reading something on the topic that you haven’t read before. This will offer you a fresh perspective to talk about, and possibly help you to understand the topic clearly enough to start making more of your own comments about it.
3. “Too long”
[pullquote] “The present letter is a very long one, simply because I had no leisure to make it shorter” – Blaise Pascal [/pullquote]It sounds counter-intuitive, but it’s actually much easier to write an essay that’s too long than one that’s too short. This is because we’re all prone to waffling when we’re not entirely sure what we want to say, and/or because we want to show the person marking our essay that we’ve read extensively, even when some of the material we’ve read isn’t strictly relevant to the essay question we’ve been set. But the word count is there for a reason: it forces you to be clear and concise, leaving out what isn’t relevant. A short (say, 500-word) essay is actually a challenging academic exercise, so if you see fit to write twice the number of words, the person marking the essay is unlikely to be impressed. Fifty to a hundred words over the limit probably won’t be too much of an issue if that’s less than 10% of the word count, and will probably go unnoticed, but if you’ve ended up with something significantly over this, it’s time to start trimming. Re-read what you’ve written and scrutinise every single line. Does it add anything to your argument? Are you saying in ten words what could be said in three? Is there a whole paragraph that doesn’t really contribute to developing your argument? If so, get rid of it. This kind of ruthless editing and rephrasing can quickly bring your word count down, and it results in a much tighter and more carefully worded essay.
4. “Contradicts itself”

Undermining your own argument is an embarrassing mistake to make, but you can do it without realising when you’ve spent so long tweaking your essay that you can no longer see the wood for the trees. Contradicting yourself in an essay is also a sign that you haven’t completely understood the issues and haven’t formed a clear opinion on what the evidence shows. To avoid this error, have a detailed read through your essay before you submit it and look in particular detail at the statements you make. Looking at them in essence and in isolation, do any of them contradict each other? If so, decide which you think is more convincing and make your argument accordingly.
5. “Too many quotations”
It’s all too easy to hide behind the words of others when one is unsure of something, or lacking a complete understanding of a topic. This insecurity leads us to quote extensively from either original sources or scholars, including long chunks of quoted text as a nifty way of upping the word count without having to reveal our own ignorance (too much). But you won’t fool the person marking your essay by doing this: they’ll see immediately that you’re relying too heavily on the words of others, without enough intelligent supporting commentary, and it’s particularly revealing when most of the quotations are from the same source (which shows that you haven’t read widely enough). It’s good to include some quotations from a range of different sources, as it adds colour to your essay, shows that you’ve read widely and demonstrates that you’re thinking about different kinds of evidence. However, if you’ve received this kind of feedback, you can improve your next essay by not quoting more than a sentence at a time, making the majority of the text of your essay your own words, and including plenty of your own interpretation and responses to what you’ve quoted. Another word of advice regarding quotations: one of my tutors once told me is that one should never end an essay on a quotation. You may think that this is a clever way of bringing your essay to a conclusion, but actually you’re giving the last word to someone else when it’s your essay, and you should make the final intelligent closing remark. Quoting someone else at the end is a cop-out that some students use to get out of the tricky task of writing a strong final sentence, so however difficult the alternative may seem, don’t do it!
6. “Not enough evidence”

In an essay, every point you make must be backed up with supporting evidence – it’s one of the fundamental tenets of academia. You can’t make a claim unless you can show what has lead you to it, whether that’s a passage in an original historical source, the result of some scientific research, or any other form of information that would lend credibility to your statement. A related problem is that some students will quote a scholar’s opinion as though it were concrete evidence of something; in fact, that is just one person’s opinion, and that opinion has been influenced by the scholar’s own biases. The evidence they based the opinion on might be tenuous, so it’s that evidence you should be looking at, not the actual opinion of the scholar themselves. As you write your essay, make a point of checking that everything you’ve said is adequately supported.
7. “All over the place” / “Confused”
An essay described as “all over the place” – or words to that effect – reveals that the student who wrote it hasn’t developed a clear line of argument, and that they are going off at tangents and using an incoherent structure in which one point doesn’t seem to bear any relation to the previous one. A tight structure is vital in essay-writing, as it holds the reader’s interest and helps build your argument to a logical conclusion. You can avoid your essay seeming confused by writing an essay plan before you start. This will help you get the structure right and be clear about what you want to say before you start writing.
8. “Misses the point”

This feedback can feel particularly damning if you’ve spent a long time writing what you thought was a carefully constructed essay. A simple reason might be that you didn’t read the question carefully enough. But it’s also a problem that arises when students spend too long looking at less relevant sources and not enough at the most important ones, because they ran out of time, or because they didn’t approach their reading lists in the right order, or because they failed to identify correctly which the most important sources actually were. This leads to students focusing on the wrong thing, or perhaps getting lost in the details. The tutor marking the essay, who has a well-rounded view of the topic, will be baffled if you’ve devoted much of your essay to discussing something you thought was important, but which they know to be a minor detail when compared with the underlying point. If you’re not sure which items on your reading list to tackle first, you could try asking your tutor next time if they could give you some pointers on which of the material they recommend you focus on first. It can also be helpful to prompt yourself from time to time with the question “What is the point?”, as this will remind you to take a step back and figure out what the core issues are.
9. “Poor presentation”
This kind of remark is likely to refer to issues with the formatting of your essay, spelling and punctuation , or general style. Impeccable spelling and grammar are a must, so proofread your essay before you submit it and check that there are no careless typos (computer spell checks don’t always pick these up). In terms of your writing style , you might get a comment like this if the essay marker found your writing either boring or in a style inappropriate to the context of a formal essay. Finally, looks matter: use a sensible, easy-to-read font, print with good-quality ink and paper if you’re printing, and write neatly and legibly if you’re handwriting. Your essay should be as easy to read as possible for the person marking it, as this lessens their workload and makes them feel more positively towards your work.
10. “Very good”

On the face of it, this is the sort of essay feedback every student wants to hear. But when you think about it, it’s not actually very helpful – particularly when it’s accompanied by a mark that wasn’t as high as you were aiming for. With these two words, you have no idea why you didn’t achieve top marks. In the face of such (frankly lazy) marking from your teacher or lecturer, the best response is to be pleased that you’ve received a positive comment, but to go to the person who marked it and ask for more comments on what you could have done to get a higher mark. They shouldn’t be annoyed at your asking, because you’re simply striving to do better every time.
General remarks on responding to essay feedback
We end with a few general pieces of advice on how to respond to essay feedback.
- Don’t take criticism personally.
- Remember that feedback is there to help you improve.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for more feedback if what they’ve said isn’t clear.
- Don’t rest on your laurels – if you’ve had glowing feedback, it’s still worth asking if there’s anything you could have done to make the essay even better.
It can be difficult to have one’s hard work (metaphorically) ripped apart or disparaged, but feedback is ultimately there to help you get higher grades, get into better universities, and put you on a successful career path; so keep that end goal in mind when you get your essay back.
Image credits: banner ; library ; snake ; magnifying glass ; dartboard ; suggestions box .

Reflection and Reflective Writing - Skills Guide
- Reflective Assignments
- Reflecting on Your Experiences
- Reflecting on Your Skills
Reflecting on Feedback
- YouTube Playlist This link opens in a new window
- Audio Playlist
- Further Reading
- Downloadable Resources
Reflecting on feedback
What is reflectiong on feedback?
Feedback is designed to help you to identify your own strengths and weaknesses in a piece of work. It can help you improve on your work by building on the positive comments and using the critical ones to inform changes in your future writing. Therefore, feedback forms a critical role in your learning and helps you to improve each piece of work. As with all reflection, reflecting on your feedback should follow the three stages of reflection outlined in earlier in this guide.
What should I do with feedback?
Try to identify the main points of the feedback. What does it say? Can you break it down into main points or areas of improvement? Writing these down can be good to refer to later. You may find keeping all of your feedback in one place helps, as it makes it easier to look back and identify common mistakes. Identifying the main points of the feedback is the descriptive stage of reflection.
Once you have done this, move on to the critical thinking stage. How do you feel about the feedback? What are you particularly proud of? Is there anything you are disappointed by? Are there any points where you need further clarification from your lecturer?
Finally, there is the future focused stage of reflection. How will this feedback influence how you complete your next assignment? What will you do the same? What will you do differently? You may find it helpful to put together an action plan ready for when you begin your next module.
VP Education's Feedback Guidance
Feedback guidance.

Reflecting on Feedback Video - 2 mins
Naomi discusses top tips for reflecting on feedback from your assignments.
Methods of Reflecting on Your Assignment
- << Previous: Reflecting on Your Skills
- Next: PebblePad >>
- Last Updated: Aug 23, 2023 3:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.derby.ac.uk/reflectivewriting
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, feedback that leads to improvement in student essays: testing the hypothesis that “where to next” feedback is most powerful.

- 1 Graduate School of Education, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, VI, Australia
- 2 Hattie Family Foundation, Melbourne, VI, Australia
- 3 Turnitin, LLC, Oakland, CA, United States
Feedback is powerful but variable. This study investigates which forms of feedback are more predictive of improvement to students’ essays, using Turnitin Feedback Studio –a computer augmented system to capture teacher and computer-generated feedback comments. The study used a sample of 3,204 high school and university students who submitted their essays, received feedback comments, and then resubmitted for final grading. The major finding was the importance of “where to next” feedback which led to the greatest gains from the first to the final submission. There is support for the worthwhileness of computer moderated feedback systems that include both teacher- and computer-generated feedback.
Introduction
One of the more powerful influences on achievement, prosocial development, and personal interactions is feedback–but it is also remarkably variable. Kluger and DeNis (1996) completed an influential meta-analysis of 131 studies and found an overall effect on 0.41 of feedback on performance and close to 40% of effects were negative. Since their paper there have been at least 23 meta-analyses on the effects of feedback, and recently Wisniewski et al. (2020) located 553 studies from these meta-analyses ( N = 59,287) and found an overall effect of 0.53. They found that feedback is more effective for cognitive and physical outcome measures than for motivational and behavioral outcomes. Feedback is more effective the more information it contains, and praise (for example), not only includes little information about the task, but it can also be diluting as receivers tend to recall the praise more than the content of the feedback. This study investigates which forms of feedback are more predictive of improvement to students’ essays, using Turnitin Feedback Studio–a computer augmented system to capture teacher- and computer-generated feedback comments.
Hattie and Timperley (2007) defined feedback as relating to actions or information provided by an agent (e.g., teacher, peer, book, parent, internet, experience) that provides information regarding aspects of one’s performance or understanding. This concept of feedback relates to its power to “fill the gap between what is understood and what is aimed to be understood” ( Sadler, 1989 ). Feedback can lead to increased effort, motivation, or engagement to reduce the discrepancy between the current status and the goal; it can lead to alternative strategies to understand the material; it can confirm for the student that they are correct or incorrect, or how far they have reached the goal; it can indicate that more information is available or needed; it can point to directions that the students could pursue; and, finally, it can lead to restructuring understandings.
To begin to unravel the moderator effects that lead to the marked variability of feedback, Hattie and Timperley (2007) argued that feedback can have different perspectives: "feed-up" (comparison of the actual status with a target status), "feed-back" (comparison of the actual status with a previous status), and "feed-forward" (explanation of the target status based on the actual status). They claimed that these related to the three feedback questions: Where am I going? How am I going? and Where to next? Additionally, feedback can be differentiated according to its level of cognitive complexity: It can refer to a task, a process, one’s self-regulation, or one’s self. Task level feedback means that someone receives feedback about the content, facts, or surface information (How well have the tasks been completed and understood?). Feedback at the level of process means that a person receives feedback on the processes or strategies of his or her performance (What needs to be done to understand and master the tasks?). Feedback at the level of self-regulation means that someone receives feedback about the individual’s regulation of the strategies they are using to their performance (What can be done to manage, guide, and monitor your own way of action?). The self-level focuses on the personal characteristics of the feedback recipient (often praise about the person). One of the arguments about the variability is that feedback needs to focus on the appropriate question and the optimal level of cognitive complexity. If not, the message can easily be ignored, misunderstood, and of low value to the recipient.
Another important distinction is between the giving and receiving of feedback. Students are more often the receiver, and this is becoming more a focus of research. Students indicate a preference for feedback that is specific, useful, and timely ( Pajares and Graham, 1998 ; Gamlem and Smith, 2013 ), relative to the criteria or standards they are assessed against ( Brown, 2009 ; Beaumont et al., 2011 ), and do not mind what form it comes provided they see it as informative to improve their learning. Dawson et al. (2019) asked teachers and students about what leads to the most effective feedback. The majority of teachers argued it was the design of the task that lead to better feedback and students argued it was the quality of the feedback provided to them in teacher comments that led to improvements in performance.
Brooks et al. (2019) investigated the prevalence of feedback relative to these three questions in upper elementary classrooms. They recorded and transcribed 12 h of classroom audio based on 1,125 grade five students from 13 primary schools in Queensland. The researchers designed a questionnaire to measure the usefulness of feedback aligned with the three feedback questions (“Where am I going?” “How am I going?” “Where to next?“) along with three of the four feedback levels (task, process, and self-regulation). Results indicated that of the three feedback questions, “How am I going?” (Feed-back) was by far the most prominent, accounting for 50% of total feedback words. This was followed by “Where am I going?” (Feed-up) (31%) and “Where to next?” (Feed-forward) (19%). When considering the focus of verbal feedback, 79% of the feedback was at the task level, 16% at process level, and <1% at the self level. The findings of such studies are significant in relation to the gap between literature and practice, which indicates that we need to know more about how effective feedback interventions are enacted in the classroom.
Mandouit (2020) developed a series of feedback questions from an intensive study of student conceptions of feedback. He found that students sought feedback as to how to “elaborate on ideas” and “how to improve.” They wanted feedback that would not only help them “next time” they complete a similar task in the future, but that would help them develop the ability to think critically and self-regulate moving forward. It is these transferable skills and understandings that students consider as important, but, as identified in this study, challenged teachers in practice as it was rarely offered. His student feedback model included four questions: Where have I done well? Where can I improve? How do I improve? What do I do next time?
One often suggested method of improving the nature of feedback is to administer it via computer-based systems. Earlier synthesis of this literature tended to focus on task or item-specific level and investigating the differences between knowledge of results (KR), knowledge of correct response (KCR), and elaborated feedback (EF). Van der Kleij, Feskens, and Eggen (2015) , for example, used 70 effects from 40 studies of item-based feedback in a computer-based environment on students’ learning outcomes. They showed that elaborated feedback (e.g., providing an explanation) produced larger effect-sizes (EF = 0.49) than feedback regarding the correctness of the answer (KR = 0.05) or providing the correct answer (KCR = 0.32). Azevedo and Bernard (1995) used 22 studies on the effects of feedback on learning from computer-based instruction with an overall effect of 0.80. Immediate feedback had an effect of 0.80 and delayed 0.35, but they did not relate their findings to specific feedback characteristics. Jaehnig and Miller (2007) used 33 studies and found elaborated feedback was more effective than KCR, and KCR was more effective than KR. The major message is the computer-delivered elaborated feedback has the largest effects.
The Turnitin Feedback Studio Model: Background and Existing Research
Turnitin Feedback Studio, one such computer-based system, is most known for its similarity checking, powered by a comprehensive database of academic, internet, and student content. Beyond that capability, however, Feedback Studio also offers functionality to support both effective and efficient options for grading and, most relevant to this study, providing feedback. Inside the system, the Feedback Studio model allows for multiple streams of feedback, depending on how instructors opt to utilize the system, with both automated options and teacher-generated options. The primary automated option is for grammar feedback, which automatically detects issues and provides guidance through an integration with the e-rater ® engine from ETS ( https://www.ets.org/erater ). Even this option allows for customization and additional guidance, as instructors are able to add elaborative comments to the automated feedback. Outside of the grammar feedback, the remaining capabilities are manual, in that instructors identify the instances requiring feedback and supply the specific feedback content. Within this structure, there are still multiple avenues for providing feedback, including inline comments, summary text or voice comments, and Turnitin’s trademarked QuickMarks ® . In each case, instructors determine what student content requires commenting and then develop the substance of the feedback.
As a vehicle for providing feedback on student writing, Turnitin Feedback Studio offers an environment in which the impact of feedback can be leveraged. Student perceptions about the kinds of feedback that most impact their learning align to findings from scholarly research ( Kluger and DeNis, 1996 ; Wisniewski et al., 2020 ). Periodically, Turnitin surveys students to gauge different aspects of the product. In studies conducted by Turnitin, student perceptions of feedback over time fall into similar patterns as in outside research. For example, a 2013 survey about students’ perceptions of the value, type, and timing of instructor feedback reported that 67% of students claimed receiving general, overall comments, but only 46% of those students rated the general comments as “very helpful.” Respondents from the same study rated feedback on thesis/development as the most valuable, but reported receiving more feedback on grammar/mechanics and composition/structure ( Turnitin, 2013 ). Turnitin (2013) suggests the disconnect between the receipt of general, overall comments compared to the perceived value provides further support that students value more specific feedback, such as comments on thesis/development.
Later, an exploratory survey examining over 2,000 students’ perceptions on instructor feedback asked students to rank the effectiveness of types of feedback. The survey found that the greatest percentage (76%) of students reported suggestions for improvement as “very” or “extremely effective.” Students also highly perceived feedback such as specific notes written in the margins (73%), use of examples (69%), and pointing out mistakes as effective (68%) ( Turnitin, 2014 ). Turnitin (2014) proposes, “The fact that the largest number of students consider suggestions for improvement to be “very” or “extremely effective” lends additional support to this assertion and also strongly suggests that students are looking at the feedback they receive as an extension of course or classroom instruction.”
Turnitin found similar results in a subsequent survey that asked students about the helpfulness of types of feedback. Students most strongly reported suggestions for improvement (83%) as helpful. Students also preferred specific notes (81%), identifying mistakes (74%), and use of examples (73%) as types of feedback. Meanwhile, the least helpful types of feedback reported by students were general comments (38%) and praise or discouragement (39%) ( Turnitin, 2015 ). As a result of this survey data, Turnitin (2015) proposed that “Students find specific feedback most helpful, incorporating suggestions for improvement and examples of what was done correctly or incorrectly.” The same 2015 survey found that students consider instructor feedback to be just as critical for their learning as doing homework, studying, and listening to lectures. From the 1,155 responses, a majority of students (78%) reported that receiving and using teacher feedback is “very” or “extremely important” for learning. Turnitin (2015) suggests that the results from the survey demonstrates that students consider feedback to be just as important to other core educational activities.
Turnitin’s own studies are not the only evidence of these trends in students’ perceptions of feedback. In a case study examining the effects of Turnitin’s products on writing in a multilingual language class, Sujee et al. (2015) found that the majority of the learners expressed that Turnitin’s personalized feedback and identification of errors met their learning needs. Students appreciated the individualized feedback and claimed a deeper engagement with the content. Students were also able to integrate language rules from the QuickMark drag-and-drop comments, further strengthening the applicability in a second language classroom ( Sujee et al., 2015 ). A 2015 study on perceptions of Turnitin’s online grading features reported that business students favored the level of personalization, timeliness, accessibility, and quantity and quality of receiving feedback in an electronic format ( Carruthers et al., 2015 ). Similarly, a 2014 study exploring the perceptions of healthcare students found that Turnitin’s online grading features enhanced timeliness and accessibility of feedback. In particular regard to the instructor feedback tools in Turnitin Feedback Studio (collectively referred to as GradeMark), students valued feedback that was more specific since instructors could add annotated comments next to students’ text. Students claimed it increased meaningfulness of feedback which further supports the GradeMark tools as a vehicle for instructors to provide quality feedback ( Watkins et al., 2014 ). In both studies, students expressed interest in using the online grading features more widely across other courses in their studies ( Watkins et al., 2014 ; Carruthers et al., 2015 ).
In addition to providing insight about students’ perception of what is most effective, Turnitin studies also surfaced issues that students sometimes encounter with feedback provided inside the system. Part of the 2015 study focused on how much students read, use, and understand feedback they receive. Turnitin (2015) reports that students most often read a higher percentage of feedback than they understand or apply. When asked about barriers to understanding feedback, students who claimed to understand a minimal amount of instructor feedback (13%) reported that most often/always the largest challenges were: comments had unclear connections to the student work or assignment goals (44.8%), feedback was too general (42.6%), and they received too many comments (31.8%) ( Turnitin, 2015 ). Receiving feedback that was too general was also considered a strong barrier for students who claimed to understand a moderate or large amount of feedback.
Research Questions
From studies investigating students’ conceptions of feedback, Mandouit (2020) found that while they appreciated feedback about “where they are going”, and “how they are going”, they saw feedback mainly in terms of helping them know where to go next in light of submitted work. Such “where to next” feedback was more likely to be enacted.
This study investigates a range of feedback forms, and in particular investigates the hypothesized claim that feedback that leads to “where to next” decisions and actions by students is most likely to enhance their performance. It uses Turnitin Feedback Studio to ask about the relation of various agents of feedback (teacher, machine program), and codes the feedback responses to identify which kinds of feedback are related to the growth and achievement from first to final submission of essays.
In order to examine the feedback that instructors have provided on student work, original student submissions and revision submissions, along with corresponding teacher- and machine intelligence-assigned feedback from Feedback Studio were compiled by the Turnitin team. All papers in the dataset were randomly selected using a postgreSQL random () function. A query was built around the initial criteria to fetch assignments and their associated rubrics. The initial criteria included the following: pairs of student original drafts and revision assignments where each instructor and each student was a member of one and only one pairing of assignments; assignments were chosen without date restrictions through random selection until the sample size (<3,000) had been satisfied; assignments were from both higher education and secondary education students; assignment pairs where the same rubric had been applied to both the original submission and the revision submission and students had received scores based on that rubric; any submissions with voice-recorded comments were excluded; and submissions and all feedback were written only in the English language. Throughout the data collection process, active measures were taken to exclude all personally identifiable information, including student name, school name, instructor name, and paper content, in accordance with Turnitin’s policies. The Chief Security Officer of Turnitin conducted a review of this approach prior to completion. After the dataset was returned, an additional column was added that assigned a random number to each data item. That random number column was then sorted and returned the final dataset of student submissions and resubmissions in random order, from which the final sample of student papers were identified for analysis.
The categories for investigation included country of student, higher education or high school setting, number of times the assignment was submitted, date and time of submission, details regarding the scoring of the assignment (like score, possible points, and scoring method), and details regarding feedback that was provided on the assignment (like mark type, page location of each mark, title of each mark, and comment text associated with each mark), and two outcome measures–achievement and growth from time 1 to time 2.
There were 3,204 students who submitted essays for feedback on at least two occasions. About half (56%) were from higher education and the other half (44%) from secondary schools. The majority (90%) were from the United States, and the others were from Australia (5.2%), Japan (1.5%), Korea (0.8%), India (0.5%), Egypt (0.5%), the Netherlands (0.4%), China (0.4%), Germany (0.3%), Chile (0.2%), Ecuador (0.2%), Philippines (0.2), and South Africa (0.03%). Within the United States, students spanned 13 states, with the majority coming from California (464), Texas (412), Illinois (401), New York (256), New Jersey (193), Washington (93), Wisconsin (91), Missouri (81), Colorado (67), and Kentucky (61).
In this study, pairs of student-submitted work—original drafts and revisions of those same assignments—along with the feedback that was added to each assignment, were examined. Student assignments were submitted to the Turnitin Feedback Studio system as part of real courses to which students submit their work via online, course-specific assignment inboxes. Upon submission, student work is reviewed by Turnitin’s machine intelligence for similarity to other published works on the Internet, submissions by other students, or additional content available within Turnitin’s extensive database. At this point in the process, instructors also have the opportunity to provide feedback and score student work with a rubric.
Feedback streams for student submissions in Turnitin Feedback Studio are multifaceted. At the highest level, holistic feedback can be provided in the Feedback Summary panel as a text comment. However, if instructors wish to embed feedback directly within student submissions, there are several options. First, the most prolific feature of Turnitin Feedback Studio is QuickMarks™, a set of reusable drag-and-drop comments derived from corresponding rubrics aligned to genre and skill-level criteria. Instructors may also choose to create their own QuickMarks and rubrics to save and reuse on future submissions. When instructors wish to craft personalized feedback not intended for reuse, they may leave a bubble comment, which appears in a similar manner to the reusable QuickMarks, or an inline comment that appears as a free-form text box they can place anywhere on the submission. Instructors also have access to a strikethrough tool to suggest that a student should delete the selected text. Automated grammar feedback can be enabled as an additional layer, offering the identification of grammar, usage, mechanics, style, and spelling errors. Instructors have the option to add an elaborative comment, including hyperlinks to instructional resources, to the automated grammar and mechanics feedback (delivered via e-rater®) and Turnitin QuickMarks. Finally, rubrics and grading tools are available to the teacher to complete the feedback and scoring process.
Within the prepared dataset, paired student assignments were presented for analysis. Work from each individual student was used only once, but appeared as a pair of assignments, comprising an original, “first draft” submission, and then a later “revision” submission of the same assignment by the same student. The first set of feedback thus can be considered formative, and the latter summative feedback. For each pair of assignments, the following information was reported: institution type, country, and state or province for each individual student’s work. Then, for both the original assignment submission and the revision assignment submission, the following information was reported: assignment ID, submission ID, number of times the assignment was submitted, date and time of submission, details regarding the scoring of the assignment (like score, possible points, and scoring method), and details regarding feedback that was provided on the assignment (like mark type, page location of each mark, title of each mark, and comment text associated with each mark). Prior to the analysis, definitions of all terms included within the dataset were created collaboratively and recorded in a glossary to ensure a common understanding of the vocabulary.
Some of the essays had various criteria scores (such as ideas, organization, evidence, style), but in this study only the total score was used. The assignments were marked out of differing totals so all were converted to percentages. On average, there were 19 days between submissions (SD = 18.4). Markers were invited by the Turnitin Feedback Studio processes to add comments to the essays and these were independently coded into various categories (see Table 1 ). One researcher was trained in applying the coding manual, and close checking was undertaken for the first 300 responses, leading to an inter-rater reliability in excess of 0.90, with all disagreements negotiated.

TABLE 1 . Codes and description of attributes coded for each essay.
There were two outcome measures. The first is the final score after the second submission, and the growth effect-size between the score after the first submission (where the feedback was provided) and the final score. The effect-size for each student was calculated using the formula for correlated or dependent samples.
A structural model was used to relate the feedback types with the final and growth effect-size. A multivariate analysis of variance investigates the nature of changes in means from the first to final scores, moderated by level of schooling (secondary, university). A regression was used to identify the source of feedback relative to the growth and final scores.
The average score at Time 1 was 71.34 (SD = 19.91) and at Time 2 was 82.97 (SD = 15.03). The overall effect-size was 0.70 (SD = 0.97) with a range from −2.26 to 4.97. The correlation between Time 1 and 2 scores was 0.60.
Figure 1 shows the number of students in each score range, and the average effect-size for that score range. Not surprising, the opportunity to improve (via the effect-size) is greater for those who scored lower in their essays at Time 1. There were between 1 and 139 total comments for the first submission essays with an average of 14 comments per essay ( Table 2 ). The most common comments related to Where to next–Specific (5.9), Needs support (4.5), Where to next–General (3.8), and Probes (2.3). The next set of common comments were about style such as references (2.0), Unclear comments (1.9), Grammar, punctuation, and spelling (1.7). There was about 1 praise comment per essay, and the other forms of feedback were more rare (Seek additional help (0.22), Uncodeable symbols (0.15), and Word count (0.10). The general message is that instructors were mostly focused on improvement, then on the style aspects of the essays.
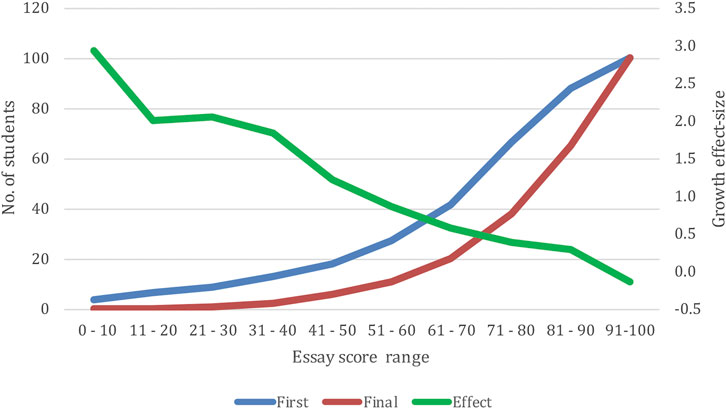
FIGURE 1 . The number of students within each first submitted and final score range, and the average effect-size for that score range based on the first submission.
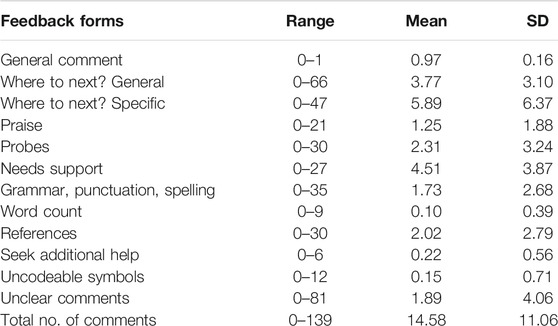
TABLE 2 . Range, mean, and standard deviation of feedback comments for first submission essay.
There are two related dependent variables–the relation between the comments and the Time 2 grade, and to the improvement between Time 1 and Time 2 (the growth effect-size). Clearly, there is a correlation between Time 2 and the effect-size (as can be seen in Figure 1 ) but it is sufficiently low ( r = 0.19) to warrant asking about the differential relations of the comments to these two outcomes.
A covariance analysis using SEM (Amos, Arbuckle, 2011 ) identified the statistically significant correlates of the Time 2 and growth effect-sizes. Using only these forms of feedback statistically significant, then a reduced model was run to optimally identify the weights of the best sub-set. The reduced model (chi-square = 18,466, df = 52) was statistically significantly better fit (chi-square = 19,686, df = 79; Δchi-square = 1,419, df = 27, p <. 001).
Thus, the best predictors of the growth improvement from Time 1 to Time 2 were the number of comments (the more comments given, the more likely the essay improved), and Specific and General Where to next comments ( Table 3 ). The best predictors of the overall Time 2 performance were Praise; and the comments that led to the lowest improvement included Praise, Probes, Grammar, Referencing, and Unclear comments. It is worth noting that Praise for a summative outcome is positive, but for formative is negative.
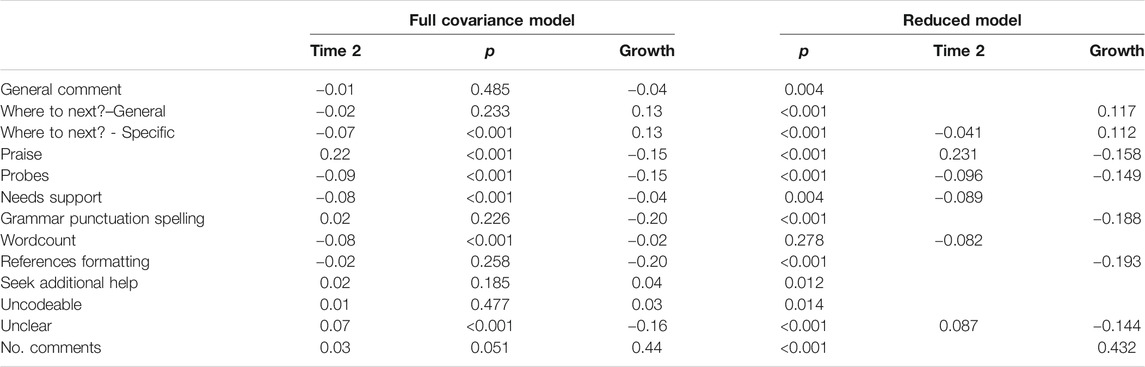
TABLE 3 . Standardized structural weights for the full and reduced covariance analyses for the feedback forms.
A closer investigation was undertaken to see if Praise indeed has a dilution effect. Each student’s first submission was coded as having no Praise and no Where-to-next ( N = 334), only Praise ( N = 416), only Where-to-next (N = 1,113), and Praise and Where-to-next feedback ( N = 1,434). When the first two sets were considered, the improvement was appreciably lower where there was Praise compared to no Praise and no Where-to-next (Mn = −0.21 vs. 0.40), and similar compared to Where-to-next and “Praise and Where-to-next” (Mn = 0.89 vs. 0.89).
There was an overall mean difference in the Time 1, Time 2, and growth effect-size relating to whether the student was at University or within a High School (Wilks Lambda = 0.965, Mult. F = 57.68, df = 2, 3,189, p < 0.001; Table 4 ). There were no differences between the mean scores at Time 1, but the University students made the greatest growth between Time 1 and Time 2, and thence in the final Time 2 grade. There were more comments for University students inviting students to seek additional help, and more Where to next comments. The instructors of University students gave more specific and general Where to next feedback comments (4.11, 6.55 vs. 3.30, 4.87) than did the instructors/markers of the secondary students. There were no differences in the number of words in the comments, Praise, the provision of general comments or not, uncodeable comments, and referencing.
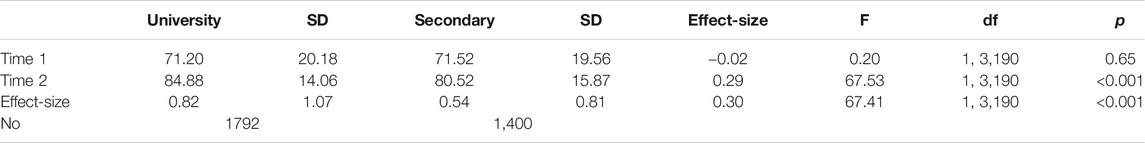
TABLE 4 . Means, standard deviations, effect-sizes, and analysis of variance statistics of comparisons between University and Secondary students.
For University students, the highest correlates of the specific coded essay comments included Where to next, the number of comments, General and Specific Where to next, Need support, Seek additional help, the total number of comments, and negatively related to Praise ( Table 5 ). For secondary students, the highest correlates were Where to next, Need support, and negative to Praise.
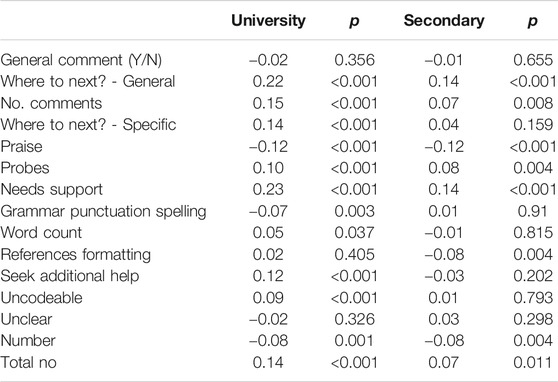
TABLE 5 . Correlations between the forms of feedback for the university and secondary students.
There are five major forms of feedback provisions, and the most commonly used were e-rater ® (grammar), QuickMarks (drag-and-drop comments), and teacher-provided comments. There were relatively few inline (instructor brief comments), and strikethroughs ( Table 6 ). Across all essays, there were significant relations between teacher inline, QuickMarks, and strikethroughs with the growth impact over time. Perhaps not surprising, these same three correlated negatively with the performance at first submission as these had the greatest opportunity for teacher comments.
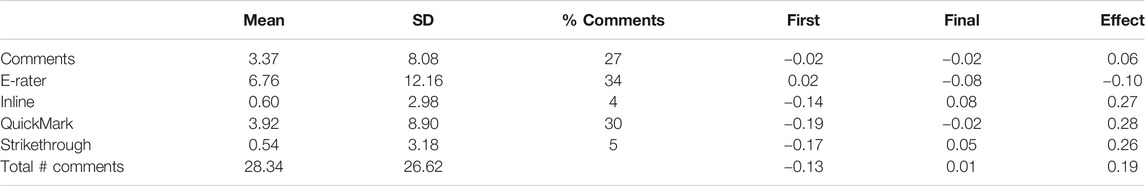
TABLE 6 . Means, standard deviations, and correlations between forms of feedback provision and first submission, final submission, and growth effect-sizes.
Feedback can be powerful but it is also most variable. Understanding this variability is critical for instructors who aim to improve their students’ proficiencies. There is so much advice about feedback sandwiches (including a positive comment, then specific feedback comment, then another positive comment), increasing the amount of feedback, the use of praise about effort, and debates about grades or comments, but these all ignore the more important issue about how any feedback is heard, understood, and actioned by students. There is also a proliferation of computer-aided tools to improve the giving of feedback, and with the inclusion of artificial intelligence engines, these are proffered as solutions to also reduce the time and investment by instructors in providing feedback. The question addressed in this study is whether the various forms of feedback is “heard and used by students” leading to improved performance.
As Mandouit (2020) argued, students prefer feedback that assists them to know where to learn next, and then how to attain this “where to next” status; although this appears to be a least frequent form of feedback ( Brooks et al., 2019 ). Others have found that more elaborate feedback produces greater gains in learning than feedback about the correctness of the answer, and this is even more likely to be the case when asked for essays rather than closed forms of answering (e.g., multiple choice).
The major finding was the importance of “where to next” feedback, which lead to the greatest gains from the first to the final submission. No matter whether more general or quite specific, this form of feedback seemed to be heard and actioned by the students. Other forms of feedback helped, but not to the same magnitude; although it is noted that the quantity of feedback (regardless of form) was of value to improve the essay over time.
Care is needed, however, as this “where to next” feedback may need to be scaffolded on feedback about “where they are going” and “how they are going,” and it is notable that these students were not provided with exemplars, worked examples, or scoring rubrics that may change the power of various forms of feedback, and indeed may reduce the power of more general forms of “where to next” feedback.
In most essays, teachers provided some praise feedback, and this had a negative effect on improvement, but a positive effect on the final submission. Praise involves a positive evaluation of a student’s person or effort, a positive commendation of worth, or an expression of approval or admiration. Students claim they like praise (Lipnevich, 2007), and it is often claimed praise is reinforcing such that it can increase the incidence of the praise behaviors and actions. In an early meta-analysis, however, Deci et al. (1999) showed that in all cases, the effects of praise were negative on increasing the desired behavior; task noncontingent–praise given from something other than engaging in the target activity (e.g., simply participating in the lesson) ( d = −0.14); task contingent–praise given for doing or completing the target activity ( d = −0.39); completion contingent–praise given specifically for performing the activity well, matching some standard of excellence, or surpassing some specific criterion ( d = −0.44); engagement contingent–praise dependent on engaging in the activity but not necessarily completing it ( d = −0.28). The message from this study is to reduce the use of praise-only feedback during the formative phase if you want the student to focus on the substantive feedback to then improve their writing. In a summative situation, however, there can be praise-only feedback, although more investigation is needed of such praise on subsequent activities in the class ( Skipper and Douglas, 2012 ).
The improvement was greater for university than high school students and this is probably because university instructors were more likely to provide where to next feedback and inviting students to seek additional help. It is not clear why high school teachers are less likely to offer “where to next” feedback, although it is noted they were more likely to request the student seek additional help. Both high school and college students do not seem to mind the source of the feedback, especially the timeliness, accessibility, and quantity of feedback provided by computer-based systems.
The strengths of the study include the large sample size and there was information from a first submission of an essay with formative feedback, then resubmission for summative feedback. The findings invite further study about the role of praise, the possible effects of combinations of forms of feedback (not explored in this study); a major message is the possibilities offered from computer-moderated feedback systems. These systems include both teacher- and automatic-generated feedback, but as important are the facilities and ease for instructors to add inline comments and drag-and-drop comments. The Turnitin Feedback Studio model does not yet provide artificial intelligence provision of “where to next” feedback, but this is well worth investigation and building. The use of a computer-aided system of feedback augmented with teacher-provided feedback does lead to enhanced performance over time.
This study demonstrates that students do appreciate and act upon “where to next” feedback that guides them to enhance their learning and performance, they do not seem to mind whether the feedback is from the teacher via a computer-based feedback tool, and were able, in light of the feedback, to decode and act on the feedback statements.
Data Availability Statement
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions: The data for the study was drawn from Turnitin’s proprietary systems in the manner described in the from Data Availability Statement to anonymize user information and protect user privacy. Turnitin can provide the underlying data (without personal information) used for this study to parties with a qualified interest in inspecting it (for example, Frontiers editors and reviewers) subject to a non-disclosure agreement. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to Ian McCullough, [email protected] .
Author Contributions
JH is the first author and conducted the data analysis independent of the co-authors employed by Turnitin, which furnished the dataset. JC, KVG, PW-S, and KW provided information on instructor usage of the Turnitin Feedback Studio product and addressed specific questions of data interpretation that arose during the analysis.
Turnitin, LLC employs several of the coauthors, furnished the data for analysis of feedback content, and will cover the costs of the open access publication fees.
Conflict of Interest
JC, KVG, PW-S, and KW are employed by Turnitin, which provided the data for analysis.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ian McCullough, James I. Miller, and Doreen Kumar for their support and contributions to the set up and coding of this article.
Arbuckle, J. L. (2011). IBM SPSS Amos 20 User’s Guide . Wexford, PA: Amos Development Corporation, SPSS Inc .
Azevedo, R., and Bernard, R. M. (1995). A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Feedback in Computer-Based Instruction. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 13 (2), 111–127. doi:10.2190/9lmd-3u28-3a0g-ftqt
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Beaumont, C., O’Doherty, M., and Shannon, L. (2011). Reconceptualising Assessment Feedback: A Key to Improving Student Learning?. Stud. Higher Edu. 36 (6), 671–687. doi:10.1080/03075071003731135
Brooks, C., Carroll, A., Gillies, R. M., and Hattie, J. (2019). A Matrix of Feedback for Learning. Aust. J. Teach. Edu. 44 (4), 13–32. doi:10.14221/ajte.2018v44n4.2
Brown, G. (2009). “The reliability of essay scores: The necessity of rubrics and moderation,” in Tertiary assessment and higher education student outcomes: Policy, practice and research. Editors L. H. Meyer, S. Davidson, H. Anderson, R. Fletcher, P. M. Johnston and M. Rees, (Wellington, NZ: Ako Aotearoa), 40–48.
Google Scholar
Carruthers, C., McCarron, B., Bolan, P., Devine, A., McMahon-Beattie, U., and Burns, A. (2015). ‘I like the Sound of that' - an Evaluation of Providing Audio Feedback via the Virtual Learning Environment for Summative Assessment. Assess. Eval. Higher Edu. 40 (3), 352–370. doi:10.1080/02602938.2014.917145
Dawson, P., Henderson, M., Mahoney, P., Phillips, M., Ryan, T., Boud, D., et al. (2019). What Makes for Effective Feedback: Staff and Student Perspectives. Assess. Eval. Higher Edu. 44 (1), 25–36. doi:10.1080/02602938.2018.1467877
Deci, E. L., Koestner, R., and Ryan, R. M. (1999). A Meta-Analytic Review of Experiments Examining the Effects of Extrinsic Rewards on Intrinsic Motivation. Psychol. Bull. 125 (6), 627–668. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.125.6.627
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Gamlem, S. M., and Smith, K. (2013). Student Perceptions of Classroom Feedback. Assess. Educ. Principles, Pol. Pract. 20 (2), 150–169. doi:10.1080/0969594x.2012.749212
Hattie, J., and Timperley, H. (2007). The Power of Feedback. Rev. Educ. Res. 77 (1), 81–112. doi:10.3102/003465430298487
Jaehnig, W., and Miller, M. L. (2007). Feedback Types in Programmed Instruction: A Systematic Review. Psychol. Rec. 57 (2), 219–232. doi:10.1007/bf03395573
Kluger, A. N., and DeNisi, A. (1996). The Effects of Feedback Interventions on Performance: A Historical Review, a Meta-Analysis, and a Preliminary Feedback Intervention Theory. Psychol. Bull. 119 (2), 254–284. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.119.2.254
Mandouit, L. (2020). Investigating How Students Receive, Interpret, and Respond to Teacher Feedback . Melbourne, Victoria, Australia: Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Melbourne .
Pajares, F., and Graham, L. (1998). Formalist Thinking and Language Arts Instruction. Teach. Teach. Edu. 14 (8), 855–870. doi:10.1016/s0742-051x(98)80001-2
Sadler, D. R. (1989). Formative Assessment and the Design of Instructional Systems. Instr. Sci. 18 (2), 119–144. doi:10.1007/bf00117714
Skipper, Y., and Douglas, K. (2012). Is No Praise Good Praise? Effects of Positive Feedback on Children's and University Students' Responses to Subsequent Failures. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 82 (2), 327–339. doi:10.1111/j.2044-8279.2011.02028.x
Sujee, E., Engelbrecht, A., and Nagel, L. (2015). Effectively Digitizing Communication with Turnitin for Improved Writing in a Multilingual Classroom. J. Lang. Teach. 49 (2), 11–31. doi:10.4314/jlt.v49i2.1
Turnitin (2013). Closing the Gap: What Students Say about Instructor Feedback . Oakland, CA: Turnitin, LLC . Retrieved from http://go.turnitin.com/what-students-say-about-teacher-feedback?Product=Turnitin&Notification_Language=English&Lead_Origin=Website&source=Website%20-%20Download .
Turnitin (2015). From Here to There: Students’ Perceptions on Feedback, Goals, Barriers, and Effectiveness . Oakland, CA: Turnitin, LLC . Retrieved from http://go.turnitin.com/paper/student-feedback-goals-barriers .
Turnitin (2014). Instructor Feedback Writ Large: Student Perceptions on Effective Feedback . Oakland, CA: Turnitin, LLC . Retrieved from http://go.turnitin.com/paper/student-perceptions-on-effective-feedback .
Van der Kleij, F. M., Feskens, R. C. W., and Eggen, T. J. H. M. (2015). Effects of Feedback in a Computer-Based Learning Environment on Students' Learning Outcomes. Rev. Educ. Res. 85 (4), 475–511. doi:10.3102/0034654314564881
Watkins, D., Dummer, P., Hawthorne, K., Cousins, J., Emmett, C., and Johnson, M. (2014). Healthcare Students' Perceptions of Electronic Feedback through GradeMark. JITE:Research 13, 027–047. doi:10.28945/1945Retrieved from http://www.jite.org/documents/Vol13/JITEv13ResearchP027-047Watkins0592.pdf .
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., and Hattie, J. (2020). The Power of Feedback Revisited: A Meta Analysis of Educational Feedback Research. Front. Psychol. 10, 3087. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.03087
Keywords: feedback, essay scoring, formative evaluation, summative evaluation, computer-generated scoring, instructional practice, instructional technologies, writing
Citation: Hattie J, Crivelli J, Van Gompel K, West-Smith P and Wike K (2021) Feedback That Leads to Improvement in Student Essays: Testing the Hypothesis that “Where to Next” Feedback is Most Powerful. Front. Educ. 6:645758. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.645758
Received: 23 December 2020; Accepted: 06 May 2021; Published: 28 May 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Hattie, Crivelli, Van Gompel, West-Smith and Wike. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Patti West-Smith, [email protected]
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu
Khan Academy Blog
Introducing Khanmigo’s New Academic Essay Feedback Tool
posted on November 29, 2023
By Sarah Robertson , senior product manager at Khan Academy

Khan Academy has always been about leveraging technology to deliver world-class educational experiences to students everywhere. We think the newest AI-powered feature in our Khanmigo pilot—our Academic Essay Feedback tool—is a groundbreaking step toward revolutionizing how students improve their writing skills.
The reality of writing instruction
Here’s a word problem for you: A ninth-grade English teacher assigns a two-page essay to 100 students. If she limits herself to spending 10 minutes per essay providing personalized, detailed feedback on each draft, how many hours will it take her to finish reviewing all 100 essays?
The answer is that it would take her nearly 17 hours —and that’s just for the first draft!
Research tells us that the most effective methods of improving student writing skills require feedback to be focused, actionable, aligned to clear objectives, and delivered often and in a timely manner .
The unfortunate reality is that teachers are unable to provide this level of feedback to students as often as students need it—and they need it now more than ever. Only 25% of eighth and twelfth graders are proficient in writing, according to the most recent NAEP scores .
An AI writing tutor for every student
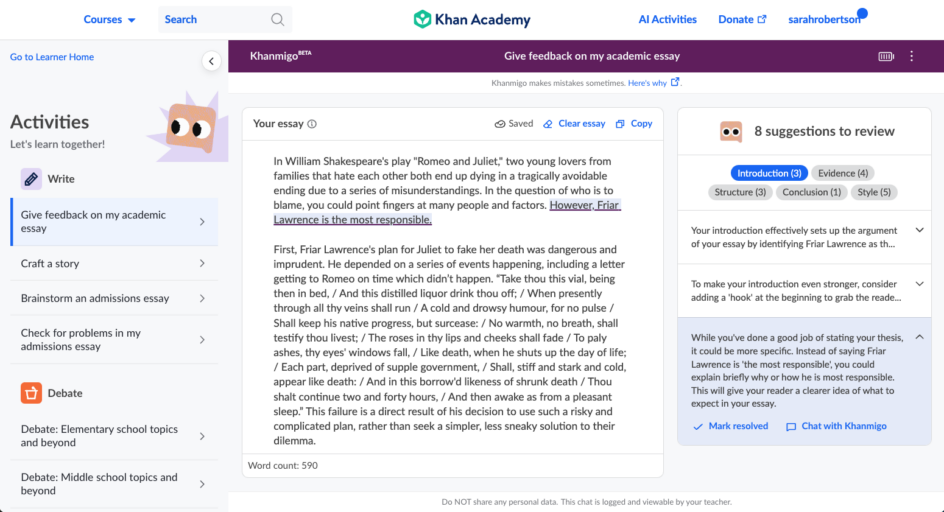
Developed by experts in English Language Arts (ELA) and writing instruction, the pilot Khanmigo Academic Essay Feedback tool uses AI to offer students specific, immediate, and actionable feedback on their argumentative, expository, or literary analysis essays.
Unlike other AI-powered writing tools, the Academic Essay Feedback tool isn’t limited to giving feedback on sentence- or language-level issues alone, like grammar or spelling. Instead, it provides feedback on areas like essay structure and organization, how well students support their arguments, introduction and conclusion, and style and tone.
The tool also doesn’t just stop at providing feedback, it also guides students through the revision process. Students can view highlighted feedback, ask clarifying questions, see exemplar writing, make revisions, and ask for further review—without the AI doing any actual writing for them.
Unique features of Khanmigo pilot Academic Essay Feedback tool
- Immediate, personalized feedback: within seconds, students get detailed, actionable, grade-level-appropriate feedback (both praise and constructive) that is personalized to their specific writing assignment and tied directly to interactive highlights in their essay.
- Comprehensive approach: feedback covers a wide range of writing skills, from crafting an engaging yet focused introduction and thesis, to overall essay structure and organization, to style and tone, to alignment and use of evidence.
- Interactive revision process: students can interact with Khanmigo to ask questions about specific pieces of feedback, get examples of model writing, make immediate revisions based on the feedback, and see if their revisions addressed the suggestion.
- Support for various essay types: the tool is versatile and assists with multi-paragraph persuasive, argumentative, explanatory, and literary analysis essay assignments for grades 8-12 (and more, coming soon).
- Focus on instruction and growth: like all Khanmigo features, the Academic Essay Feedback tool will not do the work for the student. Teachers and parents can rest assured that Khanmigo is there to improve the students’ independent writing skills, not provide one-click suggested revisions.
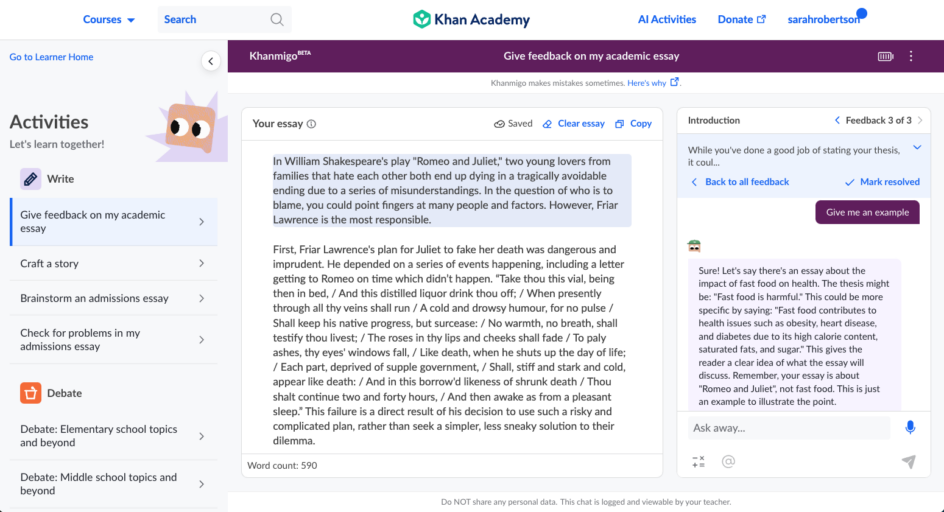
How parents can use Khanmigo’s Academic Essay Feedback tool
Any student with Khanmigo access can find the feedback tool under the “Write” category on their AI Activities menu.
For academic essays, students should simply paste their first draft into the essay field, select their grade level and essay type, and provide the essay instructions from the teacher.
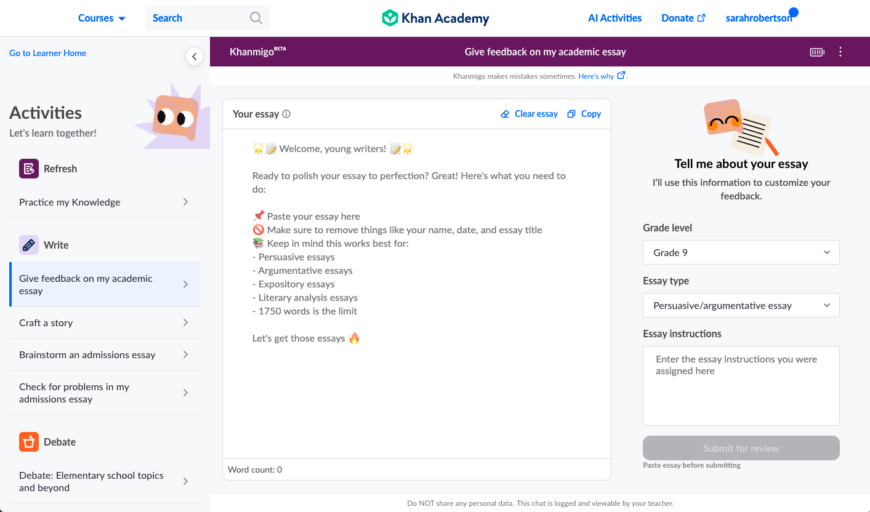
Students then click “Submit” and feedback begins generating. Once Khanmigo is done generating feedback, students can work their way through the suggestions for each category, chat with Khanmigo for help, make revisions, and resolve feedback. They can then submit their second draft for another round of feedback, or copy the final draft to submit to their teacher.
Bringing Khanmigo to your classroom, school, or district
Teachers in Khan Academy Districts partnerships can begin using the Khanmigo Academic Essay Feedback tool with their students right away. Simply direct students to the feedback tool under the “Write” category on their AI Activities menu.
Like all other Khanmigo activities, students’ interactions are monitored and moderated for safety. Teachers or parents can view the student’s initial draft, AI-generated feedback, chat history, and final draft in the student’s chat history. If anything is flagged for moderation, teachers or parents will receive an email notification.
Looking ahead
With the Academic Essay Feedback tool in our Khanmigo pilot, teachers and parents can empower students to take charge of their writing.The tool helps facilitate a deeper understanding of effective writing techniques and encourages self-improvement. For teachers, we think this tool is a valuable ally, enabling them to provide more frequent, timely, detailed, and actionable feedback for students on multiple drafts.
In the coming months, we’ll be launching exciting improvements to the tool and even more writing resources for learners, parents, teachers, and administrators:
- The ability for teachers to create an essay-revision assignment for their students on Khan Academy
- More varied feedback areas and flexibility in what feedback is given
- Support for students in essay outlining and drafting
- Insights for teachers and parents into their students’ full writing process
Stay tuned!
Sarah Robertson is a senior product manager at Khan Academy. She has a M.Ed. in Curriculum and Instruction and over a decade of experience teaching English, developing curriculum, and creating software products that have helped tens of millions of students improve their reading and writing skills.
Get Khanmigo
The best way to learn and teach with AI is here. Ace the school year with our AI-powered guide, Khanmigo.
For learners For teachers For parents
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Give Feedback on an Essay
4-minute read
- 9th May 2019
Whether you’re teaching or just helping a friend, being asked to offer feedback on an essay can be intimidating if you’ve not done it before. We do, though, have a few tips to share on this subject.
Content vs. Quality of Writing
There are two main things you may want to offer feedback on when reading an essay. These are:
- The content of the essay (i.e. what the author is arguing)
- How it is written (i.e. how well they communicate their argument)
The exact nature of the feedback you provide will depend on the topic and type of essay you are reading. But there are some things you might want to comment on for any paper, including:
- Spelling, grammar and punctuation errors
- Overall structure and readability
- Academic vocabulary and writing style
- Factual inaccuracies or ambiguities
- Whether the author provides evidence for their arguments
- Clarity and consistency of referencing
Ideally, you’ll provide feedback on all of these. However, if you’re simply reading the first draft of a paper to help a friend, you may want to check what kind of feedback they want.
Try, too, to balance the positive and negative feedback. It’s just as important to note things that are good as things that need clarifying. After all, if the author sees nothing but negative comments, they could be discouraged. Positive feedback, on the other hand, is a great motivator.
Comments in Margins vs. In-Depth Feedback
One way of leaving feedback is to make notes in the margins (either on paper or using the comment function in Microsoft Word). These should be short notes related to a specific issue, such as highlighting a misspelled word, an incorrect fact, or a missing citation.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Try not to leave too many comments in the margins, though. If there is a recurring problem, such as a word that the author has repeatedly misspelled, don’t comment on it every time. Instead, leave a comment noting the pattern of errors. This highlights the issue without overwhelming the reader.
You may also want to provide overall feedback at the end of the paper. Ideally, this in-depth feedback should:
- Start positive (e.g. This is a well-researched, well-organised paper ).
- Focus on one or two major issues rather than repeating everything you commented on in the margins. If there are too many big problems to pick one or two, you may want to speak to the author in person instead.
- Provide concrete criticism on specific problems, including page or section numbers where relevant, not just general criticisms (e.g. You are missing several citations in section three, so please check… rather than The referencing in this paper could be improved… ).
If you’re offering feedback on an essay that is currently in progress, focus on issues that the author could improve in the next draft. If you’re marking a final draft, however, you may want to focus on what they can learn from the essay’s overall strengths and weaknesses.
Marking Criteria
Finally, if you’re teaching on a university course – or even just marking papers – you should have access to the marking criteria. These will be set by the university or whoever is teaching the class. And, crucially, these guidelines will set out in detail what a good paper should do.
These criteria can also be useful when planning a paper, so it’s worth asking about the marking criteria even if you’re writing an essay rather than offering feedback! And if you’re not sure where to find the marking criteria for your course, check the university website or ask your professor.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
5 effective constructive feedback examples: Unlocking student potential

This video provides an overview of the key features instructors need to know to make best use of Feedback Studio, accessed through the Turnitin website.

At Turnitin, we’re continuing to develop our solutions to ease the burden of assessment on instructors and empower students to meet their learning goals. Turnitin Feedback Studio and Gradescope provide best-in-class tools to support different assessment types and pedagogies, but when used in tandem can provide a comprehensive assessment solution flexible enough to be used across any institution.
By completing this form, you agree to Turnitin's Privacy Policy . Turnitin uses the information you provide to contact you with relevant information. You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time.
Providing constructive feedback examples to students is an important part of the learning journey and is crucial to student improvement. It can be used to feed a student’s love of learning and help build a strong student-teacher relationship. But it can be difficult to balance the “constructive” with the “feedback” in an effective way.
On one hand, we risk the student not absorbing the information, and therefore missing an opportunity for growth when we offer criticism, even when constructive. On the other hand, there is a risk of discouraging the student, dampening their desire to learn, or even harming their self-confidence. Further complicating the matter is the fact that every student learns differently, hears and absorbs feedback differently, and is at a different level of emotional and intellectual development than their peers.
We know that we can’t teach every student the exact same way and expect the same results for each of them; the same holds true for providing constructive feedback examples. For best results, it’s important to tailor how constructive feedback is provided based on content, student needs, and a variety of other factors.
In this blog, we’ll take a look at constructive feedback examples and the value of effective instructor feedback, centering on Dr. John Hattie’s research on “Where to next?” feedback. We’ll also offer key examples for students, so instructors at different grade levels can apply best practices right away.
In 1992 , Dr. John Hattie—in a meta-analysis of multiple scientific studies—found that “feedback has one of the positive influences on student achievement,” building on Sadler’s concept that good feedback can close the gap between where students are and where they aim to be (Sadler, 1989 ).
But before getting too far into specifics, it would be helpful to talk about what “constructive feedback” is. Not everyone will define it in quite the same way — indeed, there is no singular accepted definition of the phrase.
For example, a researcher in Buenos Aires, Argentina who studies medical school student and resident performance, defines it, rather dryly, as “the act of giving information to a student or resident through the description of their performance in an observed clinical situation.” In workplace scenarios , you’ll often hear it described as feedback that “reinforces desired behaviors” or, a definition that is closer to educators’ goals in the classroom, “a supportive way to improve areas of opportunity.”
Hattie and Clarke ( 2019 ) define feedback as the information about a learning task that helps students understand what is aimed to be understood versus what is being understood.
For the purposes of this discussion, a good definition of constructive feedback is any feedback that the giver provides with the intention of producing a positive result. This working definition includes important parts from other, varied definitions. In educational spaces, “positive result” usually means growth, improvement, or a lesson learned. This is typically accomplished by including clear learning goals and success criteria within the feedback, motivating students towards completing the task.
If you read this header and thought “well… always?” — yes. In an ideal world, all feedback would be constructive feedback.
Of course, the actual answer is: as soon, and as often, as possible.
Learners benefit most from reinforcement that's delivered regularly. This is true for learners of all ages but is particularly so for younger students. It's best for them to receive constructive feedback as regularly, and quickly, as possible. Study after study — such as this one by Indiana University researchers — shows that student information retention, understanding of tasks, and learning outcomes increase when they receive constructive feedback examples soon after the learning moment.
There is, of course, some debate as to precise timing, as to how soon is soon enough. Carnegie Mellon University has been using their proprietary math software, Cognitive Tutor , since the mid-90s. The program gives students immediate feedback on math problems — the university reports that students who use Cognitive Tutor perform better on a variety of assessments , including standardized exams, than their peers who haven’t.
By contrast, a study by Duke University and the University of Texas El Paso found that students who received feedback after a one-week delay retained new knowledge more effectively than students who received feedback immediately. Interestingly, despite better performance, students in the one-week delayed feedback group reported a preference for immediate feedback, revealing a metacognitive disconnect between actual and perceived effectiveness. Could the week delay have allowed for space between the emotionality of test-taking day and the calm, open-to-feedback mental state of post-assessment? Or perhaps the feedback one week later came in greater detail and with a more personalized approach than instant, general commentary? With that in mind, it's important to note that this study looked at one week following an assessment, not feedback that was given several weeks or months after the exam, which is to say: it may behoove instructors to consider a general window—from immediate to one/two weeks out—after one assessment and before the next assessment for the most effective constructive feedback.
The quality of feedback, as mentioned above, can also influence what is well absorbed and what is not. If an instructor can offer nuanced, actionable feedback tailored to specific students, then there is a likelihood that those students will receive and apply that constructive feedback more readily, no matter if that feedback is given minutes or days after an assessment.
Constructive feedback is effective because it positively influences actions students are able to take to improve their own work. And quick feedback works within student workflows because they have the information they need in time to prepare for the next assessment.
No teacher needs a study to tell them that motivated, positive, and supported students succeed, while those that are frustrated, discouraged, or defeated tend to struggle. That said, there are plenty of studies to point to as reference — this 2007 study review and this study from 2010 are good examples — that show exactly that.
How instructors provide feedback to students can have a big impact on whether they are positive and motivated or discouraged and frustrated. In short, constructive feedback sets the stage for effective learning by giving students the chance to take ownership of their own growth and progress.
It’s one thing to know what constructive feedback is and to understand its importance. Actually giving it to students, in a helpful and productive way, is entirely another. Let’s dive into a few elements of successful constructive feedback:
When it comes to providing constructive feedback that students can act on, instructors need to be specific.
Telling a student “good job!” can build them up, but it’s vague — a student may be left wondering which part of an assessment they did good on, or why “good” as opposed to “great” or “excellent” . There are a variety of ways to go beyond “Good job!” on feedback.
On the other side of the coin, a note such as “needs work” is equally as vague — which part needs work, and how much? And as a negative comment (the opposite of constructive feedback), we risk frustrating them or hurting their confidence.
Science backs up the idea that specificity is important . As much as possible, educators should be taking the time to provide student-specific feedback directly to them in a one-on-one way.
There is a substantial need to craft constructive feedback examples in a way that they actively address students’ individual learning goals. If a student understands how the feedback they are receiving will help them progress toward their goal, they’re more likely to absorb it.
Our veteran Turnitin team of educators worked directly with Dr. John Hattie to research the impact of “Where to next?” feedback , a powerful equation for goal-oriented constructive feedback that—when applied formatively and thoughtfully—has been shown to dramatically improve learning outcomes. Students are more likely to revise their writing when instructors include the following three essential components in their feedback:
- Issue: Highlighting and clearly describing the specific issue related to the writing task.
- Relevance: Aligning feedback explicitly to the stated expectations of the assignment (i.e. rubric).
- Action: Providing the learner with their “next steps,” appropriately guiding the work, but not giving away the answer.
It’s also worth noting that quality feedback does not give the answer outright to the student; rather, it offers guidelines and boundaries so the students themselves can do their own thinking, reasoning, and application of their learning.
As mentioned earlier, it's hard to balance the “constructive” with the “feedback” in an effective way. It’s hard, but it’s important that instructors learn how to do it, because how feedback is presented to a student can have a major impact on how they receive it .
Does the student struggle with self confidence? It might be helpful to precede the corrective part of the feedback acknowledging something they did well. Does their performance suffer when they think they’re being watched? It might be important not to overwhelm them with a long list of ideas on what they could improve.
Constructive feedback examples, while cued into the learning goals and assignment criteria, also benefit from being tailored to both how students learn best and their emotional needs. And it goes without saying that feedback looks different at different stages in the journey, when considering the age of the students, the subject area, the point of time in the term or curriculum, etc.
In keeping everything mentioned above in mind, let’s dive into five different ways an instructor could give constructive feedback to a student. Below, we’ll look at varying scenarios in which the “Where to next?” feedback structure could be applied. Keep in mind that feedback is all the more powerful when directly applied to rubrics or assignment expectations to which students can directly refer.
Below is the template that can be used for feedback. Again, an instructor may also choose to couple the sentences below with an encouraging remark before or after, like: "It's clear you are working hard to add descriptive words to your body paragraphs" or "I can tell that you conducted in-depth research for this particular section."

For instructors with a pile of essays needing feedback and marks, it can feel overwhelming to offer meaningful comments on each one. One tip is to focus on one thing at a time (structure, grammar, punctuation), instead of trying to address each and every issue. This makes feedback not only more manageable from an instructor’s point of view, but also more digestible from a student’ s perspective.
Example: This sentence might be difficult for your readers to understand. Reword this sentence so your meaning is clear to your audience.
Rubrics are an integral piece of the learning journey because they communicate an assignment’s expectations to students. When rubrics are meaningfully tied to a project, it is clear to both instructors and students how an assignment can be completed at the highest level. Constructive feedback can then tie directly to the rubric , connecting what a student may be missing to the overarching goals of the assignment.
Example: The rubric requires at least three citations in this paper. Consider integrating additional citations in this section so that your audience understands how your perspective on the topic fits in with current research.
Within Turnitin Feedback Studio, instructors can add an existing rubric , modify an existing rubric in your account, or create a new rubric for each new assignment.
QuickMark comments are sets of comments for educators to easily leave feedback on student work within Turnitin Feedback Studio.
Educators may either use the numerous QuickMarks sets readily available in Turnitin Feedback Studio, or they may create sets of commonly used comments on their own. Regardless, as a method for leaving feedback, QuickMarks are ideal for leaving “Where to next?” feedback on student work.
Here is an example of “Where to next?” feedback in QuickMarks:

It can be just as helpful to see a non-example of “Where to next?” feedback. In the image below, a well-meaning instructor offers feedback to a student, reminding them of what type of evidence is required in an argumentative essay. However, Issue and Action are missing, which leaves the student wondering: “Where exactly do I need to improve my support? And what next steps ought to be taken?”
Here is a non-example of “Where to next?” feedback in QuickMarks:

As an instructor in a STEM class, one might be wondering, “How do I apply this structure to my feedback?” While “Where to next?” feedback is most readily applied to English Language Arts/writing course assignments, instructors across subject areas can and should try to implement this type of feedback on their assignments by following the structure: Issue + Relevance + Action. Below is an example of how you might apply this constructive feedback structure to a Computer Science project:
Example: The rubric asks you to avoid “hard coding” values, where possible. In this line, consider if you can find a way to reference the size of the array instead.
As educators, we have an incredible power: the power to help struggling students improve, and the power to help propel excelling students on to ever greater heights.
This power lies in how we provide feedback. If our feedback is negative, punitive, or vague, our students will suffer for it. But if it's clear, concise, and, most importantly, constructive feedback, it can help students to learn and succeed.
Study after study have highlighted the importance of giving students constructive feedback, and giving it to them relatively quickly. The sooner we can give them feedback, the fresher the information is in their minds. The more constructively that we package that feedback, the more likely they are to be open to receiving it. And the more regularly that we provide constructive feedback examples, the more likely they are to absorb those lessons and prepare for the next assessment.
The significance of providing effective constructive feedback to students cannot be overstated. By offering specific, actionable insights, educators foster a sense of self-improvement and can truly help to propel students toward their full potential.
Press ESC to close
5 Well-crafted Essay Feedback Examples That Promote Growth
- backlinkworks
- Writing Articles & Reviews
- September 15, 2023

Introduction
Providing constructive and valuable feedback is a crucial aspect of the learning process for students. By offering insightful comments, educators can guide students towards improvement and growth in their essay writing skills. In this article, we will explore five well-crafted essay feedback examples that promote growth and development in students.
Example 1: Highlighting Strengths and Areas for Improvement
One effective feedback approach is to first recognize the strengths of a student’s essay. Start by pointing out the well-developed arguments, strong use of evidence, or exceptional creativity demonstrated in the paper. By acknowledging these strengths, students gain confidence and motivation to continue their growth. However, IT is equally important to point out areas for improvement. Identify the weaker arguments, inconsistencies, or areas that lack clarity. Provide specific suggestions, such as recommending additional research or providing examples to support their claims.

Example 2: Encouraging Critical Thinking
Essay feedback should encourage students to think critically about their arguments and evidence. Prompt them to question assumptions, analyze the underlying logic, and consider alternative viewpoints. For instance, instead of simply providing answers or corrections, ask probing questions that encourage deeper reflection. By fostering critical thinking skills, students learn to evaluate their own work more objectively and develop a more nuanced understanding of the subject matter.
Example 3: Providing Clear and Actionable Suggestions
Clear feedback needs to provide specific suggestions for improvement. Rather than simply stating that the introduction is weak, provide guidance on how to make IT stronger. For instance, suggest different ways to hook the reader or restructure the introduction to create a more compelling thesis statement. Specific and actionable suggestions give students tangible steps to take to enhance their essays, enabling them to actively work towards growth.
Example 4: Focusing on Grammar and Language
In addition to addressing content and arguments, essay feedback should also focus on grammar and language. While IT is important to acknowledge that these aspects do not determine the overall quality of an essay, providing feedback on language use helps students become more effective communicators. Offer suggestions on sentence structure, word choice, and clarity. Additionally, recommend reliable resources, such as grammar guides or language learning tools, to further assist with language improvement.
Example 5: Encouraging Revision and Reflective Practice
Feedback should emphasize the importance of revision and encourage students to engage in reflective practices. Guide students in reflecting on their initial writing process and identifying specific areas for modification. Encourage multiple drafts, emphasizing that quality essays are rarely achieved with just one attempt. By promoting revision and reflection, students understand the iterative nature of writing and are motivated to continuously enhance their skills.
Effective essay feedback is a powerful tool in promoting growth and development in students’ writing abilities. By highlighting strengths and areas for improvement, encouraging critical thinking, providing clear suggestions, focusing on grammar and language, and emphasizing revision and self-reflection, educators can help students become better writers. Constructive feedback not only enhances their current work but also equips students with invaluable skills for future endeavors.
Q: How can essay feedback benefit students?
A: Essay feedback benefits students by encouraging growth and improvement in their writing skills. IT allows them to identify their strengths and weaknesses, prompts critical thinking, and offers actionable suggestions for enhancement.
Q: Should essay feedback only focus on grammar and language?
A: No, essay feedback should not be limited to grammar and language alone. While these aspects are crucial, feedback must also address content , arguments, structure, and clarity. Providing feedback on all these aspects contributes to overall growth in a student’s writing ability.
Q: How often should students receive essay feedback?
A: The frequency of essay feedback may vary depending on educational settings and assignments. However, IT is beneficial for students to receive feedback on a regular basis, ideally after each major essay submission. Frequent feedback enables students to apply the suggestions and lessons learned to subsequent assignments, fostering continuous growth.
Q: How should feedback be delivered to students?
A: Feedback can be delivered in various formats, such as written comments, in-person discussions, or even audio/video recordings. IT is essential to choose a delivery method that ensures clarity and allows students to fully understand the feedback provided. Additionally, offering opportunities for students to ask questions or seek further clarification supports their growth.
Q: Can feedback be overwhelming for students?
A: Feedback, if not properly delivered, can feel overwhelming for students. IT is essential for educators to balance constructive criticism with acknowledgment of their strengths. Providing clear and specific suggestions, along with encouragement and support, can help students navigate feedback and view IT as an opportunity for growth.
Providing well-crafted essay feedback is an art. Educators who perfect this skill empower their students to develop stronger writing abilities, critical thinking skills, and a growth mindset. By employing these five examples of effective feedback, teachers can make a lasting impact on their students’ writing journey.
10 Essential JavaScript Concepts for Beginners
10 essential factors to consider when hiring a wordpress website agency.

Recent Posts
- Driving Organic Growth: How a Digital SEO Agency Can Drive Traffic to Your Website
- Mastering Local SEO for Web Agencies: Reaching Your Target Market
- The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking Powerful Backlinks for Your Website
- SEO vs. Paid Advertising: Finding the Right Balance for Your Web Marketing Strategy
- Discover the Secret Weapon for Local SEO Success: Local Link Building Services
Popular Posts

Shocking Secret Revealed: How Article PHP ID Can Transform Your Website!

Uncovering the Top Secret Tricks for Mastering SPIP PHP – You Won’t Believe What You’re Missing Out On!

Unlocking the Secrets to Boosting Your Alexa Rank, Google Pagerank, and Domain Age – See How You Can Dominate the Web!

The Ultimate Collection of Free Themes for Google Sites

Discover the Shocking Truth About Your Website’s Ranking – You Won’t Believe What This Checker Reveals!
Explore topics.
- Backlinks (2,425)
- Blog (2,744)
- Computers (5,318)
- Digital Marketing (7,741)
- Internet (6,340)
- Website (4,705)
- Wordpress (4,705)
- Writing Articles & Reviews (4,208)
51 Constructive Feedback Examples for Students
Constructive feedback is feedback that helps students learn and grow.
Even though it highlights students’ weaknesses, it is not negative feedback because it has a purpose. It is designed to help them identify areas for improvement.
It serves both as an example of positive reinforcement and a reminder that there is always room for further improvement. Studies show that students generally like feedback that points them in the right direction and helps them to improve. It can also increase motivation for students.
Why Give Constructive Feedback?
Constructive feedback is given to help students improve. It can help people develop a growth mindset by helping them understand what they need to do to improve.
It can also help people to see that their efforts are paying off and that they can continue to grow and improve with continued effort.
Additionally, constructive feedback helps people to feel supported and motivated to keep working hard. It shows that we believe in their ability to grow and succeed and that we are willing to help them along the way.
How to Give Constructive Feedback
Generally, when giving feedback, it’s best to:
- Make your feedback specific to the student’s work
- Point out areas where the student showed effort and where they did well
- Offer clear examples of how to improve
- Be positive about the student’s prospects if they put in the hard work to improve
- Encourage the student to ask questions if they don’t understand your feedback
Furthermore, it is best to follow up with students to see if they have managed to implement the feedback provided.
General Constructive Feedback Examples for Students
The below examples are general templates that need to be edited so they are specific to the student’s work.
1. You are on the right track. By starting to study for the exam earlier, you may be able to retain more knowledge on exam day.
2. I have seen your improvement over time. As a next step, it is a good idea to…
3. You have improved a lot and should start to look towards taking on harder tasks for the future to achieve more self-development.
4. You have potential and should work on your weaknesses to achieve better outcomes. One area for improvement is…
5. Keep up the good work! You will see better results in the future if you make the effort to attend our study groups more regularly.
6. You are doing well, but there is always room for improvement. Try these tips to get better results: …
7. You have made some good progress, but it would be good to see you focusing harder on the assignment question so you don’t misinterpret it next time.
8. Your efforts are commendable, but you could still do better if you provide more specific examples in your explanations.
9. You have done well so far, but don’t become complacent – there is always room for improvement! I have noticed several errors in your notes, including…
10. It is great that you are trying your best, but don’t stop here – keep pushing yourself to get even better results. It would be good to see you editing your work to remove the small errors creeping into your work…
11. You have put in a lot of hard work, and it is starting to show. One area for improvement is your tone of voice, which sometimes comes across too soft. Don’t be afraid to project your voice next time.
12. You are making good progress, but don’t forget to focus on your weaknesses too. One weakness to focus on is…
13. Your efforts are commendable, but it would have been good to have seen you focus throughout as your performance waned towards the end of the session.
15. While your work is good, I feel you are becoming complacent – keep looking for ways to improve. For example, it would be good to see you concentrating harder on providing critique of the ideas explored in the class.
16. It is great that you are trying your best, but don’t stop here – keep pushing yourself to get even better results! Try to improve your handwriting by slowing down and focusing on every single letter.
17. You have put in a lot of hard work, and it is starting to show. Keep up the good work and you will see your grades slowly grow more and more. I’d like to see you improving your vocabulary for future pieces.
18. You are making good progress, but don’t forget to focus on your weaknesses too. One weakness to focus on is…
19. You have potential and should work on your using more appropriate sources to achieve better outcomes. As a next step, it is a good idea to…
Constructive Feedback for an Essay
1. Your writing style is good but you need to use more academic references in your paragraphs.
2. While you have reached the required word count, it would be good to focus on making sure every paragraph addresses the essay question.
3. You have a good structure for your essay, but you could improve your grammar and spelling.
4. You have made some good points, but you could develop them further by using more examples.
5. Your essay is well-written, but it would be helpful to provide more analysis of the topic.
6. You have answered the question well, but you could improve your writing style by being more concise.
7. Excellent job! You have covered all the key points and your writing is clear and concise.
8. There are a few errors in your essay, but overall it is well-written and easy to understand.
9. There are some mistakes in terms of grammar and spelling, but you have some good ideas worth expanding on.
10. Your essay is well-written, but it needs more development in terms of academic research and evidence.
11. You have done a great job with what you wrote, but you missed a key part of the essay question.
12. The examples you used were interesting, but you could have elaborated more on their relevance to the essay.
13. There are a few errors in terms of grammar and spelling, but your essay is overall well-constructed.
14. Your essay is easy to understand and covers all the key points, but you could use more evaluative language to strengthen your argument.
15. You have provided a good thesis statement , but the examples seem overly theoretical. Are there some practical examples that you could provide?
Constructive Feedback for Student Reports
1. You have worked very hard this semester. Next semester, work on being more consistent with your homework.
2. You have improved a lot this semester, but you need to focus on not procrastinating.
3. You are doing well in most subjects, but you could improve your grades by paying more attention in class and completing all your homework.
4. You are doing well in most subjects, but you could still improve your grades by studying more and asking for help when you don’t understand something.
5. You have shown great improvement this semester, keep up the good work! However, you might want to focus on improving your test scores by practicing more.
6. You have made some good progress this semester, but you need to continue working hard if you want to get good grades next year when the standards will rise again.
7. Next semester, focus on completing all your homework on time and paying more attention in class.
8. You have worked hard this semester, but you could still improve your grades by taking your time rather than racing through the work.
9. Next semester, focus on completing all your homework in advance so you have time to check it over before submission.
10. While you usually understand the instructions, don’t forget to ask for help when you don’t understand something rather than guessing.
11. You have shown great improvement this semester, but you need to focus some more on being self-motivated rather than relying on me to keep you on task.
Constructive feedback on Homework
1. While most of your homework is great, you missed a few points in your rush to complete it. Next time, slow down and make sure your work is thorough.
2. You put a lot of effort into your homework, and it shows. However, make sure to proofread your work for grammar and spelling mistakes.
3. You did a great job on this assignment, but try to be more concise in your writing for future assignments.
4. This homework is well-done, but you could have benefited from more time spent on research.
5. You have a good understanding of the material, but try to use more examples in your future assignments.
6. You completed the assignment on time and with great accuracy. I noticed you didn’t do the extension tasks. I’d like to see you challenging yourself in the future.
Related Articles
- Examples of Feedback for Teachers
- 75 Formative Assessment Examples
Giving and receiving feedback is an important part of any learning process. All feedback needs to not only grade work, but give advice on next steps so students can learn to be lifelong learners. By providing constructive feedback, we can help our students to iteratively improve over time. It can be challenging to provide useful feedback, but by following the simple guidelines and examples outlined in this article, I hope you can provide comments that are helpful and meaningful.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
2 thoughts on “51 Constructive Feedback Examples for Students”
Very helpful to see so much great developmental feedback with so many different examples.
Great examples of constructive feedback, also has reinforced on the current approach i take.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Parents & Guardians
- Faculty & Staff
BC.EDU LINKS
- Boston College
- Campus Life
- Jesuit, Catholic
- Academic Calendar
- BC Magazine
- Directories
- Offices, Services, Resources
- Agora Portal
- Maps & Directions
- Writing Sample Feedback
Examples of Submission Feedback
The following are actual responses to some of our recent submissions to the Online Writing Lab, although the names have been changed to maintain the anonymity of student writers. You can expect similarly global-oriented comments and suggestions for developing your own work. Of course, length and type of feedback vary between individual tutors and between essay submissions.
Dear Rachel: I think you touch on some really nice ideas in this paper, which I'll talk about in a minute, but first I want to address one general concern I had about your writing. You have a tendency to spend too much time summarizing the plot--this is time when you could be advancing your argument. You don't need to tell your reader what happens in the story; you can assume that he or she already knows. For example, look at this paragraph: [...] Everything that I've noted with square brackets is plot summary. The sentence that begins "Feeling rejected, the creature wanders away..." is borderline because you're making a judgment about the creature's motivations, but in general you shouldn't spend time repeating the events of the story. The second part of this paragraph is much better in that you're talking about motivations and making arguments. I think you've got some really interesting ideas in this paper, particularly in your fifth and sixth paragraphs, but you need to expand upon them. For example, you might spend more time talking about Millhauser's rationale--WHY does he think the monster should have been presented as a brutal beast throughout? What would be lost in such a presentation? Why is it better that Shelley shows the monster in terms of growth and progression? You introduce this idea in your introduction, arguing that Shelley is deliberately playing with the reader's sympathies, for the monster and for Frankenstein. Could you say more about HOW she does this? What is the effect of the reader's divided sympathies? Where does the sympathy lie at the end of the book? Why might Shelley be interested in this? In general, what is the value of making the creature sympathetic? I hope you found some of the questions I've raised valuable. You've touched on some interesting issues in this paper, and there is definitely plenty of room for you to develop them even further. If you have any questions about anything I've said, or any further questions, please feel free to write back to me. Good luck with your paper and thank you for submitting to the OWL!
Mark, Thank you for submitting your paper to the OWL; I am a Political Science major and very much enjoyed reading it. Below you will find a few suggestions for how to strengthen your writing during the revision process. You wrote that your major concerns with your paper were "abstract prose" and "elementary points." I did not find your arguments to be too simplistic or "elementary," nor did your language seem too abstract. It did, however, lack clarity and definition at some points. Specifically, there are some concepts that you repeat throughout your paper but never define. One is the "republican role." It may be that your instructor discussed this idea at length in class, or that Machiavelli does in his Discourses on Livy, but there is no such discussion in your paper. A stronger paper would define the proper role of a leader in a republican state from the beginning. Some theoretical questions you may want to consider on this point include: what is the difference between a republican leader and a tyrannical leader? How can one distinguish between the two? Why is it important to prevent against tyranny? Is the leader subservient to the will of the people? Is the leader responsible to anyone? Where does the leader draw his power or right to govern from? What does it mean to "be subordinate to a republican role"? What qualities are valuable in a leader? Which ones are dangerous? It may be beneficial to read over your paper with a critical eye looking for vague concepts. What ideas do you reference but never fully explain? Do you take certain concepts for granted? If you find such problems, generating a list of questions to focus your idea (as above) can be a helpful exercise. There were two more areas I found especially lacking in definition: the concept of tyranny and a "short time in office." Thank you again for submitting your paper to the OWL. Your arguments are strong and I hope my comments will help to fine-tune your essay. Please feel free to e-mail me for further assistance or clarification. Good luck with your revisions!
Thanks for submitting your essay-I enjoyed reading it. I hope my comments help you in your revision process.
Your personal narrative is without a doubt at its best when you give vivid details of the day from your perspective, which is, as you describe, a very unique one. The "chalky taste" of the air, for instance, is a detail that really brings the scene to life.
You asked for help with structure, and I think the most sensible structure in this case is a chronological one. It's fine to start with a vivid scene to land the reader in the event, but then it makes sense to step back and tell the story as it happened. To help you accomplish this end, you might consider listing each of the major points you want to cover and then turning them into an outline. It might help, too, to think about the overall message you want to convey. Then make sure all of your details contribute to that message.
As for constructive comments, you never really explain why you were at Ground Zero on September 12. Do you just happen to live nearby? Did you have any special connection to the firefighters or the victims? Why did you decide to help out?
I would also be careful of the very general statements you use to sum up the essay, such as , "That day brought to my attention a side of humanity that had lay dormant in my mind. That moment in time showed me that people have the capacity to act unselfishly." It's best to convey your point through examples rather than summation-the old advice to "show not tell."
It takes a lot of courage to tackle in an essay the events of September 11 and the days following, but I think you have a great perspective, and the ability to look beyond the chaos to the details of the scene.
Feel free to write back as you revise this piece. I'd be glad to talk more about it.
Hello, Angela,
Your paper is coherent, well-organized, and very informative. You do a nice job of incorporating various theorists and applying their ideas to the phenomenon of AHANA. You also do a good job of considering "the opposing viewpoint" and introducing relevant arguments to substantiate your position.
One area I would suggest giving a little more attention to how exactly AHANA functions. You mention that the term was coined as an alternative to the more negative term "minority," and that the group exists to "promote understanding..." etc. But I still want to know more about HOW the group works to achieve their goals; do they sponsor events on campus? hold workshops? etc. You did an effective job of explaining the philosophy of the group, but I would be interested in seeing just a little bit more of how it works in action, so to speak.
The second point is that you might want to explain in greater detail how subjective experiences shape the need for a group such as AHANA. You mention that racial and cultural differences do exist and that the "differing perspectives caused by these distinctions exist regardless of whether they are acknowledged." This is a very integral part of your argument, so maybe developing it further would be helpful. I realize it's a very broad concept to try and condense within your paper, but focusing on explicating that part might be helpful. Overall, I think you have a very strong paper that seems to fulfill the parameters of the assignment quite well.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Bar Exam Toolbox®
Get the tools you need for bar exam success
Essay Feedback: Why It’s Important, Where to Get It, and How to Use It to Improve
January 19, 2017 By Jennifer Warren Leave a Comment

When you’re preparing for the bar exam, whether you’re a first-time taker or a repeater, you want to use every tool available to you to improve your chances of success. One of the most valuable tools that you can employ in preparing for the written portions of the exam is feedback from someone who is experienced at evaluating bar exam essays and MPTs.
Why Feedback is Important
Getting feedback on your written work is important primarily because it gives you an objective evaluation of your work. It’s often difficult for us to fairly assess our own writing, but feedback from a good grader should help you better recognize your own strengths and weaknesses as a writer. If you’re struggling to improve your practice essay or MPTS scores, feedback can help you identify where you need to focus your attention. Are you failing to spot key issues? Is your writing disorganized? Are you not analyzing the facts thoroughly enough? Or are you simply not reciting the relevant rules? Whatever it might be, feedback from an objective source can help you isolate the problem.
Additionally, as important as it is to know the rules, spot the issues, and perform solid legal analysis, it also won’t hurt if your essays “sound good.” Bar exam graders have to review hundreds of essays in a relatively short amount of time, so they may not go through each one with a fine tooth comb. If you’re essay is stylistically well written and at least sounds like something a lawyer would write, it may help make up for a few missing elements or some superficial factual analysis. Getting feedback on your practice essays should help you refine your writing style and at the very least, make your essays sound good.
Where to Get Quality Feedback
To really improve your writing style and substantive analysis using feedback, you need to be getting quality feedback. Quality feedback will point out what you’re doing well and what you’re missing, and will also give you specific suggestions on how to improve some of your weaker areas. Most commercial bar prep courses now provide feedback on practice essays, and their graders are generally knowledgeable and experienced at providing quality feedback. If you’re signed up with a bar prep course, be sure to take advantage of this resource. If you’re not signed up with a bar prep course or your course doesn’t offer feedback, seek out an experienced bar exam tutor . Bar exam essays are a unique writing challenge, so you’ll want the person providing you the feedback to be familiar with the expectations of your state’s bar exam.
How to Use Feedback to Improve Your Performance
Once you’ve gotten some feedback on a practice essay question, you’ll want to use the comments to make positive changes for the next practice question, and then eventually the bar exam. As you’re receiving feedback and reviewing it, keep the following tips in mind to help you make the most of it.
- Don’t take it personal – The feedback is evaluating your answer, not you as a person. So don’t take it personal and try not to get defensive. Some of the feedback may seem harsh or overly critical, but try to remember that this is all part of a process designed to help you pass the exam. Ultimately, it’s better to get that criticism on a practice essay where you can correct your mistakes than on the actual bar exam.
- Submit multiple answers for feedback – Improving your performance on the essay portions of the exam is a multi-step process. You can’t expect to make significant progress by submitting one practice question for some feedback a couple weeks before the test. Instead, plan on submitting a question each week for several weeks so that you can make incremental changes based on the feedback you receive and get plenty of practice employing the recommendations the grader gives you.
- Take the practice essays under exam like conditions – It’s fine to give yourself a few extra minutes or even glance at an outline during the first practice essay you write, but otherwise all your practice essays should be taken under exam like conditions. That means you should stick to the time limits, complete them closed book, and write out complete answers. Remember, the goal is to improve your performance on the actual test. The only way to know whether you can write a passing answer is practice with the same time and resource restrictions. The feedback you receive for answers written under exam like conditions will be more useful, because your answer will more accurately reflect the strengths and weaknesses you’ll be grappling with on the actual exam.
- Try a re-write – After you received your feedback and had time to process it, try re-writing your answer based on the comments. Re-writing your answer will give you practice making the changes suggested by the feedback and help solidify those new skills.
- Pick 1 or 2 things to work on – Trying to make several changes at once is difficult and often results in failing to fully change anything at all. So instead of focusing on every comment the grader provided in their feedback, pick one or two of the most important comments and focus on improving those areas in the next practice question. Once you’ve made improvements in those areas, you can focus on the next set of skills that you need to work on.
What to Do With Negative Feedback
Quality feedback can help you make major improvements on the written portions of the bar exam, so you want to take it seriously, but you also don’t want to get discouraged by negative feedback. Try to remember that graders for practice essays are often using very rigid model answers or rubrics to evaluate answers. Sometimes these grading systems don’t leave a lot of room to award points to good answers that approached a question in a different way. So while it’s important to take the feedback seriously and make changes based on the comments, it’s also important to remember that there is no one way to write a passing essay answer. Don’t get discouraged if you’re getting negative feedback or if your answer varies somewhat from the model answer. You can usually approach a question in different ways and still write a passing answer, so long as you have the basic qualities that all good answers have: organization, issue spotting, accurate rule statements, and factual analysis.
Did you find this post helpful? Check out some other great articles:
- Don’t Do This on Your Bar Exam Essays
- Advice From a Bar Grader: Tips to Maximize Your Essay Score
- How to Approach a Uniform Bar Exam Subject Essay (MEE)
- Don’t Forget the Basics on the Bar Exam Essays
Photo credit: Shutterstock

Ready to pass the bar exam? Get the support and accountability you need with personalized one-on-one bar exam tutoring or one of our economical courses and workshops . We’re here to help!
About Jennifer Warren
Jennifer received her B.A. in Politics cum laude from New York University and her J.D. with highest distinction from the University of Oklahoma College of Law. She has several years of experience in the areas of juvenile law and civil litigation and is the Academic Achievement Coordinator at Oklahoma City University School of Law.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Need to Pass the Bar Exam?
Sign up for our free weekly email with useful tips!
- Terms & Conditions
Copyright 2024 Bar Exam Toolbox®™
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 12 April 2024
Feedback sources in essay writing: peer-generated or AI-generated feedback?
- Seyyed Kazem Banihashem 1 , 2 ,
- Nafiseh Taghizadeh Kerman 3 ,
- Omid Noroozi 2 ,
- Jewoong Moon 4 &
- Hendrik Drachsler 1 , 5
International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education volume 21 , Article number: 23 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
2270 Accesses
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
Peer feedback is introduced as an effective learning strategy, especially in large-size classes where teachers face high workloads. However, for complex tasks such as writing an argumentative essay, without support peers may not provide high-quality feedback since it requires a high level of cognitive processing, critical thinking skills, and a deep understanding of the subject. With the promising developments in Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly after the emergence of ChatGPT, there is a global argument that whether AI tools can be seen as a new source of feedback or not for complex tasks. The answer to this question is not completely clear yet as there are limited studies and our understanding remains constrained. In this study, we used ChatGPT as a source of feedback for students’ argumentative essay writing tasks and we compared the quality of ChatGPT-generated feedback with peer feedback. The participant pool consisted of 74 graduate students from a Dutch university. The study unfolded in two phases: firstly, students’ essay data were collected as they composed essays on one of the given topics; subsequently, peer feedback and ChatGPT-generated feedback data were collected through engaging peers in a feedback process and using ChatGPT as a feedback source. Two coding schemes including coding schemes for essay analysis and coding schemes for feedback analysis were used to measure the quality of essays and feedback. Then, a MANOVA analysis was employed to determine any distinctions between the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT. Additionally, Spearman’s correlation was utilized to explore potential links between the essay quality and the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT. The results showed a significant difference between feedback generated by ChatGPT and peers. While ChatGPT provided more descriptive feedback including information about how the essay is written, peers provided feedback including information about identification of the problem in the essay. The overarching look at the results suggests a potential complementary role for ChatGPT and students in the feedback process. Regarding the relationship between the quality of essays and the quality of the feedback provided by ChatGPT and peers, we found no overall significant relationship. These findings imply that the quality of the essays does not impact both ChatGPT and peer feedback quality. The implications of this study are valuable, shedding light on the prospective use of ChatGPT as a feedback source, particularly for complex tasks like argumentative essay writing. We discussed the findings and delved into the implications for future research and practical applications in educational contexts.
Introduction
Feedback is acknowledged as one of the most crucial tools for enhancing learning (Banihashem et al., 2022 ). The general and well-accepted definition of feedback conceptualizes it as information provided by an agent (e.g., teacher, peer, self, AI, technology) regarding aspects of one’s performance or understanding (e.g., Hattie & Timplerely, 2007 ). Feedback serves to heighten students’ self-awareness concerning their strengths and areas warranting improvement, through providing actionable steps required to enhance performance (Ramson, 2003 ). The literature abounds with numerous studies that illuminate the positive impact of feedback on diverse dimensions of students’ learning journey including increasing motivation (Amiryousefi & Geld, 2021 ), fostering active engagement (Zhang & Hyland, 2022 ), promoting self-regulation and metacognitive skills (Callender et al., 2016 ; Labuhn et al., 2010 ), and enriching the depth of learning outcomes (Gan et al., 2021 ).
Normally, teachers have primarily assumed the role of delivering feedback, providing insights into students’ performance on specific tasks or their grasp of particular subjects (Konold et al., 2004 ). This responsibility has naturally fallen upon teachers owing to their expertise in the subject matter and their competence to offer constructive input (Diezmann & Watters, 2015 ; Holt-Reynolds, 1999 ; Valero Haro et al., 2023 ). However, teachers’ role as feedback providers has been challenged in recent years as we have witnessed a growth in class sizes due to the rapid advances in technology and the widespread use of digital technologies that resulted in flexible and accessible education (Shi et al., 2019 ). The growth in class sizes has translated into an increased workload for teachers, leading to a pertinent predicament. This situation has directly impacted their capacity to provide personalized and timely feedback to each student, a capability that has encountered limitations (Er et al., 2021 ).
In response to this challenge, various solutions have emerged, among which peer feedback has arisen as a promising alternative instructional approach (Er et al., 2021 ; Gao et al., 2024 ; Noroozi et al., 2023 ; Kerman et al., 2024 ). Peer feedback entails a process wherein students assume the role of feedback providers instead of teachers (Liu & Carless, 2006 ). Involving students in feedback can add value to education in several ways. First and foremost, research indicates that students delve into deeper and more effective learning when they take on the role of assessors, critically evaluating and analyzing their peers’ assignments (Gielen & De Wever, 2015 ; Li et al., 2010 ). Moreover, involving students in the feedback process can augment their self-regulatory awareness, active engagement, and motivation for learning (e.g., Arguedas et al., 2016 ). Lastly, the incorporation of peer feedback not only holds the potential to significantly alleviate teachers’ workload by shifting their responsibilities from feedback provision to the facilitation of peer feedback processes but also nurtures a dynamic learning environment wherein students are actively immersed in the learning journey (e.g., Valero Haro et al., 2023 ).
Despite the advantages of peer feedback, furnishing high-quality feedback to peers remains a challenge. Several factors contribute to this challenge. Primarily, generating effective feedback necessitates a solid understanding of feedback principles, an element that peers often lack (Latifi et al., 2023 ; Noroozi et al., 2016 ). Moreover, offering high-quality feedback is inherently a complex task, demanding substantial cognitive processing to meticulously evaluate peers’ assignments, identify issues, and propose constructive remedies (King, 2002 ; Noroozi et al., 2022 ). Furthermore, the provision of valuable feedback calls for a significant level of domain-specific expertise, which is not consistently possessed by students (Alqassab et al., 2018 ; Kerman et al., 2022 ).
In recent times, advancements in technology, coupled with the emergence of fields like Learning Analytics (LA), have presented promising avenues to elevate feedback practices through the facilitation of scalable, timely, and personalized feedback (Banihashem et al., 2023 ; Deeva et al., 2021 ; Drachsler, 2023 ; Drachsler & Kalz, 2016 ; Pardo et al., 2019 ; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ; Rüdian et al., 2020 ). Yet, a striking stride forward in the field of educational technology has been the advent of a novel Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool known as “ChatGPT,” which has sparked a global discourse on its potential to significantly impact the current education system (Ray, 2023 ). This tool’s introduction has initiated discussions on the considerable ways AI can support educational endeavors (Bond et al., 2024 ; Darvishi et al., 2024 ).
In the context of feedback, AI-powered ChatGPT introduces what is referred to as AI-generated feedback (Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ). While the literature suggests that ChatGPT has the potential to facilitate feedback practices (Dai et al., 2023 ; Katz et al., 2023 ), this literature is very limited and mostly not empirical leading us to realize that our current comprehension of its capabilities in this regard is quite restricted. Therefore, we lack a comprehensive understanding of how ChatGPT can effectively support feedback practices and to what degree it can improve the timeliness, impact, and personalization of feedback, which remains notably limited at this time.
More importantly, considering the challenges we raised for peer feedback, the question is whether AI-generated feedback and more specifically feedback provided by ChatGPT has the potential to provide quality feedback. Taking this into account, there is a scarcity of knowledge and research gaps regarding the extent to which AI tools, specifically ChatGPT, can effectively enhance feedback quality compared to traditional peer feedback. Hence, our research aims to investigate the quality of feedback generated by ChatGPT within the context of essay writing and to juxtapose its quality with that of feedback generated by students.
This study carries the potential to make a substantial contribution to the existing body of recent literature on the potential of AI and in particular ChatGPT in education. It can cast a spotlight on the quality of AI-generated feedback in contrast to peer-generated feedback, while also showcasing the viability of AI tools like ChatGPT as effective automated feedback mechanisms. Furthermore, the outcomes of this study could offer insights into mitigating the feedback-related workload experienced by teachers through the intelligent utilization of AI tools (e.g., Banihashem et al., 2022 ; Er et al., 2021 ; Pardo et al., 2019 ).
However, there might be an argument regarding the rationale for conducting this study within the specific context of essay writing. Addressing this potential query, it is crucial to highlight that essay writing stands as one of the most prevalent yet complex tasks for students (Liunokas, 2020 ). This task is not without its challenges, as evidenced by the extensive body of literature that indicates students often struggle to meet desired standards in their essay composition (e.g., Bulqiyah et al., 2021 ; Noroozi et al., 2016 ;, 2022 ; Latifi et al., 2023 ).
Furthermore, teachers frequently express dissatisfaction with the depth and overall quality of students’ essay writing (Latifi et al., 2023 ). Often, these teachers lament that their feedback on essays remains superficial due to the substantial time and effort required for critical assessment and individualized feedback provision (Noroozi et al., 2016 ;, 2022 ). Regrettably, these constraints prevent them from delving deeper into the evaluation process (Kerman et al., 2022 ).
Hence, directing attention towards the comparison of peer-generated feedback quality and AI-generated feedback quality within the realm of essay writing bestows substantial value upon both research and practical application. This study enriches the academic discourse and informs practical approaches by delivering insights into the adequacy of feedback quality offered by both peers and AI for the domain of essay writing. This investigation serves as a critical step in determining whether the feedback imparted by peers and AI holds the necessary caliber to enhance the craft of essay writing.
The ramifications of addressing this query are noteworthy. Firstly, it stands to significantly alleviate the workload carried by teachers in the process of essay evaluation. By ascertaining the viability of feedback from peers and AI, teachers can potentially reduce the time and effort expended in reviewing essays. Furthermore, this study has the potential to advance the quality of essay compositions. The collaboration between students providing feedback to peers and the integration of AI-powered feedback tools can foster an environment where essays are not only better evaluated but also refined in their content and structure.With this in mind, we aim to tackle the following key questions within the scope of this study:
RQ1. To what extent does the quality of peer-generated and ChatGPT-generated feedback differ in the context of essay writing?
Rq2. does a relationship exist between the quality of essay writing performance and the quality of feedback generated by peers and chatgpt, context and participant.
This study was conducted in the academic year of 2022–2023 at a Dutch university specializing in life sciences. In total, 74 graduate students from food sciences participated in this study in which 77% of students were female ( N = 57) and 23% were male ( N = 17).
Study design and procedure
This empirical study has an exploratory nature and it was conducted in two phases. An online module called “ Argumentative Essay Writing ” (AEW) was designed to be followed by students within the Brightspace platform. The purpose of the AEW module was to improve students’ essay writing skills by engaging them in a peer learning process where students were invited to provide feedback on each other’s essays. After designing the module, the study was implemented in two weeks and followed in two phases.
In week one (phase one), students were asked to write an essay on given topics. The topics for the essay were controversial and included “ Scientists with affiliations to the food industry should abstain from participating in risk assessment processes ”, “ powdered infant formula must adhere to strict sterility standards ”, and “ safe food consumption is the responsibility of the consumer ”. The given controversial topics were directly related to the course content and students’ area of study. Students had time for one week to write their essays individually and submit them to the Brightspace platform.
In week two (phase two), students were randomly invited to provide two sets of written/asynchronous feedback on their peers’ submitted essays. We gave a prompt to students to be used for giving feedback ( Please provide feedback to your peer and explain the extent to which she/he has presented/elaborated/justified various elements of an argumentative essay. What are the problems and what are your suggestions to improve each element of the essay? Your feedback must be between 250 and 350 words ). To be able to engage students in the online peer feedback activity, we used the FeedbackFruits app embedded in the Brightspace platform. FeedbackFruits functions as an external educational technology tool seamlessly integrated into Brightspace, aimed at enhancing student engagement via diverse peer collaboration approaches. Among its features are peer feedback, assignment evaluation, skill assessment, automated feedback, interactive videos, dynamic documents, discussion tasks, and engaging presentations (Noroozi et al., 2022 ). In this research, our focus was on the peer feedback feature of the FeedbackFruits app, which empowers teachers to design tasks that enable students to offer feedback to their peers.
In addition, we used ChatGPT as another feedback source on peers’ essays. To be consistent with the criteria for peer feedback, we gave the same feedback prompt question with a minor modification to ChatGPT and asked it to give feedback on the peers’ essays ( Please read and provide feedback on the following essay and explain the extent to which she/he has presented/elaborated/justified various elements of an argumentative essay. What are the problems and what are your suggestions to improve each element of the essay? Your feedback must be between 250 and 350 words ).
Following this design, we were able to collect students’ essay data, peer feedback data, and feedback data generated by ChatGPT. In the next step, we used two coding schemes to analyze the quality of the essays and feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT.
Measurements
Coding scheme to assess the quality of essay writing.
In this study, a coding scheme proposed by Noroozi et al. ( 2016 ) was employed to assess students’ essay quality. This coding system was constructed based on the key components of high-quality essay composition, encompassing eight elements: introduction pertaining to the subject, taking a clear stance on the subject, presenting arguments in favor of the chosen position, providing justifications for the arguments supporting the position, counter-arguments, justifications for counter-arguments, responses to counter-arguments, and concluding with implications. Each element in the coding system is assigned a score ranging from zero (indicating the lowest quality level) to three (representing the highest quality level). The cumulative scores across all these elements were aggregated to determine the overall quality score of the student’s written essays. Two experienced coders in the field of education collaborated to assess the quality of the written essays, and their agreement level was measured at 75% (Cohen’s Kappa = 0.75 [95% confidence interval: 0.70–0.81]; z = 25.05; p < 0.001), signifying a significant level of consensus between the coders.
Coding scheme to assess the quality of feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT
To assess the quality of feedback provided by both peers and ChatGPT, we employed a coding scheme developed by Noroozi et al. ( 2022 ). This coding framework dissects the characteristics of feedback, encompassing three key elements: the affective component, which considers the inclusion of emotional elements such as positive sentiments like praise or compliments, as well as negative emotions such as anger or disappointment; the cognitive component, which includes description (a concise summary of the essay), identification (pinpointing and specifying issues within the essay), and justification (providing explanations and justifications for the identified issues); and the constructive component, which involves offering recommendations, albeit not detailed action plans for further enhancements. Ratings within this coding framework range from zero, indicating poor quality, to two, signifying good quality. The cumulative scores were tallied to determine the overall quality of the feedback provided to the students. In this research, as each essay received feedback from both peers and ChatGPT, we calculated the average score from the two sets of feedback to establish the overall quality score for the feedback received, whether from peers or ChatGPT. The same two evaluators were involved in the assessment. The inter-rater reliability between the evaluators was determined to be 75% (Cohen’s Kappa = 0.75 [95% confidence interval: 0.66–0.84]; z = 17.52; p < 0.001), showing a significant level of agreement between them.
The logic behind choosing these coding schemes was as follows: Firstly, from a theoretical standpoint, both coding schemes were developed based on robust and well-established theories. The coding scheme for evaluating essay quality draws on Toulmin’s argumentation model ( 1958 ), a respected framework for essay writing. It encompasses all elements essential for high-quality essay composition and aligns well with the structure of essays assigned in the chosen course for this study. Similarly, the feedback coding scheme is grounded in prominent works on identifying feedback features (e.g., Nelson & Schunn, 2009 ; Patchan et al., 2016 ; Wu & Schunn, 2020 ), enabling the identification of key features of high-quality feedback (Noroozi et al., 2022 ). Secondly, from a methodological perspective, both coding schemes feature a transparent scoring method, mitigating coder bias and bolstering the tool’s credibility.
To ensure the data’s validity and reliability for statistical analysis, two tests were implemented. Initially, the Levene test assessed group homogeneity, followed by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to evaluate data normality. The results confirmed both group homogeneity and data normality. For the first research question, gender was considered as a control variable, and the MANCOVA test was employed to compare the variations in feedback quality between peer feedback and ChatGPT-generated feedback. Addressing the second research question involved using Spearman’s correlation to examine the relationships among original argumentative essays, peer feedback, and ChatGPT-generated feedback.
The results showed a significant difference in feedback quality between peer feedback and ChatGPT-generated feedback. Peers provided feedback of higher quality compared to ChatGPT. This difference was mainly due to the descriptive and identification of the problem features of feedback. ChatGPT tended to produce more extensive descriptive feedback including a summary statement such as the description of the essay or taken action, while students performed better in pinpointing and identifying the issues in the feedback provided (see Table 1 ).
A comprehensive list featuring selected examples of feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT is presented in Fig 1 . This table additionally outlines examples of how the generated feedback was coded based on the coding scheme to assess the quality of feedback.
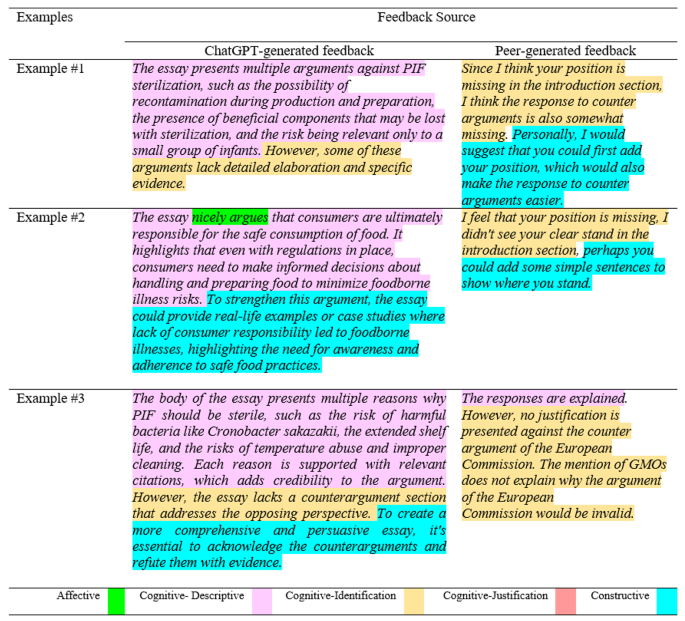
A comparative list of selected examples of peer-generated and ChatGPT-generated feedback
Overall, the results indicated that there was no significant relationship between the quality of essay writing and the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT. However, a positive correlation was observed between the quality of the essay and the affective feature of feedback generated by ChatGPT, while a negative relationship was observed between the quality of the essay and the affective feature of feedback generated by peers. This finding means that as the quality of the essay improves, ChatGPT tends to provide more affective feedback, while peers tend to provide less affective feedback (see Table 2 ).
This study was an initial effort to explore the potential of ChatGPT as a feedback source in the context of essay writing and to compare the extent to which the quality of feedback generated by ChatGPT differs from the feedback provided by peers. Below we discuss our findings for each research question.
Discussion on the results of RQ1
For the first research question, the results revealed a disparity in feedback quality when comparing peer-generated feedback to feedback generated by ChatGPT. Peer feedback demonstrated higher quality compared to ChatGPT-generated feedback. This discrepancy is attributed primarily to variations in the descriptive and problem-identification features of the feedback.
ChatGPT tended to provide more descriptive feedback, often including elements such as summarizing the content of the essay. This inclination towards descriptive feedback could be related to ChatGPT’s capacity to analyze and synthesize textual information effectively. Research on ChatGPT further supports this notion, demonstrating the AI tool’s capacity to offer a comprehensive overview of the provided content, therefore potentially providing insights and a holistic perspective on the content (Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ; Ray, 2023 ).
ChatGPT’s proficiency in providing extensive descriptive feedback could be seen as a strength. It might be particularly valuable for summarizing complex arguments or providing comprehensive overviews, which could aid students in understanding the overall structure and coherence of their essays.
In contrast, students’ feedback content entailed high quality regarding identifying specific issues and areas for improvement. Peers outperformance compared to ChatGPT in identifying problems within the essays could be related to humans’ potential in cognitive skills, critical thinking abilities, and contextual understanding (e.g., Korteling et al., 2021 ; Lamb et al., 2019 ). This means that students, with their contextual knowledge and critical thinking skills, may be better equipped to identify issues within the essays that ChatGPT may overlook.
Furthermore, a detailed look at the findings of the first research question discloses that the feedback generated by ChatGPT comprehensively encompassed all essential components characterizing high-quality feedback, including affective, cognitive, and constructive dimensions (Kerman et al., 2022 ; Patchan et al., 2016 ). This comprehensive observation could be an indication of the fact that ChatGPT-generated feedback could potentially serve as a viable source of feedback. This observation is supported by previous studies where a positive role for AI-generated feedback and automated feedback in enhancing educational outcomes has been recognized (e.g., Bellhäuser et al., 2023 ; Gombert et al., 2024 ; Huang et al., 2023 ; Xia et al., 2022 ).
Finally, an overarching look at the results of the first research question suggests a potential complementary role for ChatGPT and students in the feedback process. This means that using these two feedback sources together creates a synergistic relationship that could result in better feedback outcomes.
Discussion on the results of RQ2
Results for the second research question revealed no observations of a significant correlation between the quality of the essays and the quality of the feedback generated by both peers and ChatGPT. These findings carry a consequential implication, suggesting that the inherent quality of the essays under scrutiny exerts negligible influence over the quality of feedback furnished by both students and the ChatGPT.
In essence, these results point to a notable degree of independence between the writing prowess exhibited in the essays and the efficacy of the feedback received from either source. This disassociation implies that the ability to produce high-quality essays does not inherently translate into a corresponding ability to provide equally insightful feedback, neither for peers nor for ChatGPT. This decoupling of essay quality from feedback quality highlighted the multifaceted nature of these evaluative processes, where proficiency in constructing a coherent essay does not necessarily guarantee an equally adept capacity for evaluating and articulating constructive commentary on peers’ work.
The implications of these findings are both intriguing and defy conventional expectations, as they deviate somewhat from the prevailing literature’s stance. The existing body of scholarly work generally posits a direct relationship between the quality of an essay and the subsequent quality of generated feedback (Noroozi et al., 2016 ;, 2022 ; Kerman et al., 2022 ; Vale Haro et al., 2023 ). This line of thought contends that essays of inferior quality might serve as a catalyst for more pronounced error detection among students, encompassing grammatical intricacies, depth of content, clarity, and coherence, as well as the application of evidence and support. Conversely, when essays are skillfully crafted, the act of pinpointing areas for enhancement becomes a more complex task, potentially necessitating a heightened level of subject comprehension and nuanced evaluation.
However, the present study’s findings challenge this conventional wisdom. The observed decoupling of essay quality from feedback quality suggests a more nuanced interplay between the two facets of assessment. Rather than adhering to the anticipated pattern, wherein weaker essays prompt clearer identification of deficiencies, and superior essays potentially render the feedback process more challenging, the study suggests that the process might be more complex than previously thought. It hints at a dynamic in which the act of evaluating essays and providing constructive feedback transcends a simple linear connection with essay quality.
These findings, while potentially unexpected, are an indication of the complex nature of essay assignments and feedback provision highlighting the complexity of cognitive processes that underlie both tasks, and suggesting that the relationship between essay quality and feedback quality is not purely linear but influenced by a multitude of factors, including the evaluator’s cognitive framework, familiarity with the subject matter, and critical analysis skills.
Despite this general observation, a closer examination of the affective features within the feedback reveals a different pattern. The positive correlation between essay quality and the affective features present in ChatGPT-generated feedback could be related to ChatGPT’s capacity to recognize and appreciate students’ good work. As the quality of the essay increases, ChatGPT might be programmed to offer more positive and motivational feedback to acknowledge students’ progress (e.g., Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ; Ray, 2023 ). In contrast, the negative relationship between essay quality and the affective features in peer feedback may be attributed to the evolving nature of feedback from peers (e.g., Patchan et al., 2016 ). This suggests that as students witness improvements in their peers’ essay-writing skills and knowledge, their feedback priorities may naturally evolve. For instance, students may transition from emphasizing emotional and affective comments to focusing on cognitive and constructive feedback, with the goal of further enhancing the overall quality of the essays.
Limitations and implications for future research and practice
We acknowledge the limitations of this study. Primarily, the data underpinning this investigation was drawn exclusively from a singular institution and a solitary course, featuring a relatively modest participant pool. This confined scope inevitably introduces certain constraints that need to be taken into consideration when interpreting the study’s outcomes and generalizing them to broader educational contexts. Under this constrained sampling, the findings might exhibit a degree of contextual specificity, potentially limiting their applicability to diverse institutional settings and courses with distinct curricular foci. The diverse array of academic environments, student demographics, and subject matter variations existing across educational institutions could potentially yield divergent patterns of results. Therefore, while the current study’s outcomes provide insights within the confines of the studied institution and course, they should be interpreted and generalized with prudence. Recognizing these limitations, for future studies, we recommend considering a large-scale participant pool with a diverse range of variables, including individuals from various programs and demographics. This approach would enrich the depth and breadth of understanding in this domain, fostering a more comprehensive comprehension of the complex dynamics at play.
In addition, this study omitted an exploration into the degree to which students utilize feedback provided by peers and ChatGPT. That is to say that we did not investigate the effects of such feedback on essay enhancements in the revision phase. This omission inherently introduces a dimension of uncertainty and places a constraint on the study’s holistic understanding of the feedback loop. By not addressing these aspects, the study’s insights are somewhat partial, limiting the comprehensive grasp of the potential influences that these varied feedback sources wield on students’ writing enhancement processes. An analysis of the feedback assimilation patterns and their subsequent effects on essay refinement would have unveiled insights into the practical utility and impact of the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT.
To address this limitation, future investigations could be structured to encompass a more thorough examination of students’ feedback utilization strategies and the resulting implications for the essay revision process. By shedding light on the complex interconnection between feedback reception, its integration into the revision process, and the ultimate outcomes in terms of essay improvement, a more comprehensive understanding of the dynamics involved could be attained.
Furthermore, in this study, we employed identical question prompts for both peers and ChatGPT. However, there is evidence indicating that ChatGPT is sensitive to how prompts are presented to it (e.g., Cao et al., 2023 ; White et al., 2023 ; Zuccon & Koopman, 2023 ). This suggests that variations in the wording, structure, or context of prompts might influence the responses generated by ChatGPT, potentially impacting the comparability of its outputs with those of peers. Therefore, it is essential to carefully consider and control for prompt-related factors in future research when assessing ChatGPT’s performance and capabilities in various tasks and contexts.
In addition, We acknowledge that ChatGPT can potentially generate inaccurate results. Nevertheless, in the context of this study, our examination of the results generated by ChatGPT did not reveal a significant inaccuracies that would warrant inclusion in our findings.
From a methodological perspective, we reported the interrater reliability between the coders to be 75%. While this level of agreement was statistically significant, signifying the reliability of our coders’ analyses, it did not reach the desired level of precision. We acknowledge this as a limitation of the study and suggest enhancing interrater reliability through additional coder training.
In addition, it is worth noting that the advancement of Generative AI like ChatGPT, opens new avenues in educational feedback mechanisms. Beyond just generating feedback, these AI models have the potential to redefine how feedback is presented and assimilated. In the realm of research on adaptive learning systems, the findings of this study also echo the importance of adaptive learning support empowered by AI and ChatGPT (Rummel et al., 2016 ). It can pave the way for tailored educational experiences that respond dynamically to individual student needs. This is not just about the feedback’s content but its delivery, timing, and adaptability. Further exploratory data analyses, such as sequential analysis and data mining, may offer insights into the nuanced ways different adaptive learning supports can foster student discussions (Papamitsiou & Economides, 2014 ). This involves dissecting the feedback dynamics, understanding how varied feedback types stimulate discourse, and identifying patterns that lead to enhanced student engagement.
Ensuring the reliability and validity of AI-empowered feedback is also crucial. The goal is to ascertain that technology-empowered learning support genuinely enhances students’ learning process in a consistent and unbiased manner. Given ChatGPT’s complex nature of generating varied responses based on myriad prompts, the call for enhancing methodological rigor through future validation studies becomes both timely and essential. For example, in-depth prompt validation and blind feedback assessment studies could be employed to meticulously probe the consistency and quality of ChatGPT’s responses. Also, comparative analysis with different AI models can be useful.
From an educational standpoint, our research findings advocate for the integration of ChatGPT as a feedback resource with peer feedback within higher education environments for essay writing tasks since there is a complementary role potential for pee-generated and ChatGPT-generated feedback. This approach holds the potential to alleviate the workload burden on teachers, particularly in the context of online courses with a significant number of students.
This study contributes to and adds value to the young existing but rapidly growing literature in two distinct ways. From a research perspective, this study addresses a significant void in the current literature by responding to the lack of research on AI-generated feedback for complex tasks like essay writing in higher education. The research bridges this gap by analyzing the effectiveness of ChatGPT-generated feedback compared to peer-generated feedback, thereby establishing a foundation for further exploration in this field. From a practical perspective of higher education, the study’s findings offer insights into the potential integration of ChatGPT as a feedback source within higher education contexts. The discovery that ChatGPT’s feedback quality could potentially complement peer feedback highlights its applicability for enhancing feedback practices in higher education. This holds particular promise for courses with substantial enrolments and essay-writing components, providing teachers with a feasible alternative for delivering constructive feedback to a larger number of students.
Data availability
The data is available upon a reasonable request.
Alqassab, M., Strijbos, J. W., & Ufer, S. (2018). Training peer-feedback skills on geometric construction tasks: Role of domain knowledge and peer-feedback levels. European Journal of Psychology of Education , 33 (1), 11–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-017-0342-0 .
Article Google Scholar
Amiryousefi, M., & Geld, R. (2021). The role of redressing teachers’ instructional feedback interventions in EFL learners’ motivation and achievement in distance education. Innovation in Language Learning and Teaching , 15 (1), 13–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/17501229.2019.1654482 .
Arguedas, M., Daradoumis, A., & Xhafa Xhafa, F. (2016). Analyzing how emotion awareness influences students’ motivation, engagement, self-regulation and learning outcome. Educational Technology and Society , 19 (2), 87–103. https://www.jstor.org/stable/jeductechsoci.19.2.87 .
Google Scholar
Banihashem, S. K., Noroozi, O., van Ginkel, S., Macfadyen, L. P., & Biemans, H. J. (2022). A systematic review of the role of learning analytics in enhancing feedback practices in higher education. Educational Research Review , 100489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2022.100489 .
Banihashem, S. K., Dehghanzadeh, H., Clark, D., Noroozi, O., & Biemans, H. J. (2023). Learning analytics for online game-based learning: A systematic literature review. Behaviour & Information Technology , 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2023.2255301 .
Bellhäuser, H., Dignath, C., & Theobald, M. (2023). Daily automated feedback enhances self-regulated learning: A longitudinal randomized field experiment. Frontiers in Psychology , 14 , 1125873. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1125873 .
Bond, M., Khosravi, H., De Laat, M., Bergdahl, N., Negrea, V., Oxley, E., & Siemens, G. (2024). A meta systematic review of artificial intelligence in higher education: A call for increased ethics, collaboration, and rigour. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education , 21 (4), 1–41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00436-z .
Bulqiyah, S., Mahbub, M., & Nugraheni, D. A. (2021). Investigating writing difficulties in Essay writing: Tertiary Students’ perspectives. English Language Teaching Educational Journal , 4 (1), 61–73. https://doi.org/10.12928/eltej.v4i1.2371 .
Callender, A. A., Franco-Watkins, A. M., & Roberts, A. S. (2016). Improving metacognition in the classroom through instruction, training, and feedback. Metacognition and Learning , 11 (2), 215–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-015-9142-6 .
Cao, J., Li, M., Wen, M., & Cheung, S. C. (2023). A study on prompt design, advantages and limitations of chatgpt for deep learning program repair. arXiv Preprint arXiv:2304 08191 . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.08191 .
Dai, W., Lin, J., Jin, F., Li, T., Tsai, Y. S., Gasevic, D., & Chen, G. (2023). Can large language models provide feedback to students? A case study on ChatGPT. https://doi.org/10.35542/osf.io/hcgzj .
Darvishi, A., Khosravi, H., Sadiq, S., Gašević, D., & Siemens, G. (2024). Impact of AI assistance on student agency. Computers & Education , 210 , 104967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2023.104967 .
Deeva, G., Bogdanova, D., Serral, E., Snoeck, M., & De Weerdt, J. (2021). A review of automated feedback systems for learners: Classification framework, challenges and opportunities. Computers & Education , 162 , 104094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.104094 .
Diezmann, C. M., & Watters, J. J. (2015). The knowledge base of subject matter experts in teaching: A case study of a professional scientist as a beginning teacher. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education , 13 , 1517–1537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-014-9561-x .
Drachsler, H. (2023). Towards highly informative learning analytics . Open Universiteit. https://doi.org/10.25656/01:26787 .
Drachsler, H., & Kalz, M. (2016). The MOOC and learning analytics innovation cycle (MOLAC): A reflective summary of ongoing research and its challenges. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning , 32 (3), 281–290. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12135 .
Er, E., Dimitriadis, Y., & Gašević, D. (2021). Collaborative peer feedback and learning analytics: Theory-oriented design for supporting class-wide interventions. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 46 (2), 169–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2020.1764490 .
Farrokhnia, M., Banihashem, S. K., Noroozi, O., & Wals, A. (2023). A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: Implications for educational practice and research. Innovations in Education and Teaching International , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846 .
Gan, Z., An, Z., & Liu, F. (2021). Teacher feedback practices, student feedback motivation, and feedback behavior: How are they associated with learning outcomes? Frontiers in Psychology , 12 , 697045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.697045 .
Gao, X., Noroozi, O., Gulikers, J. T. M., Biemans, H. J., & Banihashem, S. K. (2024). A systematic review of the key components of online peer feedback practices in higher education. Educational Research Review , 100588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2023.100588 .
Gielen, M., & De Wever, B. (2015). Scripting the role of assessor and assessee in peer assessment in a wiki environment: Impact on peer feedback quality and product improvement. Computers & Education , 88 , 370–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.07.012 .
Gombert, S., Fink, A., Giorgashvili, T., Jivet, I., Di Mitri, D., Yau, J., & Drachsler, H. (2024). From the Automated Assessment of Student Essay Content to highly informative feedback: A case study. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education , 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-023-00387-6 .
Hattie, J., & Timperley, H. (2007). The power of feedback. Review of Educational Research , 77 (1), 81–112. https://doi.org/10.3102/003465430298487 .
Holt-Reynolds, D. (1999). Good readers, good teachers? Subject matter expertise as a challenge in learning to teach. Harvard Educational Review , 69 (1), 29–51. https://doi.org/10.17763/haer.69.1.pl5m5083286l77t2 .
Huang, A. Y., Lu, O. H., & Yang, S. J. (2023). Effects of artificial intelligence–enabled personalized recommendations on learners’ learning engagement, motivation, and outcomes in a flipped classroom. Computers & Education , 194 , 104684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104684 .
Katz, A., Wei, S., Nanda, G., Brinton, C., & Ohland, M. (2023). Exploring the efficacy of ChatGPT in analyzing Student Teamwork Feedback with an existing taxonomy. arXiv Preprint arXiv . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.11882 .
Kerman, N. T., Noroozi, O., Banihashem, S. K., Karami, M., & Biemans, H. J. (2022). Online peer feedback patterns of success and failure in argumentative essay writing. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2093914 .
Kerman, N. T., Banihashem, S. K., Karami, M., Er, E., Van Ginkel, S., & Noroozi, O. (2024). Online peer feedback in higher education: A synthesis of the literature. Education and Information Technologies , 29 (1), 763–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12273-8 .
King, A. (2002). Structuring peer interaction to promote high-level cognitive processing. Theory into Practice , 41 (1), 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15430421tip4101_6 .
Konold, K. E., Miller, S. P., & Konold, K. B. (2004). Using teacher feedback to enhance student learning. Teaching Exceptional Children , 36 (6), 64–69. https://doi.org/10.1177/004005990403600608 .
Korteling, J. H., van de Boer-Visschedijk, G. C., Blankendaal, R. A., Boonekamp, R. C., & Eikelboom, A. R. (2021). Human-versus artificial intelligence. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence , 4 , 622364. https://doi.org/10.3389/frai.2021.622364 .
Labuhn, A. S., Zimmerman, B. J., & Hasselhorn, M. (2010). Enhancing students’ self-regulation and mathematics performance: The influence of feedback and self-evaluative standards. Metacognition and Learning , 5 , 173–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-010-9056-2 .
Lamb, R., Firestone, J., Schmitter-Edgecombe, M., & Hand, B. (2019). A computational model of student cognitive processes while solving a critical thinking problem in science. The Journal of Educational Research , 112 (2), 243–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2018.1514357 .
Latifi, S., Noroozi, O., & Talaee, E. (2023). Worked example or scripting? Fostering students’ online argumentative peer feedback, essay writing and learning. Interactive Learning Environments , 31 (2), 655–669. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1799032 .
Li, L., & Liu, X. (2010). Steckelberg. Assessor or assessee: How student learning improves by giving and receiving peer feedback. British Journal of Educational Technology , 41 (3), 525–536. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.00968.x .
Liu, N. F., & Carless, D. (2006). Peer feedback: The learning element of peer assessment. Teaching in Higher Education , 11 (3), 279–290. https://doi.org/10.1080/13562510600680582 .
Liunokas, Y. (2020). Assessing students’ ability in writing argumentative essay at an Indonesian senior high school. IDEAS: Journal on English language teaching and learning. Linguistics and Literature , 8 (1), 184–196. https://doi.org/10.24256/ideas.v8i1.1344 .
Nelson, M. M., & Schunn, C. D. (2009). The nature of feedback: How different types of peer feedback affect writing performance. Instructional Science , 37 , 375–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-008-9053-x .
Noroozi, O., Banihashem, S. K., Taghizadeh Kerman, N., Parvaneh Akhteh Khaneh, M., Babayi, M., Ashrafi, H., & Biemans, H. J. (2022). Gender differences in students’ argumentative essay writing, peer review performance and uptake in online learning environments. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2034887 .
Noroozi, O., Biemans, H., & Mulder, M. (2016). Relations between scripted online peer feedback processes and quality of written argumentative essay. The Internet and Higher Education , 31, 20-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2016.05.002
Noroozi, O., Banihashem, S. K., Biemans, H. J., Smits, M., Vervoort, M. T., & Verbaan, C. L. (2023). Design, implementation, and evaluation of an online supported peer feedback module to enhance students’ argumentative essay quality. Education and Information Technologies , 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11683-y .
Papamitsiou, Z., & Economides, A. A. (2014). Learning analytics and educational data mining in practice: A systematic literature review of empirical evidence. Journal of Educational Technology & Society , 17 (4), 49–64. https://doi.org/10.2307/jeductechsoci.17.4.49 . https://www.jstor.org/stable/ .
Pardo, A., Jovanovic, J., Dawson, S., Gašević, D., & Mirriahi, N. (2019). Using learning analytics to scale the provision of personalised feedback. British Journal of Educational Technology , 50 (1), 128–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12592 .
Patchan, M. M., Schunn, C. D., & Correnti, R. J. (2016). The nature of feedback: How peer feedback features affect students’ implementation rate and quality of revisions. Journal of Educational Psychology , 108 (8), 1098. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000103 .
Ramsden, P. (2003). Learning to teach in higher education . Routledge.
Ray, P. P. (2023). ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems , 3 , 121–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003 .
Rüdian, S., Heuts, A., & Pinkwart, N. (2020). Educational Text Summarizer: Which sentences are worth asking for? In DELFI 2020 - The 18th Conference on Educational Technologies of the German Informatics Society (pp. 277–288). Bonn, Germany.
Rummel, N., Walker, E., & Aleven, V. (2016). Different futures of adaptive collaborative learning support. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education , 26 , 784–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-016-0102-3 .
Shi, M. (2019). The effects of class size and instructional technology on student learning performance. The International Journal of Management Education , 17 (1), 130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2019.01.004 .
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Toulmin, S. (1958). The uses of argument . Cambridge University Press.
Valero Haro, A., Noroozi, O., Biemans, H. J., Mulder, M., & Banihashem, S. K. (2023). How does the type of online peer feedback influence feedback quality, argumentative essay writing quality, and domain-specific learning? Interactive Learning Environments , 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2215822 .
White, J., Fu, Q., Hays, S., Sandborn, M., Olea, C., Gilbert, H., & Schmidt, D. C. (2023). A prompt pattern catalog to enhance prompt engineering with chatgpt. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11382 . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.11382 .
Wu, Y., & Schunn, C. D. (2020). From feedback to revisions: Effects of feedback features and perceptions. Contemporary Educational Psychology , 60 , 101826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.101826 .
Xia, Q., Chiu, T. K., Zhou, X., Chai, C. S., & Cheng, M. (2022). Systematic literature review on opportunities, challenges, and future research recommendations of artificial intelligence in education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence , 100118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100118 .
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V. I., Bond, M., & Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education–where are the educators? International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education , 16 (1), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0171-0 .
Zhang, Z. V., & Hyland, K. (2022). Fostering student engagement with feedback: An integrated approach. Assessing Writing , 51 , 100586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2021.100586 .
Zuccon, G., & Koopman, B. (2023). Dr ChatGPT, tell me what I want to hear: How prompt knowledge impacts health answer correctness. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302 .13793. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.13793 .
Download references
No funding has been received for this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Open Universiteit, Heerlen, The Netherlands
Seyyed Kazem Banihashem & Hendrik Drachsler
Wageningen University and Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Seyyed Kazem Banihashem & Omid Noroozi
Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran
Nafiseh Taghizadeh Kerman
The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, USA
Jewoong Moon
DIPE Leibniz Institute, Goethe University, Frankfurt, Germany
Hendrik Drachsler
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S. K. Banihashem led this research experiment. N. T. Kerman contributed to the data analysis and writing. O. Noroozi contributed to the designing, writing, and reviewing the manuscript. J. Moon contributed to the writing and revising the manuscript. H. Drachsler contributed to the writing and revising the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Seyyed Kazem Banihashem .
Ethics declarations
Declaration of ai-assisted technologies in the writing process.
The authors used generative AI for language editing and took full responsibility.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Banihashem, S.K., Kerman, N.T., Noroozi, O. et al. Feedback sources in essay writing: peer-generated or AI-generated feedback?. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 21 , 23 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-024-00455-4
Download citation
Received : 20 November 2023
Accepted : 18 March 2024
Published : 12 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-024-00455-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- AI-generated feedback
- Essay writing
- Feedback sources
- Higher education
- Peer feedback

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.
For Business
For Individuals
16 constructive feedback examples — and tips for how to use them

Giving constructive feedback is nerve-wracking for many people. But feedback is also necessary for thriving in the workplace.
It helps people flex and grow into new skills, capabilities, and roles. It creates more positive and productive relationships between employees. And it helps to reach goals and drive business value.
But feedback is a two-way street. More often than not, it’s likely every employee will have to give constructive feedback in their careers. That’s why it’s helpful to have constructive feedback examples to leverage for the right situation.
We know employees want feedback. But one study found that people want feedback if they’re on the receiving end . In fact, in every case, participants rated their desire for feedback higher as the receiver. While the fear of feedback is very real, it’s important to not shy away from constructive feedback opportunities. After all, it could be the difference between a flailing and thriving team.
If you’re trying to overcome your fear of providing feedback, we’ve compiled a list of 16 constructive feedback examples for you to use. We’ll also share some best practices on how to give effective feedback .
What is constructive feedback?
When you hear the word feedback, what’s the first thing that comes to mind? What feelings do you have associated with feedback? Oftentimes, feedback conversations are anxiety-ridden because it’s assumed to be negative feedback. Unfortunately, feedback has this binary stigma, it’s either good or bad.
But in reality, there are plenty of types of feedback leveraged in both personal and professional relationships. They don’t all fall into one camp or the other. And each type of feedback is serving a purpose to ultimately better an individual, team, or work environment.
For example, positive feedback can be used to reinforce desired behaviors or big accomplishments. Real-time feedback is reserved for those “in the moment” situations. Like if I’ve made a mistake or a typo in a blog, I’d want my teammates to give me real-time feedback .
However, constructive feedback is its own ball game.
What is constructive feedback?
Constructive feedback is a supportive way to improve areas of opportunity for an individual person, team, relationship, or environment. In many ways, constructive feedback is a combination of constructive criticism paired with coaching skills.
16 constructive feedback examples to use
To truly invest in building a feedback culture , your employees need to feel comfortable giving feedback. After all, organizations are people, which means we’re all human. We make mistakes but we’re all capable of growth and development. And most importantly, everyone everywhere should be able to live with more purpose, clarity, and passion.
But we won’t unlock everyone’s full potential unless your people are comfortable giving feedback. Some employee feedback might be easier to give than others, like ways to improve a presentation.
But sometimes, constructive feedback can be tricky, like managing conflict between team members or addressing negative behavior. As any leader will tell you, it’s critical to address negative behaviors and redirect them to positive outcomes. Letting toxic behavior go unchecked can lead to issues with employee engagement , company culture, and overall, your business’s bottom line.
Regardless of where on the feedback spectrum your organization falls, having concrete examples will help set up your people for success. Let’s talk through some examples of constructive feedback. For any of these themes, it’s always good to have specific examples handy to help reinforce the feedback you’re giving. We’ll also give some sample scenarios of when these phrases might be most impactful and appropriate.
Constructive feedback examples about communication skills
An employee speaks over others and interrupts in team meetings.
“I’ve noticed you can cut off team members or interrupt others. You share plenty of good ideas and do good work. To share some communication feedback , I’d love to see how you can support others in voicing their own ideas in our team meetings.”
An employee who doesn’t speak up or share ideas in team meetings.
“I’ve noticed that you don’t often share ideas in big meetings. But in our one-on-one meetings , you come up with plenty of meaningful and creative ideas to help solve problems. What can I do to help make you more comfortable speaking up in front of the team?”
An employee who is brutally honest and blunt.
“Last week, I noticed you told a teammate that their work wasn’t useful to you. It might be true that their work isn’t contributing to your work, but there’s other work being spread across the team that will help us reach our organizational goals. I’d love to work with you on ways to improve your communication skills to help build your feedback skills, too. Would you be interested in pursuing some professional development opportunities?”
An employee who has trouble building rapport because of poor communication skills in customer and prospect meetings.
“I’ve noticed you dive right into the presentation with our customer and prospect meetings. To build a relationship and rapport, it’s good to make sure we’re getting to know everyone as people. Why don’t you try learning more about their work, priorities, and life outside of the office in our next meeting?”

Constructive feedback examples about collaboration
An employee who doesn’t hold to their commitments on group or team projects.
“I noticed I asked you for a deliverable on this key project by the end of last week. I still haven’t received this deliverable and wanted to follow up. If a deadline doesn’t work well with your bandwidth, would you be able to check in with me? I’d love to get a good idea of what you can commit to without overloading your workload.”
An employee who likes to gatekeep or protect their work, which hurts productivity and teamwork .
“Our teams have been working together on this cross-functional project for a couple of months. But yesterday, we learned that your team came across a roadblock last month that hasn’t been resolved. I’d love to be a partner to you if you hit any issues in reaching our goals. Would you be willing to share your project plan or help provide some more visibility into your team’s work? I think it would help us with problem-solving and preventing problems down the line.”
An employee who dominates a cross-functional project and doesn’t often accept new ways of doing things.
“I’ve noticed that two team members have voiced ideas that you have shut down. In the spirit of giving honest feedback, it feels like ideas or new solutions to problems aren’t welcome. Is there a way we could explore some of these ideas? I think it would help to show that we’re team players and want to encourage everyone’s contributions to this project.”
Constructive feedback examples about time management
An employee who is always late to morning meetings or one-on-ones.
“I’ve noticed that you’re often late to our morning meetings with the rest of the team. Sometimes, you’re late to our one-on-ones, too. Is there a way I can help you with building better time management skills ? Sometimes, the tardiness can come off like you don’t care about the meeting or the person you’re meeting with, which I know you don’t mean.”
A direct report who struggles to meet deadlines.
“Thanks for letting me know you’re running behind schedule and need an extension. I’ve noticed this is the third time you’ve asked for an extension in the past two weeks. In our next one-on-one, can you come up with a list of projects and the amount of time that you’re spending on each project? I wonder if we can see how you’re managing your time and identify efficiencies.”
An employee who continuously misses team meetings.
“I’ve noticed you haven’t been present at the last few team meetings. I wanted to check in to see how things are going. What do you have on your plate right now? I’m concerned you’re missing critical information that can help you in your role and your career.”

Constructive feedback examples about boundaries
A manager who expects the entire team to work on weekends.
“I’ve noticed you send us emails and project plans over the weekends. I put in a lot of hard work during the week, and won’t be able to answer your emails until the work week starts again. It’s important that I maintain my work-life balance to be able to perform my best.”
An employee who delegates work to other team members.
“I’ve noticed you’ve delegated some aspects of this project that fall into your scope of work. I have a full plate with my responsibilities in XYZ right now. But if you need assistance, it might be worth bringing up your workload to our manager.”
A direct report who is stressed about employee performance but is at risk of burning out.
“I know we have performance reviews coming up and I’ve noticed an increase in working hours for you. I hope you know that I recognize your work ethic but it’s important that you prioritize your work-life balance, too. We don’t want you to burn out.”
Constructive feedback examples about managing
A leader who is struggling with team members working together well in group settings.
“I’ve noticed your team’s scores on our employee engagement surveys. It seems like they don’t collaborate well or work well in group settings, given their feedback. Let’s work on building some leadership skills to help build trust within your team.”
A leader who is struggling to engage their remote team.
“In my last skip-levels with your team, I heard some feedback about the lack of connections . It sounds like some of your team members feel isolated, especially in this remote environment. Let’s work on ways we can put some virtual team-building activities together.”
A leader who is micromanaging , damaging employee morale.
“In the last employee engagement pulse survey, I took a look at the leadership feedback. It sounds like some of your employees feel that you micromanage them, which can damage trust and employee engagement. In our next one-on-one, let’s talk through some projects that you can step back from and delegate to one of your direct reports. We want to make sure employees on your team feel ownership and autonomy over their work.”
8 tips for providing constructive feedback
Asking for and receiving feedback isn’t an easy task.
But as we know, more people would prefer to receive feedback than give it. If giving constructive feedback feels daunting, we’ve rounded up eight tips to help ease your nerves. These best practices can help make sure you’re nailing your feedback delivery for optimal results, too.
Be clear and direct (without being brutally honest). Make sure you’re clear, concise, and direct. Dancing around the topic isn’t helpful for you or the person you’re giving feedback to.
Provide specific examples. Get really specific and cite recent examples. If you’re vague and high-level, the employee might not connect feedback with their actions.

Set goals for the behavior you’d like to see changed. If there’s a behavior that’s consistent, try setting a goal with your employee. For example, let’s say a team member dominates the conversation in team meetings. Could you set a goal for how many times they encourage other team members to speak and share their ideas?
Give time and space for clarifying questions. Constructive feedback can be hard to hear. It can also take some time to process. Make sure you give the person the time and space for questions and follow-up.
Know when to give feedback in person versus written communication. Some constructive feedback simply shouldn’t be put in an email or a Slack message. Know the right communication forum to deliver your feedback.
Check-in. Make an intentional effort to check in with the person on how they’re doing in the respective area of feedback. For example, let’s say you’ve given a teammate feedback on their presentation skills . Follow up on how they’ve invested in building their public speaking skills . Ask if you can help them practice before a big meeting or presentation.
Ask for feedback in return. Feedback can feel hierarchical and top-down sometimes. Make sure that you open the door to gather feedback in return from your employees.
Start giving effective constructive feedback
Meaningful feedback can be the difference between a flailing and thriving team. To create a feedback culture in your organization, constructive feedback is a necessary ingredient.
Think about the role of coaching to help build feedback muscles with your employees. With access to virtual coaching , you can make sure your employees are set up for success. BetterUp can help your workforce reach its full potential.
Elevate your communication skills
Unlock the power of clear and persuasive communication. Our coaches can guide you to build strong relationships and succeed in both personal and professional life.
Madeline Miles
Madeline is a writer, communicator, and storyteller who is passionate about using words to help drive positive change. She holds a bachelor's in English Creative Writing and Communication Studies and lives in Denver, Colorado. In her spare time, she's usually somewhere outside (preferably in the mountains) — and enjoys poetry and fiction.
5 types of feedback that make a difference (and how to use them)
Are you receptive to feedback follow this step-by-step guide, handle feedback like a boss and make it work for you, how to give constructive feedback as a manager, should you use the feedback sandwich 7 pros and cons, how to get feedback from your employees, why coworker feedback is so important and 5 ways to give it, feedback in communication: 5 areas to become a better communicator, how managers get upward feedback from their team, similar articles, 15 tips for your end-of-year reviews, how to give negative feedback to a manager, with examples, how to embrace constructive conflict, 25 performance review questions (and how to use them), how to give feedback to your boss: tips for getting started, how to give kudos at work. try these 5 examples to show appreciation, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback
Part of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (NeurIPS 2022) Main Conference Track
Long Ouyang, Jeffrey Wu, Xu Jiang, Diogo Almeida, Carroll Wainwright, Pamela Mishkin, Chong Zhang, Sandhini Agarwal, Katarina Slama, Alex Ray, John Schulman, Jacob Hilton, Fraser Kelton, Luke Miller, Maddie Simens, Amanda Askell, Peter Welinder, Paul F. Christiano, Jan Leike, Ryan Lowe
Making language models bigger does not inherently make them better at following a user's intent. For example, large language models can generate outputs that are untruthful, toxic, or simply not helpful to the user. In other words, these models are not aligned with their users. In this paper, we show an avenue for aligning language models with user intent on a wide range of tasks by fine-tuning with human feedback. Starting with a set of labeler-written prompts and prompts submitted through a language model API, we collect a dataset of labeler demonstrations of the desired model behavior, which we use to fine-tune GPT-3 using supervised learning. We then collect a dataset of rankings of model outputs, which we use to further fine-tune this supervised model using reinforcement learning from human feedback. We call the resulting models InstructGPT. In human evaluations on our prompt distribution, outputs from the 1.3B parameter InstructGPT model are preferred to outputs from the 175B GPT-3, despite having 100x fewer parameters. Moreover, InstructGPT models show improvements in truthfulness and reductions in toxic output generation while having minimal performance regressions on public NLP datasets. Even though InstructGPT still makes simple mistakes, our results show that fine-tuning with human feedback is a promising direction for aligning language models with human intent.
Name Change Policy
Requests for name changes in the electronic proceedings will be accepted with no questions asked. However name changes may cause bibliographic tracking issues. Authors are asked to consider this carefully and discuss it with their co-authors prior to requesting a name change in the electronic proceedings.
Use the "Report an Issue" link to request a name change.

COMMENTS
Court K (2014) Tutor feedback on draft essays: Developing students' academic writing and subject knowledge. Journal of Further and Higher Education 38(3): 327-45. Crossref. Google Scholar. Covic T, Jones MK (2007) Is the essay resubmission option a formative or a summative assessment and does it matter as long as the grades improve?
Finally, we would encourage you to think about feedback on your writing as a way to help you develop better writing strategies. This is the philosophy of the Writing Center. Don't look at individual bits of feedback such as "This paper was badly organized" as evidence that you always organize ideas poorly.
Your essay should be as easy to read as possible for the person marking it, as this lessens their workload and makes them feel more positively towards your work. 10. "Very good". It's always OK to ask for more feedback. On the face of it, this is the sort of essay feedback every student wants to hear.
Feedback is designed to help you to identify your own strengths and weaknesses in a piece of work. It can help you improve on your work by building on the positive comments and using the critical ones to inform changes in your future writing. Therefore, feedback forms a critical role in your learning and helps you to improve each piece of work.
Feedback is powerful but variable. This study investigates which forms of feedback are more predictive of improvement to students' essays, using Turnitin Feedback Studio-a computer augmented system to capture teacher and computer-generated feedback comments. The study used a sample of 3,204 high school and university students who submitted their essays, received feedback comments, and then ...
Prioritise Revisions: Once you receive feedback, prioritise implementing revisions. Identify the key areas for improvement and revise your essay accordingly. This iterative process not only enhances the quality of your current work but also contributes to your growth as a writer. Reflect on Feedback: Take the time to reflect on the feedback ...
Looking ahead. With the Academic Essay Feedback tool in our Khanmigo pilot, teachers and parents can empower students to take charge of their writing.The tool helps facilitate a deeper understanding of effective writing techniques and encourages self-improvement. For teachers, we think this tool is a valuable ally, enabling them to provide more ...
There are two main things you may want to offer feedback on when reading an essay. These are: The content of the essay (i.e. what the author is arguing) How it is written (i.e. how well they communicate their argument) The exact nature of the feedback you provide will depend on the topic and type of essay you are reading.
15. "There are too many errors.". This can be a discouraging piece of essay feedback, but it's also one of the easiest to fix. It's important to have someone read and edit your draft, whether you struggle with grammar or consider yourself a word nerd. Everyone makes mistakes.
Constructive feedback example for essays . For instructors with a pile of essays needing feedback and marks, it can feel overwhelming to offer meaningful comments on each one. One tip is to focus on one thing at a time (structure, grammar, punctuation), instead of trying to address each and every issue. This makes feedback not only more ...
Effective essay feedback is a powerful tool in promoting growth and development in students' writing abilities. By highlighting strengths and areas for improvement, encouraging critical thinking, providing clear suggestions, focusing on grammar and language, and emphasizing revision and self-reflection, educators can help students become ...
Constructive Feedback for an Essay. 1. Your writing style is good but you need to use more academic references in your paragraphs. 2. While you have reached the required word count, it would be good to focus on making sure every paragraph addresses the essay question. 3. You have a good structure for your essay, but you could improve your ...
There are two things you may want to offer feedback on when reading a college paper: The content of the paper itself. How well it is written. The feedback you provide will depend on the topic and type of essay. But there are some things you could comment on for any paper, including: Spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors.
Sample Feedback - Student to Student. Dear A--, First of all, this is clearly a well-thought out and well-written essay. The first paragraph offers a strong hook, while at the same time providing important historical information. You transition smoothly into the second paragraph, which successfully sets up your thesis.
By Carolina Kuepper-Tetzel. My post today is a personal reflection on effective feedback use. Feedback is a crucial aspect of the learning process. It helps us correct errors and improve performance in the future. However, effective feedback remains a problem in education. In the most recent National Student Survey in the UK (a survey that is ...
Of course, length and type of feedback vary between individual tutors and between essay submissions. Sample 1. Dear Rachel: I think you touch on some really nice ideas in this paper, which I'll talk about in a minute, but first I want to address one general concern I had about your writing. You have a tendency to spend too much time summarizing ...
Getting feedback on your practice essays should help you refine your writing style and at the very least, make your essays sound good. Where to Get Quality Feedback. To really improve your writing style and substantive analysis using feedback, you need to be getting quality feedback. Quality feedback will point out what you're doing well and ...
Peer feedback is introduced as an effective learning strategy, especially in large-size classes where teachers face high workloads. However, for complex tasks such as writing an argumentative essay, without support peers may not provide high-quality feedback since it requires a high level of cognitive processing, critical thinking skills, and a deep understanding of the subject.
essay. The links between the ideas presented in the essay were effectively linked together in a nice way. The essay also has a clear and well-written introduction and conclusion. The language used throughout the essay was appropriate and relevant to the topic and general theme of the course. Key terminology from the
Constructive feedback examples about communication skills. An employee speaks over others and interrupts in team meetings. "I've noticed you can cut off team members or interrupt others. You share plenty of good ideas and do good work.
Sample message to authors of a reflective essay submitted to TLTHE: Dear K and A, I very much enjoyed reading your essay. It is so inspiring to see a written analysis of your partnership and the ways you worked through the challenges you faced last semester! This essay certainly could be appropriate for TLTHE if you balance the detailed ...
In this paper, we show an avenue for aligning language models with user intent on a wide range of tasks by fine-tuning with human feedback. Starting with a set of labeler-written prompts and prompts submitted through a language model API, we collect a dataset of labeler demonstrations of the desired model behavior, which we use to fine-tune GPT ...
The legal battles and signature-gathering challenges amount to financial hurdles that typically prevent independent candidates from gaining ballot access nationwide. Kennedy's campaign ended ...
In the context of ongoing global urbanization, the disparity in urban development, marked by the dual phenomena of urban sprawl and urban shrinkage at the regional level, has become increasingly evident. In this vein, two land-related governance strategies—smart growth (SG) and smart shrinkage (SS)—emerge as potential remedies to these challenges, targeting urban expansion and shrinkage ...